Page 1

Notice
The information in this guide is subject to change without notice.
COMPAQ COMPUTER CORPORATION SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR
TECHNICAL OR EDITORIAL ERRORS OR OMISSIONS CONTAINED
HEREIN; NOR FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
RESULTING FROM THE FURNISHING, PERFORMANCE, OR USE OF
THIS MATERIAL.
This guide contains information protected by copyright. No part of this
guide may be photocopied or reproduced in any form without prior
written consent from Compaq Computer Corporation.
© 2000 Compaq Computer Corporation. All rights reserved. Printed in
the U.S.A., U.K, Singapore, and Taiwan,.
Compaq
Office.
Microsoft, MS-DOS, and Windows are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks, and SpeedStep is a
trademark of Intel Corporation.
Imation and SuperDisk are trademarks of Imation Enterprises
Corporation.
Software described herein is furnished under a license agreement or
nondisclosure agreement. The software may be used or copied only in
accordance with the terms of the agreement.
Product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered
trademarks of their respective companies.
and Armada are registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark
COMPAQ ARMADA E500 S ERIES
REFERENCE GUIDE
Second Edition June 2000
First Edition January 2000
Part Number 170045-002
Compaq Computer Corporation
Page 2

CONTENTS
chapter 1
TAKING A LOOK AT THE COMPUTER
Top Components...............................................................................1-1
Left Side Components ......................................................................1-3
Right Side Components....................................................................1-4
Rear Components..............................................................................1-6
Bottom Components.........................................................................1-7
Status Indicator Lights......................................................................1-8
chapter 2
USING THE KEYBOARD
Using the Pointing Device................................................................2-1
Identifying TouchPad Components .............................................2-1
Navigating with the TouchPad.....................................................2-2
Setting TouchPad Preferences .....................................................2-2
Identifying Pointing-Stick Components ......................................2-3
Navigating with the Pointing-Stick..............................................2-4
Setting Pointing-Stick Preferences ..............................................2-5
Using Hotkeys...................................................................................2-6
Switching the Image.....................................................................2-7
Adjusting System Volume ...........................................................2-7
Initiating Quick Controls..............................................................2-8
Setting a Power Conservation Level............................................2-8
Viewing Battery Status.................................................................2-8
Adjusting Panel Contrast..............................................................2-8
Adjusting Brightness....................................................................2-9
Displaying System Information...................................................2-9
Stretching Text .............................................................................2-9
Using the Embedded Numeric Keypad..........................................2-10
Toggling the Keypad On and Off ..............................................2-10
Operating the Keypad Keys as Standard Keys..........................2-11
Enabling the Keypad at Startup .................................................2-11
Contents v
Page 3

Easy Access Buttons....................................................................... 2-12
Adding Easy Access Buttons Schemes ..................................... 2-13
Changing Easy Access Buttons Schemes.................................. 2-14
Deleting Easy Access Buttons Schemes.................................... 2-14
Disabling and Enabling the Easy Access Buttons..................... 2-15
Programming the External Keyboard Internet Buttons............. 2-15
chapter 3
USING BATTERY PACKS
Learning About Battery Packs......................................................... 3-1
Using a New Battery Pack................................................................ 3-2
Charging Battery Packs.................................................................... 3-2
Inserting and Removing the Primary Battery Pack........................ 3-3
Removing the Primary Battery Pack........................................... 3-3
Inserting the Primary Battery Pack.............................................. 3-4
Storing a Battery Pack...................................................................... 3-5
Maximizing Battery Pack Life......................................................... 3-5
Recycling Used Battery Packs......................................................... 3-6
System Beeps.................................................................................... 3-6
Beeps with a Blinking Battery Charge Light .............................. 3-6
Beeps with a Blinking Power/Suspend Light.............................. 3-7
Turning Beeps On or Off............................................................. 3-7
chapter 4
MANAGING POWER
Selecting a Power Source................................................................. 4-1
Using Suspend (Standby) and Hibernation...................................... 4-2
Managing Low-Battery Conditions ................................................. 4-5
Identifying Low-Battery Conditions ........................................... 4-5
Resolving Low-Battery Conditions............................................. 4-6
Restoring from Hibernation After Resolving a
Critical Low-Battery Condition................................................... 4-6
Charging a Battery Pack................................................................... 4-7
Monitoring the Charge in a Battery Pack.........................................4-8
Using the Battery Status Tab....................................................... 4-8
Displaying Power Source and Battery Power Status in
Windows 2000 Professional ........................................................ 4-9
Using the Battery Meter or Power Meter Icon............................ 4-9
Using the Power or Power Meter Tab....................................... 4-11
vi Contents
Page 4

Calibrating a Battery Pack..............................................................4-12
Running a Calibration ................................................................4-13
Stopping a Calibration................................................................4-14
Using Power Preferences................................................................4-15
Setting Power Preferences in Windows 95 and
Windows NT 4.0 ........................................................................4-16
Setting Power Preferences in Windows 98................................4-18
Setting Power Preferences in Windows 2000 Professional.......4-19
Turning Auto Insert Notification On or Off..............................4-20
Changing the Processor Performance Mode
(Available on Select Models).........................................................4-20
Changing Performance Modes...................................................4-21
Combining Performance Modes with
Other Power Settings..................................................................4-21
Setting SpeedStep Preferences.......................................................4-21
Using the SpeedStep Window....................................................4-21
Using the SpeedStep Icon ..........................................................4-24
Conserving Battery Power..............................................................4-24
Battery Power Conservation Checklist......................................4-24
Conserving Battery Power in Windows 95................................4-25
Conserving Battery Power in Windows 98................................4-25
Conserving Battery Power in Windows 2000 Professional......4-26
Conserving Battery Power in Windows NT 4.0........................4-26
chapter 5
WORKING WITH REMOVABLE DRIVES AND DEVICE BAYS
Bay Configuration.............................................................................5-1
Caring for Removable Drives...........................................................5-2
Changing the Startup Sequence with MultiBoot.........................5-3
Selecting Diskettes............................................................................5-4
DualBay Devices ..............................................................................5-4
Inserting a DualBay Device.........................................................5-4
Removing a DualBay Device.......................................................5-5
Second Battery Pack.....................................................................5-5
MultiBay Devices.............................................................................5-6
Inserting a MultiBay Device........................................................5-6
Removing a MultiBay Device......................................................5-7
Using the CD or DVD Drive........................................................5-8
Manually Ejecting a CD or DVD.................................................5-9
Using the LS-120 Drive ...............................................................5-9
Using the Third Battery Pack.......................................................5-9
Contents vii
Page 5

chapter 6
USING AN INTERNAL MODEM (AVAILABLE ON SELECT MODELS)
Connecting the Modem Cable.......................................................... 6-1
Setting up the Modem ...................................................................... 6-2
Selecting Communication Software................................................. 6-3
Configuring the Modem................................................................... 6-5
Using Modem Commands and Dial Modifiers................................ 6-6
Using the Modem While Traveling Internationally......................... 6-7
Using a Country-Specific Modem Adapter................................. 6-7
Selecting a Country-Specific Modem Configuration.................. 6-8
Travel Connection Checklist ....................................................... 6-9
Reinstalling or Updating Drivers
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)......................................................... 6-9
Uninstalling Modem Drivers:
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)................................................... 6-10
Reinstalling Modem Drivers:
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)................................................... 6-10
Reinstalling or Updating Drivers (Windows NT 4.0) .................. 6-10
Uninstalling Modem Drivers: (Windows NT 4.0)................... 6-11
Reinstalling Modem Drivers: (Windows NT 4.0).................... 6-11
chapter 7
CONNECTING TO A LOCAL AREA NETWORK (AVAILABLE ON SELECT MODELS)
Connecting the Network Cable........................................................ 7-1
Turning a LAN Connection On and Off.......................................... 7-2
Accessing the Network at Startup.................................................... 7-2
Reinstalling or Updating Drivers (Windows 95 or Windows 98)... 7-2
Uninstalling Modem and LAN Drivers:
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)..................................................... 7-3
Reinstalling LAN and Modem Drivers
(Windows 95 and Windows 98).................................................. 7-3
Confirming the Network Protocol
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)..................................................... 7-4
Reinstalling or Updating Drivers (Windows NT 4.0) .................... 7-5
Uninstalling Modem and LAN Drivers: (Windows NT 4.0)...... 7-5
Reinstalling Windows NT Networking: (Windows NT 4.0)...... 7-6
viii Contents
Page 6

chapter 8
CONNECTING EXTERNAL DEVICES
Connecting an External Enhanced Keyboard ..................................8-1
Connecting an External Monitor......................................................8-1
Connecting a Television Monitor.....................................................8-2
Connecting a Mouse or Other External Pointing Device.................8-3
Connecting a Serial Printer...............................................................8-3
Connecting a Parallel Printer............................................................8-3
Connecting Infrared Equipment.......................................................8-4
Configuring the Infrared Port.......................................................8-5
Enabling the Infrared Port............................................................8-5
Connecting USB Peripherals............................................................8-6
Connecting to a Docking Device......................................................8-6
chapter 9
USING PC CARDS
PC Card Types..................................................................................9-1
Inserting a PC Card...........................................................................9-1
Removing a PC Card........................................................................9-3
PC Card Device Drivers ...................................................................9-4
Changing PC Card Settings..............................................................9-4
Managing PC Card Power................................................................9-5
Zoomed Video ..................................................................................9-5
Stopping a PC Card...........................................................................9-5
chapter 10
USING AUDIO FEATURES
Identifying the Audio Components................................................10-1
Using Internal and External Microphones .....................................10-2
Using Internal and External Speakers/Headphones.......................10-3
Controlling Audio Volume.............................................................10-3
Speaker Ports ..................................................................................10-4
Contents ix
Page 7

chapter 11
UPGRADING THE COMPUTER
Upgrading System Memory........................................................... 11-1
Checking the Amount of Memory............................................. 11-1
Obtaining an Optional Memory Expansion Board.................... 11-2
Inserting a Memory Expansion Board....................................... 11-2
Removing a Memory Expansion Board.................................... 11-4
Upgrading the Hard Drive.............................................................. 11-6
Removing and Inserting the Primary Hard Drive ..................... 11-6
Attaching a Hard Drive Adapter.................................................... 11-6
Adding an Internal Modem............................................................ 11-6
chapter 12
MAINTENANCE & TRAVEL GUIDELINES
Updating the System....................................................................... 12-1
Obtaining Customized Update Information with
Info Messenger........................................................................... 12-1
Obtaining Software Updates and Enhancements
by Subscription .......................................................................... 12-1
Obtaining Software Updates from the Compaq Internet Site... 12-2
Ordering Preinstalled Software.................................................. 12-2
Updating the System ROM........................................................ 12-2
Reinstalling Software..................................................................... 12-4
Caring for the Computer................................................................. 12-4
Preparing the Computer for Shipping or Travel............................ 12-5
Traveling with the Computer ......................................................... 12-5
x Contents
Page 8

chapter 13
SECURITY FEATURES
Types of Security............................................................................13-1
Using the Cable Lock .....................................................................13-2
Using the Power-On Password.......................................................13-3
Establishing the Power-On Password........................................13-3
Establishing the Power-On Password in
Windows 2000 Professional.......................................................13-4
Entering a Power-On Password .................................................13-4
Changing the Power-On Password ............................................13-5
Deleting the Power-On Password..............................................13-6
If You Forget Your Power-On Password ..................................13-6
Establishing the Administrator Password
(Windows 2000 Professional)....................................................13-7
Using Quick Controls.....................................................................13-7
Enabling Quick Controls............................................................13-8
Initiating Quick Controls............................................................13-8
Using the Setup Password ..............................................................13-8
Establishing the Setup Password................................................13-8
Entering the Setup Password......................................................13-9
Changing the Setup Password..................................................13-10
Deleting the Setup Password....................................................13-10
Enabling and Disabling Devices ..................................................13-11
DriveLock Overview ....................................................................13-11
User and Master Passwords Overview ....................................13-12
Establishing DriveLock Protection..........................................13-13
Changing the User or Master Password...................................13-14
Removing DriveLock Protection.............................................13-15
Compaq Computer Security (Windows 2000 Professional)........13-16
Setting Port Security.................................................................13-16
Setting Boot (Start-Up) Security..............................................13-16
Displaying or Entering System Information............................13-17
Contents xi
Page 9

