
WP-17
WP-17V
OM-225 427E/multi
2012−08
WP-17FV
WP-17F
WP-17V-PSH
WP-17-PSH
Hand-Held Air-Cooled TIG
(GTAW) Torches
Torches manuelles TIG refroidies
par air
Antorchas manuales enfriadas
por aire para TIG (GTAW)
ESPAÑOL FRANÇAIS ENGLISH
Owner’s Manual
Manuel de L’utilisateur
Manual del Operador
File: TIG (GTAW)


TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 −SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR GTAW TORCHES − READ BEFORE USING 1..............
1-1. Symbol Usage 1........................................................................
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards 1..................................................................
1-3. Proposition 65 Warnings 2...............................................................
1-4. Principal Safety Standards 2.............................................................
1-5. EMF Information 2......................................................................
SECTION 2 − SPECIFICATIONS 3................................................................
2-1. Specifications 3........................................................................
2-2. Duty Cycle 4...........................................................................
SECTION 3 − INSTALLATION 4..................................................................
3-1. Required Torch Parts And Torch Assembly 4................................................
3-2. International Style Connector Assembly 5..................................................
3-3. Connecting Torch 6.....................................................................
SECTION 4 − MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING 8...........................................
4-1. Routine Maintenance 8..................................................................
4-2. Troubleshooting 8......................................................................
SECTION 5 − SELECTING AND PREPARING A TUNGSTEN FOR DC OR AC WELDING 10..............
5-1. Selecting Tungsten Electrode (Wear Clean Gloves To Prevent Contamination Of Tungsten) 10.......
5-2. Preparing Tungsten Electrode For Welding With Phase Control Machines 10......................
SECTION 6 − GUIDELINES FOR TIG WELDING (GTAW) 11..........................................
6-1. Positioning The Torch 11..................................................................
6-2. Torch Movement During Welding 12........................................................
6-3. Positioning Torch Tungsten For Various Weld Joints 12........................................
SECTION 7 − PARTS LIST 13.....................................................................


SECTION 1 −SAFETY PRECAUTIONS FOR GTAW
TORCHES − READ BEFORE USING
WC000038 − 2011-10
Protect yourself and others from injury — read, follow, and save these important safety precautions and operating instructions.
1-1. Symbol Usage
DANGER! − Indicates a hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. The
possible hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols
or explained in the text.
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury. The possible
hazards are shown in the adjoining symbols or explained in the text.
NOTICE − Indicates statements not related to personal injury.
1-2. Arc Welding Hazards
The symbols shown below are used throughout this manual
to call attention to and identify possible hazards. When you
see the symbol, watch out, and follow the related instructions
to avoid the hazard. The safety information given below is
only a summary of the more complete safety information
found in the welding power source Owner’s Manual. Read
and follow all Safety Standards.
Only qualified persons should install, operate, maintain, and
repair this unit.
During operation, keep everybody, especially children, away.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Always wear dry insulating gloves.
Insulate yourself from work and ground.
Do not touch live electrode or electrical parts.
Before welding, verify torch head is firmly attached to the torch
body.
Do not wrap torch hoses and power cable together with tape or
plastic wire ties. Wrapping restricts water flow which may cause
power cable to overheat and torch hose to burst.
Repair or replace worn, damaged, or cracked torch or cable
insulation.
Turn off welding power source before changing tungsten elec-
trode or torch parts.
Keep all covers and handle securely in place.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin.
Arc rays from the welding process produce intense
visible and invisible (ultraviolet and infrared) rays
that can burn eyes and skin. Sparks fly off from the
weld.
Wear an approved welding helmet fitted with a proper shade of
filter lenses to protect your face and eyes from arc rays and
sparks when welding or watching (see ANSI Z49.1 and Z87.1
listed in Safety Standards).
Wear approved safety glasses with side shields under your
helmet.
Use protective screens or barriers to protect others from flash,
glare and sparks; warn others not to watch the arc.
Wear protective clothing made from durable, flame-resistant
material (leather, heavy cotton, or wool) and foot protection.
Indicates special instructions.
This group of symbols means Warning! Watch Out! ELECTRIC
SHOCK, MOVING PARTS, and HOT PARTS hazards. Consult symbols and related instructions below for necessary actions to avoid the
hazards.
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous.
Keep your head out of the fumes.
Ventilate area, or use breathing device.
Read Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) and manufacturer’s
instructions for material used.
BUILDUP OF GAS can injure or kill.
Shut off compressed gas supply when not in
use.
Always ventilate confined spaces or use ap-
proved air-supplied respirator.
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
Do not weld near flammable material.
Do not weld on containers that have held com-
bustibles, or on closed containers such as tanks, drums, or pipes
unless they are properly prepared according to AWS F4.1 and
AWS A6.0 (see Safety Standards).
Watch for fire; keep extinguisher nearby.
HOT PARTS can burn.
Allow torch to cool before touching.
Do not touch hot metal.
Protect hot metal from contact by others.
NOISE can damage hearing.
Check for noise level limits exceeding those
specified by OSHA.
Use approved ear plugs or ear muffs if noise level is high.
Warn others nearby about noise hazard.
READ INSTRUCTIONS.
Read and follow all labels and the Owner’s
Manual carefully before installing, operating,
or servicing unit. Read the safety information
at the beginning of the manual and in each
section.
Use only genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer.
Perform maintenance and service according to the Owner’s
Manuals, industry standards, and national, state, and local
codes.
OM-225 427 Page 1

