Page 1
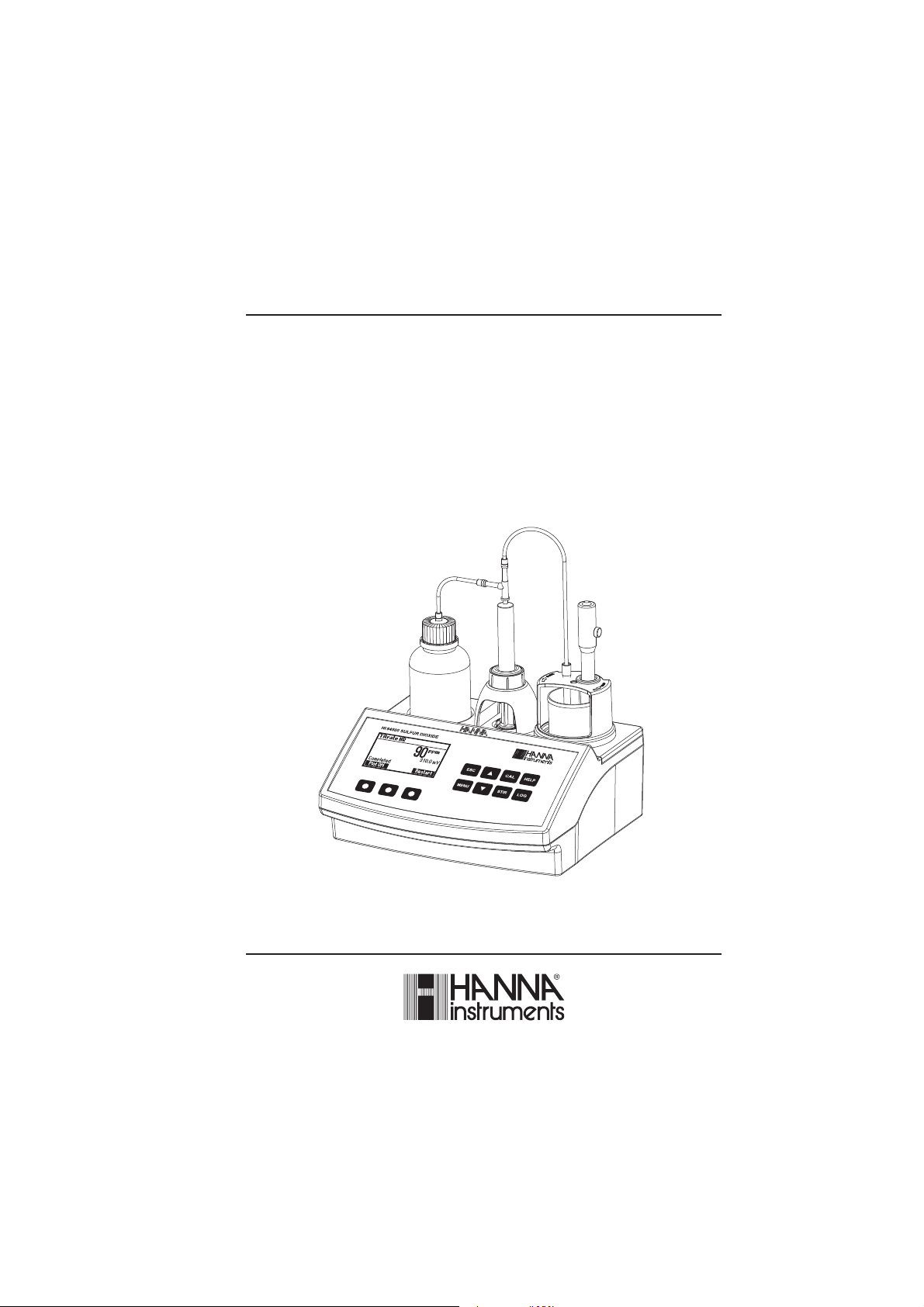
Instruction Manual
HI 84500
FREE & TOTAL SULFUR DIOXIDE
MINITITRATOR
for wine analysis
www.hannainst.com
1
Page 2

Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Instruments product.
Please read this instruction manual carefully before using this instrument. This manual will
provide you with the necessary information for correct use of this instrument, as well as a precise
idea of its versatility.
If you need additional technical information, do not hesitate to e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com
or view our worldwide contact list at www.hannainst.com.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION................................................................................................. 3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................................ 3
SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................... 5
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION .................................................................................................... 6
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION................................................................................................... 7
TITRATOR STARTUP ............................................................................................................. 9
SETUP MENU .................................................................................................................... 10
GUIDE TO DISPLAY CODES ................................................................................................... 13
ELECTRODE PREPARATION .................................................................................................. 16
DOSING PUMP INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 17
DOSING PUMP PRIME PROCEDURE ..................................................................................... 17
ELECTRODE CHECK PROCEDURE .......................................................................................... 19
PUMP CALIBRATION PROCEDURE ........................................................................................ 19
FREE SO2 MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE................................................................................ 21
TOTAL SO2 MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE .............................................................................. 24
ORP MEASUREMENT .......................................................................................................... 28
PC INTERFACE AND DATA TRANSFER ................................................................................... 30
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE ................................................................................................ 31
ELECTRODE CONDITIONING AND MAINTENANCE .................................................................. 32
ACCESSORIES ..................................................................................................................... 34
WARRANTY........................................................................................................................ 35
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the written consent
of the copyright owner, Hanna Instruments Inc., Woonsocket, Rhode Island, 02895, USA.
2
Page 3

PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
Please examine this product carefully. Make sure that the instrument is not damaged. If any
damage occurred during shipment, please notify your Dealer.
Each HI 84500 minititrator is supplied complete with:
• HI 84500-70 Reagent Kit for SO2 determination
• HI 3148B ORP electrode
• HI 7082 Electrode Fill Solution (30 mL)
• Two 100 mL beakers
• Two 20 mL beakers
• Scissors
• Dosing Pump Valve
• 5 mL Syringe
• 1 mL Plastic Pipette
• Tube set (aspiration tube with titrant bottle cap and dispensing tube with tip)
• Stir bar
• Power Adapter
• Two sachets of cleaning solution for wine deposits
• Two sachets of cleaning solution for wine stains
• Instruction manual
Note:Save all packing material until you are sure that the instrument works correctly.
Any defective item must be returned in its original packing.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The HI 84500 is a low-cost, easy to use, microprocessor-based automatic titrator that benefits
from Hanna’s years of experience as a manufacturer of analytical instrumentation.
The instrument incorporates a simple and reliable dosing pump which ensures high dosing
reproducibility. Pump calibrations, performed with the provided Hanna reagents, assure the
accuracy of the instrument.
The instrument comes with a preprogrammed method for Free and Total Sulfur Dioxide
measurements in wine. The instrument uses a powerful algorithm which analyzes the shape of
the electrode response in order to determine when the titration has reached completion.
The HI 84500 provides a simple user interface. By simply pressing the Start key in Titration
mode, the instrument will automatically titrate the sample to the equivalence point and the
results are immediately displayed in ppm. Another titration can be started immediately by
pressing Restart.
3
Page 4
Hp 0.3 1.3 2.3 3.3 4.3 5.3 6.3 7.3 8.3 9.3
OSeerF
2
41 81 22 82 53 44 55 96 78 901
A dedicated HELP key aids in setup, calibration, status and troubleshooting.
Other features:
• ORP meter
• Stirrer speed control
• Graphic mode to display the titration data
• Data can be stored using the log feature and then exported to a USB stick or transferred
to a PC using the USB connection
• Log on demand for up to 400 samples (200 for mV measurements; 200 for titration
results)
• GLP feature, to view calibration data for the pump
SIGNIFICANCE OF USE
Wine makers add sulfur dioxide to wine in order to inhibit bacteria and wild yeast growth and to
serve as an antioxidant to prevent browning.
When SO2 is added to wine, a portion of it becomes immediately bound while a remaining portion
is unbound SO2. The portion that is unbound is also called free; it is responsible for protecting the
wine. The bound and unbound SO2 together are referred to as total SO2.
The relationship between the amount of SO2 added and the amount of free SO2 is complex. This
relationship is governed by the total amount of SO2 in the wine. The exact relationship between free
and bound will vary wine to wine. The amount of free SO2 depends on how much is added, how much
was present before the addition and how much was immediately bound.
Free SO2 exists in two forms. Bisulfite (HSO3¯) is the predominante form but is relatively ineffective.
Molecular SO2 is the minor form and is responsible for protecting the wine.
The amount of molecular SO2 available in wine is depended on the amount of free SO2 present and
the pH. Typically 0.8 ppm of molecular SO2 provides adequate protection against bacteria growth
and oxidation. In order to obtain this value for a wine sample that has a pH of 3.2 you would need
22 ppm of free SO2, if the pH was at 3.5 you would need double, 44 ppm.
Molecular SO2 can be detected by human senses at about 2.0 ppm. This level is needed for
maximum protection of wine. Higher levels are needed for sweet and most notable, botrytised wine.
The HI 84500
can be used to test for free and total SO2 in all wines, including red, which are
difficult to test using traditional methods associated with a distinctive color change to determine the
end point.
4
Page 5

SPECIFICATIONS
Titrator Range Low Range: 1.0 to 40.0 ppm of SO
High Range: 30 to 400 ppm of SO
2
2
Resolution Low Range: 0.1 ppm
High Range: 1 ppm
Accuracy Low Range: 3% of reading or ±0.5 ppm @ 25 °C, whichever is greater
High Range: 3% of reading or ±1 ppm @ 25 °C, whichever is greater
Sample volume 50 mL
Titration method Ripper method
Principle Equivalence point redox titration
Pump speed 10 mL/min
Stirring speed 700 rpm
Log data Up to 200 samples
ORP meter ORP meter -2000.0 to 2000.0 mV
ORP Resolution 0.1 mV
ORP Accuracy ± 1 mV
Log data Up to 200 samples
ORP Electrode HI 3148B
Environment 0 to 50 °C (32 to 122 °F); max 95% RH non-condensing
Power supply 12 Vdc power adapter
Dimensions 235 x 200 x 150 mm (9.2 x 7.9 x 5.9”)
Weight 1.9 kg (67.0 oz.)
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code Description
HI 84500-50 Low Range Titrant
HI 84500-51 High Range Titrant
HI 84500-55 Calibration Standard
HI 84500-60 Acid Reagent
HI 84500-61 Alkaline Reagent (Total SO2)
HI 84500-62 Stabilizer Packet
5
Page 6

PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
The HI 84500 determines the free and total sulfur dioxide concentration in wine using the Ripper
method. Excess iodide added to the wine sample reacts with iodate introduced by the titrant to
produce iodine.
-
IO
+ 5I- + 6H
3
+
→ 3I
+ 3H2O
2
The iodine produced in the sample then reacts with sulfur dioxide in the wine according to the redox
reaction below:
H2SO3 + I
→ H
2
2SO4
+ 2HI
The HI 84500 utilizes an ORP electrode to monitor the redox titration. The integrated algorithm
detects when the reaction is complete (equivalence point). The volume of titrant required to reach the
equivalence point, the titrant concentration and the sample size are used to calculate the sulfur
dioxide concentration in the wine sample.
6
Page 7
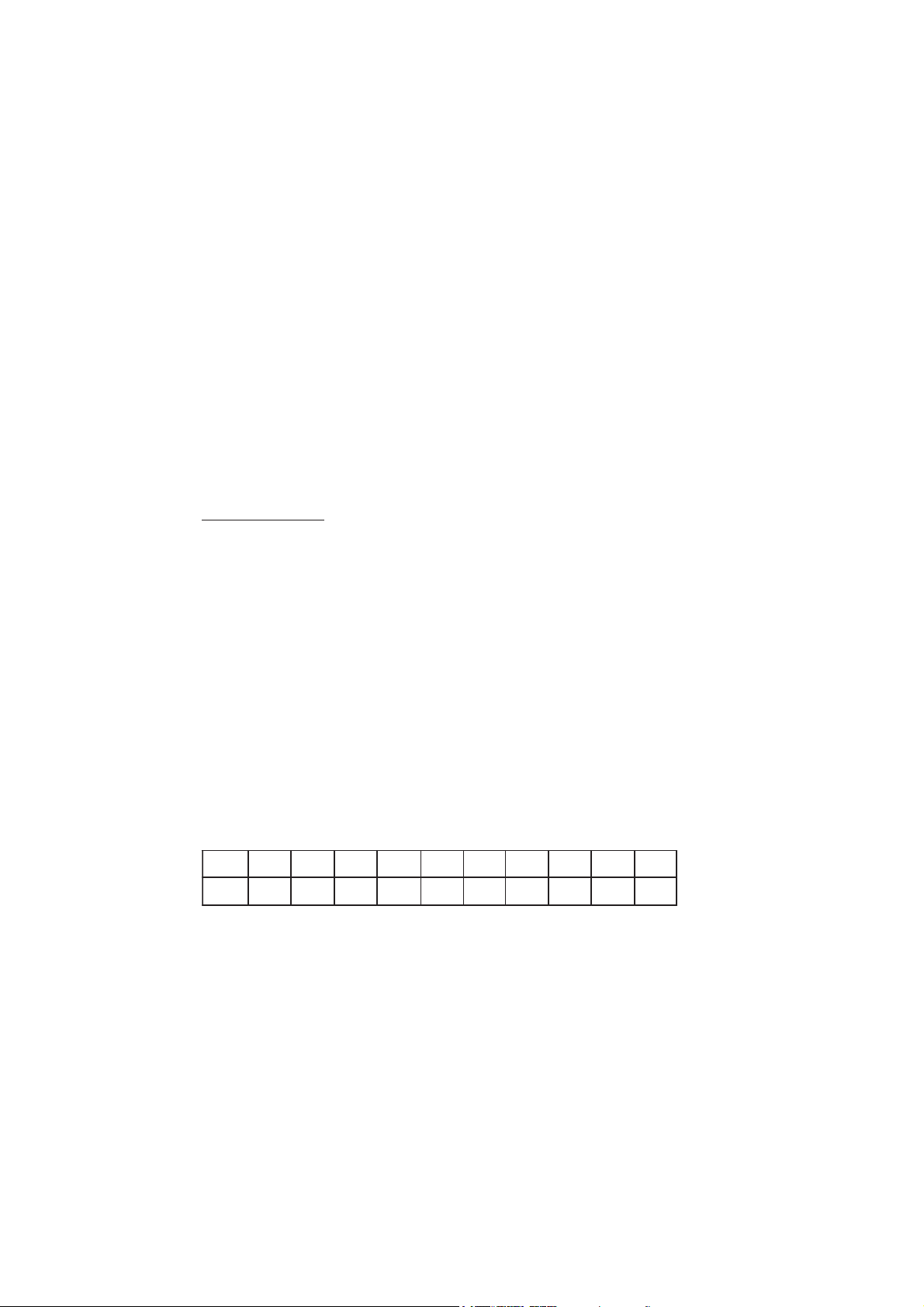
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
OVERHEAD VIEW
1) Titrant bottle
2) Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
3) Keypad
4) Electrode holder
5) Dispensing tube
FRONT VIEW
REAR VIEW
6) ORP Electrode
7) Beaker
8) Dosing pump
9) Power switch
10) Power adapter
11) USB connector (PC interface)
12) USB connector (Storage interface)
13) BNC electrode connector
14) Titrant bottle
15) Syringe
16) Aspiration tube
17) Dosing Pump Valve
7
Page 8
KEYPAD FUNCTION
ESC - used to leave the current screen and to return either to the previous screen or to the
main screen. In Setup menu, exits a parameter without changing the value.
/ - used to modify the parameter values, to scroll the information displayed while
viewing a help screen or to move between the options from the instrument’s Setup menu
CAL - used to access the Pump calibration
HELP - used to access/exit the instrument’s contextual help
LOG - used to save the current mV-ORP reading in ORP meter mode and the titration result
MENU - used to enter Setup, Recall or GLP selection menu, while instrument is in ORP or
Titration mode
STIR - used to start/stop the stirrer
Note: The stirrer starts automatically during pump calibration and titration, it cannot
be stopped by pressing STIR key.
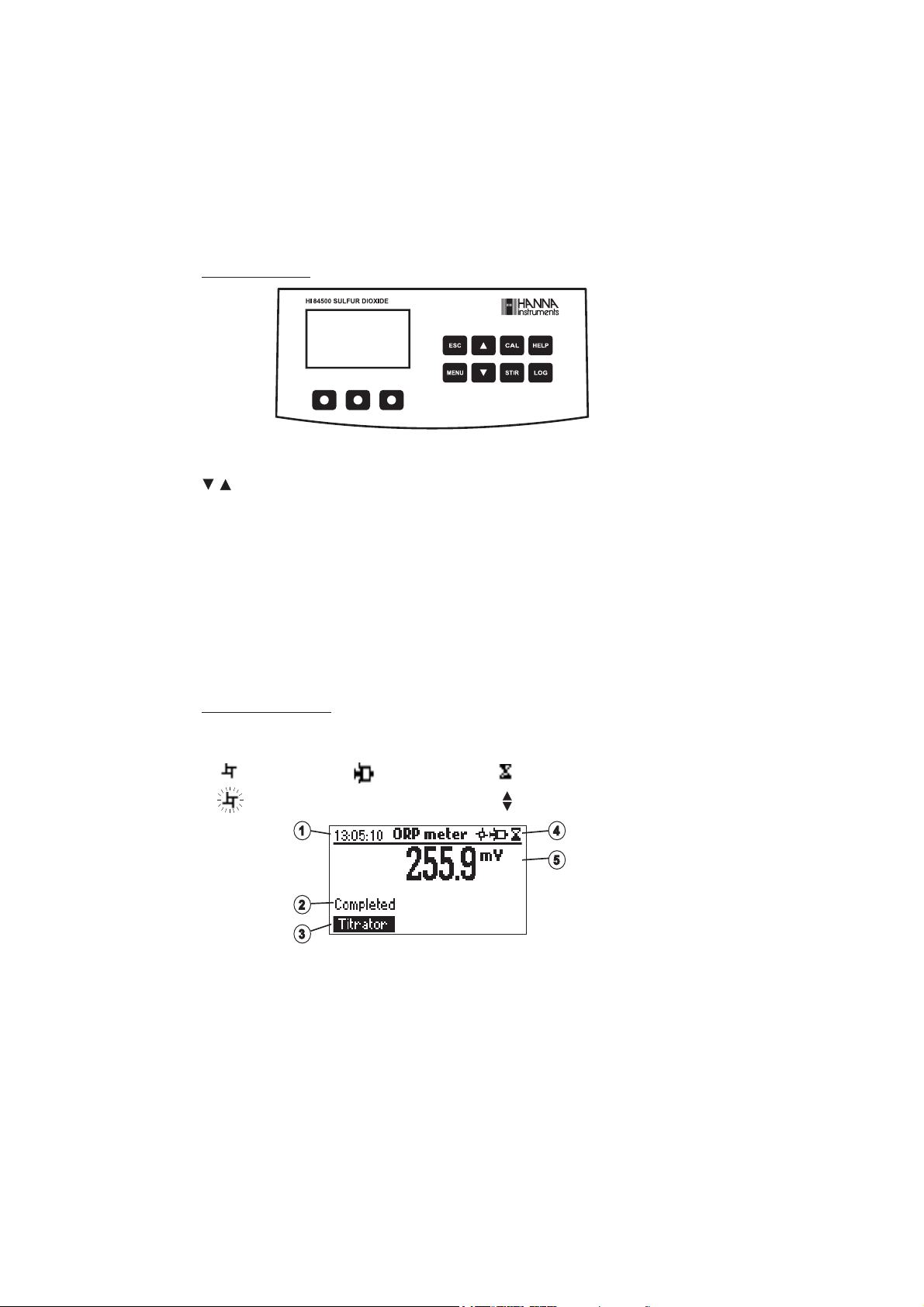
GUIDE TO INDICATORS
During the instrument’s operation information is displayed on the LCD.
Displayed icons:
Unstable reading.Stirrer on. Pump running.
Stirrer is not working properly.
1) Current time and instrument mode information (ORP meter or Titrator)
2) Instrument status
3) Virtual option keys
4) Stirrer and reading status
5) Main reading information
8
Parameter can be modified.
Page 9

