Page 1

HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
(Hardware P/N AJ087B, Version 1.1; Firmware Version:1.1)
FIPS 140-2
Security Policy
Level 2 Validation
Document Version 0.7
December 4, 2008
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 2

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Table of Contents
1 INTRODUCTION...............................................................................................................................................5
1.1 PURPOSE.........................................................................................................................................................5
1.2 REFERENCES...................................................................................................................................................5
2 HP STORAGEWORKS SECURE KEY MANAGER.....................................................................................6
2.1 OVERVIEW......................................................................................................................................................6
2.2 CRYPTOGRAPHIC MODULE SPECIFICATION....................................................................................................6
2.3 MODULE INTERFACES ....................................................................................................................................8
2.4 ROLES, SERVICES, AND AUTHENTICATION ...................................................................................................11
2.4.1 Crypto Officer Role..............................................................................................................................11
2.4.2 User Role.............................................................................................................................................12
2.4.3 HP User Role.......................................................................................................................................13
2.4.4 Cluster Member Role...........................................................................................................................14
2.4.5 Authentication......................................................................................................................................14
2.4.6 Unauthenticated Services ....................................................................................................................15
2.5 PHYSICAL SECURITY ....................................................................................................................................15
2.6 OPERATIONAL ENVIRONMENT......................................................................................................................15
2.7 CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEY MANAGEMENT..........................................................................................................15
2.7.1 Keys and CSPs.....................................................................................................................................15
2.7.2 Key Generation....................................................................................................................................19
2.7.3 Key/CSP Zeroization............................................................................................................................19
2.8 SELF-TESTS ..................................................................................................................................................19
2.9 MITIGATION OF OTHER ATTACKS.................................................................................................................20
3 SECURE OPERATION....................................................................................................................................21
3.1 INITIAL SETUP ..............................................................................................................................................21
3.2 INITIALIZATION AND CONFIGURATION .........................................................................................................21
3.2.1 First-Time Initialization.......................................................................................................................21
3.2.2 FIPS Mode Configuration ...................................................................................................................21
3.3 PHYSICAL SECURITY ASSURANCE ................................................................................................................22
3.4 KEY AND CSP ZEROIZATION ........................................................................................................................24
3.5 ERROR STATE...............................................................................................................................................24
ACRONYMS..............................................................................................................................................................25
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 2 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 3
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Table of Figures
FIGURE 1 – DEPLOYMENT ARCHITECTURE OF THE HP STORAGEWORKS SECURE KEY MANAGER ................................6
FIGURE 2 – BLOCK DIAGRAM OF SKM...........................................................................................................................7
FIGURE 3 – FRONT PANEL LEDS....................................................................................................................................9
FIGURE 4 – REAR PANEL COMPONENTS .......................................................................................................................10
FIGURE 5 – REAR PANEL LEDS.................................................................................................................................... 10
FIGURE 6 – FIPS COMPLIANCE IN CLI .........................................................................................................................22
FIGURE 7 – FIPS COMPLIANCE IN WEB ADMINISTRATION INTERFACE.........................................................................22
FIGURE 8 – TAMPER-EVIDENCE LABELS ......................................................................................................................23
FIGURE 9 – TAMPER-EVIDENCE LABEL S OVER POWER SUPPLIES.................................................................................23
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 3 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 4
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Table of Tables
TABLE 1 – SECURITY LEVEL PER FIPS 140-2 SECTION...................................................................................................6
TABLE 2 – LOGICAL INTERFACE AND PHYSICAL PORTS MAPPING..................................................................................8
TABLE 3 – FRONT PANEL LED DEFINITIONS ..................................................................................................................9
TABLE 4 – REAR PANEL COMPONENTS DESCRIPTIONS.................................................................................................10
TABLE 5 – REAR PANEL LED DEFINITIONS..................................................................................................................11
TABLE 6 – CRYPTO OFFICER SERVICES ........................................................................................................................11
TABLE 7 – USER SERVICES...........................................................................................................................................13
TABLE 8 – HP USER SERVICES .....................................................................................................................................13
TABLE 9 – CLUSTER MEMBER SERVICES......................................................................................................................14
TABLE 10 – ROLES AND AUTHENTICATIONS ................................................................................................................14
TABLE 11 – LIST OF CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEYS, CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEY COMPONENTS, AND CSPS FOR SSH....................15
TABLE 12 – LIST OF CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEYS, CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEY COMPONENTS, AND CSPS FOR TLS....................16
TABLE 13 – CIPHER SUITES SUPPORTED BY THE MODULE’S TLS IMPLEMENTATION IN FIPS MODE ...........................17
TABLE 14 – OTHER CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEYS, CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEY COMPONENTS, AND CSPS ...................................17
TABLE 15 – ACRONYMS ...............................................................................................................................................25
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 4 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 5

