Hp COMPAQ PROLIANT 6000, COMPAQ PROLIANT 5500, COMPAQ PROLIANT 3000, COMPAQ PROLIANT 1600, COMPAQ PROLIANT 5000 PCI Bus Balancing and Optimization on Compaq ProLiant Servers
Page 1

[March 1998]
Prepared By
Windows NT
Integration Team
Compaq Computer
Corporation
CONTENTS
Executive Sum mary 3
PCI Archi tecture 3
PCI Load Balancing 5
Performance Optimiz ation
Using PCI Bus Balanc ing 5
Bus Balancing Rules 5
Example Configurations 6
PCI Bus Loading with
PCI Hot Plug 7
PCI Bus
Balancing Tools 9
System Management
Performance Monitor 10
Balancing Bus Use 10
PCI Bus Loading with
Redundant Controllers 10
Online Storage Controller
Recovery Option 10
Compaq Advanced Net work
Control Utility 10
Future PCI Bus Loading
and Technical Summar y 11
ECG073/0398
WHITE PAPER
.
.
.
.
.
PCI Bus Balancing and Optimization on
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Compaq ProLiant Servers
.
.
.
.
.
With the introduction of dual-peer PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) bus
.
.
.
architecture, Compaq recommends balancing the load between the two PCI buses to
.
.
.
.
achieve opt i ma l performance on t h e s er ver .
.
.
.
.
This white paper identifies the importance of PCI Bus Balancing and provides technical
.
.
.
configurations for achieving high performance and availability on bridged PCI buses
.
.
.
.
and dual-peer PCI bus architectures.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Additional Resources include:
.
.
.
.
PCI Bus Numbering in a Microsoft Windows NT
.
.
.
February, 1998 – Doc ID ECG024/0298.
.
.
.
.
.
Configuring the Compaq
.
.
.
July 1997 – Doc ID 679A/0697.
.
.
.
.
.
Implementing Online Storage Controller Recovery Option Under Windows NT
.
.
.
1997 - Doc ID ECG066A/0797.
.
.
.
.
.
Compaq Advanced Network Error Correction Support using PCI Hot Plug with
.
.
.
Microsoft Windows NT
.
.
.
.
.
Compaq Advanced Network Error Correction Support in a Microsoft
.
.
.
Windows NT
.
.
.
.
Advanced Network Fault Detection and Correction Feature for NetWare
.
.
.
.
Part Number 385A/0696.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Help us impr ove our technical communic ation. Let us know what you think about the
.
.
.
technical information in this docum ent. Your feedback i s valuable and will help us
.
.
.
structure future communications. Please send your comments to: CompaqNT@compaq.com
.
.
1
Server Environment, June 1996 – Part Number 353A/0696.
ProLiant 5000 Server for Peak Performance, Fourth Edition,
, August 1997 – Doc ID ECG057/0897.
Environment, First Edition,
, July
, June 1996 –
Page 2

WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
NOTICE
.
.
.
.
.
The information in this publication is subject to change without notice.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
OMPAQ COM PUTER CORPORATION SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR TECHNICAL
C
.
.
.
OR EDITORIAL ERRORS OR OMISSIONS CONTAINED HEREIN
.
.
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE
.
.
.
FURNISHING
.
.
.
.
This publication does not constitute an endorsement of the product or products that were tested.
.
.
.
The configuration or configurations tested or described may or may not be the only available
.
.
.
solution. This test is not a determination of product quality or correctness, nor does it ensure
.
.
.
compliance with any federal, state or local requirements. Compaq does not warrant products
.
.
.
other than its own strictly as stated in Compaq product warranties.
.
.
.
.
.
Product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
.
.
.
respective companies.
.
.
.
.
Compaq, Contura, Deskpro, Fastar t, Compaq Insight Manager, LTE, PageMar q, Systempro,
.
.
.
Systempro/LT, ProLiant, TwinTray, ROMPaq, LicensePa q, QVision, SLT, ProLinea, SmartStart,
.
.
.
NetFlex, DirectPlus, QuickFind, RemotePaq, BackPaq, TechPaq, SpeedPaq, QuickBack, PaqFax,
.
.
.
Presario, SilentCool, CompaqCare (design), Aero, SmartStation, MiniStation, and PaqRap,
.
.
.
registered United States Patent and Trademark Office.
.
.
.
.
Netelligent, Armada, Cruiser, Concerto, QuickChoice, ProSignia, Systempro/XL, Net1, LTE
.
