Page 1

Voyager
Single-Line Laser Scanner
TM
1250g
User’s Guide
™
Page 2

Disclaimer
Honeywell International Inc. (“HII”) reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice,
and the reader should in all cases consult HII to determine whether any such
changes have been made. The information in this publication does not represent a commitment on the part of HII.
HII shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained
herein; nor for incidental or consequential damages resulting from the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright.
All rights are reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without the prior written consent of
HII.
© 2011 Honeywell International Inc. All rights reserved.
Other product names or marks mentioned in this document may be trademarks
or registered trademarks of other companies and are the property of their
respective owners.
Web Address:
www.honeywellaidc.com
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 - Getting Started
About This Manual ......................................................1-1
Unpacking Your Device............................................... 1-1
Connecting the Device ................................................ 1-1
Connecting with USB ............................................ 1-1
Connecting with Keyboard Wedge........................ 1-2
Connecting with RS232 Serial Port....................... 1-3
Connecting with RS485......................................... 1-4
Reading Techniques ................................................... 1-5
Menu Bar Code Security Settings ............................... 1-5
Setting Custom Defaults ............................................. 1-5
Resetting the Custom Defaults ................................... 1-6
Resetting the Factory Defaults.................................... 1-7
Chapter 2 - Programming the Interface
Introduction ................................................................. 2-1
Programming the Interface - Plug and Play ................ 2-1
Keyboard Wedge................................................... 2-1
IBM PS2 Keyboard................................................ 2-1
RS232 Serial Port.................................................. 2-1
RS485 ................................................................... 2-2
OPOS Mode.......................................................... 2-3
USB IBM SurePos................................................. 2-4
IBM Secondary Interface....................................... 2-4
USB PC or Macintosh Keyboard........................... 2-5
USB HID................................................................ 2-5
HID Fallback Mode................................................ 2-5
USB Serial Commands ............................................... 2-6
USB Serial Emulation............................................ 2-6
CTS/RTS Emulation.............................................. 2-6
ACK/NAK Mode..................................................... 2-7
Communication Timeout ....................................... 2-7
NAK Retries........................................................... 2-8
Support BEL/CAN in ACK/NAK............................. 2-8
1
Page 4

Verifone® Ruby Terminal Default Settings ..................2-9
Gilbarco
®
Terminal Default Settings............................2-9
Honeywell Bioptic Aux Port Configuration .................2-10
©
Datalogic™ Magellan
Bioptic
Aux Port Configuration ............................................2-10
NCR Bioptic Aux Port Configuration..........................2-10
Wincor Nixdorf Terminal Default Settings..................2-11
Wincor Nixdorf Beetle™ Terminal Default Settings...2-11
Keyboard Country Layout..........................................2-12
Keyboard Wedge Modifiers .......................................2-14
ALT Mode ............................................................2-14
Keyboard Style ....................................................2-14
Keyboard Conversion ..........................................2-15
Keyboard Modifiers..............................................2-16
Inter-Scan Code Delay ........................................2-17
<F0> Break Character .........................................2-18
Keyboard Wedge Defaults...................................2-18
RS232 Modifiers ........................................................2-19
RS232 Baud Rate................................................2-19
RS232 Word Length: Data Bits, Stop Bits,
and Parity ....................................................... 2-20
RS232 Handshaking............................................2-21
RS232 Timeout....................................................2-22
XON/XOFF ..........................................................2-22
ACK/NAK .............................................................2-23
Communication Timeout......................................2-23
NAK Retries .........................................................2-24
Support BEL/CAN in ACK/NAK ...........................2-25
RS232 Defaults.................................................... 2-25
NCR Modifiers ...........................................................2-25
NCR ACK/NAK ....................................................2-25
Block Check Character ........................................2-26
NCR Prefix...........................................................2-26
NCR Suffix ...........................................................2-26
NCR Prefix/Suffix.................................................2-27
NCR NOF (Not-on-File) Error ..............................2-27
Scanner to Bioptic Communication............................2-27
2
Page 5

Scanner-Bioptic Packet Mode............................. 2-28
ACK/NAK............................................................. 2-28
Communication Timeout ..................................... 2-28
Chapter 3 - Input/Output Settings
Power Up Beeper........................................................ 3-1
Beep on BEL Character ..............................................3-1
Good Read and Error Indicators ................................. 3-2
Beeper – Good Read ............................................ 3-2
Beeper Volume – Good Read ............................... 3-2
Beeper Pitch – Good Read ................................... 3-3
Beeper - Transmit Order ....................................... 3-3
Beeper Pitch – Error.............................................. 3-3
Beeper Duration – Good Read.............................. 3-4
Number of Beeps – Good Read............................ 3-4
Number of Beeps – Error ...................................... 3-4
LED Indicators............................................................. 3-6
LED Settings ......................................................... 3-6
LED Brightness ..................................................... 3-7
In-Stand and Out-Of-Stand Settings ...........................3-7
In-Stand and Out-of-Stand Defaults...................... 3-8
Presentation Modes .............................................. 3-8
Manual Activation Mode........................................ 3-9
End Manual Activation After Good Read............... 3-9
Manual Activation Laser Timeout -
Button Settings............................................... 3-10
CodeGate
Object Detection Mode........................................ 3-11
End Object Detection After Good Read .............. 3-12
Object Detection Laser Timeout.......................... 3-12
Object Detection Distance................................... 3-13
Character Activation Mode........................................ 3-13
Activation Character............................................ 3-13
End Character Activation After Good Read......... 3-14
Character Activation Laser Timeout.................... 3-14
Character Deactivation Mode.................................... 3-15
®
.......................................................... 3-11
3
Page 6

Deactivation Character ........................................3-15
Reread Delay.............................................................3-16
User-Specified Reread Delay ....................................3-16
Output Sequence Overview.......................................3-16
Require Output Sequence ...................................3-16
Output Sequence Editor ......................................3-17
To Add an Output Sequence ...............................3-17
Other Programming Selections............................ 3-17
Output Sequence Editor ......................................3-19
Sequence Timeout............................................... 3-19
Sequence Match Beeper .....................................3-20
Partial Sequence .................................................3-20
Require Output Sequence ...................................3-20
No Read.....................................................................3-21
Chapter 4 - Data Editing
Prefix/Suffix Overview..................................................4-1
To Add a Prefix or Suffix:.......................................4-1
To Clear One or All Prefixes or Suffixes ................4-2
To Add a Carriage Return Suffix to
All Symbologies................................................4-3
Prefix Selections..........................................................4-3
Suffix Selections ..........................................................4-4
Transmit Alternate Extended ASCII Characters ..........4-4
Function Code Transmit ..............................................4-6
Communication Check Character................................4-6
Intercharacter, Interfunction, and
Intermessage Delays.................................................4-7
Intercharacter Delay ..............................................4-7
User Specified Intercharacter Delay ......................4-7
Interfunction Delay.................................................4-8
Intermessage Delay...............................................4-9
Chapter 5 - Data Formatting
Data Format Editor Introduction...................................5-1
To Add a Data Format .................................................5-1
4
Page 7

Other Programming Selections ............................. 5-3
Terminal ID Table........................................................ 5-4
Data Format Editor Commands .................................. 5-4
Move Commands .................................................. 5-5
Search Commands................................................ 5-6
Miscellaneous Commands .................................... 5-7
Data Formatter ............................................................ 5-8
Data Format Non-Match Error Tone...................... 5-9
Primary/Alternate Data Formats................................ 5-10
Single Scan Data Format Change....................... 5-10
Chapter 6 - Symbologies
All Symbologies........................................................... 6-1
Message Length Description....................................... 6-2
Codabar ...................................................................... 6-3
Codabar Concatenation ........................................ 6-4
Code 39....................................................................... 6-7
Code 32 Pharmaceutical (PARAF)........................ 6-9
Full ASCII .............................................................. 6-9
Interleaved 2 of 5 ...................................................... 6-11
NEC 2 of 5................................................................. 6-13
Code 93..................................................................... 6-15
Straight 2 of 5 Industrial (three-bar start/stop) .......... 6-16
Straight 2 of 5 IATA (two-bar start/stop).................... 6-18
Matrix 2 of 5 .............................................................. 6-19
Code 11..................................................................... 6-21
Code 128................................................................... 6-24
ISBT 128 ................................................................... 6-25
GS1-128.................................................................... 6-31
Telepen ..................................................................... 6-33
UPC-A ....................................................................... 6-35
UPC-A/EAN-13 with Extended Coupon Code........... 6-38
UPC-A Number System 4 Addenda Required .... 6-38
UPC-A Number System 5 Addenda Required .... 6-39
UPC-E0 ..................................................................... 6-41
EAN/JAN-13.............................................................. 6-45
5
Page 8

EAN-13 Beginning with 2 Addenda Required......6-46
EAN-13 Beginning with 290 Addenda Required..6-47
EAN-13 Beginning with 378/379
Addenda Required .........................................6-47
EAN-13 Beginning with 414/419
Addenda Required .........................................6-48
EAN-13 Beginning with 434/439
Addenda Required .........................................6-49
EAN-13 Beginning with 977 Addenda Required..6-50
EAN-13 Beginning with 978 Addenda Required..6-50
EAN-13 Beginning with 979 Addenda Required..6-51
ISBN Translate ....................................................6-53
ISSN Translate ....................................................6-54
EAN/JAN-8 ................................................................6-55
MSI ............................................................................6-58
Plessey Code.............................................................6-60
GS1 DataBar Omnidirectional ...................................6-62
GS1 DataBar Limited.................................................6-63
GS1 DataBar Expanded ............................................6-64
Trioptic Code .............................................................6-65
GS1 Emulation...........................................................6-65
Postal Codes .............................................................6-66
China Post (Hong Kong 2 of 5)............................6-66
Chapter 7 - Interface Keys
Keyboard Function Relationships................................7-1
Supported Interface Keys ............................................7-2
Chapter 8 - Utilities
To Add a Test Code I.D. Prefix to All Symbologies .....8-1
Show Software Revision..............................................8-1
Show Data Format.......................................................8-1
Test Menu....................................................................8-2
EZConfig-Scanning Introduction..................................8-2
Installing EZConfig-Scanning from the Web..........8-3
6
Page 9

Chapter 9 - Serial Programming Commands
Conventions ................................................................ 9-1
Menu Command Syntax.............................................. 9-1
Query Commands ....................................................... 9-2
Responses ............................................................ 9-3
Serial Trigger Commands ........................................... 9-4
Read Time-Out...................................................... 9-4
Resetting the Standard Product Defaults.................... 9-4
Menu Commands........................................................ 9-6
Chapter 10 - Product Specifications
Voyager 1250g Scanner Product Specifications....... 10-1
Standard Cable Pinouts ............................................ 10-2
Keyboard Wedge................................................. 10-2
Serial Output ...................................................... 10-3
RS485 Output ..................................................... 10-4
USB..................................................................... 10-5
Chapter 11 - Maintenance
Repairs...................................................................... 11-1
Maintenance.............................................................. 11-1
Cleaning the Device: ........................................... 11-1
Inspecting Cords and Connectors....................... 11-1
Replacing Cables ...................................................... 11-1
Replacing an Interface Cable.............................. 11-2
Troubleshooting a Voyager Scanner......................... 11-2
Chapter 12 - Customer Support
Symbology Chart.........................................................A-1
ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) ...............A-4
Code Page Mapping of Printed Barcodes...................A-6
7
Page 10

8
Page 11

Product Agency Compliance
USA
FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class B
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio or television technician for
help.
If necessary, the user should consult the dealer or an experienced radio/
television technician for additional suggestions. The user may find the following booklet helpful: “Something About Interference.” This is available at
FCC local regional offices. Honeywell is not responsible for any radio or
television interference caused by unauthorized modifications of this equipment or the substitution or attachment of connecting cables and equipment
other than those specified by Honeywell. The correction is the responsibility of the user.
Use only shielded data cables with this system. This unit has been tested
with cables less than 3 meters. Cables greater than 3 meters may not meet
class B performance.
Caution: Any changes or modifications made to this equipment not
expressly approved by Honeywell may void the FCC authorization to operate this equipment.
UL Statement
UL listed: UL60950-1, 2nd Edition.
Page 12

