Page 1

Page 2

This manual contains proprietary information, which is protected by
copyrights. All rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be
photocopied, reproduced or translated to another language without
prior written consent of Good Will company.
The information in this manual was correct at the time of printing.
However, Good Will continues to improve products and reserves
the rights to change specification, equipment, and maintenance
procedures at any time without notice.
Good Will Instrument Co., Ltd.
No. 7-1, Jhongsing Rd., Tucheng City, Taipei County 236, Taiwan.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS....................................................5
Safety Symbols.......................................................5
Safety Guidelines...................................................5
GETTING STARTED............................................................8
Technical background.............................................9
Lineup/Features....................................................11
Front Panel...........................................................12
Rear Panel.............................................................15
Set Up...................................................................16
Operation Shortcuts..............................................18
SINE/SQUARE/TRIANGLE WAVE.....................................19
Activate waveform.................................................20
Set Frequency........................................................20
Set Amplitude.......................................................22
Set Duty Cycle (Square Waveform).........................23
Set Offset..............................................................23
TTL OUTPUT....................................................................25
Activate TTL..........................................................25
Set Frequency........................................................26
Set Duty Cycle.......................................................27
APPLICATION EXAMPLES................................................28
Reference Signal for PLL System............................28
Trouble-Shooting Signal Source.............................28
Transistor DC Bias Characteristics Test..................29
Amplifier Over-Load Characteristic Test.................30
Amplifier Transient Characteristics Test.................30
3
Page 4

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Logic Circuit Test..................................................32
Impedance Matching Network Test.......................32
Speaker Driver Test...............................................33
FAQ.................................................................................34
APPENDIX.......................................................................35
Fuse Replacement................................................35
Specification........................................................37
Declaration of Conformity.....................................39
INDEX.............................................................................40
4
Page 5

Safety Instructions
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This chapter contains important safety instructions that
you must follow when operating SFG-1000 series and
when keeping it in storage. Read the following before any
operation to insure your safety and to keep the best
condition for SFG-1000 series.
Safety Symbols
These safety symbols may appear in this manual or on SFG-1000 series.
Warning: Identifies conditions or practices that could
WARNING
CAUTION
result in injury or loss of life.
Caution: Identifies conditions or practices that could
result in damage to SFG-1000 series or to other
properties.
Attention Refer to the Manual
Earth (ground) Terminal
Safety Guidelines
General Guideline
CAUTION
• Do not place any heavy object on SFG-1000 series.
• Avoid severe impacts or handling that leads to damage.
• Do not discharge static electricity to SFG-1000 series.
• Use only mating connectors, for the terminals.
• Do not block or obstruct cooling vent opening.
• Do not perform measurements at power source and
building installation site (Note below).
• Do not disassemble SFG-1000 series unless you are
qualified as service personnel.
5
Page 6

