Page 1

User’s Guide
HP 8712ES and HP 8714ES
RF Network Analyzers
HP Part No. 08714-90012
Printed in USA
Print Date: October 1999
Supersedes: November 1998
© Copyright 1998, 1999 Hewlett-Packard Company
Page 2

Notice
The information contained in this document is subject to change without
notice. Hewlett-Packard makes no warranty of any kind with regard to
this material, including but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Hewlett-Packard
shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance,
or use of this material.
Key Conventions
This manual uses the following conventions:
FRONT PANEL KEY
This represents a key physically located on the instrument (a “hardkey”).
Softkey
This indicates a “softkey,” a key whose label is determined by the
instrument’s firmware, and is displayed on the right side of the
instrument’s screen next to the eight unlabeled keys.
Screen Text
This indicates text displayed on the instrument’s screen.
Safety Information
For safety and regulatory information seeChapter 10, “Safety and
Regulatory Information.” For warranty and assistance information see
Chapter 9, “Specifications.”
Firmware Revision
This manual documents analyzers with firmware revisions E.06.00 and
above.
ii ES User’s Guide
Page 3

Acknowledgments
Lotus® 1-2-3® are U.S. registered trademarks of Lotus Development
Corporation.
Windows, Word97, and Excel97 are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corp.
Portions of the software include source code from the Info–ZIP group.
This code is freely available on the Internet by anonymous ftp
asftp.uu.net:/pub/archiving/zip/unzip51/.tar.Z, and from CompuServe
asunz51.zip in the IBMPRO forum, library 10, (data compression).
ES User’s Guide iii
Page 4

Introducing the Analyzer
The HP 8712ES and HP 8714ES are easy-to-use RF network analyzers
optimized for production measurements of S-parameters. The
instrument integrates an RF synthesized source, S-parameter test set,
multi-mode receivers, and display in one compact box.
The source features 1 Hz resolution, 40 ms (or faster) sweep time, and up
to +13 dBm output power.
S-parameter test sets provide the capability to measure reflection and
transmission characteristics of two-port devices in either the forward or
reverse direction with a single connection. RF power can come out of
either the analyzer’s port 1 or port 2, and either port can be connected to
a receiver. S-parameter test sets also allow full two-port (12 term) error
correction, which is the most accurate form available.
The three-channel, dual mode receivers provide dynamic range of
greater than 100 dB in narrowband measurement mode. For
measurements of frequency-translating devices, the network analyzer
features broadband internal detectors and external detector inputs. The
receivers incorporate digital signal processing and microprocessor
control to speed operation and measurement throughput.
Two independent measurement channels and a large display show the
measured results of one or two receiver channels in several
user-selectable formats. An external VGA monitor can be connected to
the rear panel for enhanced measurement viewing in color.
Measurement functions are selected with front panel hardkey and
softkey menus. Measurements can be printed or plotted directly with a
compatible peripheral. Instrument states can be saved to the internal
floppy disk, internal non-volatile memory, or internal volatile memory.
Built-in service diagnostics are available to simplify troubleshooting
procedures
Measurement calibrations and data averaging provide performance
improvement and flexibility. Measurement calibrations consist of
normalizing data, utilizing the internal factory calibration, or calibrating
with external standards. Measurement calibration reduces errors
iv ES User’s Guide
Page 5

associated with crosstalk, directivity, source and load match, and
frequency response. Refer to Chapter 9, “Specifications,” for error
correction specifications.
How to Use This Guide
The first 6 chapters of this guide explain how to perform measurements,
calibrate the instrument, and use the most common instrument
functions.
Chapters 7 through 11 are reference material. Use these chapters to look
up information such as front panel features, specific key functions, and
specifications.
ES User’s Guide v
Page 6

HP 8712ES and HP 8714ES
Network Analyzer
Documentation Map
The CDROM provides the contents of all of the documents
listed below.
The User’s Guide shows how to make measurements,
explains commonly-used features, and tells you how to get
the most performance from the analyzer.
The LAN Interface User’s Guide Supplement shows
how to use a local area network (LAN) for programming and
remote operation of the analyzer.
The Automating Measurements User’s Guide
Supplement provides information on how to configure and
control test systems for automation of test processes.
The Programmer’s Guide provides programming
information including HP-IB and SCPI command references,
as well as short programming examples.
The Example Programs Guide provides a tutorial
introduction using BASIC programming examples to
demonstrate the remote operation of the analyzer
.
vi ES User’s Guide
Page 7
The Service Guide provides the information needed to
adjust, troubleshoot, repair , and verify analyzer conformance
to published specifications.
The HP Instrument BASIC User’s Handbook describes
programming and interfacing techniques using
HP Instrument BASIC, and includes a language reference.
The HP Instrument BASIC User’s Handbook
Supplement shows how to use HP Instrument BASIC to
program the analyzer.
The Option 100 Fault Location and Structural Return
Loss Measurements User’s Guide Supplement provides
theory and measurement examples for making fault location
and SRL measurements. (Shipped only with Option 100
analyzers.)
The CATV Quick Start Guide provides abbreviated
instructions for testing the quality of coaxial cables.
(Shipped only with Option 100 analyzers.)
The Cellular Antenna Quick Start Guide provides
abbreviated instructions for verifying the performance of
cellular antenna systems. (Shipped only with Option 100
analyzers.)
ES User’s Guide vii
Page 8

viii ES User’s Guide
Page 9

Contents
1. Installing the Analyzer
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Step 1. Check the Shipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Step 2. Meet Electrical and Environmental Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Step 3. Check the Analyzer Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
Connecting Peripherals and Controllers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
Installing the Analyzer in a Rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-16
Preventive Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
Clean the CRT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
Check the RF Front Panel Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
2. Getting Started
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Front Panel Tour . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Entering Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Presetting the Analyzer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Entering Frequency Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Entering Source Power Level. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Scaling the Measurement Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Entering the Active Measurement Channel and Type of Measurement. . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Viewing Measurement Channels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Performing the Operator's Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Equipment List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Make S21 and S12 Transmission Measurements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Make a Broadband Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Make S11 and S22 Reflection Measurements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
If the Analyzer Fails the Operator's Check. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
3. Making Measurements
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
The Measurement Display Icon. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Measuring S-Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Attenuation and Amplification in a Measurement Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
When to Change the System Impedance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Contents-i
Page 10

Contents
The Typical Measurement Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-13
Using the BEGIN Key to Make Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-14
BEGIN Key Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-15
Using the BEGIN Key to Configure Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-16
AUTOST files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-18
The User BEGIN Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-18
Measuring S-Parameters using a
Two-Port Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-19
Enter the Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-20
Perform a User Two-Port Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-20
View and Interpret the S-Parameter Measurement Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-40
Measuring S21 Forward
Transmission using an Enhanced Response Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-41
Enter the Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-42
Perform an Enhanced Response Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-42
Connect the DUT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-45
View and Interpret the S21 Measurement Results. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-46
Measuring S11 Reflection Port 1 using a One-Port Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-48
Enter the Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-49
Perform a User One-Port Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-49
Connect the DUT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-52
View and Interpret the S11 Measurement Results. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-54
Making a Power Measurement using Broadband Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-56
Enter the Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-56
Perform a Normalization Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-57
Connect the DUT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-58
View and Interpret the Power Measurement Results. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-59
Measuring Conversion Loss. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-61
Enter the Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-62
Perform a Normalization Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-62
Connect the DUT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-64
View and Interpret the Conversion Loss Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-65
Making Measurements with the Auxiliary Input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-67
Auxiliary Input Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-68
Measuring Group Delay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-69
Enter the Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-70
Perform a User Two-Port Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-71
Contents-ii
Page 11

Contents
Connect the DUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-71
View and Interpret the Group Delay Measurement Results. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-71
Measuring Impedance using the Smith Chart. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-73
Enter the Measurement Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-74
Perform a User Two-Port Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-74
Connect the DUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-75
View and Interpret the Impedance Measurement Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-76
Measuring Impedance Magnitude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-80
How the Reflection Measurement Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-80
How the Transmission Measurement Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-81
4. Using Instrument Functions
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Using Markers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
To Activate Markers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
To Turn Markers Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
To Use Marker Search Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
To Use Marker Math Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-18
To Use Delta (∆) Marker Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-24
To Use Other Marker Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-26
To Use Polar Format Markers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-27
To Use Smith Chart Markers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-27
Using Limit Testing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-28
To Create a Flat Limit Line. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-29
To Create a Sloping Limit Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-30
To Create a Single Point Limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-32
To Use Marker Limit Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-32
To Use Relative Limits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-36
Other Limit Line Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-37
Additional Notes on Limit Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-39
Using Reference Tracking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-42
To Track the Peak Point. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-43
To Track a Frequency. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-44
Customizing the Display. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-45
Using the Split Display Feature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-46
Enabling/Disabling Display Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-47
Contents-iii
Page 12

Contents
Modifying Display Annotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-48
Expanding the Displayed Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-52
Saving and Recalling Measurement Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-55
Saving Instrument Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-57
To Recall from a Floppy Disk or Internal Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-60
Other File Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-63
To Use Directory Utilities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-65
Formatting a Floppy Disk. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-67
Connecting and Configuring Printers and Plotters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-68
Select a Compatible Plotter or Printer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-68
Select an Appropriate Interface Cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-69
Connect the Printer or Plotter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-70
Configure the Hardcopy Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-71
Define the Printer or Plotter Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-73
Printing and Plotting Measurement Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-78
To Select the Copy Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-78
To Define the Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-79
Using a Keyboard. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-83
To Connect the Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-83
To Use the Keyboard to Edit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-84
Front Panel Control using a Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-84
Using an External VGA Monitor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-87
Customizing Color on an External Monitor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-87
Synchronizing and Positioning the Display. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-89
5. Optimizing Measurements
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-2
Increasing Sweep Speed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
Select the Appropriate Calibration Type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-3
To Increase the Start Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
To Set the Sweep Time to AUTO Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
To Widen the System Bandwidth. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
To Reduce the Amount of Averaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
To Reduce the Number of Measurement Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-5
To View a Single Measurement Channel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-6
To Turn Off Alternate Sweep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-7
Contents-iv
Page 13

Contents
To Turn Off Markers and Marker Tracking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
To Turn Off Spur Avoidance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
To Avoid Frequency Bandcrossings by
Minimizing the Span (HP 8714ES only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
Increasing Network Analyzer Dynamic Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
To Increase the Receiver Input Power. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
To Reduce the Receiver Noise Floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
Reducing Trace Noise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
To Activate Averaging for Reducing Trace Noise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
To Change System Bandwidth for Reducing Trace Noise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
To Eliminate Receiver Spurious Responses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
Reducing Mismatch Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
Reducing Mismatch Errors in a Reflection Measurement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
Reducing Mismatch Errors in a Transmission Measurement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-16
Reducing Mismatch Errors when Measuring Both Reflection and Transmission . 5-17
Compensating for Phase Shift in Measurement Setups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-18
Port Extensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-18
Electrical Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-20
Measuring Devices with Long Electrical Delay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-21
6. Calibrating for Increased Measurement Accuracy
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Measurement Calibration Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
The Calibration Reference Plane. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
Default versus User-Defined Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
When to Use a Default Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
When to Perform a User-Defined Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
Calibration Choices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-9
Retrieving Previous User-Defined Calibrations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
Presetting the Analyzer: How Calibration Is Affected. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-13
To Perform a Normalization Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-14
To Perform a Transmission Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-15
To Perform a Reflection Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-19
To Perform a Conversion Loss Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-22
Calibration Kits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-23
Selecting a Calibration Kit Stored in the Analyzer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-23
Contents-v
Page 14

Contents
Creating a User-Defined Calibration Kit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-25
Saving and Recalling the Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-33
Saving the Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-33
Recalling the Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-34
7. Front/Rear Panel
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-2
Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-3
BNC Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-4
Multi-pin Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-7
RF Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-15
Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-16
Knob . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-18
Power Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-19
Display Intensity Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-20
Disk Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-21
Line Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-22
Power Cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-22
The Line Fuse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-24
The Voltage Selector Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-25
8. Hardkey/Softkey Reference
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-2
Numeric Entries. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-3
A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-5
B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-11
C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-14
D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-20
E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-27
F. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-30
G . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-35
H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-37
I . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-42
K . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-45
L. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-46
M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-52
Contents-vi
Page 15

Contents
N . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-60
O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-63
P . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-64
R . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-69
S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-75
T . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-89
U . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-94
V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-97
W. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-99
X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-100
Y . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-101
Z . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-103
9. Specifications
Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
System Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Test Port Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-23
Test Port Input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-29
General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-39
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-45
Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-45
Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-47
Data Hardcopy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-47
Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-48
Measurement Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-49
Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-52
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-54
Limitation of Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-55
Exclusive Remedies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-55
Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Offices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-56
10. Safety and Regulatory Information
Safety and Regulatory Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2
Safety Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-3
Warnings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-3
Cautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-4
Contents-vii
Page 16

Contents
Statement of Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-4
Cleaning Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-4
Shipping Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-4
Instrument Markings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-5
Regulatory Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-6
Notice for Germany: Noise Declaration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-6
Declaration of Conformity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-6
11. Factory Preset State and Memory Allocation
Factory Preset and Peripheral States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-2
Factory Preset State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-2
Peripheral State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-8
Volatile Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-12
Save/Recall Memory Allocation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-13
Types of Storage Disks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-13
Types of Storable Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-15
How to Determine the Size of Disk Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-16
Memory Usage Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-18
Contents-viii
Page 17

1 Installing the Analyzer
ES User’s Guide 1-1
Page 18

Installing the Analyzer
Introduction
Introduction
This chapter will guide you through the four steps needed to correctly
and safely install your network analyzer. The four steps are:
1. Check the Shipment
2. Meet Electrical and Environmental Requirements
3. Check the Analyzer Operation
4. Configure the Analyzer
1-2 ES User’s Guide
Page 19

