Page 1

INVERTED VERTICAL TURNING CELL
CS20/25
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
57 SPECIFICATION
SEIKI - SEICOS å21L
Edition 2.02
Hitachi Seiki Deutschland
Werkzeugmaschinen GmbH
Page 2

Introduction
Thank you for your having purchased the machine, favoring our product lines for your use.
This manual contains fundamental information on the specification. Please read and fully understand
the contents for your safe machine operation.
In particular , the contents of the items concerning safety in this manual and the descriptions on the
“caution plates” attached to the machine are important. Please follow the instructions contained
and keep them always in mind to ensure safe operation.
The reference record papers on adjusting setting values such as a parameter list are attached to
the machine unit and enclosed in the packing. These are necessary for maintenance and
adjustment of the machine later on. Please keep them safely not to be mislaid.
The design and specifications of this machine may be changed to meet any future improvement.
As the result, there may arise some cases where explanations in this manual could become partly
inconsistent with the actual machine. Please note this point in advance.
In this manual, items on the standard and optional specifications are handled indiscriminately.
Please refer to the “delivery note” for the detailed specification of your machine confirmation.
Page 3

CONTENTS
1. General Precautions ........................................................................... 1 - 1
1-1 Precautions on Machine Operation...................................................................................1 - 1
1-2 Electric Equipment and NC Unit........................................................................................1 - 4
1-3 Weights and Measures Table............................................................................................1 - 5
2. SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................... 2 - 1
2-1 Machine Outline ................................................................................................................2 - 1
2-2 Component Units ..............................................................................................................2 - 2
2-3 Machine Specifications .....................................................................................................2 - 3
2-4 NC Unit Specifications.......................................................................................................2 - 6
2-5 Major Dimensions ...........................................................................................................2 - 10
3. REQUIRED DIMENSION FOR MACHINE ........................................... 3 - 1
3-1 Spindle Traveling Range ...................................................................................................3 - 1
3-1-1 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Type................................................................. 3 - 1
3-1-2 12-station VDI/VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Type.................................................. 3 - 6
3-2 Output Diagram ..............................................................................................................3 - 13
3-3 Chucking Pressure-Gripping Force Diagram..................................................................3 - 16
3-4 Method of Obtaining Tool Center Height.........................................................................3 - 18
4. Tooling System................................................................................... 4 - 1
4-1 CS20 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Assembly Tools (Standard)...........................4 - 1
4-2 CS20 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Assembly Tools (Selected) ...........................4 - 2
4-3 CS25 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Assembly Tools (Standard)...........................4 - 4
4-4 CS25 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Assembly Tools (Selected) ...........................4 - 5
4-5 CS20 12-station VDI Turret Head Assembly Tools (Standard).........................................4 - 7
4-6 CS25 12-station VDI Turret Head Assembly Tools (Standard).........................................4 - 8
4-7 CS20/25 12-station VDI Turret Head Assembly Tools (Selected) ....................................4 - 9
4-8 CS20 12-station VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Assembly Tools (Standard)................. 4 - 11
4-9 CS25 12-station VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Assembly Tools (Standard).................4 - 12
4-10 CS20/25 12-station VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Assembly Tools (Selected) ..........4 - 13
i
Page 4

1. General Precautions
General descriptions is very useful for making working environment against accidents and
increase productivity.
1. Be sure to put safety goggles on.
2. Be sure to put safety shoes on.
3. Operate with proper dressing, such as putting a utility cap on, fixing the sleeves and the
cuffs of working clothes.
4. Don’t operate the machine with gloves.
5. Make clean and neat environment by lighting up and keeping dry around the machine.
Also don’t put any obstacles.
6. Remove dust and chips on the machine, high voltage control panel and NC unit. Also
remove them on the floor. Avoid using compressed air as much as possible for these
cleanings.
7. Use a strong enough table to be put around the machine, and take anti-sliding measures on
the surface.
8. Don’t put tools, workpieces, and other items on the machine as well as on the moving parts
of the machine.
9. Don’t give any remodeling to the machine without our permission.
1-1 Precautions on Machine Operation
When conducting trial run, read the manual applied to the machine carefully for full
understanding beforehand. Witness of our operation instructor is most preferable.
Maintenance
1. An operator and maintenance personnel should read the precautions on the caution plate
fitted to the machine and observe them.
Don’t stain, damage or remove the caution plate becomes hard to read, contact Hitachi
Seiki.
2. Close all the doors and covers except when adjusting work is made.
As for the doors of the NC unit and the power control cabinet, be sure to close them with
special care.
3. Don’t remove or modify the limit switches for the stroke end, for the travelling axes and the
mechanism, or the electric circuit employed for safety.
4. Use regular wrenches and spanners for adjusting or repairing work.
5. When repairing the machine, be sure to perform lock-out or tag-out so that power switch
may not be operated.
1 - 1
Page 5

Coolant
This machine doesn’t mix coolant with lubrication oil by using the economy pack. But, the
soluble cutting fluid is decomposed due to the factors such as propagation of microorganisms, which causes various troubles by lowering cutting and rust prevention
performance.
When using soluble cutting fluid, care must be taken of the following points.
1. When selecting soluble cutting fluid, carefully consider lubrication, infiltration, rust
prevention, bubble prevention, separability against oil and safety needs.
2. Before operation starts and after operation ends, not only remove chips, but also wipe off
soluble cutting oil adhered to each slideway, the rotating parts, the saddle and cross-slide
of the machine and then be sure to apply lubrication oil thinly to those parts.
3. Replace soluble cutting fluid immediately if it becomes vitiated.
4. Remove the covers every 6 months and clean each slideway, X, Y, Z axes ball-screws,
each limit switch and feed motors etc.
5. As soluble cutting oil is considered for rust prevention, it may be no problem when the
workpiece is wet. However, when dry, it is apt to rust.
Therefore, it is recommendable to apply rust preventive oil before the workpiece dries after
finished machining.
6. Since soluble oil is alkalescent and has a strong decreasing action, the operator is apt to
develop dermatitis.
Therefore, the operator should take appropriate precautions.
7. As for the diluting method and soluble cutting fluid, diluting water they are different
depending on the type of soluble cutting oil, so use it in accordance with the
recommendations of the cutting fluid manufacturer.
8. Since there are instances where extensive micro-organisms are detected in industrial
water, it is recommendable either to check it before use as water for dilution or to use
service water.
9. Do not use a chemical solution type (synthetic type) in water-soluble cutting agents,
because it causes detachment of coating anf affects sealing materials and resin materials
adversely.
10. The influences of difference kinds of oil on coolant are as follows: Carefully monitor the
condition the coolant fluid.
Different kinds of oil
Lubrication oil
Rust preventive oil
Mixture
(Emulsification)
Nutritive source of
micro-organism
Instabilization
of liquid
Adhesion to
machine
Propagation of
bacilli
Density
abnormality
Propagation of
bacilli
Petrifaction,
rust & others
Lowering of density
Lowering of pH
Seal due to
surfacing
Formation of state
of aversion
1 - 2
Page 6

