Page 1

HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
Windows 2003
art number: T1634-96054
P
Fourth edition: August 2006
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2005-2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and
12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are
licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth
in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting
an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Intel, Itanium, Pentium, Intel Inside, and the Intel Inside logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its
subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows XP, and Windows NT are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Adobe and Acrobat are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Java is a US trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Oracle is a registered US trademark of Oracle Corporation, Redwood City, California.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Printed in the US.
Page 3

Contents
Preface .............................. 5
Aboutthisguide....................................... 5
Intendedaudience...................................... 5
Diskarrays......................................... 5
Relateddocumentation.................................... 5
Documentconventionsandsymbols .............................. 6
HPtechnicalsupport..................................... 7
Subscriptionservice ..................................... 7
HPwebsites ........................................ 7
Documentationfeedback ................................... 7
OtherHPwebsites ..................................... 7
1Overview ............................ 9
Simpleoverview...................................... 10
Detailedoverview..................................... 11
VirtualDiskService(VDS)................................ 11
VolumeShadowCopyService(VSS) ........................... 11
Functionalcomponents................................. 12
MicrosoftWindowsServer2003operatingsystem ..................... 13
WindowsDiskManagement .............................. 13
Management applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Microsoftcommandlineinterfaces............................ 13
Windowssoftwareproviders .............................. 13
MicrosoftVirtualDiskService(VDS) ........................... 14
MicrosoftVolumeShadowCopyService(VSS)....................... 14
Copyterminology ................................. 14
HPVDS/VSSHardwareProviders ............................ 14
HPdiskarrays..................................... 15
HPEVAarraysandVSS .............................. 15
HPHWPtypicalapplications ................................ 15
VDStypicalapplications ................................ 15
VSStypicalapplications ................................ 15
Consistent backups of open files and applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
ShadowCopyTransport .............................. 16
HPFastRecoverySolution.............................. 16
2Configuration.......................... 17
Requiredcomponents ................................... 18
Requiredhardwarecomponents ............................. 19
Requiredsoftwarecomponents.............................. 20
EVAdiskarraywithCVworkstation: ......................... 20
VDS/VSSServer.................................. 20
SecondaryServer(optional)............................. 20
Important configurationnotes .............................. 20
Importantperformancenotes .............................. 20
Configurationprocedures.................................. 21
Configurationsummary................................. 21
WindowsCVworkstation: ............................. 21
ConfiguringthearrayCVworkstation........................... 21
ConfiguringtheVDS/VSSServer............................. 22
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
3
Page 4

Configuring additional servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
ConfiguringtheEVAdiskarray ............................. 23
AddingVDS/VSShosts............................... 25
Addingdiskgroups ................................ 26
3Installation........................... 29
Installationprocedures ................................... 30
Upgradeinstallation.................................. 30
Installationsummary.................................. 30
InstallingHWP .................................... 31
ConfiguringVSS/VDStoaccessCommandView: ................... 35
Adding disk groups using the VSS ConfigurationUtility ................... 38
Verifyinginstallation .................................... 39
Checkingthelistofprograms .............................. 39
CheckingVDSdiskmanagementusingDiskRaid...................... 39
CheckingVSSvolumeshadowcopying.......................... 39
UninstallingHWP ..................................... 40
UninstallingHWPusingWindows ............................ 40
UninstallingusingHWPInstaller............................. 40
4Troubleshooting . . ....................... 41
Troubleshootingprocedures................................. 42
VDS/VSSHWPwillnotinstall.............................. 42
CVauthenticationfailure ................................ 42
VDSdiskarraymanagementnotworking ......................... 42
VSSvolumecopyingnotworking............................. 43
VSScopiesintermittentlyfailortimeout.......................... 43
Errormessages ...................................... 45
VDSerrormessages .................................. 45
VSSerrormessages .................................. 49
Glossary............................. 51
Index .............................. 53
4
Page 5

Preface
About this guide
This guide provides information about:
• HP EVA H ardware Providers version 4.01.00 for Microsoft VDS 1.1 and VSS.
• Requirements and procedures for connecting an EVA disk array to a host system
• Configuring the disk array for use with the Windows 2 003 operating system
Intended audi
This guide is intended for system administrators with knowledge of:
• Thehosthardware
• Windows 2003
• EVA disk arrays
ence
operating system
Disk arrays
Unless otherwise noted, the term “disk a rray” refers to these disk arrays:
• HP StorageWorks 3000 Enterprise Virtual Array (EVA)
• HP StorageWorks 4000 Enterprise Virtual Array (EVA)
• HP StorageWorks 5000 Enterprise Virtual Array (EVA)
• HP StorageWorks 6000 Enterprise Virtual Array (EVA)
• HP StorageWorks 8000 Enterprise Virtual Array (EVA)
Related documentation
The follow
Guides ar
• HP StorageWorks EVA User Guide
• HP StorageWorks EVA Software Guide
• HP Storag
• HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Configuration Guide
ing documents provide related information for the EVA arrays. Generic titles are listed below.
eavailableforspecific EVA models, hosts, and software:
eWorks EVA Installation and Configuration Guide
You can find these documents from the Manuals p age of the HP Business Support Center web site:
h
ttp://www.hp.com/support/manuals.
In the Storage section, click Storage array systems and then select your product.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
5
Page 6

Document conven
tions and symbols
Convention
Blue text: Document conventions and
symbols
Blue, underlined text: http://www.hp.com
Bold text
Italic text Text emphasis
Monospace
Monospace, italic text
Monospace, bold text
text
Element
Cross-reference links and e-mail addresses
Web site addre
• Keys that are pressed
• Text typed into a GUI element, such as a box
• GUI elements that a re clicked or selected, such
as menu and list items, buttons, tabs, and check
boxes
• File and d
• System ou
• Code
• Command
• Code variables
• Command variables
Emphasized monospace text
sses
irectory names
tput
s, their arguments, and argument values
WARNING!
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death.
CAUTION:
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT:
Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
NOTE:
Provides additional information.
TIP:
Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
6
Preface
Page 7

HP technical support
Telephone numbers for worldwide technical suppor t are listed on the HP support web site:
h
ttp://www.hp.com/support/.
Collect the f
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Product mod
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed q
For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
ollowing information before calling:
el names and numbers
uestions
Subscription service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber’s Choice for Business web site:
h
ttp://www.hp.com/go/e-updates.
After registering, you will receive e-mail notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
HP web si
For additional information, see the following HP web sites:
•h
•http://
•http://www.hp.com/service_locator
•http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
•http:/
tes
ttp://www.hp.com
www.hp.com/go/storage
/www.hp.com/support/downloads
Documentation feedback
HP welcomes your feedback.
To make comments and suggestions about product documentation, please send a message to
storagedocs.feedback@hp.com. All submissions become the property of HP.
Other HP web sites
For additional information, see the following HP web sites:
//www.hp.com/go/storage
ttp:
•h
•http://www.hp.com/support/
•http://www.hp.com/service_locator
•http
://www.docs.hp.com
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
7
Page 8