.
.
Elite, Vocalyst, PageMate, SoftPaq, FirstPaq, SolutionPaq, EasyPoint, EZ Help, MaxLight,
.
.
.
MultiLock, QuickBlank, QuickLock, UltraView, Innovate logo, Wonder Tools logo in black/white
.
.
.
and color, and Compaq PC Card Solution logo are trademarks and/or service marks of Compaq
.
.
.
Computer Corporation.
.
.
.
.
Other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
.
.
.
respective companies.
.
.
.
.
.
Copyright ©1998 Compaq Computer Corporation. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
.
.
.
.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT, Windows NT Server and Workstation, Microsoft SQL Server
.
.
.
for Windows NT are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
PCI Bus Balancing and Optimization on Compaq
.
.
.
.
ProLiant Servers
.
.
.
First Edition (March 1998)
.
.
Document Number: ECG073/0398
.
.
.
.
.
, PERFORMANCE, OR USE OF THIS MATERIAL.
, NOR FOR
ECG073/0398
2
Page 3
NOTE: Table 1 lists the
Compaq Pr oLiant fami ly of
servers that embody the
dual-peer P C I bus architecture.
NOTE: Table 1 lists the
Compaq Pr oLiant fami ly of
servers that embody the bridged
PCI bus ar chitecture.
WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
.
.
.
.
With the in t roduction of the Compaq ProLiant 5000 Server and its dual-peer PCI (Peripher a l
.
.
.
Component Interconnect) bus architecture, Compaq recommended certain configurations to
.
.
.
balance the load between the two PCI buses and achieve optimal performance on the server.
.
.
.
Customers now question what load balancing means, how it affects server performance and what
.
.
.
to consider for future planning and implementation of PCI bus loading.
.
.
.
.
This white paper identifies the overall importance of PCI bus balancing and provides technical
.
.
.
configurations for achieving high performance and availability on bridged and dual-peer PCI bus
.
.
.
