Page 1

HP Comware-Based Devices
Transceiver Modules User Guide
Part number: 5998-1616
Document version: 6W103-20140829
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
No part of this documentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without
prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS
MATERIAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained
herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or
use of this material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained
herein.
Page 3

Contents
Overview ······································································································································································ 1
Types of transceiver modules ··········································································································································· 2
Fiber transceiver modules ················································································································································· 3
Data rate ··································································································································································· 4
Transmission distance ·············································································································································· 4
Central wavelength ·················································································································································· 4
Fiber ··········································································································································································· 4
Connector ·································································································································································· 6
Optical parameters ·················································································································································· 7
Copper transceiver modules ············································································································································ 7
Transmission distance ·············································································································································· 7
Connector ·································································································································································· 8
SFP modules ·································································································································································· 9
100-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver module ···················································································································· 9
Models and specifications ······································································································································· 9
622-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver module ················································································································· 10
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 10
Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module ·························································································································· 11
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 11
2.5-Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module ··················································································································· 12
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 12
100-Megabit BIDI fiber transceiver module ················································································································ 13
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 13
Gigabit BIDI fiber transceiver module ·························································································································· 14
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 14
Gigabit CWDM fiber transceiver module ··················································································································· 14
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 15
Gigabit SFP copper transceiver module ······················································································································ 16
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 16
Gigabit SFP cable ·························································································································································· 16
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 17
SFP+ modules ····························································································································································· 18
10-Gigabit SFP+ fiber transceiver module ·················································································································· 18
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 18
10-Gigabit SFP+ cable ·················································································································································· 19
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 19
XFP transceiver modules ············································································································································ 20
Models and specifications ············································································································································ 20
CX4 cables ································································································································································· 23
Models and specifications ············································································································································ 23
QSFP+ modules ·························································································································································· 24
QSFP+ fiber transceiver modules that use a 12-fiber MPO connector····································································· 24
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 24
QSFP+ fiber transceiver modules that use an LC connector ······················································································ 25
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 25
40-Gigabit QSFP+ cable··············································································································································· 26
i
Page 4

Models and specifications ···································································································································· 26
QSFP+ to SFP+ cable ···················································································································································· 26
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 27
CFP transceiver modules ············································································································································ 28
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 28
CXP modules ······························································································································································· 30
CXP fiber transceiver modules ······································································································································ 30
Models and specifications ···································································································································· 30
CXP AOC ········································································································································································ 31
Models and specifications ············································································································································ 31
Support and other resources ····································································································································· 32
Contacting HP ································································································································································ 32
Subscription service ·············································································································································· 32
Related information ························································································································································ 32
Documents ······························································································································································ 32
Websites ································································································································································· 32
Conventions ···································································································································································· 33
Index ··········································································································································································· 35
ii
Page 5

Overview
This guide describes transceiver modules available on the following HP Comware-Based devices:
• HP FlexFabric 12900 Switch Series
• HP 12500 Switch Series
• HP FlexFabric 12500E Switch Series
• HP FlexFabric 119 00 Swi tc h Ser ie s
• HP 10500 Switch Series
• HP 9500 Switch Series
• HP FlexFabric 7900 Switch Series
• HP 7500 Switch Series
• HP 6125 Blade Switch Series
• HP FlexFabric 5930 Switch Series
• HP 5920 Switch Series
• HP 5900 Switch Series
• HP 5700 Switch Series
• HP 5830 Switch Series
• HP 5820X Switch Series
• HP 5800 Switch Series
• HP 5500 HI Switch Series
• HP 5500 EI Switch Series
• HP 5500 SI Switch Series
• HP 5120 EI Switch Series
• HP 5120 SI Switch Series
• HP 3600 v2 Switch Series
• HP 3100-48 v2 Switch
• HP 3100 v2 Switch Series
• HP 1920 Gigabit Ethernet Switch Series
• HP 1910 Gigabit Ethernet Switch Series
• HP 1910 Fast Ethernet Switch Series
• HP 8800 Router Series
• HP 6600 Router Series
• HP HSR6600 Router Series
• HP HSR6800 Router Series
• HP MSR1002-4 Router
• HP MSR2004-24 Router
• HP
MSR3000 Router Series
1
Page 6

• HP MSR4000 Router Series (with SPU-200 / SPU-300)
yp
• HP MSR30-40 / MSR30-60 Routers
• HP MSR50 Router Series
• HP F5000 Firewall
• HP F5000-S VPN Firewall Appliance
• HP F5000-C VPN Firewall Appliance
• HP F1000-E VPN Firewall Appliance
• HP F1000-S-EI VPN Firewall Appliance
• HP F1000-A-EI VPN Firewall Appliance
• HP U200-A Unified Threat Management Appliance
• HP 7500 VPN Firewall Module
• HP 9500 VPN Firewall Module
• HP 12500 VPN Firewall Module
• HP 6600 VPN Firewall Module
• HP 8800 VPN Firewall Module
• HP 10500/11900/7500 20Gbps VPN FW Module
• HP 12500 20Gbps VPN Firewall Module
• HP 12900 40Gbps VPN Firewall Module
• HP 7500 NetStream Monitoring Module
• HP 9500 NetStream Monitoring Module
• HP 12500 NetStream Monitoring Module
• HP 7500 Load Balancing Module
• HP 9500 Load Balancing Module
• HP 12500 Load Balancing Module
• HP 8800 Load Balancing Module
• HP 830 8-Port PoE+ Unified Wired-WLAN Switch
• HP 830 24-Port PoE+ Unified Wired-WLAN Switch
• HP 850 Unified Wired-WLAN Appliance
• HP 870 Unified Wired-WLAN Appliance
Types of transceiver modules
Table 1 Types of transceiver modules
Transceiver module t
e Connector type
100-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver module
Small form-factor pluggable (SFP)
module (transceiver)
622-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver module
Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module
2.5-Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module
2
LC
Page 7

