Gigabyte GA-7VT600 1394, GA-K8VT800 PRO, GA-K8VNXP, GA-7VM400M-P, GA-7VM400MF-P User Manual
...
SATA Host Controller
User Manual
Revision 1.01
May 19, 2003

Table of Contents
Table of Contents............................................................................................................................................... i
Introduction ....................................................................................................................................................... 1
RAID Basics...................................................................................................................................................1
RAID 0 (Striping) ........................................................................................................................................................................1
RAID 1 (Mirroring) ..................................................................................................................................................................... 1
JBOD (Spanning)......................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Key Features .................................................................................................................................................. 2
Installing The Hard Drives ...............................................................................................................................3
BIOS Configuration Utility ...............................................................................................................................4
Enter BIOS Configuration Utility ...............................................................................................................4
Create Disk Array ......................................................................................................................................... 5
Delete Disk Array.......................................................................................................................................... 8
Create and Delete Spare Hard Drive ..........................................................................................................9
Select Boot Array ........................................................................................................................................10
View Serial Number of Hard Drive........................................................................................................... 11
View Array Status ....................................................................................................................................... 11
Duplicate Critical RAID 1 Array............................................................................................................... 12
Rebuild Broken RAID 1 Array.................................................................................................................. 13
Driver and RAID Software Installation.......................................................................................................... 15
Microsoft Windows Driver Installation .................................................................................................... 15
Verify Installation .......................................................................................................................................17
RAID Software................................................................................................................................................. 18
Installation ................................................................................................................................................... 18
Getting Start ................................................................................................................................................ 19
View Controller and Device Status............................................................................................................ 22
Create Disk Array ....................................................................................................................................... 23
Delete Disk Array........................................................................................................................................ 26
Add and Remove Spare Disk Drive........................................................................................................... 28
Add Spare Disk Drive................................................................................................................................................................ 28
Remove Spare Disk Drive.......................................................................................................................................................... 30
Check All Disks ...........................................................................................................................................31
View Event Log ...........................................................................................................................................32
Verify Mirror Disk...................................................................................................................................... 34
Synchronize Mirror Disk............................................................................................................................ 36
Disk Error Detection................................................................................................................................... 38
Duplicate Critical RAID 1 Array............................................................................................................... 39
Rebuild Broken RAID 1 Array.................................................................................................................. 40
Icon View...................................................................................................................................................... 43
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 i Table of Contents
I
NTRODUCTION
This section gives a brief introduction on the RAID-related background knowledge and a brief introduction on VIA SATA RAID
Host Controller. For users wishing to install their VIA SATA RAID driver and RAID software, proceed to Driver and RAID
Software Installation section.
RAID Basics
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a method of combining two or more hard disk drives into one logical unit. The
advantage of an Array is to provide better performance or data fault tolerance. Fault tolerance is achieved through data redundant
operation, where if one drives fails, a mirrored copy of the data can be found on another drive. This can prevent data loss if the
operating system fails or hangs. The individual disk drives in an array are called “members”. The configuration information of
each member is recorded in the “reserved sector” that identifies the drive as a member. All disk members in a formed disk array
are recognized as a single physical drive to the operating system.
Hard disk drives can be combined together through a few different methods. The different methods are referred to as different
RAID levels. Different RAID levels represent different performance levels, security levels and implementation costs. The RAID
levels which the VIA VT6420 SATA RAID Host Controller supports are RAID 0, 1, and JBOD. The table below briefly
introduced these RAID levels.
RAID Level No. of Drives Capacity Benefits
RAID 0 (Striping) 2 to 4 Number drives * Smallest size Highest performance without
data protection
RAID 1 (Mirroring) 2 Smallest size Data protection
JBOD (Spanning) 2 to 4 Sum of All drives No data protection and
performance improving, but disk
capacity fully used.
RAID 0 (Striping)
RAID 0 reads and writes sectors of data interleaved between multiple drives. If any disk member fails, it affects the entire array.
The disk array data capacity is equal to the number of drive members times the capacity of the smallest member. The striping
block size can be set from 4KB to 64KB. RAID 0 does not support fault tolerance.
RAID 1 (Mirroring)
RAID 1 writes duplicate data onto a pair of drives and reads both sets of data in parallel. If one of the mirrored drives suffers a
mechanical failure or does not respond, the remaining drive will continue to function. Due to redundancy, the drive capacity of the
array is the capacity of the smallest drive. Under a RAID 1 setup, an extra drive called the “spare drive” can be attached. Such a
drive will be activated to replace a failed drive that is part of a mirrored array. Due to the fault tolerance, if any RAID 1 drive fails,
data access will not be affected as long as there are other working drives in the array.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 1 Introduction

JBOD (Spanning)
A spanning disk array is equal to the sum of the all drives when the drives used are having different capacities. Spanning stores
data onto a drive until it is full, then proceeds to store files onto the next drive in the array. When any disk member fails, the
failure affects the entire array. JBOD is not really a RAID and does not support fault tolerance.
Key Features
The VIA SATA RAID solution uses the VT6420 chip as a RAID controller, which is a 2-channel SATA and 1-channel ATA133
solution. The RAID software is a Windows-based software utility with graphical user interface that provides an easy-operating
tool to configure and manage disk drives or disk arrays connected to the VT6420 controller. Listed below are the main features
and benefits of VIA SATA RAID:
1. Support two SATA + two PATA or four SATA hard disk drives.
2. Only SATA supports RAID.
3. Supports ATA 133 high performance hard disk drive.
4. Supports hard disk drive larger than 137 GB (48-bits LBA).
5. Dual independent ATA channels and maximum connection of four hard disk drives allowed.
6. Supports Ultra DMA mode 6/5/4/3/2/1/0, DMA mode 2/1/0, and PIO mode 4/3/2/1/0.
7. Supports PCI Plug and Play. PCI interrupt sharing and coexists with mainboard IDE controller.
8. Supports IDE bus master operation.
9. Supports RAID 0, 1, and JBOD.
10. 4 KB to 64 KB striping block size support.