architectures. The supporting facts presented along with recommendations will assist system
.
.
.
administrators and network operators in attaining and maintain in g th is goal.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
PCI ARCHITECTURE
.
.
.
.
.
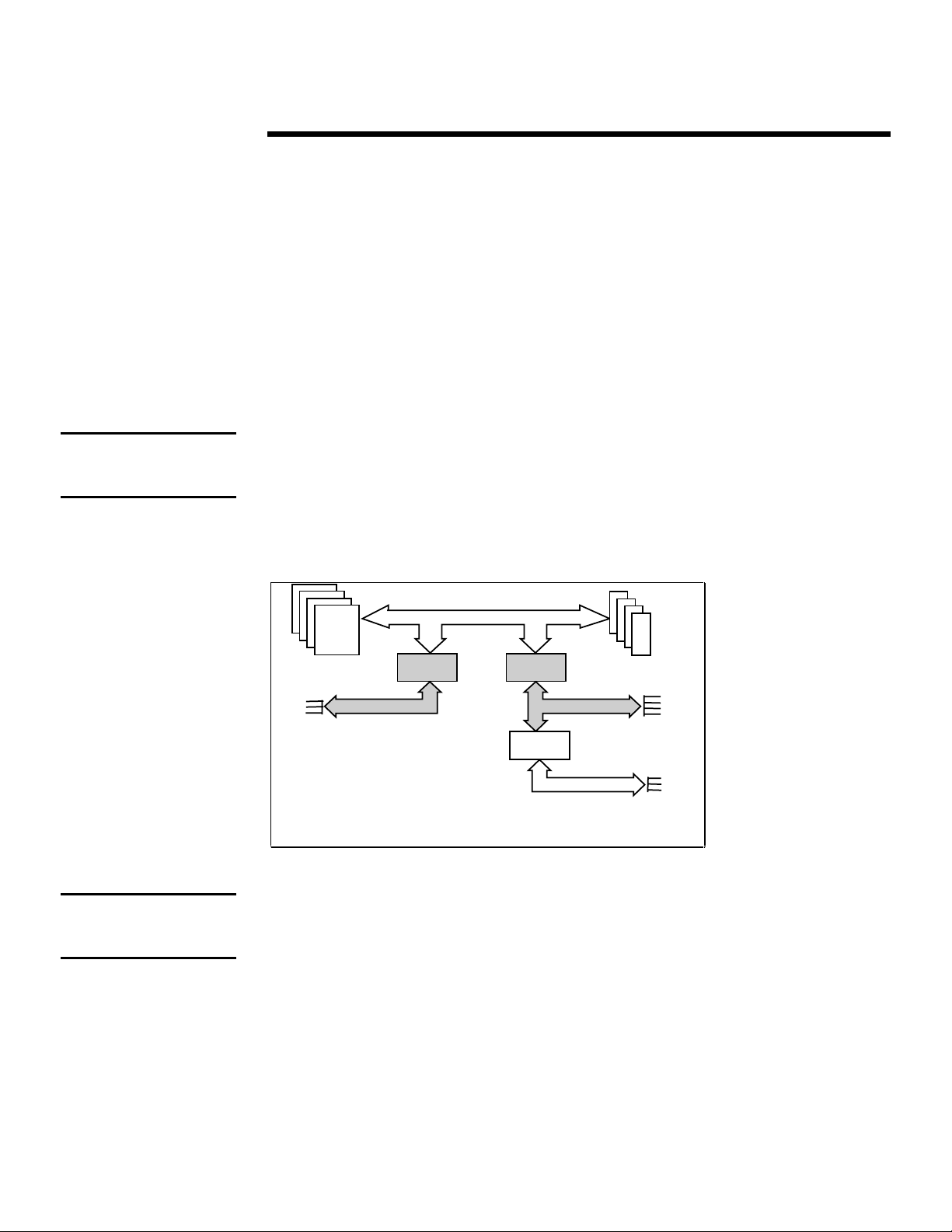
Two basic architectures are used to connect the primary and secondary PCI bus to the host bus:
.
.
the dual-peer PCI bus or the bridged PCI bus. The dual-peer bus architecture, as shown in
.
.
.
Figure 1, provides two PCI buses independently linked to the host processor bus by means of two
.
.
.
Host-to-PCI Bridges. Since each PCI bus runs independently, it is possible to have two PCI bus
.
.
.
masters transferring data simultaneously thus producing more overall throughput. This is an
.
.
.
advantage with systems that have two or more high-bandwidth peripherals. Splitting these
.
.
.
peripherals between the two buses provides an uniformed load.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Processors
Slots
Figure 1: Dual-peer PCI architecture.
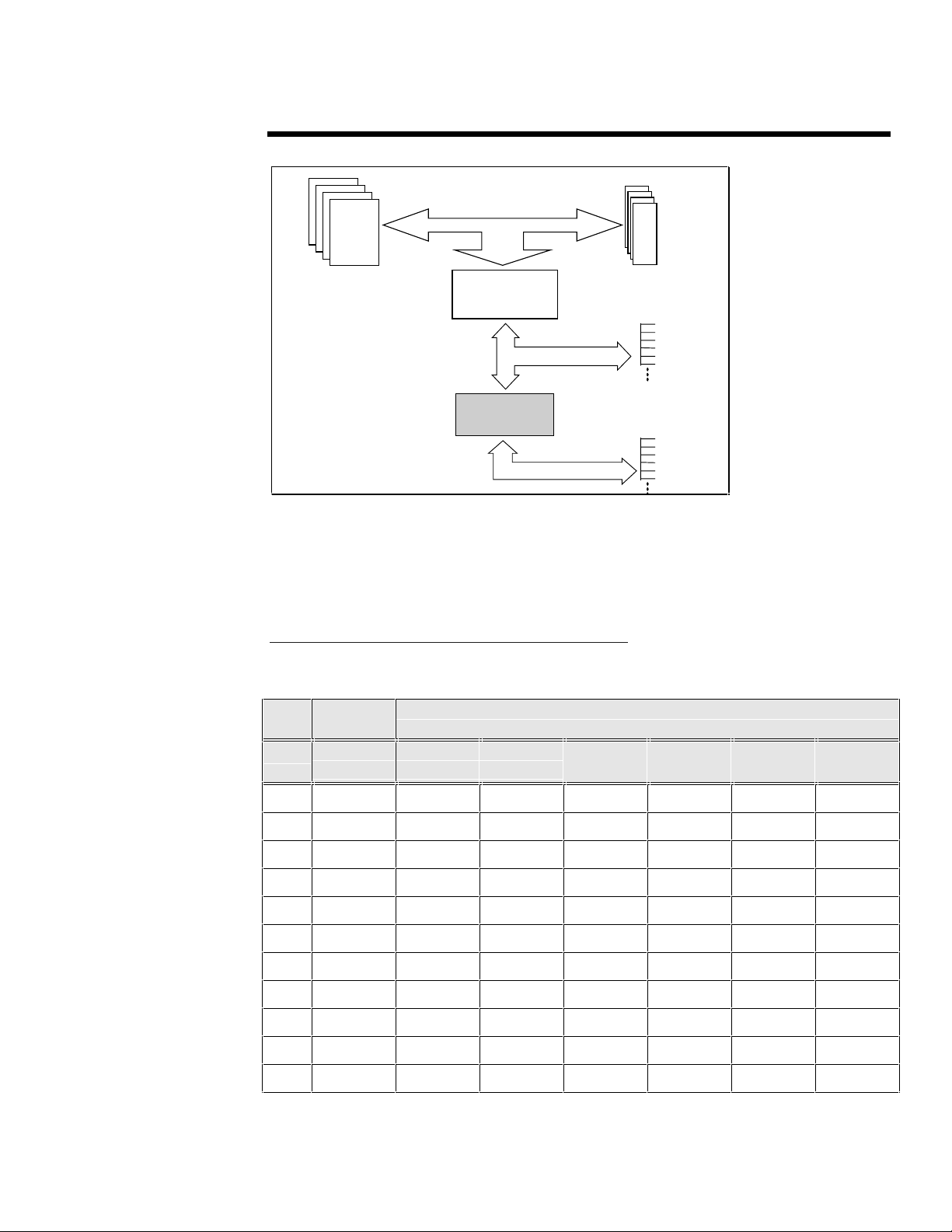
The bridged PCI architecture, as shown in Figure 2, requires all processed transactions on the
bridged PCI bus (the secondary bus) to go through the PCI-to-PCI Bridge to reach the primary
bus, then through the Host-to-PCI Bridge. In effect there is only one path to the host bus;
therefore, no load balancing is required on a system with this type of architecture.
133 MB/s 133 MB/s
Secon dary PCI Bus
Bridge
Host Bus
Host Bus
540 MB/s
Host-
Host-
to-PCI
to-PCI
PCI-to-EISA
Bridge
Primary PCI Bus
Bridge
33 MB/s
EISA Bus
Memory
Slots
Slots
ECG073/0398
3
Page 4
WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Processors Memory
Figure 2: Bridged PCI architecture.
Knowing what PCI bus specific slots are assigned can be difficult to determine; therefore, Table 1