Transceiver module type Connector type
g
100-Megabit bi-direction (BIDI) fiber
transceiver module
Gigabit BIDI fiber transceiver module
Gigabit coarse wavelength division
multiplexing (CWDM) fiber transceiver
module
Gigabit SFP copper transceiver module RJ-45
LC
LC
Gigabit SFP cable (for interconnecting
devices)
10-Gigabit SFP+ fiber transceiver module
SFP+ module (transceiver)
10-Gigabit small form-factor pluggable (XFP) module (transceiver)
10-Gigabit CX4 cable (for interconnecting devices) N/A
40-Gigabit QSFP+ fiber transceiver module MPO/LC
QSFP+ module
(transceiver)
CFP module
(transceiver)
CXP module
(transceiver)
40-Gigabit QSFP+ cable (for interconnecting QSFP+
ports)
QSFP+ to SFP+ cable (for connecting one 40-Gigabit
QSFP+ port to four 10-Gigabit SFP+ ports)
40-Gigabit/100-Gigabit CFP fiber transceiver module
100-Gigabit CXP fiber transceiver module MPO
100-Gigabit CXP AOC N/A
10-Gigabit SFP+ cable (for interconnecting
devices)
NOTE:
N/A
LC
N/A
LC
N/A
N/A
LC
• The available transceiver modules vary by HP Comware-Based device models and are subject to chan
over time. For the most up-to-date list of transceiver modules, contact your HP sales representative or
technical support engineer.
• For information about the transceiver modules available for each HP Comware-Based device model, see
the installation guides.
Fiber transceiver modules
Fiber modules transmit signals over optical fibers. Optical transmission features low loss and is fit for long
distance transmission.
The HP Comware-Based devices support fiber transceiver module models of different specifications. You
can choose fiber transceiver modules as needed for data transmission over optical fibers.
The fiber transceiver modules include optical transmitters, optical receivers, transceivers, and
transponders.
The HP Comware-Based devices support transceivers. Transceivers are mainly used for
optical-to-electrical and electrical-to-optical conversions and provide the following functions: optical
3
e
Page 8

power control, modulation transmission, signal probe, IV conversion, and limiting amplifier and decision
regeneration. In addition, transceivers provide some other functions, such as counterfeit-prevention query
and TX-disable. Common transceivers include XFP, SFP, SFP+, and QSFP+.
Data rate
Data rate is the number of bits transmitted per second. The unit of measure for data rate is Megabits per
second (Mbps) or Gigabits per second (Gbps). Fiber transceiver modules available for HP
Comware-Based devices mainly provide the following levels of data rates: 100 Mbps, 155 Mbps, 622
Mbps, 1000 Mbps, 2.5 Gbps, 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, and 100 Gbps.
Transmission distance
The transmission distance of fiber transceiver modules is divided into short and long-range types. A
distance of 2 km (1.24 miles) and below is generally considered as short-range type. 10 km (6.21 miles)
is considered as long-range type.
Transmission distances provided by fiber transceiver modules are mainly limited by certain loss and
dispersion suffered during the transmission of fiber signals over fibers.
• Loss is the optical energy loss due to the absorption, dispersion and leakage over the media when
light travels through optical fibers. This loss increases in direct ratio to transmission distance.
• Dispersion happens mainly because electromagnetic waves of different wavelengths travel at
different rates over the same medium, causing different wave components of optical signals to
reach the receiving end early or late as the transmission distance increases, which in turn causes
impulse broadening, making the signal values indistinguishable.
To meet different transmission distance requirements, choose suitable fiber transceiver modules
according to actual networking conditions.
Central wavelength
Central wavelength represents the wave band used for optical signal transmission. The following central
wavelengths are available for common fiber transceiver modules: 850 nm, 1310 nm, and 1550 nm,
respectively representing three wavebands.
• The 850 nm wave band is used for short-reach transmission.
• The 1310 nm and 1550 nm wave bands are used for middle-reach and long-haul transmissions.
Fiber
Fiber types
Fibers are classified as multimode fibers and single-mode fibers.
• Multimode fibers
Multimode fibers (MMFs) have thicker fiber cores and can transport light in multiple modes.
However, the intermodal dispersion is greater and worsens as the transmission distance increases.
Multimode fibers can be classified into multiple grades according to their diameters and modal
bandwidth. For more information, see Table 2. T
determined by the expression the modulation frequency of the maximum modulation frequency
4
he modal bandwidth of a multimode fiber is
Page 9

