Page 1
Instruction Manual
HI 38079
Magnesium
Test Kit for
Irrigation Water
www.hannainst.com
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Product.
Please read the instruction sheet carefully before using the
test kit. It will provide you with the necessary information
for correct use of the kit. If you need additional information,
do not hesitate to e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com.
Remove the test kit from the packing material and examine
it carefully to make sure that no damage has occurred
during shipping. If there is any noticeable damage, notify
your Dealer or the nearest Hanna office immediately.
Each kit is supplied with:
Buffer Reagent, 1 bottle with dropper (25 mL);
•
Oxalate Reagent, powder (100 pcs)
•
HI 38079B-0 EDTA Solution, 1 bottle (120 mL);
•
Buffer Solution pH 10.2±0.2, 1 bottle (100 mL);
•
• Calmagite Indicator,
Demineralizer Bottle with filter cap for about 12 liters
•
of deionized water (depending on the hardness level
of water to be treated)
•1 calibrated plastic vessel (20 mL);
•2 calibrated plastic vessels (50 mL);
•1 large funnel;
filter paper discs ∅
•
• 1 plastic spoon;
1 bottle with dropper (10 mL)
110 mm (100 pcs);
;
;
•1 plastic pipette (1 mL);
•1 plastic pipette (3 mL);
1 syringe (1 mL) with tip.
•
Note: Any damaged or defective item must be returned in
its original packing materials.
Range 0 to 240 mg/L (ppm) as Mg (MR)
Smallest Increment ±2.4 mg/L as Mg (MR)
Analysis Method Titration
Sample Size 25 mL
Number of Tests 100 (average)
Case Dimensions 235x175x115 mm (9.2x6.9x4.5")
Shipping Weight 873 g (30.8 oz.)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USESIGNIFICANCE AND USE
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
SIGNIFICANCE AND USESIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Magnesium is a common constituent of natural waters; its
average abundance in streams is 4 mg/L and in groundwaters
is >5 mg/L. In concentration greater than 125 mg/L it
can cause diuretic effect. The aqueous species is often Mg
and it does not normally result in precipitation (as dolomite)
in natural waters. Magnesium is also an important contributor to the hardness of water: when heated, magnesium
salts break down forming incrustation in boilers. Moreover
magnesium is necessary to plant metabolism since it is an
