
User Guide

© Copyright 2009 Hewlett-Packard
Development Company, L.P.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its
proprietor and used by Hewlett-Packard
Company under license. SD Logo is a
trademark of its proprietor.
The information contained herein is subject
to change without notice. The only
warranties for HP products and services are
set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services.
Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors
or omissions contained herein.
First Edition: August 2009
Document Part Number: 575021-001
Product notice
This user guide describes features that are
common to most models. Some features
may not be available on your computer.
To obtain the latest information in the User
Guide, go to the HP Web site at
http://www.hp.com/support.

Safety warning notice
WARNING! To reduce the possibility of heat-related injuries or of overheating the computer, do not
place the computer directly on your lap or obstruct the computer air vents. Use the computer only on a
hard, flat surface. Do not allow another hard surface, such as an adjoining optional printer, or a soft
surface, such as pillows or rugs or clothing, to block airflow. Also, do not allow the AC adapter to contact
the skin or a soft surface, such as pillows or rugs or clothing, during operation. The computer and the
AC adapter comply with the user-accessible surface temperature limits defined by the International
Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment (IEC 60950).
iii

iv Safety warning notice

Table of contents
1 Notebook tour
Identifying the hardware ....................................................................................................................... 1
Top components .................................................................................................................. 1
TouchPad ............................................................................................................ 1
Lights ................................................................................................................... 2
Buttons and fingerprint reader (select models only) ............................................ 3
Keys .................................................................................................................... 5
Front components ................................................................................................................ 5
Right-side components ........................................................................................................ 6
Left-side components .......................................................................................................... 7
Bottom components ............................................................................................................. 8
Display components ............................................................................................................ 9
Wireless antennas ............................................................................................................... 9
Additional hardware components ...................................................................................... 10
Identifying the labels ........................................................................................................................... 11
2 Wireless and local area network
Using wireless devices ....................................................................................................................... 14
Identifying wireless and network status icons .................................................................... 14
Using the wireless controls ................................................................................................ 15
Using the wireless button ................................................................................................... 15
Using Wireless Assistant software (select models only) .................................................... 15
Using operating system controls ........................................................................................ 16
Using a WLAN .................................................................................................................................... 17
Setting up a WLAN ............................................................................................................ 17
Protecting your WLAN ....................................................................................................... 17
Connecting to a WLAN ...................................................................................................... 18
Roaming to another network .............................................................................................. 19
Using HP Mobile Broadband (select models only) ............................................................................. 20
Inserting a SIM ................................................................................................................... 20
Removing a SIM ................................................................................................................ 23
Using Bluetooth wireless devices (select models only) ...................................................................... 25
Bluetooth and Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) ............................................................. 25
Troubleshooting wireless connection problems ................................................................................. 26
v

Cannot connect to a WLAN ............................................................................................... 26
Cannot connect to a preferred WLAN network .................................................................. 27
Network icon is not displayed ............................................................................................ 27
Current WLAN network security codes are unavailable .................................................... 27
WLAN connection is very weak ......................................................................................... 28
Cannot connect to the wireless router ............................................................................... 28
Connecting to a local area network (LAN) .......................................................................................... 29
3 Pointing devices and keyboard
Using pointing devices ....................................................................................................................... 30
Setting pointing device preferences ................................................................................... 30
Using the TouchPad .......................................................................................................... 30
Two-finger scrolling (select models only) .......................................................... 30
Rotating (select models only) ............................................................................ 31
Pinching (select models only) ........................................................................... 31
Using hotkeys ..................................................................................................................................... 32
Using keypads .................................................................................................................................... 35
Using the embedded numeric keypad ............................................................................... 36
Enabling and disabling the embedded numeric keypad .................................... 36
Switching key functions on the embedded numeric keypad ............................. 37
Using an optional external numeric keypad ....................................................................... 37
Cleaning the TouchPad and keyboard ............................................................................................... 37
4 Multimedia
Multimedia features ............................................................................................................................ 38
Multimedia software ........................................................................................................................... 42
Audio .................................................................................................................................................. 43
Video .................................................................................................................................................. 45
Webcam ............................................................................................................................................. 47
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................. 48
Identifying your multimedia components ........................................................................... 38
Adjusting the volume ......................................................................................................... 40
Using the media activity functions ..................................................................................... 41
Using the media activity hotkeys ....................................................................... 41
Using multimedia software ................................................................................................. 42
Installing multimedia software from a disc ......................................................................... 42
Connecting external audio devices .................................................................................... 43
Checking your audio functions ........................................................................................... 43
Connecting an external monitor or projector ...................................................................... 45
Connecting an HDMI device .............................................................................................. 45
Configuring audio for HDMI (select models only) .............................................. 46
Adjusting webcam properties ............................................................................................. 47
The disc tray does not open for removal of a disc ............................................................. 48
vi

The computer does not detect the optical drive ................................................................. 49
A disc does not play ........................................................................................................... 50
A disc does not play automatically ..................................................................................... 51
A movie stops, skips, or plays erratically ........................................................................... 51
A movie is not visible on an external display ..................................................................... 51
The process of burning a disc does not begin, or it stops before completion .................... 51
A DVD playing in Windows Media Player produces no sound or picture .......................... 52
A device driver must be reinstalled .................................................................................... 52
5 Power management
Setting power options ......................................................................................................................... 54
Using power-saving states ................................................................................................. 54
Using the battery meter ..................................................................................................... 55
Using power plans ............................................................................................................. 56
Setting password protection on wakeup ............................................................................ 56
Using external AC power .................................................................................................................... 57
Connecting the AC adapter ............................................................................................... 57
Testing an AC adapter ....................................................................................................... 58
Using battery power ........................................................................................................................... 58
Identifying batteries ............................................................................................................ 59
Finding battery information in Help and Support ............................................................... 59
Using Battery Check .......................................................................................................... 59
Displaying the remaining battery charge ........................................................................... 59
Inserting or removing the battery ....................................................................................... 60
Charging a battery ............................................................................................................. 61
Maximizing battery discharge time .................................................................................... 62
Managing low battery levels .............................................................................................. 62
Calibrating a battery ........................................................................................................... 63
Obtaining the latest HP device drivers .............................................................. 52
Obtaining the latest Windows device drivers .................................................... 53
Initiating and exiting Sleep ................................................................................ 54
Initiating and exiting Hibernation ....................................................................... 55
Viewing the current power plan ......................................................................... 56
Selecting a different power plan ........................................................................ 56
Customizing power plans .................................................................................. 56
Identifying low battery levels ............................................................................. 62
Resolving a low battery level ............................................................................. 62
Resolving a low battery level when external power is available ....... 63
Resolving a low battery level when a charged battery is
available ........................................................................................... 63
Resolving a low battery level when no power source is
available ........................................................................................... 63
Resolving a low battery level when the computer cannot exit
Hibernation ....................................................................................... 63
vii