1-3. Proposition 65 Warnings
Welding or cutting equipment produces fumes or gases
which contain chemicals known to the State of California to
cause birth defects and, in some cases, cancer. (California
Health & Safety Code Section 25249.5 et seq.)
This product contains chemicals, including lead, known to
the state of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after use.
1-4. Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, ANSI Standard Z49.1,
is available as a free download from the American Welding Society at
http://www.aws.org or purchased from Global Engineering Documents
(phone: 1-877-413-5184, website: www.global.ihs.com).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036 (phone: 212-642-4900, website: www.ansi.org).
Safe Practices for the Preparation of Containers and Piping for Welding
and Cutting, American Welding Society Standard AWS F4.1, from Glob-
al Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184, website: www.global.ihs.com).
Safe Practices for Welding and Cutting Containers that have Held Combustibles, American Welding Society Standard AWS A6.0, from Global
Engineering Documents (phone: 1-877-413-5184,
website: www.global.ihs.com).
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protection Association, Quincy, MA 02269 (phone: 1-800-344-3555, website:
www.nfpa.org and www. sparky.org).
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1,
from Compressed Gas Association, 14501 George Carter Way, Suite
103, Chantilly, VA 20151 (phone: 703-788-2700, website:
www.cganet.com).
This product contains or produces a chemical known to the
State of California to cause cancer or birth defects (or other
reproductive harm). (California Health & Safety Code Section
25249.5 et seq.)
Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes, CSA Standard
W117.2, from Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 5060
Spectrum Way, Suite 100, Ontario, Canada L4W 5NS (phone:
800-463-6727, website: www.csa-international.org).
Safe Practice For Occupational And Educational Eye And Face Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
25 West 43rd Street, New York, NY 10036 (phone: 212-642-4900, website: www.ansi.org).
Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot
Work, NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire Protection Association,
Quincy, MA 02269 (phone: 1-800-344-3555, website: www.nfpa.org.
OSHA, Occupational Safety and Health Standards for General Indus-
try, Title 29, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), Part 1910, Subpart Q,
and Part 1926, Subpart J, from U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Documents, P.O. Box 371954, Pittsburgh, PA 15250-7954
(phone: 1-866-512-1800) (there are 10 OSHA Regional Offices—
phone for Region 5, Chicago, is 312-353-2220, website:
www.osha.gov).
1-5. EMF Information
Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized electric
and magnetic fields (EMF). Welding current creates an EMF field
around the welding circuit and welding equipment. EMF fields may interfere with some medical implants, e.g. pacemakers. Protective measures for persons wearing medical implants have to be taken. For example, restrict access for passers−by or conduct individual risk assessment for welders. All welders should use the following procedures in order to minimize exposure to EMF fields from the welding circuit:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them, or using a
cable cover.
2. Do not place your body between welding cables. Arrange cables
to one side and away from the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cables around your body.
4. Keep head and trunk as far away from the equipment in the
welding circuit as possible.
5. Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as
possible.
6. Do not work next to, sit or lean on the welding power source.
7. Do not weld whilst carrying the welding power source or wire
feeder.
About Implanted Medical Devices:
Implanted Medical Device wearers should consult their doctor and the
device manufacturer before performing or going near arc welding, spot
welding, gouging, plasma arc cutting, or induction heating operations.
If cleared by your doctor, then following the above procedures is recommended.
OM-225 427 Page 2

SECTION 2 − SPECIFICATIONS
2-1. Specifications
Model
WP-17 WP-17V
Ampere Rating 150 Amps W/Argon Gas @ 60% Duty Cycle DCEN; 115 Amps W/Argon Gas @ 60% Duty Cycle ACHF
Cooling Method Air
Tungsten Size .020 Thru 1/8 in. (0.5 Thru 3.2 mm)
Cable Options 12.5 ft (3.8 m) Or 25 ft (7.6 m) One-Piece Rubber
12.5 ft (3.8 m) Or 25 ft (7.6 m) Two-Piece Rubber
ENGLISH
Dimensions Length: 7.5 in. (191 mm)
Handle Diameter: 7/8 in. (22 mm)
Weight: 6.1 oz (173 g)
Model
WP-17FV WP-17F
Ampere Rating 150 Amps W/Argon Gas @ 60% Duty Cycle DCEN; 115 Amps W/Argon Gas @ 60% Duty Cycle ACHF
Cooling Method Air
Tungsten Size .020 Thru 1/8 in. (0.5 Thru 3.2 mm)
Cable Options 12.5 ft (3.8 m) Or 25 ft (7.6 m) One-Piece Rubber
12.5 ft (3.8 m) Or 25 ft (7.6 m) Two-Piece Rubber
Dimensions Length: 9.75 in. (248 mm)
Handle Diameter: 7/8 in. (22 mm)
Weight: 9 oz (255 g)
Model
WP-17V-PSH WP-17-PSH
Length: 7.5 in. (191 mm)
Handle Diameter: 7/8 in. (22 mm)
Weight: 6.85 oz (194 g)
Length: 8 in. (203 mm)
Handle Diameter: 7/8 in. (22 mm)
Weight: 7.8 oz (221 g)
Ampere Rating 150 Amps W/Argon Gas @ 60% Duty Cycle DCEN; 115 Amps W/Argon Gas @ 60% Duty Cycle ACHF
Cooling Method Air
Tungsten Size .020 Thru 1/8 in. (0.5 Thru 3.2 mm)
Cable Options 12.5 ft (3.8 m) Or 25 ft (7.6 m) One-Piece Rubber
12.5 ft (3.8 m) Or 25 ft (7.6 m) Two-Piece Rubber
Dimensions Length: 7.5 in. (191 mm)
Handle Diameter: 7/8 in. (22 mm)
Weight: 7.05 oz (200 g)
Length: 7.5 in. (191 mm)
Handle Diameter: 7/8 in. (22 mm)
Weight: 6.15 oz (174 g)
OM-225 427 Page 3

