Page 1

Network & Internet
Communications Guide
Business Desktops
Document Part Number: 312968-001
February 2003
This guide provides definitions and instructions for using network
interface controller (NIC) features that are preinstalled on select
models. It also provides information about Internet Service Providers
and solving Internet access problems.
Page 2

© 2002 Hewlett-Packard Company © 2002 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
HP, Hewlett Packard, and the Hewlett-Packard logo are trademarks of
Hewlett-Packard Company in the U.S. and other countries.
Compaq and the Compaq logo are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Development
Company, L.P. in the U.S. and other countries.
Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the U.S.
and other countries.
All other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective
companies.
Hewlett-Packard Company shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or
omissions contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in
connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material. The
information in this document is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind,
including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and
fitness for a particular purpose, and is subject to change without notice. The
warranties for HP products are set forth in the express limited warranty
statements accompanying such products. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright.
No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to
another language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard
Company.
WARNING: Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow
Å
directions could result in bodily harm or loss of life.
CAUTION: Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow
Ä
directions could result in damage to equipment or loss of information.
Network & Internet Communications Guide
Business Desktops
First Edition (February 2003)
Document Part Number: 312968-001
Page 3

Contents
1 Network Communications
Ethernet Network Structure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
NIC-Based Alerts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
Wake-On-LAN Support (WOL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
Interpreting the Network Status Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–4
Disabling 802.3u Auto-Negotiation Capabilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–5
Installing Network Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–7
2 Internet Communications
Choosing an Internet Service Provider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Content Advisor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Restricting Internet Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Solving Internet Access Problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com iii
Page 4

