Page 1

hp 39g+ graphing calculator
Mastering the hp 39g+
A guide for teachers, students and other
users of the hp 39g+, hp 39g & hp 40g
Edition 1.1
HP part number F2224-90010
Printed Date: 2005/10/11
Page 2

Table of Contents
Introduction.................................................................................................12
How to use this Manual..............................................................................13
Early High School.........................................................................................................13
Pre-Calculus.................................................................................................................14
Calculus........................................................................................................................14
Where’s the ON button?.............................................................................15
Some Keyboard Examples.........................................................................16
Keys & Notation Conventions...................................................................17
Some essential keys .......................................................................................................17
The SHIFT key .............................................................................................................17
The ALPHA key............................................................................................................18
The Screen keys ..........................................................................................................18
Pop-up menus & short-cuts..........................................................................................18
Everything revolves around Aplets! .........................................................21
Some typical aplet views .............................................................................................. 22
The HOME view...........................................................................................25
What is the HOME view?.................................................................................................25
Exploring the keyboard...................................................................................................26
The screen keys ........................................................................................................... 26
Aplet related keys.........................................................................................................26
The arrow keys.............................................................................................................26
The SYMB, PLOT and NUM keys....................................................................................27
Intro to the VIEWS menu ..............................................................................................28
The VARS key ............................................................................................................... 28
The SETUP views .........................................................................................................30
The MODES view ...........................................................................................................30
Numeric formats ........................................................................................................... 31
The ANS key .................................................................................................................32
The negative key .......................................................................................................... 33
The CHARS key............................................................................................................ 33
The DEL and CLEAR keys ............................................................................................34
Angle and Numeric settings...........................................................................................35
Memory Management......................................................................................................37
The MEMORY MANAGER view................................................................................... 37
Downloaded aplets & memory .....................................................................................38
The GRAPHICS MANAGER ........................................................................................ 39
The LIBRARY MANAGER............................................................................................ 39
Fractions on the hp 39g+................................................................................................40
Pitfalls to watch for .......................................................................................................42
The HOME History.............................................................................................................43
COPYing calculations................................................................................................... 43
Clearing the History......................................................................................................44
SHOWing results..........................................................................................................44
Storing and Retrieving Memories..................................................................................45
Referring to other aplets from the HOME view...............................................................46
An introduction to the MATH Menu...............................................................................47
Resetting the calculator..................................................................................................48
Soft reboot....................................................................................................................48
Soft reboot (Hardware).................................................................................................49
Hard reboot (with memory wipe) .................................................................................. 49
Summary ..........................................................................................................................50
2
Page 3

The Function Aplet.....................................................................................51
∫
Choose the aplet ..........................................................................................................51
The SYMB view .............................................................................................................52
The XTθ button ............................................................................................................. 52
ing your function ...............................................................................................52
The NUM view................................................................................................................ 53
The PLOT view .............................................................................................................53
Auto Scale........................................................................................................................54
The PLOT SETUP view....................................................................................................55
Detail vs. Faster............................................................................................................ 55
Simultaneous................................................................................................................ 56
Connect ........................................................................................................................ 56
Axes.............................................................................................................................. 56
Labels ...........................................................................................................................56
Grid...............................................................................................................................56
The default axis settings ................................................................................................57
The Bar...............................................................................................................57
The MENU toggle.........................................................................................................57
The Menu Bar functions..................................................................................................58
Trace ............................................................................................................................58
Defn ..............................................................................................................................58
Goto..............................................................................................................................59
The Zoom Sub-menu ...................................................................................................60
Center...........................................................................................................................60
In/Out............................................................................................................................60
Box…............................................................................................................................61
X-Zoom In/Out x4 and Y-Zoom In/Out x4 ....................................................................62
Square ..........................................................................................................................62
Auto Scale, Decimal, Integer and Trig .........................................................................62
The FCN menu.................................................................................................................63
Root ..............................................................................................................................63
Intersection...................................................................................................................64
Slope ............................................................................................................................64
Signed area… ..............................................................................................................65
Definite integrals........................................................................................................... 65
Tracing the integral in PLOT ......................................................................................... 66
Areas between and under curves ................................................................................67
Extremum ..................................................................................................................... 68
Tips & Tricks - Function.............................................................................69
Finding a suitable set of axes....................................................................................... 69
Composite functions.....................................................................................................71
Using functions in the HOME view ...............................................................................72
Differentiating ...............................................................................................................73
Circular functions.......................................................................................................... 74
Trig functions................................................................................................................76
Retaining calculated values.......................................................................................... 77
The NUM view revisited ..............................................................................................77
ZOOM...........................................................................................................................78
Integration: The definite integral using the
function ............................................... 80
Integration: The algebraic indefinite integral ................................................................ 81
The hp 40g Computer Algebra System........................................................................82
Integration: The definite integral using PLOT variables ............................................... 83
Piecewise defined functions .........................................................................................85
‘Nice’ scales..................................................................................................................86
Use of brackets in functions ......................................................................................... 87
3
Page 4

Problems when evaluating limits..................................................................................88
Gradient at a point........................................................................................................90
Finding and accessing polynomial roots ...................................................................... 91
The VIEWS menu........................................................................................92
Plot-Detail.....................................................................................................................93
Plot-Table ..................................................................................................................... 94
Overlay Plot..................................................................................................................95
Auto Scale .................................................................................................................... 96
Decimal, Integer & Trig................................................................................................. 97
Downloaded Aplets from the Internet ...........................................................................99
Curve Areas..................................................................................................................99
Linear Programming.....................................................................................................99
The Parametric Aplet................................................................................100
Choose XRng, YRng & TRng..................................................................................... 100
The effect of TRng...................................................................................................... 101
TStep controls smoothness........................................................................................101
Tips & Tricks - Parametric equations .....................................................103
Fun and games..............................................................................................................103
Example 1...................................................................................................................103
Example 2...................................................................................................................103
Vectors ...........................................................................................................................104
Example 1...................................................................................................................104
Example 2...................................................................................................................105
The Polar Aplet.........................................................................................106
Choose XRng, YRng & θRng ..................................................................................... 106
θStep and smoothness............................................................................................... 106
Changing the default for θStep................................................................................... 106
Circular circles ............................................................................................................106
The Sequence Aplet .................................................................................107
Recursive or non-recursive ........................................................................................107
First, second & general terms ....................................................................................107
Convenient screen keys provided .............................................................................. 108
Tips & Tricks - Sequences & Series........................................................110
Defining a generalized GP and the sum to n terms. ..................................................110
Solving sequence problems ....................................................................................... 110
Modeling loans ...........................................................................................................112
The Solve Aplet.........................................................................................113
Equations vs. expressions.......................................................................................... 113
Entering the equation ................................................................................................. 113
Solving for a missing value.........................................................................................114
The INFO report ......................................................................................................... 114
Multiple solutions and the initial guess.......................................................................115
Graphing in Solve.......................................................................................................116
Transferring approximate solutions............................................................................116
Referring to functions from other aplets ..................................................................... 117
A detailed explanation of PLOT in Solve.................................................................... 118
The meaning of messages..............................................................................120
Tips & Tricks - Solve ................................................................................121
Easy problems............................................................................................................ 121
Harder problems......................................................................................................... 121
4
Page 5

The Stats Aplet - Univariate Data............................................................122
Uni vs. Bi-variate data ................................................................................................ 122
Clearing data .............................................................................................................. 122
Sorting data ................................................................................................................ 123
The STATS key .......................................................................................................... 123
Functions of columns .................................................................................................124
Registering columns as ‘in use’.................................................................................. 124
Working with frequency tables ...................................................................................125
Auto scale...................................................................................................................125
Plot Setup options ......................................................................................................126
Box and whisker graphs .............................................................................................126
The effect of HRng ..................................................................................................... 127
Grouped data & HWidth ............................................................................................. 127
Tips & Tricks - Univariate Data................................................................129
New columns as functions of old................................................................................129
Simulating Dice ..........................................................................................................129
Simulating Random Variables....................................................................................130
The Stats Aplet - Bivariate Data ..............................................................132
Uni vs. Bi-variate data ................................................................................................ 132
Clearing data .............................................................................................................. 132
Entering data as ordered pairs...................................................................................133
Adjusting the symbols used to plot points ..................................................................133
The cursor ..................................................................................................................133
Sorting paired columns............................................................................................... 134
Specifying the fit model .............................................................................................. 134
Multiple data sets .......................................................................................................134
Choosing from available fit models ............................................................................135
The User Defined model ............................................................................................135
Connected data .......................................................................................................... 136
Two Variable Statistics ...............................................................................................137
Showing the line of best fit .........................................................................................138
Predicting using PREDY..............................................................................................140
Predicting using the PLOT view..................................................................................140
RelErr as a measure of non-linear fit....................................................................... 141
Tips & Tricks - Bivariate Data..................................................................143
New columns as functions of old................................................................................143
Using values from in calculations ..................................................................143
Obtaining coefficients from the fit model ....................................................................145
Finding Fit Coefficients...............................................................................................145
Correct interpretation of the PREDX function ............................................................146
Assigning rank orders to sets of data .........................................................................147
Using Stats to find equations from point data ............................................................148
The Inference aplet...................................................................................150
Using the Chi2 test on a frequency table ................................................................... 150
Hypothesis test: T-Test 1-µ ....................................................................................... 151
Confidence interval: T-Int 1-µ .................................................................................... 153
Hypothesis test: T-Test µ1 -µ
Hypothesis test: Z-Test 1-µ ....................................................................................... 156
.....................................................................................154
2
Tips & Tricks - Inference..........................................................................158
Importing from a frequency table ...............................................................................158
5
Page 6

The Finance aplet .....................................................................................160
Parameters.................................................................................................................160
Straightforward compound interest ............................................................................ 161
Annuity........................................................................................................................162
Loan calculations........................................................................................................ 162
Amortization................................................................................................................163
The Quad Explorer teaching aplet ..........................................................164
Objectives...................................................................................................................164
Choosing the level......................................................................................................164
GRAPH mode............................................................................................................. 164
SYMB mode ...............................................................................................................165
Self test mode ............................................................................................................166
The Trig Explorer teaching aplet.............................................................167
Objectives...................................................................................................................167
SIN vs. COS ............................................................................................................... 167
SYMB vs. GRPH mode ..............................................................................................167
Using Matrices on the hp 39g+................................................................170
The MATRIX Catalog ................................................................................................ 170
Matrix calculations in the HOME view ..........................................................................171
Solving a system of equations....................................................................................172
Finding an inverse matrix ........................................................................................... 174
The dot product ..........................................................................................................175
Using Lists on the hp 39g+......................................................................176
The list variables ........................................................................................................176
Operations on lists...................................................................................................... 176
Statistical columns as lists.......................................................................................... 176
List functions...............................................................................................................177
Editing a list ................................................................................................................ 177
Operations on elements .............................................................................................177
Using the Notepad Catalog......................................................................178
Aplet notes vs. independent notes ............................................................................. 178
Independent Notes and the Notepad Catalog..........................................................179
Transferring notes using IR ........................................................................................180
Editing software..........................................................................................................180
Software .........................................................................................................................181
For the hp 38g, hp 39g & hp 40g................................................................................181
For the hp 39g+ ..........................................................................................................181
Creating a Note..............................................................................................................182
Locking ALPHA mode ................................................................................................. 182
The CHARS view .........................................................................................................183
Corrupting notes.........................................................................................................183
Using the aplet Sketchpad.......................................................................184
Adding text to a sketch ............................................................................................... 184
The DRAW menu ...........................................................................................................185
DOT+..........................................................................................................................185
LINE............................................................................................................................185
BOX ............................................................................................................................185
CIRCLE ......................................................................................................................186
Cut and paste (sort of…)............................................................................................186
Capturing the PLOT screen ....................................................................................... 187
6
Page 7

Using, Copying & Creating aplets...........................................................189
Creating a copy of a Standard aplet............................................................................190
Copying and adding to the Function aplet.................................................................. 190
Copying and adding to the Stats aplet ....................................................................... 191
Some examples of saved aplets..................................................................................192
The Triangles aplet..................................................................................................... 192
The Prob. Distributions aplet......................................................................................192
The Transformer aplet................................................................................................194
Copying from hp 39g+ to hp 39g+ via the infra-red link............................................197
The infra-red port........................................................................................................ 197
Time out...................................................................................................................... 199
Attached programs ..................................................................................................... 199
Downloading aplets from the Internet.........................................................................200
Finding aplets ............................................................................................................. 200
Organizing your collection ..........................................................................................201
Software for the hp 38g, hp 39g & hp 40g .................................................................202
Software for the hp 39g+............................................................................................203
The HPGComm Connectivity Program ......................................................................204
Deleting downloaded aplets from the calculator ........................................................207
Saving notes, aplets and sketches via the Connectivity Kit ....................................... 208
Capturing screens using the Connectivity Kit............................................................. 210
Editing Notes with the Aplet Development Kit............................................................211
Programming the hp 39g+ .......................................................................212
The design process.......................................................................................................212
An overview................................................................................................................212
Choosing the parent aplet .......................................................................................... 212
Naming conventions...................................................................................................213
Planning the VIEWS menu..........................................................................................214
The SETVIEWS command .......................................................................................... 214
Special entries in the SETVIEWS command...............................................................216
The ‘Start’ entry .......................................................................................................... 217
Example aplet #1........................................................................................................ 217
Example aplet #2........................................................................................................ 222
Example aplet #3........................................................................................................ 224
Example aplet #4........................................................................................................ 226
Programming Commands........................................................................233
The Aplet commands....................................................................................................233
CHECK & UNCHECK................................................................................................ 233
SELECT...................................................................................................................... 233
SETVIEWS.................................................................................................................234
The Branch commands.................................................................................................234
IF THEN [ELSE] END............................................................................................... 234
CASE..........................................................................................................................234
IFFERR THEN [ELSE] END......................................................................................234
RUN............................................................................................................................235
STOP..........................................................................................................................235
The Drawing commands...............................................................................................235
ARC ............................................................................................................................235
BOX ............................................................................................................................235
ERASE .......................................................................................................................236
FREEZE .....................................................................................................................236
LINE............................................................................................................................236
PIXON and PIXOFF .................................................................................................. 236
TLINE .........................................................................................................................236
7
Page 8

The Graphics commands .............................................................................................237
The Loop commands ....................................................................................................237
FOR <var> = <start> TO <end> [STEP] <statements> END ..................................... 237
DO UNTIL................................................................................................................... 237
WHILE REPEAT......................................................................................................... 237
BREAK .......................................................................................................................238
The Matrix commands...................................................................................................238
EDITMAT....................................................................................................................238
REDIM ........................................................................................................................238
The Print commands.....................................................................................................239
PRDISPLAY ...............................................................................................................239
PRHISTORY...............................................................................................................239
PRVAR ....................................................................................................................... 239
The Prompt commands.................................................................................................240
BEEP ..........................................................................................................................240
CHOOSE …. ..............................................................................................................240
DISP ........................................................................................................................... 241
DISPXY ......................................................................................................................241
DISPTIME................................................................................................................... 241
GETKEY .....................................................................................................................241
INPUT.........................................................................................................................242
MSGBOX.................................................................................................................... 242
PROMPT .................................................................................................................... 242
WAIT........................................................................................................................... 242
The MATH menu functions......................................................................243
The ‘Real’ group of functions.......................................................................................246
CEILING ..................................................................................................................... 246
DEG RAD ................................................................................................................ 246
FLOOR ....................................................................................................................... 246
FNROOT ....................................................................................................................247
FRAC..........................................................................................................................247
HMS ........................................................................................................................248
HMS........................................................................................................................248
INT..............................................................................................................................249
MANT .........................................................................................................................249
MAX............................................................................................................................249
MIN .............................................................................................................................250
MOD ........................................................................................................................... 250
% ................................................................................................................................250
%CHANGE.................................................................................................................251
%TOTAL.....................................................................................................................251
RAD DEG ................................................................................................................ 251
ROUND ......................................................................................................................252
SIGN...........................................................................................................................252
TRUNCATE................................................................................................................253
XPON .........................................................................................................................253
The ‘Stat-Two’ group of functions...............................................................................254
PREDY ....................................................................................................................... 254
PREDX ....................................................................................................................... 254
The ‘Symbolic’ group of functions..............................................................................255
The = ‘function’ ...........................................................................................................255
ISOLATE ....................................................................................................................255
LINEAR?..................................................................................................................... 256
QUAD ......................................................................................................................... 256
QUOTE.......................................................................................................................257
The | function..........................................................................................................258
8
Page 9

