Page 1

Voice over IP (VoIP) Application Note
HP iPAQ 500 series Voice Messenger
The goal of this document is to clearly and concisely state what HP iPAQ 500 series
Voice Messenger is and is not capable of supporting for mobile IP telephony, aka VoIP,
or Voice over IP. All the capabilities and interoperability scenarios haven’t been tested at
this point, and until then this document will be a work-in-progress. As new information
becomes available, it will be added to this document.
Contents
1 Overview..................................................................................................................... 2
2 Media and Signaling Protocols................................................................................... 3
3 Telephony Features..................................................................................................... 3
4 Audio Quality.............................................................................................................. 4
5 Hardware and Firmware ............................................................................................. 5
6 WLAN Infrastructure.................................................................................................. 6
7 IP-PBX and SIP Server Support ................................................................................. 6
7.1 Compatibility with Cisco unified Call Manager v5.1 .......................................... 7
7.2 Compatibility with Avaya Communication Manager v4.0 / SES v3.1.2 ............. 8
7.3 Compatibility with Nortel MCS 5100 v4.5.......................................................... 9
7.4 Compatibility with Nortel CS1000 v4.5 ............................................................ 10
7.5 Compatibility with Alcatel OmniPCX Enterprise v6.1...................................... 11
8 Accessory Support .................................................................................................... 12
9 Configuring VoIP...................................................................................................... 12
9.1 Enabling ‘Internet Calling’................................................................................. 12
9.2 Checking Wi-Fi.................................................................................................. 12
9.3 Using HP iPAQ Setup Assistant ........................................................................ 12
9.4 VoIP Dial Plan ................................................................................................... 14
9.4.1 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT EMERGENCY CALLING ...................... 14
9.5 ADDITIONAL CONFIGURATION................................................................. 16
