Page 1

HP StorageWorks
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide
This document provides information for network administrators who are managing MSA2000 G2 product from
a storage management application through SMI-S, including use of the MSA2000 Proxy Settings Manager
(PSM).
Part number: 573100-002
Second edition: December 2009
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211
and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items
are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Intel, Itanium, Pentium, Intel Inside, and the Intel Inside logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or
its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows XP, and Windows NT are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction ....................................................................................... 7
SMI-S Support ............................................................................................................................ 8
2 Installing and uninstalling the SMI-S Proxy Provider ............................... 11
Windows ................................................................................................................................. 11
Linux ....................................................................................................................................... 13
3 Configuring the Proxy Provider ........................................................... 15
First-time configuration ............................................................................................................... 15
Ports and the service utility (Windows only) .................................................................................. 15
PSM device management commands .......................................................................................... 16
Add system ....................................................................................................................... 17
Remove system ................................................................................................................... 18
Discover systems ................................................................................................................ 19
View systems ..................................................................................................................... 20
Clear systems .................................................................................................................... 22
Manage system .................................................................................................................. 23
Create user account in the MSA device ........................................................................... 24
Change user password in the MSA device ...................................................................... 25
Delete user account in the MSA device ........................................................................... 26
Get or set provider attributes ................................................................................................ 27
Set Proxy Provider timeout ............................................................................................. 28
Set indication provider polling interval ............................................................................ 29
Set proxy provider debug log level ................................................................................. 30
4 Integrating the Proxy Provider with HP SIM .......................................... 31
HP SIM storage integration ........................................................................................................ 31
Discovering an MSA2000 G2 Proxy Provider ............................................................................... 32
Identifying an MSA2000 G2 Array ............................................................................................. 33
Subscribing to and viewing events ............................................................................................... 33
Generating reports .................................................................................................................... 34
5 Client API Interface ........................................................................... 35
6 Frequently asked questions ................................................................ 39
7 Support and other resources .............................................................. 43
Document conventions and symbols ............................................................................................. 43
HP technical support ................................................................................................................. 44
Product warranties .................................................................................................................... 44
Subscription service .................................................................................................................. 44
HP websites ............................................................................................................................. 44
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 3
Page 4

Documentation feedback ........................................................................................................... 45
Glossary ............................................................................................ 47
4
Page 5

Figures
SMI-S Proxy Provider overview .................................................................................... 71
HP Package Setup dialog ......................................................................................... 112
Pegasus service in the Services window ..................................................................... 123
Pegasus installation directory .................................................................................... 134
Output of add system command ............................................................................... 175
Output of remove system command ........................................................................... 186
Output of discover systems command ........................................................................ 197
Output of view systems command .............................................................................. 208
Output of the view op command ............................................................................... 219
Output of clear systems command ............................................................................. 2210
Output of manage system command .......................................................................... 2311
Output of create user account command .................................................................... 2412
Screenshot of change user password command .......................................................... 2513
Output of delete user command ................................................................................ 2614
Output of set command options ................................................................................ 2715
HP SIM topology .................................................................................................... 3116
Link to the Identification page of the managed MSA2000 G2 Array ............................. 3317
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 5
Page 6

Tables
Supported SMI-S profiles ............................................................................................ 81
Supported indication events ....................................................................................... 92
PSM commands ...................................................................................................... 163
Pegasus CIMOM operations ..................................................................................... 374
Document conventions ............................................................................................. 435
6
Page 7
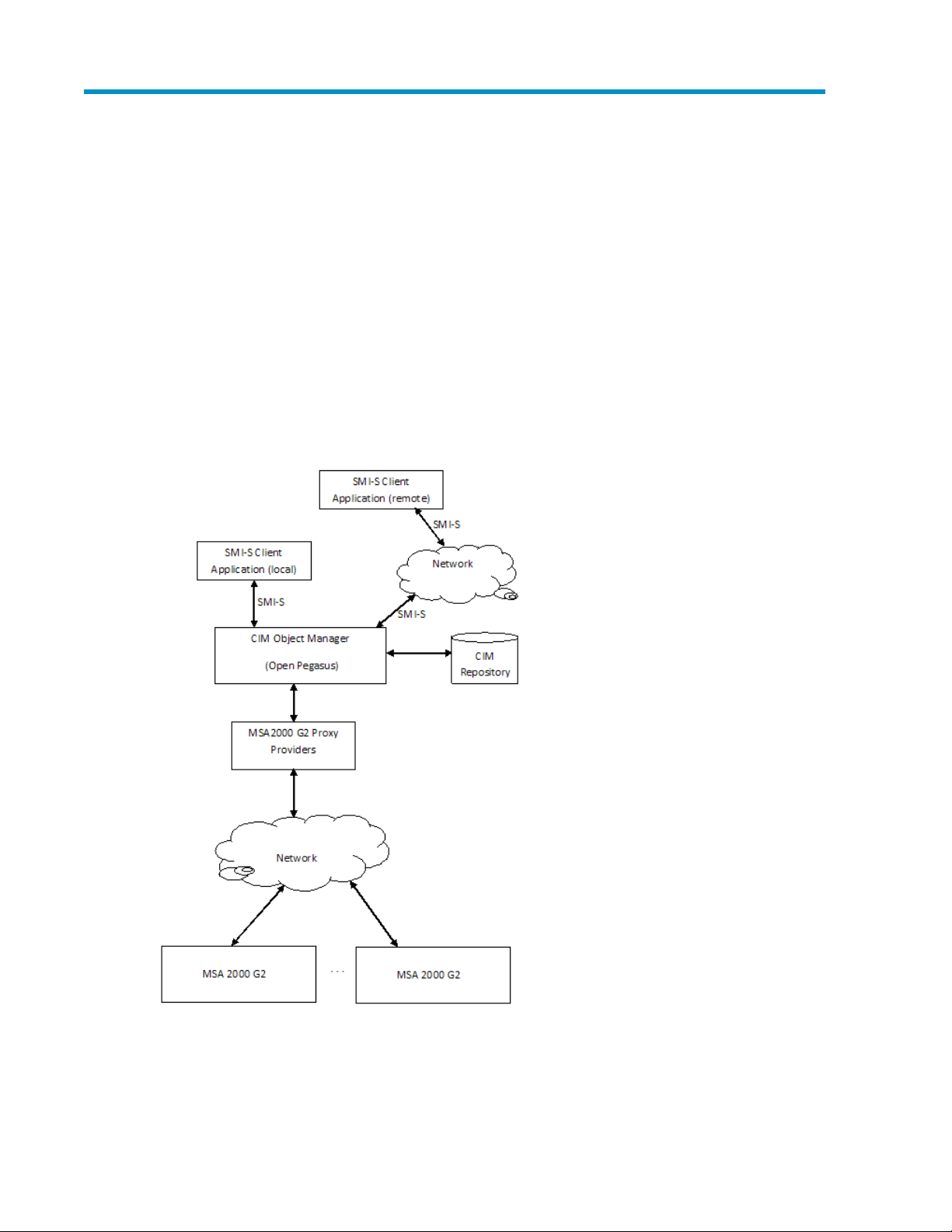
1 Introduction
The SMI-S Proxy Provider provides an industry-standard WBEM-based management software framework
for MSA2000 G2 products that can be integrated with various HP Enterprise management software
applications, such as HP SIM.
This release supports:
• MSA2312fc and 2324fc
• MSA2312sa and 2324sa
• MSA2312i and 2324i
• Passive management features
Support for the following is planned for future releases:
• Active management features, such as RAID provisioning
Figure 1 SMI-S Proxy Provider overview
.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 7
Page 8
This product carries OpenPegasus CIMOM and is supported on both Windows and Linux platforms.
The proxy provider set includes the following:
• Instance Provider
• Association Provider
• Method Provider
• Indication Provider
SMI-S Support
The SMI-S Proxy Provider supports passive management features described in Table 1, page 8.
Table 1 Supported SMI-S profiles
DescriptionProfile / Subprofile
Describes RAID array systems. It provides a high-level overview of the array system.Array
Block Services
Physical Package
Server
Profile Registration
Defines a standard expression of existing storage capacity, the assignment of capacity
to Storage Pools, and allocation of capacity to be used by external devices or applications.
Models information about a storage system’s physical package and optionally about in-
ternal sub-packages.
Defines the general mechanisms used in expressing health in SMI-S.Health
Defines the capabilities of a CIM object manager based on the communication mechanisms
that it supports.
Models the Fibre Channel specific aspects of a target storage system.FC Target Ports
Models the SAS specific aspects of a target storage system.SAS Target Ports
Models the iSCSI specific aspects of a target storage system.iSCSI Target Ports
Provides addresses of remote access points for management services.Access Points
Specializes the DMTF Fan profile by adding indications.Fan
Specializes the DMTF Power Supply profile by adding indications.Power Supply
Models the profiles registered in the object manager and associations between registration
classes and domain classes implementing the profile.
Models software or firmware installed on the systemSoftware
Extent Composition
Proxy Server System Management
Introduction8
Models device mapping and masking abilities for SCSI systemsMasking and Mapping
Models disk drive devices.Disk Drive Lite
Provides an abstraction of how it virtualizes exposable block storage elements from the
underlying Primordial storage pool.
Models the location details of product and its sub-componentsLocation
Specializes the DMTF Sensors profileSensors
Models the discovery of devices to be managed
Page 9
This provider supports the following CIM operations:
• getClass
• enumerateClasses
• enumerateClassNames
• getInstance
• enumerateInstances
• enumerateInstaneceNames
• associators
• associatorNames
• references
• referenceNames
• invokeMethod
The Proxy Provider supports the CIM Alert Indication events listed in Table 2, page 9.
Table 2 Supported indication events
Corresponding provider classEvent category
Operational status values that trigger alert
indications
DHS_TopComputerSystemController
Down, Not Installed, Unknown operational
status
Unknown, Missing, ErrorDHS_DiskDriveHard Disk
Error, Stopped, Unknown operational statusDHS_FanFan
Unknown, Error, Other, StressedDHS_PowerSupplyPower Supply
Unknown, Other, Error, NonRecoverable ErrorDHS_TemperatureSensorTemperature Sensor
Unknown, ErrorDHS_SuperCapBattery/SuperCap
Stopped, Unknown operational statusDHS_FCPortFC Port
Unknown, StoppedDHS_SASTargetPortSAS Port
Unknown, StoppedDHS_ISCSIEthernetPortiSCSI Port
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 9
Page 10