The ‘Tests’ group of functions.....................................................................................259
The ‘Trigonometric’ & ‘Hyperbolic’ groups of functions...........................................259
COT, SEC etc............................................................................................................. 259
EXP ............................................................................................................................260
ALOG.......................................................................................................................... 260
EXPM1 .......................................................................................................................260
LNP1...........................................................................................................................261
The ‘Calculus’ group of functions...............................................................................261
The ‘Complex’ group of functions...............................................................................262
ABS ............................................................................................................................263
SIGN...........................................................................................................................263
ARG............................................................................................................................264
CONJ..........................................................................................................................264
IM & RE ...................................................................................................................... 264
The ‘List’ group of functions........................................................................................265
CONCAT ....................................................................................................................265
∆LIST..........................................................................................................................266
MAKELIST..................................................................................................................266
πLIST ..........................................................................................................................267
POS ............................................................................................................................267
SIZE............................................................................................................................ 268
ΣLIST..........................................................................................................................268
REVERSE ..................................................................................................................268
SORT.......................................................................................................................... 268
The ‘Loop’ group of functions .....................................................................................269
ITERATE ....................................................................................................................269
RECURSE..................................................................................................................270
Σ (SUMMATION)........................................................................................................270
The ‘Matrix’ group of functions....................................................................................271
COLNORM ................................................................................................................. 271
COND .........................................................................................................................271
CROSS.......................................................................................................................271
DET ............................................................................................................................272
DOT ............................................................................................................................272
EIGENVAL..................................................................................................................272
EIGENVV.................................................................................................................... 272
IDENTMAT ................................................................................................................. 272
INVERSE.................................................................................................................... 273
LQ...............................................................................................................................273
LSQ ............................................................................................................................274
LU ...............................................................................................................................274
MAKEMAT..................................................................................................................274
QR .............................................................................................................................. 274
RANK.......................................................................................................................... 274
ROWNORM................................................................................................................ 274
RREF..........................................................................................................................274
SCHUR.......................................................................................................................275
SIZE............................................................................................................................ 275
SPECNORM............................................................................................................... 275
SPECRAD .................................................................................................................. 275
SVD ............................................................................................................................ 275
SVL.............................................................................................................................275
TRACE .......................................................................................................................276
TRN ............................................................................................................................ 276
9
Page 10

The ‘Polynomial’ group of functions...........................................................................277
POLYCOEF................................................................................................................277
POLYEVAL................................................................................................................. 277
POLYFORM ...............................................................................................................278
POLYROOT................................................................................................................279
The ‘Probability’ group of functions............................................................................280
COMB.........................................................................................................................280
The ! function.............................................................................................................. 280
PERM ......................................................................................................................... 281
RANDOM....................................................................................................................281
RANDSEED................................................................................................................281
UTPN..........................................................................................................................282
UTPC..........................................................................................................................283
UTPF .......................................................................................................................... 283
UTPT .......................................................................................................................... 283
Appendix A: Worked Examples...............................................................284
Finding the intercepts of a quadratic..........................................................................284
Method 1 - Using the QUAD function in HOME. ............................................................284
Method 2 - Using the Function aplet. ......................................................................... 284
Method 3 - Using the POLYROOT function..................................................................285
Finding complex solutions to a complex equation....................................................285
Method 1 - Using the QUAD function.........................................................................285
Method 2 - Using POLYROOT...................................................................................285
Finding critical points and graphing a polynomial....................................................286
Solving simultaneous equations.................................................................................288
Method 1 - Graphing the lines....................................................................................288
Second method - using a matrix.................................................................................288
Third method - using the 3x3 Solver aplet ................................................................289
Expanding polynomials................................................................................................290
Exponential growth.......................................................................................................291
Solution of matrix equations........................................................................................293
Inconsistent systems of equations .............................................................................294
Using the RREF function............................................................................................294
Finding complex roots..................................................................................................295
Analyzing vector motion and collisions......................................................................296
Circular Motion and the Dot Product...........................................................................297
Inference testing using the Chi2 test...........................................................................299
Appendix B: Teaching Calculus with an hp 39g+..................................301
Investigating
Domains and Composite Functions............................................................................302
Gradient at a Point.........................................................................................................303
Gradient Function..........................................................................................................304
The Chain Rule ..............................................................................................................305
Optimization...................................................................................................................305
Area Under Curves........................................................................................................306
Fields of Slopes and Curve Families...........................................................................306
Inequalities.....................................................................................................................307
Rectilinear Motion .........................................................................................................307
Limits..............................................................................................................................307
Piecewise Defined Functions.......................................................................................308
Sequences and Series ..................................................................................................308
Transformations of Graphs..........................................................................................309
n
yx= for n an integer..........................................................................301
10
Page 11

Appendix C: The hp 40g & its CAS .........................................................310
REGISTER YOUR PRODUCT AT: www.register.hp.com
THIS MANUAL AND ANY EXAMPLES CONTAINED HEREIN ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" AND
ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES
NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MANUAL, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, NON-INFRINGEMENT
AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
HEWLETT-PACKARD CO. SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY ERRORS OR FOR INCIDENTAL
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH THE FURNISHING,
PERFORMANCE, OR USE OF THIS MANUAL OR THE EXAMPLES CONTAINED HEREIN.
© Copyright 1993-1998, 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation of this manual is prohibited without prior written
permission of Hewlett-Packard Company, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
Hewlett-Packard Company
4995 Murphy Canyon Rd,
Suite 301
San Diego, CA 92123
Acknowledgements
Hewlett-Packard would like to thank the author Colin Croft.
Printing History
Edition 1 February 2004
Edition 2 September 2005
Notice
Introduction....................................................................................................................310
What is a CAS? .......................................................................................................... 310
What is the difference between the hp 39g, hp 40g & hp 39g+? ...............................312
Using the CAS................................................................................................................313
Entering and editing an expression............................................................................313
In-line editing mode .................................................................................................... 316
Erasing, copying, cutting and pasting ........................................................................316
Cursor mode............................................................................................................... 317
The CAS HOME History.............................................................................................317
The PUSH and POP commands................................................................................318
Pasting to an aplet...................................................................................................... 319
Evaluating algebraic expressions............................................................................... 320
Using functions in the CAS..........................................................................................321
E.g. 1 Using LIMIT.................................................................................................... 321
E.g. 2 Factorizing expressions ................................................................................. 322
E.g. 3 Solving equations........................................................................................... 323
E.g. 4 Solving simultaneous equations ....................................................................323
E.g. 5 Solving a simultaneous integration ................................................................ 325
E.g. 6 Defining a user function ................................................................................. 327
On-line help....................................................................................................................328
Configuring the CAS.....................................................................................................329
Tips & Tricks - CAS.......................................................................................................330
11
Page 12

I
NNTTRROODDUUCCTTIIOON
I
This booklet is intended to help you to master your hp 39g+ calculator but is
also aimed at users of the hp 39g and hp 40g. These are very sophisticated
calculators, having more capabilities than a mainframe computer of the ’70s,
so don’t expect to come to grips with its abilities in one or two sessions.
However, if you persevere you will gain efficiency and confidence.
The majority of readers may only have used a Scientific calculator before so
explanations are as complete as possible. However it is not the purpose of
this book to teach mathematics so knowledge will be assumed. Those who
are already familiar with another brand or type, may find that a quick skim is
sufficient, perhaps with detailed reading of the “Tips and Tricks” sections.
The impact these calculators are having on the topics taught and even more,
the way they are taught is proving to be profound. The inventiveness and
flexibility of teachers of mathematics is being stretched to the limit as we
gradually change the face of teaching in the light of these machines.
N
For those concerned with the impact of a graphical calculator on the
‘fundamentals’ of mathematics, it should be recalled that the same fears were
held for scientific calculators when they were introduced earlier. History has
shown that these fears were generally groundless. Students are learning
topics in high school that their parents did not cover until university years. In
particular, the scientific calculator proved to be a great boon to students of
middle to lower ability in mathematics, relieving them of the burden of tedious
calculations and allowing them to concentrate on the concepts. This is also
the case with graphical calculators.
This manual is not intended to replace the one supplied with the calculator. It
fills in the holes, and also provides tips to make your work smother and more
confident. Happy calculating.
About the author
Colin Croft is a teacher at St. Hilda’s Anglican School for Girls in Perth,
Western Australia. Colin has worked extensively with Hewlett Packard on the
graphic calculator family of which the hp 39g+ is a member, and was part of
the team which created the hp 39g & hp 40g in 2000. He maintains an
extensive website of material for the hp 39g/40g/39g+ series called The HP
Home view, at http://www.hphomeview.com.
12
Page 13

H
OOWW TTOO UUSSEE TTHHIISS
H
It has been attempted to design this manual to cover the full use of the
hp 39g+ calculator. This means explanations which will be useful to anyone
from a student who is just beginning to use algebra seriously, to one who is
coming to grips with advanced calculus, and also to a teacher who is already
familiar with some other brand of graphic calculator.
Readers may encounter one of two difficulties. Firstly, the information in here
will be beyond the needs of some readers and secondly, the explanations
may be too detailed for more advanced users.
For students who don’t yet need the more advanced capabilities, suggestions
on which parts of the manual to read are given below. For more advanced
users, it is suggested that you read the sections on the Function, Sequence,
Statistics, Inference, Finance and Solve aplets, and also read the ‘Tips and
Tricks’ sections which follow many of the chapters.
M
AANNUUAAL
M
L
Early High School
Typical topics covered include…
Solving linear equations, graphing linear equations and possibly
simple quadratics, examining number patterns, multiplying
polynomials, factoring simple polynomials, calculations involving
powers (
positives and negatives, scientific notation, indices, systems of
equations and inequalities, parallel and perpendicular lines, dividing
polynomials, solving quadratics, rational expressions and equations.
Suggestions…
Read about the Function aplet in full, ignoring any sections that seem
to advanced. Learn about Intersection and Root in the menu
and make sure you know how the menu, Autoscale and PLOT
SETUP work. Learn to Build Your Own in the NUM view because it
lets you find values for rules easily. Learn to use the HOME view for
routine calculations, the MODES view, and how to use the calculator’s
memories. Read about the Solve aplet and how to use it to solve
equations. Read about the Statistics aplet and how to use it to find
23
, ,......xx ), square roots, cube roots, order of operations,
13
Page 14

means and to display histograms. In the MATH menu, read about the
functions ROUND, POLYFORM and POLYROOT. Make sure you
know how to save and transfer aplets. Learn about the Sketch view
and the Notes catalog for a bit of fun.
Pre-Calculus
Typical topics covered include…
Solving complex linear and non-linear simultaneous equations, and
trig, exponential & complex quadratic equations, factoring of any
quadratic, use and re-arrangement of formulas, indices, trigonometry,
some statistics, absolute value and greatest integer functions,
matrices, logarithms and parametric equations.
Suggestions…
Cover all of the material mentioned for high school students. Read the
suggestions on how to deal with graphs whose shape you don’t know
in advance. Learn how to use the Parametric aplet. Your teacher
might best advise on which portions of the Statistics aplet will be
relevant to you. In the MATH menu, also learn about functions
CEILING, ABS and FLOOR, POLYCOEF, and POLYEVAL. Read the
section covering the Matrices catalog and the functions DET, RREF,
INVERSE, and TRN.
Calculus
Topics covered here will vary according to which course students undertake
but there are very few skills covered in this manual which will not be of use at
some time. It is suggested that students skim the whole manual, and then
re-read it at intervals as material is covered in their courses and they begin to
see which parts of the manual are particularly relevant.
14
Page 15

y g
W
W
HHEERRE
E
’
SS TTHHEE
’
OON
N
BBUUTTTTOON
N
?
?
Let’s begin by looking at the fundamentals - the layout of the keyboard and
which are the important keys that are used frequently. The sketch below
shows most of the important keys. These are the ones which control the
operation of the calculator - others are used to do calculations once the
important keys have set up the environment to do it in.
The NUM key gives you a
tabular view of your
function, sequence or data.
The PLOT key displays the
graph view for any given
environment.
These six screen keys change their
function in different contexts. The
bar at the bottom of the screen labels
them. Check this bar for special
functions in an
These are the cursor (or
arrow) keys. They let you
move within a window.
iven context.
The SYMB key nearly
always takes you to a
view in which you can
The VIEWS key gives a
different menu in each aplet.
It can be very useful, and is
always worth checking.
HOME is where you will do
most of your calculations. It
is shared by all the aplets
and oversees them all.
The APLET key is central.
This key allows you to choose
which mathematical
environment you wish to
working.
So where is the ON button?
Examples of the effects of each of these keys and many more are shown on
the pages that follow.
15
Page 16
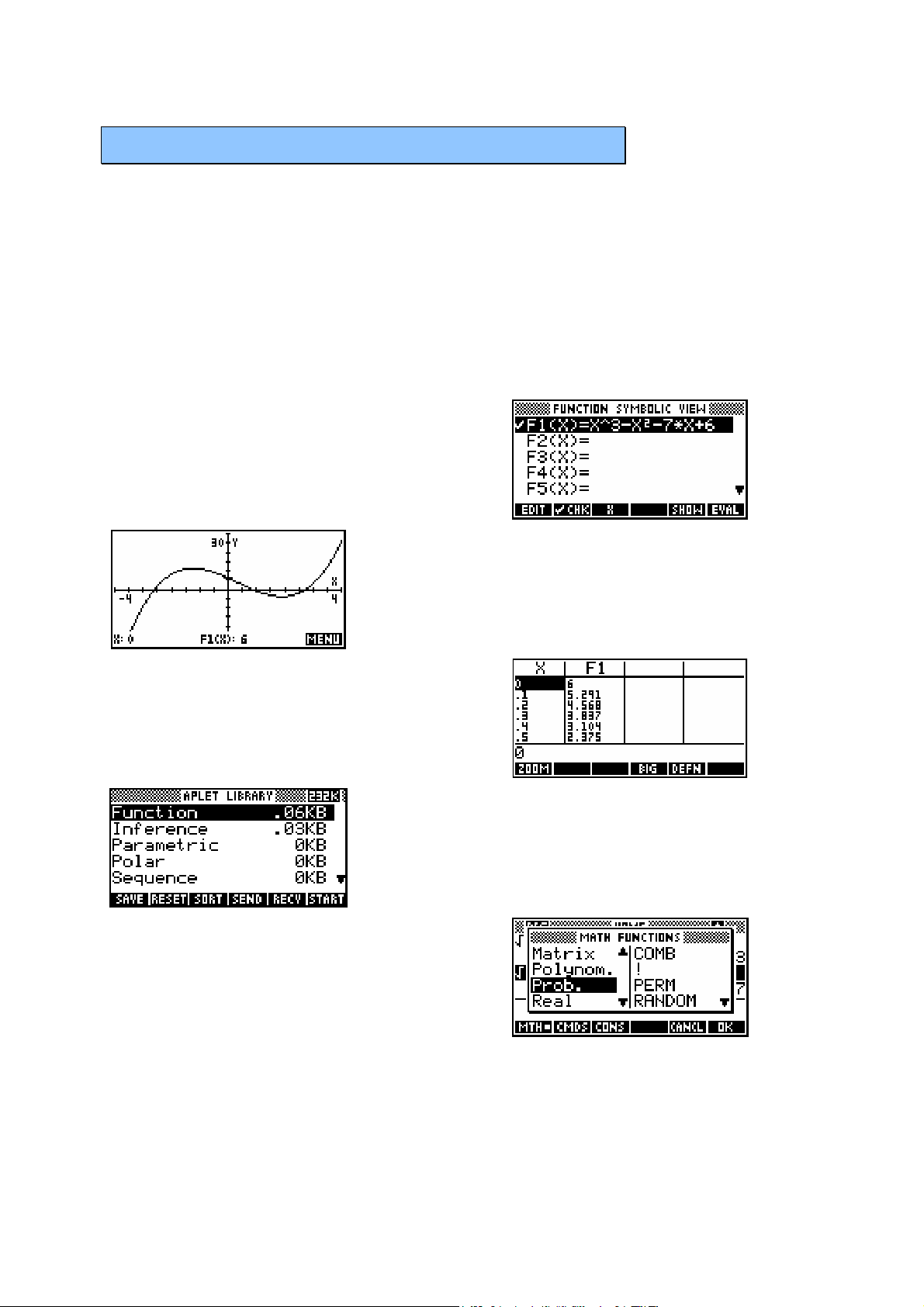
S
OOMMEE
S
Shown below are snapshots of some typical screens you might see when
you press each of the keys shown on the previous page. Exactly what you
see depends on which aplet is active at the time.
The aplet used below to illustrate this is the Function aplet, which is used to
graph and analyze Cartesian functions. Notice how the meanings of the row
of blank screen keys under the screen changes in different views.
The SYMB key - in this case it is set to graph
K
EEYYBBOOAARRDD
K
the function
E
XXAAMMPPLLEES
E
32
76yx x x=−−+.
The PLOT key - used to graph the function.
S
The NUM key showing a tabular view of the
function.
The MATH key gives access to more than a
hundred extra functions, grouped by category.
The view shown right is currently showing the
Probability section.
The APLET key is used to choose which aplet
is active. There are 10 aplets provided with
the calculator and more can be downloaded
from the internet.
16
Page 17

K
EEYYSS
K
There are a number of types of keys/buttons that are used on the hp 39g+.
&
&
N
OOTTAATTIIOONN
N
C
OONNVVEENNTTIIOONNS
C
S
SSoommee eesssseennttiiaall kkeeyyss
The basic keys are those that you see on any
calculator including scientific ones, such as the
numeric operators and the trig keys. Most of these
keys have two or more functions.
All references to keys, whether they need the SHIFT key or not, are written in
this typeface: KEY.
The SHIFT key
The SHIFT key gives you the second function for each
key. In the case of the COS key, the second function is
ACOS, sometimes referred to as arc-cos or cos-1 or
inverse cos. Most keys have these second functions that
are obtained via the SHIFT key.
When I want you to use one of these keys that needs to
have the SHIFT key pressed first I usually won’t say so.
It seems to me that you’re intelligent enough to work out
for yourself when the SHIFT key needs to be pressed.
Take for example the COS key shown left. If
you just press the key, you get the COS function.
However above left of the key and below right
you will see two additional meanings assigned
via the SHIFT and ALPHA keys.
17
Page 18

