Page 1

Title page
ISO9001:2000
GE Consumer & Industrial
Multilin
MM300
Motor Management System
COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
MM300 revision: 1.0x
Manual P/N: 1601-9025-A1
GE publication code: GEK-113392
Copyright © 2007 GE Multilin
GE Multilin
215 Anderson Avenue, Markham, Ontario
Canada L6E 1B3
Tel: (905) 294-6222 Fax: (905) 201-2098
Internet: http://www.GEmultilin.com
*1601-9023*
E83849
LISTED
IND.CONT. EQ.
52TL
T
E
S
I
R
E
G
D
E
R
G
E
GE Multilin's Quality
Management System is
registered to ISO9001:2000
QMI # 005094
N
I
M
L
I
U
T
L
Page 2

© 2007 GE Multilin Incorporated. All rights reserved.
GE Multilin MM300 Motor Management System Communications Guide for revision 1.0x.
MM300 Motor Management System, EnerVista, EnerVista Launchpad, EnerVista MM300
Setup, and FlexLogic are registered trademarks of GE Multilin Inc.
The contents of this manual are the property of GE Multilin Inc. This documentation is
furnished on license and may not be reproduced in whole or in part without the permission
of GE Multilin. The content of this manual is for informational use only and is subject to
change without notice.
Part number: 1601-9025-A1 (July 2007)
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Table of Contents
COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE ............................................................................................................................ i
Communications interfaces .........................................................................................1
RS485 interface (Modbus RTU) .....................................................................................2
Modbus Protocol...............................................................................................................................................2
Electrical Interface ..........................................................................................................................................2
Data Frame Format and Data Rate........................................................................................................ 2
Data Packet Format .......................................................................................................................................2
Error Checking................................................................................................................................................... 3
CRC-16 Algorithm............................................................................................................................................3
Timing.................................................................................................................................................................... 4
MM300 supported functions...................................................................................................................... 4
Modbus Functions............................................................................................................................................4
Function Code 03H ......................................................................................................................................... 4
Function Code 04H ......................................................................................................................................... 5
Function Code 05H ......................................................................................................................................... 6
Function Code 06H ......................................................................................................................................... 7
Function Code 07H ......................................................................................................................................... 8
Function Code 08H ......................................................................................................................................... 9
Function Code 10H ......................................................................................................................................... 9
Error Responses..............................................................................................................................................10
Modbus memory map................................................................................................................................. 11
Format codes ..................................................................................................................................................34
Performing Commands Using Function Code 10H ....................................................................... 49
Using the User Definable Memory Map..............................................................................................50
Ethernet interface ........................................................................................................52
Fieldbus interface.........................................................................................................53
Profibus protocol (DP V0) ........................................................................................................................... 53
Profibus Output Data...................................................................................................................................53
Profibus DP-Diagnostics.............................................................................................................................54
Profibus Input Data.......................................................................................................................................54
DeviceNet protocol.......................................................................................................................................57
DeviceNet Communications.....................................................................................................................57
Identity Object (Class Code 01H).............................................................................................................58
Message Router (Class Code 02H).........................................................................................................58
DeviceNet Object (Class Code 03H).......................................................................................................58
DeviceNet Connection Object (Class Code 05H).............................................................................59
DeviceNet Motor Data - Poll, Explicit Object (Class Code A0H).................................................60
DeviceNet - Explicit Motor Analog Data Object, Class Code B0H, Services........................62
DeviceNet - Explicit Motor Object, Class Code B1H.......................................................................65
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 1
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
2 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 5

GE Consumer & Industrial
Multilin
MM300 Motor Management System
Communications Guide
Communications Guide
Communications interfaces
The MM300 has three communications interfaces:
• RS485
• 10/100Base-T Ethernet
•Fieldbus
NOTE:
NOTE:
Setpoint changes related to DeviceNet, Profibus, and Ethernet, require a power cycle to be
activated.
External power must be present on the Fieldbus port at power-up, in order to correctly
initialize.
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 1
Page 6

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
NOT
RS485 interface (Modbus RTU)
The RS485 interface is a serial two-wire port intended for use as a Modbus RTU slave. The
RS485 port has the following characteristics.
• Address: 1 to 254
• Baud rate: 9600 to 115200 bps
• Supported Modbus function codes: 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 16
Modbus Protocol
The MM300 implements a subset of the Modicon Modbus RTU serial communication
standard. The Modbus protocol is hardware-independent. That is, the physical layer can be
any of a variety of standard hardware configurations. This includes RS232, RS422, RS485,
fibre optics, etc. Modbus is a single master / multiple slave type of protocol suitable for a
multi-drop configuration as provided by RS485 hardware. The MM300 Modbus
implementation employs two-wire RS485 hardware. Using RS485, up to 32 MM300s can be
daisy-chained together on a single communication channel.
The MM300 is always a Modbus slave. It can not be programmed as a Modbus master.
Computers or PLCs are commonly programmed as masters.
Both monitoring and control are possible using read and write register commands. Other
commands are supported to provide additional functions.
Electrical Interface
The hardware or electrical interface in the MM300 is two-wire RS485. In a two-wire link,
data is transmitted and received over the same two wires. Although RS485 two wire
communication is bi-directional, the data is never transmitted and received at the same
time. This means that the data flow is half duplex.
RS485 lines should be connected in a daisy chain configuration with terminating networks
installed at each end of the link (i.e. at the master end and at the slave farthest from the
master). The terminating network should consist of a 120 W resistor in series with a 1 nF
ceramic capacitor when used with Belden 9841 RS485 wire. Shielded wire should always
be used to minimize noise. The shield should be connected to all of the MM300s as well as
the master, then grounded at one location only. This keeps the ground potential at the
same level for all of the devices on the serial link.
NOTE:
Polarity is important in RS485 communications. The '+' (positive) terminals of every device
must be connected together.
E
Data Frame Format and Data Rate
One data frame of an asynchronous transmission to or from a MM300 typically consists of
1 start bit, 8 data bits, and 1 stop bit. This produces a 10 bit data frame. This is important
for transmission through modems at high bit rates (11 bit data frames are not supported
by Hayes modems at bit rates of greater than 300 bps).
Modbus protocol can be implemented at any standard communication speed. The
MM300supports operation at 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, and 115200 baud.
Data Packet Format
A complete request/response sequence consists of the following bytes (transmitted as
separate data frames):
2 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 7

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Master Request Transmission:
SLAVE ADDRESS: 1 byte
FUNCTION CODE: 1 byte
DATA: variable number of bytes depending on FUNCTION CODE
CRC: 2 bytes
Slave Response Transmission:
SLAVE ADDRESS: 1 byte
FUNCTION CODE: 1 byte
DATA: variable number of bytes depending on FUNCTION CODE
CRC: 2 bytes
SLAVE ADDRESS: This is the first byte of every transmission. This byte represents the userassigned address of the slave device that is to receive the message sent by the master.
Each slave device must be assigned a unique address and only the addressed slave will
respond to a transmission that starts with its address. In a master request transmission the
SLAVE ADDRESS represents the address of the slave to which the request is being sent. In a
slave response transmission the SLAVE ADDRESS represents the address of the slave that
is sending the response.
FUNCTION CODE: This is the second byte of every transmission. Modbus defines function
codes of 1 to 127.
DATA: This will be a variable number of bytes depending on the FUNCTION CODE. This may
be Actual Values, Setpoints, or addresses sent by the master to the slave or by the slave to
the master.
CRC: This is a two byte error checking code.
Error Checking
CRC-16 Algorithm
The RTU version of Modbus includes a two byte CRC-16 (16 bit cyclic redundancy check)
with every transmission. The CRC-16 algorithm essentially treats the entire data stream
(data bits only; start, stop and parity ignored) as one continuous binary number. This
number is first shifted left 16 bits and then divided by a characteristic polynomial
(11000000000000101B). The 16 bit remainder of the division is appended to the end of the
transmission, MSByte first. The resulting message including CRC, when divided by the
same polynomial at the receiver will give a zero remainder if no transmission errors have
occurred.
If a MM300 Modbus slave device receives a transmission in which an error is indicated by
the CRC-16 calculation, the slave device will not respond to the transmission. A CRC-16
error indicates than one or more bytes of the transmission were received incorrectly and
thus the entire transmission should be ignored in order to avoid the MM300 performing
any incorrect operation.
The CRC-16 calculation is an industry standard method used for error detection. An
algorithm is included here to assist programmers in situations where no standard CRC-16
calculation routines are available.
Once the following algorithm is complete, the working register “A” will contain the CRC
value to be transmitted. Note that this algorithm requires the characteristic polynomial to
be reverse bit ordered. The MSBit of the characteristic polynomial is dropped since it does
not affect the value of the remainder. The following symbols are used in the algorithm:
—>: data transfer
A: 16 bit working register
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 3
Page 8

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
AL: low order byte of A
AH: high order byte of A
CRC: 16 bit CRC-16 value
i, j: loop counters
(+): logical exclusive or operator
Di: i-th data byte (i = 0 to N-1)
G: 16 bit characteristic polynomial = 1010000000000001 with MSbit dropped and bit order
reversed
shr(x): shift right (the LSbit of the low order byte of x shifts into a carry flag, a '0' is shifted
into the MSbit of the high order byte of x, all other bits shift right one location
The algorithm is:
1. FFFF hex —> A
2. 0 —> i
3. 0 —> j
4. Di (+) AL —> AL
5. j+1 —> j
6. shr(A)
7. is there a carry? No: go to 8. Yes: G (+) A —> A
8. is j = 8? No: go to 5. Yes: go to 9.
9. i+1 —> i
10. is i = N? No: go to 3. Yes: go to 11.
11. A —> CRC
Timing
Data packet synchronization is maintained by timing constraints. The receiving device
must measure the time between the reception of characters. If 3.5 character times elapse
without a new character or completion of the packet, then the communication link must
be reset (i.e. all slaves start listening for a new transmission from the master). Thus at 9600
baud a delay of greater than 3.5 x 1 / 9600 x 10 x = x 3.65 x ms will cause the
communication link to be reset.
MM300 supported functions
The following functions are supported by the MM300:
• FUNCTION CODE 03 - Read Setpoints and Actual Values
• FUNCTION CODE 04 - Read Setpoints and Actual Values
• FUNCTION CODE 05 - Execute Operation
• FUNCTION CODE 06 - Store Single Setpoint
• FUNCTION CODE 07 - Read Device Status
• FUNCTION CODE 08 - Loopback Test
• FUNCTION CODE 10 - Store Multiple Setpoints
Modbus Functions
Function Code 03H
Modbus implementation: Read Holding Registers
4 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 9

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
MM300 implementation: Read Setpoints
For the MM300 implementation of Modbus, this function code can be used to read any
setpoints (“holding registers”). Holding registers are 16 bit (two byte) values transmitted
high order byte first . Thus all MM300 Setpoints are sent as two bytes. The maximum
number of registers that can be read in one transmission is 125.
The slave response to this function code is the slave address, function code, a count of the
number of data bytes to follow, the data itself and the CRC. Each data item is sent as a two
byte number with the high order byte sent first.
For example, consider a request for slave 17 to respond with 3 registers starting at address
006B. For this example the register data in these addresses is as follows:
Address Data
006B 022B
006C 0000
006D 0064
The master/slave packets have the following format:
Table 1: Master/slave packet format for function code 03H
MASTER TRANSMISSION BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message for slave
FUNCTION CODE 1 03 read registers
DATA STARTING ADDRESS 2 00 6B data starting at
NUMBER OF SETPOINTS 2 00 03 3 registers = 6
CRC 2 76 87 CRC error code
17
006B
bytes total
Function Code 04H
SLAVE RESPONSE BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message from
slave 17
FUNCTION CODE 1 03 read registers
BYTE COUNT 1 06 3 registers = 6
bytes
DATA 1 (see definition above) 2 02 2B value in address
006B
DATA 2 (see definition above) 2 00 00 value in address
006C
DATA 3 (see definition above) 2 00 64 value in address
006D
CRC 2 54 83 CRC error code
Modbus Implementation: Read Input Registers
MM300 implementation: Read Actual Values
For the MM300 implementation of Modbus, this function code can be used to read any
actual values (“input registers”). Input registers are 16 bit (two byte) values transmitted high
order byte first . Thus all MM300 Actual Values are sent as two bytes. The maximum
number of registers that can be read in one transmission is 125.
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 5
Page 10
RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
The slave response to this function code is the slave address, function code, a count of the
data bytes to follow, the data itself and the CRC. Each data item is sent as a two byte
number with the high order byte sent first .
For example, request slave 17 to respond with 1 register starting at address 0008. For this
example the value in this register (0008) is 0000.
Table 2: Master/slave packet format for function code 04H
MASTER TRANSMISSION BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message for slave
FUNCTION CODE 1 04 read registers
DATA STARTING ADDRESS 2 00 08 data starting at
NUMBER OF ACTUAL VALUES 2 00 01 1 register = 2 bytes
CRC 2 B2 98 CRC error code
SLAVE RESPONSE BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message from
FUNCTION CODE 1 04 read registers
BYTE COUNT 1 02 1 register = 2 bytes
DATA (see definition above) 2 00 00 value in address
CRC 2 78 F3 CRC error code
17
0008
slave 17
0008
Function Code 05H
Modbus Implementation: Force Single Coil
MM300 Implementation: Execute Operation
This function code allows the master to request a MM300 to perform specific command
operations.
For example, to request slave 17 to execute operation code 1 (reset), we have the following
master/slave packet format:
Table 3: Master/slave packet format for function code 05H
MASTER TRANSMISSION BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message for slave
17
FUNCTION CODE 1 05 execute operation
OPERATION CODE 2 00 01 operation code 1
CODE VALUE 2 FF 00 perform function
CRC 2 DF 6A CRC error code
SLAVE RESPONSE BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message from
slave 17
FUNCTION CODE 1 05 execute operation
OPERATION CODE 2 00 01 operation code 1
CODE VALUE 2 FF 00 perform function
CRC 2 DF 6A CRC error code
6 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 11

