Holden Commodore Common Mazda 2005 User Manual
Diesel Injection Pump
SERVICE MANUAL
New Common Rail System (HP3)
for MAZDA
OPERATION
June, 2005
00400517E

© 2005 DENSO CORPORATION
All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced
or copied, in whole or in part, without the written
permission of the publisher.

Table of Contents
Table of Contens
Operation Section
1. PRODUCT APPLICATION INFORMATION
1.1 Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.2 Application. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.3 System Components Parts Number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
2. OUTLINE OF SYSTEM
2.1 Outline of Composition and Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
3. SUPPLY PUMP
3.1 Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
3.2 Explode View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
3.3 SCV (Suction Control Valve) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
4. RAIL
4.1 Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
5. INJECTOR
5.1 Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
5.2 Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
5.3 Construction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
5.4 QR Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
6. OPERATION OF CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
6.1 Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
6.2 Engine ECU (Electronic Control Unit) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
6.3 Operation of Sensors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-12
7. CONTROL SYSTEM
7.1 Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14
7.2 Fuel Injection Timing Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-16
8. DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)
8.1 About the Codes Shown in the Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
8.2 Diagnostic Trouble Code Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
9. EXTERNAL WIRING DIAGRAM
9.1 Engine ECU External Wiring Diagram (Model Name: MAZDA 5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-33
9.2 Engine ECU External Wiring Diagram (Model Name: MAZDA 6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-37
1–1
Operation Section
1. PRODUCT APPLICATION INFORMATION
1.1 Outline
z The common rail system for the MZR-CD engine has been newly installed in the Mazda 5 and Mazda 6. The contents for the common
rail system are basically the same as those published in the previous Service Bulletin, "S/B Code: ECD02-06, Subject: New Common