The ALPHA key
The next modifier key is the ALPHA key. This is used to type alphabetic
characters, and these appear in orange just below most keys.
The Screen keys
A special type of key unique to the hp 39g+ and family is the row of blank
keys directly under the screen. These keys change their function depending
on what you are doing at the time. The easiest
way to see this is to press the APLET key. As
you can see right, the functions are listed at
the bottom of the screen. All you have to is to
press the key under the screen definition you
want to use.
All references to keys of this type are shown
as images of the label. For example, if I want
you to press the key under the SORT label it
would be written as . Do it now and you’ll
see the screen shown on the right. Notice that
the keys have now changed function. Press
the one under .
Pop-up menus & short-cuts
Sometimes pressing a key pops up a menu on the screen as you just saw.
You use the up/down arrow keys to move the highlight through the menu and
make choices by pressing the ENTER key. Choices that are listed in a menu
will usually be written using italics. As an example, I might say to press
and choose Chronologically. The manual you are given with your calculator
uses a different convention.
As mentioned before, the third way a key can be used is to get letters of the
alphabet. This is not so that you can write letters to your friends (although
you can do that with the Notepad) but so that you can use variables like X
and Y or A and B. The key above the SHIFT key labeled ALPHA is used
to type in letters of the alphabet. Lower case letters are obtained by pressing
the SHIFT key before the ALPHA key. If you want to type in more than just a
single letter, hold down the ALPHA key. Unfortunately, this doesn't work for
lowercase.
18
Page 19

Try this…
If you haven’t already, out of the menu from the
previous screen. Press the HOME key to see the
screen on the right. Yours may not be blank like mine
but that doesn’t matter.
Press 12 and then press the screen key labeled
. Now press the ALPHA key and then the
alphabetic D key (on the XTθ key). Finally, press the
ENTER key. Your screen should look like mine on the
right. You have now stored the value 12 into memory
D. Each alpha key can be used as a memory.
You can also use these memories in calculations.
Type in the following (not forgetting the ALPHA key
before the D)…. (3+D)/5 ENTER
The calculator will use the value of 12 stored earlier in
D to evaluate the expression (see right). In case you
haven’t worked it out for yourself, the / symbol
comes from the divide key ( ) and the * symbol from the multiply key.
More information on memories and detailed information on the HOME view in
general is given on pages 45.
The calculator also comes with a large number of mathematical functions that
are very useful. They can all be obtained via menus
through the MATH key. Try pressing the MATH key now
and you should find your screen looks like the screen
shot on the right.
The MATH menu is covered in detail on pages 243 but
we will have a brief look now.
The left side of the menu lists the categories of
functions. As you use the up/down arrows to scroll
through the topics, you’ll see the actual list on the right
change. Move down through the menu until you reach
Prob. (short for Probability) and then one step more
and you’ll find yourself back at Real. Now press the
right arrow key and your highlight will move into the
right hand menu (see above). Move the highlight down through this menu
until you reach Round. Press ENTER.
19
Page 20

You should now be back HOME, with the function
ROUND( entered in the display as shown right. You
can also achieve the same effect by using ALPHA to
type in the word letter by letter. Some people prefer
to do it that way.
Now type in: 4+D/18,3) and press ENTER
As you can see, the effect was to round off the answer
of 4.666666.. to 3 decimal places.
There are shortcuts for obtaining things from the MATH
menu that are covered later (see page 47).
20
Page 21

E
VVEERRYYTTHHIINNGG RREEVVOOLLVVEESS AARROOUUNNDD
E
A set of “aplets” is provided in the APLET view on the hp 39g+. This
effectively mean that it is not just one calculator but nine (or more), changing
capabilities according to which aplet is chosen.
The best way to think of these aplets is as “environments” or “rooms” within
which you can work. Although these environments may seem dissimilar at
first, they all have things in common, such as that the PLOT key produces
graphs, that the SYMB key puts you into a screen used to enter equations and
rules, and that the NUM key displays the information in tabular form.
There are ten standard aplets available via the APLET key. More can be
created by you or obtained via the Internet (see pages 212 & 200)
A
PPLLEETTS
A
S
!
!
The Function aplet (see page 51)
Provides f(x) style graphs, calculus functions etc. It will not only
graph but find intercepts, intersections, areas and turning
points.
The Inference aplet (see page 150)
Allows the investigation of inferential statistics via hypothesis
testing and confidence intervals. This was not available on the
hp 38g, the original calculator upon which the hp 39g+ was
based.
The Parametric aplet (see page 100)
Handles x(t), y(t) style graphs. Can also be used to help with
vector motion.
The Finance aplet (see page 160)
Performs calculations involving time/value of money.
The Polar aplet (see page 106)
Handles r(θ) style graphs. Quite apart from their mathematical
use, they produce some really lovely patterns!
21
Page 22

The Quadratic Explorer aplet (see page 164)
=
This is a teaching aplet, allowing the student to investigate the
properties of quadratic graphs.
The Sequence aplet (see page 107)
Handles sequences such as
23;2
TT T
nn
+= or
11
−
T−= .
n
Allows you to explore recursive and non-recursive sequences.
12n
The Solve aplet (see page 113)
Solves equations for you. Given an equation such as
2Arrh
π
=+ it will solve for any variable if you tell it the
()
values of the others.
The Statistics aplet (see page 122 & 132)
Handles descriptive statistics really well. Data entry is easy, as
is editing. It analyzes univariate and bivariate data, drawing
scatter graphs, histograms and box & whisker graphs.
The Trig Explorer aplet (see page 167)
This is a teaching aplet, allowing the student to investigate the
properties of sine and cosine graphs.
The Function aplet is probably the easiest to understand and also the one
you will use most often, so we will have a very quick look at this aplet.
Some typical aplet views
The APLET key is used to list all the aplets and start,
reset or save them.
The SYMB view is used to enter equations….
It can store up to ten functions.
The NUM view shows the function in table form…
22
Page 23
The PLOT view is used to display the function as a
graph…
The key gives access to a number of other
useful tools allowing further analysis of the function.
Although these views are superficially different in other aplets, the basic idea
is usually similar.
Having said that aplets are best thought of as “working environments”, it is
equally true that aplets are essentially programs, with the standard ones
simply being built into the calculator. This is a programmable calculator,
having its own programming language and able to perform quite
sophisticated tasks.
Unless you particularly want to learn about the programming language, there
is no reason why you should worry about it. The standard aplets will cover all
of your normal requirements in mathematics.
However one of the great strengths of the hp 39g+ is its ability to “download”
additional aplets from other calculators, from a PC or Mac and from the
Internet. See page 200.
A cable and software were provided with your hp 39g+ which you can use to
connect your PC or Mac to your calculator and then download aplets from the
computer to the calculator or to save your work to the computer. If you have
an hp 38g, hp 39g or hp 40g then you need to buy the cable separately.
If you are using an hp 39g+ then the cable connects to the USB port on your
computer. If you are using an hp 39g or an hp 40g then you will need to
purchase the cable and download the software from Hewlett-Packard’s
website.
More information on this can be found on pages 200 - 226.
Calculator Tip
Search on the web using the key word “hp 39g” and you
will find a variety of sites which contain information and
aplets.
23
Page 24
Once an aplet is transferred onto any one calculator, transferring it to another
takes only seconds using the built in infra-red link at the top of each
calculator. This is exactly like the remote control of a VCR, and allows two
calculators to talk to each other. In the interests of security in examinations
the distance over which they can communicate is limited to about 8 - 10cm
(about 3 - 4 inches). See page 197 for details on this process.
Aplets are available to do many mathematical tasks such as statistical
simulations, time series analysis and many tasks called for in calculus,
physics and chemistry. There are a number of web sites which offer aplets.
The Hewlett-Packard site is found at…
http://www.hp.com/calculators/
(follow the links to graphical calculators and then to the library
of aplets)
In addition to this you should check the site called The HP HOME view which
can be found at…
http://www.hphomeview.com
(contains not only aplets and games, but also a huge amount of
detailed information on the calculator.)
Calculator Tip
The aplets for an hp 39g, hp 40g and hp 39g+ are
interchangeable but not those of an hp 38g. If you load an
aplet from an hp 38g onto an older model then the
download will appear to be successful but the calculator
will “crash” when the aplet is run.
The entire topic of aplets is discussed in more detail in the chapter entitled
“Using, copying & creating aplets” on page 189.
24
Page 25

HHEE
HHOOMME
E
T
T
In addition to these aplets, there is also the HOME view, which can best be
thought of as a scratch pad for all the others. This is accessed via the HOME
key (just below the APLET key) and is the view in which you will do your
routine calculations such as working out 5% of $85, or finding √35. The
HOME view is the view that you will most often use, so we will explore that
view first.
WWhhaatt iiss tthhee HHOOMMEE vviieeww?
This is the HOME base for the calculator. All other
aplets can be accessed from it and affect it to varying
degrees, and all mathematical functions are available
in this view. Learn to use this view as efficiently as
possible, since a great deal of work will be done here.
We will explore the HOME view in the following order:
1. Exploring the Keyboard
W
VVIIEEW
?
2. Angle and numeric settings
3. Memory management
4. Fractions on the hp 39g+
5. The HOME History
6. Storing and retrieving memories
7. Referring to other aplets from the HOME view
8. An introduction to the MATH menu
9. Resetting the calculator
25
Page 26

EExxpplloorriinngg tthhee kkeeyybbooaarrdd
It is worth familiarizing yourself with the mathematical functions available on
the keyboard. If we examine them row by row, you will see that they tend to
fall into two categories - those which are specific to the use of aplets, and
those which are commonly used in mathematical calculations.
The screen keys
The first row of blank keys are context defined. The
reason they have no label is that their meaning is
redefined in different situations - they are the
‘screen keys’. The current meaning of each key is
listed in the row of boxes at the bottom of the
screen.
A common abbreviation used for these keys is SK1
or SK2 etc (for “screen key 1” ). In the PLOT view
shown above, some of the screen keys are labeled,
such as the key. When you press this the row of screen keys labels
appear or disappear. To see another view where all the keys are in use,
change to the APLET view.
Calculator Tip
Develop the habit of checking the screen to see if any of
those keys have been given meanings. In many views, the
screen keys have been set up with useful shortcuts and
functions.
Aplet related keys
The next two rows of keys and part of the
third are mainly aplet related, so we’ll deal
with them as a group.
The arrow keys
The arrow keys on the right are used in
most views, usually to move the cursor (a
small cross) or the highlight around on the
screen.
26
Page 27
The APLET key is used to choose between the
various different aplets available. Everything in the
calculator revolves around aplets, which you can
think of either as miniature programs or as
environments within
which you can work.
The hp 39g+ comes with ten standard aplets -
Finance, Function, Inference, Parametric,
Polar, Quadratic Explorer, Sequence, Solve,
Statistics and Trig Explorer. Which one you
want to work with is chosen via the APLET key.
Calculator Tip
The name of the active aplet is shown at the top of the
screen, as above. It is important to bear this in mind
because the angle and numeric settings are tied to the
active aplet. Changing aplets may therefore cause these
settings to change in HOME too.
See page 35 for more details on this.
In addition to the standard ten, covered in great detail in the chapters
following, many more aplets are available from the Internet written by other
programmers. Once these are downloaded into your calculator they can also
be accessed via the APLET key. For more detail on this type of aplet, see
the brief summary later in this section, and the chapter entitled “Programming
the hp 39g+” on page 212.
The
SYMB, PLOT
and
NUM
keys
The SYMB, PLOT and NUM keys are used within aplets to
move from view to view. In most aplets the PLOT view
shows the graph, the SYMB view shows the equations and
the NUM view shows the equations in tabular (numeric)
format.
The VIEWS key pops up a menu from which you can
choose various options. Part of the VIEWS menu for
the Function aplet is shown right. See page 92 for
more information.
27
Page 28
The VIEWS menu is provided for two purposes…
Intro to the
VIEWS
menu
Firstly, within the standard aplets (Function, Sequence, Solve etc.) it provides
a list of special views available to enhance the PLOT view.
For example the standard PLOT screen provides a
graph, but the VIEWS menu lets you use a split screen
such as shown right. Information on the VIEWS menu
is given in the chapter dealing with the Function aplet.
In addition to this, the VIEWS key also has a critical role when using aplets
which have been downloaded from the Internet. When a programmed aplet
is created for the hp 39g+, a menu is provided by the programmer to let you
control and use it. This menu is tied to the VIEWS key,
replacing the menu normally found on the key. For
example, the snapshot shown right is of a VIEWS
menu taken from an aplet designed to analyze and
graph Time Series data.
The next important key is the HOME key. It allows you
to change into the HOME view from wherever you are.
Above it is the MODES key, accessed by pressing
SHIFT first. Far more detailed information on these
two views follows later.
The
VARS
key
The VARS key is used (mainly by programmers) to
access all the different variables stored by the
calculator.
Shown right are two views of the VARS screen, the first
from the HOME list showing the graphic variables
(memories) G1, G2…. and the next from the APLET
list showing some of the variables in the set controlling
PLOT.
The VARS key is not generally used much, and you may not have followed
this explanation. Don’t worry. The VARS key is mostly used by programmers
who want to produce aplets of their own and is discussed in more detail in
the chapter entitled “Programming on the hp 39g+” on page 212. Uses are
also detailed in the Function aplet’s “Tips and Tricks” section on page 69.
28
Page 29
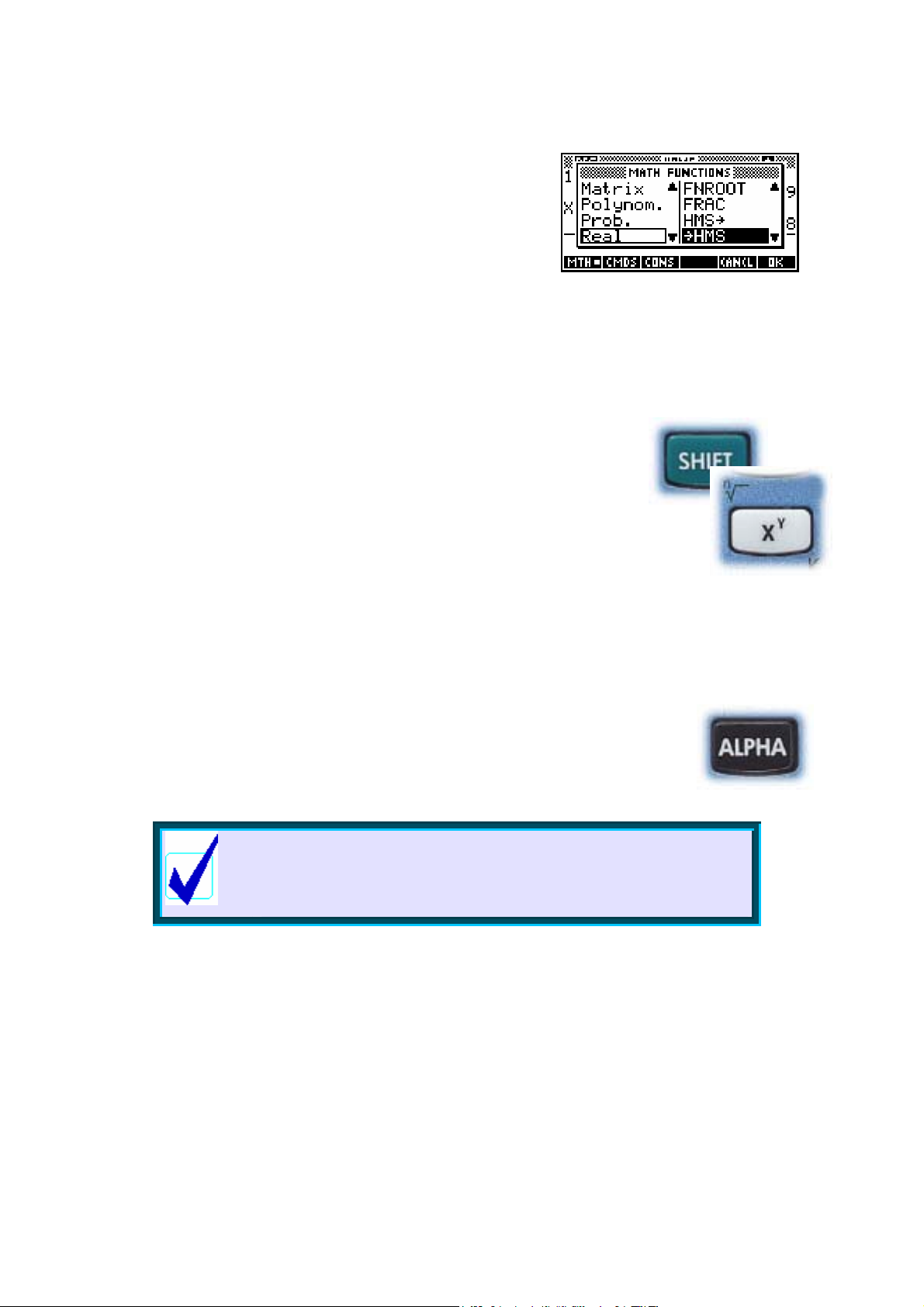
The MATH key next to VARS provides access to a
library of mathematical functions. The more
common functions have keys of their own, but there
is a limit to the number of keys that one can put on a
calculator before it takes too long to find the key
required.
The MATH menu lists all those functions that would not fit onto the keyboard
plus some which also appear on the keyboard. Shown in the screen
snapshot above is a small selection of the total list. For a listing of almost all
the functions, with examples of their use, see the chapter entitled “The MATH
Menu” on page 243.
Most of the keys have another function in light blue above the
key. The hp 39g+ gets twice the action from each key by
having this second function.
The second function is accessed via the SHIFT key on the left side of
the calculator. Although this book will sometimes tell you explicitly to press
this key, in most cases it will be assumed that you are intelligent enough to
work out for yourself when it is necessary to press it.
The ALPHA key gives alphabetical characters, shown below right of
most keys. Pressing SHIFT ALPHA gives lower case. If you press
and hold down the ALPHA key you can ‘lock’ alpha mode but this
doesn’t work for lower case. Many people use this to type in
functions by hand rather than using the MATH menu.
Calculator Tip
You can use the ALPHA button to type in functions by
hand instead of going through the MATH menu. This is
often faster.
29
Page 30
The
SETUP
views
The SETUP views, above PLOT, SYMB and NUM,
are used to customize their respective views. For
example, the PLOT SETUP screen controls things
like axes, labels etc. Their use changes in
different aplets, so for more information see the
explanations in the chapters dealing with the various aplets, particularly with
the Function aplet on page 55.
In particular, the SYMB SETUP key is only used in one place, which is to
choose the data model for bivariate statistics in the Statistics aplet. It is not
available in the other aplets and trying to access it will result only in a quick
flash of an exclamation mark on the screen to say “You’ve done something
wrong!”.
Information on the use of the SKETCH and NOTE keys
(above APLET and VEIWS) can be found in the
chapters “Using the Sketchpad” and “Using the Notepad Catalog” on pages
184 & 178. Briefly, any aplet (except for the Quad & Trig Explorer aplets)
has a note and a sketch associated with it, which are usually blank unless
you have added to them.
The main use for them comes with aplets downloaded from the Internet.
Instructions for using the aplet are sometimes included with the aplet in note
form, and sometimes as an accompanying sketch.
The
MODES
view
The MODES view (see right) controls the
numeric format used in displaying numbers
and angles in aplets. At the bottom of the
screen you will see that one of the screen keys
has been given the function
. Pressing
this key pops up a menu of choices from which
you can select the option which suits you. The
default angle setting is radians.
Calculator Tip
If you don’t want to use the menu then, rather than
pressing , highlight the field and then press the ‘+’
key repeatedly. This will cycle through the choices without
popping up a menu. This can be much faster if the menu
has only a few choices.
30
Page 31