10 Appendix A – Standards Support ............................................................................. 17
10.1 Signaling Standards Implemented.................................................................. 17
10.2 Media/Other Standards................................................................................... 18
10.3 Standards Not Implemented ........................................................................... 18
Page 2
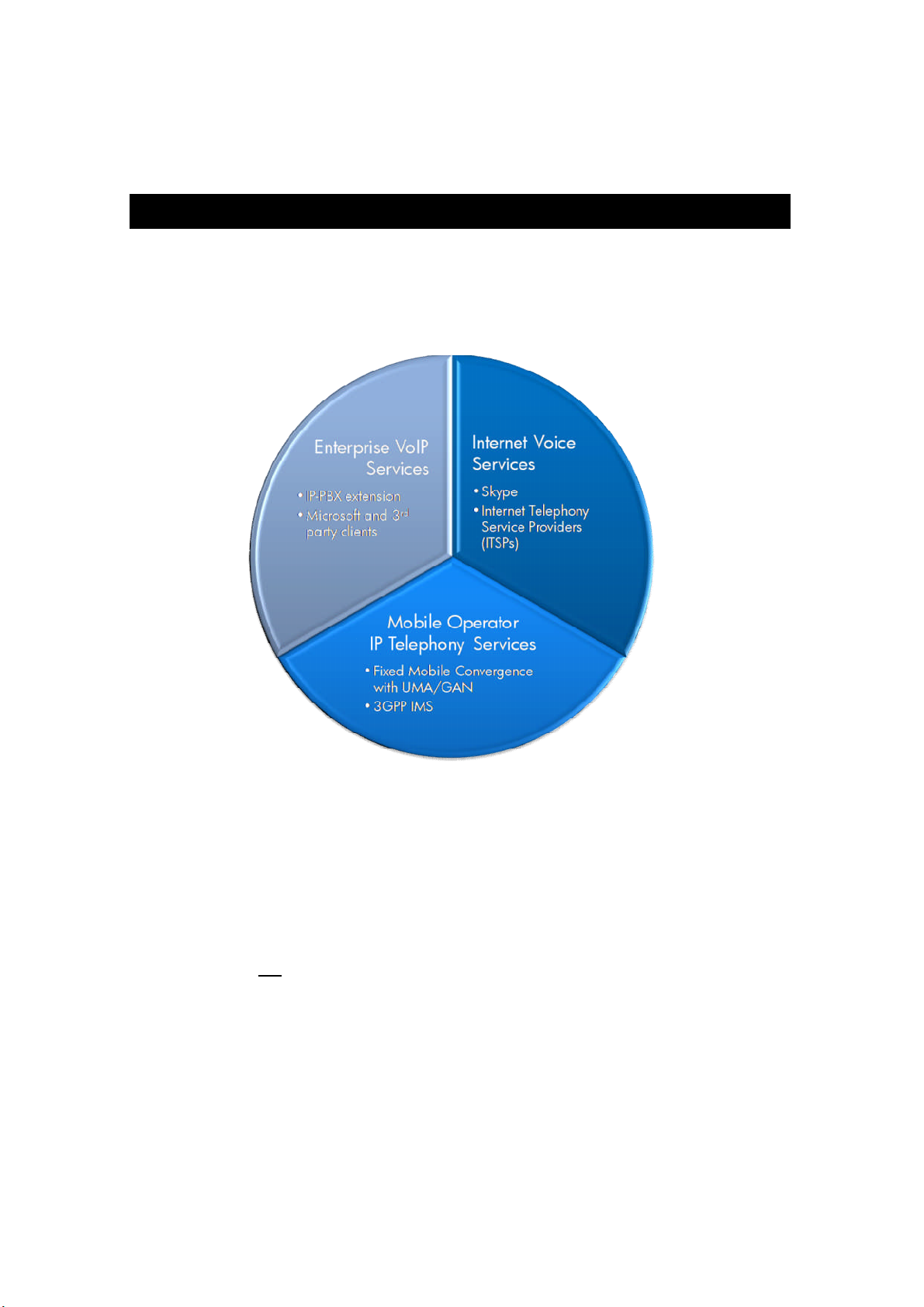
1 Overview
Mobile IP telephony services can be separated into three broad categories, each with its
own specific target markets and technologies used. These categories are illustrated below:
Tested use cases for the built-in VoIP client on the HP iPAQ 500 series smartphone cover
the enterprise VoIP segment exclusively and expect the enterprise has IT staff that
manage their own IP-PBX systems and provision devices for enterprise users. Mobile
enterprise VoIP services should be accessible anywhere the VoIP-enabled enterprise
wireless local area network (WLAN) provides coverage, typically within company
buildings and possibly around corporate campuses. Using the built-in VoIP client for
mobile access to the company’s IP-PBX from remote locations (homes, hotels, Internet
hotspots, etc.) is not a supported capability.
HP uses the native Microsoft SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) client in Windows Mobile
6 to access VoIP services, and this SIP client’s capabilities and limitations have been
further split into the following categories for the purposes of this document:
Media and Signaling Protocols
Telephony Features
Page 3
Audio Quality
Hardware and Firmware
WLAN Infrastructure
IP-PBX and SIP Server Support
Accessory Support
While Internet voice services delivered by Internet Telephony Service Providers (ITSPs)
may also be based on SIP, HP has done no testing or validation of interoperability with
these services at this time.
2 Media and Signaling Protocols
This category is related to the industry protocols that exist today for carrying control
messages and media messages.
Supported:
SIP – Session Initiation Protocol for Signaling [RFC 3261]
G.711 – Audio codec for compression/decompression of voice. Both A-law and
u-law variants are included.
Not Supported:
H.323 – signaling protocol used in some IP-PBXs
SCCP – Cisco’s proprietary call control protocol for Unified CallManager.
G.729 – Compressed audio codec more suitable for voice over WLAN compared
to G.711
Secure RTP [SRTP] – secure version of the RTP protocol [RFC 3711]
A full list of the standards supported and not supported is included in Appendix A of this
document.
3 Telephony Features
This category is related to the standard telephony features available in a VoIP
implementation.
Page 4

