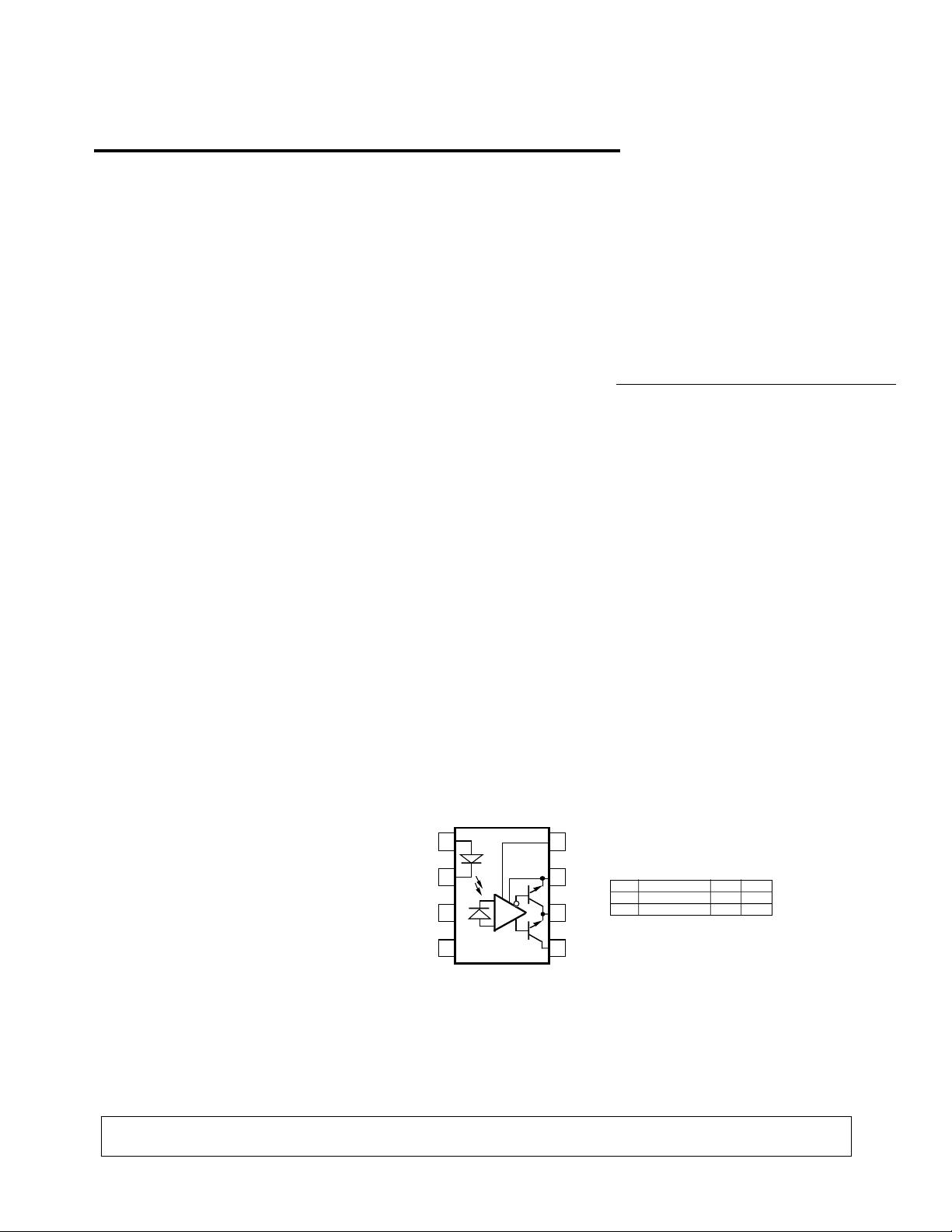
Power Bipolar Transistor
Base Drive Optocoupler
Technical Data
H
HCPL-3000
Features
• High Output Current
IO2 (2.0 A Peak, 0.6 A
Continuous)
IO1 (1.0 A Peak, 0.5 A
Continuous)
• 1.5 kV/µs Minimum Common
Mode Rejection (CMR) at
VCM = 600 V
• Wide VCC Range (5.4 to 13
Volts)
• 2 µs Typical Propagation
Delay
• Recognized under UL 1577
for Dielectric Withstand
Proof Test Voltage of 5000
Vac, 1 Minute
Applications
• Isolated Bipolar Transistor
Base Drive
• AC and DC Motor Drives
• General Purpose Industrial
Inverters
• Uninterruptable Power
Supply
Description
The HCPL-3000 consists of a
Silicon-doped GaAs LED optically
coupled to an integrated circuit
with a power output stage. This
optocoupler is suited for driving
power bipolar transistors and
power Darlington devices used in
motor control inverter applications. The high peak and steady
state current capabilities of the
output stage allow for direct