Rail System (ECD-U2P) for Mazda." The two major points that have changed for this system are the addition of the DPF system, and
injectors equipped with the QR code. Please be sure to use this Service Manual together with the Service Bulletin as this edition ex-
plains only points that have changed.
1.2 Application
Model Name Engine Destination Line Off Period
MAZDA 5
MZR-CD Europe
MAZDA 6 April, 2005
March, 2005
1.3 System Components Parts Number
Parts Name DENSO P/N Manufacturer P/N Remarks
275800-6401 RF7J 18 881B MAZDA 6
Engine ECU
Turbo pressure sensor (MAPS) 079800-7440 RF7J 18 211
Injector 095000-5780 RF7J 13 H50
Crankshaft position sensor (NE) 949979-0200 RF7J 18 221
Cylinder recognition sensor (TDC) 949979-1520 RF7J 18 230
Rail 095440-0740 RF7J 13 GC0
Rail pressure sensor 499000-6210 —
Pressure limiter 095420-0201 —
Supply pump 294000-0420 RF7J 13 800A
Suction control valve 294200-0160 —
Fuel temperature sensor 179730-0020 RF1L 18 840
Mass air flow meter 197400-2010 ZL01 13 215
275800-6441 RF7K 18 881B MAZDA 6 High Output Engine
275800-6450 RF7N 18 881A MAZDA 5
275800-6460 RF7P 18 881A MAZDA 5 High Output Engine
Coolant temperature sensor 179700-0220 B593 18 840A
Engine compartment temperature sensor 170400-6020 BP4W 18 845
Exhaust temperature sensor 1
Exhaust temperature sensor 2
265600-1050 RF7N 18 7G0 MAZDA 6
265600-1090 RF7K 18 7G0A MAZDA 5
265600-1060 RF7P 18 7G0 MAZDA 6
265600-1080 RF7J 18 7G0A MAZDA 5

Operation Section
Parts Name DENSO P/N Manufacturer P/N Remarks
1–2
Exhaust temperature sensor 3
265600-1070 RF7R 18 7G0 MAZDA 6
265600-1101 RF7L 18 7G0C MAZDA 5
A/F sensor (UHEGO) 211200-4260 RF7N 18 8G1
104990-1160 RF7N 18 2B5 MAZDA 6
Differential pressure sensor
104990-1150 RF7J 18 2B5 MAZDA 5
198800-3480 CC30 41 600
198800-3490 CC34 41 600
198800-3400 GR1L 41 600A
Accele pedal module
198800-3410 GR1M 41 600A
198800-3440 GR3D 41 600A
198800-3450 GR3E 41 600A
MAZDA 6
MAZDA 5
1–3
Operation Section
2. OUTLINE OF SYSTEM
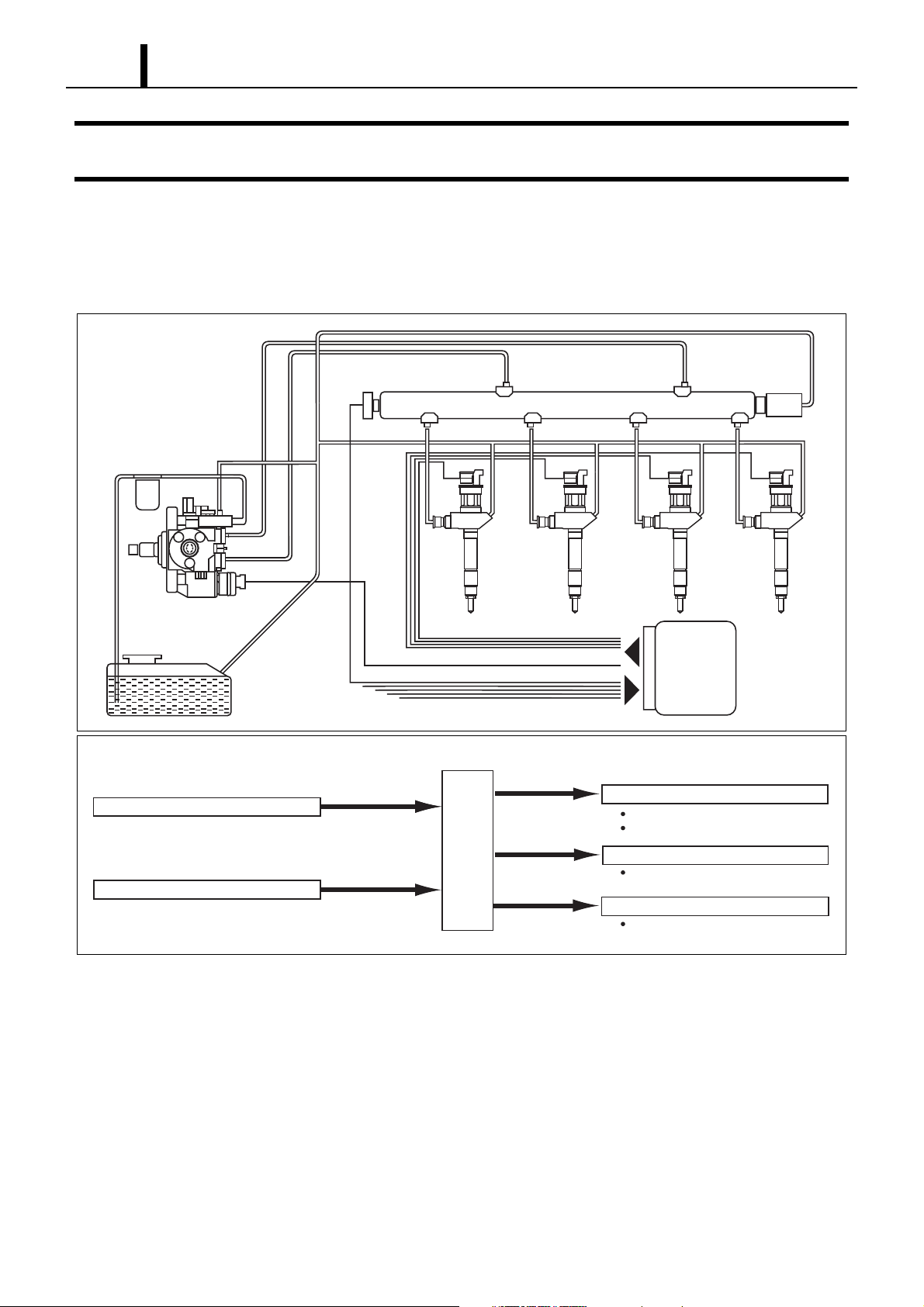
2.1 Outline of Composition and Operation
z This system is basically the same as that in Service Bulletin ECD02-06. However the EDU has been discontinued. Please refer to the
Service Bulletin for Operation.
Fuel filter
Supply pump
Fuel tank
Sensors
Engine speed sensor
Other sensors and switches
Fuel pressure
sensor
Various
sensors
Engine Speed
Engine
ECU
Pressure
limiter
Rail
Injector
Engine
ECU
Q001109E
Actuators
Injector
Fuel injection quantity control
Injection timing control, etc.
