62-0413-02
MCSS/MCSP Current Switches
CAUTION
WARNING
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
Risk of electrical shock.
Can cause severe injury, property damage or
death.
Disconnect and lock out all power sources before
installation as severe injury or death may result from
electrical shock due to contact with high voltage wires.
Never rely on the LED’s of the MCSS-A/MCSP-A to
determine whether power is present at the current
switch. The Red LED will indicate whether the current
is above the adjustable trip point. The Blue LED will
indicate that the current is below the adjustable trip
point.
The MCSS-A and MCSP-A Current Switches should be used
on Insulated Conductors Only! The current switch may be
mounted in any position using the (2) #8 x 3/4” Tek screws and
the mounting holes in the base. Leave a minimum distance of
INSTALLATION
Make sure that all installations are in compliance with all
national and local electrical codes. Only qualified individuals
that are familiar with codes, standards, and proper safety
procedures for high-voltage installations should attempt
installation. The current switches will not require external
power, since the power for the current switch is induced from
the conductor being monitored.
1” (3 cm) between the current switch and any other magnetic
devices such as contactors and transformers.
For applications in which the normal operating current is
below the 0.32Amps (MCSS-A) or 0.70Amps (MCSP-A) trip
point (See Figure 5 below), the conductor being monitored
may be looped through the sensor 6 times giving you a total
operating current of 6X the original current. Example: A small
fan operating at 0.2A should be wrapped through the sensor 7
times to give you a total operating current of 1.4 Amps flowing