Supported:
Originate and Terminate Calls
Caller ID
Call Waiting
Call Hold
Call Mute
Call Forwarding *only with a SIM card present
o The number the call is forwarded to must be in a format [E.164] that can
be validated on the GSM network.
Configuring Caller ID *only with a SIM card present
Configuring Call Waiting *only with a SIM card present
Call Barring *only with a SIM card present
Blind Transfer
In-Band and out-of-band DTMF
o Out-of-band DTMF is requested by default. If the other end-point
declines, in-band DTMF is used.
Emergency Calling (over GSM only)
Interoperability testing with SIP-enabled IP PBX systems is being done to confirm
feature functionality with each vendor’s SIP implementation. Refer to subsequent
sections of this document for test results.
Not Supported:
Conferencing a second line
Consultative Transfer
Call Park/Pick-up
‘Do Not Disturb’
Emergency Calling over IP
A full list of the RFCs supported and not supported is included in Appendix A of this
document.
4 Audio Quality
This category is related to the components that need to be in the device to handle audio
quality.
Supported:
Automatic Gain Control
Page 5

Adaptive Jitter Buffer Management
Voice Activity Detection
Silence Suppression
Comfort Noise Generation
Acoustic Echo Cancellation (3rdparty sourced, not provided by Microsoft)
5 Hardware and Firmware
This category is related to WLAN and other hardware/firmware components in the
handset that are critical to the performance and usability of VoIP.
Supported:
802.11b/g
802.11i (PEAPv0 and EAP-TLS with certificates)
Encryption suites: WEP64, WEP128, TKIP and AES CCMP
Not Supported:
Full 802.1X Supplicant – Microsoft provides the limited set of EAP
authentication noted above. Additional EAP methods may be required by some
customers.
*A 3rdparty supplicant is currently under
consideration for a future release
Fast Roaming – A basic roaming agent has been implemented, and specific
roaming performance results will be published when they become available.
802.11r “Fast Roaming” is currently unsupported.
*Fast roaming enhancements are under
consideration for a future release
Cisco Compatible Extensions (CCX) – The WLAN module firmware and driver
would have to be updated to support the CCX v4 ASD feature set.
*A CCX v4 implementation is currently
under consideration for a future release
Certain features of 802.11e [WMM] are not currently supported.
o Automatic Power Save Delivery (APSD) and Unscheduled Automatic
Power Save Delivery (U-APSD) power saving mechanisms are not
currently supported.
o Even though packet tagging [802.1p and Diffserv] is inherently supported
by Windows Mobile 6, there may not be any benefit by tagging voice
packets with a higher priority.
Page 6
6 WLAN Infrastructure
This category is related to the wireless local area network (WLAN) infrastructure to
which the handset connects to send and receive IP traffic. The key consideration from the
mobile handset perspective is typically AP-AP roaming. Given the real time requirements
of voice and the delays inherent in WLAN authentication (802.11i), the strongly
recommended answer is a VoIP-enabled pervasive enterprise WLAN infrastructure. Note
that HP Services has a well-developed practice for migrating customers’ WLANs to this
model. The baseline requirement here is a controller-based AP deployment; not
standalone APs. Examples of these controller-based WLAN product offerings include:
• Cisco Aironet APs with Wireless LAN controller(s)
• HP ProCurve Radio Ports plus Wireless Edge Services xl module(s) in 5300xl
switch chassis
• Extreme Networks Altitude APs and Summit switches
• Aruba Networks APs and Mobility Controller(s)
• Meru Networks APs and Controller(s)
Testing is underway with Cisco Aironet APs and wWireless LAN controllers. Other
WLAN infrastructure testing and results may be available in the future.
For optimal performance, all 802.11b and 802.11g data rates should be enabled on the
APs. Limiting the data rates on the APs may prevent iPAQ 500 series devices from
connecting to the AP.
7 IP-PBX and SIP Server Support
This category is related to the SIP-based IP-PBX system or server with which the
handheld device must interact for VoIP services. HP testing is underway with enterprise
IP-PBX products from Cisco, Avaya, Alcatel, and Nortel. Detailed test criteria and results
will be added to this section as they become available.
Results of other additional testing with operator-class SIP servers (Broadsoft, Sylantro,
Huawei, Alcatel, etc.) will be included when they are made available to HP.
Page 7