chapter 14
INTELLIGENT MANAGEABILITY
Intelligent Manageability Overview .............................................. 14-1
Asset Management ......................................................................... 14-2
Fault Management.......................................................................... 14-3
Fault Management Alerts........................................................... 14-3
Security Management..................................................................... 14-4
Configuration Management............................................................ 14-4
chapter 15
COMPUTER SETUP AND DIAGNOSTICS UTILITIES
Selecting Computer Setup or Compaq Diagnostics
for Windows................................................................................... 15-1
Using Computer Setup ................................................................... 15-2
Selecting from the File Menu.................................................... 15-3
Selecting from the Security Menu............................................. 15-3
Selecting from the Advanced Menu.......................................... 15-4
Using Compaq Diagnostics for Windows...................................... 15-6
Displaying System Information................................................. 15-6
Running a Diagnostic Test......................................................... 15-6
chapter 16
TROUBLESHOOTING
Troubleshooting Checklist ............................................................. 16-1
appendix A
COMPAQ CUSTOMER SUPPORT
Preparing to Call Technical Support............................................... A-1
Worldwide Telephone Numbers..................................................... A-2
appendix B
REGULATORY NOTICES
appendix C
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE
appendix D
SPECIFICATIONS
INDEX .......................................................................................................I-1
xii Contents
Page 10
chapter
1
TAKING A LOOK AT THE COMPUTER
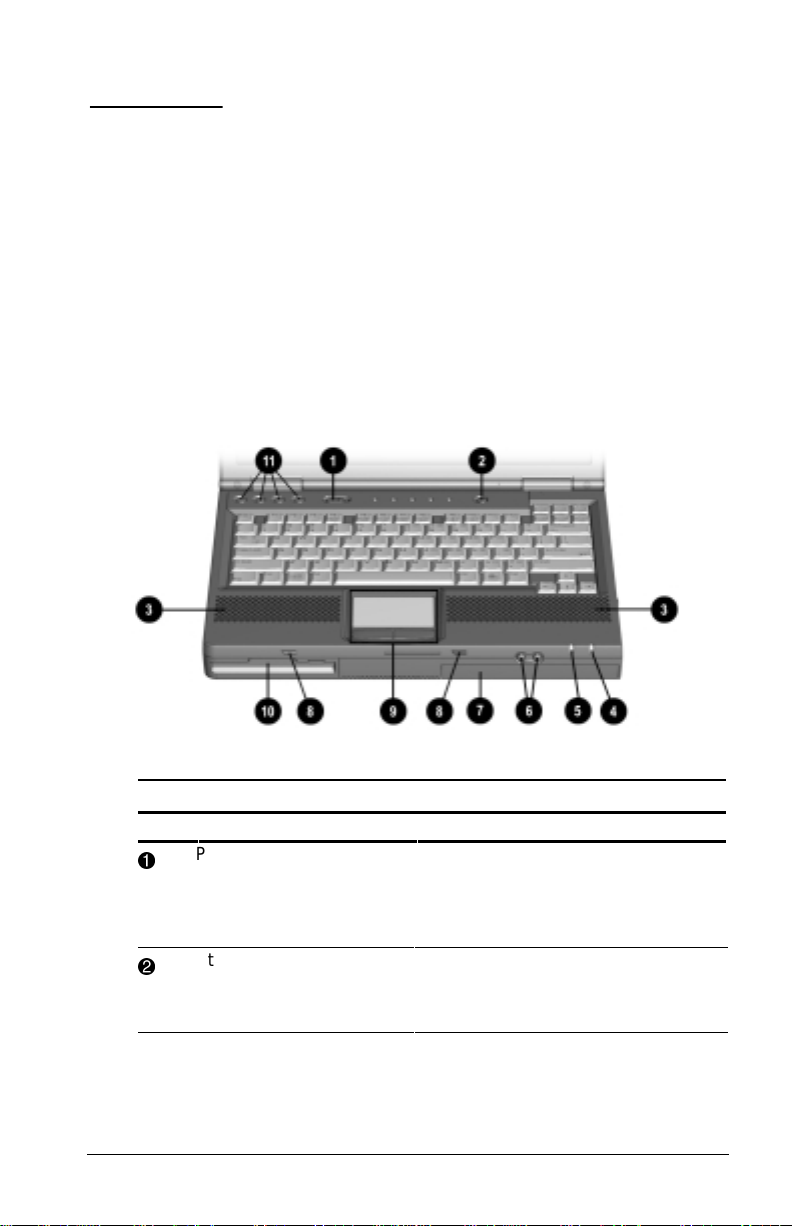
Top Components
Top Components
Component Function
Power switch Slides to turn the computer on or off.
1
Standby/Suspend switch Initiates and exits Suspend. Turns on
2
While working in Windows, click
StartÅShut Down to exit the
operating system and turn off the
computer.
the computer if it is off. When used
with the Fn key on the computer, the
Suspend button initiates Hibernation.
Taking a Look at the Computer 1-1
Continued
Page 11
Top Components Continued
Component Function
Stereo speakers Built-in speakers for high-quality
3
Battery light Indicates the battery is charging
4
Power/Suspend light Blinks every four seconds. This
5
Volume Control buttons Controls the speaker volume.
6
MultiBay Accepts a CD drive, DVD drive,
7
Speaker ports Integrated tuned loudspeaker ports
8
TouchPad Provides integrated pointing device
9
Left and right TouchPad
buttons
or
stereo sound and a multimedia
sound system.
when light is on. If the light is off, the
battery is not charging. A blinking
light indicates a low battery condition.
indicates the computer is in suspend
mode.
SuperDisk LS-120 drive, second hard
drive, third battery pack, or a weight
saver.
that allow airflow to and from the
internal stereo speakers.
functions.
Function like the left-click and right-
click buttons of an external mouse.
Used with the TouchPad, the
TouchPad button drags and
highlights.
Pointing Stick Moves the mouse cursor.
Left and right pointing
stick buttons (pointing
stick models only)
DualBay Accepts a diskette drive, a second
:
Easy Access buttons Allows direct access to predefined
q
1-2 Taking a Look at the Computer
Functions like the left-click and rightclick buttons on an external mouse.
battery pack, or a weight saver.
websites when connected to the
Internet.
Page 12

Left Side Components
Left Side Components
Component Function
Tilt foot Retractable feet on the rear base of
1
Battery bay Holds the primary battery pack.
2
the computer that open and lock into
place in order to angle the keyboard
to a more comfortable position.
Taking a Look at the Computer 1-3
Page 13
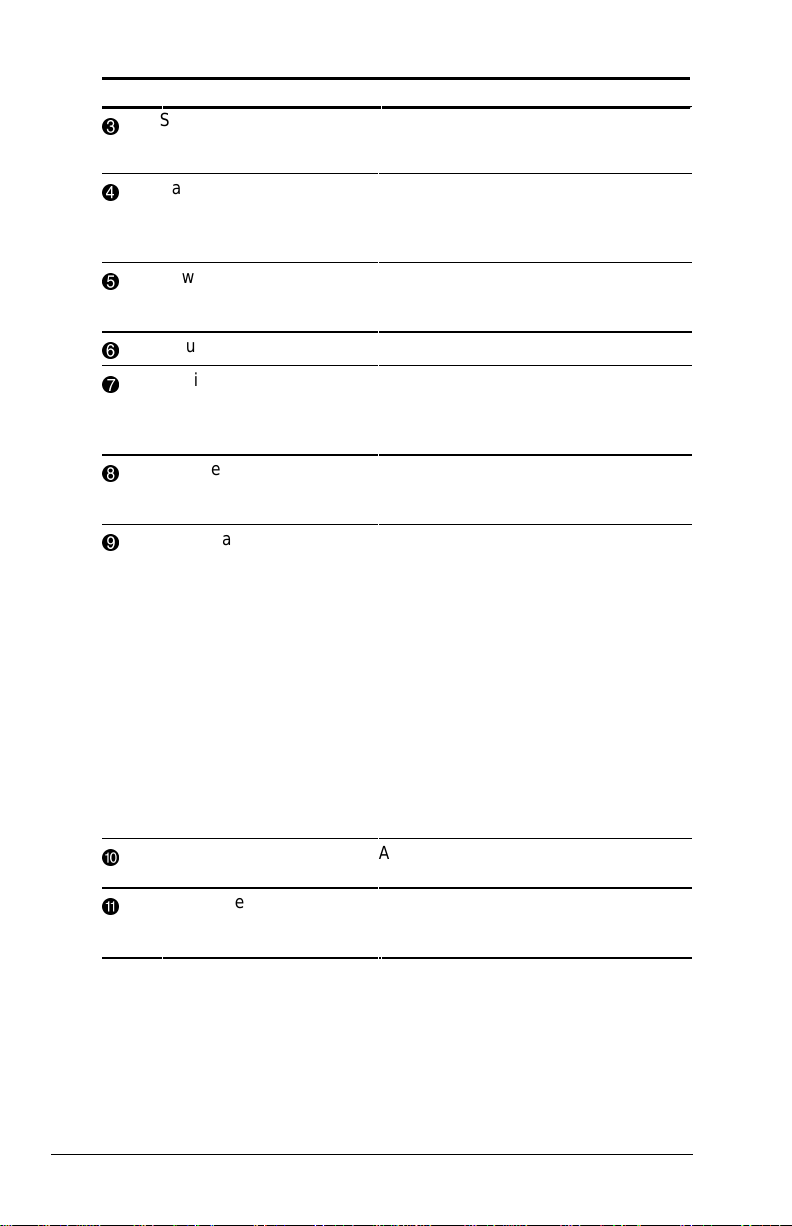
Right Side Components
Right Side Components
Component Function
1
PC Card slots Slots that support Type II or Type III
2
Microphone jack Connects to an external microphone.
3
Stereo speaker/
headphone jack
4
Lock provision Accepts an anti-theft cable that
5
RJ-45 jack Connects the Ethernet cable (NIC) to
6
RJ-11 jack Connects the RJ-11 modem cable to
PC Cards, such as modem, hard
drive, or network cards. These slots
accept 16-bit PC Cards and 32-bit
Cardbus Cards.
Connects to a headphone or external
speakers.
secures the computer to a fixed
object.
the computer. Available on models
with an internal NIC/modem
combination
the computer. Available on models
with an internal modem
Continued
1-4 Taking a Look at the Computer
Page 14

Right Side Components Continued
Component Function
7
Infrared port Infrared signals for communicating
8
Composite TV-Out jack Connects a television to the
9
Tilt foot Retractable feet on the rear base of
with another computer. Links to
another IrDA-compliant device for
wireless communication.
computer.
the computer that open and lock into
place in order to angle the keyboard
to a more comfortable position.
Taking a Look at the Computer 1-5
Page 15
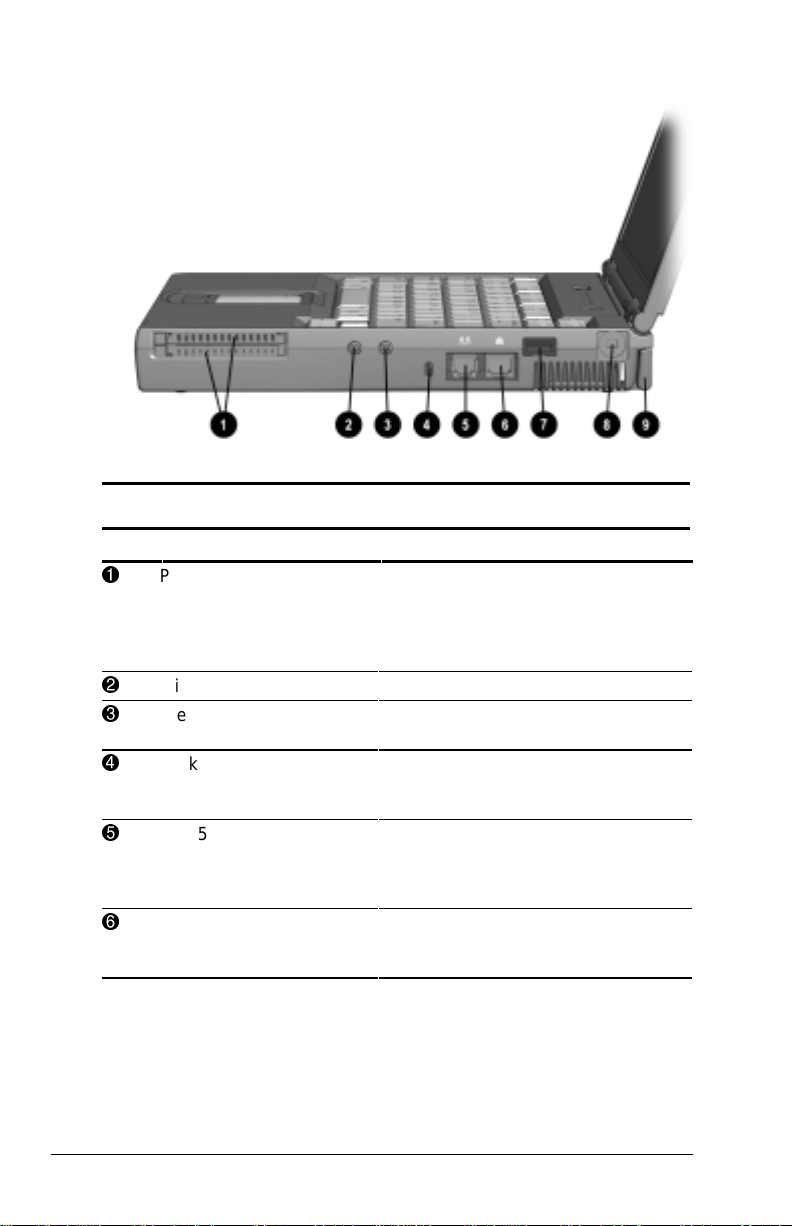
Rear Components
Rear Components
Component Function
Power connector Connects to an AC adapter when the
1
USB connector Allows connection to Universal Serial
2
Serial connector Connects an optional external serial
3
External monitor
4
connector
Docking connector A 176-pin expansion bus connector
5
Parallel connector Connects an optional parallel device
6
7
Keyboard/Mouse
connector
battery or charge battery are not
operating.
Bus (USB) devices, such as a
keyboard or mouse, or to a camera
for video conferencing.
device such as a mouse or printer.
Connects an optional external
display, such as an external CRT
monitor.
that connects the computer to the
optional docking solutions.
such as a printer.
Connects an external keyboard or
mouse.
1-6 Taking a Look at the Computer
Page 16

Bottom Components
Bottom Components
Component Function
Modem compartment Provides access to the internal
1
Keyboard security screw Keeps the keyboard secured to the
2
Hard drive release latch Releases the hard drive.
3
Hard drive compartment Provides access to the primary hard
4
Battery release latch Releases the primary battery pack.
5
DualBay release latch Releases the second battery pack or
6
MultiBay release latch Releases the MultiBay device from
7
modem. The modem is available on
select models and as an option for
other models.
computer.
drive. A security screw prevents
unauthorized access to the hard
drive. Use a standard screwdriver to
remove the screw.
diskette drive from the DualBay.
the MultiBay.
Taking a Look at the Computer 1-7
Page 17

Status Indicator Lights
The five lights located above the keyboard indicate system
operations and status.
Status Indicator Lights
Light Function
Hard drive/CD/DVD drive
1
light indicator
Diskette drive light
2
indicator
Num Lock On: embedded numeric keypad is
3
Caps Lock On: Caps Lock function is on.
4
Scroll Lock On: Scroll Lock key function is on.
5
Turns on when the hard drive or
optional CD or DVD drive is
accessed.
Turns on when the diskette drive is
accessed.
active.
1-8 Taking a Look at the Computer
Page 18

chapter
2
USING THE KEYBOARD
Using the Pointing Device
The built-in TouchPad (TouchPad models) and the EasyPoint IV
pointing stick (pointing stick models) function with any software
that supports a Microsoft-compatible mouse.
NOTE: If you are using software that does not support a Microsoft-
compatible mouse, select Advanced➔Device Options in Computer
Setup, then select the Disable Multiple Pointing Devices check
box.
Identifying TouchPad Components
1
TouchPad
2
Left TouchPad button
3
Right TouchPad button
Using the Keyboard 2-1
Page 19
Navigating with the TouchPad
TouchPad Procedures
Task Procedure
Move the cursor Move your finger directionally across the
Increase or decrease
cursor speed
Right-, left-, or center-click
or double-click
Highlight an item* Press down on the TouchPad as you move
Select text or an object* Position the cursor over the highlighted
Activate a selection* Position the cursor over the selection, then
Select, then drag and drop
an item*
*To perform this task exactly as you would with an external mouse, use
the left pointing-device button like the left button of an external mouse.
TouchPad surface.
Increase or decrease finger speed across
the TouchPad surface.
or
Adjust cursor speed using TouchPad
Preferences. See Setting TouchPad
Preferences for more information.
Press the right or left TouchPad button as
you would the corresponding button on an
external mouse.
the cursor over the item.
text or object, then quickly tap the
TouchPad once.
quickly tap the TouchPad twice.
NOTE: To select and activate a preference,
first tap the preference once to select it,
then tap the preference twice to activate it.
Press down on the TouchPad as you move
the cursor over the item, then drag the
item to the new location. To drop the item,
release the pressure.
Setting TouchPad Preferences
To access all TouchPad features and settings, including mouse
trails, cursor speed, double-click space, and Windows 98 singleclick mode, select StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅMouse. Or,
place the cursor over the TouchPad icon in the system tray and
press the left TouchPad button.
2-2 Using the Keyboard
Page 20