Installing the Analyzer
Step 1. Check the Shipment
Step 1. Check the Shipment
After you have unpacked your instrument, it is recommended that you
keep the packaging materials so they may be used if your instrument
should need to be returned for maintenance or repair.
NOTE The packaging material is designed to protect the analyzer from damage
that can happen during shipping. Returning the analyzer in anything
other than the original packaging may result in non-warranted damage.
Check the items received against the Product Checklist (included in your
shipment) to make sure that you received everything.
Inspect the analyzer and all accessories for any signs of damage that
may have occurred during shipment. If your analyzer or any accessories
appear to be damaged or missing, call your nearest Hewlett-Packard
sales or service office. Refer to Table 9-10, “Hewlett-Packard Sales and
Service Offices,” in Chapter 9 for the nearest office.
ES User’s Guide 1-3
Page 20
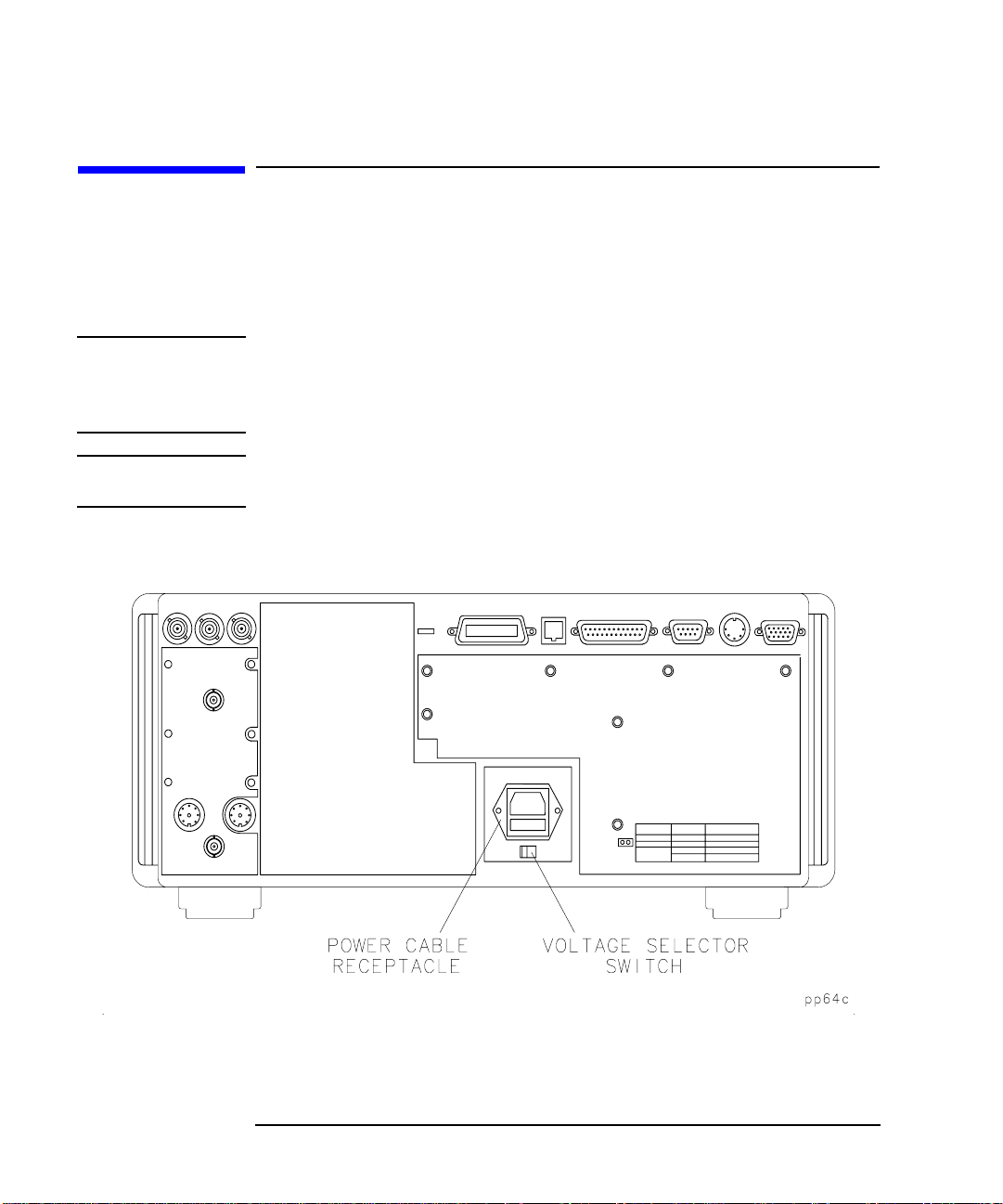
Installing the Analyzer
Step 2. Meet Electrical and Environmental Requirements
Step 2. Meet Electrical and
Environmental Requirements
1. Set the line voltage selector to the position that corresponds to the ac
power source you will be using.
CAUTION Before switching on this instrument, make sure that the line voltage
selector switch is set to the voltage of the mains supply and the correct
fuse (T 5 A 250 V) is installed. Assure the supply voltage is in the
specified range.
NOTE The working fuse and a spare are located in the power cable receptacle.
See Figure 7-12, “Location of Line Fuses,” in Chapter 7.
Figure 1-1 Voltage Selector Switch Location
1-4 ES User’s Guide
Page 21
Installing the Analyzer
Step 2. Meet Electrical and Environmental Requirements
2. Ensure the available ac power source meets the following
requirements:
Nominal
Setting
115 V
230 V
If the ac line voltage does not fall within these ranges, an
autotransformer that provides third-wire continuity to ground should
be used.
3. Ensure the operating environment meets the following requirements
for safety:
• indoor use
• altitude up to 15,000 feet (4,572 meters)
• temperature 0 °C to 55 °C
• maximum relative humidity 5 to 95 percent relative at +40 °C
(non-condensing)
CAUTION This product is designed for use in Installation Category II and Pollution
Degree 2 per IEC 1010 and 664 respectively.
NOTE The above requirements are for safety only. Separate conditions that
must be met for specified performance are noted in Chapter 9.
AC Line Power
90 to 132 Vac (47 to 63 Hz)
198 to 264 Vac (47 to 63 Hz)
ES User’s Guide 1-5
Page 22
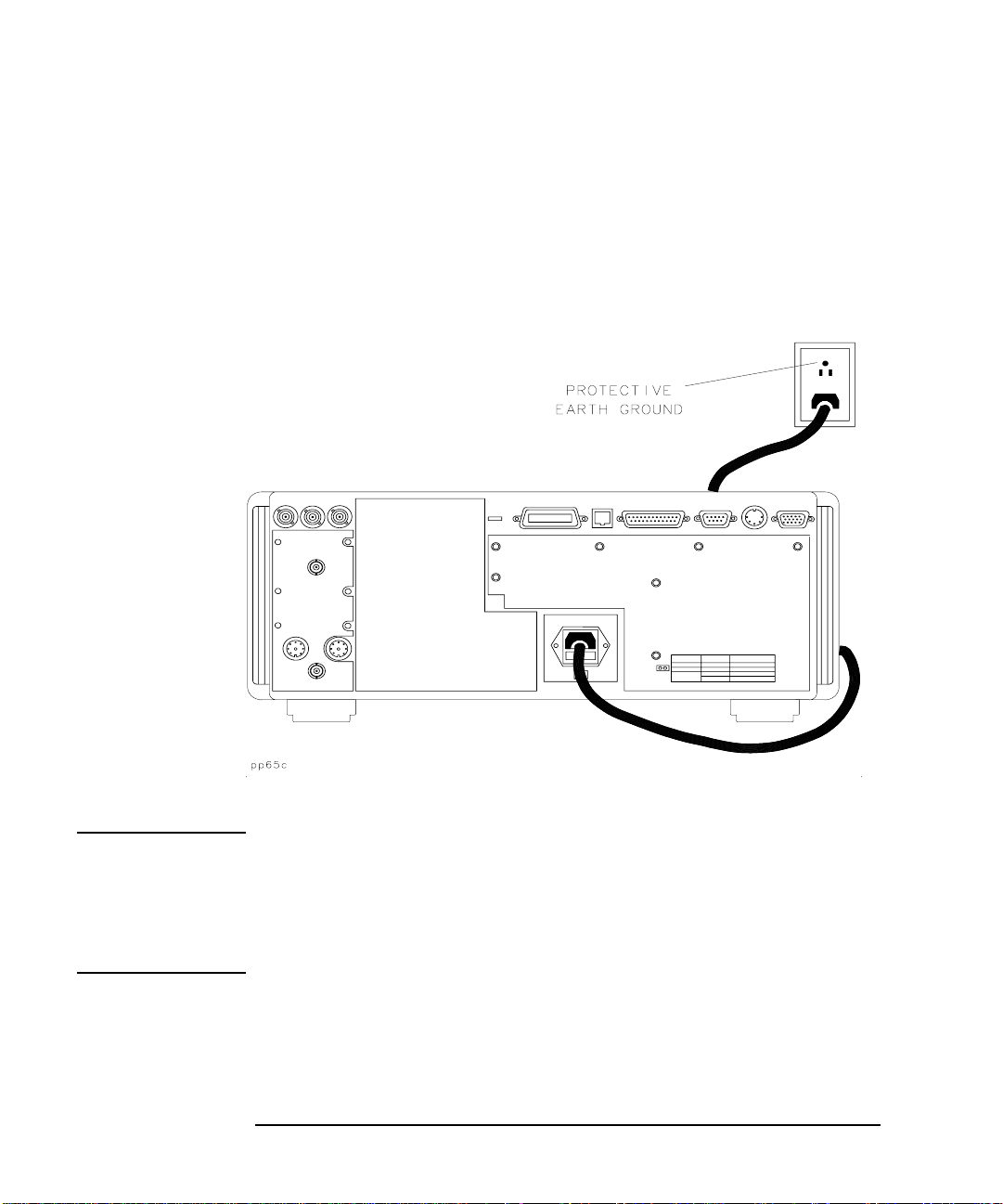
Installing the Analyzer
Step 2. Meet Electrical and Environmental Requirements
4. V erify that the power cable is not damaged, and that the power source
outlet provides a protective earth ground contact. Note that the
following illustration depicts only one type of power source outlet.
Refer to Figure 7-11 in Chapter 7 to see the different types of power
cord plugs that can be used with your analyzer.
Figure 1-2 Protective Earth Ground
WARNING This is a Safety Class I product (provided with a protective
earthing ground incorporated in the power cord). The mains
plug shall only be inserted in a socket outlet provided with a
protective earth contact. Any interruption of the protective
conductor , inside or outside the instrument, is likely to make the
product dangerous. Intentional interruption is prohibited.
1-6 ES User’s Guide
Page 23
Installing the Analyzer
Step 2. Meet Electrical and Environmental Requirements
WARNING If this instrument is to be energized via an external
autotransformer for voltage reduction, make sure that its
common terminal is connected to a neutral (earthed pole) of the
power supply.
5. Install the analyzer so that the detachable power cord is readily
identifiable and is easily reached by the operator. The detachable
power cord is the instrument disconnecting device. It disconnects the
mains circuits from the mains supply before other parts of the
instrument. The front panel switch is only a standby switch and not a
LINE switch. Alternatively, an externally installed switch or circuit
breaker (which is readily identifiable and is easily reached by the
operator) may be used as a disconnecting device.
6. Install the analyzer according to the enclosure protection provided.
This instrument does not protect against the ingress of water. It does
protect against finger access to hazardous parts within the enclosure.
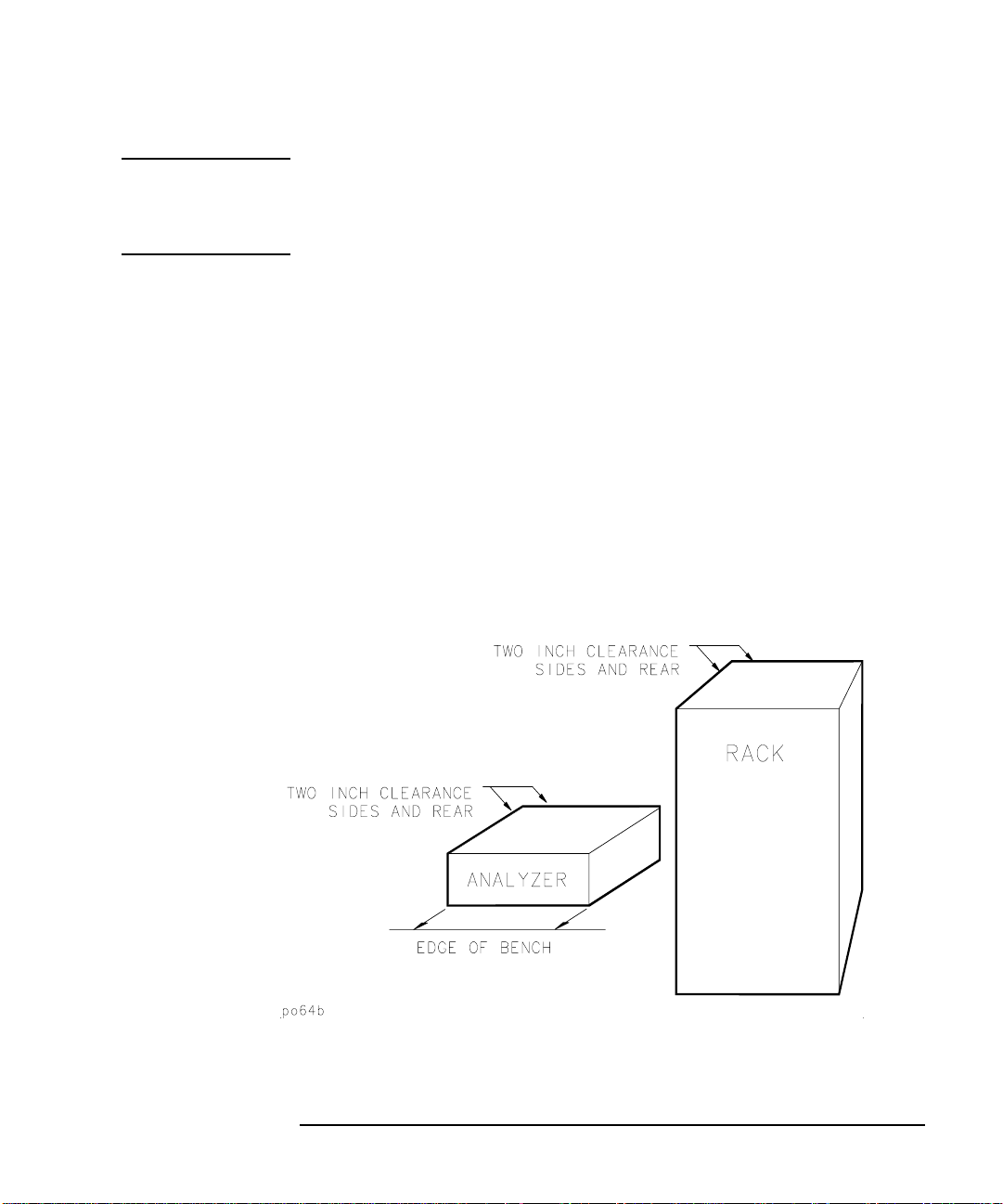
7. Ensure there are at least two inches of clearance around the sides
and back of either the stand-alone analyzer or the system cabinet.
Figure 1-3 Ventilation Clearance Requirements
ES User’s Guide 1-7
Page 24
Installing the Analyzer
Step 2. Meet Electrical and Environmental Requirements
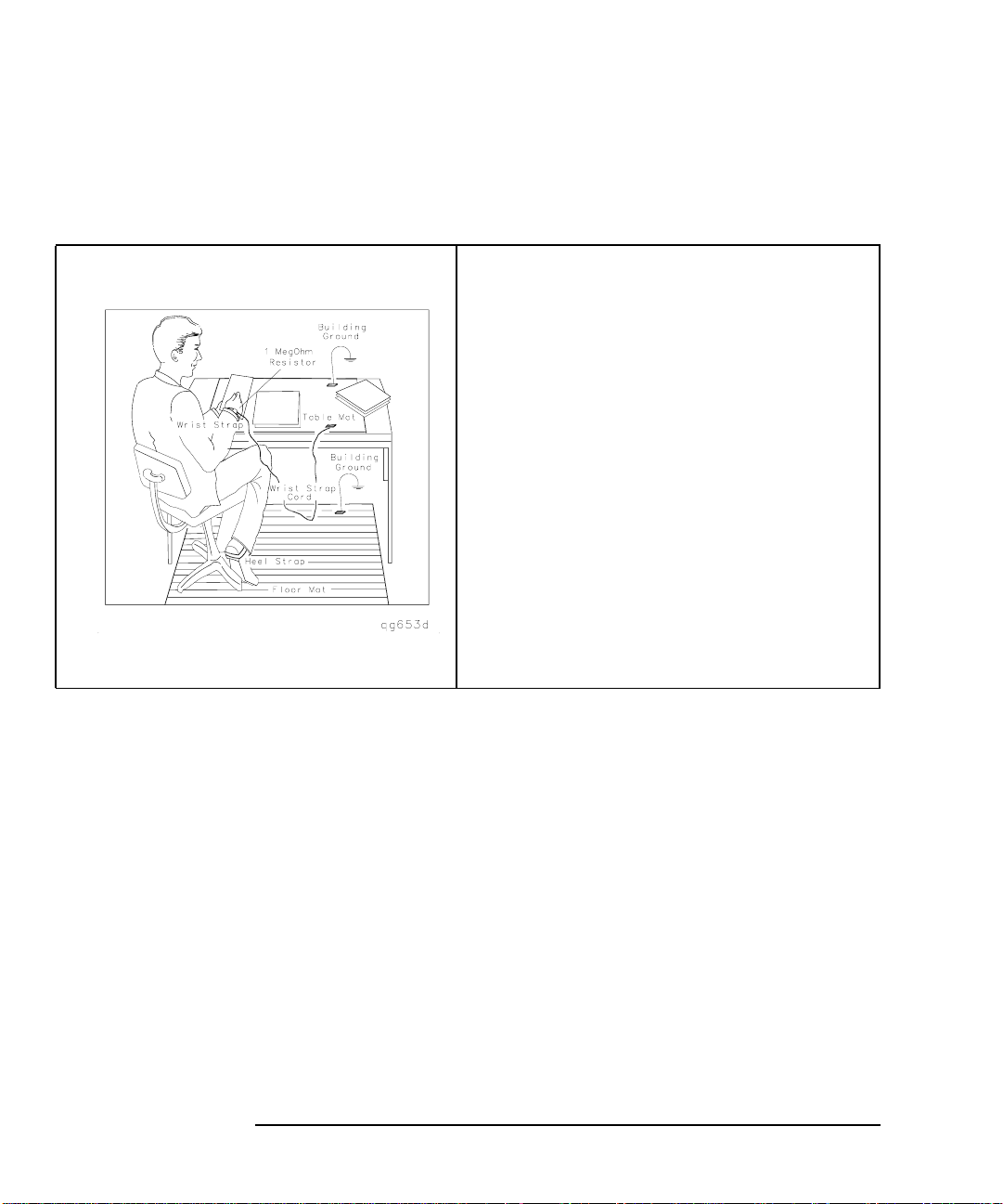
8. Set up a static-safe workstation. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can
damage or destroy components.
• table mat with earth ground wire:
HP part number 9300-0797
• wrist-strap cord with 1 Meg Ohm resistor:
HP part number 9300-0980
• wrist-strap:
HP part number 9300-1367
• heel straps:
HP part number 9300-1308
• floor mat
1-8 ES User’s Guide
Page 25