pulse that can pass a fiber × the fiber length. The modal bandwidth is a comprehensive index
g
reflecting the optical characteristics of a multimode fiber.
International Telecommunication Union (ITU) defines multimode fiber types in its G series
standards. The commonly-used multimode fiber is defined in the ITU G.651 standard. The
G.651-compliant fiber transmits light at the wavelength range 800 nm to 900 nm or 1200 nm to
1350 nm.
Table 2 Multimode fiber grades
Fiber mode Fiber grade Fiber diameter (m)
OM1 62.5/125 200
Multimode fiber
OM2 50/125 500
OM3 50/125 2000
Modal bandwidth at
850 nm (MHz*km)
Other factors that influence the transmission distance of multimode fibers include interface type,
central wavelength, and fiber grade. For more information, see Table 3.
Table 3 Multimode fiber
Interface type
1000BASE-SX 850
10GBASE-SR 850
10GBASE-LRM 1310
specifications
Central
wavelen
th (nm)
Fiber grade Transmission distance
OM1 < 275 m (902.23 ft)
OM2 < 550 m (1804.46 ft)
OM1 < 33 m (108.27 ft)
OM2 < 82 m (269.03 ft)
OM3 < 300 m (984.25 ft)
OM1 < 220 m (721.78 ft)
OM2 < 220 m (721.78 ft)
OM3 < 220 m (721.78 ft)
• Single-mode fibers
Single-mode fibers (SMFs) have a small core size, typically 9 μm or 10 μm, and can transmit light
in only one mode. Single-mode fibers suffer little intermodal dispersion and are suitable for
long-haul communication. Single-mode fibers transmit light at the central wavelength of 1310 nm
or 1550 nm.
Telecommunication Industries Alliance (TIA)/Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) defines that
single-mode fibers use yellow outer jackets with the mark "SM".
ITU defines single-mode fiber types in its G series standards. The mostly-commonly used
single-mode fibers are defined in ITU G.652 and G.655 standards. Table 4 desc
ribes features of
the G.652 and G.655-compliant fibers.
5
Page 10
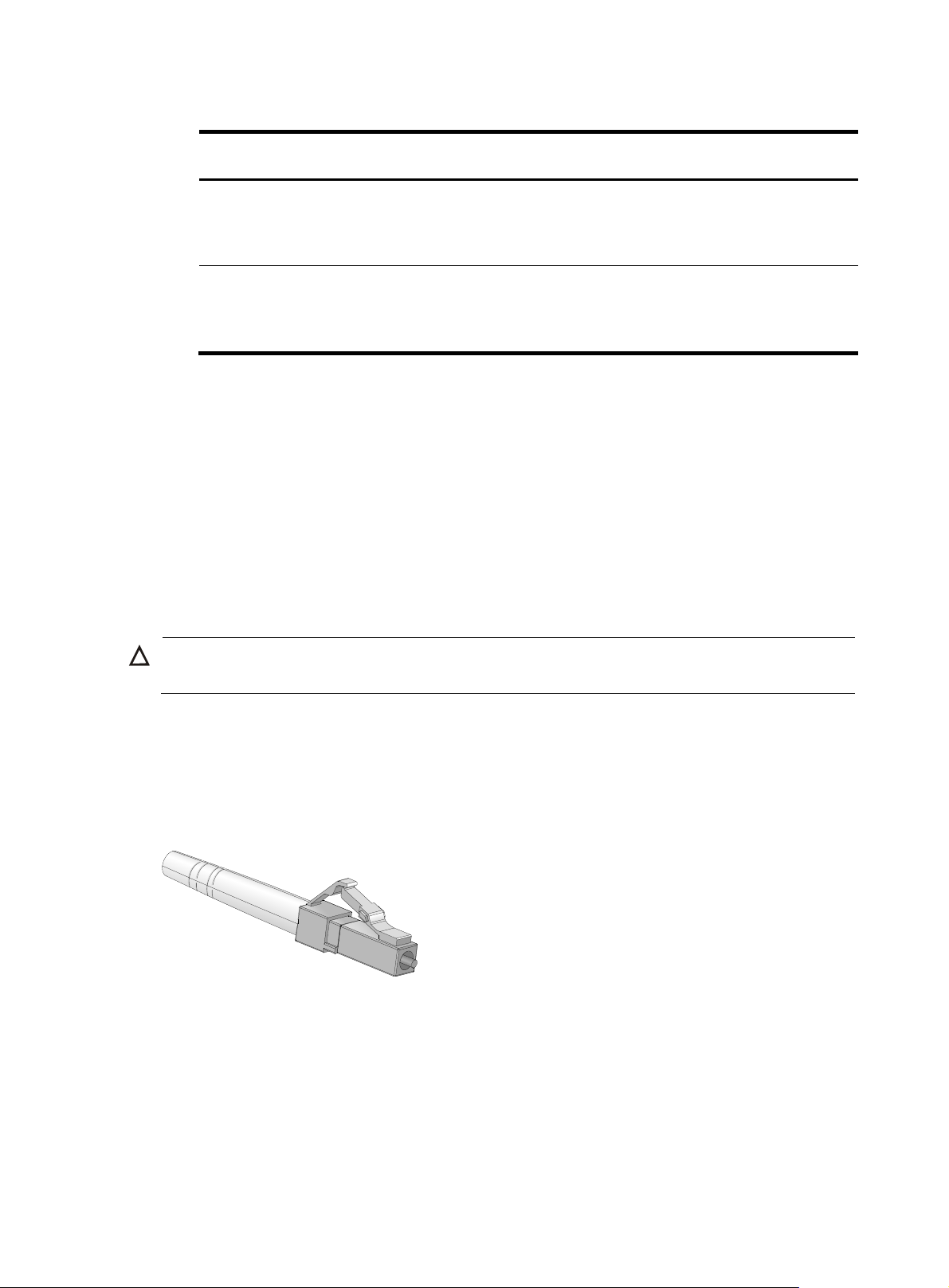
Table 4 Features of G.652 and G.655-compliant fibers
yp
Single-mode fiber
t
G.652-compliant
fiber (standard
single-mode fiber)
G.655-compliant
fiber (non-zero
dispersion shifted
fiber)
Fiber diameter
Fiber diameter is expressed as core diameter/cladding diameter, in μm. For example, 9/125 μm means
the fiber core diameter is 9 μm and the fiber cladding diameter is 125 μm.
For the HP Comware-Based devices, the following fiber diameters are recommended:
• G.652 standard single-mode fiber—9/125 μm.
• G.655 single-mode fiber—9/125 μm.
• G.651 standard multimode fiber—50/125 μm or 62.5/125 μm.
Connector
e
Wavelength (nm) Features Applications
• 1260 t o 136 0
• 153 0 t o 156 5
1530 to 1565
Zero dispersion at 1310
nm.
Near-zero dispersion
around 1550 nm.
Connecting transceiver
modules with a central
wavelength of 1310
nm or 1550 nm.
For 1550-nm
wavelength-division
multiplexing (WDM)
transmissions.
CAUTION:
Cover the connector with a dust cap when it is not connected to any optical fiber.
Connectors connect transceiver modules to the corresponding transmission media. The transceiver
modules available for the HP Comware-Based devices use the following types of connectors:
• Lucent connector or local connector (LC).
• Multi-fiber Push On connector (MPO).
Figure 1 LC connector
6
Page 11

