Page 1

Contents
HP E1411A/B 5 1/2 Digit Multimeter Service Manual
Edition 2
Click here to Return to HP TS-5400 Systems On-Line Manuals Main Contents
Chapter 1. General Informa tio n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Safety Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Warnings and Cautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Multimeter Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Multimeter Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Multimeter Serial Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Multimeter Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Recommended
Test Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Chapter 2. Ins tallation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Initial Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Preparation for Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Shipping the Multimeter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Chapter 3. Operating Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Multimeter Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Operator’s Chec k . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Self-Test Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Example: Multimeter Self-Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Chapter 4. Verification Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Test Conditions / Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Performance Test Record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Verification Test Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Function al Verification Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Self-Test Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Example: Self-Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Operatio n Verification Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Performance Verification Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Performance Test Record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Multimeter Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Measurement Uncertainty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Test Accuracy Ratio (TAR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Page 2

Chapter 5. Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Adjustment Conditions / Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
DC Voltage Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Equipment Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Adjustment Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Example: DC Voltage Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
AC Voltage Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Equipment Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Adjustment Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Resistanc e Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Equipment Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Adjustment Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Example: 4-Wire Resistance Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Calibration Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Chapter 6. Replaceable Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Exchange Assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Ordering Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Replaceable Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Chapter 7. Manual Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Chapter 8. Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Equipment Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Service Aids . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
TroubleshootingTechniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Identifyi ng the Problem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Testing Assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Repair Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
ESD Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Removing Top Shield . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Removing Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Removing Binding Posts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Soldering Printed Circuit Boards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Post-Repair Safety Checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Appendix A. C alculating Multimeter Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Multimeter Accuracy Calculations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
DC Voltage Accuracy Equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
AC Voltage Accuracy Equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
4-Wire Ohms Accuracy Equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Measurement Uncertainty Calculations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Page 3

Calculate DCV Measurement Uncertainty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Calculate ACV Measurement Uncertainty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Calculate Resistance Measurement Uncertainty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Test Accuracy Ratio (TAR) Calculations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Appendix B. Verification Tests - C Programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Function al Verification Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Example:Self Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Performance Verification Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Example: Zero Volt DCV Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Example: DC Voltage Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Example: AC Voltage Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Example: Resistance Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
DC Voltage Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
AC Voltage Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Resistanc e Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Page 4

Notes
Page 5

Certification
Hewlett-Packard Company certifies that this product met its published specifications at the time of shipment from the factory. HewlettPackard further certifies that its calibration measurements are traceable to the United States National Institute of Standards and Technology (formerly National Bureau of Standards), to the extent allowed by that organization’s calibration facility, and to the calibration
facilities of other International Standards Organization members.
Warranty
This Hewlett-Packard product is warranted against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of three years from date of shipment. Duration and conditions of warranty for this product may be superseded when the product is integrated into (becomes a part of)
other HP products. During the warranty period, Hewlett-Packard Company will, at its option, either repair or replace products which
prove to be defective.
For warranty service or repair, this product must be returned to a service facility designated by Hewlett-Packard (HP). Buyer shall prepay shipping charges to HP and HP shall pay shipping charges to return the product to Buyer. However, Buyer shall pay all shipping
charges, duties, and taxes for products returned to HP from another country.
HP warrants that its software and firmware designated by HP for use with a product will execute its programming instructions when
properly installed on that produ c t. HP do e s not war ra n t th a t th e ope ra tion of the product , or s oftware, or firmwa re w ill be uninterrupted
or error free.
Limitation Of Warranty
The foregoing wa rr a nt y s ha l l not apply to defects resulting from im p r op e r or ina d e qu a te m aintenance by Buye r, Buyer-suppli e d products or interfacing, unauthorized modification or misuse, operation outside of the environmental specifications for the product, or improper site preparation or maintenance.
The design and implement ation of any circuit on this product is th e sole respo nsi bi li ty of the Buyer. HP does not warrant the Buyer’s
circuitry or m a lfu nc tions of HP products th a t r e s ul t f rom th e Bu yer ’s c ir c u itry. In addition, HP doe s not warrant any dam a g e that occurs as a result of the Buyer’s circuit or any defects that result from Buyer-supplied products.
NO OTHER WARRANTY IS EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED. HP SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Exclusive Remedies
THE REMEDIES PROVIDED HEREIN ARE BUYER’S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES. HP SHALL NOT BE LIABLE
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, WHETHER BASED ON CONTRACT, TORT, OR ANY OTHER LEGAL THEORY.
Notice
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. HEWLETT-PACKARD (HP) MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. HP shall not be liable for errors contained
herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing , performance or use of this material. This document contains proprietary information which is protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another language witho ut the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard Company. HP assumes no
responsibility for the use or reliability of its software on equipment that is not furnished by HP.
U.S. Government Restricted Rights
The Software and Documentation have been developed entirely at private expense. They are delivered and licensed as "commercial
computer software" as defined in DFARS 252.227- 7013 (Oct 1988), DFARS 252.211-7015 (May 1991) or DFARS 252.227-7014 (Jun
1995), as a "com mercial ite m " as de fined in FAR 2.10 1(a ) , or as "R e s tricted comp uter software" as defined in FA R 52.227-19 (Jun
1987)(or any equivalent agency regulation or contract clause), whichever is app licable. You have only those rights provided for such
Software and Documentation by the applicable FAR or DFARS clause or the HP standard software agreement for the product involved.
HP E1411A/E141 1B 5 1/2-Digit Mult im e ter Service Manual
Copyright © 1996 Hewlett-Packard Company. All Rights Reserved.
Edition 2
HP E1411A/B Service Manual 5
Page 6
Documentation History
All Editions and Updates of this manual and their creation date are listed below. The first Edition of the manual is Edition 1. The Edition number increments by 1 whenever the manual is revised. Updates, which are issued between Editions, contain replacement pages
to correct or add additional information to the current Edition of the manual. Whenever a new Edition is created, it will contain all of
the Update information for the previous Edition. Each new Edition or Update also includes a revised copy of this documen tatio n history page.
Edition 1 (Part Number E1411-90000). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . October 1995
Edition 2 (Part Number E1411-90011). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . August 1996
Safety Symbols
Instructio n m a nu a l s ym b ol affixed to pro duct. Indicates that the user must refer to the
manual for specific WARNING or CAUTION information to avoid personal injury
or damage to th e product.
Indicates the field wiring terminal that must
be connected to earth ground before operating the equipment—protects against electrical shock in case of fault.
or
Frame or chassis ground terminal—typically connects to the equipment’s metal
frame.
WARNING
CAUTION
Alternating current (AC).
Direct current (DC).
Indicates hazardous voltages.
Calls attention to a procedure, practice, or
condition that c ould cau se bodi l y in ju ry or
death.
Calls attention to a procedure, practice, or condition that could possibly cause damage to
equipment or pe r m a n e nt loss of data.
WARNINGS
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation, service, and repair of this product.
Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this manual violates safety standards of design,
manufacture, and intended use of the product. Hewlett-Packard Company assumes no liabil ity for the customer’s failure to
comply with these requirements.
Ground the equipment: For Safety Class 1 equipment (equipment having a protective earth terminal), an uninterruptible safety earth
ground must be provid e d from th e mai ns po we r sourc e to the pro du c t in pu t w iring terminals or s up pl ie d powe r c a bl e .
DO NOT operate the product in an explosive atmosphere or in the presence of flammable gases or fumes.
For continued protection against fire, replace the line fuse(s) only with fuse(s) of the same voltage and current rating and type.
DO NOT use repaired fuses or short-circuited fuse holders.
Keep away from live circuits: Operating personnel must not remove equipment covers or shields. Procedures involving the removal
of covers or shields are for use by service-trained personnel only. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even with the
equipment switched off. To avoid dangerous electrical shock, DO NOT perform procedures involving cover or shield removal unless
you are qualified to do so.
DO NOT operate damaged equipment: Whenever it is possible that the safety protection features built into this product have been impaired, either through physical damage, excessive moisture, or any other reason, REMOVE POWER and do not use the product until
safe operation can be verified by service-trained personnel. If necessary, return the product to a Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Office for service and repair to ensure that safety features are maintained.
DO NOT service or adjust alone: Do not attempt internal service or adjustment unless another person, capable of rendering first aid
and resuscitation, is present.
DO NOT substitute parts or modify equipment: Because of the danger of introducing additional hazards, do not install substitute
parts or perform any unauthorized modification to the product. Return the product to a Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Office for
service and repair to ensure that safety features are maintained.
6 HP E1411A/B Service Manual
Page 7

Declaration of Conformity
according to ISO/IEC Guide 22 and EN 45014
Manufacturer’s Name: Hewlett-Packard Company
Loveland Manufacturing Center
Manufacturer’s Address: 815 14th Street S.W.
Loveland, Colorado 80537
declares, that the product:
Product Name: 5 1/2-Digit Multimeter
Model Number: HP E1411A/HP E1411B
Product Options: All
conforms to the following Product Specifications:
Safety: IEC 1010-1 (1990) Incl. Amend 1 (1992)/EN61010-1(1993)
CSA C22.2#1010.1 (1992)
UL 3111
EMC: CISPR 11:1990/EN55011 (1991): Group 1, Class A
EN50082-1:1992
IEC 801-2:1991 : 4kV CD, 8kV AD
IEC 801-3:1984 : 3 V/m
IEC 801-4:1988 : 1kV Power Line, 0.5kV signal lines
ENV50141:1993/p rE N 50 08 2-1 (1995): 3 Vrms
ENV50142:1994/prEN50082-1 (1995): 1 kV CM, 0.5kV DM
IEC1000-4-8:1993/p rEN50082-1 (1995): 3 A/m
EN61000-4-11:1994/prEN50082-1 (1995): 30%,10ms 60%,100ms
Supplementary Information: The product herewith complies with the requirements of the Low Voltage Directive
73/23/EEC and the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC (inclusive 93/68/EEC) and carries the "CE" mark accordingly.
Tested in a typical HP C-Size VXI mainframe configuration.
December 30, 1995 Jim White, QA Manager
European contact: Your local Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Office or Hewlett-Packard GmbH, Department
HQ-TRE, Herrenberger Straße 130, D-71034 Böblingen, Germany (FAX +49-7031-14-3143).
HP E1411A/B Service Manual 7
Page 8

Notes
8 HP E1411A/B Service Manual
Page 9

Please fold and tape for mailing
Reader Comment Sheet
HP E1411A/E1411B 5 1/2-Digit Multimeter Service Manual
Edition 2
You can help us improve our manuals by sharing your comments and suggestions. In appreciation of your time, we will
enter you in a quarterly drawing for a Hewlett-Packard Palmtop Personal Computer (U.S. government employees
are not eligible for the drawing).
Your Name
Company Name
Job Title
Address
City, State/Province
Country
Zip/Postal Code
Telephone Number with Area Code
Please list the system controller, operating system, programming language, and plug-in modules you are using.
fold here
UNITED STATES
BUSINESS REPLY MAIL
FIRST CLASS PERMIT NO. 37 LOVELAND, CO
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY
cut along this line
Measurement Systems Division
Learning Products Department
P.O. Box 301
Loveland, CO 80539-9984
NO POSTAGE
NECESSARY
IF MAILED
IN THE
fold here
Please pencil-in one circle for each stateme n t belo w: Disagree Agree
•
The documentation is well organized. OOOOO
•
Instructions are easy to understand. OOOOO
•The documentation is clearly written. OOOOO
•Examples are clear and useful. OOOOO
•Illustrations are clear and helpful. OOOOO
•The documentation meets my overall expectations. OOOOO
Please write any comments or suggestions below--be specific.
Page 10

10 HP E1411A/E1411B Service Manual
Page 11
Chapter 1
General Information
Introduction This manual contains information required to test, adjust, troubleshoot, and
repair the HP E1411A and HP E1411B C-Size VXI 5 1/2-Digit Multimeters
(HP E1411 multimeter). See the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the
HP E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual for additional information on the HP
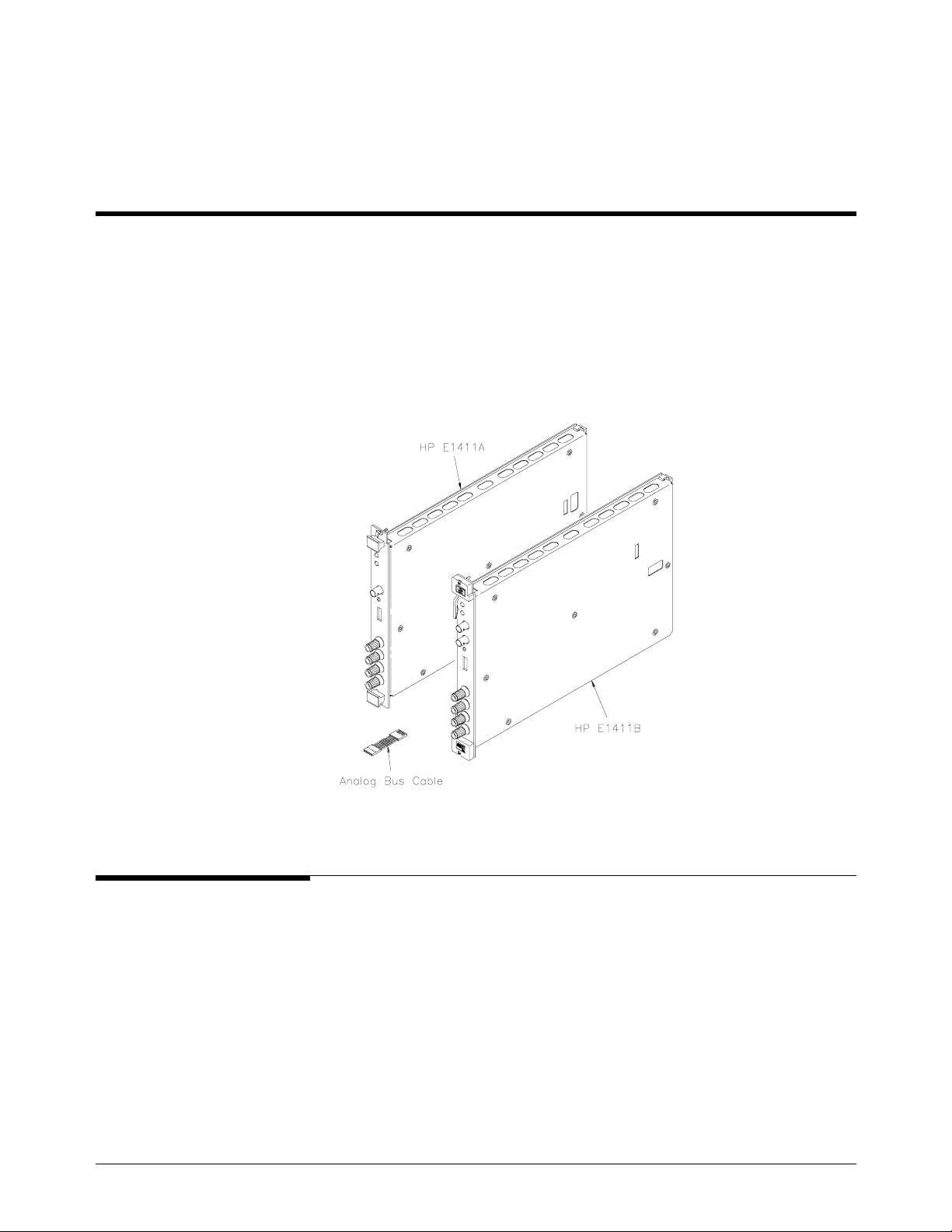
E1411 multimeter. Figure 1-1 shows the HP E1411A and E1411B
multimeters.
Figure 1-1. HP E1411A/B Multimeters
Safety
Considerations
Chapter 1 General Information 11
This product is a Safety Class I instrument that is provided with a protective
earth terminal when installed in the mainframe. The mainframe, multimeter,
and all related documentation should be reviewed for familiarization with
safety markings and instructions before operation or service.
Refer to the WARNINGS page (page 4) in this manual for a summary of
safety information. Safety information for testing, adjusting, and service
follows and is also found throughout this man ual.
Page 12