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
1 Introduction
1.1 Purpose
This document is a non-proprietary Cryptographic Module Security Policy for the HP StorageW orks Secure Key
Manager (SKM) from Hewlett-Packard Company. Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140-2, Security
Requirements for Cryptographic Modules, specifies the U.S. and Canadian Governments’ requirements for
cryptographic modules. The following pages describe how HP’s SKM meets these requirements and how to use the
SKM in a mode of operation compliant with FIPS 140-2. This policy was prepared as part of the Level 2 FIPS 140-2
validation of the HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager.
More information about FIPS 140-2 and the Cryptographic Module Validation Program (CMVP) is available at the
website of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST):
http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/STM/cmvp/index.html
In this document, the HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager is referred to as the SKM, the module, or the device.
1.2 References
This document deals only with the operations and capabilities of the module in the techn ical terms of a FIPS 140-2
cryptographic module security policy. More information is available on the module from the following sources:
.
• The HP website (http://www.hp.com
) contains information on the full line of products from HP.
• The CMVP website (http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/STM/cmvp/index.html
answers to technical or sales-related questions for the module.
) contains contact information for
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 5 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 6
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
2 HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
2.1 Overview
HP provides a range of security products for banking, the Internet, and enterprise security applications. These
products use encryption technology—often embedded in hardware—to safeguard sensitive data, such as financial
transactions over private and public networks and to offload security processing from the server.
The HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager is a hardened serv er that provides secur ity policy and key management
services to encrypting client devices and applications. After enrollment, clients, such as storage systems, application
servers and databases, make requests to the SKM for creation and management of cryptographic keys and related
metadata.
Client applications can access the SKM via its Key Management Service (KMS) server. Configuration and
management can be performed via web administration, Secure Shell (SSH), or serial console. Status-monitoring
interfaces include a dedicated FIPS status interface, a health check interface, and Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP).
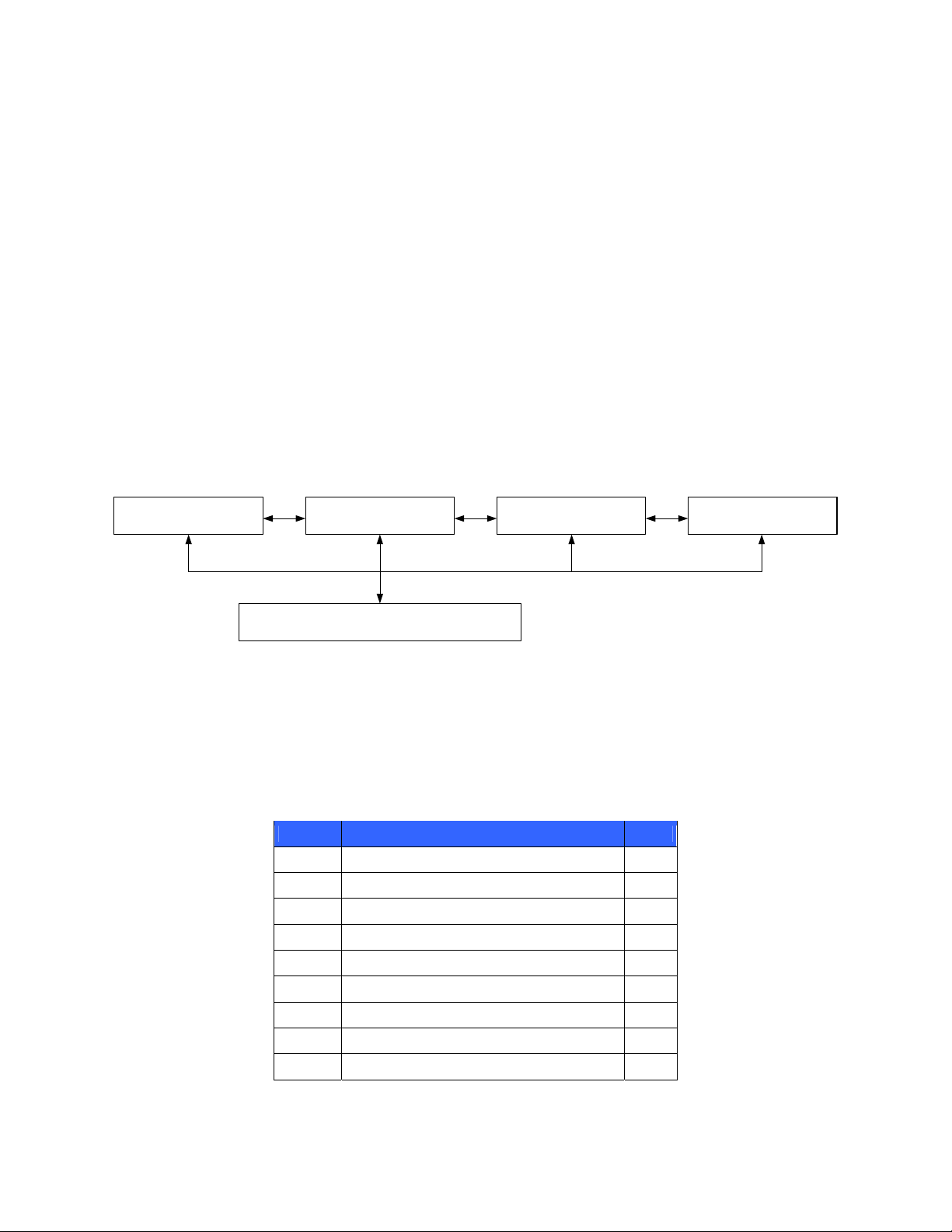
The deployment architecture of the HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager is shown in Figure 1 below.
Web Server Application Server Database Storage System
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
Figure 1 – Deployment Architecture of the HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
2.2 Cryptographic Module Specification
The HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager is validated at FIPS 140-2 section levels shown in Table 1 – Security
Level per FIPS 140-2 Section.
Table 1 – Security Level per FIPS 140-2 Section
Section Section Title Level
1 Cryptographic Module Specification 3
2 Cryptographic Module Ports and Interfaces 2
3 Roles, Services, and Authentication 3
4 Finite State Model 2
5 Physical Security 2
6 Operational Environment N/A
7 Cryptographic Key Management 2
8 EMI/EMC 2
9 Self-Tests 2
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 6 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 7
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Section Section Title Level
10 Design Assurance 2
11 Mitigation of Other Attacks N/A
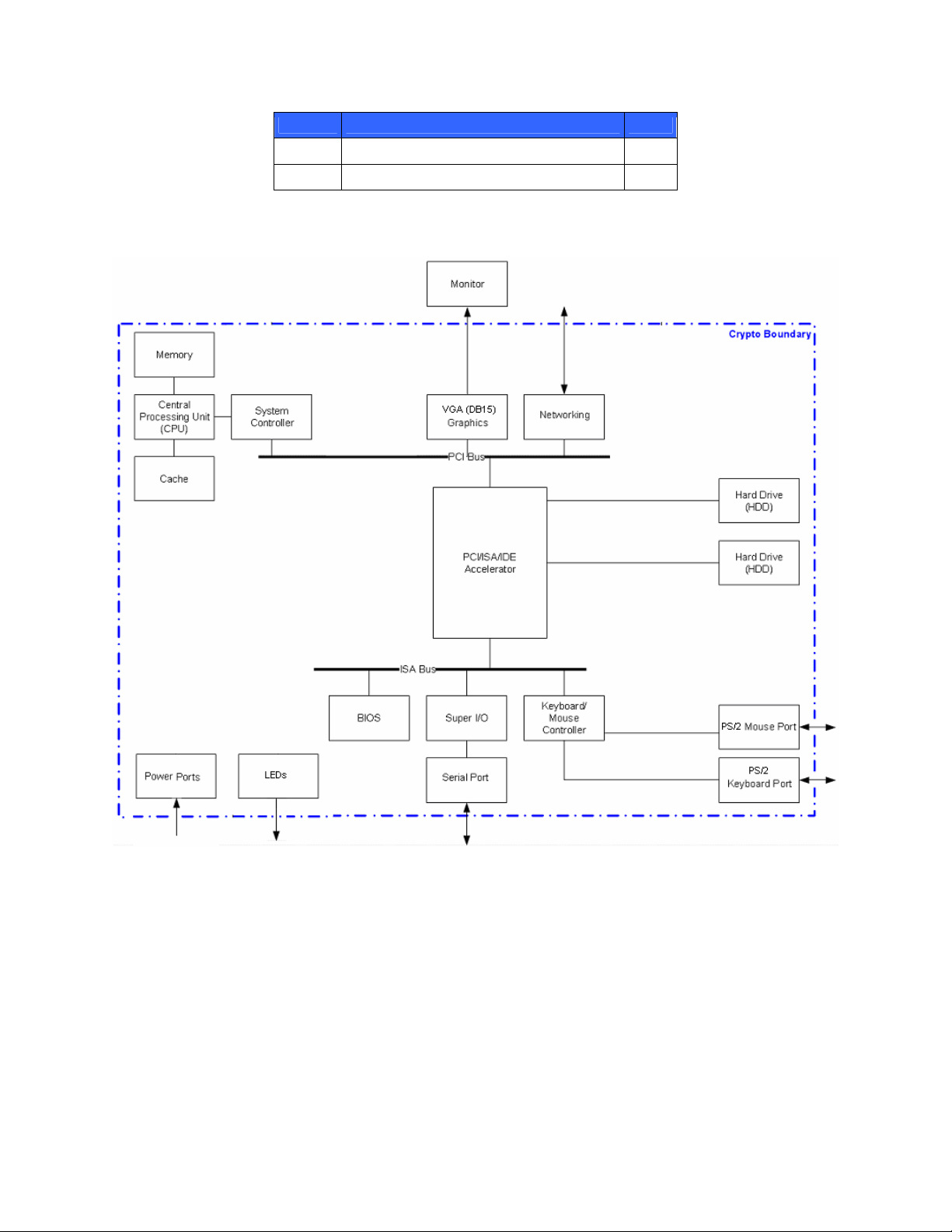
The block diagram of the module is given in Figure 2 – Block Diagram of SKM. The cryptographic boundary is
clearly shown in the figure.
Figure 2 – Block Diagram of SKM
In the FIPS mode of operation, the module implements the following Approved algorithms:
• Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption and decryption: 128, 192, and 256 bits, in Electronic
Codebook (ECB) and Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) modes (certificate # 653)
• Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) encryption and decryption: 112 and 168 bits, in ECB and CBC
modes (certificate # 604)
• Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA)-1, SHA-256, SHA- 38 4, SH A-512 (certificate # 847)
• Keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code (HMAC) SHA-1 and HMAC SHA-256 (certificate # 470)
• Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman (RSA) American National Standard Institute (ANSI) X9.31 key generation,
signature generation, and signature verification: 1024 and 2048 bits (certificate # 302)
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 7 of 26
Page 8

