Page 1

Programmable DC Power Supply
PSU Series
PROGRAMMING MANUAL
Revision 1.2 July 2014
ISO-9001 CERTIFIED MANUFACTURER
Page 2

This manual contains proprietary information, which is protected by
copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be
photocopied, reproduced or translated to another language without
prior written consent of Good Will company.
The information in this manual was correct at the time of printing.
However, Good Will continues to improve products and reserves the
rights to change specification, equipment, and maintenance
procedures at any time without notice.
Good Will Instrument Co., Ltd.
No. 7-1, Jhongsing Rd., Tucheng Dist., New Taipei City 236, Taiwan.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ................................................... 4
GETTING STARTED ........................................................... 8
PSU Series Overview .............................. 9
Appearance .......................................... 13
Configuration Settings ......................... 21
REMOTE CONTROL ........................................................ 30
Interface Configuration ........................ 31
Command Syntax ................................. 55
Command List ..................................... 58
Status Register Overview ................... 104
Error List ........................................... 115
APPENDIX ..................................................................... 124
PSU Default Settings ......................... 124
Error Messages & Messages .............. 124
LED ASCII Table Character Set ........... 126
INDEX............................................................................ 128
3
Page 4

PSU Programming Manual
WARNING
Warning: Identifies conditions or practices that
could result in injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
Caution: Identifies conditions or practices that
could result in damage to the PSU or to other
properties.
DANGER High Voltage
Attention Refer to the Manual
Protective Conductor Terminal
Earth (ground) Terminal
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This chapter contains important safety
instructions that you must follow during
operation and storage. Read the following before
any operation to insure your safety and to keep
the instrument in the best possible condition.
Safety Symbols
These safety symbols may appear in this manual or on the
instrument.
4
Page 5

SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Do not dispose electronic equipment as unsorted
municipal waste. Please use a separate collection
facility or contact the supplier from which this
instrument was purchased.
General
Guideline
CAUTION
Do not place any heavy object on the PSU.
Avoid severe impact or rough handling that
leads to damaging the PSU.
Do not discharge static electricity to the PSU.
Use only mating connectors, not bare wires, for
the terminals.
Do not block the cooling fan opening.
Do not disassemble the PSU unless you are
qualified.
(Measurement categories) EN61010-1:2010 and EN61010-2-030
specifies the measurement categories and their requirements as
follows. The PSU falls under category II.
Measurement category IV is for measurement performed at the
source of low-voltage installation.
Measurement category III is for measurement performed in the
building installation.
Measurement category II is for measurement performed on the
circuits directly connected to the low voltage installation.
0 is for measurements performed on circuits not directly
connected to Mains.
Power Supply
WARNING
AC Input voltage range: 85Vac~265Vac
Frequency: 47Hz to 63Hz
To avoid electrical shock connect the protective
grounding conductor of the AC power cord to
an earth ground.
Safety Guidelines
5
Page 6

PSU Programming Manual
Cleaning the PSU
Disconnect the power cord before cleaning.
Use a soft cloth dampened in a solution of mild
detergent and water. Do not spray any liquid.
Do not use chemicals containing harsh material
such as benzene, toluene, xylene, and acetone.
Operation
Environment
Location: Indoor, no direct sunlight, dust free,
almost non-conductive pollution (Note below)
Relative Humidity: 20%~ 85% (no condensation)
Altitude: < 2000m
Temperature: 0°C to 50°C
(Pollution Degree) EN61010-1:2010 and EN61010-2-030 specifies
the pollution degrees and their requirements as follows. The PSU
falls under degree 2.
Pollution refers to “addition of foreign matter, solid, liquid, or
gaseous (ionized gases), that may produce a reduction of dielectric
strength or surface resistivity”.
Pollution degree 1: No pollution or only dry, non-conductive
pollution occurs. The pollution has no influence.
Pollution degree 2: Normally only non-conductive pollution
occurs. Occasionally, however, a temporary conductivity caused
by condensation must be expected.
Pollution degree 3: Conductive pollution occurs, or dry, non-
conductive pollution occurs which becomes conductive due to
condensation which is expected. In such conditions, equipment
is normally protected against exposure to direct sunlight,
precipitation, and full wind pressure, but neither temperature
nor humidity is controlled.
Storage
environment
Location: Indoor
Temperature: -25°C to 70°C
Relative Humidity: ≤90%(no condensation)
Disposal
Do not dispose this instrument as unsorted
municipal waste. Please use a separate collection
facility or contact the supplier from which this
instrument was purchased. Please make sure
discarded electrical waste is properly recycled to
reduce environmental impact.
6
Page 7

SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Green/ Yellow:
Earth
Blue:
Neutral
Brown:
Live (Phase)
Power cord for the United Kingdom
When using the power supply in the United Kingdom, make sure
the power cord meets the following safety instructions.
NOTE: This lead/appliance must only be wired by competent persons
WARNING: THIS APPLIANCE MUST BE EARTHED
IMPORTANT: The wires in this lead are coloured in accordance with the
following code:
As the colours of the wires in main leads may not correspond with
the coloured marking identified in your plug/appliance, proceed
as follows:
The wire which is coloured Green & Yellow must be connected to
the Earth terminal marked with either the letter E, the earth symbol
or coloured Green/Green & Yellow.
The wire which is coloured Blue must be connected to the terminal
which is marked with the letter N or coloured Blue or Black.
The wire which is coloured Brown must be connected to the
terminal marked with the letter L or P or coloured Brown or Red.
If in doubt, consult the instructions provided with the equipment
or contact the supplier.
This cable/appliance should be protected by a suitably rated and
approved HBC mains fuse: refer to the rating information on the
equipment and/or user instructions for details. As a guide, a cable
of 0.75mm2 should be protected by a 3A or 5A fuse. Larger
conductors would normally require 13A types, depending on the
connection method used.
Any exposed wiring from a cable, plug or connection that is
engaged in a live socket is extremely hazardous. If a cable or plug is
deemed hazardous, turn off the mains power and remove the cable,
any fuses and fuse assemblies. All hazardous wiring must be
immediately destroyed and replaced in accordance to the above
standard.
7
Page 8

PSU Programming Manual
GETTING STARTED ........................................................... 8
PSU Series Overview ......................................................... 9
Series lineup .............................................................................. 9
Main Features ......................................................................... 10
Accessories ............................................................................. 11
Appearance ..................................................................... 13
PSU Series Front Panel ......................................................... 13
PSU Series Display and Operation Panel ........................... 16
Rear Panel ............................................................................... 18
Configuration Settings..................................................... 21
GETTING STARTED
This chapter describes the power supply in a
nutshell, including its main features and front /
rear panel introduction. After going through the
overview, please read the theory of operation to
become familiar with the operating modes,
protection modes and other safety considerations.
8
Page 9

GETTING STARTED
Model name
Voltage Rating1
Current Rating2
Power
PSU 6-200
6V
200A
1200W
PSU 12.5-120
12.5V
120A
1500W
PSU 20-76
20V
76A
1520W
PSU 40-38
40V
38A
1520W
PSU 60-25
60V
25A
1500W
1
Minimum voltage guaranteed to 0.2% of rating voltage.
2
Minimum current guaranteed to 0.4% of rating current.
PSU Series Overview
Series lineup
The PSU series consists of 5 models, covering a number of different
current, voltage and power capacities:
9
Page 10
Main Features
Performance
High power density: 1500W in 1U
Universal input voltage 85~265Vac, continuous
operation.
Output voltage up to 60V, current up to 200A.
Features
Active power factor correction.
Parallel master/slave operation with active
current sharing.
Remote sensing to compensate for voltage drop
in load leads.
19" rack mounted ATE applications.
A built-in Web server that lets you monitor the
instrument directly from an internet browser on
your computer.
OVP, OCP and OHP protection.
Preset memory function.
Adjustable voltage and current slew rates.
Bleeder circuit ON/OFF setting. (to prevent
over-discharging of batteries)
CV, CC priority start function. (prevents
overshoot with output ON)
Supports test scripts.
Interface
Built-in RS-232/485, LAN and USB interface.
Analog output programming and monitoring.
Optional interfaces: GPIB, Isolated Voltage (0-
5V/0-10V) and Isolated Current (4-20mA)
programming and monitoring interface.
(Factory options)
PSU Programming Manual
10
Page 11

GETTING STARTED
Standard
Accessories
Part number
Description
Qty.
Output terminal cover
1
Analog connector plug kit
1
Output terminal M8 bolt set
1
Input terminal cover
1 62SB-8K0HD101
1U Handle, ROHS
2
62SB-8K0HP101
1U BRACKET (LEFT), RoHS
1
62SB-8K0HP201
1U BRACKET (RIGHT), RoHS
1 82SU-60250E01
User manual CD
1 set
82SU-60250M01
Quick start guide
1
82SU-062H0K01
Packing list
82GW-00000C01
* CTC GW/INSTEK JAPAN
USE ,RoHS
1
Factory Installed
Options
Part number
Description
PSU-GPIB
GPIB interface
PSU-ISO-V
Voltage programming isolated
analog interface
PSU-ISO-I
Current programming isolated
analog interface
Accessories
Before using the PSU power supply unit, check the package
contents to make sure all the standard accessories are included.
11
Page 12

PSU Programming Manual
Optional
Accessories
Part number
Description
PSU-01C
Cable for 2 units of PSU-Series in
parallel mode connection
PSU-01B
Bus Bar for 2 units of PSU-Series in
parallel mode connection
PSU-02C
Cable for 3 units of PSU-Series in
parallel mode connection
PSU-02B
Bus Bar for 3 units of PSU-Series in
parallel mode connection
PSU-03C
Cable for 4 units of PSU-Series in
parallel mode connection
PSU-03B
Bus Bar for 4 units of PSU-Series in
parallel mode connection
PSU-232
RS232 cable with DB9 connector kit
PSU-485
RS485 cable with DB9 connector kit
GRM-001
Rack-mount slides (General Devices
P/N: C-300-S-116-RH-LH)
GTL-246
USB Cable 2.0-A-B Type, Approx. 1.2M
GPW-001
Power Cord SJT 12AWG/3C, 3m MAX
Length, 105 ºC, RNB5-5*3P UL/CSA
type
GPW-002
Power Cord H05W-F 1.5mm2/3C, 3m
MAX Length, 105 ºC, RNB5-5*3P VDE
type
GPW-003
Power Cord VCTF 3.5mm2/3C, 3m
MAX Length, 105 ºC, RNB5-5*3P PSE
type
Download
Name
Description
psu_cdc.inf
PSU USB driver
Other
Name
Description
Certificate of traceable calibration
12
Page 13
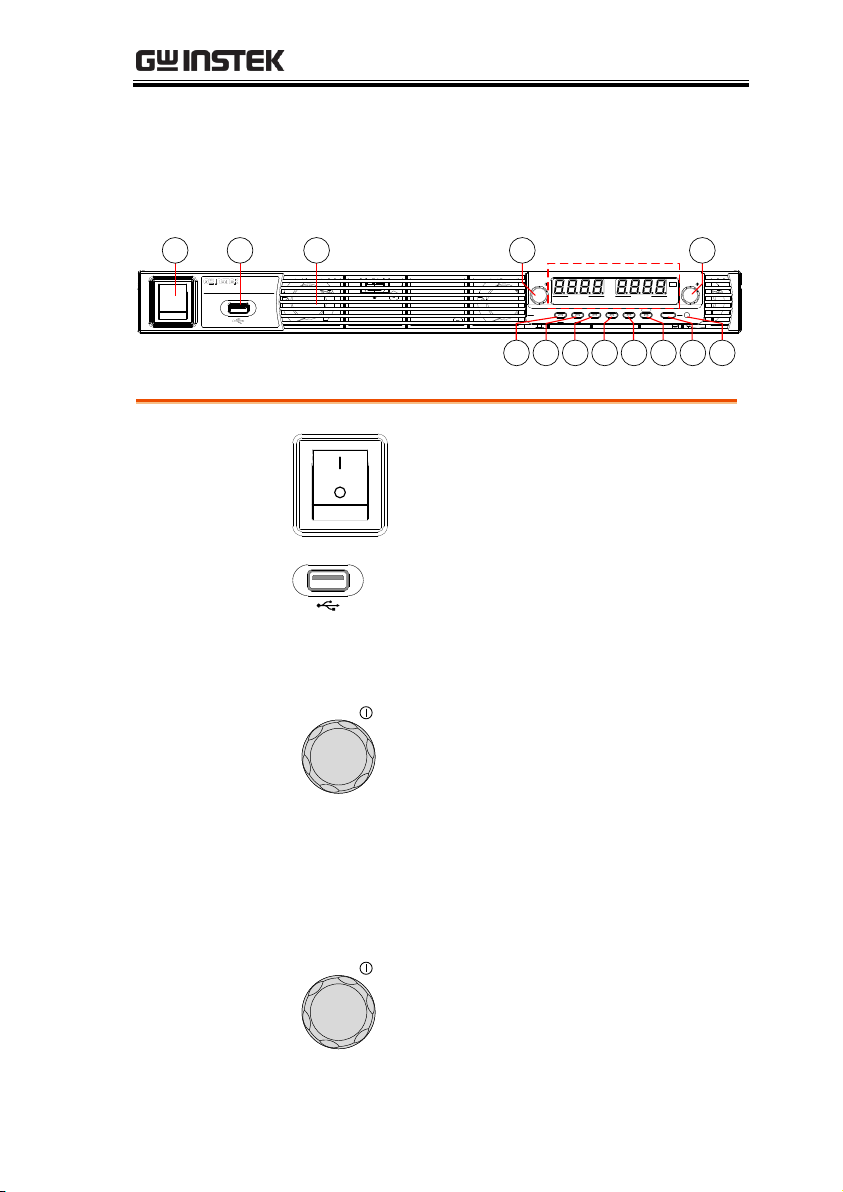
GETTING STARTED
Lock/Local PROT Function Test Set Output
Unlock ALM_CLR M 1 M 2 M 3
Shift
: Long Push
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C C
A
C V
V
VOLTAGE CURRENT
PSU 40-38
DC Power Supply
0 -40V / 0 - 38A
Voltage Current
2 3 4 5
Display Area
1
116 7 8 9 10 12 13
1.
Power Switch
Used to turn the power on/off.
2.
USB A Port
USB A port for data transfer,
loading test scripts etc.
3.
Air Inlet
Air inlet for cooling the inside of
the PSU series.
4.
Voltage Knob
Voltage
Used to set the voltage value or
select a parameter number in the
Function settings.
Display Area
The display area shows setting values, output
values and parameter settings. The function LEDs
below show the current status and mode of the
power supply. See page 16 for details.
5.
Current Knob
Current
Displays the current or the value
of a Function parameter.
Appearance
PSU Series Front Panel
13
Page 14