DOSING PUMP
The dosing pump is based on a valve that automatically moves the titrant between the titrant
bottle and syringe when filling the syringe and between the syringe and sample when
dispensing. A replaceable 5 mL plastic syringe is used to limit the amount of titrant used per test
to ensure the highest possible accuracy. Before a set of titrations, it is necessary to prime the
dosing system.
Note: Once titrations have been completed, the dosing system should be cleaned with deionized
water using the prime feature.
TITRATOR STARTUP
This is a general outline of the steps required to perform a titration. The following topics are
expanded upon in each section that follows.
• Place the instrument on a flat table. Do not place the instrument in direct sun light.
• Connect the power adapter to the instrument.
• Turn the instrument ON using the power switch from the rear panel of the instrument.
• Set up the instrument. See the “Setup Menu” section for details.
• Connect the ORP sensor to the instrument.
• Connect the tubes and the valve. See the “Dosing Pump Installation” section for the
procedure.
• Remove the titrant bottle cap and replace it with the bottle cap with tubes. Place the titrant
bottle in the appropriate place on the titrator top.
Note: Different titrants are required based on the concentration. See “Pump Calibration Procedure”
for details.
• Prime the syringe. To assure high accuracy, verify there are no air bubbles in the syringe or
tubing.
• Calibrate the pump.
Note: Different volumes of standard are required based on the concentration. See “Pump
Calibration Procedure” for details.
• Prepare the sample.
• Run a titration and log sample results.
9
Page 10

SETUP MENU
The titrator’s setup menu may be accessed from the main screen (meter or titrator mode) by
pressing the MENU key, then Setup.
A list of setup parameters will be displayed with currently configured setting.
While in the setup menu it is possible to modify the instrument’s operation parameters. The
ARROW keys permit the user to scroll the setup parameters.
Press HELP to view the contextual help.
Press ESC to return to the main screen.
Range Setup
Use Low measurement range for 1.0 - 40.0 ppm.
Use High measurement range for 30 - 400 ppm.
Use the appropriate titrant for each range.
To ensure a high accuracy, it is recommended to
recalibrate the pump after the valve, titrant or
electrode has been changed.
Time
Press the Modify key to change the time and time
format.
Date
Press Format to switch between 12 hour (am/pm)
and 24 hour mode.
Press to highlight the value to be modified. Use
the ARROW keys to change the value. Press Accept
to confirm the new value or ESC to return to the
setup.
Press the Modify key to change the date and date
format.
10
Page 11

Key Beep
Error Beep
Decimal Separator
Press Format to cycle between the available date
formats.
Press to highlight the value to be modified. Use
the ARROW keys to change the value. Press Accept
to confirm the new value or ESC to return to the
setup.
Select Enable to activate or Disable to deactivate
the Key Beep function.
If enabled, a short beep will be heard every time a
key is pressed.
Select Enable to activate or Disable to deactivate
the Error Beep function.
If enabled, a beep will be heard when an error
condition occurs.
This option allows the user to select the symbol
used for a decimal separator.
LCD Contrast
This option is used to set the display’s contrast.
Press Modify to change the display’s contrast.
The default value is 8.
Use the ARROW keys or / to increase/
decrease the value. Press Accept to confirm the value
or ESC to return to the setup menu.
11
Page 12

LCD Backlight
Language
Tutorial
Press Modify to change the backlight level.
The default value is 3.
Use the ARROW keys or / to increase/
decrease the backlight level.
Press Accept to confirm or ESC to return to the
setup menu.
Press the corresponding virtual option key to change
the language.
If the selected language cannot be loaded, the
previously selected language will be reloaded.
If no language can be loaded at startup the instrument
will work in “safe mode”. In “safe mode” all
messages are displayed in English. Tutorial and help
information are not available.
Enable or Disable the Tutorial. This helpful tool
offers additional information during calibration and
titration.
Meter Information
Press Select to view the firmware version, language
version, mV factory calibration date and time,
method version.
Press ESC to return to the setup menu.
12
Page 13

Restore Factory Settings
GUIDE TO DISPLAY CODES
Press Select to restore the factory settings.
Press Yes to confirm the restore process or No to
return without restoring.
Press ESC to return to the setup menu.
This screen appears when the instrument is turned
on during the initialization process.
Titration screen display.
Titration screen when a titration is in progress.
Prime burette screen.
13
Page 14

PUMP CALIBRATION MESSAGES
Prime burette screen when the dosing system is
running.
This error message appears when the pump is not
working properly. Check the tubing, valve and
syringe. Press Restart to try again.
Pump calibration is initiated by pressing the Start
key.
This screen appears while pump calibration is in
progress. Press ESC or Stop key to return to the
Pump Calibration screen.
This screen appears when pump calibration is
complete.
This error message appears during pump calibration
when the end point can not be reached and the
maximum amount of titrant is exceeded. Check
standard, electrode and/or dosing system and try
again.
14
Page 15

The calibration was outside the acceptable limits.
Prepare a new standard and try again.
This error message appears when the input reading
(mV) exceeds the input limits (± 2000.0 mV).
This screen appears when the stirrer is not working
properly. Check the stir bar and beaker content.
Press Restart to try again.
This error message appears when the pump is not
working properly. Check the tubing, valve and
syringe. Press Restart to try again.
TITRATION MESSAGES
This screen is displayed when the instrument is in
titration mode. Press Start to begin a titration, Meter
to enter ORP meter mode or Prime to enter into the
prime function.
The titration result, expressed as the concentration of
sulfur dioxide in ppm (mg/L), is displayed
automatically at the end of the titration. Press Restart
to start another titration or ESC to return to the main
screen.
15
Page 16