Numeric formats
The choices for ‘Number format’ are shown
on the right. Standard is probably the best
choice in most cases, although it can be a little
annoying to constantly have 12 significant
figures displayed. In Standard mode, very
large and very small numbers are displayed in scientific notation.
The Fixed, Scientific and
Engineering formats all require you to
specify how many decimal places to display.
The screenshot right shows Fixed 4, which
rounds everything off to 4 decimal places. Of
course, you can change the 4 to any other
number you want.
A setting of Scientific notation ensures that any results are displayed in
scientific notation. Of course, the calculator’s idea of scientific notation may
not be the same as yours. Since the calculator has no way of displaying
powers as superscripts, a result of
3 203 10⋅× has to be displayed as
4
3.203E4. The alternative of Engineering notation is very similar to
Scientific, except that powers are always displayed as multiples of 3.
This is done to allow easy conversion
in the Metric system, which also works
in multiples of 1000.
The screens right show the same two
numbers displayed as in turn as; Fixed 4,
Scientific 4 and Engineering 4.
Calculator Tip
If you have Labels turned on when you in (or out)
on a graph then you may end up with axes whose numeric
labels are horrible decimals (see below right).
31
Page 32

The setting of Fraction can be quite
deceptive to use and is discussed in more
detail on page 40.
The next alternative in the MODES view of
‘Decimal Mark’ controls the character which
is used as a decimal point. In some countries
a comma is used instead of a decimal point.
If you opt to use a comma rather than a full
stop then any places where a comma would normally be used (such as in
lists) will swap to using a full stop. Any functions which might normally have
terms separated by a comma will use a full stop instead. For example,
ROUND(3.456,2) will become ROUND(3,456.2).
Moving back to our tour of the keyboard, the next key is the ENTER key. This
is used as an all purpose “I’ve finished - do your thing!” signal to the
calculator. In situations where you would normally press the ‘=’ key on most
calculators, press the ENTER key instead.
The
ANS
key
Above the ENTER key is the ANS key. This can
be used to retrieve the final value of the last
calculation done. An example of this is shown
right.
If you are not confident about using brackets,
then the ANS key can be quite useful.
For example, you could calculate the value of
372
−×
23
25
by using brackets…
+
…. or you could use the ANS key.
32
Page 33

An alternative to using the ANS key is to use the History facility and the
−
function. This is discussed on page 43.
The negative key
Another important key is the (-) key (shown right).
If you want to calculate the value of (say) 2(9)
−− then
you must use the (-) key before the 2 and the 9 rather than the subtract
key. If you press the subtract key before the 2 instead of the (-) key, then
the calculator will enter instead: Ans - 2, meaning, subtract 2 from the
previous answer. Similarly, entering ‘subtract, subtract 9’ instead of ‘subtract
(-) 9’ will give an error message of “Invalid syntax”, meaning it does not make
mathematical sense to have two subtract signs instead of a subtract of a
negative.
The reason for the Ans - 2 is that a subtract cannot start a ‘sentence’ in
mathematics, while a negative sign can. Since the subtract can’t come first,
the calculator decides that you must have intended to subtract from the
previous answer. Hence the sudden appearance of an Ans. This occurs at
other times too. One of the most common
The
CHARS
key
The next important key is the CHARS key (above VARS). This key is used to
access all of the many characters that are used occasionally but not often
enough to bother putting on the keyboard.
Pressing SHIFT CHARS will pop up the screen
above right. One of the screen keys is set to
be a ‘Page Down’ key (
), and will give
access to two more pages of characters.
These special characters are obtained by
pressing the screen key labeled
. You
can press as many times as you need to
in order to obtain multiple characters. When
you have as many as you need, press the
key.
33
Page 34

The
DEL
and
CLEAR
keys
The next important key is the DEL key at the top right of the
keyboard. This serves as a backspace key when typing in
formulas or calculations, erasing the last character typed. If you
have used the left/right arrow keys to move around within a line of
typing, then the DEL key will delete the character above the
cursor. The CLEAR key above DEL can be thought of as a kind of ‘super
delete’ key. For example, if pressing DEL would erase one function only in
the SYMB view then CLEAR will erase the whole set.
Calculator Tip
Another use for the DEL key is to restore factory settings.
For example, if you move back into the MODES screen and
change to Degree mode, then pressing the DEL key will
restore the default of Radians. Pressing CLEAR in the
MODES view would restore factory settings to all the
entries. This is particularly useful in the PLOT SETUP
view.
The remaining keys of LIST, MATRIX, MEMORY , NOTEPAD and PROGRAM
have special chapters of their own.
34
Page 35

AAnnggllee aanndd NNuummeerriicc sseettttiinnggss
It is critical to your efficient use of the hp 39g+ that you understand how the
angle and numeric settings work. For those upgrading from the hp 38g this is
particularly important, since the behavior is significantly different.
On the hp 39g+, when you set the angle measure or the numeric format in
the MODES view, it applies both to the aplet and to the HOME view. However,
this setting applies only to the currently active aplet (the one highlighted in
the APLET view). This means that if you change active aplet then these
settings may change also, not only for the aplet but in the
HOME
view too.
For example, suppose you have been
performing trig calculations in the HOME view
with the Function aplet being currently active,
and have set the angle measure to DEG.
If you were to now change to the Solve aplet in
order to solve an equation then the settings
would revert to those of the Solve aplet;
probably be radians unless you had also
changed those as well.
Radian measure is the default for all aplets
and thus also for HOME unless you change it.
Performing the same calculation in HOME
would now give a different result (see right).
Although this may seem to be a strange way of doing things, there is actually
a very good reason for it. The hp 38g did not behave this way and it caused
a number of users to have difficulties as you'll see on the next page.
35
Page 36

Suppose we define a trig function in
the Function aplet as shown.
The default setting for the Function
aplet is radians, so if we set the axes to extend
from -πto π, the graph would look as shown
right.
In the PLOT view shown, the first positive root
has been found (see page 63) as x=1.0471…
On the hp 39g+, if we now change to the HOME
view and perform the calculation shown right,
we expect that the answer should be zero, as
indeed it is.
However, this is only the case because the angle measures of HOME and the
Function aplet agree. The problem was that on the hp 38g the default setting
for the Function aplet was radians, while HOME had a default setting of
degrees and its setting was independent of those of the aplet. This meant
that a calculation such as the one above would give incorrect results, and
caused considerable confusion to some students. It even resulted in users
returning their hp 38g to dealers as ‘faulty’!
The only drawback of this method is that you
might change aplets and forget that it may also
change settings. For this reason, the name of
the active aplet is shown at the top of the HOME
view as a reminder.
On the hp 39g+ you can see that if we turn Labels on and then PLOT, the
numeric mode also affects the axis labels.
36
Page 37

This setting also applies to the appearance of equations and results
displayed using the SHOW command.
Calculator Tip
Under the system used on the HP39+, if you want to work
in degrees then you will need to choose that setting in the
MODES view and possibly set it again if you change to
another aplet. Some people choose to go through and
change the setting on all the aplets at once so that they
don’t have to remember that it might change. However, if
you the aplet the default setting will return.
MMeemmoorryy MMaannaaggeemmeenntt
One of the major complaints about the hp 38g was its memory - mainly the
lack of it, but also the inability to control or manage it. This problem has been
addressed on the hp 39g+ in two ways. Firstly, the hp 39g+ has over ten
times the useable memory of the hp 38g. At 232 Kb (vs. only 23 Kb), there
are very few users who will come close to filling the hp 39g+. Depending on
size, there is enough room for at least fifty aplets, or for over 10,000 data
points.
The MEMORY MAN A GER view
In addition to extra memory, the hp 39g+
supplies a better way to control it through the
MEMORY MANAGER view. If you press the
MEMORY key you will see the view shown right.
Scrolling through it will show you exactly how
the available memory is currently being used.
The remaining memory, in Kb, is shown at the
top right of the screen. This view gives an
overview of the memory. For detailed
management the key is provided.
Pressing on any entry will take you a relevent screen in which you can
delete entries no longer needed.
For example, with the highlight on Aplets,
pressing will take you to the APLET view
(right), where you can choose to delete or
reset any aplets no longer required.
37
Page 38
As you can see in the screen snapshot on the previous page, my calculator
has a number of extra aplets. Two of them, Statistics2 and Statistics3 are
simply copies of the normal Statistics aplet containing data that I did not want
to lose. The top two aplets Curve Area and Coin Tossing are teaching aplets
that I have downloaded from the internet.
Downloaded aplets & memory
If you use teaching aplets that you download
from the internet via the Connectivity Kit, or
which are supplied to you by your teacher via
the infra-red link on your hp 39g+, then you
need to bear in mind that most of them have
‘helper’ programs that aid them in performing
their tasks. In the screens shown right you can
see some of the programs which are attached
to these two teaching aplets. The convention
which most hp 39g+ programmers follow is to
name these ‘helper’ programs in a way that
associates them clearly with the parent aplet.
The memory associated with these programs is not included in that shown for
the aplet in the APLET view but will not usually be a large amount.
Calculator Tip
The reason for this naming convention for ‘helper’
programs is that when you delete the parent aplet in the
APLET view the ‘helper’ programs are not automatically
deleted with it. You must change to the Program
Catalog view and delete them manually after you have
finished with the teaching aplet and deleted it in the APLET
view. If you don’t do this then they will continue to take up
memory on the calculator. Even on the hp 39g+ this is not
infinite and too many left over programs will eventually
cause problems.
As mentioned on the earlier, pressing
in
the MEMORY MANAGER screen takes you to a
relevent view showing greater detail. For
example, the Matrices entry right shows 0.1 Kb
in use. Pressing will take you to the
MATRIX CATALOG view which shows exactly
where the memory is being used and allows
you to delete any or all of the matrices, or you
can enter the view in the normal way by
pressing SHIFT 4.
38
Page 39

The History entry will take you to the HOME view, where pressing SHIFT
CLEAR will clear the History.
The GRAPHICS MANAGER
There are two views, shown right, for which the
only access is via the MEMORY MANAGER
screen. The first of these, the GRAPHICS
MANAGER, shows some memory in use on my
calculator due to the screen captures I am
performing to show you these views. Yours
will probably be empty.
The LIBRARY MANAGER
The second of these is the LIBRARY
MANAGER, and this will almost certainly be
empty unless you have games loaded.
Generally, the only aplets which use libraries are those such as games which
are written by expert programmers in machine code in order to make them
run as fast as possible. These games, available on the internet, are listed in
the APLET view along with the normal aplets and when you delete them the
associated library is automatically deleted with them, unlike the case of the
‘helper’ programs.
Calculator Tip
Because of the amount of memory available on the
hp 39g+, the Memory View is not one that you will normally
need to worry about. It is probably of more interest to
programmers.
39
Page 40

FFrraaccttiioonnss oonn tthhee hhpp 3399gg++
Earlier we examined the use of the MODES view, and the meaning of Number
Format. We discussed the use of the settings Fixed, Scientific and
Engineering, but left the setting of Fraction for later. The Fraction
setting can be a little deceptive.
b
Most calculators have a fraction key, often labeled
input, for example,
2
as 123¬¬ or something similar. What these
1
3
a
, that allows you to
c
calculators usually won’t do is allow you to mix fractions and decimals.
On most calculators
2
137
3
not attempt to convert the
will give a decimal result - the calculator will
+⋅
37⋅ into a fraction. The reason for this is that
while some decimals like 0.25 are easy to convert to a fraction, others, such
as recurring ones, are not so easy. Most calculators opt for the easy option
of switching to a decimal answer in any mixture of fractions and decimals.
The makers of the hp 39g+ took a very different approach. Once you select
Fraction mode, all numbers become fractions - including any decimals.
The first point to remember is that there is no
provision for inputting mixed fractions such as
2
. Fractions are entered using the divide
1
3
key and, while the calculator is quite happy
with improper fractions such as 5/3, it
correctly interprets 1/2/3 as one half divided by 3 and gives a result of 1/6
. The solution to this is simply to enter mixed fractions as (1+2/3).
Calculator Tip
You need to be careful with brackets or “order of
2
operations” problems may occur, such as
1
1
*
being
5
3
interpreted as 1+(2/3*1/5) rather than as it should be:
(1+2/3)*1/5. When in doubt, use brackets for mixed
fractions.
40
Page 41

Some examples are… (using Fraction 4 or higher)
−
1417
1.
+=
3515
11 1
2.
34 1
=−
32 6
The second point to remember involves the method the hp 39g+ uses when
converting decimals to fractions, which is basically to generate (internally and
unseen by you) a series of continued fractions which are approximations to
the decimal entered. The final fractional approximation chosen for display is
the first one found which is ‘sufficiently close’ to the decimal.
The trap lies in what constitutes ‘sufficiently close’, and this is determined by
the ‘4’ in Fraction 4. Roughly, the calculator will use the first fraction it
finds in its process of approximation which matches the decimal to that
number of significant digits.
For example, a setting in the MODES view of…
Fraction 1 changes 0.234 to
3
13
which is actually 0.2307692…
(matching to at least 1 sig. fig.)
7
Fraction 2 changes 0.234 to
30
which is actually 0.2333333…
(matching to at least 2 sig. fig.)
Fraction 3 changes 0.234 to
11
47
which is actually 0.2340425…
(matching to at least 3 sig. fig.)
117 234
Fraction 4 changes 0.234 to
or
500 1000
which is exactly 0.234
Essentially, the value of ‘n’ in ‘Fraction n’ affects the degree of
precision used in converting the decimal to a fraction. As was said earlier,
the calculator will use the first fraction it finds in its process of approximation
which matches the decimal to that number of significant digits.
41
Page 42

The Fraction setting is thus far more
powerful than most calculators but can require
that you understand what is happening. It
should also be clear why a special fraction
button was not provided: the ‘fractions’ are
never actually stored or manipulated as
fractions at all!
Pitfalls to watch for
As you can see in the screenshot right, a setting of Fraction 4 produces
a strange (but actually correct) result for 0.666, while adding one more 6 (to
take the decimal beyond 4 d.p.) will give the desired result of 2/3. In other
words, so long as you understand the approach taken by the hp 39g+ it is
capable of producing results which are closer to what was probably intended
by the user in entering 0.66666.
If you want to use this facility to convert decimals to fractions, here are some
tips…
! if you are converting a recurring decimal to a
fraction, then make sure you include at least
one more digit in the decimal than the setting
of Fraction in MODES. As you can see in
the second screenshot, failing to include
enough decimal places does not produce the
desired result.
! if you are converting an exact decimal to a
fraction, then set a Fraction n value of at
least one more than the number of decimal
places in the value entered. Both examples
right were done at Fraction 6.
Not understanding the significance of the setting of Fraction can
produce some unfortunate effects. For example, at Fraction 2, the value of
123.456 becomes 123, with the 0.456 dropped entirely.
Similarly, one of the earlier examples at the top of the previous page was
1/3 + 4/5 = 17/15.
42
Page 43