Operation
1. Be aware of the position of the push button for emergency stop so that the operator may be
able to press it instantly.
2. As for the operation of the machine, proceed in accordance with the procedure described
later.
3. During operation, keep hands away from the rotating sections and movable sect ions.
4. When disposing of chips that wound round tooling or fell onto the chip brow, etc. it is
dangerous to grasp and pull them. Further, when disposing of chips, be sure to do it after
stopping the machine.
5. When adjusting the position of the coolant nozzle, do it after stopping the machine.
Tool Setting
1. When setting up tools, stop a spindle as well as the feed in each axis.
2. Be very careful of tool length when setting them up. Do not set the tools over their specified
lengths because their tool edges may interfere with a bed, carriage, cover, tailstock, etc.
when indexing a turret.
3. Mount tools in a well balance condition. Due to high-speed turret indexing when their
mounting is unbalanced, it may lead to improper turret indexing.
4. When setting a tool to the rotating tool, it is feared that the driving side may be damaged, if
it is performed in the machine.
Whenever tools are set, be sure to do it at the outside of machine.
Workpiece Chucking
1. When chucking a workpiece, be careful of its balance. Do not turn the spindle if the
mounting of the workpiece is unbalanced badly.
2. Use standard soft jaws. Mount the jaws so that they may stay within the outer diameter of
the chuck.
3. To set pressure of chuck cylinder, determine it referring to “Chucking Pressure-Gripping
Force Diagram”.
Take note that the chuck gripping force will be suddenly reduced due to a centrifugal force
when the spindle runs at a high speed.
4. When forming the soft jaws, pay full attention to a forming ring gripping position and a
shape to which the jaws are to be formed.
After forming, check that the jaws properly grip the workpiece and that a chucking pressure
is adequate.
5. When chucking and centering a shaft work, take special note of a workpiece weight, a size
of center hole and a thrust force.
If a heavy workpiece is held with a small center hole and a load is applied, the tip of the
center may be damaged, allowing the workpiece to jump out.
1 - 3
Page 7

Operation Finish
1. After operation of the machine is over, be sure to switch the power OFF in the prescribed
order, clean the machine and apply rust preventive oil to each section of the machine such
as the slide ways.
When soluble cutting fluid is used, perform these jobs with special care.
1-2 Electric Equipment and NC Unit
When operating the machine or carrying out maintenance checks, pay special attention to the
following points, concerning the electric equipment and NC unit.
1. Do not give shocks to the NC unit, power control cabinet and other machine parts.
2. For the primary wiring of the machine, use the cable size specified in the maintenance
manual. Do not use an excessively long cabtire cable.
When the primary wiring has to be put on the floor, protect it with a cover against damage
by cutting chips and other sharp objects.
3. While test running the machine, be sure the setting parameter of the NC unit coincides with
the parameter sheet attached to the machine.
4. Do not change the current set values of thermal relays in the power control cabinet, various
control knobs or the parameter data.
5. Do not apply excessive force, e.g. bending force etc., to the connector portion of plugs,
flexible conduits (tubes) or cabtire cables etc.
6. When carrying out maintenance checks on the electric equipment, turn off the
EMERGENCY STOP button on the operation panel, the power of the NC unit, the main
switch of the power control cabinet and the power switch installed in your factory, in this
order.
Start maintenance work after making sure that these switches are turned off.
Lock the power switches in the OFF state as much as possible or put up warning signs. In
additions, place a “DO NOT TOUCH” tag near the operation buttons of the machine to
forbid other personnel from operating the machine.
7. Handle electric equipment of the machine with particular care and exercise extreme caution
not to allow the machine to get wet.
8. For equipment inside the power control cabinet, use those specified by Hitachi Seiki. Use
always specified fuses. Never use fuses with a higher capacity.
9. Never leave the control cabinet door open, because direct sunshine or camera’s strobe
flash rays may enter the cabinet and damage internal equipment.
10.In case of turning on the power again, execute power on went by equal to or more than two
seconds after power turned off. If the power is turned on during discharge from control
devise by power off, pay attention to the alarm of the machine is displayed some time, due
to normal process is not available.
1 - 4
Page 8

1-3 Weights and Measures Table
(Metric and English Conversion)
1. Liner measure
1m (meter) = 39.37 inches = 3.2808 feet = 1.0936 yards
1cm (centimeter) = 0.3937 inch
1mm (millimeter) = 0.03937 inch
2. Square measure
2
1m
(square meter) =10.764 square feet = 1.196 square yards
2
1cm
(square centimeter) = 0.155 square inch
2
1mm
(square millimeter) = 0.00155 square inch
3. Cubic measure
3
1m
(cubic meter) = 35.315 cubic feet = 1.308 cubic yards
= 264.2 U.S. gallons = 220.0 U. K. gallons
1
(liter, cubic decimeter) = 0.0353 cubic foot = 61.023 cubic inches
= 0.2642 U.S. gallon = 1.0567 U. S. quarts
= 0.2200 U.K. gallon =0.02745 bushel
3
1cm
(cubic centimeter) = 0.061 cubic inch
4. Weight
1 ton (metric ton) = 0.9842 U. S. (long) ton = .2204.6 pounds
= 1.1023 U. K. (short) ton
1 kg (kilogram) = 2.2046 pounds = 35.274 ounces avoirdupois
5. Others
0.098 MPa (Mega-Pascal)= 14.223 pounds per square inch
9.8 N.m (Newton-meter) = 7.233 foot-pounds
1 - 5
Page 9

2. SPECIFICATIONS
2-1 Machine Outline
The equipment has two sets of vertical headstocks and drum type tool posts of the same structure
installed on the integral bed. The reversing unit is installed in the center of the equipment to allow
the left and right machines to mutually transfer the work between them. The left and right machines
are simultaneous 2-axis control NC lathes for chuck work, respectively.
The following lists the features of the equipment:
1. The vertical headstock can move in the X- and Z-axis directions. In addition to cutting, it
loads and unloads the workpieces through X-directional movement to the outside of the
machine and Z-axis movement. Basic movements are as follows:
The workpiece is introduced from the feeder of the left machine. Once the workpiece is finished
with machining, it moves to the right machine via the reversing unit. After 1st- and 2nd-process
machining is completed, the finished workpiece is unloaded onto the feeder of the right machine.
2. The workpiece can be passed not only from the left to the right, but the other way around.
The left and right machines can also machine different workpieces independently. The
tools used and the machine operating methods are common to both left and right machines.
3. An AC inverter motor is used for the spindle to allow a wide range of stepless speed change.
4. The inner-diameter tools are radially arranged, offset from the outer-diameter tools to ensure
that the tools do not interfere with the workpiece within the standard machining diameter .
5. The electromechanical structure integrated with the coolant tank and circular stocker
saves the space and facilitates transportation/move.
6. A diagnostic function is added.
7. A machining range can be further expanded by adding optional accessories.
Outline of Equipment Structure
1. Mechanical Construction
・ The headstock is vertically suspended and moves along the X- and Z-axis.
・ The X-axis is provided long enough to allow the headstock to move to a workpiece
loading position outside the machine.
・ The tool post is secured under the headstock and performs only indexing.
2. Headstock
A high-torque built-in motor allows a wide range of automatic speed change as follows:
CS20 30 to 5,000 min
{
CS25 30 to 4,000 min
3. Tool Post
High indexing accuracy is ensured by a unique coupling system.
Indexing operation is driven by a servo motor and clamping operation by a hydraulic unit,
respectively, to improve certainty of operations.
4. The 12-face VDI rotary tool post allows you to mount the X- and Z-directional rotary tools
to any turret faces.
Simultaneous 3-axis control is enabled by adding a spindle C-axis control function.
}
-1
-1
2 - 1
Page 10

2-2 Component Units
1 Oil pressure unit 7 Z axis feed motor 13 Turret 19 Bed
2 Coolant tank 8 Chip box (OP) 14 Q-setter 20 Spindle cooling
system
3 X axis feed motor 9 Chip conveyor(OP) 15 Spindle 21 Stoker
4 Saddle 10 Operating panel 16
5 Coolant pump 11 Cross slide 17 Headstock
6 Power control cabinet 12 Tool post 18 Chuck pressure
adjustment manifold
2 - 2
Page 11