This error message appears when the input reading
(± 2000 mV) exceeds the input limits during a
titration.
This screen appears when the sample concentration
is out of range.
This screen appears when the stirrer is not working
properly. Check the stir bar and beaker content.
Press Restart to try again.
This error message appears when the pump is not
working properly. Check the tubing, valve and
syringe. Press Restart to try again.
ELECTRODE PREPARATION
PREPARATION PROCEDURE
Remove the electrode protective cap.
DO NOT BE ALARMED IF ANY SALT DEPOSITS ARE PRESENT. This is normal with electrodes and
they will disappear when rinsed with distilled/deionized water.
During transport tiny bubbles of air may have formed inside the glass bulb. The electrode cannot
function properly under these conditions. These bubbles can be removed by "shaking down" the
electrode as you would do with a glass thermometer.
If the bulb is dry, soak the electrode in HI 70300 Storage Solution for at least one hour.
16
Page 17

DOSING PUMP INSTALLATION
To install the dosing pump follow the procedure below:
• Extend the plunger on the 5 mL syringe to its maximum volume.
• Place the syringe in the dedicated spot on the top of the meter (1).
• Arrange the bottom of the syringe into the holder on the pump (2). Once the syringe is in place
lower the barrel until it sits flush on the holder.
• Put the o-ring and syringe-fixing nut over the syringe (3) and turn clockwise to secure it in place (4).
• Place the valve on the top of the syringe (5). Ensure it fits securely.
• Insert the aspiration tube into the left side of the valve (6) and replace the titrant bottle cap with
the attached cap (7).
• Insert the dispensing tube into the top of the valve (8).
DOSING PUMP PRIME PROCEDURE
Prime cycle should be performed:
• if you notice there is no titrant in the tip
• whenever the dosing system tubes are replaced
• whenever a new bottle of titrant is used
• before starting a pump calibration
• before starting a series of titrations
The prime cycle is used to fill the syringe before starting a set of titrations.
Two rinse cycles of the syringe are shown in the figure below. The dispensing tube is connected to
the top of the valve and the aspiration tube on the left side.
17
Page 18

Note: •The aspiration tube must be inserted in the titrant bottle. The dosing tip must be placed
over a rinse beaker.
•Before starting the prime procedure, make sure you are using the appropriate titrant
solution for the selected range.
• To prime the burette, select Prime option from Titration mode.
• Adjust the rinses number by pressing the and keys and press Start.
• The number of syringe rinses can be set between 1 and 5 (at least three rinses are recommended
to ensure that the air bubbles are completely removed).
• To pause the prime process press the Pause key; to continue press the Continue key. To stop the
prime process press the Stop key.
Note: This error message appears when the pump is
not working properly. Check the tubing, valve
and syringe. Press Restart to try again.
18
Page 19

egnaRwoL egnaRhgiH
mpp0.04ot0.1 mpp004ot03
ELECTRODE CHECK PROCEDURE
Before taking any measurements with the HI 84500 minititrator, it is recommended to check
the HI 3148B ORP electrode using the following steps:
• Press Meter to enter mV mode.
• Pour roughly 15 mL of HI 7021 into a 20 mL beaker. This does not need to be exact, as
long as the PTFE junction is covered by the solution.
• Place the electrode in the solution, stir gently for a few seconds and verify the mV reading.
If the mV reading is 240 ± 20 mV this indicates the electrode is in good condition and can
be used for titrations. A mV reading of 240 ± 30 mV indicates the electrode is beginning
to drift. Follow the “Electrode Conditioning and Maintenance”, Probe Maintenance section
on page 32. If the mV reading is greater than 240 ± 40 mV replace the electrode.
• Remove the electrode from the solution and rinse thoroughly with deionized or distilled water.
PUMP CALIBRATION PROCEDURE
Pump calibration must be performed every time the syringe, pump tube, the titrant bottle or the ORP
electrode is changed. A pump calibration is recommended before each set of titrations or after the
titrator is left idle for several hours.
• Press MENU, select Setup and select the corresponding range according to the table below:
• Ensure the pump is primed with the correct titrant for the selected range (HI 84500-50 Low
Range Titrant or HI 84500-51 High Range Titrant).
Sample preparation: Use a clean pipette to precisely add the appropriate amount of
HI 84500-55 Calibration Standard to a clean beaker as indicated below:
Low Range (Free & Total SO2) - 1 mL
High Range (Free & Total SO2) - 10 mL
Note: Failure to use a clean pipette will result in erroneous readings.
• Fill the beaker up to the 50 mL mark with the distilled or
deionized water.
• Fill the 20 mL beaker up to the 5 mL mark with the HI 84500-60
Acid Reagent and add the contents to the 100 mL beaker.
• Add the contents of one packet of HI 84500-62 Stabilizer
Packet to the sample beaker.
• Press CAL key.
Note: DO NOT PLACE THE TIP INTO THE CALIBRATION BEAKER,
PLACE THE TIP OVER A WASTE BEAKER. A SMALL AMOUNT
OF TITRANT IS DISPENSED WHEN THE PUMP RESETS.
19
Page 20

• Press Start, wait for the syringe to refill.
• Place the stir bar in the beaker and put the beaker in the
minititrator top.
• Place the probe holder on the top of the beaker and secure it
by turning clockwise.
• Rinse the ORP electrode with deionized water and immerse
into the sample until the PTFE reference junction is completely
submerged. Be sure that the tip of the electrode is not
hitting the stir bar. If necessary additional distilled or
deionized water can be added.
• Insert the dosing tip into the titrant tube sleeve. IT IS
CRITICAL THAT THE TIP BE IMMERSED APPROXIMATELY
0.25 CM (0.1”) INTO THE SOLUTION BEING TITRATED.
• Press Continue to begin the calibration and Stop to abort it.
• At the end of the calibration, “Calibration Completed“
appears on display. To repeat the calibration press Restart
and ESC to return to the main screen.
Note:
• If an erroneous situation is encountered during
the calibration, an error message is displayed
and the calibration can be restarted by pressing
Restart. Prepare a new standard, rinse electrode
and dosing tip and try again.
• If the calibration doesn’t complete and the
max titrant volume of titrant is reached, an
error message will be displayed. The calibration
can be restarted by pressing Restart. Prepare
a new standard, rinse the electrode and dosing
tip and try again.
• This error message appears when the input
reading (mV) exceeds the input limits
(± 2000.0 mV).
20
Page 21