through the MCSS-A or MCSP-A.
This product is not intended to be used for Life or
Safety applications.
This product is not intended for use in any
hazardous or classified locations.
For applications in which the normal operating current is
greater than 150 Amps or for conductor diameters larger than
0.530” (1.35 cm) in diameter, an external 5 Amp Current
Transformer (5A CT) must be used as shown in Figure 6
below. Remember that the secondary of the 5A CT must be
shorted together before the power may be turned onto the
monitored device.
MCSS/MCSP CURRENT SWITCHES
M33395
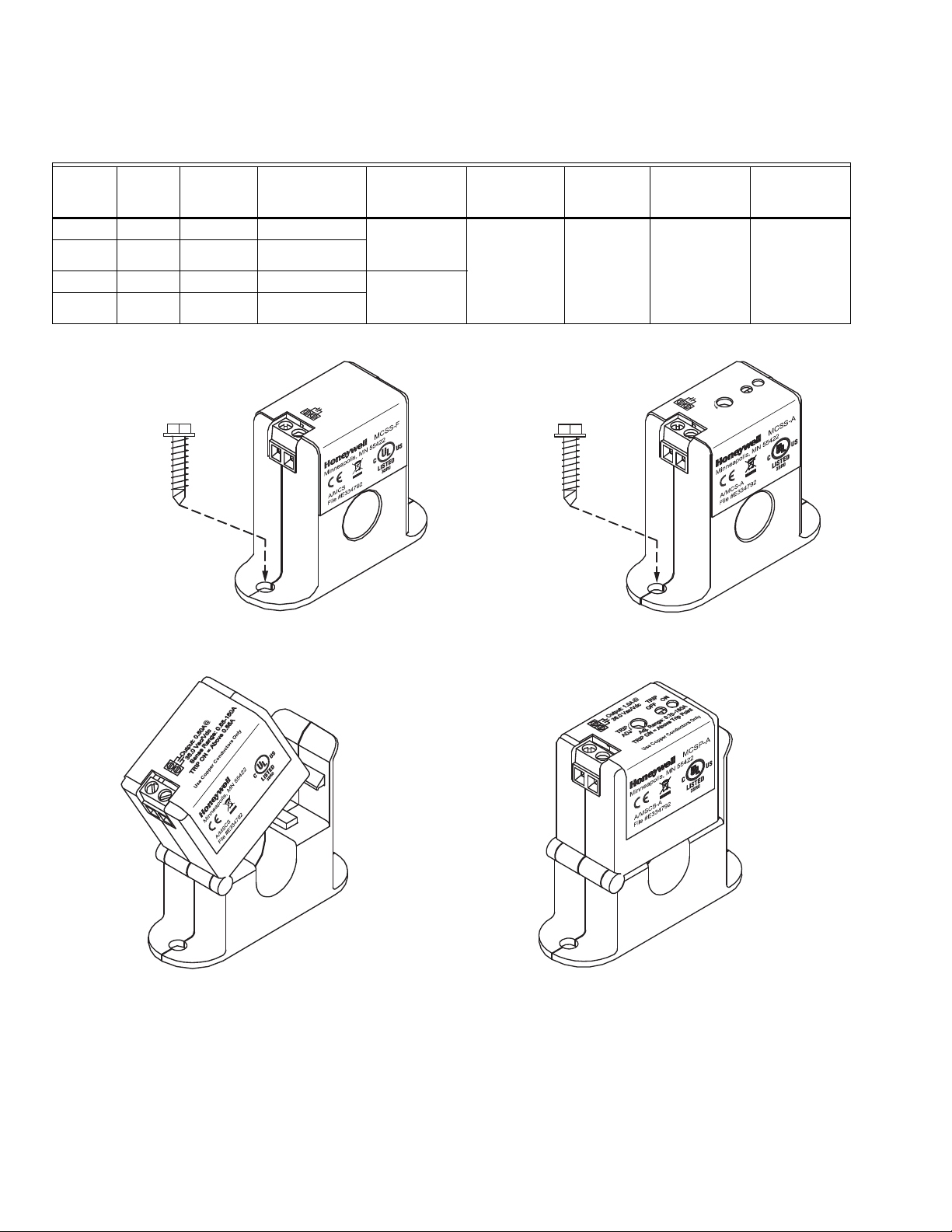
NUMBER 8 X 3/4 (19) TEK SCREW
(QUANITY 2 PER UNIT)
Use Copper Conductors Only
Output: 0.5A@
36.0 Vac/V
DC
Sense Range: 0.2-150A
TRIP ON = Above 0.2A
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1. Operating specifications.
Core
Model
Typ e
MCSS-F Solid Fixed < 0.20 Amps 0.50 Amp
MCSP-F Split Fixed < 0.55 Amps
MCSS-A Solid Adjustable 0.32 - 150 Amps 1.00 Amp
MCSP-A Split Adjustable 0.70 - 150 Amps
Switch
Type Trip Point
Output
Switch Rating
@ 36 VAC/
VDC
@ 36 VAC/
VDC
Max. Sensing
Current
Voltage
Max.
Continuous
Current
Max. Current
for
6 seconds
Max. Current
1 second
600 VAC 158 Amps 240 Amps 600 Amps
TRIP
OFF ON
Output: 1.0A@
NUMBER 8 X 3/4 (19) TEK SCREW
(QUANITY 2 PER UNIT)
36.0 Vac/Vdc
TRIP
ADJ
TRIP ON = Above Trip Point
Adj. Range: 0.32-150A
Use Copper Conductors Only
for
Fig. 1. MCSS-F
MCSP-F
Fig. 2. MCSP-F
M33397
Fig. 3. MCSS-A
M33398
M33396
Fig. 4. MCSP-A
62-0413—02 2

INSULATED
M33402
DDC CONTROLLER
RELAY/
CONTACTOR
TRANSFORMER
DI
STATUS
DO
(RELAY COIL OR
CONTACTOR)
24 VAC COIL
24 VAC
120 VAC
LINE
CONDUCTOR
MCSS/MCSP CURRENT SWITCHES
M33399
Fig. 5. Wires through sensors.
600:5 RATIO 5A C.T.
WIRE NUT
Fig. 6. Using a current transformer.