2-3 Machine Specifications
1. Machine Specifications
1) CS20
Item Unit
12-st. base holder
type turret
12-st. VDI type
turret
Capacity Max. spindle swing mm (inch) 350 (13.8”)
Chuck outer diameter mm (inch) 210 (8.25”)
Max. machining diameter mm (inch) φ350 (φ13.8”)
Max. machining length mm (inch) 150 (6”)
Travel
1310(51.5”)(Cutting area:190
X axis travel mm (inch)
(7.5”),Loader area:1120 (44”))
Z axis travel mm (inch) 370 (14.5”)
Spindle Spindle speed min
-1
(rpm) 30 ~ 5000
Spindle speed range Stepless
Spindle nose (Type, NO.) JIS A2-6
Diameter of spindle through
mm(inch) φ59 (φ2.3”)
hole
Spindle bearing inside
mm (inch) φ100 (φ4”)
diameter
Turret Type of turret
head No. of tool
12-st. base holder
12 pcs.
(O.D. 6, I.D. 6)
12-st. VDI
Shank size of O.D. tool mm (inch) 25 (1”)
32(B/H hole dia. 40) /
Boring ber size mm (inch)
1-1/4” (HOLE 1.5”)
Feedrate Rapid traverse X axis m/min (ipm) 30 (1181)
Z axis m/min (ipm) 30 (1181)
Cutting feed (Per revolution) mm/rev (ipr) 0.001 ~ 1000 (0.001 ~ 40)
Jog feed mm/min (ipm) 0 ~ 5000 (0 ~ 200)
Motor Spindle motor
AC-kW (HP) 11/7.5 (15/10)
(40%ED/continuous)
For Rotary tools(15 minutes
AC-kW (HP)E ---- ---- 3.7/2.2(5/3)
rated/continuous)
Axis feed motor X axis AC-kW(HP) 2.8 (3.8)
Z axis AC-kW (HP) 3.8 ( 5 )
Turret indexing motor kW (HP) 2.2 (2.9)
Oil pressure pump kW (HP) 0.4 (0.5)
Coolant fluid motor kW (HP) 1.1 (1.5)
Spindle coolant pump W (HP) 0.4 (0.5)
Power Power supply kVA 23
Source Pneumatic Pressure MPa (psi) 0.5 (70)
source Rate of flow
N /min (gal/min)
150 (40)
Machine
weight
kg ( bs) 5000 (11000)
12-st. VDI rotating
tool type turret
12-st. VDI
rotating tool
12
2 - 3
Page 12

2) CS25
Item Unit
12-st. base holder
type turret
12-st. VDI type
turret
Capacity Max. spindle swing mm (inch) 350 (13.8”)
Chuck outer diameter mm (inch) 254 (10”)
Max. machining diameter mm (inch) φ350 (φ13.8”)
Max. machining length mm (inch) 150 (6”)
Travel
1310(51.5”)(Cutting area:190
X axis travel mm (inch)
(7.5”),Loader area:1120 (44”))
Z axis travel mm (inch) 370 (14.6”)
Spindle Spindle speed min
-1
(rpm) 30 ~ 4000
Spindle speed range Stepless
Spindle nose (Type, NO.) JIS A2-8
Diameter of spindle through
mm(inch) φ78 (φ3.1”)
hole
Spindle bearing inside
mm (inch) φ130 (φ5.1”)
diameter
Turret Type of turret
head No. of tool
12-st. base holder
12 pcs.
(O.D. 6, I.D. 6)
12-st. VDI
Shank size of O.D. tool mm (inch) 25 (1”)
32(B/H hole dia. 40) /
Boring ber size mm (inch)
1-1/4” (HOLE 1.5”)
Feedrate Rapid traverse X axis m/min (ipm) 30 (1181)
Z axis m/min (ipm) 30 (1181)
Cutting feed (Per revolution) mm/rev (ipr) 0.001 ~ 1000 (0.001 ~ 40)
Jog feed mm/min (ipm) 0 ~ 5000 (0 ~ 200)
Motor Spindle motor
AC-kW (HP) 15/18.5 (25/20)
(40%ED/continuous)
For Rotary tools(15 minutes
AC-kW (HP)E ---- ---- 3.7/2.2(5/3)
rated/continuous)
Axis feed motor X axis AC-kW(HP) 2.8 (3.8)
Z axis AC-kW (HP) 3.8 ( 5 )
Turret indexing motor kW (HP) 2.2 (2.9)
Oil pressure pump kW (HP) 0.4 (0.5)
Coolant fluid motor kW (HP) 1.1 (1.5)
Spindle coolant pump W (HP) 0.4 (0.5)
Power Power supply kVA 26
Source Pneumatic Pressure MPa (psi) 0.5 (70)
source Rate of flow
N /min (gal/min)
150 (40)
Machine
weight
kg ( bs) 5400 (11900)
12-st. VDI rotating
tool type turret
12-st. VDI
rotating tool
12
2 - 4
Page 13

2. Standard Accessories
1. Q-Setter ........................................................................ 1 set
2. CS20: φ210 Solid chuck (With chuck open/close
confirmation equipment) ............................................... 1 set
CS25: φ254 Solid chuck (With chuck open/close
confirmation equipment) ............................................... 1 set
3. Soft jaw ......................................................................... 1 set
4. Work light...................................................................... 1 set
5. Leveling block ............................................................... 1 set
6. Spindle override ............................................................ 1 set
7. Call light (yellow)........................................................... 1 set
8. Spindle load meter (on screen)..................................... 1 set
9. Electric leakage breaker ............................................... 1 set
10. Spindle positioning device (two position indexing electric
system) ......................................................................... 1 set
11 Chuck side air blow confirmation.................................. 1 set
12 Jet coolant .................................................................... 1 set
13 Operator side door interlock ......................................... 1 set
14 Chuck open/close M function........................................ 1 set
15 Chuck open/close confirmation .................................... 1 set
16 Spindle speed meter (on screen).................................. 1 set
17 Machining completion pre-call ...................................... 1 set
18 Work counter (on screen)............................................. 1 set
19 Run hour display (on screen)........................................ 1 set
20 Spinners & wrenches.................................................... 1 set
3. Optional Accessories
• Chip conveyor backward delivery • External power transformer 32 kVA
• Chip wagon • Work tools
• Automatic power shut-off device • Coolant gun
• SEIKI DON FD card • Tool post coolant/air changeover (M-code)
• Magnet piece (In the coolant tank) • Chucking pressure 2-step changeover
• Chip conveyor intermittent feeder • Work pusher
• Chuck-side coolant/air changeover (M-code) • Spindle tachometer (Standalone)
• Work airtightness checker • Rotary tool tachometer (Standalone)
• Counter • Spindle load meter (Standalone)
• Addition of the call light • Rotary tool spindle load meter (Standalone)
• Buzzer alarm • Weekly timer
• Safety measure specifications
2 - 5
Page 14

2-4 NC Unit Specifications
Refer to the NC unit specifications list of SEIKI SEICOS instruction manual (operating section)
for details of specifications.
Item Standard specification
1 Controlled axis 2 axis, axis simultaneous
2 Least input increment 0.001mm/0.0001”
3 Interpolation Positioning, Linear, Circular
4 Inch/Metric conversion
5 Tape code EIA/ISO auto.recognition
6 Designation INC./ABS.
7 Decimal point programming
8 Buffer register
9 Feedrate command F code/feedrate direct
10 Rapid traverse override 0, 1, 10, 50, 100%
11 Feedrate override 0~200% (10% step)
12 Override cancel
13 Spindle override 50~150% (10% step)
14 Threading function F/E code direct
15 Manual feed function Rapid, Jog feed, Handle
16 Manual pulse generator ×1, ×10, ×100 (inch=×50)
17 Part program storage 80m
18 Add. registered programs 100 pcs.
19 Back ground editing
20 Extended program edit (Program copy)
21 Display 9.5" Monochrome
22 Memory lock
23 Language display English/German
24 Tape mode operation RS232C*
25 I/O interface RS232C*
1
1
26 Function G3, M3, T4
27 Spindle speed command S code/speed direct
28 Constant surface speed control
2 - 6
Page 15