Page 5

1
Network Communications
The following items are covered in this section:
■ Ethernet Network Structure
■ Network Interface Controller (NIC)-Based Alerts
■ Wake-On-Lan (WOL) Support
■ Interpreting the Network Status Lights
■ Disabling the Autosensing Capabilities
■ Installing Network Drivers
This section provides information about Ethernet networks and the
hardware connectors and software device drivers that allow you to
access an Ethernet network. Access to a computer network
immediately increases your productivity potential. Once the network
connection is active, you can share resources, such as a printer,
exchange information from computer to computer, and run common
software programs.
The computer comes network-ready, which means that it has an
integrated network controller and network device drivers already
loaded onto the computer hard drive. The computer is ready to make
the network connection.
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com 1–1
Page 6
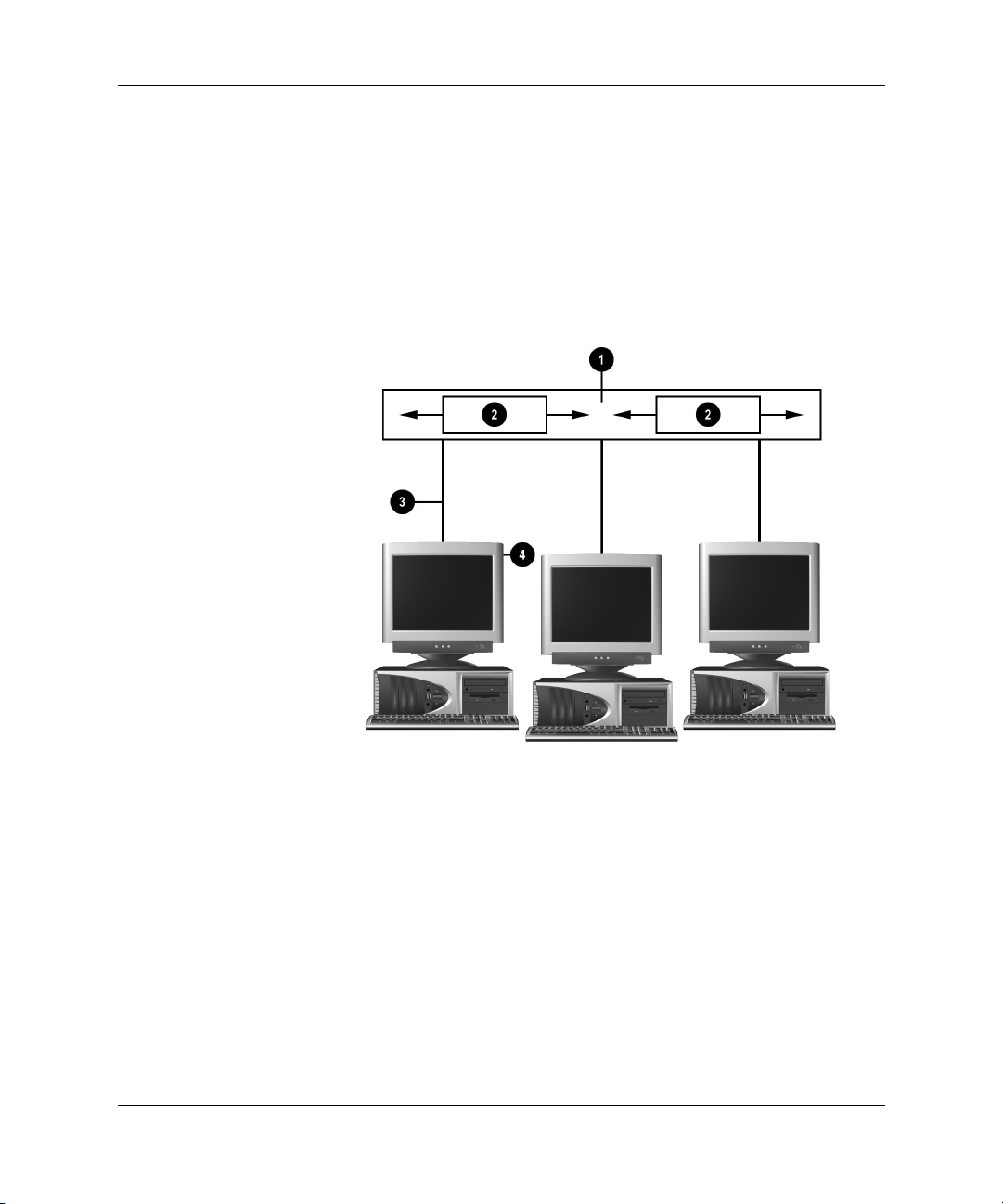
Network Communications
Ethernet Network Structure
All Ethernet networks include some combination of the following
elements:
1 Ethernet cable 3 Drop cables
2 Information packets 4 Workstations
Ethernet Network Structure
Refer to the Hardware Reference Guide for network connector
identification and connection instruction.
1–2 www.hp.com Network & Internet Communications Guide
Page 7

NIC-Based Alerts
Some NICs feature Alerting Capabilities, which allow a system
administrator to monitor the computer over the network remotely. The
computer can send hardware and operating system alerts over the
network before the operating system is loaded, while the operating
system is loaded, while the computer is in low power states, and when
the computer is powered off. Depending on the NIC model, these
alerts may include:
■ System BIOS hang
■ Operating system hang
■ Processor missing
■ Operating temperature exceeded
■ Chassis intrusion
■ Watchdog
■ Heartbeat monitoring
NICs featuring Alerting Capabilities comply with Alert Standard
✎
Format (ASF) specification 1.0. RMCP events are not supported due
to lack of security in the ASF 1.0 specification.
NIC-Based Alerts are enabled and configured by installing the
ASF 1.0 agents for the NIC you are using. These are available at
http://www.hp.com. ASF alerts can also be enabled and configured
using DMI or CIM.
Network Communications
Wake-On-LAN Support (WOL)
Wake-On-Lan (WOL) can be enabled and disabled in Windows 2000
and Windows XP.
To enable or disable Wake-On-Lan:
Windows 2000
1. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network Dial-up Connections.
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com 1–3
Page 8

