Page 1

HPE FlexNetwork MSR Router Series
Comware 7 Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide
Part number: 5998-8832
Software version: CMW710-R0305
Document version: 6PW106-20160308
Page 2

© Copyright 2016 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
The info
rmation contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for Hewlett Packard
Enterprise products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements acco mpanying such
products and services. Nothing herein should be construe d as constituting an additional warranty. Hewlett
Packard Enterprise shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions co ntained herein.
Confidential computer software. V alid license from Hewlett Packard Enterprise required for possession, use, or
copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software
Documentation, and T e chnical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor’s
standard commercial license.
Links to third-party websites take you outside the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website. Hewlett Packard
Enterprise has no control over and is not responsible for information outside the Hewlett Packard Enterprise
website.
Acknowledgments
Intel®, Itanium®, Pentium®, Intel Inside®, and the Intel Inside logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the
United States and other countries.
Microsoft® and Windows® are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies.
Adobe® and Acrobat® are trademarks of Adobe Systems In corporated.
Java and Oracle are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
UNIX® is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
i
Page 3

Contents
Configuring ARP ····························································································· 1
Overview ···························································································································································· 1
ARP message format ································································································································· 1
ARP operating mechanism ························································································································ 1
ARP table ··················································································································································· 2
Configuring a static ARP entry ··························································································································· 3
Setting the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries for a device ·································································· 4
Setting the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries for an interface ···························································· 4
Setting the aging timer for dynamic ARP entries ······························································································· 5
Enabling dynamic ARP entry check ··················································································································· 5
Enabling ARP logging ········································································································································ 5
Displaying and maintaining ARP ························································································································ 6
Configuration examples ····································································································································· 7
Long static ARP entry configuration example ···························································································· 7
Short static ARP entry configuration example ···························································································· 8
Configuring gratuitous ARP ············································································ 9
Overview ···························································································································································· 9
Gratuitous ARP packet learning ················································································································· 9
Periodic sending of gratuitous ARP packets ······························································································ 9
Configuration procedure ·································································································································· 10
Enabling IP conflict notification ························································································································ 10
Configuring proxy ARP ················································································· 12
Enabling common proxy ARP ·························································································································· 12
Enabling local proxy ARP ································································································································ 12
Displaying proxy ARP ······································································································································ 13
Common proxy ARP configuration example ···································································································· 13
Network requirements ······························································································································ 13
Configuration procedure ··························································································································· 13
Verifying the configuration ························································································································ 14
Configuring ARP fast-reply ··········································································· 15
Overview ·························································································································································· 15
Configuration procedure ·································································································································· 15
ARP fast-reply configuration example ·············································································································· 15
Network requirements ······························································································································ 15
Configuration procedure ··························································································································· 16
Configuring ARP PnP ··················································································· 17
Overview ·························································································································································· 17
Configuration prerequisites ······························································································································ 17
Configuration procedure ·································································································································· 17
Displaying and maintaining ARP PnP ·············································································································· 18
ARP PnP configuration example ······················································································································ 18
Network requirements ······························································································································ 18
Configuration procedure ··························································································································· 18
Verifying the configuration ························································································································ 19
Configuring ARP suppression ······································································· 20
Overview ·························································································································································· 20
Configuration procedure ·································································································································· 20
Displaying and maintaining ARP suppression ································································································· 21
ARP suppression configuration example ········································································································· 21
Network requirements ······························································································································ 21
Configuration procedure ··························································································································· 22
Verifying the configuration ························································································································ 22
i
Page 4

Configuring ARP direct route advertisement ················································· 23
Overview ·························································································································································· 23
Configuration procedure ·································································································································· 23
Configuring IP addressing ············································································· 24
Overview ·························································································································································· 24
IP address classes ··································································································································· 24
Special IP addresses ······························································································································· 25
Subnetting and masking ··························································································································· 25
Assigning an IP address to an interface ·········································································································· 25
Configuration guidelines ··························································································································· 26
Configuration procedure ··························································································································· 26
Configuring IP unnumbered ····························································································································· 26
Configuration guidelines ··························································································································· 26
Configuration prerequisites ······················································································································ 27
Configuration procedure ··························································································································· 27
Displaying and maintaining IP addressing ······································································································· 27
Configuration examples ··································································································································· 27
IP address configuration example ············································································································ 27
IP unnumbered configuration example ···································································································· 29
DHCP overview ····························································································· 31
DHCP address allocation ································································································································· 31
Allocation mechanisms ···························································································································· 31
IP address allocation process ·················································································································· 32
IP address lease extension ······················································································································ 32
DHCP message format ···································································································································· 33
DHCP options ·················································································································································· 34
Common DHCP options ··························································································································· 34
Custom DHCP options ····························································································································· 34
Protocols and standards ·································································································································· 36
Configuring the DHCP server ······································································· 37
Overview ·························································································································································· 37
DHCP address pool ································································································································· 37
IP address allocation sequence ··············································································································· 39
DHCP server configuration task list ················································································································· 39
Configuring an address pool on the DHCP server ··························································································· 40
Configuration task list ······························································································································· 40
Creating a DHCP address pool ················································································································ 40
Specifying IP address ranges for a DHCP address pool ········································································· 40
Specifying gateways for DHCP clients ····································································································· 43
Specifying a domain name suffix for DHCP clients ·················································································· 44
Specifying DNS servers for DHCP clients ································································································ 44
Specifying WINS servers and NetBIOS node type for DHCP clients ······················································· 44
Specifying BIMS server for DHCP clients ································································································ 45
Specifying the configuration file for DHCP client auto-configuration ························································ 45
Specifying a server for DHCP clients ······································································································· 46
Configuring Option 184 parameters for DHCP clients ············································································· 46
Customizing DHCP options ······················································································································ 47
Configuring the DHCP user class whitelist ······························································································· 48
Enabling DHCP ················································································································································ 49
Enabling the DHCP server on an interface ······································································································ 49
Applying an address pool on an interface ········································································································ 49
Configuring IP address conflict detection ········································································································· 50
Enabling handling of Option 82 ························································································································ 50
Configuring DHCP server compatibility ············································································································ 51
Configuring the DHCP server to broadcast all responses ········································································ 51
Configure the DHCP server to ignore BOOTP requests ·········································································· 51
Configuring the DHCP server to send BOOTP responses in RFC 1048 format ······································ 52
Setting the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP server ····························································· 52
ii
Page 5

Configuring DHCP binding auto backup ·········································································································· 52
Configuring address pool usage alarming ······································································································· 53
Binding gateways to a common MAC address ································································································ 53
Advertising subnets assigned to clients ··········································································································· 54
Applying a DHCP address pool to a VPN instance ·························································································· 55
Enabling client offline detection on the DHCP server ······················································································ 55
Configuring DHCP logging on the DHCP server ······························································································ 56
Displaying and maintaining the DHCP server ·································································································· 56
DHCP server configuration examples ·············································································································· 57
Static IP address assignment configuration example ·············································································· 57
Dynamic IP address assignment configuration example ········································································· 58
DHCP user class configuration example ·································································································· 60
DHCP user class whitelist configuration example ···················································································· 61
Primary and secondary subnets configuration example ·········································································· 62
DHCP option customization configuration example ················································································· 63
Troubleshooting DHCP server configuration ··································································································· 65
Symptom ·················································································································································· 65
Analysis ···················································································································································· 65
Solution ···················································································································································· 65
Configuring the DHCP relay agent ································································ 66
Overview ·························································································································································· 66
Operation ················································································································································· 66
DHCP relay agent support for Option 82 ································································································· 67
DHCP relay agent configuration task list ········································································································· 67
Enabling DHCP ················································································································································ 68
Enabling the DHCP relay agent on an interface ······························································································ 68
Specifying DHCP servers on a relay agent ······································································································ 68
Configuring the DHCP relay agent security functions ······················································································ 69
Enabling the DHCP relay agent to record relay entries ··········································································· 69
Enabling periodic refresh of dynamic relay entries ·················································································· 69
Enabling DHCP starvation attack protection ···························································································· 70
Configuring the DHCP relay agent to release an IP address ··········································································· 71
Configuring Option 82 ······································································································································ 71
Setting the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP relay agent ····················································· 72
Enabling DHCP server proxy on a DHCP relay agent ····················································································· 72
Configuring a DHCP relay address pool ·········································································································· 73
Specifying a gateway address for DHCP clients ······························································································ 74
Enabling client offline detection on the DHCP relay agent ·············································································· 74
Specifying the source address and gateway address in DHCP requests ························································ 74
Displaying and maintaining the DHCP relay agent ·························································································· 75
DHCP relay agent configuration examples ······································································································ 75
DHCP relay agent configuration example ································································································ 75
Option 82 configuration example ············································································································· 76
Troubleshooting DHCP relay agent configuration ···························································································· 77
Symptom ·················································································································································· 77
Analysis ···················································································································································· 77
Solution ···················································································································································· 77
Configuring the DHCP client ········································································· 78
Enabling the DHCP client on an interface ········································································································ 78
Configuring a DHCP client ID for an interface ································································································· 78
Enabling duplicated address detection ············································································································ 79
Setting the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP client ······························································ 79
Displaying and maintaining the DHCP client ··································································································· 79
DHCP client configuration example ················································································································· 80
Network requirements ······························································································································ 80
Configuration procedure ··························································································································· 80
Verifying the configuration ························································································································ 81
Configuring DHCP snooping ········································································· 83
Overview ·························································································································································· 83
iii
Page 6

Application of trusted and untrusted ports ································································································ 84
DHCP snooping support for Option 82 ····································································································· 85
Command and hardware compatibility ············································································································· 85
DHCP snooping configuration task list ············································································································· 85
Configuring basic DHCP snooping ·················································································································· 86
Configuring Option 82 ······································································································································ 86
Configuring DHCP snooping entry auto backup ······························································································ 87
Enabling DHCP starvation attack protection ···································································································· 88
Enabling DHCP-REQUEST attack protection ·································································································· 89
Setting the maximum number of DHCP snooping entries ··············································································· 89
Displaying and maintaining DHCP snooping ··································································································· 90
DHCP snooping configuration examples ········································································································· 90
Basic DHCP snooping configuration example ························································································· 90
Option 82 configuration example ············································································································· 91
Configuring the BOOTP client ······································································· 93
BOOTP application ·········································································································································· 93
Obtaining an IP address dynamically ··············································································································· 93
Protocols and standards ·································································································································· 93
Configuring an interface to use BOOTP for IP address acquisition ································································· 93
Displaying and maintaining BOOTP client ······································································································· 94
BOOTP client configuration example ··············································································································· 94
Network requirements ······························································································································ 94
Configuration procedure ··························································································································· 94
Verifying the configuration ························································································································ 94
Configuring DNS ··························································································· 95
Overview ·························································································································································· 95
Static domain name resolution ················································································································· 95
Dynamic domain name resolution ············································································································ 95
DNS proxy ················································································································································ 96
DNS spoofing ··········································································································································· 97
DNS configuration task list ······························································································································· 98
Configuring the IPv4 DNS client ······················································································································ 98
Configuring static domain name resolution ······························································································ 98
Configuring dynamic domain name resolution ························································································· 99
Configuring the IPv6 DNS client ······················································································································ 99
Configuring static domain name resolution ······························································································ 99
Configuring dynamic domain name resolution ······················································································· 100
Configuring the DNS proxy ···························································································································· 101
Configuring DNS spoofing ····························································································································· 101
Configuring network mode tracking for an output interface ··········································································· 102
Specifying the source interface for DNS packets ··························································································· 102
Configuring the DNS trusted interface ··········································································································· 103
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing DNS packets ······················································································· 103
Displaying and maintaining IPv4 DNS ··········································································································· 103
IPv4 DNS configuration examples ················································································································· 104
Static domain name resolution configuration example ··········································································· 104
Dynamic domain name resolution configuration example ······································································ 105
DNS proxy configuration example ·········································································································· 107
IPv6 DNS configuration examples ················································································································· 108
Static domain name resolution configuration example ··········································································· 108
Dynamic domain name resolution configuration example ······································································ 109
DNS proxy configuration example ·········································································································· 114
Troubleshooting IPv4 DNS configuration ······································································································· 115
Symptom ················································································································································ 115
Solution ·················································································································································· 115
Troubleshooting IPv6 DNS configuration ······································································································· 115
Symptom ················································································································································ 115
Solution ·················································································································································· 115
iv
Page 7

Configuring DDNS ······················································································ 116
Overview ························································································································································ 116
DDNS application ··································································································································· 116
DDNS client configuration task list ················································································································· 117
Configuring a DDNS policy ···························································································································· 117
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 118
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 118
Applying the DDNS policy to an interface ······································································································ 119
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing DDNS packets ····················································································· 119
Displaying DDNS ··········································································································································· 120
DDNS configuration examples ······················································································································· 120
DDNS configuration example with www.3322.org ················································································· 120
DDNS configuration example with PeanutHull server ············································································ 121
Configuring NAT ························································································· 123
Overview ························································································································································ 123
Terminology ··········································································································································· 123
NAT types ·············································································································································· 123
NAT control ············································································································································ 124
Command and hardware compatibility ··········································································································· 124
NAT implementations ····································································································································· 124
Static NAT ·············································································································································· 124
Dynamic NAT ········································································································································· 124
NAT Server ············································································································································ 125
DS-Lite NAT444 ····································································································································· 126
NAT entries ···················································································································································· 126
NAT session entry ·································································································································· 126
EIM entry ················································································································································ 127
NO-PAT entry ········································································································································· 127
Using NAT with other features ······················································································································· 127
VRF-aware NAT ····································································································································· 127
NAT with DNS mapping ························································································································· 128
NAT with ALG ········································································································································ 128
NAT configuration task list ····························································································································· 129
Configuring static NAT ··································································································································· 129
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 129
Configuring outbound one-to-one static NAT ························································································· 129
Configuring outbound net-to-net static NAT ··························································································· 130
Configuring inbound one-to-one static NAT ··························································································· 130
Configuring inbound net-to-net static NAT ····························································································· 131
Configuring dynamic NAT ······························································································································ 131
Configuration restrictions and guidelines ······························································································· 132
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 132
Configuring outbound dynamic NAT ······································································································ 132
Configuring inbound dynamic NAT ········································································································ 133
Configuring NAT Server ································································································································· 134
Configuring common NAT Server ·········································································································· 134
Configuring load sharing NAT Server ···································································································· 135
Configuring ACL-based NAT Server ······································································································ 136
Configuring DS-Lite NAT444 ························································································································· 136
Configuring NAT with DNS mapping ·············································································································· 137
Configuring NAT hairpin ································································································································· 137
Configuring NAT with ALG ····························································································································· 138
Configuring NAT session logging ··················································································································· 138
Displaying and maintaining NAT ···················································································································· 138
NAT configuration examples ·························································································································· 140
Outbound one-to-one static NAT configuration example ······································································· 140
Outbound dynamic NAT configuration example (non-overlapping addresses) ······································ 141
Outbound bidirectional NAT configuration example ··············································································· 144
NAT Server for external-to-internal access configuration example ························································ 147
NAT Server for external-to-internal access through domain name configuration example ···················· 150
v
Page 8

Bidirectional NAT for external-to-internal NAT Server access through domain name configuration example
······························································································································································· 153
NAT hairpin in C/S mode configuration example ··················································································· 156
NAT hairpin in P2P mode configuration example ·················································································· 159
Twice NAT configuration example ········································································································· 162
Load sharing NAT Server configuration example ·················································································· 165
NAT with DNS mapping configuration example ····················································································· 167
DS-Lite NAT444 configuration example ································································································· 170
Basic IP forwarding on the device ······························································· 173
FIB table ························································································································································· 173
Displaying FIB table entries ··························································································································· 174
Configuring load sharing ············································································· 175
Command and hardware compatibility ··········································································································· 175
Configuring per-packet or per-flow load sharing ···························································································· 175
Configuring load sharing based on bandwidth ······························································································· 176
Configuring fast forwarding ········································································· 177
Overview ························································································································································ 177
Command and hardware compatibility ··········································································································· 177
Configuring the aging time for fast forwarding entries ··················································································· 177
Configuring fast forwarding load sharing ······································································································· 177
Displaying and maintaining fast forwarding ··································································································· 178
Configuring flow classification ····································································· 179
Feature and hardware compatibility ··············································································································· 179
Specifying a flow classification policy ············································································································ 179
Displaying the adjacency table ··································································· 180
Overview ························································································································································ 180
Command and hardware compatibility ··········································································································· 181
Displaying commands ···································································································································· 181
Configuring IRDP ························································································ 182
Overview ························································································································································ 182
IRDP operation ······································································································································· 182
Basic concepts ······································································································································· 182
Protocols and standards ························································································································ 183
Configuration procedure ································································································································ 183
IRDP configuration example ·························································································································· 184
Network requirements ···························································································································· 184
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 184
Verifying the configuration ······················································································································ 185
Optimizing IP performance ········································································· 186
Command and hardware compatibility ··········································································································· 186
Enabling an interface to receive and forward directed broadcasts destined for the directly connected network
······································································································································································· 186
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 186
Configuration example ··························································································································· 187
Configuring MTU for an interface ··················································································································· 188
Configuring TCP MSS for an interface ··········································································································· 188
Configuring TCP path MTU discovery ··········································································································· 188
Enabling TCP SYN Cookie ···························································································································· 189
Configuring the TCP buffer size ····················································································································· 190
Configuring TCP timers ·································································································································· 190
Enabling sending ICMP error messages ······································································································· 190
Configuring rate limit for ICMP error messages ····························································································· 192
Specifying the source address for ICMP packets ·························································································· 192
Enabling IPv4 local fragment reassembly ······································································································ 193
Displaying and maintaining IP performance optimization ·············································································· 193
vi
Page 9

Configuring UDP helper ·············································································· 196
Overview ························································································································································ 196
Feature and hardware compatibility ··············································································································· 196
Configuration restrictions and guidelines ······································································································· 196
Configuring UDP helper to convert broadcast to unicast ··············································································· 196
Configuring UDP helper to convert broadcast to multicast ············································································ 197
Configuring UDP helper to convert multicast to broadcast or unicast ···························································· 198
Displaying and maintaining UDP helper ········································································································ 199
UDP helper configuration examples ·············································································································· 199
Configuring UDP helper to convert broadcast to unicast ······································································· 199
Configuring UDP helper to convert broadcast to multicast ···································································· 200
Configuring UDP helper to convert multicast to broadcast ···································································· 201
Configuring basic IPv6 settings ··································································· 202
Overview ························································································································································ 202
IPv6 features ·········································································································································· 202
IPv6 addresses ······································································································································ 203
IPv6 ND protocol ···································································································································· 205
IPv6 path MTU discovery ······················································································································· 207
IPv6 transition technologies ··························································································································· 208
Dual stack ·············································································································································· 208
Tunneling ··············································································································································· 208
NAT-PT ·················································································································································· 209
6PE ························································································································································ 209
Protocols and standards ································································································································ 209
Compatibility information ································································································································ 210
Command and hardware compatibility ··································································································· 210
IPv6 basics configuration task list ·················································································································· 210
Assigning IPv6 addresses to interfaces ········································································································· 211
Configuring an IPv6 global unicast address ··························································································· 211
Configuring an IPv6 link-local address ··································································································· 213
Configuring an IPv6 anycast address ···································································································· 214
Configuring IPv6 ND ······································································································································ 214
Configuring a static neighbor entry ········································································································ 214
Setting the maximum number of dynamic neighbor entries ··································································· 215
Setting the aging timer for ND entries in stale state ··············································································· 215
Minimizing link-local ND entries ············································································································· 216
Setting the hop limit ································································································································ 216
Configuring parameters for RA messages ····························································································· 216
Configuring the maximum number of attempts to send an NS message for DAD ································· 218
Enabling ND proxy ································································································································· 219
Configuring IPv6 ND suppression ·········································································································· 220
Configuring IPv6 ND direct route advertisement ···················································································· 221
Configuring path MTU discovery ···················································································································· 222
Configuring the interface MTU ··············································································································· 222
Configuring a static path MTU for an IPv6 address ··············································································· 223
Configuring the aging time for dynamic path MTUs ··············································································· 223
Controlling sending ICMPv6 messages ········································································································· 223
Configuring the rate limit for ICMPv6 error messages ··········································································· 223
Enabling replying to multicast echo requests ························································································· 224
Enabling sending ICMPv6 destination unreachable messages ····························································· 224
Enabling sending ICMPv6 time exceeded messages ············································································ 225
Enabling sending ICMPv6 redirect messages ······················································································· 225
Specifying the source address for ICMPv6 packets ··············································································· 225
Enabling IPv6 local fragment reassembly ······································································································ 226
Configuring IPv6 load sharing based on bandwidth ······················································································· 226
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 basics ········································································································· 227
IPv6 configuration examples ·························································································································· 230
Basic IPv6 configuration example ·········································································································· 230
IPv6 ND suppression configuration example ························································································· 234
Troubleshooting IPv6 basics configuration ···································································································· 235
vii
Page 10

Symptom ················································································································································ 235
Solution ·················································································································································· 235
DHCPv6 overview ······················································································· 236
Feature and hardware compatibility ··············································································································· 236
DHCPv6 address/prefix assignment ·············································································································· 236
Rapid assignment involving two messages ··························································································· 236
Assignment involving four messages ····································································································· 236
Address/prefix lease renewal ························································································································· 237
Stateless DHCPv6 ········································································································································· 238
Protocols and standards ································································································································ 238
Configuring the DHCPv6 server ·································································· 240
Overview ························································································································································ 240
IPv6 address assignment ······················································································································· 240
IPv6 prefix assignment ··························································································································· 240
Concepts ················································································································································ 241
DHCPv6 address pool ···························································································································· 241
IPv6 address/prefix allocation sequence ································································································ 242
Configuration task list ····································································································································· 243
Configuring IPv6 prefix assignment ··············································································································· 243
Configuration guidelines ························································································································· 243
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 244
Configuring IPv6 address assignment ··········································································································· 244
Configuration guidelines ························································································································· 245
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 245
Configuring network parameters assignment ································································································ 246
Configuring network parameters in a DHCPv6 address pool ································································· 246
Configuring network parameters in a DHCPv6 option group ································································· 247
Configuring the DHCPv6 server on an interface ···························································································· 247
Configuration guidelines ························································································································· 247
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 248
Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 server ··················································· 248
Configuring DHCPv6 binding auto backup ···································································································· 248
Advertising subnets assigned to clients ········································································································· 249
Applying a DHCPv6 address pool to a VPN instance ···················································································· 250
Configuring DHCPv6 logging on the DHCPv6 server ···················································································· 250
Displaying and maintaining the DHCPv6 server ···························································································· 251
DHCPv6 server configuration examples ········································································································ 252
Dynamic IPv6 prefix assignment configuration example········································································ 252
Dynamic IPv6 address assignment configuration example ···································································· 254
Configuring the DHCPv6 relay agent ·························································· 257
Overview ························································································································································ 257
DHCPv6 relay agent configuration task list ···································································································· 258
Enabling the DHCPv6 relay agent on an interface ························································································ 258
Specifying DHCPv6 servers on the relay agent ····························································································· 258
Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 relay agent ··········································· 259
Specifying a padding mode for the Interface-ID option ·················································································· 259
Configuring a DHCPv6 relay address pool ···································································································· 260
Specifying a gateway address for DHCPv6 clients ························································································ 260
Displaying and maintaining the DHCPv6 relay agent ···················································································· 261
DHCPv6 relay agent configuration example ·································································································· 261
Network requirements ···························································································································· 261
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 262
Verifying the configuration ······················································································································ 262
Configuring the DHCPv6 client ··································································· 264
Overview ························································································································································ 264
Configuration restrictions and guidelines ······································································································· 264
DHCPv6 client configuration task list ············································································································· 264
Configuring IPv6 address acquisition ············································································································· 264
viii
Page 11