lists the slots for Compaq PCI bridged and dual-peer PCI servers and which bus they populate.
Use this matrix to identify which slot is assigned to the primary or secondary bus.
For any servers not listed, refer to the server user guide for the slot information or the Compaq
and Microsoft Windows NT Frontline Partnership web site located at:
http://www.compaq.com/solutions/frontline/pciutils.html.
TABLE 1: PCI BUS TO SLOT NUMBER ASSIGNMENTS
Slot
Bridged PCI
Number
Bus Systems
ProLiant 2500 ProLiant 1200 ProLiant 1600
1 Secondary Secondary Secondary Primary Primary
2 Secondary Secondary Secondary Primary Secondary Primary
3 Secondary Secondary Secondary Primary Secondary Primary Secondary
4 Primary Primary Primary Primary Secondary Primary Secondary
5 Primary Primary Primary Secondary Primary Primary Secondary
6 Primary Primary Primary Secondary Primary Primary Secondary
7 Secondary Primary Secondary Secondary
8 Secondary Primary Secondary Secondary
9 Secondary
10 Secondary
11 Secondary
Host Bus
Host-to-PCI
Bridge
133 MB/s
PCI-to-PCI
Bridge
PCI Bus
PCI Bus
133 MB/s
Dual-Peer PCI Bus Systems
ProLiant 3000/
ProLiant 5500 ProLiant 5000
Slots
Slots
ProLiant 6000/
ProLiant 7000
ProLiant 6500
ECG073/0398
4
Page 5

WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
PCI LOAD BALANCING
.
.
.
.
One key to procuring peak server performance is optimal configuration of the I/O (Input/Output)
.
.
.
subsystems. Because of architectural changes and enhancements incorporated into these systems,
.
.
.
careful consideration of load balancing must be given before the initial system setup and
.
.
.
configuration take place.
.
.
.
.
For example, the Intel Pentium Pro processor is optimized for performance using PCI peripherals.
.
.
.
The Compaq ProLiant servers that support dua l-peer PCI bus archit ectures provide aggregate I/O
.
.
.
throughput capability as high as 267 MB/s. The dual-peer PCI bus architecture increases
.