8
Preface
Page 9

1Overview
This chapter describes the HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers (HW P) for Windows Server 2003
Enterprise Edition and explains how they operate with Microsoft’s op erating system and applications.
When you have read this chapter, you should have a functional understanding of the Hardware Providers
that will prepare you to install the providers and get them working.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
9
Page 10
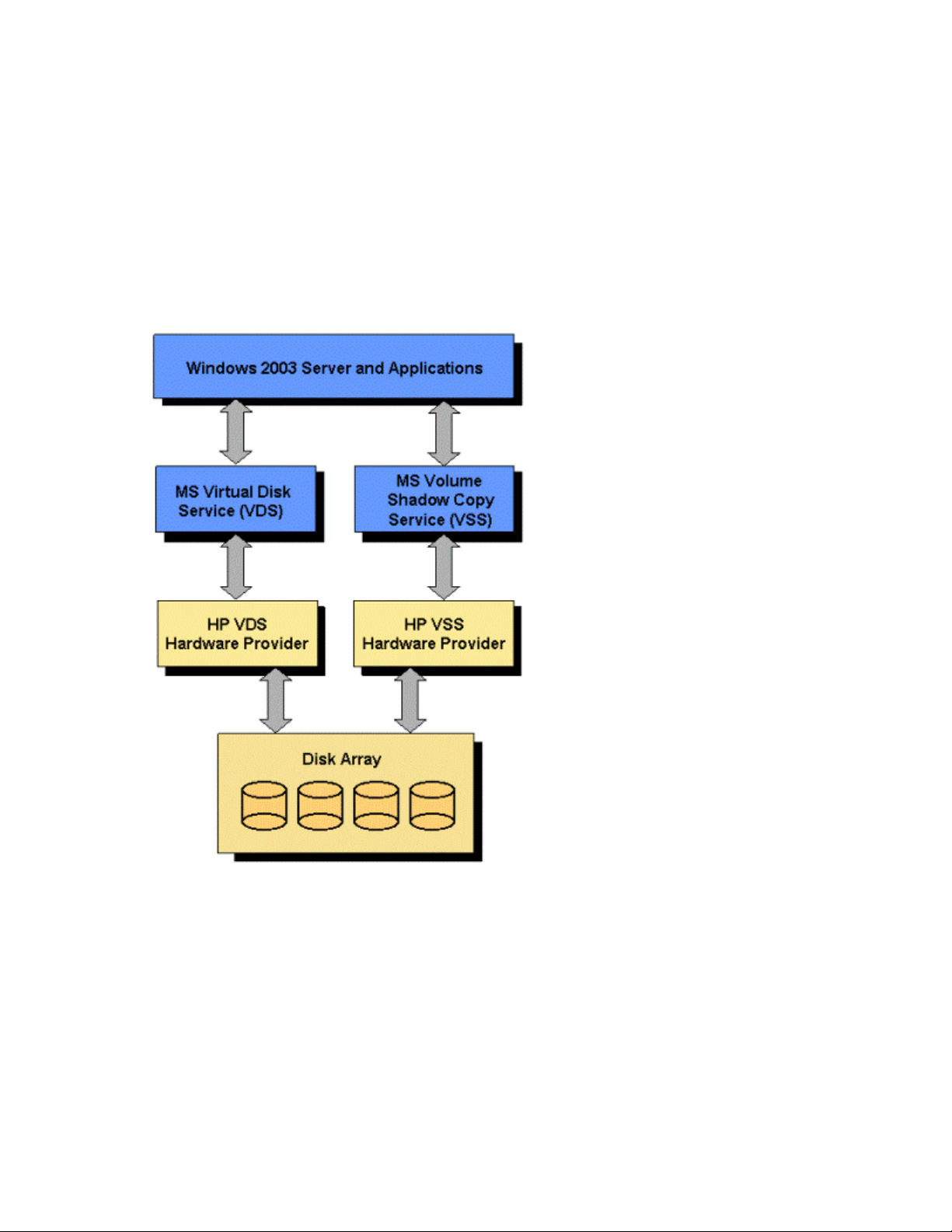
Simple overview
HP StorageWorks EVA H ardware Providers for Windows Server 2003 are solutions that install on a
Windows 2003 server connected to an HP disk array.
There are two
• HP VDS HWP and Microsoft Virtual Disk Service (VDS)
• HP VSS HWP and Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS)
The purpose
OSandapplicationstodothesetasks:
• VDS: manage the disk array using the Windows OS and applications
• VSS: creat
providers associated with two Microsoft storage services:
of the Hardware P roviders, together with the Microsoft services, is to enable the Windows
e copies of data on array volumes for backup
10 Overview
Page 11

Detailed overview
HP Hardware Providers enable Windows and its applications to use Microsoft VDS/VSS ser vices to
manage certa
Virtual Disk Service (VDS)
The V DS service provides the capability of Windows and Windows applications to recognize the HP disk
array and perform basic and dynamic disk management functions.
• Microsoft Management Console (MMC) Snap-in, Disk Manager and DiskPart command line
interface use the VDS service.
• When used with HP VDS HWP, Windows and Windows applications can perform disk array
LUN and port management tasks normally performed using proprietary array control software.
Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS)
in functions of the disk array.
Through t
primary a
these functions:
• Coordinates with business and backup applications to control the disk array through the HP
• Makes f
For detailed information about the Microsoft VDS and VSS services, see the Microsoft website.
he HP VSS HWP, the VSS ser vice provides mirroring of the active files or databases on
rray volumes to secondary array volumes for backup and restoration. The service performs
VSS HWP to make copies of array volume(s)
ull copies of data, called volume shadow copies, clones,orplexes by Microsoft.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
11
Page 12
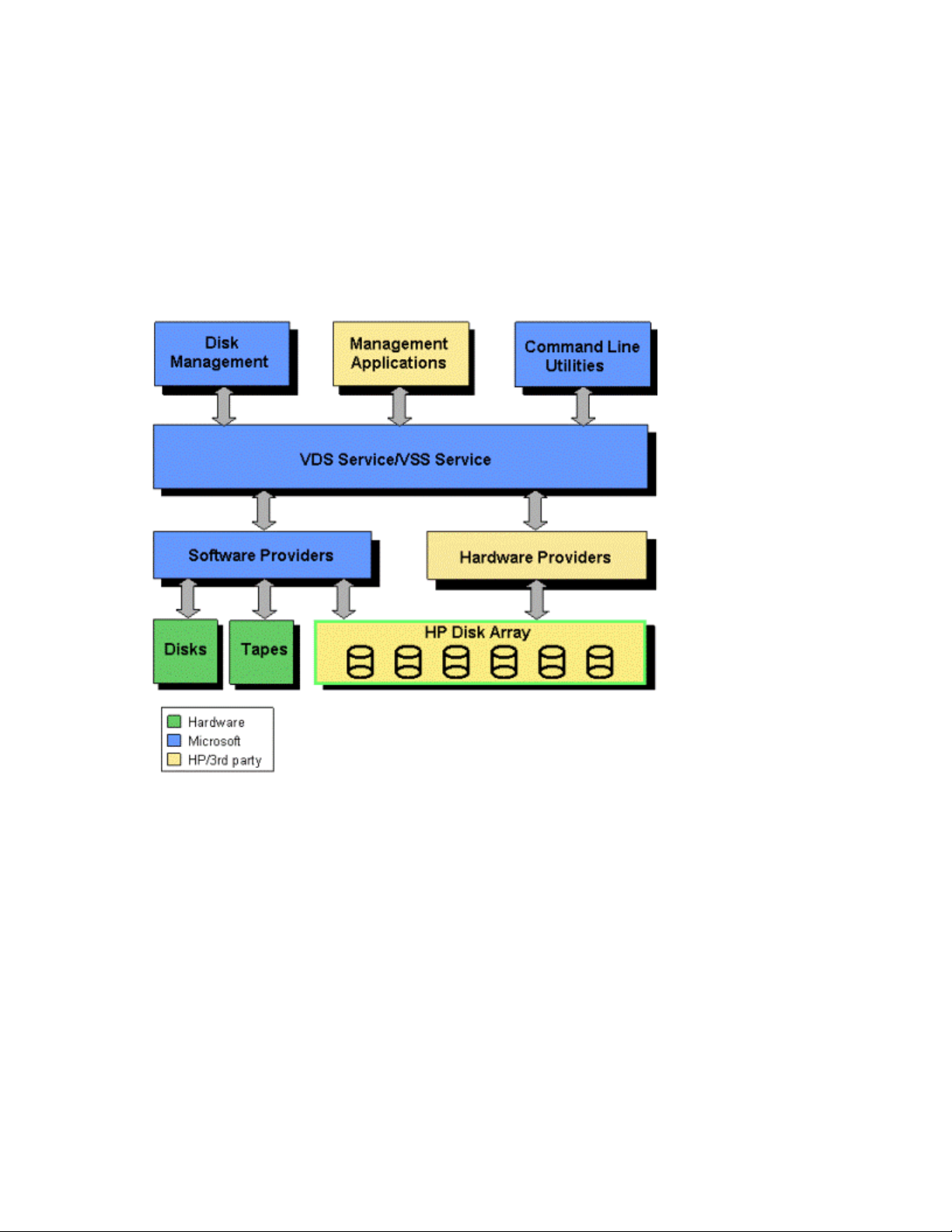
Functional c
The process of manag ing array volumes using VDS/VSS and HP HWP involves the following components:
• Microsoft Wi
• Windows Disk Management
• Management Applications, such as HP’s Fast Recovery Solution (FRS) and third party programs
• Microsoft C
• Windows Software Providers
• Windows VDS Service/VSS Service
• HP VDS/VSS
• HP Disk Array System
omponents
ndows Server 2003 OS
ommand Line Utilities
Hardware Providers
12 Overview
Page 13

