Hp COMPAQ PROLIANT 5000, COMPAQ PROLIANT 2000, COMPAQ PROLIANT 800, COMPAQ PROLIANT 2500, COMPAQ PROLIANT 1500 intraNetWare Symmetric Multiprocessing
...Page 1
INTEGRATION NOTE
.
.
October, 1997
Prepared By
Novell Integration
Business Unit, Compaq
Computer Corporation
CONTENTS
Executive Summary........ 3
Introduction ................... 3
Why Do I Need
SMP? ............................. 3
History of SMP at
Compaq .......................... 4
NetWare and
Multiprocessing .............. 4
intraNetWare SMP........... 5
Installing
intraNetWare SMP........... 6
MP Driver ............................ 6
SMP Kernel .......................... 7
SMP Tips ............................. 8
NLM Updates During
Installation ........................... 9
Uninstalling intraNetWare SMP9
MONITOR.NLM
Statistics ........................ 9
Troubleshooting
intraNetWare SMP.......... 10
Glossary of
Multiprocessing
Terminology ..................11
ECG045/1097
.
intraNetWare Symmetric Multiprocessing
.
.
.
.
.
This document looks at the evolution of Compaq multiprocessing systems, focuses on the
.
.
.
development of NetWare SMP, and provides basic installation instructions and tips for
.
.
.
using NetWare SMP on your Compaq server.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
Page 2

ECG045/1097
.
.
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
.
NOTICE
.
.
.
.
.
The information in this publication is subject to change without notice.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
COMPAQ COMPUTER CORPORATION SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR TECHNICAL
.
.
OR EDITORIAL ERRORS OR OMISSIONS CONTAINED HEREIN, NOR FOR
.
.
.
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE
.
.
.
FURNISHING, PERFORMANCE, OR USE OF THIS MATERIAL.
.
.
.
.
This publication does not constitute an endorsement of the product or products that were tested.
.
.
.
The configuration or configurations tested or described may or may not be the only available
.
.
.
solution. This test is not a determination of product quality or correctness, nor does it ensure
.
.
.
compliance with any federal, state or local requirements. Compaq does not warrant products other
.
.
.
than its own strictly as stated in Compaq product warranties.
.
.
.
.
Product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
.
.
.
respective companies.
.
.
.
.
.
Compaq, Compaq Insight Manager, ProLiant, SmartStart, NetFlex, registered United States
.
.
.
Patent and Trademark Office.
.
.
.
.
Netelligent is a trademark and/or service mark of Compaq Computer Corporation.
.
.
.
.
.
Hot Fix, intraNetWare, NetWare 3, NetWare 4, NetWare Loadable Module, NetWare Storage
.
.
Management Services, NetWare SMS, Novell, Novell Directory Services, and NDS and are
.
.
.
trademarks of Novell, Inc.
.
.
.
.
.
Btrieve is a registered trademark of Pervasive Software, Inc.
.
.
.
.
CompuServe is a registered trademark of CompuServe Incorporated.
.
.
.
.
.
ARCserve and JETserve are trademarks of Cheyenne Software, Inc.
.
.
.
.
Other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
.
.
.
respective companies.
.
.
.
.
©1997 Compaq Computer Corporation. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
NetWare Symmetric Multiprocessing
.
.
.
First Edition (October, 1997)
.
.
.
045A/1097
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2
Page 3
ECG045/1097
.
.
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
.
.
.
.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
.
.
.
.
.
The amount of information and the number of network applications on NetWare servers is
.
.
.
increasing rapidly, as is the dependence on these servers. Resource-intensive services such as
.
.
.
large databases, multimedia, imaging and document management are becoming more prominent.
.
.
intraNetWare Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) allows you to add additional processors to a
.
.
.
system without adding the overhead of an entire machine with its own hardware (disk drives and
.
.
.
network cards) and software (operating system and disk drivers). An SMP server also allows a
.
.
.
network administrator to centralize network services—file, print, communications and
.
.
.
client/server applications—within one server, which also greatly reduces the number of servers
.
.
.
that must be managed. As servers handle heavier workloads, the need for increased processing
.
.
.
power grows, making an SMP solution very attractive. This document looks at the evolution of
.
.
.
Compaq multiprocessing systems, focuses on the development of intraNetWare SMP, and
.
.
.
provides basic installation instructions and tips for using intraNetWare SMP on your Compaq
.