Configuring IPv6 prefix acquisition ················································································································· 265
Configuring IPv6 address and prefix acquisition ···························································································· 265
Configuring stateless DHCPv6 ······················································································································ 265
Setting the DSCP value for DHCPv6 packets sent by the DHCPv6 client ····················································· 265
Displaying and maintaining DHCPv6 client ···································································································· 266
DHCPv6 client configuration examples ·········································································································· 266
IPv6 address acquisition configuration example ···················································································· 266
IPv6 prefix acquisition configuration example ························································································ 268
IPv6 address and prefix acquisition configuration example ··································································· 269
Stateless DHCPv6 configuration example ····························································································· 271
Configuring DHCPv6 snooping ··································································· 274
Overview ························································································································································ 274
Application of trusted and untrusted ports ······························································································ 274
Command and hardware compatibility ··········································································································· 275
Implementation of Option 18 and Option 37 ·································································································· 275
Option 18 for DHCPv6 snooping ············································································································ 275
DHCPv6 snooping support for Option 37 ······························································································· 276
DHCPv6 snooping configuration task list ······································································································· 276
Configuring basic DHCPv6 snooping ············································································································· 277
Configuring Option 18 and Option 37 ············································································································ 277
Configuring DHCPv6 snooping entry auto backup ························································································ 278
Setting the maximum number of DHCPv6 snooping entries ·········································································· 279
Enabling DHCPv6-REQUEST check ············································································································· 279
Displaying and maintaining DHCPv6 snooping ····························································································· 280
DHCPv6 snooping configuration example ····································································································· 280
Network requirements ···························································································································· 280
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 281
Verifying the configuration ······················································································································ 281
Configuring IPv6 fast forwarding ································································· 282
Overview ························································································································································ 282
Compatibility information ································································································································ 282
Command and hardware compatibility ··································································································· 282
Configuring the aging time for IPv6 fast forwarding entries ··········································································· 282
Configuring IPv6 fast forwarding load sharing ······························································································· 283
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 fast forwarding ··························································································· 283
Configuring tunneling ·················································································· 284
Overview ························································································································································ 284
IPv6 over IPv4 tunneling ························································································································ 284
IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling ························································································································ 286
IPv4 over IPv6 tunneling ························································································································ 287
IPv6 over IPv6 tunneling ························································································································ 291
Protocols and standards ························································································································ 291
Compatibility information ································································································································ 292
Feature and hardware compatibility ······································································································· 292
Command and hardware compatibility ··································································································· 292
Tunneling configuration task list ····················································································································· 292
Configuring a tunnel interface ························································································································ 292
Configuring an IPv6 over IPv4 manual tunnel ································································································ 294
Configuration example ··························································································································· 295
Configuring an automatic IPv4-compatible IPv6 tunnel ················································································· 297
Configuration example ··························································································································· 297
Configuring a 6to4 tunnel ······························································································································· 298
6to4 tunnel configuration example ········································································································· 299
6to4 relay configuration example ··········································································································· 301
Configuring an ISATAP tunnel ······················································································································· 303
Configuration example ··························································································································· 304
Configuring an IPv4 over IPv4 tunnel ············································································································ 306
Configuration example ··························································································································· 307
Configuring an IPv4 over IPv6 manual tunnel ································································································ 308
ix
Page 12

Configuration example ··························································································································· 309
Configuring a DS-Lite tunnel ·························································································································· 311
Configuration example ··························································································································· 312
Configuring an IPv6 over IPv6 tunnel ············································································································ 314
Configuration example ··························································································································· 315
Displaying and maintaining tunneling configuration ······················································································· 316
Troubleshooting tunneling configuration ········································································································ 317
Symptom ················································································································································ 317
Analysis ·················································································································································· 317
Solution ·················································································································································· 317
Configuring GRE ························································································· 318
Overview ························································································································································ 318
GRE encapsulation format ····················································································································· 318
GRE tunnel operating principle ·············································································································· 318
GRE security mechanisms ····················································································································· 319
GRE application scenarios ····················································································································· 319
Protocols and standards ························································································································ 321
Configuring a GRE/IPv4 tunnel ······················································································································ 322
Configuration guidelines ························································································································· 322
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 322
Configuring a GRE/IPv6 tunnel ······················································································································ 323
Configuration guidelines ························································································································· 324
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 324
Displaying and maintaining GRE ··················································································································· 325
GRE configuration examples ························································································································· 326
Configuring an IPv4 over IPv4 GRE tunnel ···························································································· 326
Configuring an IPv4 over IPv6 GRE tunnel ···························································································· 328
Troubleshooting GRE ···································································································································· 330
Symptom ················································································································································ 330
Analysis ·················································································································································· 330
Solution ·················································································································································· 331
Configuring ADVPN ···················································································· 332
Overview ························································································································································ 332
ADVPN structures ·································································································································· 332
How ADVPN operates ···························································································································· 334
NAT traversal ········································································································································· 337
ADVPN configuration task list ························································································································ 337
Configuring AAA ············································································································································ 337
Configuring the VAM server ··························································································································· 337
Creating an ADVPN domain ·················································································································· 338
Enabling the VAM server ······················································································································· 338
Configuring a pre-shared key for the VAM server ·················································································· 338
Configuring hub groups ·························································································································· 339
Configuring the port number of the VAM server ····················································································· 340
Specifying authentication and encryption algorithms for the VAM server ·············································· 341
Configuring an authentication method ··································································································· 341
Configuring keepalive parameters ········································································································· 341
Configuring the retry timer ······················································································································ 342
Configuring the VAM client ···························································································································· 342
Creating a VAM client ···························································································································· 343
Enabling VAM clients ····························································································································· 343
Specifying VAM servers ························································································································· 343
Specifying an ADVPN domain for a VAM client ····················································································· 343
Configuring a pre-shared key for a VAM client ······················································································ 344
Setting the retry timer and retry times for a VAM client ·········································································· 344
Setting the dumb timer for a VAM client ································································································· 344
Configuring a username and password for a VAM client ······································································· 345
Configuring an ADVPN tunnel interface ········································································································· 345
Configuring routing ········································································································································· 347
Configuring IPsec for ADVPN tunnels ··········································································································· 347
x
Page 13

Displaying and maintaining ADVPN ··············································································································· 347
ADVPN configuration examples ····················································································································· 349
IPv4 full-mesh ADVPN configuration example ······················································································· 349
IPv6 full-mesh ADVPN configuration example ······················································································· 356
IPv4 hub-spoke ADVPN configuration example ····················································································· 364
IPv6 hub-spoke ADVPN configuration example ····················································································· 372
IPv4 multi-hub-group ADVPN configuration example ············································································ 379
IPv6 multi-hub-group ADVPN configuration example ············································································ 393
IPv4 full-mesh NAT traversal ADVPN configuration example ································································ 408
Configuring WAAS ······················································································ 417
Overview ························································································································································ 417
TFO ························································································································································ 417
DRE ························································································································································ 418
LZ compression ······································································································································ 418
Command and hardware compatibility ··········································································································· 419
Protocols and standards ································································································································ 419
WAAS configuration task list ·························································································································· 419
Configuring a WAAS class ····························································································································· 419
Configuring a WAAS policy ···························································································································· 420
Applying a WAAS policy to an interface ········································································································· 420
Configuring TFO parameters ························································································································· 421
Configuring the TFO blacklist autodiscovery feature ····················································································· 421
Deleting all WAAS settings ···························································································································· 422
Restoring predefined WAAS settings ············································································································· 422
Displaying and maintaining WAAS ················································································································ 422
WAAS configuration examples ······················································································································ 423
Predefined WAAS policy configuration example ···················································································· 423
User-defined WAAS policy configuration example ················································································· 425
Configuring AFT ·························································································· 429
Overview ························································································································································ 429
Compatibility information ································································································································ 429
Command and hardware compatibility ··································································································· 429
AFT implementations ····································································································································· 429
Static AFT ·············································································································································· 429
Dynamic AFT ········································································································································· 429
Prefix translation ···································································································································· 430
AFT internal server ································································································································· 431
AFT translation process ································································································································· 431
For IPv6-initiated communication ··········································································································· 431
For IPv4-initiated communication ··········································································································· 432
AFT with ALG ················································································································································· 433
AFT configuration task list ······························································································································ 433
For IPv6-initiated communication ··········································································································· 433
For IPv4-initiated communication ··········································································································· 434
Enabling AFT ················································································································································· 434
Configuring an IPv6-to-IPv4 destination address translation policy ······························································· 434
Configuring an IPv6-to-IPv4 source address translation policy ····································································· 435
Configuring an IPv4-to-IPv6 destination address translation policy ······························································· 436
Configuring an IPv4-to-IPv6 source address translation policy ····································································· 436
Configuring AFT logging ································································································································ 437
Setting the ToS field to 0 for translated IPv4 packets ···················································································· 437
Setting the Traffic Class field to 0 for translated IPv6 packets ······································································· 437
Displaying and maintaining AFT ···················································································································· 437
AFT configuration examples ·························································································································· 439
Allowing IPv4 Internet access from an IPv6 network ············································································· 439
Providing FTP service from an IPv6 network to the IPv4 Internet ·························································· 442
Allowing mutual access between IPv4 and IPv6 networks ···································································· 443
Allowing IPv6 Internet access from an IPv4 network ············································································· 445
Providing FTP service from an IPv4 network to the IPv6 Internet ·························································· 448
xi
Page 14

Document conventions and icons ······························································· 451
Conventions ··················································································································································· 451
Network topology icons ·································································································································· 452
Support and other resources ······································································ 453
Accessing Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support ···························································································· 453
Accessing updates ········································································································································· 453
Websites ················································································································································ 454
Customer self repair ······························································································································· 454
Remote support ······································································································································ 454
Documentation feedback ······················································································································· 454
Index ··········································································································· 456
xii
Page 15
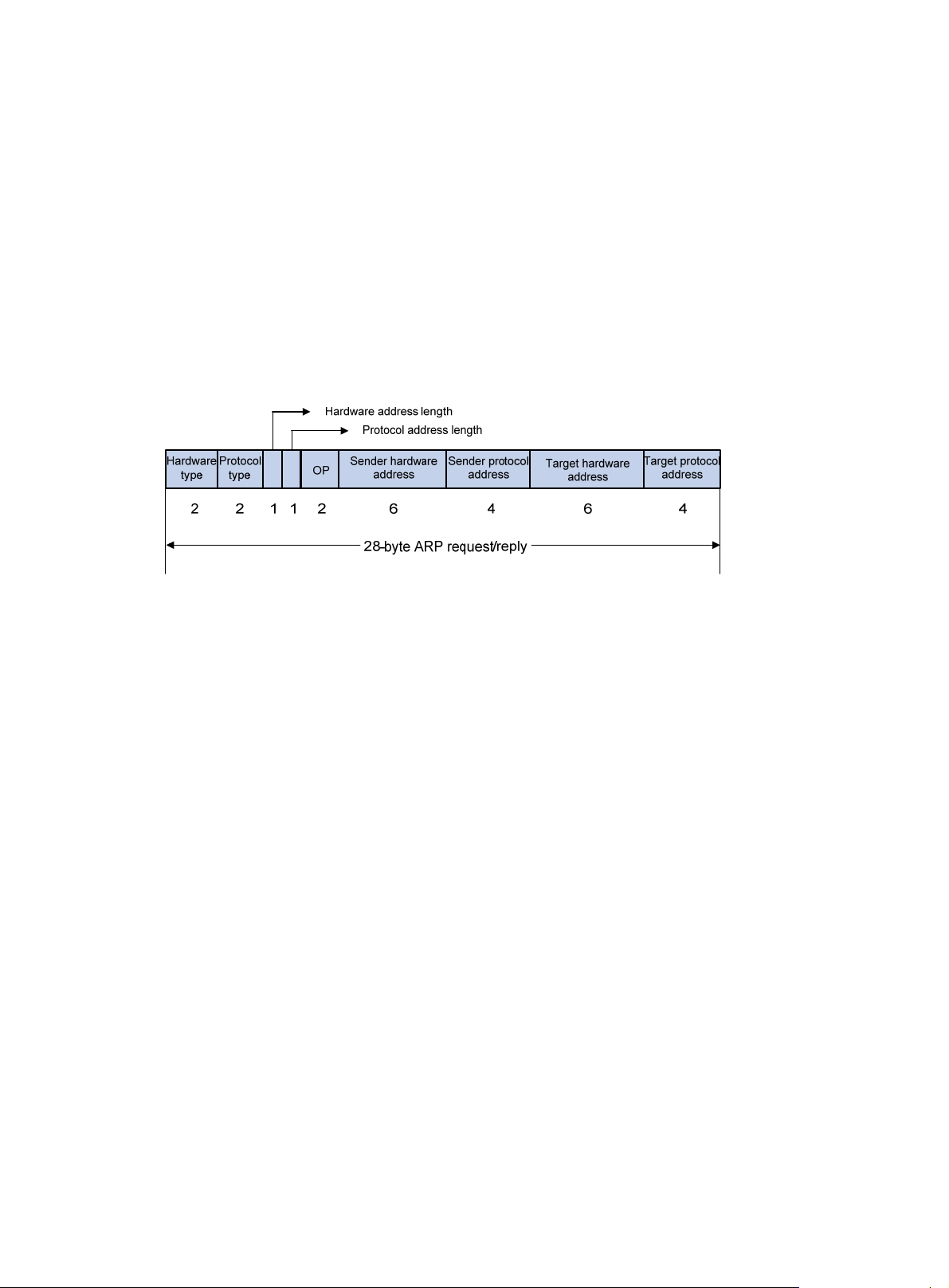
Configuring ARP
Overview
ARP resolves IP addresses into MAC addresses on Ethernet networks.
ARP message format
ARP uses two types of messages: ARP request and ARP reply. Figure 1 shows the format of ARP
request/reply messages. Numbers in the figure refer to field lengths.
Figure 1 ARP message format
• Hardware type—Hardware address type. The value 1 represents Ethernet.
• Protocol type—Type of the protocol address to be mapped. The hexadecimal value 0x0800
represents IP.
• Hardware address length and protocol address length— Length, in bytes, of a hardware
address and a protocol address. For an Ethernet address, the value of the hardware address
length field is 6. For an IPv4 address, the value of the protocol address length field is 4.
• OP—Operation code, which describes the type of ARP message. The value 1 represents an
ARP request, and the value 2 represents an ARP reply.
• Sender hardware address—Hardware address of the device sending the message.
• Sender protocol address—Protocol address of the device sendin g the message.
• Target hardware address—Hardware address of the device to which the message is being
sent.
• Target protocol address—Protocol address of the device to which the message is being sen t.
ARP operating mechanism
As shown in Figure 2, Host A and Host B are on the same subnet. Host A sends a packet to Host B as
follows:
1. Host A looks through the ARP table for an ARP entry for Host B. If one entry is found, Host A
uses the MAC address in the entry to encapsulate the IP packet into a data link layer frame.
Then Host A sends the frame to Host B.
2. If Host A finds no entry for Host B, Host A buffers the packet and broadcasts an ARP request.
The payload of the ARP request contains the following information:
{ Sender IP address and sender MAC address—Host A's IP address and MAC address.
{ Target IP address—Host B's IP address.
{ Target MAC address—An all-zero MAC address.
1
Page 16
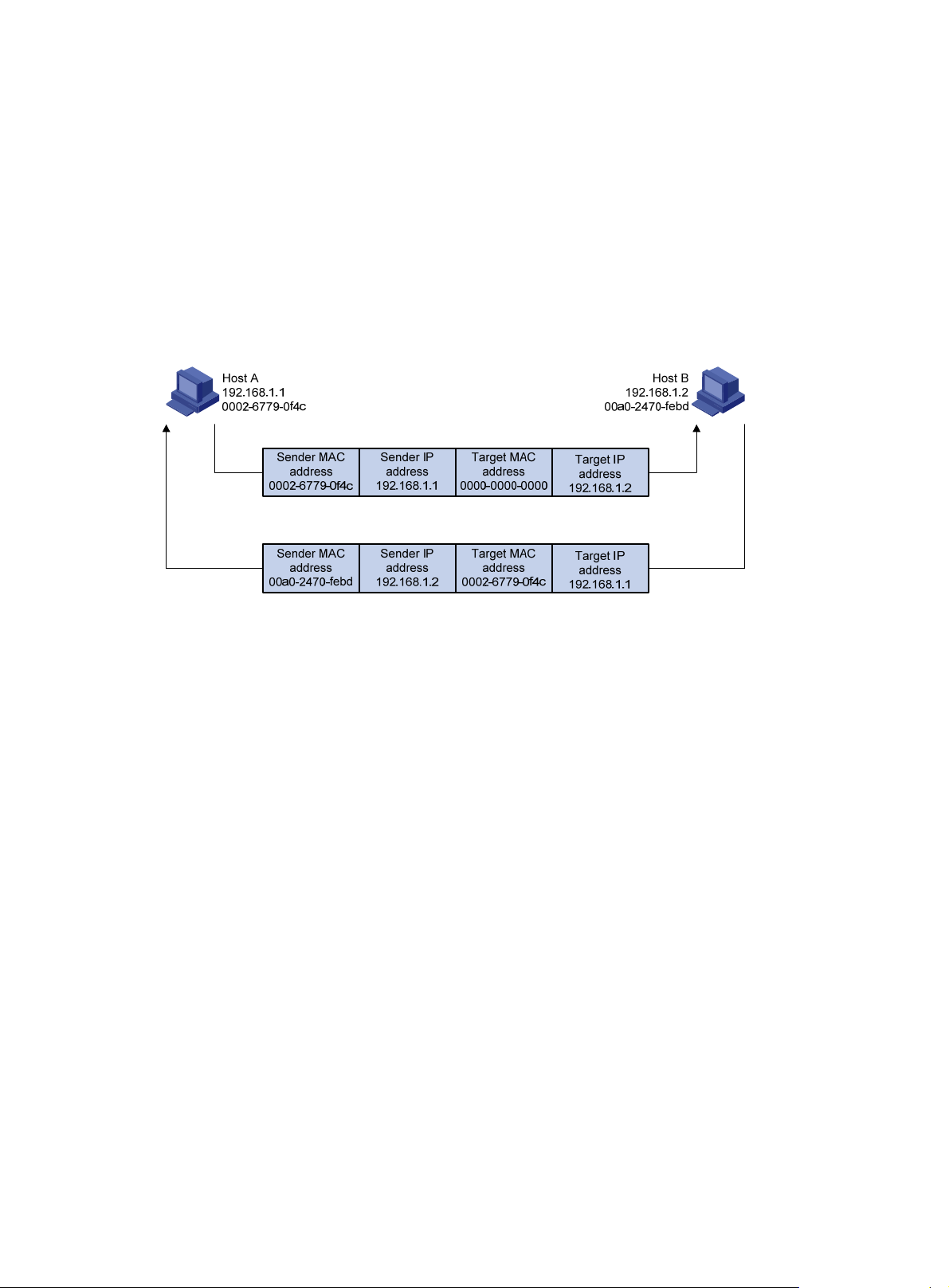
All hosts on this subnet can receive the broadcast request, but only the requested host (Host B)
processes the request.
3. Host B compares its own IP address with the target IP address in the ARP request. If they are
the same, Host B operates as follows:
a. Adds the sender IP address and sender MAC address into its ARP table.
b. Encapsulates its MAC add ress into an ARP reply.
c. Unicasts the ARP reply to Host A.
4. After receiving the ARP reply, Host A operates as follows:
a. Adds the MAC address of Host B into its ARP table.
b. Encapsulates the MAC add ress into the packet and sends the packet to Host B.
Figure 2 ARP address resolution process
If Host A and Host B are on different subnets, Host A sends a packet to Host B as follows:
1. Host A broadcasts an ARP request where the target IP address is the IP address of the
gateway.
2. The gateway responds with its MAC address in an ARP reply to Host A.
3. Host A uses the gateway's MAC address to encapsulate the packet, and then sends the packet
to the gateway.
4. If the gateway has an ARP entry for Host B, it forwards the packet to Host B directly. If not, the
gateway broadcasts an ARP request, in which the target IP address is the IP address of Host B.
5. After the gateway gets the MAC address of Host B, it sends the packet to Host B.
ARP table
An ARP table stores dynamic, static, OpenFlow, and Rule ARP entries.
Dynamic ARP entry
ARP automatically creates and updates dynamic entries. A dynamic ARP entry is removed when its
aging timer expires or the output interface goes down. In addition, a dynamic ARP entry can be
overwritten by a static ARP entry.
Static ARP entry
A static ARP entry is manually configured and maintained. It does not age out and cannot be
overwritten by any dynamic ARP entry.
Static ARP entries protect communication between devices because attack packets cannot modify
the IP-to-MAC mapping in a static ARP entry.
The device supports the following types of static ARP entries:
2
Page 17

• Long static ARP entry—It contains the IP address, MAC address, VLAN, and o utput interface.
It is directly used for forwarding packets.
• Short static ARP entry—It contains only the IP address and MAC address.
{ If the output interface is a Layer 3 Ethernet interface, the short ARP entry can be directly
used to forward packets.
{ If the output interface is a VLAN interface, the device sends an ARP request whose target IP
address is the IP address in the short entry. If the sender IP and MAC addresses in the
received ARP reply match the short static ARP entry, the device performs the following
operations:
− Adds the interface that received the ARP reply to the short static ARP entry.
− Uses the resolved short static ARP entry to forward IP packets.
To communicate with a host by using a fixed IP-to-MAC mapping, configure a short static ARP entry
on the device. To communicate with a host by using a fixed IP-to-MAC mapping through an interface
in a VLAN, configure a long static ARP entry on the device.
OpenFlow ARP entry
ARP creates OpenFlow ARP entries by learning from the OpenFlow module. An OpenFlow ARP
entry does not age out, and it cannot be updated. It can be overwritten by a static ARP entry. An
OpenFlow ARP entry can be used directly to forward packet s. For more information about OpenFlow ,
see OpenFlow Configuration Guide.
Rule ARP entry
ARP creates Rule ARP entries by learning from the IPoE or portal module. A Rule ARP entry does
not age out, and it cannot be updated. It can be overwritten by a static ARP entry. A Rule ARP entry
can be used directly to forward packets. For more information about IPoE, see Layer 2—WAN
Access Configuration Guide. For more information about portal, see Security Configuration Guide.
Configuring a static ARP entry
A static ARP entry is effective when the device functions correctly. If a VLAN or VLAN interface is
deleted, long static ARP entries in the VLAN are delet ed, and resolved short static ARP entries in the
VLAN become unresolved.
A resolved short static ARP entry becomes unresolved upon certain events. For example, it
becomes unresolved when the resolved output interface goes down.
A long static ARP entry is ineffective in either of the following situations:
• The IP address in the entry conflicts with a local IP address.
• No local interface has an IP address in the same subnet as the IP address in the ARP entry.
Follow these guidelines when you configure a long static ARP entry:
• The vlan-id argument must be the ID of an existing VLAN where the ARP entry resides. The
specified Ethernet interface must belong to that VLAN.
• The VLAN interface must be created. Its IP address and the IP address specified by the
ip-address argument must be on the same subnet.
To configure a static ARP entry:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
3
Page 18

