Page 1

INSTALLATION & SERVICE
INDUSTRIAL PUMPS
Models: D-04, G-04
WANNER ENGINEERING, INC.
1204 Chestnut Avenue, Minneapolis, MN 55403
TEL: (612) 332-5681 FAX: (612) 332-6937
TOLL-FREE FAX [US only]: (800) 332-6812
www.hydra-cell.com
email: sales@wannereng.com
Page 2

D/G-04 Contents
Page
Specifications......................................................................... 2
Dimensions ............................................................................ 4
Installation.............................................................................. 5
Maintenance .......................................................................... 9
Service (Fluid End) .............................................................. 10
Service (Hydraulic End)....................................................... 14
Troubleshooting ................................................................... 17
D/G-04 Specifications
Max Pressure 2,500 psi (170 bar)
Capacity @ Max Pressure
rpm gpm I/min
D/G-04-X 1750 2.9 11.0
D/G-04-E 1750 2.1 7.8
D/G-04-S 1750 1.6 6.1
Delivery @ Rated Pressure
revs/gal
500 psi 1500 psi 2500 psi
D/G-04-X 565 583 603
D/G-04-E 761 795 833
D/G-04-S 921 972 1,093
revs/liter
35 bar 100 bar 170 bar
D/G-04-X 149 154 159
D/G-04-E 201 211 224
D/G-04-S 244 257 287
Max Inlet Pressure 500 psi (35 bar)
Max Temperature 250°F (121°C) – consult factory for
temperatures above 160°F (71°C)
Inlet Port D-04: 1/2 inch NPT
G-04: 1/2 inch BSPT
Discharge Port D-04: 1/2 inch NPT
G-04: 1/2 inch BSPT
Shaft Diameter 7/8 inch (22.22 mm)
Shaft Rotation Bi-directional
Bearings Ball bearings
Oil Capacity 1.1 US quarts (1.05 liters)
Weight 37 lbs (16.8 kg)
Calculating Required
Horsepower (kW)*
6 x rpm
63,000
6 x rpm
84,428
* rpm equals pump shaft rpm. HP/kW is required application
power. Use caution when sizing motors with variable speed
drives.
+
+
gpm x psi
1,460 –
gpm x bar
511 –
psi – 500
(
bar – 35
(
4
20
=
electric motor HP*
)
=
electric motor kW*
)
2 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 3
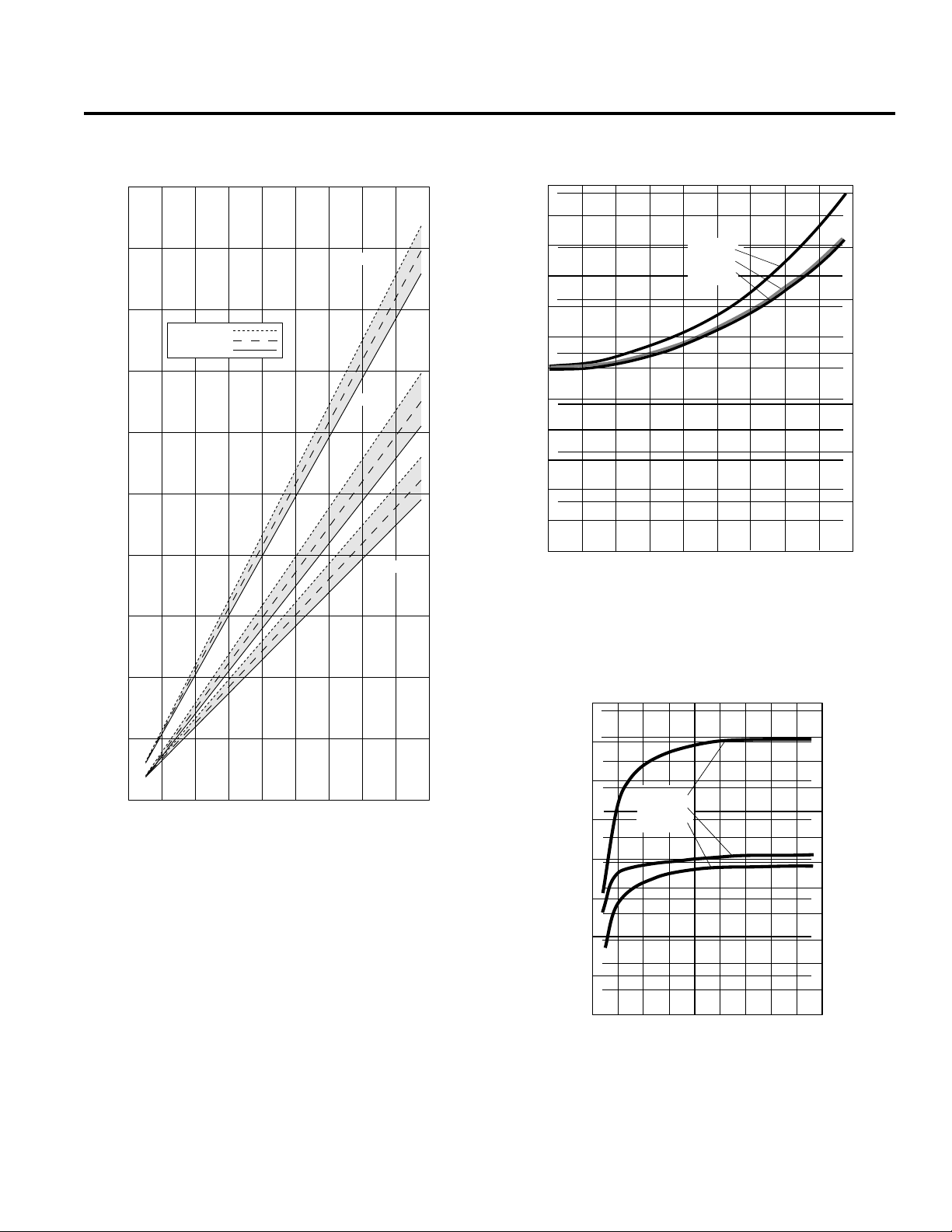
D/G-04 Specifications
Performance Net Positive Suction Head –
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
3.33
3.00
2.66
500 PSI (35 bar)
1500 PSI (100 bar)
2500 PSI (170 bar)
2.33
RPM
D/G-04-X
12.5
1750
11.25
10
8.75
NPSHr
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
D/G-04-X
D/G-04-E
D/G-04-S
3.5
1750
3.0
2.5
2.0
2.00
1.66
Gallons per Minute
1.33
1.00
0.66
0.33
D/G-04-E
D/G-04-S
7.5
6.25
Liters per Minute
5.0
3.75
2.5
1.25
0
0
5
NPSHr (feet of water)
4
3
2
1
0
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
RPM
Dry Lift
8.0
7.0
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
Lift (feet of water)
2.0
1.0
0
0
D/G-04-X
D/G-04-E
D/G-04-S
200 400 600 800 10001200 14001600 1800
RPM
240
1750
220
200
180
160
140
120
100
1.5
NPSHr (meters of water)
1.0
0 .5
Lift (cm of water)
80
60
40
20
3 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 4
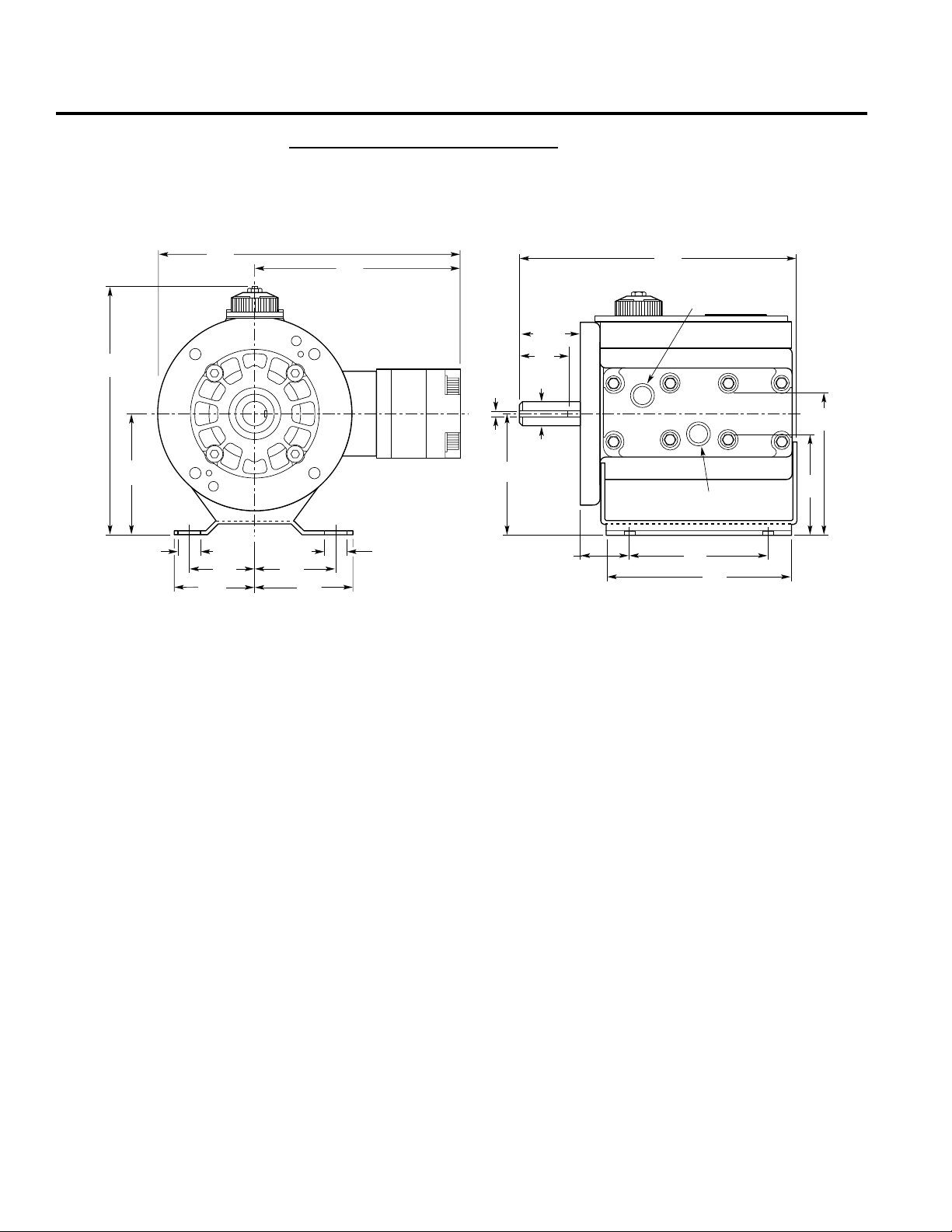
D/G-04 Dimensions