Figure 2 MPO connector
A
Optical parameters
NOTE:
verage transmit and receive power ranges are provided for transceiver modules in this guide.
Transmit power
Transmit power is the power at which the transmitter of a fiber transceiver module transmits optical
signals, in dBm.
Receive power
Receive power is the power at which the receiver of a fiber transceiver module receives optical signals,
in dBm.
Copper transceiver modules
Copper transceiver modules transmit signals over Category-5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP). UTP
transmission cover shorter distances than fiber transmission and can be used in small-sized networks
only.
The HP Comware-Based devices support the HP X120 1G SFP RJ45 T Transceiver (JD089B) copper
transceiver modules.
Transmission distance
Through UTP cables, signals can be transmitted over a distance of 100 m (328.08 ft.) only. This is
because signals attenuate during transmission through the UTP cables.
Attenuation refers to the dissipation of the power of a transmitted signal as it travels over a cable.
Attenuation occurs because signal transmission suffers certain resistance from the cable, which weakens
the signals as they travel over the cable. When signals are transmitted over a very long distance, signal
strength decreases significantly, causing the signal-to-noise ratio to drop below the accepted level. This
makes it impossible to distinguish between signals and noise, resulting in decision errors.
When signals are to be transmitted over a short distance, use copper transceiver modules only.
7
Page 12

Connector
Registered Jack-45 (RJ-45) twisted pair connectors are used as connectors for copper transceiver
modules.
Figure 3 RJ-45 connector
Table 5 RJ-45 GE connector pin assignment
Pin Signal Function
1 MX_0+ Data transmit/receive
2 MX_0- Data transmit/receive
3 MX_1+ Data transmit/receive
4 MX_2+ Data transmit/receive
5 MX_2- Data transmit/receive
6 MX_1- Data transmit/receive
7 MX_3+ Data transmit/receive
8 MX_3- Data transmit/receive
8
Page 13

g
ps)
m)
p
SFP modules
100-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver module
Figure 4 100-Megabit/622-Megabit/Gigabit/2.5-Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module
Models and specifications
100-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver modules use LC connectors.
Table 6 Specifications for 100-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JD102B
JF833A
JF832A
JD120B
JD090A
JD091A
Name
HP X115 100M SFP
LC FX Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP
LC FX Transceiver
HP X120 100M/1G
SFP LC LX Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP
LC LX Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP
LC LH40 Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP
LC LH80 Transceiver
Central
wavelen
th (nm)
1310 155 MMF
1310 125 MMF
1310 125 SMF 9/125 10 km (6.21 miles)
1310 155 SMF 9/125 15 km (9.32 miles)
1310 155 SMF 9/125 40 km (24.86 miles)
1550 155 SMF 9/125 80 km (49.71 miles)
Data
rate
(Mb
Fiber
mode
Fiber
diameter
(
50/125
62.5/125
50/125
62.5/125
Table 7 Specifications for 100-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver modules (2)
Transmission
distance
2 km (1.24 miles)
2 km (1.24 miles)
O
Product
code
JD102B
Name
HP X115 100M SFP LC FX
Transceiver
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit power
–19 to –14 –30 to –14
9
Receive power
Page 14

p
p
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
Name
O
Transmit power
Receive power
JF833A
JF832A
JD120B
JD090A
JD091A
HP X110 100M SFP LC FX
Transceiver
HP X120 100M/1G SFP LC
LX Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP LC LX
Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP LC
LH40 Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP LC
LH80 Transceiver
–20 to –14 –31.5 to –8
–15 to –8 –28 to –8
–15 to –8 –28 to –7
–5 to 0 –34 to –9
–5 to 0 –34 to –10
622-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver module
See Figure 4 for a view of the 622-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver module.
Models and specifications
622-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver modules use LC connectors.
Table 8 Specifications for 622-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JF829A
JF830A
JF831A
Central
Name
wavelen
gth (nm)
HP X120 622M SFP
LC LX 15km
Transceiver
HP X120 622M SFP
LC LH 40km 1310
Transceiver
HP X120 622M SFP
LC LH 80km 1550
Transceiver
1310 SMF 9/125 15 km (9.32 miles)
1310 SMF 9/125 40 km (24.86 miles)
1550 SMF 9/125 80 km (49.71 miles)
Fiber
mode
Fiber
diameter
(m)
Table 9 Specifications for 622-Megabit SFP fiber transceiver modules (2)
O
Product
code
JF829A
Name
HP X120 622M SFP LC LX
15km Transceiver
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit power
–15 to–8 –28 to –8
Transmission distance
Receive power
JF830A
HP X120 622M SFP LC LH
40km 1310 Transceiver
–3 to +2 –28 to –8
10
Page 15

p
g
m)
p
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
Name
O
Transmit power
Receive power
JF831A
HP X120 622M SFP LC LH
80km 1550 Transceiver
–3 to +2 –28 to –8
Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module
See Figure 4 for a view of the Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module.
Models and specifications
Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver modules provide a transmission rate of 1250 Mbps and use LC connectors.
Table 10 Specifications for Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JD118B
Name
HP X120 1G SFP LC
SX Transceiver
Central
wavelen
th (nm)
850 MMF
Fiber
mode
Fiber
diameter
(
50/125
62.5/125
Modal
bandwidth
(MHz*km)
500 550 m (1804.46 ft)
400 500 m (1640.42 ft)
200 275 m (902.23 ft)
160 220 m (721.78 ft)
Transmission
distance
SMF 9/125 N/A 10 km (6.21 miles)
JD119B
JF832A
JD061A
JD062A
JD063B
JD103A
HP X120 1G SFP LC
LX Transceiver
HP X120 100M/1G
SFP LC LX Transceiver
HP X125 1G SFP LC
LH40 1310nm
Transceiver
HP X120 1G SFP LC
LH40 1550nm
Transceiver
HP X125 1G SFP LC
LH70 Transceiver
HP X120 1G SFP LC
LH100 Transceiver
1310
1310 SMF 9/125 N/A 10 km (6.21 miles)
1310 SMF 9/125 N/A 40 km (24.86 miles)
1550 SMF 9/125 N/A 40 km (24.86 miles)
1550 SMF 9/125 N/A 70 km (43.5 miles)
1550 SMF 9/125 N/A
MMF 50/125 500 or 400 550 m (1804.46 ft)
MMF 62.5/125 500 550 m (1804.46 ft)
Table 11 Specifications for Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver modules (2)
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
Name
O
Transmit power
100 km (62.14
miles)
Receive power
JD118B
HP X120 1G SFP LC SX
Transceiver
–9.5 to 0 –17 to 0
11
Page 16