PSU Programming Manual
6.
Lock/Local
Button
Lock/Local
Unlock
Used to lock all front panel
buttons other than the Output
Button or it switches to local
mode.
Unlock
Button
(Long push) Used to unlock the
front panel buttons.
7.
PROT Button
PROT
ALM_CLR
Used to set and display OVP, OCP
and UVL.
ALM_CLR
Button
(Long push) Used to release
protection functions that have
been activated.
8.
Function
Button
Function
M1
Used to configure the various
function.
M1 Button
(+Shift) Used to recall the M1
setup.
(+Shift and hold) Used to save the
current setup to M1.
9.
Test Button
TEST
M2
Used to run customized scripts for
testing.
M2 Button
(+Shift) Used to recall the M2
setup.
(+Shift and hold) Used to save the
current setup to M2.
10.
Set Button
SET
M3
Used to set and confirm the output
voltage and output current.
M3 Button
(+Shift) Used to recall the M3
setup.
(+Shift and hold) Used to save the
current setup to M3.
14
Page 15
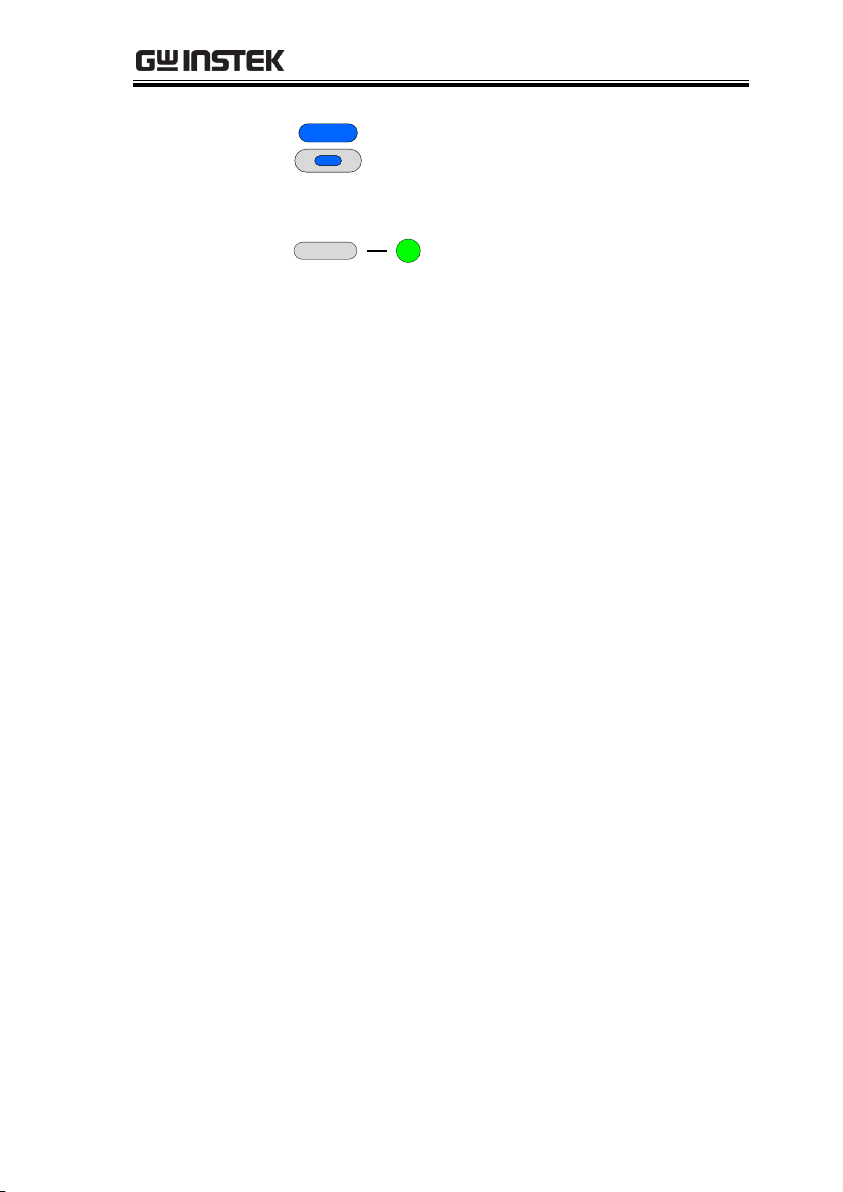
GETTING STARTED
11.
Shift Button
Shift
Used to enable the functions that
are written in blue characters
below the button.
12.
Output
Button
Output
Used to turn output on and off.
13.
Output ON
LED
Lights in green during output ON.
15
Page 16

PSU Programming Manual
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C C
A
C V
V
VOLTAGE CURRENT
Display Area
14 1516 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24
25
26 27 28
14.
Voltage
Meter
Displays the voltage or the parameter number of a
Function parameter.
15.
Current
Meter
Displays the current or the value of a Function
parameter.
16.
CV LED
Lights in green during constant voltage mode.
17.
CC LED
Lights in green during constant current mode.
18.
VSR LED
The voltage slew rate enable.
19.
LAN LED
Lights up when the LAN interface is connected.
20.
RMT LED
Lights in green during remote control.
21.
ERR LED
Lights in red when an error has occurred.
22.
DLY LED
The output on/off delay enable.
23.
ALM LED
Lights in red when a protection function has been
activated.
PSU Series Display and Operation Panel
16
Page 17

GETTING STARTED
24.
ISR LED
The current slew rate enable.
25.
M1 LED
Lights in green when the memory value are being
recalled or saved.
26.
M2 LED
Lights in green when the memory value are being
recalled or saved.
27.
M3 LED
Lights in green when the memory value are being
recalled or saved.
28.
RUN LED
Auto sequence has been activated.
Note
Only the ERR and ALM LED’s are red. All the
others are green.
17
Page 18

Rear Panel
L N
AC INPUT
DC OUTPUT
LANRS 485 / 232
OUT IN
ANALOG PROGRAMMING
S LS SLSNC
REMOTE SENSE
234 15678
9 10
87654321
0 -5V / 0 - 10V
ISOLATED PROGRAMMING
87654321
4 -20mA
ISOLATED PROGRAMMING
1.
AC Input
L N
AC INPUT
Wire clamp connector.
2.
DC Output
Output terminals for 6V to 60V
models.
3.
USB
USB port for controlling the PSU
remotely.
4.
LAN
LAN
RS 485 / 232
Ethernet port for controlling the
PSU remotely.
PSU Programming Manual
18
Page 19

GETTING STARTED
5.
Remote-IN
LAN
RS 485 / 232
Two different types of cables can
be used for RS232 or RS485-based
remote control.
PSU-232: RS232 cable with DB9
connector kit.
PSU-485: RS485 with DB9
connector kit.
6.
Remote-OUT
LAN
RS 485 / 232
RJ-45 connector that is used to
daisy chain power supplies with
the Remote-IN port to form a
communication bus.
PSU-485S: Serial link cable with
RJ-45 shielded connector.
7.
Analog
Control
ANALOG PROGRAMMING
External analog control connector.
8.
Remote
Sense
S LS SLSNC
REMOTE SENSE
Compensation of load wire drop.
9.
Option Slot
87654321
0 - 5V / 0 - 10V
ISOLATED PROGRAMMING
Blank sub-plate for standard units.
Isolated Analog connector for
units equipped with Isolated
Current and Voltage
Programming and Monitoring
option.
GPIB connector for units equipped
with IEEE programming option.
10.
Ground
Screw
Connector for grounding the output (two
positions, shown in red).
19
Page 20

PSU Programming Manual
L N
AC INPUT
DC OUTPUT
20
Page 21

GETTING STARTED
The normal function settings (F-01~F-61, F70~F-76) and F-88 ~ F-89 can be easily
configured with the Function key.
Ensure the load is not connected.
Ensure the output is off.
Function settings F-90~97 can only be
viewed.
Note
Function setting F-89 (Show Version) can only be
viewed, not edited.
Configuration settings F-90~ F-97 cannot be edited
in the Normal Function Settings. Use the Power
On Configuration Settings. See page 23 for details.
Steps
1. Press the Function key. The
function key will light up.
Function
2. The display will show F-01 on the left and the
configuration setting for F-01 on the right.
VOLTAGE CURRENT
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C V C C
V A
3. Rotate the voltage knob to change
the F setting.
Voltage
Range
F-00~F-61, F-70~F-76,
F-88~F-97
Configuration Settings
Setting Normal Function Settings
21
Page 22

PSU Programming Manual
4. Use the current knob to set the
parameter for the chosen F setting.
Current
Press the Voltage knob to save the
configuration setting. ConF will be
displayed when it is configuring.
Voltage
VOLTAGE CURRENT
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C V C C
V A
Exit
Press the Function key again to exit
the configuration settings. The
function key light will turn off.
Function
22
Page 23

GETTING STARTED
Background
The Power On configuration settings can only
be changed during power up to prevent the
configuration settings being inadvertently
changed.
Ensure the load is not connected.
Ensure the power supply is off.
Steps
1. Hold the Function key whilst turning the
power on.
Lock/Local PROT Function Test Set
Output
Unlock ALM_CLR M 1 M 2 M 3
Shift
: Long Push
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C CAC V
V
VOLTAGE CURRENT
PSU 40-38
DC Power Supply
0 - 40V / 0 - 38A
Voltage Current
2. The display will show F-90 on the left and the
configuration setting for F-90 on the right.
VOLTAGE CURRENT
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C V C C
V A
3. Rotate the voltage knob to change
the F setting.
Voltage
Range
F-90 ~ F-97
4. Use the current knob to set the
parameter for the chosen F setting.
Current
Setting Power On Configuration Settings
23
Page 24