7.1 COMPATIBILITY WITH CISCO UNIFIED CALL MANAGER V5.1
Feature Brief Description Pass/Fail Comments
Originate Calls SIP End Point to End point,
Extension, and PSTN
Terminate Calls From SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN
DTMF (in-band) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
DTMF (RFC 2833) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
Call Forward Call Forward All (CFA), Busy
(CFB) and Not Answered
(CFNA)
Message Waiting
Indicator
Blind Transfer Originator and Terminator
Call Waiting On Originator and Terminator,
Caller ID Calling Line ID Presentation
Call Barring Calling Line ID Restriction
Direct Inward Dial DID from Endpoint to Local and
Call Hold
(Music on Hold)
Voicemail notification passed
from server to Endpoint
transfer to Endpoint, Extension
and PSTN
waiting, timeout, release before
answer
(CLIP) Type I and II
(CLIR)
Remote Extension and PSTN to
Endpoint
Originator and Terminator hold
and resume with Endpoint,
Extension, and PSTN
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass Requires SIM card and
accepts valid E.164
numbers only
Fail
Pass
Pass Requires SIM card to
Pass Requires SIM card to
Pass Requires SIM card to
Pass
Pass
Cisco uses SIP Notify,
Enhancement request
submitted to Microsoft
configure
configure
configure
Page 8

7.2 COMPATIBILITY WITH AVAYA COMMUNICATION MANAGER V4.0 / SES
V3.1.2
Feature Brief Description Pass/Fail Comments
Originate Calls SIP End Point to End point,
Extension, and PSTN
Terminate Calls From SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN
DTMF (in-band) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
DTMF (RFC 2833) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
Call Forward Call Forward All (CFA), Busy
(CFB) and Not Answered
(CFNA)
Message Waiting
Indicator
Blind Transfer Originator and Terminator
Call Waiting On Originator and Terminator,
Caller ID Calling Line ID Presentation
Call Barring Calling Line ID Restriction
Direct Inward Dial DID from Endpoint to Local and
Call Hold
(Music on Hold)
Voicemail notification passed
from server to Endpoint
transfer to Endpoint, Extension
and PSTN
waiting, timeout, release before
answer
(CLIP) Type I and II
(CLIR)
Remote Extension and PSTN to
Endpoint
Originator and Terminator hold
and resume with Endpoint,
Extension, and PSTN
Testing still in progress
Page 9

7.3 COMPATIBILITY WITH NORTEL MCS 5100 V4.5
Feature Brief Description Pass/Fail Comments
Originate Calls SIP End Point to End point,
Extension, and PSTN
Terminate Calls From SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN
DTMF (in-band) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
DTMF (RFC 2833) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
Call Forward Call Forward All (CFA), Busy
(CFB) and Not Answered
(CFNA)
Message Waiting
Indicator
Blind Transfer Originator and Terminator
Call Waiting On Originator and Terminator,
Caller ID Calling Line ID Presentation
Call Barring Calling Line ID Restriction
Direct Inward Dial DID from Endpoint to Local and
Call Hold
(Music on Hold)
Voicemail notification passed
from server to Endpoint
transfer to Endpoint, Extension
and PSTN
waiting, timeout, release before
answer
(CLIP) Type I and II
(CLIR)
Remote Extension and PSTN to
Endpoint
Originator and Terminator hold
and resume with Endpoint,
Extension, and PSTN
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass Requires SIM card and
accepts valid E.164
numbers only
Pass
Pass
Pass Requires SIM card to
configure
Pass Requires SIM card to
configure
Pass Requires SIM card to
configure
Pass
Pass
Page 10