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
• Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) PQG generation, key generation, signature generation, and signature
verification: 1024 bits (certificate # 244)
• ANSI X9.31 Appendix A.2.4 with 2-key 3DES Deterministic Random Number Generator (DRNG)
(certificate # 375)
• Diffie-Hellman key agreement (SP 800-56A, vendor affirmed; key establish ment methodology provides 80
bits of encryption strength)
In the FIPS mode of operation, the module implements the following non-approved algorithms:
• A non-approved Random Number Generator (RNG) to seed the ANSI X9.31 DRNG
• The following commercially-available protocols for key establishment:
o Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.0/ Secure Socket Layer (SSL) 3.1 protocol using RSA 1024 and
2048 bits for key transport. Caveat: The RSA 1024- and 2048-bit key wrapping and key
establishment provide 80 and 112 bits of encryption strength, respectively.
In the non-FIPS mode of operation, the module also implements DES, MD5, RC4, and 512- and 768-bit RSA for
signature generation and verification, and key establishment.
2.3 Module Interfaces
FIPS 140-2 defines four logical interfaces:
• Data Input
• Data Output
• Control Input
• Status Output
The module features the following physical ports and LEDs:
• Serial port (RS232 DB9)
• Ethernet 10/100/1000 RJ-45 ports (Network Interface Card [NIC], quantity: 2)
• Mouse port (PS/2)
• Keyboard port (PS/2)
• Monitor port (VGA DB15)
• Power input (115VAC)
• LEDs (six on the front panel and seven on the rear panel)
The logical interfaces and their physical port mappings are described in Table 2 – Logical Interface and Physical
Ports Mapping.
Table 2 – Logical Interface and Physical Ports Mapping
Logical Interface Physical Ports
Data Input Keyboard, serial, Ethernet
Data Output Monitor, serial, Ethernet
Control Input Keyboard, mouse, serial, Ethernet
Status Output Monitor, serial, Ethernet, LEDs
There are no buttons or ports on the front panel. There are six LEDs on the front panel. See Figure 3 – Front Panel
LEDs.
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 8 of 26
Page 9

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Figure 3 – Front Panel LEDs
Descriptions of the LEDs are given in Table 3 – Front Panel LED Definitions.
Table 3 – Front Panel LED Definitions
Item Description Status
Green = System is on.
Power On/Standby button
1
and system power LED
Amber = System is shut down, but power is still applied.
Off = Power cord is not attached, power supply failure has
occurred, no power supplies are installed, facility power is not
available, or disconnected power button cable.
Unit Identifier (UID)
2
button/LED
Blue = Identification is activated.
Off = Identification is deactivated.
Green = System health is normal.
Amber = System health is degraded. To identify the component in
3 Internal health LED
a degraded state, refer to “HP Systems Insight Display and LEDs”.
Red = System health is critical. To identify the component in a
critical state, refer to “HP Systems Insight Display and LEDs”.
Off = System health is normal (when in standby mode).
External health LED (power
4
supply)
Green = Power supply health is normal.
Amber = Power redundancy failure occurred.
Off = Power supply health is normal when in standby mode.
Green = Network link exists.
Flashing green = Network link and activity exist.
5 NIC 1 link/activity LED
Off = No link to network exists.
If power is off, the front panel LED is not active. View the LEDs on
the RJ-45 connector for status by referring to the rear panel LEDs.
Green = Network link exists.
Flashing green = Network link and activity exist.
6 NIC 2 link/activity LED
Off = No link to network exists.
If power is off, the front panel LED is not active. View the LEDs on
the RJ-45 connector for status by referring to the rear panel LEDs
The components on the rear panel are illustrated in Figure 4 – Rear Panel Components.
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 9 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 10

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Figure 4 – Rear Panel Components
Descriptions of components on the rear panel are given in Table 4 – Rear Panel Components Descriptions.
Table 4 – Rear Panel Components Descriptions
Item Definition
1 PCI Express expansion slot 1 (Blocked)
2 PCI Express expansion slot 2 (Blocked)
3 Power supply bay 2
4 Power supply bay 1
5 NIC connector 1 (Ethernet)
6 NIC connector 2 (Ethernet)
7 Keyboard connector
8 Mouse connector
9 Video connector
10 Serial connector
11 Universal Serial Bus (USB) connector 1 (Blocked)
12 USB connector 2 (Blocked)
13 Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) 2 NIC connector (Blocked)
The seven LEDs on the rear panel are illustrated in Figure 5 – Rear Panel LEDs.
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Figure 5 – Rear Panel LEDs
Page 10 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 11
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
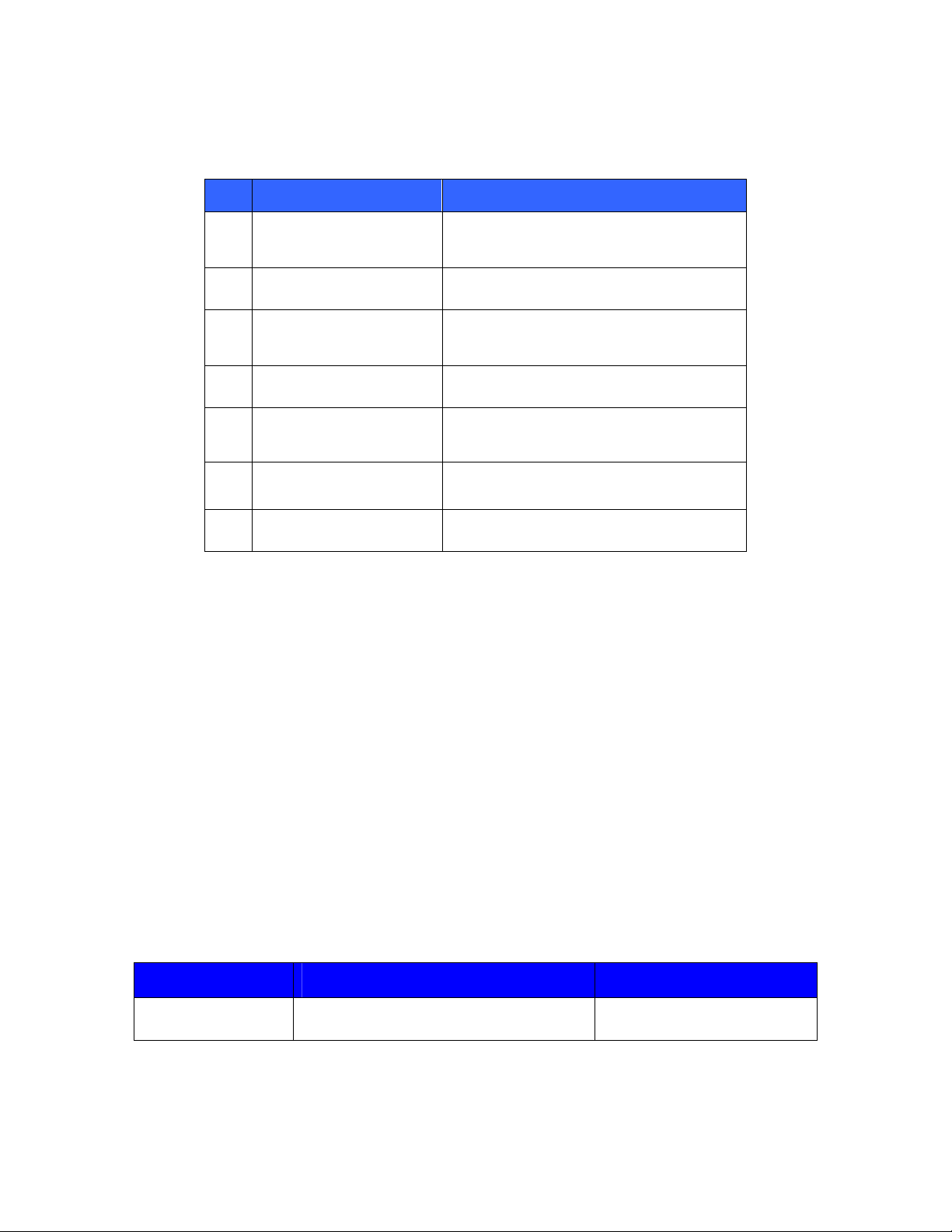
Descriptions of LEDs on the rear panel are given in Table 5 – Rear Panel LED Defi ni t i ons .
Table 5 – Rear Panel LED Definitions
Item Description Status
10/100/1000 NIC 1 activity
1
LED
10/100/1000 NIC 1 link
2
LED
10/100/1000 NIC 2 activity
3
LED
10/100/1000 NIC 2 link
4
LED
5 UID LED
6 Power supply 2 LED
7 Power supply 1 LED
Green = Activity exists.
Flashing green = Activity exists.
Off = No activity exists.
Green = Link exists.
Off = No link exists.
Green = Activity exists.
Flashing green = Activity exists.
Off = No activity exists.
Green = Link exists.
Off = No link exists.
Blue = Identification is activated.
Off = Identification is deactivated.
Green = Normal
Off = System is off or power supply has failed
Green = Normal
Off = System is off or power supply has failed
2.4 Roles, Services, and Authentication
The module supports four authorized roles:
• Crypto Officer
• User
• HP User
• Cluster Member
All roles require identity-based authentication.
2.4.1 Crypto Officer Role
The Crypto Officer accesses the module via the Web Management Console and/or the Command Line Interface
(CLI). This role provides all services that are necessary for the secure management of the module. Table 6 shows the
services for the Crypto Officer role under the FIPS mode of operation. The purpose of each service is shown in the
first column (“Service”), and the corresponding function is described in the second column (“Description”). The
keys and Critical Security Parameters (CSPs) in the rightmost column correspond to the keys and CSPs introduced
in Section 2.7.1.
Table 6 – Crypto Officer Services
Service Description Keys/CSPs
Authenticate to SKM Authenticate to SKM with a usernam e and
the associated password
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Crypto Officer passwords – read;
TLS/SSH keys – read
Page 11 of 26
Page 12