essential constituent of organic molecules such as chlorophyll.
By using the HI 38079 Hanna Test Kit, it is possible to
differentiate between calcium and magnesium, since the kit
determines only the magnesium ions.
Note:
mg/L is equivalent to ppm (parts per million).
;
CHEMICAL REACTIONCHEMICAL REACTION
CHEMICAL REACTION
CHEMICAL REACTIONCHEMICAL REACTION
The Hanna Test Kit determines Magnesium in irrigation
water via a titrimetric method. Calcium, if present, is
removed by prior filtration. Then the indicator chelates with
magnesium to form a red colored complex. As EDTA is
added, magnesium complexes with it: the reaction endpoint
is indicated by a change in color of the indicator from red to
blue.
ISTR38079 09/00 PRINTED IN ITALY
SPECIFICATIONSSPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONSSPECIFICATIONS
0 to 725 mg/L (ppm) as Mg (HR)
±7.3 mg/L as Mg (HR)
INSTRUCTIONSINSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONSINSTRUCTIONS
READ THE ENTIRE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING THE KIT
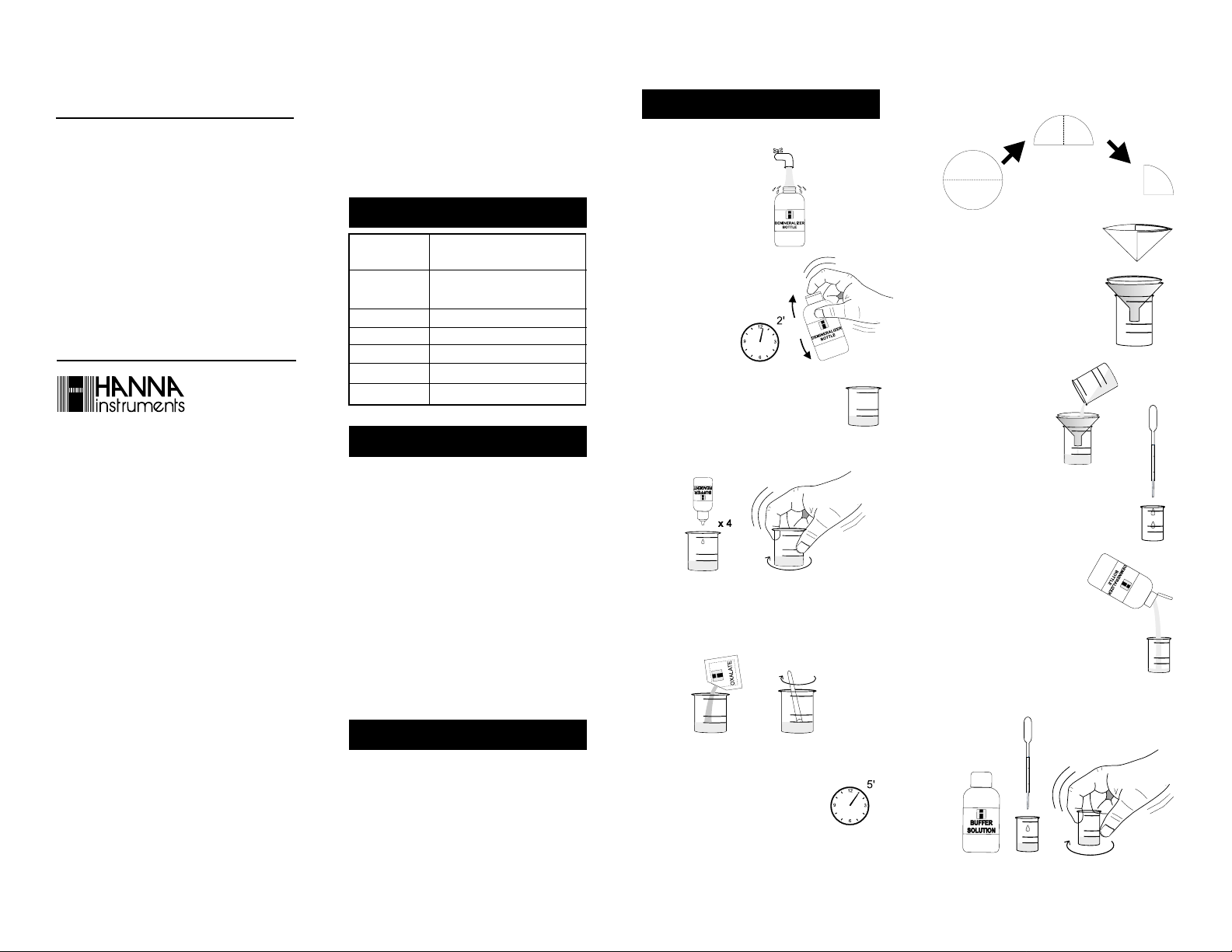
1- Remove the cap and fill
the Demineralizer Bottle
with tap water.
2- Replace the cap
and shake for
least 2 minutes.
The demineralized
water is now
ready.
3- Fill one of the large (50 mL)
plastic vessels with 25 mL of water sample, up to the mark.
4- Add 4 drops of Buffer Reagent and swirl to mix.
2+
5- Add 1 packet of HI 38079A-0 Oxalate reagent and mix
for 30 seconds by means of the plastic spoon. Some
deposits may remain, but they do not affect the measurement.
6- Wait for about 5 minutes for the
reaction to complete. If Calcium is
present, the solution will become turbid.
at
25 mL
7- Fold a filter paper disc twice as shown in the figure.
8- Separate one side from the other
three to form a cone.
9- Place the folded filter disc in the
funnel. Place the funnel over the
other large plastic vessel.
10-Pour the reacted wa-
ter sample through
the filter paper.
11- Using the 3 mL plastic pipette, carefully
transfer 3 mL of the filtered clear water
sample into the small (20 mL) plastic
vessel.
12-Flip open the top of the Dem-
ineralizer Bottle cap. By gently
squeezing the bottle, add demineralized water to the vessel
up to the 10 mL mark.
13- Using the 1 mL plastic pipette, add 1 mL of Buffer
Solution 10.2±0.2 and swirl to mix.
