Page 1

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Notice
The information in this guide is subject to change without notice.
COMPAQ COMPUTER CORPORATION SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR
TECHNICAL OR EDITORIAL ERRORS OR OMISSIONS CONTAINED HEREIN;
NOR FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM
THE FURNISHING, PERFORMANCE, OR USE OF THIS MATERIAL.
This guide contains information protected by copyright. No part of this guide may be
photocopied or reproduced in any form without prior written consent from Compaq
Computer Corporation.
1998 Compaq Computer Corporation.
All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
Compaq and LTE are registered is the U. S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Armada is a trademark of Compaq Computer Corporation.
Microsoft, MS-DOS, and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
The software described in this guide is furnished under a license agreement or
nondisclosure agreement. The software may be used or copied only in accordance with
the terms of the agreement.
Product names mentioned herein may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their
respective companies.
Maintenance and Service Guide
Compaq Armada 4100 and 4200 Families of Personal Computers
First Edition (January 1998)
Documentation Part Number 234843-002
Spare Part Number 273027-002
Compaq Computer Corporation
Page 2

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contents
Preface
..........................................................................................................................xi
Symbols........................................................................................................xi
Technician Notes..........................................................................................xi
Laser Safety................................................................................................ xii
CDRH Regulations..................................................................................... xii
Locating Additional Information............................................................... xiii
Chapter 1
Product Description
1.1 Computer Features and Models........................................................... 1-1
1.2 Models................................................................................................. 1-2
1.3 Standard Features................................................................................1-3
1.3.1 Software Fulfillment....................................................................1-5
1.3.2 Security Features..........................................................................1-5
1.3.3 Power Management...................................................................... 1-5
1.4 Options ................................................................................................1-6
1.4.1 System Memory Options ............................................................. 1-6
1.4.2 Display Options ........................................................................... 1-7
1.4.3 Secondary Cache.......................................................................... 1-7
1.4.4 Mobile CD Expansion Unit.......................................................... 1-7
1.4.5 Convenience Base........................................................................ 1-7
1.4.6 Mass Storage Options .................................................................. 1-7
1.4.7 AC Adapter..................................................................................1-8
1.4.8 Automobile Adapter..................................................................... 1-8
1.4.9 Lithium Ion Battery Pack............................................................. 1-8
1.4.10 External Battery Charger ........................................................... 1-8
1.4.11 External Keyboards....................................................................1-8
1.4.12 External Monitors ...................................................................... 1-8
1.4.13 Compaq Mouse.......................................................................... 1-9
1.4.14 Trackball Pointing Device ......................................................... 1-9
1.5 External Computer Components.........................................................1-9
1.5.1 Front and Left Side Components.................................................1-9
1.5.2 Front and Right Side Components............................................. 1-11
1.5.3 Rear Components....................................................................... 1-12
1.5.4 Bottom Components .................................................................. 1-13
1.5.5 Status Panel Lights..................................................................... 1-14
1.6 Mobile CD Expansion Unit Components......................................... 1-15
1.7 Convenience Base Connectors.......................................................... 1-17
1.8 Design Overview - Computer............................................................ 1-18
1.8.1 System Unit................................................................................ 1-18
1.8.2 System Board............................................................................. 1-18
1.8.3 Processor Board ......................................................................... 1-19
1.8.4 Processor.................................................................................... 1-19
Contents v
Page 3

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.8.5 System Memory..........................................................................1-19
1.8.6 Cache ..........................................................................................1-19
1.8.7 Local Bus Video.........................................................................1-20
Chapter 2
2.1 Preliminary Steps................................................................................2-2
2.2 Clearing the Power-On and Setup Passwords.....................................2-3
2.3 Power-On Self Test (POST)................................................................2-4
2.4 POST Error Messages.........................................................................2-4
2.5 Compaq Utilities.................................................................................2-7
2.5.1 Running Computer Setup ............................................................2-7
2.5.2 Running Computer Checkup (TEST)..........................................2-8
2.5.3 View System Information (INSPECT)......................................2-10
2.6 Diagnostic Error Codes.....................................................................2-11
2.7 Troubleshooting Without Diagnostics ..............................................2-17
2.7.1 Solving Minor Problems............................................................2-17
Chapter 3
Illustrated Parts
3.1 System Unit..........................................................................................3-2
3.2 Mass Storage Devices..........................................................................3-6
3.3 Cables and Power Cords......................................................................3-8
3.4 Standard and Optional Boards ...........................................................3-10
3.5 Display Assembly..............................................................................3-12
3.6 Options...............................................................................................3-14
3.8 Miscellaneous Parts............................................................................3-16
3.8 Shipping Boxes..................................................................................3-18
3.9 Documentation...................................................................................3-19
vi Contents
Chapter 4
Removal and Replacement Preliminaries
4.1 Electrostatic Discharge ........................................................................4-1
4.1.1 Generating Static ..........................................................................4-1
4.1.2 Preventing Electrostatic Damage to Equipment...........................4-2
4.1.3 Removing Batteries ......................................................................4-2
4.1.4 Preventing Damage to Drives.......................................................4-3
4.1.5 Grounding Methods......................................................................4-3
4.1.6 Grounding Workstations...............................................................4-4
4.1.7 Grounding Equipment ..................................................................4-4
4.1.8 Recommended Materials and Equipment.....................................4-5
4.2 Service Considerations.........................................................................4-6
4.2.1 Tool Requirements........................................................................4-6
4.2.2 Cables and Connectors .................................................................4-6
4.3 Serial Number......................................................................................4-6
Page 4

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 5
Removal and Replacement Procedures
5.1 Serial Number...................................................................................... 5-1
5.2 Disassembly Sequence Chart .............................................................. 5-2
5.3 Preparing the Computer for Disassembly............................................ 5-3
5.3.1 Disconnecting the AC Power and
External Diskette Drive Bay .................................................................5-4
5.3.2 Undocking the Computer............................................................. 5-5
5.3.3 Battery Packs.............................................................................. 5-11
5.3.4 DualBay Battery Pack and Devices ..........................................5-13
5.3.4 Pointing Devices........................................................................5-16
5.3.5 Hard Drive.................................................................................. 5-18
5.3.6 PC Card...................................................................................... 5-19
5.4 External Computer Components.......................................................5-20
5.4.1 Computer Logo.......................................................................... 5-20
5.4.2 Computer Feet............................................................................ 5-21
5.4.3 Handle........................................................................................ 5-22
5.5 CPU Base Assembly ......................................................................... 5-26
5.5.1 Memory Cover........................................................................... 5-27
5.5.2 Memory Boards.......................................................................... 5-28
5.5.3 Lithium Real Time Clock Battery.............................................. 5-30
5.5.4 CPU Base Cover ........................................................................ 5-31
5.5.5 Processor Shield and Board ...................................................... 5-34
5.5.6 CPU Cover and Keyboard Assembly........................................ 5-36
5.6 Display Assembly.............................................................................. 5-40
5.7 Clutch Assembly Components.......................................................... 5-44
5.7.1 Clutch Cover.............................................................................. 5-44
5.7.2 Clutches...................................................................................... 5-46
5.8 System Board Components...............................................................5-47
5.8.1 System Board............................................................................. 5-47
5.8.2 Ensuring ESD Protection...........................................................5-52
5.8.3 Heatsink and Video Chip Heatpipe........................................... 5-53
5.9 Frame Components............................................................................ 5-56
5.9.1 Upper PCMCIA Door................................................................ 5-56
5.9.2 Lower PCMCIA Door................................................................ 5-59
5.9.3 DualBay Eject Assembly...........................................................5-62
5.9.5 PCMCIA Assembly .................................................................. 5-64
5.9.6 PCMCIA Ejector Buttons .......................................................... 5-67
5.9.7 Display Ground Bracket............................................................. 5-69
Chapter 6
Specifications
6.1 Computer............................................................................................. 6-2
6.2 Displays.............................................................................................. 6-3
6.3 Hard Drives ......................................................................................... 6-6
Contents vii
Page 5

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.4 Diskette Drive......................................................................................6-9
6.5 CD-ROM Drives...............................................................................6-10
6.6 Battery Packs.....................................................................................6-13
6.7 Mobile CD Expansion Unit................................................................6-14
6.8 External Power Supplies....................................................................6-15
6.9 System Interrupts ...............................................................................6-18
6.10 System DMA....................................................................................6-19
6.11 System I/O Address ........................................................................6-20
6.12 System Memory Map......................................................................6-22
Appendix A
Connector Pin Assignments
...................................................................................A-1
Appendix B
Power Cord Set Requirements
3-Conductor Power Cord Set....................................................................B-1
General Requirements ..........................................................................B-1
Country-Specific Requirements............................................................B-2
Index
................................................................................................................................... I-1
..............................................................................B-1
viii Contents
Page 6
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preface
Preface
This Maintenance and Service Guide is a troubleshooting guide that can be used for
reference when servicing the Compaq Armada 4100 and 4200 Families of Personal
Computers. Additional information is available in the Service Quick Reference Guide
and in QuickFind.
Compaq Computer Corporation reserves the right to make changes to the Compaq
Armada 4100 and 4200 Families of Personal Computers without notice.
Symbols
The following symbols and words mark special messages throughout this guide:
WARNING:
!
warning could result in bodily harm or loss of life.
CAUTION:
result in damage to equipment or loss of data.
IMPORTANT: Text set off in this manner presents clarifying information or specific
instructions.
NOTE: Text set off in this manner presents commentary, sidelights, or other points
of information.
Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow directions in the
Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow directions could
Technician Notes
WARNING:
!
this equipment. All troubleshooting and repair procedures are detailed to allow only
subassembly/module level repair. Because of the complexity of the individual boards and
subassemblies, no one should attempt to make repairs at the component level or to
make modifications to any printed wiring board. Improper repairs can create a safety
hazard. Any indication of component replacement or printed wiring board modifications
may void any warranty or exchange allowances.
CAUTION:
(7.62 cm) of clearance on the front and back of the computer.
WARNING:
!
operation, plug the AC power cord into a properly grounded electrical outlet only.
Only authorized technicians trained by Compaq should attempt to repair
To properly ventilate your system, you must provide at least 3 inches
The computer is designed to be electrically grounded. To ensure proper
Preface xi
Page 7
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Laser Safety
All Compaq systems, equipped with CD-ROM drives, comply with appropriate safety
standard including IEC 825. With specific regard to the laser, the equipment complies
with laser product performance standards set by government agencies as a Class 1 laser
product. It does not emit hazardous light; the beam is totally enclosed during all modes
of customer operation and maintenance.
CDRH Regulations
The Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) of the U.S. Food and Drug
Administration implemented regulations for laser products on August 2, 1976. These
regulations apply to laser products manufactured from August 1, 1976. Compliance is
mandatory for products marketed in the United States.
WARNING:
!
other than those specified herein or in the CD ROM installation guide may
result in hazardous radiation exposure.
This system is classified as a CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT. This label is located on the
outside of your system. A similar label also appears on the internal CD-ROM installed
in your system.
LASER INFO
Laser Type: Semiconductor GaAIAs
Wave Length: 780 +/- 35 nm
Divergence Angle: 53.5 Degree +/- 1.5 Degree
Output Power: Less than
Polarization: Circular
Numerical Aperture: 0.45 +/- 0.04
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures
-1
0.2mW or 10,869 W
•
m-2sr
Only authorized technicians trained by Compaq should attempt to repair this
equipment. All troubleshooting and repair procedures are detailed to allow only
subassembly/module level repair. Because of the complexity of the individual boards
and subassemblies, no one should attempt to make repairs at the component level or to
make modifications to any printed wiring board. Improper repairs can create a safety
hazard.
xii Preface
Page 8

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Locating Additional Information
The following documentation is available to support the products:
Quick Setup
■
Reference Guide
■
Introducing Microsoft Windows 95
■
Compaq Service Quick Reference Guide
■
■
Service Training Guides
Compaq Service Advisories and Bulletins
■
Compaq QuickFind
■
Technical Reference Guide
■
Preface xiii
Page 9

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 1
Product Description
1.1 Computer Features and Models
The Compaq Armada 4100 and 4200 Families are mobile notebook computers with
advanced modularity, processors, and video graphics. Both families provide fullfunction, Pentium-based notebook computers that allow desktop functionality and
connectivity through the use of an optional Mobile CD (MCD) Expansion Unit and a
convenience base.
The 4100 Family provides light weight multimedia models with up to 166-MHz
processors with MMx technology, 8- or 16-MB of system memory, hard drive capacity
up to 2.0 GB, and primary battery power from the handle battery.
The 4200 Family provides slimline models with 233- or 266-MHz processor, 32-MB of
system memory, hard drive capacity up to 4-GB, and primary battery power from the
modular battery pack in the DualBay.
This chapter describes the features of these computer models.
■
Compaq Armada 4100
■
Compaq Armada 4110 and 4110D
■
Compaq Armada 4115
■
Compaq Armada 4120 and 4120T
■
Compaq Armada 4125D and 4125T
■
Compaq Armada 4130T
■
Compaq Armada 4131T
■
Compaq Armada 4140T
■
Compaq Armada 4150 and 4150T
■
Compaq Armada 4160T
■
Compaq Armada 4160T Slimline
■
Compaq Armada 4210T
■
Compaq Armada 4220T
Product Description 1-1
Page 10

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 1-1
. Compaq Armada 4100 and 4200
1.2 Models
The following 4200 models are available:
Table 1-1
4200 Family of Personal Computers
Model Processor Display Hard Drive Cache
4210T 233-MHz Pentium 12.1-inch CTFT 3.0-GB 256-KB (L2) 32/96
4220T 266-MHz Pentium 12.1-inch CTFT 4.0-GB 512-KB (L2) 32/96
Memory/
Upgrade
1-2 Product Description
Page 11
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The following 4100 Family models are available:
Table 1-2
Compaq Armada 4100 Family of Personal Computers
Memory/
Model Processor Display Hard Drive Cache
4120 120-MHz Pentium 11.3-inch CSTN 810-MB 256-KB 16/48*
4125D 120-MHz Pentium 11.3-inch CSTN 810-MB 256-KB 8/40
4120T 120-MHz Pentium 11.8-inch CTFT 810-MB 256-KB 8/40
4120T 120-MHz Pentium 11.8-inch CTFT 810-MB 256-KB 16/48*
4125T 120-MHz Pentium 11.8-inch CTFT 810-MB 256-KB 16/48*
4130T 133-MHz Pentium 11.8-inch CTFT 1.08-GB 256-KB 16/48
4131T 133-MHz Pentium 11.8-inch CTFT 1.4-GB 256-KB 16/48
4150 150-MHz Pentium w/ MMx 12.1-inch CSTN 1.6-GB 256-KB 16/80
4150T 150-MHz Pentium w/ MMx 12.1-inch CTFT 1.6-GB 256-KB 16/80
4160T 166-MHz Pentium w/ MMx 12.1-inch CTFT 2.0-GB 256-KB 16/80
4160T Slimline 166-MHz Pentium w/ MMx 12.1-inch CTFT 2.0-GB 256-KB 16/80
* Japan only
Upgrade
1.3 Standard Features
Depending upon your computer model, the processor, DRAM, hard drive space, and
color monitor type and size may vary:
Available in the Compaq Armada 4200 models:
■
233- or 266-MHz Pentium processors, upgradable to future Pentium technology
■
64-bit graphics controller
■
32-MB of dynamic random access memory (DRAM), expandable to 96 MB
■
3-GB or 4-GB 2.5- inch hard drives (4-GB hard drive is not compatible with the
4100 modeles)
■
12.1-inch Color Thin Film Transistor (CTFT) SVGA displays
■
External Diskette Drive Bay
■
Modular Lithium Ion (Li-ion) battery in the DualBay as the primary battery power
■
32-bit cardbus PC card slot
■
Handle battery in handle shell
Available in the Compaq Armada 4131T-4160T models:
■
4131T has a 133-MHz Pentium procesor and the 4150 has a 150-MHz Pentium
processor.The 4150 and the 4150T have 150-MHz Pentium processors with MMx
technology. The 4160T and the 4160T slimline have 166-MHz Pentium processors
with MMx technology.
■
Cirrus logic LCD graphic controller
Product Description 1-3
Page 12