p
p
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
Name
O
Transmit power
Receive power
JD119B
JF832A
JD061A
JD062A
JD063B
JD103A
HP X120 1G SFP LC LX
Transceiver
HP X120 100M/1G SFP LC LX
Transceiver
HP X125 1G SFP LC LH40
1310nm Transceiver
HP X120 1G SFP LC LH40
1550nm Transceiver
HP X125 1G SFP LC LH70
Transceiver
HP X120 1G SFP LC LH100
Transceiver
–9.5 to –3 –20 to –3
–9.5 to –3 –22 to –3
–2 to +5 –22 to –3
–4 to +1 –21 to –3
–4 to +5 –22 to –3
0 to +5 –30 to –9
2.5-Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module
See Figure 4 for a view of the 2.5-Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver module.
Models and specifications
2.5-Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver modules use LC connectors.
Table 12 Specifications for 2.5-Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JD084A
JD085A
JD086A
JD087A
Name
HP X160 2.5G SFP LC
2km Transceiver
HP X160 2.5G SFP LC
15km Transceiver
HP X160 2.5G SFP LC
40km Transceiver
HP X160 2.5G SFP LC
80km Transceiver
Central
wavelength
(nm)
1310 SMF 9/125 2 km (1.24 miles)
1310 SMF 9/125 15 km (9.32 miles)
1310 SMF 9/125
1550 SMF 9/125
Fiber
mode
Fiber diameter
(m)
Table 13 Specifications for 2.5-Gigabit SFP fiber transceiver modules (2)
O
Product
code
JD084A
Name
HP X160 2.5G SFP LC 2km
Transceiver
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit power
–10 to –3 –18 to –3
Transmission
distance
40 km (24.86
miles)
80 km (49.71
miles)
Receive power
JD085A
HP X160 2.5G SFP LC 15km
Transceiver
–5 to 0 –18 to 0
12
Page 17

p
g
p
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
Name
O
Transmit power
Receive power
JD086A
JD087A
HP X160 2.5G SFP LC 40km
Transceiver
HP X160 2.5G SFP LC 80km
Transceiver
–2 to +3 –27 to –9
–20 to –14 –31 to –12
100-Megabit BIDI fiber transceiver module
Figure 5 100-Megabit/Gigabit BIDI fiber transceiver module
Models and specifications
100-Megabit BIDI fiber transceiver modules provide a transmission rate of 155 Mbps and use LC
connectors.
Table 14 Specifications for 100-Megabit BIDI fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JD100A
JD101A
Name
HP X110 100M SFP LC
BX 10-U Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP LC
BX 10-D Transceiver
Central wavelen
Transmitting
end (TX)
1310 1550
1550 1310
th (nm)
Receiving
end (RX)
Fiber
mode
SMF 9/125
Table 15 Specifications for 100-Megabit BIDI transceiver modules (2)
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
JD100A
JD101A
Name
HP X110 100M SFP LC BX
10-U Transceiver
HP X110 100M SFP LC BX
10-D Transceiver
O
Transmit power
–15 to –8 –31 to –3
Fiber
diameter
(m)
Transmission
distance
15 km (9.32
miles)
Receive power
13
Page 18

X
g
p
NOTE:
• BIDI fiber transceiver modules use different central wavelengths in transmit and receive directions to
implement bidirectional transmission of fiber signals over the same fiber.
• You must use the HP X115 100M SFP LC BX 10-U Transceiver (JD100A) and HP X115 100M SFP LC B
10-D Transceiver (JD101A) in pairs.
Gigabit BIDI fiber transceiver module
See Figure 5 for a view of the Gigabit BIDI fiber transceiver module.
Models and specifications
Gigabit BIDI fiber transceiver modules provide a transmission rate of 1250 Mbps and use LC connectors.
Table 16 Specifications for Gigabit BIDI fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JD098B
JD099B
Name
HP X120 1G SFP LC
BX 10-U Transceiver
HP X120 1G SFP LC
BX 10-D Transceiver
Central wavelen
Transmitting
end (TX)
1310 1490
1490 1310
th (nm)
Receiving
end (RX)
Fiber
mode
SMF 9/125
Fiber
diameter
(m)
Transmission
distance
10 km (6.21
miles)
Table 17 Specifications for Gigabit BIDI transceiver modules (2)
O
Product
code
JD098B
JD099B
Name
HP X120 1G SFP LC BX 10-U
Transceiver
HP X120 1G SFP LC BX 10-D
Transceiver
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit power
–9 to –3 –18.7 to –3
Receive power
NOTE:
• BIDI fiber transceiver modules use different central wavelengths in transmit and receive directions, in
order to implement bidirectional transmission of fiber signals over the same fiber.
• You must use the HP X120 1G SFP LC BX 10-U Transceiver (JD098B) and HP X120 1G SFP LC BX 10-D
Transceiver (JD099B) in pairs.
Gigabit CWDM fiber transceiver module
Figure 6 Gigabit CWDM fiber transceiver module
14
Page 19

p
Models and specifications
Gigabit CWDM fiber transceiver modules provide a transmission rate of 1250 Mbps and use LC
connectors.
Table 18 Specifications for Gigabit CWDM fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JD113A
JD114A
JD115A
JD116A
JD109A
JD110A
JD111A
JD112A
Name
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70
1470 Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70
1490 Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70
1510 Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70
1530 Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70
1550 Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70
1570 Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70
1590 Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70
1610 Transceiver
Central
wavelength (nm)
1470
1490
1510
1530
1550
1570
1590
1610
Fiber
mode
SMF 9/125
Fiber
diameter (m)
Table 19 Specifications for Gigabit CWDM fiber transceiver modules (2)
Transmission
distance
70 km (43.5
miles)
O
Product
code
JD113A
JD114A
JD115A
JD116A
JD109A
Name
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70 1470
Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70 1490
Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70 1510
Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70 1530
Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70 1550
Transceiver
15
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit power
0 to +5 –23 to –3
Receive power
Page 20