Installing the Analyzer
Step 3. Check the Analyzer Operation
Step 3. Check the Analyzer Operation
1. Turn on the line switch of the analyzer. After approximately 30
seconds, a display box should appear on the screen with the following
information:
• the model number of your analyzer (either HP 8712ES or
HP 8714ES)
• the firmware revision
• the serial number of your analyzer
• installed options
2. Verify that the serial number and options displayed on the screen
match the information on the rear panel serial label.
3. The operator's check should be performed on the analyzer to provide a
high degree of confidence that the analyzer is working properly. Refer
to Chapter 2, “Getting Started,” for instructions on how to perform
the operator's check.
ES User’s Guide 1-9
Page 26

Installing the Analyzer
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer
You can begin making measurements by simply connecting your
analyzer to an appropriate power source and turning it on. This section,
however, will explain how to connect common peripherals and
controllers, and how to install your analyzer into a rack system.
1-10 ES User’s Guide
Page 27

Installing the Analyzer
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer
Connecting Peripherals and Controllers
Figure 1-4 Analyzer Rear Panel Line Module and Selected Connectors
Refer to Figure 1-4:
• The HP-IB port is for use with computers and peripherals (printers,
plotters, etc.).
• The parallel and RS-232 (serial) ports are also for peripherals. The
parallel and serial ports can also be programmed via IBASIC for
general I/O control. See the HP Instrument BASIC User's Handbook
for information on using IBASIC.
ES User’s Guide 1-11
Page 28

Installing the Analyzer
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer
• The VIDEO OUT COLOR VGA port allows you to connect a color
VGA monitor for enhanced viewing. See “Using an External VGA
Monitor” in Chapter 4 for more information.
• The LAN ETHERTWIST connector is for connecting your analyzer to
a LAN (local area network) for control and access. See The LAN
Interface User’s Guide Supplement for information on how to use your
analyzer in a LAN.
HP-IB
Connections
An HP-IB system may be connected in any configuration as long as the
following rules are observed:
• The total number of devices is less than or equal to 15.
• The total length of all the cables used is less than or equal to 2 meters
times the number of devices connected together up to an absolute
maximum of 20 meters. For example, the maximum cable length is 4
meters if only 2 devices are involved. The length between adjacent
devices is not critical as long as the overall restriction is met.
See Figure 1-5 for different connection configurations.
1-12 ES User’s Guide
Page 29
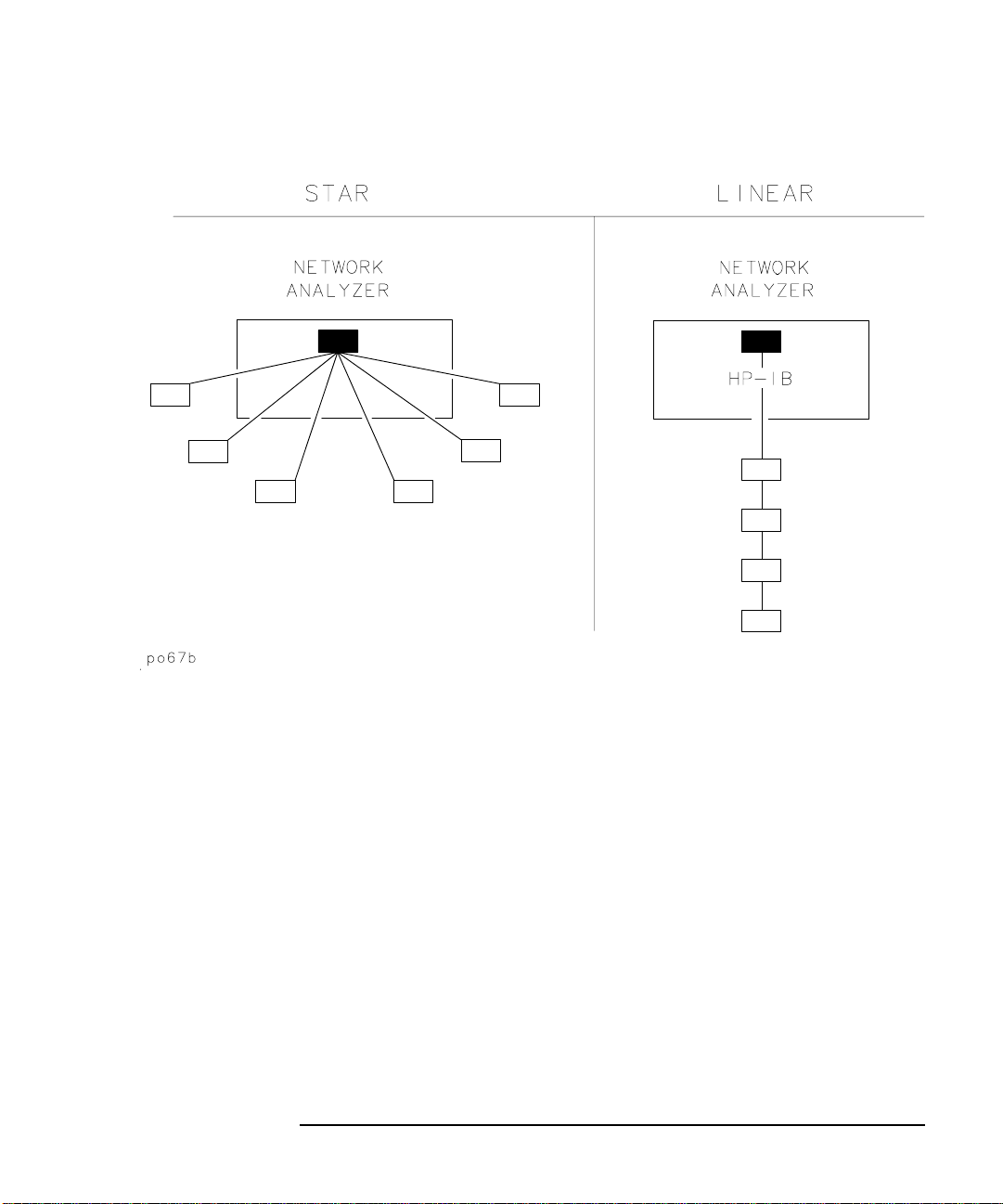
Figure 1-5 HP-IB Connection Configurations
Installing the Analyzer
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer
ES User’s Guide 1-13
Page 30
Installing the Analyzer
Select Copy Port
Select
Print/Plot HP-IB Addr
Enter
Select Copy Port
Select
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer
Table 1-1 Maximum HP-IB Cable Lengths
Instruments/Peripherals
in System
Two
Fifteen (max)
Parallel and Serial
Connections
Other Connections If you plan to use a keyboard, barcode reader, external video monitor, or
To Set HP-IB
Addresses
Parallel and serial devices often require specific cables—check their
manuals for details. Parallel cable length should not exceed 25 feet. The
analyzer may experience problems talking to a printer if this length is
exceeded. Connect the required control cables and secure them. (Tighten
the knurled screws or comparable fasteners.)
external detectors, connect them to the appropriate rear panel
connectors. See Figure 1-4, “Analyzer Rear Panel Line Module and
Selected Connectors.” Also see Chapter 7, “Front/Rear Panel,” for more
information on front and rear panel connectors.
To communicate via HP-IB, each external device must have a unique
address and the network analyzer must recognize each address. T o check
or set each external device's actual address, refer to the device's manual
(most addresses are set with switches).
The following are examples of how to check or set the device's recognized
address on the network analyzer:
Maximum HP-IB Cable
Length between Each Pair
of Devices
4 m
20 m (total)
Printer: Press . Use the
front panel knob to highlight the line that reads HP
Printer PCL HP-IB. Press . The second line
of the screen displays settings: in this case the address.
The default address is 5, however most printers are
factory set to address 1 (one). To change the recognized
address, press
Plotter: Press . Use the
front panel knob to highlight the line that reads HP
Plotter HPGL HP-IB. Press . The second
line of the screen displays settings: in this case the
address. The default address is 5 and most plotters are
factory set to address 5, so changing the address is
1-14 ES User’s Guide
HARDCOPY
number
.
HARDCOPY
Page 31