.
7.4 COMPATIBILITY WITH NORTEL CS1000 V4.5
Feature Brief Description Pass/Fail Comments
Originate Calls SIP End Point to End point,
Extension, and PSTN
Terminate Calls From SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN
DTMF (in-band) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
DTMF (RFC 2833) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
Call Forward Call Forward All (CFA), Busy
(CFB) and Not Answered
(CFNA)
Message Waiting
Indicator
Blind Transfer Originator and Terminator
Call Waiting On Originator and Terminator,
Caller ID Calling Line ID Presentation
Call Barring Calling Line ID Restriction
Direct Inward Dial DID from Endpoint to Local and
Call Hold
(Music on Hold)
Voicemail notification passed
from server to Endpoint
transfer to Endpoint, Extension
and PSTN
waiting, timeout, release before
answer
(CLIP) Type I and II
(CLIR)
Remote Extension and PSTN to
Endpoint
Originator and Terminator hold
and resume with Endpoint,
Extension, and PSTN
Testing still in progress
Page 11

7.5 COMPATIBILITY WITH ALCATEL OMNIPCX ENTERPRISE V6.1
Feature Brief Description Pass/Fail Comments
Originate Calls SIP End Point to End point,
Extension, and PSTN
Terminate Calls From SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN
DTMF (in-band) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
DTMF (RFC 2833) SIP End Point, Extension,
and PSTN send and receive
DTMF tones
Call Forward Call Forward All (CFA), Busy
(CFB) and Not Answered
(CFNA)
Message Waiting
Indicator
Blind Transfer Originator and Terminator
Call Waiting On Originator and Terminator,
Caller ID Calling Line ID Presentation
Call Barring Calling Line ID Restriction
Direct Inward Dial DID from Endpoint to Local and
Call Hold
(Music on Hold)
Voicemail notification passed
from server to Endpoint
transfer to Endpoint, Extension
and PSTN
waiting, timeout, release before
answer
(CLIP) Type I and II
(CLIR)
Remote Extension and PSTN to
Endpoint
Originator and Terminator hold
and resume with Endpoint,
Extension, and PSTN
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass Requires SIM card and
accepts valid E.164
numbers only
Not tested
Pass
Pass Requires SIM card to
Pass Requires SIM card to
Pass Requires SIM card to
Pass
Pass
No voicemail service on
test system
configure
configure
configure
Page 12

8 Accessory Support
This category is related to headsets and other accessories that may be used with the
handset in conjunction with VoIP.
Supported:
Wired headsets
Mono Bluetooth headsets
Not Supported:
Stereo Bluetooth headsets
9 Configuring VoIP
The Phone Dialer on the HP iPAQ 500 series Voice Messenger can be used to make
VoIP calls in addition to normal cellular calls. VoIP can be configured to work with SIPenabled IP-PBX or other SIP servers. Refer to Section 7 above for specific
interoperability test results.
9.1 ENABLING ‘INTERNET CALLING’
Before VoIP can be configured, ‘Internet Calling’ needs to be turned on. ‘Internet
Calling’ is turned off by default. The ‘Internet Calling’ plug-in on the Home screen
displays ‘Off’ indicating that the feature is turned off. To turn the feature on, select
‘Internet Calling’ on the Home screen and press Enter. This displays the Internet Calling
Settings page. Change the ‘Use Internet Calling:’ setting from ‘Never’ to any of the other
available options. This changes the status of the plug-in on the Home screen from’Off’ to
‘Not Available’. This indicates that even though VoIP is turned on, it hasn’t been
configured yet.
9.2 CHECKING WI-FI
Wi-Fi connectivity is required for VoIP to work. Before configuring VoIP, please set-up
Wi-Fi and make sure the phone can connect to an Access Point [AP] and that Internet
Explorer Mobile can be used to browse web pages.
9.3 USING HP IPAQ SETUP ASSISTANT
Once ‘Internet Calling’ is turned on and Wi-Fi is set-up, VoIP can be configured using
the HP iPAQ Setup Assistant software included on the Companion CD. The VoIP tab
Page 13

