Page 1
Instruction Manual
SPECIFICATIONSSPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONSSPECIFICATIONS
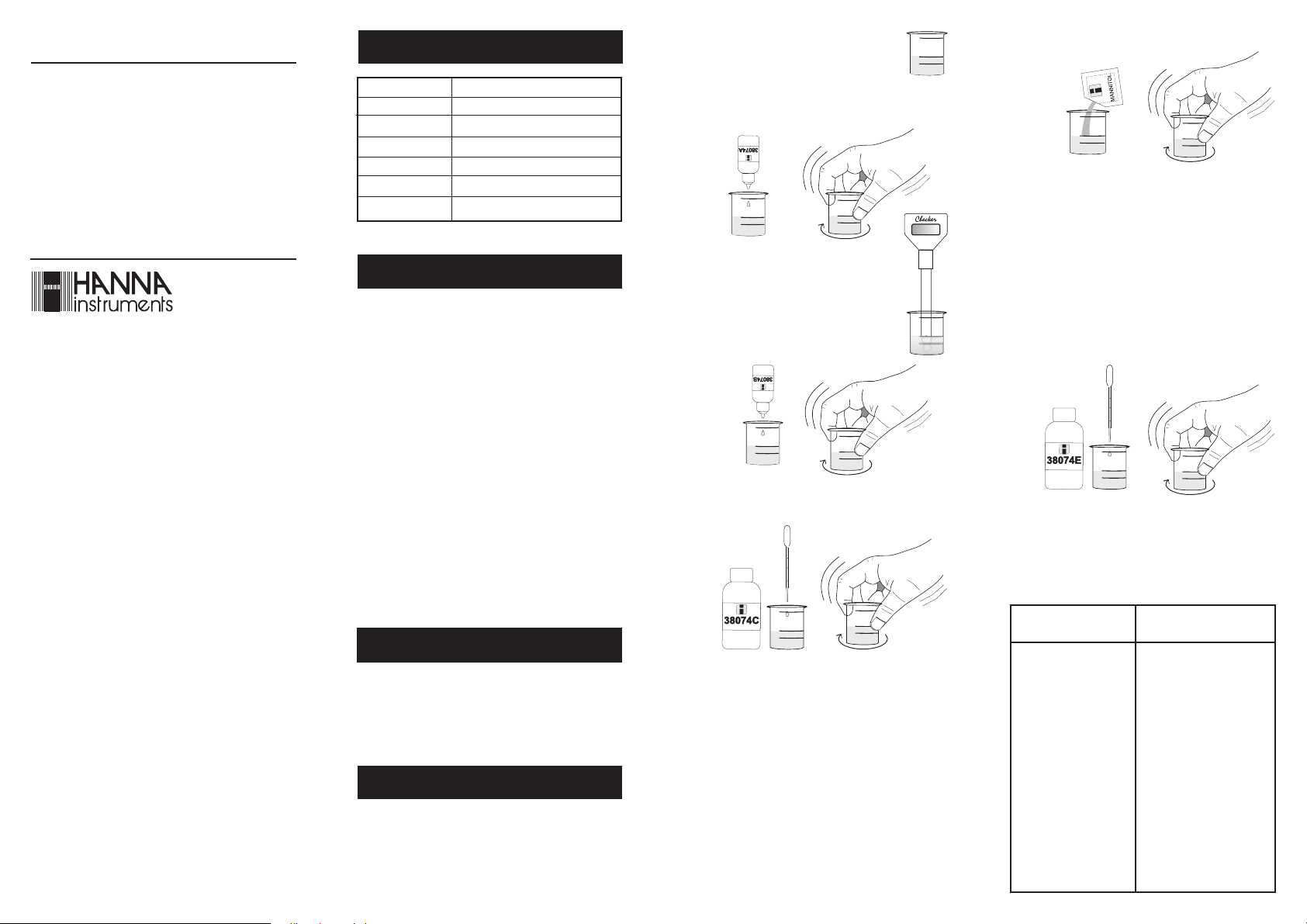
• Fill the plastic vessel with 50 mL of
sample (up to the mark).
50 mL
• Add 1 packet of Mannitol reagent and swirl gently to
dissolve.
HI 38074
Boron
Test Kit for
Irrigation Water
www.hannainst.com
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Product.
Please read the instruction sheet carefully before using the
test kit. It will provide you with the necessary information
for correct use of the kit. If you need additional information,
do not hesitate to e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com.
Remove the chemical test kit from the packing material and
examine it carefully to make sure that no damage has
occurred during shipping. If there is any noticeable damage, notify your Dealer or the nearest Hanna office
immediately.
Each kit is supplied with:
HI 38074A-0 Boron Reagent, 1 bottle with dropper
•
(30 mL);
HI 38074B-0 Boron Reagent, 1 bottle with dropper
•
(30 mL);
HI 38074C-0 Boron Reagent, 1 bottle (100 mL);
•
Mannitol, powder in packets (100 pcs);
•
HI 38074E-0 Boron Reagent, 1 bottle (100 mL);
•
• HI 70004, 1 sachet;
• HI 70007, 1 sachet;
•1Checker, pocket-sized pH-meter;
• 1 screwdriver;
• 1 empty bottle (120 mL) with cap;
• 1 calibrated plastic vessel (50 mL);
• 2 plastic pipettes (1 mL).
Note: Any damaged or defective item must be returned in
its original packing materials.