p
g
g
yp
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
Name
O
Transmit power
Receive power
JD110A
JD111A
JD112A
NOTE:
Gigabit CWDM fiber transceiver modules adopt the CWDM technology that uses wavelength division
multiplexers to multiplex optical si
fiber, thereby savin
to demultiplex the multiplexed optical signals.
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70 1570
Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70 1590
Transceiver
HP X170 1G SFP LC LH70 1610
Transceiver
nals with different wavelengths for transmission over a single optical
optical fiber resources. The receiving end uses a wavelength division demultiplexer
Gigabit SFP copper transceiver module
Figure 7 Gigabit SFP copper transceiver module
Models and specifications
Table 20 Specifications for SFP copper transceiver modules
Product
code
JD089B
Name
HP X120 1G SFP
RJ45 T Transceiver
Gigabit SFP cable
Figure 8 Gigabit SFP cable
Transmission
distance
100 m (328.08 ft) 1250 Mbps UTP/STP RJ-45
Data rate Cable type
Connector
e
t
16
Page 21

g
Models and specifications
Table 21 Specifications for Gigabit SFP cables
Product code Name Cable len
JD324A
HP A3600 Switch SFP
Stacking Kit
1.5 m (4.92 ft) 1250 Mbps UTP/STP
th
Data rate Cable type
17
Page 22

g
m)
SFP+ modules
10-Gigabit SFP+ fiber transceiver module
Figure 9 10-Gigabit SFP+ fiber transceiver module
Models and specifications
10-Gigabit SFP+ fiber transceiver modules provide a transmission rate of 10.31 Gbps and use LC
connectors.
Table 22 Specifications for 10-Gigabit SFP+ fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JD092B
JD093B
JD094B
Name
HP X130 10G SFP+
LC SR Transceiver
HP X130 10G SFP+
LC LRM Transceiver
HP X130 10G SFP+
LC LR Transceiver
Central
wavelen
th (nm)
850 MMF
1310 MMF
1310 SMF 9/125 N/A 10 km (6.21 miles)
Fiber
mode
Fiber
diameter
(
50/125
62.5/125
50/125
62.5/125
Modal
bandwidth
(MHz*km)
2000 300 m (984.25 ft)
500 82 m (269.03 ft)
400 66 m (216.54 ft)
200 33 m (108.27 ft)
160 26 m (85.30 ft)
1500 220 m (721.78 ft)
500 220 m (721.78 ft)
400 100 m (328.08 ft)
200 220 m (721.78 ft)
160 220 m (721.78 ft)
Transmission
distance
HP X130 10G SFP+
JG234A
JG915A
LC ER 40km
Transceiver
HP X130 10G SFP+
LC LH 80km
Transceiver
1550 SMF 9/125 N/A 40 km (24.86 miles)
1550 SMF 9/125 N/A 80 km (49.71 miles)
18
Page 23

p
Table 23 Specifications for 10-Gigabit SFP+ fiber transceiver modules (2)
O
Product
code
Name
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit power
Receive power
JD092B
JD093B
JD094B
JG234A
JG915A
HP X130 10G SFP+ LC SR
Transceiver
HP X130 10G SFP+ LC LRM
Transceiver
HP X130 10G SFP+ LC LR
Transceiver
HP X130 10G SFP+ LC ER
40km Transceiver
HP X130 10G SFP+ LC LH
80km Transceiver
10-Gigabit SFP+ cable
Figure 10 10-Gigabit SFP+ cable
–7.3 to –1 –9.9 to +0.5
–6.5 to +0.5 –6.5 to +1.5
–8.2 to +0.5 –14.4 to +0.5
–4.7 to +4 –15.8 to –1
0 to +4 –24 to –7
Models and specifications
Table 24 Specifications for 10-Gigabit SFP+ cables
Product
code
JD095C
JD096C
JD097C
JG081C
JC784C
Name Cable length Data rate Type
HP X240 10G SFP+ SFP+
0.65m DA Cable
HP X240 10G SFP+ SFP+
1.2m DA Cable
HP X240 10G SFP+ SFP+
3m DA Cable
HP X240 10G SFP+ SFP+
5m DA Cable
HP X240 10G SFP+ SFP+
7m Direct Attach Copper
Cable
0.65 m (2.13 ft)
1.2 m (3.94 ft)
3 m (9.84 ft)
5 m (16.40 ft)
7 m (22.97 ft)
10.31 Gbps SFP+ cable
19
Page 24

gth
ps)
m)
XFP transceiver modules
Figure 11 XFP transceiver module
Models and specifications
10-Gigabit XFP fiber transceiver modules use LC connectors.
Table 25 Specifications for XFP transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JD117B
JD108B
JD088A
JD121A
Name
HP X130 10G XFP
LC SR Transceiver
HP X130 10G XFP
LC LR 1310nm
Transceiver
HP X130 10G POS
XFP LC LR
Transceiver
HP X135 10G XFP
LC ER Transceiver
Central
wavelen
(nm)
850 10.31 MMF
1310 10.31 SMF 9/125 N/A
1310
1550
Data
rate
(Gb
9.95 to
11.3
9.95 to
10.7
Fiber
mode
SMF 9/125 N/A
SMF 9/125 N/A
Fiber
diameter
(
50/125
62.5/12
5
Modal
bandwidth
(MHz*km)
2000
500
400
200
160 26 m (85.30 ft)
Maximum
transmission
distance
300 m
(984.25 ft)
82 m (269.03
ft)
66 m (216.54
ft)
33 m (108.27
ft)
10 km (6.21
miles)
10 km (6.21
miles)
40 km (24.86
miles)
HP X130 10G XFP
JD107A
JG226A
LC ZR 1550nm
Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP
LC LH 80km
1538.98nm
DWDM Transceiver
1550
1538.98
9.95 to
10.31
9.95 to
10.31
20
SMF 9/125 N/A
SMF 9/125 N/A
80 km (49.71
miles)
80 km (49.71
miles)
Page 25