PSU Programming Manual
Press the Voltage knob to save the
configuration setting. ConF will be
displayed when it is configuring.
Voltage
VOLTAGE CURRENT
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C V C C
V A
Exit
Cycle the power to save and exit the
configuration settings.
24
Page 25

GETTING STARTED
Normal Function
Settings
Setting
Setting Range
Output ON delay time
F-01
0.00s~99.99s
Output OFF delay time
F-02
0.00s~99.99s
V-I mode slew rate select
F-03
0 = CV high speed priority (CVHS)
1 = CC high speed priority (CCHS)
2 = CV slew rate priority (CVLS)
3 = CC slew rate priority (CVLS)
Rising voltage slew rate
F-04
0.001~0.06V/msec (PSU 6-200)
0.001~0.125V/msec (PSU 12.5-120)
0.001~0.2V/msec (PSU 20-76)
0.001~0.4V/msec (PSU 40-38)
0.001~0.6V/msec (PSU 60-25)
Falling voltage slew rate
F-05
0.001~0.06V/msec (PSU 6-200)
0.001~0.125V/msec (PSU 12.5-120)
0.001~0.2V/msec (PSU 20-76)
0.001~0.4V/msec (PSU 40-38)
0.001~0.6V/msec (PSU 60-25)
Rising current slew rate
F-06
0.001~2A/msec (PSU 6-200)
0.001~1.2A/msec (PSU 12.5-120)
0.001~0.76A/msec (PSU 20-76)
0.001~0.38A/msec (PSU 40-38)
0.001~0.25A/msec (PSU 60-25)
Falling current slew rate
F-07
0.001~2A/msec (PSU 6-200)
0.001~1.2A/msec (PSU 12.5-120)
0.001~0.76A/msec (PSU 20-76)
0.001~0.38A/msec (PSU 40-38)
0.001~0.25A/msec (PSU 60-25)
Configuration Table
Please use the configuration settings listed below when applying
the configuration settings.
25
Page 26

PSU Programming Manual
Internal resistance
setting
F-08
0~0.03Ω (PSU 6-200)
0~0.104Ω (PSU 12.5-120)
0~0.263Ω (PSU 20-76)
0~1.053Ω (PSU 40-38)
0~2.4Ω (PSU 60-25)
Bleeder circuit control
F-09
0 = OFF, 1 = ON
Buzzer ON/OFF control
F-10
0 = OFF, 1 = ON
OCP Delay Time
F-12
0.1 ~ 2.0 sec
Current Setting Limit
(I-Limit)
F-13
0 = OFF, 1 = ON
Voltage Setting Limit
(V-Limit)
F-14
0 = OFF, 1 = ON
Display memory
parameter when recalling
(M1, M2, M3)
F-15
0 = OFF, 1 = ON
Auto Calibration Parallel
Control
F-16
0 = Disable, 1 = Enable, 2 = Execute
Parallel Calibration and set to Enable.
Note: Must be a short between each
unit before starting.
Measurement Average
Setting
F-17
0 = Low, 1 = Middle, 2 = High
Alarm Recovery and
Output Status
F-18
0 = Safe Mode, 1 = Force Mode
Lock Mode
F-19
0:Lock Panel, Allow Output OFF
1:Lock Panel, Allow Output ON/OFF
USB/GPIB settings
Show front panel USB
status
F-20
0 = None, 1 = Mass Storage
Show rear panel USB
status
F-21
0 = None, 1 = Linking to PC
Setup rear USB Speed
F-22
0 = Disable USB, 1 = Full Speed, 2 =
Auto Detect Speed
GPIB Address
F-23
0 ~ 30
GPIB Enable/Disable
F-24
0 = Disable GPIB, 1 = Enable GPIB
Show GPIB available
status
F-25
0 = No GPIB, 1 = GPIB is available
SCPI Emulation
F-26
0 = GW Instek, 1 = TDK GEN, 2 =
Agilent 5700, 3 = Kikusui PWX
LAN settings
Show MAC Address-1
F-30
0x00~0xFF
26
Page 27

GETTING STARTED
Show MAC Address-2
F-31
0x00~0xFF
Show MAC Address-3
F-32
0x00~0xFF
Show MAC Address-4
F-33
0x00~0xFF
Show MAC Address-5
F-34
0x00~0xFF
Show MAC Address-6
F-35
0x00~0xFF
LAN Enable
F-36
0 = OFF, 1 = ON
DHCP
F-37
0 = OFF, 1 = ON
IP Address-1
F-39
000~255
IP Address-2
F-40
000~255
IP Address-3
F-41
000~255
IP Address-4
F-42
000~255
Subnet Mask-1
F-43
000~255
Subnet Mask-2
F-44
000~255
Subnet Mask-3
F-45
000~255
Subnet Mask-4
F-46
0~255
Gateway-1
F-47
0~255
Gateway-2
F-48
0~255
Gateway-3
F-49
0~255
Gateway-4
F-50
0~255
DNS address -1
F-51
0~255
DNS address -2
F-52
0~255
DNS address-3
F-53
0~255
DNS address-4
F-54
0~255
Socket Server
Enable/Disable
F-57
0 = Disable, 1 = Enable
Web Server
Enable/Disable
F-59
0 = Disable, 1 = Enable
Web Password
Enable/Disable
F-60
0 = Disable, 1 = Enable
Web Enter Password
F-61
0000~9999
UART Settings
UART Mode
F-70
0 = Disable UART, 1 = RS232,
2 = RS485
UART Baud Rate
F-71
0 = 1200, 1 = 2400, 2 = 4800,
3 = 9600, 4 = 19200, 5 = 38400,
6 = 57600, 7 = 115200
UART Data Bits
F-72
0 = 7 bits, 1 = 8 bits
UART Parity
F-73
0 = None, 1 = Odd, 2 = Even
UART Stop Bit
F-74
0 = 1 Bit, 1 = 2 Bits
UART TCP
F-75
0 = SCPI, 1 = TDK (emulation mode)
27
Page 28
PSU Programming Manual
UART Address (For TDK)
F-76
00 ~ 31
System Settings
Factory Set Value
F-88
0 = None
1 = Return to factory default settings
Show Version
F-89
0, 1 = Version
2, 3, 4, 5 = Build date (YYYYMMDD)
6, 7 = Keyboard CPLD
8, 9 = Analog Board CPLD
A, B = Analog Board FPGA
C, D, E, F = Kernel Build
(YYYYMMDD)
G, H = Test Command Version
I, J, K, L = Test Command Build
(YYYYMMDD)
Power On Configuration Settings*
CV Control
F-90
0 = Control by Local
1 = Control by External Voltage
2 = Control by External Resistor -
Rising
3 = Control by External Resistor -
Falling
4 = Control by Isolated Board
CC Control
F-91
0 = Control by Local
1 = Control by External Voltage
2 = Control by External Resistor -
Rising
3 = Control by External Resistor -
Falling
4 = Control by Isolated Board
Output Status when
Power ON
F-92
0 = Safe Mode (Always OFF),
1 = Force Mode (Always ON),
2 = Auto Mode (Status before last
time power OFF)
Master/Slave
Configuration
F-93
0 = Independent
1 = Master with 1 slave in parallel
2 = Master with 2 slaves in parallel
3 = Master with 3 slaves in parallel
4 = Slave (parallel)
External Output Logic
F-94
0 = High ON, 1 = Low ON
Monitor Voltage Select
F-96
0 = 5V , 1 = 10V
28
Page 29

GETTING STARTED
Control Range
F-97
0 = 5V [5kΩ], 1 = 10V [10kΩ]
External Output Control
Function
F-98
0 = OFF, 1 = ON
Special Function Settings*
Calibration
F-00
0000 ~ 9999
*Note
Power On configuration settings can only be set
during power up. They can, however, be viewed
under normal operation.
29
Page 30

PSU Programming Manual
Interface Configuration ................................................... 31
Command Syntax ............................................................ 55
Command List ................................................................. 58
Status Register Overview ................................................ 103
Error List ........................................................................ 115
REMOTE CONTROL
This chapter describes basic configuration of
IEEE488.2 based remote control.
30
Page 31

REMOTE CONTROL
USB
Configuration
PC side
connector
Type A, host
PSU side
connector
Rear panel Type B, slave
Speed
1.1/2.0 (full speed/high speed)
USB Class
CDC (communications device
class)
Steps
1. Connect the USB cable to the rear
panel USB B port.
2. Change the Rear panel-USB (F-22)
setting to 2 (Auto Detect Speed) or
1 (USB Full Speed).
Page 21
Note
If you are not using the rear panel
USB device port, set F-22 to 0
(Disable USB).
Page 21
3. The RMT indicator will turn on when a remote
connection has been established.
RMT indicator
AV
VOLTAGE CURRENT
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C V C C
Interface Configuration
USB Remote Interface
Configuration
31
Page 32

Function Check
Functionality
check
Invoke a terminal application such as Realterm.
To check the COM port No., see the Device
Manager in the PC. For WinXP; Control panel
→ System → Hardware tab.
Run this query command via the terminal
application after the instrument has been
configured for USB remote control (page 31).
*idn?
This should return the Manufacturer, Model
number, Serial number, and Firmware version
in the following format.
GW-INSTEK,PSU40-38,TW123456,T0.01.12345678
Manufacturer: GW-INSTEK
Model number : PSU40-38
Serial number : TW123456
Firmware version : T0.01.12345678
PSU Programming Manual
32
Page 33

REMOTE CONTROL
Configure GPIB
1. Ensure the PSU is off before proceeding.
2. Connect a GPIB cable from a GPIB controller to
the GPIB port on the PSU.
3. Turn the PSU on.
4. Press the Function key to enter the
Normal configuration settings.
Page 21
5. Set the following GPIB settings.
F-24 = 1
Enable the GPIB port
F-23 = 0~30
Set the GPIB address (0~30)
6. Check to see that the GPIB option
is detected by the PSU. The F-25
setting indicates the GPIB port
status.
F-25 = 1
Indicates that the GPIB port is
available.
F-25 = 0
Indicates that the GPIB port is
not detected.
GPIB Remote Interface
Configuration
To use GPIB, the optional GPIB option (GW Instek part number:
PSU-GPIB) must be installed. This is a factory installed option and
cannot be installed by the end-user. Only one GPIB address can be
used at a time.
33
Page 34

PSU Programming Manual
7. The RMT indicator will turn on when a remote
connection has been established.
RMT indicator
AV
VOLTAGE CURRENT
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C V C C
GPIB constraints
Maximum 15 devices altogether, 20m cable
length, 2m between each device
Unique address assigned to each device
At least 2/3 of the devices turned On
No loop or parallel connection
Background
To test the GPIB functionality, National
Instruments Measurement and Automation
Explorer can be used. This program is available
on the NI website, www.ni.com., via a search
for the VISA Run-time Engine page, or
“downloads” at the following URL,
http://www.ni.com/visa/
Requirements
Operating System: Windows XP, 7, 8
GPIB Function Check
34
Page 35

REMOTE CONTROL
Functionality
check
1. Start the NI Measurement and Automation
Explorer (MAX) program. Using Windows,
press:
Start>All Programs>National
Instruments>Measurement & Automation
2. From the Configuration panel access;
My System>Devices and Interfaces>GPIB
3. Press Scan for Instruments.
2
3
35
Page 36

PSU Programming Manual
4. Select the device (GPIB address of PSU) that
now appears in the System>Devices and
Interfaces > GPIB-USB-HS “GPIBX” node.
5. Click on the VISA Properties tab on the bottom.
6. Click Open Visa Test Panel.
4
5
6
7. Click on Configuration.
8. Click on the GPIB Settings tab and confirm that
the GPIB settings are correct.
7
8
9. Click on the I/O Settings tab.
10. Make sure the Enable Termination Character
36
Page 37