This product is intended to be supplied by a Listed Direct Plug-In Power
unit marked "Class 2" or "LPS" and rated 5 Vdc - 5.2 Vdc, 1A.
Canada
Industry Canada ICES-003
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003. Operation is subject to the following conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Conformité à la règlementation canadienne
Cet appareil numérique de la Classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003
du Canada. Son fonctionnement est assujetti aux conditions suivantes :
1. Cet appareil ne doit pas causer de brouillage préjudiciable.
2. Cet appareil doit pouvoir accepter tout brouillage reçu, y compris le
brouillage pouvant causer un fonctionnement indésirable.
C-UL Statement
C-UL listed: CSA C22.2 No.60950-1-07, 2nd Edition.
Europe
The CE marking indicates compliance to 2004/108/EC EMC Directive
with Standards EN55022 CLASS B, EN55024, EN61000-3-2,
EN61000-3-3. In addition, complies to 2006/95/EC Low Voltage Directive, when shipped with recommended power supply.
For further information please contact:
Honeywell International Inc. shall not be liable for use of our product with
equipment (i.e., power supplies, personal computers, etc.) that is not CE
marked and does not comply with the Low Voltage Directive.
Honeywell Imaging & Mobility Europe BV
Nijverheidsweg 9-13
5627 BT Eindhoven
The Netherlands
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
Information
Honeywell complies with Directive 2002/96/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 27 January 2003 on waste electrical
and electronic equipment (WEEE).
Page 13

This product has required the extraction and use of natural resources for its
production. It may contain hazardous substances that could impact health
and the environment, if not properly disposed.
In order to avoid the dissemination of those substances in our environment
and to diminish the pressure on the natural resources, we encourage you to
use the appropriate take-back systems for product disposal. Those systems will reuse or recycle most of the materials of the product you are disposing in a sound way.
The crossed out wheeled bin symbol informs you that the product
should not be disposed of along with municipal waste and invites you to
use the appropriate separate take-back systems for product disposal.
If you need more information on the collection, reuse, and recycling systems, please contact your local or regional waste administration.
You may also contact your supplier for more information on the environmental performances of this product.
Australia/NZ
C-Tick Statement
Conforms to AS/NZS 3548
Mexico
Conforms to NOM-019.
Russia
Tawain
Gost-R certificate
BSMI Standard: CNS13438, CNS 14336
Page 14
International
Laser Safety Statement
LASER LIGHT: DO NOT STARE INTO
BEAM. CLASS 2 LASER PRODUCT.
LASERSTRAHLUNG: NICHT IN DEN
STRAHL BLICKEN. LASER KLASSE 2.
LUMIERE LASER: NE PAS REGARDER
DANS LE FAISCEAU. APPAREIL A LASER.
DE CLASSE 2 630-650nm, 1mW.
This device has been tested in accordance with and complies with
IEC60825-1 ed2.0 and 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11, except for deviations
pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50, dated June 24, 2007.
LASER LIGHT, DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM, CLASS 2 LASER PRODUCT, 1 mW MAX OUTPUT: 630-650nM.
Scanner Laser Beam
Wavelength 630 - 650 nm
Divergence < 1.5 mrad. per IEC 60825-1 worst case
Max power output < 1mw
Embedded Laser
Wavelength 630 - 650 nm
Divergence < 1.5 mrad, per IEC 60825-1 worst case
Max power output < 10 mw
Caution: Use of controls or adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may
result in hazardous radiation exposure.
CB Scheme
Certified to CB Scheme IEC60950-1, Second Edition.
Solids and Water Protection
The Voyager 1250g has a rating of IP42, immunity of foreign particles and dripping water.
Patents
For patent information, please refer to www.honeywellaidc.com/patents.
Page 15
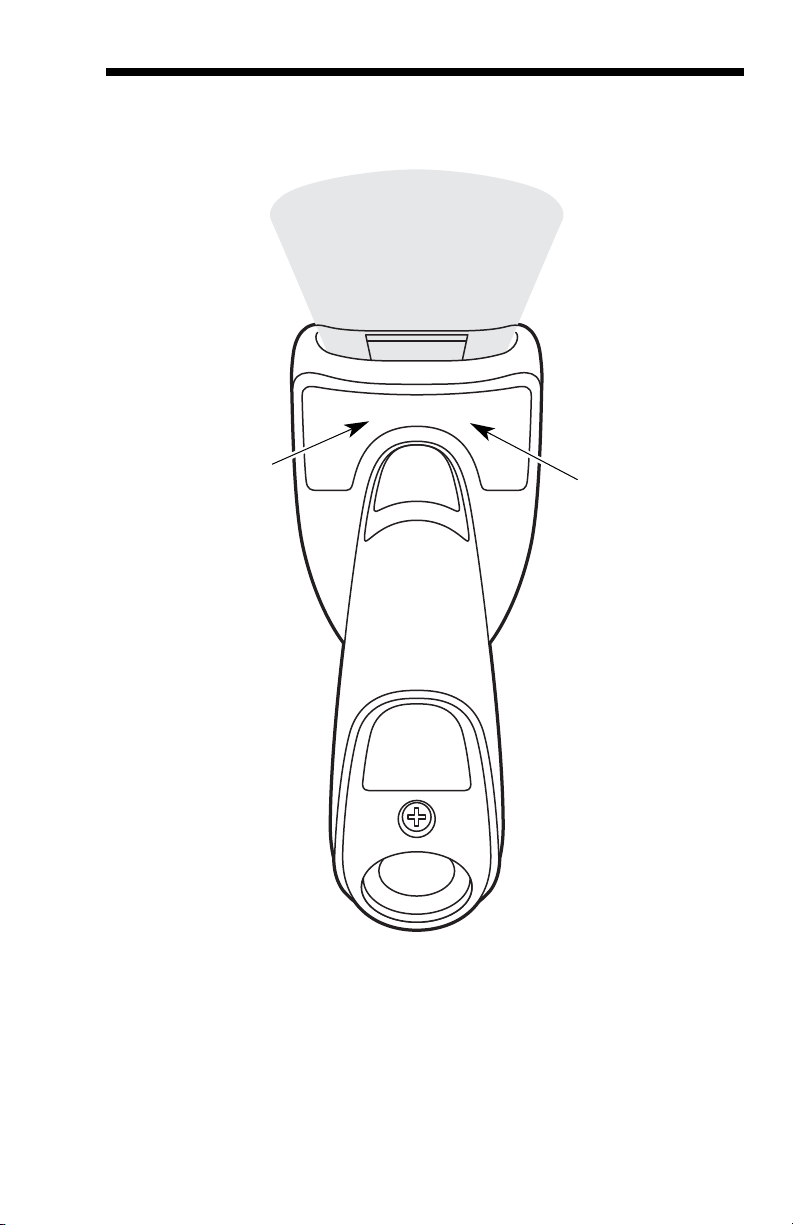
Required Safety Label Locations
Part Number,
Serial Number
Laser Label,
and Revision
Information
location
Laser Safety
information
Laser Output
Page 16

Page 17
1
Getting Started
About This Manual
This User’s Guide provides installation and programming instructions for the
Voyager 1250g single-line laser scanner. Product specifications, dimensions,
warranty, and customer support information are also included.
Honeywell bar code scanners are factory programmed for the most common
terminal and communications settings. If you need to change these settings,
programming is accomplished by scanning the bar codes in this guide.
An asterisk (*) next to an option indicates the default setting.
Unpacking Your Device
After you open the shipping carton containing the product, take the following
steps:
• Check for damage during shipment. Report damage immediately to the
carrier who delivered the carton.
• Make sure the items in the carton match your order.
• Save the shipping container for later storage or shipping.
Connecting the Device
Connecting with USB
A scanner can be connected to the USB port of a computer.
1. Connect the appropriate interface cable to the scanner first, then to
the computer.
1 - 1
Page 18

2. The scanner beeps.
only if
power
supply is
included
3. Verify the scanner operation by scanning a bar code from the Sample
Symbols in the back of this manual.
The unit defaults to a USB PC Keyboard. Refer to page 2-5 for other USB
terminal settings.
For additional USB programming and technical information, refer to “USB
Application Note,” available at www.honeywellaidc.com.
Connecting with Keyboard Wedge
A scanner can be connected between the keyboard and PC as a “keyboard
wedge,” plugged into the serial port, or connected to a portable data terminal in wand emulation or non decoded output mode. The following is an
example of a keyboard wedge connection:
1. Turn off power and disconnect the keyboard cable from the back of the
terminal/computer.
2. Connect the appropriate interface cable to the scanner and to the
terminal/computer.
3. Turn the terminal/computer power back on. The scanner beeps.
4. Verify the scanner operation by scanning a bar code from the Sample
Symbols in the back of this manual. The scanner beeps once.
The unit defaults to an IBM PC AT and compatibles keyboard wedge interface with a USA keyboard. A carriage return (CR) suffix is added to bar
code data.
1 - 2
Page 19
Connecting with RS232 Serial Port
only if
power
supply is
included
1. Turn off power to the terminal/computer.
2. Connect the appropriate interface cable to the scanner.
3. Plug the serial connector into the serial port on your computer.
Tighten the two screws to secure the connector to the port.
4. Once the scanner has been fully connected, power up the computer.
This interface programs 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit.
1 - 3
Page 20
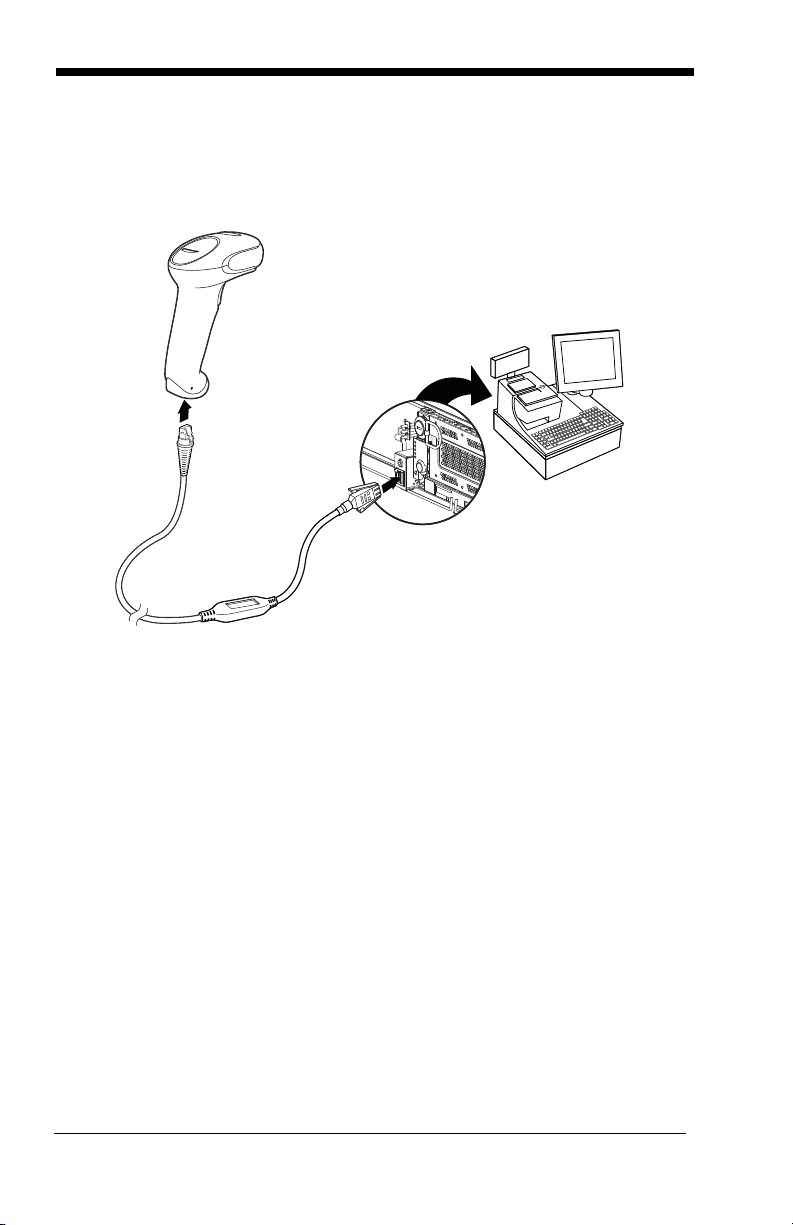
Connecting with RS485
A scanner can be connected for an IBM POS terminal interface.
1. Connect the appropriate interface cable to the device, then to the computer.
2. Turn the terminal/computer power back on. The scanner beeps.
3. Verify the scanner operation by scanning a bar code from the Sample
Symbols in the back of this manual. The scanner beeps once.
For further RS485 settings, refer to RS485, page 2-2.
1 - 4
Page 21