Introduction10
Page 11
2 Installing and uninstalling the SMI-S Proxy Provider
Windows
The Windows package comes as a Smart Component with installers for Pegasus CIMOM, HP Proxy
Settings Manager, and MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider.
The SMI-S Proxy Provider can be installed on any ProLiant Server running Windows or Linux that has
Ethernet connection to the MSA2000 G2 Storage Enclosures. The SMI-S proxy will communicate to
all of the MSA2000 G2 Storage enclosures via the Ethernet-based embedded storage management
processor.
To install the package:
1. Verify that the following management interfaces are enabled on each MSA2000 G2 storage
enclosure:
• Embedded SMI-S
• Embedded SNMP (used for initial discovery only)
2. With Windows Explorer, navigate to the directory containing the installation package.
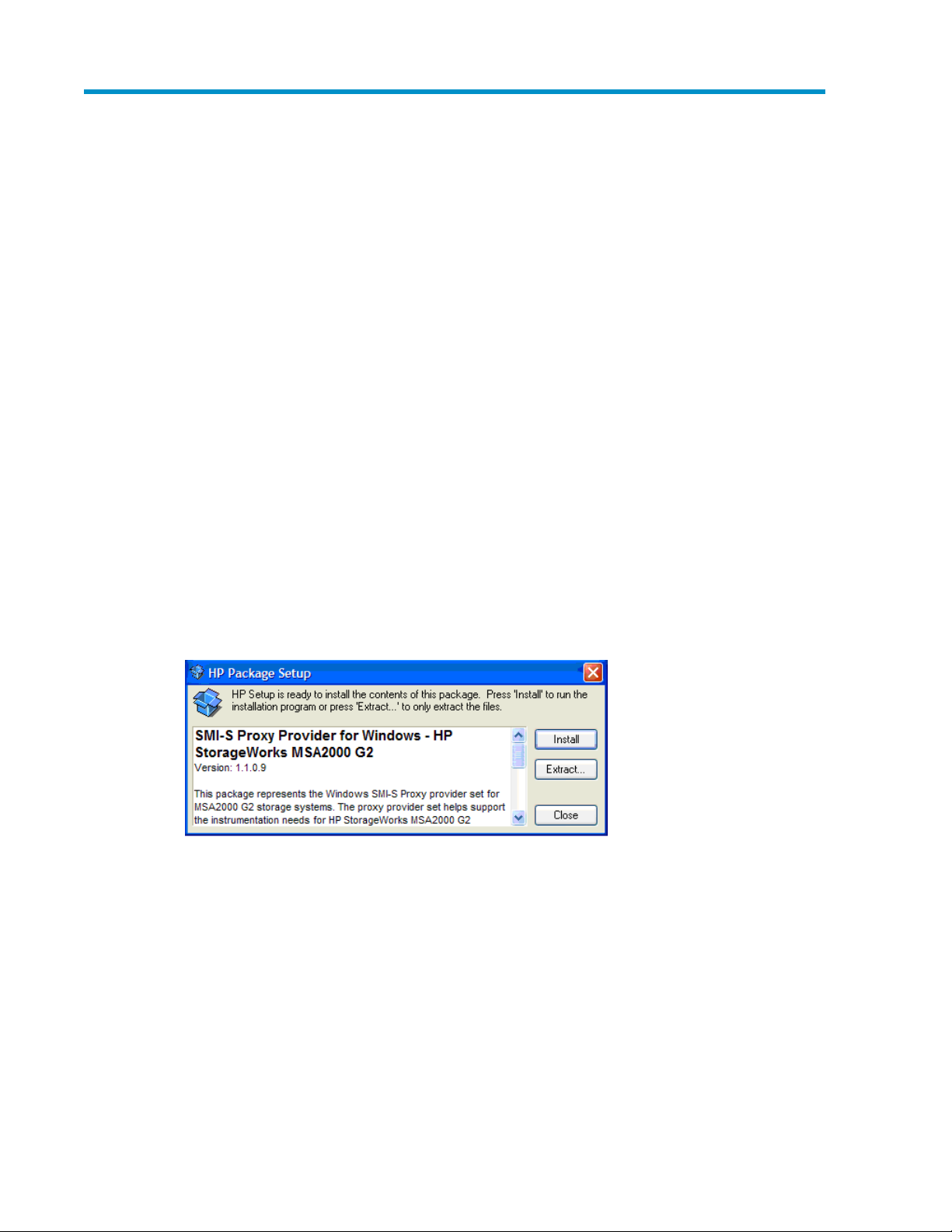
3. Click cpnnnnnn.exe.
4. Click Install in the HP Package Setup dialog. (See Figure 2, page 11.)
Figure 2 HP Package Setup dialog
.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 11
Page 12
5. Select Typical Installation and click OK to install Pegasus, the Proxy Providers, and PSM
automatically. The installation status is displayed on the user interface. Installation typically takes
6–8 minutes.
NOTE:
If a Pegasus CIMOM is already installed on the server and is version 2.7.0 or above, the
installer will skip the CIMOM installation and integrate the provider set into the existing
CIMOM installation.
If a Pegasus CIMOM is already installed on the server and is a version lower than 2.7.0,
the installer will install CIMOM version 2.7.1, but would ensure that the existing CIMOM
binaries and all the relevant folders are undisturbed. However, if the existing installation
has Pegasus installed as a Windows service, the current installation will overwrite it. After
the installation, the Pegasus service entry will refer to the CIMOM from this package, and
the existing Pegasus CIMOM can only be run as a process and not as a Windows service.
If the existing CIMOM is already using the default port 5989, the new CIMOM would choose
a different port as described in Ports and the service utility (Windows only), page 15.