Installing the Analyzer
Print/Plot HP-IB Addr
Enter
HP-IB
HP 8712ES Address
HP 8714ES Address
Enter
Select Copy Port
Select
Select Copy Port
Select
Select Copy Port
Select
LAN Printr IP Addr
Select Copy Port
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer
probably not necessary. To change the recognized
address, press
.
NOTE Only one hardcopy HP-IB address can be set at a time. Changing the
printer address, for example, changes the plotter to the same address.
number
To Configure
Peripheral
Settings
Analyzer: Press ,
The network analyzer's address will appear (the
default is 16). To change the address, press
If your system uses serial or parallel peripherals, follow the guidelines
below to configure the system. Refer to the peripheral's manual for
correct cables and settings. The parallel and serial ports have standard
Centronics DB-25 and RS232 pinouts respectively as explained in
Chapter 7.
Serial
Devices: Press . Use the
entry controls to highlight your type of printer or
plotter, and press . If the baud rate or
handshake at the top of the screen are incorrect, use
the softkeys to change them.
Parallel
Devices: Press . Use the
entry controls to highlight your type of printer or
plotter, and press .
LAN
Printer: Press . Use the
entry controls to highlight HP LaserJet PCL5/6
PCL5 LAN, and press . If the printer IP
address at the top of the screen is incorrect, press
SYSTEM OPTIONS
, or .
number
.
HARDCOPY
HARDCOPY
HARDCOPY
to enter the correct IP address.
NOTE When is selected, the first two lines in the box at
NOTE Use a PCL5 printer for fastest hardcopies. See “Configure the Hardcopy
the top of the display screen show the current settings.
Port” on page 4-71for more information.
ES User’s Guide 1-15
Page 32

Installing the Analyzer
Step 4. Configure the Analyzer
Installing the Analyzer in a Rack
Use only the recommended rack mount kit (Option 1CM when ordered
with the analyzer or HP part number 08712-60036 when ordered
separately) with this instrument; it needs side support rails. Do not
attempt to mount it by the front panel (handles) only. This rack mount
kit allows you to mount the analyzer with or without handles.
To install the network analyzer in an HP 85043D rack, follow the
instructions in the rack manual.
CAUTION To install the network analyzer in other racks, note that they may
promote shock hazards, overheating, dust contamination, and inferior
system performance. Consult your HP customer engineer about
installation, warranty, and support details.
CAUTION VENTILATION REQUIREMENTS: When installing the product in a
cabinet, the convection into and out of the instrument must not be
restricted. The ambient temperature (outside the cabinet) must be less
than the maximum operating temperature of the instrument by 4° C for
every 100 watts dissipated in the cabinet. If the total power dissipated in
the cabinet is greater than 800 watts, then forced convection must be
used.
Place other system instruments (computer, printer, plotter) where
convenient, within the HP-IB cable length limits (see Table 1-1) or other
interface cabling limits.
1-16 ES User’s Guide
Page 33

Installing the Analyzer
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance consists of two tasks. It should be performed at
least every six months—more often if the instrument is used daily on a
production line or in a harsh environment.
Clean the CRT
Use a soft cloth and, if necessary, a mild cleaning solution.
Check the RF Front Panel Connectors
Figure 1-6 Maximum and Minimum Protrusion of Center Conductor from
Visually inspect the front panel connectors. The most important
connectors are those to which the DUT is connected, typically the RF
cable end or the PORT 1 and PORT 2 connectors. All connectors should
be clean and the center pins centered. The fingers of female connectors
should be unbroken and uniform in appearance. If you are unsure
whether the connectors are good, gauge the PORT 1 and PORT 2
connectors to confirm that their dimensions are correct.
Mating Plane
ES User’s Guide 1-17
Page 34

Installing the Analyzer
Preventive Maintenance
1-18 ES User’s Guide
Page 35

2 Getting Started
ES User’s Guide 2-1
Page 36

Getting Started
Introduction
Introduction
The HP 8712ES and HP 8714ES are easy-to-use, fully integrated RF
component test systems. Each instrument includes a synthesized source,
a wide dynamic range receiver, and a built-in test set. Controls are
grouped by functional block, and settings are displayed on the
instrument screen. This section familiarizes new users with the layout of
the front panel and the process of entering measurement parameters
into the analyzer.
Figure 2-1 Network Analyzer Front Panel Features
2-2 ES User’ s Guide
Page 37

Getting Started
Softkeys
Sweep Time
Front Panel Tour
Front Panel Tour
1 The CRT Display The analyzer's large CRT displays data, markers, limit lines, Instrument BASIC
(IBASIC) programming code, softkey menus and measurement parameters quickly and
clearly. Refer to “Display” on page 7-16 in for more information.
2 The key simplifies measurement setups. The key allows quick
BEGIN BEGIN BEGIN
and easy selection of basic measurement parameters for a user-specified class of devices
(e.g., filters, amplifiers, or mixers). For example, when making an S
transmission measurement or an S
Filter as your device type puts the analyzer into narrowband detection mode,
maximizing measurement dynamic range. In comparison, selecting Mixer as your device
type puts the analyzer into broadband detection mode, enabling frequency translation
measurements. This capability allows new users to start making measurements with as
few as four keystrokes.
3 MEAS The measure keys select the measurements for each measurement channel. The
analyzer's measurement capabilities include S11 (reflection port 1), S21 (forward
transmission), S12 (reverse transmission), S22 (reflection port 2), power, conversion loss,
and multiport selection (for use with multiport test sets).
4 SOURCE The source keys select the desired source output signal to the device under test, for
example, selecting source frequency range or output power. The source keys also control
sweep time, number of points, and sweep triggering.
5 CONFIGURE The configure keys control receiver and display parameters. These parameters include
receiver bandwidth and averaging, display scaling and format, marker functions, and
instrument calibration.
6 SYSTEM The system keys control system level functions. These include instrument preset,
save/recall, and hardcopy output. HP-IB parameters and IBASIC are also controlled with
these system keys.
7 The Numeric Keypad Use the number keys to enter a specific numeric value for a chosen parameter. Use the
key or the softkeys to terminate the numeric entry with the appropriate
.
8
HARDKEYS
9
ENTER
units. You can also use the front panel knob for making continuous adjustments to
parameter values, while the keys allow you to change values in steps.
Hardkeys are front panel keys physically located on the instrument front panel. In text,
these keys will be represented by the key name with a box around it such as:
PRESET
Softkeys are keys whose labels are determined by the analyzer's firmware. The labels are
on the screen next to the 8 blank keys, which are located along the right edge of the
analyzer’s display. In text, these softkeys will be represented by the key name with
shading behind it such as: .
reverse transmission measurement, selecting
12
forward
21
ES User’s Guide 2-3
Page 38

Getting Started
42.5
.
Entering Measurement Parameters
Entering Measurement Parameters
This section describes how to input measurement parameter information
into the network analyzer.
NOTE When entering parameters, you can use the numeric key pad, as
described in each example, or you can use the keys or the
front panel knob to enter data.
NOTE When you are instructed to enter numeric values in this manual, it often
can get cluttered and confusing to depict each key stroke. So in this
manual, numbers (no matter how many characters) are depicted inside
one keycap. F or example, if you are instructed to enter the number−42.5,
it will be depicted inside one keycap like this: . To enter this
number , the following keys need to be pressed in succession:
.
5
You can follow along with these examples by connecting the filter and
cable that were supplied with your instrument as shown in Figure 2-2.
−
− 4 2
Figure 2-2 Connect the Filter to the Analyzer
2-4 ES User’ s Guide
Page 39

Getting Started
User Preset
Factory Preset
User Preset
Factory Preset
Entering Measurement Parameters
Presetting the Analyzer
Press the key and then press either or
PRESET
. The key returns the analyzer to
user-defined preset settings you may have saved as file UPRESET.STA.
If this file doesn’t exist, you can create it by following the instructions in
the pop-up message that appears when the key is pressed. When the
key is pressed, the following major default conditions
apply:
Frequency range (HP 8712 ES) 0.3 to 1300 MHz
Frequency range (HP 8714 ES) 0.3 to 3000 MHz
Power level
Measurement Channel 1
1
0 dBm
S21 Forward Transmission
measurement
Measurement Channel 2
Off
measurement
Format Log Magnitude
Number of points 201
Sweep time Auto
NOTE The measurement parameters that you enter will be retained in the
NOTE Refer to Chapter 11, “F actory Preset State and Memory Allocation, ” for a
Scale 10 dB/div
Reference 0 dB
System Bandwidth Medium wide
1. Preset power level can be set to other than 0 dBm if desired.
See “Entering Source Power Level” on page 2-6 for more
information.
analyzer's memory when the power is turned off, and will be restored
when the power is turned back on.
comprehensive table of factory preset conditions.
ES User’s Guide 2-5
Page 40

Getting Started
Start
MHz
Stop
MHz
Center
Span
Disp Freq Resolution
Level
dBm
Level
1.6
dBm
Pwr Level at Preset
2.5
dBm
Autoscale
Scale/Div
Enter
Reference Position
Enter
Reference Level
Enter
Entering Measurement Parameters
Entering Frequency Range
1. Press the key to access the frequency softkey menu.
FREQ
2. To change the low end of the frequency range to 10 MHz, press
10
.
3. To change the high end of the frequency range to 900 MHz, press
900
.
4. You can also set the frequency range by using the and
softkeys. For instance, if you set the center frequency to
160 MHz and the span to 300 MHz, the resulting frequency range
would be 10 to 310 MHz.
NOTE When entering frequencies, be sure to terminate your numeric entry
with the appropriate softkey to obtain the correct units. If you use the
ENTER
key to terminate a frequency entry, the units default to Hz.
The default displayed frequency resolution is kHz. You can change the
resolution by pressing , and then
FREQ
selecting a new resolution.
Entering Source Power Level
1. Press the key to access the power level softkey menu.
2. To change the power level to 3 dBm, press and or
ENTER
3. To change the power level to −1.6 dBm, press
or .
ENTER
POWER
3
.
−
Scaling the Measurement Trace
4. To change the power level that will always be restored when you
preset the analyzer, press and
or . This entry does not affect the current power level.
ENTER
1. Press the key to access the scale menu.
SCALE
2. To view the complete measurement trace on the display, press
.
3. To change the scale per division to 5 dB/division, press
5
.
4. To move the reference position (indicated by the symbol on the left
side of the display) to the first division down from the top of the
display, press . Figure 2-3 shows
9
how each reference position is identified.
5. To change the reference level to 0 dB, press
0
.
2-6 ES User’ s Guide
Page 41

Figure 2-3 Reference Positions
S21 Fwd Trans
S11 Refl Port1
Getting Started
Entering Measurement Parameters
Entering the
Active
Measurement
Channel and Type
of Measurement
The and keys allow you to choose which
MEAS 1 MEAS 2
measurement channel is active, and measurement parameters for that
channel. When a particular measurement channel is active, its display is
brighter than the inactive channel, and any changes made to
measurement parameters will affect only the active measurement
channel. (Some measurement parameters cannot be independently set
on each measurement channel. F or these parameters , both c hannels will
be affected regardless of active channel status.)
1. To measure S21on measurement channel 1 and S11 on measurement
channel 2, press the following keys:
PRESET MEAS 1
MEAS 2
2. Both channels' measurements are now visible on the analyzer's
display screen. Note that the active measurement channel's (channel
2) measurement trace is brighter than the other measurement
channel's trace. Refer to Figure 2-4.
ES User’s Guide 2-7
Page 42

Getting Started
Meas OFF
More Display
Split Disp FULL split
Entering Measurement Parameters
Figure 2-4 Both Measurement Channels Active
Viewing Measurement Channels
1. To view only the measurement channel 2 S11 measurement, press
MEAS 1
2. To view both measurement channels again, press .
3. To view both measurement channels separately on a split screen,
press . Refer to
Figure 2-5, “Split Display.”
2-8 ES User’ s Guide
DISPLAY
.
MEAS 1
Page 43

Figure 2-5 Split Display
Getting Started
Entering Measurement Parameters
You have now learned how to enter common measurement parameters
and how to manipulate the display for optimum viewing of your
measurement. You can now proceed on to performing the operator's
check, or refer to Chapter 3, “Making Measurements,” for detailed
information on making specific types of measurements.
ES User’s Guide 2-9
Page 44