egnaRwoL
)elpmasLm05(
egnaRhgiH
)elpmasLm05(
mpp0.04ot0.1 mpp004ot03
• This screen appears when the stirrer is not
working properly. Check the stir bar and beaker
content. Press Restart to try again.
• This error message appears when the pump is
not working properly. Check the tubing, valve
and syringe. Press Restart to try again.
FREE SO2 MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Refer to “Setup Menu” (see page 10) to set up the instrument for your measurement.
• For best accuracy, before taking any measurement, ensure that the pump is calibrated on the
selected range following the “Pump Calibration Procedure” (see page 19).
• Select the corresponding range according to the table below:
• Ensure the pump is primed with the correct titrant for the selected range (HI 84500-50 Low
Range Titrant or HI 84500-51 High Range Titrant).
Sample preparation: Use a clean pipette to precisely add the appropriate amount of wine
sample to a clean 100 mL beaker as indicated below:
Low Range (Free & Total SO2) - 50 mL
High Range (Free & Total SO2) - 50 mL
Note: •The volume of wine added is critical to the measurement
accuracy. Pipettes are recommended.
•Failure to use a clean pipette will result in erroneous
readings.
• Fill the 20 mL beaker up to the 5 mL mark with the HI 84500-60
Acid Reagent and add the contents to the 100 mL beaker.
• Add the contents of one packet of HI 84500-62 Stabilizer
Packet to the 100 mL beaker.
• Press Titrator.
21
Page 22

Note: DO NOT PLACE THE TIP INTO THE SAMPLE BEAKER.
PLACE THE TIP OVER A WASTE BEAKER. A SMALL
AMOUNT OF TITRANT IS DISPENSED WHEN THE PUMP
RESETS.
• Press Start to begin a titration.
• Wait for the syringe to refill.
• Place the stir bar in the beaker and put the beaker into the beaker
holder.
• Place the probe holder on the top of the beaker and secure it by
turning clockwise.
• Rinse the ORP electrode with deionized water and immerse into
the sample until the PTFE reference junction is completely
submerged. Be sure that the tip of the electrode is not hitting the
stir bar.
• Insert the dosing tip into the titrant tube sleeve. IT IS CRITICAL
THAT THE TIP BE IMMERSED APPROXIMATELY 0.25 CM (0.1”)
INTO THE SOLUTION BEING TITRATED.
• Press Continue to begin the titration and Stop to abort it.
• The instrument will continuously update the concentration on the display. The value will be
displayed blinking. When the reading is under range “----” symbol appears blinking.
• The titration curve can be visualized during a titration by pressing Plot ON. Press Plot OFF to
exit this mode.
22
Page 23

• At the end of the titration the instrument displays the concentration in ppm of SO2. The titration
curve can be viewed by pressing Plot ON. Press Plot OFF to exit this mode.
• Press LOG to record the concentration value and the titration curve into the instrument’s
memory. A message will be displayed for a few seconds indicating the amount of free log
space. Up to 200 log samples can be recorded in the instrument’s memory.
• Press Restart to begin a new titration or ESC to return to the titration menu.
• If the concentration exceeds the range limits (>40.0 ppm for Low Range, >400 ppm for
High Range), the exceeded range limit will be displayed blinking. Another titration can be
started by pressing Restart.
• “Wrong input” error message appears when the input reading (mV) exceeds the specified
limits. The mV value and the concentration will blink indicating an error.
• This screen appears when the stirrer is not working properly. Check the stir bar and beaker
content. Press Restart to try again.
23
Page 24

egnaRwoL
)elpmasLm05(
egnaRhgiH
)elpmasLm05(
mpp0.04ot0.1 mpp004ot03
• This error message appears when the pump is not working properly. Check the tubing, valve
and syringe. Press Restart to try again.
TOTAL SO2 MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• For best accuracy, before taking any measurement, ensure that the pump is calibrated on the
selected range following the “Pump Calibration Procedure” (see page 19).
• Select the corresponding range according to the table below:
• Ensure the pump is primed with the correct titrant for the selected range (HI 84500-50 Low
Range Titrant or HI 84500-51 High Range Titrant).
Sample preparation: Use a clean pipette to precisely add the appropriate amount of wine
sample to a clean 100 mL beaker as indicated below:
Low Range (Free & Total SO2) - 50 mL
High Range (Free & Total SO2) - 50 mL
Note: •The volume of wine added is critical to the measurement
accuracy. Pipettes are recommended.
•Failure to use a clean pipette will result in erroneous readings.
• Fill the 20 mL beaker up to the 5 mL mark with the HI 84500-61
Alkaline Reagent, add the contents to the 100 mL beaker containing
the sample.
• Cover the beaker, swirl and wait for 10 minutes.
• Fill the 20 mL beaker up to the 5 mL mark with the HI 84500-60
Acid Reagent, add the contents to the 100 mL beaker containing
the sample.
• Add the contents of one packet of HI 84500-62 Stabilizer Packet
to the 100 mL beaker.
• Place the beaker into the beaker holder.
• Press Titrator.
24
Page 25

Note: DO NOT PLACE THE TIP INTO THE SAMPLE BEAKER.
PLACE THE TIP OVER A WASTE BEAKER. A SMALL
AMOUNT OF TITRANT IS DISPENSED WHEN THE PUMP
RESETS.
• Press Start to begin a titration.
• Wait for the syringe to refill.
• Place the stir bar in the beaker and put the beaker into the
beaker holder.
• Place the probe holder on the top of the beaker and secure it by
turning clockwise.
• Rinse the ORP electrode with deionized water and immerse into
the sample until the PTFE reference junction is completely
submerged. Be sure that the tip of the electrode is not hitting
the stir bar.
• Insert the dosing tip into the titrant tube sleeve. IT IS CRITICAL
THAT THE TIP BE IMMERSED APPROXIMATELY 0.25 CM (0.1”)
INTO THE SOLUTION BEING TITRATED.
• Press Continue to begin the titration and Stop to abort it.
• At the end of the titration the instrument displays the concentration in ppm of SO2. The titration
curve can be viewed by pressing Plot ON. Press Plot OFF to exit this mode. For more information
about this feature, see page 22.
• Press LOG to record the concentration value and the titration curve into the instrument’s
memory. A message will be displayed for a few seconds indicating the amount of free log
space. Up to 200 log samples can be recorded in the instrument’s memory.
• Press Restart to begin a new titration or ESC to return to the titration menu.
25
Page 26