Reading Techniques
Good Read Bad Read
The scanner has a view finder that projects a bright red aiming beam that corresponds to the scanner’s horizontal field of view. The aiming beam should be
centered horizontally over the bar code and must highlight all the vertical bars of
the bar code. It will not read if the aiming beam is in any other direction.
The aiming beam is smaller when the scanner is closer to the code and larger
when it is farther from the code. Symbologies with smaller bars or elements (mil
size) should be read closer to the unit. Symbologies with larger bars or elements (mil size) should be read farther from the unit. To read single or multiple
symbols (on a page or on an object), hold the scanner at an appropriate distance from the target, press the button, and center the aiming beam on the symbol. If the code being scanned is highly reflective (e.g., laminated), it may be
necessary to tilt the code up 15° to 18° to prevent unwanted reflection.
Menu Bar Code Security Settings
Honeywell scanners are programmed by scanning menu bar codes or by sending serial commands to the scanner. If you want to restrict the ability to scan
menu codes, you can use the Menu Bar Code Security settings. Please contact
the nearest technical support office (see Technical Assistance on page 12-1) for
further information.
Setting Custom Defaults
You have the ability to create a set of menu commands as your own, custom
defaults. To do so, scan the Set Custom Defaults bar code below before each
menu command or sequence you want saved. If your command requires scanning numeric codes from the back cover, then a Save code, that entire
sequence will be saved to your custom defaults. Scan the Set Custom
Defaults code again before the next command you want saved to your custom
defaults.
1 - 5
Page 22

When you have entered all the commands you want to save for your custom
Save Custom Defaults
Set Custom Defaults
Activate Custom Defaults
defaults, scan the Save Custom Defaults bar code.
You may have a series of custom settings and want to correct a single setting.
To do so, just scan the new setting to overwrite the old one. For example, if you
had previously saved the setting for Beeper Volume at Low to your custom
defaults, and decide you want the beeper volume set to High, just scan the Set
Custom Defaults bar code, then scan the Beeper Volume High menu code,
and then Save Custom Defaults. The rest of the custom defaults will remain,
but the beeper volume setting will be updated.
Resetting the Custom Defaults
If you want the custom default settings restored to your scanner, scan the Activate Custom Defaults bar code below. This resets the scanner to the custom
default settings. If there are no custom defaults, it will reset the scanner to the
factory default settings. Any settings that have not been specified through the
custom defaults will be defaulted to the factory default settings.
1 - 6
Page 23

Resetting the Factory Defaults
!
Remove Custom Defaults
Activate Defaults
This selection erases all your settings and resets the scanner to the
original factory defaults.
If you aren’t sure what programming options are in your scanner, or you’ve
changed some options and want to restore the scanner to factory default settings, first scan the Remove Custom Defaults bar code, then scan Activate
Defaults. This resets the scanner to the factory default settings.
The Serial Programming Commands, beginning on page 9-1 list the factory
default settings for each of the commands (indicated by an asterisk (*) on the
programming pages).
1 - 7
Page 24

1 - 8
Page 25

2
IBM PC AT and Compatibles with CR Suffix
IBM PS2 with CR Suffix
Programming the Interface
Introduction
This chapter describes how to program your system for the desired interface.
Programming the Interface - Plug and Play
Plug and Play bar codes provide instant scanner set up for commonly used
interfaces.
Note: After you scan one of the codes, power cycle the host terminal to have
the interface in effect.
Keyboard Wedge
If you want your system programmed for an IBM PC AT and compatibles
keyboard wedge interface with a USA keyboard, scan the bar code below.
Keyboard wedge is the default interface.
Note: The following bar code also programs a carriage return (CR) suffix.
IBM PS2 Keyboard
The following bar code programs you scanner for an IBM PS2 keyboard
wedge interface with a USA keyboard.
Note: The following bar code also programs a carriage return (CR) suffix.
RS232 Serial Port
The RS232 Interface bar code is used when connecting to the serial port
of a PC or terminal. The following RS232 Interface bar code also programs a carriage return (CR) and a line feed (LF) suffix, baud rate, and
data format as indicated below.
Option Setting
Baud Rate 9600 bps
Data Format 8 data bits, no parity bit, 1 stop bit
2 - 1
Page 26
RS485
RS232 Interface
IBM Port 5B Interface
IBM Port 9B
HHBCR-1 Interface
IBM Port 17 Interface
IBM Port 9B
HHBCR-2 Interface
Scan one of the following “Plug and Play” codes to program the scanner for
an IBM POS terminal interface.
Note: After scanning one of these codes, you must power cycle the cash
register.
Each bar code above also programs the following suffixes for each symbology:
Symbology Suffix Symbology Suffix
EAN 8 0C Code 39 00 0A 0B
EAN 13 16 Interleaved 2 of 5 00 0D 0B
UPC A 0D Code 128 * 00 0A 0B
UPC E 0A Code 128 ** 00 18 0B
* Suffixes programmed for Code 128 with IBM 4683 Port 5B, IBM 4683 Port 9B
HHBCR-1, and IBM 4683 Port 17 Interfaces
**Suffixes programmed for Code 128 with IBM 4683 Port 9 HHBCR-2 Interface
2 - 2
Page 27

OPOS Mode
OPOS Mode
The following bar code configures your scanner for OPOS (OLE for Retail
Point of Sale) by modifying the following OPOS-related settings:
Option Setting
Interface RS232
Baud Rate 38400
RS232
Handshaking
Data Bits, Stop
Bits, and Parity
Prefix/Suffix
Intercharacter
Delay
Symbologies Enable UPC-A with check digit and number system
Flow Control, No Timeout
XON/XOFF Off
ACK/NAK Off
8 Data, 1 Stop, Parity None
Clear All Prefixes and Suffixes
Add Code ID and AIM ID Prefix
Add CR Suffix
Off
Enable UPC-E0 with check digit
Enable EAN/JAN-8 with check digit
Enable EAN/JAN-13 with check digit
Enable Code 128
Enable Code 39
Enable OPOS with automatic disable off
2 - 3
Page 28
USB IBM SurePos
USB IBM SurePos
(USB Handheld Scanner)
Interface
USB IBM SurePos
(USB Tabletop Scanner)
Interface
*Enable Secondary Interface
Disable Secondary Interface
Scan one of the following “Plug and Play” codes to program the scanner for
an IBM SurePos (USB handheld scanner) or IBM SurePos (USB tabletop
scanner) interface.
Note: After scanning one of these codes, you must power cycle the cash
register.
Each bar code above also programs the following suffixes for each symbology:
Symbology Suffix Symbology Suffix
EAN 8 0C Code 39 00 0A 0B
EAN 13 16 Interleaved 2 of 5 00 0D 0B
UPC A 0D Code 128 00 18 0B
UPC E 0A Code 39 00 0A 0B
IBM Secondary Interface
On some older IBM cash registers, it may be necessary to disable the secondary or management interface. In particular, it has been found necessary on IBM registers using the 4690 V2R4 operating system. The
following bar codes are used for this purpose.
Interface.
Default = Enable Secondary
2 - 4
Page 29
USB PC or Macintosh Keyboard
U
S
B
K
e
y
b
o
a
r
d
(
P
C
)
USB Keyboard (Mac)
USB Japanese Keyboard (PC)
USB HID Bar Code Scanner
Scan one of the following codes to program the scanner for USB PC Keyboard or USB Macintosh Keyboard. Scanning these codes also adds a CR
and LF.
USB HID
Scan the following code to program the scanner for USB HID bar code
scanners.
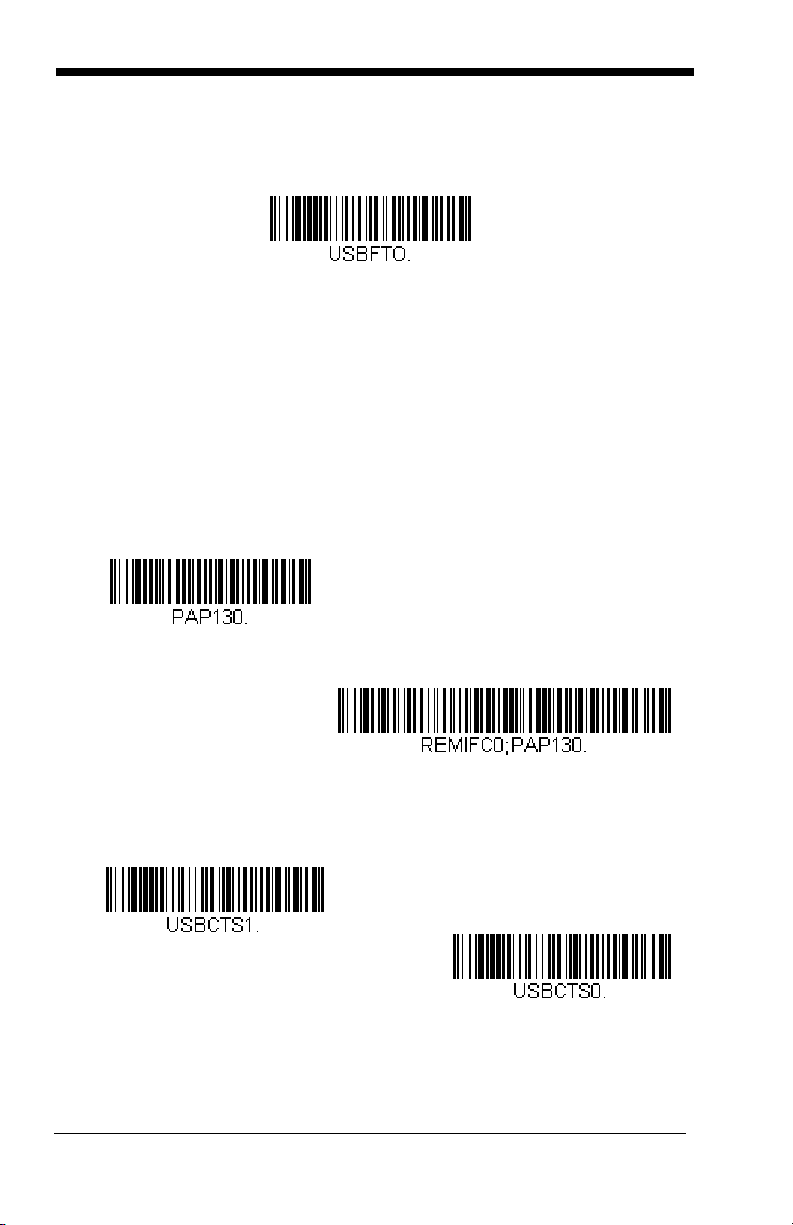
HID Fallback Mode
If you attempt to set a USB interface for your scanner, but the setup fails on
the host system, you can program the scanner to fall back to a HID keyboard interface after a set length of time. For example, if the scanner is
configured for Serial Emulation Mode, but the host system does not have
the correct driver, the scanner would fail. If you set the HID Fallback Mode
for a set length of time, for example, 5 minutes, the scanner would change
to a HID keyboard interface after 5 minutes of trying to configure as serial
emulation.
A unique beep sequence indicates that this mode has been entered. While
in HID Fallback Mode, the scanner will not scan normal bar codes and
sounds a unique beep sequence that indicates the scanner is in Fallback
Mode. Menu codes can still be scanned while in HID Fallback Mode, allowing you to change the scanner’s programming.
2 - 5
Page 30
Scan the bar code below, then set the length for the HID Fallback (from 0-
HID Fallback Mode
USB Serial Emulation for
Windows XP, Windows Server
2003, and later
USB Serial Emulation for Windows 2000
CTS/RTS Emulation On
* CTS/RTS Emulation Off
60 minutes) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning
Save.
Default = 5 minutes.
USB Serial Commands
USB Serial Emulation
Scan one of the following codes to program the scanner to emulate a regular RS232-based COM Port. If you are using a Microsoft® Windows® PC,
you will need to download a driver from the Honeywell website
(www.honeywellaidc.com). The driver will use the next available COM Port
number. Apple® Macintosh computers recognize the scanner as a USB
CDC class device and automatically uses a class driver.
Scanning either of these codes also adds a CR and LF.
Note: No extra configuration (e.g., baud rate) is necessary.
CTS/RTS Emulation
2 - 6
Page 31

ACK/NAK Mode
ACK/NAK Mode On
* ACK/NAK Mode Off
Communication Timeout
Timeout Retries
Communication Timeout
This allows you to set the length (in milliseconds) for a timeout for the host
ACK/NAK response. Scan the bar code below, then set the timeout (from
0-65535 milliseconds) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart,
then scanning Save.
Timeout Retries
This setting limits the number of Communication Timeout retries. If the
Timeout Retries is set to 0, the transmission is terminated after the initial Communication Timeout. Scan the bar code below, then set the
number of retries (from 0-255) by scanning digits from the
Programming Chart, then scanning Save. (5 is the recommended set-
Default = 0.
ting.)
Default = 2000 ms.
2 - 7
Page 32