Identifying Pointing-Stick Components
1
EasyPoint IV pointing stick
2
Left pointing-stick button
3
Right pointing-stick button
4
Scroll pointing-stick button
Using the Keyboard 2-3
Page 21
Navigating with the Pointing-Stick
Pointing-Stick Procedures
Task Procedure
Move the cursor Directionally press the pointing stick.
Increase or decrease
cursor speed
Right-, left-, or center-click
or double-click
Highlight an item* Press and hold down the pointing stick as
Select text or an object* Position the cursor over the highlighted
Activate a selection* Position the cursor over the selection, then
Select, then drag and drop
an item*
Scrolling Position the cursor over the selection, then
*To perform this task exactly as you would with an external mouse, use
the left pointing-device button like the left button of an external mouse.
Increase or decrease pressure on the
pointing stick.
or
Adjust cursor speed using Pointing-Stick
Preferences. See Setting Pointing-Stick
Preferences for more information.
Press the right, left, or scroll pointing stick
buttons as you would the right, left, or
center buttons on an external mouse.
you move the mouse cursor over the item.
text or object, then quickly tap the pointing
stick once.
quickly tap the pointing stick twice.
NOTE: To select and activate a preference,
first tap the preference once to select it,
then tap the preference twice to activate it.
Press down on the pointing stick as you
move the cursor over the item, then drag
the item to the new location. To drop the
item, release the pressure.
press the Scroll pointing-stick button to
move up or down.
2-4 Using the Keyboard
Page 22

Setting Pointing-Stick Preferences
EasyPoint IV pointing stick model
■ To access settings common to any Microsoft-compatible
mouse, such as mouse trails, cursor speed, double-click
pace, and Windows 98 single-click mode, select
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅMouse.
■ To access settings and instructions for using additional
EasyPoint IV pointing stick features, such as scrolling,
magnifying, and selecting an icon without tapping the
pointing stick, select StartÅSettingsÅControl
PanelÅTrackpoint. Or, place the cursor over the PointingStick icon in the system tray and press the left pointingstick button.
Using the Keyboard 2-5
Page 23

Using Hotkeys
Hotkeys are preset combinations of the Fn key 1 plus a second
key that activate frequently used system functions. The icons on
the function keys
F4-F10 2, Fn+T
functions.
■ To use hotkeys on an external keyboard, which does not have
Fn key, press the Scroll Lock key twice, then the second key
an
only of the hotkeys combination. For example, to use the
Fn+F10 hotkeys, press Scroll LockÅScroll Lock+F10.
NOTE:
The Fn+F6 hotkeys cannot be used on an external
keyboard connected through a USB connector.
■ To close a window opened with hotkeys, use standard
Windows procedures or press the hotkeys.
3
, and Fn+Esc 4 represent these
Hotkeys Quick Reference
Task Hotkeys
Switch the image Fn+F4
Adjust system volume Fn+F5
2-6 Using the Keyboard
Continued
Page 24

Hotkeys Quick Reference Continued
Task Hotkeys
Initiate Quick Controls Fn+F6
Set a power conservation level Fn+F7
View battery status Fn+F8
Adjust panel contrast FN+F9
Adjust screen brightness Fn+F10
Display system information Fn+Esc
Stretch text Fn+T
Switching the Image
In Windows 95 or Windows NT 4.0 toggle Fn+F4 to switch the
image among the computer display, an external display, and
simultaneous display. The external display can be connected
through the external monitor connector or the video-out jack.
In Windows 98 or Windows 2000 Professional toggle
switch the image between the computer display and an external
display that is connected to the external monitor connector.
■ When MultiMonitor is enabled, press Fn+F4 to turn off the
external display and disable MultiMonitor.
■ When MultiMonitor is disabled, toggle Fn+F4 to switch the
image among the computer display, the external display, and
simultaneous display.
Fn+F4 to
Adjusting System Volume
■ To adjust system volume:
■ Press Fn+F5 using the on-screen slide button or the keyboard
arrow keys.
or
■ Press the front-mounted volume control buttons. See Top
Components in Chapter 1.
■ To mute or restore volume:
■ Press Fn+F5+M
or
■ Press Fn+F5, then select or clear the Mute check box.
or
■ Press the front panel volume control buttons at the same
time.
Using the Keyboard 2-7
Page 25

Initiating Quick Controls
Quick Controls are security features that can disable the keyboard
and pointing device and clear the screen. Before you can use
Quick Controls, set a power-on password and enable Quick
Control preferences. For instructions, refer to Chapter 13.
■ To initiate Quick Controls, press Fn+F6.
■ To exit Quick Controls, enter your power-on password.
The
Fn+F6 hotkeys cannot be used on an external keyboard
connected through a USB connector on the computer or an
optional docking base.
Setting a Power Conservation Level
In Windows 2000 Professional press Fn+F7 to open the Power
Options Properties window. Select the Battery Conservation
Settings tab.
In Windows 98 press
In Windows 95 or Windows NT 4.0 press
Battery Conservation Settings window.
Select one of the following preset battery conservation levels:
■ High—Maximizes running time from a single charge.
■ Medium—Balances system performance with running time.
■ None (Drain)—Runs the computer at full power.
Fn+F7 to open the Power Schemes window.
Fn+F7 to open the
Viewing Battery Status
Press Fn+F8 to view the status of all installed batteries. Battery
packs are listed by location.
■ To display the location of a listed battery, select the
corresponding battery icon.
■ A lightning bolt icon beside a battery icon indicates that the
battery pack in that location is charging.
Adjusting Panel Contrast
Press Fn+F9 to adjust the panel contrast of the computer screen
with an on-screen slide button or with the arrow keys. This feature
is only available to select models.
2-8 Using the Keyboard
Page 26

Adjusting Brightness
Press Fn+F10 to adjust the brightness of the computer screen
with an on-screen slide button or with the arrow keys.
Displaying System Information
Press Fn+Esc to display information about system hardware
components and software version numbers.
NOTE: The number beside System BIOS is the version number of
your system ROM.
Stretching Text
When the computer is running MS-DOS under Windows and the
desktop area resolution is set lower than the display resolution,
Fn+T to toggle the image between Text Stretch, which
press
stretches the text to fill more of the screen, and not stretched. Text
Stretch is the default.
Using the Keyboard 2-9
Page 27

Using the Embedded Numeric Keypad
Toggling the Keypad On and Off
n
To convert the embedded numeric keypad section 1 of the
computer keyboard to a numeric keypad, press
■ When the embedded numeric keypad is enabled, the
characters upper-right on the keypad keys are active and the
num lock light is on.
■ To disable the embedded numeric keypad, toggle
Fn+Num Lk.
■ The embedded numeric keypad cannot be enabled while
an optional external keyboard or numeric keypad is connected
to the computer.
Fn+Num Lk 2.
2-10 Using the Keyboard
Page 28

Operating the Keypad Keys as Standard Keys
To use the embedded numeric keypad keys as standard keyboard
keys while the keypad is enabled:
■ Press and hold Fn to use the keys as you would when typing in
lowercase.
■ Press and hold Fn+Shift to use the keys as you would when
typing in uppercase.
Enabling the Keypad at Startup
■ To set the computer to start up with the embedded
numeric keypad enabled—
1. Turn on or restart the computer, then press F10 when the
blinking cursor appears upper-right on the screen.
■ To change the language, press F2.
■ For navigation instructions, press F1.
2. Select AdvancedÅDevice Options, then press Enter.
3. Toggle the field beside Num Lock State at Boot to On, then
F10.
press
4. To save your preferences, then close Computer Setup and
restart the computer, select FileÅSave Changes and Exit,
then press
Enter.
5. When you are prompted to confirm your action, press F10.
■ To disable the embedded numeric keypad at startup—
Repeat the above procedure with the Num Lock State at Boot
field toggled Off.
NOTE: The embedded numeric keypad can be enabled or disabled
Fn+Num Lk in either startup state.
with
Using the Keyboard 2-11
Page 29

Easy Access Buttons (Available on Select
Models)
The Easy Access Buttons located at the top of your keyboard
provide quick access to the Internet. Before using these buttons,
you must have Internet service. Reference the following
illustration and table for the location and description of your
computer’s Easy Access Buttons.
Easy Access Buttons
No. Button Function
1
2
3
4
2-12 Using the Keyboard
Armada Information Page —Direct link to
Compaq Armada mobile user information for quick
answers to your computer questions.
MyArmada—Internet start point. Connects to a
personalized Web page filled with local weather,
news, sports, and financial information.
Search—Opens the AltaVista search engine
website, which helps you locate information on the
Internet.
Email—Provides one-touch access to your default
Email application for sending and reading your
Email.
Page 30

To use the Easy Access Buttons:
■ You must be connected to the Internet. Until you set up your
Internet Service Provider (ISP), each Easy Access Button will
launch the Compaq Internet Setup process.
■ You do not have to be connected to your ISP to add, change,
or delete schemes.
n
You can also connect an external Compaq keyboard to the
computer. When an external Compaq keyboard that has seven
or eight Internet buttons is connected to your computer, the
first four buttons on the external keyboard will automatically
default to the Easy Access Buttons.
Adding Easy Access Buttons Schemes
Schemes are a collection of up to four button assignments that you
define. You can add additional schemes so that the buttons will
perform different functions depending on which scheme is
currently selected. There is no limit to the number of schemes that
can be added, but the buttons will only work for the scheme that is
currently selected.
To add a new scheme:
1. Double-click the Easy Access Buttons icon located on the
Windows Taskbar.
or
Click StartÅSettingsÅ
Control PanelÅdouble-click KeyboardÅ
click the Easy Access Buttons tab.
2. Click on Add.
3. Type the name of the scheme to be added.
4. In the Button Name box, type a name for the button being
assigned.
5. In the Button Assignment box, type the filename, program, or
website address (URL) to be assigned to the button.
6. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 for each of the Easy Access Buttons
being assigned to this scheme.
7. Click OK.
Using the Keyboard 2-13
Page 31

Changing Easy Access Buttons Schemes
To select a different scheme:
1. Double-click the Easy Access Buttons icon located on the
Windows Taskbar.
or
Click StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅdouble-click
KeyboardÅclick the Easy Access Buttons tab.
2. In the Scheme drop-down list box, select the name of the
scheme you want to make active.
3. Click OK.
Deleting Easy Access Buttons Schemes
NOTE: The default schemes can not be deleted. Only the schemes
defined by you can be deleted.
To delete a scheme:
1. Double-click the Easy Access Buttons icon located on the
Windows Taskbar.
or
Click StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅdouble-click
KeyboardÅclick the Easy Access Buttons tab.
2. In the Scheme drop-down list box, select the name of the
scheme you want to delete.
NOTE: Schemes must be deleted one at a time.
3. Click the Delete button.
4. Click OK.
2-14 Using the Keyboard
Page 32

Disabling and Enabling the Easy Access Buttons
You can turn off all Easy Access Buttons from the Internet buttons
window. When turned off, none of the buttons will operate. The
Easy Access Buttons icon on the taskbar will appear with a red X
on top to indicate the buttons have been disabled. You can still
access the button functions if you open the Easy Access Buttons
window.
To disable the Easy Access Buttons:
1. From the Windows taskbar, right-click the Easy Access
Buttons icon.
2. Click Disable Easy Access Buttons. The icon will appear with
a red X to indicate it has been disabled.
To enable the Easy Access Buttons:
1. From the Windows taskbar, right-click the Easy Access
Buttons icon with the red X (disabled).
2. Click Enable Easy Access Buttons.
Programming the External Keyboard Internet Buttons
If a Compaq external keyboard with seven or eight Internet
buttons is connected to your computer, the first four Internet
buttons automatically default to the Easy Access Buttons schemes.
You can program the remaining external keyboard Internet
buttons or change the Easy Access Buttons to match the first four
Internet buttons on the external keyboard .
To program the remaining external keyboard Internet buttons:
1. Double-click the Easy Access Button icon located on the
Windows Taskbar.
or
Click StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅdouble-click
KeyboardÅclick the Easy Access Buttons tab.
2. Click Internal and select the type of external keyboard you
have connected to the computer.
3. Click on Add, then enter the name of the filenames, programs,
or websites you want assigned to the remaining buttons on the
external keyboard.
4. Click Apply.
Using the Keyboard 2-15
Page 33

To change the Easy Access Buttons on the computer to match the
first four button schemes on the External keyboard:
1. Double-click the Easy Access Button icon located on the
Windows Taskbar.
or
Click StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅdouble-click
KeyboardÅclick the Easy Access Buttons tab.
2. Click Internal.
3. Click on Add, then enter the name of the filenames, programs,
or websites you want assigned to the four Easy Access
Buttons.
4. Click Apply. The Easy Access Buttons on the computer are
programmed to be the same as the first four buttons on the
external keyboard.
2-16 Using the Keyboard
Page 34

chapter
3
USING BATTERY PACKS
Learning About Battery Packs
The computer accommodates up to three rechargeable battery
packs at one time. Battery packs are supported in the:
■ Battery bay in the computer (primary battery pack)
■ DualBay in the computer (secondary battery pack)
■ MultiBay in the computer (third battery pack)
With the computer turned off, each battery pack will recharge in
less than three hours. With the computer turned on, each battery
pack will recharge in less than five hours.
If two fully charged battery packs are installed, one can be
removed while the computer is on without affecting system
operation. With only one battery pack installed, turn off the
computer or initiate Hibernation before removing a battery, or
connect to external AC power before removing the battery pack.
For more information on using Hibernation, see Chapter 4.
Before removing a battery pack when the computer is in suspend,
ensure that the computer is connected to a fully charged battery
pack or AC power source. For more information on using
Suspend, see Chapter 4.
WARNING: Your computer contains a lithium-ion battery pack.
!
There is a risk of fire and burns if the battery pack is not handled
properly. Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external
contacts, or dispose of in fire or water. Do not expose to
temperatures higher than 60°C. Replace only with the Compaq
spare designated for this product.
Using Battery Packs 3-1
Page 35