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
The commands that can be performed by the MM300 using function code 05 can also be
initiated by using function code 10.
Operation Code Description
1Reset
2Lockout Reset
3Stop
4Start A
5Start B
96 Clear Last Trip Data Prompt
97 Reset MWh and Mvarh Meters
99 Clear Counters
100 Clear Event Records
102 Clear Maintenance Timer
112 Clear RTD Maximums
113 Reset Motor Information
114 Auto Mode
115 Manual Mode
116 Manual Inhibit
117 Manual Restore
Function Code 06H
Modbus Implementation: Preset Single Register
MM300 Implementation: Store Single Setpoint
This command allows the master to store a single setpoint into the memory of a MM300
The slave response to this function code is to echo the entire master transmission.
For example, request slave 17 to store the value 2 in setpoint address 04 5C. After the
transmission in this example is complete, setpoints address 04 5C will contain the value
01F4. The master/slave packet format is shown below:
Table 4: Master/slave packet format for function code 06H
MASTER TRANSMISSION BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message for slave
17
FUNCTION CODE 1 06 store single
setpoint
DATA STARTING ADDRESS 2 04 5C setpoint address
04 5C
DATA 2 00 02 data for setpoint
address 04 5C
CRC 2 CB B9 CRC error code
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 7
Page 12

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
SLAVE RESPONSE BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message from
FUNCTION CODE 1 06 store single
DATA STARTING ADDRESS 2 04 5C setpoint address
DATA 2 00 02 data stored in
CRC 2 CB B9 CRC error code
slave 17
setpoint
04 5C
setpoint address
04 5C
Function Code 07H
Modbus Implementation: Read Exception Status
MM300 Implementation: Read Device Status
This is a function used to quickly read the status of a selected device. A short message
length allows for rapid reading of status. The status byte returned will have individual bits
set to 1 or 0 depending on the status of the slave device. For this example, consider the
following MM300 general status byte:
The master/slave packets have the following format:
Table 5: Function code 7 bitmask
Bit Function
0Alarm
1Trip
2 Internal fault
3Auto
4 Contactor A
5 Contactor B
6 Contact output 3
7 Drive available (communications control)
Table 6: Master/slave packet format for function code 07H
MASTER TRANSMISSION BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message for slave
FUNCTION CODE 1 07 read device status
CRC 2 4C 22 CRC error code
SLAVE RESPONSE BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message from
FUNCTION CODE 1 07 read device status
DEVICE STATUS (see
definition above)
CRC 2 22 28 CRC error code
1 2C status = 00101100
17
slave 17
(in binary)
8 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 13
COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Function Code 08H
Modbus Implementation: Loopback
Test MM300 Implementation: Loopback Test
This function is used to test the integrity of the communication link. The MM300 will echo
the request.
For example, consider a loopback test from slave 17:
Table 7: Master/slave packet format for function code 08H
MASTER TRANSMISSION BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message for slave
FUNCTION CODE 1 08 loopback test
DIAG CODE 2 00 00 must be 00 00
DATA 2 00 00 must be 00 00
CRC 2 E0 0B CRC error code
SLAVE RESPONSE BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message from
FUNCTION CODE 1 08 loopback test
DIAG CODE 2 00 00 must be 00 00
DATA 2 00 00 must be 00 00
CRC 2 E0 0B CRC error code
17
slave 17
Function Code 10H
Modbus Implementation: Preset Multiple Registers
MM300 Implementation: Store Multiple Setpoints
This function code allows multiple Setpoints to be stored into the MM300 memory. Modbus
“registers” are 16-bit (two byte) values transmitted high order byte first. Thus all MM300
setpoints are sent as two bytes. The maximum number of Setpoints that can be stored in
one transmission is dependent on the slave device. Modbus allows up to a maximum of 60
holding registers to be stored. The MM300 response to this function code is to echo the
slave address, function code, starting address, the number of Setpoints stored, and the
CRC.
For example, consider a request for slave 17 to store the value 00 02 to setpoint address
04 5C and the value 01 F4 to setpoint address 04 5D. After the transmission in this example
is complete, MM300 slave 17 will have the following setpoints information stored:
Address Data
04 5C 00 02
04 5D 01 F4
The master/slave packets have the following format:
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 9
Page 14

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Table 8: Master/slave packet format for function code 10H
MASTER TRANSMISSION BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message for slave
FUNCTION CODE 1 10 store setpoints
DATA STARTING ADDRESS 2 04 5C setpoint address
NUMBER OF SETPOINTS 2 00 02 2 setpoints = 4
BYTE COUNT 1 04 4 bytes of data
DATA 1 2 00 02 data for setpoint
DATA 2 2 01 F4 data for setpoint
CRC 2 31 11 CRC error code
SLAVE RESPONSE BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message from
FUNCTION CODE 1 10 store setpoints
DATA STARTING ADDRESS 2 04 5C setpoint address
NUMBER OF SETPOINTS 2 00 02 2 setpoints
CRC 2 82 7A CRC error code
17
04 5C
bytes total
address 04 5C
address 04 5D
slave 17
04 5C
Error Responses
When a MM300 detects an error other than a CRC error, a response will be sent to the
master. The MSBit of the FUNCTION CODE byte will be set to 1 (i.e. the function code sent
from the slave will be equal to the function code sent from the master plus 128). The
following byte will be an exception code indicating the type of error that occurred.
Transmissions received from the master with CRC errors will be ignored by the MM300.
The slave response to an error (other than CRC error) will be:
SLAVE ADDRESS: 1 byte
FUNCTION CODE: 1 byte (with MSbit set to 1)
EXCEPTION CODE: 1 byte
CRC: 2 bytes
The MM300 implements the following exception response codes:
01 - ILLEGAL FUNCTION
The function code transmitted is not one of the functions supported by the MM300.
02 - ILLEGAL DATA ADDRESS
The address referenced in the data field transmitted by the master is not an allowable
address for the MM300.
03 - ILLEGAL DATA VALUE
The value referenced in the data field transmitted by the master is not within range for the
selected data address.
10 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 15
COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
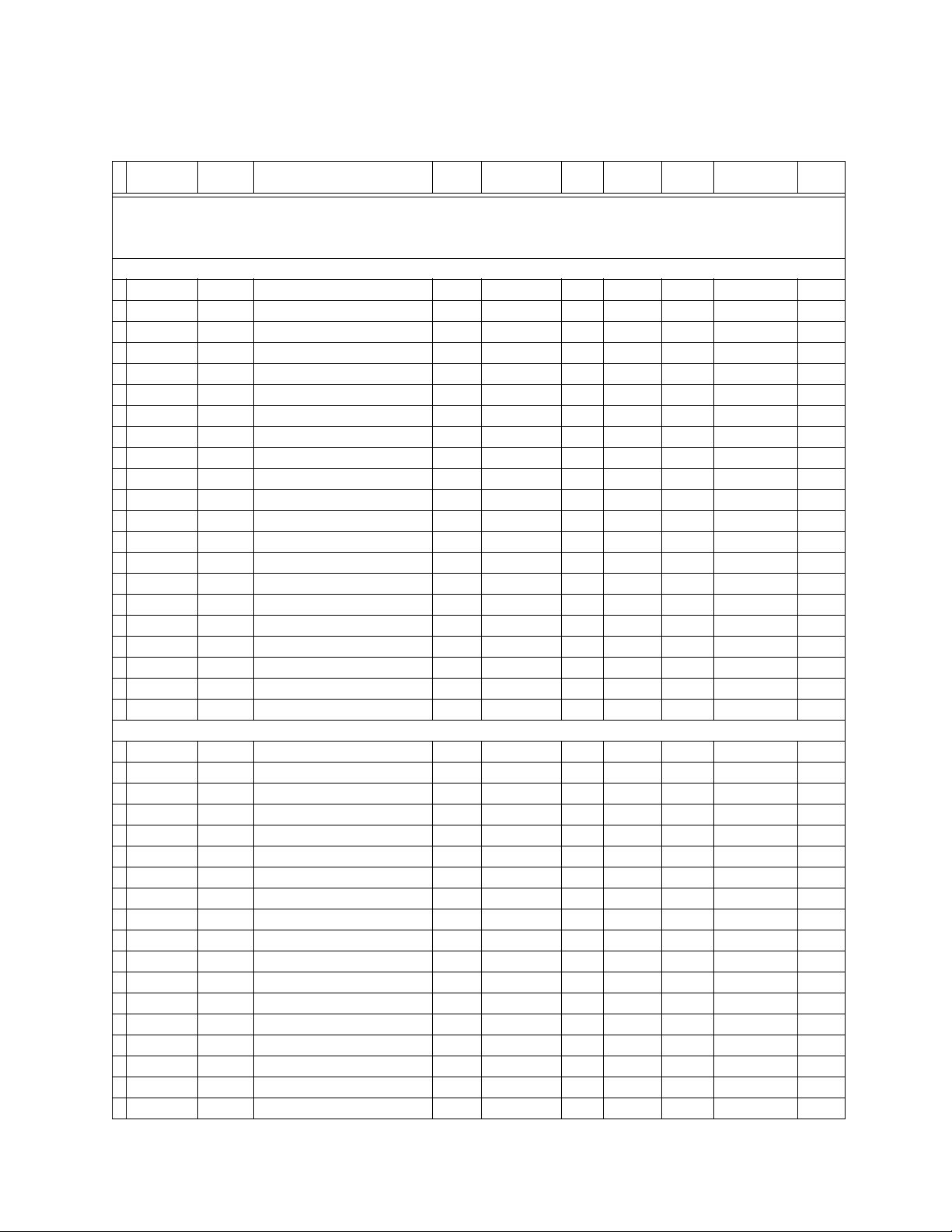
Modbus memory map
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
ACTUAL VALUES
PRODUCT INFORMATION
30001 0000 Product Device Code --- --- --- --- F22 N/A 1
30002 0001 Hardware Revision --- --- --- --- F15 N/A 1
30003 0002 Firmware Version --- --- --- --- F3 N/A 1
30004 0003 Display Software Version --- --- --- --- F3 N/A 1
30005 0004 Modification Number --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30006 0005 Boot Version --- --- --- --- F3 N/A 1
30007 0006 Boot Modification # --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30008 0007 Serial Number --- --- --- --- F22 N/A 6
30014 000D Order Code --- --- --- --- F22 N/A 16
30030 001D MAC Address --- --- --- --- F22 N/A 6
30036 0023 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30037 0024 Build Date --- --- --- --- F22 N/A 6
30043 002A Build Time --- --- --- --- F22 N/A 4
30047 002E Original Calibration Date --- --- --- --- F18 N/A 2
30049 0030 Last Calibration Date --- --- --- --- F18 N/A 2
30051 0032 Communications Build Date --- --- --- --- F22 N/A 6
30057 0038 Communications Build Time --- --- --- --- F22 N/A 4
30061 003C Communications Revision --- --- --- --- F3 N/A 1
30062 003D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30185 00B8 Reserved 1
LAST TRIP DATA
30186 00B9 Cause of Last Trip --- --- --- --- FC134 N/A 1
30187 00BA Time of Last Trip 2 words --- --- --- --- F19 N/A 2
30189 00BC Date of Last Trip 2 words --- --- --- --- F18 N/A 2
30191 00BE Motor Speed During Trip --- --- --- --- FC135 N/A 1
30192 00BF Pre Trip Ia --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30194 00C1 Pre Trip Ib --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30196 00C3 Pre Trip Ic --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30198 00C5 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30199 00C6 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30200 00C7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30201 00C8 Pre Trip Motor Load --- --- --- A F3 N/A 1
30202 00C9 Pre Trip Current Unbalance --- --- --- % F1 N/A 1
30203 00CA Pre Trip Ig --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30205 00CC Pre Trip Vab --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30206 00CD Pre Trip Vbc --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30207 00CE Pre Trip Vca --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30208 00CF Pre Trip Van --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30209 00D0 Pre Trip Vbn --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 11
Page 16