Getting Started
Performing the Operator's Check
Performing the Operator's Check
The operator's check should be performed when you receive your
instrument, and any time you wish to have confidence that the analyzer
is working properly. The operator's check does not verify performance to
specifications, but should give you a high degree of confidence that the
instrument is performing properly if it passes.
The operator's check consists of making the following measurements
with the cable that was supplied with your analyzer:
•S21 and S
• broadband power
•S11 and S
•S11 and S22 (with a 50 Ω or 75 Ω load, instead of the cable)
12
22
Equipment List
To perform the operator's check you will need the following:
• A known good cable such as the one that was supplied with your
analyzer. The cable you use should have ≤0.5 dB of insertion loss up
to 1.3 GHz and ≤0.75 dB of insertion loss from 1.3 to 3.0 GHz.
• A known good load (> 40 dB return loss) that matches the test port
impedance of your analyzer such as one from calibration kit
HP 85032B/E (50 Ω) or HP 85036B/E (75 Ω).
2-10 ES User’s Guide
Page 45
Getting Started
User Preset
Factory Preset
Enter
dBm
Default Response
Performing the Operator's Check
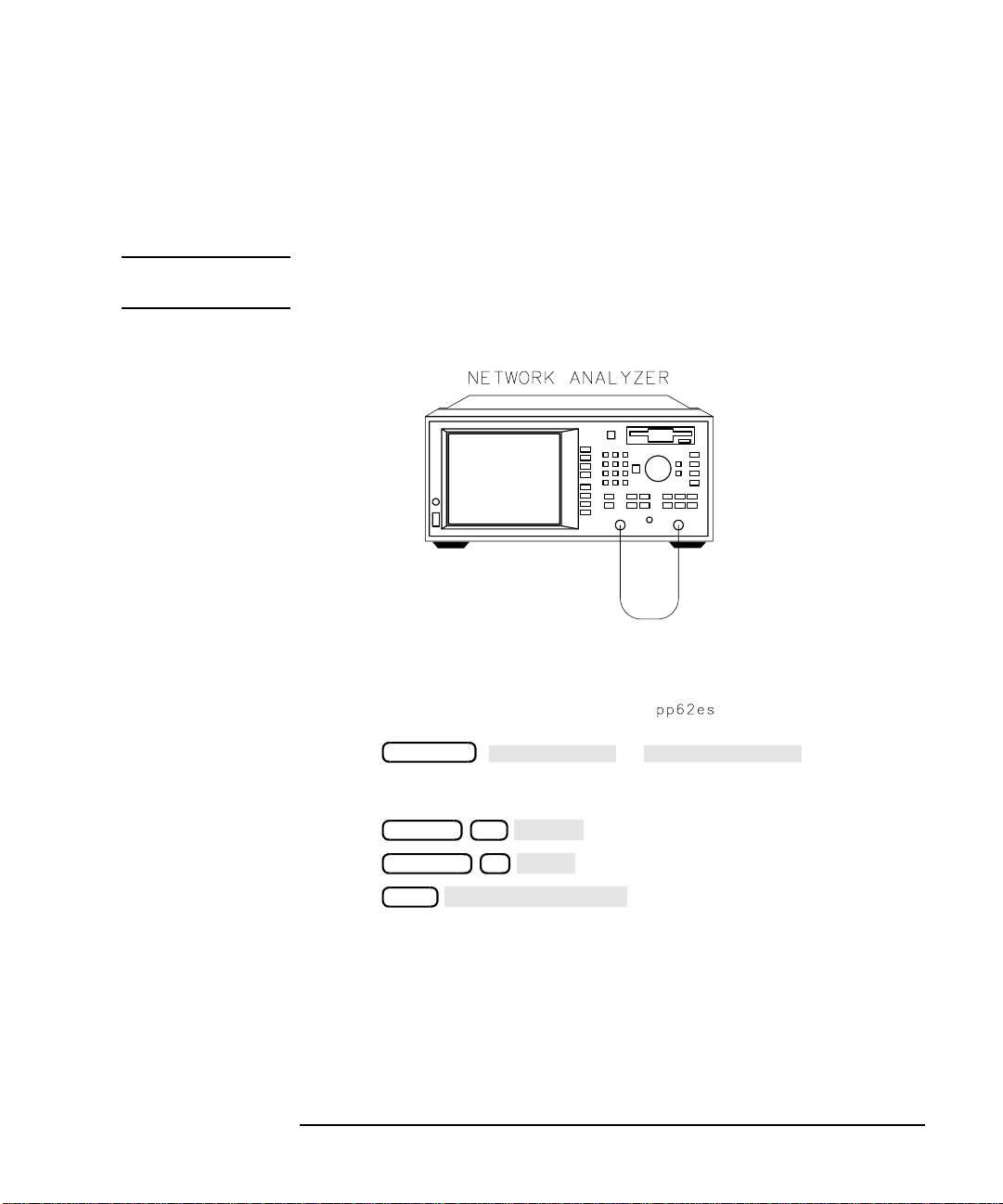
Make S21 and S12 Transmission Measurements
1. Connect the equipment as shown in Figure 2-6. Use a known good
cable such as the one that was supplied with your analyzer.
NOTE The quality of the cable will affect these measurements; make sure you
use a cable with the characteristics described in “Equipment List.”
Figure 2-6 Equipment Setup for Performing the Operator’s Check
2. Press ( or ). The
instrument is automatically set up for an S21 measurement on
measurement channel 1.
3. Press .
4. Press .
5. Press .
6. Verify that the data trace falls within ±0.5 dB of 0 dB. See Figure 2-7
for a typical HP 8714ES result. The HP 8712ES should look similar,
but end at 1300 MHz.
ES User’s Guide 2-11
PRESET
SCALE .1
POWER 0
CAL
Page 46

Getting Started
S12 Rev Trans
Default Response
Performing the Operator's Check
Figure 2-7 Verify S21 Transmission Measurement
7. Press .
8. Press .
MEAS 1
CAL
9. Verify that the data trace falls within ±0.5 dB of 0 dB. See Figure 2-7
for a typical HP 8714ES result. (Although this figure is from an S
21
measurement, the results of your S12 measurement should look
similar.) The HP 8712ES should look similar, but will end at
1300 MHz.
2-12 ES User’s Guide
Page 47

Getting Started
More
Power
Start
MHz
Enter
dBm
Performing the Operator's Check
Make a Broadband Power Measurement
1. Leave the cable connected to the analyzer as shown in Figure 2-6.
NOTE The quality of the cable will affect these measurements; make sure you
use a cable with the characteristics described in “Equipment List” on
page 2-10.
2. Press
3. Press (unless done in the previous
measurement).
4. V erify that the data trace is within±2 dB of 0 dBm. See Figure 2-8 for
a typical HP 8714ES result. The HP 8712ES should look similar, but
end at 1300 MHz.
Figure 2-8 Verify Broadband Power Measurement
MEAS 1
SCALE 1
POWER 0
FREQ
.
10
ES User’s Guide 2-13
Page 48

Getting Started
User Preset
Factory Preset
S11 Refl Port1
Enter
dBm
Default 1-Port
Performing the Operator's Check
Make S11 and S22 Reflection Measurements
1. Leave the cable connected to the analyzer as shown in Figure 2-6.
NOTE The quality of the cable will affect these measurements; make sure you
use a cable with the characteristics described in “Equipment List”.
2. Press ( or )
3. Press
4. Press .
5. Press .
6. Verify that the data trace falls completely below −16 dB. See
Figure 2-9 for a typical HP 8714ES result. The HP 8712ES should
look similar, but end at 1300 MHz.
PRESET
.
SCALE 10
POWER 0
CAL
MEAS 1
2-14 ES User’s Guide
Page 49

Figure 2-9 Verify S11 Reflection Measurement
S22 Refl Port2
Default 1-Port
Getting Started
Performing the Operator's Check
7. Press .
8. Press .
9. Verify that the data trace falls completely below −16 dB. See
Figure 2-9 for a typical HP 8714ES result. (Although this figure is
from an S11 measurement, the results of your S22 measurement
should look similar.) The HP 8712ES should look similar, but will end
at 1300 MHz.
10.Disconnect the cable and connect a known good load to port 2 as
shown in Figure 2-10.
ES User’s Guide 2-15
MEAS 1
CAL
Page 50

Getting Started
Reference Level
S11 Refl Port1
Performing the Operator's Check
Figure 2-10 Connect the Load to Port 2
11.Verify that the data trace falls below −30 dB. If the data trace is off
the screen, press and the key
until the trace moves up onto the screen.
SCALE
12.Disconnect the load from port 2 and connect it to port 1 as shown in
Figure 2-11.
Figure 2-11 Connect the Load to Port 1
13.Press .
2-16 ES User’s Guide
MEAS 1
Page 51

Getting Started
Reference Level
Trigger
Hold
Performing the Operator's Check
14.Verify that the data trace falls below −30 dB. If the data trace is off
the screen, press and the key
until the trace moves up onto the screen.
This concludes the operator's check. However, further confidence can be
obtained by performing the following:
• Measure a known filter to verify that its measured response is the
same as is expected. (A 175 MHz filter is supplied with the analyzer.)
Verify both the frequency accuracy and noise floor.
• Check broadband response with the filter using conversion-loss mode
(same as B*/R*).
• If the analyzer's frequency accuracy is critical for your application,
verify a CW frequency using a frequency counter. Verify to ±.005%
accuracy (for example, ± 2500 Hz at 500 MHz). Ensure that the
analyzer is placed in trigger-hold mode (press
) to measure frequencies.
SCALE
MENU
If the Analyzer Fails the Operator's Check
First, repeat the operator's check using a different cable and load to
eliminate these as a possible cause of failure. If your analyzer does not
meet the criteria in the operator's check, your analyzer may need
adjustment or servicing. Contact any Hewlett-Packard sales or service
office for assistance. Refer to Table 9-10, “Hewlett-Packard Sales and
Service Offices,” inChapter 9 for the nearest office. Before shipping your
analyzer, fill out and attach the blue repair tag, located at the back of the
analyzer’s Service Guide.
ES User’s Guide 2-17
Page 52

Getting Started
Performing the Operator's Check
2-18 ES User’s Guide
Page 53

3 Making Measurements
ES User’s Guide 3-1
Page 54

Making Measurements
Introduction
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of basic network analyzer
measurement theory, a section explaining the typical measurement
sequence, a segment describing the use of the key, and detailed
examples of the following measurements:
• “Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-P ort Calibration” on page 3-19
• “Measuring S21 Forw ard Transmission using an Enhanced Response
Calibration” on page 3-41
• “Measuring S11 Reflection Port 1 using a One-Port Calibration” on
page 3-48
• “Making a Power Measurement using Broadband Detection” on
page 3-56
• “Measuring Conversion Loss” on page 3-61
• “Making Measurements with the Auxiliary Input” on page 3-67
BEGIN
• “Measuring Group Delay” on page 3-69
• “Measuring Impedance using the Smith Chart” on page 3-73
• “Measuring Impedance Magnitude” on page 3-80
3-2 ES User’ s Guide
Page 55

Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
This section provides a basic overview of how the network analyzer
measures devices. The analyzer has an RF signal source that produces
an incident signal that is used as a stimulus to the device under test.
Your device responds by reflecting a portion of the incident signal and
transmitting the remaining signal. If the device is passive, some of the
transmitted signal will be absorbed, indicating a “lossy” device. If the
device is active, the transmitted signal may be amplified, indicating that
the device has gain. Figure 3-1 shows how a device under test (DUT)
responds to an RF source stimulus.
Figure 3-1 DUT Response to an RF Signal
Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
ES User’s Guide 3-3
Page 56

Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
Refer to Figure 3-2, “Simplified Block Diagram,” for the following
discussion regarding detection schemes and modes. The forward
transmitted signal (routed to input B) and the reflected signal (input A)
are measured by comparison to the incident signal. The reverse
transmitted signal (routed to input A) and the reflected signal (input B)
are also measured by comparison to the incident signal. The analyzer
couples off a small portion of the incident signal to use as a reference
signal (routed to input R). Sweeping the source frequencies, the analyzer
measures and displays the response of your test device.
Figure 3-2 Simplified Block Diagram
3-4 ES User’ s Guide
Page 57

Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
Refer to Figure 3-3, “Block Diagram,” for the following discussion. The
network analyzer receiver has two signal detection modes:
• broadband detection mode
• narrowband detection mode
There are two internal broadband detectors: B* and R*. External
broadband detectors can also be used when connected to the X and Y
ports on the rear panel of the analyzer. When the network analyzer is in
the broadband detection mode, it measures the total power of all signals
present at these measurement ports, independent of signal frequency.
This enables the characterization of frequency translation devices such
as mixers, receivers, and tuners, where the RF input and output
frequencies are not the same. Figure 3-3 labels the transmitted signal for
broadband detection input as B*, and the reference signal as R*.
When the network analyzer is in the narrowband detection mode, the
receiver is tuned to the source frequency. This technique provides greater
dynamic range by decreasing the receiver's bandwidth. Figure 3-3 shows
receiver B as the narrowband detection input for the forward
transmitted signal and the reverse reflected signal. Receiver A acts as
the narrowband detection input for the reverse transmitted signal and
the forward reflected signal. Receiver R is shown as the narrowband
detection input for the reference signal.
ES User’s Guide 3-5
Page 58

Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
Figure 3-3 Block Diagram
3-6 ES User’ s Guide
Page 59

Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
The following table shows the correlation between different types of
measurements, input channels and signals.
Measurement Detection Mode
S21 Forw ard Transmission Narrowband B/R transmitted/
S12 Reverse Transmission Narrowband A/R transmitted/
S11 Reflection Port 1 Narrowband A/R reflected/
S22 Reflection Port 2 Narrowband B/R reflected/
Power Broadband B* transmitted Forward
Conversion Loss Broadband B*/R* transmitted/
Input
Detectors
Input
Signals
incident
incident
incident
incident
incident
Source
Direction
Forw ard
Reverse
Forward
Reverse
Forward
The Measurement Display Icon
The measurement display icon, located in the lower right corner of the
analyzer’s display, indicates the signal path direction of the current
measurement. The look of this icon will vary, depending on the type of
measurement, calibration, and sweep time that have been selected. The
following table contains the icons, along with an explanation of each. (If
both measurement channels are active, you may see variations of these
icons.)
ES User’s Guide 3-7
Page 60

Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
Measurement
Display Icon
Icon Appears on the Analyzer’s Display
When Measuring:
Any of the four S-parameters (with two-port
calibration) when sweep time is less than 3.0
seconds.
Either of the two forward S-parameters (with
two-port calibration) when sweep time is more
than 3.0 seconds.
Either of the two reverse S-parameters (with
two-port calibration) when sweep time is more
than 3.0 seconds.
S11 (not with two-port calibration) or calibration
standards.
1
S22 (not with two-port calibration) or calibration
standards.
1
S21 or fault location/SRL (not with two-port
calibration), power, conversion loss, or
calibration standards.
1
S12 or fault location/SRL (not with two-port
calibration), or calibration standards.
1
1. When calibration standards are being measured, a “Cx” is displayed
on the annotation line, indicating non-corrected, non-simultaneous
measurements are being made.
3-8 ES User’ s Guide
Page 61

Measuring S-Parameters
Figure 3-4 Measuring S-Parameters
Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
Refer to Figure 3-4 for the following discussion of S-parameters.
S-parameters are used to completely describe the electrical behavior of a
linear two-port device that operates at high frequencies. An N-port
device has N2 S-parameters. So, a two-port device has four S-parameters .
The numbering convention for S-parameters is that the first number
following the “S” is the port where energy emerges, and the second
number is the port where energy enters. So, S21 is a measure of power
coming out port 2 as a result of applying an RF stimulus to port 1. When
the numbers are the same (e.g., S11), it indicates a reflection
measurement.
ES User’s Guide 3-9
Page 62

Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
NOTE When making any type of S-parameter measurement with a two-port
calibration, the analyzer takes both a forward and a reverse sweep while
collecting data.
S11 and S21 are determined by measuring the magnitude and phase of
the incident, reflected, and transmitted signals when the output is
terminated in a perfect Z0 (a load that equals the characteristic
impedance of the test system). This condition guarantees that a2 is zero.
S11 is equivalent to the input complex reflection coefficient or impedance
of the DUT, and S21 is the forward complex transmission coefficient.
Likewise, by placing the source at port 2 and terminating port 1 in a
perfect load (making a1 zero), S22 and S12 measurements can be made.
S22 is equivalent to the output complex reflection coefficient or output
impedance of the DUT, and S12 is the reverse complex transmission
coefficient.
The accuracy of S-parameter measurements depends greatly on how
good a termination we apply to the port not being stimulated. Anything
other than a perfect load will result in a1 or a2 not being zero (which
violates the definition for S-parameters). When the DUT is connected to
the test ports of a network analyzer and you don’t account for imperfect
test port match, you haven’t satisfied the condition of a perfect
termination. For this reason, two-port error correction, which corrects for
source and load match, is very important for accurate S-parameter
measurements (two-port correction is covered in more detail in
Chapter 6, “Calibrating for Increased Measurement Accuracy”).
3-10 ES User’s Guide
Page 63

Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
Attenuation and Amplification in a
Measurement Setup
The measurement setup that you use may require attenuation or
amplification. The following sections describe when to use them.
When to Use Attenuation
• For accurate measurements, use external attenuation to limit the
power at the input port to +10 dBm (for narrowband-detection
measurements) or +16 dBm (for broadband-detection measurements).
CAUTION Always use attenuation on the input port if your test device's output
power exceeds the receiver damage limit of +26 dBm or ±30 Vdc.
• For information on how to reduce mismatch errors, see “Reducing
Mismatch Errors” on page 5-15.
When to Use Amplification
• For accurate measurements, amplification may be needed on the
analyzer's output port. Use amplification when your test device
requires input power that exceeds the analyzer's maximum specified
output power.
NOTE If you use an amplifier between the analyzer’s output port and your DUT,
you won’t be able to measure the input match (S11) of your DUT.
The maximum specified output power is dependent upon the option
configuration of your analyzer as well as the frequency range of your
test setup. It ranges from +4 to +13 dBm. See Chapter 9,
“Specifications,” to determine the maximum specified output power of
your analyzer.
ES User’s Guide 3-11
Page 64

Making Measurements
More Cal
System Z0
50Ω 75
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
When to Change the System Impedance
Your analyzer has a system characteristic impedance of either 50 or 75
ohms, yet may be changed to the alternate impedance. If using
minimum-loss pads for impedance conversions, the alternate impedance
should be selected so that the measurement results are displayed
relative to the conversion impedance.
For example, if you have a 50 ohm instrument and are making 75 ohm
measurements, you may be using 50 to 75 ohm minimum-loss pads.
Measurement results can be reported relative to 75 ohms, not 50 ohms, if
the alternate system impedance is selected. This includes marker
readouts, Smith chart results, or SRL impedance computations
(Option 100).
To change the system impedance, press the following keys on the
analyzer:
CAL
οr
The built-in cal kit selections will be converted to the selected system
impedance.
3-12 ES User’s Guide
Ω
Page 65

Making Measurements
Measuring Devices with Your Network Analyzer
The Typical Measurement Sequence
A typical measurement consists of performing four major steps:
Step 1. Enter the
Measurement
Parameters
Step 2. Calibrate
the Analyzer
Step 3. Connect
the Equipment
Step 4. View and
Interpret the
Measurement
The easiest way to set up the analyzer's parameters for a simple
measurement is to use the key. When this key is selected, the
analyzer automatically sets up a generic set of parameters to match the
device type you choose. (See “Using the BEGIN Key to Make
Measurements” next, in this chapter.)
For measurements that require you to enter your own specific
measurement parameters (such as frequency range, source power level,
number of points, and sweeptime), use the instrument’s keys to enter
your selections rather than using the key. See the
measurement examples, located later in this chapter.
Your analyzer can provide highly accurate measurements without
performing any additional user-defined calibrations if certain conditions
are met. Chapter 6, “Calibrating for Increased Measurement Accuracy,”
explains when additional user-defined calibration is necessary.
Connect the DUT and any other required test equipment. See the
measurement examples later in this chapter for typical equipment setup
configurations.
Use the , , and functions to optimize
viewing of the measurement results.
Markers, limit lines, and hard copies of the display are common means of
interpreting measurement results.
SCALE DISPLAY FORMAT
BEGIN
BEGIN
See Chapter 4, “Using Instrument Functions,” for detailed information
on using instrument functions to view and interpret your measurements.
ES User’s Guide 3-13
Page 66

Making Measurements
Using the BEGIN Key to Make Measurements
Using the BEGIN Key to Make
Measurements
Figure 3-5 The BEGIN Key
The key allows you to quickly and easily configure the analyzer
BEGIN
(from the condition) to measure the following:
• amplifiers
• filters
• broadband passive devices (a cable, for example)
• mixers
• cable fault location and structural return loss (Option 100 only)
Configuring basic measurements from the key helps you
ensure correct instrument setup. The analyzer guides you through the
initial steps and configures itself for the device type you select.
3-14 ES User’s Guide
PRESET
BEGIN
Page 67

Making Measurements
Using the BEGIN Key to Make Measurements
BEGIN Key Overview
The key sets up a generic instrument state for the testing of
BEGIN
various types of devices.
The key has two different behaviors, depending on whether
BEGIN
you are selecting a new device type, or a new measurement type.
Selecting a New
Device
Selecting a New
Measurement
When you use the key to select a new device type and
measurement, the analyzer does the following:
• presets the analyzer (except for external reference parameters, and
trigger mode)
• takes a sweep
• autoscales the measurement
• places a marker on the maximum or minimum point (depending on
the type of measurement)
• makes the marker active
• modifies the sweep time (Option 100 only)
See Table 3-1, “Measurement Configurations from the BEGIN Key,” for a
table of parameters for each measurement type.
Once you have selected your device, you can use the softkeys to select the
measurement you wish to make. When you select a new measurement, a
preset is not done. It is assumed that you are simply changing
measurement types and that you may have already changed some of the
analyzer's parameters (such as frequency, power, etc.) for your DUT. In
this situation, you would probably not want these parameters changed
for subsequent measurements.
BEGIN
NOTE If the new measurement selected is a broadband measurement such as
power, or conversion loss, the start frequency is limited to at least
10 MHz. Therefore, if your customized setup contains a start frequency
below 10 MHz and you choose power, or conversion loss, the start
frequency will be changed to 10 MHz. The stop frequency will remain
unchanged, unless it was set to below 10 MHz.
The BEGIN Key
and Measurement
Channels
The key is designed to work when measurement channel 1 is
BEGIN
active. However, it does change the mode of measurement channel 2 as
well.
ES User’s Guide 3-15
Page 68

Making Measurements
User Preset
Factory Preset
S11 Refl Port1
S21 Fwd Trans
S12 Rev Trans
S22 Refl Port2
Amplifier
Filter
Broadband Passive
Mixer
Power
Power
Amplifier
Conversion Loss
Conversion Loss
Mixer
SRL
SRL
Cable
Using the BEGIN Key to Make Measurements
If measurement channel 2 is active when the key is used to
select a new device type, measurement channel 2 is turned off, and
measurement channel 1 is made active.
If measurement channel 2 is active when the key is used to
select a new measurement type, measurement channel 2 will be left on
and active. However, the analyzer then proceeds to set up channel 1 for
the requested measurement type, even though channel 2 is the active
channel.
BEGIN
BEGIN
Using the BEGIN Key to Configure
Measurements
This procedure shows you how to configure the network analyzer for
measurements.
1. Press ( or ). Presetting
the instruments puts it into a known state with predefined
parameters.
2. Press and then use a softkey to select the type of device that
you will be measuring (amplifier, filter, broadband passive device,
mixer, or cable—Option 100 only).
3. Connect your test device to the network analyzer.
4. Use the softkeys to select the type of measurement you want to make:
PRESET
BEGIN
• Press , , , or
if you want to measure a particular
S-parameter. (S-parameter selections are under the ,
, , and menus.)
• Press if you want to measure the RF power of a device.
(The selection is under the menu.)
• Press if you want to measure the conversion
loss of a device. (The selection is under the
menu.)
• Press (Option 100 only) if you want to measure the
structural return loss of a cable. (The selection is under the
menu.)
3-16 ES User’s Guide
Page 69

Making Measurements
Fault Location
Fault Location
Cable
SRL
Fault Location
Using the BEGIN Key to Make Measurements
• Press (Option 100 only) if you want to measure
the cable fault location. (The selection is under
the menu.)
Depending on your selection, the analyzer is set to one of the following
configurations. (The and configurations are
discussed in the Option 100 User's Guide Supplement.)
Table 3-1 Measurement Configurations from the BEGIN Key
Frequency
Range
(HP 8712ES)
Frequency
Range
(HP 8714ES)
Measurement
Channel 1
Detection
Mode
Measurement
Paths
S11 Refl Port 1 S21 Fwd Trans S12 Rev Trans S22 Refl Port 2
0.300 MHz to
1300 MHz
0.300 MHz to
3000 MHz
S
11
Narrowband Narrowband Narrowband Narrowband Broadband
A/R B/R A/R B/R B* B*/R*
0.300 MHz to
1300 MHz
0.300 MHz to
3000 MHz
S
21
0.300 MHz to
1300 MHz
0.300 MHz to
3000 MHz
S
12
0.300 MHz to
1300 MHz
0.300 MHz to
3000 MHz
S
22
Power
10 MHz to
1300 MHz
10 MHz to
3000 MHz
Power Conversion
Internal
Conversion
Loss
10 MHz to
1300 MHz
10 MHz to
3000 MHz
Loss
Broadband
Internal
The following measurement configurations apply to all of the
measurement types in the previous table:
Power Level Factory preset power level
Measurement
Channel 2
Off
Format Log Mag
Number of Points 201
1
Sweep Time Mode Auto
Sweep Triggering Continuous
Averaging Off
System Bandwidth Medium Wide
1. Factory preset power level is user-defined by using the “Pwr
Level at Preset” softkey. The factory default is 0 dBm.
ES User’s Guide 3-17
Page 70

Making Measurements
Autost
User BEGIN
User BEGIN
Recall Program
User BEGIN on OFF
User BEGIN
User BEGIN
User BEGIN
User BEGIN
Using the BEGIN Key to Make Measurements
AUTOST files
When the analyzer's power is turned on, it first checks for an IBASIC
autostart file (AUTOSTART.BAS) on the non-volatile RAM disk and then
on the 3.5” disk. If found, the file is loaded and run. This feature
simplifies the task of turning on an automated test station at the
beginning of a working day or test session. To manually load and run an
autostart file, press .
BEGIN
The User BEGIN Function
The softkey gives you the capability to redefine the
BEGIN
key to define macros such as:
• softkeys to implement fast save/recall
• softkeys to implement most-used functions or features
• softkeys to implement often-used features that involve a number of
Macros must be defined with an IBASIC program. If no
program is currently installed (either by AUTOST or
program.
key menu and install user-defined macro functions. Use this
steps
), the analyzer will automatically create a default
selects the key menu to "user" mode
when on, and to normal operation when off.
Once you have changed the mode to on, the same menu
will be displayed for subsequent key presses of the hardkey.
(This is not true if your IBASIC program has changed. If the program
has changed, the mode is reset to off.)
Use of the function does not restrict access to any
normally available instrument feature (such as marker functions), nor
does this key affect sweep update rates.
Refer to the IBASIC example programs provided on the Example
Programs Disk for implementation requirements. Keystroke recording
may be used to modify or update programs.
See the Automating Measurements User’s Guide Supplement for more
information.
3-18 ES User’s Guide
BEGIN
BEGIN
Page 71

Making Measurements
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Measuring S-Parameters using a
Two-Port Calibration
This section describes how to perform a two-port calibration. Once done,
this calibration can be used with all types of S-parameter measurements.
It should be noted that other types of error correction, though not as
accurate as a two-port calibration, allow faster measurement speed.
Therefore, if measurement speed is of more importance than highest
accuracy, you may want to use a different type of error correction than
the two-port calibration. See the table below for a list of all possible
calibration choices for S-parameter measurements.
TIP An optimum calibration is critical for achieving best measurement
accuracy. Refer to Chapter 6, “Calibrating for Increased Measurement
Accuracy,” for detailed information about all of the various aspects of
calibration.
Table 3-2 Calibration Choices for S-Parameter Measurements
Measurement Type Calibration Choices
S11 Refl Port 1 or
S22 Refl Port 2
S21 Fwd Trans or
S12 Rev Trans
ES User’s Guide 3-19
Default 1-Port
Default 2-Port
User 1-Port
User 2-Port
Default Response
Default 2-Port
User Response:
Response
Response & Isolation
Enhanced Response
User 2-Port
Normalize
Page 72

Making Measurements
User Preset
Factory Preset
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Enter the Measurement Parameters
1. Press the following keys on the analyzer:
PRESET
2. Press the softkey for any type of S-parameter measurement.
NOTE This example measurement uses the default instrument parameters for
the S-parameter measurement you selected. If your particular
measurement requires different parameters (such as frequency range,
source power level, number of data points, and sweeptime), enter them
now.
( or )
MEAS 1
Perform a User Two-Port Calibration
This example describes how to perform a two-port calibration. This
calibration uses known standards to correct for directivity, source match,
load match, and frequency response errors when using narrowband
detection. To correct for errors caused by crosstalk, refer to the definition
of a user two-port calibration in Chapter 6.
When you perform a two-port calibration, the analyzer performs
correction at each data point across the selected frequency band. The
default number of data points per sweep is 201, but you can select any
number between 3 and 1601. Interpolation recalculates the error
correction array for reduced frequency spans. If the frequency span is
increased, the calibration is invalidated and the default two-port
calibration is automatically restored.
To perform a two-port calibration, you will need one of the following
calibration kits depending on the nominal impedance of your analyzer:
3-20 ES User’s Guide
Page 73