If you use a setting of only Fraction 2 to
perform this, you will find to your amazement
that 1/3 + 4/5 = 8/7 , whereas using
Fraction 6 gives the correct answer.
The reason for this ‘error’ is that the 1/3 and 4/5 were converted to
decimals and added to give 1.133333…. This was converted back to a
fraction to give 8/7 (1.1428..) matching sufficiently closely in Fraction
2 to be accepted.
TThhee
The HOME page maintains a record of all your calculations called the History.
You can re-use any of the calculations or their results in subsequent
calculations.
Try this for yourself now. Type in at least four
calculations, pressing the ENTER key after
each one to tell the calculator to perform the
calculation.
You will now be looking at a screen similar to the one on the right (except
probably with different calculations).
If you now press the up arrow key, a
highlighted bar moves up the screen. When
you reach the top of the screen the previous
calculations will scroll into view. Pressing
SHIFT up-arrow takes the highlight to the top
in one movement.
E
HHOOMME
HHiissttoorryy
COPYing calculations
You may have noticed that as soon as the
highlight appeared so did two labels at the
bottom of the screen. If you now press the
screen key under you will find that the
highlighted calculation will be copied on the
edit line. This is shown in the screen shot on
the right.
43
Page 44

At this point you can use the left and right arrows and the DEL key to edit the
calculation by removing some of the characters and/or adding to it.
For example, in the screenshot right, the
calculation of 3*2*COS(35) has been edited
to 3*COS(35).
Clearing the History
Pressing enter will now cause this new calculation to be performed.
Calculator Tip
! Pressing ON during editing will erase the whole line.
! Pressing SHIFT CLEAR erases the whole history.
This is worth doing regularly, since the history uses
memory that may be needed for other things, even with
the immense amount of user memory the hp 39g+ has.
! You can calculations and results from any
number of different lines in building your new
expression.
SHOWing results
Next to the key you will see another screen key labeled . This
key will display an expression the way you would write it on the page rather
than in the somewhat difficult to read style that is forced on the calculator
when it must show the whole expression on one line. This works anywhere
the label appears, not just in HOME. Some examples…
44
Page 45

SSttoorriinngg aanndd RReettrriieevviinngg MMeemmoorriieess
×
Each of the alphabetic characters shown in orange below the keys can
function as a memory. Some examples of this are shown in the third and
fourth examples above where the values of 1, -3 and -4 are stored into A, B
and C and the value of 3 is stored into X. All of this ‘storing’ of values is
done with the key, which is one of the screen keys listed at the bottom
of the HOME view. There are ways of obtaining even more memories than
these 26 alphabetic ones, such as storing values into a list (see page 176),
but 26 is enough for most people.
Once stored into memory, a value can be used
in a calculation by typing the letter into the
place where you would normally use the value.
Typing a letter and pressing ENTER will display
memory’s contents.
There is an advantage to storing results in memories, particularly if they are
long decimals, or if you’re going to be re-using the result a number of times.
4(3)
+
5
23 5
⋅−
−
.
2
As an example, we will perform the calculation of
We will do this in two stages, calculating the top and bottom of the fraction
and storing the results in memories.
Firstly the top of the fraction, storing the result
in memory A, then the bottom, storing in B.
And then finally the result…
45
Page 46

RReeffeerrrriinngg ttoo ootthheerr aapplleettss ffrroomm tthhee
−
E
HHOOMME
vviieeww..
Once functions or sequences have been defined in other aplets, they can be
referenced in the HOME view.
e.g. 1 Suppose we use the Function aplet to
define F1(X)=X²-2 and
F2(X)=e^X as shown right.
These functions now become accessible not only from within the HOME view
but also within any other aplet also. This is shown by the screen shots
below.
The results shown will (of course) depend on
your settings in the MODES view.
The reason for the QUOTE(X-2) rather than
just X-2, is that using X-2 would tell the
calculator to use the value currently stored in
memory X, while QUOTE(X-2) tells it to use
the symbol. The QUOTE function is available
through the MATH menu under Symbolic (see
page 257).
This type of work is actually far more easily done in the Function aplet, where
QUOTE is not needed and the
key does a better job. See page 71.
e.g. 2 Suppose we use the Sequence aplet
to define a sequence with
3, 1TT==and
12
2
TTT
=+.
nnn
12
−
In the HOME view, the sequence values can be
referred to as easily as the function values in
the previous example.
46
Page 47

AAnn iinnttrroodduuccttiioonn ttoo tthhee MMAATTHH MMeennuu
The MATH menu holds all the functions that are
not used often enough to be worth a key of
their own. There is a very large supply of
functions available, many of them extremely
powerful, listed in their own chapter later in the
book. When you press the MATH key you will
see the pop up screen shown right. The left hand menu is a list of topics.
Scroll through the topics until you find the one you want, then use the right
arrow key to move into the list of functions for that topic.
For example:
The function ROUND will round off to a specified
number of decimal places.
E.g. round off 145.25667 to 3 decimal places.
! Press the MATH key & right arrow (→) into
the Real group of functions.
! Press the ‘R’ key (the 9 key) to move to
the first of the functions beginning with ‘R’,
then move down one more function to
ROUND. Press ENTER.
! Now finish off the command and press ENTER again to see the result.
See page 243 for a far more detailed look at the Math Menu.
47
Page 48

RReesseettttiinngg tthhee ccaallccuullaattoorr
It is probably inevitable as the line between calculators and computers
becomes blurred that calculators will inherit one of the more frustrating
characteristics of computers: they crash! If you find that the calculator is
beginning to behave strangely, or is locking up then there are a number of
ways to deal with this.
Calculator Tip
If you are a user of external aplets then you may find that
one will stop working with the message “Invalid syntax.
Edit program?”. There is almost certainly nothing wrong.
Press , try a soft reboot as below, then run the aplet
again.
Soft reboot
Pressing ON+SK3 will perform a soft reboot. It is perfectly safe
and will not cause any memory loss except that your HOME
History will be cleared. Hold down the ON key and, while still
holding it down, press the 3rd screen key from the left. The
calculator will very briefly display a boot screen and then
redisplay the HOME view, with the Function aplet as the active
one.
48
Page 49

Just on the rare chance that you may find that the calculator locks up so
completely that the keyboard will not respond a method of reset is provided
which is independent of the keyboard. This should never happen but it is
important to know how to deal with it in case it happened during a test or an
exam.
Soft reboot (Hardware)
On the back of the calculator is a small hole. Poke a paper clip
or a pin into this hole and press gently on the switch inside. To
the calculator this is exactly equivalent to a soft reboot as
outlined on the previous page. If you do this when the calculator
is locked up then the chances are that you will find that the
procedure will not only unlock the calculator but retain your data
intact.
Hard reboot (with memory wipe)
To completely wipe the calculator’s memory press
ON+SK1+SK6. Hold down the ON key and, while still holding it
down, press the first and then the last screen keys. Release
them in the opposite order. Don't release SK1 and SK6
together - release SK6, then SK1, then ON. This method will
always cause complete loss of data. If you find that the screen
fills with garbage, or if the calculator’s in-built diagnostic routine
starts to run, then it is just that you have not released them in
the right order. Simply try again.
Calculator Tip
As a last resort, take the batteries out, including the disk
shaped back-up battery and wait a few hours. Reinsert the
batteries. Make SURE they go in correctly as you can very
seriously damage the calculator if you insert batteries the
wrong way around.
49
Page 50

SSuummmmaarryy
1. The up/down arrow key moves the history highlight through the record
of previous calculations. When the highlight is visible, the key
can be used to retrieve any earlier results for editing using the left/right
arrow keys and the DEL key.
2. Care must be taken to ensure the your idea of order of operations
agrees with the calculator’s.
2
For example, (-5)
must be entered as (-5) 2 rather than as -52, and
54+ must be entered as √(5+4) rather than √5 + 4.
3. The ANS key can be used to retrieve the results of the calculation
immediately preceding the one you’re working on. E.g. √(5+Ans)
4. The DEL key can be used to erase single lines in the history. The
SHIFT CLEAR key will delete the entire history. Regular clearing will
ensure that memory is not gradually eroded.
5. The key displays a calculation as you would see it written.
6. The MODES view can be used to set the format in which numbers are
displayed on the HOME page, and to choose the angle measure which
is to be used.
7. Make sure you understand Fraction mode before using it.
Remember that the angle and numeric mode settings may change if
you change aplets in the APLET view.
8. Numbers are stored in memory using the key labeled . The
stored values can then be used by simply putting the letter in the
expression in place of the number.
9. You can reboot the calculator if it locks up. Make sure you know how
to do this in case it happens during a test or an examination.
For more information on the complete set of mathematical functions available
in the HOME view (and anywhere else) see the chapter “The MATH menu” on
page 243.
50
Page 51

T
T
The Function aplet is probably the one that you will use
most of all. It allows you to:
Choose the aplet
The first step for any aplet is to choose it in the
APLET LIBRARY. Press the APLET key and
you will see something similar to the screen on
the right. Use the arrow keys to move the
highlight up or down until the Function aplet is
selected. Now, looking at the list of programmable functions at the bottom of
the screen, you should see labels of
Press the key under
message shown right - press the
The reason for doing this is to clear out any
functions that you may have put in there while
playing around, and so to make sure that what
you see will be the same as the screen snapshots.
F
HHEE
UUNNCCTTIIOONN
F
! graph equations
! find intercepts
! find turning points (maxima/minima)
! find areas under curves
! find areas between curves
! find gradients
! find derivatives algebraically
! find simple integrals algebraically
! evaluate functions at particular values
! graph and evaluate algebraically expressions such as f(g(x)) or f(x+2)
A
A
T
PPLLEET
first. You’ll see the
key.
and .
51
Page 52

The
SYMB
view
Now press the key. When you do, your
screen should change so that it appears like
the one on the right. This is the SYMB view.
Notice the screen title so that you will know
where you are (if you didn’t already).
Calculator Tip
Pressing ENTER here would have had the same effect.
Whenever there is an obvious choice pressing ENTER will
usually produce the desired effect.
The
XTθ
button
Whenever you enter an aplet, one of the keys which usually changes its
function is the key labeled XTθ. As its label suggests, it supplies an X, or a
T, or a θ, depending on which aplet you are in. Let's use that key to produce
a graph of the quadratic we dealt with in the earlier section on the HOME view.
Using the up/down arrows, move the cursor (if necessary) to the line
F1(X) = .
Type in:
3 XTθ X² - 5 XTθ - 4 ENTER
This will produce the screen shown on the
right. Notice the check/tick mark next to the
function F1(X). This signifies that this
function is to be graphed, so that if you had
five functions entered but only wanted
numbers 1, 3 and 4 graphed, you could simply
ensure that only F1(X), F3(X) and F4(X) were checked.
ing your function
The key that turns the check on or off is a screen key - the one labeled with
the . It is a toggle key - when the check is off it turns it on and when on
it turns it off. In some countries a ‘check’ mark is called a ‘tick’ mark but the
idea is the same.
52
Page 53

Try turning the check on and off for function F1(X). Remember, the
highlight has to be on the function before the check can be changed. Make
sure it’s checked when you have finished.
The
NUM
view
If you now press the NUM key, you will see the
screen on the right. It shows the calculated
function values for F1(X), starting at zero and
increasing in steps of 0.1
Make sure the highlight is in the X column, and then press 4 and ENTER.
You will find that the numbers will now start at 4 instead of zero. It is also
possible to change the step size via the
key, which can be convenient
at times, particularly for trig functions. The simplest way to set the start value
and increment is in the NUM SETUP view. This will be covered in detail later
(see page 77).
The
PLOT
view
Now try pressing the PLOT key. The graph
you’ll see will not be a terribly useful one (see
right) because the axes will not be set up
correctly. We’ll look next at how to do this.
One of the easiest ways to set up the axes properly for a function whose
shape is not known in advance is to let the calculator suggest a suitable
scale. There are a number of ways of doing this. See page 86 for a
discussion of ways of finding ‘nice’ axes.
One method of finding a viable scale is to use the Auto Scale option in the
VIEWS menu (below). More information on the VIEWS menu can be found
on page 92. Another method is to use the NUM view to investigate the range
of values that will be required for the function.
53
Page 54

AAuuttoo SSccaallee
Press the VIEWS key. Use the arrow keys to
scroll down to Auto Scale and press ENTER.
The calculator will adjust the y axis in an
attempt to fit as much of the graph on to the
screen as possible.
Some points to bear in mind;
! the y axis is scaled only on the first function which has a .
! the y axis is scaled for the x axis you have chosen in PLOT SETUP. If
you’ve not chosen wisely then your result will not be good.
! it doesn’t choose ‘nice’ scales such as we would choose (going up in
0.2’s or 5’s or 10’s etc.) so we generally need to tidy up its choice a little.
If you look at the y axis of the graph you’ve just produced, you’ll see that the
axis tick marks are so close together that it looks like a solid line! To tidy this
up you must change to the PLOT SETUP view. If you look above the PLOT,
SYMB and NUM keys you will see the word ‘SETUP’. The SETUP view for
each of these keys is obtained via the SHIFT key.
See “Tips & Tricks - Function” on page 69 for more information on how to find
good choices for axes. The Auto Scale function is covered in much greater
detail on page 96.
54
Page 55

TThhee PPLLOOTT SSEETTUUPP vviieeww
If you press SHIFT then PLOT you will see
something like the view on the right.
The highlight should be on the first value of ‘XRng:’. Enter the value -4.
Calculator Tip
Don’t use the subtract key to input a negative. You MUST
use the negative key labeled (-) which is in the same row
as the ENTER key.
Type in 4 for the other ‘XRng:’ value, then -20 and 20 for the ‘YRng:’
values. When you’ve done this use the arrow keys move to ‘Ytick:’ and
change it to 5.
Detail vs. Faster
At the bottom of the screen you will see Res: (short for
‘Resolution’). If you highlight it and press the key
you will see that you have a choice of Faster or More Detail. More Detail
should be selected. If you choose Faster then every second dot is plotted
instead of every dot. This is quicker but may make some graphs appear less
smooth, particularly graphs with steep gradients.
There are two pages to this view (see the
key at the bottom of the screen). The
first page is used to set axes, the second to
control certain features of them.
Press the
key. You will now be
looking at the screen shown above right.
Using the arrow keys to move the highlight,
make sure that your checks/ticks match the
ones in my snapshot. Now press PLOT again.
Perfect!
55
Page 56

Let's have a look at the meaning of the CHKs (check marks) on the second
page of PLOT SETUP. Although they are not used often they can be quite
useful and I recommend highly that you use Simult:
Simultaneous
The first option Simult: controls whether each graph is drawn separately (one
after the other) or whether they are all drawn at the same time, sweeping
from left to right on the screen.
My preference is to turn this off. I find that if
there are more than two functions defined then
drawing them all at the same time can be
confusing. Turning off Simult: means that they
are drawn one after the other, in the order that
they are defined. This is obviously a bit
slower.
Connect
The second option Connect: controls whether the separate dots that make up
a graph are connected with lines or left as dots.
vs…
Axes
The third option Axes: controls whether axes are drawn. The fourth
Inv.Cross: controls the appearance of the cursor that is moved by the arrow
keys. It is best if you try this one yourself to see the effect.
Labels
The fifth option Labels: controls whether labels (X, Y and numbers) are put
on the axes. The only time this causes problems is if the scale is an odd
one, causing the labels to have too many decimal places.
Grid
The sixth and last check Grid: causes a grid of
dots to be drawn on the screen (see right).
The density of the grid is controlled by the
values of Xtick and Ytick. This can be quite
useful.
56
Page 57

TThhee ddeeffaauulltt aaxxiiss sseettttiinnggss
The default scale is displayed in the PLOT
SETUP view shown right. It may seem a
strange choice for axes but it reflects the
physical properties of the LCD screen, which is
131 pixels wide by 63 pixels tall. A ‘pixel’ is a
‘picture element’ and means a dot on the
screen. The default scale means that each dot
represents a ‘jump’ in the scale of 0.1 when
tracing graphs. The y value is determined by the graph, of course, and has
nothing to do with your choice of scale. Once the scale changes, the cursor
jumps from dot to dot are often not a useful size. See page 69 for
information on choosing ‘nice’ scales.
TThhee
The MENU toggle
If you look at the screen key
list at the bottom of the screen
you will see only a single entry,
labeled .
BBaarr
Press the key under it and your screen will
change to look like the one above right.
Press it again and the screen will clear
completely. Once more and you are back to the
original appearance. Try pressing it a few times
to get the feel for its behavior. This is what is
known as a ‘toggle’ switch. The key is a
triple toggle, cycling through each of the display
modes shown right. The first default mode is (X,Y) mode, which displays the
coordinates of the current cursor position. In any of these modes the up/down
arrows move the cursor from function to function, while the left/right arrows
move along the currently selected function.
Calculator Tip
Pressing SHIFT right arrow or SHIFT left arrow will jump
the cursor directly to the right or left side of the screen.
57
Page 58