6 Drives
Step 1: Fully charge the battery ........................................................................ 63
Step 2: Disable Hibernation and Sleep ............................................................. 64
Step 3: Discharge the battery ............................................................................ 64
Step 4: Fully recharge the battery ..................................................................... 65
Step 5: Reenable Hibernation and Sleep .......................................................... 65
Conserving battery power .................................................................................................. 65
Storing a battery ................................................................................................................ 66
Disposing of a used battery ............................................................................................... 66
Replacing the battery ......................................................................................................... 66
Shutting down the computer ............................................................................................................... 66
Identifying installed drives .................................................................................................................. 68
Handling drives ................................................................................................................................... 68
Using an optical drive ......................................................................................................................... 69
Identifying the installed optical drive .................................................................................. 69
Using optical discs ............................................................................................................. 70
Selecting the right disc (CDs, DVDs, and BDs) ................................................................. 70
CD-R discs ........................................................................................................ 71
CD-RW discs ..................................................................................................... 71
DVD±R discs ..................................................................................................... 71
DVD±RW discs ................................................................................................. 71
LightScribe DVD+R discs .................................................................................. 71
Blu-ray Disc ....................................................................................................... 71
Playing a CD, DVD, or BD ................................................................................................. 72
Configuring AutoPlay ......................................................................................................... 72
Changing DVD region settings .......................................................................................... 73
Observing the copyright warning ....................................................................................... 73
Copying a CD or DVD ........................................................................................................ 74
Creating (burning) a CD or DVD ........................................................................................ 74
Removing an optical disc (CD, DVD, or BD) ..................................................................... 75
Improving hard drive performance ..................................................................................................... 75
Using Disk Defragmenter ................................................................................................... 75
Using Disk Cleanup ........................................................................................................... 76
Using HP ProtectSmart Hard Drive Protection ................................................................................... 76
Identifying HP ProtectSmart Hard Drive Protection status ................................................ 76
Using HP ProtectSmart Hard Drive Protection software .................................................... 77
Replacing the hard drive .................................................................................................................... 77
7 External devices
Using a USB device ........................................................................................................................... 81
viii
Connecting a USB device .................................................................................................. 81
Removing a USB device .................................................................................................... 81

Using an eSATA device ..................................................................................................................... 83
Connecting an eSATA device ............................................................................................ 83
Removing an eSATA device .............................................................................................. 83
8 External media cards
Using Digital Media Slot cards ........................................................................................................... 85
Inserting a digital card ........................................................................................................ 85
Removing a digital card ..................................................................................................... 86
Using ExpressCards ........................................................................................................................... 87
Configuring an ExpressCard .............................................................................................. 87
Inserting an ExpressCard .................................................................................................. 87
Removing an ExpressCard ................................................................................................ 88
9 Memory modules
Adding or replacing memory modules ................................................................................................ 91
Adding or replacing a memory module in the expansion memory module slot ................. 91
Upgrading a memory module in the primary memory module slot .................................... 94
10 Security
Protecting the computer ..................................................................................................................... 98
Using passwords ................................................................................................................................ 99
Setting passwords in Windows .......................................................................................... 99
Setting passwords in Setup Utility ................................................................................... 100
Using antivirus software ................................................................................................................... 103
Using firewall software ..................................................................................................................... 104
Installing critical security updates ..................................................................................................... 105
Installing an optional security cable .................................................................................................. 106
Using the fingerprint reader (select models only) ............................................................................. 106
Locating the fingerprint reader ......................................................................................... 107
Registering fingerprints .................................................................................................... 107
Using your registered fingerprint to log on to Windows ................................................... 108
Administrator password ................................................................................... 100
Managing an administrator password ............................................. 101
Entering an administrator password ............................................... 101
Power-on password ........................................................................................ 101
Managing a power-on password .................................................... 102
Entering a power-on password ....................................................... 102
Appendix A Setup Utility
Starting Setup Utility ......................................................................................................................... 110
Using Setup Utility ............................................................................................................................ 111
Changing the language of Setup Utility ........................................................................... 111
Navigating and selecting in Setup Utility .......................................................................... 111
ix