Page 7
Safety Instructions
• Pollution degree 1: No pollution or only dry, non-conductive
pollution occurs. The pollution has no influence.
• Pollution degree 2: Normally only non-conductive pollution
occurs. Occasionally, however, a temporary conductivity caused
by condensation must be expected.
• Pollution degree 3: Conductive pollution occurs, or dry,
non-conductive pollution occurs which becomes conductive due
to condensation which is expected. In such conditions,
equipment is normally protected against exposure to direct
sunlight, precipitation, and full wind pressure, but neither
temperature nor humidity is controlled.
Storage
Environment
• Location: Indoor
• Relative Humidity: < 70%
• Temperature: −10°C to 70°C
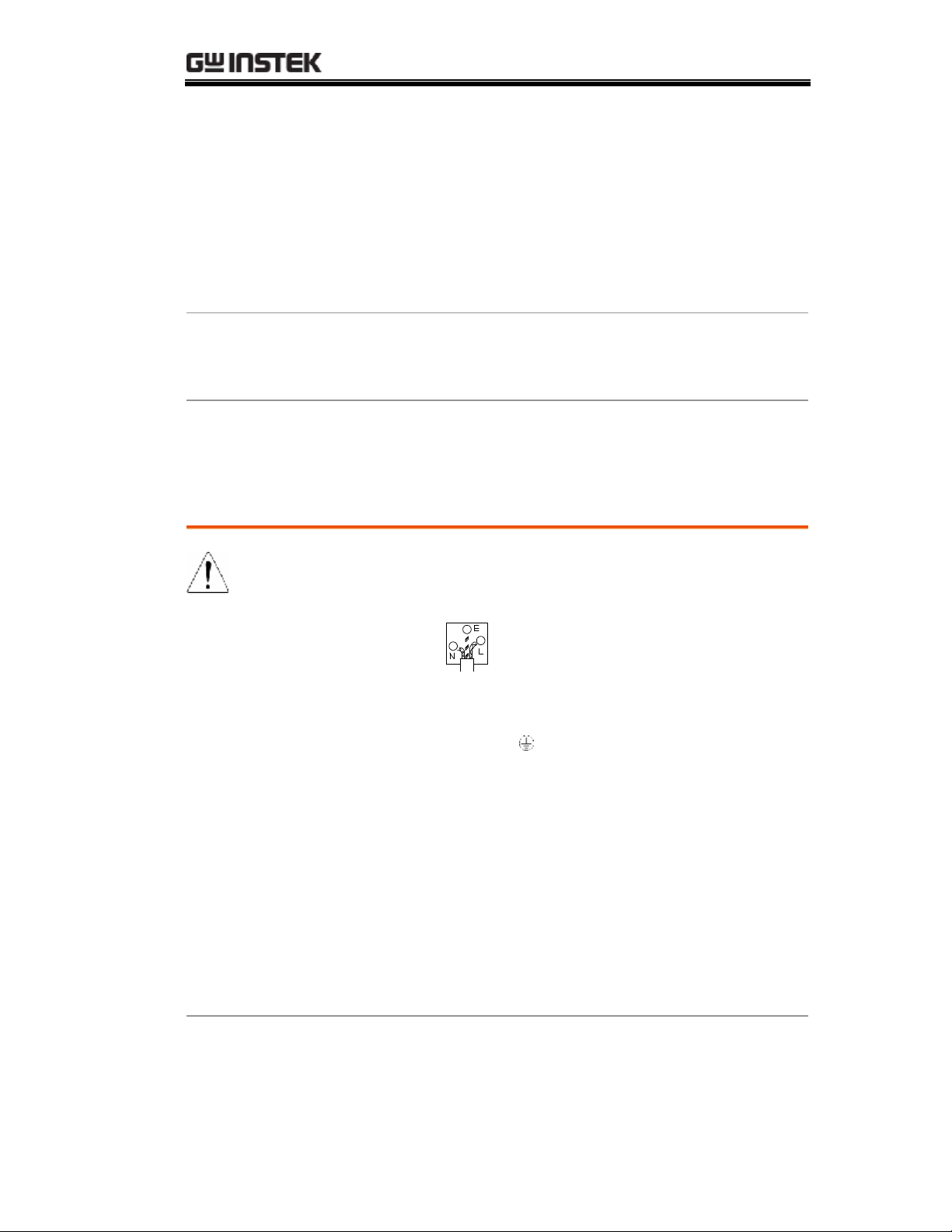
Power cord for the United Kingdom
When using SFG-1000 series in the United Kingdom, make sure the power
cord meets the following safety instructions.
NOTE: This lead / appliance must only be wired by competent persons
WARNING: THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE EARTHED
IMPORTANT: The wires in this lead are coloured in accordance with the following code:
Green/ Yellow: Earth
Blue: Neutral
Brown: Live (Phase)
As the colours of the wires in main leads may not correspond with the colours marking
identified in your plug/appliance, proceed as follows:
The wire which is coloured Green & Yellow must be connected to the Earth terminal
marked with the letter E or by the earth symbol or coloured Green or Green & Yellow.
The wire which is coloured Blue must be connected to the terminal which is marked with
the letter N or coloured Blue or Black.
The wire which is coloured Brown must be connected to the terminal marked with the
letter L or P or coloured Brown or Red.
If in doubt, consult the instructions provided with the equipment or contact the supplier.
This cable/appliance should be protected by a suitably rated and approved HBC mains
fuse: refer to the rating information on the equipment and/or user instructions for details.
As a guide, cable of 0.75mm2 should be protected by a 3A or 5A fuse. Larger conductors
would normally require 13A types, depending on the connection method used.
Any moulded mains connector that requires removal /replacement must be destroyed by
removal of any fuse & fuse carrier and disposed of immediately, as a plug with bared wires
is hazardous if a engaged in live socket. Any re-wiring must be carried out in accordance
with the information detailed on this label.
7
Page 8

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
GETTING STARTED
This chapter describes SFG-1000 series in a nutshell,
including main features and front/rear/display
introduction. Follow the Set Up section to properly
install and power up SFG-1000 series.
SFG-1000
series overview
Panel
introduction
Setup
Technical background.............................................9
Series lineup........................................................11
Main features.......................................................11
Main Display........................................................12
Entry keys.............................................................13
Others..................................................................14
Rear Panel............................................................15
Tilt stand..............................................................16
Power up..............................................................17
Functionality check...............................................17
Quick
reference
8
Operation Shortcuts.............................................18
Page 9