Step Command Remarks
• Configure a long static ARP entry:
arp static ip-address mac-address
vlan-id interface-type
2. Configure a static ARP
entry.
interface-number [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
• Configure a short static ARP entry:
arp static ip-address mac-address
[ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no static ARP entry is
configured.
Setting the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries for a device
A device can dynamically learn ARP entries. To prevent a device from holding too many ARP entries,
you can set the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries that the device can learn. When the
maximum number is reached, the device stops learning ARP entries.
If you set a value lower than the number of existing dynamic ARP entries, the device does not
remove the existing entries unless they are aged out.
To set the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries for a device:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Set the maximum
number of dynamic
ARP entries for the
device.
system-view
arp max-learning-number
number
N/A
If the value for the number argument is set to
0, the device is disabled from learning
dynamic ARP entries.
Setting the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries for an interface
An interface can dynamically learn ARP entries. To prevent an interface from holding too many ARP
entries, you can set the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries that the interface can learn. Whe n
the maximum number is reached, the interface stops learning ARP entries.
You can set limits for both a Layer 2 interface and the VLAN interface for a permitted VLAN on the
Layer 2 interface. The Layer 2 interface learns an ARP entry only when neither limit is reached.
To set the maximum number of dynamic ARP entries for an interface:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Set the maximum number
of dynamic ARP entries for
the interface.
system-view
interface
interface-number
arp max-learning-num
number
interface-type
N/A
N/A
If the value of the number argument is
set to 0, the interface is disabled from
learning dynamic ARP entries.
4
Page 19
Setting the aging timer for dynamic ARP entries
Each dynamic ARP entry in the ARP table has a limited lifetime, called an aging timer. The aging
timer of a dynamic ARP entry is reset each time the dynamic ARP entry is updated. A dynamic ARP
entry that is not updated before its aging timer expires is deleted from the ARP table.
To set the aging timer for dynamic ARP entrie s:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Set the aging timer for
dynamic ARP entries.
system-view
arp timer aging
aging-time
N/A
By default, the aging time for dynamic ARP
entries is 20 minutes.
Enabling dynamic ARP entry check
The dynamic ARP entry check function disables the device from supporting dynamic ARP entries
that contain multicast MAC addresses. The device cannot learn dynamic ARP entries containing
multicast MAC addresses. You cannot manually add static ARP entries containing multicast MAC
addresses.
When dynamic ARP entry check is disabled, ARP entries containing multicast MAC addresses are
supported. The device can learn dynamic ARP entries containing m ulticast MAC addresses obtained
from the ARP packets sourced from a unicast MAC address. You can also manually add static ARP
entries containing multicast MAC addresses.
To enable dynamic ARP entry check:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable dynamic ARP entry
check.
system-view
arp check enable
Enabling ARP logging
This function enables a device to log ARP events when ARP cannot resolve IP addresses correctly.
The device can log the following ARP events:
• On a proxy ARP-disabled interface, the target IP address of a received ARP packet is not one of
the following IP addresses:
{ The IP address of the receiving interface.
{ The virtual IP address of the VRRP group.
{ The public IP address after NAT.
• The sender IP address of a received ARP reply conflicts with one of the following IP addresses:
{ The IP address of the receiving interface.
{ The virtual IP address of the VRRP group.
{ The public IP address after NAT.
N/A
By default, dynamic ARP entry check is
enabled.
The device sends ARP log messages to the informatio n center . You can use the info-center source
command to specify the log output rules for the information center. For more information about
information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
5
Page 20

To enable the ARP logging function:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable the ARP logging
function.
system-view
arp check log enable
Displaying and maintaining ARP
IMPORTANT:
Clearing ARP entries from the ARP table might cause communication failures. Make sure the entries
to be cleared do not affect current communications.
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
Task Command
Display ARP entries (centralized devices
in standalone mode).
display arp
interface-type interface-number ] [
[ [
all
|
dynamic
N/A
By default, ARP logging is disabled.
|
static
] |
count
vlan
verbose
|
vlan-id |
interface
]
Display ARP entries (distributed devices
in standalone mode/centralized devices in
IRF mode).
Display ARP entries (distributed devices
in IRF mode).
Display the ARP entry for an IP address
(centralized devices in standalone mode).
Display the ARP entry for an IP address
(distributed devices in standalone
mode/centralized devices in IRF mode).
Display the ARP entry for an IP address
(distributed devices in IRF mode).
Display the ARP entries for a VPN
instance.
Display the aging timer of dynamic ARP
entries.
Clear ARP entries from the ARP table
(centralized devices in standalone mode).
Clear ARP entries from the ARP table
(distributed devices in standalone
mode/centralized devices in IRF mode).
display arp
vlan-id |
verbose ]
display arp
slot
slot-number ] |
interface-number ] [
display arp
display arp
display arp
slot-number ] [
display arp vpn-instance
display arp timer aging
reset arp
interface-number |
reset arp
interface-number |
all
[ [
interface
all
[ [
ip-address [
ip-address [
ip-address [
verbose ]
all
dynamic
{
|
all
dynamic
{
|
dynamic
|
interface-type interface-number ] [
dynamic
|
vlan
count
verbose ]
slot
static }
slot
slot-number |
static
|
static
|
vlan-id |
verbose ]
|
slot-number ] [
chassis
vpn-instance-name [
interface
|
interface
|
slot
] [
chassis
] [
interface
chassis-number
interface-type
interface-type
static }
slot-number ] |
count
chassis-number
interface-type
verbose ]
slot
count ]
vlan
|
Clear ARP entries from the ARP table
(distributed devices in IRF mode).
reset arp
dynamic
6
all
{
|
interface
|
chassis
chassis-number
interface-type interface-number |
slot
slot-number |
static }
Page 21
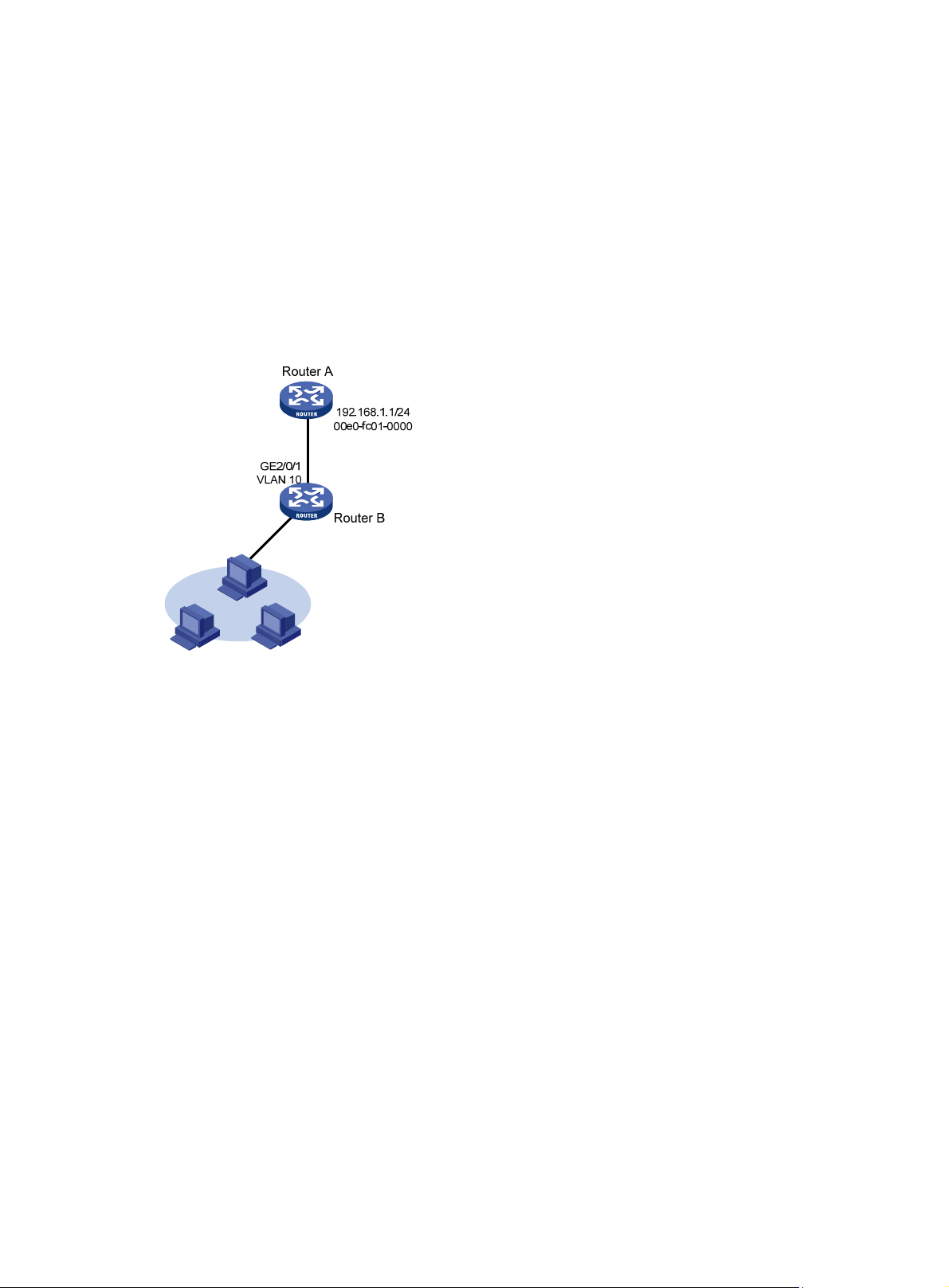
Configuration examples
Long static ARP entry configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 3, hosts are connected to Router B. Router B is connected to Router A through
interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 in VLAN 10.
To ensure secure communications between Router A and Router B, configure a long static ARP
entry for Router A on Router B.
Figure 3 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
# Create VLAN 10.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] vlan 10
[RouterB-vlan10] quit
# Add interface GigabitEthe rnet 2/0/1 to VLAN 10.
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] port access vlan 10
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create VLAN-interface 10 and configure its IP address.
[RouterB] interface vlan-interface 10
[RouterB-vlan-interface10] ip address 192.168.1.2 8
[RouterB-vlan-interface10] quit
# Configure a static ARP e ntry t hat has I P addres s 192.168. 1.1, M AC add ress 0 0e0-f c01-000 0, and
output interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 in VLAN 10.
[RouterB] arp static 192.168.1.1 00e0-fc01-0000 10 gigabitethernet 2/0/1
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Router B has a long static ARP entry for Router A.
[RouterB] display arp static
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule M-Multiport I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN Interface Aging Type
7
Page 22
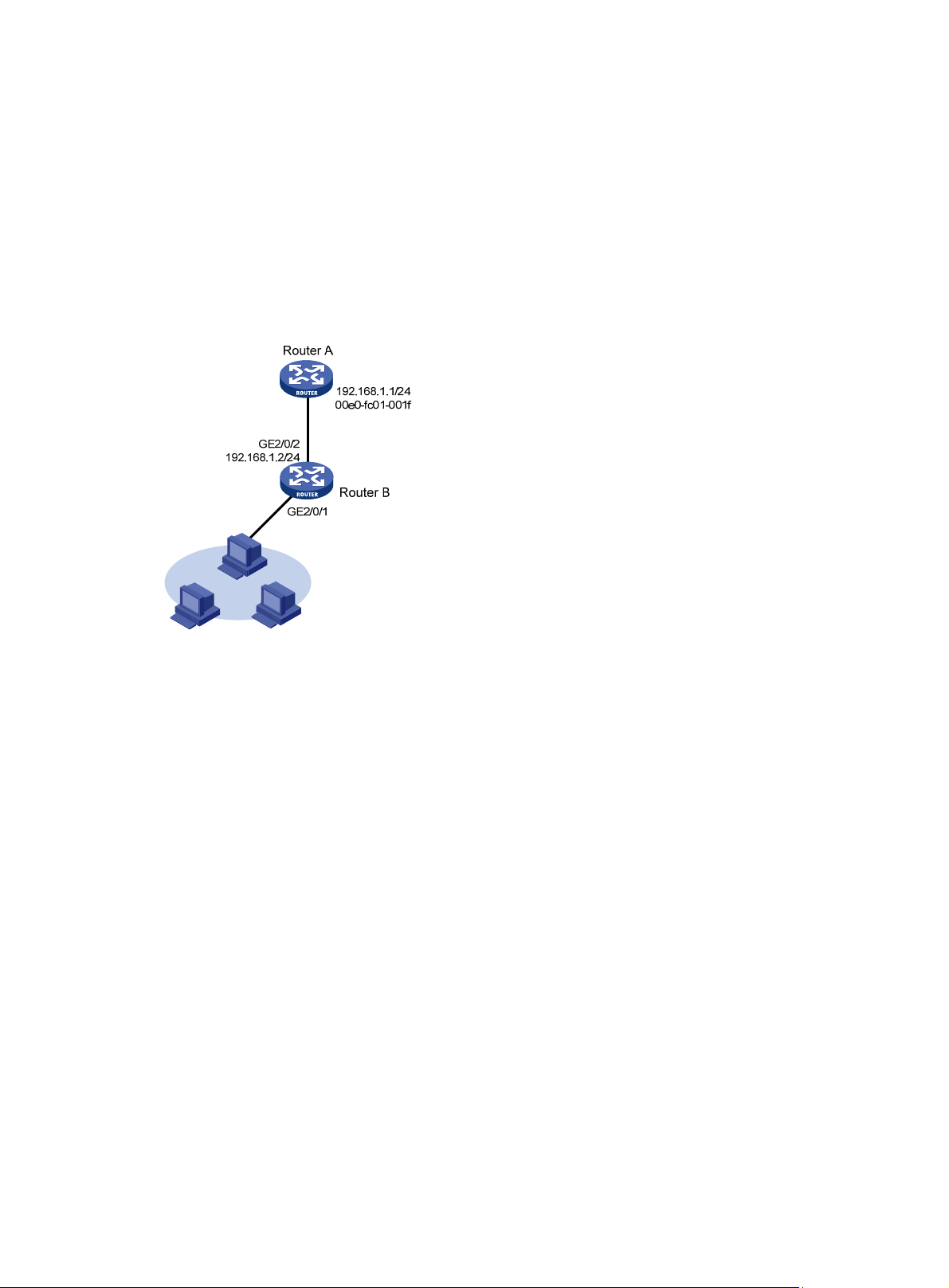
192.168.1.1 00e0-fc01-0000 10 GE2/0/1 N/A S
Short static ARP entry configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 4, hosts are connected to Router B. Router B is connected to Router A through
interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/2.
To ensure secure communications between Router A and Router B, configure a short static ARP
entry for Router A on Router B.
Figure 4 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
# Configure an IP address for GigabitEthernet 2/0/2.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] ip address 192.168.1.2/24
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] quit
# Configure a static ARP entry that has IP address 192.168.1.1 and MAC address 00e0-fc01-001f.
[RouterB] arp static 192.168.1.1 00e0-fc01-001f
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Router B has a sho rt static ARP entry for Router A.
[RouterB] display arp static
Type: S-Static D-Dynamic O-Openflow R-Rule M-Multiport I-Invalid
IP address MAC address VLAN Interface Aging Type
192.168.1.1 00e0-fc01-001f N/A N/A N/A S
8
Page 23

Configuring gratuitous ARP
Overview
In a gratuitous ARP packet, the sender IP address and the target IP address are the IP address of
the sending device.
A device sends a gratuitous ARP packet for either of the following purposes:
• Determine whether its IP address i s already used by another device. If the IP address is already
used, the device is informed of the conflict by an ARP reply.
• Inform other devices of a MAC address change.
Gratuitous ARP packet learning
This function enables a device to create or update ARP entries by using the sender IP and MAC
addresses in received gratuitous ARP packets.
When this function is disabled, the device uses received gratuitous ARP packets to update existing
ARP entries only. ARP entries are not created based on the received gratuito us ARP packets, which
saves ARP table space.
Periodic sending of gratuitous ARP packets
Enabling periodic sending of gratuitous ARP packets helps downstream devices update ARP entries
or MAC entries in a timely manner.
This feature can implement the following functions:
• Prevent gateway spoofing.
Gateway spoofing occurs when an attacker uses the gateway address to send gratuitous ARP
packets to the hosts on a network. The traffic destined for the gateway from the hosts is sent to
the attacker instead. As a result, the hosts cannot access the external network.
To prevent such gateway spoofing attacks, you can enable the gateway to send gratuitous ARP
packets at intervals. Gratuitous ARP packets contain the primary IP address and manually
configured secondary IP addresses of the gateway, so hosts can learn correct gateway
information.
• Prevent ARP entries from aging out.
If network traffic is heavy or if the host CPU usage is high, received ARP packets can be
discarded or are not promptly processed. Eventually, the dynamic ARP entries on the receiving
host age out. The traffic between the host and the corresponding devices is inte rrupted until the
host re-creates the ARP entries.
To prevent this problem, you can enable the gateway to send gratuitous ARP packets
periodically. Gratuitous ARP packets contain the primary IP address and manually configured
secondary IP addresses of the gateway, so the receiving hosts can update ARP entries in a
timely manner.
• Prevent the virtual IP address of a VRRP group from being used by a host.
The master router of a VRRP group can periodically send gratuitous ARP packets to the hosts
on the local network. The hosts can then update local ARP entries and avoid using the virtual IP
address of the VRRP group. The sender MAC address in the gratuitous ARP packet is the
virtual MAC address of the virtual router. For more information about VRRP, see High
Availability Configuration Guide.
9
Page 24
• Update MAC entries of devices in the VLANs having ambiguous Dot1q or QinQ termination
configured.
In VRRP configuration, if ambiguous Dot1q or QinQ termination is configured for multiple
VLANs and VRRP groups, interfaces configured with VLAN termination must be disabled from
transmitting broadcast/multicast packets. Also, a VRRP control VLAN must be configured so
that VRRP advertisements can be transmitted within the control VLAN only. I n such case s, you
can enable periodic sending of gratuitous ARP packets containing the following addresses:
{ The VRRP virtual IP address.
{ The primary IP address or a manually configured secondary IP address of the sending
interface on the subinterfaces.
When a VRRP f a il ov er o cc urs, d ev i ces in the VLANs can use the gratuitou s ARP packets to update
their corresponding MAC entries in a timely manner. For more information about ambiguous Dot1q
or QinQ termination, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Configuration procedure
The following conditions apply to the gratuitous ARP configuration:
• You can enable periodic sending of gratuitous ARP packets on a maximum of 1024 interfaces.
• Periodic sending of gratuitous ARP packets takes effect only when the link of the enabled
interface goes up and an IP address has been assigned to the interface.
• If you change the interval for sending gratuitous ARP packets, the configuration is effective at
the next sending interval.
• The frequency of sending gratuitous ARP packets might be much lower than the sending
interval set by the user in any of the following circumstances:
{ This function is enabled on multiple interfaces.
{ Each interface is configured with multiple secondary IP addresses.
{ A small sending interval is configured when the previous two conditions exist.
To configure gratuitous ARP:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable learning of gratuitous
ARP packets.
3. Enable the device to send
gratuitous ARP packets upon
receiving ARP requests
whose sender IP address
belongs to a different subnet.
4. Enter interface view.
5. Enable periodic sending of
gratuitous ARP packets and
set the sending interval.
system-view
gratuitous-arp-learning enable
gratuitous-arp-sending enable
interface
interface-number
arp send-gratuitous-arp
interval
[
interface-type
milliseconds ]
Enabling IP conflict notification
By default, if the sender IP address of an ARP packet is being used by the receiving device, the
receiving device sends a gratuitous ARP request. It also displays an error message after it receives
an ARP reply about the conflict.
N/A
By default, learning of gratuitous
ARP packets is enabled.
By default, a device does not send
gratuitous ARP packets upon
receiving ARP requests whose
sender IP address belongs to a
different subnet.
N/A
By default, periodic sending of
gratuitous ARP packets is
disabled.
10
Page 25

You can use this command to enable the device to display error messages before sending a
gratuitous ARP reply or request for conflict confirmation.
To enable IP conflict notification:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable IP conflict
notification.
system-view
N/A
arp ip-conflict log prompt
By default, IP conflict notification is
disabled.
11
Page 26