Displaying system information ......................................................................................... 112
Restoring default settings in Setup Utility ........................................................................ 112
Exiting Setup Utility .......................................................................................................... 112
Setup Utility Menus .......................................................................................................................... 114
Main menu ....................................................................................................................... 114
Security menu .................................................................................................................. 114
System Configuration menu ............................................................................................ 114
Diagnostics menu ............................................................................................................ 115
Appendix B Software updates
Updating the BIOS ........................................................................................................................... 117
Determining the BIOS version ......................................................................................... 117
Downloading a BIOS update ........................................................................................... 117
Updating programs and drivers ........................................................................................................ 119
Index ................................................................................................................................................................. 120
x
1 Notebook tour
Identifying the hardware
Components included with the computer may vary by region and model. The illustrations in this chapter
identify the standard features on most computer models.
To see a list of hardware installed in the computer:
1. Select Start > Control Panel > System and Security.
2. In the System area, click Device Manager.
You can also add hardware or modify device configurations using Device Manager.
Top components
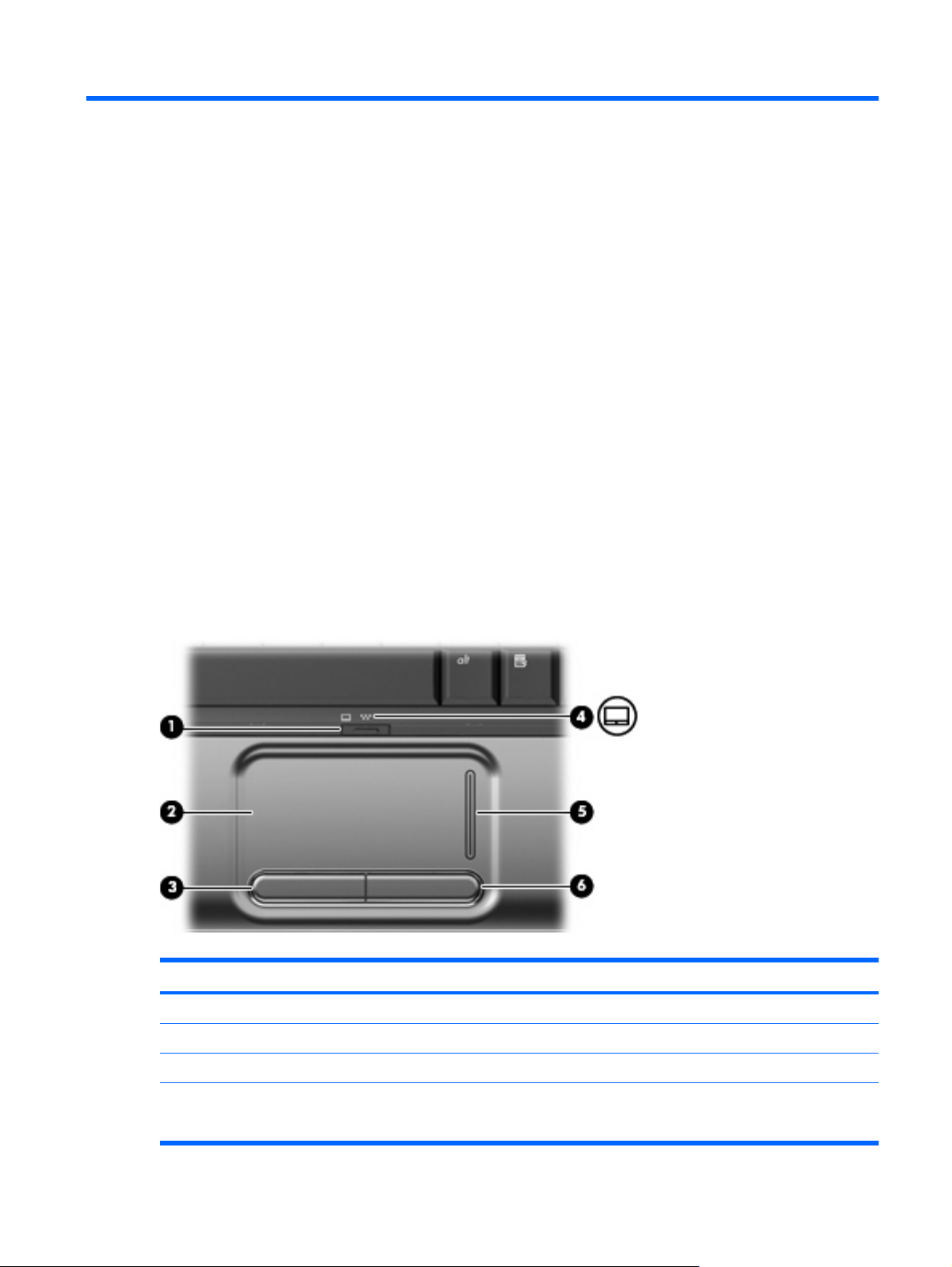
TouchPad
Component Description
(1) TouchPad on/off button Enables/disables the TouchPad.
(2) TouchPad* Moves the pointer and selects or activates items on the screen.
(3) Left TouchPad button* Functions like the left button on an external mouse.
(4) TouchPad light
White: TouchPad is enabled.
●
Amber: TouchPad is disabled.
●
Identifying the hardware 1

Lights
Component Description
(5) TouchPad scroll zone Scrolls up or down.
(6) Right TouchPad button* Functions like the right button on an external mouse.
*This table describes factory settings. To view and change pointing device preferences, select Start > Devices and Printers.
Then, right-click the device representing your computer, and select Mouse settings.
Component Description
(1) Caps lock light On: Caps lock is on.
(2) Power lights (2)*
(3) Wireless light
(4) Volume mute light
2 Chapter 1 Notebook tour
On: The computer is on.
●
Blinking: The computer is in the Sleep state.
●
Off: The computer is off or in Hibernation.
●
On: An integrated wireless device, such as a wireless local
●
area network (WLAN) device and/or a Bluetooth® device, is
on.
Off: All wireless devices are off.
●
White: Computer sound is on.
●
Amber: Computer sound is off.
●

Component Description
(5) Volume down light On: The volume scroll zone is being used to decrease speaker
volume.
(6) Volume up light On: The volume scroll zone is being used to increase speaker
(7) Num lock light On: Num lock is on or the embedded numeric keypad is enabled.
(8) Battery light
(9) Drive light Blinking: The hard drive or optical drive is being accessed.
*The 2 power lights display the same information. The light on the power button is visible only when the computer is open. The
power light on the front of the computer is visible whether the computer is open or closed.
volume.
On: A battery is charging.
●
Blinking: A battery that is the only available power source has
●
reached a low battery level. When the battery reaches a
critical battery level, the battery light begins blinking rapidly.
Off: If the computer is plugged into an external power source,
●
the light is turned off when all batteries in the computer are
fully charged. If the computer is not plugged into an external
power source, the light stays off until the battery reaches a
low battery level.
Buttons and fingerprint reader (select models only)
Identifying the hardware 3