.
.
server.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
INTRODUCTION
.
.
.
.
Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP) denotes the use of multiple processors in an intraNetWare
.
.
.
environment. Each processor has equal access to system resources, including system interrupts,
.
.
.
memory, I/O bus and peripheral support. SMP provides more processing power, often at a lower
.
.
.
cost than multiple single processor systems. The most common need for more processing power
.
.
.
is in processor-intensive database environments. intraNetWare SMP allows you to add additional
.
.
.
processors to a system without adding the overhead of an entire machine with its own hardware
.
.
.
(disk drives and network cards) and software (operating system and disk drivers). An SMP
.
.
server also allows a network administrator to centralize network services—file, print,
.
.
.
communications and client/server applications—within one server, which also greatly reduces the
.
.
.
number of servers that must be managed. This document looks at the evolution of Compaq
.
.
.
multiprocessing systems, focuses on the development of intraNetWare SMP, and provides basic
.
.
.
installation instructions and tips for using intraNetWare SMP on your Compaq server.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
WHY DO I N EED SMP?
.
.
.
.
NetWare SMP offers the greatest potential returns in environments that require intensive
.
.
.
processing power. The most common example of this can be found in application serving
.
.
.
environments where large enterprise applications stress the capacity of the typical NetWare file
.
.
.
server.
.
.
.
.
.
Often in the past, the only option users could find to address the capacity requirements of these
.
.
environments was to implement a new multiprocessing operating system. In most organizations,
.
.
.
introducing a new operating system represented a costly decision requiring a significant financial
.
.
.
commitment to develop resources to manage the new environment. However, with NetWare
.
.
.
SMP, organizations have the option of leveraging the existing skills of their support staffs to
.
.
.
implement a high-capacity enterprise application serving environment. Benchmark tests run in
.
.
.
Compaq Integration Labs suggest that NetWare SMP can provide a highly scaleable platform for
.
.
.
application serving environments.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
3
NOTE: Compaq supports intranetWare SMP. Support for
NetWare 4.10 SMP was discontinued with NPFC v3.04.
Page 4

ECG045/1097
.
.
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
To obtain this benefit in an application serving environment, your network applications must be
.
.
.
designed to take advantage of intraNetWare/NetWare 4.11 SMP. Contact your application vendor
.
.
.
to find out about current support for NetWare SMP. Novell is also updating applications, such as
.
.
.
GroupWise and MultiProtocol Router v3.0, to support the SMP architecture.
.
.
.
.
NetWare SMP also offers some opportunities for organizations using NetWare to provide basic
.
.
.
network file and print services. Large file serving environments that stress the processor capacity
.
.
.
of existing NetWare servers may see significant benefit from NetWare SMP. In
.
.
.
intraNetWare/NetWare 4.11 SMP, the LAN driver interrupts are moved to the secondary
.
.
.
processors, reducing the load on the boot processor and making more capacity available for other
.
.
.
functions. Server environments that support multiple LAN segments and maintain high
.
.
.
processor utilization are most likely to benefit from this capability.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
HISTORY OF SMP AT COMPAQ
.
.
.
.
Multiprocessing (MP) in the PC industry began with the Compaq Systempro. While this design
.
.
.
enhanced performance and supported up to two processors, the support was asymmetrical: only
.
.
.
one processor could service interrupts. In the case of the Systempro, all interrupts were processed
.
.
.
by the boot processor. The second processor could run applications but could not service
.
.
.
interrupts from peripheral boards, timers, or other components.
.
.
.
.
The Systempro/XL and ProLiant family were the first Compaq SMP servers and used the 8259
.
.
.
programmable interrupt controller. This architecture is symmetric: any processor can service any
.
.
.
interrupt and there are separate Direct Memory Access (DMA) channels, timers and
.
.
.
Programmable Interrupt Controllers (PIC) for each processor. Because of expanding customer
.
.
.
needs, Intel has introduced the Multiprocessor Specification (MPS) which is becoming a standard
.
.
.
for MP.
.
.
.
.
Intel’s MPS assumes that an Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers (APIC) are available
.
.
.
in the system. The APIC was developed for multiprocessing environments. Later versions of
.
.
.
Pentium and Pentium Pro chips have the APIC embedded in the processor to simplify design
.
.
.
requirements and to guarantee that the APIC functionality will be available for use by operating
.