Microsoft Windows Server 2003 operating system
The Windows Server 2003 OS includes Microsoft Virtual Disk Service (VDS) and Volume Shadow Copy
Service (VSS). These services allow you to manage storage array disks and volumes and to perform data
backup and re
HP EVA disk arrays.
The Microsoft Virtual Disk Service provides interfaces for managing storage devices. Windows Server
2003 included VDS 1.0. Windows Server 2003 R2 introduced VDS 1.1. Microsoft VDS 1.1 includes
new service
support DSM and M PIO multipath (per LUN) path queries and load balancing. The current HP EVA VDS
Hardware Provider supports both VDS 1.0 and VDS 1.1.
The Micros
Windows Ser ver 2003 included Volume Shadow Copy Service. With Windows Server 2003 SP1
additional improvements were made to VSS. These changes added the ability to import shadow copies
in a cluster, include many LUNs in a single copy set, and perform shadow copy revert. The current
HP EVA VSS HWP supports this version of VSS.
storation. The HP EVA Hardware Providers enable the VDS and VSS services to work with
s for querying, configuring, and maintaining storage devices. The new services primarily
oft Volume Shadow Copy Service provides interfaces for performing backups and restores.
Windows Disk Management
Windows Disk Management consists of the Windows software and user interfaces that enable you to
manage disks, volumes, and file systems. The user interface for disk management is included in the
Computer Management tool within the Administrative Tools Control Panel.
Managem
ent applications
HP StorageWorks Fast Recovery Solution (FRS) and other third party m a nagement applications work with
the Microsoft VDS and VSS services to allow you to manage array disks and volumes and to perform
data backup and restoration. For more information about FRS, see the HP website.
Microsoft command line interfaces
Microsoft offers several command line utilities for use with VDS, VSS, and the HWPs. DiskPart and
DiskRaid provide interfaces that enable you to script disk management tasks so you can automate
configuration of multiple storage disks.
The DiskPart utility, which comes standard with Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, manages disks,
volumes, and partitions. Using DiskPart, you can use the command line to manage the disk array.
The DiskRaid utility, which comes with the Windows 2003 Server Resource Kit, configures hardware
RAID subsystems. It works with any storage hardware that includes a VDS hardware provider, including
HP arrays using the HP VDS HWP. DiskRaid has a command syntax similar to DiskPart. Note that
if you display LUNs, DiskRaid shows LUNs in decimal rather than the hexadecimal numbering used in
Command View.
Additionally, Microsoft makes a snapshot copy utility called Vshadow. You can use Vshadows with VSS
and HWP to make and manage volume shadow copies and snapshots. See the Microsoft web site
for more information.
Windows software providers
e Microsoft Software Providers (called Basic Disk Provider and Dynamic Disk Provider) interface
Th
between the Windows OS, Windows applications, and disks, drives, and disk arrays. Through these
software providers and VDS, Windows sees the disks, drives, and disk array volumes and performs
actions such as partitioning, mounting, and manag ing the file system.
Other Windows software providers (not shown) are the in-box providers, such as the Windows Backup
ility and Windows Microsoft Software Shadow Copy Provider. These providers allow individual users
ut
to back up and recover user volumes and files.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
13
Page 14

HP Hardware Providers are not required in order for the Microsoft in-box or third party software providers
to per form the tasks described above on the HP disk arrays. However, the HP HWPs extend the
capabilities of various Windows providers and applications to do additional tasks that normally require
the use of proprietary HP array management software. Such tasks include LUN and port m anagement
and m ore sophisticated volume copying.
Microsoft Vir
Microsoft VDS provides a mechanism for managing volumes and logical units. Administrators can
identify, configure, and monitor supported HP StorageWorks disk array volumes from the Windows
Server 2003 Microsoft Management Console (MMC).
When used with HP disk arrays, VDS manages the array to make it appear like a Windows d isk for
Windows applications. When you use Microsoft Mana gement Console, Windows Disk Manager and
the Microsoft DiskPart or DiskRaid utility to control the array, your commands are sent to the array
through VDS and the software or hardware providers.
VDS performs the following functions:
• Coordinat
• Performs binding
• Discloses hardware LUNs to software disks
• Performs c
• Monitors volume status
• Provides fault and performance tracking
tual Disk Service (VDS)
es providers and clients (local and remote)
ommon file system functions
Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS)
Microsoft’s VSS manages creation and maintenance of data shadow copies for backup and recovery,
includingcopiesacrossmultiplevolumes. Toaccomplishthis,VSScoordinateswithHP’sFastRecovery
Solution and Business Copy software or other third party business applications, file-system services,
backup applications, and the storage hardware.
The shadow copies contain static copies of all files, such as databases, transaction logs, and checkpoint
files. Because VSS coordinates copying, the files are copied in a defined state.
Copy terminology
Understanding how Microsoft VSS terminology corresponds to standard IT industry terms for data copying
makes it easier to understand what VSS does. The following paragraphs explain the terminology.
Microsoft generally refers to a VSS copy as a “volume shadow copy.” When created using HP FRS and
HWP, this type of copy is a static replica of an original volume’s contents. It is keyed with a GUID to
allow identification of the parts of a s hadow copy set that span multiple volumes. Microsoft also refers to
aVSScopyasa“plex.”ThistypeofcopyiscommonlyreferredtointheITindustryasa“splitmirror.”
you use an EVA array to make a s hadow copy, the array makes what is known as a “snapclone.”
When
An EVA Snapclone is a complete clone copy of a specified Virtual Disk (LUN). EVA snapclones are
available almost immediately. This is accomplished by creating a point-in-time copy and making it
diately available by pointing to data on the original volume while continuing to copy data to a
imme
secondary volume in the background. When copying is complete, the snapclone is a static point-in-time
copy of the original.
HP VDS/VSS Hardware Providers
Windows Server 2003 sees, partitions, mounts, and manages file systems on the disk array using its own
software providers. HP’s Hardware Providers extend the array management capabilities of Windows and
its applications to include functions normally performed using the disk array’s proprietary control software.
These functions include managing disk array LUNs and ports and performing volume copy operations.
14
Overview
Page 15

There are two HP HWP installation executables for each HP disk array model, one installation executable
for VDS and one for VSS. These installation executables are different for each HP disk array model.
The HP Hardware Providers installation executables install the HWP files in your Windows Server
file system. The files installed consist of special sets of HP DLLs and executables. These components
extend the array management capabilities of Windows and its applications. Because they are installed
separately, you can choose to install only the VDS or VSS HWP or both.
For VSS only, HP’s Business Copy (BC) application, which installs on the disk array an d is licensed in
Command View, works with the VSS and the HP HWP components to enable the array to make VSS
shadow copies. For functional purposes, you can think of BC as a part of the hardware providers,
even though it is installed separately.
HP disk arrays
Specific HP Hardware Providers have been created to work with selected HP disk arrays. Different
supporting technologies and features within the arrays result in some differences in their methods and
capabilities of performing VDS/VSS tasks.
HP EVA arrays and VSS
TheHPEVAVSSHardwareProviderworkswithEVAarraystoenableMicrosoftVSStocreateand
manage snapclones and snapshots. During HP VSS HWP installation you specify an EVA disk group to
hold the co pies.
HP HWP typic
The follow
Microsoft
al applications
ing examples demonstrate typical applications of the H ardware Providers when used with the
VDS, and VSS software components. Many more scenarios are possible.
VDS typical applications
The advantage of VDS and the HP VDS HWP is that they allow you to manage the HP disk array using
the Windows interface. Array management tasks that would normally require the array’s proprietary
management application can be done using VDS and the third party Windows management application
of your choice. When you have multiple array models, this is par ticularly helpful because you c an
manage all arrays from a single interface.
VSS typical applications
VSS shad
purposes:
• Consistent backups of open files and applications
• Transp
• Fast recovery of files and data
Consistent backups of open files and applications
VSS captures data files from running applications by taking a snapshot of the da ta at a point in time,
minimizing interruption to the applications. This process may include cooperation from the applications,
which notify the operating system that they are momentarily pausing. During this time, the applications
make data on the disk consistent by performing actions such as flushing buffers to disk or writing data in
memory to disk. The resulting backup data copies are typically temporary, maintained for some limited
period of time until they a re superseded by newer copies.
ow copies made o n the disk array with the help of the HP VSS HWP can be used for many
ortable shadow copies for backup, testing and data mining
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
15
Page 16

Shadow Copy Transport
Using a server configured with suitable applications together with VSS and the HP HWP, you can
create shadow c
enables multiple servers to make use of the same data, allowing data mining or testing on those
servers. (However, shadow copies are read-only. If you need to write to a shadow copy, you must use a
storage-management application that works with VDS/VSS to convert the copy to read/write.)
You can also use VSS and HP HWP to create a nd transport shadow copies from the primary server onto
abackupserve
is that it rel
often than tape backups because the copying process is faster than tape and doesn’t require taking
the database offline.
opies and import them onto other servers connected to the same disk array. This
r, and then back up the shadow copy volumes to tape. The advantage of this solution
ieves the primary server of backup traffic. Additionally, shadow copies can be made more
HP Fast Recovery Solution
FRS is an HP management ap plication that works with VSS and HP VSS HWP. Using FRS, you can create
point-in-time shadow copies and use them to perform quick recovery of your data. Whether data is lost
becauseofahardwarefailureorsoftwarecorruption,itcanberestoredinminutes.
16 Overview
Page 17

2Confi guration
This chapter lists required hardware and software components and explains how to configure the disk
array and Windows 2003 servers for use with HP Hardware Providers (HWP). You must complete the
procedures in this chapter before you install HP HWP.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The right combination of software versions is crucial to configuring a working system.
Refer to the Release Notes (ReadMe file) accompanying the HP HWP installation files for information
about compatible software versions and system configurations.
For HP Hardware Providers documentation and software downloads, see the following web location:
h
ttp://www.hp.com/support/HWPEVA
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
17
Page 18

Required components
The following illustration summarizes the hardware and software in a fully configured system. A second
server is not needed for VDS and is optional for VSS, but it may be useful if you want to manage VSS
data copies without burdening the primary server.
Note that any firewall must be open between the HW P server(s) and the Command View workstation.
Anything th
at slows down access to the CV workstation will cause VSS timeout failures.
18
Configuration
Page 19