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
■
16-MB of dynamic random access memory (DRAM), expandable to 40-, 48- or 80
MB
■
1.4-GB, 1.6-GB, and 2-GB hard drives
■
Lithium Ion (Li-ion) handle battery pack primary battery power
■
16-bit PC card system
Available in the Compaq Armada 4100-4130T models:
■
All models prior to and including the 4131T can be upgraded to a 133-MHz
Pentium processor by replacing the processor board.
■
75-, 100-, 120-, or 133-MHz Pentium processors.
■
8- or 16-MB of dynamic random access memory (DRAM), expandable to 72- or 80MB
■
630-MB, 810-MB, or 1.08-GB 2.5- inch hard drives
■
10.4-inch Color Super Twist Nematic (CSTN), 11.3-inch CSTN, or 11.8-inch Color
Thin Film Transistor (CTFT) SVGA displays
■
Lithium Ion (Li-ion) handle battery pack primary battery power
The following features are standard in both the Compaq Armada 4100 and 4200
Families:
■
NTSC/PAL TV video allows full screen, full motion digital video presentation with
interleaved synchronized stereo sound. MPEG accommodates full motion video in
the range of 24 frames per second (cinema quality) to 30 frames per second
(television quality).
■
IDE hard drive in the dedicated hard drive bay. Cable select technology is employed
for device 0/device 1 selection. The hard drive is secured in place with a pair of
screws
■
3.5-inch 1.44-MB diskette drive DualBay module supports a single diskette drive
■
Supports Lithium Ion (Li-ion) and Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) handle battery
packs
■
Sound Blaster−compatible audio controller with internal stereo speakers and internal
microphone
■
Full-size 101 key compatible keyboard including 12 function keys, 8 cursor control
keys, inverted-T cursor control keys, and embedded numeric keypad
■
Four user-programmable keys
■
Touchpad pointing device
■
Operates from an internal battery pack or an AC adapter that is compatible with
domestic or international power sources
■
Power management and security features
1-4 Product Description
Page 13

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
■
Infrared interface for wireless communication with other IrDA-compliant devices at
data rates up to 115 kbaud or 4 mbps on the 4210T, 4220T, 4150, 4150T, 4160T,
and the 4160T Slimline models.
■
Two PCMCIA standard device slots that will accommodate two types I and II and
one type III PC Cards
■
120-pin expansion connector provides the interface to the Mobile CD Expansion
Unit (MCD) and the convenience base
■
Rear-panel ports provide connections for parallel and serial, video out,
keyboard/mouse, and IrDA compliant infrared devices
1.3.1 Software Fulfillment
Backup software may be ordered directly from Compaq Computer Corporation through
the Compaq Order Center. Both the model and serial numbers of the computer are
needed to identify the specific software available.
For technical questions about software for the computer, contact a Compaq Technical
Support Engineer. The model and serial numbers of the computer should be available
before making the call.
1.3.2 Security Features
The computer has the following security features:
■
Ability to secure the computer and MCD Expansion Unit to an immovable object
with an optional cable lock.
■
Ability to establish power-on and setup passwords and to disable ports and devices
from the Security menu in Computer Setup.
1.3.3 Power Management
The computer supports three power management modes:
■
Local Standby: The ability of individual subsystems to enter reduced power modes
after predetermined periods of inactivity.
■
Global Standby: The ability to place all subsystems in a reduced power mode after a
predetermined period of inactivity.
■
Hibernation: The ability to save the system configuration and user data to the hard
disk, for restoration at a later time.
■
ACPI Hardware Ready (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface): the 4200
Family models support the operation of hardware and software power specifications
to interface in a single system and be used as needed.
In addition, there are the OFF and ON states. In the OFF state, the computer appears to
be consuming no power; however, as long as there is a battery capable of supplying
current, some components will be powered up, performing housekeeping tasks and
Product Description 1-5
Page 14

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
waiting to be awakened. In the ON state, all systems are powered up and the unit is
completely functional.
1.4 Options
The 4100 and 4200 Families support the following options:
■
MCD Expansion Unit
■
Convenience base (Passthrough and Ethernet models)
■
Memory expansion boards
■
Li-ion handle battery packs
■
Li-ion modular battery pack
■
Automobile Adapter
■
AC Adapter
■
External Battery Charger
■
PCMCIA modem
■
Trackball pointing device
■
AC power cords for international travelers
■
Display upgrades (4100 Family models only)
■
Hard drive upgrades (model dependent)
■
Processor upgrades (4100 Family models only)
■
External Battery Charger
■
External keyboards
■
External diskette drive bay
■
Compaq mouse
■
USB Cardbus PC card(4200 Family models only)
1.4.1 System Memory Options
The computer supports optional 4-, 8-, 16-, 32-MB or 64-MB memory board sets. The
memory boards are 70 ns Fast Page Mode DRAM SODIMMs, without parity. System
memory can be expanded to 40, 48, or 96-MB of DRAM depending on the model.
The 4210T and 4220T models can support standard EDO and FP memory upgrades.
Compaq does not offer EDO memory upgrade kits.
The system includes two DIMM slots that must be populated in pairs with DIMMs of
equal size and type. Either parity or non-parity DIMMs may be used, but parity
checking will not be enabled by the memory controller.
1-6 Product Description
Page 15

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.2 Display Options
The 4100 Family models with 11.3-inch, 11.8-inch, or CSTN displays can be upgraded
to an 12.1-inch Color Thin Film Transistor (CTFT) SVGA display.
1.4.3 Secondary Cache
The 4200 Family models are equipped with 256-KB or 512-KB secondary (L2) cache
of write-back/write-through cache on the system I/O board.
Models 4110 through 4160T of the 4100 Family are equipped with 256-KB of writeback/write-through cache on the system I/O board.
1.4.4 Mobile CD Expansion Unit
The Mobile CD-ROM Expansion Unit provides the following multimedia capabilities:
■
CD-ROM drive
■
Integrated stereo speakers
■
Game port with MIDI support
■
Dedicated battery bay
The CD-ROM drive is available in the optional MCD Expansion unit. The drive
supports the following formats:
■
ISO-9660, the most common CD-ROM format
■
CD-ROM XA eXtended Architecture, a standard for storing multimedia information
■
Photo CD (Kodak's format for storing photographic images on CD-ROM)
1.4.5 Convenience Base
The convenience base provides the following added capabilities:
■
Pass-through ports (serial, parallel, and video)
■
Expansion features (mouse and keyboard ports, network support)
■
Five-degree tilt for the notebook keyboard
■
Charging of batteries in the system
■
Integrated Ethernet (available on models with Ethernet capability)
1.4.6 Mass Storage Options
A 4-GB hard drive is available as options for the 4210T. The 3-GB hard drive supports
both the 4100 and 4200 Family models. Only a single diskette drive may be used at any
one time with the computer. This drive may be used in the DualBay or externally with
an optional parallel cable.
Product Description 1-7
Page 16

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4.7 AC Adapter
The AC adapter supplies DC voltage to the system converter to operate and/or charge
the installed battery pack(s). The adapter provides sufficient power to charge each main
battery pack in 1.5 hours or less with the system off, or in 2.5 hours or less with the
system on. The AC adapter power specifications are presented in Chapter 6.
1.4.8 Automobile Adapter
The automobile adapter is used to charge the computer while traveling in an
automobile. The Automobile Adapter power specifications are presented in Chapter 6.
1.4.9 Lithium Ion Battery Pack
Lithium Ion (Li-ion) battery packs offer superior performance over nickel metal
hydride batteries. NiMH batteries are not recommended. Li-ion batteries weigh
approximately half as much as the NiMH battery packs and are compatible with the
External Battery Charger and its charging options. They are available in both battery
handle and modular bay forms.
1.4.10 External Battery Charger
The External Battery charger has the following features:
■
Two battery charge slots
■
Accepts Li-ion handle and modular batteries
■
Fast charges one battery in 1.5 hours
■
Fast charges two batteries in 3 hours
1.4.11 External Keyboards
The following external full-size keyboards are supported:
■
Enhanced III keyboard
■
SpaceSaver keyboard
■
Alternative design keyboard
1.4.12 External Monitors
The following external monitors are supported:
■
QVision 172 Color Monitor
■
151 FS Color Monitor
■
171 FS Color Monitor
■
V50 Color
■
V70 Color
1-8 Product Description
Page 17