D/G-04 Models with Metallic Pumping Head
Brass
304 Stainless Steel
316 Stainless Steel
8.71
(221.2)
4.25
(108)
0.75
(19.1)
10.38
(263.7)
(57.2)
2.75
(69.9)
2.25
2.75
(69.9)
3.35
(85.1)
7.01
(178)
0.75
(19.1)
0.189
(4.8)
4.250
(107.9)
2.25
(57.2)
1.73
(43.9)
Good Key
0.875
(22.23)
1.71
(43.4)
9.93
(252.2)
Outlet
5.00
(127)
Inlet
D-04: 1/2" NPT
G-04: 1/2" BSPT
D-04: 1/2" NPT
G-04: 1/2" BSPT
6.55
(166)
3.52
(89.4)
4.97
(126)
4 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 5
D/G-04 Installation
NOTE: The numbers in parentheses are the Reference
Numbers on the illustrations in the Parts Manual.
Location
Locate the pump as close to the supply source as possible.
Install it in a lighted clean space where it will be easy to inspect
and maintain. Allow room for checking the oil level, changing
the oil, and removing the pump head (manifold, valve plate and
related items).
Mounting
The pump shaft can rotate in either direction.To prevent
vibration, securely attach the pump to a rigid base.
On a belt-drive system, align the sheaves accurately; poor
alignment wastes horsepower and shortens the belt and bearing
life. Make sure the belts are properly tightened, as specified by
the belt manufacturer.
On a direct-drive system, align the shafts accurately. Unless
otherwise specified by the coupling manufacturer, maximum
parallel misalignment should not exceed .015” and angular
misalignment should be held to 1 degree maximum. Careful
alignment extends life of the coupling, pump, shafts, and support
bearings. Consult coupling manufacturer for exact alignment
tolerances.
On a close-coupled system, coat the motor shaft liberally with
anti-seize.
Important Precautions
Adequate Fluid Supply. To avoid cavitation and
premature pump failure, be sure that the pump will have
an adequate fluid supply and that the inlet line will not be
obstructed. See “Inlet Piping”.
Positive Displacement. This is a positive-displacement
pump. To avoid severe system damage if the discharge
line ever becomes blocked, install a relief valve
downstream from the pump. See “Discharge Piping”.
Safety Guards. Install adequate safety guards over all
pulleys, belts, and couplings. Follow all codes and
regulations regarding installation and operation of the
pumping system.
Shut-Off Valves. Never install shut-off valves between
the pump and discharge pressure regulator, or in the
regulator bypass line.
Freezing Conditions. Protect the pump from freezing.
See also the Maintenance Section.
Consult the Factory for the following situations:
• Extreme temperature applications above 160° F (71°C)
or below 40° F (4°C)
• Pressure feeding of pumps
• Viscous or abrasive fluid applications
• Chemical compatibility problems
• Hot ambient temperatures above 110° F(43°C)
• Conditions where pump oil may exceed 200° F (93°C)
because of a combination of hot ambient temperatures,
hot fluid temperature, and full horsepower load — an
oil cooler may be required
5 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 6