.
.
systems. The APIC design provides better interrupt handling than previous designs in SMP
.
.
.
environments. The largest benefit is that the APIC system dispatches interrupts to the processor
.
.
.
executing the least important task.
.
.
.
.
An additional performance increase is realized through the operating system scheduler. The
.
.
.
scheduler recognizes high priority tasks and avoids interrupting these tasks when possible, thus
.
.
.
increasing the overall efficiency of the system. The scheduler also attempts to schedule a task to
.
.
.
use the same processor that was last used by the task, which is called thread affinity. Because
.
.
.
each processor has its own cache, if a processor is using information that has already been called
.
.
.
from system memory and placed in its cache, performance is improved.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
NET WARE AND MULTIPROCESSING
.
.
.
.
NetWare versions prior to 4.10 are neither symmetric multiprocessing capable nor preemptive.
.
.
.
Novell’s first multiprocessing development was the NetWare SFT III architecture which uses
.
.
.
.
4
NOTE: The Compaq Advanced Network Fault Detection and
Correction feature (i.e. controller pairing) for NetFlex-3
and Netelligent controllers is not currently supported
under SMP. Compaq is actively working with Novell to
provide this feature under SMP, and it will be available
in the near future.
Page 5
ECG045/1097
.
.
SMP Applications
PSM (CPQSMP.PSM)
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
more than one processor and is asymmetric. One processor is dedicated to the I/OEngine, which
.
.
.
responds to hardware events. The second processor is dedicated to the MSEngine which provides
.
.
.
network and file services to clients. This design is asymmetric because only the I/OEngine
.
.
.
handles interrupts.
.
.
.
.
NetWare SFT III, like standard NetWare, is non-preemptive. Each NetWare Loadable Module
.
.
.
(NLM) must yield control of system resources before another NLM can begin a task. NLM code
.
.
.
must be written so that no single NLM controls the system for too long. In a preemptive
.
.
.
environment, the operating system controls how long each process is allowed to run before
.
.
.
handing control to a different one. Preemptive environments are more useful when servicing
.
.
.
priority tasks because the operating system can preempt other tasks and does not have to wait
.
.
.
until the NLM yields control.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
INTRANET WARE SMP
.
.
.
.
.
Novell features SMP functionality with intraNetWare/NetWare 4.11 SMP. The standard
.
.
NetWare operating system still exists and runs strictly on the boot processor as though there were
.
.
.
only a single processor available. The SMP functionality, called the NetWare SMP kernel, is an
.
.
.
addition to the traditional NetWare architecture and runs on the boot processor and secondary
.
.
.
processors.
.
.
.
.
.
The SMP kernel design has been added to the NetWare OS architecture to allow tasks to be
.
.
.
handled symmetrically and preemptively. The SMP kernel design includes an algorithm for
.
.
.
scheduling multiple incoming tasks to the processors available in a given system. In the past, this
.
.
.
algorithm was not required because new tasks were added to the queue and processed in sequence
.
.
by the available processor.
.
.
.
.
.
The SMP kernel is preemptive so that database applications can service priority tasks more
.
.
.
efficiently. Applications that are written to take advantage of SMP, referred to as SMP aware
.
.
.
applications, can run preemptively on an available processor in the system. Multi-threaded SMP
.
.
.
aware applications gain performance from parallelism in the SMP environment. Oracle7 Server
.
.
.
and Novell’s GroupWise are examples of SMP aware applications.
.
.
.
.