Communication Timeout Beeper
O
f
f
* On
NAK Retries
BEL/CAN On
* BEL/CAN Off
This selection programs the scanner to issue an error beep when a
communication timeout has occurred. The error beep sound is programmed using Number of Beeps – Error (page 3-4).
Default = On.
NAK Retries
This selection limits the number of NAK retries that can occur in ACK/NAK
mode. Scan the bar code below, then set the number of retries (from 0-
255) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning Save.
(5 is the recommended setting.)
Default = 0, or disabled.
Support BEL/CAN in ACK/NAK
This protocol responds to <BEL> and <CAN> commands when in ACK/
NAK mode. The scanner sounds an error tone when a <BEL> command is
sent from the host. <CAN> terminates the transmission.
CAN Off
.
Default = BEL/
2 - 8
Page 33

Verifone® Ruby Terminal Default Settings
Verifone Ruby Settings
Gilbarco Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Verifone
Ruby terminal. This bar code sets the baud rate to 1200 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, Mark parity, 1 stop bit and RTS/CTS no timeout. It also adds
a line feed (LF) suffix and programs the following prefixes for each symbology:
Symbology Prefix
UPC-A A
UPC-E A
EAN-8 FF
EAN-13 F
Gilbarco® Terminal Default Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Gilbarco
terminal. This bar code sets the baud rate to 2400 bps and the data format to 7
data bits, even parity, 2 stop bits. It also adds a carriage return (CR) suffix and
programs the following prefixes for each symbology:
Symbology Prefix
UPC-A A
UPC-E E0
EAN-8 FF
EAN-13 F
2 - 9
Page 34

Honeywell Bioptic Aux Port Configuration
Honeywell Bioptic Settings
Datalogic Magellan Bioptic Settings
NCR Bioptic Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Honeywell
bioptic scanner auxiliary port configuration. This bar code sets the baud rate to
38400 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit. Character
RTS/CTS with timeout and 232 ACK/NAK are also enabled.
Datalogic™ Magellan© Bioptic Aux Port Configuration
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Datalogic
Magellan bioptic scanner auxiliary port configuration. This bar code sets the
baud rate to 9600 bps and the data format to 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit.
NCR Bioptic Aux Port Configuration
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for an NCR bioptic scanner auxiliary port configuration. This bar code sets the baud rate to
9600 bps and the data format to 7 data bits, Even parity, 1 stop bit and Message
RTS/CTS with timeout. The following prefixes are programmed for each symbology:
Symbology Prefix Symbology Prefix
UPC-A A Code 39 B1
UPC-E E0 Interleaved 2 of 5 B2
EAN-8 FF All other bar
codes
EAN-13 F
2 - 10
B3
Page 35

Wincor Nixdorf Terminal Default Settings
Wincor Nixdorf Terminal Settings
Wincor Nixdorf Beetle Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Wincor Nixdorf terminal. This bar code sets the baud rate to 9600 bps and the data format
to 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit.
Wincor Nixdorf Beetle™ Terminal Default Settings
Scan the following Plug and Play code to program the scanner for a Wincor Nixdorf Beetle terminal. The following prefixes are programmed for each symbology:
Symbology Prefix Symbology Prefix
Code 128 K EAN-13 A
Code 93 L GS1-128 P
Codabar N Interleaved 2 of 5 I
UPC-A A0 Plessey O
UPC-E C Straight 2 of 5 IATA H
EAN-8 B All other bar codes M
2 - 11
Page 36

Keyboard Country Layout
* United States
Belgium
Finland
Germany
France
IBM Financial
Hungary
Arabic
Chinese
Italy
Japan ASCII
Korea
Scan the appropriate country code below to program the keyboard layout for
your country or language. As a general rule, the following characters are supported, but need special care for countries other than the United States:
@ | $ # { } [ ] = / ‘ \ < > ~
2 - 12
Page 37

Keyboard Country (continued)
United Kingdom
Turkey Q
Switzerland (German)
Russia
Slovenia
Spain
Thailand
Vietnam
Program Keyboard Country
Refer to the Honeywell website (www.honeywell.com/aidc) for complete keyboard country support information and applicable interfaces. If you need to program a keyboard for a country other than one listed above, scan the Program
Keyboard Country bar code below, then scan the numeric bar code(s) for the
appropriate country from the Programming Chart, then the Save bar code.
2 - 13
Page 38

Keyboard Wedge Modifiers
* Off
3 Characters
4 Characters
* Regular
Caps Lock
ALT Mode
If your bar code contains special characters from the extended ASCII chart
for example, an e with an accent grave (è), you will use ALT Mode. (See
Extended ASCII Characters on page A-5.)
Note: Scan the ALT mode bar code after scanning the appropriate
Keyboard Country code.
If your keystrokes require using the ALT key and 3 characters, scan the 3
Characters bar code. If your keystrokes require the ALT key and 4 characters, scan the 4 Characters bar code. The data is then output with the
special character(s).
Keyboard Style
This programs keyboard styles, such as Caps Lock and Shift Lock. If you
have used Keyboard Conversion settings, they will override any of the following Keyboard Style settings.
Regular is used when you normally have the Caps Lock key off.
Default = Off.
Default = Regular.
Caps Lock
2 - 14
is used when you normally have the Caps Lock key on.
Page 39

Shift Lock is used when you normally have the Shift Lock key on (not com-
Shift Lock
Autocaps via NumLock
Emulate External Keyboard
mon to U.S. keyboards).
Autocaps via NumLock
Germany, France) where the Caps Lock key cannot be used to toggle Caps
Lock. The NumLock option works similarly to the regular Autocaps, but
uses the NumLock key to retrieve the current state of the Caps Lock.
Emulate External Keyboard should be scanned if you do not have an
external keyboard (IBM AT or equivalent).
bar code should be scanned in countries (e.g.,
Note: After scanning the Emulate External Keyboard bar code, you must
power cycle your computer.
Keyboard Conversion
Alphabetic keyboard characters can be forced to be all upper case or all
lowercase. So if you have the following bar code: “abc569GK,” you can
make the output “ABC569GK” by scanning Convert All Characters to
Upper Case, or to “abc569gk” by scanning Convert All Characters to
Lower Case. These settings override Keyboard Style selections.
2 - 15
Page 40

Default = Keyboard Conversion Off
* Keyboard Conversion Off
Convert All Characters to Upper
Case
Convert All Characters to Lower
Case
.
Keyboard Modifiers
This modifies special keyboard features, such as CTRL+ ASCII codes and
Turbo Mode.
Control + ASCII Mode On: The scanner sends key combinations for ASCII
control characters for values 00-1F (refer to the ASCII chart for Non-
Printable Characters, page A-4). Windows is the preferred mode. All key-
board country codes are supported. DOS mode is a legacy mode, and it
does not support all keyboard country codes. New users should use the
Windows mode.
Windows Mode Prefix/Suffix Off: The scanner sends key combinations
for ASCII control characters for values 00-1F (refer to the ASCII chart for
Non-Printable Characters, page A-4), but it does not transmit any prefix or
suffix information.
2 - 16
Page 41

Default = Control + ASCII Mode Off.
Windows Mode Control + ASCII
Mode On
* Control + ASCII Mode Off
DOS Mode Control + ASCII Mode
On
Windows Mode Prefix/Suffix Off
Numeric Keypad Mode On
* Numeric Keypad Mode Off
Inter-Scan Code Delay
Numeric Keypad Mode: Sends numeric characters as if entered from a
numeric keypad.
Default = Off.
Inter-Scan Code Delay
When your keyboard detects that any key is being pressed, released, or
held down, the keyboard sends a packet of information known as a “scan
code” to your computer. This selection allows you to adjust the delay
between scan codes. Set the length (in milliseconds) for a delay by scanning the bar code below, then setting the delay (from 1-30) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning Save.
Default = 0 (800 µs)
.
2 - 17
Page 42

<F0> Break Character
Suppress
* Transmit
Keyboard Wedge Defaults
When your keyboard detects that any key is being pressed, released, or
held down, the keyboard sends a packet of information known as a “scan
code” to your computer. There are two different types of scan codes:
“make codes” and “break codes.” A make code is sent when a key is
pressed or held down. A break code is sent when a key is released. The
following selections allow you to suppress or transmit the character
sequence of the break code.
Default = Transmit.
Keyboard Wedge Defaults
If you want the custom keyboard wedge default settings restored to your
scanner, scan the Keyboard Wedge Defaults bar code below. This resets
the scanner to the custom default settings (see Setting Custom Defaults on
page 1-5). If there are no custom defaults, it will reset the scanner to the
factory default settings. Any settings that have not been specified through
the custom defaults will be defaulted to the factory default settings.
2 - 18
Page 43

RS232 Modifiers
300
2400
600
1200
4800
38400
* 9600
19200
115,200
57,600
RS232 Baud Rate
Baud Rate sends the data from the scanner to the terminal at the specified
rate. The host terminal must be set for the same baud rate as the scanner.
Default = 9600.
2 - 19
Page 44

RS232 Word Length: Data Bits, Stop Bits,
7 Data, 1 Stop, Parity Even
7 Data, 1 Stop, Parity None
7 Data, 1 Stop, Parity Odd
7 Data, 2 Stop, Parity Even
7 Data, 2 Stop Parity None
* 8 Data, 1 Stop, Parity None
8 Data, 1 Stop, Parity Even
7 Data, 2 Stop, Parity Odd
8 Data, 1 Stop, Parity Odd
7 Data, 1 Stop, Parity Space
and Parity
Data Bits sets the word length at 7 or 8 bits of data per character. If an
application requires only ASCII Hex characters 0 through 7F decimal (text,
digits, and punctuation), select 7 data bits. For applications that require
use of the full ASCII set, select 8 data bits per character.
Stop Bits sets the stop bits at 1 or 2.
Default = 1.
Parity provides a means of checking character bit patterns for validity.
Default = None.
Default = 8.
2 - 20
Page 45

RS232 Handshaking
7 Data, 2 Stop, Parity Space
8 Data, 1 Stop, Parity Space
7 Data, 1 Stop, Parity Mark
7 Data, 2 Stop, Parity Mark
8 Data, 1 Stop Parity Mark
RS232 Handshaking allows control of data transmission from the scanner
using software commands from the host device. When RTS/CTS is
turned Off, no data flow control is used.
Flow Control, No Timeout: The scanner asserts RTS when it has data to
send, and will wait indefinitely for CTS to be asserted by the host.
Character-Based Flow Control, No Timeout: The scanner asserts RTS
when it has a character to send, and will wait indefinitely for CTS to be
asserted by the host
Two-Direction Flow Control: The scanner asserts RTS when it is OK for
the host to transmit. The host asserts CTS when it is OK for the device to
transmit.
Flow Control with Timeout: The scanner asserts RTS when it has data
to send and waits for a delay (see RS232 Timeout on page 2-22) for CTS to
be asserted by the host. If the delay time expires and CTS is not asserted,
the device transmit buffer is cleared and scanning may resume.
Character-Based Flow Control with Timeout: The scanner asserts RTS
when it has a character to send and waits for a delay (see RS232 Timeout
on page 2-22) for CTS to be asserted by the host. If the delay time expires
2 - 21
Page 46

and CTS is not asserted, the device transmit buffer is cleared and scanning
Flow Control, No Timeout
* RTS/CTS Off
Two-Direction Flow Control
Flow Control with Timeout
Character-Based Flow Control
with Timeout
Character-Based Flow Control,
No Timeout
RS232 Timeout
may resume.
Default = RTS/CTS Off.
RS232 Timeout
When using Flow Control with Timeout, you must program the length of the
delay you want to wait for CTS from the host. Set the length (in milliseconds) for a timeout by scanning the bar code below, then setting the timeout (from 1-5100 milliseconds) by scanning digits from the Programming
Chart, then scanning Save.
Default = 1000 ms (1 second).
XON/XOFF
Standard ASCII control characters can be used to tell the scanner to start
sending data (XON/XOFF On) or to stop sending data (XON/XOFF Off).
When the host sends the XOFF character (DC3, hex 13) to the scanner,
2 - 22
Page 47

data transmission stops. To resume transmission, the host sends the XON
* XON/XOFF Off
XON/XOFF On
ACK/NAK On
* ACK/NAK Off
Communication Timeout
character (DC1, hex 11). Data transmission continues where it left off
when XOFF was sent.
Default = XON/XOFF Off
.
ACK/NAK
After transmitting data, the scanner waits for an ACK character (hex 06) or
a NAK character (hex 15) response from the host. If ACK is received, the
communications cycle is completed and the scanner looks for more bar
codes. If NAK is received, the last set of bar code data is retransmitted and
the scanner waits for ACK/NAK again. Turn on the ACK/NAK protocol by
scanning the ACK/NAK On bar code below. To turn off the protocol, scan
ACK/NAK Off.
Default = ACK/NAK Off
.
Communication Timeout
This allows you to set the length (in milliseconds) for a timeout for the host
ACK/NAK response. Scan the bar code below, then set the timeout (from
1-65535 milliseconds) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart,
then scanning Save.
Timeout Retries
This setting limits the number of Communication Timeout retries. If the
Timeout Retries is set to 0, the transmission is terminated after the initial Communication Timeout. Scan the bar code below, then set the
Default = 2000 ms.
2 - 23
Page 48

number of retries (from 0-255) by scanning digits from the
Timeout Retries
O
f
f
* On
NAK Retries
Programming Chart, then scanning Save. (5 is the recommended set-
Default = 0.
ting.)
Communication Timeout Beeper
This selection programs the scanner to issue an error beep when a
communication timeout has occurred. The error beep sound is programmed using Number of Beeps – Error (page 3-4).
Default = On.
NAK Retries
This selection limits the number of NAK retries that can occur in ACK/NAK
mode. Scan the bar code below, then set the number of retries (from 0-
255) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning Save.
(5 is the recommended setting.)
Default = 0, or disabled.
2 - 24
Page 49