Required har
• HP StorageWorks Disk Array: EVA disk array with a Windows workstation for running Command
View EVA. If multiple EVA disk arrays are used with FRS, all must be managed from one
Command Vie
• Windows VDS/VSS Server with Windows Server 2003 OS for connecting to the array. This
primary ser ver manages your primary data and contains applications (such as Exchange or SQL),
VSS/VDS, and HP HWP.
• Windows Se
manage the VSS copies on the array volumes without burdening the VDS/VSS server. Depending
on your purpose for this server, you may need to install the HP HWP and your application
software.
• Fibre Cha
Fibre Channel SAN.
• Fiber cables and fabric switch(es) to connect the hosts to the array.
• Etherne
connecting to Ethernet LAN. Important: The Windows Net work Connections control panel
Advanced Settings must be set to list first the network that provides communication between the
FRS servers and the CV workstation.
dware components
w workstation.
rver 2 (optional): Another server
nnel Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) in each server for connecting to the disk array via a
t Network Interface Cards or available network interface port in each server for
may
be connected to the array if you want to
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
19
Page 20

Required software components
The followin
IMPORTANT NO
Refer to the
software ve
g software is required to run HP HWP.
TE: The right combination of software versions is crucial to configuring a working system.
Release Notes accompanying the HP HWP installation files for information about compatible
rsions and system configurations. Follow all configuration and installation instructions carefully.
EVA disk array with CV workstation:
• Command View EVA
• Business Copy EVA license (for VSS only; not required for VDS)
• HP MPIO Full-Featured Failover Manager (if multipathing is required)
VDS/VSS Se
rver
• Windows Ser ver 2003 Enterprise edition (see Release Notes for details)
• HP MPIO Fu
• HP VDS HWP 4.01.00 (for array management)
• HP VSS HWP 4.01.00 (for shadow copying)
ll-Featured Failover (if multipathing is required)
Secondary Server (optional)
• Windows Server 2003 Enterprise edition
• HP MPIO Full-Featured Failover (if multipathing is required)
• Other software as required depending on server purpose
Important configuration notes
The following notes will help ensure a successful configuration:
• Using multiple servers is optional. However, if you use multiple servers, they must be in the same
net domain so that the DCOM communication process can communicate between servers.
Ether
• Administrator privileges are required for all devices and software. If you do not have administrator
privileges, the software and hardware will not communicate properly. If authentication fails,
consult the Release Notes for any special authentication issues and solutions.
• The firewall must be open between the CV workstation and the VDS/VSS servers.
Important performance notes
The following issues can affect the performance of HP HWP:
• Excessive traffic on the Ethernet LAN. If this becomes a problem, you may want to use a private
Ethernet LAN between the CV workstation and the VDS/VSS server(s) and connect it to the
corporate LAN through a fi rewall.
• Viruses that slow down network traffic. Be sure you regularly run a virus checker .
• A firewall that excessively slows traffic between the CV workstation and the servers hosting
VDS/VSS. Any firewall must be open between these systems.
20
Configuration
Page 21

Configuration procedures
Physically configure the servers and software as described below and in the manuals for those products.
See the overview diagram under the heading Required components. Your HP representative may perform
some installation and con figuration tasks.
Configuration summary
You will perform the following tasks during configuration:
Windows C V workstation:
• Install HP MPIO FF Failover Manager (if multipathing is required).
• Use Command View EVA to activate the BC license.
VDS/VSS servers:
• Install Windows Enterprise OS, FC HBAs, drivers and software.
• Install HP MPIO Full-Featured Failover (if multipathing is desired).
• Connect to the array’s FC SAN.
• Connect to the corporate Ethernet LAN (A firewall is optional but recommended. The firewall must
be o pen between servers.)
Disk arr
ay (Command View EVA):
• Create Windows user groups and names on the CV server.
• (VSS on
• (VSS only) C reate other disk groups as required by your application. (Exchange requires a data
diskgroupandalogdiskgroup.)
ly) Create a snapclone disk group (or use the existing production disk group).
Configuring the array CV workstation
Configure the disk array Command View server as explained below. VDS only requires that you do
step 1. All other steps support VSS:
1. If desired, connect the corporate Ethernet L A N to the CV workstation through a firewall. Make sure
the firewall is open between the CV workstation and the VDS/VSS server(s).
2. If multipathing is desired, verify existing or install HP M PIO Full-Featured Failover Manager as
explained in the documentation for that product.
3. Verify existing or add a license for Business Copy in Command View according to the instructions in
the Command View EVA Network Administration Guide.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
21
Page 22

Configuring the VDS/VSS Server
Install and configure the VDS/VSS server as follows:
1. If it is not already present, install the Windows 2 003 E nterprise Server OS on the host according to
Microsoft’s installation instructions.
2. If multipathing is desired, install the HP MPIO Full-Featured software according to the documentation
for that product.
3. Install a F
manufact
4. Install the HBA driver and utilit y software onto the server according to the HBA manufacturer’s
instructions. HP tested drivers are available by searching hp.com; follow the Release Notes for
installation.
5. Connect
external switch. Configure the switch, including zoning if required, according to the manufacturer’s
instructions. For helpful information on SAN construction, search the HP web site for the HP
StorageWorks SAN Design Reference Guide.
6. Connect the ser ver to the corporate Ethernet LAN, through a firewall if desired. Be sure the firewall
is open between the CV and VDS/VSS server(s). Use a ping command to test communication
betwe
in order for H WP to function.
7. Complete config uration in this chapter and then install the required HP HWP software o n the server
as ex
ibre Channel host bus adapter (HBA) card into the server according to the HBA
urer’s instructions.
the server to the disk array via the built-in Fibre Channel fabric switch, if present, or an
en servers. The Hardware Providers use ports 12301 and 2301; these ports must be available
plained in “Chapter 3 Installation.”
NOTE:
WhenusingtheVDSframeworktocreateandmanageLUNs,theLUNsshouldbethesamesizeasthe
physical disk size. You can make LUNs smaller than a physical disk (or disks, if spanning multiple disks),
but any space left over on the physical disk(s) cannot be used. For example, if you have three 36
GB drives totalling 108 GB and you create a LUN of 20 GB spanning all three disks, the remaining
Bareunusable.
88 G
Configuring additional servers
An additional server for managing data copies is optional, and its configuration depends on your specific
application. If you plan to use additional servers, configu re them according to the preceding instructions.
22
Configuration
Page 23

Configuring the EVA disk array
The following configuration steps are required for both VDS and VSS Hardware Providers. The current
HWPs work with EVA Command View 6.0 or higher.
1. For the HWPs t
operating system level on the CV server. In Windows, click Start > Control Panel > User Accounts.
2. Create the following two user groups:
o access the CV server, you must create new user names and user groups at the
Group
HP Storage Users
HP Storage Administrators
Description
Members can look at storage but cannot make changes
Members ca
n use CV/EVA for all storage management tasks
3. Still in User Accounts, create new users within the new user groups. For example, you might
create the following users:
User Acco
Hpuser
Hpadmin HP Storage Administrators
HWP user
HWP con
4. Start E
unt
smustloginasoneoftheseusersbeforeperformingVDS/VSSoperationsusingthe
figuration utility.
VA Command View and log into it using one of the user accounts you just created.
Group
HP Storage Users
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
23
Page 24

24
Configuration
Page 25

Adding VDS/VSS hosts
1. Click the + symbol next to the EVA disk array in the left panel to expand the contents of the array
and begin con
figuration.
2. Click the Hosts folder in the left panel. The Host Folder Properties window displays.
ick Add Host and fill in the host characteristics for the VDS/VSS server. Click Add Host to save the
3. Cl
new host information. Repeat if you are adding a second server.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
25
Page 26

Adding disk gr
oups
Follow the st
Exchange or S
1. Click the Di
eps below to add a snapclone disk group for use by VSS. Some applications, such as
QL, may also require disk groups for data and logs.
sk Groups folder in the left panel. The Disk Groups Properties window displays.
2. Click the + next to the Disk Groups folder to expand Disk Groups.
3. Click Create disk group to begin creating a new disk group.
26
Configuration
Page 27

4. Enter Basic and Advanced Settings for the disk group, and click Create disk group.
5. An “operation succeeded” message indicates the disk group was added, and the new group
appears in the left panel. Click OK.
6. Repeat the previous steps as required to add the disk groups needed for your application.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
27
Page 28

28
Configuration
Page 29

3 Installa tion
This chapter explains how to install Hardware Providers (HWP) and other required software. When
you install HWP, all the features of VDS and VSS are enabled, including point-in-time copies of LUNs
and storage virtualization management.
If you have not already configured the server and the array as instructed in “Chapter 2 Configuration,”
do so now before you install the HWP software. HWP will not work if the array and server have not
been correctly configured before you install HWP.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The right combination of software versions is crucial to configuring a working system.
Refer to the Release Notes accompanying the HP HWP installation files for information about compatible
software versions and system configurations.
For HP Hardware Providers software downloads and d ocumentation, see the following web location:
ttp://www.hp.com/support/HWPEVA
h
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
29
Page 30