Supply pump
Fuel pressure control
Other actuators
EMS control
Q001110E
Operation Section
1–4
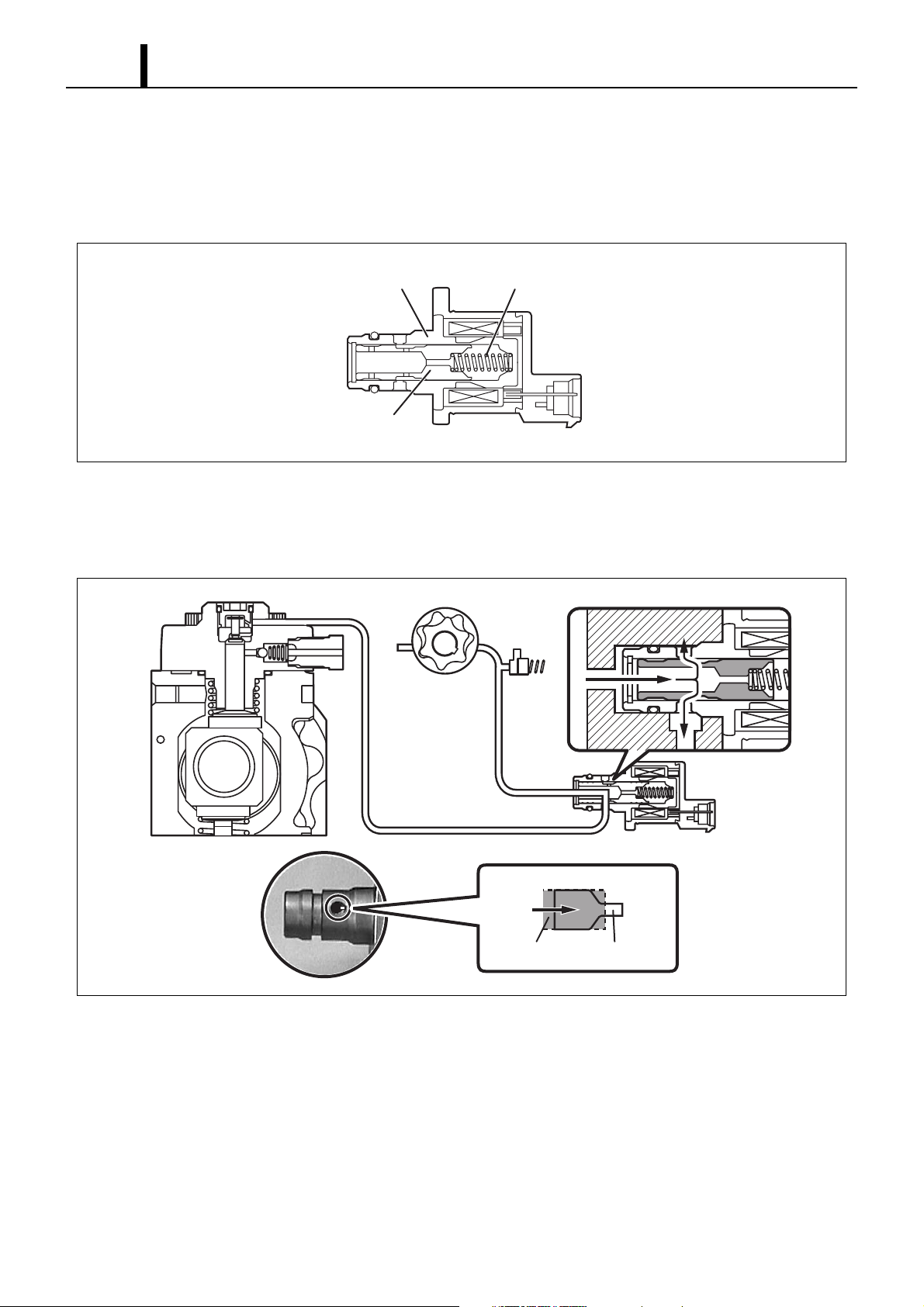
3. SUPPLY PUMP
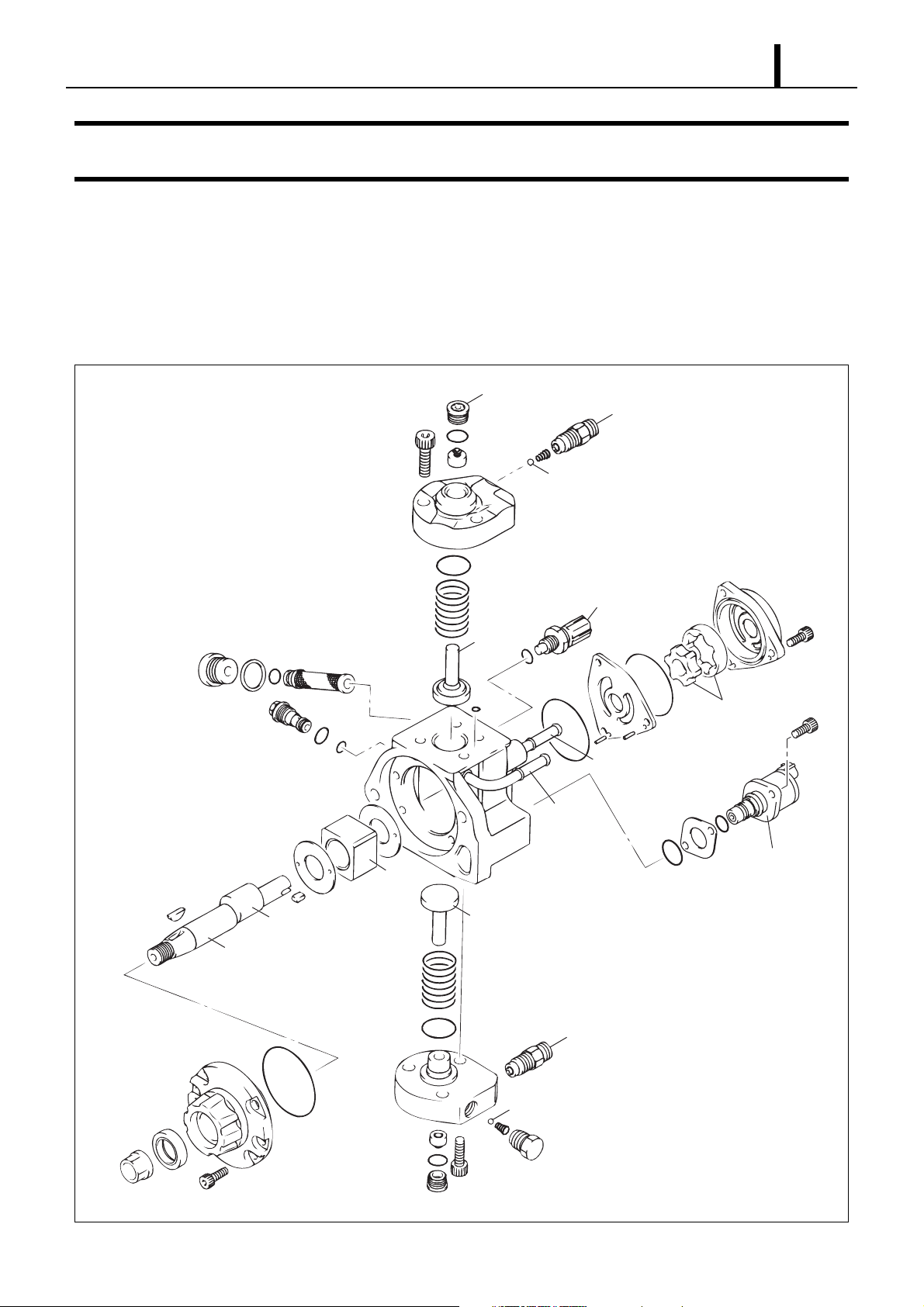
3.1 Outline
z The HP3 supply pump comes with the compact SCV (Suction Control Valve) installed. Please refer to Service Bulletin ECD02-06 as
only the SCV has changed.
3.2 Explode View
Suction valve
Discharge outlet
Delivery valve
Eccentric cam
Camshaft
Ring cam
Fuel temperature
sensor
Plunger
Feed pump
Fuel suction inlet
Overflow
fuel outlet
Suction control