Support BEL/CAN in ACK/NAK
BEL/CAN On
* BEL/CAN Off
RS232 Defaults
* NCR ACK/NAK Off
NCR ACK/NAK On
This protocol responds to <BEL> and <CAN> commands when in ACK/
NAK mode. The scanner sounds an error tone when a <BEL> command is
sent from the host. <CAN> terminates the transmission.
CAN Off
.
Default = BEL/
RS232 Defaults
If you want the custom RS232 default settings restored to your scanner,
scan the RS232 Defaults bar code below. This resets the scanner to the
custom default settings (see Setting Custom Defaults on page 1-5). If
there are no custom defaults, it will reset the scanner to the factory default
settings. Any settings that have not been specified through the custom
defaults will be restored to the factory default settings.
NCR Modifiers
NCR ACK/NAK
This is an NCR communication protocol for ACK/NAK processing.
= NCR ACK/NAK Off
.
Default
2 - 25
Page 50

Block Check Character
* Transmit
Don’t Transmit
NCR Prefix
NCR Suffix
When this selection is set to Transmit, the NCR Block Check Character
(BCC) is expected with incoming messages and transmitted with outgoing
messages.
Default = Transmit.
NCR Prefix
This selection allows you to program an NCR-specific prefix. Refer to the
ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4 to find the hex
equivalent for the characters you want for the NCR prefix (typically, 02 for
STX). Scan the bar code below, then set the hex number (from 0-FF) by
scanning digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning Save.
= 0.
Default
NCR Suffix
This selection allows you to program an NCR-specific suffix. Refer to the
ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4 to find the hex
equivalent for the characters you want for the NCR suffix (typically, 03 for
ETX). Scan the bar code below, then set the hex number (from 0-FF) by
scanning digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning Save.
= 0.
Default
2 - 26
Page 51

NCR Prefix/Suffix
Transmit
* Don’t Transmit
On
* Off
When set to Transmit, both the NCR prefix and suffix are transmitted with
bar codes. Usually, prefixes and suffixes are programmed using the Data
Editing selections (see Data Editing beginning on page 4-1), however, the
following commands override any other prefix/suffix settings.
Don’t Transmit.
Default =
NCR NOF (Not-on-File) Error
A scanner receives an NOF (Not on File) command from the POS whenever it cannot cross-reference the bar code to a price parameter. When set
to On, the error tone sounds (set via Number of Beeps – Error, page 3-4)
for an NOF, and disables the scanner while the cashier looks up the price
manually. When set to Off, no sound is emitted for an NOF.
Default = Off.
Scanner to Bioptic Communication
The following settings are used to set up communication between Honeywell
scanners and bioptic scanners.
Note: The scanner’s baud rate must be set to 38400 and the RS232 Timeout
must be set to 3000 in order to communicate with a bioptic scanner. See
RS232 Modifiers on page 2-19, and RS232 Timeout on page 2-22 for
further information.
2 - 27
Page 52

Scanner-Bioptic Packet Mode
* Packet Mode Off
Packet Mode On
ACK/NAK On
* ACK/NAK Off
Communication Timeout
Packet Mode On must be scanned to set the scanner’s format so it is com-
patible with a bioptic scanner.
Default = Packet Mode Off.
ACK/NAK
After transmitting data, the scanner waits for an ACK character (hex 06) or
a NAK character (hex 15) response from the host. If ACK is received, the
communications cycle is completed and the scanner looks for more bar
codes. If NAK is received, the last set of bar code data is retransmitted and
the scanner waits for ACK/NAK again. Turn on the ACK/NAK protocol by
scanning the ACK/NAK On bar code below. To turn off the protocol, scan
ACK/NAK Off.
Default = ACK/NAK Off
.
Communication Timeout
This allows you to set the length (in milliseconds) for a timeout for the host
ACK/NAK response. Scan the bar code below, then set the timeout (from
1-65535 milliseconds) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart,
then scanning Save.
2 - 28
Default = 2000 ms.
Page 53

3
Power Up Beeper Off -
Scanner
* Power Up Beeper On -
Scanner
*Beep on BEL Off
Beep on BEL On
Input/Output Settings
Power Up Beeper
The scanner can be programmed to beep when it’s powered up. Scan the Off
bar code(s) if you don’t want a power up beep.
- Scanner.
Beep on BEL Character
You may wish to force the scanner to beep upon a command sent from the host.
If you scan the Beep on BEL On bar code below, the scanner will beep every
time a BEL character is received from the host.
Default = Power Up Beeper On
Default = Beep on BEL Off.
3 - 1
Page 54

Good Read and Error Indicators
* Beeper - Good Read On
Beeper - Good Read Off
* High
Medium
Off
Low
Beeper – Good Read
The beeper may be programmed On or Off in response to a good read.
Turning this option off, only turns off the beeper response to a good read
indication. All error and menu beeps are still audible.
Good Read On.
Beeper Volume – Good Read
The beeper volume codes modify the volume of the beep the scanner
emits on a good read.
Default = High.
Default = Beeper -
3 - 2
Page 55

Beeper Pitch – Good Read
Low (1600 Hz)
* Medium (2350 Hz)
High (4200 Hz)
* Before Transmission
After Transmission
* Razz (100 Hz)
Medium (2000 Hz)
High (4200 Hz)
The beeper pitch codes modify the pitch (frequency) of the beep the scanner emits on a good read.
Default = Medium.
Beeper - Transmit Order
The beeper transmit order determines when the good read beep occurs.
The scanner can be set to emit the good read beep either before or after
data transmission.
Default = Before Transmission.
Beeper Pitch – Error
The beeper pitch codes modify the pitch (frequency) of the sound the scanner emits when there is a bad read or error.
Default = Razz.
3 - 3
Page 56

Beeper Duration – Good Read
* Normal Beep
Short BeepShort Beep
Number of Good Read Beeps/LED Flashes
The beeper duration codes modify the length of the beep the scanner emits
on a good read.
Default = Normal.
Number of Beeps – Good Read
The number of beeps of a good read can be programmed from 1 - 9. The
same number of beeps will be applied to the beeper and LED in response
to a good read. For example, if you program this option to have five beeps,
there will be five beeps and five LED flashes in response to a good read.
The beeps and LED flashes are in sync with one another.
Note: The LEDs can also be programmed separately. See LED
Settings on page 3-6.
To change the number of beeps, scan the bar code below and then scan a
digit (1-9) bar code and the Save bar code on the Programming Chart
inside the back cover of this manual.
Default = 1.
Number of Beeps – Error
The number of beeps and LED flashes emitted by the scanner for a bad
read or error can be programmed from 1 - 9. For example, if you program
this option to have five error beeps, there will be five error beeps and five
LED flashes in response to an error.
Note: The LEDs can also be programmed separately. See LED
Settings on page 3-6.
3 - 4
Page 57

To change the number of error beeps, scan the bar code below and then
Number of Error Beeps/LED Flashes
scan a digit (1-9) bar code and the Save bar code on the Programming
Chart inside the back cover of this manual.
Default = 1.
3 - 5
Page 58

LED Indicators
Green LED Off
* Red LED Off
* Green LED On with Good Scan
Red LED On with Good Scan
Green LED On with Laser
Red LED On with Laser
Red LED On when CodeGate
Disabled
Green LED On when CodeGate
Disabled
Green LED On when In-Stand
Red LED On when In-Stand
The green and red LEDs can be programmed to be On or Off and at different
brightness levels to indicate various scanner states. Use the following bar
codes to program the LED indicators.
LED Settings
Default = Red LED Off with Laser, Green LED On with Good Scan.
3 - 6
Page 59

LED Brightness
Red LED On with CTS
Green LED On with CTS
Green Off
Red Off
Green Low
Red Low
Green Medium
Red Medium
* Red High
* Green High
Default = Red High, Green High.
In-Stand and Out-Of-Stand Settings
The following settings program the scanner’s behavior when it is either in the
stand, or out of the stand (hand-held).
3 - 7
Page 60

Caution: When working with In-Stand and Out-of-Stand settings, enable
Out-of-Stand Defaults
In-Stand Defaults
the settings you want before disabling those you do not want to
use. If you disable settings first, you may program the scanner
so it is unable to read bar codes. if this happens, power cycle
the scanner and scan the defaults bar code on page 1-6.
In-Stand and Out-of-Stand Defaults
If you want the In-Stand or Out-of-Stand default settings restored to your
scanner, scan the appropriate Defaults bar code below. They reset the
scanner to the custom default settings (see Setting Custom Defaults on
page 1-5). If there are no custom defaults, it will reset the scanner to the
factory default settings. Any settings that have not been specified through
the custom defaults will be defaulted to the factory default settings.
Presentation Modes
When the scanner is in the stand, by default, bar codes are automatically
read when they are detected in the scanner’s field of view. When the scanner is out of the stand, by default you must push the button on top of the
scanner to read a bar code. Use the following commands to adjust how the
scanner behaves when it is out of the stand.
Presentation Mode Out-of-Stand: When the scanner is not in the stand,
it automatically detects bar codes, then scans and transmits the data. The
laser turns off afterward. (If you are accustomed to a Voyager 9520, this
setting is the same as the 9520’s default.)
3 - 8
Page 61

Presentation Mode with CodeGate® Out-of-Stand: When the scanner
Presentation Mode with
CodeGate Out-of-Stand
Presentation Mode
Out-of-Stand
* Manual Activation Mode On
In-Stand
Manual Activation Mode Off
In-Stand
* Manual Activation Mode On
Out-of-Stand
Manual Activation Mode Off
Out-of-Stand
is not in the stand, it automatically detects bar codes and decodes them.
However, the data is not transmitted until you press the button. The laser
remains on briefly after the transmission. (If you are accustomed to a Voyager 9540, this setting is the same as the 9540’s default.)
Manual Activation Mode
In Manual Activation Mode, you must press the button to scan a bar code.
The scanner scans until a bar code is read, or until the button is released.
Default = Manual Activation Mode Off In-Stand, Manual Activation On Outof-Stand.
End Manual Activation After Good Read
After a bar code is successfully read, the laser can be programmed either
to remain on and scanning, or to turn off. When End Manual Activation
After Good Read is enabled, the laser turns off and stops scanning after a
3 - 9
Page 62

good read. If you scan Do Not End Manual Activation After Good Read,
* End Manual Activation After
Good Read Out-of-Stand
Do Not End Manual Activation
After Good Read Out-of-Stand
* End Manual Activation After
Good Read In-Stand
Do Not End Manual Activation
After Good Read In-Stand
Laser Timeout - Button
Release In-Stand
Laser Timeout - Button Hold
In-Stand
Laser Timeout - Button
Release Out-of-Stand
Laser Timeout - Button Hold
Out-of-Stand
the laser remains on after a good read, but the button must be pressed to
scan the next bar code.
Default = End Manual Activation After Good Read.
Manual Activation Laser Timeout Button Settings
You can set a timeout for the length of time the laser remains on and
attempting to decode bar codes when the button is held down, and after it
is released. Set the length (in milliseconds) for a timeout by scanning one
of the bar codes below, then setting the timeout (from 1-65535 milliseconds) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning
Default = Button Hold In-Stand 5000 ms, Button Hold Out-of-Stand
Save.
30000 ms, Button Release In or Out-of-Stand 0.
3 - 10
Page 63

CodeGate
CodeGate On
In-Stand
* CodeGate Off
In-Stand
* CodeGate On
Out-of-Stand
CodeGate Off
Out-of-Stand
* Object Detection Mode On
In-Stand
Object Detection Mode Off
In-Stand
Object Detection Mode On
Out-of-Stand
* Object Detection Mode Off
Out-of-Stand
®
When CodeGate is On, the button is used to allow decoded data to be
transmitted to the host system. The scanner remains on, scanning and
decoding bar codes, but the bar code data is not transmitted until the button
is pressed. When CodeGate is Off, bar code data is transmitted when it is
decoded.
Default = CodeGate Off in-Stand, CodeGate On Out-of-Stand.
Object Detection Mode
Object Detection Mode uses an LED to detect when an object is in the
scanner’s field of view. When an object is detected, the laser turns on and
the scanner attempts to scan the bar code.
Mode On In-Stand.
Default = Object Detection
3 - 11
Page 64