Installation procedures
The following procedures describe how to install the Hardware Providers.
If you have not already configuredtheserverandthearrayasinstructedin
now before you install the HWP software.
correctly configured before you install HWP. For a summary of the configuration steps, see Configuration
procedures
.
Upgrade installation
If you are upgrading from a previous version of HWP, b efore doing the installation procedure that
follows, uninstall the previous version of HWP. The uninstallation procedure is explained under the
heading Uninstalling HWP.
Installation summary
You will p
• Run the HWP installation executable(s):
• Follow t
• Accept the license terms.
• Install the HP HWPs in the default or custom folder location.
• Enter t
• Connect to the disk array.
• Select the disk group you created for VDS/VSS operations.
erform the following tasks during installation:
hp StorageWorks VDS hardware provider for EVA.msi
hp StorageWorks VSS hardware provider for EVA.msi
he InstallShield Wizard instructions to do the following tasks.
he CV workstation IP address and log into Command View EVA.
“Uninstalling HWP,”
HWP will not work if the array and server have not been
do so
30
Installation
Page 31

Installing H
WP
Installatio
package must be installed individually. Install V DS first to provide disk management capability. If you
also want to make data copies, install VSS second.
1. Before you s
2. Download and extract the HWP files from the HP VSS/VDS web page: h
3. Double cli
n for VDS and VSS is very s imilar; therefore only VSS installation is described. However, each
tart installation, use a ping command to test communication with the Command View
EVA server.
ttp://www.hp.com/
support/HWPEVA
ck the HWP installation executable:
hp StorageWorks VDS hardware provider for EVA.msi
or
hp Storage
The InstallShield Welcome window appears.
Works VSS hardware provider for EVA.msi
4. Click Next. The License Agreement window appears.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
31
Page 32

5. Click “I accept...” to agree to the license terms, and click Next. The Destination Folder window
appears.
6. Click Next to install V DS or VSS in the default location, or click Change to browse for a new location,
and then click Next. The Ready to Install window appears.
32
Installation
Page 33

7. Click Ins ta ll to start the installation. A status window shows progress.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
33
Page 34

8. When installation is completed, click Finish. The VSS-VDS Configuration Utility opens.
34
Installation
Page 35

Configuring VSS/VDS to access Command View:
1. In the Appliance IP Address text box, enter the IP address of the server where Command View
is installed
The Enter UserName and Password window pops up.
2. Enter the administrator’s User Name and Password to the Command View system. Click OK.A
“loading
Configura
list of a
and click Logon.
...” message ap pears while the system authenticates the lo gon. The system populates the
tion Utility window HSV Storage System box with the name of the disk array and (VDS) a
vailable disk groups.
If the name of the array does not appear, the logon is incorrect or a communication problem
occurred with the CV workstation. Check your logon and password and check connectivity
has
rexample,afirewall may be interfering with commun ication). Also refer to “Chapter 4
(fo
oubleshooting” for troubleshooting information.
Tr
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
35
Page 36

Selecting the
1. For VDS, click on a d isk group in the Disk Group List, and click Add to List to add the group to the list
disk group:
of Selected Disk Groups available to V DS HWP. Then click OK.
For VSS, clic
the disk gro
k Snapclone and click Select Disk Group to open the list of disk groups (below). Select
up you created for VSS copies and click OK.
If no disk gr
server duri
oups are listed, make sure you created the disk groups and presented them to the
ng configuration.
For VDS, when you click OK, the Configuration Utility window closes.
For VSS, the Configuration Utility window appears as shown below.
2. For VSS, check that the disk group you selected is d isplayed. Then click OK.
e InstallShield Wizard Completed window appears.
Th
36
Installation
Page 37

3. Click Finish. HWP installation is complete.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
37
Page 38

Adding disk groups using the VSS Configuration Utility
After installation, if you need to add disk groups, increase storage in a disk group, or select a new
Snapclone disk group, access the VSS Configuration Utility in the Windows Start/Programs menu:
Hewlett-Packard/ Hardware Providers/Provider Configuration for EVA
1. TosettheSnapClonediskgroup,checktheSnapClone option to select the snapclone type, a nd then
click Select Disk Group. The Select Disk Group window opens.
2. In the Select Disk Group window, click a disk group in the Disk Group List, and select a redundancy
type for the snapclone vdisk from the drop-down menu. Redundancy type choices include Default
(same redundancy type as the source vdisk), RAID0, RAID1, or RAID5.
3. Click OK to confirm your selections and close the windows.
38
Installation
Page 39

Verifying installation
To verify installation, perform the following tests. If you have any trouble with installation or with verifying
installation, see “Chapter 4 Troubleshooting” in this guide.
Checking the list of programs
A simple way to verify successful installation of the HP HWPs is to make sure they are listed in the
Add/Remove Programs Control Panel in Windows. To see the list of installed programs, click Windows
Start,clickSettings,clickControl Panel, and double-click Add/Remove Programs.
You can also check that the hpEVA VSS Hardware Provider is running by making sure it is listed when
you type the following at the command line:
vssadm list providers
Checking VDS disk management using DiskRaid
You can install and run the Microsoft DiskRaid command line interface and use the “list provider” and
“list sub
2003 Resource Kit and requires the HP VDS HWP in order to work with the HP disk array. The example
output below shows the use of these commands:
system” commands to verify the HP HWP is working properly. DiskRaid comes with the Windows
DISKRAID> List Provider
Prov ### Name Version
-------- --------------------------------------------- ---------* Prov 0 HPEVA VDS Hardware Provider 4.01.00
DISKRAI
D> list subsystem
Subsys ### Name Status Health
---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ----------
Subsys 0 HP EVA (SN# 12345) Online Healthy
Checking VSS volume shadow copying
Testing the HP VSS HWP requires a third party application that can work with VSS, the HP VSS HWP,
and the disk array to create hardware volume shadow copies. One such program is Microsoft’s vshadow
utility, which comes with the VSS Software Developer’s Kit.
he HWP installation by making a shadow copy of the array volumes containing p roduction data.
Test t
check whether a copy of the production data appears on the snapclone volumes of the array. If the
Then
copyisnotsuccessful,see“Chapter4Troubleshooting.”
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
39
Page 40

Uninstalling HWP
Before uninstalling VDS or VSS, issue a net stop command from the command line, as shown in these
examples:
net stop vds
net stop vss
net stop hpevavssprv
Uninstalling HWP using Windows
1. In Windows, select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Add/Remove Programs.
3. Select the program you want to remove (VDS or VSS).
4. Click Change/Remove. Windows removes the program.
Uninstalling using HWP Installer
You can al
window. Click Remove, then click Finish.
so uninstall HP HWP by starting the HP HWP installer again. Click Next to open the Remove
40
Installation
Page 41

4 Troubleshooting
This chapter explains how to troubleshoot Hardware Providers (HWP) and also presents a list of VDS and
VSS error messages and explanations.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
41
Page 42

Troubleshooting procedures
The following instructions present typical problems and solutions.
VDS/VSS HWP will not install
The HP HWP installation works only on the Windows versions listed in the Configuration chapter of this
guide and in the Release Notes supplied with the HP HWP. The installer will not install the software on
other versions of Windows.
CV authentication failure
Smart Star
EVA API. Th
is installed.
To resolve this issue, reset the HP Command View API password. This password enables any application
that uses
this utility.
To enable the HP Command View API, follow these steps:
1. Execute t
2. In the Services window restart the HP Command View EVA service.
t v7.2 may cause login failures for applications such as HP HWP using the Command View
is issue occurs when a server is built using the new SS v7.2 CD and then CV EVA software
the HP Command View API to authenticate properly. Only a system administrator can run
he following utility/command to change the password:
c:\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\SANworks\Element Manager for
StorageWorks HSV\Bin\elmsetup.exe -pA:administrator -f
where “ad
You can use any password you wish in place of “administrator”.
Applica
API corr
remains unchanged.
ministrator” equals the password for the HP Comm a nd View A PI Administrator accou nt.
tions such as HP HWP that use the Command View API should now be able to log into the
ectly. The new password is for the HP Command View API login only. The CV GUI log in
VDS disk array management not working
Use a process of elimination to determine whether the problem is with one of the following components:
• Application managing the array
• VDS
• HP HWP
• EVA disk array
Perform these tests:
1. Do the array volumes appear in the Disk Management tool? To check, in the Windows menu bar
select Start > Control Panels > Administrative Tools > Computer Management > Storage > Disk
Management. If array LUNs are not visible, click Action > Refresh and Ac tion > Scan Disks.
2. Do the array volumes appear when you use the DiskPart utility? At the Run command line,
type diskpart.exe.Typelist disk to see a list of disk devices present. (Type “help” to see a list
of commands.)
If you receive this error message: “The disk management services could not complete the
operation,” VDS is not enabled at startup. Click Start > Control Panels > Administrative Tools >
Services >right-clickVirtual Disk Service > Properties >clickManual under Startup type and
click OK.
3. Check the Release Notes that came with your HP HWP installation files to verify you are using
compatible versions of software.
42
Troubleshooting
Page 43