Warnings and
Cautions
This section contains WARNINGS which must be followed for your
protection and CAUTIONS which must be followed to avoid damage to the
equipment when performing instrument maintenance or repair.
WARNING
SERVICE-TRAINED PERSONNEL ONLY. The information in this
manual is for service-trained personnel who are familiar with
electronic circuitry and are aware of the hazards involved. To
avoid personal injury or damage to the instrument, do not
perform procedures in this manual or do any servicing unless
you are qualified to do so.
CHECK MAINFRAME POWER SETTINGS. Before applying
power, verify that the mainframe setting matches the line
voltage and the correct fuse is installed. An uninterruptible
safety earth ground must be provided from the main power
source to the supplied power cord set.
GROUNDING REQUIREMENTS. Interruption of the protective
(grounding) conductor (inside or outside the mainframe) or
disconnecting the protective earth terminal will cause a
potential shock hazard that could result in personal injury.
(Grounding one conductor of a two-conductor outlet is not
sufficient protection.)
IMPAIRED PROTECTION. Whenever it is likely that instrument
protection has been impaired, the mainframe must be made
inoperative and be secured against any unintended operation.
REMOVE POWER IF POSSIBLE. Some procedures in this
manual may be performed with power supplied to the
mainframe while protective covers are removed. Energy
available at many points may, if contacted, result in personal
injury. (If maintenance can be performed without power applied,
the power should be removed.)
USING AUTOTRANSFORMERS. If the mainframe is to be
energized via an autotransformer (for voltage reduction) make
sure the common terminal is connected to neutral (that is, the
grounded side of the main’s supply).
CAPACITOR VOLTAGES. Capacitors inside the mainframe may
remain charged even when the mainframe has been
disconnected from its source of supply.
12 General Information Chapter 1
Page 13
WARNING
USE PROPER FUSES. For continued protection against fire
hazard, replace the line fuse(s) only with fuses of the same
current rating and type (such as normal blow, time delay, etc.).
Do not use repaired fuses or short-circuited fuseholders.
CAUTION
Multimeter
Description
NOTE
Static electricity is a major cause of component failure. To prevent
damage to the electrical components in the multimeter, observe
anti-static techniques whenever working on the multimeter.
The HP E1411 multimeter is an "instrument" in the slots of a VXIbus
mainframe. As su ch, it is assigned an er ro r qu eue, input and ou tput buffers,
status registers, and is allocated a portion of mainframe memory for reading
storage.
Instruments are based on the logical addresses of the plug-in modules. See
the HP 75000 Series C Installation and Getting Started Guide to set the
addresses to create an instrument.
The instrument may consist of a multimeter only (stand-alone operation), or
can include relay or FET multiplexers (scanning multimeter operation). The
instrument is operated from a computer using Standard Commands for
Programmable Instruments (SCPI) language.
In stand-alone operation, input signals are connected to the multimeter’s
external (faceplate) terminals. In scanning multimeter operation, input
signals are connected to the multiplexer channels. The multimeter is linked
to relay multiplexers via an analog bus cable. The multimeter is linked to
FET multiplexers via an analog bus cable and a digital bus cable.
Multimeter
Specifications
Multimeter specifications are listed in Appendix A of the HP
E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual.
These specifications are the performance standards or limits against which
the instrument may be tested.
Chapter 1 General Information 13
Page 14
Multimeter Serial
Numbers
Multimeters covered by this manual are identified by a serial number prefix
listed on the title page. Hewlett-Packard uses a two part serial number in the
form 0000A00000, where 0000 is the serial prefix, A is the country of
origin (A=USA) and 00000 is the serial suffix. The serial number prefix
identifies a series of identical instruments. The serial number suffix is
assigned sequentially to each instrument.
If the serial num b er p re fix of you r instrument is gre at er tha n the one listed
on the title page , a M an u a l Update (as required ) w il l ex plai n how to adapt
this manual to your instrument. If the serial number prefix of your
instrument is lower than the one listed on the title page, information
contained in Chapter 7- Manual Changes will explain how to adapt this
manual to your instrument.
Multimeter Options There are no electrical or mechanical options available for the HP E1411
multimeters. However, for the HP E1411B, you can order Option 1BN that
provides a MIL-STD-45662A Calibration Certificate. Contact your nearest
Hewlett-Packard Sales and Support Office for information on Option 1BN.
Recommended
Test
Equipment
Instrument Requirements Recommended
Controller, HP-IB HP-IB compatibility as def ined by IEEE
Mainframe Compatible wit h mu lt im et er HP E1400B/T or
AC Standard Voltage Range 0.1 V to 300 V Datron 4708 with
DC Standard Voltage Range 0.07 V to 300 V Datron 4708 with
Resistance Standard
Table 1-1 lists the te st equipment recom m en ded for testing, adj us ti ng and
servicing the multimeter. Essential requirements for each piece of test
equipment are described in the Requirements column.
Table 1-1. Recommended Test Equipment
Use*
Model
Standard 488-1987 and the identical
ANSI Standard MC1.1: SH1, AH1, T2,
TE0, L2, LE0, SR0, RL0, PP0, DC0,
DT0, and C1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Values 1 kΩ to 1 MΩ
HP 9000 Series 300
or
IBM Compatible PC
with HP BASIC
E1421A/B
Option 20
Option 10
Datron 4708 with
Option 30
A,F,
P,T
A,F,
P,T
A,P
A,P
A,P
Digital Multimeter General Purpose Voltage and Resistance HP 3458A T
*A = Adjustments, F = Functional Verification, P = Performance Verification Tests, T = Troubleshooting
14 General Information Chapter 1
Page 15
Chapter 2
Installation
Introduction This chapter provides information to install the HP E1411 multimeter,
including initial inspection, preparation for use, environment, storage and
shipment.
Initial
Inspection
WARNING
Inspect the shipping container for damage. If the shipping container or
cushioning material is damaged, keep the container until the shipment
contents have been checked and the instrument has been c hecked
mechanically and electrically. See Figure 1-1 in Chapter 1 - General
Informatio n fo r sh ipment contents . See Chapter 4 - Verification Tests for
procedures to check electrical performance.
To avoid possible hazardous electrical shock, do not perform
electrical tests if there are signs of shipping damage to any
portion of the outer enclosure (covers, panels, etc.).
If the contents are incomplete, if there is mechanical damage or defect, or if
the instrument does not pass the electrical performance tests, notify your
nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales and Support Office. If the shipping container
is damaged or the cushioning material shows signs of stress, notify the
carrier as well as Hewlett-Packard, and keep the shipping materials for the
carrier’s inspection.
Preparation for
Use
Chapter 2 Installation 15
See Chapter 2 of the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the
E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual to prepare an HP E1411 multimeter for
use. See the appropriate mainframe user’s manual(s) to prepare your
mainframe. If your mainframe is not manufactured by Hewlett-Packard,
consult the manufacturer for a list of available manual(s).
Recommended operating environment for the HP E1411 multimeters is 0
o
to +55
should be stored in a clean, dry environment. For storage and shipment, the
temperature range is -40
+40
C with relative humidity <65% (0 oC to +40oC). The instrum en t
o
o
C).
C to +75oC with relative humidity <65% (0oC to
o
C
Page 16

Shipping the
Multimeter
If you need to return an HP E1411 multimeter to Hewlett-Packard,
first remove any adapters or connectors before packaging the instrument for
shipment. When you return the instrument to Hewlett-Packard, attach a tag
to the instrument identifying the owner and indicating service or repair
required. In any correspondence, refer to the instrument by model number
and full serial nu mber.
When shipping the instrument, we recommend using containers and
materials identical to those used in factory packaging, which are available
through Hewlett-Packard Sales and Support Offices. Mark the shipping
container "FRAGILE" to assure careful handling.
If you use other (commercially available) shipping materials, wrap the
instrument in heavy paper or plastic. Use a strong shipping container. A
double-wall carton of 2.4 MPa (350 psi) test material is adequate.
Use enough shock-absorbing material (75 to 100 mm layer; 3 to 4 inches)
around all sides of the instrument to provide firm cushion and prevent
movement in the container. Protect the front panel with cardboard. Seal the
shipping container securely and mark the container "FRAGILE" to assure
careful handling.
16 Installation Chapter 2
Page 17

Chapter 3
Operating Instructions
Introduction This chapter lists operating information for the HP E1411 multimeter,
including:
• Multimeter operation
• Operator’s check (self-test)
Multimeter
Operation
Operator’s
Check
See the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the E1326B/E1411B User’s
Manual for multimeter operation, including:
• Getting started
• Configuring the multimeter
• Using the multimeter
• Understanding the multimeter
• Multimeter command reference
• Multimeter specifications
• Multimeter error messages
• Register-based programming
The Operator’s Check for the HP E1411 multimeter consists of sending the
self-test (*TST?) command and checking the return. The operator’s check
can be used to verify the multimeter is connected properly and is responding
to the self-tes t command.
As required, see the mainframe user’s manual for information on address
selection. See the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the
E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual for information on multimeter SCPI
commands.
Self-Test Procedure 1. Verify the multimeter is properly installed in the mainframe and
the mainframe has passed its power-on sequence test.
2. Execute the multimeter functional test using the *TST? command
(see example following).
3. A "0" returned means no self-test failure, while "1", "2", "3", or "4"
returned means a failure was detected. See Chapter 8 - Service for
troubleshooting information (see NOTE following).
Chapter 3 Operating Instructions 17
Page 18

NOTE
Test failures can be caused by improper cabling, improper selection of the
interface select code, primary, and/or secondary address setting. Verify
proper connection and address selection before troubleshooting.
Example:
Multimeter Self-Test
An example follows which uses an HP 9000 Series 300 computer with HP
BASIC and a multimeter address of 70903.
10 OUTPUT 70903;"*TST?" Send the self-test command
20 ENTER 70903;A Enter self-test result
30 PRINT A
40 END
18 Operating Instructions Chapter 3
Page 19