Network Communications
✎
3. Double-click Local Area Connection.
4. Click Properties.
5. Click Configure.
6. Click the Power Management tab, then select or clear the check
box to Allow this device to bring the computer out of standby.
Windows XP
1. Select Start > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network Connections.
3. Double-click Local Area Connection.
4. Click Properties.
5. Click Configure.
6. Click the Power Management tab, then select or clear the check
box to Allow this device to bring the computer out of standby.
For more information on Wake-On-LAN, refer to the online Desktop
Management Guide or to the Remote Management Administrators
Guide. The Remote Management Administrators Guide is included
with the Remote Management Setup Utilities and is available on the
Support Software CD or at http://www.compaq.com.
For information on filtering out unintentional Wake-On-LAN events,
✎
refer to any additional documentation provided for the NICs
advanced diagnostics/configuration utility.
Interpreting the Network Status Lights
Select Ethernet network interface controllers include network status
lights:
■ Link light—illuminates when the system is physically connected
to an active network.
■ Activity light—illuminates when the computer detects network
activity. When the system is connected to a highly used
network, the activity light will remain on almost constantly.
1–4 www.hp.com Network & Internet Communications Guide
Page 9

Network Communications
■ Operating Speed light—illuminates during 1000 Mbps or
100 Mbps operation. The color of the light identifies the
operating speed.
Some NICs include only two network status lights where link
(light on) and activity (light blinking) are indicated by one light and
1000-Mbps or 100-Mbps operation is indicated by the second light.
The integrated NIC has two network status lights on the NIC
connector:
■ Link/Activity light—Illuminates green when physically linked to
the network and blinks on and off to indicate network activity.
■ Operating Speed light—Illuminates green when operating at
1000 Mbps, yellow when operating at 100 Mbps, and is not
illuminated when operating at 10 Mbps.
Disabling 802.3u Auto-Negotiation Capabilities
Auto-Negotiation NICs automatically determine the maximum
network operating speed and duplex capabilities of the attached
network and configure themselves on the highest common
combination. The computer begins Auto-Negotiation whenever it
obtains a valid network link, or when the NIC driver is loaded.
In addition to determining the network operating speed, the computer
determines if full-duplex is supported. Full-duplex systems can
transmit and receive information on the network simultaneously.
Half-duplex systems cannot transmit and receive simultaneously.
If necessary, you can disable the Auto-Negotiation capabilities and
force the system to operate in one mode only.
Windows 2000
1. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network Connections.
3. Double-click Local Area Connection.
4. Click Properties.
5. Click Configure.
6. Click the Advanced tab.
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com 1–5
Page 10

Network Communications
7. Select Link Speed/Duplex Mode in the Property list box.
8. Change the speed and duplex values to the appropriate values,
depending on the capabilities of the network.
9. Click OK. You may be prompted to restart the computer for the
changes to take effect.
Windows XP
1. Select Start > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network Connections.
3. Double-click Local Area Connection.
4. Click Properties.
5. Click Configure.
6. Click the Advanced tab.
7. Select Link Speed & Duplex in the Property list box.
8. Change the speed and duplex values to the appropriate values,
depending on the capabilities of the network.
9. Click OK. You may be prompted to restart the computer for the
changes to take effect.
Refer to the documentation provided with the network controller for
additional information.
100Base-TX and 1000Base-Tx operation requires the use of Category
✎
5 UTP cable with an RJ-45 network connection.
1–6 www.hp.com Network & Internet Communications Guide
Page 11