WARNING: Batteries/battery packs and accumulators should not be
!
disposed of with general household waste. In order to forward them
to recycling or proper disposal, please use the public collection
system or return them to Compaq, your authorized Compaq Partners,
or other agents.
Using a New Battery Pack
Charge the battery pack in the computer’s battery bay, a DualBay,
or a MultiBay while connected to an external power source or
while docked in the optional convenience base.
You can also charge up to two battery packs in the optional battery
charger. However the battery charger has only one slot for the
main battery and one slot for the MultiBay battery. Therefore, you
can only charge two battery packs at one time if one is the main
battery and the other battery is for the MultiBay.
IMPORTANT: A new battery pack should be fully charged before it is
used for the first time. The battery pack will work without being
fully charged, but the battery gauge will not show an accurate
charge until the battery pack receives its first full charge.
Charging Battery Packs
Battery packs charge in the following sequence:
1. The primary battery in the computer battery bay
2. A second battery pack in the computer DualBay
3. A third battery pack in the computer MultiBay
Battery packs are discharged in the reverse order, with the battery
pack in the MultiBay depleted first. See Chapter 1 for bay
locations.
To charge battery packs, follow these steps:
1. With battery packs in the battery bay, DualBay, and/or
MultiBay, connect the power cord to the computer and plug it
into an electrical outlet.
2. Turn on the computer if you want to use it while the battery
packs are charging.
3-2 Using Battery Packs
Page 36

NOTE: The battery charge light is the right light on the front edge of
the computer. It turns on (solid) when a battery pack (in the
battery bay, DualBay, or MultiBay) is charging. It turns off when
fully charged. It blinks in a low-battery condition.
When the battery charge light turns off, the battery packs are fully
charged.
Inserting and Removing the Primary Battery Pack
Removing the Primary Battery Pack
CAUTION: If the battery pack you are about to remove is the only
source of power to the computer, initiate Hibernation or connect the
computer to external power before removing the battery.
1. Pull forward on the primary battery release latch to release the
battery pack.
2. Remove the battery pack from the primary battery bay.
Using Battery Packs 3-3
Page 37

Inserting the Primary Battery Pack
CAUTION: If the battery pack you are about to remove is the only
source of power to the computer, initiate Hibernation or connect the
computer to external power before removing the battery.
Insert a battery pack into the battery bay with the large label on the
battery pack facing up and the battery contacts facing in. Push the
battery pack into the battery bay until it is firmly seated.
NOTE: See Chapter 5 to insert and remove battery packs to and
from the DualBay and MultiBay.
3-4 Using Battery Packs
Page 38

Storing a Battery Pack
CAUTION: To prevent damage to a battery pack, do not expose it to
high temperatures for extended periods of time.
If the computer will be unused and unplugged from an external
power source for more than two weeks, remove and store the
battery packs.
Proper storage procedures reduce the self-discharge rate of a
battery pack. Store a battery pack in a cool, dry place within the
following temperature ranges.
Recommended Battery Pack Storage Temperatures
Storage Time Temperature Range °F Temperature Range °C
Less than
1 month
No more than
3 months
Unlimited 32°– 86° 0°–30°
32°–122° 0°–50°
32°–104° 0°–40°
Maximizing Battery Pack Life
Battery pack operating time varies depending on the system
components, options, and applications used. Battery operating
time can increase by as much as 50 percent by controlling the
energy used by the computer and the energy stored in the battery
pack.
NOTE: The display, processor, and drive components use the
majority of battery power.
To maximize battery pack life, use the following guidelines:
■ Select the High level of power management (not available
under Windows 98). See Chapter 4 for more information on
power management.
■ Initiate Suspend or Hibernation or turn the computer off when
you are not using it.
■ Reduce the display brightness and select a shorter screen save
timeout.
■ Keep a battery pack in the computer when you are using the
computer with external power.
Using Battery Packs 3-5
Page 39

■ Disconnect external equipment that does not have its own
power source. (External equipment connected to the computer
drains the battery pack.)
■ Exit modem programs when you are not using them.
■ Remove a PC Card when you are not using it.
■ When storing the computer for more than two weeks, remove
battery packs and store them separately to reduce the discharge
rate and increase battery life.
■ Store the battery pack in a cool, dry place when it is not in use.
High temperatures cause a battery pack to lose its charge more
quickly and reduce battery pack life. For more information on
storing battery packs, see "Storing a Battery Pack" in this
chapter.
■ Format diskettes while using external power when possible.
(Formatting diskettes increases the drain on a battery pack.)
Recycling Used Battery Packs
To find out if the battery pack recycling program is available in
your area, check the “Worldwide Telephone Numbers” in
Appendix A. If a number for recycling is not listed for your area,
contact your Compaq authorized dealer, reseller, or service
provider.
System Beeps
Beeps with a Blinking Battery Charge Light
When the computer beeps while the battery charge light is
blinking, the computer has entered a low battery condition.
CAUTION: When you are alerted of a low battery condition, very
little battery charge remains. Save your information and take
immediate action to resolve the low battery condition.
See “Turning Beeps On or Off” in this chapter to avoid being
alerted with system beeps.
3-6 Using Battery Packs
Page 40

Beeps with a Blinking Power/Suspend Light
When the computer beeps while the Power/Suspend light is
blinking, the computer has initiated Suspend. See Chapter 4 for
more information on using Suspend.
NOTE: When the computer is in Suspend and a low battery
condition occurs, you cannot press the power button or suspend
button to exit Suspend. Connect the computer to AC power until a
fully charged battery is available.
See the following section, “Turning Beeps On or Off,” to avoid
being alerted with system beeps.
Turning Beeps On or Off
Based on the type of beeps to be turned on or off, do one of the
following:
■ To enable or disable PC Card beeps, click Control PanelÅ
double-click PC Card iconÅGlobal Settings tab, then click the
Disable PC Card Sound Effects box.
■ To disable only low battery warning beeps, click StartÅ
SettingsÅControl PanelÅdouble-click PowerÅ
Power PropertiesÅConservation Settings tab. Then click the
Warning Beeps Off button.
NOTE: Application-specific beeps must be controlled through the
application software.
Using Battery Packs 3-7
Page 41

chapter
4
MANAGING POWER
Selecting a Power Source
Task Recommended Power Source
Work within installed
software applications
Charge a battery pack
inserted in the computer
Calibrate a battery pack External power supplied through
Modify system software External power supplied through
■ Charged battery pack inserted into
the computer
or
■ External power supplied through
■ AC adapter
■ Optional docking base
■ Optional Automobile Power
Adapter/Charger
■ Optional Aircraft Power Adapter
External power supplied through
■ AC adapter
■ Optional docking base
■ Optional Automobile Power
Adapter/Charger
■ Power cord or AC adapter
■ Optional docking base
AC adapter
NOTE: If your external monitor is not Energy Star compliant,
enabling monitor energy-saving features may cause video
distortion when the screen save timeout occurs.
Managing Power 4-1
Page 42

Using Suspend (Standby) and Hibernation
You will use the power switch 1, Suspend button 2, Fn key 3,
4
and the power/suspend light
or place it in Suspend (Standby) or Hibernation.
■ Suspend, called Standby in Windows 98 and Windows 2000
Professional, is an energy-saving feature that reduces power to
system components that are not being used. When the
computer is in Suspend (Standby), your work is saved in
random access memory (RAM) and the screen is cleared.
■ Hibernation is an energy-saving feature that saves all
information in RAM to a hibernation file on the hard drive,
then shuts down the computer.
as you turn the computer on or off
If you are leaving your work, consider:
If you plan to resume shortly—Initiating Suspend (Standby)
clears the screen, uses less power than leaving the computer on,
and your work returns instantly to the screen when you press the
suspend button. A fully charged battery pack can support Suspend
(Standby) for up to a week, unless frequent charging and
discharging has shortened battery pack life.
4-2 Managing Power
Page 43

If the computer will be disconnected from external power for
more than two weeks—To extend the useful life of the battery
pack, shut down the computer, then remove the battery pack and
store it in a cool, dry place.
If you plan to resume within two weeks—Initiating Hibernation
clears the screen, saves your work to the hard drive, and uses less
power than Suspend (Standby). Returning to work saved in
Hibernation takes a little longer than returning to work placed in
Suspend (Standby), but is much faster than returning to your place
manually after restarting the computer. A fully charged battery
pack supports Hibernation indefinitely.
Using Standby (Suspend) and Hibernation
Task Procedure Result
Turn the
computer
on from
shutdown
Shut down
the
computer
Initiate
Suspend*
*In Windows 98 and Windows 2000 Professional the term Standby
replaces the term Suspend.
**In Windows 98 and Windows 2000 Professional the term sleep button
replaces the term suspend button.
Slide power switch. Power/suspend* light turns on.
Operating system loads.
Shut down the
computer.
■ Press suspend
button.**
or
■ Select Stand by
(Windows 98 and
Windows 2000
Professional) on the
shutdown menu.
Power/suspend* light turns off.
Operating system closes and
turns off all power.
Computer turns off.
Power/suspend* light blinks.
System beeps twice.
Screen clears.
Continued
Managing Power 4-3
Page 44

Using Standby (Suspend) and Hibernation Continued
Task Procedure Result
Exit
Suspend*
Initiate
Hibernation
Restore
from
Hibernation
*In Windows 98 and Windows 2000 Professional the term Standby
replaces the term Suspend.
**In Windows 98 and Windows 2000 Professional the term sleep button
replaces the term suspend button.
■ Press suspend
button.**
or
■ Slide power switch.
Press Fn + suspend
button.
Power/suspend* light turns on.
System beeps once.
Your work returns to the screen.
Power/suspend* light turns off.
System beeps twice.
Screen clears.
Slide power switch. Power/suspend* light turns on.
System beeps once.
Your work returns to the screen.
4-4 Managing Power
Page 45

Managing Low-Battery Conditions
Identifying Low-Battery Conditions
■ When a battery pack that is the only source of power available
to the computer reaches a low-battery condition
■ The system beeps five times.
■ The battery light
■ If the low-battery condition is not resolved, the computer will
1
blinks.
enter a critical low-battery condition. In a critical low-battery
condition,
■ If Hibernation is enabled and the computer is on or in
Suspend (Standby)—The computer beeps twice, then
initiates Hibernation. Hibernation is enabled by default.
■ If Hibernation is disabled and the computer is on or in
Suspend (Standby)—The computer beeps twice, and the
2
power/suspend light
blinks. The computer remains briefly
in Suspend (Standby), then shuts down and your unsaved
work is lost.
Managing Power 4-5
Page 46

Resolving Low-Battery Conditions
■ If external power is available, do one of the following—
■ Connect the computer to an electrical outlet with the
AC adapter.
■ Dock the computer in a docking base that is connected to
external power.
■ Plug an optional Automobile Power Adapter/Charger into
the power connector on the computer and into a vehicle
cigarette lighter receptacle.
■ Plug an optional Aircraft Power Adapter into the power
connector on the computer and into the in-seat power supply
available on some commercial aircraft.
NOTE: An optional Aircraft Power Adapter can be used to run
the computer, but cannot be used to charge a battery pack.
■ If a charged battery pack is available—Save your files and
press the suspend button to initiate Suspend (Standby), then
remove the discharged battery pack and insert a charged
battery pack.
■ If neither external power nor a charged battery pack is
available—
■ Press Fn + the suspend button to initiate Hibernation
or
■ Save your work, then shut down the computer.
Restoring from Hibernation After Resolving
a Critical Low-Battery Condition
Slide the power switch. If the computer does not have
enough power to restore your work:
1. Press
2. Insert a charged battery pack or connect the computer to
3. Slide the power switch.
4-6 Managing Power
Ctrl+Alt+Del to abort the restoration.
external power.
Page 47

Charging a Battery Pack
A battery pack can be recharged wherever external power is
available. These locations include the computer battery bay,
DualBay, MultiBay, an optional Battery Charger, and the docking
base.
NOTE: Charging may be delayed if a battery pack is new, has not
been used for 2 weeks or more, or is much warmer or cooler than a
comfortable room temperature.
■ If you are charging the battery pack in the computer—
■ External power can be supplied to the computer through the
AC adapter, an optional docking base, or an optional
Automobile Power Adapter/Charger.
NOTE: An optional Aircraft Power Adapter cannot be used to
charge a battery pack.
■ The battery light, shown below, turns on while the battery
pack is charging and turns off when the battery pack is
fully charged.
Managing Power 4-7
Page 48

■ To increase the accuracy of all battery charge displays—
■ Allow a battery pack to discharge to the low-battery level
through normal use before charging it.
■ When you charge a battery pack, charge it fully.
■ Before charging a new battery pack or a battery pack that
has not been used for two weeks or more, calibrate the new
battery pack or check the calibration on the unused
battery pack.
Monitoring the Charge in a Battery Pack
NOTE: The references in Windows 98 battery charge displays to a
“standard APM battery pack” apply to all battery packs that can be
used in the computer.
Using the Battery Status Tab
NOTE: This section only applies to Windows 95, Windows 98, and
Windows NT 4.0. Please refer to the “Displaying Power Source
and Battery Power Status in Windows 2000 Professional” for
detailed information.
To access the Battery Status tab, press the
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅpower icon (named Power,
Power Management, or Compaq Power, depending on your
operating system)ÅBattery Status tab.
■ To display the location of a listed battery, select the
corresponding battery icon.
■ A lightning bolt icon beside a battery icon indicates that the
battery pack in that location is charging.
Fn+F8 hotkeys or select
4-8 Managing Power
Page 49

Displaying Power Source and Battery Power Status in
Windows 2000 Professional
To display the current power source and remaining power of each
of the battery packs in the system in Windows 2000 Professional,
use one of the following methods:
■ Press the Fn+F8 hotkeys, then click the Power Meter tab.
■ Click StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅ
Power Options iconÅPower Meter tab.
■ Right click the power meter icon on the taskbar, click Open
Power Meter.
■ To display the location of a listed battery, select the
corresponding battery icon.
■ A lightning bolt icon beside a battery icon indicates that the
battery pack in that location is charging.
Using the Battery Meter or Power Meter Icon
The battery meter icon, called the power meter icon in
Windows 98 and Windows 2000 Professional, changes shape to
indicate whether the computer is running on external power or on
a full, half-full, or nearly discharged battery pack.
To display the battery meter icon in the taskbar
■ In Windows 95 select StartÅSettingsÅControl
PanelÅPowerÅPower tab, then select the Show Battery
Meter on the Taskbar check box.
■ In Windows 98 select StartÅ SettingsÅControl
PanelÅPower ManagementÅPower Meter tab, then select the
Show Power Meter on the Taskbar check box.
■ In Windows 2000 Professional select StartÅ
SettingsÅControl PanelÅPower OptionsÅAdvanced tab,
then select the Always show icon on the taskbar check box.
■ In Windows NT 4.0 the battery meter icon displays in the
taskbar by default.
Managing Power 4-9
Page 50