Chapter 4
Verification Tests
Introduction The three levels o f te st p ro ce du re s de sc ri be d in this chapter are us ed
to verify that the HP E1411 multimeter:
• is functional (Functional Verification)
• meets selected testable specifications (Operation Verification)
• meets all testable specifications (Performance Verification)
WARNING
Test Conditions /
Procedures
Do not perform any of the following verification tests unless
you are a qualified, service-trained person and have read the
WARNINGS and CAUTIONS in
For valid tests, all test equipment and the multimeter must have a one hour
warmup, the line voltage must be 115/230 Vac ± 10%, and multimeter Auto
Zero must be set to ON. See Table 1-1, Recommended Test Equipment, for
test equipment requirements.
For best test accuracy, the ambient temperature of the test area should be
between 18
Performance Verification tests at least once a year. For heavy use or severe
operating environments, perform the tests more often.
The verification tests assume the person performing the tests understands
how to operate the mainframe, multimeter and specified test equipment. The
test procedures do not specify equipment settings for test equipment, except
in general terms. It is assumed a qualified, service-trained person will select
and connect the cables, adapters, and probes required for the test.
o
C and 28oC and stable to within ±1oC. You should perform the
Chapter 1 - General Information
.
Performance Test
Record
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 19
Table 4-1, Performance Test Record for the HP E1411 Multimeter, at the
end of this chapter, provides space to enter the results of each Performance
Verification test and to compare the results with the
upper and lower limits for the test. You can make a copy of this form,
if desired.
Page 20
The value in the "Measurement Uncertainty" column of Table 4-1 is
derived from the specifications for the source used for the test, and
represents the expected accuracy of the source. The value in the "Test
Accuracy Ratio (TAR)" column of Table 4-1 is the ratio of multimeter
accuracy to measurement uncertainty.
Verification Test
Examples
Functional
Verification
Test
Each Performance Verification Test includes an example program to
perform the te st. Eac h ex am p le u se s ad dr es s 70 90 3 fo r th e m ul tim et er , an d
an HP 9000 Series 200/300 computer running HP BASIC and Standard
Commands for Programmable Instruments (SCPI) commands. You may
need to change the multimeter address and/or command syntax to perform
the examples for your setup.
As required, see the mainframe or command module user’s manual for
information on address selection and cabling guidelines. See the HP
E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual for
information on multimeter SCPI commands.
The functional verification test for the HP E1411 multimeter consists of the
multimeter self-test. You can perform this test to verify the multimeter is
functional and is communicating with the mainframe, external computer
and/or exte rn al ter m in al .
Self-Test Procedure This test verifies the multimeter is communicating with the mainframe,
external controller, and/or external terminal by performing a multimeter
self-test. Do the fol lo w in g st ep s to perform the se lf -t es t:
1. Verify the multimeter is correctly installed in the mainframe.
2. Connect a power cable to the mainframe and set mainframe
power ON. Verify proper mainframe power-up sequence. (See
the mainframe user’s manual for additional information.) If
correct, proceed with step 3. If incorrect, troubleshoot the problem
before proceeding .
3. Execute the multimeter functional verification test using the
*TST? command. See the following exam ple which uses an HP
9000 Series 300 computer with HP BASIC and a multimeter
address of 70903.
4. A "0" returned means no failure, while "1", "2", "3", or "4" returned
means a failure w as det ec te d. See Chapter 8 - Service for troubleshooting information.
20 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 21
NOTE
Example: Self-Test
Test failures can be caused by improper selection of the interface select
code, primary address setting, and/or secondary address setting. Verify
proper address selection before troubleshooting.
10 OUTPUT 70903;"*TST?" !Send the self-test command
20 ENTER 70903;A !Enter the test result
30 PRINT A !Display the result
40 END
Operation
Verification
Tests
Performance
Verification
Tests
There are no separate operation verification tests for the HP E1411
multimeter. Use the Performance Verification tests for post-repair
checkout.
Performance verification tests are used to check the multimeter’s electrical
performance against the specifications in Appendix A - Specifications of the
HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual
as the performance standards. These tests are suitable for incoming
inspection and troubleshooting. The performance verification tests for the
HP E1411 multimeter are:
• Test 4-1: DC Voltage Test (Zero Volt Input)
• Test 4-2: DC Voltage Test (DCV Input)
• Test 4-3: AC Voltage Test
• Test 4-4: Resistance Test (4-Wire Ohms)
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 21
Page 22
Test 4-1: DC Voltage Test (Zero Volt Input)
This test verifies DC Voltage accuracy on all five ranges using a zero
volt input.
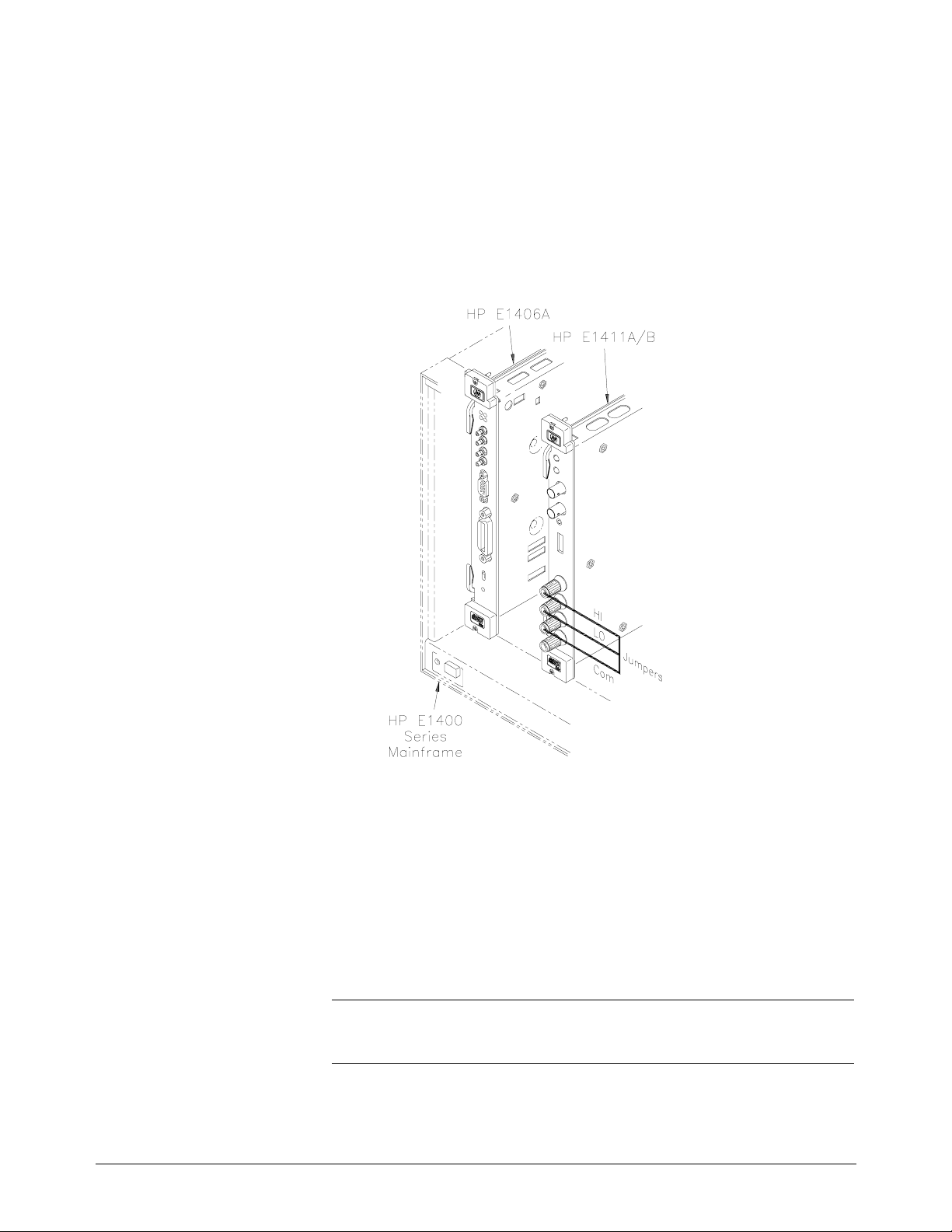
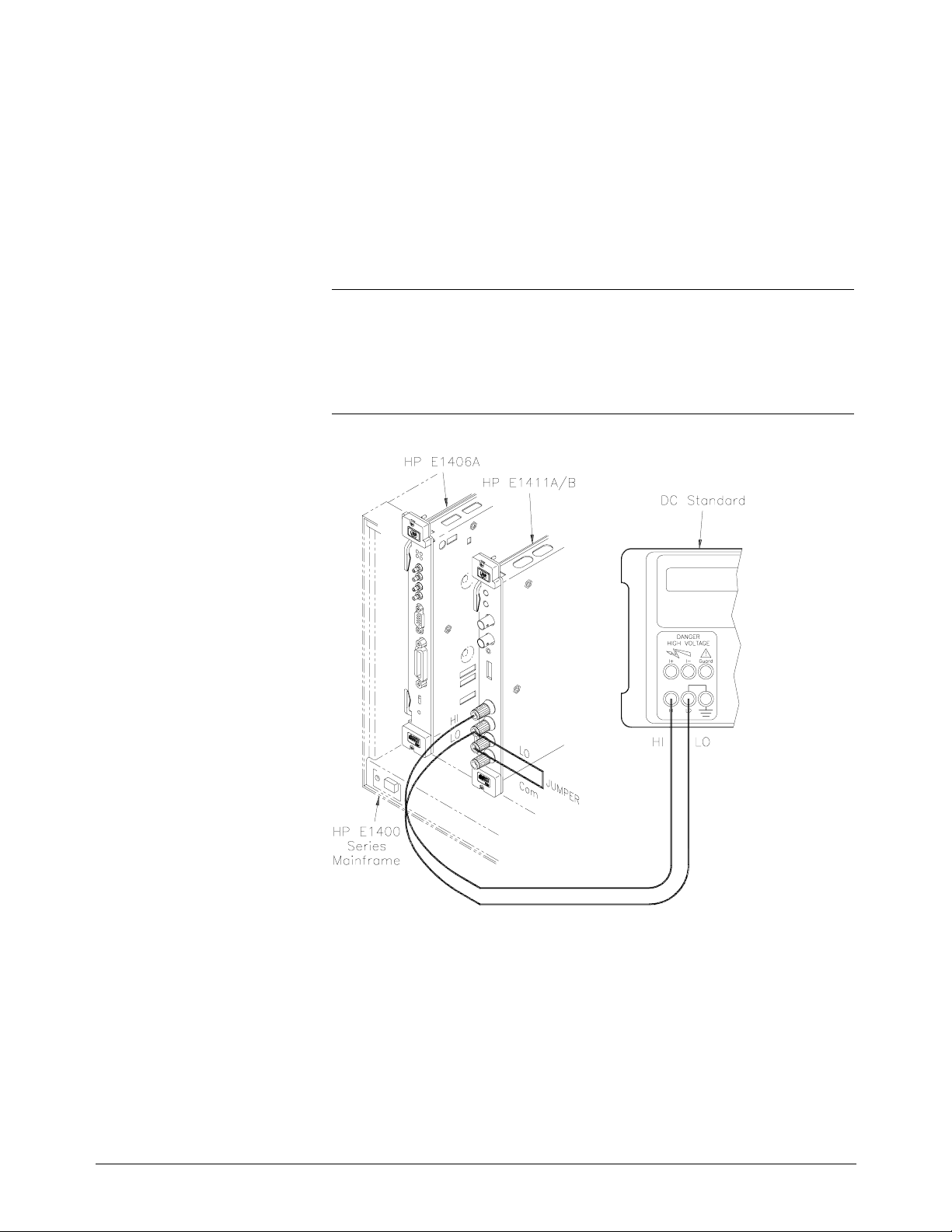
Equipment Setup 1. Connect the equipment as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1. DC Voltage (Zero Volt Input) Setup
2. Set the HP E1411 multimeter as follows:
• Reset Multimeter ..................................................*RST
• Auto Zero ............ .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .ON
• Power Line Cycles (PLC) ............................................1
• Line Freq Reference (CAL:LFR) ...... 50Hz or 60Hz
NOTE
*RST sets Auto Zero to ON and Power Line Cycles to 1.
Test Procedure
22 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 23
1. Set the HP E1411 range to 0.113 V (0.125 V with 10% over- range)
and measure the in pu t vo lt ag e w ith M E AS :VO LT: DC ? 0. 1
2. Observe the input, record the results on the Performance Test
Record, and verify th e re sults are within sp ec if ie d li m it s (a t th e
range selected for 1 PLC).
3. Repeat step s 1 and 2 for the followi ng ranges:
E1411 Range 10% Overrange Input
Example: Zero Volt
DCV Test
0.91 V
7.27 V
58.10 V
300.00 V
4. Remove power and disconnect test equipment.
64 V
None
1 V
8 V
0 V
0 V
0 V
0 V
This example performs a DCV test for zero volts input and a power line
reference frequency of 60 Hz. Change line 20 to OUTPUT
70903;"CAL:LFR 50" for 50 Hz operation.
1 !Zero Volts Performance Verification
10 OUTPUT 70903;"*RST" !Resets and sets autozero ON
20 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:LFR 60" !Sets line reference to 60 Hz
30 OUTPUT 70903;"MEAS:VOLT:DC? .1" !Measure 0.113 V range
40 ENTER 70903;A
50 PRINT A
60 OUTPUT 70903;"MEAS:VOLT:DC? .9" !Measure 0.91 V range
70 ENTER 70903;B
80 PRINT B
90 OUTPUT 70903;"MEAS:VOLT:DC? 7" !Measure 7.27 V range
100 ENTER 70903;C
110 PRINT C
120 OUTPUT 70903;"MEAS:VOLT:DC? 58" !Measure 58.1 V range
130 ENTER 70903;D
140 PRINT D
150 OUTPUT 70903;"MEAS:VOLT:DC? 300" !Measure 300 V range
160 ENTER 70903;E
170 PRINT E
180 END
and PLC to 1
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 23
Page 24
Test 4-2: DC Voltage Test (DCV Input)
This test verifies DC Voltage accuracy on all five ranges with DC voltage
inputs.
Equipment Setup 1. Connect the equipment as shown in Figure 4-2.
WARNING
The DC Standard (Datron 4708, Option 10) can produce
dangerous voltages which are present on the terminals. Do not
touch the front (or rear) panel terminals unless you are sure no
dangerous voltage is present.
Figure 4-2. DC Voltage (DCV Input) Setup
2. Set the HP E1411 multimeter as follows:
• Reset Multimeter .................................................*RST
• Auto Zero ................................................................ON
• Power Line Cycles (PLC) ...........................................1
• Line Freq Reference (CAL:LFR) ..... 50Hz or 60Hz
24 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 25

NOTE
*RST sets Auto Zero to ON and Power Line Cycles to 1.
Test Procedure 1. Set the DC Standard Output to 0.1 DCV.
2. Set the HP E1411 range to 0.113 V (0.125 V with 10% overrange)
with CONF:VOLT:DC .1
3. Measure the input with READ? and verify the results are within
specified limits (at the range selected for 1 PLC). Record results
on Performance Test Record.
4. Repeat steps 1 through 3 for the following DC Standard voltage
settings and HP E1411 ranges:
E1411 Range 10% overrange DC Std Output
Example: DC Voltage
Test (DCV Input)
NOTE
0.91 V
7.27 V
58.10 V
300.00 V
5. Remove power and disconnect test equipment.
64 V
None
1 V
8 V
0.9 V
7.0 V
58.0 V
300.0 V
This example performs a DCV test for DC volts input and a power line
reference frequency of 60 Hz. Change line 80 to OUTPUT
70903;"CAL:LFR 50" for 50 Hz operation.
When connected to the HP E1411 multimeter, some DC Standards may
exhibit voltage variations at the start of a measurement. The WAIT 1
statement (line 150) provides a one second wait before measurement to
allow settling of the DC Standard output.
1 !DC Voltage Performance Verification
10 OPTION BASE 1
20 DIM Range(5), Volts(5), Read_meas(5)
30 DATA 0.113, 0.91, 7.27, 58.1, 300.0
40 READ Range(*)
50 DATA 0.1, 0.9, 7.0, 58.0, 300.0
60 READ Volts(*)
70 OUTPUT 70903;"*RST" !Set autozero on and PLC 1
80 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:LFR 60" !Set 60 Hz line frequency
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 25
Page 26

90 FOR I=1 TO 5
100 PRINT "Set DC Standard to ";Volts(I);"VDC"
110 PRINT "Press Continue when ready"
120 PAUSE
130 CLEAR SCREEN
140 OUTPUT 70903;"CONF:VOLT:DC";Range(I) !Set DCV, range
150 WAIT 1 !Wait for settling
160 OUTPUT 70903;"READ?"
170 ENTER 70903;Read_meas(I) !Enter DC voltage
180 NEXT I
190 FOR I=1 TO 5
200 PRINT "Voltage on";Range(I);"V range =";Read_meas(I);"VDC"
210 NEXT I
220 END
Test 4-3: AC Voltage Test
This test verifies AC voltage accuracy on the 87.5 mV and 300 V ranges
using sine wave inputs at ≥50% of full scale. The input frequency varies
from 20 Hz to 10 kHz. The DC component must be <10% of the AC
component.
NOTE
The DC Voltage Performance test must be performed prior to the AC
Voltage test to check the A/D accuracy on all ranges. If the DC Voltage test
has not been performed, the AC voltage must be checked on all ranges.
Equipment Setup 1. Connect the equipment as shown in Figure 4-3.
WARNING
The AC Standard (Datron 4708, Option 20) can produce
dangerous voltages which are present on the terminals. Do not
touch the front (or rear) panel terminals unless you are sure no
dangerous voltage is present.
26 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 27

Figure 4-3. AC Voltage Setup
2. Set the HP E1411 multimeter as follows:
• Reset Multimeter ..................................................*RST
• Auto Zero ................................................................ON
• Power Line Cycles (PLC) ...........................................1
• Line Freq Reference (CAL:LFR) ..... 50Hz or 60Hz
NOTE
*RST sets Auto Zero to ON and Power Line Cycles to 1.
Test Procedure 1. Set the AC Standard Output to 0.07 Vac at 20 Hz sine wave.
2. Set the HP E1411 range to 79.5 mV (87.5 mV with 10% overrange)
using CONF:VOLT:AC .07.
3. Measure the AC input voltage with READ? and verify the
results are within specified limits (at the range selected for 1 PLC).
Record the results on the Performance Test Record.
4. Repeat steps 1 through 3 using the following AC Standard
voltage and frequency settings, and HP E1411 ranges:
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 27
Page 28