REMOTE CONTROL
check box is checked, and the terminal
character is \n (Value: xA).
11. Click Apply Changes.
10
9
11
12. Click on Input/Output.
13. Click on the Basic/IO tab.
14. Enter *IDN? in the Select or Enter Command drop
down box.
15. Click Query.
16. The *IDN? query will return the Manufacturer,
model name, serial number and firmware
version in the dialog box.
GW-INSTEK,PSU40-38,
TW123456,T0.02.20131205
37
Page 38

PSU Programming Manual
12
13
15
14
16
Overview
The PSU uses the IN & OUT ports for UART
communication coupled with RS232 (GW Part
number PSU-232) or RS485 adapters (GW part
number PSU-485)
The pin outs for the adapters are shown below.
PSU-232 RS232
cable with DB9
connector
DB-9 Connector
Remote IN Port
Remarks
Pin No.
Name
Pin No.
Name
Housing
Shield
Housing
Shield
2
RX 7 TX
Twisted
pair
3
TX 8 RX
5
SG 1 SG
UART Remote Interface
Configure UART
38
Page 39

REMOTE CONTROL
PSU-485 RS485
cable with DB9
connector
DB-9 Connector
Remote IN Port
Remarks
Pin No.
Name
Pin No.
Name
Housing
Shield
Housing
Shield
9 TXD -
6
RXD -
Twisted
pair
8
TXD +
3
RXD +
1
SG 1 SG 5
RXD -
5
TXD -
Twisted
pair
4
RXD +
4
TXD +
Steps
1. Connect the RS232 serial cable
(included in the PSU-232 kit) or
RS485 serial cable (included in the
PSU-485 kit) to the (Remote IN
port) on the rear panel.
Connect the other end of the cable
to the PC.
RS 485 / 232
2. Press the Function key to enter the
Normal configuration settings.
Page 21
Set the following UART settings:
F-70 = 1 or 2
Interface: 0= Disable UART,
1= RS232 or 2 = RS485
F-71 = 0 ~ 7
Set the baud rate:
0=1200, 1=2400, 2=4800,
3=9600, 4=19200, 5=38400,
6=57600, 7=115200
F-72 = 0 or 1
Data bits: 0=7 or 1=8
F-73 = 0 ~3
Parity: 0 = none, 1 = odd, 2 =
even
F-74 = 0 or 1
Stop bits: 0 = 1, 1 = 2
F-75 = 0 or 1
TCP: 0 = SCPI, 1 = TDK
(emulation mode)
39
Page 40

PSU Programming Manual
F-76 = 00~31
UART address if TDK is selected
for F-75.
3. The RMT indicator will turn on when a remote
connection has been established.
RMT indicator
AV
VOLTAGE CURRENT
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C V C C
Note
If TDK (emulation mode) is selected for F-75, the
TDK GENESYS legacy commands should be used
for remote commands. See the TDK Genesys user
manual for details.
40
Page 41

REMOTE CONTROL
Functionality
check
Invoke a terminal application such as Realterm.
To check the COM port No, see the Device
Manager in the PC. For WinXP; Control panel
→ System → Hardware tab.
Run this query command via the terminal
application after the instrument has been
configured for either RS232 or RS485 remote
control (page 38).
*idn?
This should return the Manufacturer, Model
number, Serial number, and Firmware version
in the following format:
GW-INSTEK,PSU40-38,,T0.01.12345678
Manufacturer: GW-INSTEK
Model number : PSU40-38
Serial number : TW123456
Firmware version : T0.01.12345678
UART Function Check
41
Page 42

PSU Programming Manual
Operation
1. Connect the first unit’s IN port to a PC via
RS232 or RS485.
Use the serial cables supplied in the PSU-
232 or PSU-485 connection kit.
2. Connect the OUT port on the first unit to the IN
port of the second unit using the serial link
cable supplied in the PSU-232 or PSU-485
connection kit.
3. Connect all the remaining units in the same
fashion until all the units have been daisychained together.
RS 485 / 232
OUT IN
Unit #1
RS 485 / 232
OUT IN
Unit #2
RS 485 / 232
OUT IN
Unit #N
End terminal
connector
To PC
RS232/RS485
serial cable
Serial link
cable
Serial link
cable
Multiple Unit Connection Using Local RS485 Bus
The PSU power supplies can have up to 31 units daisy-chained
together using the 8 pin connectors (IN OUT ports) on the rear
panel. The first unit in the chain is remotely connected to a PC
using RS232 or RS485. Each subsequent unit is daisy-chained to the
next using an RS485 local bus. The OUT port on the last terminal
must be terminated by the end terminal connector.
Only the TDK GENESYS legacy commands can be used when
using multiple units over the local RS485 bus, SCPI commands
cannot be used. When using the TDK commands, each unit is
assigned a unique address and can then be individually controlled
from the host PC. When using SCPI commands via RS232/RS485,
remote commands can only be used to control the master unit.
42
Page 43

REMOTE CONTROL
4. Terminate the OUT port of the last unit with
the end terminal connector included in the
PSU-232 or PSU-485 connection kit.
5. Press the Function key to enter the
Normal configuration settings for
the master unit.
Page 21
Set the following settings:
F-70 = 1 or 2
Configure the master unit as you
normally would for RS232 or
RS485 remote control.
F-71 = 0~7
Set the baud rate (set all units
the same).
F-72 = 1
Set to 8 data bits.
F-73 = 0
Parity to none.
F-74 = 1
1 Stop bit.
F-75 = 1
Set the UART TCP to TDK
(emulation mode).
F-76 = 00~31
Set the address of the master
unit. It must be a unique
address identifier.
6. Press the Function key to enter the
Normal configuration settings for
the slave(s).
Page 21
Set the following settings:
F-70 = 2
Set the slave unit to RS485.
F-71 = 0~7
Set the baud rate (make all
units, including the master, the
same baud).
F-72 = 1
Set to 8 data bits.
F-73 = 0
Parity to none.
F-74 = 1
1 Stop bit.
F-75 = 1
Set the UART TCP to TDK
(emulation mode).
43
Page 44

PSU Programming Manual
F-76 = 00~31
Set the address of each slave to
a unique address identifier
7. Multiple units can now be operated at the same
time, see the function check below for usage
details.
Serial link cable
with RJ-45
shielded
connectors from
PSU-232 or PSU485 connection
kit
8 Pin Connector (IN)
8 Pin Connector (OUT)
Pin No.
Name
Pin No.
Name
Housing
Shield
Housing
Shield
1
SG 1 SG 6 TXD -
6
TXD -
3
TXD +
3
TXD +
5
RXD -
5
RXD -
4
RXD +
4
RXD +
Functionality
check
Invoke a terminal application such as Realterm.
To check the COM port No, see the Device
Manager in the PC. For WinXP; Control panel
→ System → Hardware tab.
Below shows an example using the TDK
GENESYS legacy commands.
TDK Query
When using the TDK GENESYS legacy
commands, each unit can be individually
controlled using the unique address identifiers.
For this function check, we will assume that the
master unit is assigned to address 8, while a
slave is assigned address 11.
Multi-Unit Function Check
44
Page 45

REMOTE CONTROL
Run this query command via the terminal
application after the instruments have been
configured for multi-unit control. See page 42.
ADR 8
IDN?
The identity string for the Master unit will be
returned:
GW-INSTEK,PSU40-38,,T0.01.12345678
Type the following:
ADR 11
IDN?
The identity string for the slave with address 11
will be returned:
GW-INSTEK,PSU40-38,,T0.01.12345678
Note: TDK commands do not use LF (line feed)
codes to terminate commands. See the TDK
Genesys user manual for further information.
45
Page 46

PSU Programming Manual
Ethernet
configuration
Parameters
For details on how to configure the Ethernet
settings, please see the configuration chapter on
page 21.
MAC Address
(display only)
LAN Enable/Disable
DHCP
Enable/Disable
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Gateway
DNS Address
Sockets Server
Enable/Disable
Web Server
Enable/Disable
Web Password
Enable/Disable
Web Enter Password
Configuration
This configuration example will configure the
PSU as a web server and use DHCP to
automatically assign an IP address to the PSU.
1. Connect an Ethernet cable from the
network to the rear panel Ethernet
port.
LAN
Configure Ethernet Connection
The Ethernet interface can be configured for a number of different
applications. Ethernet can be configured for basic remote control or
monitoring using a web server or it can be configured as a socket
server.
The PSU series supports both DHCP connections so the instrument
can be automatically connected to an existing network or
alternatively, network settings can be manually configured.
Web Server Configuration
46
Page 47

REMOTE CONTROL
2. Press the Function key to enter the
Normal configuration settings.
Page 21
Set the following LAN settings:
F-36 = 1
Turn LAN on
F-37 = 1
Enable DHCP
F-59 = 1
Turn the web server on
F-60 = 0 or 1
Set to 0 to disable web
password, set to 1 to enable web
password
F-61 = 0000
~9999
Set the web password
3. The LAN indicator will turn on when a
network cable is plugged in.
LAN indicator
AV
VOLTAGE CURRENT
VSR LAN RMT ERR DLY ALM ISR M 1 M 2 M 3 RUN
C V C C
Note
It may be necessary to cycle the power or refresh
the web browser to connect to a network.
Functionality
check
Enter the IP address of the power supply in a
web browser after the instrument has been
configured as a web server (page 46).
The web server allows you to monitor the
function settings of the PSU.
You can check the IP address by checking F-39 to
F-42.
F-39 = AAA
IP Address part 1 of 4
F-40 = BBB
IP Address part 2 of 4
Web Server Remote Control Function Check
47
Page 48

PSU Programming Manual
F-41 = CCC
IP Address part 3 of 4
F-42 = DDD
IP Address part 4 of 4
http:// AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD
The web browser interface appears.
The web browser interface allows you to access
the following:
Network configuration settings
Analog control pinouts & usage
PSU dimensions
Operating area diagram
48
Page 49

REMOTE CONTROL
Configuration
This configuration example will configure the
PSU socket server.
The following configuration settings will
manually assign the PSU an IP address and
enable the socket server. The socket server port
number is fixed at 2268.
1. Connect an Ethernet cable from the
network to the rear panel Ethernet
port.
LAN
2. Press the Function key to enter the
Normal configuration settings.
Page 21
Set the following LAN settings:
F-36 = 1
Enable LAN
F-37 = 0
Disable DHCP
F-39 = 172
IP Address part 1 of 4
F-40 = 16
IP Address part 2 of 4
F-41 = 5
IP Address part 3 of 4
F-42 = 133
IP Address part 4 of 4
F-43 = 255
Subnet Mask part 1 of 4
F-44 = 255
Subnet Mask part 2 of 4
F-45 = 128
Subnet Mask part 3 of 4
F-46 = 0
Subnet Mask part 4 of 4
F-43 = 172
Gateway part 1 of 4
F-44 = 16
Gateway part 2 of 4
F-45 = 21
Gateway part 3 of 4
F-46 = 101
Gateway part 4 of 4
F-57 = 1
Enable Sockets
Sockets Server Configuration
49
Page 50

PSU Programming Manual
Background
To test the socket server functionality, National
Instruments Measurement and Automation
Explorer can be used. This program is available
on the NI website, www.ni.com., via a search
for the VISA Run-time Engine page, or
“downloads” at the following URL,
http://www.ni.com/visa/
Requirements
Operating System: Windows XP, 7, 8
Functionality
check
1. Start the NI Measurement and Automation
Explorer (MAX) program. Using Windows,
press:
Start>All Programs>National
Instruments>Measurement & Automation
2. From the Configuration panel access;
My System>Devices and Interfaces>Network
Devices
3. Press Add New Network Device>Visa TCP/IP
Resource…
Socket Server Function Check
50
Page 51

REMOTE CONTROL
2
3
4. Select Manual Entry of Raw Socket from the
popup window.
4
5. Enter the IP address and the port number of the
PSU. The port number is fixed at 2268.
6. Click the Validate button.
7. A popup will appear if a connection is
successfully established.
8. Click Next.
51
Page 52

PSU Programming Manual
6
5
7
8
9. Next configure the Alias (name) of the PSU
connection. In this example the Alias is:
PSU_DC1
10. Click finish.
9
10
11. The IP address of the PSU will now appear
under Network Devices in the configuration
panel. Select this icon now.
12. Click Open VISA Test Panel.
52
Page 53