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
30210 00D1 Pre Trip Vcn --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30211 00D2 Pre Trip System Frequency --- --- --- Hz F3 N/A 1
30212 00D3 Pre Trip Real Power --- --- --- kW F13 N/A 2
30214 00D5 Pre Trip Reactive Power --- --- --- kvar F13 N/A 2
30216 00D7 Pre Trip Apparent Power --- --- --- kVA F2 N/A 1
30217 00D8 Pre Trip Power Factor --- --- --- --- F21 N/A 1
30218 00D9 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30222 00DD Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
REAL-TIME CLOCK
30223 00DE Weekday --- --- --- --- FC171 N/A 1
30224 00DF Date Read Only --- --- --- --- F18 N/A 2
30226 00E1 Time Read Only --- --- --- --- F19 N/A 2
30228 00E3 Daylight Savings Active --- --- --- --- FC126 N/A 1
30229 00E4 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
TRIP COUNTERS
30230 00E5 Total Number of Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30231 00E6 Incomplete Sequence Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30232 00E7 Overload Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30233 00E8 Mechanical Jam Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30234 00E9 Undercurrent Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30235 00EA Current Unbalance Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30236 00EB Ground Fault Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30237 00EC Motor Acceleration Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30238 00ED Undervoltage Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30239 00EE Overvoltage Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30240 00EF Voltage Phase Reversal Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30241 00F0 Voltage Freq Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30242 00F1 Underpower Trips --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30243 00F2 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30256 00FF Reserved 1
GENERAL TIMERS
30257 0100 Number of Motor Starts --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30258 0101 Number of UV Restarts --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30259 0102 Motor Running Hours --- --- --- hrs F9 N/A 2
30261 0104 UVR Timer --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30262 0105 Start Timer 1 --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30263 0106 Start Timer 2 --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30264 0107 Start Timer 3 --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30265 0108 Start Timer 4 --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30266 0109 Start Timer 5 --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30267 010A TransferTimer --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30268 010B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30269 010C Motor Stopped Hours --- --- --- hrs F1 N/A 1
START BLOCKS
Words
12 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 17
COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
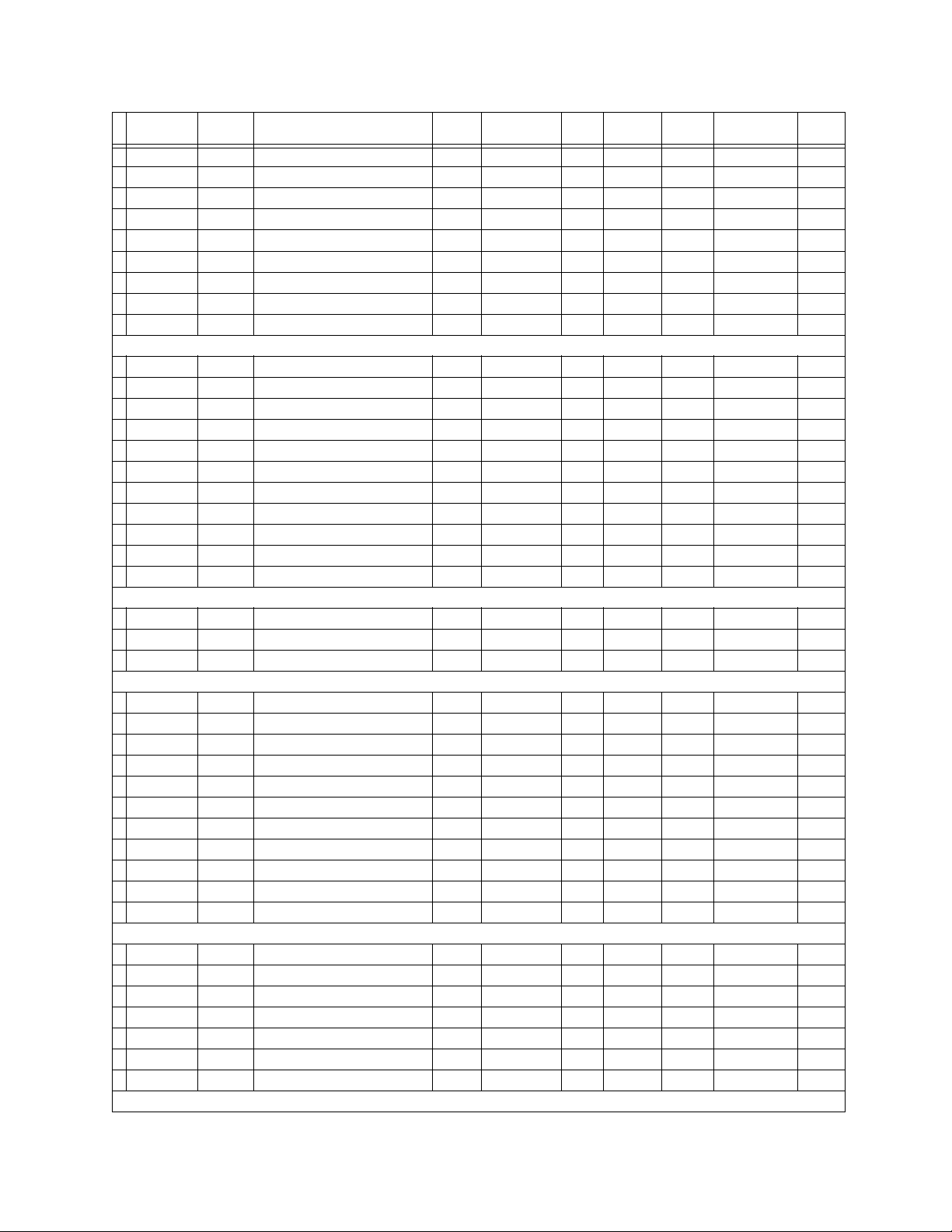
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
Words
30270 010D Overload Lockout --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30271 010E Starts/Hour Block --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30272 010F Time Between Starts --- --- --- s F1
1
N/A 1
30273 0110 Restart Block --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30274 0111 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30275 0112 Pre-Contactor Timer --- --- --- s F1 N/A 1
30276 0113 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 2
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30282 0119 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
CONTACT/VIRTUAL INPUTS/OUTPUTS STATUS
30283 011A Contact Input 64-33 (Bit Field) --- --- --- --- FC168 N/A 2
30285 011C Contact Input 32-1 (Bit Field) --- --- --- --- FC167 N/A 2
30287 011E Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30288 011F Virtual Input 32-1 (Bit Field) --- --- --- --- FC167 N/A 2
30290 0121 Virtual Output 32-1 (Bit Field) --- --- --- --- FC167 N/A 2
30292 0123 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 2
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30297 0128 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30298 0129 Contact Output 32-1 (Bit Field) --- --- --- --- FC167 N/A 2
30300 012B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30301 012C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
SECURITY
30302 012D Current Security Access Level --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30303 012E Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30304 012F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
STATUS - MOTOR
30305 0130 Motor Status --- --- --- --- FC129 N/A 1
30306 0131 Extended Status --- --- --- --- FC178 N/A 1
30307 0132 Thermal Cap Used --- --- --- % F1 N/A 1
30308 0133 Time to Overload Trip --- --- --- s F20 N/A 2
30310 0135 Drive Status --- --- --- --- FC143 N/A 1
30311 0136 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30312 0137 Command Status --- --- --- --- FC128 N/A 1
30313 0138 Time To Reset --- --- --- min F1 N/A 1
30314 0139 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30327 0146 Reserved 1
CURRENT METERING
30328 0147 Ia --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30330 0149 Ib --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30332 014B Ic --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30334 014D Iavg --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30336 014F Motor Load --- --- --- % F1 N/A 1
30337 0150 Current Unbalance --- --- --- %Ub F1 N/A 1
30338 0151 Ig --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
VOLTAGE METERING
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 13
Page 18

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
30340 0153 Va1 Angle --- --- --- ° F1 N/A 1
30341 0154 Vb1 Angle --- --- --- ° F1 N/A 1
30342 0155 Vc1 Angle --- --- --- ° F1 N/A 1
30343 0156 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30344 0157 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30357 0164 Reserved 1
30358 0165 Vab --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30359 0166 Vbc --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30360 0167 Vca --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30361 0168 Average Line Voltage --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30362 0169 Van --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30363 016A Vbn --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30364 016B Vcn --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30365 016C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30366 016D Freq --- --- --- Hz F3 N/A 1
30367 016E Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30375 0176 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30376 0177 VAux --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30377 0178 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30383 017E Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
POWER METERING
30384 017F Power Factor --- --- --- --- F21 N/A 1
30385 0180 Real Power --- --- --- kW F13 N/A 2
30387 0182 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30388 0183 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30389 0184 Reactive Power --- --- --- kvar F13 N/A 2
30391 0186 Apparent Power --- --- --- kVA F2 N/A 1
30392 0187 MWh Consumption --- --- --- MWh F17 N/A 2
30394 0189 Mvarh Consumption --- --- --- Mvarh F17 N/A 2
30396 018B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 2
30398 018D Apparent Power --- --- --- kVA F10 N/A 2
30400 018F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30427 01A9 Reserved 1
TEMPERATURE METERING
30427 01AA Hottest Stator RTD --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30428 01AB Hottest Stator RTD --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30429 01AC RTD 1 Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30430 01AD RTD 2 Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30431 01AE RTD 3 Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30432 01AF RTD 4 Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30433 01B0 RTD 5 Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30434 01B1 RTD 6 Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
Words
14 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 19
COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
30435 01B2 Thermistor --- --- --- ohms F1 N/A 1
30436 01B3 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30466 01D1 Reserved 1
MOTOR STARTING LEARNED DATA
30467 01D2 Learned Acceleration Time --- --- --- s F2 N/A 1
30468 01D3 Learned Starting Current --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30470 01D5 Learned Starting Capacity --- --- --- % F1 N/A 1
30471 01D6 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30483 01E2 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30484 01E3 Average Motor Load Learned --- --- --- %FLA F3 N/A 1
RTD MAXIMIUM TEMPERATURE
30485 01E4 RTD 1 MAX Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30486 01E5 RTD 2 MAX. Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30487 01E6 RTD 3 MAX. Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30488 01E7 RTD 4 MAX. Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30489 01E8 RTD 5 MAX. Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30490 01E9 RTD 6 MAX. Temp --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30491 01EA Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30504 01F7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
LED STATUS FOR GRAPHICAL AND BASIC CONTROL PANEL
30505 01F8 LED Status --- --- --- --- FC144 N/A 2
30507 01FA LED Flash --- --- --- --- FC130 N/A 1
30508 01FB Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
GCP FACTORY TEST
30509 01FC LCD Test Color --- --- --- --- FC212 N/A 1
30510 01FD Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30523 020A Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
USER MAP VALUES
30524 020B User Map Value 1 --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30525 020C User Map Value 2 --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30526 020D User Map Value 3 --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30527 020E User Map Value 4 --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30645 0284 User Map Value 122 --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30646 0285 User Map Value 123 --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30647 0286 User Map Value 124 --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30648 0287 User Map Value 125 --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30649 0288 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30656 028F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
SELF TEST
30657 0290 Internal Fault Cause --- --- --- --- FC188 N/A 2
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 15
Page 20
RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
EVENT RECORDER
30659 0292 Event Recorder Last Reset 2
words
30661 0294 Total Number of Events Since
Last Clear
30662 0295 Cause --- --- --- --- FC134 N/A 1
30663 0296 Contactor --- --- --- --- FC136 N/A 1
30664 0297 Time --- --- --- --- F19 N/A 2
30666 0299 Date --- --- --- --- F18 N/A 2
30668 029B Ia --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30670 029D Ib --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30672 029F Ic --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30674 02A1 Motor Load --- --- --- x FLA F3 N/A 1
30675 02A2 Iunb --- --- --- % F1 N/A 1
30676 02A3 Ig --- --- --- A F10 N/A 2
30678 02A5 Vab --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30679 02A6 Vbc --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30680 02A7 Vca --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30681 02A8 Van --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30682 02A9 Vbn --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30683 02AA Vcn --- --- --- V F1 N/A 1
30684 02AB Freq --- --- --- Hz F3 N/A 1
30685 02AC Power Factor --- --- --- --- F21 N/A 1
30686 02AD Real Power --- --- --- kW F13 N/A 2
30688 02AF Reactive Power --- --- --- kvar F13 N/A 2
30690 02B1 Apparent Power --- --- --- kVA F2 N/A 1
30691 02B2 Hottest Stator RTD --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
30692 02B3 Hottest Stator RTD --- --- --- °C F4 N/A 1
30693 02B4 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
30951 03B6 Reserved 1
STATUS BUFFER
30952 03B7 Alarm Status 4 --- --- --- --- FC182 N/A 2
30954 03B9 Alarm Status 3 --- --- --- --- FC181 N/A 2
30956 03BB Alarm Status 2 --- --- --- --- FC180 N/A 2
30958 03BD Alarm Status 1 --- --- --- --- FC179 N/A 2
30960 03BF Trip Status 4 --- --- --- --- FC186 N/A 2
30962 03C1 Trip Status 3 --- --- --- --- FC185 N/A 2
30964 03C3 Trip Status 2 --- --- --- --- FC184 N/A 2
30966 03C5 Trip Status 1 --- --- --- --- FC183 N/A 2
30968 03C7 Message Status 4 --- --- --- --- FC190 N/A 2
30970 03C9 Message Status 3 --- --- --- --- FC189 N/A 2
30972 03CB Message Status 2 --- --- --- --- FC188 N/A 2
30974 03CD Message Status 1 --- --- --- --- FC187 N/A 2
30976 03CF Ctrl Element Status 4 --- --- --- --- FC194 N/A 2
30978 03D1 Ctrl Element Status 3 --- --- --- --- FC193 N/A 2
30980 03D3 Ctrl Element Status 2 --- --- --- --- FC192 N/A 2
--- --- --- --- F18 N/A 2
--- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
Words
16 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 21