E1411
Range
10%
overrange
AC Standard Output
Voltage (Vac) Frequency (Hz)
Example: AC Voltage
Test
NOTE
79.5 mV
79.5 mV
79.5 mV
300.0 V
87.5 mV
87.5 mV
87.5 mV
None
0.07 V
0.07 V
0.07 V
300.00 V
60 Hz
5 kHz
10 kHz
5 kHz
5. Remove power and disconnect test equipment.
This example performs an ACV test for a power line reference frequency of
60 Hz. Change line 80 to OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:LFR 50" for 50 Hz
operation.
When connected to the HP E1411 multimeter, some AC Standards may
exhibit voltage variations at the start of a measurement. The WAIT 1
statement (line 160) allows settling for the AC Standard output.
1 ! AC Voltage Performance Verification
10 OPTION BASE 1
20 DIM Read_meas(5),Source_volts(5),Source_freq(5)
30 DATA 0.07, 0.07, 0.07, 0.07, 300.0
40 READ Source_volts(*)
50 DATA 20, 60, 5000, 10000, 5000
60 READ Source_freq(*)
70 OUTPUT 70903;"*RST" !Set autozero ON, PLC 1
80 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:LFR 60" !Set 60 Hz line ref frequency
90 FOR I=1 TO 5
100 PRINT "1. Set AC Standard output to";Source_volts(I);"Vac"
110 PRINT "2. Set AC Standard frequency to";Source_freq(I);"Hz"
120 PRINT "3. Press Continue when ready"
130 PAUSE
140 CLEAR SCREEN
150 OUTPUT 70903;"CONF:VOLT:AC";Source_volts(I)
160 WAIT 1 !One second settling time
170 OUTPUT 70903;"READ?"
180 ENTER 70903;Read_meas(I)
190 NEXT I
200 FOR I=1 TO 5
210 PRINT "Voltage for";Source_volts(I);"Vac range @";Source_freq(I);
"Hz=";Read_meas(I);"Vac"
220 NEXT I
28 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 29

230 END
Test 4-4: Resistance Test (4-Wire Ohms)
This test verifies the 4-wire resistance accuracy of the 2kΩ, 100kΩ, and
1MΩ ranges.
NOTE
The DC Voltage performance test must be performed prior to the Resistance
Test to check the A/D accuracy on all ranges. If the DC Voltage test has not
been performed, resistance must be checked on all ranges at 0 and at 50%
of full scale.
Figure 4-4. Resistance Test Setup
Equipment Setup 1. Connect the equipment as shown in Figure 4-4
2. Set the HP E1411 multimeter as follows:
• Reset Multimeter ..................................................*RST
• Auto Zero ............ .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ON
• Power Line Cycles (PLC) .............................................1
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 29
Page 30

• Line Freq Reference (CAL:LFR) ....50 Hz or 60 Hz
NOTE
Test Procedure 1.
*RST sets Auto Zero to ON and Power Line Cycles to 1.
Set the Resistance Standard to 1 kΩ setting
2.
Set the HP E1411 range to 1861Ω (2048Ω with 10% overrange)
with CONF:FRES 1861
3. Measure the input resistance with READ? and verify the results
are within specified limits (at the range selected for 1 PLC). Record
the results on the Performance Test Record.
NOTE
For best measurement accuracy, you may want to measure the ACTUAL
Resistance Standard value. You can do this by recording the front panel
display of the resistance value, or measuring the resistance with an HP
3458A multimeter or eq ui va le nt.
For example, supp os e th e AC TUAL res is tan ce va lue for the 1 kΩ settin g is
1001.3Ω. Then, the Lower Limit for this value = 1001.03 Ω and th e Upp er
Limit = 1001.57Ω. These limits would replace the existing limits of
999.730Ω and 1000.270Ω shown in Table 4- 1. If th e mea su re d va lu e fa ll s
within the revised limits, the test passes.
4. Repeat steps 1 through 3 using the following Resistance Standard
settings:
E1411 Range 10%
overrange
119,156 Ω
1,048,576 Ω
5. Remove power and disconnect test equipment.
131,052 Ω
N/A
Resistance
Std Setting
100 kΩ
1 MΩ
30 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 31

Example: 4-Wire Ohms
Test
This example performs a 4-wire ohms resistance test for a power line
reference frequency of 60 Hz. Change line 80 to OUTPUT
70903;"CAL:LFR 50" for 50 Hz operation.
The program also calculates the Upper Limit and Lower Limit values for
ACTUAL Resistance Standard resistance value (lines 170-190). If the
actual Resistance Standard value is different than 1kΩ, 100k Ω, or 1MΩ,
replace the Lower Limit and Upper Limit values shown in Table 4-1,
Performance Test Record for the HP E1411 Multimeter, with the values
computed by the program.
1 !4-Wire Ohms Performance Verification
10 OPTION BASE 1
20 DIM Range(3),Source(3),Read_meas(3),Limit(3),Ohms(3)
30 DATA 1861, 119156, 1048576
40 READ Range(*)
50 DATA 1000, 100000, 1000000
60 READ Source(*)
70 OUTPUT 70903;"*RST" !Set autozero on and PLC 1
80 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:LFR 60" !Set 60 Hz line ref frequency
90 FOR I=1 TO 3
100 PRINT "1. Set Resistance Standard to";Source(I);"Ohms"
110 PRINT "2. Measure ACTUAL Resistance Standard value (in Ohms)"
120 PRINT "Enter ACTUAL Resistance Standard value (in
Ohms)",Ohms(I)
130 CLEAR SCREEN
140 OUTPUT 70903;"CONF;FRES";Range(I)!Set 4-wire ohms, range
150 OUTPUT 70903;"READ?"
160 ENTER 70903;Read_meas(I)
170 IF I=1 THEN Limit(I)=.00025*Ohms(I)+2.0E-2 !2 kOhm limits
180 IF I=2 THEN Limit(I)=.00025*Ohms(I)+1 !131 kOhm limits
190 IF I=3 THEN Limit(I)=.00025*Ohms(I)+10 !1 MOhm limits
200 NEXT I
210 PRINT "Measured Source Low Limit High Limit"
220 PRINT "Resistance Resistance (Ohms) (Ohms)"
230 PRINT
240 Format:IMAGE 7D.3D,6X,7D.3D,6X,7D.3D,6X,7D.3D
250 FOR I=1 TO 3
260 PRINT USING Format;Read_meas(I),Ohms(I),Ohms(I)-Limit(I),
Ohms(I)+Limit(I)
270 NEXT I
280 END
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 31
Page 32

Performance
Test Record
Table 4-1, Performance Test Record for the HP E1411 Multimeter, is a
form you can copy and use to record performance verification test results
for the multimeter. Page 3 of Table 4-1 shows multimeter accuracy,
measurement uncertainty and test accuracy ratio (TAR) values. See
Appendix A - Calculating Multimeter Accuracy for example calculations of
Table 4-1 entrie s.
NOTE
Multimeter
Accuracy
Measurement
Uncertainty
The accuracy, mea sure m en t unce rtainty, and TAR values sho wn in Table
4-1 are valid ON LY for the specific tes t co nditions, test equ ip m en t, and
assumptions described. If you use different test equipment and/or change
the test conditions, you will need to compute the specific values for your test
setup.
Accuracy is defined for DC Voltage, AC Voltage, and 4-Wire Resistance
measurements using the 90-day specifications in Appendix A -
Specifications in the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the
E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual. In Table 4-1, the "High Limit" and "Low
Limit" columns represent the multimeter accuracy for the specified test
conditions.
For the performance verification tests in this manual, measurement
uncertainties are calculated assuming a Datron 4708 source for inputs to the
multimeter. Measurement uncertainties in Table 4-1 are calculated for the
90-day accuracy specifications in the Datron 4708 User’s Handbook.
Test Accuracy
Ratio (TAR)
In Table 4-1, the "Test Accuracy Ratio (TAR)" is calculated from (high
limit - expected measurement)/measurement uncertainty. "N/A" means
measurement uncertainty and TAR do not apply to the measurement. If the
TAR value is <10:1, the TAR value is listed. If the TAR value is >10:1, the
entry is >10:1.
32 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 33

Test Facility:
Table 4-1. Performance Test Record for the HP E1411 Multimeter (Page 1 of 3)
Name
_________________________________________
Address
________________________________________
City/State
_______________________________________
Phone
_________________________________________
Model
________________________________________
Serial No.
______________________________________
Options
_______________________________________
Firmware Rev.
__________________________________
Special Notes:
Report No.
_____________________________________
Date
___________________________________________
Customer
______________________________________
Tested by
_____________________________________
Ambient temperature
__________________________
Relative humidi ty
____________ __ __ __ _____________%
Line frequency __ __ ______________ __ ___ Hz
(nominal)
o
C
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 33
Page 34

Table 4-1. Performance Test Record for the HP E1411 Multimeter (Page 2 of 3)
Model __________ __ __ __ _____________ Rep ort No . __ __ __ __ __ __________ Date ___ __ __ __ ___________
Test Equipment Used:
Description
1. DATRON 4708
2.
________________________________
3.
________________________________
4.
________________________________
5.
________________________________
6.
________________________________
7.
________________________________
8.
________________________________
9.
________________________________
Model No. Trace No. Cal Due Date
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
10.
________________________________
11.
________________________________
12.
________________________________
11.
________________________________
12.
________________________________
13.
________________________________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
34 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 35

Table 4-1. Performance Test Record for the HP E1411 Multimeter (Page 3 of 3)
Model ____________________________ Report No. ____________________________ Date_________________
90 day Specifications
Test
No.
DC Voltage (Zero Volts Input) (Values in V)
4-1 0.0
DC Voltage (DCV Input) (Values in VDC)
4-2 0.1
AC Voltage (20 Hz, 60 Hz, 10 kHz, 5 kHz) (Valu es in VA C)
4-3 0.07
Test
Input
300.0
300.00
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.9
7.0
58.0
0.07
0.07
0.07
DMM
Range
300.000
300.000
0.113
0.910
7.270
58.100
0.113
0.910
7.270
58.100
0.0875
0.0875
0.0875
0.0875
300.00
Low
Limit
-.000005
-.000015
-.000050
-.001000
-.005000
.099972
.899868
6.999250
57.990300
299.950000
.067480
.069327
.069327
.067578
296.125000
Measured
Reading
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
__________
High
Limit
+.000005
+.000015
+.000050
+.001000
+.005000
.100028
.900132
7.000750
58.009799
300.050000
.072523
.070673
.070673
.072423
303.875000
Meas
Uncert*
.0000012
.0000044
.0000210
.0002820
.0017750
.000020
.000016
.000016
.000016
.047000
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Test Acc
Ratio
(TAR)**
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
4-Wire Resistance (Val ue s in Ohms )
4-4 1000
100000
1000000
* Measurement Uncertainty of Datron 4708 source for 90 days since calibration and 23
** TAR = multimeter accuracy/measurement uncertainty, rounded to nearest integer for <10:1 and >10:1 otherwise.
2000
131000
1000000
999.730
99974.000
999740.000
__________
__________
__________
1000.270
100026.000
1000260.000
o
C ±1oC.
0.008
0.900
22.000
>10:1
>10:1
>10:1
Chapter 4 Verification Tests 35
Page 36

Notes
36 Verification Tests Cha pt er 4
Page 37

Chapter 5
Adjustments
Introduction This chapter contains procedures to adjust the HP E1411 multimeter for
peak performance. For best performance, the instrument should be adjusted
after repair. Al l ad ju st m en ts are p er fo rmed electrically , so manual
adjustment of the multimeter is not necessary.
WARNING
NOTE
Adjustment
Conditions /
Procedures
Do not perform any of the following adjustments unless you are
a qualified, service-trained person, and have read the
WARNINGS and CAUTIONS in
ALL adjustment procedures MUST be pe rfor med in the or der sh own in this
manual (DC Voltage, then AC Voltage, and then Resistance).
For valid adjustments, the HP E1411 multimeter and test equipment used
must have at least a 60 minute warm-up, and the line voltage must be
115/230 Vac ±10%. For best accuracy, the temperature of the area where
adjustments are made should be between 18
within ±1
equipment requirements.
The adjustmen t pr oc ed ur es ass um e the per so n pe rf or min g the adjustments
understands how to operate the mainframe, multimeter and specified test
equipment. Th e ad ju st ment procedures do not specify test equipment
settings, except in general terms. It is assumed a qualified, service-trained
person will select and connect the cables and jumpers required for the
adjustments.
o
C. See Table 1-1, Recommended Test Equipment, for test
Chapter 1 - General Information.
o
C and 28oC and stable to
Chapter 5 Adjustments 37
Page 38

DC Voltage
Adjustments
This procedure adjusts HP E1411 multimeter DC voltage measurement
accuracy.
Equipment Setup 1. Connect the equipment as shown in Figure 5-1.
WARNING
The DC Standard (Datron 4708, Option 10) can produce
dangerous voltages which are present on the terminals. Do not
touch the front (or rear) panel terminals unless you are sure no
dangerous voltage is present.
2. Set the HP E1411 as follows:
Figure 5-1. DC Voltage Adjustment Setup
• Reset Multimeter ......................................................*RST
• Auto Zero ............ .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ON
• Power Line Cycles (PLC) .................................................1
• Line Freq Reference (CAL:LFR ) ....... 50 Hz or 60 Hz
38 Adjustments Chapter 5
Page 39

NOTE
Adjustment
Procedure
*RST sets Auto Zero to ON and Power Line Cycles to 1.
1. Set the DC Standard output to 7.7 V
2. Set the HP E1411 range to 8 V, and adjust the multimeter
at 7.7 V using:
VOLT:DC:RANG 8
3.
FUNC:VOLT:DC
CAL:VAL 7.7
TRIG:DEL .05
CAL?
Verify that the returned calibration error code is 0 (no error).
If not 0, see Table 5-1 for a list of calibration errors and codes.
The calibration error can be returned to an external computer
using an ENTER type statement.
4. Repeat steps 1 th rough 3 using the fo llowi ng HP E1411
voltage ranges and DC Standard settings:
HP E1411 range DC Standard Output
8 V
0.125 V
0.125 V
1 V
1 V
64 V
64 V
300 V
300 V
-7.7 V
+0.121 V
- 0.121 V
+0.97 V
- 0.97 V
+62 V
-62 V
+300 V
-300 V
5. Remove power and disconnect test equipment.
Example: DC
Voltage
Adjustments
This example performs DC voltage adjustments for a power line reference
frequency of 60 Hz. Change line 80 to OUTPUT 7090 3;" CAL:LFR 50 " for
50 Hz operation.
If no calibration error occurs (Cal_code = 0 in line 210), the program
displays an "adjustment complete" message. If a calibration error occurs,
the program displays the calibration error and prompts you to repeat the
adjustment (see Table 5-1 for a list of calibration errors).
Chapter 5 Adjustments 39
Page 40