TThhee MMeennuu BBaarr ffuunnccttiioonnss
In the examples and explanations which follow, the functions and settings
used are:
Trace
is quite a useful tool. The dot next to
the word means that it is currently switched on.
If yours isn’t then press the key underneath to
turn it on. Leave it on for now.
Press the left arrow 5 or 6 times to see a similar display to that shown right.
Pressing up or down arrow moves from function to function.
The order used is not related graph but solely to the order that they are
defined in the SYMB view. If it is turned off then the cursor is free to move
anywhere on the screen. Try this and then turn it on again.
Defn
Press the key labeled
(short for
Definition). You will find that the equation is
now listed at the bottom of the screen.
The up/down arrows will move the cursor from F1(X) to F2(X), with the
definition changing as it does so. If Trace is switched off then Defn will not
work correctly.
58
Page 59

Goto
This function allows you to move directly to a point on the graph without
having to trace along the graph. It is very powerful and useful.
Suppose we begin with the cursor at x=0 on
F1(X) as shown right.
Press and then to see the input
form shown right.
Type the value 3 and press ENTER. The cursor
will jump straight to the value x = 3, displaying
the (X,Y) coordinates at the bottom of the
screen.
A very nice feature of the key is that it will jump to values which are not
on the current screen, or which would be inaccessible for the current scale.
For example, we can jump to the value x = 100
and see the (X,Y) coordinate displayed, with
the cursor positioned at the far right side of the
screen.
If the left arrow is now pressed, tracing will resume from the right edge of the
screen, in this case at one pixel point back from x = 4.
Calculator Tip
The key will also accept calculated values. You
could, for example, jump to a value such as e2+2. If you
had recently found an intersection, then jumping to a value
of Isect would return the cursor to that point. See page
64 for information on Isect.
59
Page 60

The Zoom Sub-menu
The next menu key we’ll examine is .
Pressing the key under pops up a new
menu, shown right.
The menu is longer than will show in one
screen, so two screen shots have been
included to show most of the menu.
The list which follows covers the purpose of each of the ten options shown
right. The four extra options which follow these are covered as part of the
detailed examination of the VIEWS menu on page 92.
Center
This redraws the graph with proportionally the same scale for each
axis but re-centered around the current position of the cursor. If you
already have a ‘nice’ scale, this will preserve it, while perhaps showing
a more interesting section of graph.
In/Out
These two options zoom in or out by adjusting the scales by the factor
shown. The default factor is 4x4 but this can be adjusted through the
Set Zoom Factor option later in the menu. The most useful settings
are either 5x5 or 2x2 as these are more likely to give and preserve
‘nice’ scales.
60
Page 61

Box…
This is the most useful of the
commands. When you choose this
option a message will appear at the bottom of the screen
asking you to Select first corner.
If you use the arrow keys to move the cursor to one
corner of a rectangle containing the part of the graph you
want to zoom into and then press ENTER, the message
will change to Select second corner.
As you move the cursor this time to a
position at the diagonally opposite
corner of a box, the box will appear on
the screen.
Pressing expands the box to fill
the screen.
You’ll notice that the scale has been
disrupted so that the labels are no
longer very helpful. PLOT SETUP would give better end points for the
axes or let you switch off the labels option.
Rather than doing that however, scroll down the menu to a new
option of UnZoom. This option puts the
screen back to the way it was before you
did the
The cursor
positioned at
one corner of a
…and at the
other corner.
.
Calculator Tip
Zoom is very handy for allowing you to examine small
sections of a graph in detail, but remember Un-Zoom!
61
Page 62

X-Zoom In/Out x4 and Y-Zoom In/Out x4
These two options allow you to zoom in
(or out) by a factor of 4 on either axis.
The factors can be set using the Set
Factors… option, which gives you
access to the view shown above right.
You will also see a CHK mark next to an
option called Recenter. If this is CHKed
then the graph will be redrawn after
zooming in or out with the current position of the cursor as its center.
Changing the x factor is reflected in the menu as you can see in
the second screen snapshot.
Square
This option changes the vertical scale to proportionally match the
horizontal scale so that circles will appear circular rather than elliptical.
Auto Scale, Decimal, Integer and Trig
These four options are duplicates of those found on the VIEWS menu,
and are provided in both places simply for convenience. Information
on them can be found in the section on the VIEWS menu on pages 92.
62
Page 63

TThhee FFCCNN mmeennuu
p
Before continuing, set the axes back to the way
we set them at the start of the section on the
Menu bar.
Looking at the menu functions again, you will see that the only one we have
not yet examined is the one labeled
Tools FCN menu.
. This key pops up the Function
Move to about
this
osition.
Before you use this key, make sure is
switched on and move the cursor so that it is in
roughly the position shown right.
Root
Press the key. As you can see on the
right, this key gives you access to a number of
useful tools. If you leave the highlight on Root
(as shown) and press ENTER (or ) then
the cursor will jump to the nearest root or x
intercept for the function it is on, starting its
search at the current position. Try it now.
Notice the message at the bottom of the
screen giving the value of the root that was
found. To find the other root, you need to move
the cursor so that it is closer to the other root
than to the present one. In general that means
moving it past the turning point.
Calculator Tip
If you are working with a function which has asymptotes
then make sure the cursor is positioned on the same side
of the asymptote as the root. The internal algorithm used
does not seem to cope well with crossing asymptotes.
63
Page 64

Intersection
The next function tool in the menu is
Intersection. If you choose this option, then
you will be presented with a choice similar to
the one in the screen shown right.
Exactly what is in the menu depends on how
many functions you have showing. In the case
shown here we only have two, so the choice is
of finding the intersection of F1(X), which is the
one the cursor is on, with either the X axis, or
the other function F2(X). The results of
choosing F2(X) are shown right.
Calculator Tip
When you find an intersection or a root the value of the x
coordinate is stored in the memory X. If you immediately
change to the HOME view and type X and hit ENTER then
you can retrieve and use this value. See “Tips and Tricks Function” on page 83 for more detail and examples.
Slope
This gives the numerical value of the derivative at the point of the cursor for
the current function.
Calculator Tip
If the value at which you wish to find the slope is not
accessible for the current scale then you will need to use
the key to jump to the desired point before choosing
Slope. The value is remembered and used in the Slope
calculation, despite not being on the current scale. In the
same way, choosing Slope immediately after finding a root
or intersection will give the slope at the remembered value
rather than the nearest dot.
64
Page 65

Signed area…
x
Another very useful tool provided in the menu is the Signed Area…
tool. Before we begin to use it, make sure that is switched on, and
that the cursor is on F1(X) - the quadratic. The Signed Area… tool is similar
to the Box Zoom in that it requires you to indicate the start and end points of
the area to be calculated.
Definite integrals
3
Suppose we want to find the definite integral:
∫
2
−
2
54
xdx
−−
Choose and then Signed Area… You
will see the message shown right, asking you
to choose a starting point.
Press the key, enter the value -2 and press or ENTER. The
starting value will then be -2 so press again (or ENTER) to accept it.
Another menu will appear, asking you to
indicate what area you wish to calculate. In
this case there are only two choices - between
F1(X) and the X axis, or between F1(X) and
F2(X).
If we had defined more functions in the SYMB view then this menu would be
longer. In this case we want the area between F1(X) and the x axis, so
position the highlight as shown and press ENTER.
The graphs will then reappear, with a message
requesting that you choose an end point. In the
screenshot shown right I have pressed
and entered the value 3 to move to that point
directly.
65
Page 66

If you now press ENTER again to accept the
end point, the hp 39g+ will calculate the signed
area and display the result at the bottom of the
screen.
Calculator Tip
It should be clearly understand that although the
label at the bottom of the screen is Area it is a
little misleading.
What has actually been calculated is the definite
integral (right), with ‘areas’ below the x axis
2ndpoint
∫
1stpoint
1( )FXdx
included as negatives. This is why the label on
the original menu reads “Signed area” instead of
just “Area”.
Tracing the integral in
PLOT
Rather than using the key, an alternative
method is to use the tracing facility. The
advantage of this is that the ‘area’ is shown
visually as you go by shading, as can be seen
right.
The disadvantage of this is that you can only trace to values which are
permitted in the scale you are using. As soon as you use the shading
stops. In this case, due to the scale we chose, if you try to trace to the values
x = -3 or x = 2 you will find that they are not accessible so we will need to
change scale.
Change to the PLOT SETUP view and change
the x axis (only) back to -6.5 to 6.5, then
PLOT again.
66
Page 67

Press and again, choosing Signed
Area… as before. Use the left/right arrow keys
or the key to move the cursor to x = -2.
Press ENTER to accept the starting point.
This time, choose the boundary as F2(X)
instead of the x axis so that we will be finding
the ‘area’ between curves instead of the area
under one. Again, the result will be a signed
area (definite integral) not a true area. See
page 83 for a simple method of finding true
areas.
We now need to choose the end point. This
time do it by tracing with right arrow to move
the cursor. As you do the area will be shaded
by the calculator. The current position is shown
at the bottom of the screen. When you reach
the end point you are looking for, press the
key and the area will be calculated as
before. This is shown right.
To remove the shading, press PLOT again.
Calculator Tip
Note that common sense tells us that the answer is almost
certainly -3.75 rather than -3.75000000002. The small
error is simply due to accumulated rounding error in the
internal methods used by the calculator. For example, an
answer of 0.4999999999 should be read as 0.5. This is
quite common and students should be aware of the need
for common sense interpretation.
Areas between and under curves
If we are wanting to find true areas rather than the ‘signed areas’ given by a
simple definite integral then we must take into account any roots of the
function. This process is shown in detail on page 83, as there are certain
tricks which can be used to make the process far simpler.
67
Page 68

Extremum
The final item in the menu is the
Extremum tool. This is used to find relative
maxima and minima for the graphs.
Ensure that is switched on and that the
cursor is positioned on the cubic F2(X) in the
vicinity of the left hand maximum (turning point) as shown right. Press
and choose Extremum from the menu. You should find that the cursor will
jump to the position of the maximum.
Calculator Tip
If your graph has asymptotes then make sure that the
cursor is positioned on the side of the asymptote
containing the extremum before initiating the process. The
internal algorithm used does not cope well with intervening
asymptotes.
68
Page 69

T
IIPPSS
T
Finding a suitable set of axes
This is probably the most frustrating aspect of graphical calculators for many
users and there is unfortunately no simple answer. Part of the answer is to
know your function. If you know, for example, that your function is hyperbolic
then that immediately gives information about what to expect. If you don’t
have knowledge then here are a few tips:
1. Try just plotting the function on the default axes. You may find that
2. The NUM view can be very helpful. Try changing to NUM SETUP and
3. If the graph is part of a test or an examination then the wording of the
4. I most often use Auto Scale to get a first approximation to a good set
&
T
RRIICCKKSS
&
T
enough of the function is showing to give you a rough idea of how to
adjust them to display it better. Remember that ZOOM can work on
either axis or on both. See Tip #4 on the next page.
setting the value of NumStep to 1, or even 5 or 10. Now scroll
through the NUM view and look at what is happening to the F(X)
values. Look for two things.
Firstly, where is the function most active? For what domain on the x
axis is it changing fastest? This is likely to be the domain you are most
interested in.
Secondly, what is the range? What sort of values will you need to
display on the y axis?
Now change to the PLOT SETUP view and set what you think may be
appropriate axes. From those you can PLOT and then zoom in or out.
question will often give a clue as to what x axis domain you should
work with.
of axes. To do this you must choose your x axis domain first so try Tip
#2 above and use your knowledge of what the function might look like.
-
F
UUNNCCTTIIOON
-
F
N
69
Page 70

5. Another possible strategy for graphing which works quite well and,
perhaps importantly, always gives ‘nice’ scales is to use ZOOM.
! Enter your graphs into the SYMB
view. Remember that Auto Scale
only works on the first ticked
graph.
! Press VIEWS and choose
Decimal, or press SHIFT CLEAR
in the PLOT SETUP view. This
will give you the default axes,
probably not showing the graph
very well.
! Place the cursor so that it is in
the center of the area you are
most interested in.
! Use the menu to
adjust the view. You may
choose first to change the
zoom factors to something
other than 4x4, and to
ensure that Recenter: is
ed.
The advantage of doing it this way is that if you zoom in or out by a factor of
2 or 4 or 5, the cursor jumps will stay at (relatively) nice values allowing you
to trace more easily. In this case, the cursor now moves in jumps of 0.05,
which is ideal for most purposes. On the other hand you may not be
interested in tracing along the graph.
70
Page 71
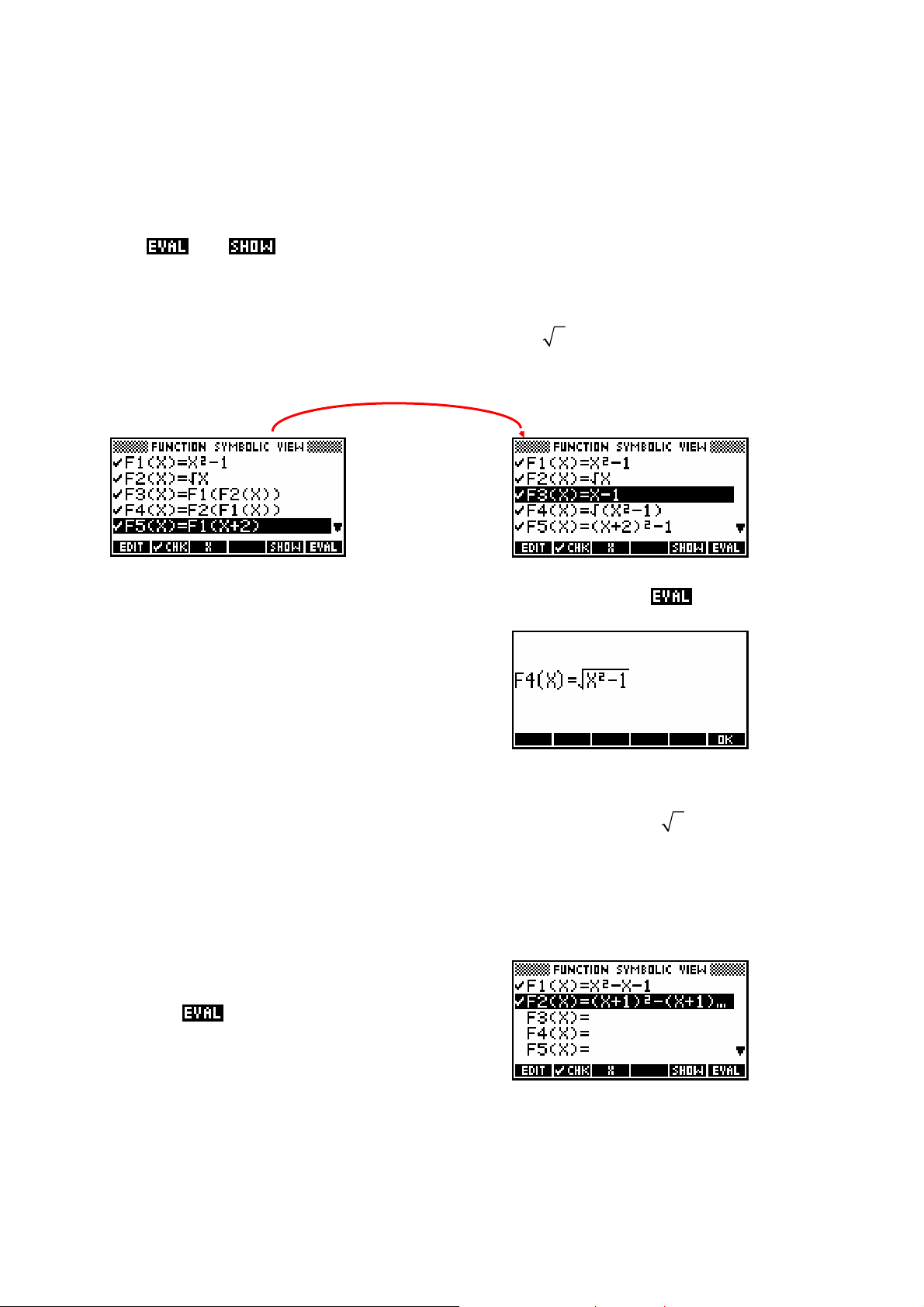
Composite functions
(
(
f
x
x
The Function aplet is capable of dealing with composite
functions such as
The and keys are particularly helpful with
this.
For example, if we define
we can use these in our defining of F3, F4. See the screen
shot on the left below.
If the highlight is now positioned on each of these in turn, and the key
pressed then the substitution is performed.
The result is shown in the upper right hand
snapshot and the F4(X) function is shown right
after pressing SHOW.
Notice that the calculator is smart enough to realize in F3(X) that
2fx+ or
)
gx in its SYMB view.
)
()
1( ) 1Fx x=− and 2( )Fx x= , then
2
2
()
1x −
is the same as 1
of the implications for the domain that F3(X) should be defined only for non-
negative x.
There is a limit to this however. If you define
1( ) 1Fx x x=−− and then 2( ) 1( 1)Fx Fx=+ ,
then the routine will not simplify
()()
2
2
111xx+−+−
− , although not, unfortunately, smart enough to keep track
2
to
1
x+−.
71
Page 72