Getting Started
Technical background
Traditional
function
generators
DDS
methodology
SFG-1000 series uses the latest Direct Digital Synthesis
(DDS) technology to generate stable, high resolution
output frequency. The DDS technology solves several
problems encountered in traditional function generators,
as follows.
Constant current circuit methodology
This analog function generating method uses a constant
current source circuit built with discrete components
such as capacitors and resistors. Temperature change
inside the generator greatly affects the components
characteristics which lead to output frequency change.
The results are poor accuracy and stability.
In DDS, the waveform data is contained in and
generated from a memory. A clock controls the counter
which points to the data address. The memory output is
converted into analog signal by a digital to analog
converter (DAC) followed by a low pass filter. The
resolution is expressed as fs/2k where fs is the frequency
and k is the control word, which contains more than
28bits. Because the frequency generation is referred to
clock signal, this achieves much higher frequency stability
and resolution than the traditional function generators.
9
Page 10
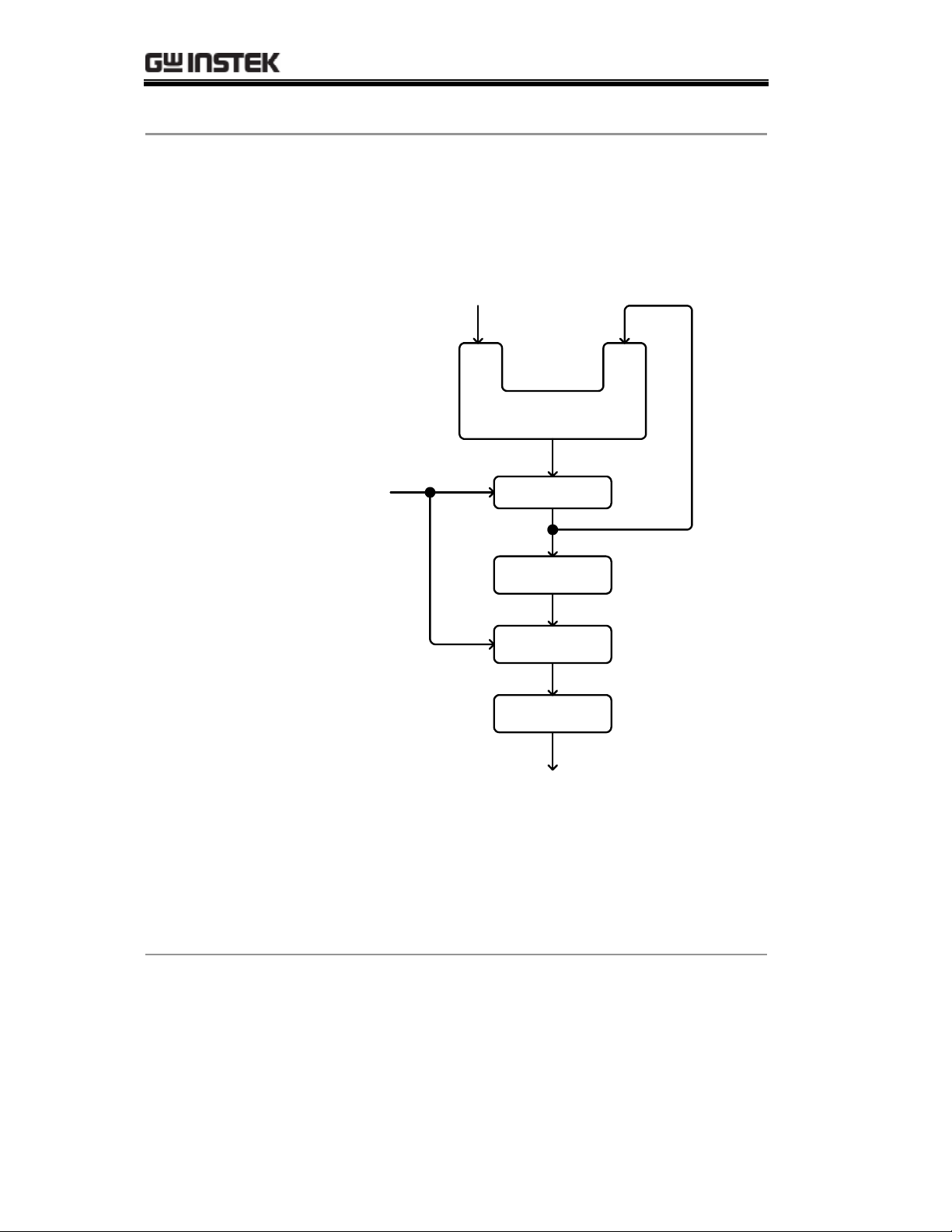
SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Block diagram
DDS synthesizer consists of Phase accumulator
(counter), lookout table data (ROM), Digital-to-analog
converter (DAC), and Low-pass filter (LPF).
Frequency
Control Word (K)
System Clock
(fs)
28bit
Phase
Accumulator
28bit
Register
Table
ROM/RAM
12bit
28bit
Digital-Analog
Converter
Low-Pass
Filter
Output (fo)
The phase accumulator adds the frequency control word
K at every clock cycle fs. The accumulator output points
to a location in the Table ROM/RAM. The DAC
converts the digital data into an analog waveform. The
LPF filters out the clock frequency to provide a pure
waveform.
10
Page 11