2-2. Duty Cycle
0
10
Minutes
Definition
Duty Cycle is percentage of 10
minutes that torch can weld at
rated load without overheating.
NOTICE − Do not exceed rated amperage or duty cycle (see Section 2-1). Exceeding
rated amperage or duty cycle can damage torch and void warranty.
SECTION 3 − INSTALLATION
3-1. Required Torch Parts And Torch Assembly
60% Duty Cycle AT 150 Amperes DCEN Using Argon Gas
60%dutycycle
6 Minutes Welding 4 Minutes Resting
sb1.5* 8/93
4
3
2
1
12
1 Cup
2 Collet Body
3 Collet
4 Backcap (Includes O-Ring)
5 Torch Body
6 Handle
7 One-Piece Power Cable
8 Weldcraft QCS (Optional)
5
11
7
6
! Before welding, insure that the torch
head is firmly attached to the torch
body.
9 Power Cable Adapter
10 International Style Adapter
11 Gas Hose For International Style Ad-
apter
10
9
8
WC0205-A
Assembling Torch Body
Keep connections tight. Replace cup, heat
shield, and backcap as needed.
12 Tungsten Electrode (See Section 5)
Installing Tungsten
To adjust tungsten position, loosen
backcap.
OM-225 427 Page 4

3-2. International Style Connector Assembly
2
Tools Needed:
1
3
1 in.
(26 mm)
5
4
3
1 Weld Output Cable
2 Insulating Boot
3 Sleeve
Slide insulating boot onto cable;
strip cable and install sleeve.
4 Connector Body
5 Setscrew
Insert cable with sleeve fully into
connector body, tighten setscrew,
and slide insulating boot over connector.
ST-156 496
ENGLISH
OM-225 427 Page 5

3-3. Connecting Torch
A. Connecting Torch With One-Piece Cable
If applicable, install high-frequency unit.
Torch Without Gas Valve
6
8
9
Torch With Gas Valve
! Turn Off welding power source
power before installing torch.
Obtain the following hose:
1 Gas Hose With 5/8-18 Right-
Hand Fittings
Connections:
4
2
3
1
5
7
4
2
3
2 Regulator/Flowmeter
3 Gas Cylinder
4 Welding Power Source
5 Gas Valve
Operating Torch Gas Valve:
Valve controls gas preflow and postflow. Open valve on torch just before
welding.
Preflow is used to purge the immediate weld area of atmosphere.
Postflow is required to cool tungsten
and weld, and to prevent contamination of tungsten and weld. After welding, leave valve open about 1 second
for every 10 amperes of weld current.
Close valve on torch when postflow is
finished.
6 One-Piece Torch Cable
7 Power Cable Adapter
Connect gas hose and power cable to
adapter before connecting adapter to
weld output terminal.
8 Work Clamp
Connect work clamp to clean, paint-
free location on workpiece, close to
weld.
Use wire brush to clean weld joint
area.
9 Foot Control
OM-225 427 Page 6
1
6
5
8
9
7
Tools Needed:
5/8, 7/8 in.
803 313