Installing Network Drivers
The device drivers in the network software enable the computer to
communicate with the network. Because Compaq does not know
which network operating system you’ll be using, the computer comes
ready to work with several different environments.
The device drivers for the network controller enable the drivers to
load correctly in the operating system used, allowing communication
with the network.
Device drivers are supplied for the Windows 2000, Windows XP
✎
Professional, and Windows XP Home operating systems, depending
on the computer model. If you are using another operating system,
device drivers may be installed from media included with the network
operating system or are available from HP. If it ever becomes
necessary to reinstall the operating system, use the Compaq Restore
Plus! CD.
Complete instructions for installing the network device drivers are
available as ASCII text files, located in the C:\COMPAQ\NIC
directory. Use the instructions found in the subdirectory that relates to
the network environment.
Network Communications
Install the correct device drivers according to the operating system
you are using, as listed below.
Windows 2000
Follow the instructions in the ASCII text files located in the
C:\CPQNET directory. Use the instructions found in the subdirectory
that relates to the network environment.
Windows XP
1. Select Start > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network Connections.
3. Double-click the New Connection Wizard icon and follow the
instructions on the screen.
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com 1–7
Page 12

Page 13

Internet Communications
The following items are covered in this section:
■ Choosing an Internet Service Provider
■ Content Advisor
■ Solving Internet Access Problems
Choosing an Internet Service Provider
An Internet service provider (ISP) gives you the dial-up (telephone or
cable networking) access and software you need to connect to the
Internet. Most ISPs also offer e-mail, access to newsgroups, space to
create Web pages, and technical support. Some ISPs offer commercial
services, such as domain hosting, to companies and individuals
wanting to do business on the Internet. You can choose from local and
national ISPs.
An online service provider, such as MSN or America Online (AOL),
offers special features, content, and technical support in addition to
providing access to the Internet. An online service provider may
provide a categorized or customizable home page that makes it easy
for you to find some of the most popular and useful sites on the
Internet.
2
To find the provider that is right for you:
■ Look in the Yellow Pages
■ Ask a friend or colleague for recommendations
■ If you have access to the Internet already, you can use a search
engine, such as Google, to help you locate an ISP or online
service provider.
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com 2–1
Page 14

Internet Communications
■ ISPs typically offer a variety of service plans for different
Content Advisor
The Internet provides you with access to a wide variety of
information, but some information may not be suitable for every
viewer.
With Content Advisor, you can:
■ Control Internet access
■ Set up a password
■ Set up a list of Web sites that people who use the computer cannot
■ Adjust the types of content people who use the computer can
customers’ needs. Be sure to review and compare plans, services
offered, and price to find the provider that is right for you and
your needs.
view
view with or without your permission
Restricting Internet Content
Windows 2000
If you have not previously enabled Content Advisor:
1. On the Windows desktop, select Start > Settings >Control
Panel.
2. Double-click Internet Options.
3. Click the Content tab.
4. In the Content Advisor area, click the Enable button.
5. Click a category in the list, then drag the slider to set the limits
you want to use. Repeat this process for each category you want
to limit.
6. Click OK, then type your password in the Password box. A
dialog box will inform you that Content Advisor has been turned
on. Click OK.
Internet Communications www.hp.com Network & Internet Communications Guide
Page 15

Internet Communications
If you have previously enabled Content Advisor:
1. Select Start > Settings >Control Panel.
2. Double-click Internet Options.
3. Click the Content tab.
4. To change the settings:
a. Click the Settings button. Type your password and click OK.
b. Click a category in the list, then drag the slider to set the
limits you want to use. Repeat this process for each category
you want to limit.
5. To disable Content Advisor:
a. Click the Disable button. Type your password and click OK.
b. A dialog box will inform you that Content Advisor has been
turned off. Click OK.
Windows XP
If you have not previously enabled Content Advisor:
1. Select Start > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Internet Options.
3. Click the Content tab.
4. In the Content Advisor area, click the Enable button. If you have
previously created a password for Internet settings, you will be
prompted for your password now.
5. Click a category in the list, then drag the slider to set the limits
you want to use. Repeat this process for each category you want
to limit.
6. Click OK, then type your password in the Password box. A
dialog box will inform you that Content Advisor has been turned
on. Click OK.
If you have previously enabled Content Advisor:
1. Select Start > Control Panel.
2. Double-click Internet Options.
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com 2–3
Page 16