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
■
P50 Color
■
P70 Color
■
P110 Color
■
P1610 Color
■
TFT500 Flat Panel
1.4.13 Compaq Mouse
The computer supports a PS/2 mouse or other external pointing device.
1.4.14 Trackball Pointing Device
The modular trackball provides an effective alternate to the touchpad or an external
mouse when the machine is used in either a portable or desktop environment.
Product Description 1-9
Page 18
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5 External Computer Components
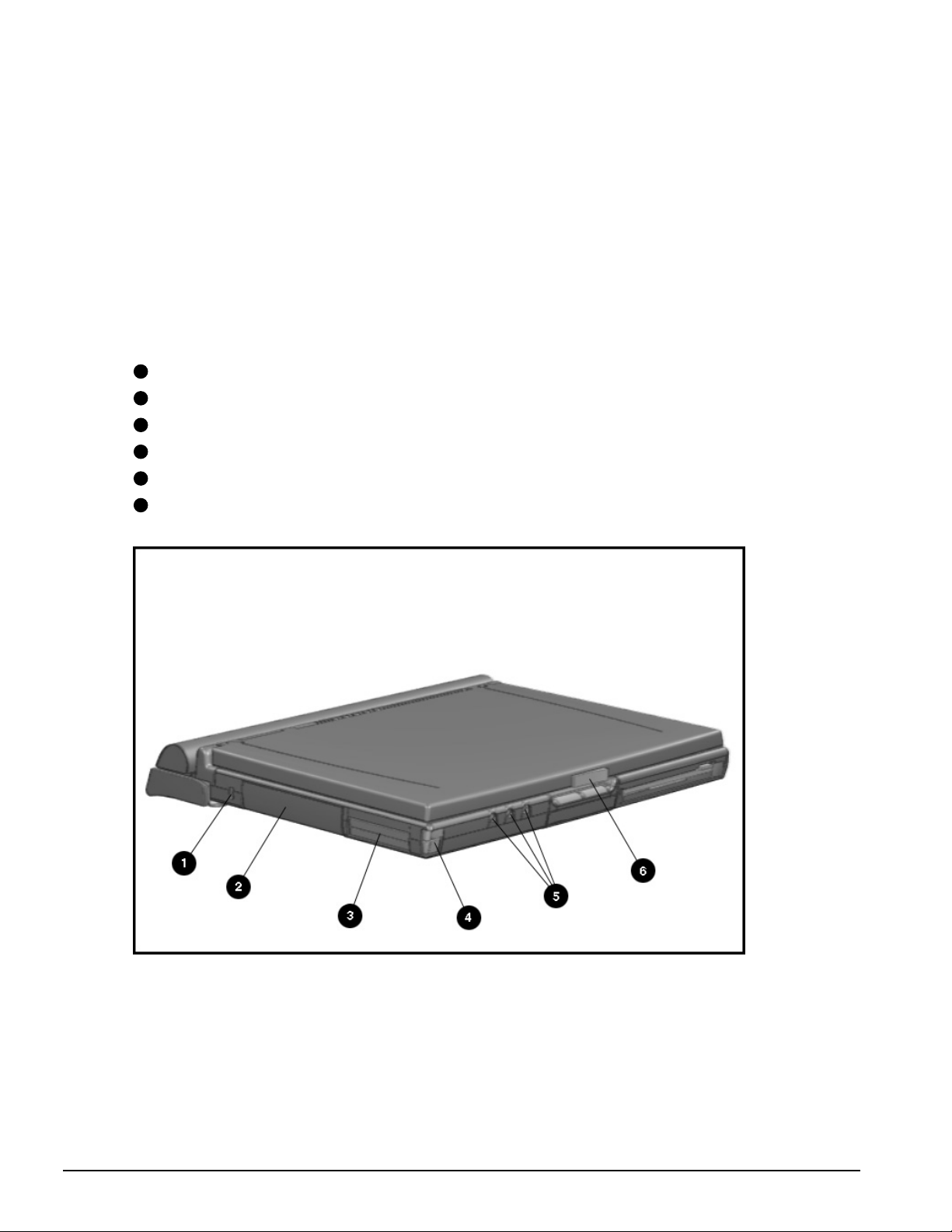
The external computer components are illustrated and described in this section.
1.5.1 Front and Left Side Components
The front and left side external components are shown in the following figure and
identified in this section:
1
Cable lock provision
2
Hard drive compartment
3
PC Card slots
4
PC Card eject buttons
5
Audio connectors
6
Display latch
Figure 1-2
1-10 Product Description
. Front and Left Side Components
Page 19
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
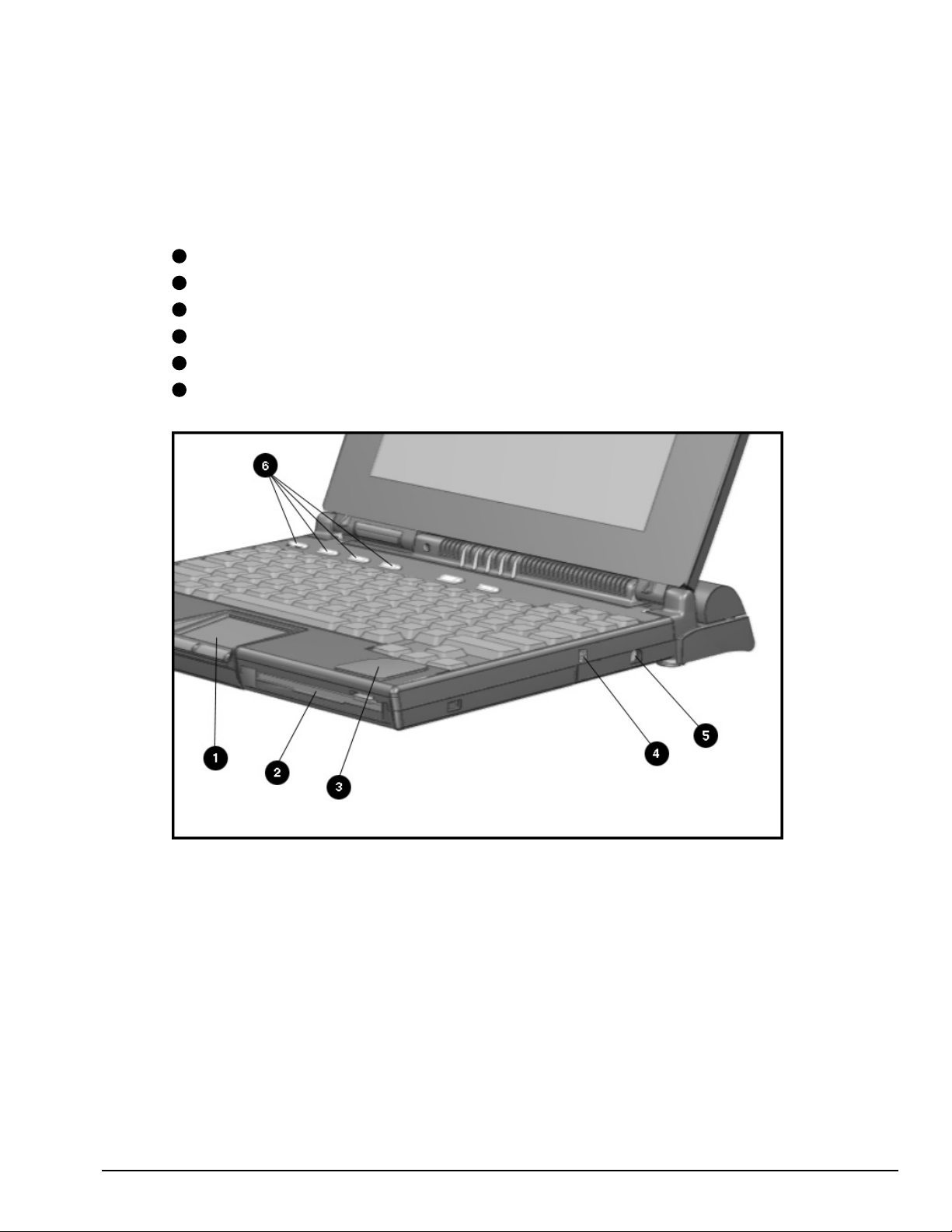
1.5.2 Front and Right Side Components
The front and right side computer components are shown and identified in this section.
1
Pointing device
2
DualBay module
3
Speaker
4
DualBay eject button
5
AC power connector
6
User programmable keys
Figure 1-3.
Front and Right Side Components
Product Description 1-11
Page 20
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
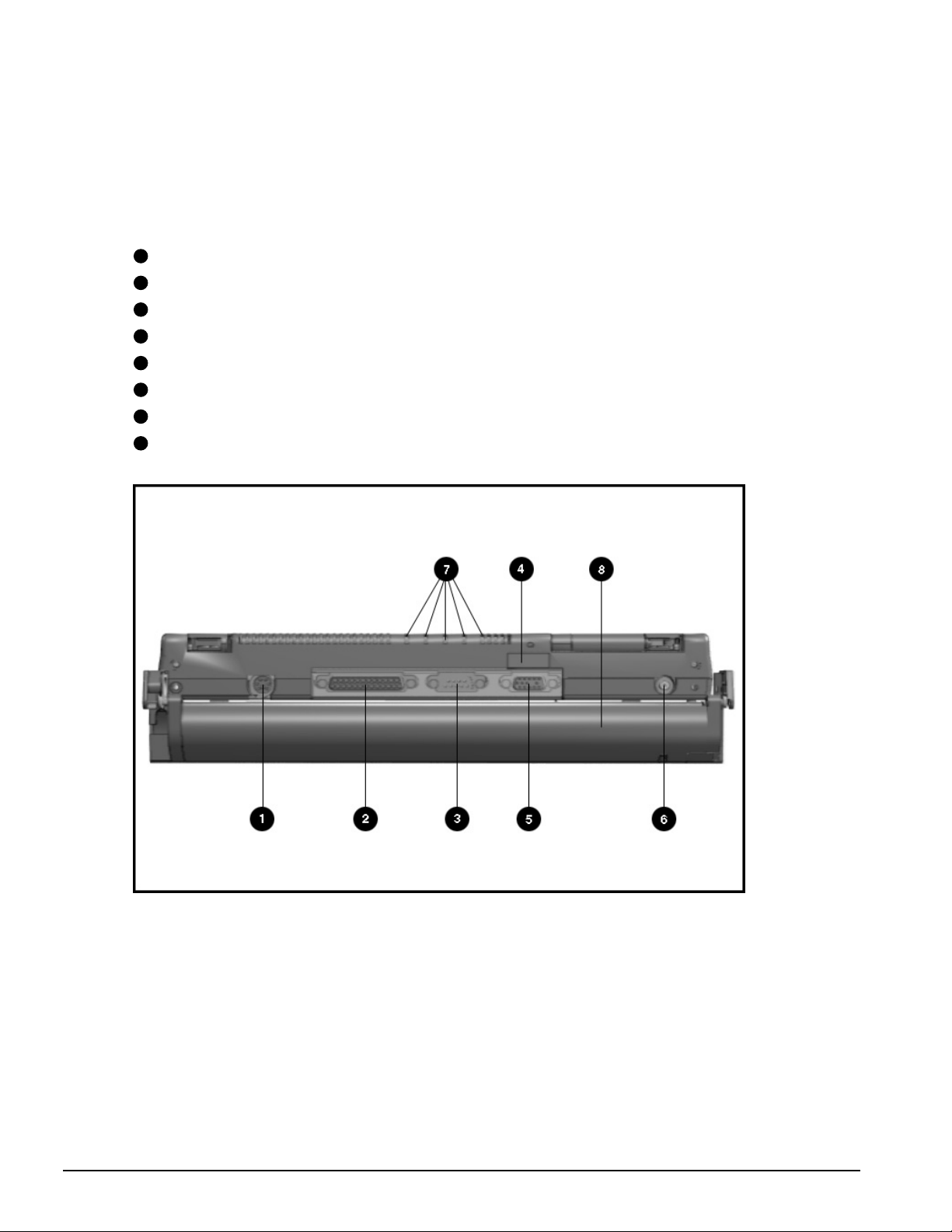
1.5.3 Rear Components
The front and right side computer components are shown and identified in this section.
1
Keyboard/mouse connector
2
Parallel connector
3
Serial connector
4
Infrared lens (IrDA compliant)
5
External monitor connector
6
NTSC/PAL video
7
Status panel indicator lights
8
Handle
Figure 1-4
1-12 Product Description
. Rear Components
Page 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
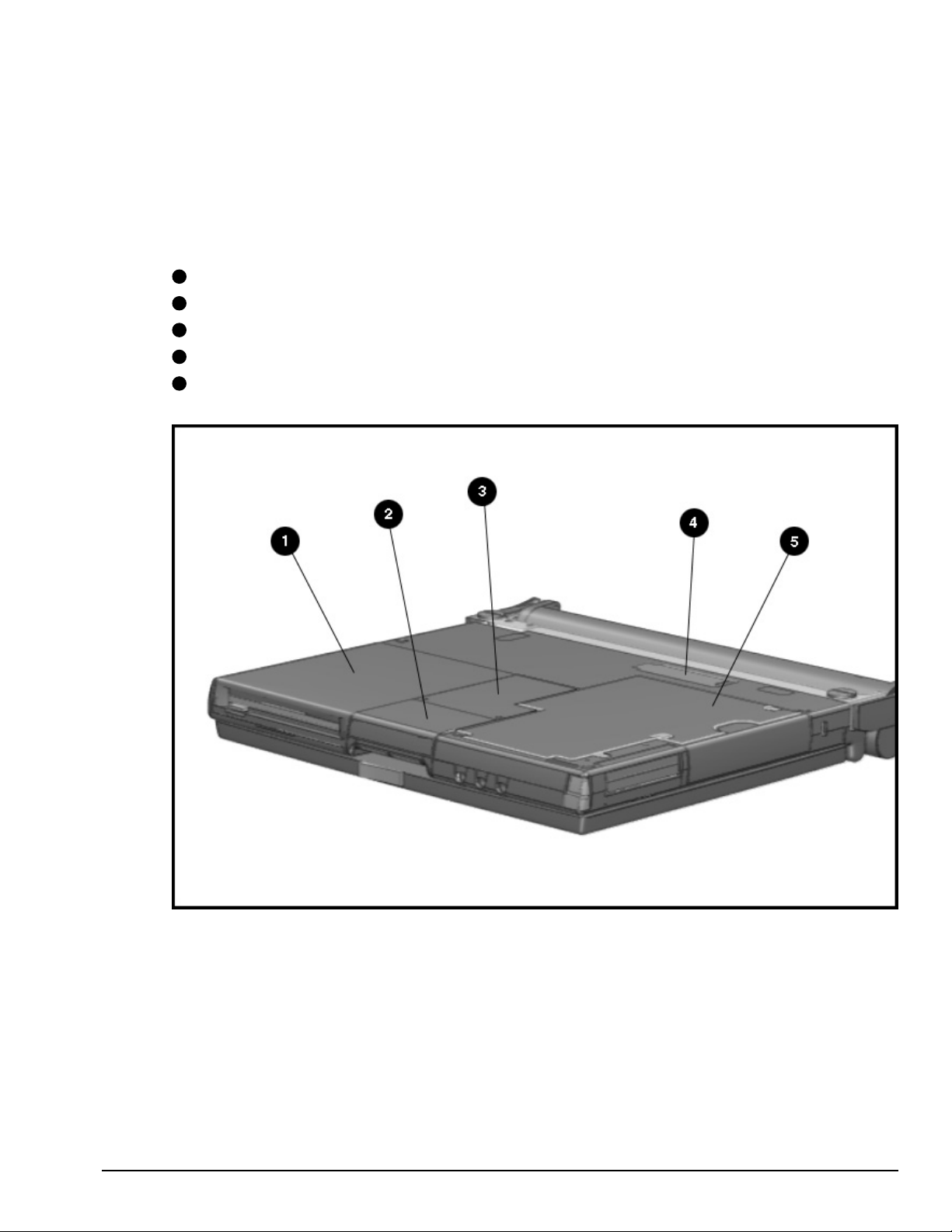
1.5.4 Bottom Components
The bottom external components are shown in the following figure and are identified in
this section:
1
DualBay
2
Pointing device
3
Memory compartment
4
Expansion slot
5
Hard drive compartment
Figure 1-5
. Bottom Components
Product Description 1-13
Page 22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
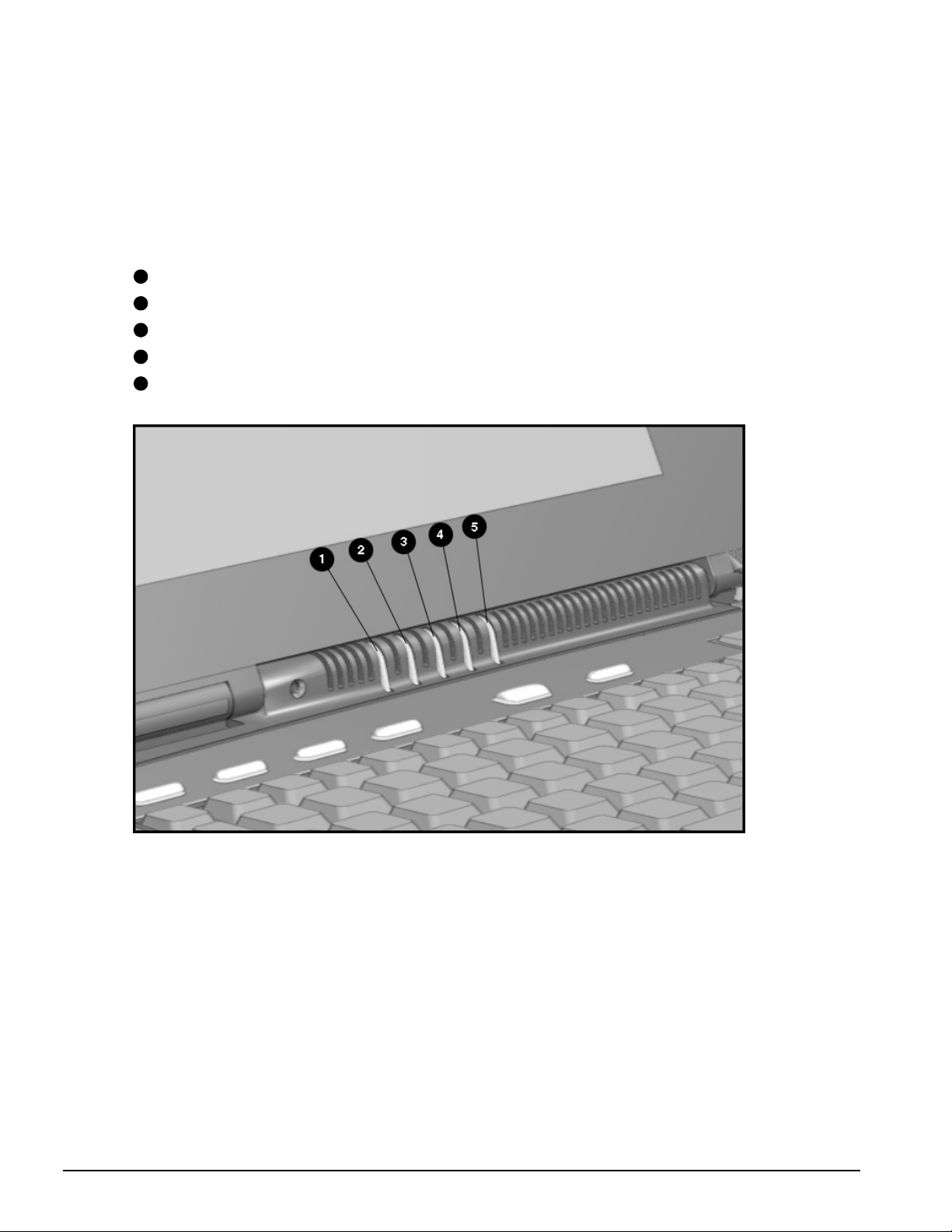
1.5.5 Status Panel Lights
The status panel lights are shown in the following figure and are identified in this
section:
1
Power/Suspend
2
Battery charge
3
Caps Lock
4
Scroll Lock
5
Num Lock
Figure 1-6.
1-14 Product Description
Status Panel Lights
Page 23
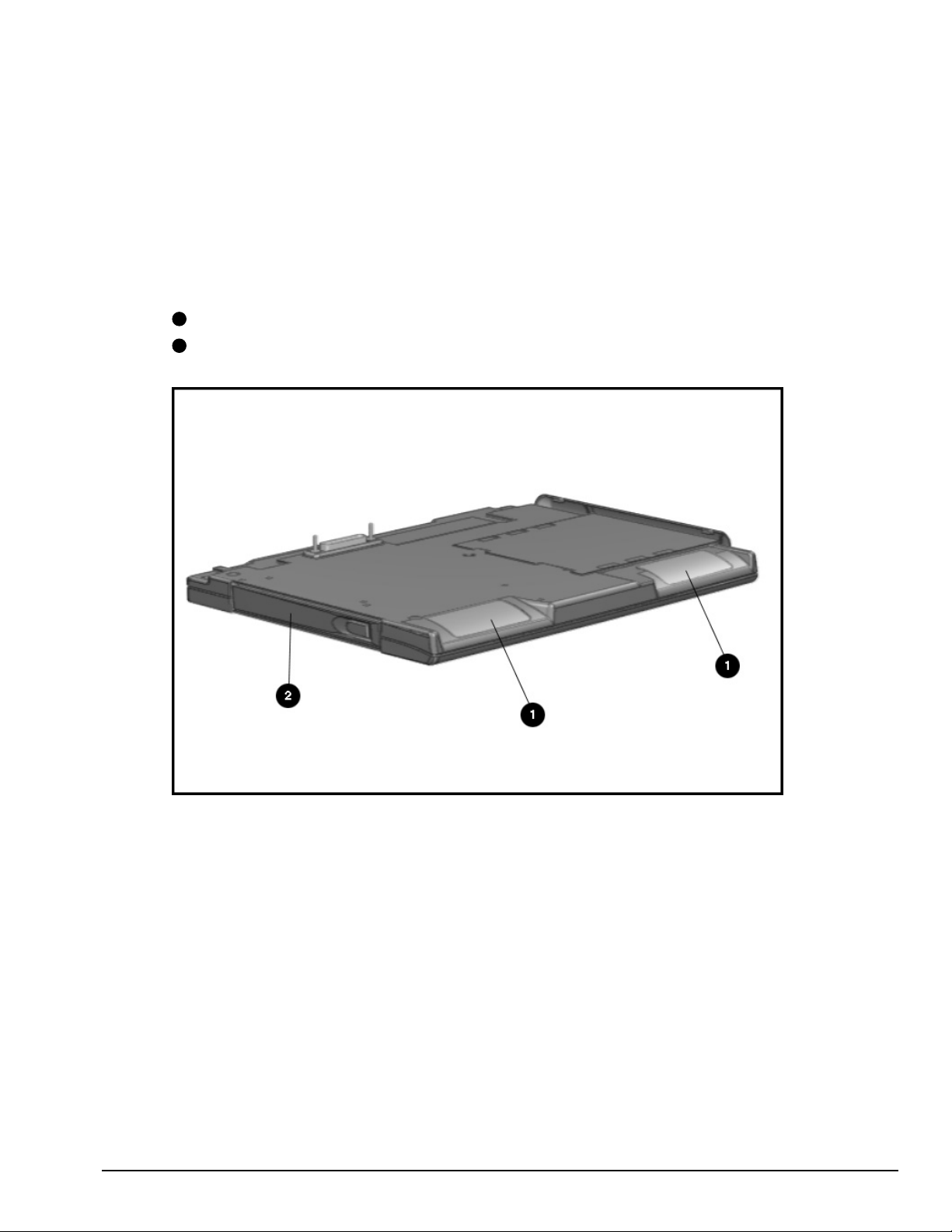
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.6 Mobile CD Expansion
Unit Components
The front and left components of the Mobile CD Expansion Unit are shown in the
following figure and are identified in this section:
1
Stereo speakers
2
CD-ROM drive
Figure 1-7
. Left and Front Components
Product Description 1-15
Page 24
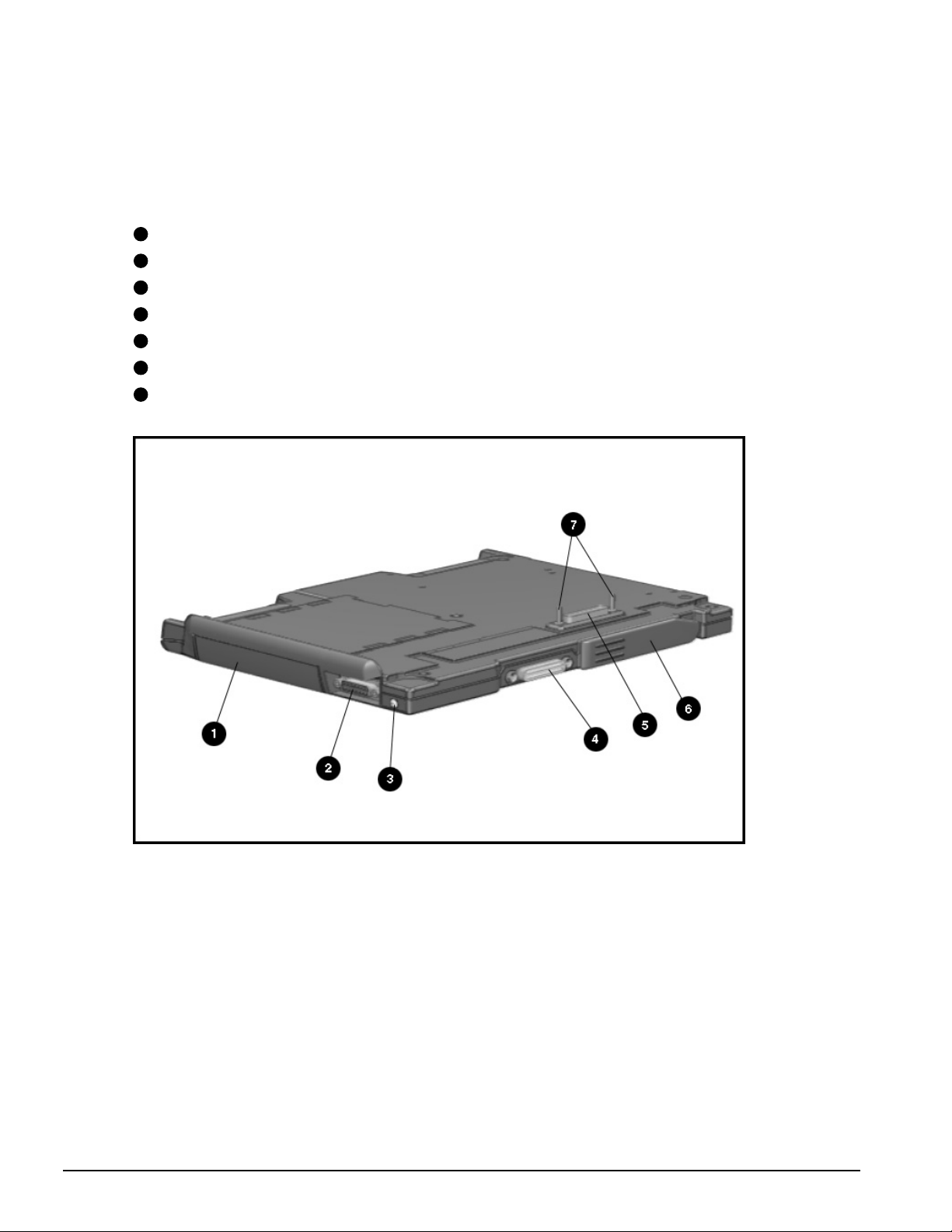
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The right and rear components are shown in the following figure and are identified in
this section:
1
Battery bay
2
MIDI/game device
3
AC adapter connector
4
Convenience Base expansion connector
5
Computer expansion connector
6
Unlocking lever
7
Expansion posts
Figure 1-8
1-16 Product Description
. Right and Rear Components
Page 25
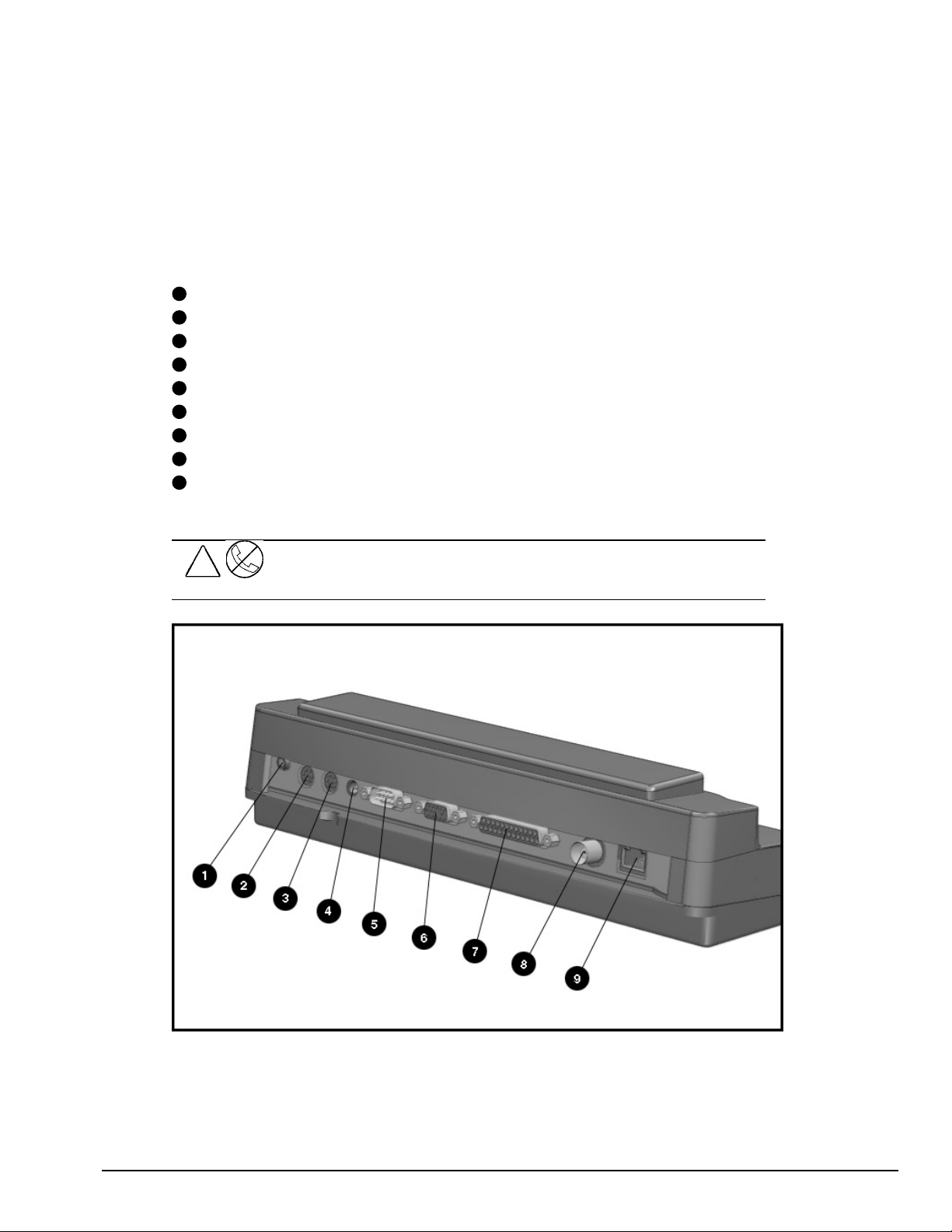
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.7 Convenience Base Connectors
The convenience base connectors are shown in the following figure and are identified
in this section:
1
Stereo speaker connector
2
External keyboard
3
Mouse
4
AC power
5
Serial port
6
Monitor
7
Parallel port
8
BNC (thin coaxial cable) connector*
9
RJ-45 connector*
* These connectors are available on the convenience base with Ethernet capability.
!
WARNING:
equipment, do not plug telecommunications/telephone connectors into the
Network Interface Card (NIC) receptacles.
To reduce the risk of electrical shock, fire or damage to the
Figure 1-9.
Convenience Base Components
Product Description 1-17
Page 26