When the battery meter or power meter icon is displayed in the
taskbar, the icon can also be used as follows.
In Windows 95 and Windows 98—
Task Procedure
View the total battery power
remaining in the system.
Enable/disable an on-screen
critical low-battery warning.
Access the Power tab in the
Power Properties window.
Open battery meter in a
popup window.
Display charge information as
a percent of a full charge or
as the run time remaining.
Rest the cursor over the icon.
Left-click the icon, select or clear
the Enable Low Battery Warning
check box, then select OK.
Right-click the icon, select Adjust
Power Properties, then press Enter.
Double-click the icon.
Left-click the icon, then select your
preference in the popup window.
In Windows 2000 Professional—
Task Procedure
View the total battery power
remaining in the system.
Display Power Schemes list. Left-click the icon.
Access the Power Options
Properties window.
Access the Power Meter tab
window.
Rest the cursor over the icon.
Right-click the icon, select Adjust
Power Properties, then press Enter.
Double-click the icon or right-click
the icon, select Open Power Meter,
then Press Enter.
In Windows NT 4.0—
Task Procedure
View the total battery power
remaining in the system.
Open the Compaq Power
Properties window.
4-10 Managing Power
Rest the cursor over the icon.
Double-click or right-click the icon.
Page 51

Using the Power or Power Meter Tab
The Power Meter tab, called the Power tab in Windows 95, is
available in Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows 2000
Professional.
■ To access the tab
■ In Windows 95 select StartÅSettingsÅ
Control PanelÅPowerÅPower tab.
■ In Windows 98 select StartÅSettingsÅ
Control PanelÅPower ManagementÅPower Meter tab.
■ In Windows 2000 Professional select
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower OptionsÅ
Power Meter tab.
■ To view the combined percent of total power remaining in all
battery packs in the system:
■ In Windows 95 and Windows 98 clear the Show the Status
of All Batteries check box.
■ In Windows 2000 Professional clear the Show details for
each battery check box.
■ To view the percent of total power remaining in each battery
pack in the system,
■ In Windows 95 and Windows 98 select the Show the
Status of All Batteries check box.
■ In Windows 2000 Professional clear the Show details for
each battery check box.
The three numbered icons correspond as follows to battery
pack locations.
1 Computer battery bay
2 Computer DualBay
3 Computer MultiBay
Managing Power 4-11
Page 52

Calibrating a Battery Pack
Calibration increases the accuracy of all battery charge displays.
The calibration utility supports all battery packs that can be used
in the computer.
Use the calibration utility both to check the calibration of a battery
pack and to calibrate or recalibrate a battery pack.
■ A battery pack cannot be calibrated unless the utility reports
that it needs calibration.
■ A new battery pack can be charged, then used to run the
computer before the battery pack is calibrated. However,
the amount of charge in the new battery pack cannot be
reported accurately until the new battery pack has been
calibrated.
■ Check the calibration of a used battery pack periodically
and whenever battery charge displays seem inaccurate.
■ While a battery pack is being calibrated, it is fully charged,
then fully discharged.
■ A battery calibration icon in the taskbar displays an Up
arrow during the charge phase and a Down arrow during the
discharge phase.
■ A calibration cannot resume if the calibration is stopped or
if the computer is shut down during a calibration. An
interrupted calibration must be restarted.
■ After calibration, a battery pack must be charged before it
can be used to run the computer.
■ The calibration utility calibrates one battery pack at a time
and can run in the background as you use the computer
or overnight.
CAUTION: To prevent loss of work, ensure that the computer
remains connected to AC power throughout a calibration.
4-12 Managing Power
Page 53

Running a Calibration
NOTE: The following section applies to Windows 95, Windows 98,
and Windows NT 4.0. Please refer to the “Running a Calibration
in Windows 2000 Professional” section below for detailed
information.
1. If you are checking the calibration of a battery
pack—Insert the battery pack into the computer battery
bay, a DualBay, or a MultiBay.
If you are calibrating a battery pack—Insert the battery
pack into the computer battery bay, a DualBay, or a MultiBay.
Then connect the computer to external power with the AC
adapter or dock the computer in a docking base that is
connected to external power.
2. Access the Battery Calibration tab.
■ In Windows 95 select StartÅSettingsÅ
Control PanelÅPowerÅBattery Calibration tab.
■ In Windows 98 select StartÅSettingsÅControl
PanelÅPower ManagementÅBattery Calibration tab.
■ In Windows NT 4.0 select StartÅSettingsÅControl
PanelÅCompaq PowerÅBattery Calibration tab.
3. View the calibration reports in the Status column. The battery
numbers in the Battery column correspond to the following
locations:
Battery Number Battery Pack Location
1 Computer battery bay
2 Computer DualBay
3 Computer MultiBay
4. Select any location number with “Needs calibration” beside it
in the Status column.
5. Select the Start Calibration button.
Managing Power 4-13
Page 54

Running a Calibration in Windows 2000 Professional
1. If you are checking the calibration of a battery
pack—Insert the battery pack into the computer battery
bay, a DualBay, or a MultiBay.
If you are calibrating a battery pack—Insert the battery
pack into the computer battery bay, a DualBay, or a MultiBay.
Then connect the computer to external power with the AC
adapter or dock the computer in a docking base that is
connected to external power.
2. To access the Compaq Power tab select
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅ
Power Options iconÅCompaq Power tab. Click the Calibrate
button for the battery pack you want to calibrate. Click OK
when prompted.
or
Right click the power meter icon in the system tray, click
Adjust PropertiesÅCompaq Power tab. Click the Calibrate
button for the battery pack you want to calibrate. Click OK
when prompted.
or
Press the
Fn+F8 hotkeys, then click the Compaq Power tab.
Click the Calibrate button for the battery pack you want to
calibrate. Click OK when prompted.
Once the calibration utility starts, you can close the Power Options
Properties dialog box and monitor the progress of the calibration
through the icon in the system tray.
Stopping a Calibration
Shut down the computer or select the Stop Calibration button on
the Battery Calibration tab. The Stop Calibration button is visible
only during a calibration.
4-14 Managing Power
Page 55

Using Power Preferences
You can increase, decrease, and allocate the power used by the
computer by setting power preferences.
■ Increasing power increases performance, while decreasing
power conserves energy and extends the running time from a
battery pack.
■ By decreasing power to unused components and functions, you
can allocate more power to the components and functions that
you are using.
Many power preferences consist of timeout settings.
■ A timeout is the period of inactivity before the system initiates
a power change or reduces power to a component. For
example, the computer is preset to initiate Suspend (Standby)
after a period of inactivity. The time interval between when
you stop using the computer and when the computer initiates
Suspend (Standby) is a Suspend (Standby) timeout.
■ Depending on your operating system, you can set timeouts that
are specific to various conditions, components, or procedures
as well as specify the duration of those timeouts.
The following tables list power preference procedures that are not
described in your operating system documentation.
■ For additional power preference options, refer to your
operating system documentation.
■ For a summary of battery conservation settings that extend the
running time from a single charge, refer to “Conserving
Battery Power” later in this chapter.
Managing Power 4-15
Page 56

Setting Power Preferences
in Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0
Refer to the following table for procedures on setting power
preferences.
Preference Procedure from Control Panel
Select a preset level of power
use that applies whenever the
computer is running on a
battery pack.
NOTE: A battery conservation
level can also be displayed and
selected with the Fn+F7 hotkeys.
Create a level of power use that
applies settings for the following
whenever the computer is
running on a battery pack
■ Suspend timeout
■ System idle timeout
■ Processor speed
■ Screen brightness
Enable/disable low-battery
warning beeps.
Set Hibernation timeout. Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
Exit Suspend after a userselected timeout.
Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
Battery Conservation Settings tab,
then select a conservation level:
■ High provides maximum battery
conservation.
■ Medium balances battery
conservation and system
performance.
■ None (drain) provides maximum
power.
Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
Battery Conservation Settings tab.
Select Custom, then enter your
preferences.
NOTE: Although a battery conservation
level can be displayed and selected
with the Fn+F7 hotkeys, Custom level
preferences must be entered on the
Battery Conservation Settings tab.
Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
Battery Conservation Settings tab,
then select the On or Off radio
button.
Hibernation tab, then select a timeout
from the Timeout drop-down list.
NOTE: This setting does not affect
system-initiated Hibernation during a
critical low-battery condition.
Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
Resume Timer tab. Select the
Enabled check box, then select a
date from the Date drop-down list
and a time from the Time drop-down
list.
Continued
4-16 Managing Power
Page 57

Preference Procedure from Control Panel
Set computer to initiate
Hibernation rather than
Suspend.
In Windows 95, turn off power
to an optional PC Card modem
Change location of Hibernation
file.
Enable/Disable Hibernation. Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
In Windows NT 4.0, create a
general level of power use that
applies whenever the computer
is running on external AC or DC
power. You can enter settings
for
■ Screen save timeout.
■ Hard drive timeout.
■ Energy-saving monitor
timeout.
Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
Hibernation tab, then select Standby
in the Timeout drop-down list.
Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
PC-Card Modems tab, then select
Turn Off Power to PC Card Modem
when not in use check box.
Select Power (or Compaq Power)Å
Hibernation tab, then select the new
location from the Drive for Hibernation
File drop-down list.
Hibernation tab, then select the On or
Off button.
CAUTION: If the computer reaches a
critical low-battery condition while
Hibernation is turned off, unsaved
work can be lost.
1. Select Compaq
PowerÅAC Energy Saver tab.
2. Select the AC Energy Saver On
radio button.
3. To set a screen save timeout,
select a timeout in the Screen
Save drop-down list.
4. To set a hard drive timeout, select
a timeout in the Hard Disk Idle
drop-down list.
5. To enable an external monitor to
enter a low-power mode following
a screen save timeout, select the
Energy Save Monitor check box.
NOTE: You will not be logged off a
network when the monitor enters
low-power mode.
Managing Power 4-17
Page 58

Setting Power Preferences in Windows 98
To access most power preference settings—Select
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower Management. For
information about setting all Power Management preferences
except the following, refer to your Windows 98 documentation.
To enable or disable Hibernation—Select the Hibernation tab,
then select the On or Off button.
To set a screen brightness level that applies when the
computer is running on a battery pack—Select the Battery
Conservation Settings tab, then select a percent from the
Brightness drop-down list.
If you are accustomed to running Windows 95 or
Windows NT 4.0 on a Compaq portable computer—You will
find most of the power preference options you formerly accessed
in Power Properties window in the Windows 98 Power
Management Properties window. However, in Windows 98
■ Processor speed is managed by the operating system.
■ The easiest way to turn off power to a PC Card is to remove
the PC Card.
■ The Fn+F7 hotkeys open the Power Schemes window.
■ The preferences you formerly set on the Resume Timer tab can
be set at StartÅProgramsÅAccessoriesÅSystem
ToolsÅScheduled Tasks.
4-18 Managing Power
Page 59

Setting Power Preferences in Windows 2000 Professional
You can increase, decrease, and allocate computer power by
setting power preferences.
Battery Conservation Level—To select a preset or set a custom
battery conservation level, use one of the following methods:
■ Press the Fn+F8 hotkeys. Click the Battery Conservation
Settings tab. Select a conservation level from the drop-down
list box.
■ Click StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅ
Power Options iconÅBattery Conservation Settings tab.
Select a conservation level from the drop-down list box.
■ Right click the power meter icon in the system tray, click
Adjust Power PropertiesÅBattery Conservation Settings tab.
Select a conservation level from the drop-down list box.
Screen Brightness and Processor Speed—To set the screen
brightness level or processor speed when the computer is running
on battery power, use one of the following methods:
■ Press the Fn+F8 hotkeys. Click the Battery Conservation
Settings tab. Select Custom from the Conservation Level dropdown list box. Select a percent from the Brightness or
Processor Speed drop-down list box.
■ Click StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower Options
iconÅBattery Conservation Settings tab. Select Custom from
the Conservation Level drop-down list box. Select a percent
from the Brightness or Processor drop-down list box.
■ Right click the power meter icon in the system tray, click
Adjust Power PropertiesÅBattery Conservation Settings tab.
Select Custom from the Conservation Level drop-down list
box. Select a percent form the Brightness or Processor Speed
drop-down list box.
PC Card Modem—To turn off power to an optional PC Card
modem, remove the PC Card from the computer.
Managing Power 4-19
Page 60

Turning Auto Insert Notification On or Off
NOTE: The Auto insert notification feature is not available in
Windows 2000 Professional.
Auto insert notification runs a CD or DVD on insertion, but drains
power and prevents system-initiated Suspend (Standby) and
prevents system-initiated hibernation.
NOTE: The Auto insert notification prevents system-initiated
(timeout) suspend/hibernation in Windows 95 and
Windows NT 4.0.
To turn off Auto insert notification:
■ In Windows 95 or Windows 98 select StartÅSettingsÅ
Control PanelÅSystemÅDevice ManagerÅCDROMÅ
Properties. Clear the Auto insert notification check box.
■ In Windows NT 4.0 select StartÅSettingsÅControl
PanelÅCompaq PowerÅBattery Conservation Settings tab.
Clear the Auto insert notification check box.
To turn on Auto insert notification, access the Auto insert
notification check box as instructed above, then select the
check box.
Changing the Processor Performance Mode (Available on Select Models)
Computer models that provide Intel Pentium III with SpeedStep
technology allows you to enable an automatic change in processor
speed when the power source changes between AC power and
battery power.
The SpeedStep technology offers two preset performance modes:
■ In Maximum Performance mode, the processor runs at full
speed to provide maximum performance.
■ In Battery Optimized mode, the processor runs at a reduced
speed to provide optimal balance between energy conservation
and performance.
The computer can run in either performance mode while it is
running on AC power or on battery power.
4-20 Managing Power
Page 61