Getting Started
Lineup/Features
Series lineup
Features
Lineup
Frequency
Offset TTL
output
−40dB
attn.
Voltage
display
SFG-1003
SFG-1013
3MHz ● ● ●
3MHz ● ● ● ●
Main features
Performance • High resolution using DDS technology
• High frequency accuracy: ±20ppm
• Low distortion: −55dBc @ ≤200kHz
• High resolution 100mHz
Features • Digital user interface with 6-digit LED display
• Various output waveforms: Sine, Square, and Triangle
• TTL output
• Amplitude control
• −40dB attenuation
• Duty control
• Variable DC offset control
• Output On/Off control
• Voltage display (SFG-1013)
• Output overload protection
―
Interface • Frequency output
• TTL output
11
Page 12
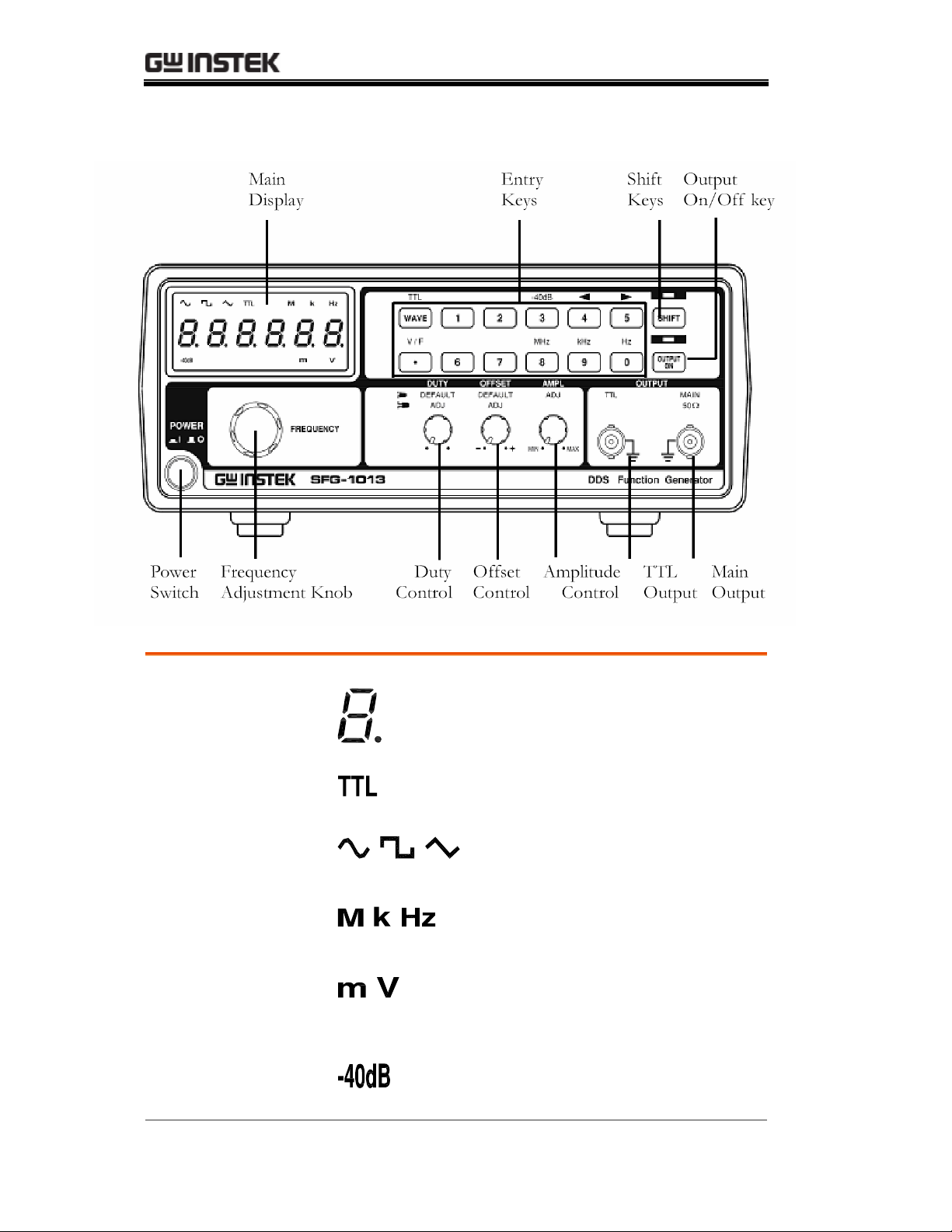
SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Front Panel
Main Display
7 segment LED
TTL indicator
Waveform
indicator
Frequency
indicator
Voltage indicator
(SFG-1013 only)
−40dB indicator
(SFG-1013 only)
Shows frequency and voltage.
Indicates that the TTL output is
enabled. For details, see page25.
Indicates the waveform shape:
Sine, Square, and Triangle.
Indicates the output frequency:
MHz, kHz, or Hz.
Indicates Voltage unit: mV, or V.
For voltage measurement detail,
see page22.
Indicates −40dB attenuation is
activated. For details, see page22.
12
Page 13

Entry keys
(9,0)
Getting Started
Waveform key
TTL activation
Numerical keys
Frequency unit
selection
Cursor selection
WAVE
SHIFT
1
SHIFT
SHIFT
Selects the waveform: sine,
square, and triangle. For details,
see page20.
Activates TTL output. For details,
WAVE
see page25.
Specifies frequency.
0
Specifies the frequency unit:
8
MHz, kHz, or Hz.
Moves the cursor (frequency
editing point) left or right. For
details, see page21.
−40dB
attenuation
(SFG-1013 only)
Frequency /
Voltage display
selection
(SFG-1013 only)
Shift key
Output On/Off
key
4
SHIFT
SHIFT
or
5
Attenuates amplitude by −40dB.
3
For details, see page22. Key
operation is for SFG-1013 only.
Switches the display between
frequency and voltage. For details,
see page22. For SFG-1013 only.
Selects the 2nd function associated
to the entry keys. The LED lights
when Shift is activated.
Turns the output On/Off. The
LED lights when the output is
On.
13
Page 14

Others
OUTPUT
AMPL
OFFSET
SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Frequency
editing knob
Main output
TTL output
Amplitude
control
Ω50
OUTPUT
Increases (right turn) or decreases (left
turn) the frequency.
Outputs sine, square, and triangle
waveform. BNC, 50Ω output impedance.
For details, see page20.
Outputs TTL output waveform, BNC
terminal. For TTL mode details, see
page25.
Sets the sine/square/triangle waveform
amplitude. Turn left (decrease) or right
(increase).
DC offset
control
-40dB
ADJ
(SFG-1003 only) When pulled
out, attenuates the sine / square / triangle
waveform amplitude by −40dB. For
details, see page22.
When pulled out, sets the DC
offset level for sine/square/triangle
waveform. Turn left (decrease) or right
(increase). The range is −5V ~ +5V, in
50Ω load. For details, see page23.
14
Page 15

Page 16

Set Up
SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Tilt stand
Pull out the
handle sideways
and rotate it.
Place SFG
horizontally,
Or tilt stand.
Place the handle
vertically for
hand carry.
16
Page 17

Getting Started
Power up
1. Check the voltage
level displayed on the
label(1) and make
sure it is identical to
the AC line. Then
connect the power
cord(2).
2. Push and turn On the
main power switch
on the front panel.
3. The display shows the default setup:
Sine wave, 1kHz
Functionality
check
1. Connect SFG main output to measurement device
such as oscilloscope.
2. Press the output key. The
output is activated and the
LED turns On.
3. Observe the output waveform: 1kHz, sine wave.
17
Page 18