under Setup Assistant provides three categories of settings – Account, Server and
VoiceMail.
Account:
Please provide the username and password for the VoIP/SIP account. Also provide the
Domain name for the account. The username and Domain are used to construct the SIP
URI for the account as in the example below:
User name- johndoe
Domain- voipservice.sip.com
SIP URI- sip:johndoe@voipservice.sip.com
The name of the VoIP Service Provider can also be specified; this is optional.
Server:
This category is for the SIP settings associated with the SIP-enabled IP-PBX or the SIP
Server. The name/s or IP Address/es of the SIP Proxy and the SIP Registrar must be
specified here. By default, ‘Register with SIP Proxy’ is checked, indicating that the SIP
Proxy is also used as the SIP Registrar. In this case, the name or IP Address of the SIP
Proxy only needs to be provided and the same name/IP address is also used for the SIP
Registrar. If the Proxy and the Registrar are different, please uncheck ‘Register with SIP
Proxy’ and provide the name/IP address for the SIP Registrar in addition to the SIP
Proxy.
Voice Mail:
If a Voice Mail number is provided with the account, please include it here. This is
optional.
The ‘Options’ button can be used to access some advanced VoIP settings. The UDP
signaling method can be toggled between symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric UDP
signaling is used by default. An option to enable early UDP packets on RTP and RTCP
ports is available. This enables opening of ports on a NAT allowing NAT traversal of
traffic. A prefix digit can be added to outgoing phone numbers. For example, if ‘9’ is
specified as the prefix digit, it is automatically pre-pended to all 11-digit, 10-digit and 7digit phone numbers. By default, no prefix digit is used. The DSCP field in the IP header
of voice packets contains a QoS number that determines the priority voice packets get
over data packets in the network. By default, 56 is used as the DSCP QoS number. This
can be modified to increase or decrease the priority of voice traffic.
Once all the appropriate information is provided, apply the configuration to the phone. If
Wi-Fi is on and connected to an AP, the phone will register with the specified SIPenabled IP-PBX or the SIP Server. If Wi-Fi is off, SIP registration will occur when the
next time Wi-Fi is turned on and connected to an AP. The status of the ‘Internet Calling’
plug-in will either be ‘Available’ or ‘Selected’. ‘Available’ means that the phone has
Wi-Fi access and is registered with the IP-PBX, but the next outgoing call will be over
cellular. ‘Selected’ means that the phone has Wi-Fi access, is registered with the IP-PBX
Page 14

and that VoIP will be used for the next outgoing call. The Phone Dialer can be used to
make and receive VoIP calls. The Internet Calling status can be toggled between
‘Available’ and ‘Selected’ by pressing the Action [Enter] button on the Internet Calling
plug-in on the home screen.
If the status of the plug-in is ‘No Service’, it indicates that the registration was
unsuccessful. This could be due to lack of Wi-Fi access, the IP-PBX being unavailable or
some other failure.
9.4 VOIP DIAL PLAN
The dial plan for VoIP consists of dialing rules. These dialing rules are constructed using
regular expressions. Please refer to the Windows Mobile 6 documentation for information
on creating dialing rules. The dial plan is an XML file based on the OMA provisioning
standard. The Voice Messenger comes with a default dial plan which may not necessarily
work for a specific set-up. The dial plan will have to be modified and to do this, a base
XML template will be provided. This should be used to add new dialing rules specific to
the infrastructure being targeted. Once the XML template is modified to add new rules, it
should be applied to the phone/s to provision the phone/s with the updated VoIP dial
plan. This can be done using any of the provisioning methods supported by Windows
Mobile 6 –
1. OTA using OMA Client provisioning [WAP push].
2. OTA using OMA Device Management provisioning. [OMA DM server is
required].
3. Using a CAB Provisioning Format [.cpf] file which can be delivered over HTTP,
or by using a SD/MMC card or copied over to the phone directly using
ActiveSync.
4. Using Remote API [RAPI] in ActiveSync to push the provisioning XML file to
the phone.
5. Application Developers can use the DMProcessConfigXML API to provision.
Please refer to the Windows Mobile 6 documentation for additional details on the
provisioning methods listed above.
HP iPAQ Setup Assistant cannot be used to make any significant changes to the dial plan.
It can only be used to add a prefix digit to 11-digit, 10-digit and 7-digit outgoing phone
numbers. It is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that any modifications/additions/deletions to
the dial plan should be done using any of the provisioning methods mentioned above. HP
iPAQ Setup Assistant MUST only be used to configure/modify SIP settings.
9.4.1 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT EMERGENCY CALLING
Emergency Calling over IP is not supported by the Voice Messenger. All emergency calls
must be placed over cellular. To ensure this, a dialing rule specifically for emergency
calling MUST be added to the VoIP dial plan. This rule will indicate what the emergency
Page 15