11. Bootable disk or disk array support.
12. Windows-based RAID configure and management software tool. (Compatible with BIOS)
13. Real-time monitoring of device status and error alarm with popup message box and beeping.
14. Supports hot-swap failed disk drive in RAID 1 array.
15. Mirroring automatic background rebuilds support.
16. ATA SMART function support.
17. Microsoft Windows 98, Me, NT4.0, 2000, XP operating systems support.
18. Event log for easy troubleshooting.
19. On-line help for easy operation for RAID software.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 2 Introduction
I
NSTALLING THE HARD DRIVES
The VT6420 SATA controller provides the following two configurations:
1. Two SATA + Two PATA Configuration:
VT6420 supports two “Master” SATA hard disk drives and one “Master”, one “Slave” PATA hard disk drives. Only SATA
hard disk drive supports RAID, so it supports RAID 0, RAID 1, and JBOD. PATA Hard disk drives must be Ultra ATA/133,
Ultra ATA/100, Ultra ATA/66, Ultra ATA/33, and/or ATA-3 compatible to operate with the VT6420 SATA RAID controller.
2. Four SATA Configuration:
Supports RAID 0, RAID 1, and JBOD.
For maximized performance, installing all identical SATA drives of the same model and capacity is recommended. Striping
(RAID 0) and JBOD both use two up to four new drives, while mirroring (RAID 1) uses two new drives. Please connect SATA
hard disk drivers according to the following table.
Number of Drives SATA Channel 0 SATA Channel 1
1 Master -----2 Master Master
3 Master & Slave Master
4 Master & Slave Master & Slave
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 3 Installing The Hard Drives
BIOS C
ONFIGURATION UTILITY
Enter BIOS Configuration Utility
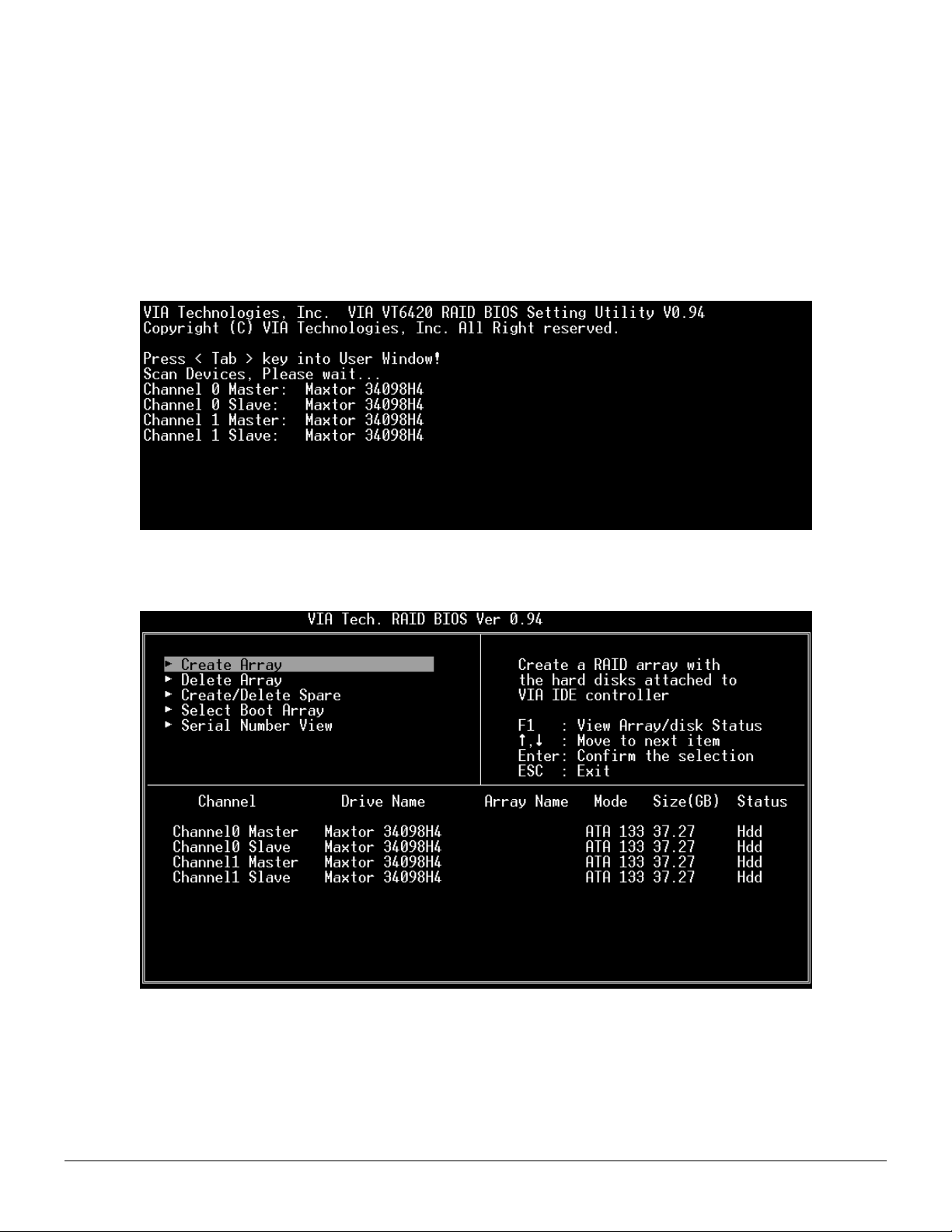
When the system powers on, the following information will appear on screen. Press the ‘Tab’ key to enter BIOS configuration
utility.
