Page 1
Instruction Manual
HI 38078
Sodium
Adsorption Ratio
(SAR)
Test Kit
www.hannainst.com
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Product.
Please read the instruction sheet carefully before using the
test kit. It will provide you with the necessary information
for correct use of the kit. If you need additional information,
do not hesitate to e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com.
Remove the chemical test kit from the packing material and
examine it carefully to make sure that no damage has
occurred during shipping. If there is any noticeable damage, notify your Dealer or the nearest Hanna office
immediately.
Each kit is supplied with:
• DiST 4 conductivity tester (with instructions and
screwdriver for calibration);
HI 70039 calibration sachet 5000 µS/cm, 2 sachets;
•
• Buffer Solution pH 10.2±0.2, 1 bottle (100 mL);
Calmagite Indicator, 1 bottle with dropper (10 mL);
•
• HI 38078-0 EDTA Solution, 1 bottle (120 mL);
• Demineralizer Bottle with filter cap for about 12 liters
of deionized water (depending on the hardness level
of water to be treated)
• 1 calibrated vessel (50 mL);
• 1 plastic pipette (3 mL);
• 1 plastic pipette (1 mL);
1 syringe (1 mL) with tip.
•
Note: Any damaged or defective item must be returned in
its original packing materials.
;
SPECIFICATIONSSPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONSSPECIFICATIONS
Range > 0 meq/L
Smallest Increment 0.5 meq/L for 1.0 mL sample
0.2 meq/L for 2.5 mL sample
Analysis Method Titration
Sample Size 1.0 mL or 2.5 mL
Number of Tests 100 (average)
Case Dimensions 235x175x115 mm (9.2x6.9x4.5")
Shipping Weight 785 g (27.7 oz.)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USESIGNIFICANCE AND USE
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
SIGNIFICANCE AND USESIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Sodium is one of the most studied elements because of its
toxic effects both to soil texture and crops:
• High concentration of sodium disperses soil colloidal
particles, rendering the soil hard and resistant to
water penetration.
• The build-up of osmotic pressure in soil due to high
sodium concentration causes difficulty in water absorption by plant roots. Plants are sensitive to varying
degrees to soil salinity and when this exceeds a
certain limit their growth is impaired, thus lowering
their productivity.
High amounts of sodium can be mitigated by presence of
large quantities of calcium and magnesium in soil or with
distribution of gypsum (calcium sulfate) directly on soil or as
an additive to irrigation water.
The Hanna Test Kit determines Sodium Hazard in irrigation
water by calculation of SAR (Sodium Adsorption Ratio) in
relation to calcium and magnesium concentration.
Note: meq/L is milliequivalent per liter.
INSTRUCTIONSINSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONSINSTRUCTIONS
READ THE ENTIRE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING THE KIT
DETERMINATION OF CONDUCTIVITY
The concentration of total soluble salts dissolved in irrigation
water is measured as the capacity to conduct electricity (EC)
and is determined with a conductivity tester. Refer to the
enclosed instructions for a proper use of the DiST 4 Conductivity Tester.
Calculate the meq/L of soluble salts by multiplying the
conductivity mS/cm by 10.
ISTR38078 02/00 PRINTED IN ITALY
meq/L Conductivity = mS/cm x 10
DETERMINATION OF CALCIUM AND MAGNESIUM
CHEMICAL REACTION