.
.
configuration flexibility and allows higher levels of overall performance. However, attaining
.
.
.
peak performance requires careful evaluation of I/O loading across both PCI buses. This means
.
.
.
the administrator must carefully plan expansion slot usage for each device before initial
.
.
.
configuration, as well as plan for future expansion.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Performance Optimization Using PCI Bus Balancing
.
.
.
.
.
Bus balancing is achieved by balancing the I/O throughput on each bus, thus producing the
.
.
.
optimum performance on a system. However, not all PCI systems (i.e., bridged PCI systems)
.
.
.
achieve performance gains when implementing bus balancing; therefore, the customer has to
.
.
.
know when to balance the load on the system. Here are some brief recommendations. Detailed
.
.
.
configurations are described later in the document:
.
.
.
.
•
For bridged architectures, load balancing is not required nor recommended. To obtain the
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
best performance on a bridged PCI system, the primary bus should be populated first.
•
For dual-peer architectures load balancing is recommended. It could be helpful to split the
workload between buses when I/O throughput i s h i gh.
•
For dual-peer architectures that have PCI Hot Plug slots, customers must consider the
trade-off between high availability and high performance. This is discussed in more detail
later in this document.
Bus Balancing Rules
Understanding how to balance the PCI load on a system can be confusing; therefore, some general
guidelines or rules for balancing bus traffic are provided:
1. When installing multiple network or array controllers, split the controllers between the buses.
2. If installing an "odd" number of controllers, for example, two NICs (Network Interface
Controller) and one drive array controller, split the two network controllers between the
buses. Network controllers consume more bandwidth than array controllers do, so it is best to
split the workload between two buses if possible.
3. Avoid putting two network controllers together in the same bus unless both buses already
have a network controller installed. Note that it is better to have a system with one dual-port
NIC in each bus than to have two single-port NICs in each bus.
ECG073/0398
5
Page 6

WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
Example Configurations
.
.
.
.
.
Table 2 explains where to place controllers to enable PCI bus balancing on Compaq ProLiant
.
.
.
servers that contain the dual-peer bus architecture. For example, a system configuration might
.
.
.
consist of one NIC and two drive array controllers (configuration #3 highlighted in Table 2). As
.
.
.
demands change and the system bandwidth needs to increase, the system administrator changes
.
.
.
the configuration to add another NIC to the system. As shown in configuration #4 (highlighted in
.
.
.
Table 2), the system administrator should place the new network controller on Bus X so the PCI
.
.
.
bus remains balanced.
.
.
.
.
.
TABLE 2 : PCI BUS BALANCING IN A DUAL-PEER ARCHITECTURE
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Config#Device Type Bus X* Bus Y*
.
.
.
.
.
.
1 1 Network Interface Controller
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
* Bus X and Y have no bearing to the prim ary and s ec ondary bus . I t could be either.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
1 Drive Array Controller
2 2 Network Interface Controllers
1 Drive Array Controller
3 1 Network Interface Controller
2 Drive Array Controllers
4 2 Network Interface Controllers
2 Drive Array Controllers
5 2 Network Interface Controllers
3 Drive Array Controllers
6 3 Network Interface Controllers
2 Drive Array Controllers
7 2 Network Interface Controllers
4 Drive Array Controllers
8 2 Network Interface Controllers
5 Drive Array Controllers
9 3 Network Interface Controller
4 Drive Array Controllers
Drive Array Controller Network Int erf ac e C ont roller
Network Interface Controller
Drive Array Controller
Drive Array Controller Network Interface Controller
Network Interface Controller
Drive Array Controller
Network Interface Controller
2 Drive Array Controllers
2 Network Interface Controllers
Drive Array Controller
Optimal Preference:
1 DualPort Network Interface Controller
1 Drive Array Controller
Network Interface Controller
2 Drive Array Controllers
Network Interface Controller
3 Drive Array Controllers
2 Network Interface Controllers
2 Drive Array Controllers
Optimal Preference:
1 DualPort Network Interface Controller
2 Drive Array Controllers
Network Interface Controller
Drive Array Controller
Network Interface Controller
Drive Array Controller
Network Interface Controller
Drive Array Controller
Network Interface Controller
Drive Array Controller
Optimal Preference:
1 Network Interface Controller
1 Drive Array Controller
Network Interface Controller
2 Drive Array Controllers
Network Interface Controller
2 Drive Array Controllers
Network Interface Controller
2 Drive Array Controllers
Optimal Preference:
1 Network Interface Controller
2 Drive Array Controllers
ECG073/0398
6
Page 7

WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
PCI BUS LOADING WITH PCI HOT PLUG
.