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Service Description Keys/CSPs
Perform first-time
initialization
Configure the module when it is used for the
first time
Crypto Officer (admin) password
– write;
Kdsa public/private – write;
Krsa private – write;
Krsa private – write;
Log signing RSA key – write;
Log signature verification RSA
key – write;
KRsaPub – write;
KRsaPriv – write.
Upgrade firmware Upgrade firmware (firmware must be FIPS-
Firmware upgrade key – read
validated)
Configure FIPS mode Enable/disable FIPS mode None
Manage keys Manage all client keys that are stored within
the module. This includes the generation,
storage, export (only public keys), import, and
Client keys – write, read, delete;
PKEK – write, read, delete.
zeroization of keys.
Manage clusters Manage all clusters that are defined within
the module. This includes the creation,
Cluster Member passwords –
write, delete
joining, and removal of a cluster from the
module.
Manage services Manage all services supported by the
None
module. This includes the starting and
stopping of all services.
Manage operators Create, modify, or delete module operators
(Crypto Officers and Users).
Crypto Officer passwords –
write, delete; User passwords –
write, delete
Manage certificates Create/import/revoke certificates KRsaPub – write, read, delete;
KRsaPriv – write, read, delete;
CARsaPub – write, read, delete;
CARsaPriv – write, read, delete;
Client RSA public keys – read.
Reset factory settings Rollback to the default firmware shipped with
All keys/CSPs – delete
the module
Restore default
configuration
Restore configuration
file
Backup configuration
Delete the current configuration file and
None
restores the default configuration settings
Restore a previously backed up configuration
None
file
Back up a configuration file None
file
Zeroize all keys/CSPs Zeroize all keys and CSPs in the module All keys and CSPs – delete
2.4.2 User Role
The User role is associated with external applications or clients that conn ect to the KMS via its XML interface.
Users in this role may exercise services—such as key generation and management—based on configured or
predefined permissions. See Table 7 – User Services for details. The keys and CSPs in the rightmost column
correspond to the keys and CSPs introduced in Section 2.7.1.
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 12 of 26
Page 13

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Table 7 – User Services
Service Description Keys/CSPs
Authenticate to SKM Authenticate to SKM with a username and the
User passwords – read
associated password
Generate key Generate a cryptographic key
Client keys – write
;
PKEK – write.
Modify key meta data Change the key o wner or update/add/delete
None
the custom attributes
Delete key Delete a cryptographic key
Client keys – delete
;
PKEK – delete.
Query key meta data Output key names and meta data that the
User is allowed to access
Client keys – read
PKEK – read.
;
Import key Import key Client keys – write;
PKEK – write.
Export key Export a cryptographic key Client keys – read;
PKEK – read.
Export Certificate Export a certificate Client certificate – read
Clone Key Clone an existing key under a different key
name
Client keys – write, read;
PKEK – write, read.
Generate random
number
Manage operators Only users with administration permission can
Generate a random number ANSI X9.31 DRNG seed – write,
read, delete
User passwords – write, delete
create, modify, or delete module operators
2.4.3 HP User Role
The HP User role can reset the module to an uninitialized state in the event that all Crypto Officer passwords are
lost, or when a self-test permanently fails. See Table 8 – HP User Services. The keys and CSPs in the rightmost
column correspond to the keys and CSPs introduced in Section 2.7.1.
Table 8 – HP User Services
Service Description Keys/CSPs
Authenticate to the
module
Reset factory settings Rollback to the default firmware shipped with
Restore default
configuration
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
Authenticate to SKM with a signed token HP User RSA public key – read
All keys/CSPs – delete
the module
Delete the current configuration file and
None
restores the default configuration settings
Page 13 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 14

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Service Description Keys/CSPs
Zeroize all keys/CSPs Zeroize all keys/CSPs in the module All keys/CSPs – delete
2.4.4 Cluster Member Role
The Cluster Member role is associated with other SKMs that can connect to this SKM and access cluster services.
See Table 9 – Cluster Member Services. The keys and CSPs in the rightmost column correspond to the keys and
CSPs introduced in Section 2.7.1.
Table 9 – Cluster Member Services
Service Description Keys/CSPs
Authenticate Cluster
Member
Authenticate to SKM via TLS Cluster Member passwords –
read; Cluster key – read; Cluster
Member RsaPub – read
Receive Configuration
Update the module’s configuration settings None
File
Zeroize Key Delete a specific key Cluster key – delete
Backup Configuration
Back up a configuration file None
File
2.4.5 Authentication
The module performs identity-based authentication for the four roles. Two authentication schemes are used:
authentication with certificate in TLS and authentication with password. See Table 10 – Roles and Authentications
for a detailed description.
Table 10 – Roles and Authentications
Role Authentication
Crypto Officer Username and password with optional digital certificate
User Username and password and/or digital certificate
HP User Digital certificate
Cluster Member Digital certificate over TLS
The 1024-bit RSA signature on a digital certificate provides 80-bits of security. There are 2
probability of a successful random guess is 2
-80
. Since 10-6 » 2
-80
, a random attempt is very unlikely to succeed. At
80
possibilities. The
least 80 bits of data must be transmitted for one attempt. (The actual number of bits that need to be transmitted for
one attempt is much greater than 80. We are considering the worst case scenario.) The processor used by the module
has a working frequency of 3.0 gigabytes, hence, at most 60×3.0×10
Since 80 bits are necessary for one attempt, at most (60×3.0×10
However, there exist 2
attempt in 60 seconds is considerably less than 10
80
possibilities. (2.25×109)/280 = 1.86×10
-5
.
9
bits of data can be transmitted in 60 seconds.
9
)/80 = 2.25×109 attempts are possible in 60 seconds.
-15
« 10-5. The probability of a successful certificate
Passwords in the module must consist of eight or more characters from the set of 90 human-readable numeric,
alphabetic (upper and lower case), and special character symbols. Excluding those combinations that do not meet
password constraints (see Section 2.7.1 – Keys and CSPs), the size of the password space is about 60
probability of a successful random guess is 60
-8
. Since 10-6 » 60-8, a random attempt is very unlikely to succeed.
8
. The
After six unsuccessful attempts, the module will be locked down for 60 seconds; i.e., at most six trials are possible
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 14 of 26
Page 15