On the other hand there is a way to further
F
x
simplify the expression. If you now the
result and enclose it with the POLYFORM
function as shown right (note the final ‘,X’),
then highlight it and press , the hp 39g+
will expand the brackets and gather terms.
Calculator Tip
These functions can all be graphed but the speed of
graphing is slowed if you don’t press first. The 39G+
is fast enough that the result can be lived with but the 39G
and 40G are usually too slow when graphing un-evaluated
composite functions.
Evaluating the function may also hide the
domain. For example, if
1( )FXX= and
2
2( )FXX= then 3( ) 1( 2( ))
the correct domain of
XFFX= will show
0x ≥
in the NUM view.
Pressing will destroy this.
Using functions in the HOME view
Once functions have been defined in the SYMB view of the Function aplet,
they can be reused in the HOME view (and indeed in any other aplet!).
For example suppose you needed to find some exact points (x = 0, 1, 2 and
3) for a graph of
fxx=
()
2
when doing a hand sketch of it.
−
2
()
Type its definition into the Function aplet SYMB
view, switch to the HOME view and then simply
type F1(0) and press ENTER. The function will
be evaluated for x = 0. Similar results can be
obtained for F1(1), F1(2) and F1(3). Notice the
error message for x = 2 caused by a divide by
zero.
72
Page 73

Differentiating
X
xx−
There are different approaches that can be taken to differentiating, most of
which are best done in the SYMB view of the Function aplet.
The syntax of the differentiation function is:
()
function∂ ,
where function is defined in terms of X.
The function can either be already defined in the SYMB view of the Function
aplet, or entered into the brackets as above.
The ∂ symbol most easily obtained by pressing the key labeled d/dx.
One point to remember is that if you use this
function in the HOME view you may not receive
the result you expect. If you try this yourself
your result will probably not be the same as
that shown.
The reason for this is that the result you see is
the derivative of
2
evaluated at whatever
value of x happens to be currently in memory.
This can be seen more clearly if we store a
specific value into the memory X beforehand.
In the example shown right, the answer of 3 is
the value of the derivative
21x− at the value of x = 2.
But what of algebraic differentiation? It is
possible but not very convenient to do this in
the HOME view using a “formal variable” of S1.
(..or S2 to S5) The drawback of this is simply
the awkwardness of having to work with S1’s
rather than with X’s.
73
Page 74
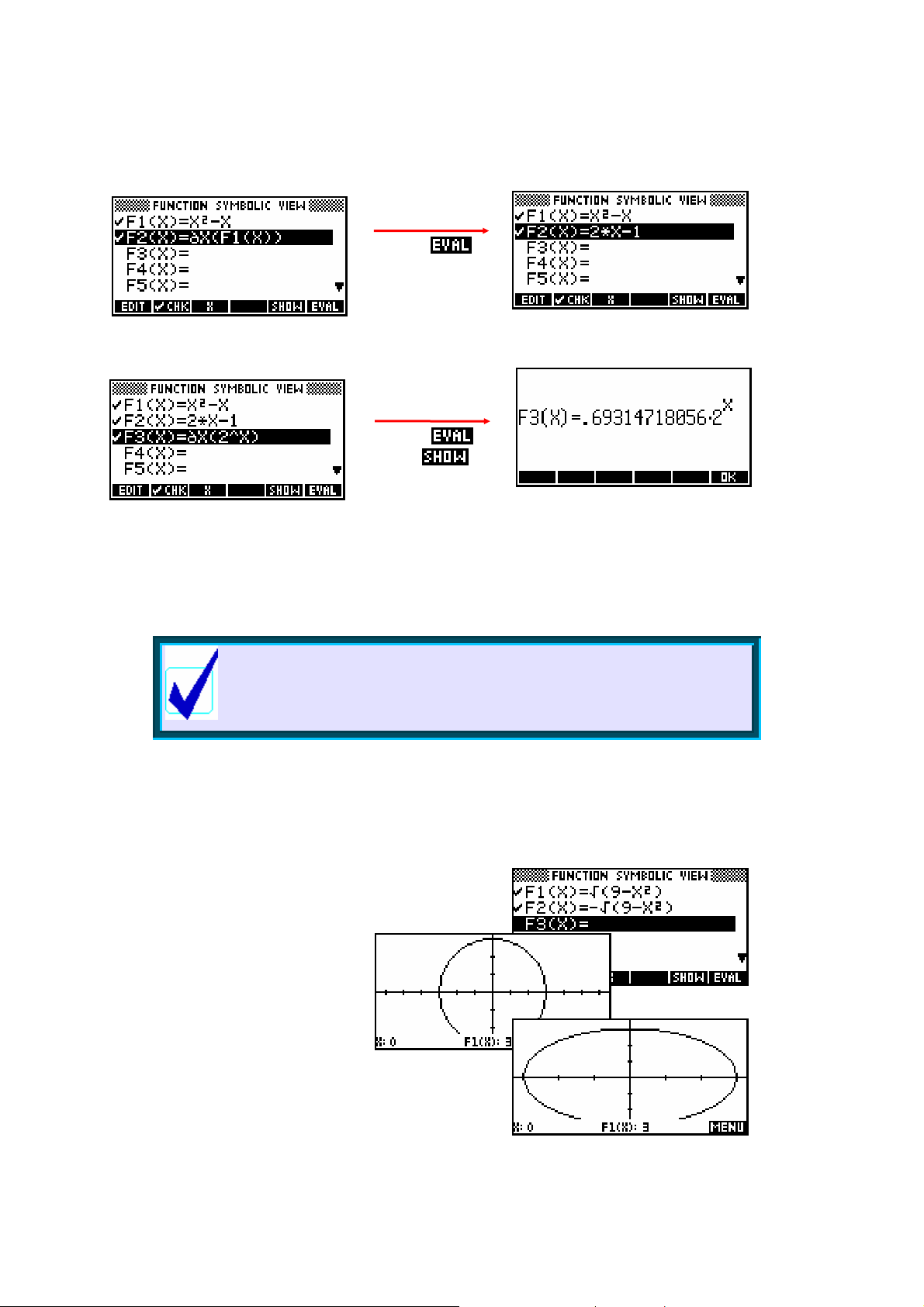
The process is easiest in the SYMB view of Function. When done this way
=
the result is algebraic rather than numeric. The best method is to define your
function as F1 and its derivative as F2 (see below)…
press
…but you can also perform the whole process in one line.
press
then
.
As you can see the calculator’s algebraic abilities do not extend to
differentiating
fx
()
2
x
as
fx′= , but at least it is numerically
ln 2 .2
()()
x
correct.
Calculator Tip
Doing your differentiation in the Function aplet is much
easier and offers the additional advantage of being able to
graph the two functions.
Circular functions
There are two issues that influence the
graphing of circular functions, both related to
the scale chosen.
The first one, illustrated on the
right, causes circles to be
ellipses if you don’t choose
scales for the x and y axes
which are ‘square’ relative to each other. The
two graphs above are both of the same
function
22
9xy+=.
74
Page 75

The simplest way to deal with this is to use
scales which are multiples of the default
scales. For example by using 13 13x−≤≤ and
6.2 6.4y−≤≤ (scale factor 2). You can also
use the ‘Square’ option on the ZOOM menu.
This adjusts the y axis so that it is ‘square’
relative to the x axis chosen.
The second issue is caused by
the domain of the circle being
undefined for some values. The
screen on your calculator is
made up of small dots called
pixels and is 131 pixels wide
and 64 pixels high. As was mentioned earlier,
this means that each pixel is 0.1 apart on the x
and y axes. This can affect your graphs and it
becomes particularly obvious with circles
because the graph does not exist for the part
of the x axis outside the circle. The two screen
shots right are an example of two images of the same graph
22
9xy+= using
two slightly different scales. You can see that the second example has
missing pieces.
Let's look at the circle
22
9xy+= as an example. This circle only exists from
-3 to 3 on the x axis and is undefined outside this domain. In order to graph it
on the hp 39g+ you have to rearrange it into
two equations of
F1(X)= (9-X2) for the top half &
F2(X)= -
(9-X2) for the bottom half.
If you enter these equations and then graph them with the default axes then
you get a perfect circle. However, if you change the x axis from the default
setting to -6 to 6 and then re-PLOT then part of the circle disappears. This is
shown in the snapshot at the start of the question.
The reason for this is that when the calculator draws the graph it does so by
‘joining the dots’. For the default scale of -6.5 to 6.5 this is not a problem
since the edges of the circle at -3 and 3 fall on a pixel. This means that the
last segment of the graph plotted extends is from 2.9 to 3 and the circle
reaches right down to the x axis.
75
Page 76

However, for the scale of -6 to 6 the pixels are no longer 'nice' values of 0.1.
π
If you try to trace the circle you'll see that the pixels fall on 0, 0.0923077,
0.1846154..... In particular, near x=3 the pixel values are 2.953846 and
3.046154. This means that the calculator can't draw anything past 2.953846
because the next value doesn't exist, being outside the circle. This is what
causes the gap in the circle. There's nothing to join to past that last point.
The solution is to use scales which allow the end points of your circle to fall
on a pixel point. If your circle has an integer radius then this is easily done
by starting with the default axes and then ZOOM in or out to show the circle.
This will tend to give 'nice' pixel points. If your circle is not centered on the
origin then just check/tick the box in the Set Zoom Factors box to Recenter.
That will allow you to turn off TRACE, move the cursor closer to the point
where you'd like the centre of screen to be and then ZOOM.
Trig functions
If graphing a trig function using
radian measure then you should
choose a scale which will cause
pixel values (screen dots) to fall at
convenient points. A good scale to
use is provided on the VIEWS menu
(see right).
This scale sets each dot to be
that multiples and most factors of
π
, ensuring
24
will fall on dots and thus helping if you
want to trace values on the graph.
Ensure the angle measure is set to Radians in the MODES view if you intend
to use this scale.
Calculator Tip
Make sure you set angle measure after you have ed
the aplet, not before, so as to ensure you are setting the
correct aplet.
76
Page 77

Retaining calculated values
When you find an extremum or an intersection,
the point is remembered until you move again
even if it is not actually on a value that would
normally be accessible for the scale you have
chosen.
For example, if you find an intersection and then return to the menu
and choose Slope, the slope calculated will be for the intersection just found
rather than for the nearest pixel point. If you have recently found a root then
pressing the
key and entering the value Root will return the cursor to it.
There are two ways to access these values. The first and simplest is via the
value stored in memory X. If you move from PLOT to the HOME view and type
X (using ALPHA) then the value it will contain will be the last position of the
cursor. If you just found a root or an intersection then this will be the value
displayed. The second way is via the reserved words of Root, Extremum,
Area, Slope and Isect. Typing any of these reserved words in any
situation will retrieve their last calculated values. If a value has not been
found yet then they will return zero.
This trick is particularly useful when calculating areas under or between
curves. See page 83.
The NUM view revisited
We saw earlier that the NUM view gives a
tabular view of the function.
It is possible to manipulate this view through
the NUM SETUP view.
77
Page 78

Firstly, one can change the start value and the step size for the view.
NumStart & NumStep
For example, values of 10 and 2 give:
Automatic vs. Build Your Own
Looking at the NUM SETUP view you will see an entry called NumType: with
the default value of Automatic. The only alternative to Automatic is the
setting of Build Your Own. Under this setting the NUM view will be empty,
waiting for you to enter your own values for X.
Typing in the values of (for example):
3 (ENTER) -2 (ENTER) 5 (ENTER)
… will give…
In this situation the function values are being calculated as you input the X
values. This can be quite useful if you are wanting to evaluate the behavior
of a function at selected points.
ZOOM
If you now use the NUM SETUP view to switch
to Automatic you will find that there is a
key at the bottom left of the NUM view. This
can be quite useful as a fast way to reset the
scale.
78
Page 79

Pressing the key pops up the menu on
π
the right. The first option of In causes the
step size to decrease from 0.1 to 0.025. This
is a factor of 4 and is changeable via the NUM
SETUP view. I find a zoom factor setting of 2
or 5 to be more useful.
The second option of Out causes the
opposite effect, changing the step size
upwards by whatever the Zoom Factor is set
to.
The Decimal option restores the default settings.
It changes from whatever is showing back to the step size of 0.1 The
Integer option on the other hand, changes the scale so the step size is 1.
The Trig option changes the scale so that the step size is
exactly. This
24
will obviously be useful when dealing with trigonometric functions.
79
Page 80

Integration: The definite integral using the ∫ function
x
+
∫
+
X
X
∂
X
The situation for integration is very similar to that of differentiation. The
difference is that both the HOME view and the Function aplet require the use
of a “formal variable” S1. As with differentiation, the results are better in the
Function aplet. The ∫symbol is obtained via the keyboard.
The syntax of the integration function is:
(,, , )a b function X
∫
where: a and b are the limits of integration
and function is defined in terms of X.
Let’s look first at the definite integral…
2
The screen left shows
ln2
followed by
∫
0
∫
1
x
edx
2
= 1.
1xdx+
= 3.3333…
It may help you to remember the syntax of the differentiation and integration
functions if you realize that they are filled in with values in exactly the same
way that they are spoken.
2
2
1
dx+
E.g.
∫
1
“the integral from 1 to 2 of
& entered:
is read as:
( 1, 2,
2
2
1x
dx ”
1X
, X )
A similar path was taken with the differentiation function,
so that:
d
2
and entered
dx
, which is read as “the derivative with respect to X of X2”
2
X
∂
()
:
X
80
2
()
Page 81

Integration: The algebraic indefinite integral
x
x
x
Algebraic integration is also possible (for simple functions), in the following
fashions:
i. If done in the SYMB view of the Function aplet, then the integration
must be done using the symbolic variable S1 (or S2, S3, S4 or S5). If
done in this manner then the results are very good, except that there is
no constant of integration ‘c’.
The screenshot right shows the results of
defining
2( ) 0, 1, 1,FX SX X=−
1( ) 1FX X=− and then
()
∫
2
2
, together with
the results of the same thing after
pressing the key (the result is placed
in F3 only for convenience of viewing). All
3
that is now necessary is to read ‘-S1+S1^3/3’ as
x−+ , or as it
3
3
should be read as
x
c−+ .
3
ii. If done in the HOME view, then S1 must
again be used as the variable of
integration.
i.e.
2
1
dx−
∫
is entered as
( 1, S1, X2 - 1, X ).
∫
This is shown right, together with the results of highlighting the answer
and pressing
. The calculator assumes that X itself may be a
function of some other variable and integrates accordingly as a ‘partial
integration’ which, while mathematically correct, is not what most of us
want.
The way to simplify this answer to a
better form is to highlight it, it, and
press ENTER again, giving the result
shown right. This is the result of the
calculator performing the substitutions
implied in the previous expression.
81
Page 82

A caveat…
x
∫
This substitution process has one implication which you need to be wary of
and so it is worth examining the process in more detail…
1
xS
1
S
2
−= −
xdx x
∫
0
1
x
3
=−−−
S
=−
3
=
3
0
x
=
33
10
S
10
S
33
3
1
1
S
The potential problem lies with the second line, where the substitution of zero
results in the second bracket disappearing. This will not always happen.
For example…
1
xS
=
1
S
∫
0
4
−=
2
xdx
()
=−
=−⋅
()()
S
()
5
−
2
x
()
5
−−
12 02
S
0
x
=
55
55
5
12
−
64
5
The final constant of 6.4 comes from substituting zero into the expression
and should not be there if we were doing this with the aim of finding an
indefinite integral. On the other hand, we all know that the answer should
have a constant of integration, so perhaps this extra constant will help you to
remember the ‘+c’!
In addition to this, there are strict limits to what the hp 39g+ can integrate.
For example, if you try to evaluate
2
sin .cos
xdx
using the calculator, it will
not be able to do it. Essentially, beyond polynomials forget it.
The hp 40g Computer Algebra System
Owners of the hp 40g will be aware that it has a CAS which allows it to
perform the most complex algebra, including complex integrations, with ease.
More information on the CAS can be found in the supplementary appendix on
the hp 40g. See the Table of Contents.
82
Page 83

Integration: The definite integral using PLOT variables
As was discussed earlier, when you find roots,
intersections, extrema or signed areas in the
PLOT view, the results are stored into variables
for later use.
For example, if we use Root to find the x
intercept of
2
() 2fx x=− then the result is stored
into a variable called Root, which can be
accessed anywhere else. Similar variables
called Isect, Area, and Extremum are
stored for the other tools.
You can access these names by typing them
in using the ALPHA key, or by using the VARS
key. Press VARS and you will see a list of the
HOME variables.
If you press SK2, labeled (not the
APLET button on the keyboard), then the
display changes to show the variables specific
to whatever aplet you are currently using.
Those shown right are for the Function aplet
and the group of Plot FCN variables is shown.
If you look at the screen shot you will see that the tag is currently
selected (showing as
) and this means that when you press the
name of the variable will be pasted into what ever view you were using when
you pressed the VARS key. Pressing the
screen key will cause the
value of the variable to be pasted instead. There is no effective difference in
most situations.
This can be very useful in finding areas, as you will see in the example
following.
83
Page 84

Suppose we want to find the area between
ff−
f
2
() 2fx x=− and () 0.5 1gx x=−from x = -2 to
the first positive intersection of the two graphs.
From the shaded screenshot shown above
right it can be seen that to find the area we
need to split it into two sections, with the
boundaries being -2 and the two
intersections.
The shortcut here is to use
Intersection
to find the first intersection, storing the results
into memory variable A.
We then do the same thing for the
second intersection, storing the
result into B.
We can now calculate the area in the HOME view, using
and
f− for the second. Use to duplicate the first integral and edit it
21
to adjust the functions and limits.
Finally,
the two solutions and add them
to give the final answer.
for the first
12
84
Page 85