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.8 Design Overview - Computer
This section presents a design overview of the 4100 and 4200 Families. The overview
is limited to field replaceable parts. All replacement parts are listed in Chapter 3.
Removal and replacement procedures are presented in Chapter 5.
The computer is a traditional clamshell design with a display unit attached to a system
unit. The computer opens to reveal a backlighted LCD display and a full-sized
keyboard. The display is designed for a continuously adjustable tilt angle. The system
unit houses the keyboard, I/O ports, operator controls and indicators, and DualBay
devices.
1.8.1 System Unit
The system unit contains the following field-replaceable parts:
■
System board
■
Processor board
■
Display assembly
■
CPU/keyboard cover
■
Internal microphone
■
Optional memory expansion boards
■
Lithium Real Time clock battery
■
Hard drive
■
Diskette drive
■
Handle
■
Pointing device
■
CPU base cover
■
PCMCIA assembly
1.8.2 System Board
The Compaq Armada system electronics are integrated on two printed circuit
assemblies; the system board and the processor board. The 4100 system boards are not
compatible with the 4200 Family system boards. Similarly, the 4200 system boards are
not compatible with the 4100 Family.
1-18 Product Description
Page 27

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.8.3 Processor Board
Prior to the 4150 model, there are two processor board PCAs with either 8-MB or 16-MB of
memory and with a level-2 cache populating the models with 100-, 120- and 133-MHz
processors. The MMX processor on the 4150 , 4150T, and 4160T are P55CLM processors
operating at 150 or 166 MHz. These processors are not compatible with 4131T, 4130T,
4120T, 4120, 4110, and 4100 models.
In each of the 4100 and 4200 systems there are two processor board PCAs with a level2 cache. The processor board contains the CPU, the OPTi 82C557 system Controller,
the OPTi 82C556 data buffer controller, and, if populated on the PCB, cache data
RAM. Also mounted on the processor board is an electronic temperature sensor that
2
interfaces to the system through the I
The 4210T and 4220T processor boards include the 233- and 266-MHz MMX
processors and the MTXC controller, part of the Intel 430TX mobile chipset. The 4200
Family processor boards also include the electronic sensor that interfaces to the system
2
through the I
C bus.
C bus.
1.8.4 Processor
The P54LM and the P55CLM Intel Pentium processors are fully compatible with the entire
installed base of applications for DOS, Windows, and OS/2, branch predition, and separate
code and data caches all provide increased performance over previous x86 processors.
Reduced voltage operation and enhanced SL power management features provide significant
power savings over other Pentium versions.
For the 4200 Family, the 233 MHz CPU core runs on a 1.8 V supply. The 266 MHz CPU core
runs on a 2.0 V supply. The interface for the 4200 Family is 2.5 V to 3.3 V.
For the 4100 Family, the CPU core runs on a 2.9V supply for lower power operation, while
the I/O buffers are powered at 3.3V for compatibility with the rest of the system.
1.8.5 System Memory
See Tables 1-1 and 1-2 for the system memory contained on models for the 4100 and
4200 Families. Up to 96-MB of expansion memory is available. Base memory is
onboard memory built into the system I/O board. Expansion memory consists of
memory expansion board kits available as user installable options.
1.8.6 Cache
The 4200 Family models have 256-KB or 512-KB of cache data RAM and 64-KB of
cache tag RAM if populated on the PCB are mounted on the processor module.
The 4110-4160T models have 256-KB of cache data RAM and 32-KB of cache tag
RAM if populated on the PCB are mounted on the processor module.
Product Description 1-19
Page 28

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.8.7 Local Bus Video
The standard Compaq Armada video subsystem consists of:
■
An internal LCD display.
■
One Megabyte frame buffer (Two Megabyte frame buffer for the 42210T and
4220T)
■
An inverter to supply AC power to the LCD back-light system
■
A standard external VGA connector for use with CRTs and other VGA compatible
displays
■
32-KB of video ROM (44KB of video ROM for the 4210T aand 4220T)
■
NTSC/PAL encoder
1-20 Product Description
Page 29
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 2
Troubleshooting
This chapter contains troubleshooting information for the computer and the
convenience base. The basic steps in troubleshooting the computer include:
1. Completing the preliminary steps listed in Section 2.1.
2. Running the Power-On Self-Test (POST) as described in Section 2.2.
2. Running Computer Setup as described in Section 2.5
4. Running the Computer Checkup (TEST) as described in Section 2.5.
5. Performing the recommended actions described in the diagnostic tables in Section
2.6 if you are unable to exercise POST or Computer Checkup or if the problem
persists after running POST and Computer Checkup.
Follow these guidelines when troubleshooting:
■
Complete the recommended actions in the order in which they are given.
■
Repeat POST and Computer Checkup after each recommended action until the
problem is resolved and the error message does not return.
■
Once the problem is resolved, do not complete the remaining recommended actions.
■
Refer to Chapter 5 for any removal and replacement procedures.
■
If the problem is intermittent, check the computer or convenience base several times
to verify that the problem is solved.
Use the following table for quick reference to troubleshooting information:
If You Want To: Run:
Check for POST error messages POST
Check that computer components are recognized and
running properly
View information about the computer and installed or
connected devices
Perform any of the following:
Check the system configuration
Set the system power management
parameters
Return the system to its original
configuration
Check system configuration of installed devices
Computer Checkup (TEST) under Compaq
Utilities
View System Information
(INSPECT)under Compaq Utilities
Computer Setup
Troubleshooting 2-1
Page 30

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 Preliminary Steps
IMPORTANT: Use AC Power when running POST, Computer Setup, or Computer
Checkup. A low-battery condition could initiate Suspend or Hibernation and interrupt
the test.
Before running POST and Computer Checkup, complete the following steps:
1. Obtain established passwords. If you must clear the passwords, go to Section 2.2.
2. Ensure that the hard drive is installed in the computer.
2. Ensure that the battery pack is installed in the computer and the AC power is
connected to the computer and plugged into an AC power source.
4. Turn on the computer.
5. If a power-on password has been established, type the password and press Enter.
NOTE:
that QuickLock/QuickBlank has been initiated. Type the power-on password to
exit QuickLock/QuickBlank. If the password is unknown, it must be cleared (see
Section 2.2).
6. Run Computer Setup (Section 2.5).
7. Use the Hotkeys to adjust the contrast (Fn+F9) and brightness (Fn+F10) to the center
8. Turn off the computer and all external devices.
9. Disconnect any external devices that you do not want to test. If you want to use the
NOTE:
the problem could be with the external device or its cable. Isolate the problem by
running POST with and without the external device connected.
10. Use Advanced Diagnostics and loopback plugs in the serial and parallel connectors
If you are running Diagnostics from the hard drive, complete the following steps:
The key icon appears on the display when the computer is turned on to indicate
of their ranges and leave the display open. On models with color TFT displays,
contrast is not applicable.
printer to log error messages, leave it connected to the computer.
If a problem only occurs when an external device is connected to the computer,
if you plan to test these ports. You may run Advanced Diagnostics from the hard
drive or from a diskette.
a. Turn on or restart the computer.
b. Press F10 when the cursor appears in the upper right corner of the screen. If you
do not press F10 in time, restart the computer and try again. The Welcome screen
appears.
2-2 Troubleshooting
Page 31

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
If you are running Diagnostics from a diskette, complete the following steps:
a. Insert the Diagnostics diskette into the diskette drive and turn on the computer.
b. At the Welcome Screen, press Enter to accept OK.
c. Select Computer Checkup (TEST).
d. Select Prompted Diagnostics after "Identifying System Hardware" completes.
e. Select Interactive Testing and follow the displayed instructions.
Refer to Chapter 3 for the description and spare part number of the loopback plugs.
After completing the preliminary steps, run POST (Section 2.3) and Computer Checkup
(Section 2.5).
2.2 Clearing the Power-On and Setup Passwords
The power-on password prevents use of the computer until the password is entered. The
setup password prevents unauthorized changes to Computer Setup. To clear the
passwords, you must remove all power from the system board. If you do not know the
passwords, use the following procedure to clear the password:
1. Remove all battery packs from the battery bay and DualBay, if applicable.
2. Disconnect the AC power.
2. Remove the real time clock battery.
4. Wait five minutes.
5. Reconnect the AC power.
6. Restart the computer. During the Power-On Self Test (POST), a "162 System
Options not Set" message appears. (See Section 2.4 for additional POST error
messages).
7. Shut down the computer, then turn off the power again.
8. Replace the real time clock battery.
9. Install the battery pack(s).
10. Proceed with the troubleshooting procedures.
Troubleshooting
2-3
Page 32

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Power-On Self Test (POST)
The Power-On Self-Test (POST) is a series of tests that run every time the computer is turned on. POST
verifies that the system is configured and functioning properly
To run POST, complete the following steps:
1. Complete the preliminary steps. (Section 2.1).
2. Turn on the computer.
If POST does not detect any errors, the computer beeps once or twice to indicate that
POST has run successfully and boots from the hard drive or from a bootable diskette if
one is installed in the diskette drive.
2.4 POST Error Messages
This section contains typical error messages that may occur during the power-on selftest (POST).
If you receive an error message read the description and follow the recommended
action or run Computer Checkup from the Diagnostics diskette. Information about
running Computer Checkup is presented later in this chapter.
If POST detects an error, one of the following events occurs:
■
A message with the prefix "WARNING" appears informing you where the error
occurred. The system pauses until you press F1 to continue.
■
A message with the prefix "FATAL" appears informing you where the error
occurred. After the message, the system emits a series of audible beeps. The system
then stops.
■
The system emits a series of audible beeps. The system then stops.
Warning messages indicate a potential problem exists such as a system configuration
error. When F1 is pressed, the system should resume. You should be able to correct
problems that produce WARNING messages.
IMPORTANT: When a WARNING message includes the prompt to "RUN SCU," run
Computer Setup. (Computer Setup replaces the SCU utility.)
Fatal errors emit a beep and may display a FATAL message. Fatal errors indicate
severe problems, such as a hardware failure. Fatal errors do not allow the system to
resume. Some of the fatal error beep codes are listed at the end of this section.
2-4 Troubleshooting
Page 33

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-1
Warning Messages
Message Description
Clock not ticking correctly The real-time clock is not ticking. Replace the real time clock
CMOS checksum invalid, run SCU CMOS RAM information has been corrupted and needs to be
reinitialized by running Computer Setup.
CMOS failure, run SCU CMOS RAM has lost power and needs to be reinitialized by running
Computer Setup.
Floppy controller failed The diskette drive controller failed to respond to the reset
command. Power - down the system and check all appropriate
connections. If the diskette drive controller continues to fail, you
may need to replace the system board.
Floppy disk track 0 failed The diskette drive cannot read track 0 of the diskette in the drive.
Try another diskette. If the problem persists, you may need to
replace the diskette drive.
Floppy information invalid, run SCU The drive parameters stored in CMOS RAM do not match the
diskette drives detected in the system. Run Computer Setup.
Hard disk controller error The hard drive controller failed to respond to the reset command.
Check the drive parameters. Power down the system and check all
appropriate connections.
Hardware info does not match video
card, run SCU
Keyboard controller failure The keyboard failed the self-test command. Replace the keyboard.
Keyboard failure The keyboard failed to respond to the RESET ID command.
No interrupts from Timer 0 The periodic timer interrupt is not occurring. Press F1.
RAM parity error at location xxxx A RAM parity error occurred at the specified (hex) location.
ROM at xxxx (LENGTH yyyy) with
nonzero checksum (zz)
Time/Date corrupt - run SCU The time and date stored in the real time clock have been
Unexpected amount of memory,
run SCU
Hard disk xx failure (or error) A failure or an error occurred when trying to access the hard drive.
The video adapter type specified in CMOS RAM does not match the
installed hardware. Run Computer Setup.
Press F1.
Press F1.
An illegal adapter ROM was located at the specified address. An
external adapter (such as a video card) may be causing the conflict.
Run Computer Setup.
corrupted, possibly by a power loss. Run Computer Setup.
The amount of memory detected by POST does not match the
amount specified in CMOS RAM. Run Computer Setup.
Press F1 and continue.
Troubleshooting
2-5
Page 34