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
in 60 seconds. Since 10-5 » 6×60-8, the probability of a successful password attempt in 60 seconds is considerably
less than 10
-5
.
2.4.6 Unauthenticated Services
The following services do not require authentication:
• SNMP statistics
• FIPS status services
• Health check services
• Network Time Protocol (NTP) services
• Initiation of self-tests by rebooting the SKM
• Negotiation of the XML protocol version for communications with the KMS
SNMP is used only for sending statistical information (SNMP traps). FIPS status and health check are status-report
services, unrelated to security or cryptography. NTP is a date/time synchronization service that does not involve
keys or CSPs. Initiation of self-tests and negotiation of the XML protocol version do not involve keys or CSPs.
2.5 Physical Security
The module was tested and found conformant to the EMI/EMC requirements specified by Title 47 of the Code of
Federal Regulations, Part 15, Subpart B, Unintentional Radiators, Digital Devices, Class A (that is, for business
use).
The HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager is a multi-chip standalone cryptographic modu le. The entire con tents of
the module, including all hardware, software, firmware, and data, are enclosed in a metal case. The case is opaque
and must be sealed using tamper-evident labels in order to prevent the case cover from being removed without signs
of tampering. All circuits in the module are coated with commercial standard passivation. Once the module has been
configured to meet FIPS 140-2 Level 2 requirements, the module cannot be accessed without signs of tampering.
See Section 3.3 – Physical Security Assurance of this document for more information.
2.6 Operational Environment
The operational environment requirements do not apply to the HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager—the module
does not provide a general purpose operating system and only allows the updating of image components after
checking an RSA signature on the new firmware image. Crypto Officers can install a new firmware image on the
SKM by downloading the image to the SKM. This image is signed by an RSA private key (which never enters the
module). The SKM verifies the signature on the new firmware image using the public key stored in the module. If
the verification passes, the upgrade is allowed. Otherwise the upgrade process fails and the old image is reused.
2.7 Cryptographic Key Management
2.7.1 Keys and CSPs
The SSH and TLS protocols employed by the FIPS mode of the module are security-related. Table 11 – List of
Cryptographic Keys, Cryptographic Key Components, and CSPs for SSH and Table 12 – List of Cryptographic
Keys, Cryptographic Key Components, and CSPs for TLS, introduce cryptographic keys, key components, and
CSPs involved in the two protocols, respectively.
Table 11 – List of Cryptographic Keys, Cryptographic Key Components, and CSPs for SSH
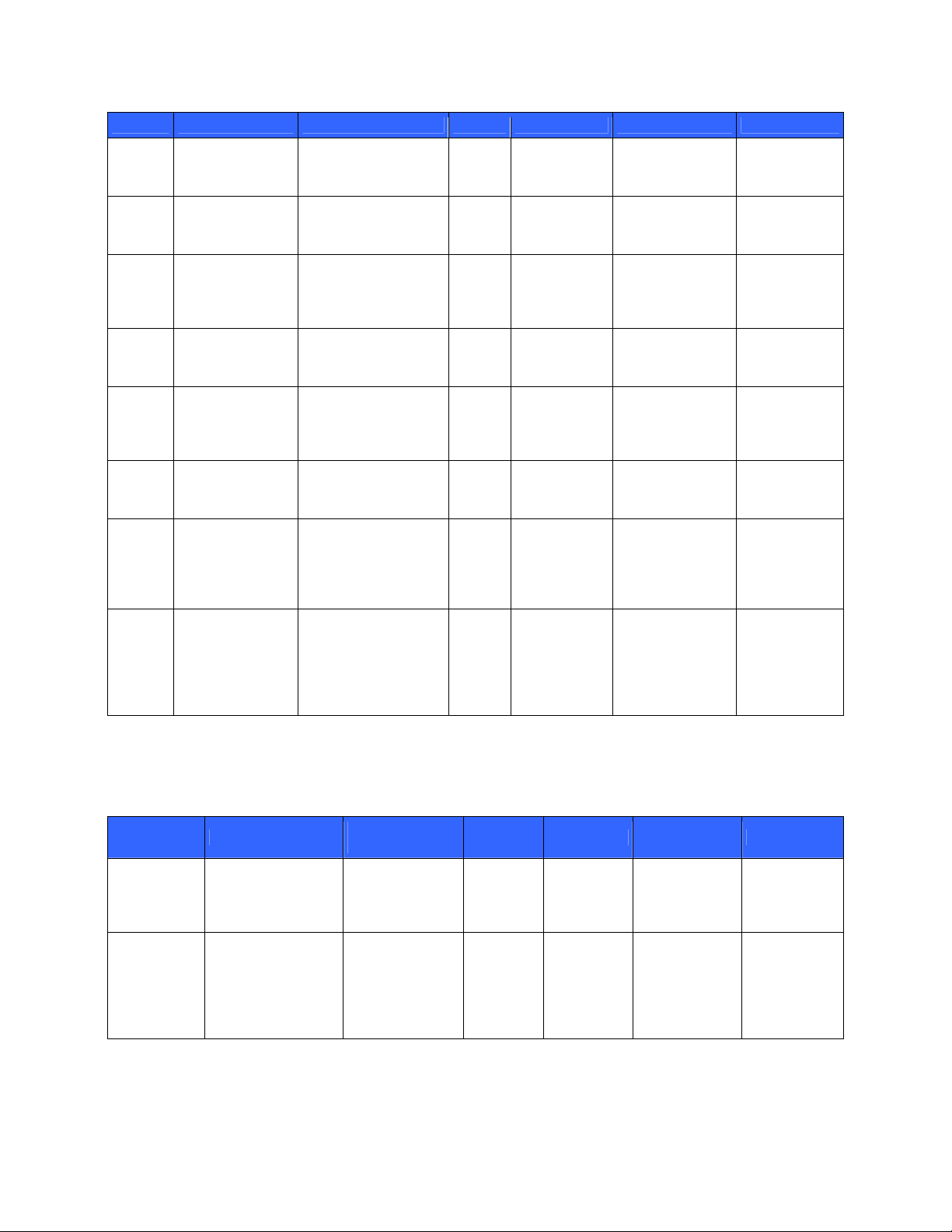
Key Key Type Generation / Input Output Storage Zeroization Use
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 15 of 26
Page 16
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Key Key Type Generation / Input Output Storage Zeroization Use
DH
public
param
DH
private
param
Kdsa
public
1024-bit DiffieHellman public
parameters
1024-bit DiffieHellman private
parameters
1024-bit DSA
public keys
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
session initialization
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
session initialization
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
first-time initialization
In
plaintext
In volatile
memory
Never In volatile
memory
In
plaintext
In non-volatile
memory
Upon session
termination
Upon session
termination
At operator delete
or zeroize request
Negotiate SSH
Ks and SSH
Khmac
Negotiate SSH
Ks and SSH
Khmac
Verify the
signature of the
server’s
message.
Kdsa
private
Krsa
public
1024-bit DSA
private keys
1024-bit RSA
public keys
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
first-time initialization
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
first-time initialization
Never In non-volatile
memory
In
plaintext
In non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or zeroize request
At operator delete
or zeroize request
Sign the
server’s
message.
Verify the
signature of the
server’s
message.
Krsa
private
SSH Ks SSH session
1024-bit RSA
private keys
168-bit 3DES key,
128-, 192-, 256-bit
AES key
Generated by ANSI
X9.31 DRNG during
first-time initialization
Diffie-Hellman key
agreement
Never In non-volatile
memory
Never In volatile
memory
At operator delete
or zeroize request
Upon session
termination or
when a new Ks is
generated (after a
Sign the
server’s
message.
Encrypt and
decrypt data
certain timeout)
SSH
Khmac
SSH session 512bit HMAC key
Diffie-Hellman key
agreement
Never In volatile
memory
Upon session
termination or
Authenticate
data
when a new
Khmac is
generated (after a
certain timeout)
Notice that SSH version 2 is explicitly accepted for use in FIPS mode, according to section 7.1 of the NIST FIPS
140-2 Implementation Guidance.
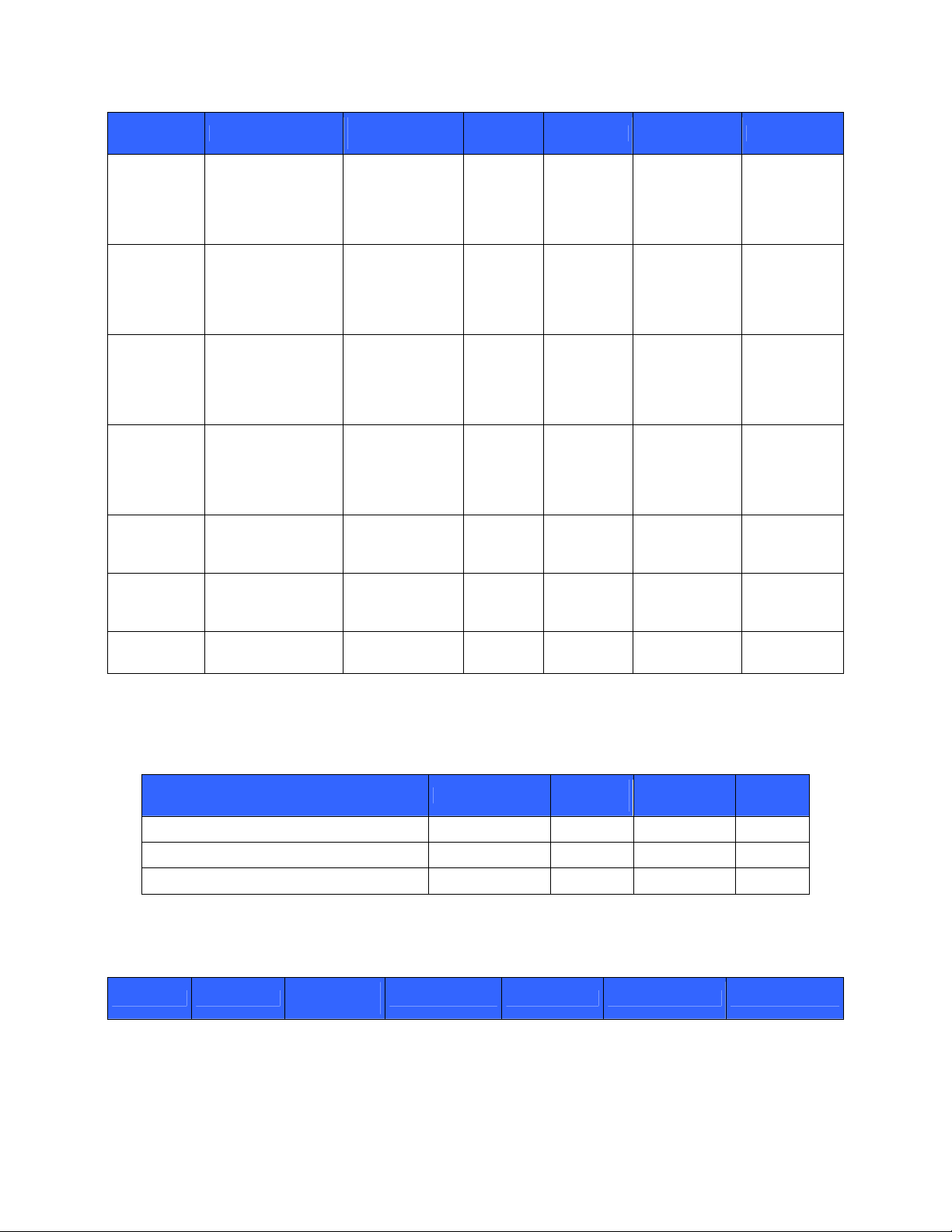
Table 12 – List of Cryptographic Keys, Cryptographic Key Components, and CSPs for TLS
Key Key Type
Pre-MS TLS pre-master
secret
MS TLS master secret Derived from Pre-
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Generation /
Input
Input in
Output Storage Zeroization Use
Never In volatile
encrypted form
from client
Never In volatile
MS using FIPS
Approved key
derivation
function
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
memory
memory
Upon session
termination
Upon session
termination
Derive MS
Derive TLS Ks
and TLS
Khmac
Page 16 of 26
Page 17
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Key Key Type
KRsaPub Server RSA public
key (1024- or 2048bit)
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG during
first-time
initialization
KRsaPriv Server RSA private
key (1024- or 2048bit)
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG during
first-time
initialization
CARsaPub Certificate Authority
(CA) RSA public key
(1024- or 2048-bit)
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG during
first-time
initialization
CARsaPriv CA RSA private key
(1024- or 2048-bit)
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG during
first-time
initialization
Cluster
Member
RsaPub
TLS Ks TLS session AES or
Cluster Member
RSA public key
(1024- or 2048-bit)
Input in plaintext Never In volatile
Derived from MS Never In volatile
3DES symmetric
key(s)
TLS Khmac TLS session HMAC
Derived from MS Never In volatile
key
Generation /
Input
Output Storage Zeroization Use
In plaintext
a X509
certificate.
In nonvolatile
memory
At operator
delete request
Client encrypts
Pre-MS. Client
verifies server
signatures
Never In non-
volatile
memory
At operator
delete or
zeroize request
Server
decrypts PreMS. Server
generates
signatures
In plaintext In non-
volatile
At operator
delete request
Verify CA
signatures
memory
never In non-
volatile
memory
memory
At operator
delete or
zeroize request
Upon session
termination
Sign server
certificates
Verify Cluster
Member
signatures
memory
memory
Upon session
termination
Upon session
termination
Encrypt and
decrypt data
Authenticate
data
Table 13 details all cipher suites supported by the TLS protocol implemented by the module. The suite n ames in the
first column match the definitions in RFC 2246 and RFC 4346.
Table 13 – Cipher Suites Supported by the Module’s TLS Implementation in FIPS Mode
Suite Name Authentication
Key
Transport
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA RSA RSA AES (256-bit) SHA-1
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA RSA RSA AES (128-bit) SHA-1
TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA RSA RSA 3DES (168-bit) SHA-1
Symmetric
Cryptography
Hash
Other CSPs are tabulated in Table 14.
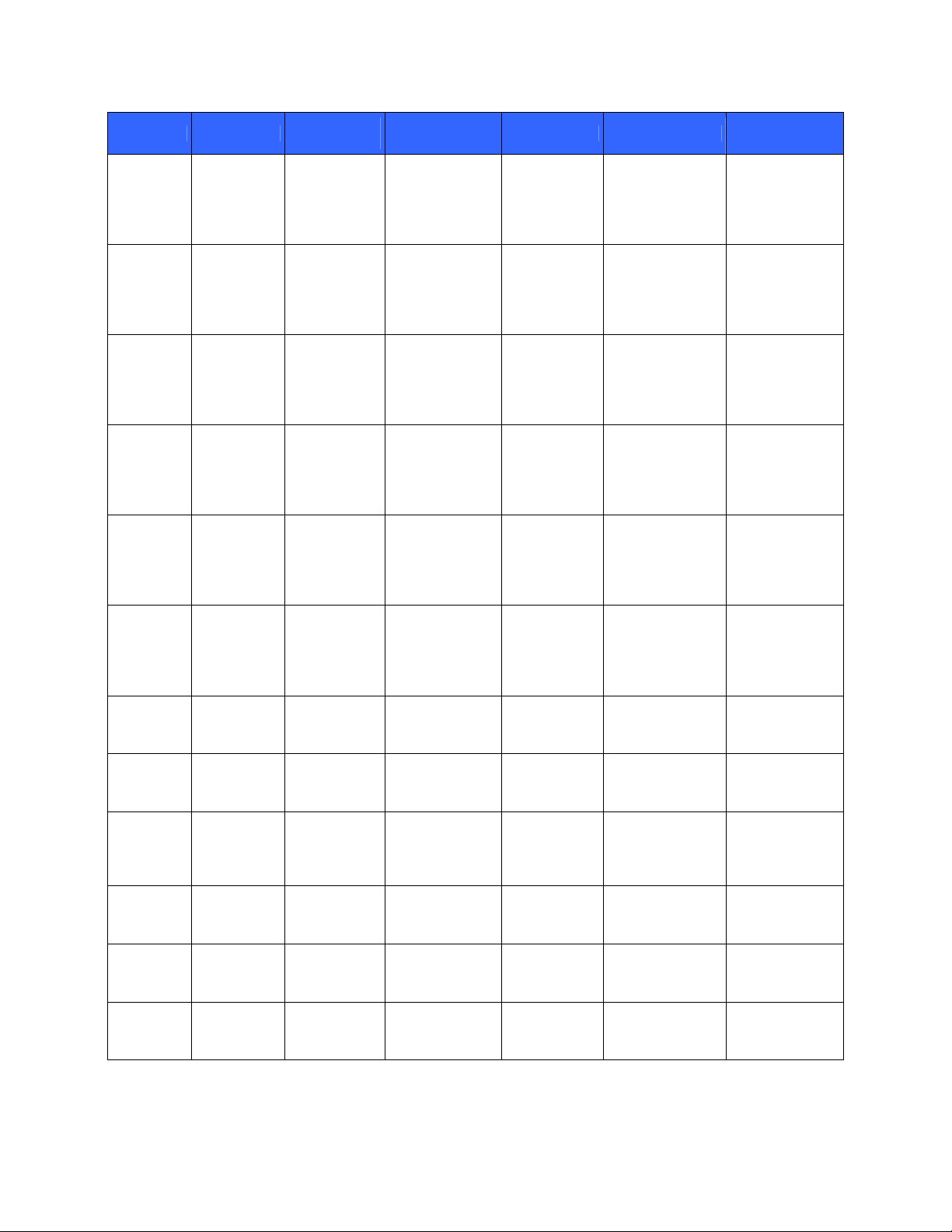
Table 14 – Other Cryptographic Keys, Cryptographic Key Components, and CSPs
Key Key Type
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
Generation /
Input
Output Storage Zeroization Use
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 17 of 26
Page 18
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Key Key Type
Client AES
key
128, 192 or
256-bit AES
key
Client
3DES key Generated by
3DES key
Client RSA
public keys
Client RSA
keys
Client
RSA public
key
RSA private
keys
HMAC keys Generated by
HMAC keys
Client
certificate
Crypto
Officer
X.509
certificate
Character
string
passwords
User
passwords
Cluster
Member
Character
string
Character
string
password
HP User
RSA public
2048-bit RSA
public key
key
Cluster key Character
string
Firmware
upgrade
1024-bit RSA
public key
key
Generation /
Input
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG
ANSI X9.31
DRNG
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG
ANSI X9.31
DRNG
Input in
ciphertext
over TLS
Input in
plaintext
Input in
plaintext
Input in
ciphertext
over TLS
Input in
plaintext at
factory
Input in
ciphertext
over TLS
Input in
plaintext at
factory
Output Storage Zeroization Use
Via TLS in
encrypted form
(encrypted with
Encrypted in
non-volatile
memory
Per client’s
request or zeroize
request
TLS Ks) per
client’s request
Via TLS in
encrypted form
(encrypted with
Encrypted in
non-volatile
memory
Per client’s
request or zeroize
request
TLS Ks) per
client’s request
Via TLS in
encrypted form
(encrypted with
Encrypted in
non-volatile
memory
At operator delete Sign
TLS Ks) per
client’s request
Via TLS in
encrypted form
(encrypted with
Encrypted in
non-volatile
memory
Per client’s
request or zeroize
request
TLS Ks) per
client’s request
Via TLS in
encrypted form
(encrypted with
Encrypted in
non-volatile
memory
Per client’s
request or zeroize
request
TLS Ks) per
client’s request
Via TLS in
encrypted form
(encrypted with
In non-volatile
memory
Per client’s
request or by
zeroize request
TLS Ks) per
client’s request
Never In non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or by zeroize
request
Never In non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or by zeroize
request
Never In non-volatile
memory
Never In non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or zeroize request
At installation of a
patch or new
firmware
Never In non-volatile
memory
At operator delete
or by zeroize
request
Never In non-volatile
memory
When new
firmware upgrade
key is input
Encrypt
plaintexts/decrypt
ciphertexts
Encrypt
plaintexts/decrypt
ciphertexts
messages/verify
signatures
Sign
messages/verify
signatures
Compute keyedMACs
Encrypt
data/verify
signatures
Authenticate
Crypto Officer
Authenticate
User
When a device
attempts to
become a
Cluster Member
Authenticate HP
User
Authenticate
Cluster Member
Used in firmware
upgrade integrity
test
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 18 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 19