REMOTE CONTROL
11
12
13. Click the Configuration icon,
14. Click on I/O Settings.
15. Make sure the Enable Termination Character
check box is checked, and the terminal
character is \n (Value: xA).
16. Click Apply Changes.
14
13
15
16
17. Click the Input/Output icon.
18. Enter *IDN? in the Select or Enter Command
dialog box if it is not already.
19. Click the Query button.
53
Page 54

PSU Programming Manual
20. The *IDN? query will return the Manufacturer,
model name, serial number and firmware
version in the dialog box.
GW-INSTEK,PSU40-38,TW123456,T0.02.20131205
18
17
19
20
54
Page 55
REMOTE CONTROL
Compatible
Standard
IEEE488.2
Partial compatibility
SCPI, 1999
Partial compatibility
Command
Structure
SCPI commands follow a tree-like structure,
organized into nodes. Each level of the
command tree is a node. Each keyword in a
SCPI command represents each node in the
command tree. Each keyword (node) of a SCPI
command is separated by a colon (:).
For example, the diagram below shows an SCPI
sub-structure and a command example.
DC
MEASure
SCALar
POWer
VOLTage
CURRent
DC
DC
MEASure:SCALar:CURRent:DC?
Command types
There are a number of different instrument
commands and queries. A command sends
instructions or data to the unit and a query
receives data or status information from the
unit.
Command types
Simple
A single command
with/without a parameter
Example
*IDN?
Command Syntax
55
Page 56

PSU Programming Manual
Query
A query is a simple or
compound command
followed by a question mark
(?). A parameter (data) is
returned.
Example
meas:curr:dc?
Compound
Two or more commands on
the same command line.
Compound commands are
separated with either a semicolon (;) or a semi-colon and a
colon (;:).
A semi-colon is used to join
two related commands, with
the caveat that the last
command must begin at the
last node of the first
command.
A semi-colon and colon are
used to combine two
commands from different
nodes.
Example
meas:volt:dc?;:meas:curr:dc?
56
Page 57

REMOTE CONTROL
Command Forms
Commands and queries have two different
forms, long and short. The command syntax is
written with the short form of the command in
capitals and the remainder (long form) in lower
case.
The commands can be written in capitals or
lower-case, just so long as the short or long
forms are complete. An incomplete command
will not be recognized.
Below are examples of correctly written
commands.
Long
form
STATus:OPERation:NTRansition?
STATUS:OPERATION:NTRANSITION?
status:operation:ntransition?
Short
form
STAT:OPER:NTR?
stat:oper:ntr?
Square Brackets
Commands that contain square brackets
indicate that the contents are optional. The
function of the command is the same with or
without the square bracketed items, as shown
below.
Both “DISPlay:MENU[:NAME]?” and
“DISPlay:MENU?” are both valid forms.
Command
Format
1.5,5.2
1 2 3 4 5
APPLY
1. Command header
2. Space
3. Parameter 1
4. Comma (no space
before/after comma)
5. Parameter 2
Parameters
Type
Description
Example
<Boolean>
Boolean logic
0, 1
57
Page 58

PSU Programming Manual
<NR1>
integers
0, 1, 2, 3
<NR2>
decimal
numbers
0.1, 3.14, 8.5
<NR3>
floating point
4.5e-1, 8.25e+1
<NRf>
any of NR1, 2, 3
1, 1.5, 4.5e-1
<block data>
Definitive length arbitrary block
data. A single decimal digit
followed by data. The decimal
digit specifies how many 8-bit
data bytes follow.
Message
Terminator
LF
Line feed code
Display
Commands
:DISPlay:MENU[:NAME] ................................................... 62
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT:CLEar .................................... 62
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT[:DATA] ................................. 63
:DISPlay:BLINk ..................................................................... 63
Initiate
Commands
:INITiate:CONTinuous[:TRANsient] ................................ 64
:INITiate[:IMMediate]:NAME ............................................ 64
:INITiate[:IMMediate][:TRANsient] ................................... 65
Measure
Commands
:MEASure[:SCALar]:ALL[:DC] ........................................... 66
:MEASure[:SCALar]:CURRent[:DC] .................................. 66
:MEASure[:SCALar]:VOLTage[:DC] ................................. 66
:MEASure[:SCALar]:POWer[:DC] ...................................... 67
Command List
58
Page 59

REMOTE CONTROL
Output
Commands
:OUTPut:DELay:ON ............................................................ 68
:OUTPut:EXTernal:LOGic ................................................. 68
:OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] ............................................... 69
:OUTPut:DELay:OFF .......................................................... 69
:OUTPut:MODE ................................................................... 69
:OUTPut:PON[:STATe] ....................................................... 70
:OUTPut[:STATe][:IMMediate] .......................................... 70
:OUTPut[:STATe]:TRIGgered ............................................ 71
:OUTPut:PROTection:CLEar ............................................. 71
Status
Commands
:STATus:OPERation[:EVENt] ........................................... 72
:STATus:OPERation:CONDition ...................................... 72
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle ............................................ 73
:STATus:OPERation:PTRansition ...................................... 73
:STATus:OPERation:NTRansition ..................................... 73
:STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt] ...................................... 73
:STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition ................................. 74
:STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle ....................................... 74
:STATus:QUEStionable:PTRansition ................................. 74
:STATus:QUEStionable:NTRansition ................................ 74
:STATus:PRESet .................................................................... 75
Source
Commands
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:RANGe ........................... 76
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:SOURce .......................... 77
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]77
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude] . 78
[:SOURce]:CURRent:LIMit:AUTO .................................... 78
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:DELay ........................ 78
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel]....................... 79
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:STATe ........................ 79
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped .................... 80
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:RISing ................................... 80
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:FALLing ............................... 81
[:SOURce]:MODE? ............................................................... 81
[:SOURce]:RESistance[:LEVel][:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude] .......................................................................... 81
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:RANGe ...................... 82
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:SOURce ..................... 82
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel][:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude] .......................................................................... 83
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel]:TRIGgered
59
Page 60

PSU Programming Manual
[:AMPLitude] .......................................................................... 83
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:AUTO ............................... 84
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:LOW ................................. 84
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection[:LEVel] ................. 85
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection:TRIPped ............... 85
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:RISing .............................. 86
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:FALLing .......................... 86
System
Commands
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BEEPer[:STATe] ............................ 88
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BLEeder[:STATe] .......................... 88
:SYSTem:CONFigure:CURRent:CONTrol ....................... 88
:SYSTem:CONFigure:VOLTage:CONTrol ...................... 89
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:PON[:STATe] ................ 89
:SYSTem:CONFigure:PROTection:RECovery ................. 90
:SYSTem:CONFigure:MSLave ............................................ 90
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:EXTernal[:MODE] ....... 90
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ENABle ...................................... 91
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDRess .......... 91
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:IPADdress ....................... 92
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:GATEway ........................ 92
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:SMASk .............................. 93
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:MAC ................................. 93
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DHCP ............................... 93
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DNS .................................. 94
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:TCPip:CONTrol ....................... 94
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial:LANGuage[:SELect] .... 94
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]
:TRANsmit:BAUD ................................................................ 95
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]
:TRANsmit:BITS ................................................................... 95
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:PARity .................................................................................... 96
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:SBITs ...................................................................................... 96
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:FRONt:STATe ................. 97
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:MODE .................. 97
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:STATe ................... 97
:SYSTem:ERRor .................................................................... 98
:SYSTem:KLOCk .................................................................. 98
:SYSTem:KEYLock:MODE ................................................ 98
:SYSTem:ERRor:ENABle .................................................... 98
:SYSTem:LANGuage:EMULation ...................................... 99
:SYSTem:LANGuage:[:SELect] ........................................... 99
60
Page 61

REMOTE CONTROL
:SYSTem:PREset ................................................................... 99
:SYSTem:VERSion ................................................................ 99
:SYSTem:REBoot ................................................................ 100
Common
Commands
*CLS ...................................................................................... 100
*ESE ...................................................................................... 100
*ESR ...................................................................................... 101
*IDN ..................................................................................... 101
*OPC ..................................................................................... 101
*RCL ...................................................................................... 102
*RST ...................................................................................... 102
*SAV ...................................................................................... 102
*SRE ...................................................................................... 102
*STB ...................................................................................... 103
*TRG ..................................................................................... 103
*TST ...................................................................................... 103
*WAI ..................................................................................... 103
61
Page 62

PSU Programming Manual
:DISPlay:MENU[:NAME] ................................................... 62
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT:CLEar .................................... 62
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT[:DATA] ................................. 63
:DISPlay:BLINk ..................................................................... 63
:DISPlay:MENU[:NAME]
Set
Query
Description
The DISPlay MENU command selects a screen
menu or queries the current screen menu.
Syntax
Query Sytax
:DISPlay:MENU[:NAME] <NR1>
:DISPlay:MENU[:NAME]?
Parameter/
Return parameter
<NR1>
Description
0
Measure voltage & current
1~2
Not Used
3
Set Menu
4
OVP / OCP Menu
5~99
Not Used.
100~199
F-00~99 Menu.
Example
DISP:MENU:NAME 0
Sets the display to the Voltage/Current display screen.
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT:CLEar
Set
Description
Clears the text on the main screen from
the :DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT[:DATA] command.
Syntax
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT:CLEar
Display Commands
62
Page 63
REMOTE CONTROL
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT[:DATA]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the data text that will be written to
the display. Writing to the display will overwrite
data that is currently on the screen. Overwriting a
display area with a shorter string may or may not
overwrite the screen. The string must be enclosed
in quotes: “STRING”. Only ASCII characters 20H
to 7EH can be used in the <string>.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT[:DATA] <string>
:DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT[:DATA]?
Parameter/
Return parameter
<string>
ASCII character 20H to 7EH can be used to in
the string parameter. The string must be
enclosed in quotes: “STRING”
Example
DISP:WIND:TEXT:DATA “STRING”
Writes STRING to the display.
Query Example
DISP:WIND:TEXT:DATA?
“STRING”
Returns the text data string on the screen.
:DISPlay:BLINk
Set
Query
Description
Turns blink on or off for the display. Blink is set to
OFF by default.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:DISPlay:BLINk {<bool>|OFF|ON}
:DISPlay:BLINk?
Parameter
OFF | 0
Turns blink OFF
ON | 1
Turns blink ON
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns the blink status.
Example
DISP:BLIN 1
Turns blink ON.
63
Page 64

PSU Programming Manual
:INITiate:CONTinuous[:TRANsient] ................................ 64
:INITiate[:IMMediate]:NAME ............................................ 64
:INITiate[:IMMediate][:TRANsient] ................................... 65
:INITiate:CONTinuous[:TRANsient]
Set
Query
Description
This command continuously initiates software
triggers for the transient or output triggers.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:INITiate:CONTinuous[:TRANsient] {<bool>|OFF|ON}
:INITiate:CONTinuous[:TRANsient]?
Parameter
OFF | 0
OFF
ON | 1
ON
Return parameter
0
OFF
1
ON
Example
INIT:TRAN 1
Turns on the continuous trigger.
:INITiate[:IMMediate]:NAME
Set
Description
The INITiate command starts the TRANsient or
OUTPut trigger.
Syntax
:INITiate[:IMMediate]:NAME {TRANsient|OUTPut}
Parameter
TRANSient
Starts the TRANsient trigger.
OUTPut
Starts the OUTPut trigger.
Example
INITiate:NAME TRANient
Starts the TRANSient trigger.
Initiate Commands
64
Page 65

REMOTE CONTROL
:INITiate[:IMMediate][:TRANsient]
Set
Description
This command controls the enabling of output
triggers. When a trigger is enabled, a trigger causes
the specified action to occur. If the trigger system
is not enabled, all triggers are ignored.
Syntax
:INITiate[:IMMediate][:TRANsient]
Example
INIT
65
Page 66