The main interface of BIOS configuration utility is as below:
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 4 BIOS Configuration Utility
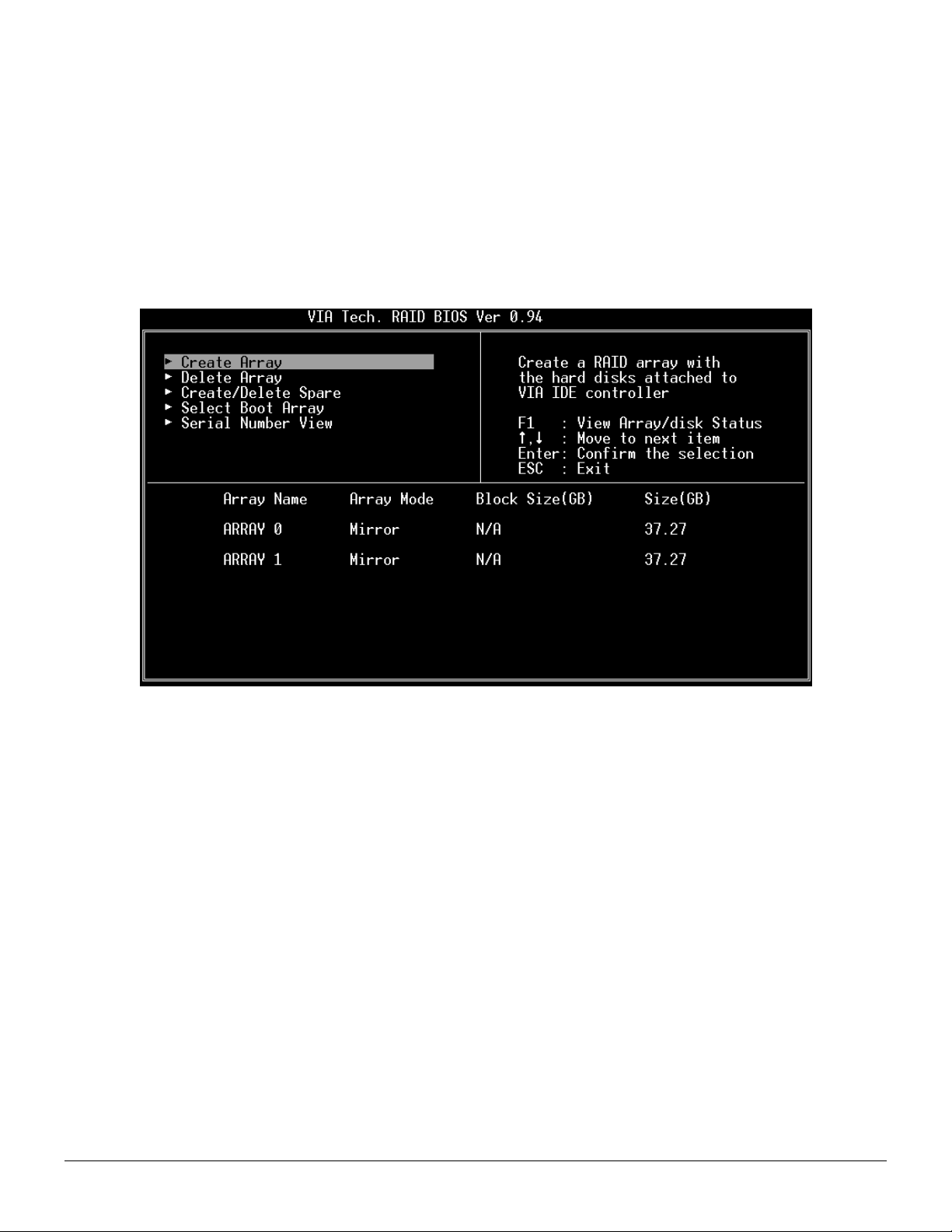
Create Disk Array
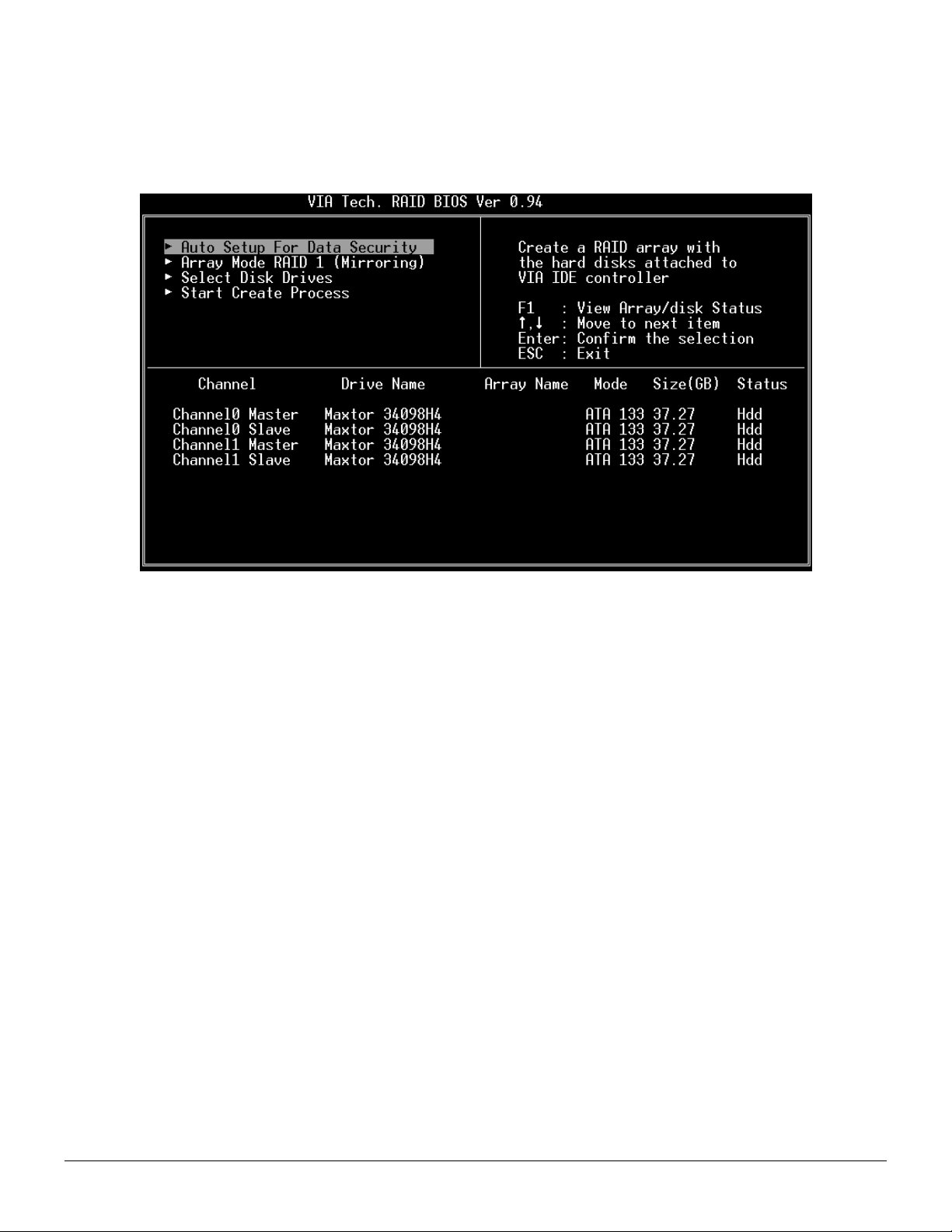
1. Use the arrow keys to navigate the main menu. Use the up and down arrow keys to select the Create Array command and
press <Enter> to call out the list of creation steps.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 5 BIOS Configuration Utility
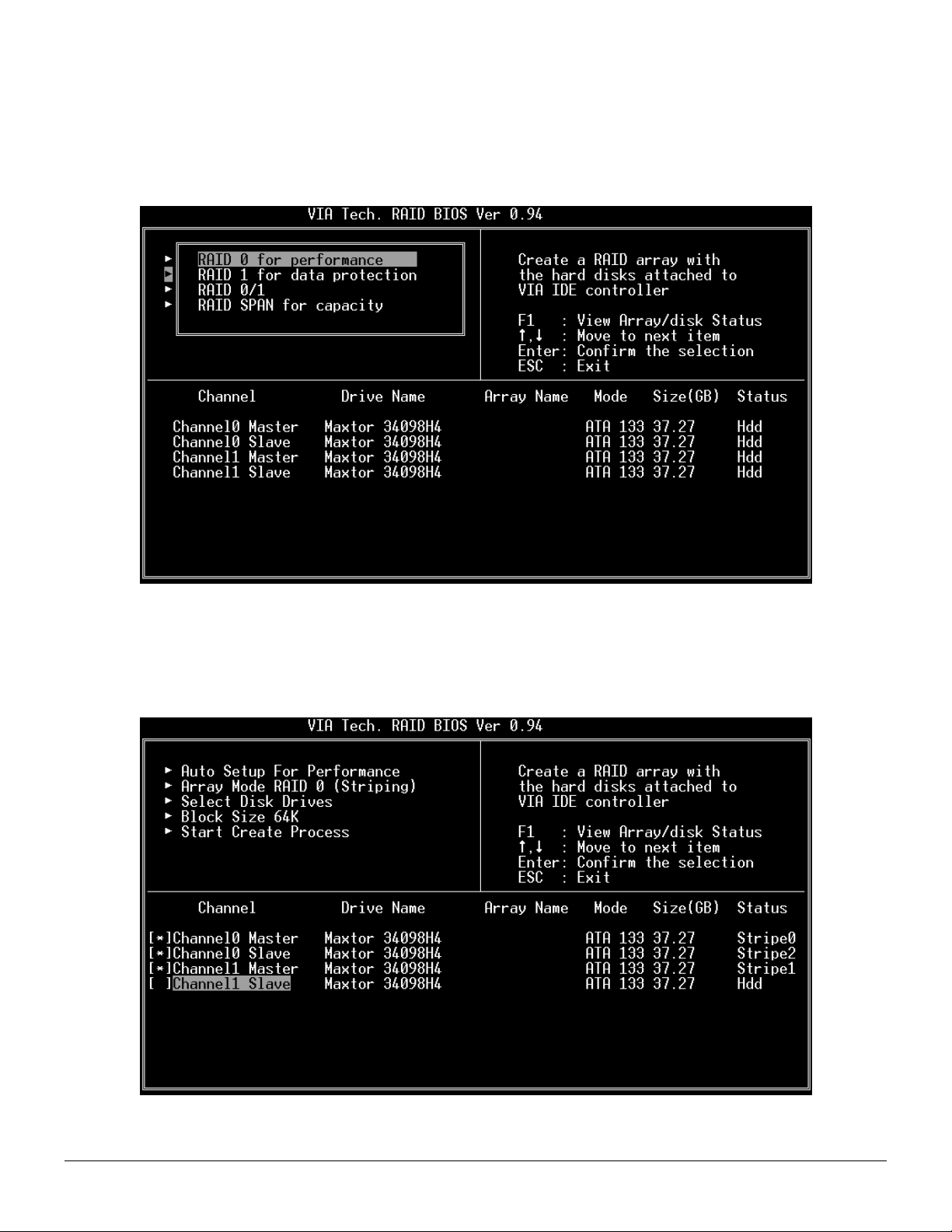
2. Select Array Mode and press <Enter>, a list of array modes will appear. Highlight the target array mode that you want to
create, and press <Enter> to confirm the selection. If RAID 1 or RAID 0/1 is selected, an option list will popup and enable the
users to select Create only or Create and duplicate. Create only will allow BIOS to only create an array. The data on the
mirroring drive may be different from the source drive. Create and duplicate lets BIOS copy the data from the source to the
mirroring drive.