Component Description
(1) Power button*
(2) Wireless button Turns the wireless feature on or off but does not create a wireless
(3) Volume mute button Mutes and restores speaker sound.
(4) Volume scroll zone To decrease the volume, slide your finger to the left on the scroll
When the computer is off, press the button to turn on the
●
computer.
When the computer is on, press the button briefly to initiate
●
Sleep.
When the computer is in the Sleep state, press the button
●
briefly to exit Sleep.
When the computer is in Hibernation, press the button briefly
●
to exit Hibernation.
If the computer has stopped responding and Windows® shutdown
procedures are ineffective, press and hold the power button for at
least 5 seconds to turn off the computer.
To learn more about your power settings, select Start > Control
Panel > System and Security > Power Options.
connection.
NOTE: To establish a wireless connection, a wireless network
must already be set up.
zone or tap the minus sign. To increase the volume, slide your
finger to the right on the scroll zone or tap the plus sign.
(5) Fingerprint reader (select models only) Allows a fingerprint logon to Windows, instead of a password
*This table describes factory settings. For information about changing factory settings, refer to the user guides located in Help
and Support.
logon.
4 Chapter 1 Notebook tour
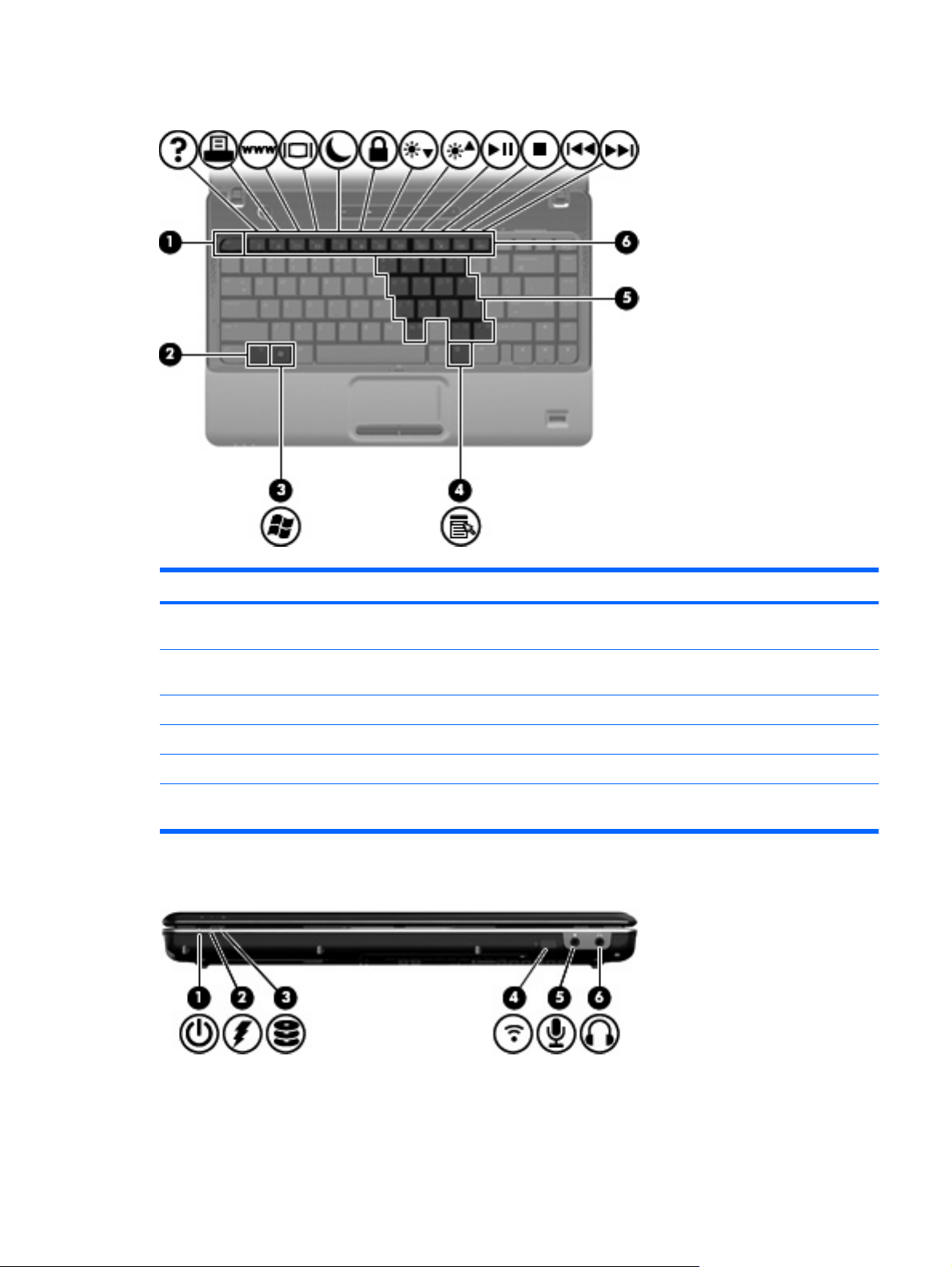
Keys
Component Description
(1) esc key Displays system information when pressed in combination with the
(2) fn key Executes frequently used system functions when pressed in
(3) Windows logo key Displays the Windows Start menu.
(4) Windows applications key Displays a shortcut menu for items beneath the pointer.
(5) Embedded numeric keypad keys Can be used like the keys on an external numeric keypad.
(6) Function keys Execute frequently used system functions when pressed in
Front components
fn key.
combination with a function key or the esc key.
combination with the fn key.
Identifying the hardware 5

Component Description
(1) Power light
(2) Battery light
(3) Drive light Blinking: The hard drive or optical drive is being accessed.
(4) Consumer infrared lens Receives a signal from the remote control (provided with select
(5) Audio-in (microphone) jack Connects an optional computer headset microphone, stereo array
(6) Audio-out (headphone) jack Produces sound when connected to optional powered stereo
On: The computer is on.
●
Blinking: The computer is in the Sleep state.
●
Off: The computer is off or in Hibernation.
●
On: A battery is charging.
●
Blinking: A battery that is the only available power source has
●
reached a low battery level or a critical battery level.
Off: If the computer is plugged into an external power source,
●
the light is turned off when all batteries in the computer are
fully charged. If the computer is not plugged into an external
power source, the light stays off until the battery reaches a low
battery level.
models only).
microphone, or monaural microphone.
speakers, headphones, ear buds, a headset, or television audio.
Right-side components
Component Description
(1) ExpressCard slot Supports an optional ExpressCard/34 module.
(2) Digital Media Slot Supports the following optional digital card formats: Secure Digital
(3) Digital Media Slot light Blinking: The media card is being accessed.
(4) eSATA/USB port Connects a high-performance eSATA component, such as an
(5) HDMI port Connects an optional video or audio device, such as a high-
(SD) Memory Card, Secure Digital Input/Output (SD I/O),
MultiMediaCard (MMC), Memory Stick (MS), Memory Stick Pro
(MSP), xD-Picture Card (XD).
eSATA external hard drive, or connects an optional USB device.
definition television, or any compatible digital or audio component.
6 Chapter 1 Notebook tour
NOTE: Depending on your computer model, the computer may
include an HDMI port or a USB port at this location.