B. Connecting Torch With Two-Piece Cable
If applicable, install high-frequency unit.
Torch Without Gas Valve
Torch With Gas Valve
Tools Needed:
956
5/8, 7/8 in.
2
4
6
7
8
2
4
−
5
803 314
3
! Turn Off welding power source
power before installing torch.
Obtain the following hose:
3
1 Gas Hose With 5/8-18 Right-
1
Hand Fittings
Connections:
2 Regulator/Flowmeter
3 Gas Cylinder
4 Welding Power Source
5 Torch Gas-In Hose
6 Torch Power Cable
7 Work Clamp
Connect work clamp to a clean, paint-
free location on workpiece, close to
weld area.
Use wire brush to clean weld joint
area.
8 Foot Control
9 Gas Valve
Valve controls gas preflow and post-
flow. Open valve on torch just before
welding.
Preflow is used to purge the immediate weld area of atmosphere.
Postflow is required to cool tungsten
and weld, and to prevent contamination of tungsten and weld. After welding, leave valve open about 1 second
for every 10 amperes of weld current.
Close valve on torch when postflow is
finished.
ENGLISH
7
C. Connecting Torch With Flow-Through Type Connection
4
If applicable, install high-frequency unit.
Torch Without Gas Valve
6
Tools Needed:
7
5/8, 7/8 in.
803 664-A
! Turn Off welding power source
2
1
5
power before installing torch.
Obtain the following hose:
3
1 Gas Hose With 5/8-18 Right-
Hand Fittings
Connections:
2 Regulator/Flowmeter
3 Gas Cylinder
4 Welding Power Source
5 Gas Valve
Located on back of machine.
6 One-Piece Torch Cable
7 Work Clamp
Connect work clamp to clean, paint-
free location on workpiece, close to
weld area.
Use wire brush to clean metal at weld
joint area.
804 330-A
OM-225 427 Page 7
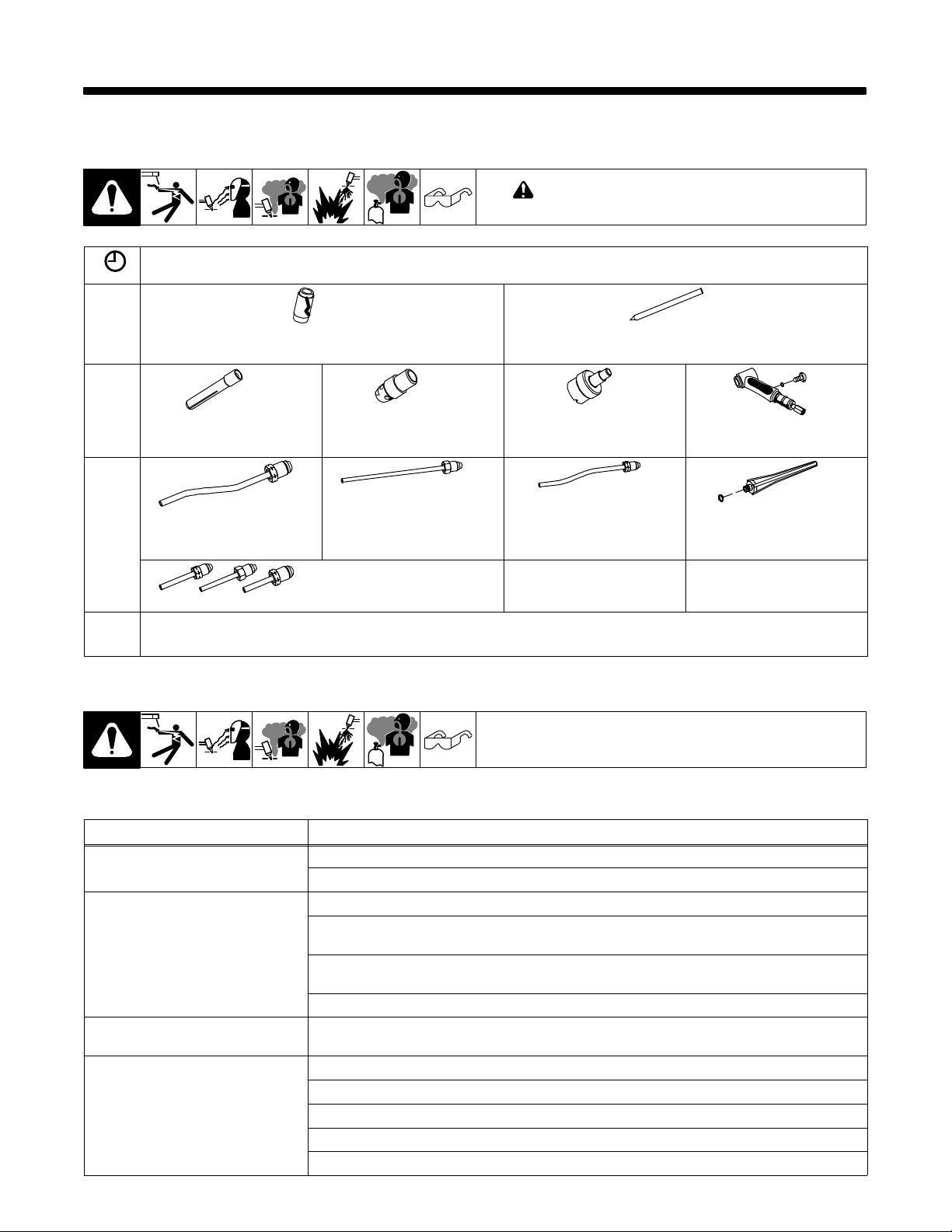
SECTION 4 − MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
4-1. Routine Maintenance
! Disconnect torch before maintaining.
= Check = Change = Clean = Replace
* To be done by Factory Authorized Service Agent
Daily
Weekly
Monthly
Nozzle For Cracks − If Necessary
Collet For Wear −
If Necessary
Power Cable For Cracks,
Wear − If Necessary
*
When using a water-cooled torch, maintain cooling equipment according to the manufactures recommendations.
Collet Body Threads −
If Necessary
Gas Hose For
Cracks, Leaks, Wear −
If Necessary
Power, Gas, And Water
Cable Connections To Ensure They Are Tight
Check Tungsten Preparation (See Section 5)
Gas Lens Screen −
If Necessary
*
Water Hose, If Applicable, For Cracks, Leaks,
Wear − If Necessary
Cable Cover For
Tears, Holes, Or Wear −
If Necessary
Gas Valve, If Applicable −
If Necessary
4-2. Troubleshooting
Before using troubleshooting table, check selection and preparation of tungsten electrode according to Section 5.
Back Cap O-Ring −
If Necessary
Trouble Remedy
Arc will not start. High frequency present
and visible at the torch.
Lack of high frequency; difficulty in establishing arc.
Torch gas valve not working properly (if
applicable).
No shielding gas flow from torch. Be sure valves on gas supply are open.
OM-225 427 Page 8
Check cable and work connections. Be sure weld circuit is complete (see Section 3-3).
Check and be sure shielding gas is present.
Select proper size and type of tungsten. Properly prepare tungsten according to Section 5.
Check cables and torch for cracks or bad connections. Be sure that torch cables are not close to any
grounded metal. Repair or replace necessary parts.
Check torch consumables. Be sure collet and collet body are correctly installed and tightened (see Section 3-1).
Check welding power source High Frequency control, and if necessary, check and adjust spark gaps.
Have Factory Authorized Service Station/Service Distributor check valve.
Check cable for kinks or blockage.
Check and tighten all gas supply fittings.
Check cables and torch for cracked insulation or bad connections. Repair or replace (see Section 4-1).
Make sure collet is installed correctly (see Section 3-1).