TIPS FOR AN ACCURATE MEASUREMENT
The instructions listed below should be followed carefully to ensure measurements are conducted
with the highest possible accuracy and precision.
• IT IS CRITICAL THAT THE TIP BE IMMERSED IN THE SOLUTION BEING TITRATED
(APPROXIMATELY 0.25 CM).
• Use a clean, volumetric pipette to measure and transfer the wine sample into the titration
beaker.
• Calibrate the pump prior to each series of titrations.
• Calibrate the pump if the meter is left idle for several hours.
• Analyze the wine sample immediately after it is obtained.
• Clean the electrode with HI 700635 or HI 700636 cleaning solutions specially designed for
the wine industry.
VIEW/DELETE TITRATOR RECORDED DATA
Press MENU then Recall to access the Titrator logs.
When an external USB storage device is connected, the Export key is displayed. It saves the meter
and titrator logs in two text format files on the storage device.
Press Meter or Titrator to view the respective logs.
The instrument will display a list of all the records stored in the log.
Use the ARROW keys to scroll the stored records list.
If the saved concentration was out of range, the “<” or “>” symbols are displayed in front of
the reading.
Press Delete to delete the selected log from the memory.
Press Del.All to delete all records.
Press Info to see detailed information about the highlighted record.
26
Page 27

The selected record data and the titration curve data file name are displayed.
When a USB storage device is connected, the Export key is displayed. It saves the titration curve
data as a text file on the storage device using the displayed file name.
Use the ARROW keys when is displayed to scroll between the log records.
Press ESC to return to the previous screen.
Press Plot
to visualize the titration curve or ESC to return to the previous screen. On the titration
curve, the end point volume and mV are displayed. The titration data (Total Titrant Volume on the
x-axis and mV on the y-axis) can be scanned through with the dotted line by using the ARROW keys.
To zoom on the titration curve press Zoom.
If Delete or Del.All is pressed the instrument will ask for confirmation.
Press Yes to delete the record or No to return to the previous screen.
Deleting a single record will renumber the list of records.
If the titrator log is empty, the message “No records available!” will be displayed.
27
Page 28

TITRATOR GLP INFORMATION
Press MENU then GLP.
The pump’s last calibration time, date and slope is displayed.
If a calibration hasn’t been performed, the message “Not Calibrated” will be displayed.
ORP MEASUREMENT
The HI 84500 can be used as an ORP meter for direct measurements.
Set the instrument to ORP meter. From titrator mode press Meter until mV units are displayed.
Rinse the ORP tip with distilled or deionized water.
Place ORP electrode into electrode holder.
For a faster response and to avoid cross-contamination of the samples, rinse the electrode tip
with a few drops of the solution to be tested before taking measurements.
Immerse the ORP sensor in the sample until the PTFE reference junction is completely
submerged and stir gently for a few seconds.
When the reading becomes stable the (unstable measurement) symbol will disappear.
If the potential reading is less than -2000.0 mV or greater than 2000.0 mV the closest full-scale
value will be displayed blinking.
28
Page 29

Press LOG to save the current reading.
During ORP measurements with stirrer on, the stirrer icon will be displayed. In case of a stirrer
malfunction, the stirrer will stop and the stirrer icon will start blinking.
VIEW/DELETE RECORDED ORP DATA
To view or delete previously logged ORP records, press MENU then Recall to access meter logs.
When an external USB storage device is connected, the Export key is displayed. It saves the
meter and titrator logs in two text format files on the storage device.
Press Meter or Titrator to view the respective logs.
The instrument will display a list of all the records stored in the log.
Use the ARROW keys to scroll the list of records.
If the saved ORP measurements are out of range, the “<” or “>” symbols are displayed in front
of the reading.
Press Delete to delete the selected log from the memory.
Press Del.All to delete all records.
Press Info to see detailed information about the highlighted record.
Use ARROW keys when is displayed to scroll between the records.
29
Page 30

If Delete or Del.All is pressed the instrument will ask for confirmation.
Press Yes to delete the record or No to return to the previous screen without deleting.
Deleting a single record will renumber the list of records.
If the ORP log is empty, the message “No records available!” will be displayed.
PC INTERFACE AND DATA TRANSFER
Data stored on the meter with the LOG function during mV measurement and titrations can be
transferred from the meter to a USB stick using the Export function from the log recall menu.
Two text files are transferred on the USB stick. These files can be used for further analysis on a PC.
The logged data can also be transferred from the instrument to the PC using a USB cable.
Connect the USB cable and the following screen will be displayed.
Press Meter to generate the text file with Meter log data.
Press Titrator to generate the text file with Titrator log data.
Press Plot to generate the text files with Titration Plots.
The generated files are now visible and can be used fot further analysis.
If the instrument has no logged Meter or Titrator records, the PC connected screen is displayed.
30
Page 31

TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
SMOTPMYS MELBORP NOITULOS
evissecxe/esnopserwolS
.tfird
.edortcelePROytriD
nipitedortceleehtkaoS
1607IH noitulosgninaelc
setunim03rof . htiwllifeR
.noitulosllifhserf
pusetautculfgnidaeR
.)esion(nwoddna
.noitcennocelbaC
nipitedortceleehtkaoS
1607IH noitulosgninaelc
setunim03rof . htiwllifeR
.noitulosllifhserf
oitcennocelbackcehC otn
retem evitcetorpyfirevdna
.ffosipac
retemPROnielihW
ro0002-,edom
siVm0002+
.gniknilbdeyalpsid
.egnarfotuognidaeR
otnoitcennocelbackcehC
evitcetorpyfirevdnaretem
ehtkcehC.ffosipac
.elpmasehtfoytilauq
llifeR.sedortceleehtnaelC
.noitulosllifhserfhtiw
noitarbilacpmupehT
demrofrepebt'nac
ro,gnibut,evlaV
.eussiegnirys
detanimatnocrognorW
noitarbilacpmup
.noitulos
.edortcelePROnekorB
,evlav,gnibutyfireV
dnatcatnieraegnirys
nehwsessapnoitulos
ondnademirpsipmup
.tneserperaselbbubria
pmupehtkcehC
.noitulosnoitarbilac
,dradnatsrehtonaeraperP
dnapmupehtemirp
.noitarbilacehttratser
eht,noitartitaretfA
syalpsidtnemurtsni
,RL-L/gm0.04
RH-L/gm004
.gniknilb
.edortcelenekorB
fotuonoitartnecnoC
.egnar
.detcelesegnargnorW
.edortceleehtnaelc/kcehC
.pmupehtetarbilaceR
,egnartcerrocehttceleS
.pmupehtetarbilacer
retemehtputratstA
ANNAHehtsyalpsid
.yltnenamrepogol
.kcutssisyekehtfoenO
rodraobyekehtkcehC
.rodnevehttcatnoc
siegassem"xxrorrE"
.deyalpsid
.rorrelanretnI
dnaretemehtfforewoP
fI.niaganotirewopneht
tcatnoc,stsisreprorreeht
.rodneveht
31
Page 32