Making Measurements
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Cal Kit Model
Number
HP 85039B 75 Ω type-F ✓✓
HP 85036B 75 Ω type-N ✓✓
HP 85036E 75 Ω type-N ✓
HP 85032B 50 Ω type-N ✓✓
HP 85032E 50 Ω type-N ✓
HP 85031B 50 Ω APC-7 N/A N/A
HP 85033D 50 Ω 3.5 mm ✓✓
HP 85038A 50 Ω 7-16 ✓✓
HP 85038F 50 Ω 7-16 ✓
HP 85038M 50 Ω 7-16 ✓
Impedance
Connector
Type
For Use
with Male
Test Ports
For Use
with Female
Test Ports
NOTE By convention, cal kit labels in the analyzer indicate the sex of the port
with which they are used. For example, the default cal kit for the
analyzer is type-N female because the front panel RF ports are female
(the calibration standards, in turn, have male connectors).
Calibrating for Insertable Devices
When measuring a through-standard during calibration, the test ports
normally mate directly together. For example, two cables with the
appropriate connectors can be connected directly without a
through-adapter, resulting in a zero-length through-standard. An
insertable device is a device that can be inserted in place of a zero-length
through-standard. It has the same type of connector on each port, but
with a different sex, or the same type of sexless connector on each port
(APC-7, for example).
ES User’s Guide 3-21
Page 74

Making Measurements
More Cal
Cal Kit
Type-N(m)
Prior Menu
Prior Menu
User 2-Port
User 2-Port
Isolation on OFF
Measure Standard
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Chapter 6 provides detail about when a user-defined calibration is
necessary, and information about other calibrations available for
S-parameter measurements. If you wish to perform a two-port
calibration on your insertable device, execute the following steps:
1. Select calibration kits for both ports: since port 1 will use the default
calibration kit (female type-N), this selection is already made for you.
For port 2, press and use the front
panel knob or the keys to highlight Port 2 in the
display’s table. Press .
2. Press . If
you want to correct for crosstalk errors, toggle the
refer to the definition of a user two-port calibration in Chapter 6).
3. When the instrument prompts you to connect a through cable, insert
a cable with type-N(m) connectors between port 1 and port 2 as
shown in the Figure 3-6. Press . When done,
disconnect the cable from port 1 but leave it connected to port 2.
4. The instrument prompts you to connect three standards (open, short,
and load) to port 1 as shown in the graphic on the next page.
CAL
key ON (for more information about isolation,
Figure 3-6 Through-Cable Connection
3-22 ES User’s Guide
Page 75

Making Measurements
Measure Standard
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Port 1: Open, Short, Load Connections Port 2: Open, Short, Load Connections
NOTE Changing sweep frequencies (and other source parameters) may affect
5. Press after connecting each standard.
6. Next, the instrument prompts you to connect three standards (open,
short, and load) to port 2. Instead of connecting the standards directly
to port 2, connect them to the open end of the cable. This end of the
cable will become the calibrated port 2 for measurements. See the
graphic above.
7. The analyzer will measure each standard and then calculate new
calibration coefficients. The message "Calibration complete."
will appear for a few seconds when the analyzer is done calculating
the new error correction array.
your calibration. See Chapter 6 for more information.
ES User’s Guide 3-23
Page 76

Making Measurements
Autoscale
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Connect the DUT.
Figure 3-7 Equipment Setup for an S-Parameter Measurement of an
Insertable Two-Port Device
View and Interpret the S-Parameter Measurement
Results.
1. To view the entire measurement trace on the display, press
2. To interpret the measurement, refer to other S-parameter
measurement examples later in this chapter.
3-24 ES User’s Guide
SCALE
Page 77

Making Measurements
More Cal
Cal Kit
Type-N(m)
Type-N(m)
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Calibrating for Noninsertable Devices
A noninsertable device is one that cannot be inserted in place of a
zero-length through-standard. It has the same connectors on each port
(type and sex) or has a different type of connector on each port (SMA on
one port, and type-N on the other, for example). The following two
calibration methods are available for noninsertable devices:
• swap equal adapters
• modify the calibration kit definition of the through standard
Method A: Swap Equal Adapters.
In the following example, the noninsertable device is type-N , with female
input and output connectors.
With this method, you use two precision matched adapters which are
“equal.” To be equal, the adapters must have the same match,
characteristic impedance (Z0), insertion loss, and electrical delay. The
adapters in most HP calibration kits have matched electrical lengths,
even if the physical lengths appear different.
NOTE For analyzers with 50 ohm input impedance only: in the 50 ohm type-N
calibration kit (HP 85032B), there are four equal adapters: two
APC-7 to type-N(f), and two APC-7 to type-N(m). To create adapter A in
the following example, connect an APC-7-to-type-N(f) adapter with an
APC-7 to type-N(m) adapter. To create adapter B, connect two
APC-7 to type-N(m) adapters.
NOTE By convention, cal kit labels in the analyzer indicate the sex of the port
with which they are used. For example, the default cal kit for the
analyzer is type-N female because the front panel RF ports are female
(the calibration standards, in turn, have male connectors).
1. Connect a test cable with type-N(m) connectors to port 2.
2. To select calibration kits for both ports, press
, and use the front panel knob or the keys to
highlight Port 1 in the display’s table. Press . Now,
highlight Port 2 and again press .
3. Connect adapter A (type-N(m) to type-N(f)) to port 1.
ES User’s Guide 3-25
CAL
Page 78

Making Measurements
Prior Menu
Prior Menu
User 2-Port
User 2-Port
Isolation on OFF
Measure Standard
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
4. Press . If
you want to correct for crosstalk errors, toggle the
key ON (for more information about isolation,
refer to the definition of a user two-port calibration in Chapter 6).
5. When the instrument prompts you to connect a through cable,
connect the port 2 test cable to adapter A on port 1 as shown in
Figure 3-8. Press .
Figure 3-8 Through-Cable Connection
3-26 ES User’s Guide
Page 79

Making Measurements
Measure Standard
Measure Standard
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Port 1: Open, Short, Load Connections Port 2: Open, Short, Load Connections
6. Remove adapter A, and place adapter B (type-N(m) to type-N(m)) on
port 1. Adapter B becomes the effective test port.
7. When the instrument prompts you, connect three standards (open,
short, and load) to adapter B—as shown in the above graphic.
8. Press after connecting each standard.
9. When the instrument prompts you, connect three standards (open,
short, and load) to the port 2 cable—as shown in the above graphic.
10.Press after connecting each standard.
11.The analyzer will measure each standard and then calculate the new
calibration coefficients. The message "Calibration complete."
will appear for a few seconds when the analyzer is done calculating
the new error correction array.
ES User’s Guide 3-27
Page 80

Making Measurements
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
NOTE Changing sweep frequencies (and other source parameters) may affect
your calibration. See Chapter 6 for more information.
Connect the DUT.
12.Measure the test device with adapter B in place as shown in
Figure 3-9.
Figure 3-9 Equipment Setup for an S-Parameter Measurement of a
Noninsertable Two-Port Device
3-28 ES User’s Guide
Page 81

Making Measurements
User Preset
Factory Preset
More Cal
Cal Kit
Type-N(m)
S22 Refl Port2
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Method B: Modify the Calibration Kit Definition of the
Through Standard.
With this method, it is only necessary to use one adapter. The calibration
kit through-standard definition is modified to compensate for the
adapter and then saved as a user kit. However, the electrical delay of the
adapter must first be found. Two examples of this method will be
described: in example #1, the noninsertable device’s input and output
connectors are the same, and in example #2, the connectors are different.
NOTE By convention, cal kit labels in the analyzer indicate the sex of the port
with which they are used. For example, the default cal kit for the
analyzer is type-N female because the front panel RF ports are female
(the calibration standards, in turn, have male connectors).
EXAMPLE #1: the noninsertable device has type-N female input
and output connectors.
NOTE For analyzers with 50 ohm input impedance only: in the 50 ohm type-N
calibration kit (HP 85032B), there are four equal adapters: two
APC-7-to-type-N(f), and two APC-7-to-type-N(m). To create the adapter
in the following example, connect two APC-7-to-type-N(f) adapters.
1. Connect a test cable with type-N(m) connectors to the analyzer’s
port 1.
2. Connect a test cable with type-N(m) connectors to the analyzer’s
port 2.
3. To select a calibration kit for port 2, press (
or ) , and use the
front panel knob or the keys to highlight Port 2 in the
display’s table. Press .
4. Press . Perform a one-port reflection
calibration using type-N(f) standards on the type-N(m) open-end of
the port 2 cable. Refer to “Perform a User One-Port Calibration” on
page 3-49.
5. Connect the type-N female-to-female adapter to the type-N(m) openend of the port 2 cable.
6. Add a type-N(m) short to the open end of the adapter as shown in
Figure 3-10.
ES User’s Guide 3-29
MEAS 1
CAL
PRESET
Page 82

Making Measurements
Delay
2:
Marker Functions
Marker Math
Statistics
More Cal
Cal Kit
Type-N(f)
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Figure 3-10 Port 2: Short Connection to the Adapter
7. Select the delay format for your measurement by pressing
FORMAT
8. Press to automatically select marker 1 as the active
marker. Position marker 1 to the left edge of the measurement trace.
9. Press to select marker 2 as the active marker. Position marker 2
to the right edge of the measurement trace.
10.Press . Find the
mean value, located in the upper right corner of the display.
11.Divide the mean value by 2. Record this value for use later in the
procedure.
12.Select a type-N(f) calibration kit for port 2. This is necessary because
the type-N(m) short (connected to the adapter on port 2) is a
component in a type-N(f) calibration kit. Press
highlight Port 2 in the display’s table. Press .
3-30 ES User’s Guide
MARKER
, and use the front panel knob or the keys to
.
CAL
Page 83

Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Operating Parameters
Next Screen
More Cal
Cal Kit
Type-N(m)
More Cal
Cal Kit
Modify Type-N(m)
Thru
Delay
Prior Menu
Mod Kit SaveRecall
Save
Add Kit Description
Select Char
Enter
13.Determine the offset delay of the calibration short:
Making Measurements
• Press
SYSTEM OPTIONS
• Press until the Cal Kit screen is displayed. In the
“CAL KIT: Port 2,” display, find the numeric value for the delay of
the short.
14.Subtract this value from the value calculated in Step 11. This
corresponds to the delay of the adapter.
15.Remove the short from the adapter.
16.Reselect a type-N(m) calibration kit for port 2. This is necessary
because the type-N(m) short has been removed from the adapter.
Press , and use the front panel knob or
CAL
the keys to highlight Port 2 in the display’s table. Press
.
17.Modify the calibration kit definition of the through-standard by
entering the electrical delay of the adapter. To do so:
• Press
CAL
. Enter the delay value with the keypad and softkeys.
18.Save (and automatically assign) the modified cal kit buffer as a
user-defined cal kit for port 2. To do so:
• Press . Use the front panel
knob or the keys to highlight the desired User Kit in
the display’s table. (In this example, highlight Cal Kit A.) Press
.
If you want to enter a cal kit description in the display’s table,
press . Use a keyboard connected to the
analyzer’s DIN KEYBOARD connector to enter the description.
(If you don’t have a keyboard, you can use the analyzer’s
keys or the front panel knob and the
key to select and enter characters from the top of the analyzer’s
display. Press when done.)
ES User’s Guide 3-31
Page 84

Making Measurements
Prior Menu
More Cal Kits
User Cal Kit A
Prior Menu
User 2-Port
User 2-Port
Isolation on OFF
Measure Standard
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
19.Assign User Cal Kit A to port 1. (This User Cal Kit is assigned to both
port 1 and port 2 since these ports are connected with the same
adapter during the calibration.) To do so:
• Press . Use the front panel knob or the
keys to highlight Port 1 in the display’s table. Press
20.Start the calibration process by pressing until the
Reflection Cal menu is displayed. Next, press
. If you want to correct for crosstalk errors, toggle ON
the key. (For more information about isolation,
refer to the definition of a user two-port calibration in Chapter 6.)
21.When the instrument prompts you to connect a through cable, insert
the female-to-female adapter between the test cables connected to
port 1 and port 2 as shown in Figure 3-11. Press
.
Figure 3-11 Through-Cable Connection
.
22.Remove the adapter between the test cables connected to port 1 and
port 2.
3-32 ES User’s Guide
Page 85

Making Measurements
Measure Standard
Measure Standard
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
23.When the instrument prompts you, connect three standards (open,
short, and load) to the port 1 test cable as shown in the graphic on the
following page.
24.Press after connecting each standard.
Port 1: Open, Short, Load Connections Port 2: Open, Short, Load Connections
25.When the instrument prompts you, connect three standards (open,
short, and load) to the port 2 test cable—as shown in the graphic
above.
26.Press after connecting each standard.
27.The analyzer will measure each standard and then calculate new
calibration coefficients. The message "Calibration complete."
will appear for a few seconds when the analyzer is done calculating
the new error correction array.
ES User’s Guide 3-33
Page 86

Making Measurements
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
NOTE Changing sweep frequencies (and other source parameters) may affect
your calibration. See Chapter 6 for more information.
Connect the DUT.
28.Measure the test device using the setup shown in Figure 3-12.
Figure 3-12 Equipment Setup for an S-Parameter Measurement of a
Type-N(f) Two-Port Noninsertable Device
3-34 ES User’s Guide
Page 87

Making Measurements
User Preset
Factory Preset
More Cal
Cal Kit
3.5 mm
Type-N(m)
S22 Refl Port2
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
EXAMPLE #2: the noninsertable device has a 3.5 mm(f) input
connector, and a type-N(f) output connector.
NOTE For analyzers with 50 ohm input impedance only: in the 50 ohm type-N
calibration kit (HP 85032B), select the APC-7-to-type-N(f) adapter and in
the 3.5 mm calibration kit (HP 85033D), select the APC-7-to-3.5 mm(f)
adapter. Connect these two adapters to create the type-N-to-3.5 mm
female-to-female adapter in the following example.
1. Connect a test cable with 3.5 mm(m) connectors to the analyzer’s
port 1. (This example assumes a type-N(m)-to-3.5 mm(f) adapter is
connected directly to the analyzer’s port 1.)
2. Connect a test cable with type-N(m) connectors to the analyzer’s
port 2.
3. Press ( or )
4. Select the proper calibration kits for each port:
• For port 1, use the front panel knob or the keys to
• For port 2, use the front panel knob or the keys to
5. Press . Perform a one-port reflection
calibration using type-N(f) standards on the type-N(m) open-end of
the port 2 test cable. Refer to “Perform a User One-Port Calibration”
on page 3-49.
6. Connect the type-N-to-3.5 mm female-to-female adapter to the
type-N(m) open-end of the port 2 test cable.
7. Add a 3.5 mm short to the open end of the adapter as shown in Figure
3-13.
PRESET
.
highlight Port 1 in the display’s table. Press .
highlight Port 2 in the display’s table. Press .
MEAS 1
CAL
ES User’s Guide 3-35
Page 88