3. After array mode is selected, there are two methods to create a disk array. One method is “Auto Setup” and the other one is
“Select Disk Drives”. Auto Setup allows BIOS to select the disk drives and create arrays automatically, but it does not
duplicate the mirroring drives even if the user selected Create and duplicate for RAID 1. It is recommended all disk drives are
new ones when wanting to create an array. Select Disk Drives lets the user select the array drives by their requirements. When
using Select Disk Drives, the channel column will be activated. Highlight the target drives that you want to use and press
<Enter> to select them. After all drives have been selected, press <Esc> to go back to the creation steps menu.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 6 BIOS Configuration Utility
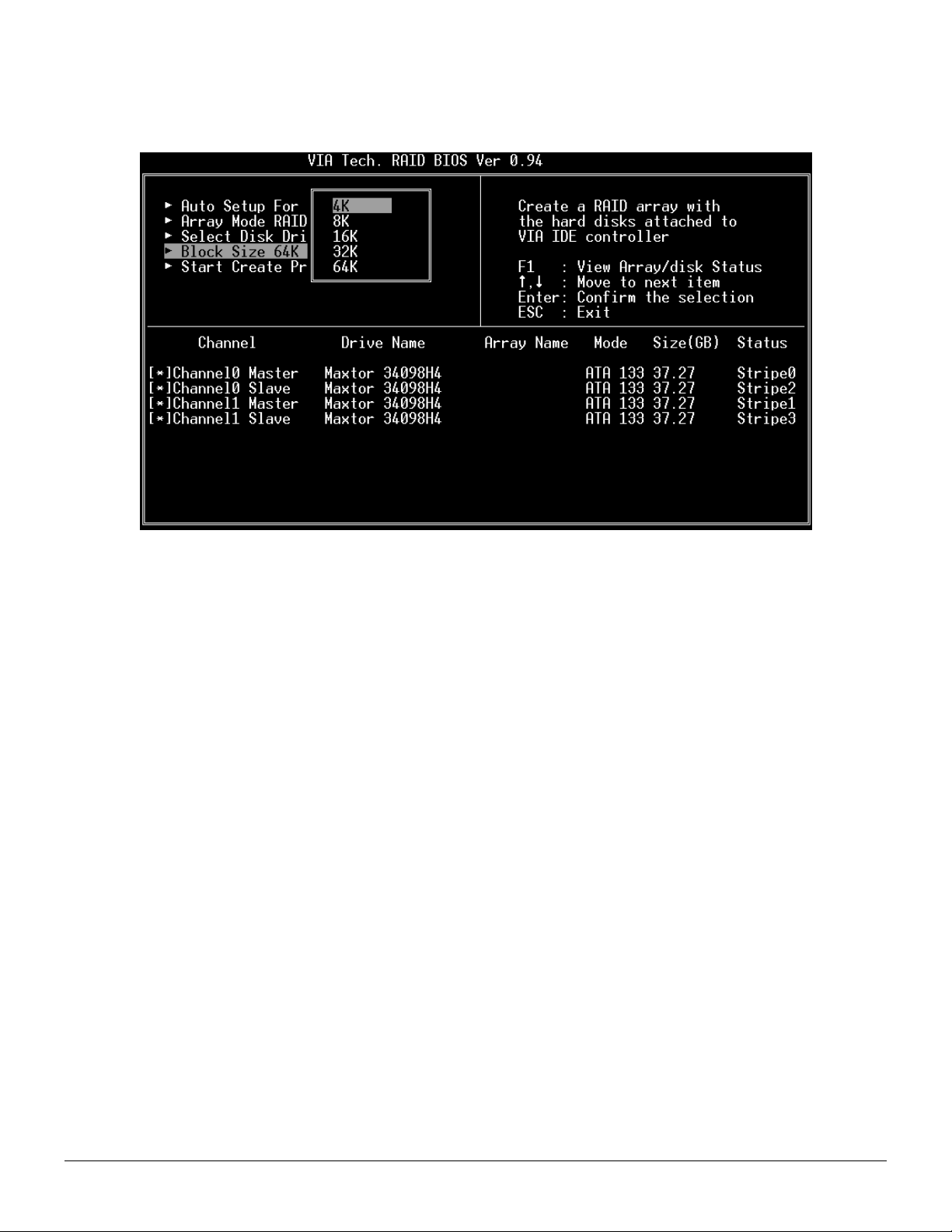
4. If user selects a RAID 0 array in step 2, the block size of the array can also be selected. Use the arrow key to highlight Block
Size and press <Enter>, then select a block size from the popup menu. The block size can be 4KB to 64KB.
5. Use the arrow key to highlight Start Create Process and press <Enter>. A warning message will appear, Press Y to finish the
creation, or press N to cancel the creation.