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Key Key Type
Log signing
keys
ANSI X9.31
DRNG
seed
PKEK 256-bit AES
1024-bit RSA
public and
private keys
DRNG seed Generated by
key
Generation /
Input
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG at firsttime
initialization
non-Approved
RNG
Generated by
ANSI X9.31
DRNG
Output Storage Zeroization Use
Never In non-volatile
memory
Never In non-volatile
memory
In encrypted
form for backup
purposes only
In non-volatile
memory
When new log
signing keys are
generated on
demand by
Crypto Officer
When module is
powered off
At operator delete
or by zeroize
request
Sign logs and
verify signature
on logs
Initialize ANSI
X9.31 DRNG
Encrypt client
keys
2.7.2 Key Generation
The module uses an ANSI X9.31 DRNG with 2-key 3DES to generate cryptographic keys. This DRNG is a FIPS
140-2 approved DRNG as specified in Annex C to FIPS PUB 140-2.
2.7.3 Key/CSP Zeroization
All ephemeral keys are stored in volatile memory in plaintext. Ephemeral keys are zeroized when they are no long er
used. Other keys and CSPs are stored in non-volatile memory with client keys being stored in encrypted form.
To zeroize all keys and CSPs in the module, the Crypto Officer should execute the reset factory settings
zeroize command at the serial console interface. For security reasons, this command is available only through the
serial console.
2.8 Self-Tests
The device implements two types of self-tests: power-up self-tests and conditional self-tests.
Power-up self-tests include the following tests:
• Firmware integrity tests
• Known Answer Test (KAT) on 3DES
• KAT on AES
• KAT on SHA-1
• KAT on SHA-256
• KAT on SHA-384
• KAT on SHA-512
• KAT on HMAC SHA-1
• KAT on HMAC SHA-256
• KAT on ANSI X9.31 DRNG
• KAT on Diffie-Hellman
• KAT on SSH Key Derivation Function
• KAT on RSA signature generation and verification
• Pairwise consistency test on DSA signature generation and verification
Conditional self-tests include the following tests:
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 19 of 26
Page 20