4. Make sure you configured the VDS/VSS Configuration Utility as explained in Chapter 3
Installation.
5. Check configuration as explained in “Chapter 2 Configuration”:
• Check LAN connectivity between all servers and the array.
• Make sure the firewall is open between all servers and the array.
• Check Command View server NIC bindings: the LAN that connects to the VDS/VSS server
must be listed first.
• Make sure you logged into all devices and software using administrator privileges.
• Visit the Microsoft website support knowledge base and search for “VDS logging.” Turn on logging
as instructed by Microsoft and use the Microsoft procedure for testing VDS and checking the log.
VSS volume c
1. Is the VSS HWP running? At the command prompt, type:
vssadm lis
You should see the hpEVA VSS hardware provider listed.
2. Verify that the Business Copy license is installed. A BC license is required in order to produce
data copie
3. Make sure
4. Check con
• Check CV workstation and VDS/VSS server connectivity.
• VDS/VSS server not connected to the SAN correctly.
•Afirewal
5. Review the Windows application event log, Windows system event log, and VSS trace to locate
errors in the snapshot process. See the Microsoft website and Windows help for information about
the log and trace files.
6. Use a process of elimination to determine which components are not working. You ca n do this
by tes
• TestVSSandthearraybyusingtheMicrosoftvshadow utility available in the Microsoft VSS
• Test your backup application and VSS together by making a backup copy on a local drive,
opying not working
tproviders
susingVSS.
you configured the VDS/VSS Utility as explained in Chapter 3 Installation.
figuration as explained in Chapter 2 Configuration:
l may be interfering with connectivity between servers.
ting components individually:
Software Developer’s Kit to create snapshots. At the command line, type:
vshadow [drive letter]
ive letter is the production LUN you want to copy. See the Microsoft documentation
The dr
for details about using vshadow.
ssing HWP and the disk array.
bypa
VSS copies intermittently fail or time out
VSS allows only 30 seconds for the entire snapshot process, including only 10 seconds for actually
making the copy. This narrow time window can cause any limitation in your system to hamper successful
snapshots. The following issues may affect system performance:
• Firewall or LAN traffic slowing or preventing communication. Reconfigure the firewall or LAN to
increase throughput.
• Viruses slowing server operation. Check for and clean off viruses.
• VDS/VSS server is too slow. Use a fast, late mode CPU with sufficient memory.
• Inadequate privileges. Administrator privileges are required in all applications and on all
hardware used with HP VSS HWP .
• Writer application not configured according to best practices. Consult the soft ware manufacturer
for recommended practices. For example, keeping database files small by creating more rather
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
43
Page 44

than larger files may speed up overall operation and database copying. Saving transaction logs
to a different volume than the database may also speed up performance.
• Review the Windows application event log, Windows system event log, and VSS trace to locate
errors in the snapshot process. See the Microsoft website and Windows help for information
about the log and trace files.
44
Troubleshooting
Page 45

Error messages
The following tables list error messages and their meanings.
VDS error messages
Message Id MessageID Value
(hex)
VDS_E_NOT_SUPPORTED 0x80042400L
VDS_E_INITIALIZED_FAILED 0x80042401L
VDS_E_INITIALIZE_NOT_CALLED 0x80042402L
VDS_E_ALREADY_REGISTERED 0x80042403L
VDS_E_ANOTHER_CALL_IN_PROGRESS 0x80042404L
VDS_E_OBJECT_NOT_FOUND 0x80042405L
VDS_E_INVALID_SPACE 0x80042406L
VDS_E_PARTITION_LIMIT_REACHED 0x80042407L
VDS_E_PARTITION_NOT_EMPTY 0x80042408L
VDS_E_O
VDS_E_OPERATION_DENIED 0x8004240AL
VDS_E_OBJECT_DELETED
VDS_E_CANCEL_TOO_LATE 0x8004240CL
VDS_E_OPERATION_CANCELED 0x8004240DL
VDS_E_CANNOT_EXTEND 0x8004240EL
VDS_E
VDS_E_NOT_ENOUGH_DRIVE 0x80042410L
PERATION_PENDING
_NOT_ENOUGH_SPACE
0x80042
0x8004240BL
0x800
409L
4240FL
Message Text
The operati
or there is i
The service failed to initialize.
The initialization method is not called.
The provid
A concurrent second call is made on a n
object before the first is completed.
The object is not found.
The specified space is not free or not valid.
Number of partitions has reached the limit
on a disk.
The extended partition is not empty.
The operation has not been completed yet.
This operation is not allowed on the current
boot, system or page file volume.
The object has been deleted.
The ope
it is to
The operation has b een cancelled.
Thevolumecannotbeextendedbecause
the file system does not support it.
There
opera
Not enough drives are specified to complete
this operation.
on is not supported by the object,
nadequate disk space.
er is already registered.
ration cannot be cancelled because
olate.
is not enough usable space for this
tion.
VDS_E_BAD_COOKIE 0x80042411L
E_NO_MEDIA
VDS_
VDS_E_DEVICE_IN_USE 0x80042413L
VDS_E_DISK_NOT_EMPTY 0x80042414L
VDS_E_INVALID_OPERATION 0x80042415L
VDS_E_PATH_NOT_FOUND 0x80042416L
VDS_E_DISK_NOT_INITIALIZED 0x80042417L
VDS_E_NOT_AN_UNALLOCATED_DISK 0x80042418L
VDS_E_UNRECOVERABLE_ERROR 0x80042419L
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
0x80
042 412L
The cookie is not found.
There is no media in the device.
The device is in use.
The disk is not empty.
lid operation.
Inva
The path is not found.
The disk is not initialized.
disk is not unallocated.
The
Unrecoverable error happened. The service
must shut down.
45
Page 46

Message Id MessageID Value
(hex)
Message Text
VDS_S_DISK_PARTIALLY_CLEANED 0x0004241AL
VDS_E_DMADMIN_SERVICE_
CONNECTION_FA ILED
VDS_E_PROVIDER_INITIALIZATION_ FAILED 0x8004241CL
VDS_E_OBJECT_EXISTS
VDS_E_NO_DISKS_FOUND 0x8004241EL
VDS_E_PROVID
VDS_E_DMADMIN_METHOD_CALL_FAILED
VDS_S_PROVIDER_ERROR_LOADING_CACHE
VDS_E_PROV
VICE_NAME_
VDS_E_PROVIDER_VOL_OPEN 0x80042423L
VDS_E_DMADMIN_CORRUPT_NOTIFICATION
VDS_E_INC
VDS_E_INCOMPATIBLE_MEDIA 0x80042426L
VDS_E_ACCESS_DENIED 0x80042427L
VDS_E_ME
ER_CACHE_CORRUPT
IDER_VOL_DE-
NOT_FOUND
OMPATIBLE_FILE_SYSTEM
DIA_WRITE_PROTECTED
0x8004241BL
0x8004241DL
0x8004241FL
0x80042420L
0x00042421L
0x80042422L
0x80042424L
0x8004242
0x800424
5L
28L
The disk is not fully cleaned due to I/O error.
The provider failed to connect to the Logical
Disk Management Administrative service.
The provider failed to initialize.
The object already exists.
No disks were found on the target machine.
The provider’s cache has become corrupt.
A method call to the Logical Disk
Management Administrative service failed.
The provider encountered errors while
loading the cache. See the NT Event Log
for more i nformation.
The device form of the volume pathname
could not be retrieved.
Failed to open the volume device.
A corrupt notificationwassentfromthe
Logical Disk Manager Administrative
service.
The file sys
The media is incompatible.
Access is denied.
The media is write protected.
tem is incompatible.
HRESULT VDS_E_BAD_LABEL 0x80042429L
VDS_E_CANT_QUICK_FORMAT 0x8004242AL
VDS_E_IO_ERROR
VDS_E_VOLUME_TOO_SMALL 0x8004242CL
VDS_E_VOLUME_TOO_BIG 0x8004242DL
VDS_E_C
VDS_E_CLUSTER_SIZE_TOO_BIG
VDS_E_CLUSTER_COUNT_BEYOND_32BITS
VDS_E_
VDS_E_VOLUME_INCOMPLETE 0x80042432L
VDS_E_EXTENT_SIZE_LESS_THAN_MIN 0x80042433L
VDS_S_
VDS_S_BOOT_PARTITION_NUMBER_CHANGE
LUSTER_SIZE_TOO_SMALL
OBJECT_STATUS_
UPDATE_BOOTFILE_FAILED
0x800424
0x80042
0x8004242FL
0x80042430L
0x8004
0x0004
0x00042436L
2BL
42EL
2431L
2434L
The label is illegal.
Can not quick format the volume.
IO error o
Thevolumesizeistoosmall.
Thevolumesizeistoobig.
The cluster size is too small.
The cluster size is too big.
Thenumberofclustersistoobigfor32bit
integer.
The obj
All extents for the volume could not be
found.
Thesizeoftheextentislessthanthe
minimum.
Failed
The boot partition’s partition number
will change as a result of the migration
operation.
ccurred during format.
ect is in failed status.
to update the boot.ini file or NVRAM.
46
Troubleshooting
Page 47