Configuring proxy ARP
Proxy ARP enables a device on one network to answer ARP requests for an IP address on another
network. With proxy ARP, hosts on different broadcast domains can communi cate with each other as
they would on the same broadcast domain.
Proxy ARP includes common proxy ARP and local proxy ARP.
• Common proxy ARP—Allows communication between hosts that conne ct to diff erent Layer 3
interfaces and reside in different broadcast domains.
• Local proxy ARP—Allows communication between hosts that connect to the same Layer 3
interface and reside in different broadcast domains.
Enabling common proxy ARP
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable common
proxy ARP .
system-view
interface
interface-number
proxy-arp enable
interface-type
N/A
The following interface types are supported:
• VLAN interface.
• Layer 3 Ethernet interface.
• Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface.
• Layer 3 aggregate interface.
• Layer 3 aggregate subinterface.
By default, common proxy ARP is disabled.
Enabling local proxy ARP
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable local proxy ARP.
system-view
interface
interface-number
local-proxy-arp enable
ip-range
[
interface-type
startIP to endIP ]
N/A
The following interface types are
supported:
• VLAN interface.
• Layer 3 Ethernet interface.
• Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface.
• Layer 3 aggregate interface.
• Layer 3 aggregate subinterface.
By default, local proxy ARP is
disabled.
12
Page 27
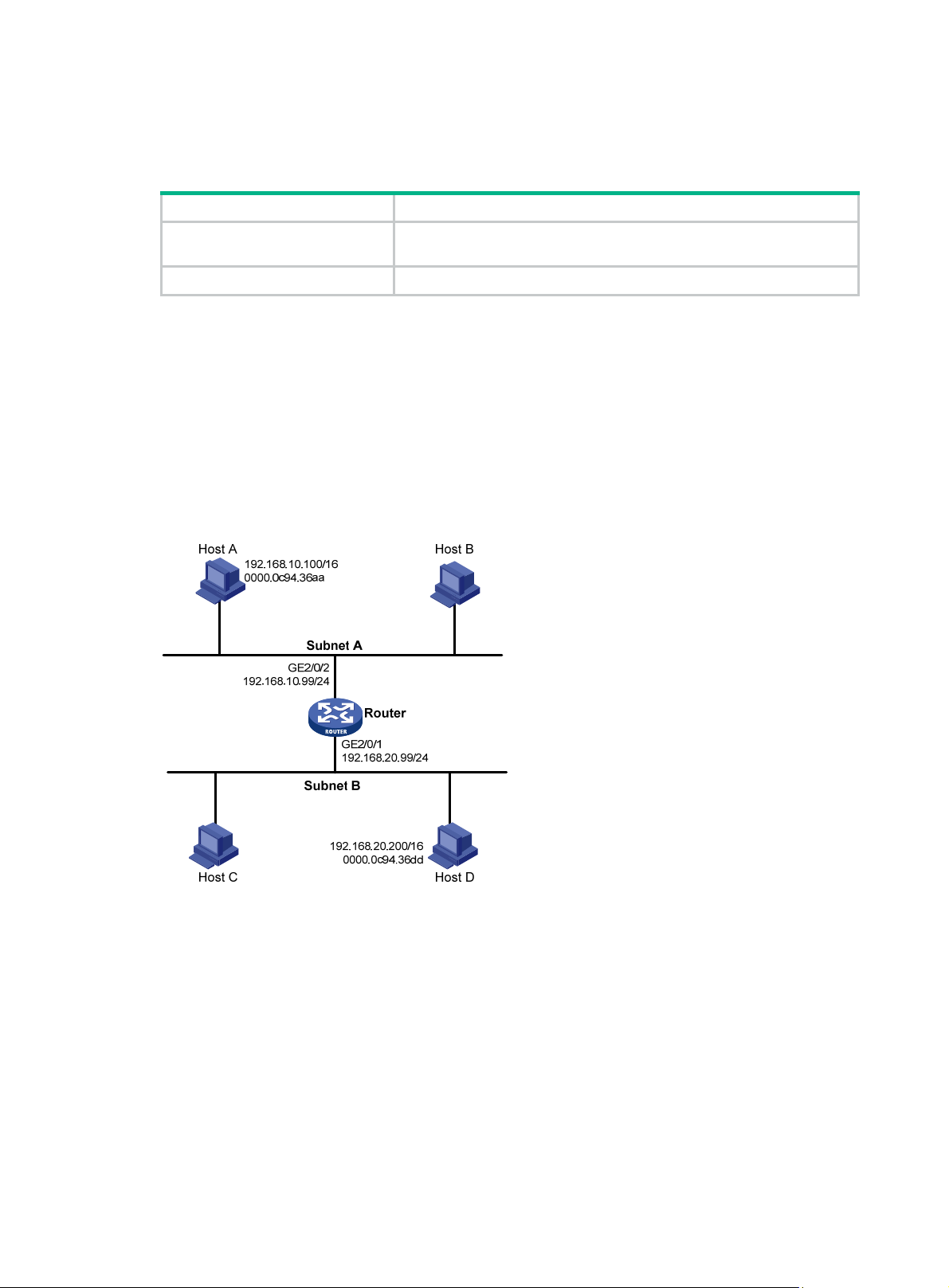
Displaying proxy ARP
Execute display commands in any view .
Task Command
Display common proxy ARP
status.
display proxy-arp [ interface
interface-type interface-number ]
Display local proxy ARP status.
display local-proxy-arp [ interface
interface-type interface-number ]
Common proxy ARP configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 5, Host A and Host D have the same prefix and mask, but they are located on
different subnets. No default gateway is configured on Host A and Host D.
Configure common proxy ARP on the router to enable communication between Host A and Host D.
Figure 5 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
# Configure the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/2.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] ip address 192.168.10.99 255.255.255.0
# Enable common proxy ARP on interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/2.
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] proxy-arp enable
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] quit
# Configure the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
13
Page 28

[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 192.168.20.99 255.255.255.0
# Enable common proxy ARP on interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] proxy-arp enable
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Host A and Host D can ping each other.
14
Page 29
Configuring ARP fast-reply
Overview
ARP fast-reply enables a device to directly answer ARP requests according to DHCP snooping
entries. ARP fast-reply functions in a VLAN. For information about DHCP snooping, see "Configuring
snooping."
DHCP
If the target IP address of a received ARP request is the IP address of the VLAN i nterface, the device
delivers the request to the ARP module. If not, the device takes the following steps to process the
packet:
1. Search the DHCP snooping table for a match by using the target IP address.
2. If a match is found, whether the device returns a reply depends on the type of interface in the
matching entry.
{ If the interface is the Ethernet interface that received the ARP request, the device does not
return a reply.
{ If the interface is a wireless interface or an Ethernet interface other than the receiving
interface, the device returns a reply according to the matching entry.
3. If no matching DHCP snooping entry is found, the ARP request is forwarded to other interfaces
except the receiving interface in the VLAN, or delivered to other modules.
Configuration procedure
To configure ARP fast-reply:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter VLAN view.
3. Enable ARP fast-reply.
system-view
vlan
vlan-id N/A
arp fast-reply enable
N/A
By default, ARP fast-reply is disabled.
ARP fast-reply configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 6, the router is a DHCP snooping device. All clients are in VLAN 2, and access
the network through the router. The clients obtain IP addresses from the DHCP server through
DHCP.
Enable ARP fast-reply for VLAN 2. The router directly returns an ARP reply without broadcasting
received ARP requests in the VLAN.
15
Page 30
Figure 6 Network diagram
Client 1
Router
Client 17
VLAN 2
……
……
VLAN 2
Configuration procedure
# Enable ARP fast-reply for VLAN 2 on the router.
[Router-vlan2] arp fast-reply enable
[Router-vlan2] quit
Client 16
DHCP server
Client 32
16
Page 31

Configuring ARP PnP
Overview
The ARP plug and play (PnP) feature is typically configured on a gateway. This feature allows end
users to access the gateway without changing their IP addresses on subnets different from the
subnet where the gateway resides.
After ARP PnP is enabled on an interface, it provides the following functions:
• ARP PnP enables the interface to alway s reply to users' ARP requests with the interface's MAC
address.
• Upon receiving a packet from the user, ARP PnP replaces the source IP address of the packet
with an agent IP address. The agent IP address is on the same subnet as the interface IP
address.
• Upon receiving the return packet destine d to the agent IP address, ARP PnP replaces the agent
IP with the user's original IP address.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure the ARP PnP feature on an interface, perform the following tasks:
• Assign the interface a primary IP address. ARP PnP generates agent IP addresses based on
the primary IP address and mask length of the interface.
• Use the reset arp command to delete all ARP entries on the interface.
• Configure NAT on the interface that connects to the external network. For more information
about NAT, see "Configuring NAT."
Configuration procedure
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure an address group
and enter its view.
3. Add an IP address range to
the address group.
4. Enter interface view of the
interface that connects to the
external network.
system-view
nat address-group
group-number
address
end-address
interface
interface-number
start-address
interface-type
N/A
By default, no address group exists.
By default, an address group has no
IP address range.
You can add multiple IP address
ranges to an address group.
The IP address ranges must not
overlap.
The following interface types are
supported:
• Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces.
• Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces.
5. Configure outbound dynamic
NAT.
6. Return to system view.
nat outbound
address-group
group-number
quit
17
By default, outbound dynamic NAT is
not configured.
N/A
Page 32

Step Command Remarks
7. Enter interface view of the
interface that connects to the
internal network.
interface
interface-number
interface-type
The following interface types are
supported:
• Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces.
• Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces.
8. Enable the ARP PnP feature.
arp pnp
By default, the ARP PnP feature is
disabled.
Displaying and maintaining ARP PnP
Execute display commands in any view .
Task Command
Display ARP PnP mappings.
display arp pnp [ interface
interface-type interface-number ]
ARP PnP configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 7, configure the ARP PnP feature to allow the host at 1.2.3.4 to access the
external server through GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
Figure 7 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure NAT:
# Specify IP addresses for GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 2/0/2.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 192.168.0.2 24
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] ip address 202.38.1.100 24
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] quit
# Configure ACL 2000 to identify packets from subnet 192.168.0.0/24.
[Router] acl number 2000
[Router-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255
[Router-acl-basic-2000] quit
# Create address group 1, and add address 202.38.1.100 to the group.
[Router] nat address-group 1
[Router-nat-address-group-1] address 202.38.1.100 202.38.1.100
18
Page 33

[Router-nat-address-group-1] quit
# Enable outbound PAT on interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/2 to translate the source address of
outgoing packets matching ACL 2000 into the address in address group 1.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] nat outbound 2000 address-group 1
2. Enable the ARP PnP feature on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] arp pnp
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the router creates an ARP PnP mapping for the host IP address 1.2.3.4 on
GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[Router] display arp pnp interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
Total number of entries : 1
Agent IP address User IP address MAC address Interface Aging
192.168.0.3 1.2.3.4 00e0-fc00-0001 GE2/0/1 10
19
Page 34

Configuring ARP suppression
Overview
The ARP suppression feature enables a device to directly answer ARP requests by using ARP
suppression entries. The device generates ARP suppression entrie s based on dy namic ARP entries
that it learns. This feature is typically configured on the PEs connected to base stations in an MPLS
L2VPN that provides access to an L3VPN network.
You can also configure the ARP suppression push function to push ARP suppression entries at
intervals by broadcasting gratuitous ARP packets.
Figure 8 s
to the base station. The PE generates ARP suppression entries for the base station, PE-agg 1, and
PE-agg 2, and it directly replies subsequent ARP requests for these devices.
Figure 8 Typical application
hows a typical application scenario. ARP suppression is enabled on the PE that connects
Configuration procedure
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a cross-connect
group and enter its view.
3. Create a cross-connect
and enter its view.
4. Enable ARP
suppression.
system-view
xconnect-group
connection
arp suppression enable
N/A
group-name
connection-name
20
By default, no cross-connect group
exists.
For more information about this
command, see MPLS Command
Reference.
By default, no cross-connect exists.
For more information about this
command, see MPLS Command
Reference.
By default, ARP suppression is
disabled.
Page 35

Step Command Remarks
5. Return to cross-connect
group view.
6. Return to system view.
7. (Optional.) Enable the
ARP suppression push
function and set a push
interval.
quit
quit
arp suppression push interval
interval
N/A
N/A
By default, the ARP suppression push
function is disabled.
Displaying and maintaining ARP suppression
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
Task Command
Display ARP suppression entries (centralized
devices in standalone mode).
display arp suppression xconnect-group
group-name ] [
count
]
name
[
Display ARP suppression entries (distributed
devices in standalone mode/centralized devices
in IRF mode).
Display ARP suppression entries (distributed
devices in IRF mode).
Clear ARP suppression entries (centralized
devices in standalone mode).
Clear ARP suppression entries (distributed
devices in standalone mode/centralized devices
in IRF mode).
Clear ARP suppression entries (distributed
devices in IRF mode).
display arp suppression xconnect-group
group-name ] [
display arp suppression xconnect-group
group-name ] [
slot-number ] [
reset arp suppression xconnect-group
reset arp suppression xconnect-group
group-name ] [
reset arp suppression xconnect-group
group-name ] [
slot-number ]
slot
slot-number ] [
chassis
count ]
slot
slot-number ]
chassis
chassis-number
chassis-number
ARP suppression configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 9, the base station, Router A, and Router B are in an MPLS L2VPN. The base
station can reach the L3VE interface VE-L3VPN 1 of Router B.
count ]
slot
slot
name
[
name
[
name
[
name
[
Enable ARP suppression on Router A to directly reply to ARP requests for Router B.
Figure 9 Network diagram
21
Page 36

Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for the interfaces as shown in Figure 9. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure ARP suppression on Router A:
# Create a cross-connect group named vpna and create a cross-connect named svc in the
group.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] xconnect-group vpna
[RouterA-xcg-vpna] connection svc
# Enable ARP suppression for the cross-connect svc in cross-connect group vpna.
[RouterA-xcg-vpna-svc] arp suppression enable
Verifying the configuration
1. On the base station, clear ARP entries, and ping the L3VE interface VE-L3VPN 1 of Router B.
(Details not shown.)
2. Verify that Router A has ARP suppression entries for the base station and Router B.
[RouterA-xcg-vpna-svc] display arp suppression xconnect-group
IP address MAC address Xconnect-group Connection Aging
10.1.1.1 00e0-fc04-582c vpna svc 25
10.1.1.3 0023-89b7-0861 vpna svc 25
3. Enable ARP debugging on Router B to verify that Router B does not receive an ARP request
from the base station under the following conditions (details not shown):
a. Clear ARP entries on the base station.
b. Ping the L3VE interface VE-L3VPN 1 of Router B from the base station.
22
Page 37

Configuring ARP direct route advertisement
Overview
The ARP direct route advertisement feature advertises host route s instead of advertising the network
route. This feature is typically configured on PE-aggs to advertise host routes to the connected PEs
in the L3VPN.
Figure 10
destined to a base station in the L2VPN. Traf fic from the PE in the L3VPN to the base station can be
load shared by PE-agg 1 and PE-agg 2. If PE-agg 1 fails, the PE uses the host route thro ugh PE-agg
2 to forward traffic.
Figure 10 Typical application
shows a typical application scenario where the PE in the L3VPN has ECMP routes
Configuration procedure
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create an L3VE
interface and enter its
view.
3. Enable the ARP direct
route advertisement
feature.
system-view
interface ve-l3vpn
interface-number
arp route-direct advertise
N/A
23
By default, no L3VE interface exists.
For more information about this
command, see MPLS Command
Reference.
By default, the ARP direct route
advertisement feature is disabled.
Page 38

Configuring IP addressing
The IP addresses in this chapter refer to IPv4 addresses unless ot herwise specified.
This chapter describes IP addressing basics and manual IP address assignment for interfaces.
Dynamic IP address assignment (BOOTP and DHCP) and PPP address negotiation are bey ond the
scope of this chapter.
Overview
This section describes the IP addressing basics.
IP addressing uses a 32-bit address to identify each host on an IPv4 network. To make addresses
easier to read, they are written in dotted decimal notation, each address being four octets in length.
For example, address 00001010000000010000000100000001 in binary is written as 10.1.1.1.
IP address classes
Each IP address breaks down into the following sections:
• Net ID—Identifies a network. The first several bits of a net ID, known as the class field or class
bits, identify the class of the IP address.
• Host ID—Identifies a host on a network.
IP addresses are divided into five classes, as shown in Figure 11. The shade
address class. The first three classes are most commonly used.
Figure 11 IP address classes
Table 1 IP address classes and ranges
Class Address range Remarks
The IP address 0.0.0.0 is used by a host at startup for
temporary communication. This address is never a
valid destination address.
A 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255
Addresses starting with 127 are reserved for loopback
test. Packets destined to these addresses are
processed locally as input packets rather than sent to
the link.
d areas represent the
B 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255 N/A
C 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 N/A
D 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 Multicast addresses.
24
Page 39

Class Address range Remarks
E 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Special IP addresses
The following IP addresses are for special use and cannot be used as ho st IP addresses:
• IP address with an all-zero net ID—Ide ntifies a host on the local network. For example, IP
address 0.0.0.16 indicates the host with a host ID of 16 on the local network.
• IP address with an all-zero host ID—Identifies a network.
• IP address with an all-one host ID—Identifies a dire cted broadcast address. For example, a
packet with the destination address of 192.168.1.255 will be broadcast to all the hosts on the
network 192.168.1.0.
Subnetting and masking
Subnetting divides a network into smaller networks called subnet s by using som e bits of the h ost ID
to create a subnet ID.
Masking identifies the boundary between the host ID and the combination of net ID and subnet ID.
Reserved for future use, except for the broadcast
address 255.255.255.255.
Each subnet mask comprises 32 bits that corre spond to the bits i n an IP address. In a subnet mask,
consecutive ones represent the net ID and subnet ID, and consecutive zeros represent the host ID.
Before being subnetted, Class A, B, and C networks use these default masks (also called natural
masks): 255.0.0.0, 255.255.0.0, and 255.255.255.0, respectively.
Figure 12 Subnetting a Class B network
Subnetting increases the number of addresses that cannot be assigned to hosts. Therefore, using
subnets means accommodating fewer hosts.
For example, a Class B network without subnetting can accommodate 1022 more hosts than the
same network subnetted into 512 subnets.
16
• Without subnetting—65534 (2
address, which has an all-one host ID, and the network address, which has an all-zero host ID.)
• With subnetting—Using the first nine bits of the host-id for subnetting provides 512 (2
subnets. However, only sev en bits remain available for the host ID. This allows 126 (2
hosts in each subnet, a total of 64512 (512 × 126) hosts.
– 2) hosts. (The two deducted addresses are the broadcast
9
)
7
– 2)
Assigning an IP address to an interface
An interface must have an IP address to communicate with other hosts. You can either manually
assign an IP address to an interface, or configure the interface to obtain an IP address through
BOOTP, DHCP, or PPP address negotiation. If you change the way an interface obtains an IP
address, the new IP address will overwrite the previous address.
25
Page 40

An interface can have one primary address and multiple secondary addresses.
Typically, you need to configure a primary IP address for an interface. If the interface connects to
multiple subnets, configure primary and secondary IP addresses on the interface so the subnets can
communicate with each other through the interface.
Configuration guidelines
Follow these guidelines when you assign an IP address to an interface:
• An interface can have only one primary IP address. A newly configured primary IP address
overwrites the previous one.
• You cannot assign secondary IP addresses to an interface that obtains an IP address through
BOOTP, DHCP, PPP address negotiation, or IP unnumbered.
• The primary and secondary IP addresses assigned to the interfa ce can be located on the same
network segment. Different interfaces on your device must reside on different network
segments.
Configuration procedure
To assign an IP address to an interface:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Assign an IP address to the
interface.
system-view
interface
interface-number
ip address
mask-length } [
interface-type
ip-address { mask |
sub
Configuring IP unnumbered
Typically, you assign an IP address to an interface either manually or through DHCP. If the IP
addresses are not enough, or the interface is used only occasionally, you can configure an interface
to borrow an IP address from other interfaces. This is called IP unnumbered, and the interface
borrowing the IP address is called IP unnumbered interface.
You can use IP unnumbered to save IP addresses either when available IP addresses are
inadequate or when an interface is brought up only for occasional use.
Configuration guidelines
Follow these guidelines when you configure IP unnum bered:
• Loopback interfaces cannot borrow IP addresses of other interfaces, but other interfaces can
borrow IP addresses of loopback interfaces.
• An interface cannot borrow an IP address from an unnumbered interface.
• Multiple interfaces can use the same unnumbered IP address.
• If an interface has multiple manually configured IP ad dresses, only the manually configured
primary IP address can be borrowed.
N/A
N/A
By default, no IP address is
]
assigned to the interface.
26
Page 41

Configuration prerequisites
Assign an IP address to the interface from which you want to borrow the IP address. Alternatively,
you can configure the interface to obtain one through BOOTP, DHCP, or PPP address negotiation.
Configuration procedure
To configure IP unnumbered on an interface:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter interface view.
3. Specify the interface to borrow
the IP address of the specified
interface.
A dynamic routing proto col cannot be enabled on the interface where IP unnumbered is configured.
T o enable the interface to communicate with other devices, configure a static route to the peer device
on the interface. For more configuration information, see "IP unnumbered co nfiguration example."
interface
interface-number
ip address unnumbered
interface
interface-number
interface-type
interface-type
N/A
By default, the interface does
not borrow IP addresses from
other interfaces.
Displaying and maintaining IP addressing
Execute display commands in any view .
Task Command
Display IP configuration and statistics for the
specified or all Layer 3 interfaces.
Display brief IP configuration for Layer 3 interfaces.
display ip interface
interface-number ]
display ip interface
[ interface-number ] ]
[ interface-type
[ interface-type
brief [ description
Configuration examples
]
IP address configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 13, GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on the router is connected to a LAN comprising two
segments: 172.16.1.0/24 and 172.16.2.0/24.
To enable the hosts on the two network segments to communicate with the external network through
the router, and to enable th e hosts on the LAN to communicate with each other:
• Assign a primary IP address and a secondary IP address to GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on the router .
• Set the primary IP address of the router as the gateway address of the PCs on subnet
172.16.1.0/24. Set the secondary IP address of the router as the gateway address of the PCs
on subnet 172.16.2.0/24.
27
Page 42

Figure 13 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
# Assign a pri m ary IP address and a secondary IP address to GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
<Router> system-view
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 sub
# Set the gateway address to 172.16.1.1 on the PCs attached to subnet 172.16.1.0/24, and to
172.16.2.1 on the PCs attached to subnet 172.16.2.0/24.
Verifying the configuration
# Verify the connectivity between a host on subnet 172.16.1.0/24 and the router.
<Router> ping 172.16.1.2
Ping 172.16.1.2 (172.16.1.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 172.16.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=128 time=7.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.1.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 172.16.1.2 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/2.600/7.000/2.245 ms
# Verify the connectivity between a host on subnet 172.16.2.0/24 and the router.
<Router> ping 172.16.2.2
Ping 172.16.2.2 (172.16.2.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 172.16.2.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=128 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.2.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=7.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.2.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.2.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.2.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=1.000 ms
28
Page 43

--- Ping statistics for 172.16.2.2 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/2.600/7.000/2.245 ms
# Verify the connectivity between a host on subnet 172.16.1.0/24 and a host on subnet 172.16. 2.0/24.
The ping operation succeeds.
IP unnumbered configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 14, two routers on an intranet are connected to each other through serial
interfaces across a Digital Data Network. Each router connects to a LAN through an Ethernet
interface.
To save IP addresses, configure the serial interfaces to borrow IP addresses from the Ethernet
interfaces.
Figure 14 Network diagram
DDN
Ser2/1/1
GE2/0/1
172.16.10.1/24
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Router A:
# Assign a primary IP address to GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Configure Serial 2/1/1 to borrow an IP address from GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterA] interface serial 2/1/1
[RouterA-Serial2/1/1] ip address unnumbered interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-Serial2/1/1] quit
# Configure a static route to the subnet attached to Router B, specifying Serial 2/1/1 as the
outgoing interface.
[RouterA] ip route-static 172.16.20.0 255.255.255.0 serial 2/1/1
2. Configure Router B:
# Assign a primary IP address to GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 172.16.20.1 255.255.255.0
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
Ser2/1/1
Router BRouter A
GE2/0/1
172.16.20.1/24
29
Page 44

# Configure interface Serial 2/1/1 to borrow an IP address from GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterB] interface serial 2/1/1
[RouterB-Serial2/1/1] ip address unnumbered interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterB-Serial2/1/1] quit
# Configure a static route to the subnet attached to Router A, specifying Serial 2/1/1 as the
outgoing interface.
[RouterB] ip route-static 172.16.10.0 255.255.255.0 serial 2/1/1
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that a host attached to Router B can be pinged from Router A.
[RouterA] ping 172.16.20.2
Ping 172.16.20.2 (172.16.20.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 172.16.20.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=128 time=7.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.20.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=2.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.20.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.20.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 172.16.20.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for 172.16.20.2 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/2.600/7.000/2.245 ms
30
Page 45

DHCP overview
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provides a framework to assign configuration
information to network devices.
Figure 15 sho
reside on the same subnet. The DHCP clients can also obtain configuration parameters from a
DHCP server on another subnet through a DHCP relay agent. For more information about the DHCP
relay agent, see "Configuring the DHCP relay agent."
Figure 15 A typical DHCP application
ws a typical DHCP application scenario where the DHCP clients and the DHCP server
DHCP address allocation
Allocation mechanisms
DHCP supports the following allocation mechanisms:
• Static allocation—The network administrator assigns an IP address to a client, such as a
WWW server, and DHCP conveys the assigned address to the client.
• Automatic allocation—DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a client.
• Dynamic allocation—DHCP assigns an IP address to a client for a limited period of time,
which is called a lease. Most DHCP clients obtain their addresses in this way.
31
Page 46