10 mL
Page 2
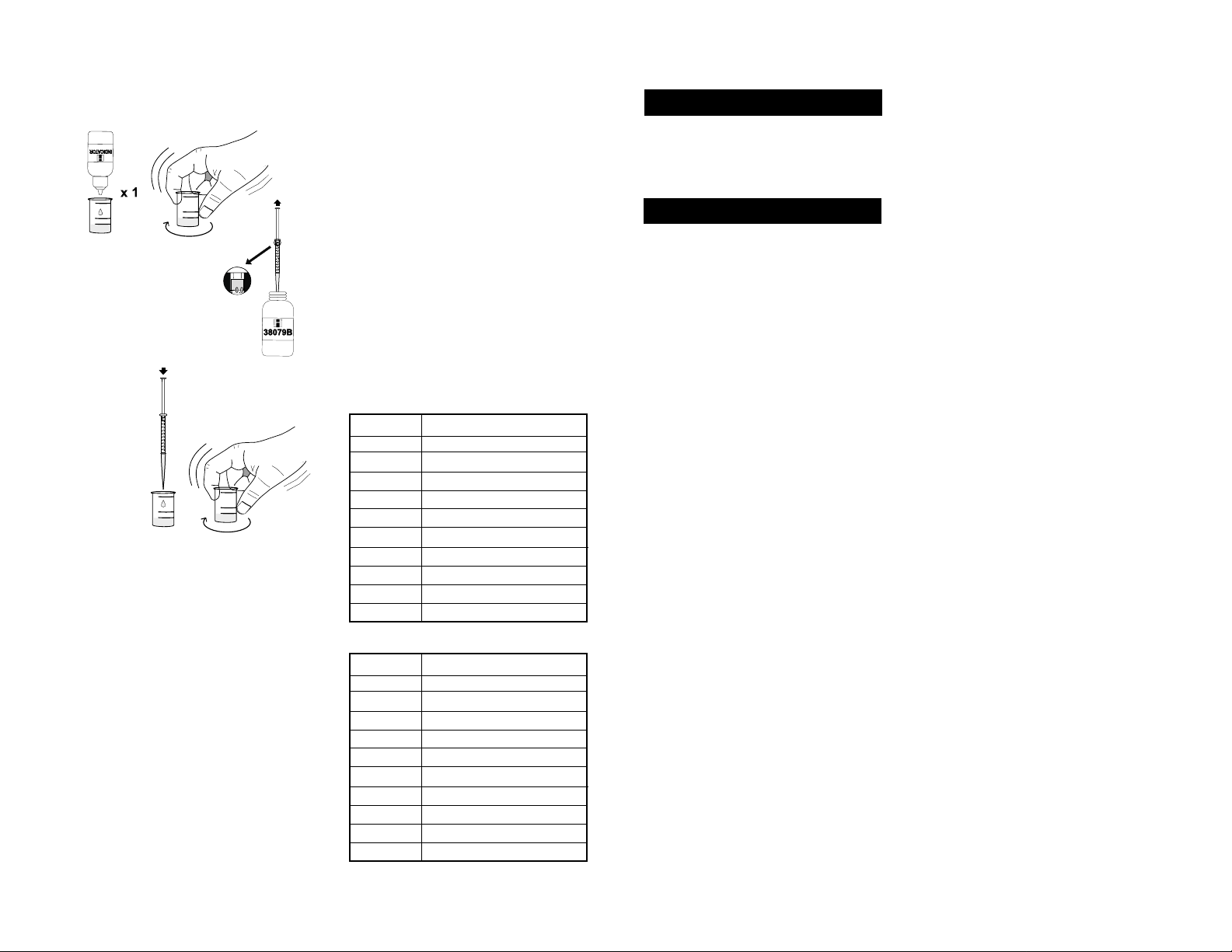
14-Add 1 drop of Calmagite Indicator and swirl to mix; if
magnesium is present, the solution will turn wine red.
15-Take the syringe and push the
plunger completely into the syringe.
Insert tip into the HI 38079B-0
EDTA Solution bottle and pull the
plunger out until the lower edge of
the seal is on the 0.0 mL mark of
the syringe.
16- Slowly add the
titration solution
drop by drop,
swirling after
each drop.
17-As the color changes from pink to purple, swirl for 15
seconds after each additional drop, until the solution
turns pure blue. Read off the milliliters of titration
solution from the syringe.
18-Calculate the mg/L (ppm) of Magnesium in your sample
as follows:
ppm of Mg = mL of titrant x 243
19- If your sample requires more than 1 mL of titrant to
turn pure blue, repeat the test from step 11 using, in
this case, 1 mL of filtered water sample, instead of 3
mL.
20-Follow then the instructions from step 12 to 17.
21-Calculate the mg/L (ppm) of Magnesium in your sample
as follows:
ppm of Mg = mL of titrant x 729
22-To convert the reading in mg/L of CaCO3, multiply the
ppm of magnesium by 4.114.
23-Rinse all labware with demineralized water after each
analysis and shake dry.
Note: High amounts of copper in your sample will alter the
final endpoint color. The solution will change from wine
red to purple without turning pure blue. In this case
add drops of titrant until no visible change in color is
obtained.
CONVERSION TABLES
for 3 mL sample:
mLof titrant ppm as Mg ppm as CaCO
0.1 24 100
0.2 49 200
0.3 73 300
0.4 97 400
0.5 122 500
0.6 146 600
0.7 170 700
0.8 194 800
0.9 219 900
1.0 243 1000
for 1 mL sample:
mLof titrant ppm as Mg ppm as CaCO
0.1 73 300
0.2 146 600
0.3 219 900
0.4 292 1200
0.5 365 1500
0.6 437 1800
0.7 510 2100
0.8 583 2400
0.9 656 2700
1.0 729 3000
3
3
REFERENCESREFERENCES
REFERENCES
REFERENCESREFERENCES
Adaptation of Standard Methods for the Examination of
Water and Wastewater, 18
HEALTH AND SAFETYHEALTH AND SAFETY
HEALTH AND SAFETY
HEALTH AND SAFETYHEALTH AND SAFETY
The chemicals contained in this kit may be hazardous if
improperly handled. Read the relevant Health and Safety
Data Sheet before performing this test.
th
edition, 1992, APA AWWA WEF.
 Loading...
Loading...