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
AMPL
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
OFFSET
OUTPUT
DUTY
Operation Shortcuts
Sine wave
250Hz, −40dB
amplitude
50
Ω
三
Triangle wave
8kHz,+2V Offset
Ω50
1. Press Wave key and
select Sine
2. Press 2 + 5 + 0 + Shift
+ 0(Hz) key
3. (SFG-1003) Press
Output key, then pull
Amplitude knob
4. (SFG-1013) Press
Output key, then press
Shift + 3 (−40dB) key
1. Press Wave key and
select Triangle
2. Press 8 + Shift +
9(kHz) key
3. Press Output key, then
pull Offset knob and
Rotate
WAVE
2
WAVE
8
5
SHIFT
SHIFT
SHIFT
0
3
9
0
Square Wave
1MHz, 45% duty
Ω50
TTL Output 10kHz
OUTPUT
1. Press Wave key and
select Square
2. Press 1 + Shift +
8(MHz) key
3. Press Output key, then
pull Duty knob and
rotate
1. Press Output key
2. Press Shift + Wave
(TTL) key
3. Press 1 + 0 + Shift +
9(kHz) key
WAVE
1
1 0
SHIFT
WAVESHIFT
8
SHIFT
ADJ
ADJ
9
18
Page 19

Sine/Square/Triangle Wave
SINE/SQUARE/TRIANGLE WAVE
Select
waveform
Set frequency
Set amplitude
Set duty cycle
(square wave)
Activate waveform................................................20
Enter frequency....................................................20
Edit frequency.....................................................21
Maximum frequency limit error............................21
Minimum frequency limit error.............................22
Set Amplitude......................................................22
View amplitude (SFG-1013)..................................22
Attenuate by −40dB..............................................22
Enter duty cycle....................................................23
Set offset
19
Activate offset......................................................23
Adjust offset........................................................23
Limitation............................................................24
Page 20

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
OUTPUT
Activate waveform
Sine / Square
/ Triangle
WAVE
1. Press the wave key repeatedly. The
corresponding indicator appears on
the display.
Sine waveform
Square waveform
Triangle waveform
2. Press the output key. The LED
turns On.
3. The waveform comes out from the
Ω50
main terminal.
10Vp-p (50Ω load)
20Vp-p (no load)
Set Frequency
Enter
frequency
45Hz
20
Enter the waveform frequency using the numerical keys.
1.2MHz
37kHz
1
3
4
7
5
2
SHIFT
SHIFT
SHIFT
9
0
8
Page 21

Sine/Square/Triangle Wave
Edit
frequency
SHIFT
SHIFT
Left cursor key moves the active
4
cursor left.
Right cursor key moves the active
5
cursor right.
Turn the Frequency knob left to
decrease the frequency.
Turn the frequency knob right to
increase the frequency.
Maximum
frequency
limit error
For full error message list, see page37.
Sine and square waveform
frequency is limited to
maximum 3MHz. When the
input exceeds it, an error
message (Err-1) appears and
forces the frequency to 3MHz.
Triangle waveform frequency is
limited to maximum 1MHz.
When the input exceeds it, an
error message (Err-2) appears
and forces the frequency to
1MHz.
21
Page 22

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
AMPL
AMPL
Minimum
For full error message list, see page37.
frequency
limit error
The minimum frequency is
0.1Hz. When the frequency
input becomes less than 0.1Hz,
an error message (Err-4)
appears and forces the
frequency to 0.1Hz.
Set Amplitude
Amplitude setting does not apply to TTL output (page25).
Set
Amplitude
Turn the Amplitude knob right
(increase) or left (decrease).
The range is 2mVpp ~ 10Vpp for
50Ω output impedance.
View
amplitude
(SFG-1013)
Attenuate by
−40dB
SFG-1003
To view the voltage level
SHIFT
(amplitude), press the Shift key
and dot (V/F) key. The display
shows the voltage level. Repeat
this procedure to go back to the
frequency level view.
Both SFG-1003 and SFG-1013 can attenuate the main
output by −40dB, in different method.
Pull out the Amplitude knob. The
output amplitude is attenuated by
−40dB.
-40dB
22
Page 23

Sine/Square/Triangle Wave
DUTY
OFFSET
SFG-1013
SHIFT
3
Press the Shift key, then 3
(−40dB). The main output is
attenuated by −40dB, and the
−40dB display indicator in the
display turns On.
Set Duty Cycle (Square Waveform)
The duty cycle setting is not available in sine/triangle waveform.
Enter duty
cycle
Pull out the Duty knob. Turn right
(left) to increase (decrease) the duty
cycle. The default is set at 50%.
ADJ
Range
25% ~ 75%
Set Offset
Offset setting does not apply to TTL output (page25).
Activate
offset
Adjust offset
SFG can add or delete offset to the sine/square/triangle
waveform, thus changing the waveform vertical position.
Pull the OFFSET knob to turn On
Offset setting.
Turn the knob right (higher position)
or left (lower position).
ADJ
Range
−5V ~ +5V for 50Ω output load
23
Page 24

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Limitation
Positive peak
clip (50Ω)
Negative peak
clip (50Ω)
Note that the output amplitude, including the offset, is
still limited to:
−5 ~ +5V (50Ω load)
−10 ~ +10V (no load)
Therefore excessive offset leads to peak clip as below.
Clipped
+5V
Offset
-5V
+5V
Offset
-5V
Clipped
24
Page 25