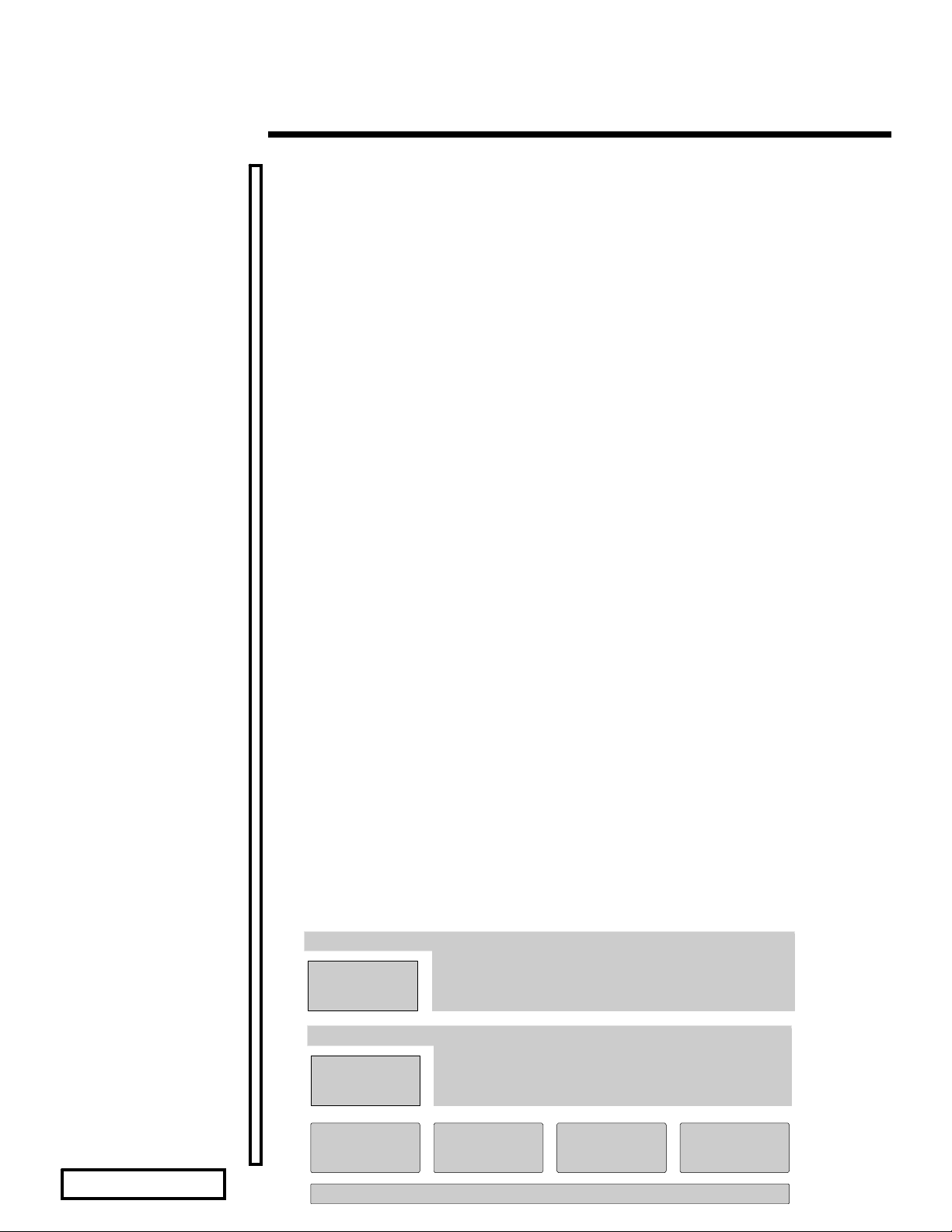
Two other NLMs are necessary to enable the SMP environment. These components are the
.
.
.
Platform Support Module (PSM) and the MP driver. The MP driver activates the secondary
.
.
.
processors (processors beyond the boot processor). The PSM is provided by the hardware vendor
.
.
.
in order for the SMP kernel to communicate with the processors. The PSM that Compaq supplies
.
.
.
for intranetWare/NetWare 4.11 SMP is CPQSMP.PSM. This hardware support provides the
.
.
.
same functionality as any device driver. For example, a network interface card requires a device
.
.
.
driver to communicate between the network card and the operating system. The PSM is the same
.
.
.
type of essential communication layer between the OS and the symmetric multiprocessing
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
5
NOTE: NetWare SFT-III servers do not currently support SMP.
NetWare
Apps
NetWare
SMP Kernel
OS
MP
Driver
MP
Driver
MP
Driver
MP
Driver
Page 6

ECG045/1097
.
.
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
hardware.
.
.
.
.
intraNetWare/NetWare 4.11 SMP is scaleable; the more processors in a system, the better the
.
.
.
potential performance. Keep in mind that standard NetWare NLMs are not actually SMP aware;
.
.
.
they run strictly on the boot processor (P0). NetWare does not schedule standard NLMs on
.
.
.
secondary processors.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
INSTALLING INTRANET WARE SMP
.
.
.
.
.
If you do not install intraNetWare SMP using the SmartStart installation utility,
.
.