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-2
Fatal Error Messages
Message Description Beep Code
CMOS RAM test failed A walking bit test of CMOS RAM location 0E (Hex) -
3F (Hex) failed.
DMA controller faulty A sequential read/write of the transfer count and
transfer address registers within the primary and
secondary DMA controllers failed.
Faulty DMA page registers A walking bit read/write of the 16 DMA controller
page registers starting at location 80 Hex failed.
Faulty refresh circuits A continuous read/write test of port 61h found that
bit 4 (Refresh Detect) failed to toggle within an
allotted amount of time.
Interrupt controller failed A sequential read/write of various Interrupt
Controller registers failed.
ROM checksum incorrect A checksum of the ROM BIOS does not match the
byte value at F000:FFFF.
RAM error at location xxxx RAM error occurred during memory test. None
Parity error at unknown location Parity error occurred. None
3
4
0
1
5
2
The following table lists some of the Fatal Error beep codes, along with the beep
sequence (short, long, pause) and the meaning of the beeps.
Table 2-3
Fatal Error Beep Codes
Beep Code Beep Sequence Explanation Remedy
0 S-S-S-P-S-S-L-P The DMA page registers are
faulty.
1 S-S-S-P-S-L-S-P The refresh circuitry is faulty. Replace system board.
2 S-S-S-P-S-L-L-P The ROM checksum is incorrect. 1. Flash the ROM.
3 S-S-S-P-L-S-S-P The CMOS RAM test failed. Replace system board.
4 S-S-S-P-L-S-L-P The DMA controller is faulty. Replace system board.
5 S-S-S-P-L-L-S-P The interrupt controller failed. Replace system board.
6 S-S-S-P-L-L-L-P The keyboard controller failed. Replace system board.
7 S-S-L-P-S-S-S-P Graphics adapter is faulty. Replace system board.
8 S-S-L-P-S-S-L-P Internal RAM is faulty. Replace processor board.
S = Short, L = Long, P = Pause
Replace system board.
2.Replace system board.
2-6 Troubleshooting
Page 35

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.5 Compaq Utilities
Run the Compaq Utilities to view or test system information and installed or connected devices. Run
Compaq Utilities from either the computer hard drive or from diskette.
If running Compaq Utilities from a diskette, note the following:
Use version 10.13c or later.
You will not be able to make a utilities diskette.
Use the Computer Setup diskette to run Computer Setup.
The Utilities menu includes the following:
Computer Setup
Computer Checkup (TEST)
View System Information (INSPECT)
Create Diagnostics diskette (hard drive only)
Manage Diagnostics Partition (diskette only)
If the problem persists, call for support. Follow these steps to prepare for the support call:
1. Run Computer Checkup and save the device list to a file and print or save the log of errors.
2. Run the View System Information (INSPECT) utility and print or save that information.
2. Have the files or the printed information available when calling for support.
2.5.1 Running Computer Setup
Computer Setup contains a group of utilities that give you an overall picture of the
computer’s hardware configuration and aid in troubleshooting. Use these utilities to set
custom features, such as security options, power conservation levels, and startup
preferences.
A computer running Windows 95 automatically recognizes and configures the system
for new devices. However, if there is a configuration problem, or you want to view or
reset configuration settings, use Computer Setup.
Computer Setup provides two methods to view the computer’s configuration - by type
or connection. The default method for viewing Computer Setup is by type.
Troubleshooting
2-7
Page 36

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Categories by type include:
System Features—security, power, boot management
Communication—ports, modem, other communication devices
Storage—storage-related devices such as hard drive or diskette
Input Devices—keyboard, mouse, and other input devices
Network—Network adapter, or other network-related devices (Available only when
docked or when PC Card is installed
Audio—sound properties and audio device settings
Video—monitor video device resources
Other devices—devices that could not be categorized
Categories by connection include:
System Features—security, power, boot management
System Devices—keyboard, mouse, parallel and serial ports
ISA—ISA bus and related devices
PCI—PCI bus and connected devices
PC Card (PCMCIA) —PC Card bus and PC Card devices
2.5.2 Running Computer Checkup (TEST)
Computer Checkup (TEST) determines whether the various computer components and
devices are recognized by the system and are functioning properly. You can display,
print, or save the information generated by Computer Checkup.
Computer Checkup is installed on the hard drive. If the hard drive is nonfunctional, you
can run it from a diskette.
NOTE:
keep them available for future needs. A current copy can be obtained from the Compaq
Customer Support Center.
It is recommended that you make diskette copies of Computer Checkup and
2-8 Troubleshooting
Page 37

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Computer Checkup
To run Computer Checkup from the hard drive, complete the following steps:
1. Close all applications and shut down the computer.
2. Turn off the computer.
2. Turn on the computer.
4. When the cursor moves to the right side of the screen, press F10.
A Welcome Screen is displayed that is followed by the Compaq Utilities main menu.
5. From the Compaq Utilities main menu, select Computer Checkup (TEST).
A diagnostics menu is displayed.
6. Select the option to view the device list.
A list of the installed hardware devices is displayed.
NOTE:
Computer Checkup does not detect all non-Compaq devices.
7. Verify that Computer Checkup correctly detected the installed devices.
If the list is correct, select OK. The Computer Checkup option menu is displayed
again.
If the list is incorrect, verify that the new devices are installed properly.
8. Select one of the following from the diagnostics menu:
■
Quick Check Diagnostics. Runs a quick, general test on each device with a
minimal number of prompts. If errors occur, they display when the testing is
complete. You cannot print or save the error messages.
■
Automatic Diagnostics. Runs an unattended, maximum testing of each device
with minimal prompts. You can choose how many times to run the tests, to stop
on errors, or to print or save a log of errors.
■
Prompted Diagnostics. Allows maximum control over testing the devices. You
can choose attended or unattended testing, decide to stop on errors, or choose to
print or save a log of errors.
9. Follow the instructions on the screen as the devices are tested. When testing is
complete, the Diagnostics menu appears.
10. Exit the Diagnostics menu.
NOTE:
changes.
Exiting the Compaq Utilities menu restarts the computer and saves the
Troubleshooting
2-9
Page 38

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11. Look up the Computer Checkup error codes that were displayed by referring to
"Computer Checkup (TEST) Error Codes" and take the recommended action.
12. Rerun POST and Computer Checkup, taking the recommended actions in given
order until the problem is solved and no error messages occur.
Computer Checkup (TEST) Error Codes
IMPORTANT:
Rerun Computer Checkup each time you complete a recommended action
step. If the problem is resolved when POST and Computer Checkup are rerun (i.e., with
no error codes) do not perform the remaining recommended action steps.
Computer Checkup (TEST) error codes occur if the system recognizes a problem while
running Computer Checkup. These error codes help identify possible defective
assemblies. Tables 2-4 through 2-14 list Computer Checkup error codes, a description
of the error condition, and the recommended action for resolving the condition. For
removal and replacement procedures for the computer, refer to Chapter 7. For removal
and replacement procedures for the convenience base, refer to Chapter 8.
NOTE:
The error codes in the following tables are listed in an AYE-XX format, where:
A or AA = Number that represents the faulty assembly.
Y = Test or action that failed.
XX = Specific problem.
2.5.3 View System Information (INSPECT)
The View System Information (INSPECT) utility provides information about the
computer and installed or connected devices. You can display, print, or save the
information.
Follow these steps to run INSPECT from the hard drive:
1. Turn on the external devices that you want to test. Connect the printer if you want to
print the information.
2. Turn on or restart the computer.
2. Press F10 when the prompt appears in the right side of the display. The Compaq
Utilities screen appears.
4. Select View System Information (INSPECT) from the Diagnostics menu.
5. Select the item you want to view from the following list:
System Memory
ROM Audio
Keyboard Operating system
System ports System files
System storage Windows files
Graphics Miscellaneous
2-10 Troubleshooting
Page 39

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6. Follow the instructions on the screen to cycle through the screens, to return to the list
and choose another item, or to print the information.
2.6 Diagnostic Error Codes
Diagnostic error codes occur if the system recognizes a problem while running the
Compaq Diagnostic program. These error codes help identify possibly defective
subassemblies.
Tables 2-4 through 2-14 list possible error codes, a description of the error condition,
and the action required to resolve the error condition.
IMPORTANT:
Retest the system after completing each step. If the problem has been
resolved, do not proceed with the remaining steps.
For assistance in the removal and replacement of a particular subassembly, see
Chapter 5, "Removal and Replacement Procedures."
Table 2-4
Processor Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
101-xx CPU test failed Replace the processor board and retest.
102-xx Coprocessor or Weitek Error
102-xx DMA page registers test failed Replace the system board and retest.
104-xx Interrupt controller master test failed
105-xx Port 61 error
106-xx Keyboard controller self-test failed
107-xx CMOS RAM test failed
108-xx CMOS interrupt test failed
109-xx CMOS clock test failed
110-xx Programmable timer load data test failed
112-xx Protected mode test failed
114-01 Speaker test failed
1. Check system configuration.
2.Verify cable connections to speaker.
2. Replace the system board and retest.
Troubleshooting
2-11
Page 40

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-5
Memory Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
200-xx Memory machine ID test failed The following steps apply to error codes 200-xx and
202-xx:
202-xx Memory system ROM checksum failed
202-xx Write/Read test failed The following steps apply to error codes 202-xx
204-xx Address test failed 1.Remove the memory board and retest.
211-xx Random pattern test failed 2 Install a new memory board and retest.
214-xx Noise test failed
215-xx Random address test failed
Keyboard Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
300-xx Failed ID Test The following steps apply to error codes 300-xx
301-xx Failed Selftest/Interface Test 1.Check the keyboard connection. If disconnected,
302-xx Failed Individual Key Test 2. Replace the keyboard and retest.
304-xx Failed Keyboard Repeat Test 2. Replace the system board and retest.
1.Flash the system ROM and retest.
2.Replace the system board and retest.
through 215-xx:
Table 2-6
through 304-xx :
turn off the computer and connect the keyboard.
Table 2-7
Parallel Printer Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
401-xx Printer failed or not connected The following steps apply to error codes 401-xx
through 402-xx :
402-xx Failed Port Test 1. Connect the printer.
402-xx Printer pattern test failed 2. Check power to the printer.
2. Install the loop-back connector and retest.
4. Check port and IRQ configuration.
5. Replace the system board and retest.
2-12 Troubleshooting
Page 41

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-8
Diskette Drive Test
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
600-xx Diskette ID drive types test
failed
601-xx Diskette format failed 1. Replace the diskette media and retest.
602-xx Diskette read test failed 2.Check and/or replace the diskette power and signal
602-xx Diskette write, read, compare test failed 2.Replace the diskette drive and retest.
604-xx Diskette random read test failed 4.Replace the system board and retest.
605-xx Diskette ID media failed
606-xx Diskette speed test failed
609-xx Diskette reset controller test failed
610-xx Diskette change line test failed
697-xx Diskette type error
698-xx Diskette drive speed not within limits
699-xx Diskette drive/media ID error Run Computer Setup.
Serial Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
1101-xx Serial port test failed
Hard Drive Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
1701-xx Hard drive format test failed The following steps apply to error codes 1701-xx
1702-xx Hard drive read test failed 1.Run Computer Setup.
1702-xx Hard drive write/read/compare test
failed
1704-xx Hard drive random seek test failed 2.Replace the system board and retest.
1705-xx Hard drive controller test failed
1706-xx Hard drive ready test failed
1707-xx Hard drive recalibration test failed
1708-xx Hard drive format bad track test failed
1709-xx Hard drive reset controller test failed
1710-xx Hard drive park head test failed
1715-xx Hard drive head select test failed
1716-xx Hard drive conditional format test failed
1717-xx Hard drive ECC* test failed
1719-xx Hard drive power mode test failed
1724-xx Network preparation test failed
1736-xx Drive monitoring test failed
* ECC = Error Correction Code
The following steps apply to error codes 600-xx
through 698-xx:
cables and retest.
Table 2-9
1. Check port configuration.
2.Replace the system board and retest.
Table 2-10
through 1736-xx :
2. Replace the hard drive and retest.
Troubleshooting
2-13
Page 42

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-11
Video Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
501-xx Video controller test failed
502-xx Video memory test failed
502-xx Video attribute test failed
504-xx Video character set test failed
505-xx Video 80 × 25 mode 9 × 14 character
cell test failed
506-xx Video 80 × 25 mode 8 × 8 character
cell test failed
507-xx Video 40 × 25 mode test failed
508-xx Video 320 × 200 mode color set 0 test
failed
509-xx Video 320 × 200 mode color set 1 test
failed
510-xx Video 640 × 200 mode test failed
511-xx Video screen memory page test failed
512-xx Video gray scale test failed
514-xx Video white screen test failed
516-xx Video noise pattern test failed
2402-xx Video memory test failed
2402-xx Video attribute test failed
2404-xx Video character set test failed
2405-xx Video 80 × 25 mode 9 × 14 character
cell test failed
2406-xx Video 80 × 25 mode 8 × 8 character
cell test failed
2408-xx
2409-xx Video 320 × 200 mode color set 1 test
failed
2410-xx Video 640 × 200 mode test failed
2411-xx Video screen memory page test failed
2412-xx Video gray scale test failed
2414-xx Video white screen test failed
2416-xx Video noise pattern test failed
2418-xx ECG/VGC memory test failed
The following apply to error codes 501-xx through
516-xx:
1. Connect and external monitor and retest.
2.Replace the LED status board and retest.
2. Replace the display and retest.
4. Replace the system board and retest.
The following steps apply to error codes 2402-xx
through 2456-xx:
1. Run Computer Setup.
2. Disconnect external monitor and test with
internal LCD display.
2.Replace the display assembly and retest.
4. Replace the system board and retest.
Continued
2-14 Troubleshooting
Page 43

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-11
Continued
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
2419-xx ECG/VGC ROM checksum test failed The following steps apply to error codes 2402-xx
through 2456-xx:
2421-xx ECG/VGC 640 × 200 graphics mode test
failed
2422-xx ECG/VGC 640 × 350 16 color set test
failed
2422-xx ECG/VGC 640 × 350 64 color set test
failed
2424-xx ECG/VGC monochrome text mode test
failed
2425-xx ECG/VGC monochrome graphics mode test
failed
2431-xx 640 × 480 graphics test failure
2432-xx 320 × 200 graphics (256 color mode) test
failure
2448-xx Advanced VGA Controller test failed
2451-xx 132-column Advanced VGA test failed
2456-xx Advanced VGA 256 Color
test failed
2458-xx Advanced VGA BitBLT test The following applies to error codes 2458-xx through
2468-xx Advanced VGA DAC test Replace the system board and retest.
2477-xx Advanced VGA data path test
2478-xx Advanced VGA BitBLT test
2480-xx Advanced VGA Linedraw test
1. Run Computer Setup.
2.Disconnect external monitor and test with internal
LCD display.
2. Replace the display assembly and retest.
4. Replace the system board and retest.
2480-xx:
Table 2-12
Audio Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
3206-xx Audio System Internal Error Replace the audio board and retest.
Troubleshooting
2-15
Page 44

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-13
Pointing Device Interface Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
8601-xx Mouse test failed The following steps apply to 8601-xx and 8602-xx:
1. Replace the top cover assembly.
8602-xx Interface test failed 2. Replace the system board and retest.
Table 2-14
CD-ROM Test Error Codes
Error
Code Description Recommended Action
3301-xx CD-ROM drive read test failed The following steps apply to error codes 3301-xx
through 3305-xx and 6600-xx through 6622-xx:
3305-xx CD-ROM drive seek test failed 1. Replace the CD and retest.
6600-xx ID test failed 2.Replace the CD-ROM drive and retest.
6605-xx Read test failed 2. Replace the system board and retest.
6608-xx Controller test failed
6622-xx Random read test failed
2-16 Troubleshooting
Page 45