TTL Output
TTL OUTPUT
Activate TTL
Set frequency
Set duty cycle
Activate TTL.........................................................25
Enter frequency....................................................26
Edit frequency......................................................26
Maximum frequency limit error............................27
Minimum frequency limit error.............................27
Enter duty cycle....................................................27
Activate TTL
Select TTL
SHIFT
1. Press the Output key. The LED
turns On. (TTL does not activate
WAVE
unless the output is already On)
2. Press the Shift key, then the
Wave key. TTL indicator appears
on the display.
25
OUTPUT
3. The waveform comes out from
the TTL output terminal.
Level: ≥3Vp-p
Page 26

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Set Frequency
Enter
Enter the waveform frequency using the numerical keys.
frequency
45Hz
1.2MHz
37kHz
Edit
frequency
SHIFT
SHIFT
1
3
4
7
5
2
SHIFT
SHIFT
SHIFT
9
0
8
Left cursor key moves the active
4
cursor left.
Right cursor key moves the active
5
cursor right.
Turn the Frequency knob left to
decrease the frequency.
Turn the frequency knob right to
increase the frequency.
26
Page 27

TTL Output
DUTY
Maximum
For full error message list, see page37.
frequency
limit error
For full error message list, see page37.
Minimum
frequency
limit error
Set Duty Cycle
TTL frequency is limited to
maximum 3MHz. When the
input exceeds it, an error
message (Err-1) appears and
forces the frequency to 3MHz.
The minimum frequency is
0.1Hz. When the frequency
input becomes less than 0.1Hz,
an error message (Err-4)
appears and forces the
frequency to 0.1 Hz.
Enter duty
cycle
Range
ADJ
25% ~ 75%
1. Pull out the Duty knob. Turn
right (left) to increase (decrease)
the duty cycle. The default is set
at 50%.
2. Press the Duty knob. The duty
cycle is reset to 50%.
27
Page 28
SFG-1000 Series User Manual
APPLICATION EXAMPLES
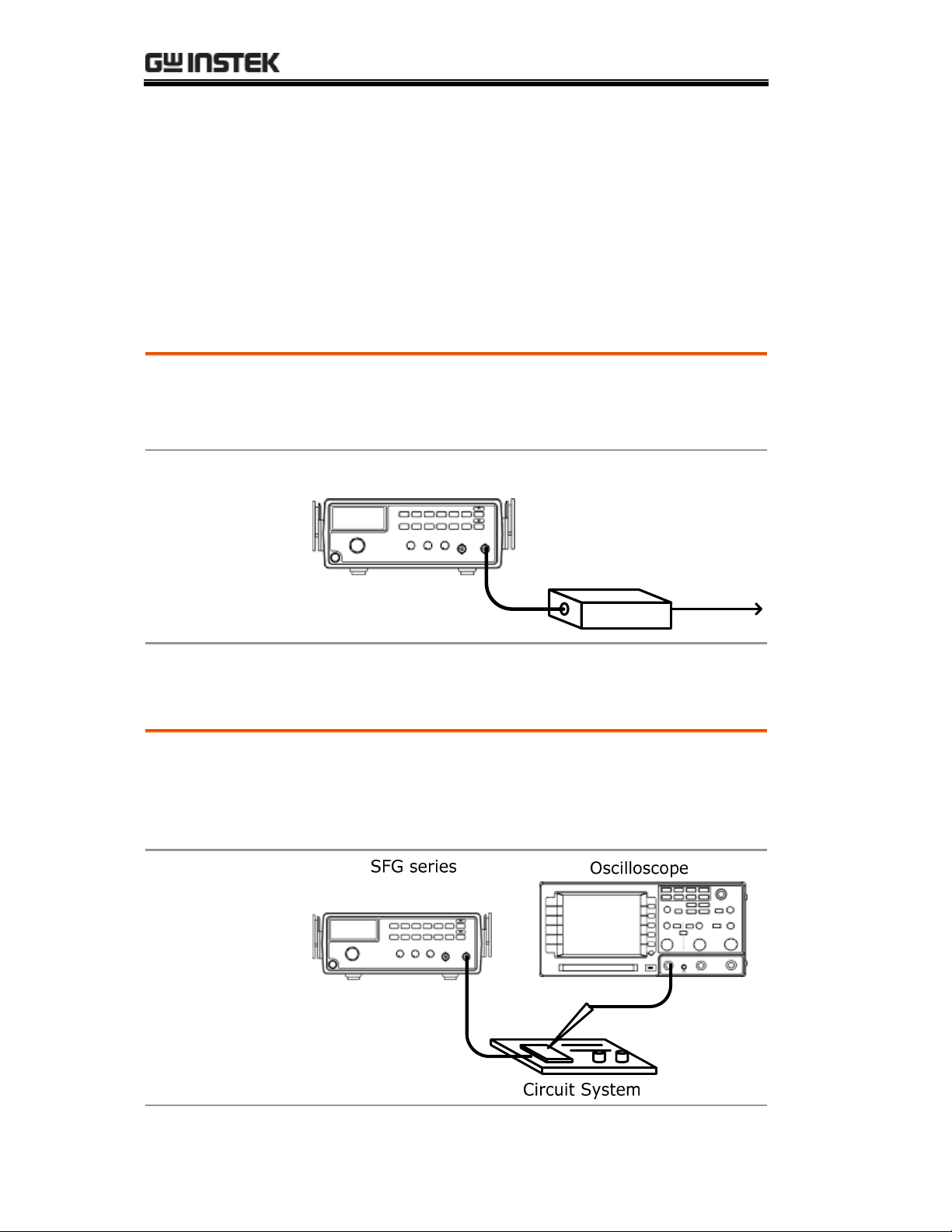
Reference Signal for PLL System
Description
Block diagram
The SFG output can be used as a cost-effective reference
signal for Phase-Locked-Loop system. Directly connect
SFG output to PLL input.
SFG series
Reference InOutput
Trouble-Shooting Signal Source
Description
The SFG output can be used as the signal source to test
the failed part in a circuit system. Isolate the problematic
part from the rest, feed the SFG output as a stimulus,
and observe the outcome using an oscilloscope.
PLL
Block diagram
28
Page 29