Message Id MessageID Value
(hex)
Message Text
VDS_E_BOOT_PARTITION_NUMBER_CHANGE
VDS_E_NO_FREE_SPACE 0x80042437L
VDS_E_ACTIVE_PARTITION 0x80042438L
VDS_E_PARTITION_OF_UNKNOWN_TYPE 0x80042439L
VDS_E_LEGACY_VOLUME_FORMAT 0x8004243AL
VDS_E_NON
PARTITION
VDS_E_MIGRATE_OPEN_VOLUME 0x8004243CL
VDS_E_VOLUME_NOT_ONLINE 0x8004243DL
VDS_E_VOLUME_NOT_HEALTHY 0x8004243EL
_CONTIGUOUS_DATA_
S
0x80042436L
0x8004243
BL
The migration operation failed. The boot
partition’s partition number will change as
a result of the migration operation.
The migration operation failed. The selected
disk does not have enough free space to
complete the operation.
The migration operation failed. An active
partition was detected on the selected disk,
and it is not the active partition used to boot
the currently running OS.
The migration operation failed. Cannot
read partition information.
The migration operation failed. A partition
with an unknown type was detected on the
selected disk.
The migrat
selected GPT formatted disk contains a
non-basic-data partition, which is both
preceded, and followed, by a basic data
partition(s).
The migration operation failed. A volume
on the selected disk could not be opened.
Operation failed. The volume is not online
Operation failed. The volume is not healthy.
ion operation failed. The
VDS_E_VOLUME_SPANS_DISKS 0x8004243FL
VDS_E_REQUIRES_CONTIGUOUS_DISK_SPACE
VDS_E_BAD_PROVIDER_DATA 0x80042441L
VDS_E_PROVIDER_FAILURE 0x80042442L
VDS_S_VOLUME_COMPRESS_FAILED 0x00042443L
VDS_E_PACK_OFFLINE 0x80042444L
VDS_E_VOLUME_NOT_A_MIRROR 0x80042445L
VDS_E_NO_EXTENTS_FOR_VOLUME 0x80042446L
VDS_E_DISK_NOT_LOADED_TO_CACHE 0x80042447L
VDS_E_INTERNAL_ERROR 0x80042448L
VDS_S_ACCESS_PATH_NOT_DELETED 0x000042449L
_PROVIDER_TYPE_NOT_SUPPORTED
VDS_E
VDS_E_DISK_NOT_ONLINE 0x8004244BL
0x80042440L
4244AL
0x800
Operation failed. The volume spans multiple
disks.
Operation failed. The volume consists of
multiple extents.
Aprovid
A provider failed to complete an operation.
Failed to compress the volume.
The operation failed. The pack is not online.
Break or remove plex operation failed. The
volume is not a mirror.
No extents were found for the volume.
Themigrateddiskfailedtoloadtothe
cache.
Check the event log for errors.
The access paths on the volume may not
be deleted.
The me
speci
The repair operation failed. The disk is
already in use by the volume.
er returned bad data.
thod call is not supported for the
fied provider type.
VDS_S_IN_PROGRESS 0x0004244DL
VDS_E_ASYNC_OBJECT_FAILURE 0x8004244EL
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
The asynchronous operation is in progress.
ure initializing the asynchronous object.
Fail
47
Page 48

Message Id MessageID Value
(hex)
Message Text
VDS_E_VOLUME_NOT_MOUNTED 0x8004244FL
VDS_E_PACK_NOT_FOUND 0x80042450L
VDS_E_IMPORT_
VDS_E_DISK_NOT_IMPORTED 0x80042452L
VDS_E_OBJECT_OUT_OF_SYNC 0x80042453L
VDS_E_MISSING_ 0x80042454L
VDS_E_DISK_PNP_REG_CORRUPT 0x80042455L
VDS_E_LBN_REMAP_ENABLED_FLAG 0x80042456L
VDS_E_NO_D
VDS_E_REVERT_ON_CLOSE 0x80042458L
VDS_E_REVERT_ON_CLOSE_SET 0x80042459L
VDS_E_REV
SET_INCOMPLETE
RIVELETTER_FLAG
ERT_ON_CLOSE_MISMATCH
0x80042451L
0x80042457
0x8004245
9L
Thevolumeisnotmounted.
The pack was not found.
Import failed.
the disks in the
A disk in the import’s source pack was not
imported.
The system’s information about the object
may not be up to date.
Operation failed. The disk is missing.
The provider’s list of Pnp registered disks
has become corrupt.
The provider does not support the LBN
REMAP ENABLED volume flag.
L
The provider does not support the NO
DRIVELETTER volume flag.
REVERT ON CLOSE should only be set if the
HIDDEN or READ ONLY volume flag is set.
AREVERTONCLOSEvolumeflag is already
set for this volume.
When clear
been set us
combination of HIDDEN and/or READ
ONLY flags must be passed to both the
SetFlags and ClearFlags calls.
Attempt to import a subset of
foreign pack.
ing volume flags that have
ing revert on close, the same
VDS_E_IA64_BOOT_MIRRORED_TO_MBR 0x8004245AL
VDS_S_IA64_BOOT_MIRRORED_TO_MBR 0x0004245AL
VDS_S_UNABLE_TO_GET_GPT_ATTRIBUTES
VDS_E_VOLUME_TEMPORARILY_
DISMOUNTED
VDS_E_VOLUME_PERMANENTLY_
DISMOUNTED
VDS_E_VOLUME_HAS_PATH 0x8004245EL
VDS_E_TIMEOUT 0x8004245FL
VDS_E_REPAIR_VOLUMESTATE 0x80042460L
S_E_LDM_TIMEOUT
VD
0x0004245BL
0x8004245CL
0x8004245DL
80042461L
0x
Not Used! You have mirrored your boot
volume on a GPT disk, to a n MBR disk. You
willnotbeabletobootyourmachinefrom
the secondary pl ex.
You have mirrored your boot volume on
a GPT disk, to an MBR disk. You will not
be able to boot your machine from the
secondary plex.
Unable to retrieve the GPT attributes for this
volume, (hidden, read only and no drive
letter).
The volume is temporarily dismounted.
Thevolumeispermanentlydismounted.
volume still has access path to it.
The
The operation timed out.
The operation could not be completed. To
repair a volume, both the volume and plex
must be online, and must not be healthy or
rebuilding.
The operation timed out in the Logical Disk
Manager Administrative service. Retry the
operation.
48
Troubleshooting
Page 49

Message Id MessageID Value
(hex)
Message Text
VDS_E_PLEX_NOT_REGENERATED 0x80042462L
VDS_E_RETRY
VDS_E_ONLINE_PACK_EXISTS 0x80042464L
VSS error messages
Error
VSS_E_BAD_STATE 0x80042301L
VSS_E_PROVIDER_ALREADY_REGISTERED 0x80042303L
VSS_E_PROVIDER_NOT_REGISTERED 0x80042304L
VSS_E_PROVIDER_VETO
VSS_E_PROVIDER_IN_USE 0x80042307L
VSS_E_OB
VSS_S_ASYNC_PENDING 0x00042309L
JECT_NOT_FOUND
The operation failed. Cannot retain plex
that has not regenerated.
0x80042463L
The operation failed. Retry the operation.
Create pack operation failed. An online
pack already exists.
Meaning Corrective A
A function call was invalid because of
the state of either the backup extensions
or the coordinator. For example calling
AddToSnapshot set prior to calling
StartSnapshotSet.
Calling RegisterProvider.
registerProvider.
0x80042306L
0x800423
08L
Calling Un
Calling DoSnapshotSet.
Calling UnregisterProvider, StartSnapshotSet.
Calling DeleteSnapshots, Q uery.
Calling IVssAsync:: QueryStatus.
ction
VSS_S_ASYNC_FINISHED 0x0004230AL
VSS_S_ASYNC_CANCELLED 0x0004230BL
VSS_E_VOLUME_NOT_SUPPORTED 0x8004230CL
VSS_E_OBJECT_ALREADY_EXISTS 0x8004230DL
VSS_E_V
BY_PRO
VSS_E_UNEXPECTED_PROVIDER_ERROR 0x8004230FL
VSS_E_CORRUPT_XML_DOCUMENT 0x80042310L
VSS_E
VSS_E_MAXIMUM_NUMBER_OF_VOLUMES_REACHED
VSS_E_FLUSH_WRITES_TIMEOUT 0x80042313L
VSS_E_HOLD_WRITES_TIMEOUT 0x80042314L
VSS_E_UNEXPECTED_WRITER_ERROR 0x80042315L
VSS_E_SNAPSHOT_SET_IN_PROGRESS 0x80042316L
OLUME_NOT_SUPPORTED_
VIDER
_INVALID_XML_DOCUMENT
0x80042
0x800
0x80042312L
30EL
42311L
Calling IVssAsync::QueryStatus.
Calling
Calling AddToSnapshotSet.
Calling ExposeCurrentState.
Calling AddToSnapshotSet.
Calling several methods supported by the
providers.
XML document unexpectedly does not match
schema.
AnXMLdocumentpassesasanargumentis
not va
XML o
We cannot add any more volumes since we
passed the maximum limit.
VSS couldn’t flush I/O writes anymore.
VSS couldn’t hold I/O writes anymore.
VSS encountered problems while sending
events to writers.
StartSnapshotSet was called when another
snapshot set in in the process of being
created.
IVssAsync::QueryStatus.
lid, i.e., is either not correctly formed
r does not match the schema.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
49
Page 50