The x86 version of the provider set will not work with an x64 version of the CIMOM and
hence while installing on an x64 server, if an x64 version of Pegasus CIMOM already exists,
the installation would fail.
NOTE:
To select components or specify a different installation directory, select Custom Install and
follow the instructions on the screen. Only the selected components will be installed.
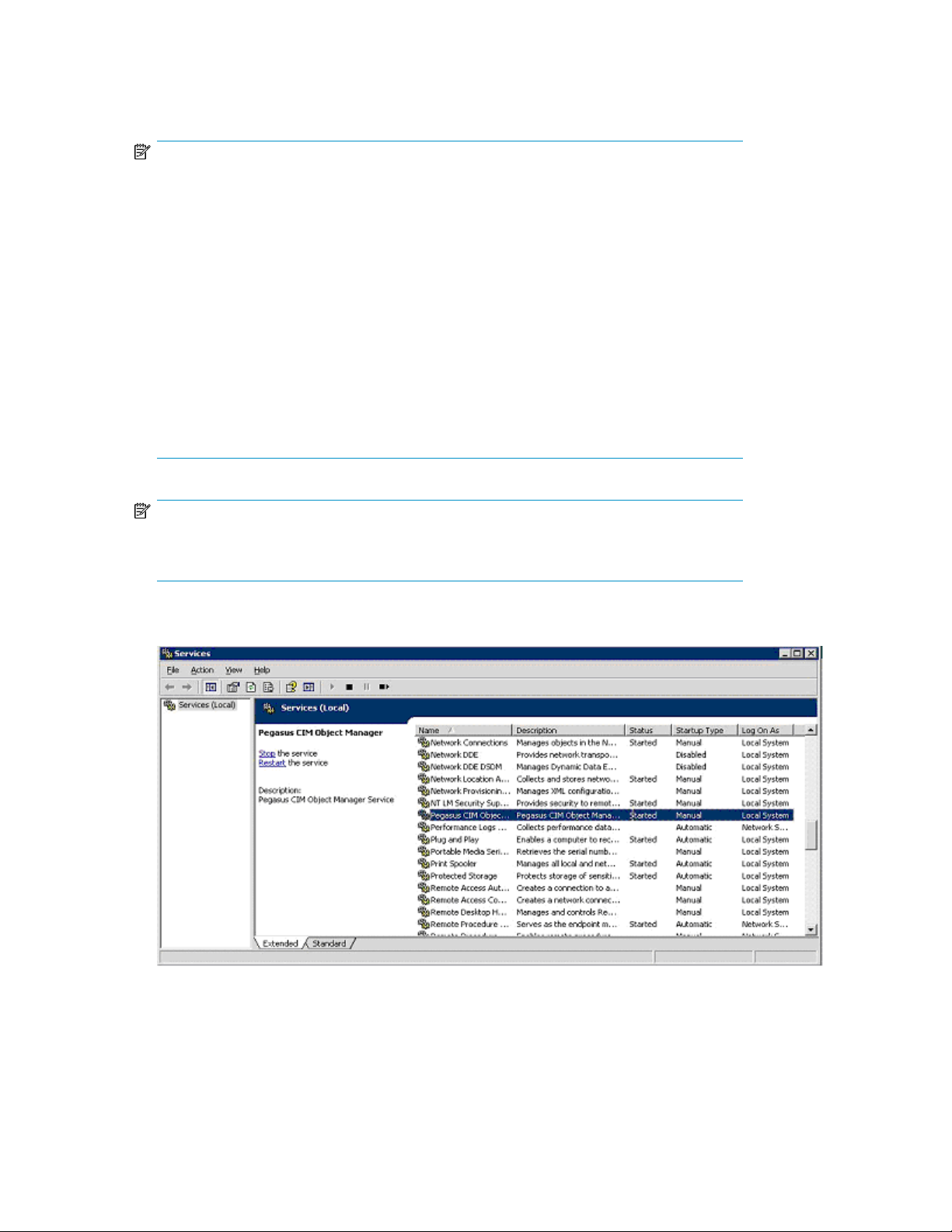
6. After the installation script completes, you can validate the installation by verifying that the Pegasus
service is started in the Services window as shown in Figure 3, page 12.
Figure 3 Pegasus service in the Services window
.
Installing and uninstalling the SMI-S Proxy Provider12
Page 13
7. Click View Logs to see the installation logs. For additional log files see:
• <systemdrive>/cpqsystem/log/Installbat.log — log of scripts run during install-
ation
• <systemdrive>/cpqsystem/log/msiexec_PSM.log — log of PSM msi installation
• <systemdrive>/cpqsystem/log/cp009873.log — log of SmartComponent installation
NOTE:
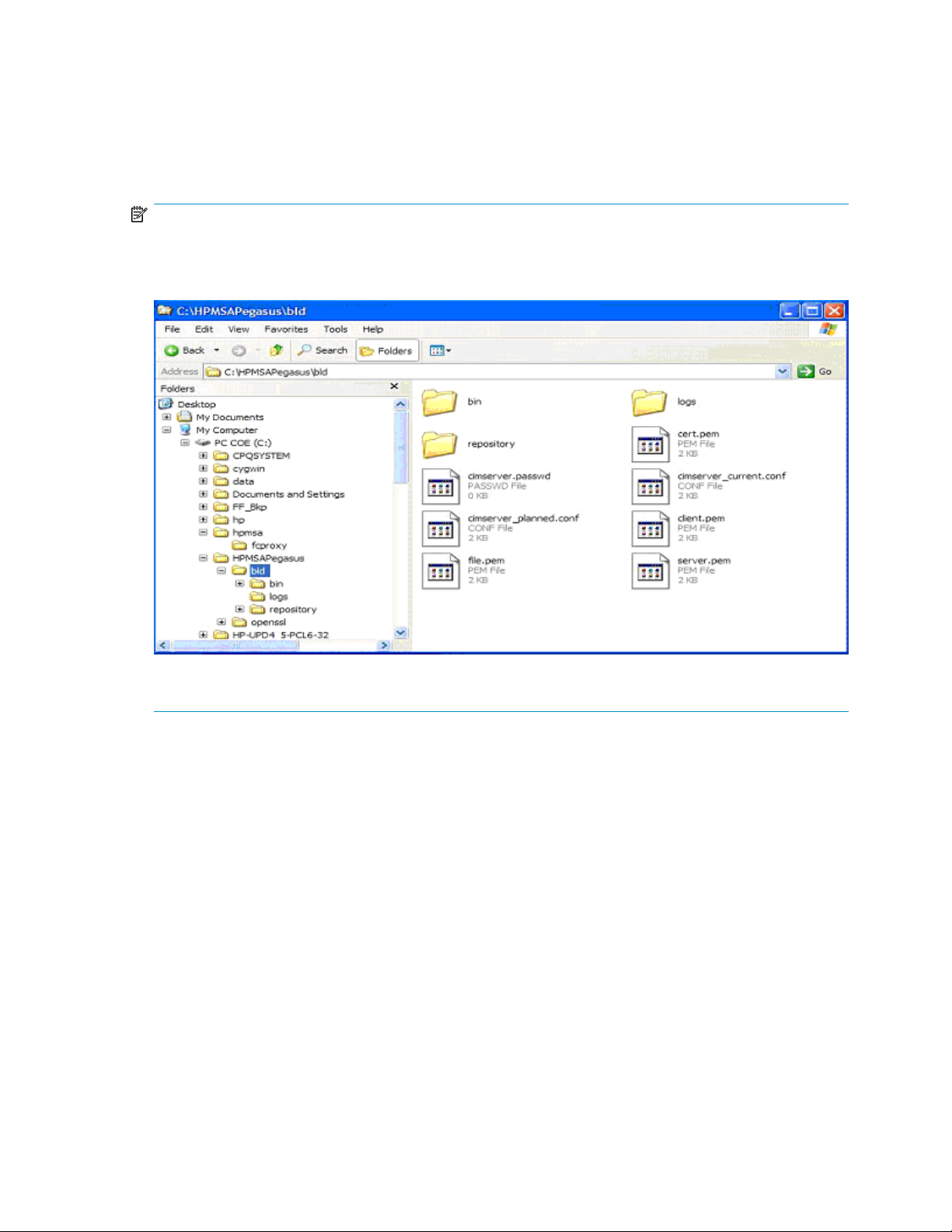
For a typical installation, Open Pegasus and Proxy Providers are installed into the HPMSAPegasus folder
under the Windows system drive as shown in Figure 4, page 13. The Proxy Settings Manager is installed
into Program Files or Program Files x64.
Linux
Figure 4 Pegasus installation directory
.
To uninstall the Proxy Provider:
1. Navigate to the Control Panel Add or Remove Programs window and uninstall the components
in the sequence listed.
2. To remove PSM, select HP StorageWorks MSA2000 SMI-S Proxy Settings Manager and then click
Remove.
3. To remove the Proxy Provider, select HP StorageWorks MSA2000 Proxy Provider for Windows
and then click Remove.
4. To remove Pegasus, select Open Pegasus and then click Remove.
The Linux package is bundled as a .tgz file, which includes the SMI-S Proxy Providers and PSM.
This version of Proxy providers has the following constraints defined:
• It has dependency on tog-pegasus rpm. This is required in SLES also. It does not use open-wbem
in SLES. Requires tog-pegasus version 2.7.0 or later.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 13
Page 14