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
30982 03D5 Ctrl Element Status 1 --- --- --- --- FC191 N/A 2
30984 03D7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30985 03D8 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
30986 03D9 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
FLEXLOGIC
30987 03DA Element Flag --- --- --- --- FC145 N/A 384
31371 055A Program Status --- --- --- --- FC109 N/A 1
31372 055B Flex Lines Used --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
31373 055C Error Line --- --- --- --- F1 N/A 1
31374 055D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
31375 055E Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
31376 055F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
31377 0560 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
COMMUNICATION
31378 0561 Serial Status --- --- --- --- FC112 N/A 1
31379 0562 Ethernet Status --- --- --- --- FC112 N/A 1
31380 0563 Profibus Status --- --- --- --- FC112 N/A 1
31381 0564 DeviceNet Status --- --- --- --- FC112 N/A 1
31382 0565 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
32272 08DF Reserved 1
Words
SETPOINTS
COMMANDS
40001 0000 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40128 007F Reserved 1
40129 0080 Command address 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40130 0081 Command Function 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40131 0082 Command Data 1 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40132 0083 Command Data 2 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40133 0084 Command Data 3 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40134 0085 Command Data 4 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40135 0086 Command Data 5 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40136 0087 Command Data 6 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40137 0088 Command Data 7 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40138 0089 Command Data 8 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40139 008A Command Data 9 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40140 008B Command Data 10 0 65535 0 --- F1 0 1
40141 008C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40171 00AA Reserved 1
COMMUNICATION SETTINGS
40172 00AB Slave Address 1 254 1 --- F1 254 1
40173 00AC RS485 Baud Rate 0 4 1 --- FC101 4 1
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 17
Page 22

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
40174 00AD Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40175 00AE Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40176 00AF Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40177 00B0 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40178 00B1 DeviceNet MAC ID 0 63 1 --- F1 63 1
40179 00B2 DeviceNet Baud Rate 0 2 1 --- FC156 0 1
40180 00B3 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40181 00B4 NTP IP Address 0 0xFFFFFFFF 1 --- FC150 0 2
40183 00B6 Ethernet IP address 0 0xFFFFFFFF 1 --- FC150 0 2
40185 00B8 Ethernet subnet mask 0 0xFFFFFFFF 1 --- FC150 0xFFFFFC00 2
40187 00BA Ethernet gateway address 0 0xFFFFFFFF 1 --- FC150 0 2
40189 00BC Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40190 00BD Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40191 00BE Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40192 00BF Profibus address 1 125 1 --- F1 125 1
40193 00C0 Profibus Baud Rate 1 2018 1 --- FC155 2018 1
40194 00C1 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40227 00E2 Reserved 1
REAL-TIME CLOCK/DAYLIGHT SAVINGS
40228 00E3 Set Date 0 0x0C1F082E 0 --- F18 0 2
40230 00E5 Set Time 0 0x173B3B63 0 --- F19 0 2
40232 00E7 Time Offset From UTC -2400 2400 25 hrs F6 0 1
40233 00E8 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40234 00E9 Daylight Savings 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40235 00EA DST Start Month 0 12 1 --- FC169 0 1
40236 00EB DST Start Week 0 5 1 --- FC170 0 1
40237 00EC DST Start Weekday 0 7 1 --- FC171 0 1
40238 00ED DST End Month 0 12 1 --- FC169 0 1
40239 00EE DST End Week 0 5 1 --- FC170 0 1
40240 00EF DST End Weekday 0 7 1 --- FC171 0 1
40241 00F0 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40261 0104 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
VIRTUAL INPUT
40262 0105 Virtual Input 32-1 (Bit Field) 0 0xFFFFFFFF 1 --- FC167 0 2
40264 0107 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40265 0108 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
CURRENT SENSING
40266 0109 Phase CT Type 0 3 1 --- FC105 0 1
40267 010A CT Primary 5 1000 1 A F1 5 1
40268 010B Ground CT Type 0 2 1 --- FC104 2 1
40269 010C High Speed CT Primary 5 1000 1 A F1 5 1
40270 010D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40275 0112 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
Words
18 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 23

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
VOLTAGE SENSING
40276 0113 3 Phase Voltage Connection 0 1 1 --- FC106 0 1
40277 0114 Aux VT Connection 0 8 1 --- FC176 0 1
40278 0115 Aux VT Primary 110 690 1 V F1 415 1
40279 0116 Aux VT Secondary 110 300 1 V F1 110 1
40280 0117 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40281 0118 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40282 0119 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40283 011A Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
MOTOR DATA SETUP
40284 011B Supply Frequency 0 1 1 Hz FC107 0 1
40285 011C Motor Name 0 10 0 --- F22 3 10
40295 0126 Starter Type 0 7 1 --- FC139 0 1
40296 0127 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40297 0128 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40298 0129 Motor FLA 5 10001 1 A F2* 10001 1
40299 012A High Speed FLA 5 10001 1 A F2* 10001 1
40300 012B Motor Nameplate Voltage 100 690 1 V F1 690 1
40301 012C Change Over Current 10 51 1 x FLA F2* 15 1
40302 012D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40303 012E Transfer Time 0 125 1 s F1 1 1
40304 012F High Speed Start Block 0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
40305 0130 Ramp Up Time 0 125 1 s F1 1 1
40306 0131 Ramp Down Time 0 125 1 s F1 1 1
40307 0132 Pre-contactor Time 0 60 1 s F1 0 1
40308 0133 Motor Rating 3 11001 1 kW F2* 11001 1
40309 0134 High Speed Motor Rating 3 11001 1 kW F2* 11001 1
40310 0135 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40316 013B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
PROCESS INTERLOCK
40317 013C IL Ignore In Test 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40318 013D IL A Name 0 10 1 --- F22 4 10
40328 0147 IL A Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40329 0148 IL A Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40330 0149 IL A Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40331 014A IL A Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40332 014B IL A Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40333 014C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40337 0150 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40338 0151 IL B Name 0 10 1 --- F22 5 10
40348 015B IL B Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40349 015C IL B Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40350 015D IL B Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40351 015E IL B Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 19
Page 24

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
40352 015F IL B Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40353 0160 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40357 0164 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40358 0165 IL C Name 0 10 1 --- F22 6 10
40368 016F IL C Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40369 0170 IL C Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40370 0171 IL C Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40371 0172 IL C Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40372 0173 IL C Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40373 0174 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40377 0178 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40378 0179 IL D Name 0 10 1 --- F22 7 10
40388 0183 IL D Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40389 0184 IL D Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40390 0185 IL D Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40391 0186 IL D Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40392 0187 IL D Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40393 0188 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40397 018C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40398 018D IL E Name 0 10 1 --- F22 8 10
40408 0197 IL E Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40409 0198 IL E Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40410 0199 IL E Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40411 019A IL E Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40412 019B IL E Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40413 019C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40417 01A0 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40418 01A1 IL F Name 0 10 1 --- F22 9 10
40428 01AB IL F Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40429 01AC IL F Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40430 01AD IL F Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40431 01AE IL F Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40432 01AF IL F Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40433 01B0 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40437 01B4 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40438 01B5 IL G Name 0 10 1 --- F22 10 10
40448 01BF IL G Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40449 01C0 IL G Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40450 01C1 IL G Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40451 01C2 IL G Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40452 01C3 IL G Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
Words
20 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 25

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
40453 01C4 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40457 01C8 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40458 01C9 IL H Name 0 10 1 --- F22 11 10
40468 01D3 IL H Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40469 01D4 IL H Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40470 01D5 IL H Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40471 01D6 IL H Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40472 01D7 IL H Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40473 01D8 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40477 01DC Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40478 01DD IL I Name 0 10 1 --- F22 12 10
40488 01E7 IL I Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40489 01E8 IL I Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40490 01E9 IL I Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40491 01EA IL I Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40492 01EB IL I Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40493 01EC Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40497 01F0 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40498 01F1 IL J Name 0 10 1 --- F22 13 10
40508 01FB IL J Function 0 3 1 --- FC140 0 1
40509 01FC IL J Inst Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40510 01FD IL J Startup Override 0 3600 1 s F1 0 1
40511 01FE IL J Running Override 0 3601 1 s F1* 0 1
40512 01FF IL J Healthy State 0 1 1 --- FC116 1 1
40513 0200 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40514 0201 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40515 0202 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40516 0203 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
COMMUNICATION SETUP
40517 0204 Comms OK Evaluation 0 64 1 --- FC131 1 1
40518 0205 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40519 0206 Comm Failure Trip 5 30 5 s F1* 30 1
40520 0207 Comm Failure Alarm 5 30 5 s F1* 30 1
OPEN CONTROL CIRCUIT
40521 0208 Open Ctrl Circuit Trip 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40522 0209 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40523 020A Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
USER MAP ADDRESSES
40524 020B User Map Address 1 30001 43763 1 --- F1 30001 1
40525 020C User Map Address 2 30001 43763 1 --- F1 30001 1
40526 020D User Map Address 3 30001 43763 1 --- F1 30001 1
40527 020E User Map Address 4 30001 43763 1 --- F1 30001 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 21
Page 26

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
40645 0284 User Map Address 122 30001 43763 1 --- F1 30001 1
40646 0285 User Map Address 123 30001 43763 1 --- F1 30001 1
40647 0286 User Map Address 124 30001 43763 1 --- F1 30001 1
40648 0287 User Map Address 125 30001 43763 1 --- F1 30001 1
40649 0288 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40658 0291 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
EVENT RECORDER
40659 0292 Event Recorder Function 0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
40660 0293 Recording of Trip Events 0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
40661 0294 Recording of Alarm Events 0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
40662 0295 Recording of Control Events 0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
40663 0296 Recording of Logic Input
Events
40664 0297 Recording of Level Events 0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
40665 0298 Recording of Dropout Events 0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
40666 0299 Recording of Set Time/Date
Events
40667 029A Event Record Selector 1 65535 1 --- F1 1 1
40668 029B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40700 02BB Reserved 1
RESET SETUP
40701 02BC Reset Lockout Using Reset Key 0 1 0 --- FC126 0 1
THERMAL MODEL SETUP
40702 02BD Overload Pickup Level 101 125 1 x FLA F3 101 1
40703 02BE Unbalance K Factor 0 19 1 --- F1 0 1
40704 02BF Cool Time Constant Running 1 1000 1 min F1 15 1
40705 02C0 Cool Time Constant Stopped 1 1000 1 min F1 30 1
40706 02C1 Hot/Cold Safe Stall Ratio 1 100 1 % F1 75 1
40707 02C2 Thermal Capacity Alarm Level 10 101 1 % F1* 101 1
40708 02C3 Standard Overload Curve 1 15 1 --- F1 4 1
40709 02C4 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40710 02C5 RTD Bias - Minimum T 0 251 1 °C F1* 251 1
40711 02C6 RTD Bias - Center T 0 251 1 °C F1* 251 1
40712 02C7 RTD Bias - Maximum T 0 251 1 °C F1* 251 1
40713 02C8 Minimize Reset Time 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40714 02C9 Overload Reset Mode 0 1 1 --- FC160 1 1
40715 02CA Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40716 02CB Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40717 02CC Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40718 02CD Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
MECHANICAL JAM
40719 02CE Mechanical Jam Level 101 451 1 x FLA F3* 451 1
40720 02CF Mechanical Jam Delay 1 300 1 s F2 1 1
40721 02D0 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
Words
22 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 27

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
40728 02D7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
RTD OPEN/SHORT CIRCUIT (REQUIRED=IO_G)
40729 02D8 RTD Open/Short Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40730 02D9 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40734 02DD Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
RTD #1 (REQUIRED=IO_G)
40735 02DE RTD 1 Application 0 4 1 --- FC121 0 1
40736 02DF RTD 1 Name 0 10 1 --- F22 14 10
40746 02E9 RTD 1 Alarm Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
40747 02EA RTD 1 Trip Voting 0 6 1 --- FC122 0 1
40748 02EB RTD 1 Trip Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
RTD #2 (REQUIRED=IO_G)
40749 02EC RTD 2 Application 0 4 1 --- FC121 0 1
40750 02ED RTD 2 Name 0 10 1 --- F22 15 10
40760 02F7 RTD 2 Alarm Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
40761 02F8 RTD 2 Trip Voting 0 6 1 --- FC122 0 1
40762 02F9 RTD 2 Trip Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
RTD #3 (REQUIRED=IO_G)
40763 02FA RTD 3 Application 0 4 1 --- FC121 0 1
40764 02FB RTD 3 Name 0 10 1 --- F22 16 10
40774 0305 RTD 3 Alarm Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
40775 0306 RTD 3 Trip Voting 0 6 1 --- FC122 0 1
40776 0307 RTD 3 Trip Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
RTD #4 (REQUIRED=IO_G)
40777 0308 RTD 4 Application 0 4 1 --- FC121 0 1
40778 0309 RTD 4 Name 0 10 1 --- F22 17 10
40788 0313 RTD 4 Alarm Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
40789 0314 RTD 4 Trip Voting 0 6 1 --- FC122 0 1
40790 0315 RTD 4 Trip Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
RTD #5 (REQUIRED=IO_G)
40791 0316 RTD 5 Application 0 4 1 --- FC121 0 1
40792 0317 RTD 5 Name 0 10 1 --- F22 18 10
40802 0321 RTD 5 Alarm Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
40803 0322 RTD 5 Trip Voting 0 6 1 --- FC122 0 1
40804 0323 RTD 5 Trip Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
RTD #6 (REQUIRED=IO_G)
40805 0324 RTD 6 Application 0 4 1 --- FC121 0 1
40806 0325 RTD 6 Name 0 10 1 --- F22 19 10
40816 032F RTD 6 Alarm Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
40817 0330 RTD 6 Trip Voting 0 6 1 --- FC122 0 1
40818 0331 RTD 6 Trip Temp -50 251 1 °C F4* 251 1
40819 0332 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40824 0337 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
THERMISTOR (CPU)
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 23
Page 28