valve (SCV)
Plunger
Discharge outlet
Delivery valve
Q001112E
1–5
Operation Section
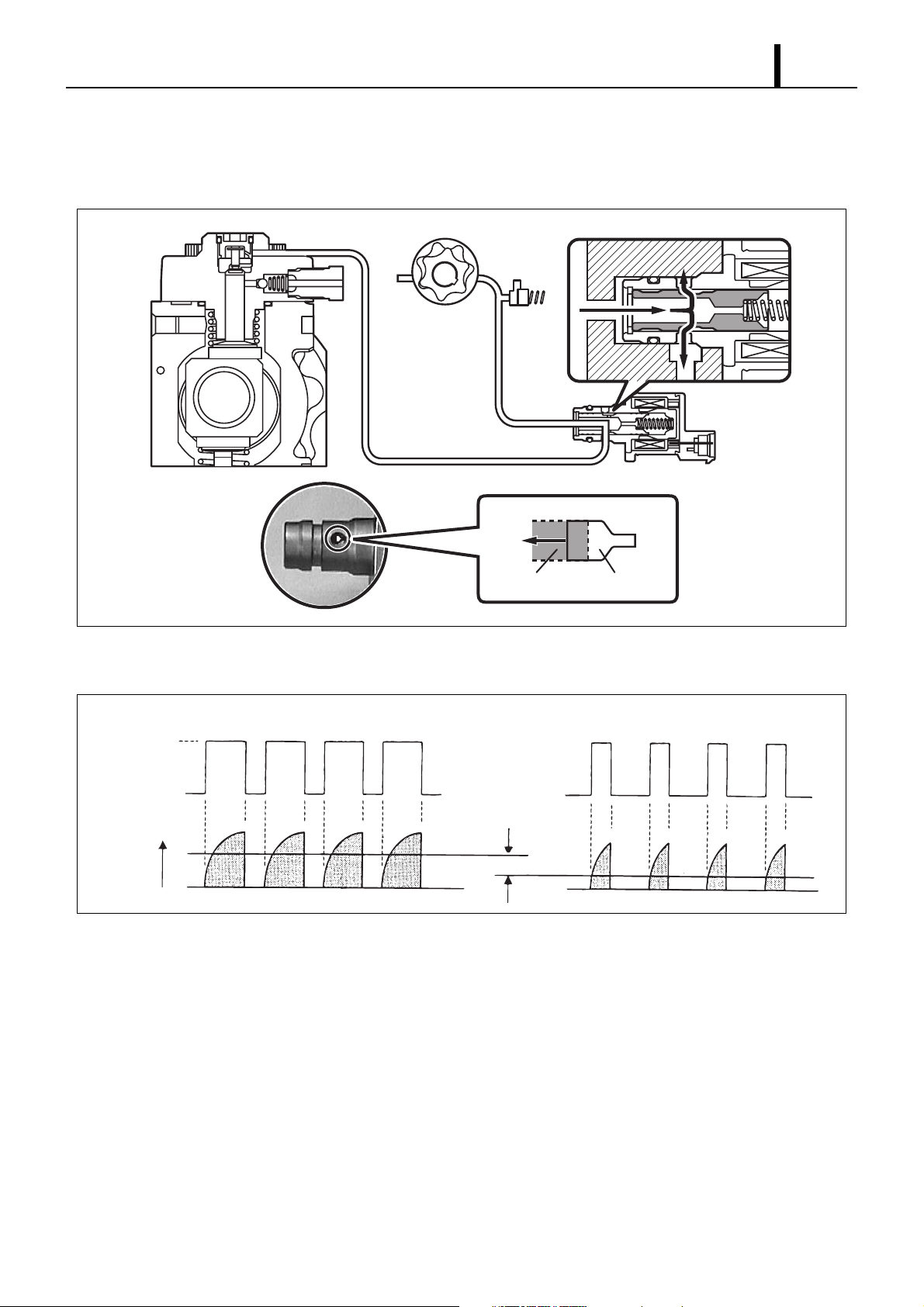
3.3 SCV (Suction Control Valve)
z A linear solenoid type solenoid valve has been adopted. The length of time in which the ECU applies current to the SCV is controlled
(duty cycle control) in order to regulate the volume of suction of fuel into the pumping area. Because only the volume of fuel that is
required by the target rail pressure is drawn in, the drive load on the supply pump decreases, thus resulting in improved fuel economy.