number is and will also indicate that this number should be placed on the cellular network
only. The emergency dialing rule for the U.S is shown below:
<rule pattern='911' display='911' restrict='VoIP' />
The base template for the VoIP Dial Plan is specified below. It is HIGHLY
RECOMMENDED that the rules included in the base template should not be removed.
<wap-provisioningdoc>
<characteristic type="VoIP">
<parm name="DialPlan" value="<dialplan xmlns='http://schemas.microsoft.com/embedded/VoIP'>
<dialplan-header>
<host>#use_sipsrv_host_name#</host>
</dialplan-header>
<!-- Dial Plan rules -->
<!-- IP address rules -->
<!-- EQUIVALENT OF '\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}' -->
<rule pattern='(\d|\d\d|\d\d\d)\.(\d|\d\d|\d\d\d)\.(\d|\d\d|\d\d\d)\.(\d|\d\d|\d\d\d)' restrict='Cell,SMS' />
<!-- EQUIVALENT OF '(\d{1,3})\*(\d{1,3})\*(\d{1,3})\*(\d{1,3})' -->
<rule pattern='(\d|\d\d|\d\d\d)\*(\d|\d\d|\d\d\d)\*(\d|\d\d|\d\d\d)\*(\d|\d\d|\d\d\d)' dial='\1.\2.\3.\4'
display='\1.\2.\3.\4' restrict='Cell,SMS' />
<!—Add Emergency Dialing Rules here -->
<!—Add Other Dialing Rules here -->
<!-- SIP URI rules -->
<!-- EQUIVALENT OF '[Ss][Ii][Pp][Ss]?:\w*(\d{3})(\d{3})(\d{4})@(.+)' -->
<rule pattern='[Ss][Ii][Pp][Ss]?:\w*(\d\d\d)(\d\d\d)(\d\d\d\d)@(.+)' display='(\1) \2-\3'
restrict='Cell,SMS' />
<rule pattern='([Ss][Ii][Pp][Ss]?:)?\w*([a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)@(.+)' display='\2' restrict='Cell,SMS' />
<rule pattern='[Ss][Ii][Pp][Ss]?:\w*([^@]+)' display='\1' restrict='Cell,SMS' />
<!—Catch All -->
<rule pattern='(\d+)' dial='sip:\1@$host$' display='\1' transfer='sip:\1@$host$' />
<rule pattern='([a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)' dial='sip:\1@$host$' display='\1' transfer='sip:\1@$host$' />
</dialplan>" />
</characteristic>
</wap-provisioningdoc>
A sample dialing rule for 10-digit phone numbers is shown below. This rule pre-pends a
‘9’ to 10-digit dialed phone numbers.
<rule pattern='(\d{3})\s*(\d{3})\s*-?\s*(\d{4})(\s*[Xx]\s*\d+)?' dial='sip:9\1\2\3@$host$'
display='(\1) \2-\3'
Page 16

transfer='sip:\1\2\3@$host$' />
Please refer to the Windows Mobile 6 documentation for additional details about the
VoIP Dial Plan and some examples.
9.5 ADDITIONAL CONFIGURATION
Windows Mobile 6 provides a set of registry keys to customize the WM6 SIP Client.
Some of the key customization features are provided by HP iPAQ Setup Assistant as
explained in section 9.3. The other customization options can be set by modifying the
registry. Below are some examples of the configuration options provided using the
registry –
Enable/disable redirection of SIP calls.
Allow/disallow listening for incoming SIP traffic on port 5060.
Modify the registration expiry time (default is 19 seconds).
Modify Session Timers, specifically ‘Session-Expires’ and ‘Min-SE’ (default is
90 seconds).
Please refer to the Windows Mobile 6 documentation for complete coverage of all
available configuration options and the associated registry entries.
Page 17