.
.
.
For servers with PCI Hot Plug slots on a single bus, customers must pay close attention to
.
.
.
requirements for availability and determine whether a trade-off is needed between high
.
.
.
availability and high performance. Consider the following scenarios:
.
.
.
.
.
.
Configuration 1
.
.
.
.
.
For high availability and high performance, place the active controllers in the hot-plug slots, with
.
.
.
the standby controllers in the non-hot-plug slots. This splits the load so that a single NIC and
.
.
.
array controller is on each bus, as shown in Table 3.
.
.
.
.
This configuration provides moderately high availability along with high performance. However
.
.
.
sin ce the standby network controller (#4) is in a non-hot-plug slot, if it were to fail replacing the
.
.
.
controller would require shutting down the server. The active NIC (#3), on the other hand, is still
.
.
.
available and in a hot-plug slot thus allowing the system administrator time to replace the failed
.
.
.
NIC (#4) during n on-peak h ours, when a ccess to the server is at a minimum.
.
.
.
.
This configuration uses the minimum number of PCI hot-plug slots while providing redundancy
.
.
.
to controllers. It also enables hot replacement of the primary devices (active) in the event that
.
.
.
any of the active controllers should fail.
.
.
.
.
.
.
TABLE 3 : HIGH AVAILABILITY AND HIGH PERFORMANCE
.
.
.
.
.
.
# Device Type PCI Hot Plug Slot Non-PCI Hot Plug Slot
.
.
.
.
1 SMART 2/P Drive Array (Active) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
.
2 SMART 2/P Driv e Array (St andby ) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
3 NetFlex-3/P Controller (Active) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
.
4 NetFlex-3/P C ont roller (St andby ) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Configuration 2
.
.
.
.
If high availability is a primary concern, place all four controllers (active and standby) in the
.
.
.
hot-plug slots as shown in Table 4. Even though this configuration breaks rule number three in
.
.
.
the "Bus Balancing Rules" section, having two network controllers on the same bus does not
.
.
.
impact performance since the second NIC is in standby mode and therefore generates minimal
.
.
.
traffic on the bus.
.
.
.
.
This configuration works well for high availability because the I/O traffic emitted here is not
.
.
.
enough to saturate the PCI bus; therefore, there is no bottleneck to slow I/O traffic. If only two
.
.
.
NICs and two drive array controllers are needed, as in Table 4, both drive arrays and network
.
.
.
controllers could be placed on s ame bus withou t receivin g any performance degradation.
.
.
.
.
.
.
TABLE 4 : HIGHER AVAILABILITY AND HIGH PERFORMANCE
.
.
.
.
.
.
# Device Type PCI Hot Plug Slot Non-PCI Hot Plug Slot
.
.
.
.
.
1 SMART 2/P Drive Array (Active) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
2 SMART 2/P Driv e Array (St andby ) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
3 NetFlex-3/P Controller (Active) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
.
4 NetFlex-3/P C ont roller (St andby ) XXXXXX
.
.
.
ECG073/0398
7
Page 8

NOTE: A controller pair is
defined as two Compaq NICs that
are configured so that network
connectivity is maintained, even if
a connection is l os t or a
controller fails. For more
information, refer to the white
paper "The Compaq A dvanced
Network Error Correction
Support in a Microsoft Windows
NT Server Envi r onm ent."
WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
Configuration 3
.
.
.
.
.
When the configuration consists of an additional stand-alone device, for example, a network
.
.
.
controller pair plus a single network controller, the active NIC should be on separate bus. If, on
.
.
.
the other hand, the customer has an array controller pair plus a single array controller, the active
.
.
.
array controllers should be on the same bus for best performance. Placing the stand-alone array
.
.
controller in a hot-plug slot provides similar performance to placing it in the non-hot-plug slot.
.
.
.
Since the performance is similar, using a hot-plug slot provides additional availability.
.
.
.
.
.
Table 5 displays a configuration using an additional stand-alone NIC. Placing the stand-alone
.
.
.
NIC in a non-hot-plug slot provides the best performance, as this configuration splits the active
.
.
.
NICs between buses. If availability is of greater concern than performance, place the stand-alone
.
.
.
NIC in a hot-plug slot.
.
.
.
.
.