Valve body
Needle valve
Return Spring
Q001113E
(1) SCV Opening Small (Duty ON time long - Refer to the "Relationship Between Actuation
Signal and Current" Diagram.)
• When the opening of the SCV is small, the fuel suction area is kept small, which decreases the transferable fuel volume.
Feed Pump
Needle valve Small Opening
Q001114E
Operation Section
1–6
(2) SCV Opening Large (Duty ON time short - Refer to the "Relationship Between Actuation
Signal and Current" Diagram.)
• When the opening of the SCV is large, the fuel suction area is kept large, which increases the transferable fuel volume.
Feed Pump
Needle valve Large Opening
Q001115E
(3) Diagram of Relationship Between Actuation Signal and Current (Magnetomotive Force)
Small Suction Volume Large Suction Volume
ON
Actuation
Voltage
OFF
Current
Average Current Difference
Q001116E
1–7
Operation Section
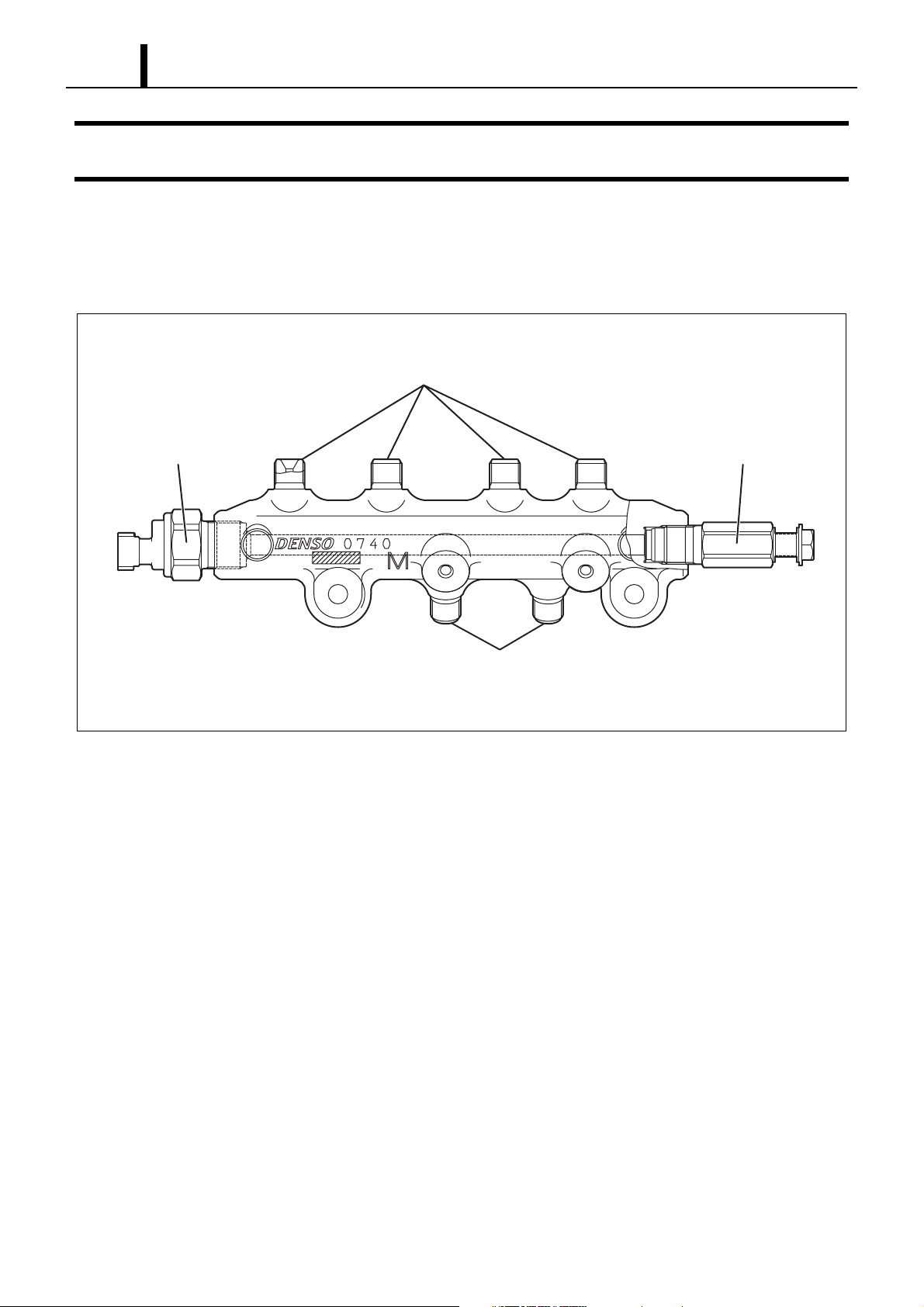
4. RAIL
4.1 Outline
z Although the characteristics of both the Fuel Pressure Sensor and Pressure limiter have not changed, the shape of the Rail Pressure
Sensor has been altered. Please refer to Service Bulletin ECD02-06.