• Port 5989 should be free and available for use by the Pegasus CIMOM.
To install the package:
1. 1. Untar the package using the following command:
nl
tar -zxvf HPMSA2000_Proxy.tgz
This creates the HPMSA2000_Proxy directory and extracts all of the files into it.
2. Navigate into the HPMSA2000_Proxy folder.
3. Execute the install script, ./install.sh, to install the Proxy Providers and PSM products.
The installation log is in the msaproxyinstall.log file.
To uninstall the package:
1. Navigate to the HPMSA2000_Proxy folder.
2. Execute the uninstall script, ./uninstall.sh, to uninstall the Proxy Providers and PSM products.
Installing and uninstalling the SMI-S Proxy Provider14
Page 15

3 Configuring the Proxy Provider
The PSM is a CLI-based MSA storage management software tool that provides simple configuration
and management tasks of the proxy providers. The PSM is installed as part of the SMI-S Proxy Provider.
The PSM provides the following device management options:
• Add a System
• Remove a System
• Discover Systems
• View Systems
• Clear Systems
• Manage a System
• Create a new Manage/Monitor user account
• Change the password of an existing user account
• Delete a user account
• Get or set Provider attributes
• Set Proxy Provider Timeout
• Set Indication Provider Polling Interval
• Set Loglevel
Use any of the following methods to launch the PSM:
• Click Launch PSM from the installer.
• Click the PSM short cut from the desktop.
• Execute msapsm.exe from the installation folder.
The tool executes as a standalone process. The tool requires Pegasus CIMOM to be installed on the
system where it is executed. When the tool starts, PSM prompts for the IP address and the port number
where the cimserver is running. A single session of the PSM application is associated with a specific
cimserver. To change the cimserver IP, start a new PSM session. The MSA storage device must be
added to the cimserver before it can be managed with PSM.
First-time configuration
MSA2000 G2 devices must be added to the proxy provider repository with PSM before the Proxy
Provider can be configured to proxy MSA2000 G2 systems.
Ports and the service utility (Windows only)
By default, CIMOM listens on two ports - 5989 (to support SSL connections) and 5988 (to support
non-SSL connections). For the SSL port, the installer contains a utility, called service, which attempts
to use port 5989 for initiating the CIMOM for SSL connection. However, if that port is not available,
it will try one of the following ports: 49152, 49153, 49154, 49155. If none of these ports are
available, it will exit with an error.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 15
Page 16

To assign a free port, edit the service.properties configuration file located in the
<systemdrive>\hpmsa\fcproxy folder with the SSL port number (httpsPort=xxxx) and try starting
the CIMOM again through the service application. If the service application is successful in starting
the CIMOM, it updates the service.properties file with the actual port number.
For the non-SSL connections, port 5988 must be available for the CIMOM to support non-SSL connection
requests from clients such as PSM.
On Linux, port 5989 should be free for the CIMOM to use. If it is not free, the CIMOM will fail to
start and the installation will not continue.
PSM device management commands
The PSM provides the commands described in Table 3, page 16.
Table 3 PSM commands
DescriptionShortcutOption
Adds an MSA2000 system to the server.aadd
Removes all the systems from the server.cclear
Discovers the MSA2000 storage systems in the subnet.ddiscover
Exits PSM.xexit
gget
sset
s intervalset interval
Displays the Indication Provider Polling Interval, Proxy Provider
Debug Log Level, and Connection Timeout values
Displays PSM help.?help
Provides a user interface to manage a specific device.mmanage
Removes an MSA2000 system from the server.rremove
Sets the provider parameters to the specified values. When entered
without input attributes it displays the values.
Sets the indication provider polling interval cycle to the specified
value.
Sets the proxy provider connection timeout value.s timeoutset timeout
Sets the proxy provider log level.s loglevelset loglevel
Displays the PSM version.verversion
Displays the version of the currently installed pegasus CIMOM.ver pegversion peg
Displays the systems currently added in the CIM server.vview
Displays the systems along with their object paths.v opview op
On Windows, PSM allows connection to CIMOM running on the local host or on a different system.
On Linux, PSM only allows connection to CIMOM running on the local host.
Configuring the Proxy Provider16
Page 17