Application Examples
Transistor DC Bias Characteristics Test
Description
Block diagram
Use SFG-1000 series as the signal source for a transistor.
Compare the transistor input/output waveform using the
oscilloscope. Adjust the DC voltage source to find out
the maximum output without distorting the waveform.
Oscilloscope
display
29
Page 30

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Amplifier Over-Load Characteristic Test
Description
Block diagram
Use the triangle wave output from SFG-1000 series to
check the amplifier output distortion caused by overload.
The common sine wave is not the ideal source in this
case. Observe the linearity of the triangle waveform
using an oscilloscope.
SFG series
Triangle wave
Amplifier
Oscilloscope
Load
Amplifier Transient Characteristics Test
Description
Block diagram
Use the square wave output from SFG-1000 series to
check the transient frequency response of an amplifier.
The common sine wave is not the ideal source in this
case. Observe the waveform using an oscilloscope.
30
Page 31

Application Examples
Test step
Transient
characteristiclist
1. Apply a triangle waveform to the amplifier first.
Adjust the waveform amplitude to make sure there
is no clipping.
2. Switch to square waveform and adjust its frequency
to the middle of the amplifier pass band, such as
20Hz, 1kHz, and 10kHz.
3. Observe the shape of the amplifier output. The
following table shows the possible output
distortions and their explanations.
• Amplitude reduction at low
frequency
• No phase shift
• Low frequency boosted (accentuated
fundamental)
• High frequency loss
• No phase shift
• Low frequency phase shift
• Trace thickened by hum-voltage
• High frequency loss
• Phase shift
• Low frequency loss
• Phase shift
• Low frequency loss
• Low frequency phase shift
• High frequency loss
• Low frequency phase shift
• Damped oscillation
Note
31
For narrow band amplifier testing, square wave may not
be suitable.
Page 32

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
Logic Circuit Test
Description
Use the TTL output from SFG-1000 series to test digital
circuits. Observe the timing relation of input/output
waveform using an oscilloscope.
Block diagram
Impedance Matching Network Test
Description
Block diagram
Test step
Use SFG-1000 series for impedance matching network:
testing its frequency characteristic and matching the
impedance.
Adjust the potentiometer until V2 becomes the half of
V1 (V2=0.5V1). Then the impedance Z of the network
becomes identical to the potentiometer.
32
Page 33

Application Examples
Speaker Driver Test
Description
Block diagram
Graph
Use SFG-1000 series for testing the frequency
characteristics of audio speakers. Record the volt reading
versus the input signal frequency.
Oscilloscope (or Voltmeter)
SFG series
Speaker
The peak voltage occurs on the resonant frequency of
the speaker.
Correspondent
Response (dB)
Peak of Audio Drive Response
Frequency (Hz)
33
Page 34

SFG-1000 Series User Manual
FAQ
●
I pressed the Power switch on the front panel but nothing happens.
●
How can I get out of TTL/−40dB mode?
●
The device accuracy does not match the specification.
●
What are these error messages?
I pressed the Power switch on the front panel but nothing happens.
Make sure the AC source voltage is set at the rating
±10%, 50/60Hz. For power up sequence, see page17.
Otherwise the internal fuse might be blown out. For fuse
replacement procedure, see page35.
TTL does not activate (pressed Shift + Wave key)
You need to turn On the output first. Press the Output
key, then press Shift+Wave. For details, see page25.
How can I get out of TTL/−40dB mode?
For TTL: press the Shift key, then the wave key. For
details, see page25.
For −40dB mode, press the Shift key, then 3. For details,
see page22.
The device accuracy does not match the specification.
Make sure the device is powered On for at least 30
minutes, within +18°C~+28°C. This is necessary to
stabilize the unit to match the specification.
What are these error messages?
Several messages appear when trying to set the frequency
in irregular ways. Page37 summarizes the messages.
If there is still a problem, please contact your local dealer or GWInstek at
www.gwinstek.com.tw / marketing@goodwill.com.tw.
34
Page 35

Appendix
APPENDIX
Fuse Replacement
1. Take off
the Handle
2. Take off
the Cover
In order to detach the handle from the unit, turn the
handle down 90 degrees, then pull it off sideways.
z
H
0
6
/
0
5
V
0
2
2
C
A
G
N
I
N
R
E
V
A
O
M
W
E
R
,
K
C
G
O
N
I
H
N
S
PE
D
O
I
O
V
E
A
R
O
O
F
T
E
B
S
T
U
P
N
I
A
V
1
2
W
7
1
Take off the two metal holdings from the handle joint.
Then take the top screw off from the rear panel.
35
z
H
0
6
/
0
5
V
0
2
2
C
A
G
N
I
N
R
E
V
A
O
W
M
E
R
,
K
C
G
O
N
I
H
N
S
PE
D
O
I
O
V
E
A
R
O
F
O
T
BE
S
T
U
P
N
I
A
V
1
2
W
7
1
Page 36