interfacing to the power device
without the need for an intermediate amplifier stage. With a CMR
Functional Diagram
HCPL-3000
V
ANODE
CATHODE
1
2
3
4
8
7
GND
Q2
6
V
Q1
5
V
rating of 1.5 kV/µs this optocoupler readily rejects transients found
in inverter applications.
The LED controls the state of the
output stage. Transistor Q2 in the
output stage is on with the LED
off, allowing the base of the
power device to be held low.
Turning on the LED turns off
transistor Q2 and switches on
transistor Q1 in the output stage
which provides current to drive
the base of a power bipolar
device.
CC
TRUTH TABLE
LED
OUTPUT
ON
HIGH LEVEL
OFF
O2
O1
LOW LEVEL
Q1
ON
OFF
Q2
OFF
ON
THE USE OF A 0.1µF BYPASS CAPACITOR CONNECTED BETWEEN PINS 8 AND 7 IS RECOMMENDED. ALSO, CURRENT LIMITING
RESISTORS ARE RECOMMENDED (SEE FIGURE 1, NOTE 2, AND NOTE 7).
CAUTION: It is advised that normal static precautions be taken in handling and assembly of this component to
prevent damage and/or degradation which may be induced by ESD.
5965-3584E
1-329
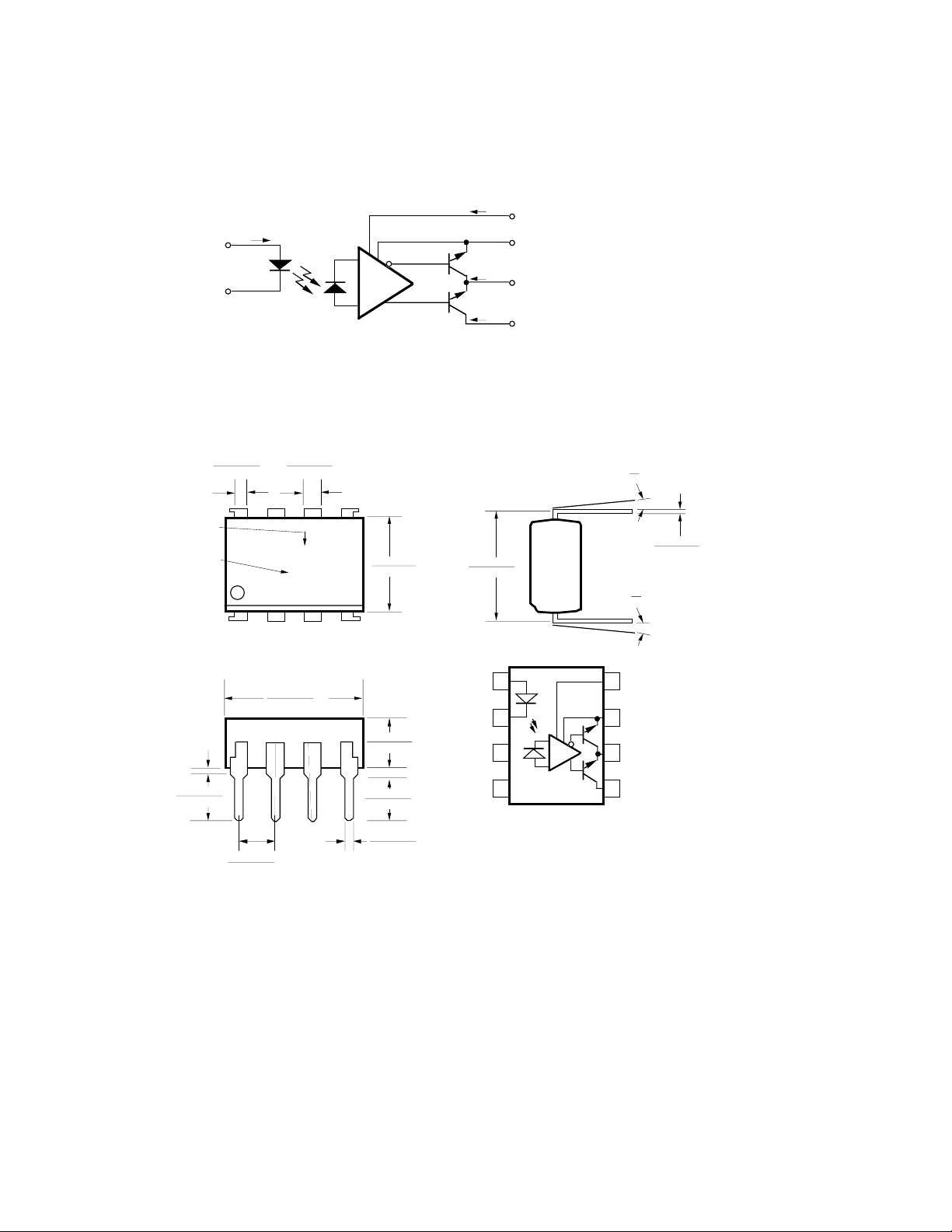
Schematic
1
ANODE
CATHODE
I
+
-
2
Outline Drawing
I
CC
V
CC
8
F
Q2
Q1
GND
7
I
O2
V
O2
6
I
O1
V
O1
5
TYPE
NUMBER
DATE
CODE
0.50
(0.020)
TYP
2.90 (0.114)
3.90 (0.154)
0.65 (0.026)
1.05 (0.041)
87 65
12 34
2.29 (0.090)
2.79 (0.110)
0.90 (0.035)
1.50 (0.059)
HP XXXX
YYWW
9.16 (0.361)
10.16 (0.400)
6.00 (0.236)
7.00 (0.276)
3.00 (0.118)
4.00 (0.157)
2.55 (0.100)
3.55 (0.140)
0.40 (0.016)
0.60 (0.024)
7.32 (0.288)
7.92 (0.312)
ANODE
CATHODE
1
2
3
4
HCPL-3000
0°
13°
0.16 (0.006)
0.36 (0.014)
0°
13°
V
8
CC
7
GND
Q2
6
V
O2
Q1
5
V
O1
Regulatory Information
The HCPL-3000 has been
approved by the following
organizations:
Demonstrated ESD Performance
Human Body Model: MIL-STD-
883 Method 3015.7: Class 2
Machine Model: EIAJ IC-121-
UL
Recognized under UL 1577,
Component Recognition Program,
1988 (1988.3.28 Version 2),
Test Method 20, Condition C:
1200 V
File E55361.