TABLE 5 : HIGH AVAILABILITY FOR ADDITIONAL STAND-ALONE DEVICES
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
# Device Type PCI Hot Plug Slot Non-PCI Hot Plug Slot
.
.
.
.
1 SMART 2/P Drive Array (Active) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
2 SMART 2/P Driv e Array (St andby ) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
.
3 NetFlex-3/P Controller (Active) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
4 NetFlex-3/P C ont roller (St andby ) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
.
5 NetFlex-3/P C ont roller (St and-alone) XXXXXX
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Configuration 4
.
.
.
.
For multiple pairs of network controllers, the same general guidelines apply. The customer must
.
.
.
evaluate the importance of availability and weigh that against any potential non-optimal
.
.
.
performance configurations.
.
.
.
.
.
Configuration 4 offers better availability than Configuration 3. Performance is optimal and a
.
.
.
higher level of availability is achieved. In the third configuration, if the standby network
.
.
controller failed, no network users would have access to any resources on that server while the
.
.
.
system administrator shuts down the system to replace the failed controller.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
ECG073/0398
8
Page 9

WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
If controller #5 fails in Configuration 4, network traffic would be "switched" or routed over to the
.
.
.
standby controller (#6), creating a slight decrease in performance because the bus is no longer
.
.
.
balanced. To eliminate the performance degradation, manually switch controller #3 to standby
.
.
.
mode and controller #4 to active mode, thus achieving a balanced load again. For details on how
.
.
.
to manually switch controllers using this utility, refer to the following white papers online at:
.
.
.
http://www.compaq.com/support/techpubs/index.html.
.
.
.
.
•
Compaq Advanced Network Error Correction Support using PCI Hot Plug with Microsoft
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Windows NT
•
Advanced Network Fault Detection and Correction Feature for NetWare
Another benefit in using this configuration is that if a controller fails, the system administrator
can schedule downtime during non-business hours to replace the failed NIC. Once the
administrator, however, replaces the failed controller, the original controller should be switched
back to being the active controller.
The only limitation in this configuration is that one of the active network controllers is located in
a non-hot plug slot and therefore cannot be replaced while the system is running.
TABLE 6 : HIGH AVAILABILITY FOR MULTIPLE NETWORK PAIRS
# Device Type PCI Hot Plug Slot Non-PCI Hot Plug Slot
1 SMART 2/P Drive Array (Active) XXXXXX
2 SMART 2/P Driv e Array (St andby ) XXXXXX
3 NetFlex-3/P Controller (Active) XXXXXX
4 NetFlex-3/P C ont roller (St andby ) XXXXXX
5 NetFlex-3/P Controller (Active) XXXXXX
6 NetFlex-3/P C ont roller (St andby ) XXXXXX
PCI Hot Plug Balancing Review
Overall, the key to balancing the PCI bus is keeping the amount of data traffic on each bus
balanced. Use the following list of guidelines as a review for PCI Hot Plug bus balancing.
•
When adding new controllers, keep the system balanced (see Table 2 for detailed
information).
•
Evaluate the importance of high availability and weigh that against any potential non-optimal
performance configurations.
•
If a controller fails, rebalancing of the system might be necessary to keep p erformance
optimal.
PCI BUS BALANCING TOOLS
Compaq offers a variety of helpful tools to assist in keeping the PCI busload balanced on Compaq
servers. Some tools specifically help users optimize their system containing PCI technology. A
brief descr iption of each tool is provided.
ECG073/0398
9
Page 10

NOTE: Compaq Insight
Manager also monitors PCI bus
utilization on SCO UNIX and
Novell NetWare servers.