.
intranetWare/NetWare 4.11 will automatically detect multiple processors during initial
.
.
.
installation and give you the option to install SMP. If you choose this option,
.
.
.
intraNetWare/NetWare 4.11 suggests that you install the PSM driver, CPQSMP.PSM.
.
.
.
.
However, if you add an additional processor board to an existing non-SMP server, you must use
.
.
.
the intraNetWare/NetWare 4.11 INSTALL module to install intraNetWare/NetWare 4.11 SMP.
.
.
.
Be sure to have the License diskette available.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
1. Boot the server into the System Configuration Utility.
.
.
.
.
.
2. Select the "Configure Hardware" option.
.
.
.
.
3. Select the "Review or modify hardware settings" option.
.
.
.
.
.
4. Select the "View or edit details" option.
.
.
.
.
5. Select "NetWare 4.1 SMP/intraNetWare SMP" for the Primary Operating System. (On older
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
6. Save the configuration changes and exit the System Configuration Utility.
.
.
.
.
.
7. Restart the server.
.
.
.
.
8. Load INSTALL from the server console prompt.
.
.
.
.
.
9. Select "Multi CPU options" from the INSTALL menu.
.
.
.
.
10. Choose "Select a Platform Support Module".
.
.
.
.
11. Select CPQSMP.PSM from Compaq, and follow the prompts. The latest version of
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
12. intraNetWare will support up to four processors without additional licensing. Exit
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
13. After installation is complete, down and restart the server.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
MP Driver
.
.
.
.
During installation, the following commands are automatically added to STARTUP.NCF.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The last command loads the MP driver, MPDRIVER.NLM, once for each secondary processor
.
.
.
(any processor beyond the boot processor). If you wish to use only selected secondary processors,
.
.
.
6
NOTE: The server must be configured with NetWare 4.1
SMP/intraNetWare SMP as the primary operating
system in the System Configuration Utility.
versions of the System Configuration Utility, the choice is listed as NetWare SMP.)
CPQSMP.PSM is available on NSSD Disk 1.
INSTALL, and restart the server for the changes to take effect.
LOAD CPQSMP.PSM
LOAD SMP.NLM
LOAD MPDRIVER.NLM ALL
Page 7

ECG045/1097
.
.
SMP Aware
P1
P2
NetWare
Applications
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
you must unload the MP drivers for all of the secondary processors, and then load the MP driver
.
.
.
for the selected processors. For example, if there are four processors in a system, the MP driver
.
.
.
may be loaded for any of the three secondary processors using the following commands:
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
To see which processors are on line, use MONITOR.NLM.
.
.
.
.
.
.
SMP Kernel
.
.
.
.
.
The SMP kernel support, SMP.NLM, is added to STARTUP.NCF during the installation process.
.
.
.
The SMP kernel provides support for SMP-aware applications by coordinating the scheduling
.
.
.
process on all active processors in the system. SMP-aware applications may be able to run on a
.
.
.
system without the SMP kernel loaded; however, they will not realize the scaling benefit provided
.
.
.
by the use of multiple processors in the system.
.
.
.
.
.
Dedicated Boot processor is dedicated to NetWare. NetWare request from SMP aware applications are queued
.
.
.
.
.
Shared NetWare and SMP aware applications share the boot processor. (The default mode.)
.
.
.
Priority Boot processor is dedicated to NetWare, but NetWare requests from SMP aware applications have
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
To change the SMP mode, use one of the SET parameters described below.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Dedicated Mode
.
.
.
.
Dedicated Mode should be used when you want file server response (NetWare NLMs) to be
.
.
.
minimally affected by the SMP aware applications. The boot processor is dedicated to NetWare.
.
.
.
Even when extra CPU time is available, SMP aware applications cannot use the boot processor to
.
.
.
service SMP application calls. When an SMP aware application makes a NetWare call, the call
.
.
.
will be added to the tail of the queue and serviced by the boot processor when the request reaches
.
.
.
the front of the queue.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
7
NOTE: The server is in shared mode by default unless the
NetWare NLMs
UNLOAD MPDRIVER (unloads SMP support for all secondary processors)
LOAD MPDRIVER 1 (brings up the second processor in the system)
LOAD MPDRIVER 2 (brings up the third processor in the system)
LOAD MPDRIVER 3 (brings up the fourth processor in the system)
with requests from standard NetWare NLMs.
priority on the boot processor over requests from standard NetWare NLMs.