D/G-04 Installation
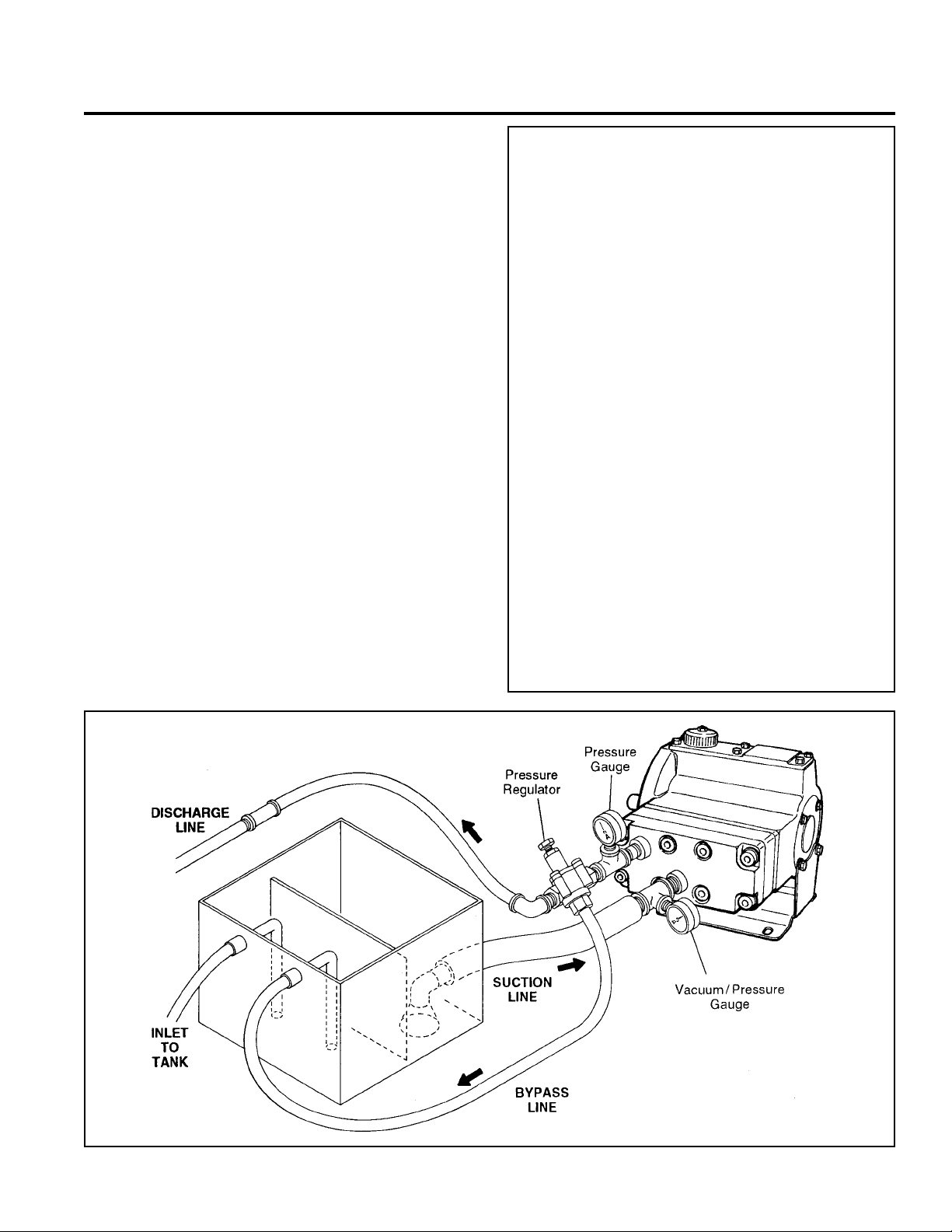
Inlet Piping (Suction Feed)
CAUTION: When pumping at temperatures above 160° F
(71
° C), use a pressure-feed system.
Install draincocks at any low points of the suction line, to permit
draining in freezing conditions.
Provide for permanent or temporary installation of a vacuum
gauge to monitor the inlet suction. To maintain maximum flow,
vacuum at the pump inlet should not exceed 7 in. Hg at 3 gpm
and 70° F (180 mm Hg at 11.4 liters/min and 21° C). Do not
supply more than one pump from the same inlet line.
Supply Tank
Use a supply tank that is large enough to provide time for any
trapped air in the fluid to escape. The tank size should be at
least twice the maximum pump flow rate.
Isolate the pump and motor stand from the supply tank, and
support them separately.
Install a separate inlet line from the supply tank to each pump.
Install the inlet and bypass lines so they empty into the supply
tank below the lowest water level, on the opposite side of the
baffle from the pump suction line.
If a line strainer is used in the system install it in the inlet line to
the supply tank.
To reduce aeration and turbulence, install a completely
submerged baffle plate to separate the incoming and outgoing
liquids.
Install a vortex breaker in the supply tank, over the outlet port
to the pump.
Place a cover over the supply tank, to prevent foreign objects
from falling into it.
Inlet Piping (Pressure Feed)
Provide for permanent or temporary installation of a vacuum/
pressure gauge to monitor the inlet vacuum or pressure.
Pressure at the pump inlet should not exceed 500 psi (34 bar);
if it could get higher, install an inlet pressure regulator.
Do not supply more than one pump from the same inlet line.
Inlet Calculations
Acceleration Head
Calculating the Acceleration Head
Use the following formula to calculate acceleration head losses.
Subtract this figure from the NPSHa, and compare the result to
the NPSHr of the Hydra-Cell pump.
Ha = (L x V x N x C) ÷ (K x G)
where:
Ha = Acceleration head (ft of liquid)
L= Actual length of suction line (ft) — not equivalent length
V= Velocity of liquid in suction line (ft/sec) [V = GPM x (0.408 ÷
N=RPM of crank shaft
C=Constant determined by type of pump — use 0.066 for the
K= Constant to compensate for compressibility of the fluid —
G=Gravitational constant (32.2 ft/sec2)
2
pipe ID
D-04 and G-04 Hydra-Cell pumps
use: 1.4 for de-aerated or hot water; 1.5 for most liquids;
2.5 for hydrocarbons with high compressibility
)]
Hose Size and Routing
Use the shortest, most-direct route from the supply tank to the
pump. If elbows are needed, 45° are recommended. Any
restrictions in the inlet piping may cause pump output to drop.
Do not install any 90
• Use flexible noncollapsible hose between the pump and rigid
piping or supply tank. This will absorb vibration, and allow
for expansion or contraction.
• Use the largest practical hose. The smallest permissible size
is 5/8 in. (16 mm) I.D.
• All valves, fittings, and unions must also have 5/8-in. (16
mm) minimum I.D. Do not exceed 5 feet of hose and piping
between and supply tank and the pump inlet.
• Support the pump and piping independently.
• Make sure all joints are sealed and tight, to prevent the pump
from drawing air into the inlet.
• Do not use a line strainer or filter in the suction line unless
regular maintenance is assured. If used, it should have a
free-flow area of at least three times the free-flow area of
the inlet.
Loctite is a registered trademark of Loctite Corporation.
Teflon is a registered trademark of E. I. DuPont de Nemours & Co. Inc.
° elbows in the pump inlet.
6 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 7