Making Measurements
Delay
2:
Marker Functions
Marker Math
Statistics
Operating Parameters
Next Screen
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
Figure 3-13 Port 2: Short Connection to the Adapter
8. Select the delay format for your measurement by pressing
FORMAT
9. Press to automatically select marker 1 as the active
marker. Position marker 1 to the left edge of the measurement trace.
10.Press to select marker 2 as the active marker. Position marker 2
to the right edge of the measurement trace.
11.Press . Find the
mean value, located in the upper-right corner of the display.
12.Divide the mean value by 2. Record this value for use later in the
procedure.
13.Determine the offset delay of the calibration short:
• Press .
• Press until the Cal Kit screen is displayed. In the
3-36 ES User’s Guide
MARKER
SYSTEM OPTIONS
“CAL KIT: Port 1,” display, find the numeric value for the delay of
the short. (This Port 1 heading is appropriate because the 3.5 mm
short used in Step 7 is from the calibration kit assigned to port 1.)
.
Page 89

Making Measurements
More Cal
Cal Kit
Modify 3.5 mm
Thru
Delay
Prior Menu
Mod Kit SaveRecall
Save
Add Kit Description
Select Char
Enter
More Cal
Cal Kit
Modify Type-N(m)
Thru
Delay
Prior Menu
Mod Kit SaveRecall
Save
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
14.Subtract this value from the value calculated in Step 12. This
corresponds to the delay of the adapter.
15.Remove the short from the adapter.
16.Modify the Port 1 calibration kit definition of the through-standard by
entering the electrical delay of the female-to-female adapter. To do so:
•Press and use the front panel knob or
CAL
the keys to highlight Port 1 in the display’s table.
Press . Enter the delay value with
the keypad and softkeys.
17.Save (and automatically assign) the modified cal kit buffer as a
user-defined cal kit for port 1. To do so:
• Press . Use the front panel
knob or the keys to highlight the desired User Kit in
the display’s table. (In this example, highlight Cal Kit A.) Press
.
If you want to enter a cal kit description in the display’s table,
press . Use a keyboard connected to the
analyzer’s DIN KEYBOARD connector to enter the description.
(If you don’t have a keyboard, you can use the analyzer’s
keys or the front panel knob and the
key to select and enter characters from the top of the analyzer’s
display. Press when done.)
18.Modify the Port 2 calibration kit definition of the through-standard by
entering the electrical delay of the female-to-female adapter. To do so:
•Press and use the front panel knob or
CAL
the keys to highlight Port 2 in the display’s table.
Press . Enter the delay value
with the keypad and softkeys.
19.Save (and automatically assign) the modified cal kit buffer as a
user-defined cal kit for port 2. To do so:
• Press . Use the front panel
knob or the keys to highlight the desired User Kit in
the display’s table. (In this example, highlight Cal Kit B.) Press
.
ES User’s Guide 3-37
Page 90

Making Measurements
Add Kit Description
Select Char
Enter
Prior Menu
User 2-Port
User 2-Port
Isolation on OFF
Measure Standard
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
If you want to enter a cal kit description in the display’s table,
press . Use a keyboard connected to the
analyzer’s DIN KEYBOARD connector to enter the description.
(If you don’t have a keyboard, you can use the analyzer’s
keys or the front panel knob and the
key to select and enter characters from the top of the analyzer’s
display. Press when done.)
20.Start the calibration process by pressing until the
Reflection Cal menu is displayed. Next, press
. If you want to correct for crosstalk errors, toggle ON
the key (for more information about isolation,
refer to the definition of a user two-port calibration in Chapter 6).
21.When the instrument prompts you to connect a through cable, insert
the type-N-to-3.5 mm female-to-female adapter between the test
cables connected to port 1 and port 2 as shown in Figure 3-14. Press
.
Figure 3-14 Through-Cable Connection
22.Remove the adapter between the test cables connected to port 1 and
port 2.
3-38 ES User’s Guide
Page 91

Making Measurements
Measure Standard
Measure Standard
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
23.When the instrument prompts you, connect three 3.5 mm standards
(open, short, and load) to the port 1 test cable as shown in the graphic
on the following page.
24.Press after connecting each standard.
Port 1: Open, Short, Load Connections Port 2: Open, Short, Load Connections
25.When the instrument prompts you, connect three type-N standards
(open, short, and load) to the port 2 test cable—as shown in the
graphic above.
26.Press after connecting each standard.
27.The analyzer will measure each standard and then calculate new
calibration coefficients. The message "Calibration complete."
will appear for a few seconds when the analyzer is done calculating
the new error correction array.
ES User’s Guide 3-39
Page 92

Making Measurements
Autoscale
Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-Port Calibration
NOTE Changing sweep frequencies (and other source parameters) may affect
your calibration. See Chapter 6 for more information.
Connect the DUT.
28.Measure the test device using the setup shown in Figure 3-15.
Figure 3-15 Equipment Setup for an S-Parameter Measurement of a
Type-N(f)-to-3.5 mm(f) Two-Port Noninsertable Device
View and Interpret the S-Parameter
Measurement Results
1. To view the entire measurement trace on the display, press
.
2. To interpret the measurement, refer to other S-parameter
measurement examples later in this chapter.
3-40 ES User’s Guide
SCALE
Page 93

Making Measurements
Measuring S21 Forward Transmission using an Enhanced Response Calibration
Measuring S21 Forward
Transmission using an Enhanced
Response Calibration
This section uses an example measurement to describe how to calibrate
for and make an S21 measurement. The same general concepts apply for
an S12 measurement. This example uses an enhanced response
calibration, but other calibration choices are also available. For example,
a two-port calibration, explained earlier in this chapter, could be used for
this measurement. Although the two-port calibration is the most
accurate form of error correction, it results in a slower measurement
speed than when using other calibrations. See the table below for a list of
all possible calibration choices for S21 or S12 measurements.
TIP An optimum calibration is critical for achieving best measurement
accuracy. Refer to Chapter 6, “Calibrating for Increased Measurement
Accuracy,” for detailed information about all of the various aspects of
calibration.
Table 3-3 Calibration Choices for S21 and S12 Measurements
Measurement Type Calibration Choices
S21 Fwd Trans or
S12 Rev Trans
In this example, an insertable bandpass filter like the one that was
supplied with your network analyzer is used.
ES User’s Guide 3-41
Default Response
Default 2-Port
User Response:
Response
Response & Isolation
Enhanced Response
User 2-Port
Normalize
Page 94

Making Measurements
User Preset
Factory Preset
Measuring S21 Forward Transmission using an Enhanced Response Calibration
Enter the Measurement Parameters
Press ( or ) on the analyzer
to set the analyzer to the default mode which includes measuring S21 on
measurement channel 1.
NOTE This example measurement uses the default instrument parameters for
an S21 measurement. If your particular measurement requires different
parameters (such as frequency range, source power level, number of data
points, and sweeptime), enter them now.
PRESET
Perform an Enhanced Response Calibration
An enhanced response calibration uses known standards to correct for
source match and frequency response errors when using narrowband
detection. When you perform an enhanced transmission response
calibration, the analyzer performs correction at each data point across
the selected frequency band. The default number of data points per
sweep is 201, but you can select any number between 3 and 1601.
Interpolation recalculates the error correction array for reduced
frequency spans. If the frequency span is increased, the calibration is
invalidated, and the default response calibration is automatically
restored.
3-42 ES User’s Guide
Page 95

Making Measurements
More Cal
Cal Kit
Measuring S21 Forward Transmission using an Enhanced Response Calibration
To perform an enhanced transmission response calibration, you will need
one of the following calibration kits depending on the nominal impedance
of your analyzer:
Cal Kit Model
Number
HP 85039B 75 Ω type-F ✓✓
HP 85036B 75 Ω type-N ✓✓
HP 85036E 75 Ω type-N ✓
HP 85032B 50 Ω type-N ✓✓
HP 85032E 50 Ω type-N ✓
HP 85031B 50 Ω APC-7 N/A N/A
HP 85033D 50 Ω 3.5 mm ✓✓
HP 85038A 50 Ω 7-16 ✓✓
HP 85038F 50 Ω 7-16 ✓
HP 85038M 50 Ω 7-16 ✓
Impedance
Connector
Type
For Use
with Male
Test Ports
For Use
with Female
Test Ports
NOTE By convention, cal kit labels in the analyzer indicate the sex of the port
with which they are used. For example, the default cal kit for the
analyzer is type-N female because the front panel RF ports are female
(the calibration standards, in turn, have male connectors).
NOTE If you are going to be using calibration standards other than the default
(female type-N), you must select a calibration kit to match the port(s) at
your calibration reference plane. Do this by pressing
and then selecting the appropriate type.
ES User’s Guide 3-43
CAL
Page 96

Making Measurements
User Response
Enhanced Response
Measure Standard
Measuring S21 Forward Transmission using an Enhanced Response Calibration
Calibrating for Insertable Devices
When doing a through-standard calibration, normally the test ports
mate directly together. For example, two cables with the appropriate
connectors can be connected directly without a through adapter,
resulting in a zero-length through-standard. An insertable device is a
device that can be inserted in place of a zero-length through-standard. It
has the same type of connector on each port, but with a different sex, or
the same type of sexless connector on each port (APC-7, for example).
Chapter 6 provides detail about when a user-defined calibration is
necessary, and information about other calibrations available for S
measurements. If you wish to perform an enhanced response calibration
on your instrument for an S21 measurement, execute the following steps:
21
1. Press .
2. The instrument prompts you to connect four standards—open, short,
load, and through cable—as shown in the following graphic.
Open, Short, Load Connections Through Cable Connection
CAL
3. Press after connecting each standard.
3-44 ES User’s Guide
Page 97

Making Measurements
Enhanced Response
User 2-Port
Measuring S21 Forward Transmission using an Enhanced Response Calibration
4. The analyzer will measure each standard and then calculate the new
calibration coefficients. The message "Calibration complete."
will appear for a few seconds when the analyzer is done calculating
the new error correction array.
NOTE Changing sweep frequencies (and other source parameters) may affect
your calibration. See Chapter 6 for more information.
Calibrating for Noninsertable Devices
A non-insertable device is one that cannot be inserted in place of a
zero-length through-standard. It has the same connectors on each port
(type and sex) or has a different type of connector on each port (SMA on
one port, and Type-N on the other, for example). To review two methods
of calibration for non-insertable devices, refer to the previous section
“Measuring S-Parameters using a Two-P ort Calibration” on page 3-19. In
both methods, you will need to select from the
calibration menu instead of .
Connect the DUT
Figure 3-16 Equipment Setup for an S21 Measurement
ES User’s Guide 3-45
Page 98

Making Measurements
Autoscale
Marker Search
Max Search
Mkr−> Max
Measuring S21 Forward Transmission using an Enhanced Response Calibration
View and Interpret the S21 Measurement Results
1. To view the entire measurement trace on the display, press
.
2. To interpret the measurement, refer to Figure 3-17, “Example of an
S21 Measurement Display,” or your analyzer's display if you are
making this measurement on your instrument.
a. The values shown on the horizontal axis are the frequencies in
MHz. The values shown on the vertical axis are the power ratios
in decibels (dB) of the transmitted signal through the device
divided by the incident power. To display the result in logarithmic
magnitude format (designated by "Log Mag" at the top of the
measurement screen), the analyzer computes the measurement
trace using the following formula:
P
trans
Transmission dB() 10 log
where P
where P
b. A level of 0 dB would indicate a perfect through cable or device (no
loss or gain). Values greater than 0 dB indicate that the DUT has
gain. Values less than 0 dB indicate loss.
3. To quickly determine the filter's minimum insertion loss, press
MARKER
= the power transmitted through the device and
trans
= the incident power.
inc
=
------------- -
P
inc
SCALE
.
4. Note the marker readout in Figure 3-17 provides the frequency and
amplitude of the minimum insertion-loss point.
3-46 ES User’s Guide
Page 99

Measuring S21 Forward Transmission using an Enhanced Response Calibration
Figure 3-17 Example of an S21 Measurement Display
Making Measurements
5. See “Using Markers” on page 4-3 in for more detailed information on
using markers to interpret measurements.
NOTE For the measurement to be valid, input signals must fall within the
dynamic range of the analyzer. See Chapter 5, “Optimizing
Measurements,” for techniques to increase the dynamic range of the
analyzer.
ES User’s Guide 3-47
Page 100

Making Measurements
Measuring S11 Reflection Port 1 using a One-Port Calibration
Measuring S11 Reflection Port 1 using a
One-Port Calibration
This section uses an example measurement to describe how to calibrate
for and make an S11 measurement. The same general concepts apply for
an S22 measurement. This example uses a one-port reflection calibration,
but a two-port calibration, explained earlier in this chapter, could also be
used for this measurement. Although the two-port calibration is the most
accurate form of error correction for a two-port device, it results in a
slower measurement speed. See the table below for a list of all possible
calibration choices for S11 or S22 measurements.
TIP An optimum calibration is critical for achieving best measurement
accuracy. Refer to Chapter 6, “Calibrating for Increased Measurement
Accuracy,” for detailed information about all of the various aspects of
calibration.
Table 3-4 Calibration Types for S11 and S22 Measurements
Measurement Type Calibration Choices
S11 Refl Port 1 or
S22 Refl Port 2
In this example, a bandpass filter like the one that was supplied with
your network analyzer is used.
3-48 ES User’s Guide
Default 1-Port
Default 2-Port
User 1-Port
User 2-Port
 Loading...
Loading...