PSU Programming Manual
:MEASure[:SCALar]:ALL[:DC] ........................................... 66
:MEASure[:SCALar]:CURRent[:DC] .................................. 66
:MEASure[:SCALar]:VOLTage[:DC] ................................. 66
:MEASure[:SCALar]:POWer[:DC] ...................................... 67
:MEASure[:SCALar]:ALL[:DC]
Query
Description
Takes a measurement and returns the average
output current and voltage
Syntax
:MEASure[:SCALar]:ALL[:DC]?
Return parameter
"+0.0000,+0.0000"
<voltage>,<current>
Returns the voltage (V) and
current (A), respectively.
:MEASure[:SCALar]:CURRent[:DC]
Query
Description
Takes a measurement and returns the average
output current
Syntax
:MEASure[:SCALar]:CURRent[:DC]?
Return parameter
"+0.0000"
Returns the current in amps.
:MEASure[:SCALar]:VOLTage[:DC]
Query
Description
Takes a measurement and returns the average
output voltage.
Syntax
:MEASure[:SCALar]:VOLTage[:DC]?
Return
"+0.0000"
Returns the voltage in volts.
Measure Commands
66
Page 67

REMOTE CONTROL
:MEASure[:SCALar]:POWer[:DC]
Query
Description
Takes a measurement and returns the average
output power.
Syntax
:MEASure[:SCALar]:POWer[:DC]?
Return
"+0.0000"
Returns the power measured in watts.
67
Page 68

PSU Programming Manual
:OUTPut:DELay:ON ........................................................... 68
:OUTPut:EXTernal:LOGic ................................................. 68
:OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] ............................................... 69
:OUTPut:DELay:OFF .......................................................... 69
:OUTPut:MODE .................................................................. 69
:OUTPut:PON[:STATe] ....................................................... 70
:OUTPut[:STATe][:IMMediate] .......................................... 70
:OUTPut[:STATe]:TRIGgered ............................................ 71
:OUTPut:PROTection:CLEar ............................................. 71
:OUTPut:DELay:ON
Set
Query
Description
Sets the Delay Time in seconds for turning the
output on. The delay is set to 0.00 by default.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:OUTPut:DELay:ON {<NR2>|MINimum|MAXimum}
:OUTPut:DELay:ON?
Parameter
<NR2>
0.00~99.99 seconds, where 0=no delay.
Return parameter
"0.00"
Returns the delay on time in seconds until the
output is turned on.
:OUTPut:EXTernal:LOGic
Set
Query
Description
Sets the logic used to turn the output on or off
when using an external contact. This is the
equivalent to the F-94 (External Output Logic)
power on configuration settings.
Syntax
Return Syntax
:OUTPut:EXTernal:LOGic {LOW|HIGH}
:OUTPut:EXTernal:LOGic?
Parameter/
Return parameter
LOW
The output is turned on with a low
signal.
HIGH
The output is turned on with a high
signal.
Output Commands
68
Page 69

REMOTE CONTROL
:OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe]
Set
Query
Description
Sets whether the output will be turned on or off
externally. By default this setting is turned off.
Syntax
Return Syntax
:OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] {<bool>|OFF|ON}
:OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe]?
Parameter
ON | 1
External control is performed.
OFF | 0
External control is not performed.
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns output status of the instrument.
:OUTPut:DELay:OFF
Set
Query
Description
Sets the Delay Time in seconds for turning the
output off. The delay is set to 0.00 by default.
Syntax
Return Syntax
:OUTPut:DELay:OFF {<NR2>| |MINimum|MAXimum}
:OUTPut:DELay:OFF?
Parameter
<NR2>
0.00~99.99 seconds, where 0=no delay.
Return parameter
"0.00"
Returns the delay off time in seconds until the
output is turned off.
:OUTPut:MODE
Set
Query
Description
Sets the PSU output mode. This is the equivalent to
the F-03 (V-I Mode Slew Rate Select) settings.
Syntax
Return Syntax
:OUTPut:MODE {<NR1>|CVHS|CCHS|CVLS|CCLS}
:OUTPut:MODE?
Parameter
CVHS | 0
CV high speed priority
CCHS | 1
CC high speed priority
CVLS | 2
CV slew rate priority
CCLS | 3
CC slew rate priority
Return parameter
<NR1>
Returns the output mode.
69
Page 70

PSU Programming Manual
:OUTPut:PON[:STATe]
Set
Query
Description
Sets the output state at power-on. This is the
equivalent to the F-92 (Output Status when Power
ON) power on configuration settings. These
settings only apply after the unit has been reset.
Syntax
Return Syntax
:OUTPut:PON[:STATe] {<NR1>|SAFE|FORCe |AUTO}
:OUTPut:PON[:STATe]?
Parameter
SAFE | 0
The PSU turns on in the same state the unit
was in prior to the previous shut down. The
output is set to off (default).
FORCe | 1
The PSU turns on in the same state the unit
was in prior to the previous shut down. The
output is set to on.
AUTO | 2
The PSU turns on in the same state the unit
was in prior to the previous shut down, but
with the same output on/off setting.
Return parameter
0
The power on output setting is “SAFE”.
1
The power on output setting is “FORCe”.
2
The power on output setting is “AUTO”.
:OUTPut[:STATe][:IMMediate]
Set
Query
Description
Turns the output on or off.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:OUTPut[:STATe][:IMMediate] { <bool> | OFF | ON }
:OUTPut[:STATe][:IMMediate]?
Parameter
OFF | 0
Turns the output off.
ON | 1
Turns the output on.
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns output status of the instrument.
70
Page 71

REMOTE CONTROL
:OUTPut[:STATe]:TRIGgered
Set
Query
Description
Turns the output on or off when a software trigger
is generated.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:OUTPut[:STATe]:TRIGgered { <bool>|OFF|ON }
:OUTPut[:STATe]:TRIGgered?
Parameter
OFF | 0
Turns the output off when a software trigger
is generated (*TRG).
ON | 1
Turns the output on when a software trigger
is generated (*TRG).
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns output trigger status of the
instrument.
:OUTPut:PROTection:CLEar
Set
Description
Clears over-voltage, over-current and overtemperature (OVP, OCP, OTP) protection circuits.
It also clears the shutdown and sense protection
circuit. The AC failure protection cannot be
cleared.
Syntax
:OUTPut:PROTection:CLEar
71
Page 72

PSU Programming Manual
:STATus:OPERation[:EVENt] ........................................... 72
:STATus:OPERation:CONDition ...................................... 72
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle ............................................ 73
:STATus:OPERation:PTRansition ...................................... 73
:STATus:OPERation:NTRansition ..................................... 73
:STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt] ...................................... 73
:STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition ................................. 74
:STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle ....................................... 74
:STATus:QUEStionable:PTRansition ................................ 74
:STATus:QUEStionable:NTRansition ................................ 74
:STATus:PRESet ................................................................... 75
:STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]
Query
Description
Queries the Operation Status Event register and
clears the contents of the register.
Syntax
:STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?
Return
<NR1>
Returns the bit sum of the Operation Status
Event register.
:STATus:OPERation:CONDition
Query
Description
Queries the Operation Status register. This query
will not clear the register.
Syntax
:STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
Return
<NR1>
Returns the bit sum of the Operation
Condition register.
Status Commands
For an overview of all the status registers, their associated register
contents and the system diagram, please see the status overview on
page 103
72
Page 73

REMOTE CONTROL
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the bit sum of the Operation Status
Enable register.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle <NR1>
:STATus:OPERation:ENABle?
Parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
Return parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
:STATus:OPERation:PTRansition
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the bit sum of the positive
transition filter of the Operation Status register.
Syntax
:STATus:OPERation:PTRansition <NR1>
:STATus:OPERation:PTRansition?
Parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
Return parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
:STATus:OPERation:NTRansition
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the bit sum of the negative
transition filter of the Operation Status register.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:STATus:OPERation:NTRansition <NR1>
:STATus:OPERation:NTRansition?
Parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
Return parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
:STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt]
Query
Description
Queries the bit sum of the Questionable Status
Event register. This query will also clear the
contents of the register.
Query Syntax
:STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt]?
Return parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
73
Page 74

PSU Programming Manual
:STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition
Query
Description
Queries the status (bit sum) of the Questionable
Status register. This query will not clear the
register.
Query Syntax
:STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Return parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
:STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the bit sum of the Questionable
Status Enable register.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle <NR1>
:STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle?
Parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
Return parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
:STATus:QUEStionable:PTRansition
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the bit sum of the positive
transition filter of the Questionable Status register.
Syntax
Return Syntax
:STATus:QUEStionable:PTRansition <NR1>
:STATus:QUEStionable:PTRansition?
Parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
Return parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
:STATus:QUEStionable:NTRansition
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the negative transition filter of the
Questionable Status register.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:STATus:QUEStionable:NTRansition <NR1>
:STATus:QUEStionable:NTRansition?
74
Page 75

Parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
Return parameter
<NR1>
0~32767
:STATus:PRESet
Set
Description
This command resets the ENABle register, the
PTRansistion filter and NTRansistion filter on the
Operation Status and Questionable Status
Registers. The registers/filters will be reset to a
default value.
Default Register/Filter Values
Setting
QUEStionable Status Enable
0x0000
QUEStionable Status Positive Transition
0x7FFF
QUEStionable Status Negative Transition
0x0000
Operation Status Enable
0x0000
Operation Status Positive Transition
0x7FFF
Operation Status Negative Transition
0x0000
Summary: The Questionable Status Enable
registers and the Operation Status Enable registers
are both reset to 0.
The Questionable Status and Operation Status
Positive Transition filters are all set high (0x7FFF)
and the Negative Transition filters are all set low
(0x0000). I.e., only positive transitions will be
recognized for the Questionable Status and
Operation Status registers.
Syntax
:STATus:PRESet
REMOTE CONTROL
75
Page 76

PSU Programming Manual
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:RANGe ........................... 76
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:SOURce .......................... 77
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude] .......................................................................... 77
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude] . 78
[:SOURce]:CURRent:LIMit:AUTO .................................... 78
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:DELay ........................ 78
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel] ...................... 79
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:STATe ........................ 79
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped .................... 80
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:RISing ................................... 80
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:FALLing ............................... 81
[:SOURce]:MODE? .............................................................. 81
[:SOURce]:RESistance[:LEVel][:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude] .......................................................................... 81
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:RANGe ...................... 82
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:SOURce ..................... 82
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel][:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude] .......................................................................... 83
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel]:TRIGgered
[:AMPLitude] .......................................................................... 83
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:AUTO ............................... 84
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:LOW ................................. 84
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection[:LEVel] ................. 85
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection:TRIPped ............... 85
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:RISing .............................. 86
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:FALLing .......................... 86
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:RANGe
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the CC or CV control range that is
used during external control. Note: the setting will
only be valid after the power has been cycled.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:RANGe {LOW|HIGH}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:RANGe?
Parameter/Return
parameter
LOW
A range of 0 V to 5 V is used.
HIGH
A range of 0 V to 10 V is used.
Source Commands
76
Page 77

REMOTE CONTROL
Example
CURR:EXT:RANG?
LOW
Returns LOW range.
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:SOURce
Set
Query
Description
Sets whether constant current will be controlled
externally or not. Note: the setting will only be
valid after the power has been cycled.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:SOURce
{NONE|VOLTage}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:EXTernal:SOURce?
Parameter/Return
parameter
NONE
External control is not used.
VOLTage
External control is used.
Example
CURR:EXT:SOUR?
NONE
External control is not used.
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the current level in amps. For
externally set current levels (from the analog
control connector) the set current level is returned.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]
{<NR2>(A)|MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]?
Parameter/Return
parameter
<NR2>
0~105% of the rated current output level.
MIN
Minimum current level.
MAX
Maximum current level.
Example
SOUR:CURR:LEV:IMM:AMPL?
38.000
Returns the current level in amps.
77
Page 78