6. Important note: All existing content in the hard drive will be destroyed after array creation.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 7 BIOS Configuration Utility
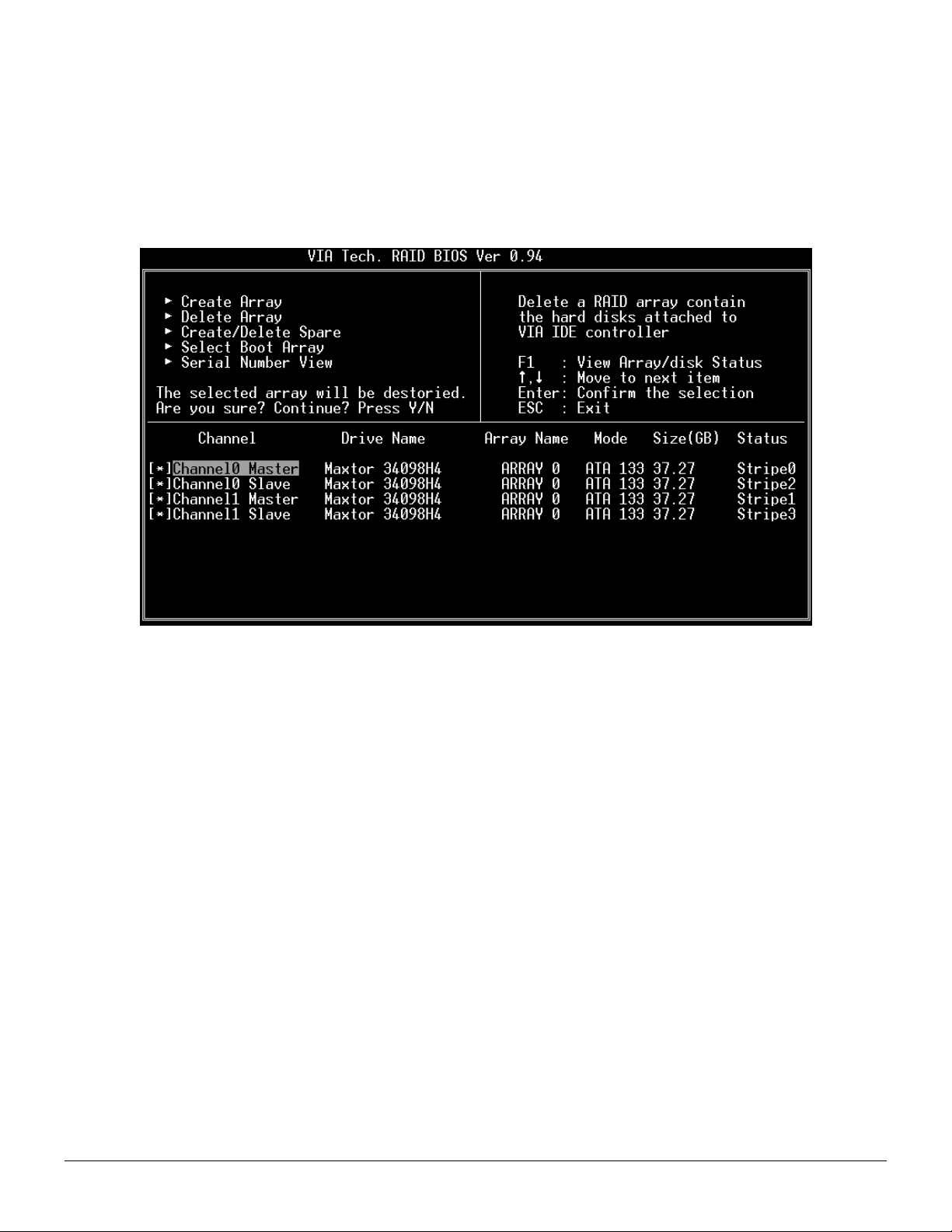
Delete Disk Array
A RAID can be deleted after it has been created. To delete a RAID, use the following steps:
1. Select Delete Array in the main menu and press <Enter>. The channel column will be activated.
2. Select the member of an array that is to be deleted and press <Enter>. A warning message will show up, press Y to delete or
press N to cancel.
Deleting a disk array will destroy all the data on the disk array except RAID 1 arrays. When a RAID is deleted, the data on these
two hard disk drives will be reserved and become two normal disk drives.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 8 BIOS Configuration Utility
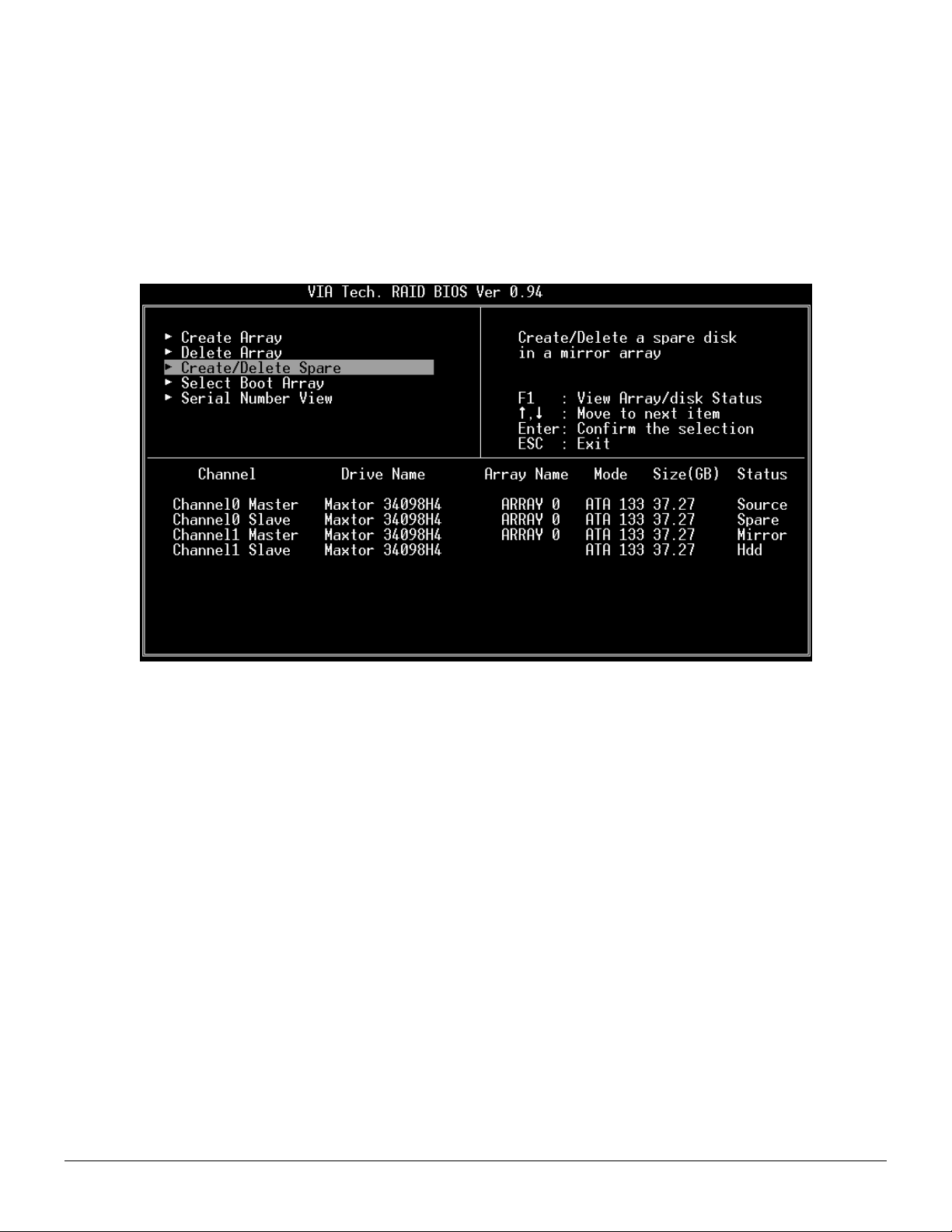
Create and Delete Spare Hard Drive
If a RAID 1 array is created and there are drives that do not belong to other arrays, the one that has a capacity which is equal to or
greater than the array capacity can be selected as a spare drive for the RAID 1 array. Select Create/Delete Spare and press