Internet Communications
3. Click the Content tab.
4. To change the settings:
a. Click the Settings button. Type your password and click OK.
b. Click a category in the list, then drag the slider to set the
limits you want to use. Repeat this process for each category
you want to limit.
5. To disable Content Advisor:
a. Click the Disable button. Type your password and click OK.
b. A dialog box will inform you that Content Advisor has been
turned off. Click OK.
Solving Internet Access Problems
If you encounter Internet access problems, consult the ISP or refer to
the common causes and solutions listed in the following table.
Solving Internet Access Problems
Problem Cause Solution
Unable to connect to the
Internet.
Internet Communications www.hp.com Network & Internet Communications Guide
Internet Service Provider
(ISP) account is not set
up properly.
Modem is not set up
properly.
Web browser is not set
up properly.
Cable/ DSL modem is
not plugged in.
Cable/DSL service is
not available or has
been interrupted due to
bad weather.
Verify Internet settings or contact the
ISP for assistance.
Reconnect the modem. Verify the
connections are correct using the
quick setup documentation.
Verify that the Web browser is
installed and set up to work with the
ISP.
Plug in cable/DSL modem. You
should see a “power” LED light on
the front of the cable/DSL modem.
Try connecting to the Internet at a
later time or contact the ISP. (If the
cable/DSL service is connected, the
“cable” LED light on the front of the
cable/DSL modem will be on.)
Page 17

Solving Internet Access Problems (Continued)
Problem Cause Solution
Unable to connect to the
Internet. (continued)
The CAT5 10/100
cable is disconnected.
Connect the CAT5 10/100 cable
between the cable modem and the
computers’s RJ-45 connector. (If the
connection is good, the “PC” LED
light on the front of the cable/DSL
modem will be on.
Internet Communications
Cannot automatically
launch Internet programs.
IP address is not
configured properly.
Cookies are corrupted.
(A “cookie” is a small
piece of information
that a Web server can
store temporarily with
the Web browser. This
is useful for having the
browser remember
some specific
information that the
Web server can later
retrieve.)
You must log on to the
ISP before some
programs will start.
Contact the ISP for the correct IP
address.
Windows 2000
1. Select Start > Settings >
Control Panel.
2. Double-click Internet
Options.
3. On the General tab, click the
Delete Cookies button.
Windows XP
1. Select Start > Control
Panel.
2. Double-click Internet
Options.
3. On the General tab, click the
Delete Cookies button.
Log on to the ISP and launch the
desired program.
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com 2–5
Page 18

Internet Communications
Solving Internet Access Problems (Continued)
Problem Cause Solution
Internet takes too long to
download Web sites.
Modem is not set up
properly.
Verify that the correct modem speed
and COM port are selected.
Windows 2000
1. Select Start > Settings >
Control Panel.
2. Double-click System.
3. Click the Hardware tab.
4. In the Device Manager area,
click the Device Manager
button.
5. Double-click Ports (COM &
LPT).
6. Right-click the COM port the
modem uses, then click
Properties.
7. U n d e r Device status, verify
that the modem is working
properly.
8. Under Device usage, verify
the modem is enabled.
9. If there are further problems,
click the Troubleshoot button
and follow the on-screen
instructions.
Internet Communications www.hp.com Network & Internet Communications Guide
Page 19

Solving Internet Access Problems (Continued)
Problem Cause Solution
Internet takes too long to
download Web sites.
(continued)
Modem is not set up
properly. (continued)
Verify that the correct modem speed
and COM port are selected.
(continued)
Windows XP
1. Select Start > Control
Panel.
2. Double-click System.
3. Click the Hardware tab.
4. In the Device Manager area,
click the Device Manager
button.
5. Double-click Ports (COM &
LPT).
6. Right-click the COM port the
modem uses, then click
Properties.
7. U n d e r Device status, verify
that the modem is working
properly.
8. Under Device usage, verify
the modem is enabled.
9. If there are further problems,
click the Troubleshoot button
and follow the on-screen
instructions.
Internet Communications
Network & Internet Communications Guide www.hp.com 2–7
Page 20

 Loading...
Loading...