Range 0 to 5 mg/L (ppm) as Boron
Smallest Increment 0.2 ppm Boron
Analysis Method Titration
Sample Size 50 mL
Number of Tests 100
Case Dimensions 235x175x115 mm (9.2x6.9x4.5")
Shipping Weight 780 g (27.5 oz.)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USESIGNIFICANCE AND USE
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
SIGNIFICANCE AND USESIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Boron is one of the micronutrients essential for plant growth. It
may be present naturally in water or may find its way into a
watercourse through industrial waste effluents. Boron in excess
of 2.0 mg/L in irrigation water is detrimental to many plants,
but some plants may even be affected adversely by concentrations lower than 1.0 mg/L.
The US Department of Agriculture reports the following classification:
ppm of Boron effect on crops
<0.5 good (except for very sensitive
crops)
0.5-2.0 some risks (many crops must
be excluded)
>2.0 dangerous (may only be used
for very tolerant crops)
Note: mg/L is equivalent to ppm (parts per million).
CHEMICAL REACTIONCHEMICAL REACTION
CHEMICAL REACTION
CHEMICAL REACTIONCHEMICAL REACTION
The Hanna Test Kit allows the determination of boron
concentration in irrigation waters by direct titration of boric
acid.
INSTRUCTIONSINSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONSINSTRUCTIONS
READ THE ENTIRE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING THE KIT
• Calibrate the pH electrode following the instructions in
ISTR38074 10/00 PRINTED IN ITALY
the Checkerinstrument manual.
• Add 3 drops of HI 38074A-0 Boron Reagent and swirl
to mix.
x3
• Insert the CheckerpH electrode into the
vessel and measure the pH. The pH must be
lower than 7. If pH is higher than 7, add
HI 38074B-0 reagent drop by drop, swirling after each drop, until pH becomes lower
than 7.
• Using one of the plastic pipettes, add drops of HI 38074C-0
Boron Reagent, swirling after each drop.
• Keep on adding HI 38074C-0 reagent until the pH
reaches the 7.8±0.2 value. Write down the exact pH
value and report it as pH
Note 1: If pH stabilizes at a value higher than 8, too
many drops of HI 38074C-0 reagent have been
added. In this case, add 1 drop of HI 38074B-0
reagent and swirl, then add again drops of
HI 38074C-0 to adjust the pH to 7.8±0.2.
Note 2: If carbonates are present, the pH readings will
show a drift after each addition. Wait until the pH
stabilizes before adding the next drop of HI 38074C-0
reagent.
start
(e.g.: pH
=7.85).
start
• Measure the pH:
- If pH is lower than pH
the other plastic pipette to add HI 38074E-0 Boron
Reagent drop by drop, swirling after each drop, while
keeping an accurate count of the number of drops being
added to the solution. Keep adding the reagent until
pH becomes equal or higher than pH
Boron Conversion Table below to convert the number of
drops added in mg/L (or ppm) of Boron (e.g.: 10 drops
of HI 38074E-0 reagent correspond to 2.0 mg/L of
Boron).
- If pH does not change after addition of the
powder packet, boron is absent. As a confirmation, add
one drop of HI 38074E-0 reagent and pH will immediately increase a lot.
(e.g.: pH=7.52), use
start
(7.85). Use the
start
BORON CONVERSION TABLE
number mg/L number mg/L
of drops Boron of drops Boron
1 0.2 14 2.8
2 0.4 15 3.0
3 0.6 16 3.2
4 0.8 17 3.4
5 1.0 18 3.6
6 1.2 19 3.8
7 1.4 20 4.0
8 1.6 21 4.2
9 1.8 22 4.4
10 2.0 23 4.6
11 2.2 24 4.8
12 2.4 25 5.0
13 2.6 26 5.2
Page 2
Interferences
• Compounds with buffering capacity (substances that
keep the pH of sample at a constant value, e.g.
phosphate buffer, ammonia buffer): if after Mannitol
reagent has been added pH of sample does not change,
verify if pH increases a little (0.05 pH units) by adding
HI 38074E-0 reagent drop by drop. In this case boron
may be present, but a buffer interferes with boron
determination. It is possible to have only an indication
for boron concentration. Use the Boron Conversion Table
below to convert the number of drops added in mg/L
(or ppm) of Boron and record the concentration of boron
in your sample as lower than the value found (e.g.: 2
drops correspond to 0.4 mg/L of Boron, thus boron
concentration in your sample is lower than 0.4 mg/L).
• Bicarbonates: if hardness of sample is about 150 ppm
CaCO3, bicarbonates are present at pH 8.3, and they
interfere with boron determination. In this case the
sample needs to be pretreated before analysis as described in the following paragraph.
Pretreatment to eliminate carbonate interference
• Fill the plastic vessel with 50 mL of sample and pour it
into the empty bottle.
• Add HI 38074B-0 reagent until pH is lower than 4.5.
Place the cap, but DO NOT SCREW IT.
• Heat the sample for about 45 seconds in a microwave
oven at 500W (do not boil the sample). Swirl several
times to eliminate air bubbles and allow the sample to
cool down to room temperature. Pour the sample into
the plastic vessel and perform the test as described
above.
REFERENCESREFERENCES
REFERENCES
REFERENCESREFERENCES
P.Sequi, Chimica del suolo, Patron editore, Ed. 1991
HEALTH AND SAFETYHEALTH AND SAFETY
HEALTH AND SAFETY
HEALTH AND SAFETYHEALTH AND SAFETY
The chemicals contained in this kit may be hazardous if
improperly handled. Read the relevant Health and Safety
Data Sheet before performing this test.
 Loading...
Loading...