gth
ps)
m)
p
Product
code
JG227A
JG228A
JG229A
JG230A
JG231A
Name
HP X180 10G XFP
LC LH 80km
1539.77nm
DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP
LC LH 80km
1540.56nm
DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP
LC LH 80km
1542.14nm
DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP
LC LH 80km
1542.94nm
DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP
LC LH 80km
1558.98nm
DWDM Transceiver
Central
wavelen
(nm)
1539.77
1540.56
1542.14
1542.94
1558.98
Data
rate
(Gb
9.95 to
10.31
9.95 to
10.31
9.95 to
10.31
9.95 to
10.31
9.95 to
10.31
Fiber
mode
SMF 9/125 N/A
SMF 9/125 N/A
SMF 9/125 N/A
SMF 9/125 N/A
SMF 9/125 N/A
Fiber
diameter
(
Modal
bandwidth
(MHz*km)
Maximum
transmission
distance
80 km (49.71
miles)
80 km (49.71
miles)
80 km (49.71
miles)
80 km (49.71
miles)
80 km (49.71
miles)
HP X180 10G XFP
JG232A
JG233A
LC LH 80km
1559.79nm
DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP
LC LH 80km
1560.61nm
DWDM Transceiver
1559.79
1560.61
9.95 to
10.31
9.95 to
10.31
SMF 9/125 N/A
SMF 9/125 N/A
Table 26 Specifications for XFP transceiver modules (2)
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
JD117B
JD108B
JD088A
JD121A
Name
HP X130 10G XFP LC SR
Transceiver
HP X130 10G XFP LC LR 1310nm
Transceiver
HP X130 10G POS XFP LC LR
Transceiver
HP X135 10G XFP LC ER
Transceiver
O
Transmit power
–7.3 to –1.08 –9.9 to –1
–8.2 to +0.5 –14.4 to +0.5
–6 to –1 –10.3 to +0.5
–1 to +2 –14.1 to –1
80 km (49.71
miles)
80 km (49.71
miles)
Receive power
JD107A
JG226A
HP X130 10G XFP LC ZR
1550nm Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP LC LH 80km
1538.98nm DWDM Transceiver
0 to +4 –24 to –7
–1 to +3 –24 to –7
21
Page 26

p
g
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
Name
O
Transmit power
Receive power
JG227A
JG228A
JG229A
JG230A
JG231A
JG232A
JG233A
HP X180 10G XFP LC LH 80km
1539.77nm DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP LC LH 80km
1540.56nm DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP LC LH 80km
1542.14nm DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP LC LH 80km
1542.94nm DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP LC LH 80km
1558.98nm DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP LC LH 80km
1559.79nm DWDM Transceiver
HP X180 10G XFP LC LH 80km
1560.61nm DWDM Transceiver
–1 to +3 –24 to –7
–1 to +3 –24 to –7
–1 to +3 –24 to –7
–1 to +3 –24 to –7
–1 to +3 –24 to –7
–1 to +3 –24 to –7
–1 to +3 –24 to –7
NOTE:
The 9/125μm single-mode fibers used by transceiver modules JG226A throu
h JG233A should conform
to ITU-T G.655, and those used by other transceiver modules should conform to ITU-T G.652.
22
Page 27

CX4 cables
Figure 12 CX4 cable
Models and specifications
Table 27 Specifications for CX4 cables
Product code Name Cable length Data rate Description
JD363B
JD364B
JD365A
HP X230 Local Connect
50cm CX4 Cable
HP X230 Local Connect
100cm CX4 Cable
HP X230 CX4 to CX4 3m
Cable
0.5 m (1.64 ft)
1 m (3.28 ft)
3 m (9.84 ft)
12 Gbps
Used for interconnecting
deices, and supports IRF
23
Page 28

p
p
QSFP+ modules
QSFP+ modules provide a transmission rate of 40 Gbps.
QSFP+ fiber transceiver modules that use a 12-fiber MPO connector
Figure 13 QSFP+ fiber transceiver module that use a 12-fiber MPO connector
Models and specifications
Table 28 Specifications for QSFP+ fiber transceiver modules that use a 12-fiber MPO connector (1)
Product
code
JG325B
JG709A
Table 29 Specifications for QSFP+ fiber transceiver modules using a 12-fiber MPO connector (2)
HP description
HP X140 40G QSFP+
MPO SR4 Transceiver
HP X140 40G QSFP+
MPO MM 850nm CSR4
300m Transceiver
Central
wavelen
gth (nm)
850 MMF 50/125
850 MMF 50/125
Fiber
mode
Fiber
diamete
r (m)
Modal
bandwidth
(MHz*km)
2000 100 m (328.08 ft)
4700 150 m (492.12 ft)
2000 300 m (984.25 ft)
4700 400 m (1312.33 ft)
Transmission
distance
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
JG325B
Name
HP X140 40G QSFP+ MPO
SR4 Transceiver
O
Transmit
–7.6 to 0 –9.5 to +2.4
24
ower
Receive power
Page 29

p
p
g
m)
p
p
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
JG709A
Name
HP X140 40G QSFP+ MPO
MM 850nm CSR4 300m
Transceiver
O
Transmit
–7.6 to 0 –9.9 to +2.4
ower
Receive power
NOTE:
The 40G QSFP+ ports of the JG325B and JG709A fiber transceiver modules can be split into four
channels. You can connect a 40G QSFP+ port to four 10G SFP+ ports. The QSFP+ fiber transceiver
module and SFP+ fiber transceiver modules to be connected must be the same in specifications, includin
central wavelength and fiber type.
QSFP+ fiber transceiver modules that use an LC connector
Figure 14 QSFP+fiber transceiver module that use an LC connector
Models and specifications
Table 30 Specifications for QSFP+ transceiver modules that use an LC connector (1)
Product
code
JG661A
Name
HP X140 40G
QSFP+ LC LR4 SM
10km 1310nm
Transceiver Module
Table 31 Specifications for QSFP+ transceiver modules that use an LC connector (2)
Product
code
Name
Central
wavelength
(nm)
Four lanes:
• 12 71
• 12 91
• 1311
• 13 31
Fiber
mode
SMF 9/125 N/A
O
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit
Fiber
diameter
(
ower
Modal
bandwidth
(MHz*km)
Receive power
Transmission
distance
10 km (6.21
miles)
25
Page 30