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
40825 0338 Cold Resistance 1 300 1 k ohms F2 1 1
40826 0339 Hot Resistance 1 300 1 k ohms F2 50 1
40827 033A Thermistor Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40828 033B Thermistor Trip 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40829 033C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40833 0340 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
UNDERCURRENT (REQUIRED=IO_A)
40834 0341 Undercurrent Alarm Level 1 101 1 %FLA F1* 101 1
40835 0342 Undercurrent Alarm Delay 1 60 1 s F1 1 1
40836 0343 Undercurrent Trip Level 1 101 1 %FLA F1* 101 1
40837 0344 Undercurrent Trip Delay 1 60 1 s F1 1 1
40838 0345 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40839 0346 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40840 0347 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40841 0348 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
UNDERPOWER (IO_A + IO_C) OR (IO_A + IO_B)
40842 0349 Underpower Alarm Level 1 101 1 %MNR F1* 101 1
40843 034A Underpower Alarm Delay 1 60 1 s F1 1 1
40844 034B Underpower Trip Level 1 101 1 %MNR F1* 101 1
40845 034C Underpower Trip Delay 1 60 1 s F1 1 1
40846 034D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40850 0351 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
ACCELERATION
40851 0352 Acceleration Alarm Timer 5 2501 1 s F2* 2501 1
40852 0353 Acceleration Trip Timer 5 2501 1 s F2* 2501 1
40853 0354 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40854 0355 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40855 0356 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40856 0357 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
CURRENT UNBALANCE (REQUIRED=IO_A)
40857 0358 Current Unbalance Alarm Level 4 41 1 % F1* 15 1
40858 0359 Current Unbalance Alarm
Delay
40859 035A Current Unbalance Trip Level 4 41 1 % F1* 30 1
40860 035B Current Unbalance Trip Delay 1 60 1 s F1 1 1
40861 035C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40862 035D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40863 035E Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40864 035F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
GROUND FAULT
40865 0360 Ground Alarm Level 10 101 1 %FLA F1* 101 1
40866 0361 CBCT Ground Alarm Level 5 151 1 A F2* 151 1
40867 0362 Ground Alarm Delay On Start 0 60 1 s F1 10 1
40868 0363 Ground Trip Level 10 101 1 %FLA F1* 101 1
160 1s F11 1
Words
24 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 29

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
40869 0364 CBCT Ground Trip Level 5 151 1 A F2* 151 1
40870 0365 Ground Trip Delay On Start 0 100 1 s F2 0 1
40871 0366 Ground Alarm Delay On Run 0 60 1 s F1 10 1
40872 0367 Ground Trip Delay On Run 0 50 1 s F2 0 1
40873 0368 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40874 0369 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
LOAD INCREASE
40875 036A Load Increase Alarm Level 50 151 1 %FLA F1* 151 1
40876 036B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40877 036C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40878 036D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
PHASE UNDERVOLTAGE (REQUIRED=IO_B)
40879 036E Undervoltage Alarm Level 60 100 1 %MNV F1* 100 1
40880 036F Undervoltage Alarm Delay 1 60 1 s F1 30 1
40881 0370 Undervoltage Trip Level 60 100 1 %MNV F1* 100 1
40882 0371 Undervoltage Trip Delay 1 60 1 s F1 30 1
40883 0372 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
40887 0376 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
AUXILIARY UNDERVOLTAGE PROTECTION (REQUIRED=IO_C)
40888 0377 Aux U/V Alarm 60 91 1 %NCV F1* 91 1
40889 0378 Aux U/V Alarm Delay 1 60 1 s F1 5 1
40890 0379 Aux UV Trip 60 91 1 %NCV F1* 91 1
40891 037A Aux UV Trip Delay 1 60 1 s F1 5 1
40892 037B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40893 037C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40894 037D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
PHASE OVERVOLTAGE (REQUIRED=IO_B)
40895 037E Overvoltage Alarm Level 101 121 1 %MNV F1* 121 1
40896 037F Overvoltage Alarm Delay 1 60 1 s F1 30 1
40897 0380 Overvoltage Trip Level 101 121 1 %MNV F1* 121 1
40898 0381 Overvoltage Trip Delay 1 60 1 s F1 30 1
40899 0382 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40900 0383 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40901 0384 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40902 0385 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
PHASE REVERSAL (REQUIRED=IO_B)
40903 0386 Voltage Phase Reversal 0 2 1 --- FC140 1 1
40904 0387 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40905 0388 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40906 0389 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40907 038A Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
VT FUSE FAIL (REQUIRED=IO_B)
40908 038B VT Fuse Fail 0 2 1 --- FC140 0 1
40909 038C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40910 038D Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 25
Page 30
RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
40911 038E Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
MAINTENANCE
40912 038F Drive Greasing Interval 100 50100 100 hrs F1* 50100 1
40913 0390 Contactor Inspection Interval 100 65000 100 ops F1* 65000 1
40914 0391 Max Motor Stopped Time 10 10010 10 hrs F1* 10010 1
40915 0392 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40916 0393 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
START INHIBIT
40917 0394 Start Inhibit Margin 0 11 1 % F1* 11 1
40918 0395 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40919 0396 Starts/Hour Limit 1 6 1 --- F1* 6 1
40920 0397 Time Between Starts 1 3601 1 s F1* 3601 1
40921 0398 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
CHANGE MODE
40922 0399 Change Mode on Comm Alarm 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40923 039A Change Mode when running 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
40924 039B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
40925 039C Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
RESTART BLOCK
40926 039D Restart Block Time 1 50001 1 s F1* 50001 1
40927 039E Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41039 040E Reserved 1
CALIBRATION
41040 040F Calibration Date 0 203360302 1 --- F18 0 2
41042 0411 Calibration Time 0 389757795 1 --- F19 0 2
41044 0413 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41105 0450 Reserved 1
SECURITY
41106 0451 Passcode Level 1 11111 55556 1 --- F1* 11111 1
41107 0452 Passcode Level 2 11111 55556 1 --- F1* 22222 1
41108 0453 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41109 0454 Access Switch Level 1 3 1 --- F1 1 1
41110 0455 Comms Security 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
41111 0456 MCC Setpoint Access 0 1 1 --- FC126 1 1
41112 0457 Passcode Entry 0 55555 1 --- F1 0 1
41113 0458 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41114 0459 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41115 045A Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41116 045B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
FLEXLOGIC TIMERS
41117 045C Timer 1 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41118 045D Timer 1 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41119 045E Timer 1 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41120 045F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
Words
26 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 31

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41124 0463 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41125 0464 Timer 2 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41126 0465 Timer 2 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41127 0466 Timer 2 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41128 0467 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41132 046B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41133 046C Timer 3 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41134 046D Timer 3 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41135 046E Timer 3 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41136 046F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41140 0473 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41141 0474 Timer 4 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41142 0475 Timer 4 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41143 0476 Timer 4 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41144 0477 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41148 047B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41149 047C Timer 5 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41150 047D Timer 5 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41151 047E Timer 5 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41152 047F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41156 0483 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41157 0484 Timer 6 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41158 0485 Timer 6 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41159 0486 Timer 6 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41160 0487 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41164 048B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41165 048C Timer 7 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41166 048D Timer 7 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41167 048E Timer 7 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41168 048F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41172 0493 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41173 0494 Timer 8 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41174 0495 Timer 8 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41175 0496 Timer 8 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41176 0497 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41180 049B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41181 049C Timer 9 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41182 049D Timer 9 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 27
Page 32

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
41183 049E Timer 9 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41184 049F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41188 04A3 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41189 04A4 Timer 10 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41190 04A5 Timer 10 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41191 04A6 Timer 10 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41192 04A7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41196 04AB Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41197 04AC Timer 11 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41198 04AD T imer 11 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41199 04AE T imer 11 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41200 04AF Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41204 04B3 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41205 04B4 Timer 12 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41206 04B5 Timer 12 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41207 04B6 Timer 12 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41208 04B7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41212 04BB Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41213 04BC Timer 13 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41214 04BD T imer 13 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41215 04BE T imer 13 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41216 04BF Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41220 04C3 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41221 04C4 Timer 14 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41222 04C5 Timer 14 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41223 04C6 Timer 14 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41224 04C7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41228 04CB Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41229 04CC Timer 15 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41230 04CD T imer 15 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41231 04CE T imer 15 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41232 04CF Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41236 04D3 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41237 04D4 Timer 16 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41238 04D5 Timer 16 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41239 04D6 Timer 16 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41240 04D7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41244 04DB Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
Words
28 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 33

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
41245 04DC T imer 17 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41246 04DD Timer 17 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41247 04DE Timer 17 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41248 04DF Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41252 04E3 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41253 04E4 Timer 18 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41254 04E5 Timer 18 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41255 04E6 Timer 18 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41256 04E7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41260 04EB Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41261 04EC T imer 19 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41262 04ED Timer 19 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41263 04EE Timer 19 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41264 04EF Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41268 04F3 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41269 04F4 Timer 20 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41270 04F5 Timer 20 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41271 04F6 Timer 20 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41272 04F7 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41276 04FB Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41277 04FC Timer 21 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41278 04FD Timer 21 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41279 04FE T imer 21 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41280 04FF Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41284 0503 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41285 0504 Timer 22 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41286 0505 Timer 22 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41287 0506 Timer 22 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41288 0507 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41292 050B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41293 050C Timer 23 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41294 050D Timer 23 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41295 050E Timer 23 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41296 050F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41300 0513 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41301 0514 Timer 24 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41302 0515 Timer 24 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41303 0516 Timer 24 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41304 0517 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 29
Page 34

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41308 051B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41309 051C Timer 25 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41310 051D Timer 25 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41311 051E Timer 25 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41312 051F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41316 0523 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41317 0524 Timer 26 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41318 0525 Timer 26 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41319 0526 Timer 26 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41320 0527 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41324 052B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41325 052C Timer 27 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41326 052D Timer 27 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41327 052E Timer 27 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41328 052F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41332 0533 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41333 0534 Timer 28 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41334 0535 Timer 28 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41335 0536 Timer 28 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41336 0537 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41340 053B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41341 053C Timer 29 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41342 053D Timer 29 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41343 053E Timer 29 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41344 053F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41348 0543 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41349 0544 Timer 30 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41350 0545 Timer 30 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41351 0546 Timer 30 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41352 0547 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41356 054B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41357 054C Timer 31 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41358 054D Timer 31 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41359 054E Timer 31 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41360 054F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41364 0553 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41365 0554 Timer 32 Type 0 2 1 --- FC141 0 1
41366 0555 Timer 32 Pickup Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
Words
30 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 35

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
41367 0556 Timer 32 Dropout Delay 0 1000 1 --- F1 1 1
41368 0557 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41372 055B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
CONTACT INPUT ASSIGNMENT
41373 055C U/V Restart Inhibit 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41374 055D Lockout Reset 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41375 055E Access Switch 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41376 055F Field Permissive 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41377 0560 Comms Permissive 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41378 0561 Forward Limit 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41379 0562 Reverse Limit 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41380 0563 Remote Reset 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41381 0564 MCC Permissive 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41382 0565 Hard Wired Start A 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41383 0566 Hard Wired Start B 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41384 0567 Hard Wired Stop 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41385 0568 Hard Wired Permissive 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41386 0569 Field Start A 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41387 056A Field Start B 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41388 056B Field Stop 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41389 056C Contactor Status A 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41390 056D Contactor Status B 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41391 056E Auto/Manual Switch 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41392 056F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41393 0570 Test Switch 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41394 0571 Process Interlock A 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41395 0572 Process Interlock B 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41396 0573 Process Interlock C 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41397 0574 Process Interlock D 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41398 0575 Process Interlock E 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41399 0576 Process Interlock F 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41400 0577 Process Interlock G 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41401 0578 Process Interlock H 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41402 0579 Process Interlock I 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41403 057A Process Interlock J 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41404 057B Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41470 05BD Reserved 1
SELF TEST
41471 05BE Self Test Action 0 1 1 --- FC111 0 1
41472 05BF Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41473 05C0 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41474 05C1 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41475 05C2 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
LEDs
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 31
Page 36

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
41476 05C3 Orange LED Intensity 0 15 1 --- FC147 0 1
41477 05C4 Green LED Intensity 0 15 1 --- FC147 0 1
41478 05C5 Red LED Intensity 0 15 1 --- FC147 0 1
41479 05C6 LED colour invert 0 1 1 --- FC177 0 1
41480 05C7 Tripped LED Flasher 0 1 1 --- FC103 0 1
41481 05C8 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41494 05D5 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
41495 05D6 USER1 LED Assignment 0 57344 1 --- FC142 0 1
41496 05D7 USER1 LED Colour 0 3 1 --- FC157 1 1
41497 05D8 USER2 LED Assignment 0 57344 1 --- FC142 0 1
41498 05D9 USER2 LED Colour 0 3 1 --- FC157 1 1
41499 05DA USER3 LED Assignment 0 57344 1 --- FC142 0 1
41500 05DB USER3 LED Colour 0 3 1 --- FC157 1 1
41501 05DC Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41514 05E9 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
CONTACT OUTPUTS
41515 05EA Contact Output 1 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41516 05EB Contact Output 2 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41517 05EC Contact Output 3 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41518 05ED Contact Output 4 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41543 0606 Contact Output 29 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41544 0607 Contact Output 30 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41545 0608 Contact Output 31 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41546 0609 Contact Output 32 0 57344 0 --- FC142 0 1
41547 060A Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41552 060F Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
UNDERVOLTAGE RESTART
41553 0610 Under Voltage Restart 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
41554 0611 UVR Short Dip Time 100 510 10 ms F1* 200 1
41555 0612 UVR Med Dip Time 1 100 1 s F2 20 1
41556 0613 UVR Long Dip Time 5 605 5 min F2* 605 1
41557 0614 UVR Med Dip Delay 2 600 2 s F2 20 1
41558 0615 UVR Long Dip Delay 2 12000 2 s F2 100 1
41559 0616 UVR Dropout Level 60 100 1 % F1 65 1
41560 0617 UVR Pickup Level 60 100 1 % F1 90 1
41561 0618 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41571 0622 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
AUTO / MANUAL CONTROL
41572 0623 Comms Start Ctrl 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
41573 0624 Comms Stop Mode 0 1 1 --- FC172 0 1
41574 0625 Hard Wired Start Ctrl 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
Words
32 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 37