When connected to the HP E1411 multimeter, some DC Standards may
exhibit voltage variations at the start of a measurement. TRIG:DEL .05 (line
190) adds a 0.8 sec wait before calibration begins to allow settling time for
the DC Standard output. TRIG:DEL .05 is used since the input is sampled
16 times before the calibration is performed. Thus, total delay added = 0.05
seconds x 16 = 0.8 seconds.
1 ! DC Voltage Adjustments
10 OPTION BASE 1
20 DIM Range(10),Volts(10)
30 DATA 8.0, 8.0, 0.125, 0.125, 1.0, 1.0, 64.0, 64.0, 300.0, 300.0
40 READ Range(*)
50 DATA 7.7, -7.7, .121, -.121, .97, -.97, 62.0, -62.0, 300.0, -300.0
60 READ Volts(*)
70 OUTPUT 70903;"*RST" !Set autozero on and PLC 1
80 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:LFR 60" !Set 60 Hz line ref frequency
90 FOR I=1 TO 10
100 Re_try: !
110 CLEAR SCREEN
120 PRINT "Set DC Standard to";Volts(I);"VDC"
130 PRINT "Press Continue when ready"
140 PAUSE
150 CLEAR SCREEN
160 OUTPUT 70903;"FUNC:VOLT:DC" !Set DCV function
170 OUTPUT 70903;"VOLT:RANG ";Range(I) !Set E1411 range
180 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:VAL";Volts(I) !Set CAL:VAL value
190 OUTPUT 70903;"TRIG:DEL .05" !Wait for settling
200 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL?" !Perform calibration
210 ENTER 70903 USING "K";Cal_code !Return cal error code
220 IF Cal_code <>0 THEN
230 PRINT "Calibration Error";Cal_code;"for ";Volts(I);"VDC input."
240 PRINT "Check source value/connections, then"
250 PRINT "press Continue to retry this adjustment"
260 PAUSE
270 GOTO Re_try
280 ELSE
290 PRINT "Adjustment complete for";Volts(I);"VDC input"
300 END IF
310 PRINT "Press Continue for the next adjustment"
320 PAUSE
330 CLEAR SCREEN
340 NEXT I
350 END
40 Adjustments Chapter 5
Page 41

AC Voltage
Adjustments
This procedure adjusts the HP E1411 AC voltage measurement accuracy.
NOTE
The DC Voltage adjustment MUST be performed before the AC Voltage
adjustment.
Equipment Setup 1. Connect the equipment as shown in Figure 5-2
Figure 5-2. AC Voltage Adjustment Setup
2. Set the HP E1411 as follows:
• Reset Multimeter ....................................................*RST
• Auto Zero .................................................................... ON
• Power Line Cycles (PLC) .............................................. 1
• Line Freq Reference (CAL:LFR ) ...... 50 Hz or 60 Hz
Chapter 5 Adjustments 41
Page 42

NOTE
Adjustment
Procedure
*RST sets Auto Zero to ON and Power Line Cycles to 1.
1. Set the AC Standard output to 5.6 Vac at 1 kHz
2. Set the HP E1411 range to 5.6 V, and adjust the multimeter
at 5.6 V using:
FUNC:VOLT:AC
VOLT:AC:RANG 5.6
CAL:VAL 5.6
TRIG:DEL .05
CAL?
Verify that the returned calibration error code is 0 (no error).
3.
If not 0, see Table 5-1 for a list of calibration errors and codes.
4. Remove power and disconnect test equipment
Example: AC Voltage
Adjustments
This example performs an AC voltage adjustment for a power line reference
frequency of 60 Hz. Change line 20 to OUTPUT 7090 3;" CAL:LFR 50 " for
50 Hz operation.
If no calibration error occurs (Cal_code = 0 in line 130), the program
displays an "adjustment complete" message. If a calibration error occurs,
the program displays the calibration error (see Table 5-1 for a list of
calibration errors).
When connected to the HP E1411 multimeter, some AC Standards may
exhibit voltage variations at the start of a measurement. TRIG:DEL .05 (line
110) adds a 0.8 sec wait before calibration begins to allow settling time for
the AC Standard output. TRIG:DEL .05 is used since the input is sampled
16 times before the calibration is performed. Thus, total delay added = 0.05
seconds x 16 = 0.8 seconds.
42 Adjustments Chapter 5
Page 43

1 ! AC Voltage Adjustments
10 OUTPUT 70903;"*RST" !Set autozero on and PLC 1
20 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:LFR 60" !Set 60 Hz line ref frequency
30 Re_try: !
40 PRINT "Set AC Standard to 5.6 Vac at 1.0 kHz"
50 PRINT "Press Continue when ready"
60 PAUSE
70 CLEAR SCREEN
80 OUTPUT 70903;"FUNC:VOLT:AC" !Set ACV function
90 OUTPUT 70903;"VOLT:RANG 5.6" !Set 5.6 Vac range
100 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:VAL 5.6" !Set 5.6 Vac cal value
110 OUTPUT 70903;"TRIG:DEL .05" !Wait for settling
120 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL?" !Perform calibration
130 ENTER 70903 USING "K";Cal_code
140 IF Cal_code <> 0 THEN
150 PRINT "Calibration Error";Cal_code;"on 5.6 Vac range"
160 PRINT "Check source value/connections, then"
170 PRINT "press Continue to retry this adjustment"
180 PAUSE
190 CLEAR SCREEN
200 GOTO Re_try
210 ELSE
220 PRINT "AC Voltage adjustment complete"
230 END IF
240 END
Chapter 5 Adjustments 43
Page 44

Resistance
Adjustments
This procedure adjusts the HP E1411 multimeter 4-wire resistance
measurement accuracy.
NOTE
The DC Voltage adjustment and the AC Voltage adjustment MUST be
performed before the Resistance adjustment.
Equipment Setup 1. Connect the equipment as shown in Figure 5-3
Figure 5-3. Resistance Adjustments Setup
2. Set the HP E1411 as follows:
• Reset Multimeter .................................................... *RST
• Auto Zero ................................................................... ON
• Power Line Cycles (PLC) .............................................. 1
• Line Freq Reference (CAL:LFR) .......... 50 Hz or 60 Hz
44 Adjustments Chapter 5
Page 45

NOTE
Adjustment
Procedure
*RST sets Auto Zero to ON and Power Line Cycles to 1.
1.
Set the Resistance Standard to 1 kΩ.
2.
Set the HP E1411 range to 2 kΩ, and adjust the multimeter
at 1 kΩ using:
FUNC:FRES
FRES:RANG 2000
CAL:VAL 1000
CAL?
NOTE
For best adjustment accuracy, you may want to measure the ACTUAL
resistance value of the Resistance Standard and use the value in the
CAL:VAL command. You can read the actual resistanc e va lue from th e
Datron front panel or you can measure the value with an HP 3458A
multimeter or equivalent.
3. Verify that the returned calibration error code is 0 (no error).
If not 0, see Table 5-1 for a list of calibration errors and codes. The
calibration error can be returned to the external computer using
an ENTER type statement.
4. Repeat steps 1 th rough 3 using the fo llowi ng HP E1411
(and FRES:RANG) ranges, and Resistance Standard
(and CAL:VAL) values:
HP E1411 Range Resistance Standard
16000 Ω
1000000 Ω
* Or, use actual measured source resistance value
10000 Ω*
1000000 Ω*
5. Remove power and disconnect test equipment.
Chapter 5 Adjustments 45
Page 46

Example: 4-Wire
Resistance
Adjustments
This example performs a 4-wire ohms resistance adjustment for a power
line reference frequency of 60 Hz. Change line 80 to OUTPUT
70903;"CAL:LFR 50" fo r 50 Hz ope rati on . If a cali br atio n er ro r oc cu rs , th e
program displays the calibration error and prompts you to repeat the
adjustment (see Table 5-1 for a list of calibration errors).
1 ! 4-Wire Resistance Adjustments
10 OPTION BASE 1
20 DIM Range(3),Source(3)
30 DATA 2000, 16000, 1048576
40 READ Range(*)
50 DATA 1000, 10000, 1000000
60 READ Source(*)
70 OUTPUT 70903;"*RST" !Set autozero on and PLC 1
80 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:LFR 60" !Set 60 Hz line ref frequency
90 FOR I=1 TO 3
100 Re_try: !
110 PRINT "1. Set Resistance Standard to";Source(I);"Ohms"
120 PRINT "2. Measure ACTUAL Resistance Standard value (in Ohms)"
130 PRINT "Enter ACTUAL Resistance Standard value (in
Ohms)",Ohms_actual
140 CLEAR SCREEN
150 OUTPUT 70903;"FUNC:FRES" !Set 4-wire ohms
160 OUTPUT 70903;"FRES:RANG ";Range(I)!Set resistance range
170 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL:VAL";Ohms_actual(I)!Set cal value
180 OUTPUT 70903;"CAL?" !Perform calibration
190 ENTER 70903;Cal_code
200 IF Cal_code <> 0 THEN
210 PRINT "Calibration Error";Cal_code;"with";Source(I);"Ohms input."
220 PRINT "Check source value/connections, then"
230 PRINT "Press Continue to repeat this adjustment"
240 PAUSE
250 CLEAR SCREEN
260 GOTO Re_try
270 ELSE
280 PRINT "Adjustment complete with";Source(I);"Ohms source"
290 PRINT "Press Continue for the next adjustment"
300 PAUSE
310 CLEAR SCREEN
320 END IF
330 NEXT I
340 PRINT "Resistance adjustments completed"
350 END
46 Adjustments Chapter 5
Page 47

Calibration
Errors
Error Title Description Code*
0 No Error N o erro r has occurre d si nc e la st tim e th e erro r code was read.
Table 5-1 summarizes calibration error numbers, titles and descriptions for
the HP E1411 multimeter. Note that an error is returned if the adjustment
(calibration) standard used is outside the calibration range of the multimeter
(between ±[0.5 full scale and full scale]).
Table 5-1. HP E1411 Multimeter Calibration Errors
4 Reading
Overrun
6Calibration
Error
7 Checksum
Error
8 Invalid
CAL
Request
9Bad CAL
Target
11 No
Inguard
Response
13 Lineari ty
CAL Error
14 Pacer
Overrun
Error
The FIFO memory was still full at the time the new reading
was ready, or a new command was received while in the
middle of outputting a reading. TRIGGER ARM is disabled
and the multimet er waits for a new command.
An error occurred when computing a calibration constant,
probably due to an improper input or a defective Unit Under
Test (UUT). Calibr at io n cy cl e aborted.
The non-volatile RA M co nt ai ns a che cksu m erro r. Th e da ta is
assumed to be corrupt ed .
Calibration requested for an invalid combination of multimeter
range and function.
The target value for the calibration was outside the range of
±(0.5 full scale to full scale).
No response from inguard (expected data and got nothing).
Timed out instea d.
An error has occurred during a line ari ty cal ib ration sequence.
Probably a hardware failure of the A/D inguard section.
The pacer is in use and the pacer rate is faster than the
maximum A/D conv ers io n rat e ba se d on in t eg r at ion time,
autorange setting, autozero setting, and interrupts enabled.
U
U/H
H
U
U
H
H
U
15 Input
Overload
* U = improper operation, H = hardware failure
A potentially damaging overload has been applied to the
multimeter terminals and the multimeter has disconnected
from the input. A new SET RANGE command is necessary to
restore normal operation. A damaging overload is defined as:
1. Applying >±40 volts Hl to LO or Hl to COMMON while in
manual range with RAN GE ≤ 8 vo lts.
2. Applying >±40 volts between LO and COMMON under any
circumstances.
U
Chapter 5 Adjustments 47
Page 48

Notes
48 Adjustments Chapter 5
Page 49

Chapter 6
Replaceable Parts
Introduction This chapter co n ta in s in formation to or de r re pl ac ea bl e pa rt s fo r th e H P
E1411A and E1411B multimeters.
Exchange
Assemblies
Ordering
Information
Replaceable
Parts List
Tables 6-1 and 6-2 list assemblies that may be replaced on an exchange
basis (EXCHANGE ASSEMBLIES). Exchange, factory-repaired, and
tested assemb lie s ar e av ai la ble only on a trade-in bas is . D ef ec tive
assemblies mu st be re turned for cred it. Ass em b li es req ui re d fo r spare parts
stock must be ordered by the new assembly part number. Contact your
nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales and Support Office for details.
To order a part listed in Table 6-1 or 6-2, specify the Hewlett-Packard part
number and the quantity required. Send the order to your nearest
Hewlett-Packard Sales and Support Office.
Table 6-1, HP E1411A Replaceable Parts, lists replaceabl e pa rt s fo r th e H P
E11411A multimeter. See Figure 6-1 (page 6-3) for locations of parts listed
in Table 6-1. Table 6-2, HP E1411B Replaceable Parts, lists replaceable
parts for the HP E11411B multimeter. See Figure 6-2 (page 6-5) for
locations of parts listed in Table 6-2.
Chapter 6 Replaceable Parts 49
Page 50