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
• Pairwise consistency test for new DSA keys
• Pairwise consistency test for new RSA keys
• Continuous random number ge nerator test on ANSI X9.31 DRNG
• Continuous random number generator test on non-Approved RNG
• Firmware upgrade integrity test
• Diffie-Hellman primitive test
The module has two error states: a Soft Error state and a Fatal Error state. When one or more power-up self-tests
fail, the module may enter either the Fatal Error state or the Soft Error State. When a conditional self-test fails, the
module enters the Soft Error state. See Section 3 of this document for more information.
2.9 Mitigation of Other Attacks
This section is not applicable. No claim is made that the module mitigate s against an y attacks beyond the FIPS 1402 Level 2 requirements for this validation.
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 20 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 21

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
3 Secure Operation
The HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager meets Level 2 requirements for FIPS 140-2. The sections below
describe how to place and keep the module in the FIPS mode of operation.
3.1 Initial Setup
The device should be unpacked and inspected according to the User Guide. The User Guide also contains
installation and configuration instructions, maintenance information, safety tips, and other information. The device
itself must be affixed with tamper-evident labels that are included in the packaging. See Figure 8 – TamperEvidence Labels for locations of tamper-evidence labels.
3.2 Initialization and Configuration
3.2.1 First-Time Initialization
When the module is turned on for the first time, it will prompt the operator for a password for a default Crypto
Officer. The module cannot proceed to the next state until the operator provides a password that conforms to the
password policy described in Section 2.7.1. The default username associated with the entered password is “admin”.
During the first-time initialization, the operator must configure minimum settings for the module to operate
correctly. The operator will be prompted to configure the following settings via the serial interface:
• Date, Time, Time zone
• IP Address/Netmask
• Hostname
• Gateway
• Management Port
3.2.2 FIPS Mode Configuration
In order to comply with FIPS 140-2 Level 2 requirements, the following functionality must be disabled on the SKM:
• Global keys
• File Transfer Protocol (FTP) for importing certificates and downloading and restoring backup files
• Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) authentication
• Use of the following algorithms: RC4, MD5, DES, RSA-512, RSA-768
• SSL 3.0
• Hot-swappable drive capability
• RSA encryption and decryption operations (note, however, that RSA encryption and decryption associated
with TLS handshakes and Sign and Sign Verify are permitted)
These functions need not be disabled individually. There are two approaches to configuring the module such that it
works in the Approved FIPS mode of operation:
Through a command line interface, such as SSH or serial console, the Crypto Officer should use the fips
compliant command to enable the FIPS mode of operation. This will alter various server settings as described
above. See Figure 6 – FIPS Compliance in CLI. The fips server command is used for the FIPS status server
configuration. The show fips status command returns the current FIPS mode configuration.
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 21 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 22