ELECTRODE CONDITIONING AND MAINTENANCE
SMOTPMYS MELBORP NOITULOS
siegassem"rorrererritS"
fodneehttadeyalpsid
ronoitarbilacpmup
.noitartit
dnarabritsehtkcehC
.tnetnocrekaeb
tcatnoc,stsisreprorreehtfI
.rodneveht
nocirerritsgninnips-noN
retemPROnigniknilb
.edom
dnarabritsehtkcehC
.tnetnocrekaeb
tcatnoc,stsisreprorreehtfI
.rodneveht
siegassem"rorrepmuP"
.deyalpsid
evlav,gnibutehtkcehC
.egnirysdna
tcatnoc,stsisreprorreehtfI
rodneveht .
retemehtputratstA
sdohteM"syalpsid
."detpurroc
sawelifdohtemehT
.detpurroc
.rodnevehttcatnoC
PREPARATION PROCEDURE
Remove the protective cap of the ORP electrode (HI 3148B).
DO NOT BE ALARMED IF SALT DEPOSITS ARE PRESENT. This is normal with electrodes. They will
disappear when rinsed with distilled/deionized water.
During transport, tiny bubbles of air may have formed inside the glass bulb, affecting proper
functioning of the electrode. These bubbles can be removed by "shaking down" the electrode as
you would do with a glass thermometer.
32
Page 33

If the bulb and/or junction is dry, soak the electrode in HI 70300L Storage Solution for at least
one hour.
If the fill solution (electrolyte) is more than 2½ cm (1”) below the fill hole, add HI 7082 3.5M
KCl Electrolyte Solution.
For faster response, unscrew the fill hole screw during measurements.
STORAGE PROCEDURE
To minimize clogging and assure a quick response time, the glass bulb and junction of the
electrode should be kept moist and not allowed to dry out.
Replace the solution in the protective cap with a few drops of HI 70300L Storage Solution or,
in its absence, HI 7082 Fill Solution. Follow the Preparation Procedure before taking
measurements.
Note: NEVER STORE THE ELECTRODE IN DISTILLED OR DEIONIZED WATER.
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
Inspect the electrode and the cable. The cable used for connection to the instrument must be
intact and there must be no points of broken insulation on the cable or cracks on the electrode
stem or bulb. Connectors must be perfectly clean and dry. If any scratches or cracks are present,
replace the electrode. Rinse off any salt deposits with water.
PROBE MAINTENANCE
Refill the reference chamber with fresh electrolyte (HI 7082). Allow the electrode to stand
upright for 1 hour. Follow the Storage Procedure above.
CLEANING PROCEDURE
•
Wine deposits
•
Wine stains
IMPORTANT: After performing any of the cleaning procedures, rinse the electrode thoroughly
with distilled water, refill the reference chamber with fresh electrolyte and soak the electrode in
HI 70300 Storage Solution for at least 1 hour before taking measurements.
Soak in Hanna HI 70635 cleaning solution for 15 minutes
Soak in Hanna HI 70636 cleaning solution for 15 minutes
33
Page 34

ACCESSORIES
REAGENTS
HI 84500-50 Low Range Titrant (230 mL)
HI 84500-51 High Range Titrant (230 mL)
HI 84500-55 Calibration Standard (120 mL)
HI 84500-60 Acid Reagent (230 mL)
HI 84500-61 Alkaline Reagent (120 mL)
HI 84500-62 Stabilizer Packet (100 pcs.)
ELECTRODE TEST SOLUTION
HI 7021M ORP Test Solution (230 mL)
HI 7021L ORP Test Solution (500 mL)
ELECTRODE
HI 3148B ORP Electrode
ELECTRODE FILL SOLUTION
HI 7082 Electrode fill solution (4 x 30 mL)
ELECTRODE STORAGE SOLUTION
HI 70300L Electrode storage solution (500 mL)
CLEANING SOLUTION
HI 70635L Cleaning solution for wine deposits (500 mL)
HI 70636L Cleaning solution for wine stains (500 mL)
OTHER ACCESSORIES
HI 70500 Tube set with cap for titrant bottle, tip and valve
HI 71005/8 115 Vac to 12 Vdc, 800 mA
HI 71006/8 230 Vac to 12 Vdc, 800 mA
HI 731319 Stir bar (10 pcs., 25 x 7 mm)
HI 740036P Beaker 100 mL (10 pcs.)
HI 740037P Beaker 20 mL (10 pcs.)
HI 740236 5 mL Syringe for minititrator
HI 920013 PC Connection Cable
34
Page 35

WARRANTY
HI 84500 is guaranteed for two years against defects in workmanship and materials when used
for it’s intended purpose and maintained according to instructions. Electrodes and probes are
guaranteed for six months. This warranty is limited to repair or replacement free of charge.
Damage due to accidents, misuse, tampering or lack of prescribed maintenance is not covered.
If service is required, contact your dealer from whom you purchased the instrument. If under
warranty, report the model number, date of purchase, serial number and the nature of the
problem. If the repair is not covered by the warranty, you will be notified of the charges incurred.
If the instrument is to be returned to Hanna Instruments, first obtain a Returned Goods
Authorization number from the Technical Service department and then send it with shipping costs
prepaid. When shipping any instrument, make sure it is properly packed for complete protection.
To validate your warranty, fill out and return the enclosed warranty card within 14 days from the
date of purchase.
RECOMMENDATION FOR USERS
Before using this product, make sure that it is entirely suitable for your specific application and for the
environment in which it is used.
Operation of this instrument may cause unacceptable interferences to other electronic equipment, this
requiring the operator to take all necessary steps to correct interferences.
Any variation introduced by the user to the supplied equipment may degrade the instrument’s EMC
performance.
To avoid damages or burns, do not put the instrument in microwave ovens. For your’s and the instrument’s
safety do not use or store the instrument in hazardous environments.
Hanna Instruments reserves the right to modify the design, construction or appearance of its products
without advance notice.
35
Page 36

Hanna Instruments Inc.
Highland Industrial Park
584 Park East Drive
Woonsocket, RI 02895 USA
Technical Support for Customers
Tel. (800) 426 6287
Fax (401) 765 7575
E-mail tech@hannainst.com
www.hannainst.com
Local Sales and Customer Service Office
Printed in ROMANIA
MAN84500 12/12
36
 Loading...
Loading...