Trouble Remedy
Tungsten electrode oxidizing and not remaining bright after conclusion of weld.
Excessive tungsten electrode consumption.
Wandering arc Shield weld zone from drafts.
Yellow powder or smoke on cup. Use proper type shielding gas.
Erratic arc Make sure base material is clean and free of contaminates.
Porosity in weld. Check for proper type gas and correct flow rate. Check manufacture’s recommendations.
Shield weld zone from drafts.
Increase postflow time.
Increase gas flow rate. Check manufacture’s recommendations.
Check and tighten all gas fittings.
Check gas valve and flow meter/regulator.
Select proper size and type of tungsten. Properly prepare tungsten (see Section 5).
Select proper size and type of tungsten. Properly prepare tungsten according to Section 5.
Check polarity setting on welding power source (see welding power source Owner’s manual).
Check for proper gas flow rate. Check manufacture’s recommendations.
If torch is water cooled, check torch and cables for water leaks. Repair or replace if necessary (see Sec-
tion 4-1).
Reduce gas flow rate.
Select proper size and type of tungsten. Properly prepare tungsten according to Section 5.
When using AC, check welding power source High Frequency control setting, and increase setting if nec-
essary.
Check for proper gas flow rate. Check manufacture’s recommendations.
Increase postflow time.
Check torch cup size. Match cup size to joint being welded.
When using DC, check polarity, and/or polarity of welding cables.
Select proper size and type of tungsten. Properly prepare tungsten according to Section 5.
Use proper arc length. Arc length may be too long or too short.
When using AC, check welding power source High Frequency control setting, and be sure it is operating
continuously.
When using AC, slow travel speed can cause erratic arc. Adjust travel speed.
Check and tighten gas fittings.
Make sure base material and filler material is clean and free of contaminates.
Check for impurities and moisture in gas lines. Purge if necessary.
If torch is water cooled, check torch and cables for water leaks. Repair or replace if necessary (see Sec-
tion 4-1).
ENGLISH
OM-225 427 Page 9

SECTION 5 − SELECTING AND PREPARING A TUNGSTEN
FOR DC OR AC WELDING
gtaw_Phase_2011−06
! Whenever possible and practical, use DC weld output instead of AC weld output.
5-1. Selecting Tungsten Electrode (Wear Clean Gloves To Prevent Contamination Of Tungsten)
Not all tungsten electrode manufacturers use the same colors to identify tungsten type. Contact the tungsten electrode manufacturer or reference
the product packaging to identify the tungsten you are using.
Amperage Range - Gas Type - Polarity
Electrode Diameter (DCEN) − Argon
Direct Current Electrode Negative
(For Use With Mild Or Stainless Steel)
2% Ceria, 1.5% Lanthanum, Or 2% Thorium Alloy Tungstens
.040” (1 mm) 25-85 20-80
1/16” (1.6 mm) 50-160 50-150
3/32” (2.4 mm) 130-250 135-235
1/8” (3.2 mm) 250-400 225-360
Pure Tungsten
.040” (1 mm) Pure Tungsten Not Recommended
1/16” (1.6 mm) 50-100
3/32” (2.4 mm) 100-160
1/8” (3.2 mm) 150-210
For DCEN − Argon
Balance Control @ 65% Electrode Negative
Typical argon shielding gas flow rates are 11 to 35 cfh (cubic feet per hour).
Figures listed are a guide and are a composite of recommendations from American Welding Society (AWS) and electrode manufacturers.
AC − Argon
(For Use With Aluminum)
10-60
5-2. Preparing Tungsten Electrode For Welding With Phase Control Machines
! Grinding the tungsten electrode produces dust and flying sparks which can cause injury and start fires. Use
local exhaust (forced ventilation) at the grinder or wear an approved respirator. Read MSDS for safety information. Consider using tungsten containing ceria, lanthana, or yttria instead of thoria. Grinding dust from
thoriated electrodes contains low-level radioactive material. Properly dispose of grinder dust in an environmentally safe way. Wear proper face, hand, and body protection. Keep flammables away.
A. Preparing Tungsten For DC Electrode Negative (DCEN) Welding
Radial Grinding
Causes Wandering Arc
Wrong Tungsten Preparation
B. Preparing Tungsten For AC Welding
1
2-1/2 Times
Electrode Diameter
2
4
Ideal Tungsten Preparation − Stable Arc
1 − 1-1/2 Times
Electrode Diameter
2
1 Grinding Wheel
Grind end of tungsten on fine grit, hard
3
abrasive wheel before welding. Do not use
wheel for other jobs or tungsten can become
contaminated causing lower weld quality.
1
2 Tungsten Electrode
A 2% ceriated tungsten is recommended.
3 Flat
Diameter of this flat determines amperage
capacity.
4 Straight Ground
Grind lengthwise, not radial.
1 Tungsten Electrode
A pure tungsten is recommended..
2 Balled End
Ball end of tungsten by applying AC amper-
age recommended for a given electrode
diameter (see Section 5-1). Let ball on end of
the tungsten take its own shape.
OM-225 427 Page 10