Table 6-1. HP E1411A Replaceable Parts
Reference*
Designator
A1
A1F1
A1F2
A1J2
A1J102
A1J103
A1JM1
A1JM3
A1K104
A1K105
A1K106
A1P1
A1P2
A1P3
A1SP1
A1XU23
A1XU104
A1XU124
CBL1
CBL2
MP1
MP2
MP3
MP4
MP5
MP6
MP7
MP8
PNL1
SHD1
SHD2
HP Part
Number
E1411-66201
E1411-69201
E1411-66501
2110-0712
2110-0712
1250-1846
1251-3712
1252-3416
1251-4927
1251-4927
0490-1556
0490-1556
0490-1555
1252-1596
1251-7892
1258-0247
3101-3066
1200-0817
1200-0817
1200-0853
E1326-61601
E1326-61605
E1400-84105
E1400-84106
1510-0091
1510-0091
1510-0091
1510-0091
8160-0686
1400-0249
E1411-00201
E1411-00602
E1411-00601
Qty Description Mfr**
Code
EXCHANGE ASSEMBLIES
E1411A Multimeter Module (New)
1
E1411A Multimeter Module (Exchange)
1
MULTIMETER PCA [a]
1
Fuse - Sub Miniature - 4A
2
Fuse - Sub Miniature - 4A
Connector - Right Angle BNC
1
Connector - Post 2 x 6
1
Connector - 4 Pin Right Angle
1
Connector - Header 16 Pin
2
Connector - Header 16 Pin
Relay - Reed
2
Relay - Reed
Relay - Reed
1
Connector - Right Angle - 96 Pin
1
Connector - Right Angle - 64 Pin
1
4-Position Jumper
1
Switch - Rocker 8 Position 5 V 0.1 A
1
Socket - 40 Pin Integrated Circuit
2
Socket - 40 Pin Integrated Circuit
Socket - 16 Pin Integrated Circuit
1
CABLE ASSEMBLIES
Cable Assembly - 6 Conductor
1
Cable Assembly - 4 Conductor
1
MECHANICAL PARTS
Handle Kit-Bottom
2
Handle Kit-Top
Binding Post - Red
4
Binding Post - Red
Binding Post - Red
Binding Post - Red
Clip-RFI Strip
1
Cable Tie - 0.062-0.625 IN DIA
1
Panel - Faceplate
1
Shield - Bottom
1
Shield - Top
1
28480
28480
28480
75915
75915
24931
18873
27264
18873
18873
71707
71707
71707
06776
18873
18873
81073
00779
00779
00779
28480
28480
28480
28480
28480
28480
28480
28480
30817
59730
28480
28480
28480
Mfr Part Number
E1411-66201
E1411-69201
E1411-66501
R251004T1
R251004T1
28JR342-1
68668-004
705-53-0108
67997-616
67997-616
3500-0050
3500-0050
3500-0051
DIN96CPCSRITR
75882-364
69146-204
76YY22968S
2-640379-1
2-640379-1
2-640358-1
E1326-61601
E1326-61605
E1400-84105
E1400-84106
1510-0091
1510-0091
1510-0091
1510-0091
00786-185
TY-23M-8
E1411-00201
E1411-00602
E1411-00601
COMMON HARDWARE
Screw Pan-Head M2.5 X 12 Torx T8
SCW1, SCW2
SCW3-SCW8,
SCW15
SCW 9-SCW11
SCW12-SCW13
HDW1-HDW4
HDW5-HDW8
* See Table 6-3 for Reference Designator definitions
** See Table 6-4 for Code List of Manufacturers
[a] Repair limited to replacement of parts listed - see Introduction for ordering information
0515-0368
0515-1135
0515-1375
0515-1968
2950-0001
3050-0593
2
Screw Pan-Head M3 X 25 Torx T8
7
Screw Flat-Head M2.5 X 6 Torx T8
3
Screw Pan-Head M2.5 X 11 Pozidriv
2
Nut-Hex-DBL Chamfer 3/8 - 32 THD
4
Washer-Spring NO. 3/8
4
00000
00000
00000
00000
00000
00000
Order by Description
Order by Description
Order by Description
Order by Description
Order by Description
Order by Description
50 Replaceable Parts Chapter 6
Page 51

Figure 6-1. HP E1411A Replaceable Parts
Chapter 6 Replaceable Parts 51
Page 52

Table 6-2. HP E1411B Replaceable Parts
Reference*
Designator
A1
A1F1
A1F2
A1J2
A1J102
A1J103
A1J301
A1JM1
A1JM3
A1K104
A1K105
A1K106
A1P1
A1P2
A1P3
A1SP1
A1XU23
A1XU104
A1XU124
CBL1
CBL2
HP Part
Number
E1411-66511***
E1411-69511***11
E1411-66511
2110-0712
2110-0712
1250-1846
1251-3712
1252-3416
1250-1846
1251-4927
1251-4927
0490-1556
0490-1556
0490-1555
1252-1596
1251-7892
1258-0247
3101-3066
1200-0817
1200-0817
1200-0853
E1326-61601
E1326-61605
Qty Description Mfr**
Code
EXCHANGE ASSEMBLIES
E1411B Multimeter Module (New)
E1411B Multimeter Module (Exchange)
1
MULTIMETER PCA [a]
2
Fuse - Sub Miniature - 4A
Fuse - Sub Miniature - 4A
Connector - Right Angle BNC
1
Connector - Post 2 x 6
1
Connector - 4 Pin Right Angle
1
Connector - Right Angle BNC
Connector - Header 16 Pin
2
Connector - Header 16 Pin
Relay - Reed
2
Relay - Reed
Relay - Reed
1
Connector - Right Angle - 96 Pin
1
Connector - Right Angle - 64 Pin
1
4-Position Jumper
1
Switch - Rocker 8 Position 5 V 0.1 A
1
Socket - 40 Pin Integrated Circuit
2
Socket - 40 Pin Integrated Circuit
Socket - 16 Pin Integrated Circuit
1
CABLE ASSEMBLIES
Cable Assembly - 6 Conductor
1
Cable Assembly - 4 Conductor
1
28480
28480
28480
75915
75915
24931
18873
27264
24931
18873
18873
71707
71707
71707
06776
18873
18873
81073
00779
00779
00779
28480
28480
Mfr Part Number
E1411-66511
E1411-69511
E1411-66511
R251004T1
R251004T1
28JR342-1
68668-004
705-53-0108
28JR342-1
67997-616
67997-616
3500-0050
3500-0050
3500-0051
DIN96CPCSRITR
75882-364
69146-204
76YY22968S
2-640379-1
2-640379-1
2-640358-1
E1326-61601
E1326-61605
MECHANICAL PARTS
Handle Bottom Metal Injection
MP1
MP2
MP3
MP4
MP5
MP6
MP7
MP8
PNL1
SHD1
SHD2
SCW1-SCW2
SCW3-SCW8,
SCW15
SCW11
HDW1-HDW4
HDW5-HDW8
* See Table 6-3 for Reference Designator definitions
** See Table 6-4 for Code List of Manufacturers
*** PC Board Replacement only
[a] Repair limited to replacement of parts listed - see Introduction for ordering information
† These parts are not compatible with older versions of the E1411B that have plastic handles. To replace one of these parts on an
older E1411B, you must order all four of the parts marked with a †
E1400-45102†
E1400-45101†
1510-0091
1510-0091
1510-0091
1510-0091
8160-0686
1400-0249
E1411-00202†
E1411-00612
E1411-00611
E1400-00610†
0515-1135
0515-1375
2950-0001
3050-0593
1
Handle Top Metal Injection
1
Binding Post - Red
4
Binding Post - Red
Binding Post - Red
Binding Post - Red
Clip-RFI Strip
1
Cable Tie - 0.062-0.625 IN DIA
1
Panel - Faceplate
1
Shield - Bottom
1
Shield - Top
1
COMMON HARDWARE
Shoulder Screw Assembly
2
Screw Pan-Head M3 X 25 Torx T8
7
Screw Flat-Head M2.5 X 6 Torx T8
1
Nut-Hex-DBL Chamfer 3/8 - 32 THD
4
Washer-Spring NO. 3/8
4
and
a new top shield.
28480
28480
28480
28480
28480
28480
30817
59730
28480
28480
28480
28480
00000
00000
00000
00000
E1400-45102
E1400-45101
1510-0091
1510-0091
1510-0091
1510-0091
00786-185
TY-23M-8
E1411-00202
E1411-00602
E1411-00601
E1400-00610
Order by Description
Order by Description
Order by Description
Order by Description
52 Replaceable Parts Chapter 6
Page 53

Figure 6-2. HP E1411B Replaceable Parts
Chapter 6 Replaceable Parts 53
Page 54

Table 6-3. HP E1411 Reference Designators
HP E1411 Reference Designators
A .......................................... assembly
CBL ............................................ cable
F ................................................... fuse
J ................ electrical connector (jack)
JM ........ electrical connector (header)
K ............ .. .. .. .............. .. .............. .. .re la y
MP .................. misc. mechanical part
P ............... electrical connector (plug)
PNL ............................................ panel
SHD ............ .. .. .. .............. .. ......... shield
SP ............ .. .. .. .............. .. ........... switc h
XU ............ .. . so ck et , in te gra t e d circu it
Table 6-4. HP E1411 Code List of Manufacturers
Mfr Code Manufacturer Name Address
00000
00779
06776
18873
24931
27264
28480
30817
59730
71707
75915
81073
Any satisfac tory supplier
AMP INC
Robinson Nugent Inc
Dupont E I DE Nemours & Co
Specialty Connector Co
Molex Inc
Hewlett Packard Company
Instrument Specialties Co Inc
Thomas & Betts Corp
Coto Wabash
Littelfuse Inc
Grayhill Inc
Harrisburg, PA 17111
New Albany, IN 47150
Wilmington, DE 19801
Franklin, IN 46131
Lisle, IL 60532
Palo Alto, CA 94304
Del Water Gap, PA 07424
Raritan, NJ 08869
Providence, RI 02907
Des Plaines, IL 60016
La Grange, IL 6052 5
54 Replaceable Parts Chapter 6
Page 55

Chapter 7
Manual Changes
Introduction This chapter co n ta in s in formation to ad ap t this manual to in st ru m en ts for
which the content does not directly apply. Since this manual applies directly
to instruments with serial numbers listed on the title page, change
information is not required. See Multimeter Serial Number s in Chapter 1 -
General Information for HP E1411 multimeter serial number information.
Chapter 7 Manual Changes 55
Page 56

56 Manual Changes Chapter 7
Page 57

Chapter 8
Service
Introduction This chapter contains information to service the HP E1411 multimeter
including troubleshooting guidelines and repair/maintenance guidelines.
WARNING
Equipment
Required
Do not perform any of the service procedures shown unless
you are a qualified, service-trained person, and have read the
WARNINGS and CAUTIONS in
Equipment required for multimeter troubleshooting and repair is listed in
Table 1-1, Recommended Test Equipment. Any equipment that satisfies the
Requirements in the table may be substituted. To avoid damage to the screw
head slots, use Pozi dr iv or Tor x dr iv er s as spe ci fied in the instructions.
Pozidriv and Torx drivers used are listed in Table 8-1.
Table 8-1. Pozidriv/Torx Drivers
Description HP Part Number
No. 1 Pozidr iv
No. 2 Pozidr iv
Size T-8 Torx
Size T-10 Torx
Size T-15 Torx
8710-0899
8710-0900
8710-1673
8710-1284
8710-1816
Chapter 1 - General Information
.
Service Aids There are no test po in ts o r man ua l ad justment locati on s fo r th e H P E1411
multimeter. Service aids on printed circuit boards include pin numbers,
some reference designations, and assembly part numbers. See Chapter 6 -
Replaceable Parts for descriptions and location of HP E1411 replaceable
parts.
Service notes, manual updates, and service literature for the HP E1411
multimete r ma y be av ai la bl e th rough Hewlett- Pa c ka rd . F or inf or m at io n,
contact your nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales and Support Office.
Chapter 8 Service 57
Page 58

Troubleshooting
Techniques
There are two main steps to troubleshoot an HP E1411 multimeter
problem: (1) identify the problem, and (2) test assemblies to isolate the
cause to a user-replaceable component.
Identifying the
Problem
Error Description Typical Causes
Multimeter problems can be divided into four general categories:
• Self-test errors
• Operator errors
• Catastrophic failures
• Performance out of specification
Self-Test Errors
An error number (1, 2, 3, or 4) is returned when the multimeter self-test
fails. If a self-test error occurs, recycle power and repeat the self-test. If the
error repeats, see "Testing Assemblies" to troubleshoot the multimeter.
Table 8-2 shows some typical causes of self-test errors.
Table 8-2. Self-Test Errors
1
2
3
Multimeter does not respond to
self-test
Invalid communication between A1
and A2 processors
Data line betwee n mu ltimeter and
mainframe failed
. Bad connections/settings
. Incorrect operation
. Hardware failure (exchange)
. Bad A1/A2 communication
. Hardware failure (exchange)
. Bad connections/settings
. Incorrect operation
. Hardware failure (exchange)
4
Invalid commun ic ation between
multimeter and mainframe
. Bad connections/settings
. Incorrect operation
. Hardware failure (exchange)
Operator Errors
Apparent failures may result from operator errors. See App endix B - Error
Messages in the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the
E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual for information on operator errors.
Catastrophic Failure
If a catastrophic failure occurs, see "Testing Assemblies" to troubleshoot the
multimeter.
58 Service Chapter 8
Page 59

Performance Out of Specification
If the multimeter performance is out of specification limits, use the
adjustment procedures in Chapter 5 - Adjustments to correct the problem. If
the condition repeats, see "Testing Assemblies" to troubleshoot the
multimeter.
Testing Assemblies You can use the tests and checks in Table 8-3 to isolate the problem to a
user-replaceable part on the multimeter frame or PCA. See Figure 6-1 (HP
E1411A) or Figure 6-2 (HP E1411B) in Chapter 6 - Replaceable Parts for
locations of us er -r ep la ce ab le p ar ts .
NOTE
If the problem cannot be traced to a user-replaceable part listed in Table
6-1 or Table 6-2, return the multimeter to Hewlett-Packard for exchange.
See Chapter 6 - Replaceable Parts for procedures.
Table 8-3. HP E1411 Tests/Checks
Test/Check Reference Desig na tor Check:
Heat Damage - - - - - - - - - - Discolored PC boards
Damaged insulation
Evidence of arcing
Switch/Jumper
Settings
Frame CBL1, CBL2
A1 Printed
Circuit
Assembly
JM1, JM3, P3
SP1
MP3, MP4, MP5 , MP 6
F1, F2
J2, J102, J103, J3 01
K104, K105, K106
P1,P2
XU23, XU104, XU124
IRQ Level sett in g
LADDR setting
Cable contact damage
Panel bindin g posts
Fuse continuity
Mating connector contacts
Relay opening/closure
Connector contacts
IC contact/connections
Checking Heat Damage
Inspect the multimeter for signs of abnormal internally generated heat such
as discolored printed circuit boards or components, damaged insulation, or
evidence of arcing. If there is damage, do not operate
the multimeter until you correct the problem.
Chapter 8 Service 59
Page 60

Checking Switches/Jumpers
Verify the logical address setting is set correctly (factory set at 24). Verify
the interrupt priority jumpers are set correctly (factory set at level 1). See
the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the E1326B/E1411B User’s
Manual for information.
Testing Multimeter Frame
To test the multimeter frame, see Table 8-3 for guidelines to check binding
posts MP3, MP4, MP5, and MP6, and cables CBL1 and CBL2. If you need
to remove and/or replace the binding posts, see "Removing Binding Posts"
in this chapter.
Testing Printed Circuit Assembly
To test the PCA, remove mainframe power and remove the multimeter from
the mainframe. Next, remove the Top Shield (see "Removing Top Shield"
for instructions). Then, see Table 8-3 for guidelines to isolate the problem to
a user-replaceable part.
Repair
This section gives guidelines to repair the HP E1411 multimeter, including:
Guidelines
• ESD precautions
• Removing top shield
• Removing front panel/bottom shield
• Removing binding posts
• Soldering printed circuit boards
• Post-repair safety checks
ESD Precautions Electrostatic discha rg e (ESD) may da m ag e M OS, CM OS and oth er
static-sensitive devices in the HP E1411 multimeter. This damage can range
from slight parameter degradation to catastrophic failure. When handling
multimeter assemblies, follow these guidelines to avoid damaging
multimeter components:
• Always use a static-free work station with a pad of conductive
rubber or similar material when handling multimeter components.
• After you remove an assembly from the multimeter, place the
assembly on a conductive surface to guard against ESD damage. Do
not stack assemblies.
60 Service Chapter 8
Page 61