D/G-04 Installation
Friction Losses
Calculating Friction Losses in Suction Piping
When following the above recommendations (under “inlet
Piping”) for minimum hose/pipe I.D. and maximum length,
frictional losses in the suction piping are negligible (i.e., Hf = 0)
if you are pumping a water-like fluid.
When pumping more-viscous fluids such as lubricating oils,
sealants, adhesives, syrups, varnishes, etc., frictional losses
in the suction piping may become significant. As Hf increases,
the available NPSH (NPSHa) will decrease, and cavitation will
occur.
In general, frictional losses increase with increasing viscosity,
increasing suction-line length, increasing pump flowrate, and
decreasing suction-line diameter. Changes in suction-line
diameter have the greatest impact on frictional losses: a 25%
increase in suction-line diameter cuts losses by more than two
times, and a 50% increase cuts losses by a factor of five times.
Consult the factory before pumping viscous fluids.
Minimizing Acceleration Head and Frictional Losses
To minimize the acceleration head and frictional losses:
• Keep inlet lines less than 3 ft (1 m) long
• Use at least 5/8 in. (16 mm) I.D. inlet hose
• Use soft hose (low-pressure hose, noncollapsing) for the
inlet lines
• Minimize fittings (elbows, valves, tees, etc.)
• Use a suction stabilizer on the inlet.
Net Positive Suction Head
NPSHa must be equal to or greater than NPSHr. If not, the
pressure in the pump inlet will be lower than the vapor pressure
of the fluid— and cavitation will occur.
Calculating the NPSHa
Use the following formula to calculate the NPSHa:
NPSHa = Pt + Hz - Hf - Ha - Pvp
where:
Pt = Atmospheric pressure
Hz = Vertical distance from surface liquid to pump centerline (if
liquid is below pump centerline, the Hz is negative)
Hf = Friction losses in suction piping
Ha = Acceleration head at pump suction
Pvp = Absolute vapor pressure of liquid at pumping temperature
NOTES:
• In good practice, NPSHa should be 2 ft greater than NPSHr
• All values must be expressed in feet of liquid
Atmospheric Pressure at Various Altitudes
Altitude Pressure Altitude Pressure
(ft) (ft of H
0 33.9 1500 32.1
500 33.3 2000 31.5
1000 32.8 5000 28.2
O) (ft) (ft of H2O)
2
Discharge Piping
NOTE: Consult the Factory before manifolding two or more
pumps together.
NOTE: Single-acting pumps create a pulsing flow. Using
pulsation dampening devices in the discharge line can
reduce or eliminate this.
Hose and Routing
Use the shortest, most-direct route for the discharge line.
Select pipe or hose with a working pressure rating of at least
1.5 times the maximum system pressure. EXAMPLE: Select a
3000-psi W.P.-rated hose for systems to be operated at 2000psi-gauge pressure.
Use about 6 ft (1.8 m) of flexible hose between the pump and
rigid piping.
Support the pump and piping independently.
Pressure Regulation
IInstall a pressure regulator or unloader in the discharge
line. Bypass pressure must not exceed the pressure limit of
the pump.
Size the regulator so that, when fully open, it will be large enough
to relieve the full capacity of the pump without overpressurizing
the system.
Locate the valve as close to the pump as possible and ahead
of any other valves.
Adjust the pressure regulating valve to no more than 10% over
the maximum working pressure of the system. Do not exceed
the manufacturer’s pressure rating for the pump or regulator.
Route the bypass line to the supply tank, or to the suction line
as far as possible from the pump (to reduce the chance of
turbulence and cavitation).
If the pump may be run for a long time with the discharge closed
and fluid bypassing, install a thermal protector in the bypass
line (to prevent severe temperature buildup in the bypassed
fluid).
CAUTION: Never install shutoff valves in the bypass line
or between the pump and pressure regulator or relief valve.
Provide for permanent or temporary installation of a pressure
gauge to monitor the discharge pressure at the pump.
For additional system protection, install a “pop-off” safety relief
valve in the discharge line, downstream from the pressure
regulator.
7 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 8