Page 37

Appendix
Error Messages
Frequency
error
Err-1
Err-2
Err-4
Sine, square, and TTL wave frequency over
range. This message appears when entering
sine / square / TTL waveform frequency
larger than 3MHz. The frequency is
automatically forced to 3MHz.
Triangle wave Frequency over range. This
message appears when entering triangle
waveform frequency larger than 1MHz. The
frequency is automatically forced to 1MHz.
Frequency over resolution. This message
appears when trying to enter frequency less
than 0.1Hz. The frequency is automatically
forced to 0.1 Hz.
Specification
• SFG series must be powered for at least 30 minutes within the ambient
temperature 18°C~28°C to meet this spec.
Output Function Sine, Square, Triangle
Main
Frequency
Amplitude Range
Amplitude Accuracy
Impedance
Attenuator
DC Offset < −5V ~ >+5V (50Ω load)
Duty Range
Display 6 digits LED display
Sine/Square
Waveform Range
Triangle Waveform
Range
Resolution 0.1Hz maximum
Stability ±20ppm
Accuracy ±20ppm
Aging ±5ppm/year
10Vpp (50Ω load)
±20% at maximum position
(SFG-1013 only)
50Ω ± 10%
−40dB ± 1dB x1
25% ~ 75%, ≤1MHz (Square Wave)
0.1Hz ~ 3MHz
0.1Hz ~ 1MHz
37
Page 38

Page 39

Appendix
Declaration of Conformity
We
GOOD WILL INSTRUMENT CO., LTD.
(1) No.7-1, Jhongsing Rd., Tucheng City, Taipei County, Taiwan
(2) No. 69, Lu San Road, Suzhou City (Xin Qu), Jiangsu Sheng, China
declare, that the below mentioned product
Type of Product: Synthesized Function Generator
Model Number: SFG-1003, SFG-1013
are herewith confirmed to comply with the requirements set out in the
Council Directive on the Approximation of the Law of Member States
relating to Electromagnetic Compatibility (89/336/EEC, 92/31/EEC,
93/68/EEC) and Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC, 93/68/EEC).
For the evaluation regarding the Electromagnetic Compatibility and Low
Voltage Directive, the following standards were applied:
◎ EMC
EN 61326-1: Electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory
use –– EMC requirements (1997 + A1:1998 + A2:2001 + A3:2003)
Conducted Emission
Radiated Emission
EN 55011: Class A 1998 +
A1:1999 + A2:2002
Current Harmonics
EN 61000-3-2: 2000 + A2:2005
Voltage Fluctuations
EN 61000-3-3: 1995 + A1:2001 +
A2:2005
------------------------- Surge Immunity
------------------------- Conducted Susceptibility
------------------------- Power Frequency Magnetic Field
------------------------- Voltage Dip/ Interruption
Electrostatic Discharge
EN 61000-4-2: 1995 + A1:1998 +
A2:2001
Radiated Immunity
EN 61000-4-3: 2002 + A1:2002
Electrical Fast Transients
EN 61000-4-4: 2004
EN 61000-4-5: 1995 + A1:2001
EN 61000-4-6: 1996 + A1:2001
EN 61000-4-8: 1993 + A1:2001
EN 61000-4-11: 2004
◎ Safety
Low Voltage Equipment Directive 73/23/EEC & amended by 93/68/EEC
Safety Requirements
IEC/EN 61010-1: 2001
39
Page 40

INDEX
SFG-1000 Series User Manual
4
40dB attenuation
faq........................................................34
step.......................................................22
A
amplifier application example....................30
C
caution symbol............................................5
cleaning.......................................................6
constant current circuit................................9
control knob overview...............................14
D
default display...........................................17
digital direct synthesis
block diagram.......................................10
direct digital synthesis.................................9
display contents overview..........................12
duty cycle
faq........................................................34
sine/square/triangle.............................23
TTL......................................................27
E
EN55011...................................................39
EN61010
declaration of conformity......................39
measurement category............................6
pollution degree......................................6
error message
error1....................................................21
error2....................................................21
error4....................................................22
summary...............................................37
F
FAQ..........................................................34
feature list..................................................11
frequency editing
sine/square/triangle..............................20
TTL......................................................26
frequency faq.............................................34
front panel key overview............................13
fuse
rating.....................................................36
replacement...........................................35
safety instruction.....................................6
G
ground terminal
location.................................................15
symbol....................................................5
I
impedance application example.................32
in/out terminal overview...........................14
L
logic application example...........................32
M
model lineup..............................................11
O
offset..........................................................23
example setting......................................18
operation environment
safety instruction.....................................6
specification..........................................38
40
Page 41

Appendix
operation shortcut......................................18
P
peak clip....................................................24
PLL example application...........................28
power supply
safety instruction....................................6
power up sequence.....................................17
faq.........................................................34
R
rear panel overview....................................15
S
setup step...................................................16
sine wave
example setting......................................18
selection................................................20
speaker application example.......................33
specification...............................................37
FAQ......................................................34
square wave
example setting......................................18
selection................................................20
storage environment
safety instruction.....................................7
specification..........................................38
T
table of contents..........................................3
tilt stand....................................................16
transistor application example...................29
triangle wave
example setting.....................................18
selection................................................20
troubleshooting example............................28
TTL
activation..............................................25
example setting.....................................18
U
UK power cord............................................7
V
voltage viewing..........................................22
W
warning symbol...........................................5
41
 Loading...
Loading...