10 Appendix A – Standards Support
10.1 SIGNALING STANDARDS IMPLEMENTED
Standardor Reference Title/ Decription
RFC 3261 SIP: Session Initiation Protocol
RFC 3261 Call Waiting
RFC 2327 SDP : Session Description Protocol
RFC 2246 TLS Protocol
RFC 3263 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): Locating SIP
Servers
RFC 3263 (obsoletes 2543) SIP: Locating servers
RFC 2782 (obsoletes 2052) DNS SRV
RFC 3264 An Offer/Answer Model with the Session
Description Protocol (SDP)
RFC 3262 Reliability of Provisional Responses :
Provisional Response ACKnowledgement
(PRACK)
RFC 3361 DHCP Option for location the outbound SIP
Proxy server
RFC 3265 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)-Specific Event
Notification (SUBSCRIBE/NOTIFY)
RFC 3842 A Message Summary and Message Waiting
Indication
RFC 3863 Presence Information Data Format (PIDF)
RFC 2976 The SIP INFO Method
RFC 3428 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Extension for
Instant Messaging
RFC 3711 Secure RTP (SRTP)
RFC 3856 Presence Event Package for the Session
Initiation Protocol (SIP)
RFC 3515 The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Refer
Method
RFC 3515 SIP: Refer Method/ Call Transfer
RFC 3323 Privacy Mechanism for SIP
RFC 3324 Short term requirements for Network asserted
identity
RFC 3325 Private extensions to SIP of asserted identify
within trusted networks
RFC 1321 MD5
RFC 2387 MIME content type
RFC 2605 RTCP in SDP
RFC 3841 Call Preferences
RFC 1321 MD5
RFC 2474 Diffserv
RFC 2617 (obsoletes 2069) An Extension to HTTP: Digest Access
Authentication
Page 18

10.2 MEDIA/OTHER STANDARDS
Standard or Reference Description
RFC 3550 (obsoletes RFC 1889) RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time
Applications
RFC 3551 (obsoletes RFC 1889) RTP Profile for Audio and Video Conferences
with Minimal Control
draft-wing-behave-symmetric-rtprtcp-01.txt Symmetric RTP/RTCP ports over UDP
RFC 2833 RTP Payload for DTMF Digits, Telephony
Tones and Telephony Signals (in-band and out
of band)
G711 u/A Voice codec
RFC 2198 RTP Payload for Redundant Audio Data
10.3 STANDARDS NOT IMPLEMENTED
Standard or Reference Decription
Draft-ietf-core-23 XMPP core implementation
Draft-ietf-xmpp-cpim-04 Mapping of XMPP to CPIM
RFC 3326 The Reason Header Fields of the SIP
RFC 4028 Session Timers in the SIP
RFC 3611 RTP Control Protocol Extended Reports
(RTCP XR)
RFC 3389 (RTP) Payload for Comfort Noise (CN)
RFC 3311 SIP Update Method
Draft-ietf-sip-join-xx SIP Join header
Draft-ietf-sipping-cc-conferencing-xx SIP Call Control - Conferencing for User
Agents
RFC 3891 SIP 'Replaces' Header
RFC 3266 Support for IPv6 in Session Description
Protocol (SDP)
RFC 3581 Symmetric Routing
Call Park/Call Pickup Call Park/Call Pickup (through ‘Replaces’
header)
RFC 3903 (Draft-ietf-sup-publish-04) Extension to SIP event notification
framewirking for aggregation of notification
under the same AOR?
UPnP IDG Internet Gateway Device (IGD) Standardized
Device Control Protocol V 1.0
RFC 3047 RTP Payload Format for ITU-T
Recommendation G.722.1
G.722.1 Voice codec
G.723 Supported if a 3rd party codec is used
G.723.1 Supported if a 3rd party codec is used
Page 19

iLBC Supported if a 3rd party codec is used
G.726 Supported if a 3rd party codec is used
G.729 Supported if a 3rdparty codec is used
SIP Auth -AKA AKA - Auth based on USIM
3GPP Specific RFCs/Headers
 Loading...
Loading...