Piecewise defined functions
It is possible to graph piecewise defined functions using the Function aplet,
although it involves literally splitting the function into pieces.
3; 2
xx
+<−
For example:
() 2 ; 2 1
fx x x
2
=− −≤≤
3;1
xx
−≥
To graph this we need to enter it into the SYMB view as
three separate functions:
F1(X)=(X+3)/(X < -2)
F2(X)=(X2-2)/(X ≥ -2 AND X ≤ 1)
F3(X)=(3-X)/(X ≥ 1)
Note: AND can be found on the (-) key.
The reason why this works is that the (X < -2)
and the (X ≥ -2 AND X ≤ 1) expressions are
evaluated as being either true (which for
computers has a value of 1) or false (which
has a value of 0).
By dividing by the domain expression we are effectively dividing by 1 inside
the range (no effect) or dividing by zero outside the domain, making the
function undefined. Since undefined values are not graphed, this produces
the desired effect.
85
Page 86

‘Nice’ scales
As discussed earlier, the reason
for the seemingly strange
default scale of -6.5 to 6.5 is to
ensure that each dot on the screen is exactly
0.1 apart.
There are other scales, basically
multiples of these numbers, that
also give nice values if you want
to along the graph. For
example, halving each of -6.5
and 6.5 will place the dots 0.05
apart.
To zoom out instead of in simply
double the values, producing
dots that are 0.2 apart.
Similarly, if you want to center
the graph around a particular
value then just add that value to
the range values. The example
right is centered around x = 1 by
adding 1 to -3.25 and 3.25.
A time when ‘nice’ scales are more important
is when you use the Plot-Table option in the
VIEWS menu. If you use the default axes you
will find that the dots, and hence the table
values are no longer ‘nice’ because of the 3
dots consumed by the line down the middle of
the screen.
86
Page 87

This can be solved by changing the
x axis scale to -6.4 to 6.4, which
gives table values of 0.2.
Using -3.2 to 3.2 is even better since it makes
the graph ‘square’ again, with both axes
proportional. Another good choice of scale for
the Plot-Table view is -8 to 8, giving table
values of 0.25. Basically any power of 2 is a
good choice. Again, adding or subtracting a
constant from each end of the axes will produce a graph where the y axis is
not centred.
Use of brackets in functions
One problem commonly encountered by new
users is misinterpretation of brackets. The
hp 39g+ will correctly interpret
F1(X) = X2(X+1) as X2*(X+1) but will not
understand F(X)=X(X+1). When used in either
Function or Solve, it will result in the error
message of “Invalid User Function”.
Similarly if you want to use the sum to n terms formula for a GP in the Solve
aplet and enter it as S=A(1-R^N)/(1-R) then you will see a similar message
until you change it to read S=A*(1-R^)/(1-R).
The reason for this apparent ‘error’ is that all of the built-in functions such as
SIN(....) and COS(....) and ROUND(....) work with brackets. When the
calculator encounters X(X+1) it interprets this as asking it to evaluate a
function called X(....) at the value X+1. Since there is no such function it
returns the error message that you are trying to use a function that is
unknown.
The solution is simple: just remember to put the * sign in when you use
letters immediately before a bracket.
87
Page 88

Problems when evaluating limits
In evaluating limits to infinity using substitution, problems can be encountered
if values are used which are too large.
x
For example: lim
x
→∞
e
x
+26
e
It is possible to gain a good idea of the value of
this limit by entering the function
F1(X)=e^X/(2*e^X+6) into the Function aplet,
changing to the NUM view and then trying
increasingly large values. As you can see
(right) the limit appears to be 0.5, which is correct.
However, if you continue to use larger values
then the limit appears to change to 1 (see
right). The reason for this is that the value of
x
e
passes the limit of the capacity of the
calculator (10
500
), and so the top and bottom of
the fraction become equal (both at a value of
500
10
) instead of the true situation of the bottom being roughly twice the top.
This is most likely to happen with limits involving power functions as they will
overflow for smaller values of x.
A related effect happens when investigating the behavior of the commonly
n
1
lim 1
+
used calculus limit of
n
→∞
.
n
Suppose that you wish to use the Function
aplet to evaluate what happens to
F1(X)=(1+1/X)^X by changing to the NUM view
and choosing the ‘Build Your Own’ facility (see
right). The convergence towards e can also be
seen graphically in the PLOT view but is very
slow to reach high accuracy.
88
Page 89

The problem lies in the fact that the slow
×
⋅
convergence will mean that people will often
try to graph this function for very large values
of x. The first graph on the right shows the
graph of this function for the domain of 0 to
100. The second graph shows how instability
develops in the domain 0 to 1E11 (
110
11
).
This apparent instability is caused by the
internal rounding of the calculator. It works to
16 bits accuracy, which means that it can store 12 significant digits (for
reasons only of interest to programmers). This means that when you invert a
really large number and add it to one, you lose a lot of accuracy.
For example: if X =
285 10⋅× then 1/X is
10
2 5087719298 10
-11
× . When you
add 1 to this, the calculator is forced to discard all but the last decimal place.
Thus 1 + 1/X = 1.00000000003 (rounded off from 1.00000000002508...)
There are naturally a whole range of numbers
which will all round off to the same value of
1.00000000003, so that (for that range of
numbers) the expression (1+1/X)^X is
equivalent mathematically (on the HP) to
(1.00000000003)^X. This produces a short section of an exponential graph,
which only looks linear because you don't see enough of it.
Eventually the calculator reaches a value on the x axis which is large enough
that it rounds off to a smaller number than 1.00000000003, which is
1.00000000002. This produces the sudden drop in the graph as the plot
changes from a section of a 1.00000000003^X graph to a section of a
1.00000000002^X graph (which has a shallower gradient).
This section is maintained until the next drop, and so on. Finally, at the value
x =
11
210× the inverted value is so small that 1+1/X becomes exactly 1 and
the graph becomes horizontal. Of course this is completely the wrong value!
Although this explanation may be beyond the level of many students it is
quite important that they have some understanding of these ideas if they use
the calculator to evaluate limits. The solution to all problems of this type is to
simply be aware of their existence and to allow for them rather than simply
accepting the results shown in the NUM view.
89
Page 90

Gradient at a point
(
)
)
f
This can be introduced via the Function aplet.
In the Function aplet, enter the function being studied into F1(X).
To examine the gradient at x=3, store 3 into
memory A in the HOME view as shown right.
Return to the SYMB view, un-CHK F1(X) and
enter the expression
F2(X)=(F1(A+X)-F1(A))/X in F2(X).
This is the basic differentiation formula with X
taking the role of h and A being the point of
evaluation.
fa
=
'lim
()
0
h
→
ah fa
+−
h
Change to the NUM SETUP view and change
the NumType to “Build Your Own”. By
entering successively smaller values for X you
can now investigate the limit as h tends
towards zero.
To investigate the gradient at a different point simply change back to the
HOME view, enter a new value into A and then return to the NUM view.
The disadvantage of the previous
method is that it is not very visual. An
alternative is to use an aplet
downloaded from the web.
(
90
Page 91

Finding and accessing polynomial roots
The POLYROOT function can be used to find roots very quickly, but the results
are often difficult to see in the HOME view, particularly if they include complex
roots. This can be dealt with easily by storing the results to a matrix.
For example, suppose we want to find the
roots of
() 3 3fx x x=− +. We will use the
32
POLYROOT function and store the results into
M1.
The advantage of this is that
you can now view the roots
by changing to the Matrix
Catalog. and pressing .
See page 170 for more
detailed information on matrices.
In addition to this, you can access the roots in
the HOME view as shown.
Calculator Tip
This trick is particularly helpful if you are working with
complex roots. Not only does it make it easier to re-use
them it makes it easier to tell at a glance which are real
and which complex.
91
Page 92

T
T
In addition to the views of PLOT, SYMB and NUM (together with their SETUP
views), there is another key which we have so far only used very fleetingly the VIEWS key.
It may seem odd to devote an entire chapter to what might appear to be an
inconsequential key. In fact, however, this button is very useful to the
effective use of the calculator, and crucial if you intend to use aplets
downloaded from the internet.
The contents of the VIEWS menu changes according to which aplet you are
currently using. The Function aplet contents are covered here but the others
differ in only small ways.
However, aplets downloaded from the Internet
will usually have a radically different VIEWS
menus created by the person who wrote the
program for the aplet. See page 214 for more
information on this process if you intend to program the calculator.
The VIEWS key pops up the menu on the right.
We have already seen the use of the Auto
Scale option (see page 96) and this is probably
the one most used. The other options are also
very useful at times.
Shown on the right is the graph of
the menu above will pop up.
HHEE
VVIIEEWWS
1( ) 1FX X=−. If we press the VIEWS key,
S
MMEENNU
2
U
92
Page 93

Plot-Detail
Choosing Plot-Detail from the menu splits the
screen into two halves and re-plots the graph
in each half. The right hand side can now be
used to without affecting the left screen.
For example a Box zoom shows the result on
the right allowing easy comparison of ‘before’
and ‘after’ views.
The left hand graph is always the active one, with results
of actions shown on the right. We can now use the left
graph again to zoom in on another section of interest, or
alternatively, press the key under the
label. This switches the right hand graph onto
the left screen.
Using or the FCN menu you
can then find or examine points of
interest. Alternatively you can zoom
in again using another Box zoom.
Any of the normal tools such as Signed
Area… or Extremum can be used in this split screen.
All the normal function
tools are available
except for
.
93
Page 94

Plot-Table
The next item on the VIEWS menu is PlotTable. This option plots the graph on the right,
with the Numeric view on the right half screen.
Using the left/right arrow keys moves the
cursor in both the graph and the numeric
windows. See page 95 for information on how
to keep nice scales in the table view. When more than one function defined
in the SYMB view, pressing the up or down arrows changes the table focus
from one to another. In this case, with only one, it centers the table.
Let us switch now to a graph of the two
functions
2( ) 2 5 4FX X X X=+ −−. This shown on
1( ) 1FX X=− &
32
2
the right, using an XRng of -8 to 8.
Changing to Plot-Table gives the result shown
left. As you can see, the scale has been
preserved unchanged, although without labels.
The table on the right also uses a sensible
scale of 0.25 because of the choice of an x
axis scale of -8 to 8. Choice of scale in the
Plot-Table view is discussed in detail in the
“Tips and Tricks – Nice Scales” immediately following the chapter on the
Function aplet.
Looking at the table heading you will see that it
currently shows the function F1(X). The
left/right arrow keys move within that function,
with the cursor keeping track. Pressing the
up/down arrows now not only centers the table
highlight but, more importantly switches from
F1(X) to F2(X). The X column will not change.
94
Page 95

Nice table values
What makes this view even more useful is that
the table keeps its ‘nice’ scale even while the
usual ‘FCN’ tools are being used. As you can
see in the screenshot left, the table is
automatically repositioned to show the closest
pixel value to that of the extremum found.
The Signed Area… tool is also available in this view and when the cursor is
moved the values in the table follow it. Unfortunately, the highlighted value in
the table doesn’t change as the cursor moves to create the shaded area. For
this reason the best strategy is to use the
key to jump to the end point.
This means that the area will not be shaded but this should not be a problem.
Overlay Plot
Another possibility from the VIEWS menu is Overlay Plot. This option can be
used to add another graph over the top of an existing one, without the screen
being blanked first as it usually is. As an example, if you have already
graphed functions F1(X) through to F6(X) and then add another one in the
SYMB view, then you don’t really want to have to wait while all the earlier
ones are redrawn. If you un-
the earlier graphs and then use Overlay
Plot for the new one then it will be drawn over the top of the existing ones.
Of course the results will not be good if the scales don’t match!.
You can even use this to combine different
styles of graphs. For example, the screen shot
right was produced by drawing a circle in the
Parametric aplet and then superimposing the
equations y = x and
y = -x in the Function aplet. This could be used
to show, for example, enclosing curves for conic sections.
You can also use this technique to overlay functions on top of statistical
graphs.
95
Page 96

Auto Scale
Auto Scale is an good way to ensure that you get a reasonable picture of the
graph if you are not sure in advance of the scale. After using Auto Scale you
can then use the PLOT SETUP view to adjust the results.
It is important to understand two points about how Auto Scale works.
1. It works by using the X-axis range that is currently chosen in PLOT
SETUP to adjust the Y-axis range to include as much of the graph as
possible. It will not adjust the x axis.
2. Auto Scale is done only for the first
graph with a . If there are other
graphs and they don’t fit the scale then
they will not benefit. As you can see in
the example shown right, the quadratic
shows well but the second graph (a
cubic) shows only an ascending section. Zooming out would be an
option at this stage, as would un- ing the quadratic in the hopes
that Auto Scaling the cubic might give better results (unlikely).
3. The resulting y scale is
often not a very ‘nice’
one. You will usually
have to adjust it in the
PLOT SETUP view to
make it look good.
The excessively thick axis in
the first screen shot of the
sequence of three on the right
is a common result of Auto
Scale and is caused by the value of
Ytick being too small. The third graph
has a Ytick value of 10 instead of 1.
96
Page 97

Decimal, Integer & Trig
π
π
π
π
The next option of Decimal resets the scales
so that each pixel (dot on the screen) is exactly
.
0
1. The result is an X scale of 65 65x−⋅ ≤ ≤ ⋅
and a Y scale of 31 32y−⋅≤ ≤ ⋅ . This may not
give the best view of the function. Personally I
don’t often use it, as it is generally easier to go
to the PLOT SETUP view and press SHIFT CLEAR.
The Integer option is similar to decimal, except
that it sets the axes so that each pixel is 1
rather than 0.1 thus giving an X scale of
65 65X−≤≤ .
The usual result of this is rather horrible.
The final option of Trig is designed for
graphing trig functions. It sets the scale so
each pixel is
. This means that if you
24
were graphing 1( ) 2 sin( )FX X= then 24
presses of the left or right arrows would move
you through exactly π and the value would be exactly 2 instead of a horrible
decimal.
If you zoom in or out from this, the jumps will still stay relatively nice,
particularly since 24 has so many factors. For example, with a zoom factor of
2, zooming out once would mean each pixel was now
would give a pixel jump of
12
.
, while zooming in
48
As you can see, the cursor is nicely at a value
of
, giving a y value of exactly 1 instead of
2
only very close.
97
Page 98

The default axes under the Trig option is 2
π
−
π
to 2
. If you are primarily
interested in the first 2π of the graph then simply change Xmin to zero.
Alternatively you can move the cursor to π (the middle) and then zoom in.
The example below uses zoom factors of 2x2 with Recenter: ed.
Calculator Tip
In the graphs above the cursor is at x = π. The coordinates at
the bottom of the screen should show F1(X)=0 but doesn’t due
to the fact that the value of π stored internally is not (and of
course cannot) be exact. The rounding of π in the 13th decimal
place means that the resulting trig values will be ‘wrong’ in the
11th to 15th decimal place depending on the function used.
98
Page 99

DDoowwnnllooaaddeedd AApplleettss ffrroomm tthhee IInntteerrnneett
The most powerful feature of the hp 39g+ is that you can download aplets
and programs from the internet to help you to learn and to do mathematics.
Two quick examples of aplets that are available are shown here. More are
listed in the supplementary appendix on “Teaching Calculus using the
hp 39g+”. Notice that in each case the aplet is controlled by a menu. This
menu is created by the programmer and ‘attached’ to the VIEWS button so
that it displays in place of the normal menu.
Curve Areas
This aplet allows the user to find
approximations to the area under a curve by
finding either the lower rectangular area, the
upper rectangular area, or the trapezoidal area.
The user can choose the end points of the interval,
the type of calculation and the number of rectangles
to be used. The rectangles are drawn on the screen. A worksheet
introduces the idea of integration to find areas.
Linear Programming
This aplet visually solves linear
programming problems, finding the vertices
of the feasible region and the max/min of
an objective function. The final stage of
finding the vertices is a bit slow on an hp 39g but
more acceptable on an hp 39g+.
99
Page 100

π
T
T
This aplet is used to graph functions where x and y are both functions of a
third independent variable t. It is generally very similar to the Function aplet
and so we will look mainly at the way it differs.
An example of a graph from this aplet is:
Although it you can graph equations of this
type, only some of the usual PLOT tools are present. As you can see in the
screen shot above, the key is not shown, meaning that none of its tools
are available. Thinking about the nature of these equations will tell you why.
As usual the first step is to choose it in the
Aplet Library. Press the APLET key, highlight
Parametric and press . If you wish to
ensure that you see the same thing as the
examples following then press the
button before pressing .
As with the Function aplet, this aplet begins in
the SYMB view by allowing you to enter
functions, but the functions are paired. Each
function consists of a function in T for X and
another for Y.
P
HHEE
xt t
yt t
AARRAAMMEETTRRIICC
P
() 5cos
=
() 3sin 3
=
()
()
02
t
≤≤
A
A
which gives:
T
PPLLEET
Choose XRng, YRng & TRng
Looking at the PLOT SETUP view, you will see
that we now have to enter a range for T as well
as the usual ranges for X and Y. It is crucial to
understand the different effect of the T range
to that of the X and Y.
Calculator Tip
The default setting for TStep is 0.1. In my experience this
is too large and can result in graphs that are not sufficiently
smooth. It is worth developing the habit of changing it to
0.05.
100
 Loading...
Loading...