1-330
Insulation and Safety Related Specifications
Parameter Symbol Value Units Conditions
Min. External Air Gap L(IO1) 6.0 mm Shortest distance measured through air, between
(External Clearance) two conductive leads, input to output
Min. External Tracking L(IO2) 6.0 mm Shortest distance path measured along outside surface
Path (External Creepage) of optocoupler body between the input and output leads
Min. Internal Plastic 0.15 mm Through insulation distance conductor to conductor
Gap (Internal Clearance) inside the optocoupler cavity
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Min. Max. Unit Conditions Fig. Note
Storage Temperature T
Operating Temperature T
Input Continuous Current I
Reverse Voltage V
Supply Voltage V
Output 1 Continuous Current I
S
A
F
R
CC
O1
Peak Current 1.0 A Pulse Width < 5 µs, 1
Voltage V
Output 2 Continuous Current I
O1
O2
Peak Current 2.0 A Pulse Width < 5 µs, 12 1
Output Power Dissipation P
Total Power Dissipation P
O
T
Lead Solder Temperature 260° C for 10 s, 1.0 mm below seating plane
-55 125 °C
-20 80 °C
25 mA 9 1
6VT
18 V
0.5 A 10,11 1
18 V
0.6 A 10,11,12 1
500 mW 10 1
550 mW 11 1
= 25°C
A
Duty cycle = 1%
Duty cycle = 1%
Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol Min. Max. Units
Power Supply Voltage V
Input Current (ON) I
Input Current (OFF) I
Operating Temperature T
*The initial switching threshold is 5 mA or less.
CC
F(ON)
F(OFF)
A
Recommended Protection for Output Transistors
During switching transitions, the
output transistors Q1 and Q2 of
the HCPL-3000 can conduct large
amounts of current. Figure 1
describes a recommended circuit
design showing current limiting
resistors R1 and R2 which are
necessary in order to prevent
5.4 13 V
8* 20 mA
- 0.2 mA
-20 80 °C
damage to the output transistors
Q1 and Q2 (see Note 7). A bypass
capacitor C1 is also recommended
to reduce power supply noise.
1-331

+5 V
CONTROL
INPUT
TTL
OR
LSTTL
1
240 Ω
TOTEM
POLE
OUTPUT
GATE
1
2
R1 = 5 - 250 Ω
R
= 1 - 2 Ω
2
BYPASS CAPACITOR C
HCPL-3000
= 0.1 µF
1
8
C
1
Q2
Q1
7
6
R
2
5
R
1
I
O1
V (+ 5.4 V + 13 V)
CC
POWER TRANSISTOR
MODULE
+ HVDC
3-PHASE
AC
- HVDC
Figure 1. Recommended Output Transistor Protection and Typical Application Circuit.
Electrical Specifications
Over recommended temperature (TA = -20°C to +80°C) unless otherwise specified.
Parameter Sym. Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions Fig. Note
Input Forward Voltage V
Input Reverse Current I
Input Capacitance C
Output 1 Low Level V
F
R
IN
O1L
Voltage RL2 = 10 Ω, IF = 5 mA 17
Leakage I
O1L
Current IF = 0 mA
Output 2 High Level V
O2H
Voltage IF = 5 mA, VO1 = 6 V 19
Low Level V
O2L
Voltage IF = 0 mA 21
Leakage I
O2L
Current VO2 = 13 V
Supply High Level I
CCH
Current
Low Level I
Low to High I
CCL
FLH
Threshold Input 6, 14, 3
Current 0.2 - 5.0 mA VCC = 6 V, RL1 = 5 Ω,15
- 1.1 1.4 V IF = 5 mA, TA = 25°C13
0.6 0.9 - V IF = 0.2 mA, TA = 25°C
--10µAVR = 3 V, TA = 25°C
- 30 250 pF VF = 0 V, f = 1 kHz,
TA = 25°C
- 0.2 0.4 V VCC = 6 V, IO1 = 0.4 A, 2, 16, 2
- - 200 µAVCC = VO1 = 13 V, VO2 = 0 V, 4