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Modbus Hex Description Min Max Step Units Format Default Size in
41575 0626 Hard Wired Stop Mode 0 1 1 --- FC172 0 1
41576 0627 Hard Wired Stop Actn 0 1 1 --- FC174 0 1
41577 0628 Hard Wired 2W/3W 0 1 1 --- FC173 1 1
41578 0629 Field Start Ctrl 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
41579 062A Field Stop Mode 0 1 1 --- FC172 0 1
41580 062B Field Stop Action 0 1 1 --- FC174 0 1
41581 062C Field 2W/3W 0 1 1 --- FC173 1 1
41582 062D MCC Start Ctrl 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
41583 062E MCC Stop Mode 0 1 1 --- FC172 0 1
41584 062F MCC Stop Action 0 1 1 --- FC174 0 1
41585 0630 Test Auto Mode 0 2 1 --- FC175 1 1
41586 0631 Test Manual Mode 0 2 1 --- FC175 0 1
41587 0632 External Stop Action 0 1 1 --- FC174 0 1
41588 0633 Auto/Manual Key 0 1 1 --- FC126 0 1
41589 0634 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 7
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
41696 069F Reserved 1
FLEXLOGIC EQUATION
41697 06A0 Flex Equation 0 65535 1 --- FC142 1024 512
42209 08A0 Reserved --- --- --- --- --- --- 1
▼▼▼ ▼▼ ▼▼▼▼ ▼
43763 0EB2 Reserved 2
1.Maximum setpoint values represent OFF.
Words
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 33
Page 38

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Format codes
Code Type Definition
F1 16 bits UNSIGNED VALUE
Example: 1234 stored as 1234
F2 16 bits UNSIGNED VALUE, 1 DECIMAL PLACE
Example: 123.4 stored as 1234
F3 16 bits UNSIGNED VALUE, 2 DECIMAL PLACES
Example: 12.34 stored as 1234
F4 16 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT SIGNED VALUE
Example: -1234 stored as -1234 i.e. 64302
F6 16 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT SIGNED VALUE, 2 DECIMAL PLACES
Example: -12.34 stored as -1234 i.e. 64302
F9 32 bits UNSIGNED LONG VALUE
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long Value
Example: 123456 stored as 123456
i.e. 1st word: 0001 hex, 2nd word: E240 hex
F10 32 bits UNSIGNED LONG VALUE, 1 DECIMAL PLACE
1st 16 bits UNSIGNED LONG VALUE, 1 DECIMAL PLACE
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long Value
Example: 12345.6 stored as 123456
i.e. 1st word: 0001 hex, 2nd word: E240 hex
F13 32 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT SIGNED LONG VALUE, 1 DECIMAL PLACE
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long Value
Example: -12345.6 stored as -123456
i.e. 1st word: FFFE hex, 2nd word: 1DC0 hex
F15 16 bits HARDWARE REVISION
0Prototype
1A
2B
3C
4D
5E
6F
7G
8H
9I
10 J
11 K
12 L
13 M
14 N
15 O
16 P
17 Q
34 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 39

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Code Type Definition
18 R
19 S
20 T
21 U
22 V
23 W
24 X
25 Y
26 Z
F17 32 bits UNSIGNED LONG VALUE, 3 DECIMAL PLACES
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long Value
Example: 123456 stored as 123456
i.e. 1st word: 0001 hex, 2nd word: E240 hex
F18 32 bits DATE MM/DD/YYYY
1st byte Month 1 to 12
2nd byte Day 1 to 31
3rd and 4th byte Year 1995 to 2094
Example: Feb 20, 1995 stored as 34867142
i.e. 1st word: 0214, 2nd word 07C6
F19 32 bits TIME HH:MM:SS:hh
1st byte Hours 0 to 23
2nd byte Minutes 0 to 59
3rd byte Seconds 0 to 59
4th byte Hundredths of seconds 0 to 99
Example: 2:05pm stored as 235208704
i.e. 1st word: 0E05, 2nd word 0000
F20 32 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT SIGNED LONG VALUE
1st 16 bits High Order Word of Long Value
2nd 16 bits Low Order Word of Long Value
Note: -1 means “Never”
F21 16 bits 2’s COMPLEMENT SIGNED VALUE, 2 DECIMAL PLACES
< 0 Leading Power Factor - Negative
> 0 Lagging Power Factor - Positive
Example: Power Factor of 0.87 lag is used as 87
i.e. 0057
F22 16 bits TWO 8-BIT CHARACTERS PACKED INTO 16-BIT UNSIGNED
MSB First Character
LSB Second Character
Example: String ‘AB’ stored as 4142 hex
FC101 16 bits RS 485 Baud Rate
0 9600 baud
1 19200 baud
2 38400 baud
3 57600 baud
4 115200 baud
Power Factor
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 35
Page 40

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Code Type Definition
FC103 16 bits Off / On or No / Yes Selection
0OFF / NO
1 ON / YES
FC104 16 bits Ground CT Type
0None
1Residual
2 CBCT 2000:1
FC105 16 bits Differential CT Type
0None
1 1 A Secondary
2 5 A Secondary
3 Direct Connect
FC106 16 bits Voltage Transformer Connection Type
0Wye
1Delta
FC107 16 bits Supply Frequency
060
150
FC109 16 bits Flex Logic Status
0OK
1 Unknown Token
2 Too Many Latches
3 Too Many Timers
4 Too Many + OneShots
5 Too Many - OneShots
6 Too Many Duel OneShots
7 Stack Overflow
8Stack Underflow
9 Program Too Long
FC111 16 bits Trip Relays
0Trip
1Alarm
FC112 16 bits Communication Status
0Error
1OK
FC116 16 bits Switch Type
0Open
1Closed
FC121 16 bits RTD Application
0None
1Stator
2Bearing
3Ambient
4Other
FC122 16 bits RTD Voting Selection
0OFF
1RTD #1
36 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 41

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Code Type Definition
2RTD #2
3RTD #3
4RTD #4
5RTD #5
6RTD #6
FC126 16 bits Disabled / Enabled Selection
0Disabled
1 Enabled
FC128 16 bits Command Status
0Manual
1Auto
2 Manual Inhibit
3 Auto/ Manual
4Hardwired Auto
5None
FC129 16 bits Quick Status Status
Bit 0 Alarm
Bit 1 Trip
Bit 2 Self Test Fault
Bit 3 Auto
Bit 4 Contactor A
Bit 5 Contactor B
Bit 6 Contact Output 3
Bit 7 Drive Available
FC130 16 bits LED Flash
Bit 0 Running
Bit 1 Stopped
Bit 2 Tripped
Bit 3 Alarm
Bit 4 Comms OK
Bit 5 Auto
Bit 6 Manual
Bit 7 USER1
Bit 8 USER2
Bit 9 USER3
Bit 10 50%
Bit 11 80%
Bit 12 100%
FC131 16 bits Comm Fail Mode
1 Serial
2 Serial & Ethernet
4 Serial & FieldBus
8Ethernet
16 FieldBus
32 Ethernet & Fieldbus
64 All
FC134 16 bits Cause of Event
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 37
Page 42
RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Code Type Definition
0No Event/Trip To Date
1 Control Power Lost
2 Control Power Applied
3 Date or Time Set
4Reset
5Lockout Reset
0x8002 Any Trip
0x8042 Thermal O/L Trip
0x8082 Ground Fault Trip
0x80C2 Acceleration Trip
0x8102 Phase Reversal Trip
0x8142 UnderPower Trip
0x8182 UnderVoltage Trip
0x81C2 OverVoltage Trip
0x8202 Mechanical Jam Trip
0x8242 UnderCurrent Trip
0x8282 Unbalance Trip
0x82C2 RTD 1 Trip
0x8302 RTD 2 Trip
0x8342 RTD 3 Trip
0x8382 RTD 4 Trip
0x83C2 RTD 5 Trip
0x8402 RTD 6 Trip
0x8442 Comm Fail Trip
0x8482 Relay Not Configured
0x84C2 Process ILock A Trip
0x8502 Process ILock B Trip
0x8542 Process ILock C Trip
0x8582 Process ILock D Trip
0x85C2 Process ILock E Trip
0x8602 Process ILock F Trip
0x8642 Process ILock G Trip
0x8682 Process ILock H Trip
0x86C2 Process ILock I Trip
0x8702 Process ILock J Trip
0x8742 Hard Wired Trip
0x8782 Field Trip
0x87C2 MCC Trip
0x8802 Aux U/V Trip
0x8842 Emergency Stop
0x8882 Fuse Fail Trip
0x88C2 Open Control Circuit Trip
0x8902 Thermistor Trip
0x89C2 Self Test Trip
0xA002 Any Alarm
0xA042 Thermal Level Alarm
0xA082 Ground Fault Alarm
38 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 43

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Code Type Definition
0xA0C2 Acceleration Alarm
0xA102 Phase Reversal Alarm
0xA142 UnderPower Alarm
0xA182 UnderVoltage Alarm
0xA1C2 OverVoltage Alarm
0xA242 UnderCurrent Alarm
0xA282 Unbalance Alarm
0xA2C2 RTD 1 Alarm
0xA302 RTD 2 Alarm
0xA342 RTD 3 Alarm
0xA382 RTD 4 Alarm
0xA3C2 RTD 5 Alarm
0xA402 RTD 6 Alarm
0xA442 RTD Open/Short Alarm
0xA482 RTD Open/Short Alarm
0xA4C2 Process ILock A Alarm
0xA502 Process ILock B Alarm
0xA542 Process ILock C Alarm
0xA582 Process ILock D Alarm
0xA5C2 Process ILock E Alarm
0xA602 Process ILock F Alarm
0xA642 Process ILock G Alarm
0xA682 Process ILock H Alarm
0xA6C2 Process ILock I Alarm
0xA702 Process ILock J Alarm
0xA742 Drive Failed to Start
0xA782 Inverter Failed
0xA7C2 Drive Stop Failed
0xA802 Aux U/V Alarm
0xA842 External Stop Alarm
0xA882 Fuse Fail Alarm
0xA8C2 Open Ctrl Cct Alarm
0xA902 Thermistor Alarm
0xA982 External Start A Alarm
0xA9C2 External Start B Alarm
0xAA02 Welded Contactor
0xAB02 Load Increase Alarm
0XAB42 Drive Greasing Alarm
0xAB82 Contactor Inspect Alarm
0xABC2 Max Stopped Alarm
0xAC82 Comm Fail Alarm
0xC002 Any Stop
0xC042 Thermal Inhibit
0xC082 AutoMode
0xC0C2 Manual Mode
0xC102 Auto/Manual Mode Input
0xC142 Restart Inhibit
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 39
Page 44

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Code Type Definition
0xC182 Contactor A
0xC1C2 Contactor B
0xC202 Forward Limit
0xC242 Reverse Limit
0xC282 Starts/Hr Inhibit
0xC2C2 Time Between Inhibit
0xC3C2 Comms Ctrl Active
0xC402 Hard Wired Ctrl Active
0xC442 Field Ctrl Active
0xC482 MCC Ctrl Active
0xC4C2 Process ILock A Stop
0xC502 Process ILock B Stop
0xC542 Process ILock C Stop
0xC582 Process ILock D Stop
0xC5C2 Process ILock E Stop
0xC602 Process ILock F Stop
0xC642 Process ILock G Stop
0xC682 Process ILock H Stop
0xC6C2 Process ILock I Stop
0xC702 Process ILock J Stop
0xC742 HW Stop
0xC782 Field Stop
0xC7C2 MCC Stop
0xC802 Access Switch Closed
0xC842 Test Switch Closed
0xC882 Hard Wired Start A
0xC8C2 Hard Wired Start B
0xC902 Start A
0xC942 Start B
0xC982 Field Start A
0xC9C2 Field Start B
0xCA02 Contactor A Status
0xCA42 Contactor B Status
0xCA82 Remote Reset Closed
0xCAC2 Lockout Reset Closed
0xCB02 UV Restart
0xCB42 Pre-Contactor
0xCB82 MCC Start A
0xCBC2 MCC Start B
0xCC02 Bypass Contact
0xCC42 Comm Start A
0xCC82 Comm Start B
0xCCC2 Comm Stop
0xCD02 Fuse Fail Inhibit
0xCD42 Phase Reversal Inhibit
0xCD82 Low Aux Voltage Inhibit
FC135 16 bits Motor Speed During Trip / Motor Speed During Event
40 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 45

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Code Type Definition
0 Low Speed
1 High Speed
FC136 16 bits Motor Speed During Trip / Motor Speed During Event
0None
1A
2B
FC139 16 bits Starter Type
0None
1 FV Nonreversing
2FV Reversing
3Two Speed
4Wye-Delta
5Inverter
6 Soft Starter
7 Custom Starter
FC140 16 bits Interlock Function
0Disabled
1Trip
2Alarm
3Stop
FC141 16 bits Timer Type
0 Millisecond
1 Second
2 Minute
FC142 16 bits FlexLogic Bit Field EEETTTTTTTSSSSSS S-Bits denotes the
0x0000 OFF
0x0001 ON
0x0040 Contact Inputs
0x0080 Virtual Inputs
0x00C0 Virtual Outputs
0x01C0 Remote Inputs
0x0380 Insert
0x0400 End
0x0440 NOT
0x0480 XOR
0x04C0 LATCH
0x0500 OR
0x0540 AND
0x0580 NOR
0x05C0 NAND
0x0600 TIMER
0x0640 ASSIGN
0x8000 Trip
0xA000 Alarm
element state or Operator specific data Number of inputs
T-Bits denote Flex logic Operands and Parameters or
when one of the E bits are set they denote specific details
for the Element Type E-Bits
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 41
Page 46