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.7 Troubleshooting Without Diagnostics
This section provides information about how to identify and correct some common
hardware, memory, and software problems. It also explains several types of common
messages that may be displayed on the screen. The following pages contain
troubleshooting information on:
■
Audio
■
Battery/Battery gauge
■
Diskette/Diskette drive
■
Hard drive
■
CD-ROM drive
■
Hardware installation
■
Infrared connection
■
Keyboard (Numeric keypad)
■
Pointing device
■
Memory
■
PC Card
■
Power
■
Printer
■
Screen (LCD and CRT)
■
Software
2.7.1 Solving Minor Problems
Some minor problems and possible solutions are outlined in the following tables. If the
problem appears related to a software application, check the documentation provided
with the software.
Solving Audio Problems
Some common audio problems and solutions are listed in the following table.
Table 2-15
Solving Audio Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Computer beeps once after
you turn it on.
Computer does not beep after
the Power-On Self-Test
(POST).
This is typical; it indicates
successful completion of the
Power-On Self-Test (POST).
Speaker volume is off or has
been turned down.
Beeps have been turned off.
No action is required.
If the speaker icon is not displayed on the
display, press
Run Computer Setup and turn on beeps.
Fn+F5
to adjust the volume.
Troubleshooting
2-17
Page 46

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Battery and Battery Gauge Problems
Some common causes and solutions for battery problems are listed in the following
table. The "Solving Power Problems" section in this chapter also may be applicable.
Table 2-16
Solving Battery and Battery Gauge Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Computer won't turn on when
battery pack is inserted and
power cord is unplugged.
Computer is beeping
and battery light is blinking.
Computer battery light blinks
to indicate low- battery
condition, but computer does
not beep.
Battery light doesn't light and
battery pack won't fast
charge.
Computer turned off and
information in memory was
lost when replacing the
battery pack.
Battery is discharged. Connect the computer to an external power
source and charge the battery pack.
Replace the battery pack with a fully charged
battery pack.
Check the battery connectors on the system
board to verify they are evenly spaced and
that they are not bent or broken.
Battery charge is low. Immediately save any open file(s). Then do
any one of the following:
■
Connect the computer to an external power
source to charge the battery pack.
■
Initiate Suspend and replace the battery
pack with a fully charged battery pack.
■
Turn the computer off or initiate
Hibernation until you can find another
power source or charge the battery pack.
Low - battery beeps were
turned off.
Volume is turned off or turned
down too low.
Battery pack is already
charged.
Battery pack was exposed to
temperature extremes.
Battery pack is at end of its
life.
The battery pack was not
replaced.
Run Computer Setup to turn on the low battery warning beeps.
Fn+F5
Press
adjust the volume.
No action is necessary.
Allow time for the battery pack to return to
room temperature.
Replace battery pack.
Turn off the computer and restart.
to turn the speaker on and then
Continued
2-18 Troubleshooting
Page 47

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continued
Table 2-16
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Battery charge does not last
as long as expected.
Battery pack is warm to the
touch after charging.
Battery gauge is inaccurate. The battery pack is new or
Battery pack operating time
is far less than the
documented average
operating time.
Battery is being exposed to
high temperatures or
extremely cold temperatures.
Battery has partially selfdischarged.
Power management is
disabled.
An external device or PC Card
is draining the battery.
Normal warming has occurred
due to charging.
has not been used for a long
period.
Power management is turned
off or disabled.
An external device or PC Card
is draining the battery.
Battery pack has partially
self-discharged.
Fuel gauge is inaccurate. Use the low battery warning beeps to
Battery pack is being drained
by high power-use accessory.
Battery pack is being exposed
to high temperatures or
extremely cold temperatures.
Keep the battery pack within the
recommended temperature ranges.
Operating: 50°F to 104°F(10°C to 40°C)
Storage: -4°F to 86°F (-20°C to 30°C )
Recharge the battery pack.
Recharge the battery. Discharge the battery
completely and then recharge it.
Set a power management level in Computer
Setup.
Turn off or disconnect external devices
when not using them.
No action is required.
Fully charge the battery pack until the
battery light on the computer turns off.
Condition the battery pack by fully charging,
then fully discharging, and then fully
recharging. If condition persists, replace the
battery. If the battery gauge is still
inaccurate, replace the system board.
Enable power management in Computer
Setup and in Windows Power Properties.
The power management icon should be
visible on the status panel.
Turn off or disconnect external devices
when not using them.
To maintain the charge, leave battery packs
in the computer when it is connected to
external power.
If the computer is disconnected from
external power for more than two weeks,
remove battery packs from the computer to
reduce the discharge rate.
determine the low battery condition.
Reduce use of accessories which drain
power such as the CD-ROM drive or PC
Card.
Keep the battery pack within the
recommended temperature ranges:
Operating: 50°F to 104°F(10°C to 40°C)
Storage: -4°F to 86°F (-20°C to 30°C ).
Recharge the battery pack.
Troubleshooting
2-19
Page 48

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Diskette and Diskette Drive Problems
Some common causes and solutions for diskette and diskette drive problems are listed
in the following table.
Table 2-17
Solving Diskette and Diskette Drive Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Diskette drive light does not
turn on.
Diskette drive light stays on. Diskette is damaged. Run SCANDISK on the diskette. At the
Diskette drive cannot write to
a diskette.
Diskette drive cannot read a
diskette.
Cannot boot from diskette. Bootable diskette is not in
Diskette drive is not installed
properly.
Diskette is incorrectly
inserted.
Software program is
damaged.
Diskette is write-protected. Disable the diskette's write-protect feature
Computer is writing to
the wrong drive.
Not enough space is left
on the diskette.
Drive error has occurred. Run Computer Checkup from the Compaq
Diskette is not formatted. Format the diskette. At the system prompt,
The wrong type of diskette is
being used.
Diskette has a bad sector. Copy files to hard drive or another diskette.
Drive error has occurred. Run Computer Checkup from the Compaq
Diskette is not
formatted.
drive A.
Diskette Boot is disabled in
Computer Setup.
Remove the diskette drive and install it
properly.
system prompt, enter
SCANDISK A:
Remove diskette and reinsert.
Check the program diskettes.
or use a diskette that is not write-protected.
Check the drive letter in the path statement.
Use another diskette.
Diagnostics diskette.
enter
FORMAT A:
Use the type of diskette required by the
drive.
Reformat bad floppy.
Diagnostics diskette.
Format the diskette. At the system prompt,
enter
FORMAT A:
Put the bootable diskette in drive A. If a
diskette drive is in the computer DualBay,
that is drive A.
Run Computer Setup and enable Diskette
Boot from the Boot Management menu.
2-20 Troubleshooting
Page 49

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Hard Drive Problems
Some common causes and solutions for hard drive problems are listed in the following
table.
Table 2-18
Solving Hard Drive Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution( s)
Reading hard drive takes an
unusually long time after
restarting the computer.
Hard drive error occurs. Hard drive has bad sectors or
Hard drive does not work. Hard drive is not seated
Solving CD-ROM Drive Problems
System entered Hibernation
due to low-battery condition
and is now exiting from it.
has failed.
properly.
Hard drive is damaged. Replace the hard drive.
Give the system time to restore the
previously saved data to its exact state
before Hibernation.
Run Computer Checkup.
See POST error messages.
Turn off the computer, remove and reinsert
the hard drive, then turn the computer on.
Some common causes and solutions for CD-ROM drive problems are listed in the
following table.
Table 2-19
Solving CD-ROM Drive Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution( s)
CD-ROM drive cannot read a
compact disc.
CD-ROM drive does not
work.
Compact disc is upside down
or is improperly inserted in
the CD-ROM drive.
CD-ROM drive is not seated
properly.
CD-ROM drive was inserted
while the computer was on, in
Suspend, or in Hibernation.
Open the CD loading tray, lay the compact
disc in it (label side up), then close the tray.
Shut down the computer, remove and
reinsert the drive, then turn on the
computer.
Shut down computer; then turn it on again.
The drive is initialized during power up.
Troubleshooting
2-21
Page 50

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Hardware Installation Problems
Some common causes and solutions for hardware installation problems are listed in the
following table.
Table 2-20
Solving Hardware Installation Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solutions(s)
A new device is not
recognized as part of
the computer system.
Solving Infrared Connection Problems
Cable(s) of new external
device are loose or
power cables are unplugged.
Power switch of new external
device is not turned on.
Device is not seated properly. Turn off the computer and reinsert the
Ensure that all cables are properly and
securely connected.
Turn off the computer, turn on the external
device, then turn on the computer to
integrate the device with the computer
system.
device.
Some common causes and solutions for infrared connection problems are listed in the
following table.
Table 2-21
Solving Infrared Connection Problems
Problem Cause Solution(s)
Cannot link with another
computer.
Data transmission problem. Direct sunlight, fluorescent
Interrupt request (IRQ) conflict. Check IRQ assignments for conflicts and
reassign as necessary.
Baud rate conflict. Select the same baud rate for both
computers.
Remove the interfering light sources.
light, or flashing incandescent
light is close to the infrared
connections.
Interference from other
wireless devices.
Physical obstruction. Do not place objects between the two units
Movement. Do not move either unit during data
Orientation. Adjust devices so that they point within
Distance. Verify that devices are not more than
Keep remote control units such as wireless
headphones and other audio devices away
from the infrared connections
that will interfere with a line-of-sight data
transmission.
transmission.
30 degrees of each other.
3 feet (1 m) apart.
2-22 Troubleshooting
Page 51

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Keyboard/Numeric Keypad Problems
Some common causes and solutions for keyboard/numeric keypad problems are listed
in the following table.
Table 2-22
Solving Keyboard/Numeric Keypad Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Embedded numeric keypad
on computer keyboard is
disabled.
Keyboard is locked. QuickLock initiated. Enter the password to exit QuickLock.
Num Lock function is not
enabled.
Press the
Num Lock function and embedded numeric
keypad. The Num Lock icon on the status
panel turns on.
Solving Pointing Device Problems
Some common causes and solutions for pointing device problems are listed in the
following table.
Fn+NumLk
keys to enable the
Table 2-23
Solving Pointing Device Problems
Problem Cause Solution( s)
External pointing device does
not work.
Integrated pointing device
does not work.
Incorrect device driver or no
device driver is installed.
The device driver is not
installed in Windows.
An external pointing device
is connected and the system
has disabled the internal
pointing device.
Install the device driver.
Install the device driver in Windows.
Initiate Suspend and disconnect the external
pointing device.
Troubleshooting
2-23
Page 52

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Memory Problems
Some common causes and solutions for memory problems are listed in the following
table.
Table 2-24
Solving Memory Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Memory count during PowerOn Self-Test (POST) is
incorrect.
"Out of Memory" message is
displayed on the screen or
insufficient memory
error occurs during operation.
Optional memory expansion
board is installed incorrectly,
is incompatible with
the computer, or is defective.
System ran out of memory for
the application.
Too many TSR (terminate and
stay resident) applications are
running.
Ensure that the optional memory expansion
board is installed correctly.
Check the application documentation for
memory requirements.
Install additional memory.
Remove from memory any TSR applications
that you do not need.
2-24 Troubleshooting
Page 53

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving PC Card Problems
Some common causes and solutions for PC Card problems are listed in the following
table.
Table 2-25
Solving PC Card Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
PC Card error messages
appear when the computer is
turned on.
Computer does not beep
when PC Card is inserted
butt PC Card works correctly
When turned on, the
computer does not beep
when a PC Card is inserted.
The PC Card drivers (Socket
Services, Card Services,
Card ID) fail with error
messages when the
computer is turned on.
PC Card modem, fax, or
network card does not
work.
The PC Card slot is disabled. Run Computer Setup and enable the PC
Card slots on the Security Menu.
System beeps are turned
down.
Card is not inserted properly
PC Card beeps are disabled.
Speaker is turned off or
volume is turned down.
PC Card drivers are not
installed.
The PC Card slots are
disabled.
Card or card driver is not
supported.
The PC Card slot is disabled. Run Computer Setup and select the Security
Card is not fully inserted
into the slot or is not
inserted properly.
Telephone cord is not
plugged in all the way.
Necessary drivers are not
installed (turned on).
Press Fn+F5, then press the right arrow key
to increase the system beeps volume.
In Windows 95, double-click PC Card icon,
click the Global Settings tab. Deselect
Disable PC Card Sound Effects.
Increase the volume.
Double-click the Add New Hardware icon in
the Control Panel for installation instructions.
Run Computer Setup and then select the
Security menu to enable PC Card slots.
Check the list of PC Cards tested
successfully in Compaq PC Card platforms.
menu to enable PC Card slots.
Ensure the card is inserted in the correct
orientation.
Check and secure telephone connection.
Install drivers.
Continued
Troubleshooting
2-25
Page 54

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-25
Continued
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
PC Card modem or fax card
does not work.
Modem network PC Card
does not work.
Memory or storage card
does not work.
You are trying to access the
card using the wrong COM
port.
The card conflicts with a serial
device.
The card is not supported. Use supported cards only.
Network driver is not installed
or is not set up properly.
Telephone cord is not properly
connected.
SRAM and flash memory cards
require the memory card
driver to be loaded (turned on).
Flash memory cards require
the Microsoft FlashFile System
to be loaded.
Hard drives on flash
mass storage cards require
the PC Card ATA driver to
be loaded.
You are trying to access the
hard drive card using the
wrong drive letter.
The card is not
supported.
See Chapter 9 to verify COM port.
See Chapter 9 to verify address.
Install driver.
Verify telephone connection.
Install driver.
Double-click My Computer to verify the drive
letter assigned to the card.
Check the list of PC Card cards tested
successfully in Compaq PC Card platforms.
2-26 Troubleshooting
Page 55

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Power Problems
Also see "Solving Battery and Battery Gauge Problems" in this chapter.
Table 2-26
Solving Power Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Computer won't turn on and
LEDs aren't lit.
Computer turned off while it
was left unattended and the
power /suspend light is off.
Computer initiated Suspend
automatically or turned off
automatically when it was
docked in expansion base.
Computer is not connected
to a power source.
Power cords to the external
power source are unplugged.
DC-DC Converter is defective. Replace the DC-DC power board.
Integrated AC Power is defective. Replace the integrated AC Power and restart.
System initiated Hibernation
due to a critical low-battery
condition.
System initiated Hibernation
after a preset timeout.
The unit temperature
was exceeded.
Insert battery or connect an external power
source.
Ensure that power cords connecting the
computer and the external power source are
plugged in properly.
Replace the battery pack with a fully charged
battery pack or connect the computer to an
external power source. Then turn on the
computer.
Turn on the computer.
NOTE: To change the Hibernation setting in
Windows 95, click the Hibernation tab in
Power properties. Windows NT, run Computer
Setup and select Power Management.
Computer is in an exceedingly hot
environment. Let the computer cool down.
Make sure the ventilation intake and exhaust
are not obstructed.
Troubleshooting
2-27
Page 56

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Printer Problems
If you experience problems printing, run a printer self-test. Refer to the documentation
provided with the printer for instructions. If the self-test fails, it is a printer-specific
problem. Also refer to the printing section of the application documentation.
Table 2-27
Solving Printer Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Printer will not turn on. The signal cable may not be
connected properly, or the
printer is unplugged.
Printer will not print. Printer is not turned on or is
off line.
The device drivers for the
application are not installed.
Printer that is set up for a
network is not connected
to the network.
Printer cable is too long,
unshielded, or defective.
Paper tray is empty. Fill the paper tray with paper and set the
Printer prints garbled
information.
Correct printer drivers are
not installed.
Cable is not connected
properly.
Cable is defective. Replace the printer cable and retest.
Ensure that the signal cable is properly
connected and that the power cord is
connected to the electrical outlet.
Turn the printer on and set it to on-line.
Refer to the printer documentation to install
the correct printer driver.
Connect the printer to the network.
Replace the cable.
printer to on-line.
Refer to the printer documentation to install
the correct printer driver.
Ensure that the printer signal cable is
properly connected to the computer.
Solving Screen Problems
This section lists some common causes and solutions for computer display and external
monitor problems.
You can perform a monitor self-test on an external VGA color or monochrome monitor
by disconnecting the monitor from the computer. To do so, complete the following
steps:
1. Turn off the monitor.
2. Turn off the computer.
2. Disconnect the monitor signal cable from the computer.
4. Turn on the monitor and allow it to warm up for one minute.
The screen should be white. A narrow black border may also appear on the left and
right sides of the display. Either of these displays indicates that the monitor is
working properly.
2-28 Troubleshooting
Page 57