Component Description
(6) RJ-45 (network) jack Connects a network cable.
(7) External monitor port Connects an external VGA monitor or projector.
(8) Vent Enables airflow to cool internal components.
(9) Security cable slot Attaches an optional security cable to the computer.
Left-side components
NOTE: The computer fan starts up automatically to cool internal
components and prevent overheating. It is normal for the internal
fan to cycle on and off during routine operation.
NOTE: The security cable is designed to act as a deterrent, but
it may not prevent the computer from being mishandled or stolen.
Component Description
(1) Power connector Connects an AC adapter.
(2) AC adapter light
(3) USB ports (2) Connect optional USB devices.
(4) Optical drive Reads optical discs and, on select models, also writes to optical
(5) Optical drive light Blinking: The drive is being accessed.
On: The computer is connected to external power.
●
Off: The computer is not connected to external power.
●
discs.
Identifying the hardware 7
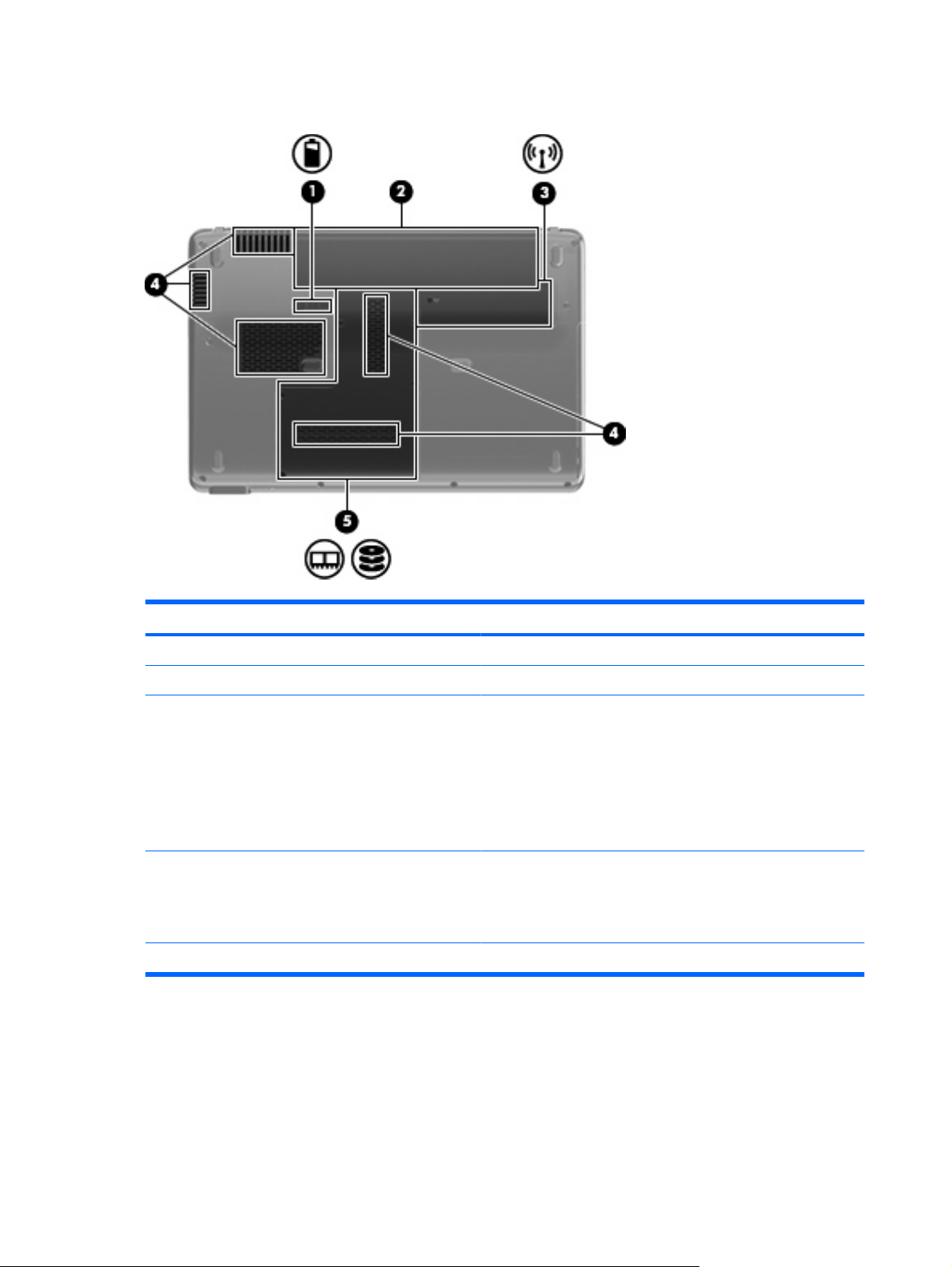
Bottom components
Component Description
(1) Battery release latch Releases the battery from the battery bay.
(2) Battery bay Holds the battery.
(3) Wireless module compartment Holds a wireless LAN module.
NOTE: To prevent an unresponsive system, replace the wireless
module only with a wireless module authorized for use in the
computer by the governmental agency that regulates wireless
devices in your country or region. If you replace the module and
then receive a warning message, remove the module to restore
computer functionality, and then contact technical support through
Help and Support.
(4) Vents (5) Enable airflow to cool internal components.
NOTE: The computer fan starts up automatically to cool internal
components and prevent overheating. It is normal for the internal
fan to cycle on and off during routine operation.
(5) Hard drive bay Holds the hard drive and the memory module slots.
8 Chapter 1 Notebook tour

Display components
Component Description
(1) Webcam light On: The webcam is in use.
(2) Webcam (select models only) Records audio and video and captures still photographs.
(3) Internal microphone Records sound.
(4) Internal display switch Turns off the display and initiates Sleep if the display is closed while
Wireless antennas
On select computer models, at least 2 antennas send and receive signals from one or more wireless
devices. These antennas are not visible from the outside of the computer.
the power is on.
Identifying the hardware 9
NOTE: For optimal transmission, keep the areas immediately around the antennas free from
obstructions.
To see wireless regulatory notices, refer to the section of the Regulatory, Safety and Environmental
Notices that applies to your country or region. These notices are located in Help and Support.
Additional hardware components
Component Description
(1) Power cord* Connects an AC adapter to an AC outlet.
(2) AC adapter Converts AC power to DC power.
10 Chapter 1 Notebook tour