Item Standard specification
29 Automatic tool nose radius
compensation
30 Grooving width offset (I.D., O.D., Face)
31 Tool offsets 32 sets
32 Q-setter repeat function
33 Cutting point coordinate system
setting
34 Reference point return Manual, Auto G27~29
35 2nd reference point return G30
36 Graphic display Before and synchronized machining
37 16-character program name
38 Single block
39 Block skip Total 9 pcs. (with switch 5 pcs.)
40 Optional stop
41 Program check function Dry run + Spindle stop + coolant stop
42 Machine lock
43 Program number O 8 digit
44 Program number search
45 Sequence number search,
Sequence number comparison
46 Program comparison
47 Manual absolute [ON] fixed
48 Custom macro Common variable 300 pcs.
49 Soft jaws forming function
by graphic
50 Fixed cycle G90, G92, G94
51 Multiple repetitive cycle G70~G76
52 Mirror image Setting via screen
53 Chamfering/corner R any angle
54 Radius designation on arc
55 Exact stop G09 G61 G64
56 Programmable data input G10
2 - 7
Page 16

Item Standard specification
57 Backlash compensation
58 Run hour display/Spindle (On screen)
speed display
59 Cycle completion pre-call (On screen)
60 Cycle time display (On screen)
61 Work counter (On screen)
62 Following up
63 Stored stroke limit 1•2•3
64 NC self diagnostics
*1 : Interface only.
Not include cable.
2 - 8
Page 17

Item Optional specification
1 Direct tapping (Rotating tool)
2 Variable lead threading
3 Thread cutting cycle retract
4 Multiple start thread cutting
5 Custom macro Common variable 600 pcs.
6 Drilling cycle (Rotating tool) G80~89
7 Macro print func. (Need printer w/ RS232C I/F) *
8 Tool diameter compensation (Rotating tool)
9 Part program storage Total 160 m
10 Part program storage Total 320 m
11 Add. registerable prog. Total 200 pcs. (Need 160m)
12 Add. registerable prog. Total 400 pcs. (Need 320m)
13 Tool offset Total 64 pcs.
14 Tool offset Total 99 pcs.
1
15 Return to cycle interrupted
point
16 48-character program name
17 Program restart
18 Angle program for linear
interpolation
19 Cylindrical interpolation (Including tool diameter compensation)
20 Polar coordinate interpolation (Including tool diameter compensation)
21 External data input Need technical discussion
22 Skip function High-speed
23 Tool life management (Count
only)/Sp are tool call
24 Each program, cycle time 10 pcs. (On screen)
display
25 Each program, cycle time 50 pcs. (On screen)
display
26 Cutting monitor (Incl. tool llife management (Count only) / Spare tool call)
27 C-axis control (Rotating tool and C-axis must needed) *
28 Multiple axis control *
*1 : Interface only .
2
2
Not include cable.
*2 : When selected C axis must choose multiple axis control
2 - 9
Page 18

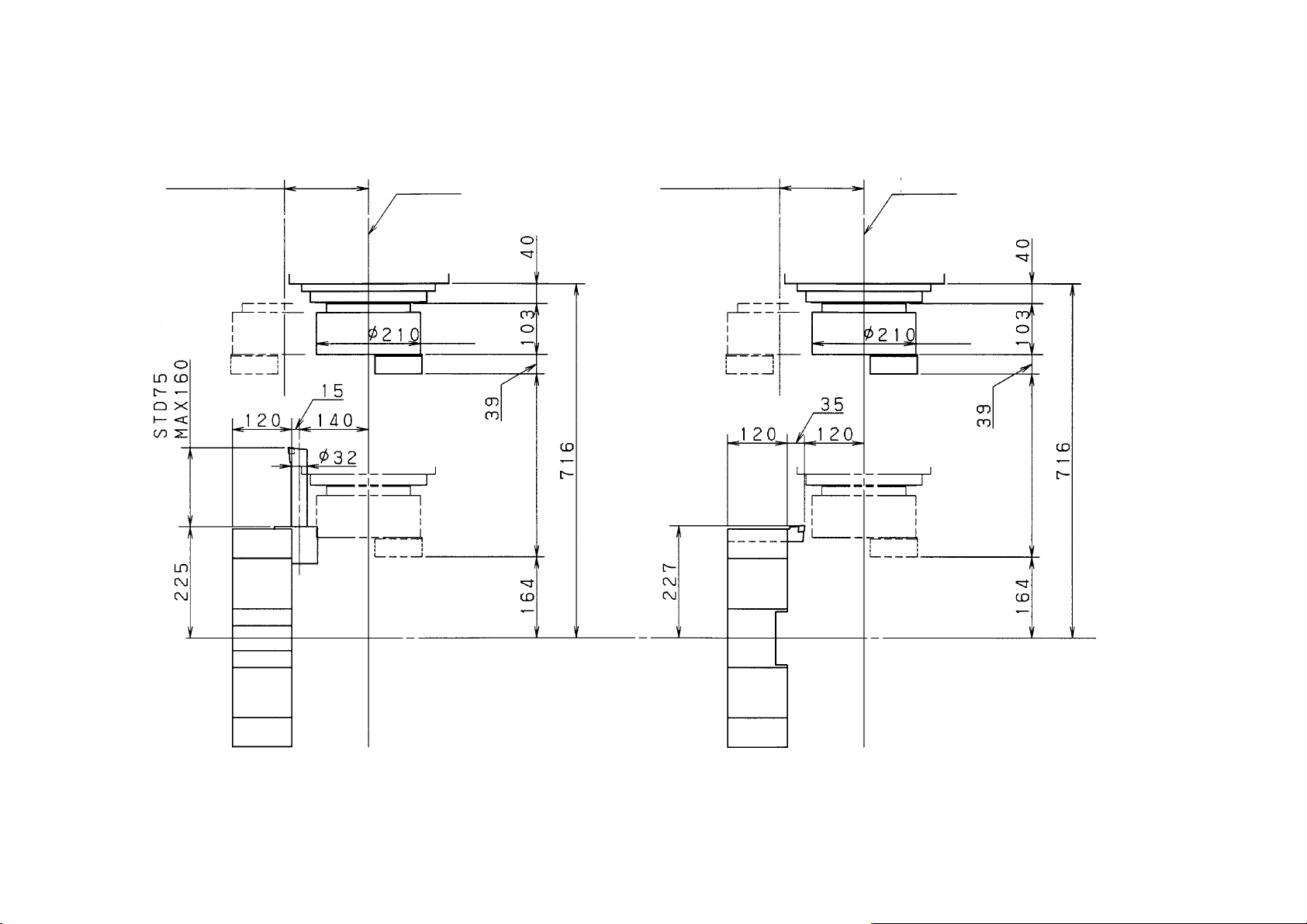
2-5 Major Dimensions
1.CS20/25 Major Dimension
(1) 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Type
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
2 - 10
Page 19

(2) 12-station VDI/VDI Rotating Tool Turret Type
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
2 - 11
Page 20

2. Spindle
CS20 Spindle
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
2 - 12
Page 21

CS25 Spindle
637,1
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
2 - 13
Page 22

3. Turret Head
(1) Turret Head list
No. Turret Head
1 12-BH
2 12-station VDI
3 12-station VDI Rotating Tool
2 - 14
Page 23

(2) 12-station Base Holder Turret Head
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
2 - 15
Page 24

(3) 12-station VDI/VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
2 - 16
Page 25

• How to Use Base Holder of VDI System
Mounting Method to Turret Head
A mounting method of a holder to the turret is as follows;
With an attached 10mm hexagon bar wrench inserted into the hexagon socket head cap
screw and turned rightward, the base holder is tightly fitted to the turret head.
Caution
• To mount a tool holder on the turret, do not tighten it with excessive force. Guideline
of tightening force applied is as in the right drawing.
• To take off a holder form the turret, loosen the clamp bolt by about 4 turnings.
2 - 17
Page 26