Error
VSS_E_MAXIMUM_NUMBER_
OF_SNAPSHOTS_REACHED
VSS_E_WRITER
VSS_E_WRITER_NOT_RESPONDING 0x80042319L
VSS_E_WRITER_ALREADY_SUBSCRIBED 0x8004231AL
_INFRASTRUCTURE
Meaning Corrective Actio n
0x80042317L
0x80042318L
AddToSnapshotSet was called on a volume
that has already reached its maximum
number.
The Writer infr
properly. Che
theVolumeSna
and check for e
services in t
A writer did not respond to a GetWriterStatus
call. This means that the process containing
the writer died or is hung.
A writer has already successfully called the
Subscribe function. It cannot call subscribe
multiple times.
astructure is not operating
ck tha t the Event Service and
pshot Service are started
rrors associated with these
he error log.
VSS_E_UNSUPPORTED_CONTEXT 0x8004231BL
VSS_E_VOLUME_IN_USE 0x8004231DL
VSS_E_MAXIMUM_DIFFAREA_
ASSOCIATIONS_REACHED
VSS_E_IN
VSS_E_NO_SNAPSHOTS_IMPORTED 0x80042320L
VSS_S_SOME_SNAPSHOTS_NOT_IMPORTED
VSS_E_
TENTSN
VSS_E_WRITERERROR_OUTOFRESOURCES 0x800423F1L
VSS_E_WRITERERROR_TIMEOUT 0x800423F2L
VSS_E_WRITERERROR_RETRYABLE 0x800423F3L
VSS_E_WRITERERROR_NONRETRYABLE 0x800423F4L
VSS_E_WRITERERROR_RECOVERY_FAILED 0x800423F5L
SUFFICIENT_STORAGE
WRITERERROR_ INCONSIS-
APSHOT
0x8004231EL
0x800423
0x00042320L
0x8004
1FL
23F0L
Attempt to
Calling Chan geD iffAreaMaximumSize
Calling AddDiffArea.
Calling EndPrepareSnapshots,
ChangeDi
Calling ImportSnapshots, no volumes were
successfully imported.
Calling ImportSnapshots, some volumes
were not successfully imported.
Indicates that the snapshot contains only a
subset of the volumes needed to correctly
backup an application component.
Indicates that the writer failed due to an out
of memory, out of handles, or other resource
allocation failure.
Indicates that the writer failed due to a
timeout between freeze and thaw.
Indicates that the writer failed due to
an error that m ight not occur if another
snapshot is created.
Indicates that the writer failed due to an
error that most likely would occur if another
snapshot were created.
Indicates that auto recovery of the snapshot
volume failed.
use an unsupported context.
ffAreaMaximumSize
50
Troubleshooting
Page 51

Glossary
This glossary defines acronyms and terms used in this guide or related to this product and is not a
comprehensive glossary of computer terms.
API Application Programming Interface, an interface that allows a software
clone A full copy of a volume, usable by an application.
CV HP StorageWorks CommandView, a browser-based interface that allows
application to connect to and work with a third party software application.
management of an HP disk array.
differential copy A copy of a database consi
the last full copy.
disk array A RAID. A collection of disk drives within a cabinet or multiple cabin ets and
including a controller and software allowing d rives to be ganged together in
various configurations to create virtual drives (LUNs).
EVA HP StorageWorks Enterprise Vir
FC Fibre Channel, a fiber optic interconnection standard commonly used for
storage area networks.
GUI Graphical User Interface.
HBA Host bus adapter. The FC interface card that installs in a host to connect the
host to a fabric SAN.
HWP Hardware Providers. A collection of software that executes on the host, a bus
adapter, and the disk array to enable managing and/or copying of array LUNs
through the Windows OS and applications.
LAN Local Area Network.
LUN Logical Unit Number. A physically addressable storage unit as surfaced by a
hardware RAID subsystem. A virtual disk, consisting of multiple portions of
physical disks addressed as a single unit.
mirror Synonymous with “clone.”
sting only of the differences in the database since
tual Array.
MSA HP StorageWorks Modular Smart Array.
plex A Microsoft term denoting a full copy of data that has been split off from the
original and is no longer being updated. Synonymous with “split mirror.”
PVOL Primary volume. Typically the volume where application data is stored.
RAID Redundant array of independent disks.
SVOL Secondary volume. The volume that receives backup copies of data.
SAN fabric The Fibre Channel hardware and cabling that connects servers to storage
devices in a Storage Area Network (SAN) is referred to as a “fabric.” A fabric
switch provides automatically-switched connectivity between servers a nd storage
in the fabric.
SNMP Simple Network Manag em ent Protocol.
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
51
Page 52

shadow copy A Microsoft term describing a point-in-time copy of an original volume. The
original volume continues to change as the process continues, but the shadow
copyofthevolumeremainsconstant.
snapclone An HP EVA disk array term denoting a full copy of a volume that becomes
immediately usable by an application. Created much faster than ordinary
clones by taking a snapshot and updating to a full copy in the b ackground.
snapshot A generic term meaning a static point-in-time copy of a volume, typically used
for backup.
split mirror A full copy of data that has been split off from the original and is no longer
being updated.
subsystem Synonym for “disk array” or “RAID.”
SVP Service processor. A laptop PC built into the HP XP Disk Array. The SVP
provides a direct interface into the disk array, and is used by the HP service
representative only.
volume Generic term for a number of physical disks or portions of disks logically
bound together as a virtual disk containing contiguous logical blocks. Volume
can also be software shorthand for a mapped volume (Windows drive letter
or mount point).
VDS Microsoft Virtual Disk Service, the Windows service that manages storage
through hardware providers.
volume shadow
See “shadow copy.”
copy
VSC Volume Size Configuration, a feature of HP disk arrays that allows creation of
logical volumes custom-sized according to user requirements.
VSS Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Ser vice, the Windows ser vice that creates data
copies. Works through HP HWP to make copies of disk array volumes.
XP HP StorageWorks XP Disk Array.
52
Glossary
Page 53

Index
A
additional servers
configuring,22
applications
HWP,15
VDS,15
VSS,15
array
configuration,17,21
audience,5
B
Business Copy,20
C
command line utilities,13
Command View,20
configuration for HWP ,21
Command View management station,19
components,12
hardware,19
HWP,11
required,18
software,20
configuration,17
additional servers,22
array,17
array and server,21
disk array,23
important notes,20
summary,21
configuration diagram,18
conventions
text symbols,6
conventions, document,
D
disk array,19
configuring,23
overview,15
disk group
installation,36
disk management,13
DiskPart,13
DiskRaid,13
document conventions,
documentation
providing feedback,7
related,5
documentation, HP web site,5
E
error messages,41,45
F
fabric switch,19
fibre cables,19
files
EVA.msi,31
FRS,13,16
functional components,12
G
glossary,51
H
hardware components,19
HBAs,19
help
obtaining,7
HP
storage web site,7
technical support,7
HWP,20
applications,15
installing,31
uninstalling,40
HWP overview,14
HWP server
configuring,22
I
installation,29
disk group,36
HWP,31
summary,30
upgrade,30
verifying,39
M
management applications,13
MPIO,20
N
network interface cards,19
HP StorageWorks EVA Hardware Providers administration guide
53
Page 54

O
overview,9
components,12
detailed,11
disk array,15
HWP,9,14
simple,10
VDS,11,14
VSS, 11, 14
Windows,13
P
passwords
Enter CV Password field,31
performance issues,20
R
related documentation,5
S
server configuration,21
server, HWP
configuring,22
software components,20
software providers,13
Subscriber’s Choice, HP,7
symbols in text,6
T
technical support
HP,7
service locator web site,7
text symbols,6
third party applications,13
troubleshooting, 41, 42
U
uninstalling HWP,40
upgrade
installation,30
V
VDS
applications,15
overview,11
VDS overview,14
VDS/VSS server,19
verifying installation,39
Vshadow,13
VSS
applications,15
overview, 11, 14
VSS process flow,14
W
web sites,5
HP,7
HP documentation,7
HP storage,7
HP Subscriber’s Choice for Business,7
Windows
overview,13
54
 Loading...
Loading...