PSU Programming Manual
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered
[:AMPLitude]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the current level in amps when a
software trigger has been generated.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude]
{<NR2> (A)| MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude]?
Parameter
<NR2>
0%~105% of the rated current output in amps.
MIN
Minimum current level.
MAX
Maximum current level.
Return Parameter
<NR2>
Returns the current level.
Example
SOUR:CURR:LEV:TRIG:AMPL?
38.000
Returns the maximum possible current level in amps.
[:SOURce]:CURRent:LIMit:AUTO
Set
Query
Description
Enables or disables the limit on the current setting.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:LIMit:AUTO {<bool>|OFF|ON}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:LIMit:AUTO?
Parameter
OFF | 0
Disable the setting current limit
ON | 1
Enable the setting current limit
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns the setting in <bool> format.
Example
SOUR:CURR:LIM:AUTO 0
Disables the current limit.
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:DELay
Set
Query
Description
Sets the Delay Time for OCP in seconds for turning
the output off. The delay is set to 0.1 by default.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:DELay
{<NR2>|MINimum|MAXimum}
78
Page 79

REMOTE CONTROL
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:DELay?
Parameter
<NR2>
0.1~2.0 seconds, where 0=no delay
MAX
The maximum allowed delay time
MIN
The minimum allowed delay time
Return parameter
<NR2>
Returns the delay time in seconds
Example
SOUR:CURR:PROT:DEL MAX
Sets the current protection delay to the maximum.
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the OCP (over-current protection)
level in amps.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel] {<NR2>(A)
|MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel]?
Parameter
<NR2>
Current protection level.
Minimum: Depend on the unit type:
if Irated * 0.1 > 5A, then minimum = 5A,
else minimum = Irated * 0.1
Maximum: Irated * 1.1
MIN
Minimum current level.
MAX
Maximum current level.
Return parameter
<NR2>
Returns the current protection level.
Example
SOUR:CURR:PROT:LEV?
+5.000
Returns the minimum possible current level in amps.
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:STATe
Set
Query
Description
Turns OCP (over-current protection) on or off.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:STATe
{<bool>|OFF|ON}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:STATe?
79
Page 80

PSU Programming Manual
Parameter
OFF | 0
Turns the OCP off.
ON | 1
Turns the OCP on.
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns the over current protection state in
<bool> format.
Example
SOUR:CURR:PROT:STAT OFF
Turns OCP off.
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped
Set
Query
Description
Returns the state of the current protection circuits.
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped?
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns protection status.
Example
SOUR:CURR:PROT:TRIP?
>0
The protection circuit has not been tripped.
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:RISing
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the rising current slew rate. This is
only applicable for CC slew rate priority mode.
Syntax
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:RISing
{<NR2>(A)|MINimum|MAXimum}
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:RISing?
Parameter
<NR2>
Per step is Rated Current divided by 100 ms.
MIN
Minimum rising current slew rate.
MAX
Maximum rising current slew rate.
Return parameter
<NR2>
Returns the step current in amps.
Example
SOUR:CURR:SLEW:RIS?
0.950
Sets the rising current slew rate to 0.950 A/ms.
80
Page 81

REMOTE CONTROL
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:FALLing
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the falling current slew rate. This is
only applicable for CC slew rate priority mode.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:FALLing
{<NR2>(A)|MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:CURRent:SLEW:FALLing?
Parameter
<NR2>
Per-Step is Rated Current divided by 100msec
MIN
Minimum falling current slew rate
MAX
Maximum falling current slew rate
Return Parameter
<NR2>
Returns the step current
Example
SOUR:CURR:SLEW:FALL MAX
Sets the falling current slew rate to the maximum.
[:SOURce]:MODE?
Set
Query
Description
Returns the status of the output mode (CC, CV,
Off) of the power supply.
The interface will return “CV’ if the supply is in
Constant Voltage Mode, “CC” if the supply is in
Constant Current Mode or “OFF” if the supply
output is off.
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:MODE?
Return parameter
<string>
Returns the output state as a string, “CC”,
“CV”, “OFF”
Example
:SOUR:MODE?
>CC
The power supply is currently in CC mode.
[:SOURce]:RESistance[:LEVel][:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the internal resistance in ohms.
81
Page 82

PSU Programming Manual
Syntax
[:SOURce]:RESistance[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude
] {<NR2>(OHM)|MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:RESistance[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude
]?
Parameter
<NR2>
Resistance in ohms:
0 ohm ~ Rrated = Vrated/Irated
MIN
Minimum internal resistance in ohms
MAX
Maximum internal resistance in ohms
Return parameter
<NR2>
Returns the internal resistance in ohms.
Example
SOUR:RES:LEV:IMM:AMPL 0.1
Sets the internal resistance to 100mΩ.
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:RANGe
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the CC or CV control range that is
used during external control. Note: the setting will
only be valid after the power has been cycled.
Syntax
[:SOURce] :VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:RANGe {LOW|HIGH}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce] :VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:RANGe?
Parameter/Return
parameter
LOW
A range of 0 V to 5 V is used.
HIGH
A range of 0 V to 10 V is used.
Example
VOLT:EXT:RANG?
LOW
Returns LOW range.
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:SOURce
Set
Query
Description
Sets whether constant current will be controlled
externally or not. Note: the setting will only be
valid after the power has been cycled.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:SOURce
{NONE|VOLTage}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:EXTernal:SOURce?
Parameter/Return
parameter
NONE
External control is not used.
VOLTage
External control is used.
82
Page 83

REMOTE CONTROL
Example
VOLT:EXT:SOUR?
NONE
External control is not used.
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel][:IMMediate]
[:AMPLitude]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the voltage level in volts.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude
] {<NR2>(V)|MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude
]?
Parameter
<NRf>
0~105% of the rated output voltage in volts.
MIN
Minimum voltage level
MAX
Maximum voltage level
Return parameter
<NR2>
Returns the voltage level in volts
Example
SOUR:VOLT:LEV:IMM:AMPL 10
Sets the voltage level to 10 volts.
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel]:TRIGgered
[:AMPLitude]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the voltage level in volts when a
software trigger has been generated.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude]
{<NR2>(V)|MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0][:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude]?
Parameter
<NR2>
0%~105% of the rated voltage output in volts.
MIN
Minimum current level.
MAX
Maximum current level.
Return parameter
<NR2>
Returns the voltage level.
Example
SOUR:VOLT:LEV:TRIG:AMPL 10
Sets the voltage level to 10 volts when a software
trigger is generated.
83
Page 84
PSU Programming Manual
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:AUTO
Set
Query
Description
Sets whether to limit the voltage setting so that it
does not exceed the OVP setting or become lower
than the UVP setting.
If you enable the limit when the OVP setting is
lower than the voltage setting, the OVP setting will
be set to 105 % of the voltage setting.
If you enable the limit when the UVP setting is
higher than the voltage setting, the UVP setting
will be set equal to the voltage setting.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:AUTO {<bool>|OFF|ON}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:AUTO?
Parameter
OFF | 0
Disable the limit setting
ON | 1
Enable the limit setting
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns the setting in <bool> format.
Example
SOUR:VOLT:LIM:AUTO 0
Disables the limit setting.
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:LOW
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the under voltage (UVL) trip point.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:LOW
<NR2>(V)|MINimum|MAXimum
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:LIMit:LOW?
Parameter/Return
<NR2>
0 ~ the present setting voltage
MIN
Minimum allowed voltage level
MAX
Maximum allowed voltage level
Example
SOUR:VOLT:LIM:LOW MAX
Sets the UV> level to its maximum.
84
Page 85

REMOTE CONTROL
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection[:LEVel]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the overvoltage protection level.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection[:LEVel]
{<NR2>(V)|MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection[:LEVel]?
Parameter/Return
<NR2>
Minimum: Depends on the unit type:
if Vrated * 0.1 > 5V, then Minimum = 5V,
else Minimum = Vrated * 0.1
Maximum: Vrated * 1.1
MIN
Minimum OVP level
MAX
Maximum OVP level
Example
SOUR:VOLT:PROT:LEV MAX
Sets the OVP level to its maximum.
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection:TRIPped
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the overvoltage protection level.
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:PROTection:TRIPped?
Return parameter
<bool>
0
Protection not tripped
1
Protection tripped
Example
SOUR:VOLT:PROT:TRIP?
>0
Indicates that the OVP protection has not been
tripped.
85
Page 86

PSU Programming Manual
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:RISing
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the rising voltage slew rate. This is
only applicable for CV slew rate priority mode.
Syntax
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:RISing
{<NR2>(V)|MINimum|MAXimum}
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:RISing?
Parameter
<NR2>
0 ~ Vrated/100msec
MIN
Minimum rising voltage slew rate
MAX
Maximum rising voltage slew rate
Return parameter
<NR2>
Returns the slew rate in A/ms.
Example
SOUR:VOLT:SLEW:RIS MAX
Sets the rising voltage slew rate to its maximum.
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:FALLing
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the falling voltage slew rate. This is
only applicable for CV slew rate priority mode.
Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:FALLing
{<NR2>(V)|MINimum|MAXimum}
Query Syntax
[:SOURce]:VOLTage[0]:SLEW:FALLing?
Parameter
<NR2>
0 ~ Vrated/100msec
MIN
Minimum voltage falling slew rate
MAX
Maximum voltage falling slew rate
Return parameter
<NR2>
Returns the voltage slew rate in A/ms
Example
SOUR:VOLT:SLEW:FALL MIN
Sets the falling voltage slew rate to its minimum.
86
Page 87

REMOTE CONTROL
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BEEPer[:STATe] ............................ 88
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BLEeder[:STATe]........................... 88
:SYSTem:CONFigure:CURRent:CONTrol ....................... 88
:SYSTem:CONFigure:VOLTage:CONTrol ...................... 89
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:PON[:STATe] ................ 89
:SYSTem:CONFigure:PROTection:RECovery ................. 90
:SYSTem:CONFigure:MSLave ............................................ 90
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:EXTernal[:MODE] ....... 90
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ENABle ...................................... 91
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDRess .......... 91
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:IPADdress ....................... 92
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:GATEway ........................ 92
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:SMASk .............................. 93
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:MAC ................................. 93
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DHCP ............................... 93
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DNS .................................. 94
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:TCPip:CONTrol ....................... 94
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial:LANGuage[:SELect] .... 94
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]
:TRANsmit:BAUD ................................................................ 95
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]
:TRANsmit:BITS ................................................................... 95
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:PARity .................................................................................... 96
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:SBITs ...................................................................................... 96
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:FRONt:STATe ................. 97
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:MODE .................. 97
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:STATe ................... 97
:SYSTem:ERRor .................................................................... 98
:SYSTem:KLOCk .................................................................. 98
:SYSTem:KEYLock:MODE ................................................ 98
:SYSTem:ERRor:ENABle .................................................... 98
:SYSTem:LANGuage:EMULation ...................................... 99
:SYSTem:LANGuage:[:SELect] ........................................... 99
:SYSTem:PREset ................................................................... 99
:SYSTem:VERSion ................................................................ 99
:SYSTem:REBoot ................................................................ 100
System Function Command
87
Page 88

PSU Programming Manual
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BEEPer[:STATe]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the buzzer state on/off.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BEEPer[:STATe]
{<bool>|OFF|ON}
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BEEPer[:STATe]?
Parameter
OFF | 0
Turns the buzzer off.
ON | 1
Turns the buzzer on.
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns the buzzer status.
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BLEeder[:STATe]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the status of the bleeder resistor.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BLEeder[:STATe]
{<bool>|OFF|ON}
:SYSTem:CONFigure:BLEeder[:STATe]?
Parameter
OFF | 0
Turns the bleeder resistor off.
ON | 1
Turns the bleeder resistor on.
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns bleeder resistor status.
:SYSTem:CONFigure:CURRent:CONTrol
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the CC control mode (local control
(panel), external voltage control, external
resistance control). This setting is applied only
after the unit is reset.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:CONFigure:CURRent:CONTrol { <NR1> }
:SYSTem:CONFigure:CURRent:CONTrol?
Parameter/Return
<NR1>
Description
0
Local (Panel) control
1
External voltage control
2
External resistance control; 10kΩ = Io max,
0kΩ = Io min.
88
Page 89