4. Solid Chuck and Soft Jaws
Jaw stroke(in diameter): J/Shifter stroke: Y
Soft Jaw
Details of Serrated Part
Symbol
Chuck T ype
HG-715-210 (Made by KITAGAWA) HG-730-254 (Made by KITAGA WA )
A 210 ( 8.3”) 254 (10”)
B 103 (4.1”) 127 (5”)
C 39 (1.5”) 46 (1.8”)
D 51 (2”) 51 (2”)
E 133.4 ( 5.25”) 171.4 ( 6.75”)
F 106.375 ( 4.188”) 139.719 ( 5.50”)
G 38 ( 1.5”) 45 (1.8”)
H M12x 30 M12x 35
I M12x 105 M16x 135
J/Y 12/28.5 (0.47/1.12”) 14.8/5 ( 0.58/1.38”)
K/L 95/35 (3.7”/1.4”) 110/40 (4.3”/1.6”)
M 12 (0.5”) 15 (0.6”)
N 38 (1.5”) 42 (1.7”)
O/P 33/14 (1.3”/0.5”) 37/16 (1.5”/0.6”)
Q 75 (3”) 90 (3.5”)
CS20 CS25
S/T 24/25 (0.9”/1”) 30/30 (1.2”/1.2”)
U/R 19/23 ( 0.7”/0.9”) 19/27 ( 0.7”/1.1”)
V M20 P2.5 M20 P2.5
W 111.5-83 (4.4”~3.3”) 125-90 (4.9”~3.5”)
2 - 18
Page 27

2 - 19
5. Connecting Parts for
φ210 Solid Chuck
No. Name Drawing No. or type Q‘ty
1 Rod 61Q3465830 1
2 Adapter B 61Q3465812 1
3 Adapter A 61Q3465223 1
4 Bolt with hexagonal hole 4B1235 6
5 Bolt with hexagonal hole 4B1030 6
6 Washer 4B825 6
7 Washer 1682-95-443-** 1
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
Page 28

2 - 20
Connecting Parts for
φ254 Solid Chuck
No. Name Drawing No. or type Q‘ty
1 Rod
2 Adapter B 1682-00-840-00 Each
3 Adapter A 1
4 Bolt with hexagonal hole 4B1235 6
5 Bolt with hexagonal hole 4B1040 6
6 Bolt with hexagonal hole 4B1030 6
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
Page 29

3. REQUIRED DIMENSION FOR MACHINE
3-1 Spindle Traveling Range
3-1-1 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Type
CS20 Spindle Traveling Range (Base Holder Type)
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
3 - 1
Position Area
C Feeder Area
D Area where initial stage one-touch
original point return is possible
Page 30
CS20 (Base Holder Turret Head Type)
3 - 2
STROKE 190
(7.5”)
(2.9”)
(5.5”)
(4.7”)
(8.8”)
I.D.
TOOL
(5.5”)
(0.6”)
(φ 1.3”)
X-AXIS ORIGIN
CHUCK
(
φ
8.3”)
STROKE 190
(7.5”)
(1.6”)
(4”)
(1.5”)
(14.6”)
(28.1”)
(4.7”)
(4.7”)
X-AXIS ORIGIN
8.3”)
CHUCK
(1.4”)
(
φ
(1.6”)
(4”)
(1.5”)
(14.6”)
(28.1”)
STROKE 370
STROKE 370
O.D.
(8.9”)
(6.4”)
TOOL
(6.4”)
Dimension: metric (mm)
Inch (”)
Page 31

3 - 3
CS25 Spindle Traveling Range (Base Holder Type)
Position Area
C Feeder Area
D Area where initial stage one-touch original point return is possible
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
Page 32

(7.5”)
STROKE 190
X-AXIS ORIGIN
(7.5”)
STROKE 190
X-AXIS ORIGIN
CS25 (Base Holder Turret Head Type)
3 - 4
inch (”)
TOOL
Dimension : metric (mm)
I.D.
(2.9”)
(4.7”)
(1.7”)
CHUCK
(
φ
10”)
(5.5”)
(6.3”)
(1.3”)
(5”)
φ
(
(1.8”)
(30.2”)
(14.5”)
(1.4”)
(4.7”)
(4.7”)
CHUCK
10”)
STROKE
(0.6”)
(8.9”)
(7.1”)
O.D.
TOOL
(8.9”)
(1.7”)
(5”)
(1.8”)
(30.2”)
(14.5”)
STROKE
(7.1”)
Page 33

12-station Base Holder Turret Head Type Interference Drawing
(1.4”)
8.3”)
φ
(
(
φ
10”)
(0.3”)
(φ 8.3”)
3 - 5
Dimension: metric (mm)
Inch (”)
Page 34

3-1-2 12-station VDI/VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Type
CS20 Spindle Traveling Range (VDI Type)
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
3 - 6
Position Area
C Feeder Area
D Area where initial stage one-touch
original point return is possible
Page 35

CS20 (VDI/VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Type)
I.D. Tool
3 - 7
STROKE 190
(2.9”)
(5.5”)
(9.6”)
Dimension: metric (mm)
(7.5”)
(
φ
1.3”)
STROKE 190
X-AXIS ORIGIN
(1.6”)
(φ 8.3”)
(5.3”)(2.7”)(2.7”)
CHUCK
(1.5”)
(4”)
(14.6”)
(28.1”)
STROKE 370
(11”)
(6.4”)
I.D. TOOL
(7.5”)
(2.7”)
(2.7”)
(φ 8.3”)
(1”)
(4.3”)
(1.3”)
O.D. TOOL
X-AXIS ORIGIN
CHUCK
• O.D. Tool
(1.6”)
(4”)
(1.5”)
(14.6”)
(28.1”)
STROKE 370
(6.4”)
Inch (”)
Page 36

STROKE 190
(7.5”)
X-AXIS ORIGIN
STROKE 190
(7.5”)
CS20 (VDI Rotating T ool Turret Head Type)
Rotary Tool
X-AXIS ORIGIN
3 - 8
Dimension: metric (mm)
(1.6”)
CHUCK
(φ 8.3”)
(1.5”)
(3.6”)(4.4”)
(4”)
(14.6”)
(28.1”)
(3.4”)
(3.5”)
(6.1”)
(φ 8.3”)
CHUCK
(1.5”)
STROKE 370
(8.3”)
(8.3”)
X-AXIS
(6.4”)
(2.7”)
ROTATION TOOL
(1.9”)
(1.1”)
Z-AXIS
ROTATION TOOL
(1.6”)
(4”)
(14.6”)
(28.1”)
STROKE 370
(6.4”)
(8”)(2.7”)
Inch (”)
Page 37

CS25 Spindle Traveling Range (VDI Type)
Dimension : metric (mm)
inch (”)
3 - 9
Position Area
C Feeder Area
D Area where initial stage one-touch
original point return is possible
Page 38

(7.5”)
STROKE 190
X-AXIS ORIGIN
(7.5”)
STROKE 190
X-AXIS ORIGIN
CS25 (VDI/VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Type)
3 - 10
(2.6”)
(1.3”)
(2.6”)
(1.2”)
I.D. TOOL
(5.5”)
(2.9”)
(
φ
10”)
(9.6”)
CHUCK
(5.5”)
(1.7”)(5”)
(1.8”)
(14.5”)
(30.2”)
STROKE 370
(7.1”)
(2.6”)
(2.6”)(1”)
O.D. TOOL
(
φ
(10.9”)
CHUCK
10”)
(1.7”)
I.D. Tool
(5”)
• O.D. Tool
(1.8”)
(14.5”)
(30.2”)
STROKE 370
(7.1”)
Page 39