• Do not use pliers to remove a MOS or CMOS device from a
high-grip socket. Instead, use a small screwdriver to pry the device
up from one end. Slowly lift the device up, one pair of pins at a time.
• After you remove a MOS or CMOS device from an assembly, place
the device onto a pad of conductive foam or other suitable holding
material.
• If a device requires soldering, be sure the assembly is placed on a
pad of conductive material. Also, be sure you, the pad, and the
soldering iron tip are grounded to the assembly. Apply as little heat
as possible when soldering.
Removing Top
Shield
Use the following steps to remove the top shield from the printed circuit
assembly (PCA). See Figure 8-1 for component locations.
1. Remove seven Torx T8 screws
2. Lift top shield from the back until front slots can be
disengaged from tabs.
3. Remove the top shield .
4. Reverse steps 1 through 3 to replace top shield.
Figure 8-1. Removing Top Shield
Chapter 8 Service 61
Page 62

NOTE
When reinstalling the top shield, verify that the slots are aligned with the
tabs, then se t th e top shield into pl ac e.
Removing Front
Panel
Use the follow i ng ste p s to re m ov e the front panel an d bo tt om sh ie ld from
the printed circuit assembly (PCA). See Figure 8-2 for component locations.
1. Remove Torx T8 screw from front panel
2. Remove two Torx T8 screws from PCA
3. Remove cable assembly fr om cl ip
4. Slide PCA off bottom shield
5. Reverse steps 1 through 4 to rep la ce fro nt pan el and
bottom shield
Figure 8-2. Removing Front Panel
62 Service Chapter 8
Page 63

Removing Binding
Posts
Use the following steps to remove the HP E1411 front panel binding posts
(MP3, MP4, MP5, and MP6) (see Figure 8-3).
1. Unsolder wire
2. Remove the 3/8-32 nut and spring washer
3. Remove the binding post
4. Reverse the order to reinstall the binding posts
Figure 8-3. Removing Binding Posts
Soldering Printed
Circuit Boards
CAUTION
The etched circuit boards in the multimeter have plated-through holes that
allow a solder path to both sides of the insulating material. Soldering can be
done from either side of the board with equally good results. When
soldering to any circuit board, keep in mind the following guidelines:
Do not use a sharp metal object such as an awl or twist drill, since
sharp objects may damage the plated-through conductor.
Chapter 8 Service 63
Page 64

• Avoid unnecessary component unsoldering and soldering. Excessive
replacement can result in damage to the circuit board and/or
adjacent components.
• Do not use a high power solder in g ir on on etched circuit board s as
excessive heat may lift a conductor or damage the board.
• Use a suction device or wooden toothpick to remove solder from
component mounting holes. When using a suction device, be sure
the equipment is properly grounded to prevent electrostatic
discharge from damaging CMOS devices.
Post-Repair Safety
Checks
After making repairs to the HP E1411 multimeter, inspect the multimeter
for any signs of abnormal internally generated heat, such as discolored
printed circuit boards or components, damaged insulation, or evidence of
arcing. Determine and correct the cause of the condition. Then run the
self-test (*TST? command) to verify that the multimeter is functional.
64 Service Chapter 8
Page 65

Appendix A
Calculating Multimeter Accuracy
Introduction This appendix shows how multimeter accuracy, measurement uncertainty,
and test accuracy ratio (TAR) values are defined and calculated for the
performance verification tests for the HP E1411 multimeter.
See Table 4-1, "Performance Tes t Recor d fo r th e H P E141 1 M ul tim eter " for
90-day spec if ic atio n va lues of multimeter acc ur ac y, me as ur em e nt
uncertainty, and test accuracy ratios (TARs).
NOTE
Multimeter Accuracy
Definition
Measurement
Uncertainty Definition
NOTE
Multimeter accuracy, measurement uncertainty, and test accuracy ratios in
Table 4-1 are valid ONLY for the specified test conditions and assumptions
described in this manual. For the test conditions describ ed, all TARs ex ceed
the 4:1 requirement of MIL-STD-45662A.
Multimeter accuracy is the expected accuracy of the measurement due
ONLY to the multimeter. The "Low Limit" entry in Table 4-1 is the lower
(-) value of multimeter accuracy, while the "High Limit" entry is the upper
(+) value of multimeter accuracy.
Measurement Uncertainty is the expec te d ac cu ra cy o f th e so ur ce use d to
input signals to the multimeter. Since the Datron 4708 Autocal
Multifunction Standard is the source used for measurements in this manual,
the measurement uncertainty of the source is that of the Datron 4708.
This value is shown in the "Measurement Uncertainty" column of Table
4-1. See the Datron 4708 User’s Handbook for additional information on
calculating measurement uncertainty for the Datron 4708 source.
Measurement Uncertainty does not apply to the DC Voltage (Zero Volts
Input) test, since no input is applied.
Appendix A Calculating Multimeter Accuracy 65
Page 66

Test Accuracy Ratio
(TAR) Definition
Test Accuracy Ratio (TAR) is the ratio of multimeter accuracy to
measurement uncertainty. For the HP E1411 multimeter performance tests,
test accuracy ratio = (High Limit value - Test Input value)/Measurement
Uncertainty va lu e. Th is valu e is sh own in th e " T es t Acc ur ac y R at io (TAR )"
column of Table 4-1.
NOTE
Multimeter
Accuracy
Calculations
DC Voltage
Accuracy Equations
Test accuracy ratio does not apply to the DC Voltage (Zero Volts Input)
test, since no measurement uncertainty value applies.
For the HP E1411 multimeter performance verification tests, multimeter
accuracy is defined for DC Voltage, AC Voltage, and 4-Wire Resistance
measurements using the 90-day specifications in Appendix A -
Specifications of the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s Manual or the
E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual. The assumed test conditions are:
• 90 days since calibration
• Temperature within ± 5
• Module calibration temperature 18
• One hour warmup
• 4-wire ohms resistance measurements
• Aperture = 16.7 msec (60 Hz) or 20 msec (50 Hz)
• Autozero ON
o
C of calibration temperature
o
C to 28oC
From Appendix A - Specifications of the HP E1326A/E1411A User’s
Manual or the E1326B/E1411B User’s Manual, DC voltage 90-day
accuracy = ±(% of reading + volts). The accuracy equations for the ranges
and apertures used in the performance verification tests are:
Range
125 mV
1 V
8 V
64 V
300 V
Accuracy [±(% of reading + Volts)]
0.023 + 5.0 µV
0.013 + 15.0 µV
0.010 + 50.0 µV
0.015 + 1.0 mV
0.015 + 5.0 mV
Example: Calculate DC Voltage Accuracy
For a 7.0 DCV input to the multimeter, using the 8 V range and 16.7/20
msec aperture, multimeter accuracy (90-days) = ±(.010% reading + 50.0
µV) = ±(.0001 x 7.0 + 50 x 10
-6
) = ±0.00075 Volts. Thus, for a 7.0 DCV
input the High Limit in Table 4-1 = 7.00075 Volts and the Low Limit =
6.99925 Volts.
66 Calculating Multimeter Accuracy Appendix A
Page 67

AC Voltage
Accuracy Equations
From Appendix A- Sp ec if ic ations of the HP E1326A /E1411A or E1326B
/E1411B User’s Manual, AC voltage 90-day accuracy = ±(% of reading +
volts). The accuracy equations for the ranges, frequencies and apertures
used in the performance verification tests are:
4-Wire Ohms
Accuracy Equations
Range Frequency
87.5 mV
87.5 mV
87.5 mV
87.5 mV
300 V
20 Hz
60 Hz
5 kHz
10 kHz
5 kHz
Accuracy [±(% of reading + Volts)]
2.175 + 1 mV
0.675 + 200 µV
0.675 + 200 µV
3.175 + 200 µV
1.125 + 500 mV
Example: Calculate AC Voltage Accuracy
For a 0.07 ACV input to the multimeter, using the 87.5 mV range, 60 Hz
frequency, and 16.7/20 msec aperture, multimeter accuracy (90-days) =
±(0.675% re ad ing + 200 µV) = ±(.00675 x 0.07 + 200 x 10
-6
) = ±0.000673
Volts. Thus, for a 0.07 ACV input the High Limit in Table 4-1 = 0.070673
Volts and the Low Limit = 0.069327 Volts.
From Appendix A- Sp ec if ic ations of the HP E1326A /E1411A or E1326B
/E1411B User’s Manual, 4-Wire resistance 90-day accuracy = ±(% of
reading + Ohms). The accuracy equations for the ranges and apertures used
in the performance verification te sts ar e:
Range
Accuracy [±(% of reading + Ohms)]
2 kΩ
131 kΩ
1 MΩ
0.025 + 20 mΩ
0.025 + 1 Ω
0.025 + 10 Ω
Example: Calc ul ate 4-Wire Resistance Ac curacy
For a 1 kΩ input to the multimeter, us i ng th e 2 k Ω range and 16.7/20 msec
aperture, multimeter accuracy (90-days) = ±(.025% reading
-3
+ 20 mΩ) = ±(.00025 x 1000 + 20 x 10
) = ±0.270 Ω. Thus, for a 1 kΩ
input the High Limit in Table 4-1 = 1000.27 Ω and the Low Limit = 999.73
Ω.
Appendix A Calculating Multimeter Accuracy 67
Page 68

Measurement
Uncertainty
Calculations
Measurement uncertainties for the Datron 4708 source are calculated using
the 90-day accuracy specifications in the Datron 4708 User’s Handbook:
Measurement Uncertainty = Datron Accuracy + Calibration Uncertainty,
where Datro n A cc ur ac y (p pm ) = Ac cu ra cy Rel at iv e to Ca li br ation
Standards = ±(ppm OUTPUT + ppm FS)
and FS = 2 x range for all ranges except 1000V
FS = 1100 for the 1000V range
The assumed test conditions are:
o
• Temperature of 23
• 90 days since calibration
• 4-wire sense function for ohms measurements
C±1
o
C
Calculate DCV
Measurement
Uncertainty
From Section 6 - Sp ec ific at io ns of the Datron 4708 User’s Handbook, DC
oC ±1o
Voltage (Op tion 1 0) Accu ra cy (90 days since ca libr at io n and 23
follows, where Datron Accuracy = ±(ppm OUTPUT + ppm FS).
Datron
OUTPUT
(DCV)
0.1
0.9
7.0
58.0
300.0
Datron
Range
(Volts)
1.0000000V
1.0000000V
10.000000V
100.00000V
1000.0000V
Datron
Accuracy
(ppm)
2 + 0.4
2 + 0.4
1 + 0.15
2 + 0.25
3 + 0.25
Calibration
Uncertainty
2
2
1.5
2
2
(ppm)
C)
Example: Calculate DC Voltage Measurement Uncertainty
Since Measurement Uncertainty = Datron Accuracy + Calibration
Uncertainty, for a 7.0 DCV OUTPUT and the Datron 4708 range set to
10.000000 V, Measurement Uncertainty (µV)=±[(1.0 x 7.0) + (2 x 0.15 x
10)] + (1.5 x 7.0)] = ±20.5 µV = ±0.000021 V.
Or, with a 300 DCV OUTPUT and the 1000.0000V range, Measurement
Uncertainty (µV) = ±[(3.0 x 300) + (0.25 x 1100)
+ (2.0 x 300)] = ± 1775 µV = ±0.001775 V.
68 Calculating Multimeter Accuracy Appendix A
Page 69

Calculate ACV
Measurement
Uncertainty
From Section 6 - Sp ec if ic at io ns of the Datron 4708 User’s Handbook , AC
oC ±1o
Voltage (Op tion 2 0) Accu ra cy (90 days since ca libr at io n an d 23
C)
where Datron Accuracy = ±(ppm OUTPUT + ppm FS).
Datron
Output
(ACV)
0.07
0.07
0.07
0.07
300.0
Datron
Range
100 mV
100 mV
100 mV
100 mV
1000 V
Datron
Freq
20 Hz
60 Hz
5 kHz
10 kHz
5 kHz
Datron
Accuracy
(ppm)
110 + 20 + 5 µV
60 + 20 + 5 µV
50 + 20 + 5 µV
50 + 20 + 5 µV
90 + 10
Calibration
Uncertainty
30 + 1 µV
30 + 1 µV
30 + 1 µV
30 + 1 µV
30
Example: Calculate AC Voltage Measurement Uncertainty
Since Measurement Uncertainty = Datron Accuracy + Calibration
Uncertainty, for a 0.07 ACV OUTPUT to the multimeter and the Datron
4708 range set to 100 mV at 60 Hz, Measurement Uncertainty
(µV)=±[(60.0 x 0.07) + (2 x 20 x .1) + 5 + (30 x .07 +1)] = ±16.3 µV =
±0.000016 V.
Or, for a 300 ACV OUTPUT to the multimeter and the Datron 4708 range
set to 1000 V at 5 kHz, Measurement Uncertainty (µV)
= ±[(90.0 x 300.0) + (10 x 1100) + (30 x 300)] = ± 47000 µV = ±0.047 V.
(ppm)
Calculate
Resistance
Measurement
Uncertainty
From Section 6 - Specifications of the Datron 4708 User’s Handbook,
4-Wire Resistance (Option 30) Accuracy (90 days since calibration and
o
C ±1o C) follows, where Datron Accuracy =±(ppm OUTPUT + ppm
23
FS).
Datron
Output
1 k Ω
100 k Ω
1 M Ω
Datron
Range
(Ohms)
1.0000000k
100.00000k
1.0000000M
Datron
Accuracy
(ppm)
3
3
10
Calibration
Uncertainty
(ppm)
5
6
12
Example: Calculate 4-Wire Ohms Measurement Uncertainty
For the 100 kΩ range, measurement uncertainty = [(3 x 10
+ (6 x 10
-6 x 105
)] Ω = (0.3 + 0.6) Ω = 0. 90 0 Ω .
-6
x 10 5)
Appendix A Calculating Multimeter Accuracy 69
Page 70

Test Accuracy
Ratio (TAR)
Calculations
For the HP E1411 multimeter, Test Accuracy Ratio (TAR) = [High Limit
- Input Value]/Measurement Uncertainty where the source input value is in
DCV, ACV, or Ohms.
Example: Calc ul ate DCV Test Accuracy Rati o
For a 7.0 DCV measurement if the High Limit value = 7.000750 DCV and
the Measurement Uncertainty = .0000115 DCV, Test Accuracy Ratio
(TAR) = (7.000750 V - 7.0000000 V)/.0000115 V = 65:1 (rounded to the
nearest integer value). Since this value is >10:1, the entry in Table 4-1 is
">10:1".
70 Calculating Multimeter Accuracy Appendix A
Page 71