Add system
Description Adds an MSA2000 device to the proxy provider management repository.
Syntax add
Prompts IP address of the device to be added
Output On success, displays the TopComputerSystem object path. Additionally,
retrieves the list of devices currently added to the server as shown in Figure
5, page 17. Refer to View Systems section for the output of the view systems
option.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
Figure 5 Output of add system command
.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 17
Page 18

Remove system
Description Removes an already added MSA2000 device from the proxy provider
Syntax remove
Prompts Retrieves the list of devices currently added in the server and prompts the
Output On success, acknowledges removal of the system as shown in Figure
management repository.
user to enter the index number of the device to be removed. The index
number is a unique number generated by the proxy settings manager application per device in the proxy provider management repository.
Refer to View Systems section for the output of the view systems option.
6, page 18.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
Figure 6 Output of remove system command
.
Configuring the Proxy Provider18
Page 19

Discover systems
Description Discovers all the MSA2000 devices present in the local subnet where the
Syntax discover
Prompts Displays a warning message This might take a very long time
Output On success, displays the number of devices discovered. Additionally, re-
application is running. Subsequently, adds all the discovered devices to the
proxy provider management repository. The discover option can only be
run when Pegasus CIMOM and PSM are running on the same system.
depending on the subnet and asks the user whether to proceed or
not.
trieves the list of devices currently added to the server, as shown in Figure
7, page 19. Refer to View Systems section for the output of the view systems
option.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
Figure 7 Output of discover systems command
.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 19
Page 20

View systems
Description Displays the list of MSA2000 devices currently in the proxy provider man-
Syntax view
Output On success, the view command displays information about all devices cur-
agement repository.
rently added in the proxy provider management repository in the format
nl
<index number> <IP Address of the device>
as shown in Figure 8, page 20.
On success, the view op command displays information about all devices
currently added in the proxy provider management repository in the format
nl
<index number> <IP Address of the device> <TopComputerSystem Object Path>
as shown in Figure 9, page 21.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
Figure 8 Output of view systems command
.
Configuring the Proxy Provider20
Page 21

Figure 9 Output of the view op command
.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 21
Page 22

Clear systems
Description Removes all the currently added MSA2000 devices in the proxy provider
Syntax clear
Prompts Retrieves the list of currently added devices in the proxy provider manage-
Output On success, acknowledges the removal of all the devices from the proxy
management repository.
ment repository and asks the user whether to proceed or not.
provider management repository as shown in Figure 10, page 22.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
Figure 10 Output of clear systems command
.
Configuring the Proxy Provider22
Page 23

Manage system
Description Helps user to perform some simple management tasks on a particular
Syntax manage
Prompts Displays the list of currently added MSA2000 devices in the proxy provider
Output On success, accesses the MSA device management console PSM Manage
MSA2000 device. Only the devices that are part of the proxy provider
management repository can be managed through this interface. The manage
command lets the user to create a user account, delete a user account, and
change the password of an existing user account in the MSA2000 device.
management repository. Prompts the user for the index number of the device
to manage.
prompt for the specified device as shown in Figure 11, page 23. To manage
another device, quit from the PSM Manage prompt and invoke the manage
command on the other device.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
Figure 11 Output of manage system command
.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 23
Page 24

Create user account in the MSA device
Description Creates a Manage/Monitor user account in the MSA device. This command
is invoked from the PSM MANAGE prompt.
Syntax create
Prompts User login details necessary to create new user account if not yet entered
in this session. Then prompts for all the input parameters required to create
a new user account – username, password, account level, account type and
interfaces. Enter nothing to consider the default values.
The default values are:
• User Account Level: monitor
• User Account Type: advanced
• Interfaces: cli and wbi
Output On success, acknowledges the creation of the user account as shown in
Figure 12, page 24.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
If the login fails, the correct user login details must be entered again while
re-issuing the command. Otherwise, the user login details are not required
to be entered for the remainder of the current ‘PSM Manage’ session.
Figure 12 Output of create user account command
.
Configuring the Proxy Provider24
Page 25

Change user password in the MSA device
Description Changes the password of an existing Manage/ Monitor user account in the
MSA device.
Syntax change
Prompts User login details needed to change the password for an existing user ac-
count, if not yet entered in this session, and then prompts for the user name
and the new password.
Output On success, acknowledges the change of the password as shown in Figure
13, page 25.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
If the login fails, the correct user login details must be entered again while
re-issuing the command. Otherwise, the user login details are not required
to be entered for the remainder of the current ‘PSM Manage’ session.
Figure 13 Screenshot of change user password command
.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 25
Page 26

Delete user account in the MSA device
Description Deletes an existing Manage/ Monitor user account in the MSA device.
Syntax delete
Prompts User login details needed to change the password for an existing user ac-
count, if not yet entered in this session, and then prompts for the user name
to delete.
Output On success, acknowledges the deletion of the user account as shown in
Figure 14, page 26.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
If the login fails, the correct user login details must be entered again while
re-issuing the command. Otherwise, the user login details are not required
to be entered for the remainder of the current ‘PSM Manage’ session.
Figure 14 Output of delete user command
.
Configuring the Proxy Provider26
Page 27

Get or set provider attributes
Description Gets or sets the Proxy Provider timeout value, the indication provider polling
interval value, and the debug log level currently set for the proxy provider.
When entered without any parameters, retrieves the respective values of
the attributes from the proxy provider.
Syntax get
set
Output On success, displays the attribute values as shown in Figure 15, page 27.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
If the attributes are not already set, displays a message unable to re-
trieve.
Figure 15 Output of set command options
.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 27
Page 28

Set Proxy Provider timeout
Description Sets the Proxy Provider timeout value for the proxy providers.
Syntax set timeout
Prompts Enter the timeout value in seconds. The minimum proxy timeout value is 60
Output On success, acknowledges setting of the timeout value as shown in Figure
seconds and the maximum value is 300 seconds. The default value is 60
seconds.
15, page 27.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
Configuring the Proxy Provider28
Page 29

Set indication provider polling interval
Description Sets the indication provider polling interval value for the proxy providers.
Syntax set interval
Prompts Enter the interval value in seconds. The minimum polling interval value is
60 seconds and the maximum value is 300 seconds. The default value is
60 seconds.
Output On success, acknowledges setting of the interval value as shown in Figure
15, page 27.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 29
Page 30

Set proxy provider debug log level
Description Gets or sets the debug log level for the proxy providers.
Syntax set loglevel
Prompts Enter the log level value. The default value is 0.
Supported log levels
• 0 — log comment, status, and critical
• 1 — log status, and critical
• 2 — log only critical
• 3 — disable logging
Output On success, acknowledges setting of the log level value as shown in Figure
15, page 27.
On failure, displays the error message with possible cause.
Configuring the Proxy Provider30
Page 31

4 Integrating the Proxy Provider with HP SIM
HP SIM is the foundation of the HP unified server-storage management strategy. HP SIM is a
hardware-level management product that supports multiple operating systems on HP ProLiant, Integrity
and HP 9000 servers, HP StorageWorks MSA, EVA, XP arrays, and third-party arrays.
Through a single management view of Microsoft Windows, HP-UX 11iv1, HP-UX 11iv2, HP-UX 11iv3,
and Red Hat, and SuSE Linux, HP SIM provides the basic management features of:
• System discovery and identification
• Single-event view
• Inventory data collection
• Reporting
HP SIM can provide systems management with plug-ins for HP clients, storage, power, and printer
products.
HP SIM leverages a distributed architecture that can be broken into three types of systems: Central
Management Server (CMS), Managed Systems, and Network Clients.
The CMS and the managed systems together are called the HP SIM Management Domain.
Figure 16 HP SIM topology
.
HP SIM storage integration
HP SIM discovers SNMP and SMI-S storage devices. This document only covers SMI-S. HP SIM uses
WBEM SMI-S providers to discover and collect data from storage systems.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 31
Page 32