(7.5”)
STROKE 190
X-AXIS ORIGIN
(7.5”)
STROKE 190
X-AXIS ORIGIN
CS25 (VDI/VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Type)
3 - 11
CHUCK
(
φ
10”)
(5.5”)
(4.4”)
(3.5”)
X-AXIS
ROTATION TOOL
(1.7”)
(5”)
(1.8”)
(14.5”)
(30.2”)
(6.3”)
(
φ
CHUCK
10”)
(3.4”)
STROKE 370
(3.5”)
(2.6”)
(1.9”)
(8.3”)
(7.1”)
(1.1”)
Z-AXIS
(8.3”)
(1.7”)
(5”)
(1.8”)
(14.5”)
(30.2”)
STROKE 370
(7.1”)
Rotary Tool
ROTATION TOOL
(2.6”)
(8.3”)
Page 40

12-station VDI/VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Type Interference Drawing
(2.7”)
(1”)
8.3”)
φ
(
(
φ
10”)
(0.6”)
(φ 10”)
3 - 12
Dimension: metric (mm)
Inch (”)
Page 41

3-2 Output Diagram
(1) S pindle Output Diagram
The equipment is equipped with variable AC motors. Output in a torque constant range differs
depending on the current spindle speed.
If heavy cutting (roughing, etc.) is carried out in the torque constant range, the spindle may
stop, not being able to endure a cutting force.
Therefore, select a speed range so that heavy cutting will be carried out in an output constant
range.
CS20
The following chart shows the output constant range which ensures the rated output of
the machine, "11 kW."
POWER
TORQUE
SPINDLE SPEED [min-1]
3 - 13
Page 42

CS25
The following chart shows the constant output range which ensures the rated output of
the machine, "18.5 kW."
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm)
TORQUE
POWER
Low-speed range M40 range 450to 1,200 min
High-speed range M41 range 1,200 to 4,000 min
LOW-SPEED WINDING TORQUE
CONST ANT RANGE
HIGH-SPEED WINDING TORQUE
CONST ANT RANGE
SPINDLE SPEED
How to Read the Diagram
Read the spindle speed you want to use on the bottom scale. Draw a line upward from that
point to make it intersect with a thick full line. Read the value of the intersecting point on the left
scale. This value indicates the maximum output(kW) at that spindle speed.
Read the spindle speed you want to use on the bottom scale. Draw a line upward from that
point to make it intersect with a thick dotted line. Read the value of the intersecting point on the
right scale. This value indicates the torque(kgf-m, N-m) at that spindle speed.
The top lines in the chart indicate the short-time rating.(ON for 5 minutes and OFF for 5
minutes in the 10-minute cycle) The bottom lines are used for continuous operation.
3 - 14
Page 43

(2) Rotating Tool Spindle Output Diagram
15-minute Rating
Continuous
Rating
3 - 15
Page 44
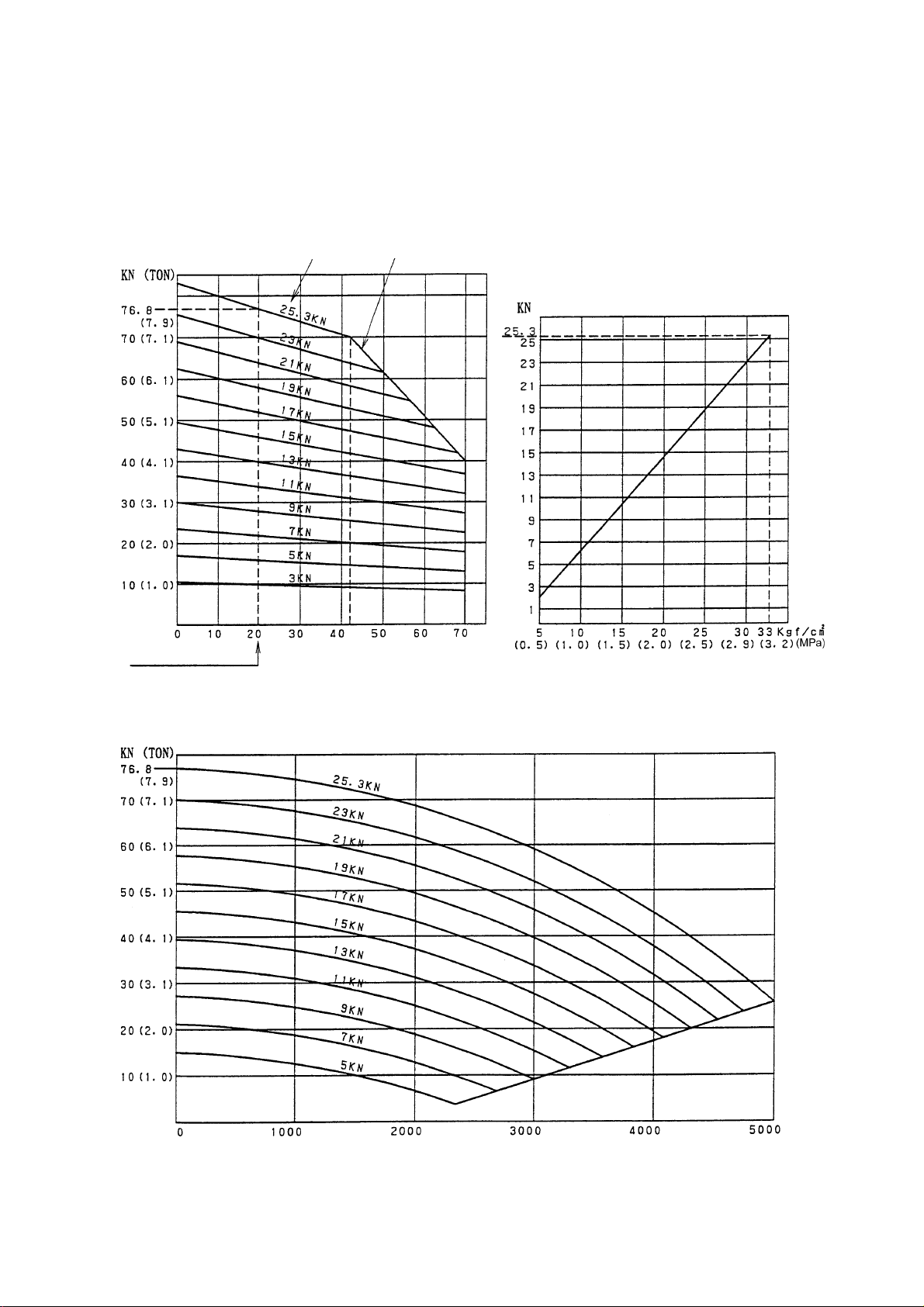
3-3 Chucking Pressure-Gripping Force Diagram
1. CS20
Chucking HG-715-210 (KITAGA WA)
Cylinder Y1230RE25 (KITAGA WA)
ST ATIC GRIPPING POWER
LINEAR DIAGRAM
INPUT
GRIPPING POWER LIMIT
INPUT
STANDARD SOFT JAW
GRIPPING SELECTION
CYLINDER SET PRESSURE
CENTER HEIGHT (mm)
GRIPPING POWER DECREASING LINEAR DIAGRAM (ST ANDARD SOFT JA W)
SPINDLE SPEED min
3 - 16
-1
(r.p.m)
Page 45

2. CS25
Chucking HG-730-254 (KITAGA WA)
Cylinder Y1235RE25 (KITAGA WA)
ST ATIC GRIPPING POWER
LINEAR DIAGRAM
INPUT
GRIPPING POWER LIMIT
INPUT
STANDARD SOFT JAW
GRIPPING SELECTION
CENTER HEIGHT (mm)
CYLINDER SET PRESSURE
GRIPPING POWER DECREASING LINEAR DIAGRAM (ST ANDARD SOFT JA W)
INPUT
SPINDLE SPEED min
3 - 17
-1
(r.p.m)
Page 46

3-4 Method of Obtaining Tool Center Height
The center height of O.D. tools is 25 mm.
If the O.D. tool needs center height adjustment, place a spacer, etc. and adjust the center height.
Block
Flat Place Such as Surface Plate
Adjust the center height with a 25-mm block outside the machine and attach to the tool post.
Place a face plate if necessary.
3 - 18
Page 47