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 2-28
Solving Screen Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
Characters are dim. The brightness or contrast
Screen is blank. You initiated QuickLock/
Computer screen is blank and
the screen on an external
monitor displays information.
Screen is blank and the
power/suspend light is blinking
Screen is blank, the power/
suspend light is blinking, and
the battery light is blinking
External monitor does not
display information
Distorted or garbled characters
on the screen are mixed with
text.
Garbled characters on internal
display or flashing internal
display when connected to
external monitor.
(if applicable) control is not
set properly.
Computer screen is in direct light. Tilt the display or move computer.
Display is damaged. Replace the display.
QuickBlank.
You may have another screen -
blanking utility installed.
Screen save was initiated after
the Power Management timeout
period of inactivity
If an STN screen is used, brightness/
contrast needs adjusting.
Screen has overheated If the computer is in direct sunlight,
Suspend was initiated. Press the suspend button to exit
Display was switched to the
external monitor.
System is in Suspend Press the Suspend button to exit
System has entered a low-battery
condition
External monitor was connected
after the computer was turned on
The external monitor signal cable
or power cord is not properly
connected.
ANSI.SYS
The
CONFIG.SYS
incorrect.
You are using 800 × 600 or higher
resolution on external display and
have toggled back to internal
display, which only supports
640 × 480 resolution.
driver is not in the
file or the path is
Adjust the control(s)using
(contrast) and
Enter the password to exit
QuickLock/QuickBlank.
Press any key and/or enter the
password.
Press any key or click the mouse.
Use the hotkeys to adjust the
brightness/contrast.
move it an allow it to cool.
Suspend.
Press the
information on the computer screen.
Suspend. Enter the power-on
password if prompted.
Immediately connect the computer
to an external power source or
replace the battery pack.
Press the
the external monitor
Verify the cables are properly
connected.
Add the
CONFIG.SYS
line: DEVICE=C:\ANSI.SYS
Restart the computer. If
simultaneous display is desired, use
640 × 480 resolution.
Fn+F10
Fn+F4
hotkey to display
Fn+F4
hotkey to switch to
ANSI.SYS
file. Add the following
Fn+F9
(brightness).
driver to the
Continued
Troubleshooting
2-29
Page 58

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ry
t
g
Table 2-28
Continued
Problem Probable Cause Solution(s)
The image on the external
monitor does not fill the screen.
Small red, green, or blue spots
appear on the computer TFT
display.
When in MS-DOS mode,
the image on the computer
display does not fill the screen.
When displaying simultaneously,
the image on the external
monitor may not be centered.
You are using an external monitor
and simultaneously displaying an
image on the computer display.
Small spots, called on-pixels, often
appear on TFT screens. Compaq
limits the number of these on-pixels
to 0.003% of the approximately
1 million transistors that are on a
12.1-, or 11.2-inch display.
To maintain a high-quality image,
the 800 × 600 models do not
stretch the lower-resolution
image of MS-DOS mode to fill the
screen.
This is typical; no action is required.
This is typical; no action is required.
This is typical; no action is required.
Solving Software Application Problems
Most software application or installation problems occur as a result of one or more of
the following:
■
The application was not installed correctly.
■
Memory was not allocated correctly.
■
A conflict exists between applications.
Table 2-29
Solving Software Application Problems
Problem Probable Cause Solution( s)
Cannot use an application. The application has not been
added to the PATH statement.
Insufficient memory to
run application.
System ran out of memory for
the application.
Too many TSR (terminate and
stay resident) applications are
running.
Application requires Windows
to be run in enhanced mode.
Run the program with the full path name.
Check the application documentation for memo
requirements.
Install additional memory.
Remove from memory any TSR applications tha
you do not need.
Exit Windows and enter again using the followin
command to run in enhanced mode:
WIN/3
2-30 Troubleshooting
Page 59

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
d
Solving Convenience Base Problems
Table 3-30
Display Problems and Solutions
Problem Possible Cause Solution(s)
Garbled characters
on internal display
or flashing internal
display when
connected to
external monitor.
External monitor
display is distorted.
Computer screen
and external
monitor do not
display information
simultaneously.
Toggled to internal monitor
from an external monitor that
is using higher resolution than
that supported by the
computer.
Energy Star Monitor is
selected on the Power
Management menu, and the
external monitor is not Energy
Star compliant.
Display was switched using the
hotkeys.
External monitor was not
turned on before the system
was turned on.
External monitor was
connected after the
computer was turned on.
Restart the system. If simultaneous display is desired, use
the resolution supported by the computer.
Press any key or move the mouse to restore the display. If
the display remains distorted, turn the monitor off and then
back on. Deselect the Energy Star Monitor setting.
Press the
display possibilities.
Initiate Suspend, turn on external monitor, then exit Suspen
to integrate new monitor.
Initiate Suspend, connect external monitor, turn on the
monitor, then exit Suspend.
hotkeys to toggle through the three
Fn+F4
Table 3-31
Docking Problems and Solutions
Problem Possible Cause Solution(s)
The computer is not
properly docked in
the convenience
base.
The computer is not
properly centered over
docking latch.
The computer is not coupled
to docking connector.
Slide computer forward from convenience base. Center over
docking latch and replace. Push docking lever back to dock.
Pull docking lever forward to release computer and re-dock.
Table 3-32
Undocking Problems and Solutions
Problem Possible Cause Solution(s)
The computer will
not undock.
Connectors are tight. Grasp the computer with one hand and pull forward while
pulling forward on docking lever with other hand.
Security cable is locked. Unlock security cable.
PC Card cable is attached to
the computer.
The docking lever in the
convenience base may be
defective.
Remove cable from PC Cards before undocking.
Replace the Convenience Base.
Troubleshooting
2-31
Page 60

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
Table 3-33
External Device Installation Problems and Solutions
Problem Possible Cause Solution(s)
new device is not
recognized as part of
the computer
system.
Problem Possible Cause Solution(s)
External keyboard
does not work.
Power switch of the new
external device was not turned
on before the system was
turned on.
External device was connected
after system was turned on.
The signal cable or power
cord of the new device is
loose or disconnected.
The signal cable or power
cord of the new device may
be defective.
Table 3-34
Keyboard Problems and Solutions
External keyboard may not
be securely connected or
may be connected to an
incorrect external connector.
Initiate Suspend, turn on external devices with power
switches, then exit Suspend to integrate the new device.
Windows 95: Initiate Suspend, plug in and turn on external
devices with power switches, then exit Suspend to integrate
the new device.
Windows NT: Power off computer and external devices.
Power back on to integrate new device.
Ensure that all cables are properly and securely connected.
Ensure that all power cords are properly and securely
plugged into an electrical outlet.
Try connecting a different signal cable and/or power cord.
Ensure that the external keyboard is properly and securely
connected to the external keyboard connector.
Table 3-35
Mouse Problems and Solutions
Problem Possible Cause Solution(s)
External mouse does
not work.
External mouse may not be
securely connected or may
be connected to an incorrect
external connector.
Mouse was connected after
system was turned on.
Ensure that the external mouse is securely connected to the
mouse connector or the correct external connector.
Turn off the unit, connect the mouse, then turn the unit on
to integrate the mouse.
2-32 Troubleshooting
Page 61

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
Solving Network Problems
This section provides guidelines for troubleshooting common Ethernet network
problems. Refer to these guidelines when you have determined that the computer in the
convenience base is not communicating with the network. These guidelines do not
discuss the process of debugging the network cabling.
These are common problems to check first. Refer to the tables on the following pages
for additional problems and solutions.
■
Ensure that the cabling is securely attached to the convenience base. A loose cable is
the most common cause of network problems. If the cable is loose, secure it and see
if the computer can communicate with the network.
■
Determine whether the current computer or another computer has communicated
with the network from the convenience base. If so, determine whether anything was
added or changed that could have stopped the network interface from working.
■
Run Diagnostics before installing the network drivers to verify that the network
interface is working correctly.
Table 3-36
Solving Ethernet Network Problems
Problem Possible Cause Solution( s)
When turned on, the
computer does not
detect the network.
fter installing
network operating
system, computer
does not detect
network interface.
The computer is not connected
to the Ethernet network.
Suspend or Hibernation was
initiated.
The network driver fails to
load during system
initialization.
If using a network interface
card connected to a parallel
port, the port has been
disabled.
Suspend or Hibernation was
initiated.
Connect the computer to the Ethernet network.
Exit Suspend or Hibernation.
Windows 95: Restart the computer by clicking Start, Shut
Down, Restart the Computer.
Windows NT: Click Start, Shut Down. Power the computer
back on.
Ensure that network drivers are loaded and that the drive
path is correct.
Enable the parallel port. Restart the computer. Press F10
immediately when the cursor moves to the top right side of
the screen.
Exit Suspend or Hibernation.
Windows 95: Restart the computer by clicking Start, Shut
Down, Restart the Computer.
Windows NT: Click Start, Shut Down. Power computer back
on.
Continued
Troubleshooting
2-33
Page 62

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Solving Ethernet Network Problems
Continued
Problem Possible Cause Solution( s)
Diagnostics reports
a failure.
Diagnostics reports
no errors, but the
computer does not
communicate with
the network.
The computer
stopped
communicating with
the network after
exiting Suspend.
The computer
stopped
communicating with
the network for no
apparent reason.
The cable is not securely
connected to the network
connector on the Ethernet
network.
There is a problem with the
cable or a device at the other
end of the cable.
Possible hardware failure. Replace the Convenience Base.
Network drivers are
not loaded.
A network configuration error
may have occurred (i.e., *.ini,
*.inf, *.nif, or
may need to be modified).
Suspend or Hibernation was
initiated.
The computer does not detect
network drivers.
The cable is not securely
connected to the network
connector on the Ethernet.
General network failure.
The files for the network
drivers have been corrupted.
CONFIG.SYS
Ensure that the cable is securely connected to the proper
network connector on the Ethernet network.
Ensure that the cable and device at the other end of the
network connection are operating properly.
Load the network drivers.
Windows 95: Restart the computer by clicking Start, Shut
Down, Restart the Computer.
Windows NT: Click Start, Shut Down. Power the computer
back on.
Contact the network administrator.
files
Exit Suspend or Hibernation.
Windows 95: Restart the computer by clicking Start, Shut
Down, Restart the Computer.
Windows NT: Click Start, Shut Down. Power computer back
on.
Windows 95: Restart the computer by clicking Start, Shut
Down, Restart the Computer.
Windows NT: Click Start, Shut Down. Power computer back
on.
Ensure that the cable is securely connected to the
convenience base and Ethernet network.
Ensure that the network you are connected to is running and
has not experienced problems that would prevent the
connection.
Reinstall the network drivers.
IMPORTANT:
module before returning the convenience base for replacement.
2-34 Troubleshooting
If the 100BaseT Ethernet upgrade module has been installed, remove this
Page 63

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 3
Illustrated Parts
This chapter provides illustrated parts and references for spare parts for the Compaq
Armada 4100 and 4200 Families. To review an illustrated parts breakdown of the
computers, refer to the Illustrated Parts Map that comes with this guide.
Illustrated Parts 3-1
Page 64

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 System Unit
Figure 3-1.
System Unit
3-2 Illustrated Parts
Page 65

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-1
System Unit
Item Description Spares Part Number
1* CPU cover (Belgian) 290865-181
2* CPU cover (Brazilian) 290865-201
3* CPU cover (Danish) 290865-081
4* CPU cover (French) 290865-051
5* CPU cover (French Canadian) 290865-121
6* CPU cover (German) 290865-041
7* CPU cover (Hangeul) 290865-AB1
8* CPU cover (Int) 290865-002
9* CPU cover (Italian) 290865-061
10* CPU cover (Japanese) 290865-291
11* CPU cover (Latin American Spanish) 290865-161
12* CPU cover (Norwegian) 290865-091
13* CPU cover (Portuguese) 290865-131
14* CPU cover (Spanish) 290865-071
15* CPU cover (Swedish/Finnish) 290865-101
16* CPU cover (Swiss) 290865-111
17* CPU cover (Thai) 290865-AB1
18* CPU cover (UK English) 290865-031
19 CPU cover (US/Canada) 290865-001
20 Touchpad 218078-001
21 Clutch cover assembly (includes) 258620-001
Clutch cover
* Microphone
* Microphone housing
* Ir lens
22 Heatsink assembly (includes) 258632-001
Heatsink
* Thermal pad
23 Heatpipe assy, CPU board 287310-001
Continued
Illustrated Parts 3-3
Page 66

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 1-1
Continued
Item Description Spares Part Number
24 CPU base assembly (includes) 258626-001
CPU base
* Expansion door
* Foot (3 ea)
* Foot (1 ea)
25 Magnesium frame assembly (includes) 258619-001
* Right speaker gasket
* Front cover
* Right cover
** Upper PCMCIA door
** Lower PCMCIA door
** Upper PCMCIA door spring
** Lower PCMCIA door spring
** Diskette eject hook
** Diskette eject button
* Eject shoulder screw
** Eject module spring
** Latch module spring
** Display ground bracket
** Front foot
* Hard drive insulator
26 Clutch kit (includes) 258621-001
Left clutch assembly
Right clutch assembly
27 Handle assembly 258618-001
28 Diskette Drive 290837-001
* Not illustrated
**Included in Small Mechanical Parts Kit #258607-001
3-4 Illustrated Parts
Page 67

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 3-2.
System Unit (continued)
Illustrated Parts 3-5
Page 68

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 Mass Storage Devices
Figure 3-3.
Mass Storage Devices
3-6 Illustrated Parts
Page 69

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-2
Mass Storage Devices
Item Description Spares Part Number
1 3.5-inch, 1.44-MB, diskette drive 258611-001
2 630-MB hard drive 258612-001
3 810-MB hard drive 258614-001
*4 1.08-GB hard drive 258616-001
*5 1.4-GB hard drive 259263-001
*6 1.6-GB hard drive 287290-001
*7 2-GB hard drive 287207-001
*8 3-GB hard drive 290810-001
*9 4-GB hard drive 290811-001
* Not illustrated
Illustrated Parts 3-7
Page 70

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Cables and Power Cords
Figure 3-4.
Cables
3-8 Illustrated Parts
Page 71

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-3
Cables and Power Cords
Item Description Spares Part Number
1* AC Power cord (Australia/New Zealand) 246959-011
2* AC Power cord (Denmark) 246959-081
3* AC Power cord (Europe) 246959-021
4* AC Power cord (Italy) 246959-061
5* AC Power cord (Japan) 246959-291
6* AC Power cord (Korea) 246959-AD1
7** AC Power cord (Switzerland) 246959-AG1
8* AC Power cord (UK and Singapore) 246959-031
9 AC Power cord (US/Canada) 246959-001
10 Diskette drive cable, parallel port to
external drive unit (External Diskette Drive
Bay)
11* Cable for SpeedPaq 288 Telephony
modems
Australia 234409-011
Belgium 234409-181
Denmark 234409-081
Finland 234409-351
France 234409-051
Germany 234409-041
Italy 234409-061
Korea 234409-AD1
Netherlands 234409-331
Norway 234409-091
Singapore, Thailand, Malasia 234409-AF1
Spain 234409-071
Sweden 234409-101
Switzerland 234409-111
UK 234409-031
US/Canada 234409-001
* Not illustrated
258575-001
Illustrated Parts 3-9
Page 72

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.4 Standard and Optional Boards
Figure 3-5.
Standard and Optional Boards
3-10 Illustrated Parts
Page 73

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-4
Standard and Optional Boards
Item Description Spares Part Number
1 Processor board, 75-MHz CPU 258627-001
2* Processor board, 100-MHz CPU with L2
cache
3* Processor board, 120-MHz CPU with L2
cache
4* Processor board, 133-MHz CPU with L2
cache
5* Processor board, 150-MHz MMX CPU with
L2 cache
6* Processor board, 166-MHz MMX CPU with
L2 cache
7* Processor board, 200-MHz CPU with L2
cache
8* Processor board, 233-MHz CPU with L2
cache
9* Processor board, 266-MHz CPU with L2
cache
10* System Board, 8-MB RAM (includes Left
speaker gasket, battery shroud
11* System Board, 16-MB RAM (includes) Left
speaker gasket, battery shroud
12* System Board, 32-MB RAM (includes) Left
speaker gasket, battery shroud
13* Memory board (DIMM), 4-MB, 70 ns,
nonparity (2 ea)
14* Memory board (DIMM), 8-MB, 70 ns,
nonparity (2 ea)
15* Memory board (DIMM), 16-MB, 70 ns,
nonparity (2 ea)
16* Memory board (DIMM), 32-MB, 70 ns,
nonparity (2 ea)
17* Netelligent 56K PC Card Fax Modem
(North America)
* Not illustrated
258628-001
258629-001
258630-001
287286-001
287287-001
290827-001
290828-001
290830-001
258631-001
287288-001
290829-001
218069-001
218070-001
218071-001
218072-001
295050-001
Illustrated Parts 3-11
Page 74

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.5 Display Assembly
Figure 3-6.
Display Assembly
3-12 Illustrated Parts
Page 75

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-5
Display Assembly
Item Description Spares Part Number
1 10.4-inch CSTN display assembly 258608-001
2* 11.3-inch CSTN display assembly 258609-001
3* 11.8-inch CTFT display assembly 258610-001
4 12.1-inch CSTN display assembly 287283-001
5* 12.1-inch CTFT display assembly 290766-001
* Not illustrated
Illustrated Parts 3-13
Page 76

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.6 Options
Figure 3-7.
3-14 Illustrated Parts
Options
Page 77

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-6
Options
Item Description Spares Part Number
1 Trackball 246970-001
2 Mobile CD Expansion Unit 218073-001
3 Convenience base (pass thru) US 218075-001
4* Convenience base (Ethernet) US 218074-001
5 Convenience base adapter 258541-001
6 AC adapter without power cord (for
domestic and international use)
7 External battery charger 218076-001
8 Automobile adapter 218079-001
9 Li-ion modular battery pack 218077-001
10* Li-ion handle battery pack 246957-001
11 NiMH handle battery pack 258509-001
12* Portfolio Carrying Case 246958-001
13* USB Cardbus PC Card 296501-001
* Not illustrated
246960-001
Illustrated Parts 3-15
Page 78