WIRING
Honeywell recommends the use of a two conductor 16 to 22
AWG shielded cable or twisted pair copper wire only for all
current switch applications. A maximum wire length of less
than 30 meters (98.4 feet) should be used between the
MCSS-A and MCSP-A current switches and the Building
Management System or controller.
NOTE: When using a shielded cable, be sure to connect
only one (1) end of the shield to ground at the
controller. Connecting both ends of the shield to
ground may cause a ground loop.
When removing the shield from the sensor end, make sure to
properly trim the shield so as to prevent any chance of
shorting. The current switch output terminals represent a
solid-state switch for controlling both AC and DC loads and is
not polarity sensitive. The recommended torque to be used on
the terminal block connections is 0.67 Nm or 5.93 in-lbs.. The
aperture (hole) size of the current switch is 0.53” (1.35 cm)
and will accept a 1 AWG maximum wire diameter.
See Figure 7 and Figure 8 for two different current switch
applications using your Building Management System (DDC/
PLC Controller). Figure 7 is showing the use of the Go/No Go
Current Switch as a Digital Input to your DDC Controller,
whereas Figure 8 is showing you how to use the Go/No Go
Current Switch in conjunction with your building management
system to control a fan or pump for example.
M33400
DIGITAL INPUT 1
BUILDING
MANAGEMENT
SYSTEM
M33401
Fig. 7. Digital circuit.
Fig. 8. Analog circuit.
3 62-0413—02

MCSS/MCSP CURRENT SWITCHES
Calibration of Adjustable Trip Point (MCSS-A, MCSP-A models only)
The adjustable current switch has an operating range of 0-150
Amps. Do not exceed! The adjustable current switch comes
with its fifteen-turn adjustment potentiometer set to the 100
Amp trip point position. The adjustable current switch can be
used to monitor Under Load, Normal Load, and Over Load
conditions, depending on how it’s set. The procedure below is
for the Normal load condition for part numbers MCSS-A &
MCSP-A.
Table 2. Troubleshooting.
Problem Solution
Red LED is on but the current switch didn’t
activate( -A models)
Current switch didn’t activate( - F models)
Red LED didn’t turn on and the current switch
didn’t activate (- A models)
Current switch didn’t activate ( -F models)
Sensor doesn't switch at all, regardless of
current level. (-A models)
Disconnect the wires from the current switch output. Measure the
resistance across the contacts with an Ohmmeter.
Verify that the conductor you are monitoring is above the adjustable trip point. If
the sensor is monitoring less than the minimum trip point, see Fig. 5.
Adjustment potentiometer is probably set to its maximum or minimum
position. Turn the Pot counter-clockwise all the way and verify if the
LED switches from Red to Blue.
Normal Loads (MCSS-A, MCSP-A models only)
With current flowing through the aperature of the MCSS-A and
MCSP-A current switches, first verify that the Blue LED is on.
If the Blue LED is on, now slowly adjust the potentiometer
clockwise until the Red LED just turns on and stop
immediately. This will set the trip point at your normal
operating load current. If the RED LED is on after initial power
up, this means that you will need to slowly adjust the
potentiometer counter-clockwise until the Blue LED turns on
and then slowly adjust the potentiometer clockwise until the
Red LED just turns on and stop immediately. The adjustable
current switch is now tripped. Now verify the output with an
Ohmmeter to verify that the contacts of the switch are
approximately 0.200 Ohms. The adjustable current switch
Hysteresis (Dead Band) is typically 10% of the trip point.
By using this Honeywell literature, you agree that Honeywell will have no liability for any damages arising out of your use or modification to,
the literature. You will defend and indemnify Honeywell, its affiliates and subsidiaries, from and against any liability, cost, or damages,
including attorneys’ fees, arising out of, or resulting from, any modification to the literature by you.
Automation and Control Solutions
Honeywell International Inc.
® U.S. Registered Trademark
© 2012 Honeywell International Inc.
62-0413—02 M.S. 07-12
Printed in United States
 Loading...
Loading...