4.5 5.0 - V VCC = 6 V, IO2 = -0.4 A 3, 18, 2
- 0.2 0.4 V VCC = 6 V, IO2 = 0.5 A, 20,
- - 200 µAVCC = 13 V, IF = 5 mA, 5
-913mAT
--17 V
-1115mAT
--20 V
= 25°C222
A
= 6 V, IF = 5 mA
CC
= 25°C23
A
= 6 V, IF = 0 mA
CC
0.3 1.5 3.0 mA TA = 25°C
R
= 10 Ω
L2
1-332

Switching Specifications (T
= 25°C)
A
Parameter Sym. Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions Fig. Note
Propagation Delay t
PLH
-25µsVCC = 6 V, IF = 5 mA, 7, 2, 6
Time to High Output RL1 = 5 Ω, RL2 = 10 Ω 24,
Level 25
Propagation Delay Time t
PHL
-25
to Low Output Level
Rise Time t
Fall Time t
r
f
- 0.2 1
- 0.1 1
Output High Level |CMH| 1500 - - V/µsVCM = 600 V Peak,82
Common Mode IF = 5mA, RL1 = 470 Ω,
Transient Immunity RL2 = 1 kΩ, ∆V
02H
= 0.5 V
Output Low Level |CML| 1500 - - V/µsVCM = 600 V Peak,
Common Mode IF = 0 mA, RL1 = 470 Ω,
Transient Immunity RL2 = 1 kΩ, ∆V
= 0.5 V
02L
Package Characteristics
Parameter Sym. Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions Fig. Note
Input-Output Momentary V
Withstand Voltage* t = 1 min., TA = 25°C
Resistance R
(Input-Output) RH = 40% to 60%
Capacitance C
(Input-Output)
*The Input-Output Momentary Withstand Voltage is a dielectric voltage rating that should not be interpreted as an input-output
continuous voltage rating. For the continuous voltage rating refer to the VDE 0884 Insulation Characteristics Table (if applicable), your
equipment level safety specification, or HP Application Note 1074, “Optocoupler Input-Output Endurance Voltage.”
5000 V rms RH = 40% to 60%, 4, 5
ISO
I-O
I-O
5x101010
– 1.2 – pF f = 1 MHz 4
11
– Ω V
= 500 V, TA = 25°C, 4
I-O
Notes:
1. Derate absolute maximum ratings with ambient temperatures as shown in Figures 9, 10, and 11.
2. A bypass capacitor of 0.01 µF or more is needed near the device between VCC and GND when measuring output and transfer
characteristics.
3. I
represents the forward current when the output goes from low to high.
FLH
4. Device considered a two terminal device; pins 1-4 are shorted together and pin 5-8 are shorted together.
5. For devices with minimum V
insulation test voltage ≥ 6000 V rms for one second (leakage current detection limit, I
6. The t
7. R1 sets the base current (I
and t
PLH
is turning off. For more applications and circuit design information see Application Note “Power Transistor Gate/Base Drive
Optocouplers.”
propagation delays are measured from the 50% level of the input pulse to the 50% level of the output pulse.
PHL
specified at 5000 V rms, in accordance with UL1577, each optocoupler is proof-tested by applying an
ISO
in Figure 1) supplied to the power bipolar device. R2 limits the peak current seen by Q2 when the device
O1
≤ 200 µA).
I-O
1-333

HCPL-3000
V
CC
GND
8
+
V
CC
-
I
F
7
R
Q2
Q1
L2
6
V
O2
5
V
O1
–
V
O1L
+
I
O1
1
I
F
2
3
4
HCPL-3000
V
CC
GND
8
+
V
CC
7
Q2
6
V
O2
Q1
-
–
V
O2H
I
+
O2
5
V
O1
1
2
3
4
Figure 2. Test Circuit for Low Level Output Voltage V
I
F
I
F
SWEEP
HCPL-3000
1
2
3
4
HCPL-3000
1
2
3
4
V
GND
V
GND
CC
8
+
V
CC
-
7
Q2
6
V
O2
Q1
V
CC
Q2
V
Q1
V
I
5
O1
O1L
O1L
.