IP address allocation process
Figure 16 IP address allocation process
As shown in Figure 16, a DHCP server assigns an IP address to a DHCP client in the following
process:
1. The client broadcasts a DHCP-DISCOVER message to locate a DHCP server.
2. Each DHCP server offers configuration parameters such as an IP address to the client in a
DHCP-OFFER message. The sending mode of the DHCP-OFFER is determined by the flag
field in the DHCP-DISCOVER message. For more information, see "DHCP message format."
3. If the client receives multiple offers, it accepts the first received offer, and broadcasts it in a
DHCP-REQUEST message to formally request the IP address. (IP addresses offered by other
DHCP servers can be assigned to other clients.)
4. All DHCP servers receive the DHCP-REQUEST message. However, only the server sele cted
by the client does one of the following operations:
{ Returns a DHCP-ACK message to confirm that the IP address has been allocated to the
client.
{ Returns a DHCP-NAK message to deny the IP address allocation.
After receiving the DHCP-ACK message, the client verifies the following details before using the
assigned IP address:
• The assigned IP address is not in use. To verify this, the client broadcasts a gratuitous ARP
packet. The assigned IP address is not in use if no response is received within the specified
time.
• The assigned IP address is not on the sa me subnet as any IP address in use on the client.
Otherwise, the client sends a DHCP-DECLINE message to the server to request an IP address
again.
IP address lease extension
A dynamically assigned IP address has a lease. When the lease expires, the IP address is reclaimed
by the DHCP server. To continue using the IP address, the client must extend the lease duration.
When about half of the lease duration elapses, the DHCP client unicasts a DHCP-REQUEST to the
DHCP server to extend the lease. Depending on the availability of the IP address, the DHCP server
returns one of the following messages:
• A DHCP-ACK unicast confirming that the client's lease duration has been extended.
• A DHCP-NAK unicast denying the request.
32
Page 47

If the client receives no reply, it broadcasts another DHCP-REQUEST message for lease extension
when about seven-eighths of the lease duration elapses. Again, depending on the availability of the
IP address, the DHCP server returns either a DHCP-ACK unicast or a DHCP-NAK unica st.
DHCP message format
Figure 17 shows the DHCP message format. DHCP uses some of the fields in significantly different
ways. The numbers in parentheses indicate the size of each field in bytes.
Figure 17 DHCP message format
• op—Message type defined in options field. 1 = REQUEST, 2 = REPLY
• htype, hlen—Hardware address type and length of the DHCP client.
• hops—Number of relay agents a request message traveled.
• xid—Transaction ID, a random number chosen by the client to identif y an IP address allocation.
• secs—Filled in by the client, the number of seconds elapsed since the client began address
acquisition or renewal process. This field is reserved and set to 0.
• flags—The leftmost bit is defined as the BROADCAST (B) flag. If this flag is set to 0, the DHCP
server sent a reply back by unicast. If this flag is set to 1, the DHCP server se nt a reply back by
broadcast. The remaining bits of the flags field are reserved for future use.
• ciaddr—Client IP address if the client has an IP address that is valid and usable. Otherwise, set
to zero. (The client does not use this field to request an IP address to lease.)
• yiaddr—Your IP address. It is an IP address assigned by the DHCP server to the DHCP client.
• siaddr—Server IP address, from which the client obtained configuration parameters.
• giaddr—Gateway IP address. It is the IP address of the first relay agent to which a requ est
message travels.
• chaddr—Client hardware address.
• sname—Server host name, from which the client obtained configuration parameters.
• file—Boot file (also called system software image) name and path information, defined by the
server to the client.
• options—Optional parameters field that is variable in length. Optional parameters include the
message type, lease duration, subnet mask, domain name server IP address, and WINS IP
address.
33
Page 48

DHCP options
DHCP extends the message format as an extension to BOOTP for compatibility. DHCP uses the
options field to carry information for dynamic address allocation and provide additional co nfiguration
information for clients.
Figure 18 DHCP option format
Common DHCP options
The following are common DHCP options:
• Option 3—Router option. It specifies the gateway address.
• Option 6—DNS server option. It specifies the DNS server's IP address.
• Option 33—Static route option. It specifies a list of classful static routes (the destination
addresses in these static routes are classful) that a client should add into its routing table. If
both Option 33 and Option 121 exist, Option 33 is ignored.
• Option 51—IP address lease option.
• Option 53—DHCP message type option. It identifies the type of the DHCP message.
• Option 55—Parameter request list option. It is used by a DHCP client to request specified
configuration parameters. The option includes values that correspond to the parameters
requested by the client.
• Option 60—Vendor class identifier option. A DHCP client use s this option to identify it s vendor .
A DHCP server uses this option to distinguish DHCP clients, and assigns IP addresses to them.
• Option 66—TFTP server name option. It specifies a TFTP server to be assigned to the client.
• Option 67—Boot file name option. It specifies the boot file name to be assigned to the client.
• Option 121—Classless route option. It specifies a list of classless st atic routes (the destination
addresses in these static routes are classless) that a client should add into its routing table. If
both Option 33 and Option 121 exist, Option 33 is ignored.
• Option 150—TFTP server IP address option. It specifies the TFTP server IP address to be
assigned to the client.
For more information about DHCP options, see RFC 2132 and RFC 3442.
Custom DHCP options
Some options, such as Option 43, Option 82, and Option 184, have no standard definitions in RFC
2132.
Vendor-specific option (Option 43)
DHCP servers and clients use Option 43 to exchange vendor-specific configuration information.
The DHCP client can obtain the following information through Option 43:
• ACS parameters, including the ACS URL, username, and password.
34
Page 49

• Service provider identifier, which is acquired by the CPE from the DHCP server and sent to the
ACS for selecting vender-specific configurations and parameters. For more information about
CPE and ACS, see Network Ma nagement and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
• PXE server address, which is used to obtain the boot file or other control information from the
PXE server.
• AC address, which is use d by an AP to obtain the boot file or other control information from the
AC.
1. Format of Option 43:
Figure 19 Option 43 format
Network configuration parameters are carried in different sub-options of Option 43 as shown
in Figure 19.
{ Sub-option type—The field value can be 0x01 (ACS parameter sub-option), 0x02 (service
provider identifier sub-option), or 0x80 (PXE server address sub-option).
{ Sub-option length—Excludes the sub-option type and sub-option length fields.
{ Sub-option value—The value format varies by sub-option.
2. Sub-option value field formats:
{ ACS parameter sub-option value field—Includes the ACS URL, username, and
password separated by spaces (0x20) as shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20
ACS parameter sub-option value field
{ Service provider identifier sub-option value field—Includes the service provider
identifier.
{ PXE server address sub-option value field—Includes the PXE server type that can only
be 0, the server number that indicates the number of PXE servers contained in the
sub-option, and server IP addresses, as shown in Figure 21.
Figure 21 PXE ser
ver address sub-option value field
35
Page 50

Relay agent option (Option 82)
Option 82 is the relay agent option. It records the location information about the DHCP client. When
a DHCP relay agent or DHCP snooping device receives a client's request, it adds Option 82 to the
request and sends it to the server.
The administrator can use Option 82 to locate the DHCP client and further implement security control
and accounting. The DHCP server can use Option 82 to provide individual configuration policies for
the clients.
Option 82 can include up to 255 sub-options and must have one sub-option at least. Option 82
supports two sub-options: sub-option 1 (Circuit ID) and sub-option 2 (Remote ID). Option 82 has no
standard definition. Its padding formats vary by vendor.
• Circuit ID has the following padding modes:
{ String padding mode—Includes a character string specified by the user.
{ Normal padding mode—Includes the VLAN ID and interface number of the interface that
receives the client's request.
{ Verbose padding mode—Includes the access node identifier specified by the user, and
the VLAN ID, interface number and interface type of the interface that receives the client's
request.
• Remote ID has the following padding modes:
{ String padding mode—Includes a character string specified by the user.
{ Normal padding mode—Includes the MAC address of the DHCP relay agent interface or
the MAC address of the DHCP snooping device that receives the client's request.
{ Sysname padding mode—Includes the device name of the device. To set the device name
for the device, use the sysname command in system view.
Option 184
Option 184 is a reserved option. You can define the parameters in the option as needed. The device
supports Option 184 carrying voice related parameters, so a DHCP client with voice functions can
get voice parameters from the DHCP server.
Option 184 has the following sub-options:
• Sub-option 1—Specifies the IP address of the primary network calling processor. The primary
processor acts as the network calling control source and provides p rogram downl oad se rvices.
For Option 184, you must define sub-option 1 to make other sub-options take effe ct.
• Sub-option 2—Specifies th e IP address of the backup network callin g processor. DHCP clients
contact the backup processor when the primary one is unreachable.
• Sub-option 3—Specifies the voice VLAN ID and the result whether the DHCP client takes this
VLAN as the voice VLAN.
• Sub-option 4—Specifies the failover route that includes the IP address and the number of the
target user. A SIP VoIP user uses this IP address and number to directly establi sh a connection
to the target SIP user when both the primary and backup calling processors are unreachable.
Protocols and standards
• RFC 2131, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
• RFC 2132, DHCP Options and BOOTP Vendor Extensions
• RFC 1542, Clarifications and Extension s for the Bootstrap Protocol
• RFC 3046, DHCP Relay Agent Information Option
• RFC 3442, The Classless Static Route Option for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
version 4
36
Page 51

Configuring the DHCP server
Overview
The DHCP server is well suited to networks where:
• Manual configuration and centralized management are difficult to implement.
• IP addresses are limited. For example, an ISP limits the number of concurrent online users, and
users must acquire IP addresses dynamically.
• Most hosts do not need fixed IP addre s ses.
An MCE acting as the DHCP server can assign IP addresses not only to clients on publi c networks,
but also to clients on private networks. The IP address rang es of public and private networks or those
of private networks on the DHCP server cannot overlap. For more information about MCE, see
MPLS Configuration Guide.
DHCP address pool
Each DHCP address pool has a group of assignable IP addresses and network configuration
parameters. The DHCP server selects IP addresses and other parameters from the address pool
and assigns them to the DHCP clients.
Address assignment mechanisms
Configure the following address assignment mechanisms as needed:
• Static address allocation—Manually bind the MAC address or ID of a client to an IP address
in a DHCP address pool. When the client requests an IP address, the DHCP server assigns the
IP address in the static binding to the client.
• Dynamic address allocation—Specify IP address ranges in a DHCP address pool. Upon
receiving a DHCP request, the DHCP server dynamic ally selects an IP address from the
matching IP address range in the address pool.
You can specify IP address ranges in an address pool by using either of the following methods:
• Method 1—Specify a primary subnet in an address pool and divide the subnet into multiple
address ranges. These address ranges include a common IP address range and IP address
ranges for DHCP user classes.
Upon receiving a DHCP request, the DHCP server finds a user class matching the client and
selects an IP address in the address range of the user class for the client. A user class can
include multiple matching rules, and a client matches the user class as long a s it matches any of
the rules. In address pool view, you can specify different address ranges for different user
classes.
The DHCP server selects an IP address for a client by performing the following steps:
a. DHCP server compares the client against DHCP user classes in the order they are
configured.
b. If the client matches a user class, the DHCP serve r selects an IP addre ss from the addres s
range of the user class.
c. If the matching user class has no assignable addresses, the DHCP server compares the
client against the next user class. If all the matching user classes have no assignable
addresses, the DHCP server selects an IP address from the common address range.
d. If the DHCP client does not match any DHCP user class, the DHCP server selects an
address in the IP address range specified by the address range command. If the add ress
range has no assignable IP addresses or it is not configured, the address allocation fails.
37
Page 52

NOTE:
All address ranges must belong to the primary subnet. If an address range does not reside on
the primary subnet, DHCP cannot assign the addresses in the address range.
• Method 2—Specify a primary subnet and multiple secondary subnets in an address pool.
The DHCP server selects an IP address from the primary subnet first. If there is no assignable
IP address on the primary subnet, the DHCP server selects an IP address from secondary
subnets in the order they are configured.
Principles for selecting an address pool
The DHCP server observes the following principles to select an addres s pool for a client:
1. If there is an address pool where an IP address is statically bound to the MAC address or ID of
the client, the DHCP server selects this address pool and assigns the statically bound IP
address and other configuration parameters to the client.
2. If the receiving interface has an address pool applied, the DHCP server selects an IP address
and other configuration parameters from this address pool.
3. If no static address pool is configured and no address pool is applied to the receiving interface,
the DHCP server selects an address pool depending on the client location.
{ Client on the same subnet as the server—The DHCP server compare s the IP address of
the receiving interface with the primary subnets of all address pools.
− If a match is found, the server selects the address pool with the longest-matching
primary subnet.
− If no match is found, the DHCP server compares the IP address wit h the secondary
subnets of all address pools. The server selects the address pool with the
longest-matching secondary subnet.
{ Client on a different subnet than the server—The DHCP server compares the IP
address in the giaddr field of the DHCP request with the primary subnets of all address
pools.
− If a match is found, the server selects the address pool with the longest-matching
primary subnet.
− If no match is found, the DHCP server compares the IP address wit h the secondary
subnets of all address pools. The server selects the address pool with the
longest-matching secondary subnet.
For example, two address pools 1.1.1.0/24 and 1.1.1.0/25 are configured but not applied to any
DHCP server's interfaces.
• If the IP address of the receiving interface is 1.1.1.1/25, the DHCP server selects the address
pool 1.1.1.0/25. If the address pool has no available IP addresses, the DHCP server will not
select the other pool and the address allocation will fail.
• If the IP address of the receiving interface is 1.1.1.130/2 5, the DHCP server selects the address
pool 1.1.1.0/24.
To ensure correct address allocation, keep the IP addresses used for dynamic allocation on one of
the subnets:
• Clients on the same subnet as the server —Subnet where the DHCP server receiving
interface resides.
• Clients on a different subnet than the server—Subnet where the first DHCP relay interface
that faces the clients resides.
38
Page 53

NOTE:
As a best practice, configure at least one matching primary subnet in your network. Otherwise, the
DHCP server selects only the first matching secondary subnet for address alloca tion. If the network
has more DHCP clients than the assignable IP addresses in the secondary subnet, not all DHCP
clients can obtain IP addresses.
IP address allocation sequence
The DHCP server selects an IP address for a client in the following sequence:
1. IP address statically bound to the client's MAC address or ID.
2. IP address that was ever assigned to the client.
3. IP address designated by the Option 50 field in the DHCP-DISCOVER message sent by the
client.
Option 50 is the Requested IP Address option. The client uses this option to spe cify the wanted
IP address in a DHCP-DISCOVER message. The content of Option 50 is user defined.
4. First assignable IP address found in the way discussed in "DHCP address pool."
5. IP addre
server does not respond.
ss that was a conflict or passed its lease duration. If no IP address is assignable, the
NOTE:
• If a client moves to another subnet, the DHCP server selects an IP address in the address pool
matching the new subnet. It does not assign the IP address th at was once assign ed to the client.
• Conflicted IP addresses can be assigned to other DHCP clients only after the addresses are in
conflict for an hour.
DHCP server configuration task list
Tasks at a glance
(Required.) Configuring an address pool on the DHCP server
(Required.) Enabling DHCP
(Required.) Enabling the DHCP server on an interface
(Optional.) Applying an address pool on an interface
(Optional.) Configuring IP address conflict detection
(Optional.) Enabling handling of Option 82
(Optional.) Configuring DHCP server compatibility
(Optional.) Setting the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP server
(Optional.) Configuring DHCP binding auto backup
(Optional.) Configuring address pool usage alarming
(Optional.) Binding gateways to a common MAC address
(Optional.) Advertising subnets assigned to clients
(Optional.) Applying a DHCP address pool to a VPN instance
(Optional.) Enabling client offline detection on the DHCP server
39
Page 54

Tasks at a glance
(Optional.) Configuring DHCP logging on the DHCP server
Configuring an address pool on the DHCP server
Configuration task list
Tasks at a glance
(Required.) Creating a DHCP address pool
Perform at least one of the following tasks:
• Specifying IP address ranges for a DHCP address pool
• Specifying gateways for DHCP clients
• Specifying a domain name suffix for DHCP clients
• Specifying DNS servers for DHCP clients
• Specifying WINS servers and NetBIOS node type for DHCP clients
• Specifying BIMS server for DHCP clients
• Specifying the configuration file for DHCP
• Specifying a server for DHCP clients
• Configuring Option 184 parameters for DHCP clients
• Customizing DHCP options
• Configuring the DHCP user class whitelist
client auto-configuration
Creating a DHCP address pool
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
Specifying IP address ranges for a DHCP address pool
Y ou can configure both static and dynamic ad dress allocation mechanism s in a DHCP add ress pool.
For dynamic address allocation, you can specify either a primary subnet with multiple address
ranges or a primary subnet with multiple secondary subnets for a DHCP address pool. You cannot
configure both.
Specifying a primary subnet and multiple address ranges for a DHCP address pool
Some scenarios need to classify DHCP clients on the same subnet into dif ferent address groups. To
meet this need, you can configure DHCP user classes and specify different address ranges for the
classes. The clients matching a user class can then get the IP addresses of an address range. In
addition, you can specify a common address range for the clients that do not match any user class. If
no common address range is specified, such clients fail to obtain IP addresses.
If there is no need to classify clients, you do not need to configure DHCP user classes or their
address ranges.
Follow these guidelines when you specify a primary subnet and multiple address ranges for a DHCP
address pool:
40
Page 55

• If you use the network or address range command multiple times f or the same address pool,
the most recent configuration takes effect.
• IP addresses spe cified by the forbidden-ip command are not assignable in the current ad dress
pool, but are assignable in other address pools. IP addresses specified by the dhcp server
forbidden-ip command are not assignable in any address pool.
To specify a primary subnet and multiple address ranges for a DHCP address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP user class and
enter DHCP user class view.
system-view
dhcp class
class-name
N/A
Required for client
classification.
By default, no DHCP user
class exists.
3. Configure the match rule for
the DHCP user class.
4. Return to system view.
5. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
6. Specify the primary subnet for
the address pool.
7. (Optional.) Specify the
common address range.
8. (Optional.) Specify an IP
address range for a DHCP user
class.
9. (Optional.) Set the address
lease duration.
if-match rule
option-code [
mask |
length ] ] |
hardware-address
hardware-address-mask }
quit
dhcp server ip-pool
network
[ mask-length |
address range
[ end-ip-address ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
class
class-name
start-ip-address end-ip-address
expired
minute
[
second ] ] ] |
rule-number {
hex
hex-string [
offset
hardware-address
network-address
day
{
minute [
length
offset
mask
mask
start-ip-address
vpn-instance
range
hour
day [
second
unlimited }
option
pool-name
mask ]
hour
mask
Required for client
classification.
By default, no match rule is
configured for a DHCP user
class.
N/A
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
By default, no primary subnet
is specified.
By default, no IP address
range is specified.
By default, no IP address
range is specified for a user
class.
The DHCP user class must
already exist.
To specify address ranges for
multiple DHCP user classes,
repeat this step.
The default setting is 1 day.
10. (Optional.) Exclude the
specified IP addresses in the
address pool from dynamic
allocation.
11. Return to system view.
12. (Optional.) Exclude the
specified IP addresses from
automatic allocation globally.
forbidden-ip
quit
dhcp server forbidden-ip
start-ip-address [ end-ip-address ]
ip-address&<1-8>
41
By default, all the IP
addresses in the DHCP
address pool are assignable.
To exclude multiple address
ranges from dynamic
allocation, repeat this step.
N/A
By default, except for the IP
address of the DHCP server
interface, all IP addresses in
address pools are assignable.
To exclude multiple IP
address ranges, repeat this
step.
Page 56

Specifying a primary subnet and multiple secondary subnets for a DHCP address pool
If an address pool has a primary subnet and multiple secondary subnets, the server assigns IP
addresses on a secondary subnet when the primary subnet has no assignable IP addresses.
Follow these guidelines when you specify a primary subnet and secondary subnets for a DHCP
address pool:
• You can specify only one primary subnet in each address pool. If you use the network
command multiple times, the most recent configuration takes effect.
• You can specify a maximum of 32 secondary subnets in each address pool.
• IP addresses spe cified by the forbidden-ip command are not assignable in the current ad dress
pool, but are assignable in other address pools. IP addresses specified by the dhcp server
forbidden-ip command are not assignable in any address pool.
To specify a primary subnet and secondary subnets for a DHCP address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP
address pool exists.
3. Specify the primary subnet.
4. (Optional.) Specify a secondary
subnet.
5. (Optional.) Return to address
pool view.
6. (Optional.) Set the address lease
duration.
7. (Optional.) Exclude the specified
IP addresses from dynamic
allocation.
8. Return to system view.
9. (Optional.) Exclude the specified
IP addresses from dynamic
allocation globally.
network
[ mask-length |
network
[ mask-length |
secondary
quit
expired
[
second ] ] ] |
forbidden-ip
quit
dhcp server forbidden-ip
start-ip-address [ end-ip-address ]
network-address
network-address
{
minute
minute [
mask
mask ]
mask
mask ]
day
hour
day [
second
unlimited
ip-address&<1-8>
hour
}
By default, no primary subnet
is specified.
By default, no secondary
subnet is specified.
N/A
The default setting is 1 day.
By default, all the IP
addresses in the DHCP
address pool can be
dynamically allocated.
To exclude multiple address
ranges from the address
pool, repeat this step.
N/A
Except for the IP address of
the DHCP server interface,
IP addresses in all address
pools are assignable by
default.
To exclude multiple address
ranges globally, repeat this
step.
Configuring a static binding in a DHCP address pool
Some DHCP clients, such as a WWW server , need fixed IP addre sses. To provide a fixed IP address
for a client, you can statically bind the MAC address or ID of the client to an IP address in a DHCP
address pool. When the client requests an IP address, the DHCP server assigns the IP address in
the static binding to the client.
42
Page 57

Follow these guidelines when you configure a static binding:
• One IP address can be bound to only one client MAC or client ID. You cannot modify bindings
that have been created. To change the binding for a DHCP client, you must delete the existing
binding first.
• The IP address of a static binding cannot be the address of the DHCP server interface.
Otherwise, an IP address conflict occurs and the bound client cannot obtain an IP address
correctly.
• Multiple interfaces on the same device might all use DHCP to request a static IP addres s. In this
case, use client IDs rather than the device's MAC address to identify the interfaces. Otherwise,
IP address allocation will fail.
To configure a static binding:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
3. Configure a static binding.
4. (Optional.) Set the lease
duration for the IP address.
static-bind ip-address
] }
day
{
day [
minute [
unlimited
mask
[ mask-length |
client-identifier
{
hardware-address
hardware-address [
token-ring
expired
minute
[
second ] ] ] |
ip-address
mask ]
client-identifier |
ethernet
hour
second
}
Specifying gateways for DHCP clients
DHCP clients send packets destined for other networks to a gateway. The DHCP server can assign
the gateway address to the DHCP clients.
You can specify gateway addresses in each address pool on the DHCP server . A maximum of eight
gateways can be specified in DHCP address pool view or secondary subnet view.
The DHCP server assigns gateway addresses to clients on a secondary subnet in the following
ways:
• If gateways are specified in both address pool view and secondary subnet view, DHCP assigns
those specified in the secondary subnet view.
• If gateways are specified in address pool view but not in second ary subnet view , DHCP assigns
those specified in address pool view.
hour
By default, no static binding is
configured.
|
To add more static bindings,
repeat this step.
The default setting is 1 day.
To configure gateways in the DHCP address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
3. Specify gateways.
4. (Optional.) Enter secondary
subnet view
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
gateway-list
network
mask
|
ip-address&<1-8>
network-address [ mask-length
secondary
mask ]
43
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP
address pool exists.
By default, no gateway is
specified.
N/A
Page 58