4. TOOLING SYSTEM
4-1 CS20 12-station Base Holder T urret Head Assembly T ools (St andard)
CI.
1594-108-96-00
1594-108-97-00
Chucks
1594-108-98-00
1594-113-13-00
PARTS
NAME
Power chuck
(Solid)
Power chuck
(1 set)
Cylinder
(1 set)
Soft jaw
SKETCH DESCRIPTION
1.210 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
2. Solid cylinder
Cylinder
Cylinder
Chuck
Draw bar
3. Soft jaws (1 set)
1.210 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
HG-715-210
1. Solid cylinder
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
Y1230RE25
2. Proximity switch
BES516-329-E3R-3
3. Draw bar
1. For 210 chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
08001351801(SB08B1)
1593-329-57-00
Base
Holder
1593-028-01-00
O.D. T oolsDrilling T ool
1593-668-08-00
1593-668-09-00
1593-668-10-00
I.D. T ool
Boring
base holder
Reverse
cutting spacer
32 shank boring
bar socket
25 shank boring
bar socket
20 shank boring
bar socket
6 pieces included as standard
accessories
1682-40-208-
1745-40-430-
1593-668-51-
1593-668-52-
1593-668-53-
1596-337-21-00
MT No. 2
drill socket
For MT No. 2 shank drill
(14.5 to 23)
1682-95-337-
4 - 1
Page 48

4-2 CS20 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Assembly Tools (Selected)
(1/2)
CI.
1593-329-59-00
Base
Holder
1593-668-1 1-00
1593-668-12-00
1593-668-06-00
I.D. T ools
1593-668-07-00
1593-337-04-00
PARTS
NAME
U-drill
base holder
16 shank boring
bar socket
12 shank boring
bar socket
10 shank boring
bar socket
8 shank boring
bar socket
MTNo.2~MTNo.1
SKETCH DESCRIPTION
1. Cover
2. Socket ( 32, 25, 20)
1682-40-21 1-
1593-668-54-
1593-668-55-
1593-668-56-
1593-668-57-
08001380001
1596-337-19-00
1596-337-20-00
1593-340-56-00
Drilling T ools
1593-340-57-00
drill sleeve
MTNo.1
drill sleeve
MTNo.3
drill sleeve
8 center drill
socket
5 center drill
socket
For MT No. 1 shank drill
( 2 to 14)
1682-95-314-
For MT No. 3 shank drill
(23.5 to 32)
1682-95-313-
1. Used for the boring base
holder
2. JIS-1A type for 2 x 60
1682-95-312-
1. Used for the boring base
holder
2. JIS-1A type for 2 x 60
1682-95-31 1-
4 - 2
Page 49

(2/2)
CI. SKETCH DESCRIPTION
T ap Holders
Other T ools
PARTS
1593-347-01-00
1593-347-02-00
08
1594-331-19-00
T ap holder
Collet
(Alone)
Cleaning tool
NAME
1. Tapper made by NIKKEN;
S32-Z12-87.5L, M3 to M16
(W/o torque limiter)
2. Collet excluded
3.40,32 socket required
1. Collet made by NIKKEN
(ZMK12 - Tap size)
2. Size:M3, M4, M5, M6, M8,
M10, M12, M14, M16
1. Cover
2. Nozzle
3. Pipe
1682-40-21 1-
4 - 3
Page 50

4-3 CS25 12-station Base Holder T urret Head Assembly T ools (St andard)
CI. SKETCH DESCRIPTION
Chucks
PARTS
1594-109-21-00
1594-109-19-00
1594-109-20-00
1594-1 13-13-00
Power chuck
(Solid)
Power chuck
(1 set)
NAME
Cylinder
(1 set)
Soft jaws
Cylinder
Cylinder
Chuck
Draw bar
1.254 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
2. Solid cylinder
3. Soft jaws (1 set)
1.254 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
HG-730-254
2. Pressure gauge 33kgf/m
1. Solid cylinder
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
Y1235RE25
2. Proximity switch;
BES516-329-E4 (2 pcs.)
3. Draw bar, stopper stay
1. For 254 chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
08001351845(SB10B1)
}
Included as stan-
dard accessories
2
1593-329-57-00
Base
Holder
1593-028-01-00
O.D. T ool
1593-668-08-00
1593-668-09-00
1593-668-10-00
I.D. T ools
Boring
base holder
Reverse cutting
spacer
32 shank
boring bar socket
25 shank
boring bar socket
20 shank
boring bar socket
6 pieces included as standard accessories
1682-40-208-
1745-40-430-
1593-668-51-
1593-668-52-
1593-668-53-
4 - 4
Page 51

4-4 CS25 12-station Base Holder Turret Head Assembly Tools (Selected)
(1/2)
CI.
1593-329-59-00
Base
Holder
1593-668-1 1-00
1593-668-12-00
1593-668-06-00
I.D. T ools
1593-668-07-00
1593-337-04-00
PARTS
NAME
U-drill
base holder
16 shank
boring bar socket
12 shank
boring bar socket
10 shank
boring bar socket
8 shank
boring bar socket
MTNo.2 - MTNo.1
drill sleeve
SKETCH
DESCRIPTION
1. Cover
2. Socket (I.D. 32/25/20)
included 1682-40-21 1-
1593-668-54-
1593-668-55-
1593-668-56-
1593-668-57-
08001380001
1596-337-19-00
1596-337-21-00
1596-337-20-00
Drilling T ools
1593-340-56-00
1593-340-57-00
MTNo.1
drill socket
MTNo.2
drill socket
MTNo.3
drill socket
8 center
drill socket
5 center
drill socket
For MT No. 1 shank drill
( 2 to 14)
1682-95-314-
For MT No. 2 shank drill
(14.5 to 23)
1682-95-337-
For MT No. 3 shank drill
(23.5 to 32)
1682-95-313-
1. Used for the boring base
holder
2. JIS-1A type for 2 x 60
1682-95-312-
1. Used for the boring base
holder
2. JIS-1A type for 2 x 60
1682-95-31 1-
4 - 5
Page 52

(2/2)
CI. SKETCH
T ap Holders
PARTS
1593-347-01-00
1593-347-02-00
08
Tap holder 1. Tapper made by NIKKEN;
Collet
(Alone)
NAME
DESCRIPTION
S32-Z12-87.5L, M3 to M16
(W/o torque limiter)
2. Collet excluded
3.40 x32 socket required
1.Collet made by NIKKEN
(ZMK12 - Tap size)
2.Size:M3, M4, M5, M6, M8,
M10, M12, M14, M16
Other T ools
4 - 6
Page 53

4-5 CS20 12-station VDI Turret Head Assembly Tools (Standard)
CI. SKETCH DESCRIPTION
Chucks
PARTS
1594-108-96-00
1594-108-97-00
1594-108-98-00
1594-1 13-13-00
NAME
Power chuck
(Solid)
Power chuck
(1 set)
Cylinder
(1 set)
Soft jaws
Cylinder
Cylinder
Chuck
Draw bar
1.210 solid chuck
(Made by KITAGAWA)
2. Solid cylinder
3. Soft jaws
1.210 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
HG-715-210
1. Solid cylinder
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
Y1230RE25
2. Proximity switch
BES516-329-E3R-3
3. Draw bar
1. For 210 chuck
(Made by KITAGAWA)
08001351801(SB08B1)
4 - 7
Page 54