SECTION 6 − GUIDELINES FOR TIG WELDING (GTAW)
6-1. Positioning The Torch
2007−04
10−25
2
1
10−15
4
3/16 in
Bottom View Of Gas Cup
90
5
3
5
6
6
1/16 in
! Grinding the tungsten elec-
trode produces dust and flying sparks which can cause
injury and start fires. Use local exhaust (forced ventilation) at the grinder or wear an
approved respirator. Read
MSDS for safety information.
Consider using cerium or
lanthanum based tungsten
instead of thoriated. Thorium dust contains low-level
4
radioactive material. Properly dispose of grinder dust in
an environmentally safe way.
Wear proper face, hand, and
body protection. Keep flammables away.
1 Workpiece
Make sure workpiece is clean
before welding.
2 Work Clamp
Place as close to the weld as
possible.
3 Torch
4 Filler Rod (If Applicable)
5 Gas Cup
6 Tungsten Electrode
Select and prepare tungsten
according to Section 5.
Guidelines:
The inside diameter of the gas cup
should be at least three times the
tungsten diameter to provide adequate shielding gas coverage. (For
example, if tungsten is 1/16 in
diameter, gas cup should be a
minimum of 3/16 in diameter.
Tungsten extension is the distance
the tungsten extends out gas cup of
torch.
The tungsten extension should be
no greater than the inside diameter
of the gas cup.
Arc length is the distance from the
tungsten to the workpiece.
ENGLISH
Ref. ST-161 892
OM-225 427 Page 11

6-2. Torch Movement During Welding
Tungsten Without Filler Rod
Welding direction
Form pool Tilt torch Move torch to front
Tungsten With Filler Rod
Welding direction
Form pool Tilt torch Add filler metal
Remove rod
75
75
15
Move torch to front
of pool. Repeat process.
6-3. Positioning Torch Tungsten For Various Weld Joints
Butt Weld And Stringer Bead
of pool. Repeat process.
ST-162 002-B
“T” Joint
90
20-40
30
20
15
Lap Joint
70
75
90
10
15
20
75
15
Corner Joint
75
ST-162 003 / S-0792
OM-225 427 Page 12

Notes
ENGLISH
OM-225 427 Page 13

SECTION 7 − PARTS LIST
4
3
2
1
6
5
18
9
8
7
11
10
20
19
12
21
13
14
22
15
16
23
17
24
25
31
35
29
26
36
37
38
32
39
33
27
28
34
40
45
44
30 41
42
43
46
48
47
OM-225 427 Page 14
WC0206−A
Figure 7-1. Complete Torch Assembly

Quantity
WP-17 Series
Item
No.
1 57N75 Nozzle, Alumina GL LG #6 (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ............. .... .... .... .... ....
1 57N74 Nozzle, Alumina GL LG #8 (1/2 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ............. .... .... .... .... ....
1 53N88 Nozzle, Alumina GL LG #10 (5/8 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ............ .... .... .... .... ....
1 53N87 Nozzle, Alumina GL LG #12 (3/4 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ............ .... .... .... .... ....
1 53N89 Nozzle, Alumina GL LG Short #15 (15/16 in.) 1111 1 1... ... .... .... .... .... .... ....
2 45V0204 Gas Lens, Large 0.020−0.040 in. (0.5−1.0 mm) 1111 1 1... . .. .... .... .... .... ....
2 45V116 Gas Lens, Large 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1... .. ............. .... .... .... .... ....
2 45V64 Gas Lens, Large 3/32 in. (204 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ............. .... .... .... .... ....
3 10N21 Collet, 0.020 in (0.5 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
3 10N22 Collet, 0.040 in (1.0 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
3 10N23 Collet, 1/16 in (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ....................... .... .... .... .... ....
3 10N24 Collet, 3/32 in (2.4 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ....................... .... .... .... .... ....
4 54N63 Insulator, Gas Lens Lg 1111 1 1... ... ........................ .... .... .... .... ....
5 54N17L Nozzle, Alumina GL Long #5 (5/16 in.) 1111 1 1... .. .......... .... .... .... .... ....
5 54N16L Nozzle, Alumina GL Long #6 (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1... .. ........... .... .... .... .... ....
5 54N15L Nozzle, Alumina GL Long #7 (7/16 in.) 1111 1 1... .. .......... .... .... .... .... ....
6 54N18 Nozzle, Alumina GL #4 (1/4 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ................ .... .... .... .... ....
6 54N17 Nozzle, Alumina GL #5 (5/16 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ............... .... .... .... .... ....
6 54N16 Nozzle, Alumina GL #6 (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ................ .... .... .... .... ....
6 54N15 Nozzle, Alumina GL #7 (7/16 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ............... .... .... .... .... ....
6 54N14 Nozzle, Alumina GL #8 (1/2 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ................ .... .... .... .... ....
6 54N19 Nozzle, Alumina GL Short #11 (11/16 in.) 1111 1 1... ... ........ .... .... .... .... ....
7 45V29 Gas Lens, 0.020 in. (0.5 mm) 1111 1 1... ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
7 45V24 Gas Lens, 0.040 in. (1.0 mm) 1111 1 1... ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
7 45V25 Gas Lens, 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ................... .... .... .... .... ....
7 45V26 Gas Lens, 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ................... .... .... .... .... ....
8 10N21 Collet, 0.020 in. (0.5 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
8 10N22 Collet, 0.040 in. (1.0 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
8 10N23 Collet, 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ....................... .... .... .... .... ....
8 10N24 Collet, 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) 1111 1 1... ... ....................... .... .... .... .... ....
9 54N01 Insulator, Gas Lens 1111 1 1... ... ........................... .... .... .... .... ....
10 53N58 Nozzle, Alumina GL #4 (1/4 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................ .... .... .... .... ....
10 53N59 Nozzle, Alumina GL #5 (5/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .............. .... .... .... .... ....
10 53N60 Nozzle, Alumina GL #6 (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................ .... .... .... .... ....
10 53N61 Nozzle, Alumina GL #7 (7/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .............. .... .... .... .... ....
10 53N61S Nozzle, Alumina GL #8 (1/2 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ................ .... .... .... .... ....
11 17GL040 Gas lens, Stubby 0.040 in. (1.0 mm) 1111 1 1.. . ............ .... .... .... .... ....
11 17GL116 Gas lens, Stubby 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1.. . ............. .... .... .... .... ....
11 17GL332 Gas lens, Stubby 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) 1111 1 1.. . ............. .... .... .... .... ....
11 17GL18 Gas lens, Stubby 1/8 in. (3.2 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. .............. .... .... .... .... ....
12 10N22S Collet, Stubby 0.040 in. (1.0 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. ............... .... .... .... .... ....
12 10N23S Collet, Stubby 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. ................ .... .... .... .... ....
12 10N24S Collet, Stubby 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. ................ .... .... .... .... ....
12 10N25S Collet, Stubby 1/8 in. (3.2 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. ................. .... .... .... .... ....
13 17GLG20 Insulator, Gas Lens Stubby 1111 1 1.. .................... .... .... .... .... ....
14 13N08 Nozzle, Alumina #4 (1/4 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................... .... .... .... .... ....
14 13N09 Nozzle, Alumina #5 (5/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
14 13N10 Nozzle, Alumina #6 (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................... .... .... .... .... ....
14 13N11 Nozzle, Alumina #7 (7/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
14 13N12 Nozzle, Alumina #8 (1/2 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................... .... .... .... .... ....
14 13N13 Nozzle, Alumina #10 (5/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
15 17CB20 Collet Body, Stubby 0.040−1/8 in. (1.0−3.2 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. .. .... .... .... .... ....
16 10N22S Collet, Stubby 0.040 in. (1.0 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. ............... .... .... .... .... ....
16 10N23S Collet, Stubby 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. ................ .... .... .... .... ....
16 10N24S Collet, Stubby 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) 1111 1 1.. .. ................ .... .... .... .... ....
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description
Figure 7-1. Complete Torch Assembly
17F17FV17V17
17V-PSH17-PSH
OM-225 427 Page 15
ENGLISH