The default collection Storage Systems is listed under Systems by Type in the tree in the System and
Event Collections panel. The following collections are available under Storage Systems:
• All Storage Systems — includes all devices that were discovered through an SMI-S provider.
• All Storage Hosts — includes all servers, desktops, and workstations that are connected by an
HBA to a SAN Storage host. Storage hosts are also included in the All Servers and All Systems
collections.
• All Storage Switches — includes Fibre Channel switches that are connected to a SAN. Storage
switches are also included in the All Systems and All Network Devices collections.
• All Storage Arrays — includes disk arrays that use a Fibre Channel controller to connect to a SAN.
Storage arrays are also included in the All Systems collection.
• All Tape Libraries — includes tape drives that are connected to SAN. Tape libraries are also in-
cluded in the All Systems collection.
HP SIM provides predefined and customized storage system reports. If HP Storage Essentials is
installed, no data appears in the HP SIM storage system reports.
• Existing storage system reports
• Storage Device Capacity—All Storage Arrays — lists capacity usage details for all storage arrays.
• Storage Device Controllers—All Storage Arrays — lists the status, port count, and number of ports
utilized for each storage array controller.
• Storage Device Inventory—All Storage Arrays — lists vendor, status, and port information for each
storage array.
• Storage Device Inventory—All Storage Switches — lists vendor, status, and port information for
each storage switch
• Storage HBAs—All Storage Hosts — lists vendor, status, and port information for each host bus
adapter (HBA) that is installed on a storage host.
• Storage Logical Units—All Storage Arrays — lists LUN information and status for all LUNs on all
storage arrays.
• Storage Ports—All Storage Arrays — lists port information for all storage arrays.
• Storage Ports—All Storage Hosts — lists port information for all storage host HBAs.
• Storage Ports—All Storage Switches — lists port information for all storage switches.
• Changer Devices—All Tape Libraries — lists the name, firmware version, and status for all tape
libraries.
• Media Access Devices—All Tape Libraries — lists the name, firmware version, and status for all
tape libraries.
Discovering an MSA2000 G2 Proxy Provider
Discovery is the process of finding systems in the management domain so that they can be managed
from the CMS by HP SIM. A system must first be discovered to collect data and track system health
status. The primary source for automatic discovery is ping sweeps configured in the automatic discovery
tasks page. Other sources might include receiving events from unknown systems or from a management
processor that has information about a server. Identification automatically runs on discovered systems.
Event-based automatic discovery is disabled by default. You can perform discovery only if you have
administrative rights.
To discover an MSA2000 G2 Proxy Provider
1. In HP SIM, click the Discovery link in the Options tab.
2. Click New and create a new task to discover the MSA2000 G2 Proxy Provider. You must specify
the IP address.
Integrating the Proxy Provider with HP SIM32
Page 33

3. Click Run Now to run the newly created discovery task. Click View Task results to see the discovery
processing flow.
Identifying an MSA2000 G2 Array
The identification process follows automatic or manual system discovery and identifies the following
information about the discovered system:
• Management protocol the system uses (for example SNMP or WBEM).
• Type of system (for example, storage)
• Product name of the system
• Product serial number
• Associations, such as iLO in server
To identify an MSA2000 G2 Array
1. Using the Search bar on the top left hand corner of HP SIM window, search for the Proxy Provider
IP address (same as the one used to discover the Proxy Provider). Click the IP address to navigate
to the Identification page of the proxy server.
2. In the Product Description pane, click the link associated with the Managed Systems item, as
shown in Figure 17, page 33.
Figure 17 Link to the Identification page of the managed MSA2000 G2 Array
.
3. Click the Tools & Links tab to find useful information, such as the SMU for the MSA2000 G2
Array and the data collection report.
Subscribing to and viewing events
With HP SIM, you can subscribe to WBEM events. MSA2000 G2 Proxy Provider currently only
supports hardware alert indications.
To subscribe and view events:
1. Click the EventsSubscribe to WBEM events link under the Options tab.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 33
Page 34

2. Create a new task for subscribing to WBEM events for the MSA2000 G2 array that is being
managed.
3. Return to the MSA2000 G2 Array Identification page and click the Events tab. The events will
be logged in this tab.
4. Click an event type to display the full details for each of the reported events.
Generating reports
With HP SIM, you can generate reports, both for a single managed system and a collection of managed
systems. Please refer to the HP SIM manual for more details on this feature.
Integrating the Proxy Provider with HP SIM34
Page 35

5 Client API Interface
Client applications can use any supported client interface that is supported by the Pegasus CIMOM.
Please refer to http://cvs.opengroup.org/pegasus-doc/ClientInterfaces.html for more details on the
client interfaces supplied by Open Pegasus.
Provided below is a sample C++ client application to collect Disk asset information using the HP
MSA2000 G2 proxy provider. This application assumes that the proxy provider has already been
configured to manage at least one MSA2000 G2 system.
#include <Pegasus/Common/Thread.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/Config.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/Constants.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/PegasusVersion.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/PegasusAssert.h>
#include <Pegasus/Client/CIMClient.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/CIMName.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/OptionManager.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/FileSystem.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/Stopwatch.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/Exception.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/XmlWriter.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/AutoPtr.h>
#include <Pegasus/Common/HostLocator.h>
PEGASUS_USING_PEGASUS;
PEGASUS_USING_STD;
static AtomicInt errorCount(0);
Array<CIMObjectPath> instanceRef;
void connectClient(
CIMClient *client,
String host,
Uint32 portNumber,
String userName,
String password,
Boolean useSSL,
Boolean localConnection,
Uint32 timeout)
{
try
{
client->setTimeout(timeout);
if (useSSL)
{
cout << "SSL not supported " << endl;
exit(1);
}
else
{
if (localConnection)
{
cout << "Using local connection mechanism " << endl;
client->connectLocal();
}
else
{
cout << "Connecting to " << host << ":" << portNumber << endl;
client->connect (host, portNumber, userName, password);
#define NAMESPACE CIMNamespaceName ("root/HPQ")
#define CLASSNAME CIMName ("DHS_TopComputerSystem")
// Locate the Top Computer System instance
Array<CIMInstance> cimNInstances =
client->enumerateInstances(NAMESPACE, CLASSNAME,
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 35
Page 36