D/G-04 Installation
Before Initial Start-Up
Before you start the pump, be sure that:
• All shutoff valves are open, and the pump has an adequate
supply of fluid.
• All connections are tight.
• The oil level is 1/4 inch (6 mm) above the cast surface in
the upper oil reservoir.
• The relief valve on the pump outlet is adjusted so the pump
starts under minimum pressure.
• All pulleys and belts are properly aligned, and belts are
tensioned according to specification.
• All pulleys and belts have adequate safety guards.
Initial Start-Up Procedure
1. Turn on power to the pump motor.
2. Check the inlet pressure or vacuum. To maintain maximum
flow, inlet vacuum must not exceed 7 in. Hg at 70° F (180
mm Hg at 21° C). Inlet pressure must not exceed 500 psi
(34 bar).
3. Listen for any erratic noise, and look for unsteady flow. If
the pump does not clear, refer to the Trouble-shooting
Section.
4. If the system has an air lock and the pump fails to prime:
a. Turn off the power.
b. Remove the pressure gauge or plug from the tee fitting
at the pump outlet (refer to the illustration on page 3).
NOTE: Fluid may come out of this port when the plug
is removed. Provide an adequate catch basin for fluid
spillage, if required. Fluid will come out of this port when
the pump is started, so we recommend that you attach
adequate plumbing from this port so fluid will not be
sprayed or lost. Use high-pressure-rated hose and
fittings from this port. Take all safety precautions to
assure safe handling of the fluid being pumped.
c. Jog the system on and off until the fluid coming from
this port is air-free.
d. Turn off the power.
e. Remove the plumbing that was temporarily installed,
and reinstall the pressure gauge or plug.
5. Adjust the discharge pressure regulator to the desired
operating and bypass pressures. Do not exceed the
maximum pressure rating of the pump.
6. After the pressure regulator is adjusted, set the “pop-off”
safety relief valve at 100 psi (7 bar) higher than the desired
operating pressure. To verify this setting, adjust the
discharge pressure regulator upward until the relief valve
opens. Follow the recommendations in the above NOTE
(step 4b) for handling the fluid that will come from the relief
valve.
7. Reset the discharge pressure regulator to the desired system
pressure.
8. Provide a return line from the relief valve to the supply tank,
similar to the bypass line from the pressure regulator.
8 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 9

D/G-04 Maintenance
NOTE: The numbers in parentheses are the Ref. Nos. on
the illustrations in the Parts Manual.
Daily
Check the oil level and the condition of the oil. The oil level
should be 1/4 in. (6 mm) above the cast surface in the upper oil
reservoir.
Use the appropriate Hydra-Oil for the application (contact
Wanner Engineering if in doubt).
CAUTION: If you are losing oil but don’t see any external
leakage, or if the oil becomes discolored and contaminated,
one of the diaphragms (17) may be damaged. Refer to the
Fluid-End Service Section. Do not operate the pump with a
damaged diaphragm.
CAUTION: Do not leave contaminated oil in the pump
housing or leave the housing empty. Remove contaminated
oil as soon as discovered, and replace it with clean oil.
Periodically
Change the oil after the first 100 hours of operation, then change
according to the quidelines below. When changing, remove the
drain plug (60) at the bottom of the pump so all oil and
accumulated sediment will drain out.
Hours Between Oil Changes @ Various
Process Fluid Temperatures
<90°F <139°F<180°F
Pressure RPM (32°C) (60°C) (82°C)
<1500 psi (100 bar) <1200 6,000 4,000 2,000
<1800 3,000 2,000 1,500
<2500 psi (170 bar) <1200 3,000 2,000 1,500
<1800 1,500 — 1,000
Shutdown Procedure During
Freezing Temperatures
Take all safety precautions to assure safe handling of the
fluid being pumped. Provide adequate catch basins for fluid
drainage and use appropriate plumbing from drain ports,
etc., when flushing the pump and system with a compatible
antifreeze.
1. Adjust the discharge pressure regulating valve so the pump
runs under minimum pressure. Stop the pump.
2. Drain supply tank; open any draincocks in system piping
and collect drainage. Drain as much fluid from the pump
manifold and plumbing attached directly to the pump
manifold by loosening fittings or removing plugs or gauges.
3. Close draincocks in system piping and tighten or replace
any fittings, gauges or plugs.
4. Fill supply tank with enough antifreeze to fill system piping
and pump.
NOTE: Disconnect the system return line from the
supply tank and connect it to a separate reservoir.
5. Start the pump and allow it to run until the system is filled
with antifreeze. NOTE: If the system has an airlock and
the pump fails to prime, follow step 4 of the Initial Startup Procedure to clear the air.
6. When mostly antifreeze is flowing from the system return
line, stop the pump. Connect the system return line back to
the supply tank and circulate the antifreeze for a short period.
7. It is also good practice to change the oil in the hydraulic end
before storage for an extended period. This will remove any
accumulated condensation and sediment from the oil
reservoir. Drain and refill the hydraulic end with the
appropriate Hydra-Oil and operate the pump for a short
period to assure smooth performance.
NOTE: Minimum oil viscosity for proper hydraulic end
lubrication is 16-20 cST (80-100 SSU).
NOTE: Use of an oil cooler is recommended when process
fluid and/or hydraulic end oil exceeds 180
CAUTION: Do not turn the drive shaft while the oil reservoir
is empty.
Check the inlet pressure or vacuum periodically with a gauge.
If vacuum at the pump inlet exceeds 7 in. Hg (180 mm Hg),
check the inlet piping system for blockages. If the pump inlet is
located above the supply tank, check the fluid supply level and
replenish if too low.
CAUTION: Protect the pump from freezing. Refer also to
the “Shutdown Procedure”.
°F (82°C).
9 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 10