To injector
Rail pressure sensor Pressure limiter
From supply pump
Q001117E
Operation Section
1–8
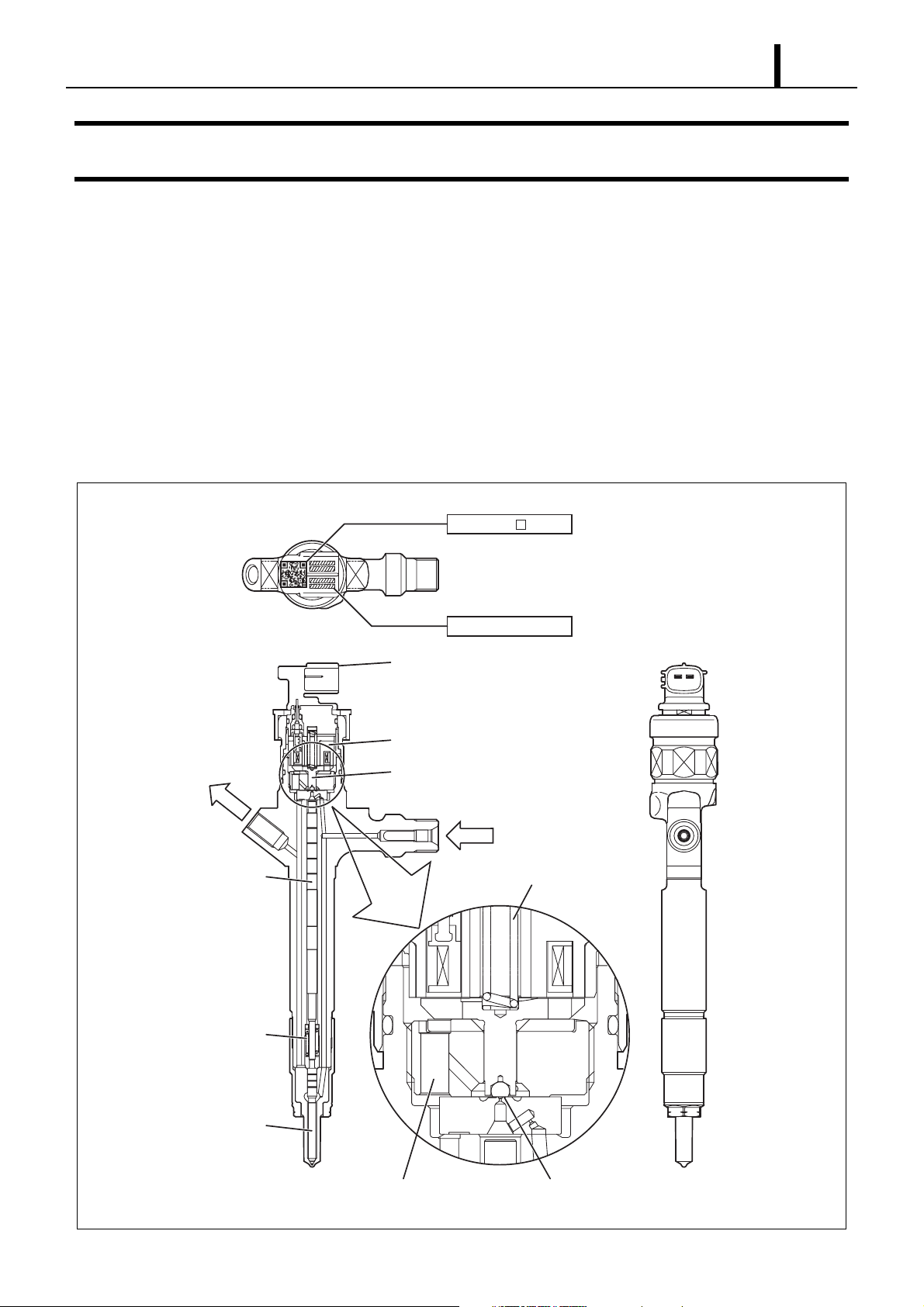
5. INJECTOR
5.1 Outline
z The injectors inject the high-pressure fuel from the rail into the combustion chambers at the optimum injection timing, rate, and spray
condition in accordance with the commands received from the ECU. In addition, the correction resistor has been discontinued and
replaced by a QR code injector.