Component Description
(3) Battery* Powers the computer when the computer is not plugged into
*Batteries and power cords vary in appearance by region and country.
Identifying the labels
The labels affixed to the computer provide information you may need when you troubleshoot system
problems or travel internationally with the computer.
Service tag—Provides important information including the following:
●
The service tag label is affixed to the bottom of the computer.
Product name (1). This is the product name affixed to the front of your notebook.
◦
external power.
Serial number (s/n) (2). This is an alphanumeric identifier that is unique to each product.
◦
Part number/Product number (p/n) (3). This number provides specific information about the
◦
product's hardware components. The part number helps a service technician to determine
what components and parts are needed.
Model description (4). This is the alphanumeric identifier you use to locate documents, drivers,
◦
and support for your notebook.
Warranty period (5). This number describes the duration (in years) of the warranty period for
◦
this computer.
Have this information available when you contact technical support. The service tag label is affixed
to the bottom of the computer.
Microsoft® Certificate of Authenticity—Contains the Windows® Product Key. You may need the
●
Product Key to update or troubleshoot the operating system. This certificate is affixed to the bottom
of the computer.
Regulatory label—Provides regulatory information about the computer. The regulatory label is
●
affixed inside the battery bay.
Wireless certification label(s) (select models only)—Provide information about optional wireless
●
devices and the approval markings of some of the countries or regions in which the devices have
been approved for use. An optional device may be a wireless local area network (WLAN) device
or an optional Bluetooth® device. If your computer model includes one or more wireless devices,
one or more certification labels are included with your computer. You may need this information
when traveling internationally. Wireless certification labels are affixed inside the Mini Card
compartment.
Identifying the labels 11

SIM (subscriber identity module) label (select models only)—Provides the ICCID (Integrated Circuit
●
Card Identifier) of your SIM. This label is located inside the battery bay.
HP Mobile Broadband Module serial number label (select models only)—Provides the serial
●
number of your HP Mobile Broadband Module. This label is located inside the battery bay.
12 Chapter 1 Notebook tour

2 Wireless and local area network
13

Using wireless devices
Wireless technology transfers data across radio waves instead of wires. Your computer may be
equipped with one or more of the following wireless devices:
Wireless local area network (WLAN) device—Connects the computer to wireless local area
●
networks (commonly referred to as Wi-Fi networks, wireless LANs, or WLANs) in corporate offices,
your home, and public places such as airports, restaurants, coffee shops, hotels, and universities.
In a WLAN, each mobile wireless device communicates with a wireless router or a wireless access
point.
HP Mobile Broadband Module—A wireless wide area network (WWAN) device that provides
●
access to information wherever mobile network operator service is available. In a WWAN, each
mobile device communicates to a mobile network operator’s base station. Mobile network operators
install networks of base stations (similar to cell phone towers) throughout large geographic areas,
effectively providing coverage across entire states, regions, or even countries.
Bluetooth® device—Creates a personal area network (PAN) to connect to other Bluetooth-enabled
●
devices such as computers, phones, printers, headsets, speakers, and cameras. In a PAN, each
device communicates directly with other devices, and devices must be relatively close together—
typically within 10 meters (approximately 33 feet) of each other.
Computers with WLAN devices support one or more of the following IEEE industry standards:
802.11b, the first popular standard, supports data rates of up to 11 Mbps and operates at a
●
frequency of 2.4 GHz.
802.11g supports data rates of up to 54 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz. An 802.11g
●
WLAN device is backward compatible with 802.11b devices, so they can operate on the same
network.
802.11a supports data rates of up to 54 Mbps and operates at a frequency of 5 GHz.
●
NOTE: 802.11a is not compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g.
802.11n supports data rates of up to 450 Mbps and may operate at 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, making it
●
backward compatible with 802.11a, b, and g.
For more information on wireless technology, refer to the information and Web site links provided in
Help and Support.
Identifying wireless and network status icons
Icon Name Description
Wireless (connected) Identifies the location of the wireless light and the wireless
Wireless (disconnected) Identifies the Wireless Assistant software on the computer
function key on the computer. Also identifies the Wireless
Assistant software on the computer and indicates that one or
more of the wireless devices are on.
and indicates that all of the wireless devices are off.
HP Connection Manager Opens HP Connection Manager, which enables you to create
14 Chapter 2 Wireless and local area network
a connection with an HP Mobile Broadband device (select
models only).

Wired network (connected) Indicates that one or more of your network drivers are
installed and one or more network devices are connected to
the network.
Wired network (disabled/disconnected) Indicates that one or more of your network drivers are
Network (disabled/disconnected) Indicates that one or more of your network drivers are
Network (connected) Indicates that one or more of your network drivers are
Network (disconnected) Indicates that one or more of your network drivers are
Using the wireless controls
You can control the wireless devices in your computer using these features:
Wireless button or wireless switch
●
installed, all network devices or all wireless devices are
disabled in Windows® Control Panel, and no network
devices are connected to a wired network.
installed, no wireless connections are available or all wireless
network devices are disabled by the wireless button or
Wireless Assistant, and no network devices are connected
to a wired network.
installed, one or more network devices are connected to a
wireless network, and one or more network devices are
connected to a wired network.
installed and wireless connections are available, but no
network devices are connected to a wired or wireless
network.
Wireless Assistant software
●
HP Connection Manager software (select models only)
●
Operating system controls
●
Using the wireless button
The computer has a wireless button, one or more wireless devices, and one or two wireless lights,
depending on the model. All of the wireless devices on your computer are enabled at the factory, so the
wireless light is on (blue) when you turn on the computer.
The wireless light indicates the overall power state of your wireless devices, not the status of individual
devices. If the wireless light is blue, at least one wireless device is on. If the wireless light is off, all
wireless devices are off.
NOTE: On some models, the wireless light is amber when all wireless devices are off.
Because the wireless devices are enabled at the factory, you can use the wireless button to turn on or
turn off the wireless devices simultaneously. Individual wireless devices can be controlled through
Wireless Assistant software (select models only).
Using Wireless Assistant software (select models only)
A wireless device can be turned on or off using Wireless Assistant software. If a wireless device is
disabled in Setup Utility, it must be reenabled in Setup Utility before it can be turned on or off using
Wireless Assistant.
Using wireless devices 15