End Object Detection After Good Read
* End Object Detection After
Good Read In-Stand
Do Not End Object Detection
After Good Read In-Stand
* End Object Detection After
Good Read Out-of-Stand
Do Not End Object Detection
After Good Read Out-of-Stand
Object Detection Laser
Timeout In-Stand
Object Detection Laser
Timeout Out-of-Stand
After a bar code is successfully detected and read from the scanner, the
laser can be programmed either to remain on and scanning, or to turn off.
When End Object Detection After Good Read is enabled, the laser turns
off and stops scanning after a good read. If you scan Do Not End Object
Detection After Good Read, the laser remains on after a good read.
Default = End Object Detection After Good Read.
Object Detection Laser Timeout
You can set a timeout for the length of time the laser remains on and
attempting to decode bar codes after an object is detected. Set the length
(in milliseconds) for a timeout by scanning the bar code below, then setting
the timeout (from 1-65535 milliseconds) by scanning digits from the
Programming Chart, then scanning Save.
Default = 5000 ms.
3 - 12
Page 65

Object Detection Distance
Long
In-Stand
* Short
In-Stand
* Long
Out-of-Stand
Short
Out-of-Stand
* Off
On
When the scanner is in the stand and you are using Object Detection
Mode, you can set the distance range for detecting objects. Short sets the
scanner to detect objects approximately 5 inches (12.7cm) away from the
nose. Long sets it to detect objects approximately 10 inches (25.4cm)
Default = Short In-Stand, Long Out-of-Stand.
away.
Character Activation Mode
You may use a character sent from the host to trigger the scanner to begin
scanning. When the activation character is received, the scanner continues
scanning until either the Character Activation Laser Timeout (page 3-14), the
deactivation character is received (see Deactivation Character on page 3-15),
or a bar code is transmitted. Scan the On bar code below to use character activation, then use Activation Character (following) to select the character you will
send from the host to start scanning.
Default = Off.
Activation Character
This sets the character used to trigger scanning when using Character Activation Mode. On the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252), page A4, find the hex value that represents the character you want to use to trig-
3 - 13
Page 66

ger scanning. Scan the bar code below, then use the Programming Chart
Activation Character
* End Character Activation After
Good Read
Do Not End Character Activation
After Good Read
Character Activation Laser
Timeout
to read the alphanumeric combination that represents that ASCII character.
Scan Save to finish.
End Character Activation After Good Read
After a bar code is successfully detected and read from the scanner, the
laser can be programmed either to remain on and scanning, or to turn off.
When End Character Activation After Good Read is enabled, the laser
turns off and stops scanning after a good read. If you scan Do Not End
Character Activation After Good Read, the laser remains on after a good
Default = End Character Activation After Good Read.
read.
Character Activation Laser Timeout
You can set a timeout for the length of time the laser remains on and
attempting to decode bar codes when using Character Activation Mode.
Set the length (in milliseconds) for a timeout by scanning the bar code
below, then setting the timeout (from 1-65535 milliseconds) by scanning
digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning Save.
ms.
Default = 5000
3 - 14
Page 67

Character Deactivation Mode
* Off
On
Deactivation Character
If you have sent a character from the host to trigger the scanner to begin scanning, you can also send a deactivation character to stop scanning. Scan the On
bar code below to use character deactivation, then use Deactivation Character
(following) to select the character you will send from the host to terminate scan-
Default = Off.
ning.
Deactivation Character
This sets the character used to terminate scanning when using Character
Deactivation Mode. On the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page
1252), page A-4, find the hex value that represents the character you want
to use to terminate scanning. Scan the bar code below, then use the
Programming Chart to read the alphanumeric combination that represents
that ASCII character. Scan Save to finish.
3 - 15
Page 68

Reread Delay
Short (500 ms)
* Medium (750 ms)
Long (1000 ms)
Extra Long (2000 ms)
User-Specified Reread Delay
This sets the time period before the scanner can read the
ond time. Setting a reread delay protects against accidental rereads of the
same bar code. Longer delays are effective in minimizing accidental rereads.
Use shorter delays in applications where repetitive bar code scanning is
required.
Default = Medium.
same
bar code a sec-
User-Specified Reread Delay
If you want to set your own length for the reread delay, scan the bar code below,
then set the delay (from 0-30,000 milliseconds) by scanning digits from the
Programming Chart, then scanning Save.
Output Sequence Overview
Require Output Sequence
When turned off, the bar code data will be output to the host as the scanner
decodes it. When turned on, all output data must conform to an edited
sequence or the scanner will not transmit the output data to the host
device. See Require Output Sequence on page 3-20 for further information.
3 - 16
Page 69

Output Sequence Editor
This programming selection allows you to program the scanner to output
data (when scanning more than one symbol) in whatever order your application requires, regardless of the order in which the bar codes are
scanned. Reading the
the Universal values, shown below. These are the defaults. Be certain
you want to delete or clear all formats before you read the
Sequence
Note: If CodeGate is enabled, you must hold the button down while reading
Note: To make Output Sequence Editor selections, you’ll need to know the
symbol.
each bar code in a sequence.
code I.D., code length, and character match(es) your application
requires. Use the Alphanumeric symbols on the Programming Chart
to read these options.
Default Sequence
symbol programs the scanner to
Default
To Add an Output Sequence
1. Scan the
Sequence, page 3-20).
2. Code I.D.
On the Symbology Chart on page A-1, find the symbology to which you
want to apply the output sequence format. Locate the Hex value for that
symbology and scan the 2 digit hex value from the Programming Chart
(inside back cover).
3. Length
Specify what length (up to 9999 characters) of data output will be
acceptable for this symbology. Scan the four digit data length from the
Programming Chart. (Note: 50 characters is entered as 0050. 9999 is
a universal number, indicating all lengths.) When calculating the length,
you must count any programmed prefixes, suffixes, or formatted
characters as part of the length (unless using 9999).
Enter Sequence
symbol (see Require Output
4. Character Match Sequences
On the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252), page A-4, find the
Hex value that represents the character(s) you want to match. Use the
Programming Chart to read the alphanumeric combination that
represents the ASCII characters. (99 is the Universal number,
indicating all characters.)
5. End Output Sequence Editor
F F
Scan
Save
to enter an Output Sequence for an additional symbology, or
to save your entries.
Other Programming Selections
•
Discard
This exits without saving any Output Sequence changes.
3 - 17
Page 70

Output Sequence Example
A - Code 39
B - Code 128
C - Code 93
In this example, you are scanning Code 93, Code 128, and Code 39 bar
codes, but you want the scanner to output Code 39 1st, Code 128 2nd, and
Code 93 3rd, as shown below.
Note: Code 93 must be enabled to use this example.
You would set up the sequence editor with the following command line:
SEQBLK62999941FF6A999942FF69999943FF
The breakdown of the command line is shown below:
SEQBLKsequence editor start command
62 code identifier for Code 39
9999 code length that must match for Code 39, 9999 = all lengths
41 start character match for Code 39, 41h = “A”
FF termination string for first code
6A code identifier for Code 128
9999 code length that must match for Code 128, 9999 = all lengths
42 start character match for Code 128, 42h = “B”
FF termination string for second code
69 code identifier for Code 93
9999 code length that must match for Code 93, 9999 = all lengths
43 start character match for Code 93, 43h = “C”
FF termination string for third code
To program the previous example using specific lengths, you would have to
count any programmed prefixes, suffixes, or formatted characters as part of
the length. If you use the example on page 3-18, but assume a <CR> suffix and specific code lengths, you would use the following command line:
SEQBLK62001241FF6A001342FF69001243FF
The breakdown of the command line is shown below:
3 - 18
Page 71

SEQBLKsequence editor start command
Default Sequence
Enter Sequence
Sequence Timeout
62 code identifier for Code 39
0012 A - Code 39 sample length (11) plus CR suffix (1) = 12
41 start character match for Code 39, 41h = “A”
FF termination string for first code
6A code identifier for Code 128
0013 B - Code 128 sample length (12) plus CR suffix (1) = 13
42 start character match for Code 128, 42h = “B”
FF termination string for second code
69 code identifier for Code 93
0012 C - Code 93 sample length (11) plus CR suffix (1) = 12
43 start character match for Code 93, 43h = “C”
FF termination string for third code
Output Sequence Editor
Sequence Timeout
You may wish to set the maximum time between bar code scans in an output sequence. If that maximum time is not met, the output sequence operation is terminated. Set the length (in milliseconds) for a timeout by
scanning the bar code below, then setting the timeout (from 1-65535 milliseconds) by scanning digits from the Programming Chart, then scanning
Default = 5000 msec.
Save.
3 - 19
Page 72

Sequence Match Beeper
Sequence Match Beeper Off
* Sequence Match Beeper On
Transmit Partial Sequence
* Discard Partial Sequence
By default, the scanner beeps when a sequence match is found. If you
want the scanner to remain silent, scan the Sequence Match Beeper Off
bar code below.
Default = Sequence Match Beeper On.
Partial Sequence
If an output sequence operation is terminated before all your output
sequence criteria are met, the bar code data acquired to that point is a
“partial sequence.”
Scan Discard Partial Sequence to discard partial sequences when the
output sequence operation is terminated before completion.
Scan Transmit Partial Sequence to transmit partial sequences. (Any
fields in the sequence where no data match occurred will be skipped in the
output.)
the timeout is reached, the partial sequence is transmitted.
card Partial Sequence.
If you have programmed a Sequence Timeout (page 3-19) and
Default = Dis-
Require Output Sequence
When an output sequence is Required, all output data must conform to an
edited sequence or the scanner will not transmit the output data to the host
device. When it’s On/Not Required, the scanner will attempt to get the
output data to conform to an edited sequence but, if it cannot, the scanner
transmits all output data to the host device as is.
3 - 20
Page 73

When the output sequence is
Required
On/Not Required
*Off
On
* Off
the scanner decodes it.
Off
, the bar code data is output to the host as
Default = Off.
No Read
With No Read turned On, the scanner notifies you if a code cannot be read. If
using an EZConfig-Scanning Tool Scan Data Window (see page 8-2), an “NR”
appears when a code cannot be read. If No Read is turned Off, the “NR” will
not appear.
Default = Off.
If you want a different notation than “NR,” for example, “Error,” or “Bad Code,”
you can edit the output message (see Data Formatting beginning on page 5-1).
The hex code for the No Read symbol is 9C.
3 - 21
Page 74

3 - 22
Page 75

4
Data Editing
Prefix/Suffix Overview
When a bar code is scanned, additional information is sent to the host computer
along with the bar code data. This group of bar code data and additional,
user-defined data is called a “message string.” The selections in this section
are used to build the user-defined data into the message string.
Prefix and Suffix characters are data characters that can be sent before and
after scanned data. You can specify if they should be sent with all symbologies,
or only with specific symbologies. The following illustration shows the breakdown of a message string:
Prefix
alpha numeric &
control characters
Scanned Data
variable length1-11
Suffix
1-11
alpha numeric &
control characters
Points to Keep In Mind
• It is not necessary to build a message string. The selections in this
chapter are only used if you wish to alter the default settings.
prefix = None. Default suffix is dependent on interface
• A prefix or suffix may be added or cleared from one symbology or all
symbologies.
• You can add any prefix or suffix from the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code
Page 1252), beginning on page A-4, plus Code I.D. and AIM I.D.
• You can string together several entries for several symbologies at one
time.
• Enter prefixes and suffixes in the order in which you want them to appear
on the output.
• When setting up for specific symbologies (as opposed to all
symbologies), the specific symbology ID value counts as an added prefix
or suffix character.
• The maximum size of a prefix or suffix configuration is 32 characters,
which includes header information.
.
Default
To Add a Prefix or Suffix:
Step 1. Scan the Add Prefix or Add Suffix symbol (page 4-3).
Step 2. Determine the 2 digit Hex value from the Symbology Chart
(included in the Symbology Chart, beginning on page A-1) for the
4 - 1
Page 76

symbology to which you want to apply the prefix or suffix. For
example, for Code 128, Code ID is “j” and Hex ID is “6A”.
Step 3. Scan the 2 hex digits from the Programming Chart inside the back
cover of this manual or scan 9, 9 for all symbologies.
Step 4. Determine the hex value from the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code
Page 1252) on page A-4, for the prefix or suffix you wish to enter.
Step 5. Scan the 2 digit hex value from the Programming Chart inside the
back cover of this manual.
Step 6. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 for every prefix or suffix character.
Step 7. To add the Code I.D., scan 5, C, 8, 0.
To add AIM I.D., scan 5, C, 8, 1.
To add a backslash (\), scan 5, C, 5, C.
Note: To add a backslash (\) as in Step 7, you must scan 5C twice – once
to create the leading backslash and then to create the backslash
itself.
Step 8. Scan Save to exit and save, or scan Discard to exit without saving.
Repeat Steps 1-6 to add a prefix or suffix for another symbology.
Example: Add a Suffix to a specific symbology
To send a CR (carriage return)Suffix for U.P.C. only:
Step 1. Scan Add Suffix.
Step 2. Determine the 2 digit hex value from the Symbology Chart
(included in the Symbology Chart, beginning on page A-1) for
U.P.C.
Step 3. Scan 6, 3 from the Programming Chart inside the back cover of this
manual.
Step 4. Determine the hex value from the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code
Page 1252) on page A-4, for the CR (carriage return).
Step 5. Scan 0, D from the Programming Chart inside the back cover of this
manual.
Step 6. Scan Save, or scan Discard to exit without saving.
To Clear One or All Prefixes or Suffixes
You can clear a single prefix or suffix, or clear all prefixes/suffixes for a
symbology. If you have been entering prefixes and suffixes for single symbologies, you can use Clear One Prefix (Suffix) to delete a specific char-
acter from a symbology. When you Clear All Prefixes (Suffixes), all the
prefixes or suffixes for a symbology are deleted.
4 - 2
Page 77