Step Command Remarks
5. (Optional.) Specify gateways.
gateway-list
ip-address&<1-8>
By default, no gateway is
specified.
Specifying a domain name suffix for DHCP clients
You can specify a domain name suffix in a DHCP address pool on the DHCP server. With this suffix
assigned, the client only needs to input part of a domain name, and the system adds the domain
name suffix for name resolution. For more information about DNS, see "Configur ing DNS ."
o configure a domain name suffix in the DHCP address pool:
T
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
3. Specify a domain name suffix.
domain-name
domain-name
By default, no domain name is
specified.
Specifying DNS servers for DHCP clients
T o a ccess hosts on the Internet through domain names, a DHCP cl ient must contact a DNS server to
resolve names. You can specify up to eight DNS servers in a DHCP address pool.
To specify DNS servers in a DHCP address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
3. Specify DNS servers.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
dns-list
ip-address&<1-8>
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP
address pool exists.
By default, no DNS server is
specified.
Specifying WINS servers and NetBIOS node type for DHCP clients
A Microsoft DHCP client using NetBIOS protocol must contact a WINS server for name resolution.
You can specify up to eight WINS servers for such clients in a DHCP address pool.
In addition, you must specify a NetBIOS node type for the clients to approach name resol ution. There
are four NetBIOS node types:
• b (broadcast)-node—A b -node client sends the destination name in a broadcast message.
The destination returns its IP address to the client after receiving the message.
• p (peer-to-peer)-node—A p-node client sends the destination name in a unicast message to
the WINS server. The WINS server returns the destination IP address.
• m (mixed)-node—An m-node client broadcasts the destination name. If it receives no
response, it unicasts the destination name to the WINS server to get the destination IP address.
• h (hybrid)-node—An h-node client unicasts the destination name to the WINS server. If it
receives no response, it broadcasts the destination name to get the destination IP address.
44
Page 59

To configure WINS servers and NetBIOS node type in a DHCP address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address
pool and enter its view.
3. Specify WINS servers.
4. Specify the NetBIOS node
type.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
nbns-list
netbios-type
m-node
ip-address&<1-8>
b-node
{
p-node
|
}
pool-name
h-node
|
|
Specifying BIMS server for DHCP clients
Perform this task to provide the BIMS server IP address, port number, and shared key for the clients.
The DHCP clients contact the BIMS server to get configuration files and perform software upgrade
and backup.
To configure the BIMS server IP address, port number , and shared key in the DHCP address pool:
N/A
By default, no DHCP address pool
exists.
This step is optional for b-node.
By default, no WINS server is
specified.
By default, no NetBIOS node type
is specified.
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
3. Specify the BIMS server IP
address, port number, and
shared key.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
bims-server ip
port-number ]
simple
} key
ip-address [
sharekey
pool-name
port
cipher
{
N/A
By default, no DHCP
address pool exists.
|
By default, no BIMS server
information is specified.
Specifying the configuration file for DHCP client auto-configuration
Auto-configuration enables a device to obtain a set of configuration settings automatically from
servers when the device starts up without a configuration file. It requires the cooperation of the
DHCP server, HTTP server, DNS server, and TFTP server. For more information about
auto-configuration, see Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Follow these guidelines to specify the parameters on the DHCP server for configuration file
acquisition:
• If the configuration file is on a TFTP server, specify the IP address or name of the TFTP server,
and the configuration file name.
• If the configuration file is on an HTTP server, specify the configuration file URL.
The DHCP client uses the obtained parameters to contact the TFTP server or the HTTP server to get
the configuration file.
To specify the configuration file name in a DHCP address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
45
Page 60

Step Command Remarks
2. Create a DHCP address
pool and enter its view.
3. Specify the IP address or
the name of a TFTP
server.
4. Specify the configuration
file name.
To specify the configuration file URL in a DHCP address pool:
dhcp server ip-pool
• Specify the IP address of the TFTP
server:
tftp-server ip-address ip-address
• Specify the name of the TFTP server:
tftp-server domain-name
domain-name
bootfile-name
pool-name
bootfile-name
By default, no DHCP
address pool exists.
You can specify both the IP
address and name of the
TFTP server.
By default, no TFTP server
is specified.
By default, no configuration
file name is specified.
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
3. Specify the URL of the
configuration file.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
bootfile-name
url
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP
address pool exists.
By default, no configuration
file URL is specified.
Specifying a server for DHCP clients
Some DHCP clients need to obtain configuration information from a server, such as a TFTP server.
You can specify the IP address of that server. The DHCP server sends the server's IP address to
DHCP clients along with other configuration information.
To specify the IP address of a server:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
3. Specify the IP address of a
server.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
next-server
ip-address By default, no server is specified.
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
Configuring Option 184 parameters for DHCP clients
To assign calling parameters to DHCP clients with voice service, you must configure Option 184 on
the DHCP server. For more information about Option 184, see "Option 184."
To configure option 184 parameters in a DHCP address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool and
enter its view.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
pool-name
N/A
By default, no DHCP address pool
exists.
46
Page 61

Step Command Remarks
3. Specify the IP address of the
primary network calling
processor.
4. (Optional.) Specify the IP address
for the backup server.
5. (Optional.) Configure the voice
VLAN.
6. (Optional.) Specify the failover IP
address and dialer string.
voice-config ncp-ip
ip-address
voice-config as-ip
ip-address
voice-config voice-vlan
vlan-id {
voice-config fail-over
ip-address dialer-string
Customizing DHCP options
IMPORTANT:
Use caution when customizing DHCP options because the configuration might affect DHCP
operation.
You can customize options for the following purposes:
• Add newly released options.
• Add options for which the vendor defines the contents, for example, Option 43.
• Add options for which the CLI does not provide a d edicated configuration command. For
example, you can use the option 4 ip-address 1.1.1.1 command to define the time server
address 1.1.1.1 for DHCP clients.
• Add all option values if the actual requirement exceeds the limit for a dedicated option
configuration command. For example, the dns-list command can specify up to eight DNS
servers. To specify more than eight DNS servers, you must use the option 6 command to
define all DNS servers.
disable
enable
|
By default, no primary network
calling processor is specified.
After you configure this command,
the other Option 184 parameters
take effect.
By default, no backup network
calling processor is specified.
By default, no voice VLAN is
}
configured.
By default, no failover IP address or
dialer string is specified.
To customize a DHCP option in a DHCP address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address
pool and enter its view.
3. Customize a DHCP
option.
To customize a DHCP option in a DHCP option group:
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
pool-name
option
ascii-string |
hex-string |
ip-address&<1-8> }
code {
hex
ip-address
ascii
N/A
By default, no DHCP address pool exists.
By default, no DHCP option is customized in a
DHCP address pool.
DHCP options specified in DHCP option
groups take precedence over those specified in
DHCP address pools.
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP user
class and enter DHCP
user class view.
system-view
dhcp class
class-name
47
N/A
By default, no DHCP user class
exists.
Page 62

Step Command Remarks
3. Configure a match rule for
the DHCP user class.
4. Return to system view.
5. Create a DHCP option
group and enter DHCP
option group view.
6. Customize a DHCP
option.
7. Create a DHCP address
pool and enter DHCP
address pool view.
8. Specify the DHCP option
group for the DHCP user
class.
if-match rule
option-code [
mask |
hardware-address
|
hardware-address
hardware-address-mask }
quit
dhcp option group
option-group-number
option
hex-string |
ip-address&<1-8> }
dhcp server ip-pool
class
class-name
option-group-number
offset
code {
ip-address
rule-number {
hex
hex-string [
length
offset
mask
ascii
ascii-string |
option group
option
mask
length ] ]
pool-name
By default, no match rule is
configured for a DHCP user class.
N/A
By default, no DHCP option group
exists.
By default, no DHCP option is
customized in a DHCP option
group.
hex
DHCP options specified in DHCP
option groups take precedence
over those specified in DHCP
address pools.
By default, no DHCP address pool
exists.
By default, no DHCP option group
is specified for a DHCP user class.
Table 2 Common DHCP options
Option Option name
3 Router Option
6 Domain Name Server Option
15 Domain Name
44
46
66 TFTP server name
67 Boot file name
43 Vendor Specific Information N/A
NetBIOS over TCP/IP Name
Server Option
NetBIOS over TCP/IP Node
Type Option
Corresponding
command
gateway-list ip-address
dns-list ip-address
domain-name ascii
nbns-list ip-address
netbios-type hex
tftp-server ascii
bootfile-name ascii
Configuring the DHCP user class whitelist
The DHCP user class whitelist allows the DHCP serv er to process requests only from clients on the
DHCP user class whitelist. The whitelist does not take effect on clients who request static IP
addresses, and the server always processes their request s.
To configure the DHCP user class whitelist:
Recommended option
command parameters
hex
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
48
N/A
Page 63

Step Command Remarks
2. Create a DHCP user class
and enter DHCP user class
view.
dhcp class
class-name
By default, no DHCP user class
exists.
3. Configure a match rule for
the DHCP user class.
4. Return to system view.
5. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter DHCP address
pool view.
6. Enable the DHCP user class
whitelist.
7. Add DHCP user classes to
the DHCP user class
whitelist.
Enabling DHCP
You must enable DHCP to validate other DHCP configurations.
To enable DHCP:
if-match rule
option
{
hex-string [
length
offset
hardware-address
hardware-address
hardware-address-mask }
quit
dhcp server ip-pool
verify class
valid class
rule-number
option-code [
mask
length ] ] |
class-name&<1-8>
hex
mask |
mask
pool-name
offset
By default, no match rule is
configured for a DHCP user class.
N/A
By default, no DHCP address pool
exists.
By default, the DHCP user class
whitelist is disabled.
By default, no DHCP user class is
on the DHCP user class whitelist.
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable DHCP.
system-view
dhcp enable
N/A
By default, DHCP is disabled.
Enabling the DHCP server on an interface
Perform this task to enable the DHCP server on an interface. Upo n receiving a DHCP requ est on the
interface, the DHCP server assigns the client an IP address and other configuration pa rameters from
a DHCP address pool.
To enable the DHCP server on an interface:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable the DHCP server on
the interface.
system-view
interface
interface-number
dhcp select server
interface-type
N/A
N/A
By default, the DHCP server on
the interface is enabled.
Applying an address pool on an interface
Perform this task to apply a DHCP address pool on an interface.
49
Page 64

Upon receiving a DHCP request from the interfa ce, the DHCP serv er performs a ddress allo cation in
the following ways:
• If a static binding is found for the client, the server assigns the static IP address and
configuration parameters from the address pool that contains the static binding.
• If no static binding is found for the client, the server uses the address pool applied to the
interface for address and configuration parameter allocation.
To apply an address pool on an interface:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter interface view.
3. Apply an address pool on the
interface.
interface
interface-number
dhcp server apply ip-pool
pool-name
interface-type
N/A
By default, no address pool is applied
on an interface.
If the applied address pool does not
exist, the DHCP server fails to perform
dynamic address allocation.
Configuring IP address conflict detection
Before assigning an IP address, the DHCP server pings that IP address.
• If the server receives a response within the specified period, it selects and pings another IP
address.
• If it receives no response, the server cont inues to ping the IP address until a spe cific number of
ping packets are sent. If still no response is received, the server assigns the IP address to the
requesting client. The DHCP client uses gratuitous ARP to perform IP address conflict
detection.
To configure IP address conflict detection:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. (Optional.) Set the maximum
number of ping packets to be
sent for conflict detection.
3. (Optional.) Set the ping
timeout time.
dhcp server ping packets
number
dhcp server ping timeout
milliseconds
Enabling handling of Option 82
Perform this task to enable the DHCP server to handle Option 82. Upon receiving a DHCP request
that contains Option 82, the DHCP server adds Option 82 into the DHCP response.
If you disable the DHCP to handle Option 82, it does not add Optio n 82 into the resp onse m essag e.
You must enable handling of Option 82 on both the DHCP server and the DHCP relay agent to
ensure correct processing for Option 82. For information about enabling handling o f Option 82 on the
DHCP relay agent, see "Configuring Option 82."
50
The default setting is one.
The value 0 disables IP address
conflict detection.
The default setting is 500 ms.
The value 0 disables IP address
conflict detection.
Page 65

To enable the DHCP server to handle Option 82:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable the server to handle
Option 82.
system-view
dhcp server relay information
enable
N/A
By default, handling of
Option 82 is enabled.
Configuring DHCP server compatibility
Perform this task to enable the DHCP server to support DHCP clients that are incompliant with RFC.
Configuring the DHCP server to broadcast all responses
By default, the DHCP server broadcasts a response only when the broadcast flag in the DHCP
request is set to 1. You can configure the DHCP server to ignore the broadcast flag and always
broadcast a response. This function is useful when some clients set the broadcast flag to 0 but do not
accept unicast responses.
The DHCP server always unicasts a response in the following situations, regardless of whether this
function is configured or not:
• The DHCP request is from a DHCP client that has an IP address (the ciaddr field is not 0).
• The DHCP request is forwa rded by a DHCP relay agent from a DHCP client (the giaddr field is
not 0).
To configure the DHCP server to broadcast all responses:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable the DHCP server
to broadcast all
responses.
system-view
dhcp server
always-broadcast
N/A
By default, the DHCP server looks at the
broadcast flag to decide whether to
broadcast or unicast a response.
Configure the DHCP server to ignore BOOTP requests
The lease duration of the IP addresses obtained by the BOOTP clients is unlimited. For some
scenarios that do not allow unlimited leases, you can configure the DHCP server to ignore BOOTP
requests.
To configure the DHCP server to ignore BOOTP requests:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure the DHCP server to
ignore BOOTP requests.
system-view
dhcp server bootp ignore
N/A
By default, the DHCP server
processes BOOTP requests.
51
Page 66

Configuring the DHCP server to send BOOTP responses in RFC 1048 format
Not all BOOTP clients can send requests that are compatible with RFC 1048. By default, the DHCP
server does not process the Vend field of RFC 1048-incompliant requests but copies the Vend field
into responses.
This function enables the DHCP server to fill the Vend field in RFC 1048-compliant format in DHCP
responses to RFC 1048-incompliant requests sent by BOOTP clients.
This function is effective for the BOOTP clients that request statically bound addresses.
To configure the DHCP server to send BOOTP responses in RFC 1048 format:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable the DHCP server to send
BOOTP responses in RFC 1048 format
to the RFC 1048-incompliant BOOTP
requests for statically bound addresses.
system-view
dhcp server bootp
reply-rfc-1048
N/A
By default, the DHCP server
directly copies the Vend field of
such requests into the responses.
Setting the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP server
The DSCP value of a packet specifies the priority level of the packet and affects the transmission
priority of the packet.
To set the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP server:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Set the DSCP value for DHCP
packets sent by the DHCP
server.
system-view
dhcp dscp
dscp-value
N/A
By default, the DSCP value in DHCP
packets sent by the DHCP server is 56.
Configuring DHCP binding auto backup
The auto backup function saves bindings to a backup file and allows the DHCP server to download
the bindings from the backup file at the server reboot. The bindings include the lease bindings and
conflicted IP addresses. They cannot survive a reboot on the DHCP server.
The DHCP server does not provide services during the download process. If a connection error
occurs during the process and cannot be repaired in a short amount of time, you can terminate the
download operation. Manual interruption allows the DHCP server to provide se rvices without waiting
for the connection to be repaired.
To configure DHCP binding auto backup:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
52
N/A
Page 67

Step Command Remarks
By default, the DHCP server
does not back up the DHCP
bindings.
With this command executed,
|
the DHCP server backs up its
bindings immediately and runs
auto backup.
N/A
2. Configure the DHCP server to
back up the bindings to a file.
3. (Optional.) Manually save the
DHCP bindings to the backup
file.
dhcp server database filename
{ filename |
username [
simple
dhcp server database update
now
url
password
} key ] ] }
url [
username
cipher
{
4. (Optional.) Set the waiting
time after a DHCP binding
change for the DHCP server
to update the backup file.
5. (Optional.) Terminate the
download of DHCP bindings
from the backup file.
dhcp server database update
interval
dhcp server database update
stop
seconds
The default waiting time is 300
seconds.
If no DHCP binding changes,
the backup file is not updated.
N/A
Configuring address pool usage alarming
Perform this task to set the threshold for address pool usage alarming. When the threshold is
exceeded, the system sends log messages to the information center. According to the log
information, you can optimize the address pool configuration. For more information about the
information center, see Network Man agement and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
To configure address pool usage alarming:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
3. Set the threshold for address
pool usage alarming.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
ip-in-use threshold
threshold-value
N/A
pool-name
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
The default threshold is 100%.
Binding gateways to a common MAC address
This feature enables DHCP clients of different types to obtain dif ferent gateway IP addresses but the
same MAC address. In addition to assigning gateway IP addresses to the clients, the DHCP server
adds the gateway IP addresses and server's MAC address to the address ma nagement module. The
ARP module can use the entries to reply ARP requests from the clients.
As shown in Figure 22, the DHCP
clients of different service types, such as broadband, IP TV, and IP telephone. The clients of different
types obtain IP addresses on different subnets. For the clients to access the network, the access
interface typically has no IP address configured. You must bind the gateways to a MAC address
when specifying gateways for the DHCP clients.
server is configured on the access device that provides acces s for
53
Page 68

Figure 22 Network diagram
...
The gateway binding feature on the master device takes effect if the DHCP add ress pool is bound to
a VSRP instance. If the address pool is applied to a VPN instance, the VPN instance must exist.
To bind the gateways to a common MAC address:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
3. Bind the gateways to the
device's MAC address.
system-view
N/A
dhcp server ip-pool
gateway-list
ip-address&<1-8>
export-route
pool-name
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
By default, gateways are not
bound to any MAC address.
Advertising subnets assigned to clients
This feature enables the route management module to advertise subnets assign ed to DHCP clients.
This feature achieves symmetric routing for traffic of the same host.
As shown in Figure 23, Ro
The BRAS devices send accounting packets to the RADIUS server. To enable the BRAS device s to
collect correct accounting information for each RADIUS user, configure the DHCP server to
advertise subnets assigned to clients. The upstream and downstream traffic of a RADIUS user will
pass through the same BRAS device.
Figure 23 Network diagram
Host A
Host B
Layer 2 switch
Host C
The subnet advertising on the master device of a VSRP instance takes effect. If the address pool is
applied to a VPN instance, the VPN instance must exist.
uter A and Router B act as both the DHCP server and the BRAS device.
Router A
DHCP server
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/1
BRAS
Router B
DHCP server
GE1/0/2
2.2.2.2/24
IP network
GE1/0/2
2.2.2.3/24
BRAS
RADIUS server
Upstream traffic
Downstream traffic
54
Page 69

To configure the subnet advertisement function:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
N/A
pool-name
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
3. Advertise subnets assigned to
DHCP clients.
network
[ mask-length |
export-route
network-address
mask
mask ]
secondary ]
[
By default, the subnets
assigned to DHCP clients are
not advertised.
Applying a DHCP address pool to a VPN instance
If a DHCP address pool is applied to a VPN instance, the DHCP server assigns IP addresses in this
address pool to clients in the VPN instance. Addresses in this address pool will not be assigned to
clients on the public network.
The DHCP server can obtain the VPN instance to which a DHCP client belongs from the following
information:
• The client's VPN information stored in authenticatio n modules, such as IPoE.
• The VPN information of the DHCP se rver's interface that receives DHCP packets from the
client.
The VPN information from authentication modules takes priority over the VPN information of the
receiving interface.
To apply a DHCP address pool to a VPN instance:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP address pool
and enter its view.
3. Apply the address pool to a
VPN instance.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
vpn-instance
N/A
vpn-instance-name
pool-name
By default, no DHCP address
pool exists.
By default, no VPN instance is
applied to the address pool.
Enabling client offline detection on the DHCP server
The client offline detection feature reclaims an assigned IP address and deletes the binding entry
when the ARP entry for the IP address ages out. The feature does not function if an ARP entry is
manually deleted.
To enable client offline detection on the DHCP server:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable client offline detection.
system-view
interface
interface-number
dhcp client-detect
N/A
interface-type
55
N/A
By default, client offline detection is
disabled on the DHCP server.
Page 70

Configuring DHCP logging on the DHCP server
The DHCP logging feature enables the DHCP server to generate DHCP logs and send them to the
information center. For information about the log destination and output rule configuration in the
information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Disable this feature when the log generation affects the device performanc e or reduces the addre ss
allocation efficiency. For example, this situation might occur when a large number of clients
frequently come online or go offline.
To configure DHCP logging on the DHCP server:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable DHCP logging.
system-view
dhcp log enable
N/A
By default, DHCP logging is disabled.
Displaying and maintaining the DHCP server
IMPORTANT:
A restart of the DHCP server or execution of the reset dhcp server ip-in-use command deletes all
lease information. The DHCP server denies any DHCP request for lease extension, and the client
must request an IP address again.
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
Task Command
Display information about IP address
conflicts.
Display information about DHCP binding
auto backup.
Display information about lease-expired IP
addresses.
Display information about assignable IP
addresses.
Display information about assigned IP
addresses.
Display DHCP server statistics.
Display information about DHCP address
pools.
Clear information about IP address conflicts.
Clear information about lease-expired IP
addresses.
Clear information about assigned IP
addresses.
display dhcp server conflict
vpn-instance
[
display dhcp server database
display dhcp server expired
vpn-instance
[
display dhcp server free-ip [ pool
vpn-instance
display dhcp server ip-in-use
vpn-instance
[
display dhcp server statistics [ pool
vpn-instance
display dhcp server pool [
vpn-instance-name ]
reset dhcp server conflict [ ip
vpn-instance-name ]
reset dhcp server expired
vpn-instance
[
reset dhcp server ip-in-use
vpn-instance
[
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ] |
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ] |
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ] |
vpn-instance-name ] |
[ ip ip-address ]
[ [ ip ip-address ]
pool-name |
[ [ ip ip-address ]
pool-name |
ip-address ] [
[ [ ip ip-address ]
[ [ ip ip-address ]
pool
pool-name ]
pool
pool-name ]
pool-name |
vpn-instance
vpn-instance
pool
pool-name ]
pool
pool-name ]
Clear DHCP server statistics.
reset dhcp server statistics [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ]
56
Page 71