D/G-04 Service (Fluid End)
Bolt Torque Specifications
Ref. No. D-04 G-04
1 50 ft-lbs 70 Nm
17 10 in-lbs 110 Ncm
10 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 11

D/G-04 Service (Fluid End)
NOTE: The number in parentheses are the Reference
numbers on the illustration at right and in the Parts Manual.
This section explains how to disassemble and inspect all easily
serviceable parts of the pump. Repair procedures for the
hydraulic end (oil reservoir) of the pump are included in a later
section of the manual.
CAUTION: Do not disassemble the hydraulic end unless you
are a skilled mechanic. For assistance, contact Wanner
Engineering (TEL 612-332-5681 or FAX 612-332-6937) or the
distributor in your area.
CAUTION: The two capscrews (16) that screw through the
diaphragm plate in the pump housing hold the diaphragm plate
over the hydraulic end of the pump. Do not remove them except
when repairing the hydraulic end.
Tools and Supplies
• Straightedge (at least 6 in. long)
• Grease or petroleum jelly
• Torque wrench, rated to at least 50 ft-lbs (70 N-m)
• Emery cloth
• 1/2-in. drive socket wrench
• 5/16-in. (8-mm) open-end wrench
• 5-mm hex Allen wrench
• 8-mm hex bit socket (1/2 inch drive)
• Wanner D-04/G-04 Tool Kit, which includes the following:
• Seat puller
• Plunger holder
• Plunger guide lifter
• Shaft rotator
2. Inspect Valves (5-11)
The three inlet and three outlet valve assemblies are identical
(but face in opposite directions). Inspect each valve as
follows:
a. Check the spring retainer (10), and replace if worn.
b. Check the valve spring (8). If shorter than a new spring,
replace it (do not stretch a used spring).
c. Check the valve (7). If worn excessively, replace it.
d. Remove the valve seat (6), O-ring (5), and dampening
washer (11) (See note below). A seat puller is included
in the Wanner Tool Kit. Inspect all parts for wear. In all
instances, O-ring (5) should be replaced. Replace the
valve seat and/or dampening washer if necessary.
NOTE: On newer pump models, the dampening
washer (11) is not used because the valve seat (6) is
thicker. When replacing the valve seat on an older
pump model which has dampening washers, do
reinstall the dampening washers as the new valve
seat is thicker than the original.
e. Reinstall the valve assemblies:
• Clean the valve ports and shoulders with emery cloth,
and lubricate them with lubricating gel or petroleum jelly.
• Install the O-ring (5) on the valve seat (6).
• Inlet (3 lower valves in the illustration below). Insert
the spring retainer (10) into the valve plate, then insert
the spring, valve, Tetra seal, valve seat, and dampening
washer (8,7,9,6,11). A flat O-ring (Tetra seal, 9) goes
between the retainer and seat.
• Outlet (3 upper valves in the illustration below).
Insert the dampening washer, valve seat, Tetra seal,
valve, and spring, then the retainer. Install the flat O-ring
(Tetra seal, 9) between the retainer and seat.
not
Service Procedures
1. Remove Manifold (3) and Valve
Plate (12)
a. Remove all eight capscrews (1) around the manifold.
Use an 8-mm hex Allen wrench.
b. Remove the manifold (3).
c. Inspect the manifold for warping or wear around the inlet
and outlet ports. If wear is excessive, replace the
manifold.
To check if the manifold is warped, place a straightedge
across it. A warped manifold should be replaced.
d. Remove the two socket-head capscrews (14) that hold
the valve plate to the pump housing. Use a 5-mm hex
Allen wrench.
e. Inspect the valve plate in the same manner as the
manifold, for excessive wear and/or warping. Replace if
necessary.
11 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 12

D/G-04 Service (Fluid End)
3. Inspect and Replace
Diaphragms (17)
a. Lift a diaphragm by one edge, and turn the pump shaft
until the diaphragm moves up to “top dead center”. This
will expose machined cross-holes in the plunger shaft
behind the diaphragm.
b. Insert the plunger holder tool through one of the
machined cross-holes, to hold the diaphragm up. (Don’t
remove the tool until the new diaphragm is installed in
step “f” below.)
c. Unscrew the diaphragm. Use a 5/16-in. (8-mm) open-
end wrench, and turn counterclockwise.
d. Inspect the diaphragm carefully. A damaged diaphragm
generally indicates a pumping system problem and
replacing only the diaphragm will not solve the larger
problem. Inspect the diaphragm for the following:
• Small puncture. Usually caused by a sharp foreign
object in the fluid, or by an ice particle.
• Diaphragm pulled away from the metal insert. Usually
caused by excessive inlet vacuum, or by
overpressurization of the pump inlet.
• Outer diaphragm bead extruded. Usually caused by
overpressurization of the pump.
• Diaphragm becoming stiff and losing flexibility.
Usually caused by pumping a fluid that is incompatible
with the diaphragm material.
• Cut diaphragm convolute. Usually caused by
excessive inlet vacuum.
CAUTION: If a diaphragm has ruptured and foreign
material or water has entered the oil reservoir, do
not operate the pump. Check all diaphragms, then
flush the reservoir completely (as outlined below)
and refill it with fresh oil. Never let the pump stand
with foreign material or water in the reservoir, or with
the reservoir empty.
e. Clean away any spilled oil.
f. Install a good or new diaphragm and tighten to 10 in.-lbs
(110 N-cm).
g. Repeat the above inspection procedure (and
replacement, if necessary) with the other two
diaphragms.
4. Flush Contaminant from
Hydraulic End
(only if a diaphragm has ruptured)
a. With the valve plate and manifold still removed (see
above), remove the oil drain cap (60) allow all oil and
contaminant to drain out.
b. Fill the reservoir with kerosene or solvent, manually turn
the pump shaft to circulate the kerosene, and drain.
Dispose of this contaminated fluid properly.
c. Repeat the flushing procedure (step “b” above).
d. Fill the reservoir with fresh oil, manually turn the pump
shaft to circulate the oil, and drain again.
e. Refill the reservoir. If the oil appears milky, there is still
contaminant in the reservoir. Repeat the flushing
procedure until the oil appears clean.
5. Prime the Hydraulic Cells
a. With the pump horizontal, fill the reservoir with the
appropriate Hydra-oil for the application.
b. All air in the oil within the hydraulic cell (behind the
diaphragms) must be forced out by turning the shaft —
and thus pumping the piston. Use a glove when turning
the shaft by hand.
Turn the shaft until a bubble-free flow of oil comes from
behind all the diaphragms. Watch the oil level in the
reservoir: if it gets too low during priming, air will be drawn
into the piston (inside the hydraulic end). This will cause
the pump to run rough, and you will have to start over
again with priming the hydraulic cells.
c. After the Hydra-Cells are fully primed, ensure that the
oil level is 1/4 in. (6 mm) above the cast surface in the
upper oil reservoir.
d. Wipe excess oil from the diaphragm plate and
diaphragms.
12 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 13