Changing Performance Modes
Before the performance mode changes from Battery
Optimized to Maximum Performance mode in Windows 95 or
Windows NT 4.0 —You are prompted to restart the computer.
The restart selection on the prompt restarts the computer and
returns your work to the screen.
It is not necessary to restart the computer to change from
■ Battery Optimized to Maximum Performance mode in
Windows 98 or Windows 2000 Professional.
or from
■ Maximum Performance to Battery Optimized mode in any
operating system.
Combining Performance Modes with Other Power Settings
The SpeedStep technology performance modes are independent of
all other power settings available on the computer except the
Custom processor speed settings available in Windows 95 and
Windows NT 4.0.
In Windows 95 or Windows NT 4.0 only—
■ Custom processor speed settings can be set by selecting
StartÅSettingsÅ Control PanelÅPower or Compaq
PowerÅBattery Conservation Settings tabÅCustom.
■ The Custom processor speed applies any time the computer is
running on battery power.
Setting SpeedStep Preferences
NOTE: If the SpeedStep window and icon are not accessible, they
may be disabled in Computer Setup. To enable the window and
icon, refer to Chapter 15 in this guide.
Using the SpeedStep Window
To open the SpeedStep window from the desktop—
■ In Windows 95 or Windows NT 4.0, select
StartÅProgramsÅIntel SpeedStep technology.
■ In Windows 98, select StartÅSettingsÅControl
PanelÅPower MangementÅIntel SpeedStep technology tab.
■ In Windows 2000 Professional, select
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower Options iconÅIntel
SpeedStep technology tab.
Managing Power 4-21
Page 62

Setting SpeedStep Preferences
Preference Procedure
Assign a performance mode that
applies any time the computer is
running on battery power.
Assign a performance mode that
applies any time the computer is
running on AC power.
Set the computer to change
between the assigned power
modes whenever the power
source changes.
Set the computer to prompt for
confirmation before initiating a
performance mode change.
Set the computer to remain in the
same performance mode even if
the power source changes.
Turn off the audible alert of a
performance mode change.
Set the computer to change
automatically between Maximum
Performance mode while running
on AC power and Battery
Optimized mode while running on
battery power
and
Disable all settings in the main
SpeedStep window.
Select a performance mode from
the drop-down list under Running on
Batteries, then select OK.
Select a performance mode from
the drop-down list under Plugged In,
then select OK.
Select the checkbox for
Automatically Change Performance
When the Power Source Changes,
then select OK.
1. Select the checkbox for
Automatically Change
Performance When the Power
Source Changes.
2. Select the checkbox for Ask me
Before Automatically Changing
Performance.
3. Select OK.
Select the same performance mode
from the drop-down lists for Running
on Batteries and Plugged In, then
select OK.
Select the Advanced button, then:
1. Select the checkbox for Disable
Audio Notification When
Performance Changes.
2. Select OK in the Advanced
window.
3. Select OK or Apply in the main
SpeedStep window.
Select the Advanced button, then.
1. Select the checkbox for Disable
Intel SpeedStep Technology
Control.
2. Select OK in the Advanced
window.
3. Select OK or Apply in the main
SpeedStep window.
Continued
4-22 Managing Power
Page 63

Setting SpeedStep Preferences Continued
Preference Procedure
Enable all settings in the main
SpeedStep window.
Remove the SpeedStep icon
from the taskbar.
Select the Advanced button, then:
1. clear the checkbox for Disable
2. Select OK in the Advanced
3. Select OK or Apply in the main
NOTE: Under some circumstances, it
may be necessary to restart the
computer after completing this
procedure.
Select the Advanced button, then:
1. Select the checkbox for
2. Select OK in the Advanced
3. Select OK or Apply in the main
Intel SpeedStep Technology
Control.
window.
SpeedStep window.
Remove Icon from Taskbar.
window.
SpeedStep window.
Managing Power 4-23
Page 64

Using the SpeedStep Icon
The SpeedStep icon displays in the system tray by default and
changes to indicate whether the computer is running in Maximum
Performance or Battery Optimized mode. The icon can also be
used for the following tasks:
SpeedStep Icon Tasks
Task Procedure
Display current performance
mode.
Open the SpeedStep window. Double-click the icon.
Change the current performance
mode.
Rest the pointer over the icon.
Right-click the icon, then select a
performance mode with the up or
down arrow key.
Conserving Battery Power
Battery Power Conservation Checklist
■ Exit modem applications and turn off local area network
(LAN) connections when you are not using them.
■ Disconnect external equipment you are not using that is not
connected to an external power source.
■ If you leave your work, initiate Suspend (Standby) or
Hibernation or shut down the computer.
■ Remove PC Cards you are not using.
■ Use the Fn+F10 hotkeys to quickly raise and lower display
brightness as you work.
■ Run the computer on external power while formatting
a diskette.
4-24 Managing Power
Page 65

Conserving Battery Power in Windows 95
■ Select StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower. Then:
■ On the Battery Conservation Settings tab, select the High
battery conservation level or select the Custom battery
conservation level, then enter even lower settings.
■ On the Disk Drives tab, set a low When Powered By
Batteries timeout for the disk drive.
■ If you are using a PC Card modem, click the PC-Card
Modems tab, then select the Turn Off PC-Card Modems
When Not in Use check box.
■ If Infrared Monitor is enabled, select StartÅSettingsÅControl
PanelÅInfraredÅOptions tab, then clear the Search for and
Provide Status for Devices in range check box.
IMPORTANT: You cannot establish an infrared link while this
check box is cleared. For more information about infrared,
refer to Chapter 8.
■ If a CD or DVD drive is in the system, clear the Auto insert
notification check box.
Conserving Battery Power in Windows 98
■ Select StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower
ManagementÅPower Schemes tab, then create a power
scheme that conserves battery power.
■ Select StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower
ManagementÅBattery Conservation Settings. Then select a
low screen brightness.
■ Select the infrared icon in the task barÅOptions tab, then
clear the Search for and Provide Status for Devices in range
check box.
IMPORTANT: You cannot establish an infrared link while this
check box is cleared. For more information about infrared,
refer to Chapter 8.
Managing Power 4-25
Page 66

Conserving Battery Power in Windows 2000 Professional
■ Select StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower Options
iconÅPower Schemes tab, then create a power scheme that
conserves battery power.
■ Select StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPower Options
iconÅBattery Conservation Settings tab. On the Battery
Conservation Settings tab, select the High battery conservation
level or select the Custom battery conservation level, then
enter even lower settings.
Conserving Battery Power in Windows NT 4.0
■ Select the Start buttonÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅCompaq
PowerÅBattery Conservation Settings tab. Then:
■ Select the High battery conservation level
or
■ Select the Custom battery conservation level, then enter
even lower settings.
4-26 Managing Power
Page 67

chapter
5
WORKING WITH REMOVABLE
DRIVES AND DEVICE BAYS
Bay Configuration
The three computer bays support standard as well as optional
devices. Some devices can be hot plugged, while others must be
inserted after the computer has been turned off. The following
table is a list of devices supported in all bays, as well as the
computer power state required before inserting the device (see
Chapter 1 for bay locations):
Bay Configuration
Functional Bay Devices Supported Power State
MultiBay CD drive On
DVD drive On
LS-120 Drive Off
Second hard drive Off
Diskette Drive On
Third battery pack On
DualBay Diskette drive On
Second battery pack On
Battery bay Primary battery pack On
NOTE: If two 3.5-inch/8.89-cm diskette drives are inserted in the
MultiBay and the DualBay at the same time, only the DualBay
diskette drive will work.
Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays 5-1
Page 68

Caring for Removable Drives
Removable drives such as the hard drive, CD or DVD drive,
diskette drive, and LS-120 drive are fragile computer components
that must be handled with care.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from hot surfaces,
!
allow the internal system components to cool before touching them.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the computer or removable drive
or to prevent loss of information, observe the following precautions.
■ Back up the information on a hard drive before removing it.
Failure to back up the hard drive can result in loss of
information if the drive is handled improperly.
■ If there is a diskette, compact disc, or digital video disc in a
drive, remove it prior to removing the media from the
computer.
■ Do not remove a CD or DVD drive with the tray extended.
Before removing the drive, push the drive tray into the drive.
■ Ensure that you are discharged of static electricity before
handling a removable drive. Electrostatic discharge can
damage electronic components. When handling a removable
drive, always grasp the outer case and avoid touching the
connectors.
■ Do not use force when inserting a drive into a bay. Excessive
force may damage the connectors.
■ Carefully handle the removable drive. DO NOT DROP IT.
■ Avoid exposing a hard drive to products with magnetic fields
such as video and audio tape erasure products, monitors, and
speakers.
■ Do not spray the drive with cleaners or expose it to liquids.
■ Avoid exposing the drive to temperature extremes.
5-2 Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays
Page 69

Changing the Startup Sequence with MultiBoot
If more than one drive is in the system, the computer selects the
drive to start from by searching for (1) a bootable CD or DVD; (2)
a bootable diskette; and (3) a bootable hard drive. The computer
can start from:
■ A bootable hard drive in the computer or diskette drive.
■ Any bootable diskette or hard drive in an optional docking
base.
■ Any bootable CD or DVD.
NOTE: A bootable hard drive, CD, DVD, or diskette contains files
needed by the computer to start up and operate properly.
By default, MultiBoot is disabled and the computer selects the
startup drive by searching these locations in this sequence:
1. Diskette drive
2. Computer hard drive
3. Computer MultiBay
To enable MultiBoot and change the sequence of the computer
drive bay locations that the computer searches during startup:
1. Restart the computer, then press
appears upper-right on the screen.
■ To change the language, press F2.
■ For navigation instructions, press F1.
2. Select Advanced➔Boot Options, then press
3. Toggle the MultiBoot field to Enable.
4. Toggle the Boot Order fields to the boot sequence you prefer.
5. To safe your preferences and exit Boot Options, press
6. To confirm saving your changes and restart the computer,
select File➔Save Changes and Exit, then press
F10 when the blinking cursor
Enter.
F10.
F10.
When the computer restarts and searches for a startup drive, it
considers only the first drive of each type.
Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays 5-3
Page 70

Selecting Diskettes
The diskette drive, which is housed in the computer DualBay,
reads and writes information onto a 3.5-inch/8.89-cm diskette.
The MultiBay also accommodates an optional LS-120 drive.
Each drive accepts the following diskettes:
Type of Drive Diskettes Accepted
Diskette Drive 1.44-MB high-density (HD)
720-Kbyte double-density (DD)
1.2-MB Japanese format
LS-120 Drive 120-MB SuperDisk
1.44-MB high-density (HD)
720-Kbyte double-density (DD)
DualBay Devices
Inserting a DualBay Device
1. Turn off the computer, if desired.
2. Insert the device into the DualBay until it locks into place.
5-4 Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays
Page 71

Removing a DualBay Device
1. Turn off the computer, if desired.
2. Press the DualBay release lever to release the device.
3. Remove the device.
Second Battery Pack
The computer is designed to use up to three battery packs: the
primary battery pack is in the computer, the secondary battery
pack in the DualBay, and the third battery pack is in the MultiBay.
A second battery pack can be used in the DualBay Drive or the
primary battery bay. (See Chapter 3 for more information on
batteries.)
Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays 5-5
Page 72

MultiBay Devices
The MultiBay supports a CD drive, DVD drive, LS-120 drive,
second hard drive, or a third battery pack.
CAUTION: Some but not all MultiBay devices can be hot plugged.
Refer to "Bay Configuration" in this chapter to determine if the
computer must be on or off before inserting or removing MultiBay
devices. This helps protect the computer or the device from damage
or data loss.
Electrostatic discharge can damage electronic components. Before
touching the hard drive, ensure that you are discharged of static
electricity by touching a grounded metal object.
Inserting a MultiBay Device
1. If your device is not hot-pluggable, turn off the computer.
2. Insert the device into the MultiBay until it locks into place.
IMPORTANT: If installing a second hard drive, insert the hard drive
into a hard drive adapter before installing the drive into the
MultiBay.
5-6 Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays
Page 73

Removing a MultiBay Device
1. If your device is not hot-pluggable, turn off the computer.
2. Press the MultiBay release lever to release the device.
IMPORTANT: When removing a second hard drive, first remove
the adapter from the MultiBay, then remove the hard drive
from the adapter.
3. Remove the device.
Using a Second Hard Drive
The computer is designed to use up to two hard drives: one in the
computer and one in the computer MultiBay. Refer to the section
“Changing the Startup Sequence with MultiBoot” in this chapter.
Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays 5-7
Page 74

Using the CD or DVD Drive
Inserting a CD or DVD
1. Turn on the computer.
2. Press the eject button on the bezel of the CD or DVD drive to
release the loading tray.
3. Slowly pull out the loading tray until it is fully extended.
4. Remove the CD from its protective case and place it in the
loading tray, label side up. Handle the CD or DVD by the
edges, not by the flat surfaces.
5. Push lightly on the bezel of the loading tray to close it.
The light on the CD or DVD drive turns on while the computer
reads the CD’s or DVD’s table of contents. The light turns off
when the CD or DVD drive is ready to receive commands.
Removing a CD or DVD
1. Turn on the computer.
2. Press the eject button on the front panel to open the loading
tray.
3. Slowly pull out the loading tray until it is fully extended.
4. Remove the CD or DVD from the tray. Handle the CD or
DVD by the edges, not by the flat surfaces.
5. Place the CD or DVD in its protective case.
6. Gently push the front panel of the loading tray to close it.
5-8 Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays
Page 75

Manually Ejecting a CD or DVD
If a CD or DVD becomes lodged in the CD or DVD drive, remove
it by using the following steps:
1. Insert a paper clip or similar thin metal rod into the manual
release hole on the front bezel of the CD or DVD drive. Press
firmly.
2. Slowly pull the tray out from the drive until it is fully
extended.
3. Remove the CD or DVD.
Using the LS-120 Drive
The LS-120 Drive is a high-capacity diskette drive that resembles
a 3.5-inch/8.89-cm diskette drive. The LS-120 drive can read a
3.5-inch/8.89-cm disk, and has a capacity of 120 MB.
Using the Third Battery Pack
The computer is designed to use up to three battery packs: the
primary battery pack is in the computer, the secondary battery
pack is in the in the DualBay, and the third battery pack is in the
MultiBay.
A third battery pack can be used in the MultiBay Drive. However,
this battery pack does not use the same type battery as the primary
battery pack in the battery bay and second battery pack in the
DualBay. (See Chapter 3 for more information on batteries.)
Working with Removable Drives and Device Bays 5-9
Page 76

chapter
6
USING AN INTERNAL MODEM
(AVAILABLE ON SELECT MODELS)
Connecting the Modem Cable
To connect the modem to a standard telephone wall jack:
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electrical shock, always ensure
!
that the modem line is disconnected from the telephone network
when opening the equipment’s enclosure.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electrical shock, fire, or damage to
!
the equipment, do not plug a telephone cable into the Ethernet RJ45 jack.
1. Connect one end of the modem cable 1 into the RJ-11 jack on
the right side of the computer.
IMPORTANT: The internal modem uses a universal DAA
(Direct Access Arrangement) that supports multiple countries.
However, some countries may require an adapter to connect
the modem to the telephone wall jack.
The modem cable may include EMI suppression circuitry near
the end of the computer. For continued EMI emissions
compliance, plug that end of the cable into the computer.
Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models) 6-1
Page 77