true, false, false, false);
std::cout << "Completed EI..." << endl;
// There should always be one and only one Top Computer System instance
if (cimNInstances.size() == 0)
{
std::cout << "No instances. Disconnecting..." << endl;
client->disconnect();
return;
}
// Print the properties of Top Computer System instance
std::cout<< "DHS_TopComputerSystem Instance" << std::endl;
std::cout << "====================================================" << std::endl;
for (Uint32 j = 0; j < cimNInstances[0].getPropertyCount(); j++)
{
CIMName propertyName = cimNInstances[0].getProperty(j).getName();
std::cout<< propertyName << "="
<< cimNInstances[0].getProperty(j).getValue().toString()
<< endl;
}
std::cout << "====================================================" << std::endl;
// Traverse through CIM_SystemDevice association to grab the CIM_DiskDrive instances
Array<CIMObject> cimNAssocs =
client->associators(NAMESPACE, cimNInstances[0].getPath(),
CIMName("CIM_SystemDevice"), CIMName("CIM_DiskDrive"));
if (cimNAssocs.size() == 0)
{
std::cout << "No DiskDrive instances. Disconnecting..." << endl;
client->disconnect();
return;
}
for (int i=0; i < cimNAssocs.size(); ++i)
{
std::cout<< "DiskDrive " << i << std::endl;
std::cout << "====================================================" << std::endl;
// Print the properties of each of the Disk Drive instances
for (Uint32 j = 0; j < cimNAssocs[i].getPropertyCount(); j++)
{
CIMName propertyName = cimNAssocs[i].getProperty(j).getName();
std::cout<< propertyName << "="
<< cimNAssocs[i].getProperty(j).getValue().toString()
<< endl;
}
// Take the CIM_realizes association and go to CIM_PhysicalPackage class which
// has some rich set of information about each of these Disk drives
Array<CIMObject> diskAssocs = client->associators(NAMESPACE,
cimNAssocs[i].getPath(), CIMName("CIM_Realizes"), CIMName("CIM_PhysicalPackage"));
for (Uint32 k = 0; k < diskAssocs[0].getPropertyCount(); k++)
{
CIMName propertyName = diskAssocs[0].getProperty(k).getName();
std::cout<< propertyName << "="
<< diskAssocs[0].getProperty(k).getValue().toString()
<< endl;
}
std::cout << "====================================================" << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
catch(ConnectionTimeoutException& e)
{
PEGASUS_STD(cerr) << "Warning: " << e.getMessage() << PEGASUS_STD(endl);
exit(2);
}
catch(Exception& e)
{
PEGASUS_STD(cerr) << "Error: " << e.getMessage() << PEGASUS_STD(endl);
exit(1);
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// MAIN
Client API Interface36
Page 37

///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
char *address_string = NULL;
Boolean localConnection = false;
Boolean useSSL = false;
Uint32 timeout = 60000;
char host[20], userName[20], password[20];
Uint32 portNumber;
char ch;
std::cout << "Enter Proxy Provider IP:";
std::cin >> host;
std::cout << "Enter Port Number:";
std::cin >> portNumber;
std::cout << "Enter User Name:";
std::cin >> userName;
std::cout << "Enter Password:";
std::cin >> password;
CIMClient* client;
client = new CIMClient();
connectClient(client, String(host), portNumber, String(userName),
String(password), useSSL, localConnection, timeout);
// clean up
delete client;
}
Also, OpenPegasus releases provide simple CIM utilities that can be used for interacting with the
Pegasus CIMOM and the providers. Cimcli is a CLI tool that provides an interactive/non-interactive
interface to interact with the Pegasus CIMOM through CIM operations.
Table 4 Pegasus CIMOM operations
deleteInstancedi
Enumerate instancenames of <instancename>enumerateInstanceNamesni
Enumerate all instancenames in namespaceenumallInstanceNamesniall
Enumerate instances of <classname>enumerateInstancesei
Enumerate Class Names of [ <classname> ]enumerateClassNamesnc
Enumerate classes of [ <classname> ]enumerateClassesec
Get class of <classname>getClassgc
Get instance of <objectname> | <classname>getInstancegi
Create one Instance of <Class> *<name=param>createInstanceci
Delete Instance of <objectname> or interactive of
<className>
Not supportedcreateClasscc
Not supportedmodifyInstancemi
Delete Class of <classname>deleteClassdc
TBDgetPropertygp
TBDsetPropertysp
Get Qualifier of <qualifiername>getQualifiergq
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 37
Page 38

Not supportedsetQualifiersq
Enumerate all QualifiersenumerateQualifierseq
Delete qualifier of <qualifiername>deleteQualifierdq
Enumerate Associators of <classname>|<instancename>associatorsa
associatorNamesan
Enumerate Associator Names of <classname>|<instancename>
Enumerate References of <classname>|<instancename>referencesr
referenceNamesrn
Enumerate Reference Names <classname>|<instancename>
Invoke Method for <object> <method> {<inputParams>}invokeMethodim
Execute Query <query-expresssion> [<query-language>]execQueryxq
Enumerate all namespaces on the serverenumerateNamespacesns
Turn on CIM Server Statistics GatheringTurn On Statisticsson
Turn off CIM Server Statistics GatheringTurn Off Statisticssoff
Show List of Commandsshow command options?
Command examples
• To list registered namespaces:
nl
cimcli ns
• Command to enumerate a class instance:
nl
cimcli –n root/<namespace> ei <CIM / DHS classname>
• To get an instance of a class:
nl
cimcli –n root/HPQ gi <objectpath of CIM class instance>
Examples of commands for when the CIMOM is running on a remote system
• cimcli -l <Remote IP Address > –n root/HPQ ei <CIM / DHS classname>
• cimcli –n root/<namespace> -l <Remote IP Address> a <object path of
CIM_DHS class> -ac <association class>
Client API Interface38
Page 39

6 Frequently asked questions
6.1. Which servers can this be installed on?
x86- and x64-based servers or workstations.
6.2. What operating systems are supported?
Windows 2003 Server edition (x86 and x86_64) and 2008 Server edition (x86 and
x86_64).
Linux RedHat4 (U7 onwards), RHEL5 (U2 onwards) and SLES10 (SP2 onwards).
6.3. Is it supported on SLES9?
No, this release of proxy provider package is supported only on SLES10
6.4. Is it supported on 64-bit Linux distros?
No, this release of proxy provider package is supported only on 32-bit Linux (RHEL/SLES) distros.
6.5. What version of SMI-S Specification does this proxy provider adhere to?
This release of proxy providers adheres to SMI-S 1.2 specification.
6.6. What is the CIM schema version that this proxy provider adheres to?
This release of proxy providers adheres to CIM schema 2.6.
6.7. What CIMOMs does this proxy provider package support?
This proxy provider package works only with Open Pegasus CIMOM. (WMI on Windows and
Open-Wbem on SLES are not supported).
6.8. What Open Pegasus version is compatible with this proxy provider package?
This proxy provider package works with Open Pegasus version 2.7.0 and above.
6.9. Does this proxy provider package include Pegasus CIMOM?
Windows Yes this proxy provider package includes Open Pegasus CIMOM version 2.7.1.
But if a Pegasus CIMOM is already installed and the version is 2.7.0 or higher, this package
does not overwrite the existing CIMOM. However, if the Pegasus CIMOM version is lower than
2.7.0, this package installs Pegasus CIMOM, along with proxy provider and PSM.
Linux No, this proxy provider package does not include Open Pegasus CIMOM. The clients
must install the Pegasus CIMIOM before installing the proxy provider package. (Requires
tog-pegasus version 2.7.0 or later.)
6.10. What is the website from which I can download Open Pegasus?
Open Pegasus can be downloaded from:
nl
http://openpegasus.org/
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 39
Page 40