Calcium and Magnesium in irrigation water are determined
via a titrimetric method: the indicator chelates with the
Calcium and Magnesium ions to form a red colored complex.
As EDTA is added, calcium and magnesium complex with it:
the reaction end point is indicated by a change in color of
the indicator from red to blue.
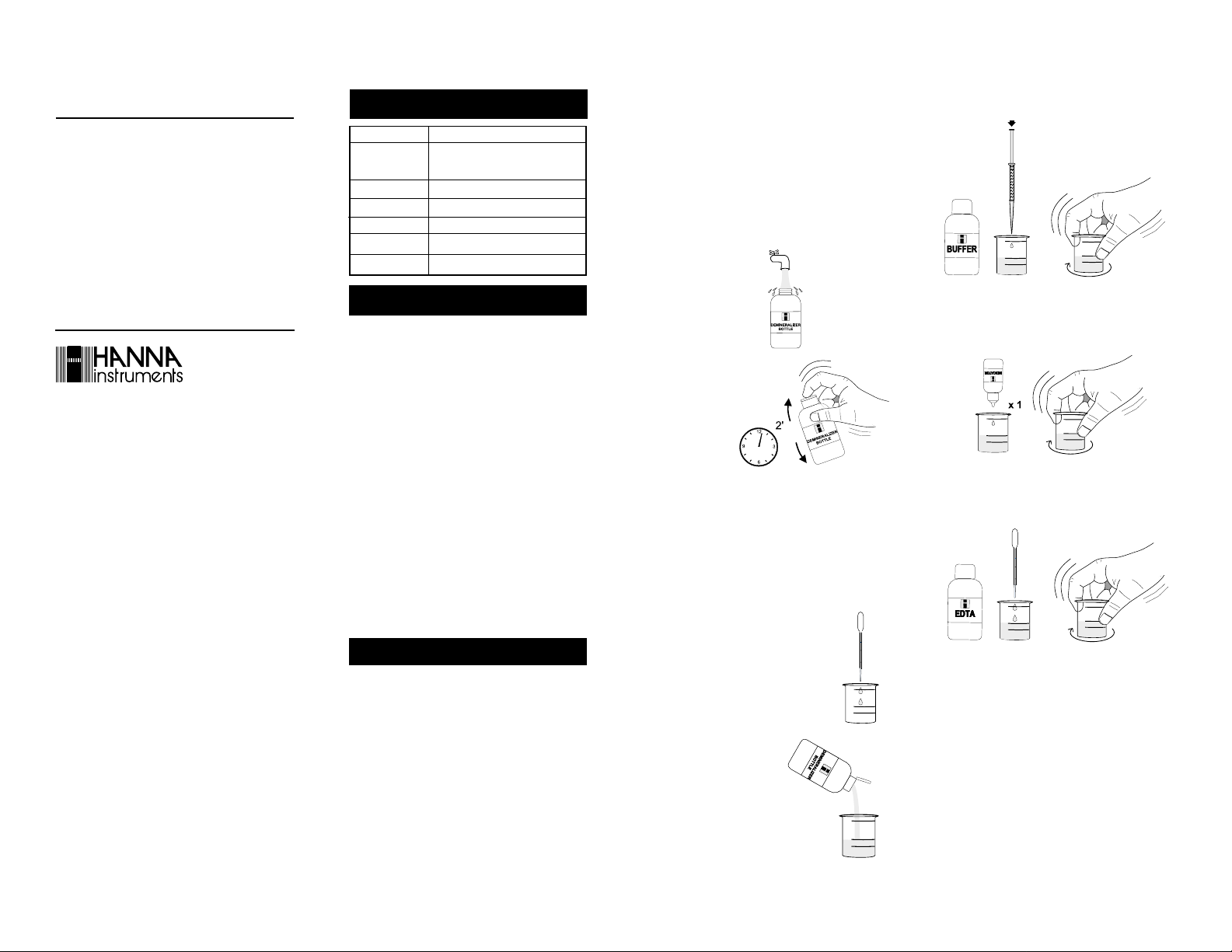
INSTRUCTIONS
• Remove the cap and
fill the Demineralizer
Bottle with tap water.
• Replace the cap
and shake for
least 2 minutes.
The demineralized
water is now
ready.
• Determine the conductivity of your sample using the
Hanna DiST 4 Conductivity Tester (for accurate results,
follow the DiST 4 instructions attentively):
- if the conductivity is < 2.00 mS/cm, take 2.5 mL of
water sample;
- if the conductivity is > 2.00 mS/cm, take 1.0 mL of
water sample.
• Use the 3 mL plastic pipette and transfer
2.5 mL or 1.0 mL of your sample (see
above) to the vessel.
• Flip open the top of the
Demineralizer Bottle cap.
Squeeze the bottle gently to
add demineralized water to
the vessel up to the 25 mL
mark.
at
• Using the syringe, add 1 mL of Buffer Solution and swirl
to mix.
1 mL
• Add 1 drop of Calmagite Indicator and swirl to mix. If
calcium and magnesium are present, the solution will
turn wine red.
• Using the 1 mL plastic pipette, add drops of HI 38078-0
EDTA Solution. Swirl after each drop and keep an accurate
count of the number of drops being added to the solution.
• As the color changes from pink to purple, swirl for 15
seconds after each additional drop, until the solution
turns pure blue. Record the number of drops needed to
obtain the final color change (from wine red to pure
blue).
Note: high amounts of copper in your sample will alter the
final end point color. The solution will change from wine
red to purple without turning pure blue. In this case
add drops of titrant until no visible change in color is
obtained.
Page 2

• Calculate the meq/L of Calcium and Magnesium in your
sample as follows:
where mL of sample is equal to:
a) 2.5 mL if the conductivity is < 2.00 mS/cm;
b) 1.0 mL if the conductivity is > 2.00 mS/cm.
• Rinse all labware with demineralized water after each
analysis and shake dry.
SODIUM ESTIMATION
To estimate the sodium content in your irrigation water,
subtract from the conductivity value (in meq/L) the value of
Calcium and Magnesium (in meq/L):
Sodium Estimation (meq/L) =
= Conductivity (meq/L) - [Ca+Mg] (meq/L)
SODIUM ADSORPTION RATIO CALCULATION
SAR is a parameter that evaluates the Sodium Hazard in
relation to Calcium and Magnesium concentration.
The Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) is calculated as:
REFERENCESREFERENCES
REFERENCES
REFERENCESREFERENCES
Adaptation of the Standard Methods for the Examination
of water and wastewater, 18
WEF.
P. Sequi, Chimica del suolo, Patron Editore, Ed. 1991
HEALTH AND SAFETYHEALTH AND SAFETY
HEALTH AND SAFETY
HEALTH AND SAFETYHEALTH AND SAFETY
The chemicals contained in this kit may be hazardous if
improperly handled. Read the relevant Health and Safety
Data Sheet before performing this test.
th
Ed. 1992, APA AWWA
PERMEABILITY HAZARD TABLE
It is possible to draw general indications about the permeability hazards in relation to EC
water tested [from Ayers and Westcot, FAO#29, Rev.1,
Rome, 1985].
Note: EC
is the electrical conductivity of the irrigation water
w
and can be expressed as mS/cm (or dS/m) @25°C.
and SAR of the irrigation
w
 Loading...
Loading...