<Enter>, the channel column will then be activated. Select the drive that you want to use as a spare drive and press <Enter>, the
selected drive will be marked as Spare. The spare drive cannot be accessed in an OS.
To delete a spare drive, highlight Create/Delete Spare and press <Enter>. The spare drive will be highlighted, press <Enter> to
delete the spare drive.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 9 BIOS Configuration Utility
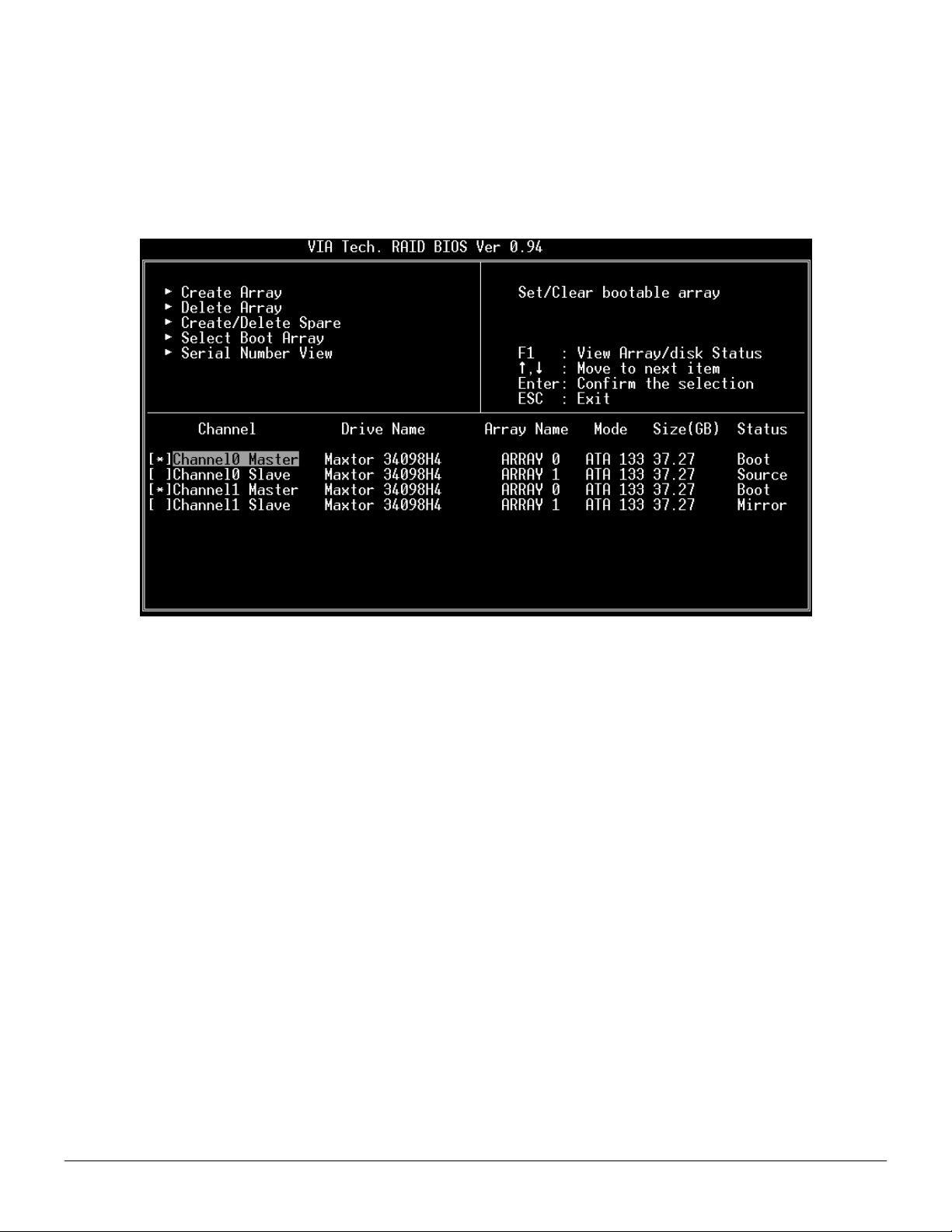
Select Boot Array
User can select a disk array as boot device if user wants to boot operating system from an array. Boot disk array cannot be
selected if the operating system does not boot from the disk array. Highlight the Select Boot Array item; press <Enter> and the
channel column will be activated. Then highlight the target disk array and press <Enter>. If user selects a disk array that has a
boot mark and press <Enter>, its boot setting will be canceled.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 10 BIOS Configuration Utility
View Serial Number of Hard Drive
Highlight Serial Number View and press <Enter>. Use arrow key to select a drive, the selected drive’s serial number can be
viewed in the last column. The serial number is assigned by the disk drive manufacturer.