NOTE: Enabling or turning on a wireless device does not automatically connect the computer to a
network or a Bluetooth-enabled device.
To view the state of the wireless devices, click the Show hidden icons icon, the arrow at the left of the
notification area, and position the mouse pointer over the wireless icon.
If the wireless icon is not displayed in the notification area, complete the following steps to change
Wireless Assistant properties:
1. Select Start > Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Windows Mobility Center.
2. Click the wireless icon in the Wireless Assistant tile, which is located in the bottom row of Windows®
Mobility Center.
3. Click Properties.
4. Select the check box next to HP Wireless Assistant icon in notification area.
5. Click Apply.
6. Click Close.
For more information, refer to the Wireless Assistant software Help:
1. Open Wireless Assistant by clicking the wireless icon in Windows Mobility Center.
2. Click the Help button.
Using operating system controls
Some operating systems also offer a way to manage integrated wireless devices and the wireless
connection. For example, Windows provides the Network and Sharing Center that allows you to set up
a connection or network, connect to a network, manage wireless networks, and diagnose and repair
network problems.
To access the Network and Sharing Center, select Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet >
Network and Sharing Center.
For more information, select Start > Help and Support.
16 Chapter 2 Wireless and local area network
Using a WLAN
With a WLAN device, you can access a wireless local area network (WLAN), which is composed of other
computers and accessories that are linked by a wireless router or a wireless access point.
NOTE: The terms wireless router and wireless access point are often used interchangeably.
A large-scale WLAN, such as a corporate or public WLAN, typically uses wireless access points
●
that can accommodate a large number of computers and accessories and can separate critical
network functions.
A home or small office WLAN typically uses a wireless router, which allows several wireless and
●
wired computers to share an Internet connection, a printer, and files without requiring additional
pieces of hardware or software.
To use the WLAN device in your computer, you must connect to a WLAN infrastructure (provided through
a service provider or a public or corporate network).
Setting up a WLAN
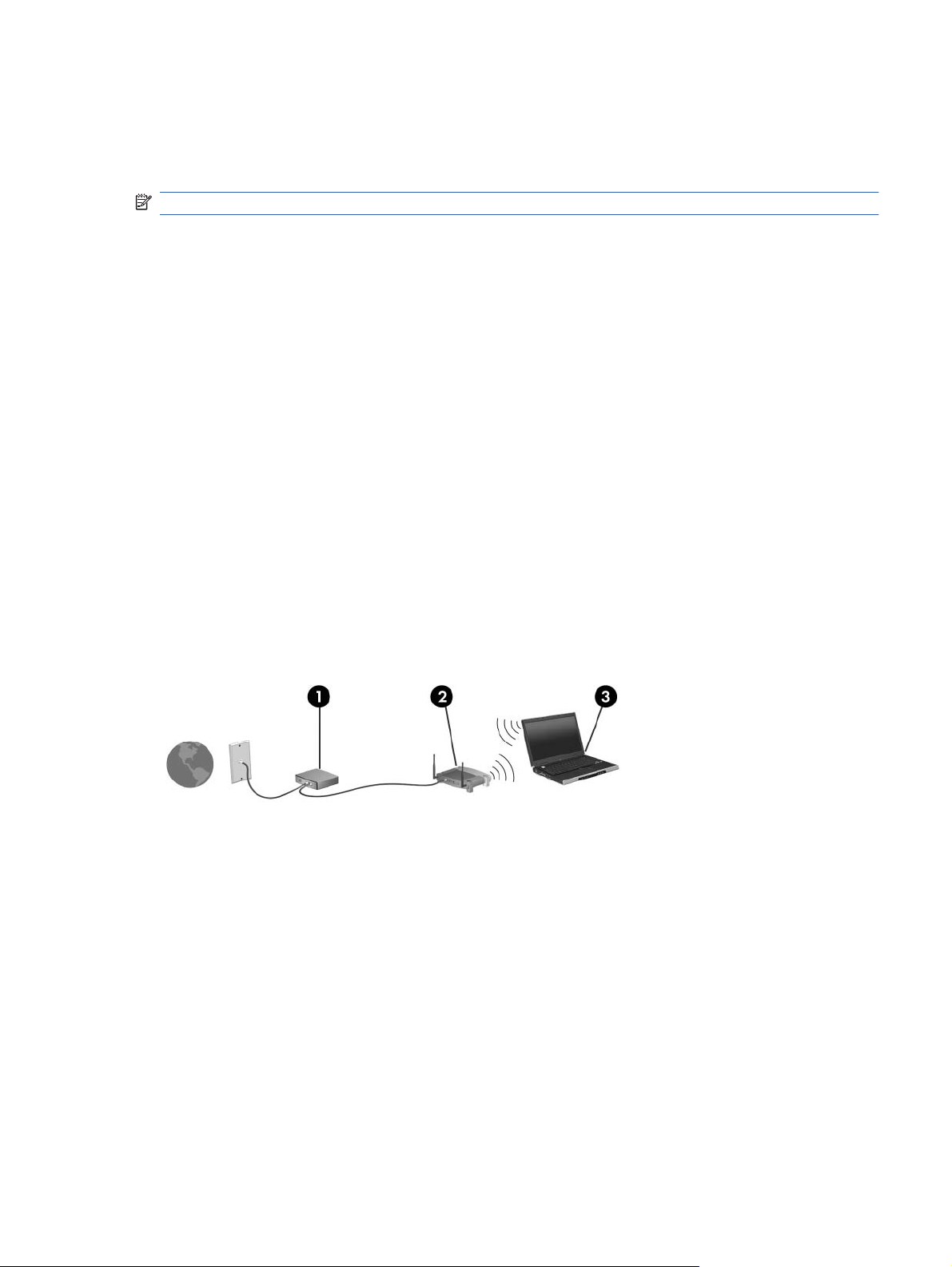
To set up a WLAN and connect to the Internet, you need the following equipment:
A broadband modem (either DSL or cable) (1) and high-speed Internet service purchased from an
●
Internet service provider (ISP)
A wireless router (purchased separately) (2)
●
The wireless computer (3)
●
The following illustration shows an example of a wireless network installation that is connected to the
Internet.
As your network grows, additional wireless and wired computers can be connected to the network to
access the Internet.
For help in setting up your WLAN, refer to the information provided by your router manufacturer or your
ISP.
Protecting your WLAN
Because the WLAN standard was designed with only limited security capabilities—basically to foil casual
eavesdropping rather than more powerful forms of attack—it is essential to understand that WLANs are
vulnerable to well-known and well-documented security weaknesses.
WLANs in public areas, or “hotspots,” like coffee shops and airports may not provide any security. New
technologies are being developed by wireless manufacturers and hotspot service providers that make
the public environment more secure and anonymous. If you are concerned about the security of your
computer in a hotspot, limit your network activities to noncritical e-mail and basic Internet surfing.
Using a WLAN 17