Step 1. Scan the Clear One Prefix or Clear One Suffix symbol.
Add CR Suffix
All Symbologies
Add Prefix
Clear One Prefix
Clear All Prefixes
Step 2. Determine the 2 digit Hex value from the Symbology Chart
(included in the Symbology Chart, beginning on page A-1) for the
symbology from which you want to clear the prefix or suffix.
Step 3. Scan the 2 digit hex value from the Programming Chart inside the
back cover of this manual or scan 9, 9 for all symbologies.
Your change is automatically saved.
To Add a Carriage Return Suffix to All Symbologies
Scan the following bar code if you wish to add a carriage return suffix to all
symbologies at once. This action first clears all current suffixes, then programs a carriage return suffix for all symbologies.
Prefix Selections
4 - 3
Page 78

Suffix Selections
Add Suffix
Clear One Suffix
Clear All Suffixes
* Transmit Alternate Extended
ASCII
Transmit Normal Extended
ASCII
Transmit Alternate Extended ASCII Characters
You may need to emulate special keyboard functions, such as up or down
arrows, Alt/Make or Alt/Break commands, that are not supported in the
Extended ASCII Character table. Refer to Alternate Extended ASCII
Characters (page 4-5) for a range of keyboard function keys and corresponding
decimal and hex characters. If you scan the Transmit Alternate Extended
ASCII code, any hex entries in a prefix or suffix will result in the corresponding
Keyboard Function output.
Example: Transmit Alternate Extended ASCII is enabled, and you scan Add
When Transmit Normal Extended ASCII is selected, the normal extended
ASCII character is transmitted (see ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252)
on page A-4).
Example: Transmit Normal Extended ASCII is enabled, and you scan Add
Default = Transmit Alternate Extended ASCII.
Suffix, then scan 9 9 8 9. All symbologies (99) would have a suffix
of a Page Down (hex 89) added to them.
Suffix, then scan 9 9 8 9. All symbologies (99) would have a suffix
‰ character added to them.
of a
4 - 4
Page 79

Alternate Extended ASCII Characters
DEC HEX Keyboard Function DEC HEX Keyboard Function
128 80
129 81
130 82
131 83
132 84 Insert 156 9C Numeric Keypad +
133 85 Delete 157 9D Numeric Keypad 134 86 Home 158 9E Numeric Keypad *
135 87 End 159 9F Caps Lock
136 88 Page Up 160 A0 Num Lock
137 89 Page Down 161 A1 Left Alt
138 8A Right ALT 162 A2 Left Ctrl
139 8B Right CTRL 163 A3 Left Shift
140 8C Reserved 164 A4 Right Shift
141 8D Reserved 165 A5 Print Screen
142 8E Numeric Keypad Enter 166 A6 Tab
143 8F Numeric Keypad / 167 A7 Shift Tab
144 90 F1 168 A8 Enter
145 91 F2 169 A9 Esc
146 92 F3 170 AA Alt Make
147 93 F4 171 AB Alt Break
148 94 F5 172 AC Control Make
149 95 F6 173 AD Control Break
150 96 F7 174 AE Alt Sequence with 1 Character
151 97 F8 175 AF Ctrl Sequence with 1 Character
up arrow ↑
down arrow ↓
right arrow →
left arrow ←
152 98 F9
153 99 F10
154 9A F11
155 9B F12
4 - 5
Page 80

Function Code Transmit
* Enable
Disable
* None
LRC Starts on 1st Character
LRC Starts on 2nd Character
CRC
When this selection is enabled and function codes are contained within the
scanned data, the scanner transmits the function code to the terminal. Charts
of these function codes are provided in Supported Interface Keys starting on
page 7-2. When the scanner is in keyboard wedge mode, the scan code is con-
verted to a key code before it is transmitted.
Default = Enable.
Communication Check Character
To enhance security, you can specify the transmission type of a check character; either LRC where the calculation starts on the first transmitted character,
LRC where the calculation starts on the second transmitted character, or CRC.
Note: This option adds a check character to the bar code data for all
symbologies. If you need to enable or disable check characters for
individual symbologies, see Symbologies beginning on page 6-1.
Scan the bar code below to set the communication check character type.
Default = None.
4 - 6
Page 81

Intercharacter, Interfunction, and
1 234 5
Intercharacter Delay
Prefix Scanned Data Suffix
Intercharacter Delay
Intermessage Delays
Some terminals drop information (characters) if data comes through too quickly.
Intercharacter, interfunction, and intermessage delays slow the transmission of
data, increasing data integrity.
Intercharacter Delay
An intercharacter delay of up to 5000 milliseconds (in 5ms increments) may
be placed between the transmission of each character of scanned data.
Scan the Intercharacter Delay bar code below, then scan the number of
5ms delays, and the Save bar code using the Programming Chart inside
the back cover of this manual.
To remove this delay, scan the Intercharacter Delay bar code, then set the
number of delays to 0. Scan the Save bar code using the Programming
Chart inside the back cover of this manual.
Note: Intercharacter delays are not supported in USB serial emulation.
User Specified Intercharacter Delay
An intercharacter delay of up to 5000 milliseconds (in 5ms increments)
may be placed after the transmission of a particular character of scanned
data. Scan the Delay Length bar code below, then scan the number of
5ms delays, and the Save bar code using the Programming Chart inside
the back cover of this manual.
4 - 7
Page 82

Next, scan the Character to Trigger Delay bar code, then the 2-digit hex
Delay Length
Character to Trigger Delay
Interfunction Delays
Prefix Scanned Data Suffix
1 2345STX HT CR LF
Interfunction Delay
value for the ASCII character that will trigger the delay ASCII Conversion
Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4.
To remove this delay, scan the Delay Length bar code, and set the number
of delays to 0. Scan the Save bar code using the Programming Chart
inside the back cover of this manual.
Interfunction Delay
An interfunction delay of up to 5000 milliseconds (in 5ms increments) may
be placed between the transmission of each segment of the message
string. Scan the Interfunction Delay bar code below, then scan the number of 5ms delays, and the Save bar code using the Programming Chart
inside the back cover of this manual.
To remove this delay, scan the Interfunction Delay bar code, then set the
number of delays to 0. Scan the Save bar code using the Programming
Chart inside the back cover of this manual.
4 - 8
Page 83

Intermessage Delay
2nd Scan Transmission1st Scan Transmission
Intermessage Delay
Intermessage Delay
An intermessage delay of up to 5000 milliseconds (in 5ms increments)
may be placed between each scan transmission. Scan the Intermessage
Delay bar code below, then scan the number of 5ms delays, and the Save
bar code using the Programming Chart inside the back cover of this man-
ual.
To remove this delay, scan the Intermessage Delay bar code, then set the
number of delays to 0. Scan the Save bar code using the Programming
Chart inside the back cover of this manual.
4 - 9
Page 84

4 - 10
Page 85

5
* Default Data Format
Data Formatting
Data Format Editor Introduction
You may use the Data Format Editor to change the scanner’s output. For example, you can use the Data Format Editor to insert characters at certain points in
bar code data as it is scanned. The selections in the following pages are used
only if you wish to alter the output.
Normally, when you scan a bar code, it gets outputted automatically; however
when you create a format, you must use a “send” command (see Send
Commands on page 5-4) within the format program to output data.
Multiple formats may be programmed into the scanner. They are stacked in the
order in which they are entered. However, the following list presents the order
in which formats are applied:
1. Specific Terminal ID, Actual Code ID, Actual Length
2. Specific Terminal ID, Actual Code ID, Universal Length
3. Specific Terminal ID, Universal Code ID, Actual Length
4. Specific Terminal ID, Universal Code ID, Universal Length
5. Universal Terminal ID, Actual Code ID, Actual Length
6. Universal Terminal ID, Actual Code ID, Universal Length
7. Universal Terminal ID, Universal Code ID, Actual Length
8. Universal Terminal ID, Universal Code ID, Universal Length
The maximum size of a data format configuration is 256 bytes, which includes
header information. No format can contain more than 50 bytes.
If you have changed data format settings, and wish to clear all formats and
return to the factory defaults, scan the Default Data Format code below.
Default Data Format setting = None.
To Add a Data Format
Step 1. Scan the Enter Data Format symbol (page 5-2).
Step 2. Select Primary/Alternate Format
Determine if this will be your primary data format, or one of 3 alternate
formats. This allows you to save a total of 4 different data formats. To
program your primary format, scan 0 using the Programming Chart
inside the back cover of this manual. If you are programming an
alternate format, scan 1, 2, or 3, depending on which alternate format
5 - 1
Page 86

you are programming. (See Primary/Alternate Data Formats on page
Enter Data Format
Save
Discard
5-10 for further information.)
Step 3. Terminal Type
Refer to Terminal ID Table (page 5-4) and locate the Terminal ID
number for your PC. Scan three numeric bar codes on the
Programming Chart to program the scanner for your terminal ID (you
must enter 3 digits). For example, scan 0 0 3 for an AT wedge.
Note: The wildcard for all terminal types is 099.
Step 4. Code I.D.
In the Symbology Chart, beginning on page A-1, find the symbology to
which you want to apply the data format. Locate the Hex value for that
symbology and scan the 2 digit hex value from the Programming Chart
inside the back cover of this manual.
Step 5. Length
Specify what length (up to 9999 characters) of data will be acceptable
for this symbology. Scan the four digit data length from the
Programming Chart inside the back cover of this manual. (Note: 50
characters is entered as 0050. 9999 is a universal number, indicating
all lengths.)
Step 6. Editor Commands
Refer to (page 5-4). Scan the symbols that represent the command you
want to enter. 94 alphanumeric characters may be entered for each
symbology data format.
Step 7. Scan Save to save your data format, or Discard to exit without saving
your changes.
5 - 2
Page 87

Other Programming Selections
Clear One Data Format
Clear All Data Formats
Save
Discard
Clear One Data Format
This deletes one data format for one symbology. If you are clearing the
primary format, scan 0 from the Programming Chart inside the back
cover of this manual. If you are clearing an alternate format, scan 1, 2,
or 3, depending on the format you are clearing. Scan the Terminal Type
and Code I.D. (see Symbology Chart on page A-1), and the bar code
data length for the specific data format that you want to delete. All other
formats remain unaffected.
Clear all Data Formats
This clears all data formats.
Save to exit and save your data format changes.
Discard to exit without saving any data format changes.
5 - 3
Page 88

Terminal ID Table
Terminal Model(s)
IBM PC/AT and compatibles
PS2 Keyboard
USB SurePOS Handheld
Scanner
USB SurePOS Tabletop
Scanner
RS232 True
TTL
RS485
USB Serial
PC Keyboard
Mac Keyboard
Japanese Keyboard (PC)
HID POS
Terminal
Data Format Editor Commands
Send Commands
Send all characters
F1 Include in the output message all of the characters from the input
message, starting from current cursor position, followed by an insert
character.
value for its ASCII code.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4
for decimal, hex and character codes.
Send a number of characters
F2 Include in the output message a number of characters followed by an
insert character. Start from the current cursor position and continue for
“nn” characters or through the last character in the input message,
followed by character “xx.”
numeric value (00-99) for the number of characters, and xx stands for
the insert character’s hex value for its ASCII code.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4
for decimal, hex and character codes.
Syntax = F1xx
where xx stands for the insert character’s hex
Syntax = F2nnxx
where nn stands for the
ID
003
002
128
129
000
000
051
130
124
125
134
131
5 - 4
Page 89