DHCP server configuration examples
DHCP networking includes the following types:
• The DHCP server and clients reside on the same subnet.
• The DHCP server and clients are not on the same subnet and communicate with each other
through a DHCP relay agent.
The DHCP server configuration for the two types is identical.
Static IP address assignment configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 24, Router A (DHCP server) assigns a static IP address, a DNS server address,
and a gateway address to Router B (DHCP client) and Router C (BOOTP client).
The client ID of the interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on Router B is:
0030-3030-662e-6532-3030-2e30-3030-322d-4574-6865-726e-6574.
The MAC address of the interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on Router C is 000f-e200-01c0.
Figure 24 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Specify an IP address for GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 on Router A:
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 25
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
2. Configure the DHCP server:
# Enable DHCP.
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Enable the DHCP server on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select server
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create DHCP address pool 0.
[RouterA] dhcp server ip-pool 0
# Configure a static binding for Router B.
57
Page 72

[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] static-bind ip-address 10.1.1.5 25 client-identifier
0030-3030-662e-6532-3030-2e30-3030-322d-4574-6865-726e-6574
# Configure a static binding for Router C.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] static-bind ip-address 10.1.1.6 25 hardware-address
000f-e200-01c0
# Specify the DNS server and gateway.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] dns-list 10.1.1.2
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] gateway-list 10.1.1.126
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] quit
[RouterA]
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Router B can obtain IP address 10.1.1.5 and all other network param eters from Router A.
(Details not shown.)
# Verify that Router C can obtain IP address 10.1.1.6 and all other network parameters from Route r
A. (Details not shown.)
# On the DHCP server, display the IP addresses assigned to the clients.
[RouterA] display dhcp server ip-in-use
IP address Client identifier/ Lease expiration Type
Hardware address
10.1.1.5 0030-3030-662e-6532- Jan 21 14:27:27 2014 Static(C)
3030-2e30-3030-322d 4574-6865-726e-6574
10.1.1.6 000f-e200-01c0 Unlimited Static(C)
Dynamic IP address assignment configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 25, the DHCP server (Router A) assigns IP addresses to clients on subnet
10.1.1.0/24, which is subnetted into 10.1.1.0/25 and 10.1.1.128/25.
Configure DHCP server on Router A to implement the following assignment scheme.
Table 3 Assignment scheme
DHCP clients IP address Lease Other configuration parameters
Clients that connect
to GigabitEthernet
2/0/1
Clients that connect
to GigabitEthernet
2/0/2
IP addresses on
subnet 10.1.1.0/25
IP addresses on
subnet 10.1.1.128/25
10 days and 12
hours
Five days
• Gateway: 10.1.1.126/25
• DNS server: 10.1.1.2/25
• Domain name: aabbcc.com
• WINS server: 10.1.1.4/25
• Gateway: 10.1.1.254/25
• DNS server: 10.1.1.2/25
• Domain name: aabbcc.com
58
Page 73

Figure 25 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Specify IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the DHCP server:
# Enable DHCP.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Enable the DHCP server on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 2/0/2.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select server
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] dhcp select server
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/2] quit
# Exclude addresses of the DNS server, WINS server, and gateways from dynamic allocation.
[RouterA] dhcp server forbidden-ip 10.1.1.2
[RouterA] dhcp server forbidden-ip 10.1.1.4
[RouterA] dhcp server forbidden-ip 10.1.1.126
[RouterA] dhcp server forbidden-ip 10.1.1.254
# Configure DHCP address pool 1 to assign IP addresses and other configurat ion parameters
to clients on subnet 10.1.1.0/25.
[RouterA] dhcp server ip-pool 1
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-1] network 10.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.128
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-1] expired day 10 hour 12
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-1] domain-name aabbcc.com
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-1] dns-list 10.1.1.2
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-1] gateway-list 10.1.1.126
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-1] nbns-list 10.1.1.4
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-1] quit
# Configure DHCP address pool 2 to assign IP addresses and other configurat ion parameters
to clients on subnet 10.1.1.128/25.
[RouterA] dhcp server ip-pool 2
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-2] network 10.1.1.128 mask 255.255.255.128
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-2] expired day 5
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-2] domain-name aabbcc.com
59
Page 74

[RouterA-dhcp-pool-2] dns-list 10.1.1.2
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-2] gateway-list 10.1.1.254
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that clients on subnets 10.1.1.0/25 and 10.1.1.128/25 can obtain correct IP addresses and
all other network parameters from Router A. (Details not shown.)
# On the DHCP server, display the IP addresses assigned to the clients.
[RouterA] display dhcp server ip-in-use
DHCP user class configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 26, the DHCP relay agent (Router A) forwards DHCP packets between DHCP
clients and the DHCP server (Router B). Enable Router A to handle Option 82 so that it can add
Option 82 in DHCP requests and then convey them to the DHCP server.
Configure the address allocation scheme as follows:
Assign IP addresses To clients
10.10.1.2 to 10.10.1.10 The DHCP request contains Option 82.
10.10.1.11 to 10.10.1.26
Router B assigns the DNS server address 10.10.1.20/24 and the gateway address 10.10.1.254/24 to
clients on subnet 10.10.1.0/24.
Figure 26 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Specify IP addresses for the interfaces on DHCP server. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure DHCP:
# Enable DHCP and configure the DHCP server to handle Option 82.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] dhcp enable
[RouterB] dhcp server relay information enable
# Enable the DHCP server on the interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select server
The hardware address in the request is six bytes long and
begins with
aabb-aabb-aab
.
60
Page 75

[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create DHCP user class tt and configure a match rule to match DHCP requests that contain
Option 82.
[RouterB] dhcp class tt
[RouterB-dhcp-class-tt] if-match rule 1 option 82
[RouterB-dhcp-class-tt] quit
# Create DHCP user class ss and configure a match rule to match DHCP requests in which the
hardware address is six bytes long and begins with aabb-aabb-aab.
[RouterB] dhcp class ss
[RouterB-dhcp-class-ss] if-match rule 1 hardware-address aabb-aabb-aab0 mask
ffff-ffff-fff0
[RouterB-dhcp-class-ss] quit
# Create DHCP address pool aa.
[RouterB] dhcp server ip-pool aa
# Specify the subnet for dynamic allocation.
[RouterB-dhcp-pool-aa] network 10.10.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
# Specify the address range for dynamic allocation.
[RouterB-dhcp-pool-aa] address range 10.10.1.2 10.10.1.100
# Specify the address range for the user class tt.
[RouterB-dhcp-pool-aa] class tt range 10.10.1.2 10.10.1.10
# Specify the address range for the user class ss.
[RouterB-dhcp-pool-aa] class ss range 10.10.1.11 10.10.1.26
# Specify the gateway and the DNS server.
[RouterB-dhcp-pool-aa] gateway-list 10.10.1.254
[RouterB-dhcp-pool-aa] dns-list 10.10.1.20
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that clients mat ching the DHCP user clas ses can obtain IP addresse s in the specified ranges
and all other configuration parameters from the DHCP server. (Details not shown.)
# On the DHCP server, display the IP addresses assigned to the clients.
[RouterB] display dhcp server ip-in-use
DHCP user class whitelist configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 27, configure the DHCP user class whitelist to allow the DHCP server to assign
IP addresses to clients whose hardware addresses are six bytes long and begin with aabb-aabb.
Figure 27 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Specify IP addresses for the interfaces on the DHCP server. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure DHCP:
# Enable DHCP.
61
Page 76

<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Enable DHCP server on interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select server
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create DHCP user class ss and configure a match rule to match DHCP requests in which the
hardware address is six bytes long and begins with aabb-aabb.
[RouterA] dhcp class ss
[RouterA-dhcp-class-ss] if-match rule 1 hardware-address aabb-aabb-0000 mask
ffff-ffff-0000
[RouterA-dhcp-class-ss] quit
# Create DHCP address pool aa.
[RouterA] dhcp server ip-pool aa
# Specify the subnet for dynamic allocation.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa] network 10.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
# Enable DHCP user class whitelist.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa] verify class
# Add DHCP user class ss to the DHCP user class whitelist.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa] valid class ss
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that clients matching the DHCP user class can obtain IP addresses on subnet 10.1.1.0/24
from the DHCP server. (Details not shown.)
# On the DHCP server, display the IP addresses assigned to the clients.
[RouterA] display dhcp server ip-in-use
Primary and secondary subnets configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 28, the DHCP server (Router A) assigns IP addresses to DHCP clients in the
LAN.
Configure two subnets in the address pool on the DHCP server: 10.1.1.0/24 as the primary subnet
and 10.1.2.0/24 as the secondary subnet. The DHCP server selects an IP address from the
secondary subnet when the primary subnet has no assignable addresses.
Router A assigns the following parameters:
• The default gateway 10.1.1.254/24 to clients on subnet 10.1.1.0/24.
• The default gateway 10.1.2.254/24 to clients on subnet 10.1.2.0/24.
62
Page 77

Figure 28 Network diagram
Router A
DHCP server
GE2/0/1
10.1.1.1/24
10.1.2.1/24 sub
...
Configuration procedure
# Enable DHCP.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Configure the primary and secondary IP addresses of interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1, and enable
the DHCP server on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 10.1.2.1 24 sub
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select server
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create DHCP address pool aa.
[RouterA] dhcp server ip-pool aa
# Specify the primary subnet and the gateway for dynamic allocation.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa] network 10.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa] gateway-list 10.1.1.254
# Specify the secondary subnet and the gateway for dynamic allocation.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa] network 10.1.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 secondary
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa-secondary] gateway-list 10.1.2.254
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa-secondary] quit
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-aa]
GatewayDHCP client DHCP client DHCP client
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the DHCP server assigns clients IP addre sses and gateway address from the secondary
subnet when no assignable address is available from the primary subnet. (Details not shown.)
# On the DHCP server, display IP addresses assigned to the clients.
[RouterA] display dhcp server ip-in-use
DHCP option customization configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 29, DHCP clients obtain IP addresses and PXE server addresses from the DHCP
server (Router A). The subnet for address allocation is 10.1.1.0/24.
63
Page 78

Configure the address allocation scheme as follows:
Assign PXE addresses To clients
2.3.4.5 and 3.3.3.3
1.2.3.4 and 2.2.2.2. Other clients.
The hardware address in the request is six bytes long and
begins with
aabb-aabb
.
The DHCP server assigns PXE server addresses to DHCP clients through Option 43, a custom
option. The formats of Option 43 and PXE server address sub-option are shown in Figure 19
and Figure 21. For example
, the value of Option 43 configured in the DHCP address pool is 80 0B 00
00 02 01 02 03 04 02 02 02 02.
• The number 80 is the value of the sub-option type.
• The number 0B is the value of the sub-option length.
• The numbers 00 00 are the value of the PXE server type.
• The number 02 indicates the number of servers.
• The numbers 01 02 03 04 02 02 02 02 indicate that the PXE server addresses are 1.2.3.4 and
2.2.2.2.
Figure 29 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Specify an IP address for interface GigabitEthernet 2/0/1. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the DHCP server:
# Enable DHCP.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Create DHCP user class ss and configure a match rule to match DHCP requests in which the
hardware address is six bytes long and begins with aabb-aabb.
[RouterA] dhcp class ss
[RouterA-dhcp-class-ss] if-match rule 1 hardware-address aabb-aabb-0000 mask
ffff-ffff-0000
[RouterA-dhcp-class-ss] quit
# Create DHCP option group 1 and customize Option 43.
[RouterA] dhcp option-group 1
[RouterA-dhcp-option-group-1] option 43 hex 800B0000020203040503030303
# Enable the DHCP server on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select server
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Create DHCP address pool 0.
[RouterA] dhcp server ip-pool 0
# Specify the subnet for dynamic address allocation.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] network 10.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
# Customize Option 43.
64
Page 79

[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] option 43 hex 800B0000020102030402020202
# Associate DHCP user class ss with option group 1.
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] class ss option-group 1
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Router B can obtain an IP address on subnet 10.1.1.0/24 and the corresponding PXE
server addresses from Router A. (Details not shown.)
# On the DHCP server, display the IP addresses assigned to the clients.
[RouterA] display dhcp server ip-in-use
Troubleshooting DHCP server configuration
Symptom
A client's IP address obtained from the DHCP server conflicts with another IP address.
Analysis
Another host on the subnet might have the same IP address.
Solution
1. Disable the client's network adapter or disconnect the client's network cable. Ping the IP
2. If a ping response is received, the IP address has been manually configured on a host. Execute
3. Enable the network adapter or connect the network cable, release the IP address, and obtain
address of the client from another host to check whether there is a host using the same IP
address.
the dhcp server forbidden-ip command on the DHCP server to exclude the IP address from
dynamic allocation.
another one on the client. For example, to release the IP address and obtain another one on a
Windows XP DHCP client:
a. In Windows environment, execute the cmd command to enter the DOS environment.
b. Enter ipconfig /release to relinquish the IP address.
c. Enter ipconfig /renew to obtain another IP address.
65
Page 80

Configuring the DHCP relay agent
Overview
The DHCP relay agent enables clients to get IP addresses from a DHCP server on another subnet.
This feature avoids deploying a DHCP server for ea ch subnet to centralize management a nd reduce
investment. Figure 30 sh
Figure 30 DHCP relay agent application
ows a typical application of the DHCP relay agent.
An MCE device acting as the DHCP relay agent can forward DHCP packets between a DHCP server
and clients on either a public network or a private network. For more information about MCE, see
MPLS Configuration Guide.
Operation
The DHCP server and client interact with each other in the same way reg ardless of whether the relay
agent exists. For the interaction details, see "IP address allocation process." The follo
describes steps related to the DHCP relay agent:
1. After receiving a DHCP-DISCOVER or DHCP-REQUEST broadcast message from a DHCP
client, the DHCP relay agent processes the message as follows:
a. Fills the giaddr field of the message with its IP address.
b. Unicasts the message to the designated DHCP server.
2. Based on the giaddr field, the DHCP server returns an IP address and other configuration
parameters in a response.
3. The relay agent conveys the response to the client.
wing only
66
Page 81

Figure 31 DHCP relay agent operation
DHCP relay agent support for Option 82
Option 82 records the location information about the DHCP client. It enables the administrator to
perform the following tasks:
• Locate the DHCP client for security and accounting purposes.
• Assign IP addresses in a specific range to clients.
For more information about Option 82, see "Relay agent option (Option 82)."
If the DHCP relay agent supports Option 82, it handles DHCP requests by following the strategies
described in Table 4.
If a respon
se returned by the DHCP server contains Option 82, the DHCP relay agent removes the
Option 82 before forwarding the response to the client.
Table 4 Handling strategies of the DHCP relay agent
If a DHCP request
has…
Option 82
No Option 82 N/A
Handling
strategy
Drop Drops the message.
Keep Forwards the message without changing Option 82.
Replace
The DHCP relay agent…
Forwards the message after replacing the original Option 82 with
the Option 82 padded according to the configured padding format,
padding content, and code type.
Forwards the message after adding Option 82 padded according to
the configured padding format, padding content, and code type.
DHCP relay agent configuration task list
Tasks at a glance
(Required.) Enabling DHCP
(Required.) Enabling the DHCP relay agent on an interface
(Required.) Specifying DHCP servers on a relay agent
(Optional.) Configuring the DHCP relay agent security functions
67
Page 82

Tasks at a glance
(Optional.) Configuring the DHCP relay agent to release an IP address
(Optional.) Configuring Option 82
(Optional.) Setting the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP relay agent
(Optional.) Enabling DHCP server proxy on a DHCP relay agent
(Optional.) Configuring a DHCP relay address pool
(Optional.) Specifying a gateway address for DHCP clients
(Optional.) Enabling client offline detection on the DHCP relay agent
(Optional.) Specifying the source address and gateway address in DHCP requ ests
Enabling DHCP
You must enable DHCP to validate other DHCP relay agent settings.
To enable DHCP:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable DHCP.
system-view
dhcp enable
N/A
By default, DHCP is disabled.
Enabling the DHCP relay agent on an interface
With the DHCP relay agent enabled, an interface forwards incoming DHCP requests to a DHCP
server.
An IP address pool that contains the IP address of the DHCP relay interface must be configured on
the DHCP server . Otherwise, the DHCP clients connected to the relay agent cannot obtain co rrect IP
addresses.
To enable the DHCP relay agent on an interface:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable the DHCP relay
agent.
system-view
interface
interface-number
dhcp select relay
interface-type
N/A
N/A
By default, when DHCP is
enabled, an interface operates in
the DHCP server mode.
Specifying DHCP servers on a relay agent
To improve availability, you can specify several DHCP servers on the DHCP relay agent. When the
interface receives request messages from clients, the relay agent forwards them to all DHCP
servers.
Follow these guidelines when you specify a DHCP server address on a relay agent:
68
Page 83

• The IP address of any specified DHCP server must not reside on the same subnet as the IP
address of the relay interface. Otherwise, the clients might fail to obtain IP addresses.
• You can specify a maximum of eight DHCP servers.
To specify a DHCP server address on a relay agent:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter interface view.
3. Specify a DHCP server
address on the relay agent.
interface
interface-number
dhcp relay server-address
ip-address
interface-type
N/A
By default, no DHCP server
address is specified on the relay
agent.
Configuring the DHCP relay agent security functions
Enabling the DHCP relay agent to record relay entries
Perform this task to enable the DHCP relay agent to automatically record clients' IP-to-MAC bindings
(relay entries) after they obtain IP addresses through DHCP.
Some security functions use the relay entries to check incoming packets and block packets that do
not match any entry. In this way, illegal hosts are not able to access external networks through the
relay agent. Examples of the security functions are ARP address check, authorized ARP, and IP
source guard.
To enable the DHCP relay agent to record relay entries:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable the relay agent to
record relay entries.
system-view
dhcp relay client-information record
N/A
By default, the relay agent
does not record relay entries.
NOTE:
The DHCP relay agent does not record IP-to-MAC bindings for DHCP clients running on
synchronous/asynchronous serial interfaces.
Enabling periodic refresh of dynamic relay entries
A DHCP client unicasts a DHCP-RELEASE message to the DHCP server to release its IP address.
The DHCP relay agent conveys the message to the DHCP server and does not remove the
IP-to-MAC entry of the client.
With this feature, the DHCP relay agent uses the following information to periodically send a
DHCP-REQUEST message to the DHCP server:
• The IP address of a relay entry.
• The MAC address of the DHCP relay interface.
The relay agent maintains the relay entries depending on what it receives from the DHCP server:
69
Page 84

• If the server returns a DHCP-ACK message or does not return any message within an interval,
the DHCP relay agent removes the relay entry. In addition, upon receiving the DHCP-ACK
message, the relay agent sends a DHCP-RELEASE message to release the IP address.
• If the server returns a DHCP-NAK message, the relay agent keeps the relay entry.
To enable periodic refresh of dynamic relay entries:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enable periodic refresh of
dynamic relay entries.
3. Set the refresh interval.
dhcp relay client-information refresh
enable
dhcp relay client-information refresh
auto | interval
[
interval ]
Enabling DHCP starvation attack protection
A DHCP starvation attack occurs when an attacker constantly sends forged DHCP requests using
different MAC addresses in the chaddr field to a DHCP server. This exhausts the IP address
resources of the DHCP server so legitimate DHCP clients cannot obtain IP addresses. The DHCP
server might also fail to work because of exhaustion of system resources. The following methods ar e
available to relieve or prevent such attacks.
• To relieve a DHCP starvation attack that uses DHCP packets encapsulated with different
source MAC addresses, you can use one of the following methods:
{ Limit the number of ARP entries that a Layer 3 interface can learn.
{ Limit the number of MAC addresses that a Layer 2 port can learn.
{ Configure an interface that has learned the maximum MAC addresses to discard packets
whose source MAC addresses are not in the MAC address table.
• To prevent a DHCP starvation attack that uses DHCP requests encapsulated with the same
source MAC address, you can enable MAC address check on the DHCP relay agent. The
DHCP relay agent compares the chaddr field of a received DHCP request with the source MAC
address in the frame header . If they are the same, the DHCP relay agent forwards the request
to the DHCP server. If not, the relay agent discards the request.
By default, periodic refresh
of dynamic relay entries is
enabled.
By default, the refresh
interval is
calculated based on the
number of total relay entries.
auto
, which is
Enable MAC address check only on the DHCP relay agent di rectly connected to the DHCP clients. A
DHCP relay agent changes the source MAC address of DHCP packets before sending them. If you
enable this feature on an intermediate relay agent, it might discard valid DHCP packets. Then the
sending clients will not obtain IP addresses.
A MAC address check entry has an aging time. When the aging time expires, both of the following
occur:
• The entry ages out.
• The DHCP relay agent rechecks the validity of DHCP requests sent from the MAC address in
the entry.
To enable MAC address check:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
70
N/A
Page 85

Step Command Remarks
The default aging time is 30
seconds.
2. Set the aging time for MAC
address check entries.
dhcp relay check mac-address
aging-time
time
This command takes effect
only after you execute the
dhcp relay check
mac-address
command.
3. Enter the interface view.
4. Enable MAC address check.
interface
interface-number
dhcp relay check mac-address
interface-type
N/A
By default, MAC address
check is disabled.
Configuring the DHCP relay agent to release an IP address
Configure the relay agent to release the IP address for a relay entry. The relay agent sends a
DHCP-RELEASE message to the server and meanwhile deletes the relay entry. Upon receiving the
DHCP-RELEASE message, the DHCP server releases the IP address.
To configure the DHCP relay agent to release an IP address:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure the DHCP relay
agent to release an IP
address.
system-view
dhcp relay release ip
vpn-instance
[
vpn-instance-name ]
client-ip
N/A
This command can release only
the IP addresses in the recorded
relay entries.
Configuring Option 82
Follow these guidelines when you configure Option 82:
• To support Option 82, you must perform related configuration on both the DHCP server and
relay agent. For DHCP server Option 82 configuration, see "Enabling handling of Option 82."
• If the handling strategy is replace, configure a padding mode and padding format for Option 82.
If the handling strategy is keep or drop, you do not need to configure any padding mode or
padding format for Option 82. The settings do not take effect even if you configure them.
• The device name (sysname) must not include spaces if it is configured as the padding conte nt
for sub-option 1. Otherwise, the DHCP relay agent will fail to add or replace Option 82.
To configure Option 82:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable the relay agent to handle
Option 82.
system-view
interface
interface-number
dhcp relay information enable
interface-type
N/A
N/A
By default, handling of
Option 82 is disabled.
71
Page 86