When you set up a WLAN or access an existing WLAN, always enable security features to protect your
network from unauthorized access. The common security levels are Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)Personal and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). Because wireless radio signals travel outside the
network, other WLAN devices can pick up unprotected signals and either connect to your network
(uninvited) or capture information being sent across it. However, you can take precautions to protect
your WLAN:
Use a wireless transmitter with built-in security
●
Many wireless base stations, gateways, or routers provide built-in security features such as
wireless security protocols and firewalls. With the correct wireless transmitter, you can protect your
network from the most common wireless security risks.
Work behind a firewall
●
A firewall is a barrier that checks both data and requests for data that are sent to your network,
and discards any suspicious items. Firewalls are available in many varieties, both software and
hardware. Some networks use a combination of both types.
Use wireless encryption
●
A variety of sophisticated encryption protocols is available for your WLAN. Find the solution that
works best for your network security:
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a wireless security protocol that encodes or encrypts all
◦
network data before it is transmitted using a WEP key. Usually, you can allow the network to
assign the WEP key. Alternatively, you can set up your own key, generate a different key, or
choose other advanced options. Without the correct key, others will not be able to use the
WLAN.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), like WEP, uses security settings to encrypt and decrypt data
◦
that is transmitted over the network. However, instead of using one static security key for
encryptions as WEP does, WPA uses “temporal key integrity protocol” (TKIP) to dynamically
generate a new key for every packet. It also generates different sets of keys for each computer
on the network.
Connecting to a WLAN
To connect to the WLAN, follow these steps:
1. Be sure that the WLAN device is on. If it is on, the wireless light is on. If the wireless light is amber,
press the wireless button.
2. Click the network icon in the notification area, at the far right of the taskbar.
3. Select your WLAN from the list.
4. Click Connect.
If the network is a security-enabled WLAN, you are prompted to enter a network security key, which
is a security code. Type the code, and then click OK to complete the connection.
NOTE: If no WLANs are listed, you are out of range of a wireless router or access point.
NOTE: If you do not see the network you want to connect to, click Open Network and Sharing
Center, and then click Set up a new connection or network. A list of options is displayed. You
can choose to manually search for and connect to a network or to create a new network connection.
18 Chapter 2 Wireless and local area network
After the connection is made, place the mouse pointer over the network icon in the notification area, at
the far right of the taskbar, to verify the name and status of the connection.
NOTE: The functional range (how far your wireless signals travel) depends on WLAN implementation,
router manufacturer, and interference from other electronic devices or structural barriers such as walls
and floors.
More information about using a WLAN is available through the following resources:
Information from your ISP and the manufacturer's instructions included with your wireless router
●
and other WLAN equipment
Information and Web site links provided in Help and Support
●
For a list of public WLANs near you, contact your ISP or search the Web. Web sites that list public
WLANs include Cisco Internet Mobile Office Wireless Locations, Hotspotlist, and Geektools. Check with
each public WLAN location for cost and connection requirements.
For additional information on connecting your computer to a corporate WLAN, contact your network
administrator or IT department.
Roaming to another network
When you move your computer within range of another WLAN, Windows attempts to connect to that
network. If the attempt is successful, your computer is automatically connected to the new network. If
Windows does not recognize the new network, follow the same procedure you used initially to connect
to your WLAN.
Using a WLAN 19
Using HP Mobile Broadband (select models only)
HP Mobile Broadband enables your computer to use wireless wide area networks (WWANs) to access
the Internet from more places and over larger areas than it can by using WLANs. Using HP Mobile
Broadband requires a network service provider (called a mobile network operator), which in most cases
is a mobile phone network operator. Coverage for HP Mobile Broadband is similar to mobile phone voice
coverage.
When used with mobile network operator service, HP Mobile Broadband gives you the freedom to stay
connected to the Internet, send e-mail, or connect to your corporate network whether you are on the
road or outside the range of Wi-Fi hotspots.
HP Mobile Broadband supports UNDP (Universal Notebook Data Platform), which enables data
connectivity for notebook computers.
You may need the HP Mobile Broadband Module serial number to activate mobile broadband service.
The serial number is printed on a label inside the battery bay of your computer.
Some mobile network operators require the use of a subscriber identity module (SIM). A SIM contains
basic information about you, such as a personal identification number (PIN), as well as network
information. Some computers include a SIM that is preinstalled in the battery bay. If the SIM is not
preinstalled, it may be provided in the HP Mobile Broadband information provided with your computer,
or the mobile network operator may provide it separately from the computer.
For information on inserting and removing the SIM, refer to the “Inserting a SIM” and “Removing a SIM”
sections in this chapter.
For information on HP Mobile Broadband and how to activate service with a preferred mobile network
operator, refer to the HP Mobile Broadband information included with your computer. For additional
information, see the HP Web site at
Inserting a SIM
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the connectors, use minimal force when inserting a SIM.
To insert a SIM:
1. Shut down the computer. If you are not sure whether the computer is off or in Hibernation, turn the
computer on by pressing the power button. Then shut down the computer through the operating
system.
2. Close the display.
3. Disconnect all external devices connected to the computer.
4. Unplug the power cord from the AC outlet.
5. Turn the computer upside down on a flat surface, with the battery bay toward you.
6. Remove the battery.
7. Lift the compartment cover (1) to release it, and then lift and rotate the compartment cover (2).
http://www.hp.com/go/mobilebroadband (United States only).
20 Chapter 2 Wireless and local area network