SET SMP NETWARE KERNEL MODE=DEDICATED
SET SMP NETWARE KERNEL MODE=SHARED
SET SMP NETWARE KERNEL MODE=PRIORITY
parameter is changed manually.
Standard
NetWare
call added
to queue
P0
Page 8

ECG045/1097
.
.
P2
SMP Aware
SMP Aware
SMP Aware
P1
P2
Applications
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
.
.
.
Shared Mode
.
.
.
.
.
In shared mode (the default mode), both NetWare and SMP aware applications use the boot
.
.
.
processor. This mode should be used when the file server activity does not need priority service
.
.
.
and the SMP aware application could benefit from more processing power. CPU time is
.
.
.
distributed on a first come, first served basis. In shared mode, NetWare NLMs running on P0 will
.
.
.
be more affected than when using dedicated mode.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
NetWare
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Priority Mode
.
.
.
.
.
Priority mode is designed for a system containing eight or more processors. The boot processor is
.
.
.
reserved for NetWare, but if an SMP aware application makes a NetWare call, that call is placed
.
.
.
at the front of the queue and will be the next request serviced. SMP aware applications do not
.
.
.
interrupt a NetWare task being serviced, but numerous NetWare requests from SMP aware
.
.
applications queued ahead of other outstanding NetWare requests will slow down their
.
.
.
processing. Priority mode, more than the other two modes, affects the servicing of NetWare
.
.
.
NLMs running on P0 the most.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
8
Standard
NetWare NLMs
NetWare
P0
SMP Tips
· If you are trying to run an SMP aware application, but the SMP NLMs are not loaded, the
application may not load. However, some SMP aware applications, such as MSM, will load
and adapt themselves to the single processor environment.
· At least 64 megabytes of memory is recommended. The minimum requirement is 32
megabytes. (A minimum of 16 megabytes of main memory for each active processor is
suggested.)
· All intraNetWare patches should be applied before loading SMP.
SMP Aware
Applications
P0
NetWare SMP
front
call added
to
of queue
Applications
P1
Applications
Page 9

ECG045/1097
.
.
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
· The latest intraNetWare Support Pack can be obtained from the Novell Support Connection
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
9
Web Site, http://support.novell.com.
· You should use the latest support modules as they become available. CPQSMP.PSM,
MSM.NLM, ETHERTSM.NLM and TOKENTSM.NLM ship on the Novell Support
Software Install/DOS & Server Support disk. Other support modules can be obtained from
Novell. To disable SMP, follow the steps in the section, Uninstalling NetWare SMP.
NLM Updates During Installation
NOTE: This section is not applicable to intraNetWare/NetWare
4.11.
Several NLMs necessary for the SMP server to operate properly are added or upgraded
automatically during the installation process. As new versions of the NLMs become available,
they should be upgraded.
The following NLMs are upgraded automatically during the installation process of SMP to
NetWare 4.1x:
CLIB.NLM
STREAMS.NLM
ETHERTSM.NLM
or
TOKENTSM.NLM
MSM.NLM
You must use a special CLIB.NLM when running SMP aware applications.
CLIB.NLM is backwards compatible for use with non-SMP servers and legacy
NLMs.
Uninstalling intraNetWare SMP
If you decide to uninstall intraNetWare SMP, update the primary operating system in the System
Configuration to prevent unstable server performance. Otherwise, lost interrupts, spurious
interrupts or server ABEND may occur. First, update the STARTUP.NCF file to prevent attempts
to automatically load SMP.
1. Remove the following lines from the STARTUP.NCF file.
LOAD CPQSMP.PSM
LOAD SMP.NLM
LOAD MPDRIVER.NLM ALL
2. Down and exit the server, and reboot the system.
Next, modify the primary operating system in the Compaq System Configuration Utility:
1. Run the Compaq System Configuration Utility.
2. At the System Configuration menu, select Configure Hardware and press ENTER.
3. Select View or Edit Details and choose NetWare or NetWare 4.10 or later as the Primary
Operating System and press ENTER.
4. Select Save and Exit to save the configuration, and choose Save the Configuration to restart
the server.
You may start MONITOR.NLM from the server console to verify that SMP is not loaded.
MONITOR.NLM STATISTICS
MONITOR.NLM also includes multiprocessing statistics. When you load MONITOR.NLM, you
will see several new statistics that will help you inspect the state of your SMP server. In addition
Page 10

ECG045/1097
.