D/G-04 Service (Fluid End)
6. Reinstall Valve Plate (12) and
Manifold (3)
a. Reinstall the valve plate (12), with the valve assemblies
installed as outlined above, onto the diaphragm plate
(18) and alignment pins (29).
Tighten the two socket-head capscrews evenly and
snugly to compress the outer diaphragm beads and hold
the valve plate in place.
b. Reinstall the O-rings (4) on the front side of the valve
plate. Use petroleum jelly or lubricating gel to hold them
in place.
c. Reinstall the manifold onto the valve plate.
d. Insert all capscrews (1), with washers (2), around the
edge of the manifold, and alternately tighten opposite
bolts until all are secure. Torque to 50 ft-lbs (70 N-m).
e. Recheck all bolts for tightness and proper torque.
13 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 14

D/G-04 Service (Hydraulic End)
14 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 15

D/G-04 Service (Hydraulic End)
NOTE: The numbers in parentheses are the Ref. Nos. on
the illustrations in the Parts Manual.
This section explains how to disassemble and inspect the
hydraulic end (oil reservoir) of the pump.
CAUTION: Do not disassemble the hydraulic end unless
you are a skilled mechanic. For assistance, contact Wanner
Engineering (TEL 612-332-5681 or F AX 612-332-6937) or the
distributor in your area.
Depending on the repair you are attempting, you may or may
not have to remove the motor from a direct-drive pump/motor
unit.
Internal piston components (21-27) can be serviced without
removing the motor or crankshaft. The motor and crankshaft
must be removed to service the connecting rod (59), piston
housing (20), crankshaft (57), front bearing (68), back bearing
(56), or seal (54).
Tools and Supplies
• Tools required for hydraulic end only:
• Snap-ring pliers
• Small hook
• 8-mm socket wrench
T o Service Pistons Without
Removing Motor or Crankshaft
1. Disassemble Pistons
With the manifold, valve plate, diaphragm plate, and
diaphragms removed, and the oil drained from the pump
(see the Fluid-End Service Section):
a. Remove the snap ring (27) from one of the pistons, using
a standard snap-ring pliers.
b. Pull out the valve plunger (24). This also removes the
washer (26) and spring (25).
c. Insert a small hook through the center hole of the valve
cylinder (22), and pull the cylinder out of the piston. Be
careful not to damage the piston.
d. Inspect all parts, and replace the O-ring and any other
parts that are worn or may be damaged.
e. Repeat steps “a” through “d” for the remaining pistons.
2. Reassemble Pistons
a. Tip the pump so the pistons are vertical.
b. Drop a ball (21) into the opening in the bottom of the
piston.
c. Insert the valve plunger (24) into a valve cylinder (22).
Slide a spring (25) over the plunger, inside the valve
cylinder.
d. Slide the assembled valve cylinder, plunger, and spring
(22-25) into the piston (20).
e. Insert the washer (26) over the plunger.
f. Using the snap-ring pliers, insert a snap ring (27) into
the piston.
g. Repeat the above procedure for the other two pistons.
To Service Remainder of
Hydraulic End
1. Remove Pump Housing
a. Remove the manifold, valve plate, diaphragm plate, and
diaphragms, as outlined in the Fluid-End Service Section.
b. Drain the oil from the pump housing by removing the
drain plug (60).
c. Stand the pump on end, with the drive shaft up.
d. Remove the bolts (50) that secure the back cover (52)
to the housing (78). Use an 8-mm socket wrench. Save
the O-rings (51).
e. Remove the cover and the cover O-ring (53).
f. Remove the crankshaft (57) by pulling it through the
connecting rods (59).
2. Remove and Replace Pistons
To remove the pistons (20), first remove the connecting rod
(59) and pin (58) by pressing the pin through the connecting
rod.
Reverse the process to reinstall the piston.
Refer to Steps 5 and 6 below to replace the diaphragm and
reassemble the pump.
15 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 16