8
+
V
CC
7
6
O2
5
O1
-
R
–
V
L2
O2
+
R
L1
Figure 6. Test Circuit for Threshold Input Current I
FLH
O1L
Figure 3. Test Circuit for High Level Output Voltage V
.
O2H
.
HCPL-3000
V
CC
GND
8
+
V
CC
-
7
Q2
V
Q1
I
6
O2
O2L
5
V
O1
.Figure 4. Test Circuit for Leakage Current I
O2L
1
I
F
2
3
4
Figure 5. Test Circuit for Leakage Current I
HCPL-3000
V
IN
I
F
t = t = 0.01µs
rf
Z = 50 Ω
o
47 Ω
1
2
3
4
V
GND
CC
8
7
Q2
6
V
O2
Q1
5
V
O1
+
V
CC
-
R
R
–
V
L2
O2
+
L1
50%
V WAVE FORM
IN
t
PLH
.
t
PHL
90%
50%
V WAVE FORM
02
10%
1-334
Figure 7. Test Circuit for t
, tr and tf.
PHL
t
f
t
r
, t
PLH

I
F
SW
AB
V
CM
CM , V
HO2
SW AT A, I = 5 mA
F
CM , V
LO2
SW AT B, I = 0 mA
F
HCPL-3000
1
2
3
4
∆ V
V
V
GND
CM
O2L
CC
8
V
V
CC
–
O2
+
V
GND
V
V
GND
CM
O2L
O2H
+
-
30
25
F
20
15
10
5
LED FORWARD CURRENT I (mA)
0
-20 0 25 50 75
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE T (°C)
100
80
A
R
L1
7
Q2
Q1
–+
R
L2
6
V
O2
5
V
O1
∆ V
O2H
Figure 9. LED Forward Current vs. Ambient Temperature.Figure 8. Test Circuit for CMH and CML.
600
(mW)
o
500
400
300
200
100
IC OUTPUT POWER DISSIPATION P
0
-20 0 25 50 75
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE TA (°C)
100
80
Figure 10. Maximum IC Output Power
Dissipation vs. Ambient Temperature.
600
550
500
(mW)
tot
400
300
(LED AND IC)
200
100
TOTAL POWER DISSIPATION P
0
-20 0 25 50 75
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE T
80
(°C)
A
Figure 11. Maximum Total Power
Dissipation vs. Ambient Temperature.
10.0
5.0
02P
I MAX (PULSE)
02
2.0
1.0
I MAX (CONTINUOUS)
02
0.5
0.2
PEAK OUTPUT 2 CURRENT I (A)
0.1
100
0.2 0.5 1.0 2.0 5.0 10.0 20.0
DC (T = 80°C)
100 ms•
10 ms• 1 ms•
A
V (MAX)
CC
OUTPUT 2 VOLTAGE V (V)
Figure 12. Typical Peak Output 2
Current vs. Output 2 Voltage (Safe
Operating Area Q2).
• SINGLE OSC.
PULSE
T = 25°C
A
I •
S
DC
02
1-335

500
TA = 75°C
200
50°C
25°C
100
(mA)
F
0°C
50
-20°C
20
10
5
FORWARD CURRENT I
2
1
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
FORWARD VOLTAGE V
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.9
0.8
NORMALIZED THRESHOLD INPUT CURRENT
3.5
(V)
F
0.7
4
6 8 10 12 14
SUPPLY VOLTAGE V (V)
T = 25°C
A
CC
1.6
VCC = 6 V
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
NORMALIZED THRESHOLD INPUT CURRENT
0.6
-25 0 25 50 75 100
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE TA (°C)
Figure 13. Typical Forward Current
vs. Forward Voltage.
0.4
(V)
01L
LOW LEVEL OUTPUT 1 VOLTAGE V
V = 6 V
CC
R = 10 Ω
L2
0.2
T = 25°C
A
I = 5 mA
0.1
F
0.05
0.02
0.01
0.005
0.01 0.02 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.5 1.0
OUTPUT 1 CURRENT I
(A)
01
Figure 16. Typical Low Level Output 1
Voltage vs. Output 1 Current.