Quantity
WP-17 Series
Item
No.
Dia.
Mkgs.
Part
No.
Description
17V-PSH 17-PSH
17F17FV17V17
Figure 7-1. Complete Torch Assembly
17 18CG20 Insulator, Nozzle Stubby 1111 1 1.. . ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
18 12N03 Nozzle, Lava Long #4L (1/4 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................ .... .... .... .... ....
18 105Z60 Nozzle, Lava Long #5L (5/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ............... .... .... .... .... ....
18 12N02 Nozzle, Lava Long #6L (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................ .... .... .... .... ....
18 105Z61 Nozzle, Lava Long #7L (7/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ............... .... .... .... .... ....
19 105Z43 Nozzle, Lava #4 (1/4 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
19 105Z42 Nozzle, Lava #5 (5/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
19 105Z44 Nozzle, Lava #6 (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
19 105Z45 Nozzle, Lava #7 (7/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
19 08N78 Nozzle, Lava #8 (1/2 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
19 08N79 Nozzle, Lava #10 (5/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
19 08N80 Nozzle, Lava #12 (3/4 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
20 10N49L Nozzle, Alumina Long #5L (5/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ............ .... .... .... .... ....
20 10N48L Nozzle, Alumina Long #6L (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ............. .... .... .... .... ....
20 10N47L Nozzle, Alumina Long #7L (7/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. .. ............ .... .... .... .... ....
21 10N50 Nozzle, Alumina #4 (1/4 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................... .... .... .... .... ....
21 10N49 Nozzle, Alumina #5 (5/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
21 10N48 Nozzle, Alumina #6 (3/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................... .... .... .... .... ....
21 10N47 Nozzle, Alumina #7 (7/16 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
21 10N46 Nozzle, Alumina #8 (1/2 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... ................... .... .... .... .... ....
21 10N45 Nozzle, Alumina #10 (5/8 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
21 10N44 Nozzle, Alumina #12 (3/4 in.) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
22 10N29 Collet Body, 0.020 in. (0.5 mm) 1111 1 1.. ... ................. .... .... .... .... ....
22 10N30 Collet Body, 0.040 in. (1.0 mm) 1111 1 1.. ... ................. .... .... .... .... ....
22 10N31 Collet Body, 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
22 10N32 Collet Body, 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) 1111 1 1.. ... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
23 10N21 Collet, 0.020 in. (0.5 mm) 1111 1 1.. ... ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
23 10N22 Collet, 0.040 in. (1.0 mm) 1111 1 1.. ... ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
23 10N23 Collet, 1/16 in. (1.6 mm) 1111 1 1.. ... ....................... .... .... .... .... ....
23 10N24 Collet, 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) 1111 1 1.. ... ....................... .... .... .... .... ....
24 18CG Insulator, Nozzle 1111 1 1.. ... ............................. .... .... .... .... ....
25 WP-17 Torch Body, 150 A A/C 1.. ... ........................
26 WP-17V Torch Body, 150 A A/C VLV 1.. . ..........................
27 WP-17FV Torch Body, 150 A A/C FX VLV (Includes) 1.. ....................
150VTB Torch Body, 150 VTB 1..... .... ....................................
28 WP-17F Torch Body, 150 A A/C FX (Includes) 1.. . ..............................
150TB Torch Body, 150 TB 1..... ..... ...........................................
29 WP-17V-PSH Torch Body, 150 A A/C VLV Thrd 1.. ......................................
30 WP-17-PSH Torch Body, 150 A A/C Thrd 1.. ..................................................
31 18-7 Insulator, Backcap 1 1 1 1.. ..... ............................ .... ................. ....
32 VS-2 Knob, Valve 1 1 1.. .... ....................................... .... ...........
33 VS-2 Knob, Valve 1 1 1.. .... ....................................... .... ...........
34 VS-2 Knob, Valve 1 1 1.. .... ....................................... .... ...........
35 57Y02 Backcap, Long 1111 1 1.. ... ............................... .... .... .... .... ....
36 300M Backcap, Medium 1 1 1 1 1.. .... .................................. .... .... .... ....
37 57Y04 Backcap, Short 1111 1 1.. ... .............................. .... .... .... .... ....
38 H-100R Handle, Ribbed (WP-17, WP-17V) 1 1.. .. .............. ....
39 H-100 Handle, Knurled (WP-17, WP-17V) 1 1.. ... ............. ....
40 105Z55R Handle, Ribbed.. .
(WP-17FV, WP-17F, WP-17V-PSH, WP-17-PSH)) 1 1 1 1................. ............. .... .... ....
41 105Z55 Handle, Knurled.. ..
(WP-17FV, WP-17F, WP-17V-PSH, WP-17-PSH)) 1 1 1 1................. ............. .... .... ....
42 57Y01 Cable, Power 12.5 Ft (3.8 m) Vinyl 1111 1 1.. ... ............. .... .... .... .... ....
42 57Y01R Cable, Power 12.5 Ft (3.8 m) Rubber 1111 1 1.. .. ........... .... .... .... .... ....
42 57Y03 Cable, Power 25 Ft (7.6 m) Vinyl 1111 1 1.. ... ............... .... .... .... .... ....
OM-225 427 Page 16