REMOTE CONTROL
3
External resistance control; 10kΩ = Io min,
0kΩ = Io max.
:SYSTem:CONFigure:VOLTage:CONTrol
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the CV control mode (local control
(panel), external voltage control, external
resistance control). This setting is applied only
after the unit is reset.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:CONFigure:VOLTage:CONTrol { <NR1> }
:SYSTem:CONFigure:VOLTage:CONTrol?
Parameter/Return
<NR1>
Description
0
Local (Panel) control
1
External voltage control
2
External resistance control; 10kΩ = Io max,
0kΩ = Io min.
3
External resistance control; 10kΩ = Io min,
0kΩ = Io max.
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:PON[:STATe]
Set
Query
Description
Sets the output state at power-on. This is the
equivalent to the F-92 (Output Status when Power
ON) power on configuration settings.
Syntax
Return Syntax
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:PON[:STATe]
{<NR1>|SAFE|FORCe |AUTO}
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:PON[:STATe]?
Parameter
SAFE | 0
The PSU turns on in the same state the unit
was in prior to the previous shut down. The
output is set to off (default).
FORCe | 1
The PSU turns on in the same state the unit
was in prior to the previous shut down. The
output is set to on.
AUTO | 2
The PSU turns on in the same state the unit
was in prior to the previous shut down, but
with the same output on/off setting.
Return parameter
0
The power on output setting is “SAFE”.
1
The power on output setting is “FORCe”.
2
The power on output setting is “AUTO”.
89
Page 90

PSU Programming Manual
:SYSTem:CONFigure:PROTection:RECovery
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries how the OHP, FAN, AC-FAIL, and
SD alarms are cleared.
Syntax
Return Syntax
:SYSTem:CONFigure:PROTection:RECovery
{SAFE|AUTO}
:SYSTem:CONFigure:PROTection:RECovery?
Parameter
SAFE
The output is not turned on automatically
when the cause of the alarm is fixed.
AUTO
The output is turned on automatically
when the cause of the alarm is fixed.
:SYSTem:CONFigure:MSLave
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the unit operation mode. This
setting is only applied after the unit has been reset.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:CONFigure:MSLave { <NR1> }
:SYSTem:CONFigure:MSLave?
Parameter/Return
<NR1>
Description
0
Master/Local
1
Master/with 1 unit in Parallel (total:2 units)
2
Master/with 2 units in Parallel (total: 3 units)
3
Master/with 3 units in Parallel (total: 4 units)
4
Slave
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:EXTernal
[:MODE]
Set
Query
Description
Sets the external logic as active high or active low.
This setting is only applied after the unit has been
reset.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:EXTernal[:MODE]
{<NR1>|LOW|HIGH}
:SYSTem:CONFigure:OUTPut:EXTernal[:MODE]?
90
Page 91

REMOTE CONTROL
Parameter
HIGH | 0
Active high
LOW | 1
Active low
Return Parameter
<NR1>
Returns the logic setting.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ENABle
Set
Query
Description
Enables/Disables GPIB, USB or other remote
interfaces such as Sockets and the Web Server.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ENABle {<bool>
|OFF|ON,GPIB|USB|SOCKets|WEB|SERial}
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:ENABle?
{GPIB|USB|SOCKets|WEB|SERial}
Parameter 1
OFF | 0
Disables the selected interface.
ON | 1
Enables the selected interface.
Parameter 2
GPIB
Select GPIB
USB
Select USB
SOCKets
Select Sockets
WEB
Select the web server
SERial
Selected Serial (UART)
Return Parameter
<bool>
Returns the status of the selected mode.
Example
SYST:COMM:ENAB 1,USB
Turns the USB interface on.
Query Example
SYST:COMM:ENAB? USB
1
Queries the USB state, returns 1 (USB is on).
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDR
ess
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the GPIB address. Note: the setting
will only be valid after the power has been cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDRess
<NR1>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:GPIB[:SELF]:ADDRess?
Parameter/Return
<NR1>
0~30
91
Page 92

PSU Programming Manual
Example
SYST:COMM:GPIB:SELF:ADDR 15
Sets the GPIB address to 15.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:IPADdress
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries LAN IP address. Note: the setting
will only be valid after the power has been cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:IPADdress <string>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:IPADdress?
Parameter/Return
<string>
LAN IP address in string format ( “address”)
Applicable ASCII characters: 20H to 7EH
Example
SYST:COMM:LAN:IPAD “172.16.5.111”
Sets the IP address to 172.16.5.111.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:GATEway
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the Gateway address. Note: the
setting will only be valid after the power has been
cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:GATEway <string>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:GATEway?
Parameter/Return
<string>
Gateway address in string format ( “address”)
Applicable ASCII characters: 20H to 7EH
Example
SYST:COMM:LAN:GATE “172.16.0.254”
Sets the LAN gateway to 172.16.0.254.
92
Page 93

REMOTE CONTROL
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:SMASk
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the LAN subnet mask. Note: the
setting will only be valid after the power has been
cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:SMASk <string>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:SMASk?
Parameter/Return
<string>
Subnet mask in string format ( “mask”)
Applicable ASCII characters: 20H to 7EH
Example
SYST:COMM:LAN:SMASk “255.255.0.0”
Sets the LAN mask to 255.255.0.0.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:MAC
Query
Description
Returns the unit MAC address as a string. The
MAC address cannot be changed.
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:MAC?
Return parameter
<string>
Returns the MAC address in the following
format “FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF”
Example
SYST:COMM:LAN:MAC?
02-80-AD-20-31-B1
Returns the MAC address.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DHCP
Set
Query
Description
Turns DHCP on/off. Queries the DHCP status.
Note: the setting will only be valid after the power
has been cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DHCP
{<bool>|OFF|ON}
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DHCP?
Parameter
OFF | 0
DHCP off
ON | 1
DHCP on
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns the DHCP status.
93
Page 94

PSU Programming Manual
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DNS
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the DNS address. Note: the setting
will only be valid after the power has been cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DNS <string>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:LAN:DNS?
Parameter/Return
<string>
DNS in string format ( “mask”)
Applicable ASCII characters: 20H to 7EH
Example
SYST:COMM:LAN:DNS “172.16.1.252”
Sets the DNS to 172.16.1.252.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:TCPip:CONTrol
Query
Description
Queries the socket port number.
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:TCPip:CONTrol?
Return parameter
<NR1>
0000 ~ 9999
Example
SYST:COMM:TCP:CONT?
>2268
Returns the socket port number.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial:LANGuage[
:SELect]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the communication protocol for the
serial port.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial:LANGuage[:SELect]
{"SCPI"|"LEGACY"}
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial:LANGuage[:SELect]?
Parameter/Return
parameter
"SCPI"
Sets the communication protocol to SCPI.
"LEGACY"
Sets the communication protocol to legacy
mode. (Emulate TDK Genesys)
Example
SYST:COMM:SER:LANG?
>SCPI
Indicates that the communication protocol is set to SCPI.
94
Page 95

REMOTE CONTROL
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]
:TRANsmit:BAUD
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the UART baud rate. Note: the
setting will only be valid after the power has been
cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:BAUD <NR1>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:BAUD?
Parameter/Return
<NR1>
2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600,
115200
Example
SYST:COMM:SER:TRAN:BAUD?
>2400
Returns the baud rate settings.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]
:TRANsmit:BITS
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the UART number of data bits.
Note: the setting will only be valid after the power
has been cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:BITS <NR1>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:BITS?
Parameter/Return
parameter
<NR1>
0 7 bits
1
8 bits
Example
SYST:COMM:SER:TRAN:BITS?
>1
Indicates that 8 data bits are used for the UART
connection.
95
Page 96

PSU Programming Manual
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:T
RANsmit:PARity
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the parity of the UART connection.
Note: the setting will only be valid after the power
has been cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:PARity <NR1>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:PARity?
Parameter/Return
parameter
0
None
1
Odd
2
Even
Example
SYST:COMM:SER:TRAN:PARity?
>1
Indicates that odd parity is used for the UART
connection.
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:T
RANsmit:SBITs
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the number of stop bits used for the
UART connection. Note: the setting will only be
valid after the power has been cycled.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:SBITs<NR1>
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:SERial[:RECeive]:TRANsmit
:SBITs?
Parameter/Return
parameter
0
1 stop bit
1
2 stop bits
Example
SYST:COMM:SER:TRAN:SBITs?
>1
Indicates that one stop bit is used for the UART
connection.
96
Page 97
REMOTE CONTROL
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:FRONt:STATe
Query
Description
Queries the front panel USB-A port state.
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:FRONt:STATe?
Return parameter
0
<NR1>Absent
1
<NR1>Mass Storage
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:MODE
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the speed of the rear panel USB B
port. This setting is applied only after the unit is
reset.
Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:MODE
{<NR1>|DISable|AUTO|FULL}
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:MODE?
Parameter
0 | DISable
Disable
1 | AUTO
Auto detect speed
2 | FULL
Full speed
Return parameter
<NR1>
0
Disable
1
Auto detect speed
2
Full speed
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:STATe
Query
Description
Queries the rear panel USB-B port state.
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:COMMunicate:USB:REAR:STATe?
97
Page 98

PSU Programming Manual
Return parameter
0
<NR1>Absent
1
<NR1>Connected to the PC
:SYSTem:ERRor
Query
Description
Queries the error queue. The last error message is
returned. A maximum of 32 errors are stored in the
error queue.
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:ERRor?
Return parameter
<string>
Returns an error code followed by
an error message as a single string.
Example
SYSTem:ERRor?
-100, “Command error”
:SYSTem:KLOCk
Set
Query
Description
Enables or disables the front panel key lock.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:KLOCk {<bool>|OFF|ON }
:SYSTem:KLOCk?
Parameter
OFF | 0
Panel keys unlocked
ON | 1
Panel keys locked
Return parameter
<bool>
Returns the key lock status.
:SYSTem:KEYLock:MODE
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the keylock mode. This setting is
the equivalent to the F-19 function setting.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:KEYLock { 0|1 }
:SYSTem:KEYLock?
Parameter/Return
parameter
0
Panel lock: allow output off.
1
Panel lock: allow output on/off.
:SYSTem:ERRor:ENABle
Set
Description
Clears the Error Queue and enables all error
messages to be placed in the System Error Queue.
98
Page 99

REMOTE CONTROL
Syntax
:SYSTem:ERRor:ENABle
:SYSTem:LANGuage:EMULation
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the command language.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:LANGuage:EMULation
NONE|N5700|GEN|PWX
:SYSTem:LANGuage:EMULation?
Parameter/
Return parameter
NONE
Emulation is not used. This is the default
setting
N5700
N5700/N8700 emulation is used.
GEN
GENESYS emulation is used.
PWX
PAG emulation is used.
:SYSTem:LANGuage:[:SELect]
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the command language.
Syntax
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:LANGuage[:SELect] SCPI|GEN
:SYSTem:LANGuage[:SELect]?
Parameter/
Return parameter
SCPI
Use the SCPI command language. This the
default language
GEN
Use the GEN command language.
:SYSTem:PREset
Set
Description
Presets all the Operation Enable and Questionable
Enable registers.
Syntax
:SYSTem:PREset
:SYSTem:VERSion
Query
Description
Returns the version of the PSU SCPI version.
Query Syntax
:SYSTem:VERSion?
Return
<string>
Returns the SCPI version as a string.
99
Page 100

PSU Programming Manual
Query Example
SYST:VERS?
>1999.9
:SYSTem:REBoot
Set
Description
Reboots the PSU system.
Syntax
:SYSTem:REBoot
*CLS ...................................................................................... 100
*ESE ...................................................................................... 100
*ESR ...................................................................................... 101
*IDN ..................................................................................... 101
*OPC ..................................................................................... 101
*RCL ..................................................................................... 102
*RST ...................................................................................... 102
*SAV ..................................................................................... 102
*SRE ...................................................................................... 102
*STB ...................................................................................... 103
*TRG ..................................................................................... 103
*TST ...................................................................................... 103
*WAI ..................................................................................... 103
*CLS
Set
Description
The *CLS command clears all the event registers,
including the status byte, event status and error
queue.
Syntax
*CLS
*ESE
Set
Query
Description
Sets or queries the Standard Event Status Enable
register.
IEEE 488.2 Common Commands
100
 Loading...
Loading...