Step Command Remarks
4. (Optional.) Configure the strategy
for handling DHCP requests that
contain Option 82.
5. (Optional.) Configure the padding
mode and padding format for the
Circuit ID sub-option.
dhcp relay information strategy
drop
keep
{
|
dhcp relay information circuit-id
bas
string
{
|
verbose
sysname
node-identifier } ] [
format { ascii | hex
[
replace }
|
circuit-id | {
node-identifier
[
user-defined
|
interface
} ] }
normal
mac
{
] }
|
|
By default, the handling
strategy is
By default, the padding
mode for Circuit ID
sub-option is
the padding format is
replace
normal
.
, and
hex
.
6. (Optional.) Configure the padding
mode and padding format for the
Remote ID sub-option.
dhcp relay information remote-id
normal
{
string
format { ascii | hex
[
remote-id |
sysname }
By default, the padding
mode for the Remote ID
} ] |
sub-option is
the padding format is
normal
, and
hex
.
Setting the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP relay agent
The DSCP value of a packet specifies the priority level of the packet and affects the transmission
priority of the packet.
To set the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP relay agent:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Set the DSCP value for DHCP
packets sent by the DHCP
relay agent.
system-view
dhcp dscp
dscp-value
N/A
By default, the DSCP value in DHCP
packets sent by the DHCP relay agent is
56.
Enabling DHCP server proxy on a DHCP relay agent
The DHCP server proxy feature isolates DHCP servers from DHCP clients and protects DHCP
servers against attacks.
Upon receiving a response from the server , the DHCP server proxy modifies the server's IP address
as the relay interface's IP address before sending out the response. The DHCP client takes the
DHCP relay agent as the DHCP server.
To configure DHCP server proxy on a DHCP relay agent:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable DHCP relay agent and
DHCP server proxy on the
interface.
system-view
interface
interface-number
dhcp select relay proxy
N/A
interface-type
72
N/A
By default, the interface
operates in DHCP server mode.
Page 87

Configuring a DHCP relay address pool
This feature allows DHCP clients of the same type to obtain IP addresses and other configuration
parameters from the DHCP servers specified in the matching relay address pool.
It applies to scenarios where the DHCP relay agent connects to clients of the sa me acce ss type but
classified into different types by their locations. In this case, the relay interface typically has no IP
address configured. You can use the gateway-list command to specify the gateway address for
clients matching the same relay address pool and bind the gateway address to the device's MAC
address.
Upon receiving a DHCP DISCOVER or REQUEST from a client that matches a relay address pool,
the relay agent processes the packet as follows:
• Fills the giaddr field of the packet with the specified gateway address.
• Forwards the packet to all DHCP servers in the matching relay address pool.
The DHCP servers select an address pool according to the gateway address.
If PPPoE users are in the network, follow these restrictions and guidelines when you configure the
relay address pool:
• Enable the DHCP relay agent to record DHCP relay entries by using the dhcp relay
client-information record command. When a PPPoE user goes offline, the DHCP relay agent
can find a matching relay entry and send a DHCP-RELEASE message to the DHCP server.
This mechanism ensures the DHCP server to be aware of the releasing of the IP address in a
timely manner.
• The remote-server command also configures the device as a DHCP relay agent. You do not
need to enable the DHCP relay agent by using the dhcp select relay command.
To configure a DHCP relay address pool:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Create a DHCP relay
address pool and enter its
view.
3. Specify gateway addresses
for the clients matching the
relay address pool.
4. Specify DHCP servers for
the relay address pool.
system-view
dhcp server ip-pool
gateway-list
export-route ]
[
remote-server
ip-address&<1-8>
N/A
ip-address&<1-8>
pool-name
By default, no DHCP relay address
pool exists.
This command is the same for
creating DHCP address pools on a
DHCP server. However, the relay
address pool names are not
necessarily the same as the server
address pool names.
By default, no gateway address is
specified.
You can specify a maximum of eight
gateway addresses, but only the first
one takes effect.
By default, no DHCP server is
specified for the relay address pool.
You can specify a maximum of eight
DHCP servers for one relay address
pool for high availability. The relay
agent forwards DHCP DISCOVER
and REQUEST packets to all DHCP
servers in the relay address pool.
73
Page 88

Specifying a gateway address for DHCP clients
By default, the DHCP relay agent fills the giaddr field of DHCP DISCOVER and REQUEST packets
with the primary IP address of the relay interface. You can specify a gateway address on the relay
agent for DHCP clients. The DHCP rela y agent uses the specified gateway address to fill the giaddr
field of DHCP DISCOVER and REQUEST packets.
To specify a gateway address for DHCP clients:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter interface view.
3. Specify a gateway address for
DHCP clients.
interface
interface-number
dhcp relay gateway
interface-type
ip-address
N/A
By default, the DHCP relay
agent uses the primary IP
address of the relay interface as
the clients' gateway address.
Enabling client offline detection on the DHCP relay agent
When an ARP entry ages out, the client offline detection feature deletes the relay entry for the IP
address and sends a RELEASE message to the DHCP server. The feature does not function if an
ARP entry is manually deleted.
To enable client offline detection on the DHCP relay agent:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable the DHCP relay agent.
system-view
interface
interface-number
dhcp select relay
N/A
interface-type
N/A
By default, when DHCP is enabled,
an interface operates in the DHCP
server mode.
By default, the relay agent does not
4. Enable the relay agent to
record relay entries.
5. Enable client offline detection.
dhcp relay
client-information record
dhcp client-detect
record relay entries.
Without relay entries, client offline
detection cannot function correctly.
By default, client offline detection is
disabled on the DHCP relay agent.
Specifying the source address and gateway address in DHCP requests
Perform this task to configure the relay agent to pad the source address and gateway address in
DHCP requests with the public IP addre ss of the loopback interface. This configuration is required for
successful packet forwarding when the DHCP server is in the public network and the DHCP clients
are in a private network.
74
Page 89

If DHCP server proxy is enabled, you must configure the sub-option 72 in Option 82 to carry the
index of the interface that processes the DHCP request. When receiv ing a DHCP response, the relay
agent forwards the response according to the interface index in sub-option 72.
To specify the source address and gateway address in DHCP requests:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enter interface view.
3. Specify an IP address as the
source address and gateway
address in DHCP requests.
interface
interface-number
dhcp relay source-address
ip-address
interface-type
N/A
By default, the IP address of the
interface is used as the source
address and gateway address in
DHCP requests.
Displaying and maintaining the DHCP relay agent
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
Task Command
Display information about DHCP servers on an
interface.
Display Option 82 configuration information on the
DHCP relay agent.
Display relay entries on the DHCP relay agent.
Display packet statistics on the DHCP relay agent.
display dhcp relay server-address [ interface
interface-type interface-number ]
display dhcp relay information [ interface
interface-type interface-number ]
display dhcp relay client-information [ interface
interface-type interface-number | ip ip-address
vpn-instance
[
display dhcp relay statistics [ interface
interface-type interface-number ]
vpn-instance-name ] ]
Display MAC address check entries on the DHCP
relay agent.
Clear relay entries on the DHCP relay agent.
Clear packet statistics on the DHCP relay agent.
display dhcp relay check mac-address
reset dhcp relay client-information [ interface
interface-type interface-number | ip ip-address
vpn-instance
[
reset dhcp relay statistics
interface-number ]
vpn-instance-name ] ]
interface
[
DHCP relay agent configuration examples
DHCP relay agent configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 32, configure the DHCP relay agent on Router A. The DHCP relay ag ent enables
DHCP clients to obtain IP addresses and other configuration parameters from the DHCP server on
another subnet.
Because the DHCP relay agent and server are on different subnets, you need to configure static or
dynamic routing to make them reachable to each other.
interface-type
75
Page 90

DHCP server configuration is also required to guarantee the client-server communication through
the DHCP relay agent. For DHCP server configuration information, see "DHCP server configuration
example
s."
Figure 32 Network diagram
DHCP clientDHCP client
10.10.1.1/24
DHCP client DHCP client
Configuration procedure
# Specify IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Enable DHCP.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Enable the DHCP relay agent on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select relay
# Specify the IP address of the DHCP server on the relay agent.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp relay server-address 10.1.1.1
Verifying the configuration
GE2/0/1
Router A
DHCP relay agent
GE2/0/2
10.1.1.2/24
GE2/0/1
10.1.1.1/24
Router B
DHCP server
# Verify that DHCP clients can obtain IP addresses an d all other network parameters from the DHCP
server through the DHCP relay agent. (Details not shown.)
# Display the statistics of DHCP packets forwarded by the DHCP relay agent.
[RouterA] display dhcp relay statistics
# Display relay entries if you have enabled relay entry recording on the DHCP relay agent.
[RouterA] display dhcp relay client-information
Option 82 configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 32, the DHCP relay agent (Router A) replaces Option 82 in DHCP requests
before forwarding them to the DHCP server (Router B).
• The Circuit ID sub-option is company001.
• The Remote ID sub-option is device001.
To use Option 82, you must also enable the DHCP server to handle Option 82.
Configuration procedure
# Specify IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
76
Page 91

# Enable DHCP.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Enable the DHCP relay agent on GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp select relay
# Specify the IP address of the DHCP server on the relay agent.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp relay server-address 10.1.1.1
# Enable the DHCP relay agent to handle Option 82, and perform Option 82 related configuration.
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp relay information enable
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp relay information strategy replace
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp relay information circuit-id string company001
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] dhcp relay information remote-id string device001
Troubleshooting DHCP relay agent configuration
Symptom
DHCP clients cannot obtain configuration parameters through the DHCP relay agent.
Analysis
Some problems might occur with the DHCP relay agent or server configuration.
Solution
To locate the problem, enable debugging and execute the display command on the DHCP relay
agent to view the debugging information and interface state information.
Check that:
• DHCP is enabled on the DHCP server and relay agent.
• The DHCP server has an address pool on the same subnet as the DHCP clients.
• The DHCP server and DHCP relay agent can reach each other.
• The DHCP server address specified on the DHCP relay interface connected to the DHCP
clients is correct.
77
Page 92

Configuring the DHCP client
With DHCP client enabled, an interface uses DHCP to obtain configuration parameters from the
DHCP server, for example, an IP address.
The DHCP client configuration is supported only on Layer 3 Ethernet interfaces (or subinterfaces),
VLAN interfaces, and Layer 3 aggregate interfaces.
Enabling the DHCP client on an interface
Follow these guidelines when you enable the DHCP client on an int erface:
• On some device models, if the number of IP address request failures reaches the
system-defined amount, the DHCP client-enabled interface u ses a default IP address.
• An interface can be configured to acquire an IP address in multiple ways. The new configuration
overwrites the old.
• Secondary IP addres ses cannot be configured on an interface that is enabled with the DHCP
client.
• If the interface obtains an IP address on the same seg ment as anot her interfa ce on the device,
the interface does not use the assigned address. Instead, it requests a new IP addres s from the
DHCP server.
To enable the DHCP client on an interface:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Configure an interface to use
DHCP for IP address
acquisition.
system-view
interface
interface-number
ip address dhcp-alloc
interface-type
N/A
N/A
By default, an interface does not
use DHCP for IP address
acquisition.
Configuring a DHCP client ID for an interface
A DHCP client ID is added to the DHCP option 61. A DHCP server can specify IP addresses for
clients based on the DHCP client ID.
Make sure the IDs for different DHCP clients are unique.
To configure a DHCP client ID for an interface:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
system-view
interface
interface-number
interface-type
N/A
N/A
3. Configure a DHCP
client ID for the
interface.
dhcp client identifier
hex
string |
interface-type
interface-number }
string |
78
mac
{
ascii
By default, an interface generates the
DHCP client ID based on its MAC address.
If the interface has no MAC address, it uses
the MAC address of the first Ethernet
interface to generate its client ID.
Page 93

Step Command Remarks
DHCP client ID includes ID type and type
value. Each ID type has a fixed type value.
You can check the fields for the client ID to
verify which type of client ID is used:
• If an ASCII string is used as the client ID,
the type value is 00.
• If a hex string is used as the client ID, the
type value is the first two characters
in the string.
• If the MAC address of an interface is
used as the client ID, the type value
is 01.
4. Verify the client ID
configuration.
display dhcp client
verbose
[
interface-type
interface-number ]
interface
] [
Enabling duplicated address detection
DHCP client detects IP addre ss conflict through ARP packets. An attacker can act as the IP address
owner to send an ARP reply. The spoofing attack makes the client unable to use the IP address
assigned by the server. As a best practice, disable duplicate address detection when ARP attacks
exist on the network.
To enable duplicated address detection:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable duplicate address
detection.
system-view
dhcp client dad enable
N/A
By default, the duplicate address
detection feature is enabled on an
interface.
Setting the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP client
The DSCP value of a packet specifies the priority level of the packet and affects the transmission
priority of the packet.
To set the DSCP value for DHCP packets sent by the DHCP client:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Set the DSCP value for DHCP
packets sent by the DHCP
client.
system-view
dhcp client dscp
dscp-value
N/A
By default, the DSCP value in DHCP
packets sent by the DHCP client is 56.
Displaying and maintaining the DHCP client
Execute display command in any view .
79
Page 94

Task Command
Display DHCP client information.
display dhcp client [ verbose
interface-number ]
DHCP client configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 34, Router B contacts the DHCP server through GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 to obtain
an IP address, a DNS server address, and static route information. The DHCP client's IP address
resides on subnet 10.1.1.0/24. The DNS server address is 20.1.1.1. The next hop of the static route
to subnet 20.1.1.0/24 is 10.1.1.2.
The DHCP server uses Option 121 to assign static route information to DHCP clients. Figure 33
ws the Option 121 format. The destination descriptor field contains the following parts: subnet
sho
mask length and destination network address, both in hexadecimal notation. In this example, the
destination descriptor is 18 14 01 01 (the subnet mask length is 24 and the network address is
20.1.1.0 in dotted decimal notation). The next hop address is 0A 01 01 02 (10.1.1.2 in dotted de cimal
notation).
Figure 33 Option 121 format
interface
] [
interface-type
Figure 34 Network diagram
GE2/0/1
10.1.1.1/24
Router A
DHCP server
GE2/0/1
Router B
DHCP Client
10.1.1.2/24 20.1.1.2/24
Router C
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Router A:
# Specify the IP address of GigabitEthernet 2/0/1.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
# Enable DHCP.
[RouterA] dhcp enable
# Exclude an IP address from dynamic allocation.
20.1.1.1/24
DNS server
80
Page 95

[RouterA] dhcp server forbidden-ip 10.1.1.2
# Configure DHCP address pool 0. Specify the subnet, lease duration, DNS server address,
and a static route to subnet 20.1.1.0/24.
[RouterA] dhcp server ip-pool 0
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] network 10.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] expired day 10
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] dns-list 20.1.1.1
[RouterA-dhcp-pool-0] option 121 hex 181401010A010102
2. Configure Router B:
# Configure GigabitEthernet 2/0/1 to use DHCP for IP address acquisition.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] ip address dhcp-alloc
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet2/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display the IP address and other network parameters assigned to Router B.
[RouterB] display dhcp client verbose
GigabitEthernet2/0/1 DHCP client information:
Current machine state: BOUND
Allocated IP: 10.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
Allocated lease: 864000 seconds, T1: 331858 seconds, T2: 756000 seconds
Lease from May 21 19:00:29 2012 to May 31 19:00:29 2012
DHCP server: 10.1.1.1
Transaction ID: 0xcde72232
Classless static route:
Destination: 20.1.1.0, Mask: 255.255.255.0, NextHop: 10.1.1.2
DNS server: 20.1.1.1
Client ID type: acsii(type value=00)
Client ID value: 000c.29d3.8659-GE2/0/1
Client ID (with type) hex: 0030-3030-632e-3239 6433-2e38-3635-392d 4574-6830-2f30-2f32
T1 will timeout in 3 days 19 hours 48 minutes 43 seconds.
# Display the route information on Router B. The output shows that a static route to subnet
20.1.1.0/24 is added to the routing table.
[RouterB] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 11 Routes : 11
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.3 GE2/0/1
10.1.1.3/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
20.1.1.0/24 Static 70 0 10.1.1.2 GE2/0/1
10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.3 GE2/0/1
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
81
Page 96

127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
82
Page 97

Configuring DHCP snooping
This feature is supported only on the following ports:
• Layer 2 Ethernet ports on the following modules:
{ HMIM-8GSW.
{ HMIM-24GSW.
{ HMIM-24GSWP.
{ SIC-4GSW.
{ SIC-4GSWP.
• Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports on MSR2004-24/2004-48 routers.
• Fixed Layer 2 Ethernet ports on MSR1002-4/1003-8S routers.
Overview
DHCP snooping works between the DHCP client and server, or between the DHCP client and DHCP
relay agent. It guarantees that DHCP clients obtain IP addresses from authorized DHCP servers.
Also, it records IP-to-MAC bindings of DHCP clients (called DHCP snooping entries) for security
purposes.
DHCP snooping does not work between the DHCP server and DHCP relay agent.
DHCP snooping defines trusted and untrusted ports to make sure clients obtain IP addresses only
from authorized DHCP servers.
• Trusted—A trusted port can forward DHCP me ssages correctly to make sure the client s get I P
addresses from authorized DHCP servers.
• Untrusted—An untrusted port discards received DHCP-ACK and DHCP-OFFE R messages to
prevent unauthorized servers from assigning IP addresses.
DHCP snooping reads DHCP-ACK messages received from trusted ports and DHCP-REQUEST
messages to create DHCP snooping entries. A DHCP snooping entry includes the MAC and IP
addresses of a client, the port that connects to the DHCP client, and the VLAN.
The following features need to use DHCP snooping entries:
• ARP fast-reply—Uses DHCP snooping entries to reduce ARP broadcast traffic. For more
information, see "Configuring ARP fast-reply."
• ARP detecti
on—Uses DHCP snooping entries to filter ARP packets from unauthorized clients.
For more information, see Security Configuration Guide.
• MAC-forced forwarding (MFF)—Auto-mode MFF performs the following tasks:
{ Intercepts ARP requests from clients.
{ Uses DHCP snooping entries to find the gateway address.
{ Returns the gateway MAC address to the clients.
This feature forces the client to send all traffic to the gateway so that the gateway can monitor
client traffic to prevent malicious attacks among clients. For more information, see Security
Configuration Guide.
• IP source guard—Uses DHCP snooping entries to filter illegal packets on a per-port basis. For
more information, see Security Configuration Guide.
• VLAN mapping—Uses DHCP snooping entries to replace service provider VLAN in packets
with customer VLAN before sending the packets to clients. For more information, see Layer
2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
83
Page 98

Application of trusted and untrusted ports
Configure ports facing the DHCP server as trusted ports, and configure other ports as untrusted
ports.
As shown in Figure 35, co
nfigure the DHCP snooping device's port that is connected to the DHCP
server as a trusted port. The trusted port forwards response messages from the DHCP server t o the
client. The untrusted port connected to the unauthorized DHCP server discards incoming DHCP
response messages.
Figure 35 Trusted and untrusted ports
In a cascaded network as shown in Figure 36, configure each DHCP snooping device's ports
connected to other DHCP snooping devices as trusted ports. To save system resources, you can
disable the untrusted ports that are not directly connected to DHCP clients from generating DHCP
snooping entries.
Figure 36 Trusted and untrusted ports in a cascaded network
DHCP client
Host A
DHCP client
Host B
DHCP client
Host C
DHCP client
Host D
DHCP snooping
Switch A
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/3
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/4
GE1/0/3
GE1/0/2
GE1/0/2
DHCP snooping
GE1/0/4
Switch B
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/3
DHCP server
Device
GE1/0/2 GE1/0/1
DHCP snooping
Switch C
Untrusted ports enabled to record snooping entries
Untrusted ports disabled from recording snooping entries
Trusted ports
84
Page 99

DHCP snooping support for Option 82
Option 82 records the location information about the DHCP client so the administrator can locate the
DHCP client for security and accounting purposes. For more information about Option 82, see
"Relay agent option (Option 82)."
snooping uses the same strategies as the DHCP relay agent to handle Option 82 for DHCP
DHCP
request messages, as shown in Table 5. If a re
82, DHCP snooping removes Option 82 before forwarding the re sponse to the client. If the response
contains no Option 82, DHCP snooping forwards it directly.
Table 5 Handling strategies
sponse returned by the DHCP server contains Option
If a DHCP request
has…
Option 82
No Option 82 N/A
Handling
strategy
Drop Drops the message.
Keep Forwards the message without changing Option 82.
Replace
DHCP snooping…
Forwards the message after replacing the original Option 82 with
the Option 82 padded according to the configured padding format,
padding content, and code type.
Forwards the message after adding the Option 82 padded
according to the configured padding format, padding content, and
code type.
Command and hardware compatibility
Commands and descriptions for centralized devices apply to the followin g routers:
• MSR1002-4/1003-8S.
• MSR2003.
• MSR2004-24/2004-48.
• MSR3012/3024/3044/3064.
• MSR954(JH296A/JH297A/JH298A/JH299A)
Commands and descriptions for distributed devices apply to MSR4060 and MSR4080 routers.
DHCP snooping configuration task list
The DHCP snooping configuration does not take effect on a Layer 2 Ethernet interface that is an
aggregation member port. The configuration takes effect when the interface leaves the aggregation
group.
Tasks at a glance
(Required.) Configuring basic DHCP snooping
(Optional.) Configuring Option 82
(Optional.) Configuring DHCP snooping entry auto backup
(Optional.) Enabling DHCP starvation attack protection
(Optional.) Enabling DHCP-REQUEST attack protection
(Optional.) Setting the maximum number of DHCP snooping entries
85
Page 100

Configuring basic DHCP snooping
Follow these guidelines when you configure basic DHCP snooping:
• Specify the ports connected to authorized DHCP servers as trusted ports to make sure that
DHCP clients can obtain valid IP addresses. The trusted ports and the ports connected to
DHCP clients must be in the same VLAN.
• You can specify Layer 2 Ethernet interfaces and Layer 2 aggregate interfaces as trusted ports.
For more information about aggregate interfaces, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration
Guide.
• The DHCP snoopi ng configuration on a Layer 2 Ethernet interface that has been added to an
aggregation group does not take effect unless the interface leaves the aggregation group.
• DHCP snoopi ng can work with QinQ to record VLAN tags for DHCP packets received from
clients. For more information about QinQ, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
To configure basic DHCP snooping:
Step Command Remarks
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2. Enable DHCP snooping.
3. Enter interface view.
4. Specify the port as a trusted
port.
5. Return to system view.
6. Enter interface view.
7. (Optional.) Enable recording
of DHCP snooping entries.
dhcp snooping enable
interface
interface-number
dhcp snooping trust
quit
interface
interface-number
dhcp snooping binding
record
Configuring Option 82
Follow these guidelines when you configure Option 82:
• The Option 82 configuration on a Layer 2 Ethernet interface that has been added to an
aggregation group does not take effect unless the interface leaves the aggregation group.
• To support Option 82, you must configure Option 82 on both the DHCP server and the DHCP
snooping device. For information about configuring Option 82 on the DHCP server, see
"Enabling handling of Option 82."
• If
• If Option 82 contains the device name, the device name must contain no spaces. Otherwi se,
• DHCP snooping uses "outer VLAN tag.inner VLAN tag" to fill the VLAN ID field of sub-option 1
the handling strategy is replace, configure a padding mode and padding format for Option 82.
If the handling strategy is keep or drop, you do not need to configure any padding mode or
padding format for Option 82. The settings do not take effect even if you configure them.
DHCP snooping drops the message. You can use the sysname command to specify the device
name. For more information about this command, see Fundamentals Command Reference.
in verbose padding format if either of the following conditions exists:
{ DHCP snooping and QinQ work together.
interface-type
interface-type
By default, DHCP snooping is
disabled.
This interface must connect to the
DHCP server.
By default, all ports are untrusted
ports after DHCP snooping is
enabled.
N/A
This interface must connect to the
DHCP client.
By default, after DHCP snooping is
enabled, recording of DHCP
snooping entries is disabled.
86
 Loading...
Loading...