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8 Miscellaneous Parts
Figure 3-8.
3-16 Illustrated Parts
Miscellaneous Parts
Page 79

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-7
Miscellaneous Parts
Item Description Spares Part Number
Small mechanical parts kit (includes) 258607-001
1 Upper PCMCIA door
2 Upper PCMCIA door spring (5 ea)
3 Lower PCMCIA door
4 Lower PCMCIA door spring (5 ea)
5 Diskette eject hook
6 Diskette eject button
7 Display ground bracket
8 Memory cover
9 DualBay latch spring (1 ea)
10 DualBay eject spring (1 ea)
11 Rear foot (3 ea)
12 Front foot (1 ea)
13 Processor board shield
14* Screw kit (For 5 units. See table 3-8 for
contents and where-used matrix)
15* Tool kit (includes connector removal tool,
loop back plugs, and case utility tool)
16 Real-Time clock battery 258634-001
PCMCIA rail kit (includes) 258818-001
17a Top PCMCIA button
17b Bottom PCMCIA button
17c PCMCIA assembly
* Not illustrated
258819-001
100767-001
Illustrated Parts 3-17
Page 80

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Table 3-8
Miscellaneous Screw Kit Contents and Use (258819-001)
Description Size Quantity Where Used
CPU aligning socket 7 mm socket 10 expansion connector
Shoulder screw, diskete eject T8/Slotted 5 diskette drive eject mechanism
4-40 × 5/16-inch screwlock 3/16 socket 30 I/O connectors at rear of unit
M2 × 0.4 × 4.0 mm T8/Slotted 10 secures hard drive to magnesium frame
M2 × 0.4 × 12.0 mm T8/Slotted 10 secures PCMCIA assembly
M2.5 × 0.45 × 6.5 mm T8/Slotted 45 secures processor board shield
secures heatsink to system board
secures system board to magnesium frame
M2.5 × 0.45 × 21.0 mm T8/Slotted 20 secures front cover
secures CPU cover/keyboard to magnesium
frame
M2.5 × 0.45 × 7.5 mm T8/Slotted 25 secures plastic to clutches
secures base plastic to magnesium frame
M3 × 0.5 × 8.0 mm T8/Slotted 10 secures clutches to display assembly
3.8 Shipping Boxes
Table 3-9
Shipping Boxes
Description Spares Part Number
Shipping Carton (5 ea) 213623-001
Shipping Carton w/packing (1 ea) 213619-001
Shipping Carton, display (1 ea) 213620-001
3-18 Illustrated Parts
Page 81

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
A
A
A
3.9 Documentation
Table 1-10
Documentation
Description Spare Part Number
rmada 4100 Family Illustrated Parts Map
(10 ea)
rmada 4200 Family Illustrated Parts Map
(10 ea)
rmada 4100 Family Quick Setup poster
and Reference Guide
rmada 4200 Family Quick Setup poster
and Reference Guide
258623-001
258624-002
258625-001
258625-002
Illustrated Parts 3-19
Page 82

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 3
Illustrated Parts 3-20
Page 83

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 4
Removal and Replacement
Preliminaries
This chapter provides general service information for the Compaq Armada 4100 and
4200 Families.
Adherence to the procedures and precautions described in this chapter is essential for
proper service.
4.1 Electrostatic Discharge
A sudden discharge of static electricity from a finger or other conductor can destroy
static-sensitive devices or microcircuitry. Often the spark is neither felt or heard, but
damage occurs. An electronic device exposed to electrostatic discharge (ESD) may not
be affected at all and will work perfectly throughout a normal cycle. Or it may function
normally for a while, then degrade in the internal layers, reducing its life expectancy.
Networks built into many integrated circuits provide some protection, but in many
cases, the discharge contains enough power to alter device parameters or melt silicon
junctions.
4.1.1 Generating Static
Table 4-1 shows how different activities generate static electricity and at different
electrostatic voltage levels.
Table 4-1
Typical Electrostatic Voltages
Relative Humidity
Event 10% 40% 55%
Walking across carpet 35,000 V 15,000 V 7,500 V
Walking across vinyl floor 12,000 V 5,000 V 3,000 V
Motions of bench worker 6,000 V 800 V 400 V
Removing DIPS from plastic tubes 2,000 V 700 V 400 V
Removing DIPS from vinyl trays 11,500 V 4,000 V 2,000 V
Removing DIPS from Styrofoam 14,500 V 5,000 V 3,500 V
Removing bubble pack from PCBs 26,000 V 20,000 V 7,000 V
Packing PCBs in foam-lined box 21,000 V 11,000 V 5,000 V
NOTE:
700 volts can degrade a product.
Removal and Replacement Preliminaries 4-1
Page 84

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.2 Preventing Electrostatic Damage
to Equipment
Many electronic components are sensitive to ESD. Circuitry design and structure
determine the degree of sensitivity. The following proper packaging and grounding
precautions are necessary to prevent damage:
■
Protect all electrostatic parts and assemblies with conductive or approved
containers or packaging.
■
Keep electrostatic-sensitive parts in their containers until they arrive at
static-free stations.
■
Place items on a grounded surface before removing them from their
container.
■
Always be properly grounded when touching a sensitive component or
assembly.
■
Place reusable electronic-sensitive parts from assemblies in protective
packaging or conductive foam.
Use transporters and conveyors made of antistatic belts and metal roller bushings.
Mechanized equipment used for moving materials must be wired to ground and proper
materials selected to avoid static charging. When grounding is not possible, use an
ionizer to dissipate electric charges.
4.1.3 Removing Batteries
Compaq recommends that you remove all batteries from the computer before beginning
the disassembly procedures. Failure to do so could cause damage to computer
components.
4-2 Removal and Replacement Preliminaries
Page 85

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
4.1.4 Preventing Damage to Drives
To prevent static damage to hard drives, use the following precautions:
■
Handle drives gently, using static-guarding techniques.
■
Store drives in the original shipping containers.
■
Avoid dropping drives from any height onto any surface.
■
Handle drives on surfaces that have at least one inch of shockproof foam.
■
Always place drives with the PCB assembly-side down on the foam.
4.1.5 Grounding Methods
The method for grounding must include a wrist strap or a foot strap at
a grounded workstation. When seated, wear a wrist strap connected to a grounded
system. When standing, use footstraps and a grounded floor mat.
Table 4-2
Static-Shielding Protection Levels
Method Voltages
ntistatic plastic 1,500
Carbon-loaded plastic 7,500
Metallized laminate 15,000
Removal and Replacement Preliminaries 4-3
Page 86

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.6 Grounding Workstations
To prevent static damage at the workstation, use the following precautions:
■
Cover the workstation with approved static-dissipative material. Provide a
wrist strap connected to the work surface and properly grounded tools and
equipment.
■
Use static-dissipative mats, heel straps, or air ionizers to give added protection.
■
Handle electrostatic sensitive components, parts, and assemblies by the case or PCB
laminate. Handle them only at static-free workstations.
■
Avoid contact with pins, leads, or circuitry.
■
Turn off power and input signals before inserting and removing connectors or test
equipment.
■
Use fixtures made of static-safe materials when fixtures must directly contact
dissipative surfaces.
■
Keep work area free of non-conductive materials such as ordinary plastic assembly
aids and Styrofoam.
■
Use field service tools, such as cutters, screwdrivers and, vacuums, that are
conductive.
■
Use a portable field service kit with a static dissipative vinyl pouch that folds out of
a work mat. Also use a wrist strap and a ground cord for the work surface. Ground
the cord to the chassis of the equipment undergoing test or repair.
4.1.7 Grounding Equipment
Use the following equipment to prevent static electricity damage to the equipment:
Wrist Straps are flexible straps with a minimum of 1 megohm +/- 10% resistance to
the ground cords. To provide proper ground, a strap must be worn snug against the
skin. On grounded mats without banana-plug connectors, connect a wrist strap with
alligator clips.
Heel straps/Toe straps/Bootstraps can be used at standing workstations and are
compatible with most types of boots and shoes. On conductive floors or dissipative
floor mats, use straps on both feet with a minimum of 1 megohm resistance between
operator and ground. To be effective, the conductive strips must be worn in contact
with the skin.
4-4 Removal and Replacement Preliminaries
Page 87

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1.8 Recommended Materials and Equipment
Other materials and equipment that are recommended for use in preventing static
electricity include:
■
Antistatic tape
■
Antistatic smocks, aprons, or sleeve protectors
■
Conductive bins and other assembly or soldering aids
■
Conductive foam
■
Conductive table-top workstations with ground cord of 1 megohm
of resistance
■
Static dissipative table or floor mats with hard tie to ground
■
Field service kits
■
Static awareness labels
■
Wrist straps and footwear straps providing 1 megohm +/- 10% resistance
■
Material handling packages
■
Conductive plastic bags
■
Conductive plastic tubes
■
Conductive tote boxes
■
Metal tote boxes
■
Opaque shielding bags
■
Transparent metallized shielding bags
■
Transparent shielding tubes
Removal and Replacement Preliminaries 4-5
Page 88

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 Service Considerations
Listed below are some considerations to keep in mind during the disassembly and
assembly of the computer.
4.2.1 Tool Requirements
■
Torx T-8 screwdriver
■
Flat-bladed screwdriver
■
Tool kit, Compaq part number 100767-001 (includes case utility tool, connector
removal tool, and loop back plugs)
■
7-mm socket wrench
■
3/16-inch socket wrench
■
Preloaded application diskettes
4.2.2 Cables and Connectors
Apply only the tension required to seat or unseat the cables during insertion or removal
from connectors. Handle cables by the connector or pull tabs whenever possible. In all
cases, avoid bending, twisting, or tearing the cables, and ensure that cables are placed
in such a way that they cannot be caught or snagged by parts being removed or
replaced.
CAUTION:
When servicing these computers, ensure that cables are placed in
their proper location during the reassembly process. Improper cable placement
can cause severe damage to the unit.
4.3 Serial Number
The computer serial numbers should be provided to Compaq whenever requesting
information or ordering spare parts. The serial number is located on the bottom of the
CPU on the left front corner.
4-6 Removal and Replacement Preliminaries
Page 89

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 5
Removal and Replacement
Procedures
This chapter presents the removal and replacement procedures for both the 4100 and
4200 Families.
5.1 Serial Number
The computer serial number should be provided to Compaq when requesting
information or ordering spare parts. The serial number is displayed on the bottom of the
CPU on the left front corner (Figure 5.1).
Figure 5-1.
Serial Number Location
Removal and Replacement Procedures 5-1
Page 90

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2 Disassembly Sequence Chart
Use the chart below to determine the section number and disassembly sequence for
removing components from the computer.
5.3.1 Disconnect AC Power
5.3.1 Disconnect External Diskette Drive Bay
5.3.2 Undock the Computer
5.3.7 PC Card
5.4.1 Computer Logo
5.4.2 Computer Feet
5.3.3 Remove Handle Battery Pack
5.4.3 Handle
5.3.4 Remove DualBay Device (Optional Battery)
5.3.5 Pointing Device
5.3.6 Hard Drive
5.5.1 Memory Cover
5.5.2 Memory Board
5.5.3 Lithium Clock Battery
5.5.4 CPU Base Cover
5.5.5 Processor Shield and Board
5.5.6 CPU Cover/Keyboard
5.9.1 Upper PCMCIA Door
5.9.5 PCMCIA Buttons
5.6 Display Assembly
5.7.1 Clutch Cover
5.7.2 Clutch
5.8.1 System Board
5.8.2 Heat Sink
5.9.2 Lower PCMCIA Door
5.9.3 DualBay Eject Button
5.9.4 PCMCIA
5.9.6 Display Ground Bracket
Figure 5-2
. Computer Disassembly Chart
5-2 Removal and Replacement Procedures
Page 91

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3 Preparing the Computer for Disassembly
Before beginning the removal and replacement procedures, complete the following
procedures:
1. Disconnect the AC power and any external devices (Section 5.3.1).
2. Undock the computer from the auxiliary base, if necessary (Section 5.3.2).
3. Remove the handle battery or DualBay pack (Section 5.3.3).
4. Remove the DualBay device (Section 5.3.4).
5. Remove the pointing device (Section 5.3.5).
6. Remove any PC Cards (Section 5.3.7).
7. Disconnect the External Diskette Drive Bay, if connected.
Removal and Replacement Procedures 5-3
Page 92

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3.1 Disconnecting the AC Power and External
Diskette Drive Bay
The first procedure that should be performed on the computer is to disconnect the
power supply and any external devices.
1. Turn off the computer.
2. Disconnect the AC adapter power cord from the wall.
3. Disconnect the AC adapter from the computer.
Figure 5-3
4. Disconnect the External Diskette Drive Bay from the computer.
5. Turn off and disconnect any external devices.
If the computer is docked in an auxiliary station, see Section 5.3.2 for undocking
instructions.
5-4 Removal and Replacement Procedures
. Disconnecting the AC Power
Page 93

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3.2 Undocking the Computer
If the computer is docked in an auxiliary station, it must be undocked from the
convenience base and from the adapter or detached from the Mobile CD Expansion
Unit (MCD) before performing additional work. Complete the following steps to
undock the computer. If the computer is not docked in an auxiliary station, proceed to
Section 5.3.3.
Convenience Base
The computer must be undocked from the convenience base before performing
additional work. The same procedure is followed for removing the adapter and
removing the MCD from the convenience base. These procedures are shown in Figures
5-4 and 5-5, respectively. To remove and replace the convenience base, complete the
following steps:
1. Disconnect the AC power and any external devices (Section 5.3.1).
2. Close the computer.
If you are removing an adapter from the convenience base proceed with step 3. If
detaching an MCD, go to step 5.
3. Grasp the adapter and the convenience base and lift the convenience base slightly to
disengage it from the adapter.
4. Pull the two pieces apart.
Removal and Replacement Procedures 5-5
Page 94

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 5-4
5. To remove the convenience base from the MCD, lift the assembly slightly and pull
6. Grasp the MCD and the convenience base, then pull apart.
. Disconnecting the Convenience Base from the Adapter
the lever on the right bottom of the convenience base. This will separate the two
pieces.
5-6 Removal and Replacement Procedures
Page 95

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 5-5.
Reverse the above procedure to dock the convenience base and the MCD.
Disconnecting the Mobile CD Expansion Unit from the Convenience Base
Removal and Replacement Procedures 5-7
Page 96

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Convenience Adapter Base
To undock the computer from the adapter, complete the following steps:
1. Grasp both the computer and adapter, then pull apart.
Figure 5-6.
2. Reach underneath the computer and close the expansion cover on the bottom of the
computer.
Reverse the above procedure to dock the computer into the adapter base.
Undocking the Computer from the Adapter Base
5-8 Removal and Replacement Procedures
Page 97

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mobile CD Expansion Unit
Before detaching the computer from the MCD, disconnect it from the convenience
base.
CAUTION:
To detach the computer from the MCD, complete the following steps:
1. Turn the computer and MCD assembly over, bottom side up. Turn the two
thumbscrews on the bottom of the MCD counterclockwise to loosen the MCD from
the computer.
Make sure the computer display is closed before beginning this procedure
.
Figure 5-7.
Loosening the Thumbscrews
Removal and Replacement Procedures 5-9
Page 98

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2. Turn the computer and MCD over, top side up.
1
3. Rotate the eject lever on the back of the MCD
Remove the computer from the guide hooks on the MCD by sliding the computer
up and away from the MCD.
down to pry the two pieces apart.
2
Figure 5-8.
Detaching the Computer from the MCD
5-10 Removal and Replacement Procedures
Page 99

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4. Close the expansion slot cover on the bottom of the computer.
Figure 5-9.
Closing the Expansion Slot Cover
Reverse the above procedures to attach the computer to the MCD.
CAUTION:
the MCD. Falure to do so may cause damage to the hard drive.
Power to the computer should be turned off when connecting the computer to
Removal and Replacement Procedures 5-11
Page 100

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3.3 Battery Packs
The handle battery pack and the DualBay battery pack should be removed before
performing any internal maintenance on the computer.
WARNING:
!
the battery compartment. To prevent damage, do not allow metal objects to touch the
battery contacts. Place only the battery pack for the Compaq Armada Personal Computer
into the battery compartment. Do not force the battery pack into the handle if insertion
does not occur easily.
WARNING:
!
water. Do not expose to temperatures higher than 60°C. Do not open a battery pack, as
this damages the pack, makes it unserviceable, and exposes potentially harmful battery
components. There are no field-serviceable parts located inside the battery pack.
Metal objects can damage the battery pack as well as the battery contacts in
Do not crush, puncture, or incinerate the battery pack. Do not dispose of in
To remove the battery pack from the handle, complete the following steps:
1. Place the computer in its normal operating position with the handle in the carry
position.
1
2. Grasp the battery cap on the top and bottom
2
handle
.
and pull the battery pack out of the
Figure 5-10
5-12 Removal and Replacement Procedures
. Removing the Battery Pack from the Handle
 Loading...
Loading...