5.2 Characteristics
z A compact, energy-saving, solenoid-control type TWV (Two-Way Valve) injector has been adopted.
5.3 Construction
To fuel tank
Command position
QR Codes ( 9.9mm)
Connector
Solenoid valve
TWV
High-pressure fuel
(from rail)
ID Codes
Valve spring
Nozzle spring
Nozzle needle
Seat areaLeak passage
Q001118E
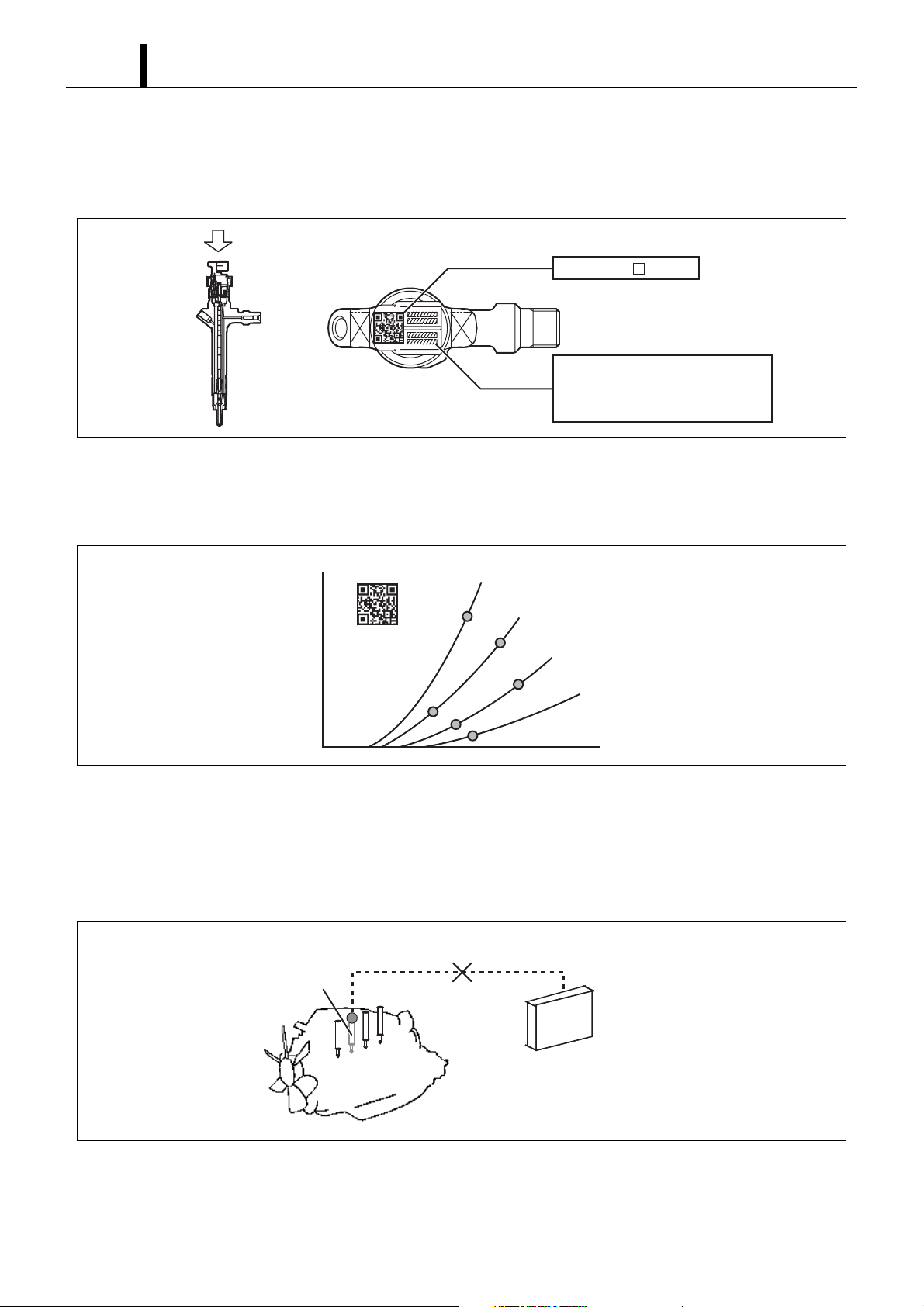
1–9
Operation Section
5.4 QR Codes
z Conventionally the whole injector Ass'y was replaced during injector replacement, but QR (Quick Response) codes have been adopted
to improve injector quantity precision.
QR Codes ( 9.9mm)
ID Codes (30 base 16 characters)
Base 16 characters noting fuel
injection quantity correction
information for market service use
z QR codes have resulted in a substantial increase in the number of fuel injection quantity correction points, greatly imimproving pre-
cision. The characteristics of the engine cylinders have been further unified, contributing to improvements in combustion efficiency,
reductions in exhaust gas emissions and so on.