2. Plug the opposite end of the cable 2 into a standard telephone
wall jack.
IMPORTANT: Wall jacks for digital PBX systems may resemble
standard telephone jacks but are not compatible with analog
devices such as modems. Be sure the modem cable is
connected to a regular analog phone line. Plugging the modem
into a digital line will result in no dial tone and is not
recommended. The modem includes protective circuitry
against the digital lines producing excess current. A warning
buzz will sound briefly when excessive current is detected
during a call attempt and the attempt is terminated with the
phone line back on-hook.
Setting up the Modem
NOTE: The following procedures are necessary only if your modem
is not installed. If your modem is installed, the name will display
in the Modem Properties window in Windows 95 and Windows
98, and Windows NT 4.0 or in the Phone and Modem Options
window under the Modems tab in Windows 2000 Professional.
In Windows 95 or Windows 98—Select StartÅSettingsÅ
Control PanelÅModem. In Windows 2000 Professional—Select
StartÅSettingsÅ Control PanelÅPhone and Modem Options.
6-2 Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models)
Page 78

The Install New Modem setup wizard displays. To set up the
modem with this wizard:
1. On the first screen, select Other, then select the Next button.
2. On the second screen, select your modem model name or
select the Next button to prompt your operating system to
detect the modem.
3. Follow the instructions on the screen.
In Windows NT 4.0—
1. Go to C:\Program Files\Compaq.
2. Select your modem model name.
3. Select Modem\NT40. Then,
■ If your modem is a network model, select Combo folder\
Setup.exe.
■ If your modem is not a network model, select Setup.exe.
Selecting Communication Software
You can operate the modem with preinstalled or optional software.
To use preinstalled modem software, select StartÅPrograms.
Then,
■ Select AccessoriesÅHyperTerminal for terminal emulation and
data transfer.
■ In Windows 95 select AccessoriesÅFaxÅCompose New Fax.
■ In Windows 98 or Windows NT 4.0 select RingCentral Fax.
■ In Windows 2000 Professional select
AccessoriesÅCommunicationsÅFaxÅFax Service
Management.
To use Lotus cc:Mail 7.0, Lotus Notes, or Microsoft
MS-Mail 3.2 Remote—You must load a script file. Script files
for these applications are preinstalled on the computer.
Loading a Lotus Script File
The Lotus Notes and Lotus cc:Mail script files provided by
Compaq support all versions of Lotus Notes and Lotus cc:Mail,
but loading procedures vary among Lotus applications.
Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models) 6-3
Page 79

To load a script file for Lotus cc:Mail or a Lotus Notes version
earlier than 4.x— Use the installation procedures in your Lotus
documentation. The script files for these applications are at
C:\Program Files\Compaq\CPQLANModem\Modem\Scripts.
■ If you are using Lotus cc:Mail, select script file
cc56kcom.mdm.
■ If you are using a Lotus Notes version earlier than 4.x,
select script file LN56kcom.mdm.
To load a script file for Lotus Notes version 4.x or later—
1. In Windows Explorer select C:\Program Files\Compaq\
CPQLANModem\Modem\Scripts.
2. Copy the LN56kcom.mdm file in the Scripts folder to the
Notes\Data\Modems folder.
3. Open the Lotus Notes application.
4. From the menu bar, select FileÅToolsÅUser
PreferencesÅPorts icon.
5. Make sure the Port Enabled checkbox is selected.
6. Make sure the modem COM port selected is COM2.
7. Select the COMx Options button.
8. From the Modem Type list in the Additional Setup dialog
box, select Compaq 56K (V.90) Mini PCI Card.
9. Make sure that Hardware Flow Control is selected and the
following options are set:
■ Maximum port speed—115200.
■ Port number—COM2.
10. To confirm your settings and close the Additional Setup
dialog box, select OK.
6-4 Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models)
Page 80

Loading a Microsoft MS-Mail 3.2 Remote Script File
1. In Windows Explorer select C:\Program Files\Compaq\
CPQLANModem\Modem\Scripts.
2. Copy the ms56kcom.scr file in the Scripts folder to the
C:\Windows\MS-Mail\MSRMT\GLB folder.
3. Open the MS-Mail Remote application.
4. Select MailÅCommunicationsÅScript menu.
5. From the modem list, select Compaq 56K (V.90) Mini
PCI Card.
6. In the Communication boxes, make sure the following options
are set:
■ Baud rate—57600.
■ Port—COM2.
7. To confirm your settings, select OK.
Configuring the Modem
The settings you may be required to enter vary among
communication software applications. The following settings are
recommended:
■ Modem initialization string—AT&F.
NOTE: Newer initialization strings may be available from the
Compaq Web site at http://www.compaq.com.
■ COM port settings—
■ In Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows 2000 Professional,
or Windows NT 4.0 select COM2.
■ Fax class—Select 1.
■ Parity—Select NONE.
■ Word length—Select 8.
■ Stop bits—Select 1.
■ Hardware flow control—Select RTS/CTS.
Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models) 6-5
Page 81

■ Speed—Select the highest transmission speed or baud rate.
■ The maximum connection speed is determined by the speed
of the slowest modem on the connection. The internal
modem negotiates the fastest speed possible with the remote
modem.
■ The internal modem supports
ITU (International Telecommunications Union) analog
modem recommendations for speeds up to 33.6 Kbps.
ITU digital/analog modem pair recommendations for
speeds up to 56 Kbps.
NOTE: The digital/analog modem pair rates allow faster
downloads only from compliant digital sources. Maximum
achievable download rates are currently unknown, may not
reach 56Kbps, and will vary with line conditions. Maximum
achievable upload rates are limited to 31.2Kbps, may not
reach 31.2Kbps, and will vary with line conditions.
Using Modem Commands and Dial Modifiers
You can configure most communications software without the use
of AT commands or dial modifiers.
■ If you prefer to configure the modem using AT commands,
select StartÅProgramsÅAccessoriesÅHyperTerminal.
■ Command sets for all modem models are available at the
Compaq Web site at http://www.compaq.com and on the
Armada Reference Library & Quick Restore CD included with
the computer. The command sets list and describe AT
commands, Status registers, and result codes.
■ To view, print, or install modem commands from the CD—
Insert the Armada Reference Library & Quick Restore CD into
the CD drive, choose to install the modem commands for your
modem, then follow the installation instructions on the screen.
6-6 Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models)
Page 82

Using the Modem While Traveling Internationally
Using a Country-Specific Modem Adapter
Telephone jacks vary by country. The modem cable included with
the computer plugs directly into an RJ-11 telephone jack. To plug
the modem cable into a different type of telephone jack, you must
use a country-specific modem cable adapter. A cable adapter is
provided with the computer. To obtain the country-specific
adapters required for your itinerary, refer to Appendix A to contact
a Compaq-authorized dealer, reseller, or service provider.
To connect the modem using a country-specific modem adapter:
1. Plug the end of the modem cable with the EMI suppression
circuitry included with the computer into the RJ-11 jack on the
1
computer
2. Plug the country-specific modem adapter into the telephone
2
jack
3. Plug the modem cable into the country-specific modem
adapter
.
.
3
.
Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models) 6-7
Page 83

Selecting a Country-Specific Modem Configuration
The internal modem is configured to meet operating approval in
the country where you purchased your computer. If the modem is
used in other countries during travel, the country selection setting
for the modem needs to change to meet the telecommunications
regulations for that country.
Modem country configuration is performed through the country
drop-down box on the Dialing Properties screen of the modem
Control Panel. To confirm that the modem has been approved for
use by the telecommunications agency in the desired country,
check the approvals label on the bottom of the computer. Or, for
the most up-to-date information, refer to the Compaq Internet Web
site at www.compaq.com.
NOTE: The internal modem supports a subset of the countries that
are listed under the Dialing Properties. If you select an
unsupported country, a warning will appear and USA will be
selected if you don’t choose a different supported country.
To confirm your country selection:
In Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows NT 4.0 click
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅModemsÅDialing
PropertiesÅand then view your country in the “I am in:” dropdown box. In Windows 2000 Professional click
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPhone and Modem
OptionsÅclick a locationÅEdit buttonÅand then view your
country or region in the Country/region drop-down box.
To change your country selection if you are traveling:
In Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows NT 4.0 click
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅModemsÅDialing
PropertiesÅand then select your new country in the “I am in:”
drop-down box. In Windows 2000 Professional click
StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅPhone and Modem
OptionsÅclick a locationÅEdit buttonÅand then select your new
country in the Country/region drop-down box.
NOTE: For proper modem operation and to ensure compliance with
local regulatory requirements when traveling, change your modem
country selection whenever you operate your modem in a different
country.
6-8 Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models)
Page 84

Travel Connection Checklist
If you experience connection problems while using the modem
outside your home country, the following suggestions may help.
■ Check the telephone line type—the modem requires an
analog, not a digital, telephone line. A telephone line described
as a data line, fax machine line, modem line, or standard
telephone line, is probably an analog line.
■ Check for pulse or tone dialing—Dial a few digits on the
telephone and listen for clicks (pulses) or tones. Then set your
communication software to the corresponding dialing mode
(pulse or tone).
■ Check the telephone number you are dialing and the
response of the remote modem—Dial the telephone number
on the telephone, wait for the remote modem to answer, then
hang up.
■ Set the modem to ignore dial tones—If the modem receives a
dial tone it does not recognize, it will not dial and will display a
No Dial Tone error message. To set the modem to ignore all
dial tones before dialing:
1. Select StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅModems.
2. Select your modem, then select PropertiesÅConnections
tab, then clear the Wait for Dial Tone Before Dialing check
box.
NOTE: If you continue to receive the No Dial Tone error
message after clearing the checkbox, click StartÅSettingsÅ
Control PanelÅDialing PropertiesÅselect USA in the “I am
in:” drop-down box, then again clear the Wait for Dial Tone
Before Dialing check box.
Reinstalling or Updating Drivers (Windows 95 or Windows 98)
To update or reinstall modem drivers:
■ First, uninstall the currently loaded modem drivers.
■ Second, install or restore the modem drivers.
Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models) 6-9
Page 85

Uninstalling Modem Drivers:
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)
1. Select StartÅSettingsÅControl Panel, then double-click
Add/Remove Programs and select the Install/Uninstall tab.
2. Select Compaq 56K (V.90) Mini PCI from the program list.
3. Select the Add/Remove button.
4. Select Yes to confirm the removal.
5. To complete the removal, restart the computer.
Reinstalling Modem Drivers:
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)
When you restart the computer, the computer displays the New
Hardware Found “PCI Serial Controller” dialog box.
1. Select the Next button in the dialog box, then continue to
select the Next button on succeeding screens until you are
prompted to enter a driver location.
2. At the driver location prompt, type the path to the Compaq
56K (V.90) Mini PCI drivers:
3. Select the Next button, then continue to select the Next button
on succeeding screens until the operation is complete.
4. To complete the installation, select Finish.
C:\Program Files\Compaq\CPQLANModem\Modem\Win9x
Reinstalling or Updating Drivers (Windows NT 4.0)
IMPORTANT: To uninstall or reinstall modem or LAN drivers in
Windows NT 4.0, you must log in to Windows NT with
Administrator privileges.
To update or reinstall modem drivers:
■ First, uninstall the currently loaded modem drivers.
■ Second, install or restore the modem drivers.
6-10 Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models)
Page 86

Uninstalling Modem Drivers:
(Windows NT 4.0)
To uninstall modem drivers—
1. Select StartÅSettingsÅControl Panel, then double-click
Add/Remove Programs and select the Install/Uninstall tab.
2. Select Compaq 56K (V.90) Mini PCI from the list of
programs.
3. Select the Add/Remove button.
4. Select Yes to confirm the removal.
5. To complete the removal, restart the computer.
Reinstalling Modem Drivers:
(Windows NT 4.0)
1. Select StartÅRun. In the Open box, type
C:\Program Files\Compaq\CPQLANModem\Modem\NT40\
Combo\Setup
2. Select the OK button, then select the Next button on
succeeding screens until the computer copies the modem
drivers.
3. Select Finish.
4. Restart the computer.
Using an Internal Modem (Available on Select Models) 6-11
Page 87

chapter
7
CONNECTING TO A
LOCAL AREA NETWORK
(AVAILABLE ON SELECT MODELS)
A network computer model includes
■ An internal modem/NIC (network interface card) combination
card
■ Has an RJ-45 jack on the right side
■ Supports network speeds up to
■ 10 Mbps when connected to a 10BaseTX network.
■ 100 Mbps when connected to a 100BaseTX network.
■ Can be connected to a LAN whether or not the internal modem
is connected to a telephone line.
■ Provides preinstalled LAN (local area network) drivers
allowing you to connect the computer to a LAN.
Connecting the Network Cable
IMPORTANT: The network cable may contain noise suppression
circuitry near one end of the cable. This circuitry prevents
interference with TV and radio reception. Orient the cable so that
the noise suppression circuitry is closest to the computer.
1. Plug one end of the LAN cable (may not be included with the
computer) into the RJ-45 jack on the computer.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to a network jack.
3. Restart the computer, then connect to the network.
Connecting to a Local Area Network (available on select models) 7-1
Page 88

IMPORTANT: Consult with your information services department
before loading a network driver or changing a network setting.
Turning a LAN Connection On and Off
To conserve power, you can turn a LAN connection off and on as
you work.
To turn off a LAN connection—
1. Log off the network.
2. Disconnect the network cable.
To turn on a LAN connection—
1. Connect the network cable.
2. Log on to the network.
Accessing the Network at Startup
A network computer model supports both the PXE (Preboot
eXecution Environment) and RPL (Remote Program Load)
preboot network protocols.
To connect to your PXE or RPL server during startup—Press
F12 when the “Network Service Boot” message appears very
briefly in the lower-right corner of the screen.
To set the computer to connect to your PXE or RPL server at
start up—Refer to “Changing the Startup Sequence with
MultiBoot” in Chapter 5.
Reinstalling or Updating Drivers (Windows 95 or Windows 98)
To update or reinstall modem and LAN drivers:
■ First, uninstall the currently loaded modem drivers.
■ Second, uninstall the currently loaded LAN drivers.
■ Third, install or restore the LAN drivers.
■ Fourth, install or restore the modem drivers.
After completing the installation or restoration, Compaq
recommends that you confirm the network protocol.
7-2 Connecting to a Local Area Network (available on select models)
Page 89