Figure 14. Normalized Low to High
Threshold Input Current vs. Supply
Voltage.
0.5
01L
0.4
0.3
I = 0.5 A
01
0.4 A
0.2
0.1
0.1 A
LOW LEVEL OUTPUT 1 VOLTAGE V (V)
0
-25 0 25 50 75 100
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE T (°C)
V = 6 V
CC
R = 10 Ω
L2
I = 5 mA
F
A
Figure 17. Typical Low Level Output 1
Voltage vs. Ambient Temperature.
Figure 15. Normalized Low to High
Threshold Input Current vs. Ambient
Temperature.
5.4
02L
5.3
5.2
5.1
5.0
4.9
HIGH LEVEL OUTPUT 2 VOLTAGE V (V)
4.8
0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.3 -0.4 -0.5 -0.6
OUTPUT 2 CURRENT I (A)
V = 6 V
CC
T = 25°C
A
I = 5 mA
F
02
Figure 18. Typical High Level Output 2
Voltage vs. Output 2 Current.
5.4
(V)
02H
5.3
I = -0.1 A
5.2
5.1
5.0
4.9
HIGH LEVEL OUTPUT 2 VOLTAGE V
4.8
-25 0 25 50 75 100
O2
-0.4 A
-0.5 A
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE TA (°C)
V = 6 V
CC
I = 5 mA
F
Figure 19. Typical High Level Output 2
Voltage vs. Ambient Temperature.
1-336
0.4
V = 6 V
CC
T = 25°C
A
02L
0.2
I = 0 mA
F
0.1
0.05
0.02
0.01
0.005
LOW LEVEL OUTPUT 2 VOLTAGE V (V)
0.01 0.02 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.5 1.0
OUTPUT 2 CURRENT I (A)
02
Figure 20. Typical Low Level Output 2
Voltage vs. Output 2 Current.
0.5
02L
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
LOW LEVEL OUTPUT 2 VOLTAGE V (V)
0
-25 0 25 50 75 100
I = 0.6 A
O2
0.5 A
0.1 A
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE TA (°C)
V = 6 V
CC
I = 0 mA
F
Figure 21. Typical Low Level Output 2
Voltage vs. Ambient Temperature.

14
I = 5 mA
F
12
CCH
10
8
6
HIGH LEVEL SUPPLY CURRENT I (mA)
4
4 6 8 101214
SUPPLY VOLTAGE V (V)
T = -20°C
A
25°C
80°C
CC
16
I = 0 mA
F
14
CCL
12
10
8
LOW LEVEL SUPPLY CURRENT I (mA)
6
4 6 8 101214
SUPPLY VOLTAGE V (V)
T = -20°C
A
25°C
80°C
CC
6
5
PHL PLH
4
3
2
1
T = 80°C
PROPAGATION DELAY TIME t , t (µs)
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
A
FORWARD CURRENT I (mA)
V = 6 V
CC
R = 5 Ω
L1
R = 10 Ω
L2
I = 5 mA
F
t
PLH
25°C
T = 80°C
F
t
PHL
A
25°C
-20°C
-20°C
Figure 22. Typical High Level Supply
Current vs. Supply Voltage.
5
4
PHL PLH
3
2
1
PROPAGATION DELAY TIME t , t (µs)
0
-25 0 25 50 75 100
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE TA (°C)
V = 6 V
CC
R = 5 Ω
L1
R = 10 Ω
L2
I = 5 mA
F
t
PLH
t
PHL
Figure 25. Typical Propagation Delay
Time vs. Ambient Temperature.
Figure 23. Typical Low Level Supply
Current vs. Supply Voltage.
Figure 24. Typical Propagation Delay
Time vs. Forward Current.
1-337
 Loading...
Loading...