Quantity
WP-17 Series
Item
No.
42 57Y03R Cable, Power 25 Ft (7.6 m) Rubber 1111 1 1.. .. ............. .... .... .... .... ....
43 57Y01-2 Cable, Power.. .
43 57Y03-2 Cable, Power 2pc 25 Ft (7.6 m) Rubber (Includes) 1111 1 1.. . .... .... .... .... ....
44 WC-3-10 Cover, Cable 10 Ft (3 m) 1111 1 1.. . ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
44 WC-3-2 Cover, Cable 22 Ft (6.7 m) 1111 1 1.. .. .................... .... .... .... .... ....
45 195378 Adapter, Gas Torch-Intnl 1111 1 1.. .. ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
46 Q5GT-150 Conn, Quick 150 A 50 mm Flow Thru 1111 1 1.. ........... .... .... .... .... ....
47 Q5G-150 Conn, Quick 150 A 50 mm w/Hose (Includes) 1111 1 1.. . .... .... .... .... .... ....
48 105Z57 Adapter, Power Cable 1111 1 1.. .. ......................... .... .... .... .... ....
Optional
BE SURE TO PROVIDE MODEL AND STYLE NUMBER WHEN ORDERING REPLACEMENT PARTS.
Dia.
Mkgs.
45V09R Hose, Gas 12.5 Ft (3.8 m) 1111 1 1..... .... .................. .... .... .... .... ....
45V10R Hose, Gas 25 Ft (7.6 m) Braided 1111 1 1..... .... ............ .... .... .... .... ....
PCA-5-16 Hose, Gas 18 in. (0.2 m) RH 1111 1 1..... .. ................ .... .... .... .... ....
AK-2 Kit, Accessory Thoriated 1111 1 1..... .... ...................... .... .... .... .... ....
AK-2C Kit, Accessory Ceriated 1111 1 1..... ... . ..................... .... .... .... .... ....
Mak-2S Kit, Starter 1111 1 1..... .. .................................. .... .... .... .... ....
Part
No.
2pc 12.5 Ft (3.8 m) Rubber (Includes) 1111 1 1................. ........... .... .... .... .... ....
Description
Figure 7-1. Complete Torch Assembly
17V-PSH 17-PSH
17F17FV17V17
ENGLISH
OM-225 427 Page 17

Notes
ENGLISH

Notes
ENGLISH

Owner’s Record
Please complete and retain with your personal records.
Model Name Serial/Style Number
Purchase Date (Date which equipment was delivered to original customer.)
Distributor
Address
City
State Zip
For Service
Contact a DISTRIBUTOR or SERVICE AGENCY near you.
Always provide Model Number.
Contact your Distributor for:
To locate a Distributor or Service Agency call 1-800-752-7620 or 920-882-6800
Welding Supplies and Consumables
Options and Accessories
Personal Safety Equipment
Service and Repair
Replacement Parts
Welding Process Handbooks
Weldcraft
An Illinois Tool Works Company
2741 N. Roemer Rd
Appleton, WI 54911 USA
1-800-752-7620 Toll Free
1-920-882-6800 Phone
1-920-882-6844 FAX
www.Weldcraft.com
Contact the Delivering Carrier to:
PRINTED IN USA 2012 Weldcraft Products Inc. 2012−01
File a claim for loss or damage during
shipment.
For assistance in filing or settling claims, contact
your distributor and/or equipment manufacturer’s
Transportation Department.
 Loading...
Loading...