View Array Status
Press the F1 key to show the array status on the lower screen. If there are no disk arrays then nothing will be displayed on the
screen.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 11 BIOS Configuration Utility
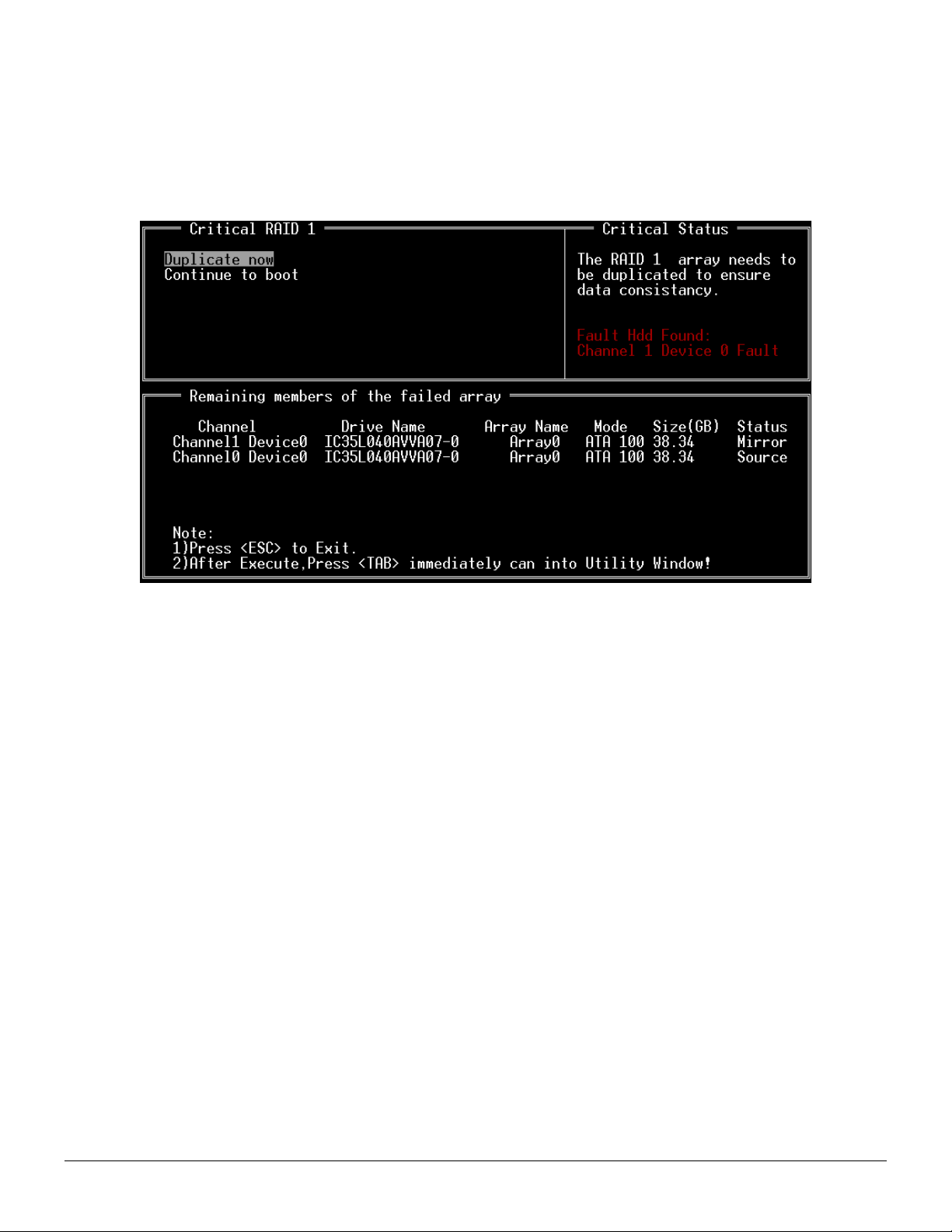
Duplicate Critical RAID 1 Array
When booting up the system, BIOS will detect if the RAID 1 array has any inconsistencies between user data and backup data. If
BIOS detects any inconsistencies, the status of the disk array will be marked as critical, and BIOS will prompt the user to duplicate
the RAID 1 in order to ensure the backup data consistency with the user data.
If user selects Continue to boot, it will enable duplicating the array after booting into OS.
Revision 1.01, May 19, 2003 12 BIOS Configuration Utility
 Loading...
Loading...