D/G-04 Service (Hydraulic End)
3. Replace Shaft Seal
NOTE: Inspect the shaft seal (54) before continuing. If
it looks damaged in any way, replace it.
a. Press the back bearing (55) and seal (54) out of the cover
(52). Discard the seal.
b. Apply a coating of Loctite High-Performance Pipe Sealant
with Teflon
surface of a new seal and the inside surface of the
opening in the back cover (52) where the seal will rest.
c. Press the new seal into the back cover.
d. Inspect the bearing (55). If pitted or damaged, replace
it.
e. Apply a coating of Loctite Rc/609 Retaining Compound
or comparable product to the outer surface of the bearing.
Press the bearing into the back cover until it rests on the
shoulder. The shield on the bearing must face away from
the back cover.
©
, or a comparable product, to the outer
4. Reassemble Housing and
Back Cover
a. Stand the pump on end.
b. With the pistons and connecting rods in place, reinstall
the crankshaft by threading it through the connecting
rods.
c. Reinstall the back cover, cover O-ring, and bolts (with
their O-rings).
5. Reinstall Diaphragms
a. Screw the plunger guide lifter (from the Wanner T ool Kit
or Repair Kit) into the valve plunger (24). Pull out to
expose the cross holes in the plunger. Rotate the shaft
until the piston is at top dead center.
b. Insert the plunger holder tool (from the Wanner T ool Kit),
through the plunger hole — to hold the plunger away
from the diaphragm plate (18), and to keep the plunger
from turning when the diaphragm is being installed.
c. Engage the diaphragm insert threads to the plunger
threads, and turn the diaphragm by hand until the insert
hits the shoulder of the valve plunger (24).
d. Hold the plunger holder tool to secure the valve plunger,
and torque the diaphragm insert to 10 in.-lbs (110 N-cm)
using a 5/16-in. (8-mm) open-end wrench.
e. Repeat the above procedure for the plungers and
diaphragms of the other two cylinders.
f. Fill the reservoir with fresh oil and prime the pump, as
outlined in the Fluid-End Service Section.
6. Reassemble Pump
Reassemble the pump as outlined in the Fluid-End Service
Section.
16 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 17

D/G-04 Troubleshooting
Cavitation
• Inadequate fluid supply because:
— Inlet line collapsed or clogged
— Clogged line strainer
— Inlet line too small or too long
— Air leak in inlet line
— Worn or damaged inlet hose
— Suction line too long
— Too many valves and elbows in inlet line
• Fluid too hot for inlet suction piping system.
• Air entrained in fluid piping system.
• Aeration and turbulence in supply tank.
• Inlet vacuum too high (refer to “Inlet Calculations”, page 3).
Symptoms of Cavitation
• Excessive pump valve noise
• Premature failure of spring or retainer
• Volume or pressure drop
• Rough-running pump
• Premature failure of diaphragms
Pump Runs Rough
• Worn pump valves
• Airlock in outlet system
• Oil level low
• Wrong weight of oil for cold operating temperatures (change
to lighter weight)
• Cavitation
• Air in suction line
• Restriction in inlet/suction line
• Hydraulic cells not primed after changing diaphragm
• Foreign material in inlet or outlet valve
• Damaged diaphragm
• Fatigued or broken valve spring
Premature Failure of Diaphragm
• Frozen pump
• Puncture by a foreign object
• Elastomer incompatible with fluid being pumped
• Pump running too fast
• Excess pressure
• Cavitation
Drop in Volume or Pressure
A drop in volume or pressure can be caused by one or more of
the following:
• Air leak in suction piping
• Clogged suction line or suction strainer
• Suction line inlet above fluid level in tank
• Inadequate fluid supply
• Pump not operating at proper RPM
• Relief valve bypassing fluid
• Worn pump valve parts
• Foreign material in inlet or outlet valves
• Loss of oil prime in cells because of low oil level
• Ruptured diaphragm
• Cavitation
• Warped manifold from overpressurized system
• O-rings forced out of their grooves from overpressurization
• Air leak in suction line strainer or gasket
• Cracked suction hose.
• Empty supply tank
• Excessive aeration and turbulence in supply tank
• Cavitation
• Abrasives in the fluid
• Valve incompatible with corrosives in the fluid
• Pump running too fast
• Worn and slipping drive belt(s)
• Worn spray nozzle(s)
Water (or Process Fluid) in Oil
Reservoir
• Condensation
• Ruptured diaphragm
• Hydraulic cell not properly primed after diaphragm
replacement
• Frozen pump
Strong Water (or Process Fluid)
Pulsations
NOTE: Small pulsations are normal in single-acting pumps
with multiple pumping chambers.
• Foreign object lodged in pump valve
• Loss of prime in hydraulic cell because of low oil level
• Air in suction line
• Valve spring (8) broken
• Cavitation
• Aeration or turbulence in supply tank
17 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 18

D/G-04 Troubleshooting
Valve Wear
• Normal wear from high-speed operation
• Cavitation
• Abrasives in the fluid
• Valve incompatible with corrosives in the fluid
• Pump running too fast
Loss of Oil
• External seepage
• Rupture of diaphragm
• Frozen pump
• Worn shaft seal
• Oil drain piping or fill cap loose.
• Valve plate and manifold bolts loose
• Pump housing porosity
Premature Failure of V alve
Spring or Retainer
• Cavitation
• Foreign object in the pump
• Pump running too fast
• Spring/retainer material incompatible with fluid being
pumped
• Excessive inlet pressure.
18 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 19

Limited Warranty
Wanner Engineering, Inc. extends to the original purchaser
of equipment manufacturerd by it and bearing its name, a
limited one-year warranty from the date of purchase against
defects in material or workmanship, provided that the
equipment is installed and operated in accordance with
the recommendations and instructions of Wanner
Engineering, Inc. Wanner Engineering, Inc. will repair or
replace, at its option, defective parts without charge if such
parts are returned with transportation charges prepaid to
Wanner Engineering, Inc., 1204 Chestnut Avenue,
Minneapolis, Minnesota 55403.
This warranty does not cover:
1. The electric motors (if any), which are covered by the
separate warranties of the manufacturers of these
components.
2. Normal wear and/or damage caused by or related to
abrasion, corrosion, abuse, negligence, accident, faulty
installation or tampering in a manner which impairs normal
operation.
3. Transportation costs.
This limited warranty is exclusive, and is in lieu of any other
warranties (express or implied) including warranty of
merchantability or warranty of fitness for a particular
purpose and of any noncontractual liabilities including
product liabilities based on negligence or strict liability.
Every form of liability for direct, special, incidental or
consequential damages or loss is expressly excluded and
denied.
19 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
Page 20

WANNER ENGINEERING, INC.
1204 Chestnut Avenue, Minneapolis, MN 55403
TEL: (612) 332-5681 FAX: (612) 332-6937
TOLL-FREE FAX [US only]: (800) 332-6812
www.hydra-cell.com
email: sales@wannereng.com
©2004 Wanner Engineering, Inc. Printed in USA
20 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
 Loading...
Loading...