4-6 CS25 12-station VDI Turret Head Assembly Tools (Standard)
CI. SKETCH DESCRIPTION
PARTS
1594-109-21-00
Power chuck
(Solid)
1594-109-19-00
NAME
Power chuck
(1 set)
Cylinder
Chuck
1.254 solid chuck
(Made by KITAGAWA)
2. Solid cylinder
3. Soft jaws (1 set)
1.254 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
HG-730-254
2. Pressure gauge 33kgf/m
Chucks
1594-109-20-00
Cylinder
(1 set)
Draw bar
Cylinder
1. Solid cylinder
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
Y1235RE25
2. Proximity switch
BES516-329-E4(2 pcs.)
3. Draw bar, stopper stay
1594-1 13-13-00
Soft jaws
1. For Bedienung 254 chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
08001351845(SB10B1)
2
4 - 8
Page 55

4-7 CS20/25 12-station VDI Turret Head Assembly Tools (Selected)
(1/2)
CI. SKETCH DESCRIPTION
Base HoldersI.D. T ools
PARTS
1594-331-18-00
1596-331-16-00
1593-668-08-00
1593-668-09-00
1593-668-10-00
NAME
Outer figure cutting
base holder
Boring
base holder
32 shank
boring bar socket
25 shank
boring bar socket
20 shank
boring bar socket
1682-67-201-
1682-67-400-
1593-668-51-
1593-668-52-
1593-668-53-
1593-668-11-00
1593-668-12-00
1593-668-06-00
1593-668-07-00
1593-337-04-00
1596-337-19-00
Drilling T ools
1596-337-21-00
16 shank
boring bar socket
12 shank
boring bar socket
10 shank
boring bar socket
8 shank
boring bar socket
MTNo.2 - MTNo.1
drill sleeve
MTNo.1
drill socket
MTNo.2
drill socket
1593-668-54-
1593-668-55-
1593-668-56-
1593-668-57-
08001380001
For MT No. 1 shank drill
( 2 to 14)
1682-95-314-
For MT No. 2 shank drill
(14.5 to 23)
1682-95-337-
4 - 9
Page 56

(2/2)
CI. SKETCH DESCRIPTION
Drilling T ools
T ap HoldersOther T oolsU-drill
PARTS
1596-337-20-00
1593-340-56-00
1593-340-57-00
1593-347-01-00
1593-347-02-00
08
NAME
MTNo.3
drill socket
8 center
drill socket
5 center
drill socket
T ap holder
Collet
(Alone)
For MT No. 3 shank drill
(23.5 to32)
1682-95-313-
1. Used for the boring base holder
2. JIS-1A type for 2 x 60
1682-95-312-
1. Used for the boring base holder
2. JIS-1A type for 2 x 60
1682-95-311-
1. T apper made by NIKKEN;
S32-Z12-87.5L, M3 to M16
(W/o torque limiter)
2. Collet excluded
3.40 x32 socket required
1. Collet made by NIKKEN
(ZMK12 - Tap size)
2. Size:M3, M4, M5, M6, M8,
M10, M12, M14, M16
1593-355-03-00
1594-331-20-00
1596-331-17-00
Plug
Cleaning tool
1742-67-568-
1. Cover
2. Nozzle
3. Pipe
1682-67-204-
(Socket 32/25/20),
1642-67-401- Cover
1682-67-204- Base holder
4 - 10
Page 57

4-8 CS20 12-station VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Assembly Tools
(Standard)
CI.
1594-108-96-00
1594-108-97-00
1594-108-98-00
Chucks
1594-113-13-00
PARTS
NAME
Power chuck
(Solid)
Power chuck
(1 set)
Cylinder
(1 set)
Soft jaws
SKETCH DESCRIPTION
1.210 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
2. Solid cylinder
Cylinder
Cylinder
Chuck
Draw bar
3. Soft jaws
1.210 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
HG-715-210
1. Solid cylinder (Made by
KIT AGAWA) Y1230RE25
2. Proximity switch
BES516-329-E3R-3
3. Draw bar
1. For 210 chuck
(Made by KITAGAWA)
08001351801(SB08B1)
4 - 11
Page 58

4-9 CS25 12-station VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Assembly Tools
(Standard)
Cl. SKETCH
Chucks
PARTS
1594-109-21-00
1594-109-19-00
1594-109-20-00
1594-113-13-00
Cylinder
(1 set)
NAME
Power chuck
(Solid)
Cylinder
Power chuck
(1 set)
Draw bar
Cylinder
Soft jaws
Chuck
DESCRIPTION
1.254 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
2. Solid cylinder
3. Soft jaws (1 set)
1.254 solid chuck
(Made by KIT AGA W A)
HG-730-254
2. Pressure gauge 33kgf/m
1. Solid cylinder (Made by
KITAGA W A) Y1235RE25
2. Proximity switch
BES516-329-E4 (2 pcs.)
3. Draw bar, stopper stay
1. For 254 chuck
(Made by KITAGAWA)
08001351845(SB10B1)
2
4 - 12
Page 59

4-10 CS20/25 12-st ation VDI Rotating Tool Turret Head Assembly Tools (Selected)
(1/2)
CI. SKETCH DESCRIPTION
Base Holders
PARTS
1594-331-18-00
1596-331-16-00
1742-68-002-00
1742-68-001-00
1593-668-08-00
NAME
Outer figure cutting
base holder
Boring
base holder
Z-axis rotary
tool holder
X-axis rotary
tool holder
32 shank
boring bar socket
1682-67-201-
1682-67-400-
Collet dependent on the selected
tool
Collet dependent on the selected
tool
1593-668-51-
1593-668-09-00
1593-668-10-00
1593-668-1 1-00
I.D. T oolsDrilling T ool
1593-668-12-00
1593-668-06-00
1593-668-07-00
25 shank
boring bar socket
20 shank
boring bar socket
16 shank
boring bar socket
12 shank
boring bar socket
10 shank
boring bar socket
8 shank
boring bar socket
1593-668-52-
1593-668-53-
1593-668-54-
1593-668-55-
1593-668-56-
1593-668-57-
1596-337-21-00
MTNo.2
drill socket
For MT No. 2 shank drill
(14.5 to 23)
1682-95-337-
4 - 13
Page 60

(2/2)
CI. SKETCH DESCRIPTION
Drilling T ools
PARTS
1593-337-04-00
1596-337-19-00
1596-337-20-00
1593-340-56-00
1593-340-57-00
NAME
MTNo.2 - MTNo.1
drill sleeve
MTNo.1
drill socket
MTNo.3
drill socket
8 center drill
socket
5 center drill
socket
08001380001
For MT No. 1 shank drill
( 2 to 14)
1682-95-314-
For MT No. 3 shank drill
(23.5 to32)
1682-95-313-
1. Used for the boring base holder
2. JIS-1A type for 2 x 60
1682-95-312-
1.Used for the boring base holder
2.JIS-1A type for 2 x 60
1682-95-311-
1593-347-01-00
1593-347-02-00
T ap HoldersRotary T oolsOther T ools
08
1596-352-09-00
13
1593-347-08-00
05
1593-355-03-00
1594-331-20-00
T ap holder
Collet
(Alone)
Collet
(Alone)
T ap collet
Plug
Cleaning tool
1. T apper made by NIKKEN;
S32-Z12-87.5L, M3 to M16
(W/o torque limiter)
2. Collet excluded
3.40 x 32 socket required
1. Collet made by NIKKEN
(ZMK12 - Tap size)
2. Size:M3, M4, M5, M6, M8,
M10, M12, M14, M16
1. Collet (ESX20-D)
2. Size: 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
8, 9, 10, 11, 12
1. Tap collet (ET -1-20)
2. Size: M3, M4, M5, M6, M8, M10
1742-67-568-
1. Cover
2. Nozzle
3. Pipe
1682-67-204-
1596-331-17-00
U-drill
(Socket 32/25/20),
1642-67-401- Cover
1682-67-204- Base holder
4 - 14
Page 61

INVERTED VERTICAL TURNING CELL
CS20/25
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
SPECIFICATIONS
SEIKI-SEICOS Σ21L
Version 2.02
12-2001
03-1998 First Edition
 Loading...
Loading...