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Figure 6 – FIPS Compliance in CLI
In the web administration interface, the Crypto Officer should use the “High Security Configuration” page to enable
and disable FIPS compliance. To enable the Approved FIPS mode of operation, click on the “Set FIPS Compliant”
button. See Figure 7 – FIPS Compliance in Web Administration In terface. This will alter various server settings as
described above.
Figure 7 – FIPS Compliance in Web Administration Interface
In the web administration interface, the User can review the FIPS mode configuration by reading the “High Security
Configuration” page.
The Crypto Officer must zeroize all keys when switching from the Approved FIPS mode of operation to the nonFIPS mode and vice versa.
3.3 Physical Security Assurance
Serialized tamper-evidence labels have been applied at four locations on the metal casing. See Figure 8 – TamperEvidence Labels. The tamper-evidence labels have a special adhesive backing to adhere to the module’s surface.
The tamper-evidence labels have individual, unique serial numbers. They should be inspected periodically and
compared to the previously-recorded serial numbers to verify that fresh labels have not been applied to a tampered
module.
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 22 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 23

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Figure 8 – Tamper-Evidence Labels
Figure 9 provides a better view of the positioning of the tamper-evidence labels over the power supplies.
Figure 9 – Tamper-Evidence Labels over Power Supplies
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 23 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 24

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
3.4 Key and CSP Zeroization
To zeroize all keys and CSPs in the module, the Crypto Officer should execute re set factory settings
zeroize command in the serial console interface. Notice that, for security reasons, the command cannot be
initiated from the SSH interface.
When switching between different modes of operations (FIPS and non-FIPS), the Crypto Officer must zeroize all
CSPs.
3.5 Error State
The module has two error states: a Soft Error state and a Fatal Error state.
When a power-up self-test fails, the module may enter either the Fatal Error state or the Soft Error State. When a
conditional self-test fails, the module will enter the Soft Error state. The module can recover from the Fatal Error
state if power is cycled or if the SKM is rebooted. An HP User can reset the module when it is in the Fatal Error
State. No other services are available in the Fatal Error state. The module can recover from the Soft Error state if
power is cycled. With the exception of the firmware upgrade integrity test and Diffie-Hellman primitive test, the
only service that is available in the Soft Error state is the FIPS status output via port 9081 (default). A User can
connect to port 9081 and find the error message indicating the failure of FIPS self-tests. Access to port 9081 does
not require authentication.
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 24 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 25

Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
Acronyms
Table 15 – Acronyms
Acronym Definition
3DES Triple Data Encryption Standard
AES Advanced Encryption Standard
ANSI American National Standard Institute
BIOS Basic Input/Output System
CA Certificate Authority
CBC Cipher Block Chaining
CLI Command Line Interface
CMVP Cryptographic Module Validation Program
CPU Central Processing Unit
CRC Cyclic Redu ndancy Check
CRL Certificate Revocation List
CSP Critical Security Parameter
DES Data Encryption Standard
DRNG Deterministic Random Number Generator
DSA Digital Signature Algorithm
ECB Electronic Codebook
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
EMI Electromagnetic Interference
FIPS Federal Information Processing Standard
FTP File T r ansfer Protocol
HDD Hard Drive
HMAC Keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code
HP Hewlett-Packard
IDE Integrated Drive Electronics
iLO Integrated Lights-Out
I/O Input/Output
IP Internet Protocol
ISA Instruction Set Architecture
KAT Known Answer Test
KMS Key Management Service
LDAP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
LED Light Emitting Diode
MAC Message Authentication Code
N/A Not Applicable
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 25 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 26
Security Policy, version 1.0 January 31, 2008
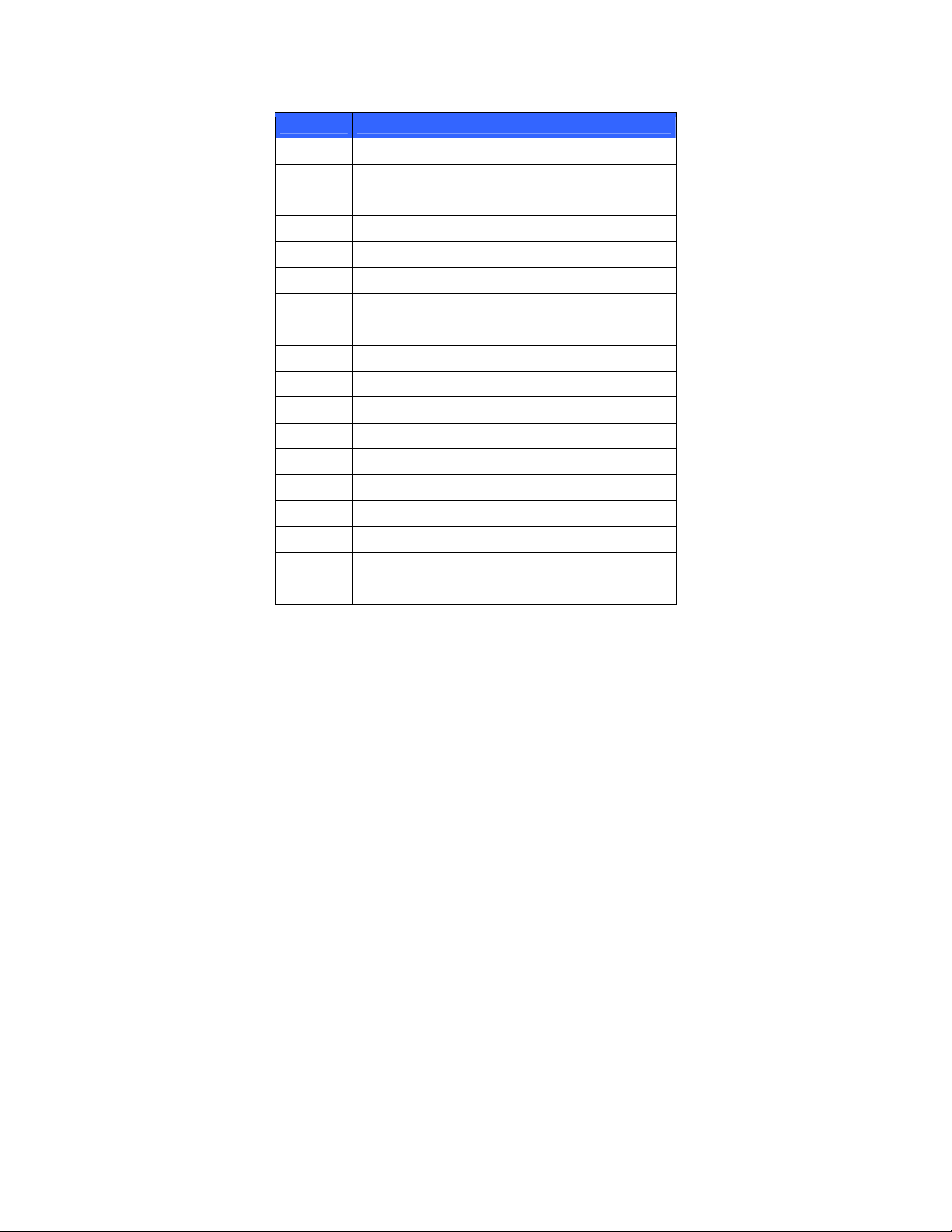
Acronym Definition
NIC Network Interface Card
NIST National Institute of Standards and Technology
NTP Network Time Protocol
PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect
PRNG Pseudo Random Number Generator
RFC Request for Comments
RNG Random Number Generator
RSA Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman
SHA Secure Hash Algorithm
SKM Secure Key Manager
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
SSH Secure Shell
SSL Secure Socket Layer
TLS Transport Layer Security
UID Unit Identifier
USB Universal Serial Bus
VGA Video Graphics Array
XML Extensible Markup Language
HP StorageWorks Secure Key Manager
This document may be freely reproduced in its original entirety.
Page 26 of 26
© 2008 Hewlett-Packard Company
 Loading...
Loading...