.
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
to seeing the number of processors in a system and the percentage utilization of each processors,
.
.
.
you can tell if the processors are on-line or off-line.
.
.
.
.
You can also monitor the amount of activity on each processor. This statistic can help you
.
.
.
determine whether bottlenecks exist within the system. For example, if your system is configured
.
.
.
in dedicated mode and you see that very little activity is occurring on the boot processor, you may
.
.
.
want to change the mode to shared mode.
.
.
.
.
.
In particular, you may want to watch the behavior of your SMP aware applications by checking
.
.
.
the Mutex Information. This statistic indicates that a thread is locking a resource. Any resource,
.
.
.
such as buffers, registers, memory, and devices can be locked by an SMP thread (multiple threads
.
.
make up an application). Upon completing an operation, an SMP thread unlocks the resource it
.
.
.
used; however, during the time a resource is locked, no other thread can use it. Resources that are
.
.
.
shared by multiple SMP aware threads need locks to ensure the integrity of an operation being
.
.
.
serviced. For example, the Mutex list may be locked temporarily by an SMP aware thread. This
.
.
.
prevents any other SMP aware thread from changing or adding to that list while the first thread is
.
.
.
completing its operation. The longer and more frequently resources are locked, the more likely
.
.
.
performance will be affected. If you are concerned about performance, you may want to consider
.
.
.
removing applications that lock resources.
.
.
.
.
MONITOR.NLM can also be used to determine whether your system is running SMP aware
.
.
.
applications. Because NetWare always runs on the boot processor, you can check
.
.
.
MONITOR.NLM for any tasks that are being run on the secondary processors. If the secondary
.
.
.
processors are being utilized, your system is running SMP aware applications.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
TROUBLESHOOTING INTRANET WARE SMP
.
.
.
.
.
Changing the operating system from intraNetWare SMP to intraNetWare requires the Primary
.
.
.
Operating System option to be changed in the System Configuration. See Uninstalling NetWare
.
.
.
SMP in this file to change this setting
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
10
Page 11

ECG045/1097
.
.
INTEGRATION NOTE (cont.)
.
.
.
.
GLOSSARY OF MULTIPROCESSING TERMINOLOGY
.
.
.
.
.
.
Bandwidth
.
.
.
Increasing the network operating system server capacity by reducing CPU utilization and
.
.
.
allowing more services and applications to run.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Cache Coherency
.
.
.
The monitoring of the state of data stored in multiple caches to ensure that no processor acts on
.
.
.
stale data. Locks: Controls within multithreaded software that prevent more than one thread from
.
.
.
accessing the same area of memory simultaneously.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Multitasking
.
.
.
The execution of multiple applications or threads to provide simultaneous execution.
.
.
.
.
.
Multithreading
.
.
.
The multitasking of separate threads within a process or application.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Mutex
.
.
.
Mutual Exclusion refers to atomic lock variables which are used to prevent multiple processors
.
.
.
from accessing shared data structures at the same instant.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Platform Specific Module (PSM)
.
.
.
A driver or layer that interfaces between the operating system and the hardware, freeing the OS
.
.
.
from being dependent upon particular hardware components.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Process
.
.
.
One or more threads and the resources allocated to them, including a virtual address space. Each
.
.
.
instance of any application runs within its own process.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Processor Affinity
.
.
The assignment of threads to a given CPU or subset of CPUs to capitalize on processor caches. A
.
.
.
high percentage of cache hits results in improved performance.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Scaling
.
.
.
The percentage of increase in throughput, or work accomplished--relative to processor 0--when
.
.
.
additional processors are added. Scalability is the incremental increased related to the addition of
.
.
.
each processor.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Semaphore
.
.
.
Restricts access to global variables or system-level resources. For example, it blocks additional
.
.
.
threads from writing to a serial port while another thread is using it. When a thread obtains a
.
.
.
semaphore, it changes the resource's state to owned, then when completed, changes the
.
.
.
state back to unowned and releases the semaphore.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP)
.
.
.
The ability of an operating system to distribute tasks to all available CPUs in a hardware platform
.
.
.
and to execute these tasks in parallel.
.
.
.
.
.
Thread
.
.
.
A single path or entity of execution within one process.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
11
 Loading...
Loading...