Appendix B
Verification Tests - C Programs
Functional
This program is designed to do the Functional Verification Test found in
Chapter 4 - Verification Tests.
Verification
Test
Example:Self Test This example performs a multimeter self-test to ensure that the multimeter
is communicating with the mainframe, external controller, and/or external
terminal.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sicl.h>
#define ADDR "hpib7,9,03" /* Address of device */
void main ()
{
INST id; /* Define id as an instrument */
char a[256] = {0}; /* Result variable */
id = iopen (ADDR); /* Open instrument session */
ipromptf(id, "*TST?\n", "%t", a); /* Self test command */
printf("\n %s", a); /* Print result */
getchar(); /* Pause */
iclose (id); /* Close instrument session */
}
Appendix B Verification Tests - C Programs 71
Page 72

Performance
Verification
Tests
These programs are designed to do the Performance Verification Tests
found in Chapter 4 - Verification Tests.
Example: Zero Volt
DCV Test
This example performs a DCV test for zero volts input and a power line
reference frequency of 60 Hz.
/* Zero Volt DCV Test E1411A/B */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sicl.h>
#define ADDR "hpib7,9,03" /* Address of HP E1326B */
void main (void)
{
INST id; /* Define id as an instrument */
char volt[256] = {0}; /* Result variable */
#if defined(__BORLANDC__) && !defined(__WIN32__)
_InitEasyWin();
#endif
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT);
id = iopen (ADDR); /* Open instrument session */
iprintf (id, "*RST\n"); /* Resets and set autozero
ON and PLC to 1 */
iprintf (id, "CAL:LFR 60\n"); /* Sets line reference to 60 Hz */
ipromptf (id, "MEAS:VOLT:DC? .1\n", "%t", volt);
/* Measure 0.113 V range */
printf ("Voltage for 0.113 V range = %s\n", volt);
ipromptf (id, "MEAS:VOLT:DC? .9\n", "%t", volt);
/* Measure 0.91 V range */
printf ("Voltage for 0.91 V range = %s\n", volt);
ipromptf (id, "MEAS:VOLT:DC? 7\n", "%t", volt);
/* Measure 7.27 V range */
printf ("Voltage for 7.27 V range = %s\n", volt);
ipromptf (id, "MEAS:VOLT:DC? 58\n", "%t", volt);
/* Measure 58.1 V range */
printf ("Voltage for 58.1 V range = %s\n", volt);
ipromptf (id, "MEAS:VOLT:DC? 300\n", "%t", volt);
/* Measure 300 V range */
printf ("Voltage for 300 V range = %s\n", volt);
iclose (id); /* Close instrument session */
}
72 Verification Tests - C Programs Appendix B
Page 73

Example: DC
Voltage Test
This test performs a DC Voltage test for positive input DC volts and a
power line reference frequency of 60 Hz.
/* DC Voltage Test (DCV Input) E1411A/B */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sicl.h>
#define ADDR "hpib7,9,03" /* Address of HP E1326B */
void main ()
{
INST id; /* Define id as an instrument */
float range[5] = {0.113, 0.910, 7.270, 58.10, 300.0};
float volts[5] = {0.1, 0.9, 7.0, 58.0, 300.0};
char measurement[5][256], complete[256]; /* Result variable */
int i;
#if defined(__BORLANDC__) && !defined(__WIN32__)
_InitEasyWin();
#endif
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT); /* Exit on error */
id = iopen (ADDR); /* Open instrument session */
iprintf (id, "*RST\n"); /* Resets and set autozero
ON and PLC to 1 */
iprintf (id, "CAL:LFR 60\n"); /* Sets line reference to 60 Hz */
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) /* Take voltage measurements */
{
printf("\n Set DC Standard to %.1f VDC", volts[i]);
printf("\n press ENTER when ready\n");
getchar ();
iprintf(id, "CONF:VOLT:DC %f\n", range[i]); /* Voltage range */
ipromptf(id, "*OPC?\n", "%s", complete); /* Wait for settling */
ipromptf(id, "READ?\n", "%t", measurement[i]); /* Read voltage */
}
for (i=0; i < 5; i++) /* Print voltage measurements */
printf("\n Voltage on %4f V range = %s ", range[i], measurement[i]);
iclose (id); /* Close instrument session */
}
Appendix B Verification Tests - C Programs 73
Page 74

Example: AC
Voltage Test
This example performs an AC voltage test for a power line reference
frequency of 60 Hz.
/* AC Voltage Test E1411A/B */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sicl.h>
#define ADDR "hpib7,9,03" /* Address of HP E1326B */
void main ()
{
INST id; /* Define id as an instrument */
float source_volts[5] = {0.07, 0.07, 0.07, 0.07, 300.0};
float source_freq[5] = {20, 60, 5000, 10000, 5000};
char measurement[5][256], complete[256]; /* Result variable */
int i;
#if defined(__BORLANDC__) && !defined(__WIN32__)
_InitEasyWin();
#endif
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT); /* Exit on error */
id = iopen (ADDR); /* Open instrument session */
iprintf (id, "*RST\n"); /* Resets and set autozero
ON and PLC to 1 */
iprintf (id, "CAL:LFR 60\n"); /* Sets line reference to 60 Hz */
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) /* Take voltage measurements */
{
printf("\n 1. Set AC Standard output to %.2f VAC",
source_volts[i]);
printf("\n 2. Set AC Standard frequency to %.1f
Hz",source_freq[i]);
printf("\n 3. Press ENTER when ready\n");
getchar ();
iprintf(id, "CONF:VOLT:AC %f\n", source_volts[i]);
/* Set voltage range */
ipromptf(id, "*OPC?\n", "%s", complete);
ipromptf(id, "READ?\n", "%t", measurement[i]);
/* Read voltage */
}
for (i=0; i < 5; i++) /* Print voltage measurements */
printf("\n Voltage for %4f V range at %.1f Hz = %s ", source_volts[i],
source_freq[i], measurement[i]);
iclose (id); /* Close instrument session */
}
74 Verification Tests - C Programs Appendix B
Page 75

Example:
Resistance Test
This example perf or ms a 4- wir e oh ms re si stance test. The program also
calculates the Upper and Lower Limit values for the ACTUAL resistance
values. Use these values in Table 4-1 if they differ from the given values.
/* Resistance Test (4-wire Ohms) E1411A/B */
#include <sdtio.h>
#include <sicl.h>
#define ADDR "hpib7,9,03" /* Address of HP E1326B */
void main ()
{
INST id; /* Define id as an instrument */
float range[3] = {1861, 119156, 1048576};
float source[3] = {1000, 100000, 1000000};
char measurement[3][256], complete[256];
float limit[3], actual[3];
int i;
#if defined(__BORLANDC__) && !defined(__WIN32__)
_InitEasyWin();
#endif
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT); /* Exit on error */
id = iopen (ADDR); /* Open instrument session */
iprintf (id, "*RST\n"); /* Resets and set autozero
ON and PLC to 1 */
iprintf (id, "CAL:LFR 60\n"); /* Sets line reference to 60 Hz */
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) /* Take measurements */
{
printf("\n 1. Set Resistance Standard to %.1f Ohms", source[i]);
printf("\n 2. Measure ACTUAL resistance standard value (in
Ohms)");
printf("\n 3. Enter ACTUAL resistance standard (in Ohms): ");
scanf("%f", &actual[i]);
iprintf(id, "CONF:FRES %f\n", range[i]);
/* Set resistance range */
ipromptf(id, "*OPC?\n", "%s", complete); /* Wait for settling */
ipromptf(id, "READ?\n", "%t", measurement[i]);
/* Read resistance */
if (i == 0)
limit[i] = .00025*actual[i] + 0.02; /* 2kOhm limits */
if (i == 1)
limit[i] = .00025*actual[i] + 1.0; /* 131 kOhm limits */
if (i == 2)
limit[i] = .00025*actual[i] + 10; /* 1 MOhm limits */
}
printf("\nMeasured Source Low Limit High Limit");
printf("\nResistance Resistance (Ohms) (Ohms)\n");
for (i=0; i < 3; i++) /* Print measurements and limits */
printf("\n%s %10.2f %10.2f %10.2f",
measurement[i],actual[i], actual[i]-limit[i], actual[i]+limit[i]);
iclose (id); /* Close instrument session */
}
Appendix B Verification Tests - C Programs 75
Page 76

Adjustments These programs are designed to do the adjustments found in Ch ap te r 5 -
Adjustments.
DC Voltage
Adjustments
This example performs DC Voltage adjustments for a power line reference
frequency of 60 Hz. If no calibration error occurs, the program displays an
"adjustment complete" message. If a calibration error occurs, the program
displays the calibration error and prompts you to repeat the adjustment (see
Table 5-1 for a list of calibration errors).
/* DC Voltage Adjustments E1411A/B */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sicl.h>
#define ADDR "hpib7,9,03" /* Address of device */
void main ()
{
INST id; /* Define id as an instrument */
float range[10] = {8.0, 8.0, 0.125, 0.125, 1.0, 1.0, 64.0, 64.0,
300.0, 300.0};
float volts[10] = {7.7, -7.7, .121, -.121, .97, -.97, 62.0, -62.0,
300.0, -300.0};
char cal_code[5][256];
int i;
#if defined(__BORLANDC__) && !defined(__WIN32__)
_InitEasyWin();
#endif
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT); /* Exit on error */
id = iopen (ADDR); /* Open instrument session */
iprintf (id, "*RST\n"); /* Resets and set autozero
ON and PLC to 1 */
iprintf (id, "CAL:LFR 60\n"); /* Sets line reference to 60 Hz */
for(i = 0; i 10; i++) /* Take voltage measurements */
{
retry:
printf("\n Set DC Standard to %.1f VDC", volts[i]);
printf("\n press ENTER when ready\n");
getchar ();
iprintf(id, "FUNC:VOLT:DC\n"); /* Set DCV function */
iprintf(id, "VOLT:RANG %f\n", range[i]); /* Set E1326B range */
iprintf(id, "CAL:VAL %f\n", volts[i]); /* Set CAL:VAL value */
iprintf(id, "TRIG:DEL .05\n"); /* Wait for settling */
ipromptf(id, "CAL?\n", "%t", cal_code[i]); /* Read voltage */
if (cal_code != 0)
{
printf ("\nCalibration Error %s for %f Vdc input", cal_code,
volts[i]);
printf ("\nCheck source value/connections, then");
printf ("\npress ENTER to retry this adjustment");
getchar ();
goto retry;
}
else
printf ("\nAdjustment complete for %f Vdc input", volts[i]);
}
iclose (id); /* Close instrument session */
}
76 Verification Tests - C Programs Appendix B
Page 77

AC Voltage
Adjustments
This example performs an AC Voltage adjustment for a power line
reference frequency of 60 Hz and an input of 5.6 Vac at 1 kHz. If no
calibration error occurs, the program displays an "adjustment complete"
message. If a calibration error occurs, the program displays the calibration
error and prom pt s yo u to rep ea t th e ad ju st m en t (s ee Table 5- 1 fo r a li st of
calibration errors).
/* AC Voltage Adjustments E1411A/B */
#include <sdtio.h>
#include <sicl.h>
#define ADDR "hpib7,9,03" /* Address of device */
void main ()
{
INST id; /* Define id as an instrument */
char cal_code[256];
#if defined(__BORLANDC__) && !defined(__WIN32__)
_InitEasyWin();
#endif
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT); /* Exit on error */
id = iopen (ADDR); /* Open instrument session */
iprintf (id, "*RST\n"); /* Resets and set autozero
ON and PLC to 1 */
printf (id, "CAL:LFR 60\n"); /* Sets line reference to 60 Hz */
retry:
printf("\n Set AC Standard to 5.6 Vac at 1.0 kHz");
printf("\n press ENTER when ready\n");
getchar (); iprintf(id, "FUNC:VOLT:AC\n"); /* Set DCV function */
iprintf(id, "VOLT:RANG 5.6\n"); /* Set E1326B range */
iprintf(id, "CAL:VAL 5.6\n"); /* Set CAL:VAL value */
iprintf(id, "TRIG:DEL .05\n"); /* Wait for settling */
ipromptf(id, "CAL?\n", "%t", cal_code[i]); /* Read voltage */
if (cal_code != 0)
{
printf ("\nCalibration Error %s on 5.6 Vac range", cal_code);
printf ("\nCheck source value/connections, then");
printf ("\npress ENTER to retry this adjustment");
getchar ();
goto retry;
}
else
printf ("\nAdjustment complete for %f Vdc input", volts[i]);
iclose (id); /* Close instrument session */
}
Appendix B Verification Tests - C Programs 77
Page 78

Resistance
Adjustments
This example performs a 4-wire ohms resistance adjustment for a power
line reference frequency of 60 Hz. If a calibration error occurs, the program
displays the calibration error and prompts you to repeat the adjustment (see
Table 5-1 for a list of calibration errors).
/* 4-wire Resistance Adjustments E1411A/B */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sicl.h>
#define ADDR "hpib7,9,03" /* Address of device */
void main ()
{
INST id; /* Define id as an instrument */
float range[3] = {2000, 16000, 1048576};
float source[3] = {1000, 10000, 1000000};
char cal_code[5][256];
float actual[3];
int i;
#if defined(__BORLANDC__) && !defined(__WIN32__)
_InitEasyWin();
#endif
ionerror(I_ERROR_EXIT); /* Exit on error */
id = iopen (ADDR); /* Open instrument session */
iprintf (id, "*RST\n"); /* Resets and set autozero
ON and PLC to 1 */
iprintf (id, "CAL:LFR 60\n"); /* Sets line reference to 60 Hz */
for(i = 0; i 3; i++) /* Take voltage measurements */
{
retry:
printf("\n Set Resistance Standard to %.1f Ohms", source[i]);
printf("\n Measure ACTUAL Resistance Standard value (in
Ohms):");
scanf ("%f", &actual[i]);
iprintf(id, "FUNC:FRES\n"); /* Set DCV function */
iprintf(id, "FRES:RANG %f\n", range[i]); /* Set E1326B range */
iprintf(id, "CAL:VAL %f\n", actual[i]); /* Set CAL:VAL value */
ipromptf(id, "CAL?\n", "%t", cal_code[i]); /* Read voltage */
if (cal_code != 0)
{
printf ("\nCalibration Error %s for %f Ohms", cal_code,
source[i]);
printf ("\nCheck source value/connections, then");
printf ("\npress ENTER to retry this adjustment");
getchar ();
goto retry;
}
else
printf ("\nAdjustment complete with %f Ohms source\n",
source[i]);
}
iclose (id); /* Close instrument session */
}
78 Verification Tests - C Programs Appendix B
 Loading...
Loading...