ECG073/0398
WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
System Management Performance Monitor
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Compaq offers Windows NT Performance Monitor Add-On Enha ncem ent T ool s to ai d i n the easy
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
installation and removal of Objects and Object Counters for the Compaq EISA and PCI Buses,
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Power Supply and NetFlex-3 Controllers.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The System Management Performance Monitor, specifically, adds several System Management
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Objects to the Windows NT Performance Monitor. These counters include items concerning the
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
EISA Bus, PCI Bus, and Power Supply. These counters require Compaq Support Software
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Version 1.21A or later for Microsoft Windows NT and Compaq Insight Manager 3.30 or later.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
These tools are available on the Compaq Resource Paq for Microsoft Windows NT. To obtain a
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
copy of the Compaq Resource Paq, go to the Compaq Microsoft Frontline Partnership page
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
located on the web at:
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
//www.compaq.com/solutions/frontline
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Once the System Management Performance Monitor utility is installed, view the counter data
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
collected by the drivers through the Performance Monitor Utility included with Microsoft
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Windows NT.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Balancing Bus Use
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Compaq Insight Manager supports bus use measurements on ea ch PCI bus and on the EISA bus.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The bus use measurement tools provide a good way to check the I/O configuration to ensure that
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
peripherals are properly balanced across the two PCI buses. An indication of unbalanced bus use
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
implies that the system might need to be reconfigured to optimize performance. Refer to Compaq
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Insight Manager documentation for more information about using these tools.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
PCI BUS LOADING WITH REDUNDANT CONTROLLERS
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Compaq has offered many innovative solutions to reducing network downtime on Compaq server
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
networks. Some of these solutions include:
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
•
Online Storage Controller Recovery Option
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
•
Compaq Advanced Network Control Utility
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Online Storage Controller Recovery Option
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The Compaq Online Storage Controller Recovery Option provides redundancy at the mass storage
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
controller level by merging two SMART-2 controllers into a controller p air. In such a pair, one
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
controller is active, and the other remains in standby mode. Should a problem occur with the
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
active controller, the device driver switches traffic to the standby controller without loss of data or
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
interruption of service. A complete description of this fault tolerance feature can be found in the
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
white paper called Implementing Online Storage Controller Recovery in Windows NT, July 1997
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
– Doc ID 066A/0797.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Compaq Advanced Network Cont rol Utility
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The Compaq Advanced Network Control Utility is a network-monitoring tool that allows a user to
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
install, uninstall, configure and monitor NetFlex-3 controllers. This utility also displays PCI bus
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
number assignments, bus type and slot numbers associated with each device.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
10
Page 11

ECG073/0398
WHITE PAPER (cont.)
.
.
.
.
.
A complete description of all the capabilities and features of this utility are documented in the
.
.
.
utility Help File, and in the white paper Compaq Advanced Network Error Correction Support
.
.
.
using PCI Hot Plug with Microsoft Windows NT, August 1997 – Doc ID ECG057/0897. This
.
.
.
white paper is available on the Compaq Resource Paq for Windows NT.
.
.
.
.
To obtain a copy of the Compaq Resource Paq, go to the Compaq Microsoft Frontline Partnership
.
.
.
page located on the web at:
.
.
.
.
//www.compaq.com/solutions/frontline
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
FUTURE PCI BUS LOADING AND TECHNICAL SUMMARY
.
.
.
.
Compaq’s first server using PCI technology contained a single PCI bus. A short time later,
.
.
.
Compaq introduced the dual-peer PCI bus architecture having two PCI buses independently
.
.
.
linked to the host processor bus, thus providing the capability of more I/O throughput on the
.
.
.
server. As technology moves forward, the natural progression for PCI architecture could move to
.
.
.
three or more buses. The same bus balancing rules discussed in this document apply to future bus
.
.
.
architectures.
.
.
.
.
The key for future PCI bus loading is to balance the system today while planing ahead for
.
.
.
tomorrow. It is important to remember to weigh the current performance needs along with future
.
.
.
performance requirements. For this reason, try to choose the best performance configuration for
.
.
.
the current server, and at the same time allow enough room in the configuration to fulfill growth
.
.
.
and increasing capacity requirements. For instance, a server configuration currently consists of
.
.
.
one network controller, yet planning for future capacity requirements dictates the addition of two
.
.
.
more NICs to the server. In this case, the network administrator should purchase a dual-port NIC
.
.
.
to meet the new capacity requirements and initiate redundancy on this server.
.
.
.
.
Before making any modifications, evaluate all of the current network server configurations first.
.
.
.
The server configuration might not need to change; therefore, the system administrator might not
.
.
.
have to reconfigure all of the machines if the PCI buses are currently balanced.
.
.
.
.
A question to ask is - "Do I need to reconfigure all of my systems to make sure the PCI buses are
.
.
.
balanced?" If your system consists of just a few devices (one network controller and one disk
.
.
.
array controller), then the total PCI bus bandwidth the devices will use will be small compared to
.
.
.
the I/O throughput capabilities of the PCI bus. In this case, there would be no significant
.
.
.
performance difference whether the controllers were on the same bus or split between buses. If
.
.
.
the system is using multiple disk and network controllers and you need to improve the
.
.
.
performance of your system, then balancing the PCI buses on your system might improve the
.
.
.
overall performance of your system.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
11
 Loading...
Loading...