Send all characters up to a particular character
F3 Include in the output message all characters from the input message,
starting with the character at the current cursor position and continuing
to, but not including, the search character “ss,” followed by an insert
character. The cursor is moved forward to the “ss” character.
= F3ssxx
ASCII code, and xx stands for the insert character’s hex value for its
ASCII code.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4 for
decimal, hex and character codes.
where ss stands for the search character’s hex value for its
Syntax
Send all but the last characters
E9 Include in the output message all but the last “nn” characters, starting
from the current cursor position. The cursor is moved forward to one
position past the last input message character included.
where nn stands for the numeric value (00-99) for the number of
characters that will not be sent at the end of the message.
Syntax = E9nn
Insert a character multiple times
F4 Send “xx” character “nn” times in the output message, leaving the
cursor in the current position.
insert character’s hex value for its ASCII code, and nn is the numeric
value (00-99) for the number of times it should be sent.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4 for
decimal, hex and character codes.
Syntax = F4xxnn
where xx stands for the
Insert symbology name
B3 Insert the name of the bar code’s symbology in the output message,
without moving the cursor. Only symbologies with a Honeywell ID are
included (see Symbology Chart on page A-1).
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4 for
decimal, hex and character codes.
Insert bar code length
B4 Insert the bar code’s length in the output message, without moving the
cursor. The length is expressed as a numeric string and does not
include leading zeroes.
Move Commands
Move the cursor forward a number of characters
F5 Move the cursor ahead “nn” characters from current cursor position.
Syntax = F5nn
of characters the cursor should be moved ahead.
Move the cursor backward a number of characters
F6 Move the cursor back “nn” characters from current cursor position.
Syntax = F6nn
of characters the cursor should be moved back.
where nn is the numeric value (00-99) for the number
where nn is the numeric value (00-99) for the number
5 - 5
Page 90

Move the cursor to the beginning
F7 Move the cursor to the first character in the input message.
F7.
Syntax =
Move the cursor to the end
EA Move the cursor to the last character in the input message.
EA.
Syntax =
Search Commands
Search forward for a character
F8 Search the input message forward for “xx” character from the current
cursor position, leaving the cursor pointing to the “xx” character.
Syntax = F8xx
its ASCII code.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4
for decimal, hex and character codes.
Search backward for a character
F9 Search the input message backward for “xx” character from the current
cursor position, leaving the cursor pointing to the “xx” character.
Syntax = F9xx
its ASCII code.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4
for decimal, hex and character codes.
Search forward for a string
B0 Search forward for “s” string from the current cursor position, leaving
cursor pointing to “s” string. Syntax = B0nnnnS where nnnn is the string
length (up to 9999), and S consists of the ASCII hex value of each
character in the match string. For example, B0000454657374 will
search forward for the first occurrence of the 4 character string “Test.”
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4
for decimal, hex and character codes.
Search backward for a string
B1 Search backward for “s” string from the current cursor position, leaving
cursor pointing to “s” string. Syntax = B1nnnnS where nnnn is the string
length (up to 9999), and S consists of the ASCII hex value of each
character in the match string. For example, B1000454657374 will
search backward for the first occurrence of the 4 character string “Test.”
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4
for decimal, hex and character codes.
where xx stands for the search character’s hex value for
where xx stands for the search character’s hex value for
5 - 6
Page 91

Search forward for a non-matching character
E6 Search the input message forward for the first non-“xx” character from
the current cursor position, leaving the cursor pointing to the non-“xx”
character.
hex value for its ASCII code.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4 for
decimal, hex and character codes.
Syntax = E6xx
where xx stands for the search character’s
Search backward for a non-matching character
E7 Search the input message backward for the first non-“xx” character
from the current cursor position, leaving the cursor pointing to the non“xx” character.
character’s hex value for its ASCII code.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4 for
decimal, hex and character codes.
Syntax = E7xx
where xx stands for the search
Miscellaneous Commands
Suppress characters
FB Suppress all occurrences of up to 15 different characters, starting at the
current cursor position, as the cursor is advanced by other commands.
When the FC command is encountered, the suppress function is
terminated. The cursor is not moved by the FB command.
Syntax = FBnnxxyy . .zz where nn is a count of the number of
suppressed characters in the list, and xxyy .. zz is the list of characters
to be suppressed.
Stop suppressing characters
FC Disables suppress filter and clear all suppressed characters.
FC.
Replace characters
E4 Replaces up to 15 characters in the output message, without moving
the cursor. Replacement continues until the E5 command is
encountered.
count of the number of characters in the list (characters to be replaced
plus replacement characters); xx
and xx
zz
.
2
Syntax = E4nnxx1xx2yy1yy2...zz1zz
defines characters to be replaced
defines replacement characters, continuing through zz1 and
2
1
where nn is the total
2
Stop replacing characters
E5 Terminates character replacement.
Syntax = E5.
Syntax =
5 - 7
Page 92

Compare characters
Data Formatter Off
FE Compare the character in the current cursor position to the character
“xx.” If characters are equal, move the cursor forward one position.
Syntax = FExx
value for its ASCII code.
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4
for decimal, hex and character codes.
where xx stands for the comparison character’s hex
Compare string
B2 Compare the string in the input message to the string “s.” If the strings
are equal, move the cursor forward past the end of the string. Syntax
= B2nnnnS where nnnn is the string length (up to 9999), and S consists
of the ASCII hex value of each character in the match string. For
example, B2000454657374 will compare the string at the current
cursor position with the 4 character string “Test.”
Refer to the ASCII Conversion Chart (Code Page 1252) on page A-4
for decimal, hex and character codes.
Check for a number
EC Check to make sure there is an ASCII number at the current cursor
position. The format is aborted if the character is not numeric.
Check for non-numeric character
ED Check to make sure there is a non-numeric ASCII character at the
current cursor position. The format is aborted if the character is
numeric.
Insert a delay
EF Inserts a delay of up to 49,995 milliseconds (in multiples of 5), starting
from the current cursor position. Syntax = EFnnnn where nnnn stands
for the delay in 5ms increments, up to 9999. This command can only
be used with keyboard wedge interfaces.
Data Formatter
When Data Formatter is turned Off, the bar code data is output to the host as
read, including prefixes and suffixes.
You may wish to require the data to conform to a data format you have created
and saved. The following settings can be applied to your data format:
Data Formatter On, Not Required, Keep Prefix/Suffix
Scanned data is modified according to your data format, and prefixes and
suffixes are transmitted.
5 - 8
Page 93

Data Formatter On, Not Required, Drop Prefix/Suffix
* Data Formatter On,
Not Required,
Keep Prefix/Suffix
Data Formatter On,
Not Required,
Drop Prefix/Suffix
Data Format Required,
Keep Prefix/Suffix
Data Format Required,
Drop Prefix/Suffix
Scanned data is modified according to your data format. If a data format is
found for a particular symbol, those prefixes and suffixes are not
transmitted.
Data Format Required, Keep Prefix/Suffix
Scanned data is modified according to your data format, and prefixes and
suffixes are transmitted. Any data that does not match your data format
requirements generates an error tone and the data in that bar code is not
transmitted. If you wish to process this type of bar code without generating
an error tone, see Data Format Non-Match Error Tone.
Data Format Required, Drop Prefix/Suffix
Scanned data is modified according to your data format. If a data format is
found for a particular symbol, those prefixes and suffixes are not
transmitted. Any data that does not match your data format requirements
generates an error tone. If you wish to process this type of bar code without
generating an error tone, see Data Format Non-Match Error Tone.
Choose one of the following options.
Default = Data Formatter On, Not
Required, Keep Prefix/Suffix.
Data Format Non-Match Error Tone
When a bar code is encountered that doesn’t match your required data format, the scanner normally generates an error tone. However, you may
want to continue scanning bar codes without hearing the error tone. If you
scan the Data Format Non-Match Error Tone Off bar code, data that
doesn’t conform to your data format is not transmitted, and no error tone
5 - 9
Page 94

will sound. If you wish to hear the error tone when a non-matching bar
* Data Format Non-Match Error
Tone On
Data Format Non-Match
Error Tone Off
Primary Data Format
Data Format 1
Data Format 2
Data Format 3
code is found, scan the Data Format Non-Match Error Tone On bar code.
Default = Data Format Non-Match Error Tone On
.
Primary/Alternate Data Formats
You can save up to four data formats, and switch between these formats. Your
primary data format is saved under 0. Your other three formats are saved under
1, 2, and 3. To set your device to use one of these formats, scan one of the bar
codes below.
Single Scan Data Format Change
You can also switch between data formats for a single scan. The next bar
code is scanned using an alternate data format, then reverts to the format
you have selected above (either Primary, 1, 2, or 3).
5 - 10
Page 95

For example, you may have set your device to the data format you saved as
Single Scan-Data Format 1
Single Scan-Data Format 2
Single Scan-Data Format 3
Single Scan-Primary
Data Format
Data Format 3. You can switch to Data Format 1 for a single button press
by scanning the Single Scan-Data Format 1 bar code below. The next bar
code that is scanned uses Data Format 1, then reverts back to Data Format
3.
5 - 11
Page 96

5 - 12
Page 97

6
All Symbologies On
All Symbologies Off
Symbologies
This programming section contains the following menu selections. Refer to
Chapter 9 for settings and defaults.
• All Symbologies • GS1-128
• Airline Code 5 - see Straight 2 of 5
IATA (two-bar start/stop)
• China Post (Hong Kong 2 of 5) • ISBT 128
• Codabar • Matrix 2 of 5
• Code 11 • MSI
• Code 128 • NEC 2 of 5
• Code 32 Pharmaceutical (PARAF) • Plessey Code
• Code 39 • Postal Codes
• Code 93
•EAN/JAN-13
• EAN/JAN-8 • Telepen
• GS1 DataBar Expanded • Trioptic Code
• GS1 DataBar Limited • UPC-A
• GS1 DataBar Omnidirectional
• GS1 Emulation • UPC-E0
• Interleaved 2 of 5
• Straight 2 of 5 IATA (two-bar start/
stop)
• Straight 2 of 5 Industrial (three-bar
start/stop)
• UPC-A/EAN-13 with Extended
Coupon Code
All Symbologies
If you want to decode all the symbologies allowable for your scanner, scan the
All Symbologies On
particular symbology, scan All Symbologies Off followed by the On symbol for
that particular symbology.
code. If on the other hand, you want to decode only a
6 - 1
Page 98

Message Length Description
You are able to set the valid reading length of some of the bar code symbologies. If the data length of the scanned bar code doesn’t match the valid reading length, the scanner will issue an error tone. You may wish to set the same
value for minimum and maximum length to force the scanner to read fixed
length bar code data. This helps reduce the chances of a misread.
EXAMPLE: Decode only those bar codes with a count of 9-20 characters.
EXAMPLE: Decode only those bar codes with a count of 15 characters.
For a value other than the minimum and maximum message length defaults,
scan the bar codes included in the explanation of the symbology, then scan the
digit value of the message length and Save bar codes on the Programming
Chart inside the back cover of this manual. The minimum and maximum
lengths and the defaults are included with the respective symbologies.
Min. length = 09Max. length = 20
Min. length = 15Max. length = 15
6 - 2
Page 99

Codabar
* On
Off
Transmit
* Don’t Transmit
<Default All Codabar Settings>
Codabar On/Off
Codabar Start/Stop Characters
Start/Stop characters identify the leading and trailing ends of the bar code.
You may either transmit, or not transmit Start/Stop characters.
Default = Don’t Transmit
.
Codabar Check Character
Codabar check characters are created using different “modulos.” You can
program the scanner to read only Codabar bar codes with Modulo 16, Modulo 7 CD, or CLSI check characters.
No Check Character
code data with or without a check character.
When Check Character is set to
only read Codabar bar codes printed with a check character, and will transmit this character at the end of the scanned data.
indicates that the scanner reads and transmits bar
Default = No Check Character.
Validate and Transmit
, the scanner will
6 - 3
Page 100

When Check Character is set to
* No Check Character
Validate Modulo 16
and Transmit
Validate Modulo 16, but
Don’t Transmit
Validate Modulo 7 CD, but Don’t
Transmit
Validate CLSI, but Don’t
Transmit
Validate Modulo 7 CD and
Transmit
Validate CLSI and Transmit
only read Codabar bar codes printed
Validate, but Don’t Transmit
with
a check character, but will not
transmit the check character with the scanned data.
, the unit will
Codabar Concatenation
Codabar supports symbol concatenation. When you enable concatenation, the scanner looks for a Codabar symbol having a “D” start character,
adjacent to a symbol having a “D” stop character. In this case the two messages are concatenated into one with the “D” characters omitted.
6 - 4
A12 3 4D
D5 6 7 8 A
 Loading...
Loading...