p
p
Product
code
JG661A
Name
HP X140 40G QSFP+ LC LR4
SM 10km 1310nm
Transceiver Module
O
Transmit
–7 to +2.3 –13.7 to +2.3
40-Gigabit QSFP+ cable
Figure 15 40-Gigabit QSFP+ cable
tical parameters (dBm)
ower
Receive power
Models and specifications
Table 32 Specifications for 40-Gigabit QSFP+ cables
Product
code
JG326A
JG327A
JG328A
Name Cable length Data rate Description
HP X240 40G QSFP+ QSFP+ 1m
Direct Attach Copper Cable
HP X240 40G QSFP+ QSFP+ 3m
Direct Attach Copper Cable
HP X240 40G QSFP+ QSFP+ 5m
Direct Attach Copper Cable
QSFP+ to SFP+ cable
One end of a QSFP+ to SFP+ cable provides a 40-Gigabit QSFP+ module, and the other end provides
four 10-Gigabit SFP+ modules.
1 m (3.28 ft)
3 m (9.84 ft)
5 m (16.40 ft)
40 Gbps
Used for interconnecting
40-Gigabit QSFP ports
26
Page 31

Figure 16 QSFP+ to SFP+ cable
Models and specifications
Table 33 Specifications for QSFP+ to SFP+ cables
Product
code
JG329A
JG330A
JG331A
Name Cable length Data rate Description
HP X240 40G QSFP+ to
4x10G SFP+ 1m Direct Attach
Copper Splitter Cable
HP X240 40G QSFP+ to
4x10G SFP+ 3m Direct Attach
Copper Splitter Cable
HP X240 40G QSFP+ to
4x10G SFP+ 5m Direct Attach
Copper Splitter Cable
1 m (3.28 ft)
3 m (9.84 ft)
5 m (16.40 ft)
40 Gbps
Used for connecting a
40-Gigabit QSFP+ port to
four 10-Gigabit SFP+ ports
27
Page 32

m)
p
p
CFP transceiver modules
Figure 17 CFP transceiver module
Models and specifications
CFP transceiver modules use LC connectors.
Table 34 Specifications for CFP transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JC857A
Name
HP X140 40G
CFP LC LR4 10km
SM Transceiver
Central
wavelength
(nm)
Four lanes:
• 12 71
• 12 91
• 1311
Data
rate
40
Gbps
• 13 31
Four lanes:
JG829A
(end of
sale)
HP X150 100G
CFP LC LR4 10km
SM Transceiver
• 1295.56
• 13 0 0 . 0 5
• 1304.58
100
Gbps
• 1309.14
Four lanes:
• 1295.56
• 13 0 0 . 0 5
• 1304.58
100
Gbps
JG829B
HP X150 100G
CFP LC LR4 10km
SM Transceiver
• 1309.14
Fiber
mode
SMF 9/125 10 km (6.21 miles)
SMF 9/125 10 km (6.21 miles)
SMF 9/125 10 km (6.21 miles)
Fiber
diameter
(
Maximum
transmission distance
Table 35 Specifications for CFP transceiver modules (2)
O
Product
code
JC857A
Name
HP X140 40G CFP LC LR4
10km SM Transceiver
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit
–4 to +3 per lane –11.5 to +3 per lane
28
ower
Receive power
Page 33

p
p
tical parameters (dBm)
Product
code
Name
O
Transmit
ower
Receive power
JG829A
(end of
sale)
JG829B
HP X150 100G CFP LC LR4
10km SM Transceiver
HP X150 100G CFP LC LR4
10km SM Transceiver
–4.3 to +4.5 per lane –10.6 to +4.5 per lane
–4.3 to +4.5 per lane –10.6 to +4.5 per lane
29
Page 34

p
p
CXP modules
CXP fiber transceiver modules
Figure 18 CXP fiber transceiver module
Models and specifications
CXP fiber transceiver modules provide a transmission rate of 100 Gbps and use 24-fiber MPO
connectors.
Table 36 Specifications for CXP fiber transceiver modules (1)
Product
code
JG881A
Table 37 Specifications for CXP fiber transceiver modules (2)
Product
code
JG881A
Name
HP X150 100G
CXP MPO SR
100m Multimode
Transceiver
Name
HP X150 100G CXP MPO
SR 100m Multimode
Transceiver
Central
wavelength
(nm)
850 MMF 50/125 100 m (328.08 ft)
Fiber
mode
O
tical parameters (dBm)
Transmit
–7.6 to +2.4 –9.5 to +2.4
Fiber diameter
(m)
ower
Maximum transmission
distance
Receive power
30
Page 35

CXP AOC
Figure 19 CXP AOC
Models and specifications
Table 38 Specifications for CXP AOCs
Product code Name Cable length Data rate
HP X2A0 100G CXP
JG883A
JG882A
CXP 30m Active
Optical Cable
HP X2A0 100G CXP
CXP 10m Active
Optical Cable
30 m (98.43 ft) 100 Gbps
10 m (32.81 ft) 100 Gbps
31
Page 36

Support and other resources
Contacting HP
For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website:
http://www.hp.com/support
Before contacting HP, collect the following information:
• Product model names and numbers
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
Subscription service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber's Choice for Business website:
http://www.hp.com/go/wwalerts
After registering, you will receive email notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
Related information
Documents
To find related documents, browse to the Manuals page of the HP Business Support Center website:
http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
• For related documentation, navigate to the Networking section, and select a networking category.
• For a complete list of acronyms and their definitions, see HP FlexNetwork Technology Acronyms.
Websites
• HP.com http://www.hp.com
• HP Networking http://www.hp.com/go/networking
• HP manuals http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
• HP download drivers and software http://www.hp.com/support/downloads
• HP software depot http://www.software.hp.com
• HP Education http://www.hp.com/learn
32
 Loading...
Loading...