6.11. Can HP SIM running on Windows discover a CIMOM running on Linux and vise versa?
Yes, the HP SIM running on Windows discover a CIMOM running on Linux and vise versa.
6.12. I am not able to create Indication subscription through HP SIM. What could be the issue?
CIMOM running on Windows:
• The server on which the CIMOM is running might have firewall turned ON. Turn OFF the
firewall and try again.
CIMOM running on Linux:
• Edit the wbemportlist.xml file and add an entry interopnamespace name=”root/
msainterop”/ under interopnamespacelist and then restart HP SIM.
• The server on which the CIMOM is running might have firewall turned ON. Turn OFF the
firewall and try again.
6.13. What Interop and Device namespaces does this proxy provider use?
Following are the Interop and Device namespaces used by this proxy provide:
Windows: InterOP Namespace = /root/PG_InterOp
nl
Device Namespace = /root/HPQ
Linux: InterOP Namespace = /root/msainterop
nl
Device Namespace = /root/HPQMSA
6.14. Why is there a discrepancy in the storage capacity values displayed by HP SIM (using the Proxy
Provider) and the SMU/CLI of the MSA2000 G2 device itself?
Currently there are two standards for displaying the capacity info:
• SI standard, 1024 bytes = 1 kilo byte (KB) (base 2)
• IEC standard, 1000 bytes = 1 kilo byte (KB) (base 10)
By default, the SMU/CLI of the MSA2000 G2 displays the capacity information using the IEC
standard while HP SIM (using the Proxy Provider) displays the capacity information using the
SI standard. So the capacity information displayed by HP SIM will be less than the actual value
displayed by SMU/CLI. To get the correct value, multiply the value shown by HP SIM by a factor
of 1.024 for each KB or adjust the SMU/CLI settings to use base 2 notation.
For example:
nl
The volume capacity displayed by SMU/CLI : 28.9 GB (default base 10)
nl
The same volume capacity displayed by HP SIM : 27.01 GB (default base 2)
The correct volume capacity value is: 27.01 * 1.024 * 1.024 * 1.024 = 29 GB.
nl
The volume capacity displayed by SMU/CLI : 27.01 GB (after changing base to 2)
6.15. What are the MSA2000 G2 interfaces that this Proxy Provider uses for data collection?
For data collection the Proxy Provider uses both SMI-S and CLI (telnet) interfaces of the MSA2000
G2 system. The Proxy Settings Manager uses SNMP interface for device discovery. Verify that
all of these interfaces are enabled so the Proxy Provider can work correctly.
6.16. Can I disable telnet service on the MSA2000 G2 system?
No. For data collection, the Proxy Provider needs telnet service to be running on MSA2000 G2
system.
6.17. Does this release of Proxy Providers support Life Cycle Indications?
Frequently asked questions40
Page 41

This release of Proxy Providers does not support Life Cycle Indications only hardware Alert
Indications are supported.
6.18. How can I increase the resolution for indication reporting?
By setting the polling interval via the PSM, the indication resolution can be fine tuned. See Set
indication provider polling interval, page 29.
6.19. How can I set the timeout value for CIM query?
By setting the timeout value via the Proxy Settings Manager (PSM), CIM query timeout value
can be controlled. SeeSet Proxy Provider timeout, page 28.
6.20. How can I enable/disable developer debug logs?
By setting the proxy debug log level via the PSM, the developer debug log level can be controlled.
See Set proxy provider debug log level, page 30.
6.21. The HP SIM discovery goes through without any errors but the MSA2000 system is not listed
under "All Storage Systems". What should I do?
Log in to the MSA2000 system and check if the field "System Name" is empty. If empty, set this
field and rerun the discovery.
6.22. HP SIM cannot communicate with the CIMOM. What could be the problem?
The likely reasons could be:
• The CIMOM is probably not running. Please start CIMOM (see Q: 6.24. , page 41) and
retry the operation.
• The CIMOM is running on a non-default port (other than 5989). Please identify the port on
which CIMOM is running and configure the SMI-S client to use that port instead.
• The server on which the CIMOM is running might have a firewall turned ON and the firewall
may be blocking some of the ports. Please turn OFF the firewall or change the firewall configuration and try again.
• If the CIMOM is running on Linux, the SMI-S client may not be using the correct interop
namespace. Please edit the wbemportlist.xml file and add an entry <interopnamespace name="root/msainterop" /> under <interopnamespacelist> and
restart HP SIM.
6.23. PSM times out on the view command. What could be the problem?
The PSM can time out for various reasons. The likely reasons are:
• The CIMOM is not running. Please start CIMOM (see Q: 6.24. , page 41) and retry the
operation.
• The CIMOM is running but on port than the one PSM is using to communicate with it.
• The MSA2000 G2 box is not reachable.
6.24. It appears that the CIMOM (cimserver) is not running. How do I start it?
Use the following command to start the CIMOM:
Windows service start cimserver
Linux /etc/init.d/tog-pegasus start
6.25. After installation how do I figure out on which SSL port the CIMOM is running?
Windows (do either a or b):
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 41
Page 42

Under <system drive>\hpmsa\fcproxy there is a file service.properties. This
a.
will have an entry similar to httpsPort=PortNumber. Do not edit this file. Open this file in
an editor, such as Notepad or Wordpad, and note the value for PortNumber.
b. Run netstat –abn and redirect the output to a file. Open the file in a editor, such as
Notepad or Wordpad, and search for process cimserver.
Linux By default the SSL port is 5989.
6.26. Which SSL port the CIMOM will use if 5989 is in use?
Windows If 5989 is not free then CIMOM tries to use one of the ports from this list: 49152,
49153, 49154, 49155.
Linux If 5989 is not free, CIMOM fails to start.
6.27. To discover the CIMOM through HPSIM do I need to provide authentication?
Windows No need to provide any authentication.
Linux Yes, you must provide the authentication for the root user (root/<root passwd>).
Frequently asked questions42
Page 43

7 Support and other resources
Document conventions and symbols
Table 5 Document conventions
ElementConvention
Cross-reference links and e-mail addressesBlue text: Table 5
Website addressesBlue, underlined text: http://www.hp.com
• Keys that are pressed
Bold text
Monospace text
• Text typed into a GUI element, such as a box
• GUI elements that are clicked or selected, such as menu
and list items, buttons, tabs, and check boxes
Text emphasisItalic text
• File and directory names
• System output
• Code
• Commands, their arguments, and argument values
Monospace, italic text
Monospace, bold text
WARNING!
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death.
CAUTION:
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT:
Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
• Code variables
• Command variables
Emphasized monospace text
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 43
Page 44

NOTE:
Provides additional information.
TIP:
Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
HP technical support
For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website:
http://www.hp.com/support
Before contacting HP, collect the following information:
• Product model names and numbers
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
Product warranties
For information about HP StorageWorks product warranties, see the warranty information website:
http://www.hp.com/go/storagewarranty
Subscription service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber's Choice for Business website:
http://www.hp.com/go/e-updates
After registering, you will receive e-mail notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
HP websites
For additional information, see the following HP websites:
• http://www.hp.com
• http://www.hp.com/go/storage
• http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
• http://www.hp.com/go/hpsim — HP SIM website
• http://h18006.www1.hp.com/storage/smisproviders.html — HP SMI-S provider website, where
updates to this product can be found
• http://h18006.www1.hp.com/storage/smis.html
Support and other resources44
Page 45

• http://www.compaq.com/storage/smis-matrix.html
• http://h18013.www1.hp.com/products/servers/management/hpsim/providers.html — HP SMI-
S provider information on the HP SIM website, where updates to this product can be found
Documentation feedback
HP welcomes your feedback.
To make comments and suggestions about product documentation, please send a message to
storagedocsFeedback@hp.com. All submissions become the property of HP.
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 45
Page 46

Support and other resources46
Page 47

Glossary
CMS Central management server — server on which the management is installed
HP SIM HP Systems Insight Manager — a hardware-level management product
PSM MSA2000 Proxy Settings Manager
MSA2000 G2 SMI-S Proxy Provider User Guide 47
Page 48

48
 Loading...
Loading...