Uninstalling Modem and LAN Drivers:
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)
To uninstall modem drivers—
1. Select StartÅSettingsÅControl Panel, then double-click
Add/Remove Programs and select the Install/Uninstall tab.
2. Select Compaq 56K (V.90) Mini PCI from the list of
programs.
3. Select the Add/Remove button.
4. Select Yes to confirm the removal.
5. If you are prompted to restart the computer, select No, then
begin uninstalling the LAN drivers.
To uninstall LAN drivers—
1. On the Install/Uninstall tab, select Intel PRO Ethernet Adapter
and Software from the list of programs.
2. Select the Add/Remove button.
3. Select OK to confirm the removal.
4. Restart the computer, then begin installing the modem drivers.
Reinstalling LAN and Modem Drivers
(Windows 95 and Windows 98)
To reinstall LAN drivers—
When you start the computer, the computer displays the New
Hardware Found “PCI Ethernet Controller” dialog box.
1. Select the Next button in the dialog box, then continue to
select the Next button on succeeding screens until you are
prompted to enter a driver location.
2. At the driver location prompt, type the path to the Intel
PRO/100+ MiniPCI drivers:
C:\Program Files\Compaq\CPQLANModem\Network
3. Select the Next button, then continue to select the Next button
on succeeding screens until the computer copies the LAN files.
4. To continue, select Finish.
5. To complete the installation of the LAN drivers, restart the
computer.
Connecting to a Local Area Network (available on select models) 7-3
Page 90

To reinstall modem drivers—
When you restart the computer, the computer displays the New
Hardware Found “PCI Serial Controller” dialog box.
1. Select the Next button in the dialog box, then continue to
select the Next button on succeeding screens until you are
prompted to enter a driver location.
2. At the driver location prompt, type the path to the Compaq
56K (V.90) Mini PCI drivers:
C:\Program Files\Compaq\CPQLANModem\Modem\Win9x
3. Select the Next button, then continue to select the Next button
on succeeding screens until the computer copies the
modem drivers.
4. To complete the installation of the modem drivers, select
Finish.
NOTE: It is not necessary to restart the computer after installing
the modem drivers.
Confirming the Network Protocol
(Windows 95 or Windows 98)
After reinstalling the LAN and modem drivers, it is recommended
that you confirm the network protocol setting:
1. Select StartÅSettingsÅControl Panel. Double-click Network,
then select the Configuration tab.
2. Verify that the desired protocols are included on the list of
installed network components.
NOTE: For information about adding a network protocol, refer to
your operating system documentation.
7-4 Connecting to a Local Area Network (available on select models)
Page 91

Reinstalling or Updating Drivers (Windows NT 4.0)
IMPORTANT: To uninstall or reinstall modem or LAN drivers in
Windows NT 4.0, you must log in to Windows NT with
Administrator privileges.
To update or reinstall modem and LAN drivers:
■ First, uninstall the currently loaded modem drivers.
■ Second, uninstall the currently loaded LAN drivers.
■ Third, reinstall Windows NT Networking (if required).
■ Fourth, install or restore the LAN drivers.
■ Fifth, install or restore the modem drivers.
Uninstalling Modem and LAN Drivers:
(Windows NT 4.0)
To uninstall modem drivers—
1. Select StartÅSettingsÅControl Panel, then double-click
Add/Remove Programs.
2. Select Compaq 56K (V.90) Mini PCI from the list of
programs.
3. Select the Add/Remove button.
4. Select Yes to confirm the removal.
5. If you are prompted to restart the computer, select No.
6. Select OK to close the Add/Remove Programs window.
To uninstall LAN drivers—
1. In the Control Panel window, double-click Network, then
select the Adapters tab.
2. Select Intel PRO/100+ Mini PCI, then select Remove.
3. Select Yes to continue.
4. Select Yes to confirm the file removal.
5. Restart the computer.
Connecting to a Local Area Network (available on select models) 7-5
Page 92

Reinstalling Windows NT Networking:
(Windows NT 4.0)
If it has become necessary to reinstall LAN drivers, you may also
need to reinstall Windows NT Networking.
To determine whether you must reinstall Windows NT
Networking, select StartÅ SettingsÅControl Panel, then doubleclick Network.
■ If you are not prompted to install Windows NT
Networking— Go to “Reinstalling LAN Drivers: Compaq
56K (V.90) MiniPCI Modem (Windows NT 4.0)” next in this
section.
■ If you are prompted to install Windows NT Networking—
Select Yes, then use the following procedure.
To install Windows NT Networking—
1. Select StartÅSettingsÅControl Panel, then double-click
Network.
2. At the Windows NT Networking installation prompt, select
Yes.
3. Select Wired to the Network, then select the Next button.
4. Select the Select from List button.
5. Select the Have Disk button.
6. When prompted, type the path to the Intel PRO/100+ Mini PCI
drivers:
C:\Program Files\Compaq\CPQLANModem\Network
7. Select the OK button.
8. Select Intel PRO Adapter.
9. Select the OK button.
10. Select the Next button.
11. Select the network protocol(s) for your LAN environment,
then select the Next button.
12. Select the network service(s) for your LAN environment.
Select the Next button, then continue to select the Next button
on succeeding screens until you are prompted to enter a drive
designator.
13. When prompted, type the drive designator for your
Windows NT 4.0 operating system. For example, if
Windows NT 4.0 is on your hard drive, type
C: (where C: is the
designator of your hard drive).
7-6 Connecting to a Local Area Network (available on select models)
Page 93

14. Select the binding(s) for your LAN environment. Select the
Next button, then continue to select the Next button on
succeeding screens until you are prompted to enter the
computer name and workgroup/domain information.
15. When prompted, enter the computer name and the
workgroup/domain information for your LAN environment,
then select the Next button.
16. Select the Finish button.
17. Restart the computer.
Reinstalling LAN Drivers:
(Windows NT 4.0)
1. Select StartÅSettingsÅControl Panel, then double-click
Network.
2. Select the Adapters tabÅAdd buttonÅHave Disk button.
3. When prompted for the path to the Intel PRO/100+ Mini PCI
drivers, type the following, then select OK.
C:\Program Files\Compaq\CPQLANModem\Network
4. Select Intel PRO AdapterÅOK.
5. Select the properties for your LAN environment, then
select OK.
6. Restart the computer.
Reinstalling Modem Drivers:
(Windows NT 4.0)
1. Select StartÅRun. In the Open box, type
C:\Program Files\Compaq\CPQLANModem\Modem\NT40\Setup
2. Select the OK button, then select the Next button on
succeeding screens until the operation is complete.
3. Select Finish.
4. Restart the computer.
Connecting to a Local Area Network (available on select models) 7-7
Page 94

chapter
8
CONNECTING EXTERNAL DEVICES
Connecting an External Enhanced Keyboard
To connect an external enhanced keyboard to the computer,
connect the keyboard cable to the keyboard/mouse connector on
the computer.
Connecting an External Monitor
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the computer, turn off the monitor
before connecting it to the computer or disconnecting it from the
computer. To prevent damage to the computer display, do not place
an external monitor or any other object on top of the computer when
the computer is closed.
To connect an external VGA monitor:
1. Turn off the monitor.
2. Plug the monitor signal cable into the external monitor
connector on the back of the computer.
3. Plug the monitor power cord into a properly grounded
electrical outlet.
4. Turn on the monitor.
5. Ensure that the computer recognizes your monitor type. Click
StartÅSettingsÅControl Panel then double-click Display.
Select the appropriate manufacturer and model, if necessary.
NOTE: If the external monitor does not immediately show a display,
try using the
Fn+F4 hotkeys.
Connecting External Devices 8-1
Page 95

Connecting a Television Monitor
CAUTION: To prevent damage to the computer display, do not place
a television monitor or any other object on top of the computer when
the computer is closed.
A Composite TV-Out is provided that allows you to switch your
screen output from the computer display (panel and/or monitor) to
a television monitor. To switch your computer output to the
television monitor, use the Microsoft Windows Control Panel.
1. Turn off the television and plug the RCA-style television
signal cable into the Composite TV-Out on the computer.
NOTE: You can purchase an RCA-style television signal cable
at any home electronics store.
2. Plug the television power cord into a properly grounded
electrical outlet.
3. If you are running Windows 95 or later: to ensure that the
computer recognizes your television format, click Start
ÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅDisplay. Select the Settings tab,
then the Advanced options. Click the Displays tab and select
TV. Select the appropriate television format (NTSC, NTSC-J,
PAL, or PAL-M).
If you are running Windows NT 4.0: to ensure that the
computer recognizes your television format, click
StartÅProgramsÅ ATI UtilitiesÅATI Display Utility. Select
the appropriate television format (NTSC, NTSC-J, PAL, or
PAL-M).
4. Turn on the television.
5. If the television does not display the correct image, repeat Step
3 and select a different television format.
6. To switch back to the computer display, toggle the
hotkeys back to the panel and/or monitor display mode, or
follow the sequence in Step 3 and select Panel and/or Monitor.
Fn+F4
8-2 Connecting External Devices
Page 96

Connecting a Mouse or Other External Pointing Device
A PS/2-compatible mouse or external TouchPad can be connected
to the computer.
To connect an external pointing device, insert the pointing device
cable into the keyboard/mouse connector.
External pointing devices need software device drivers to operate.
The necessary drivers should be provided by the manufacturer or
may be preinstalled with Microsoft Windows.
Connecting a Serial Printer
1. Turn off the printer.
2. Plug the printer end of the printer signal cable into the printer.
3. Connect the serial printer signal cable to the serial connector
on the back of the computer.
4. Plug the printer power cord into a properly grounded electrical
outlet.
5. Turn on the printer and resume your work.
NOTE: Windows should prompt you to set up your printer before
printing for the first time. If setup fails, consult the printer
documentation for printer device driver configuration information
and instructions.
Connecting a Parallel Printer
1. Turn off the printer.
2. Plug the printer end of the printer signal cable into the printer.
3. Connect the parallel printer signal cable to the parallel
connector on the back of the computer.
4. Plug the printer power cord into a properly grounded electrical
outlet.
5. Turn on the printer and resume your work.
NOTE: Windows should prompt you to set up your printer before
printing for the first time. If setup fails, you may need to consult
the printer documentation for printer device driver configuration
information and instructions.
Connecting External Devices 8-3
Page 97

Connecting Infrared Equipment
NOTE: Infrared-equipped computers are IrDA-compliant. Infrared
performance may vary depending on peripherals, distance between
infrared devices, and applications used. The infrared port is
available only on specific models.
The infrared port allows wireless communication between your
computer and other infrared-equipped devices. Operating system
support for infrared communication is currently available with
Microsoft Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows 2000
Professional but not for Windows NT 4.0. To operate infrared on
computers running Windows NT 4.0, you will need to purchase
optional software.
The infrared port produces an invisible beam of infrared light to
communicate with another infrared-equipped device.
To establish an infrared link:
■ Be sure the infrared ports on both devices are turned on and
facing each other at a distance no greater than 1.5 feet (about
0.5 meter).
■ Avoid moving the infrared ports away from each other during
data transmission.
■ Avoid interference from remote control units, such as wireless
headphones or audio devices, pointed at the infrared ports.
■ Avoid direct sunlight, fluorescent light, or flashing
incandescent light close to the infrared ports.
■ Keep the path between the infrared ports free of any objects
that might interfere with data transmission.
■ Do not point one of the ports more than 30 degrees (plus or
minus 15 degrees off the center line) away from the infrared
port of the device you are connecting with.
8-4 Connecting External Devices
Page 98

Configuring the Infrared Port
As you set up your infrared software, the following information
may be helpful.
■ The infrared port default settings are: Port, COM3; address, 3;
Interrupt Request (IRQ), 3.
■ If you use Direct Cable Connection and the utility asks you to
choose a port for the infrared connection, you can select Serial
Cable on COM5 or, if the computer is running a preinstalled
Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows 2000 Professional
operating system, select Parallel Cable on LPT3.
Enabling the Infrared Port
In Windows 95 the infrared port must be enabled each time the
computer is turned on or restarted. To enable the infrared port,
select StartÅSettingsÅControl PanelÅInfrared.
In Windows 98 and Windows 2000 Professional the infrared port
is enabled by default each time the computer starts up.
■ When the infrared port is enabled, the infrared icon appears on
the taskbar and Infrared Monitor Search is enabled by default.
■ While the Infrared Monitor Search is enabled
■ You can establish an infrared link.
■ The system cannot initiate Suspend (Standby). User-
initiated Suspend (Standby) is not affected.
■ When the Infrared Monitor Search is disabled
■ Power is conserved.
■ You cannot establish an infrared link.
■ The system can initiate Suspend (Standby).
Connecting External Devices 8-5
Page 99

Connecting USB Peripherals
Your computer comes equipped with a port that connects
Universal Serial Bus (USB) devices to the computer.
Your computer can support certain USB devices without any
special drivers. These include hubs and keyboards. To connect
USB devices for which the device manufacturer provided no
special drivers, you will need an operating system that has USB
support, such as Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows 2000
preinstalled by Compaq. Later versions of the Windows operating
systems will add functionality that may allow you to attach any
USB device to your computer (for example, a video camera) and
allow many USB devices to be connected and working
simultaneously.
A USB keyboard and mouse, optionally connected through a hub,
offer the same functionality as a standard keyboard and mouse
connected through the keyboard/mouse connector. Future
operating systems will have extended USB capabilities which will
replace the USB capabilities built into the computer.
Connecting to a Docking Device
The computer is compatible with Armada docking stations. To
connect the computer to a port replicator or docking station, refer
to the instructions that came with the docking device.
8-6 Connecting External Devices
Page 100

chapter
9
USING PC CARDS
PC Card Types
This computer can support two Type II PC Cards or one Type III
PC Card. It supports both 16-bit and 32-bit CardBus PC Cards.
Several kinds of PC Cards are supported, such as network cards,
hard drive cards, memory cards, and fax/modem cards.
For a current list of third-party PC Cards qualified on this
computer, call your Compaq authorized dealer, reseller, or service
provider.
Inserting a PC Card
1. If you are running Windows NT 4.0 but not CardWare 5.0
provided by Compaq, turn off the computer. If you are running
Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows 2000 Professional,
you do not need to turn off the computer or initiate Suspend
before inserting a PC Card.
NOTE: If you are running Windows NT 4.0 and CardWare 5.0
provided by Compaq, most PC Cards can be inserted while the
computer is on. Contact your PC Card vendor directly for
information about the level of support they offer for hot
insertion with CardWare 5.0.
Using PC Cards 9-1
 Loading...
Loading...