Q001119E
Injection Quantity Q
QR Codes
Actuating Pulse Width TQ
Q001132E
(1) Repair Procedure Changes (Reference)
• When replacing injectors with QR codes, or the engine ECU, it is necessary to record the ID codes in the ECU. (If the ID codes for
the installed injectors are not registered correctly, engine failure such as rough idling and noise will result). The ID codes will be reg-
istered in the ECU at a MAZDA dealer using approved MAZDA tools.
Replacing the Injector
"No correction resistance, cannot be detected electrically"
Replaced injector
Engine ECU
* Injector ID code must be registered with the engine ECU
Q001133E

Replacing the Engine ECU
"No correction resistance, cannot be detected electrically"
Vehicle injectors
Operation Section
1–10
Replaced engine ECU
* Injector ID code must be registered with the engine ECU
Q001134E
1–11
Operation Section
6. OPERATION OF CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
6.1 Outline
z The EDU (Electronic Driving Unit) functions have been built into the Engine ECU (Electronic Control Unit). Therefore the EDU has
been done away with. In addition the system sensor has been changed. Please refer to Service Bulletin ECD02-06 as only this sensor
has changed.
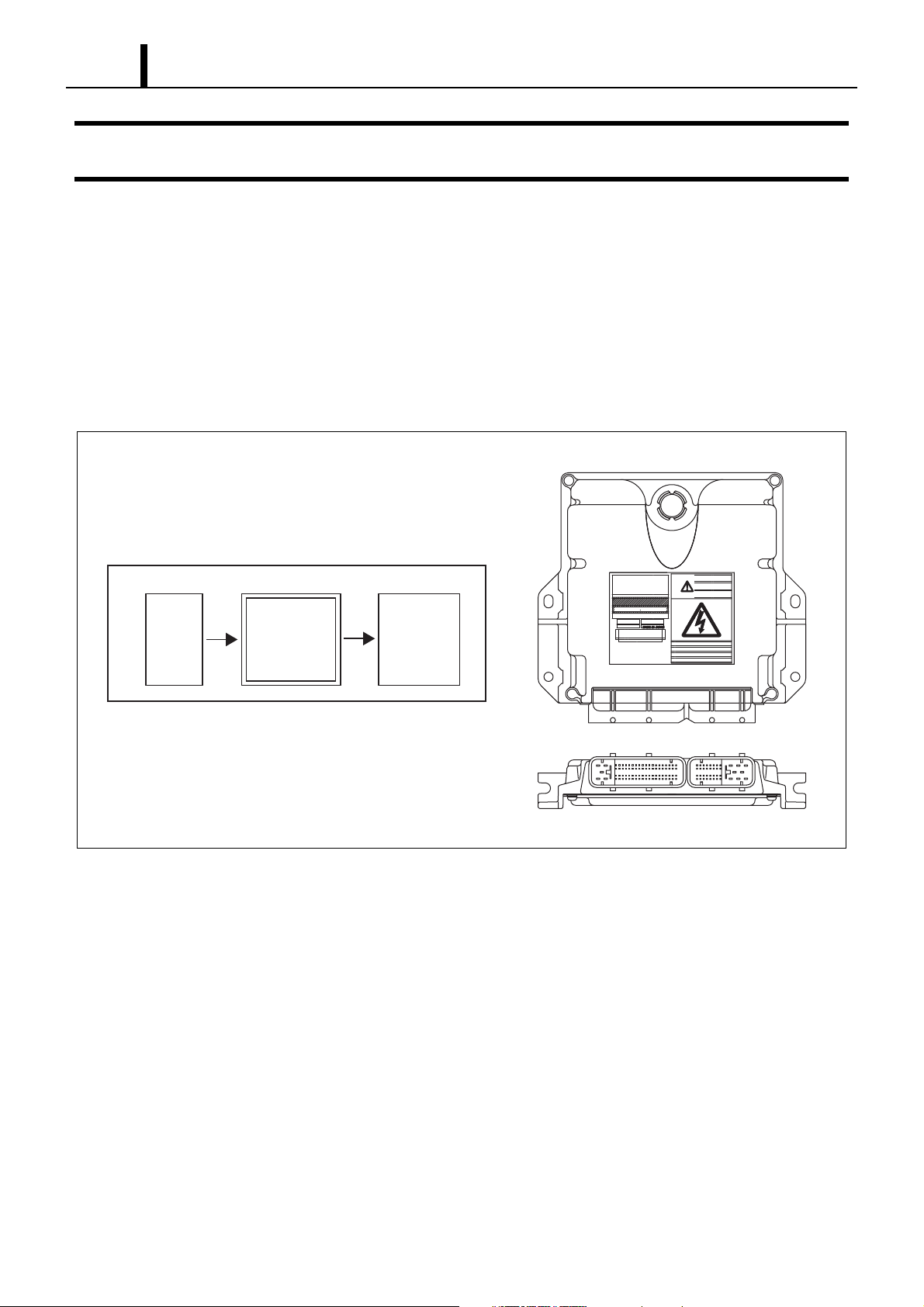
6.2 Engine ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
z This is the command center that controls the fuel injection system and the engine operation in general.
Sensor
Detection
<Outline Diagram>
Engine ECU
Calculation
Actuator
Actuation
Q001135E
 Loading...
Loading...