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Code Type Definition
0xC000 Control
FC143 16 bits Drive Status
0 Drive Unavailable
1 Available Auto
2 Available Manual
3 Available
4 Running
FC144 32 bits LED Status
Bit 0 Running Red
Bit 1 Running Green
Bit 2 Stopped Red
Bit 3 Stopped Green
Bit 4 Tripped Red
Bit 5 Tripped Green
Bit 6 Alarm Red
Bit 7 Alarm Green
Bit 8 Auto Red
Bit 9 Auto Green
Bit 10 Manual Red
Bit 11 Manual Green
Bit 12 Comms OK Red
Bit 13 Comms OK Green
Bit 14 USER1 Red
Bit 15 USER1 Green
Bit 16 USER2 Red
Bit 17 USER2 Green
Bit 18 USER3 Red
Bit 19 USER3 Green
Bit 20 50% Red
Bit 21 50% Green
Bit 22 80% Red
Bit 23 80% Green
Bit 24 100% Red
Bit 25 100% Green
FC145 16 bits Element Status 1
Bit 0 Level
Bit 1 Operated
Bit 2 Latched
Bit 3 Spare
FC147 16 bits LED Intensity
0Level 1
3Level 2
6Level 3
9Level 4
12 Level 5
15 Level 6
FC150 32 bits IP Address
42 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 47

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Code Type Definition
IP address, subnet mask or default gateway Each byte in this register represents one octet of an IP address
For example: 0x015EDA1F represents address 19421831
FC155 16 bits Profibus Baud Rate
0x0001 9600
0x0002 19200
0x0004 31250
0x0008 45450
0x0010 93750
0x0020 187500
0x0040 500000
0x0080 1500000
0x07E2 Auto Detect
FC156 16 bits DeviceNet Baud Rate
0 125 kbps
1 250 kbps
2 500 kbps
FC157 16 bits LED Colour
0None
1Red
2 Green
3Orange
FC160 16 bits Auto/Manual Mode
0Auto
1Manual
FC167 32 bits Contact/Virtual Input/Output Status
Bit 0 Input/Output 1
Bit 1 Input/Output 2
Bit 2 Input/Output 3
Bit 3 Input/Output 4
Bit 4 Input/Output 5
Bit 5 Input/Output 6
Bit 6 Input/Output 7
Bit 7 Input/Output 8
Bit 8 Input/Output 9
Bit 9 Input/Output 10
Bit 10 Input/Output 11
Bit 11 Input/Output 12
Bit 12 Input/Output 13
Bit 13 Input/Output 14
Bit 14 Input/Output 15
Bit 15 Input/Output 16
Bit 16 Input/Output 17
Bit 17 Input/Output 18
Bit 18 Input/Output 19
Bit 19 Input/Output 20
Bit 20 Input/Output 21
Bit 21 Input/Output 22
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 43
Page 48

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Code Type Definition
Bit 22 Input/Output 23
Bit 23 Input/Output 24
Bit 24 Input/Output 25
Bit 25 Input/Output 26
Bit 26 Input/Output 27
Bit 27 Input/Output 28
Bit 28 Input/Output 29
Bit 29 Input/Output 30
Bit 30 Input/Output 31
Bit 31 Input/Output 32
FC168 32 bits Contact/Virtual Input/Output Status
Bit 0 Input/Output 33
Bit 1 Input/Output 34
Bit 2 Input/Output 35
Bit 3 Input/Output 36
Bit 4 Input/Output 37
Bit 5 Input/Output 38
Bit 6 Input/Output 39
Bit 7 Input/Output 40
Bit 8 Input/Output 41
Bit 9 Input/Output 42
Bit 10 Input/Output 43
Bit 11 Input/Output 44
Bit 12 Input/Output 45
Bit 13 Input/Output 46
Bit 14 Input/Output 47
Bit 15 Input/Output 48
Bit 16 Input/Output 49
Bit 17 Input/Output 50
Bit 18 Input/Output 51
Bit 19 Input/Output 52
Bit 20 Input/Output 53
Bit 21 Input/Output 54
Bit 22 Input/Output 55
Bit 23 Input/Output 56
Bit 24 Input/Output 57
Bit 25 Input/Output 58
Bit 26 Input/Output 59
Bit 27 Input/Output 60
Bit 28 Input/Output 61
Bit 29 Input/Output 62
Bit 30 Input/Output 63
Bit 31 Input/Output 64
FC169 16 bits Month
0 Not Set
1 January
2February
44 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 49

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Code Type Definition
3March
4April
5May
6 June
7July
8 August
9 September
10 October
11 November
12 December
FC170 16 bits Count of Week
0 Not Set
11st
22nd
33rd
44th
5Last
FC171 16 bits Weekdays
0 Not Set
1SUN
2MON
3TUE
4WED
5THU
6FRI
7SAT
FC172 16 bits Auto/Manual Control Stop Mode
0 Always Enabled
1Follow Ctrl Mode
FC173 16 bits Wire Selection
02W
13W
FC174 16 bits Source Stop Action
0Stop
1Trip
FC175 16 bits Test Auto/Manual Mode
0ON
1OFF
2 Unaffected
FC176 16 bits Auxiliary VT Connection
0 Vab VT
1Vbc VT
2Vca VT
3Van VT
4Vbn VT
5Vcn VT
6Van Direct
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 45
Page 50

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Code Type Definition
7Vbn Direct
8 Vcn Direct
FC177 16 bits LED Color Invert
0 Green/Red
1Red/Green
FC178 16 bits Motor Status
Bit 0 Lockout
Bit 1 Non-Lockout Trip
Bit 2 UVR Pending
Bit 4 Running
Bit 5 Precontactor
Bit 6 Starting
Bit 8 Inhibit
Bit 9 Stopped
Bit 10 Self Test Fault
Bit 11 Alarm
Bit 12 Forward
Bit 13 Reverse
Bit 14 Low Speed
Bit 15 High Speed
FC179 32 bits Alarm Status 1
Bit 0 Any Alarm
Bit 1 Thermal Level Alarm
Bit 2 Ground Fault Alarm
Bit 3 Acceleration Alarm
Bit 4 Phase Reversal Alarm
Bit 5 UnderPower Alarm
Bit 6 UnderVoltage Alarm
Bit 7 OverVoltage Alarm
Bit 9 UnderCurrent Alarm
Bit 10 Unbalance Alarm
Bit 11 RTD 1 Alarm
Bit 12 RTD 2 Alarm
Bit 13 RTD 3 Alarm
Bit 14 RTD 4 Alarm
Bit 15 RTD 5 Alarm
Bit 16 RTD 6 Alarm
Bit 17 RTD Open/Short Alarm
Bit 18 RTD Open/Short Alarm
Bit 19 Process ILock A Alarm
Bit 20 Process ILock B Alarm
Bit 21 Process ILock C Alarm
Bit 22 Process ILock D Alarm
Bit 23 Process ILock E Alarm
Bit 24 Process ILock F Alarm
Bit 25 Process ILock G Alarm
Bit 26 Process ILock H Alarm
46 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 51

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Code Type Definition
Bit 27 Process ILock I Alarm
Bit 28 Process ILock J Alarm
Bit 29 Drive Failed to Start
Bit 30 Inverter Failed
Bit 31 Drive Stop Failed
FC180 32 bits Alarm Status 2
Bit 0 Aux U/V Alarm
Bit 1 External Stop Alarm
Bit 2 Fuse Fail Alarm
Bit 3 Open Ctrl Cct Alarm
Bit 4 Thermistor Alarm
Bit 6 External Start A Alarm
Bit 7 External Start B Alarm
Bit 8 Welded Contactor
Bit 12 Load Increase Alarm
Bit 13 Drive Greasing Alarm
Bit 14 Contactor Inspect Alarm
Bit 15 Max Stopped Alarm
Bit 18 Comm Fail Alarm
FC181 32 bits Alarm Status 3 (Reserved)
FC182 32 bits Alarm Status 4 (Reserved)
FC183 32 bits Trip Status 1
Bit 0 Any Trip
Bit 1 Thermal O/L Trip
Bit 2 Ground Fault Trip
Bit 3 Acceleration Trip
Bit 4 Phase Reversal Trip
Bit 5 UnderPower Trip
Bit 6 UnderVoltage Trip
Bit 7 OverVoltage Trip
Bit 8 Mechanical Jam Trip
Bit 9 UnderCurrent Trip
Bit 10 Unbalance Trip
Bit 11 RTD 1 Trip
Bit 12 RTD 2 Trip
Bit 13 RTD 3 Trip
Bit 14 RTD 4 Trip
Bit 15 RTD 5 Trip
Bit 16 RTD 6 Trip
Bit 17 Comm Fail Trip
Bit 18 Relay Not Configured
Bit 19 Process ILock A Trip
Bit 20 Process ILock B Trip
Bit 21 Process ILock C Trip
Bit 22 Process ILock D Trip
Bit 23 Process ILock E Trip
Bit 24 Process ILock F Trip
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 47
Page 52

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Code Type Definition
Bit 25 Process ILock G Trip
Bit 26 Process ILock H Trip
Bit 27 Process ILock I Trip
Bit 28 Process ILock J Trip
Bit 29 Hard Wired Trip
Bit 30 Field Trip
Bit 31 MCC Trip
FC184 32 bits Trip Status 2
Bit 0 Aux U/V Trip
Bit 1 Emergency Stop
Bit 2 Fuse Fail Trip
Bit 3 OpenControl Circuit
Bit 4 Thermistor Trip
FC185 32 bits Trip Status 3 (Reserved)
FC186 32 bits Trip Status 4 (Reserved)
FC187 32 bits Message Status 1
Bit 1 Transfer Timer
Bit 2 FLA Not Set
Bit 3 CT Type Not Set
Bit 4 Starter Type Not Set
Bit 5 No Control Source
Bit 6 Clock Not Set
Bit 7 FLA Too High
FC188 32 bits Message Status 2
Bit 1 IO Communication Failure
Bit 2 Metering Failure
Bit 3 Order Code Error
Bit 4 Clock Error
Bit 5 Calibration Error
Bit 6 EEPROM Error
Bit 7 IO Input Read Error
Bit 8 IO 3.3V Error
Bit 9 IO 5V Error
Bit 10 IO -5V Error
Bit 11 IO Input Overvoltage
Bit 12 IO Frequency Error
Bit 13 DPRAM Error
Bit 14 System Health Error
FC189 32 bits Message Status 3 (Reserved)
FC190 32 bits Message Status 4 (Reserved)
FC191 32 bits Ctrl Element Status 1
Bit 0 Any Stop
Bit 1 Thermal Inhibit
Bit 2 AutoMode
Bit 3 Manual Mode
Bit 4 AutoManualMode
Bit 5 Restart Inhibit
48 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 53

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
Code Type Definition
Bit 8 Forward Limit
Bit 9 Reverse Limit
Bit 10 Starts/Hr Inhibit
Bit 11 Time Between Inhibit
Bit 15 Comms Ctrl Active
Bit 16 Hard Wired Ctrl Active
Bit 17 Field Ctrl Active
Bit 18 MCC Ctrl Active
Bit 19 Process ILock A Stop
Bit 20 Process ILock B Stop
Bit 21 Process ILock C Stop
Bit 22 Process ILock D Stop
Bit 23 Process ILock E Stop
Bit 24 Process ILock F Stop
Bit 25 Process ILock G Stop
Bit 26 Process ILock H Stop
Bit 27 Process ILock I Stop
Bit 28 Process ILock J Stop
FC192 32 bits Ctrl Element Status 2
Bit 0 Access Switch
Bit 1 Test Switch
Bit 10 Remote Reset
Bit 11 Lockout Reset
Bit 13 Pre-Contactor
Bit 20 Fuse Fail Inhibit
Bit 21 Phase Reversal Inhibit
Bit 22 Low Aux Voltage Inhibit
FC193 32 bits Ctrl Status 3 (Reserved)
FC194 32 bits Ctrl Status 4 (Reserved)
FC212 16 bits LCD Test Paint Color
0None
1Red
2 Green
3Blue
Performing Commands Using Function Code 10H
Commands can be performed using function code 16 as well as function code 5. When
using FUNCTION CODE 16, the Command Function register must be written with a value of
5. The Command Operation register must be written with a valid command operation
number. The Command Data registers must be written with valid data; this is dependent
upon the command operation.
For example, consider a request for slave 17 to perform command operation 1 (RESET): The
master/slave packets have the following format:
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 49
Page 54

RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU) COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Table 9: Master/slave packet format for performing commands
MASTER TRANSMISSION BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message for slave
FUNCTION CODE 1 10 store multiple
DATA STARTING ADDRESS 2 00 80 setpoint address
NUMBER OF SETPOINTS 2 00 02 2 setpoints = 4
BYTE COUNT 1 04 4 bytes of data
DATA 1 2 00 05 data for address
DATA 2 2 00 01 data for address
CRC 2 7E CE CRC error code
SLAVE RESPONSE BYTES EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
SLAVE ADDRESS 1 11 message from
FUNCTION CODE 1 10 store multiple
DATA STARTING ADDRESS 2 00 80 setpoint address
NUMBER OF SETPOINTS 2 00 02 2 setpoints
CRC 2 42 B0 CRC error code
17
setpoints
00 80
bytes total
00 80
00 81
slave 17
setpoints
00 80
Using the User Definable Memory Map
The MM300 contains a User Definable area in the memory map. This area allows remapping of the addresses of any Actual Values or Setpoints registers. The User Definable
area has two sections:
1. A Register Index area (memory map addresses 020BH-0287H) that contains 125
Actual Values or Setpoints register addresses.
2. A Register area (memory map addresses 020BH-0287H) that contains the data at the
addresses in the Register Index.
Register data that is separated in the rest of the memory map may be re-mapped to
adjacent register addresses in the User Definable Registers area. This is accomplished by
writing to register addresses in the User Definable Register Index area. This allows for
improved throughput of data and can eliminate the need for multiple read command
sequences. The User Definable Register Index is stored as a setpoint and therefore it is
“remembered” even when the power is removed.
For example, if the values of MOTOR LOAD (register address 014FH; modbus address
30336) and DRIVE STATUS (register address 0135H; modbus address 30310) are required to
be read from a MM300, their addresses may be re-mapped as follows:
1. Write 30336 to address 020BH (40524) (User Definable Register Index 0000) using
function code 06 or 16.
2. Write 30310 to address 020CH (40525) (User Definable Register Index 0001) using
function code 06 or 16.
The MM300PC software can be used to write these locations to the User Definable Register
Index using the Setpoints > Modbus Memory Map > User Map screen.
50 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 55

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE RS485 INTERFACE (MODBUS RTU)
It is now possible to read these two data registers with one read, at addresses 020BH,
020CH. Address 020BH will contain MOTOR LOAD. Address 020CH will contain DRIVE
STATUS.
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 51
Page 56

ETHERNET INTERFACE COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Ethernet interface
The 10/100Base-T Ethernet interface is configured as a Modbus RTU slave. The Ethernet
port has the following characteristics.
• Configuration: setup using IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address.
• Supported Modbus function codes: 3, 4, 5, 6, and 16.
• Supports time/date synchronization via the Network Time Protocol (NTP).
• Ethernet port 502.
• Supports a maximum of 5 virtual connections.
The Ethernet interface has the same memory map layout as the serial Modbus RTU
interface.
Network Time Protocol is enabled if the NTP address is non-zero and the source is
detected.
Once connected to the source, the clock is updated every 30 seconds.
52 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 57

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE FIELDBUS INTERFACE
Fieldbus interface
The fieldbus interface is configurable as either Profibus DPV0 or DeviceNet. Both Fieldbus
interfaces support control and status – refer to the specific data map below for details.
Note that external power, 5 to 24 VDC, is required for this interface to operate. (Ensure that
switches 7 and 8 of the DIPswitch on the communication card, are ON.)
Profibus protocol (DP V0)
To enable the Profibus physical interface, ensure that switches 3 and 4 of the DIP switch on
the communications card (on the CPU module) are on. The external connections through
the Fieldbus interface are as follows.
Table 10: Fieldbus interface external connections (Profibus)
Pin Connection (external device)
V– Pin 5
L Pin 8, line A (negative TX/RX)
CCommon drain
H Pin 3, line B (positive TX/RX)
V+ Pin 6
Profibus Output Data
The Modbus status (MS) and network status (NS) LEDs indicate the status of the Fieldbus
interface.
Table 11: Profibus LED indications
LED Color Description
MS Green Processor OK
Off Processor FAIL
NS Green Communications to master OK
Red Communications to master FAIL
When used for Profibus, the fieldbus port has the following characteristics.
• Baud rate: 9600, 19200, 31250, 45450, 93750, 187500, 500000, and 1.5M bps (auto-
detect)
• Address: 1 to 125
• Vendor ID: 3005 (hex)
• Data table size: inputs = 240 bytes, outputs = 240 bytes
Output bit must be 1 for a minimum time of 100 ms, to be actioned.
Bit Description
1Reset
2Lockout Reset
3Stop
4Start A
5Start B
Commands are actioned on rising edge (0 to 1 transition).
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 53
Page 58

FIELDBUS INTERFACE COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Profibus DP-Diagnostics
MM300 supports both slave mandatory and slave specific diagnostic data.
Table 12: System Standard Diagnostics Bytes 1 through 6
Byte Description
1 Station Status 1
2 Station Status 2
3 Station Status 3
4 Diagnostic Master Address
5 Identification Number (High Byte)
6 Identification Number (Low Byte)
The extended diagnosis for the relay is composed of 49 bytes (bytes 7 to 55) and contains
diagnostic information according to the following table, with bit descriptions listed in the
following pages.
Address (By Bytes) Description Format
7 No. of Extended Diagnostic Bytes Unsigned
8-11 Trip Status 3 FC185
12-15 Trip Status 2 FC184
16-19 Trip Status 1 FC183
20-23 Alarm Status 3 FC181
24-27 Alarm Status 2 FC180
28-31 Alarm Status 1 FC179
32-35 Message Status 3 FC189
36-39 Message Status 2 FC188
40-43 Message Status 1 FC187
44-47 Ctrl Element Status 3 FC193
48-51 Ctrl Element Status 2 FC192
52-55 Ctrl Element Status 1 FC191
Profibus Input Data
Category Address (By Bytes) Description Format
Status-Motor 0 Motor Status FC129
2 Extended Status FC178
4 Thermal Cap Used F1
6 Time to Overload Trip F20
10 Reserved NA
Start Blocks 12 Starts/Hour Block F1
14 Time Between Starts Lockout F1B
16 Restart Block Lockout F1
18 Reserved NA
20 Reserved NA
22 Reserved NA
24 Reserved NA
Learned 26 Average Motor Load Learned F3
28 Learned Acceleration Time F2
30 Learned Starting Current F10
54 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 59

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE FIELDBUS INTERFACE
Category Address (By Bytes) Description Format
34 Learned Starting Capacity F1
Counters 36 Number of Motor Starts F1
38 Number of UV Restarts F1
40 Motor Running Hours F9
44 Motor Stopped Hours F1
46 Reserved NA
48 Reserved NA
50 Reserved NA
52 Reserved NA
54 Reserved NA
56 Reserved NA
58 Reserved NA
Current Metering 60 Ia F10
64 Ib F10
68 Ic F10
72 Reserved NA
74 Reserved NA
76 Reserved NA
78 Iavg F10
82 Igrd F10
86 Motor Load F1
88 I Unb F1
Voltage Metering 90 Vab F1
92 Vbc F1
94 Vca F1
96 Va1 Angle F1
98 Vb1 Angle F1
100 Vc1 Angle F1
102 Van F1
104 Vbn F1
106 Vcn F1
108 VAux F1
110 Reserved NA
112 Reserved NA
114 Reserved NA
116 Frequency F3
118 Reserved NA
Power Metering 120 Power Factor F21
122 Real Power F13
126 Reserved NA
128 Reactive Power F13
132 Apparent Power F2
134 MWh Consumption F17
138 Reserved NA
140 Reserved NA
142 Mvarh Consumption F17
146 Reserved NA
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 55
Page 60

FIELDBUS INTERFACE COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Category Address (By Bytes) Description Format
148 Reserved NA
150 Reserved NA
Sensor Metering 152 Hottest Stator RTD F1
154 Hottest Stator RTD Temp F4
156 RTD 1 Temp F4
158 RTD 2 Temp F4
160 RTD 3 Temp F4
162 RTD 4 Temp F4
164 RTD 5 Temp F4
166 RTD 6 Temp F4
168 Reserved NA
170 Reserved NA
172 Reserved NA
174 Reserved NA
176 Reserved NA
178 Reserved NA
Last Trip Data 180 Cause of Last Trip FC134
182 Date of Last Trip 2 words F18
186 Time of Last Trip 2 words F19
190 Pre Trip Ia F10
194 Pre Trip Ib F10
198 Pre Trip Ic F10
202 Pre Trip Motor Load F3
204 Pre Trip Current Unbalance F1
206 Pre Trip Igrd F10
210 Reserved NA
212 Reserved NA
214 Pre Trip Vab F1
216 Pre Trip Vbc F1
218 Pre Trip Vca F1
220 Pre Trip Van F1
222 Pre Trip Vbn F1
224 Pre Trip Vcn F1
226 Pre Trip System Frequency F3
228 Pre Trip Real Power F13
232 Pre Trip Reactive Power F13
236 Pre Trip Apparent Power F2
238 Pre Trip Power Factor F21
56 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 61

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE FIELDBUS INTERFACE
DeviceNet protocol
To enable the DeviceNet physical interface, ensure that switches 1 and 2 of the DIP switch
communications card (on the CPU module) are on. The external connections through the
fieldbus interface are as follows.
Table 13: Fieldbus interface external connections (DeviceNet)
Path Connection (external) Wire color
V– Pin 3, CAN_GND Black
L Pin 2, CAN_L Blue
C Pin 5, CAN_SHLD Bare
H Pin 7, CAN_H White
V+ Pin 9, CAN_V Red
The Modbus status (MS) and network status (NS) LEDs indicate the status of the Fieldbus
interface.
Table 14: DeviceNet LED indications
LED LED operation Description
MS Green on, red on, green on Device self-test
Flashing green Device in standby state
Green on Device operational
Flashing red Recoverable fault
Red on Unrecoverable fault
NS Flashing green Online, not connected
Green on Online, connected
Flashing red Connection timeout
Red on Critical link failure
Red and green Network access detected
DeviceNet Communications
When used for DeviceNet, the fieldbus port has the following characteristics.
• Baud rate: 125, 250, and 500 kbps
• MAC ID: 0 to 63
•Vendor ID: 928
• Product Code: 0x4D39
• Message types: poll, and explicit messaging
The device profile is an extension of the Communications Adapter Device Profile (0xC0). It is
a group 2 only server. The MAC ID and baud rate are programmable through the EnerVista
MM300 Setup software and the Graphical Control Panel. The MM300 supports the
following DeviceNet object classes.
CLASS OBJECT
01H Identify
02H Message Router
03H DeviceNet
05H Connection
A0H Generic Data - Polling/Explicit
B1H Explicit Control Writes
B0H Analog Data - Explicit
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 57
Page 62

FIELDBUS INTERFACE COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
The MM300 supports poll and explicit messaging types.
The Poll function will return 38 bytes of status and metering data as described in User
Object Class A0h, Instance 01h, Attribute 01h.
USINT, UINT, UDINT and DINT, stated in this document, stand for the following data types :
USINT = Unsigned integer byte
UINT = Unsigned integer word
UDINT = Unsigned integer double word
DINT = Signed integer double word
Identity Object (Class Code 01H)
Table 15: Identity Object, Class Code 01h, Services:
CODE SERVICES AVAILABLE TO THIS OBJECT
NAME DESCRIPTION
0x05 Reset Reset the device to power up conf iguration
0x0E Get_Attribute_Single Returns the contents of the given attribute
Table 16: Identity Object, Class Code 01h, Attributes:
ATTRIBUTE ACCESS NAME/DESCRIPTION DATA TYPE VALUE
01h Get Revision of Identity Object UINT 1
Table 17: Identity Object, Class Code 01h, Instance 01h, Attributes:
ATTRIBUTE ACCESS NAME/DESCRIPTION DATA TYPE VALUE
01h Get Vendor ID UINT 928
02h Get Device Type UINT 12
03h Get Product Code UINT 0x4D39
04h Get Revision (Major, Minor) USINT 1.00
Message Router (Class Code 02H)
The message router (class code 2) object provides a messaging connection point through
which a client may address a service to any object or instance residing in the physical
device. There is no external visible interface to the message router object.
DeviceNet Object (Class Code 03H)
Table 18: Identity Object, Class Code 03h, Services:
CODE SERVICES AVAILABLE TO THIS OBJECT
0x0E Get_Attribute_Single Returns the contents of the given attribute
Table 19: Identity Object, Class Code 03h, Attributes:
ATTRIBUTE ACCESS NAME/DESCRIPTION DATA TYPE VALUE
01h Get Revision of DeviceNet Object UINT 1
NAME DESCRIPTION
58 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 63

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE FIELDBUS INTERFACE
Table 20: Identity Object, Class Code 03h, Instance 01h, Attributes:
ATTRIBUTE ACCESS NAME/
DESCRIPTION
01h Get Vendor ID UINT 928 (to be defined)
02h Get Baud Rate USINT 0 = 125 kbps
05h Get Allocation Choice BYTE Bit 0: Explicit Messaging
Master/s MAC ID USINT 0 to 63: address; 255 = unallocated
DATA TYPE VALUE
1 = 250 kbps
2 = 500 kbps
Bit 1: polled I/O
Bit 6: acknowledge suppression
DeviceNet Connection Object (Class Code 05H)
Table 21: Connection Object, Class Code 05h, Services:
CODE SERVICES AVAILABLE TO THIS OBJECT
NAME DESCRIPTION
0x05 Reset Reset the device to power up conf iguration
0x0E Get_Attribute_Single Returns the contents of the given attribute
0x10 Set_Attribute_Single Sets the contents of the given attribute
Table 22: Connection Object, Class Code 05h, Instance 01h (Explicit Message Connection):
ATTRIBUTE ACCESS NAME/DESCRIPTION DATA TYPE VALUE
01h Get State BYTE 0x03
02h Get Instance type BYTE 0x00
03h Get Export class trigger BYTE 0x83
04h Get Produced connection ID UINT 10xxxxxx011,
05h Get Consumed connection ID UINT 10xxxxxx100,
06h Get Initial comm. characteristics USINT 0x21
07h Get Produced connection size UINT 0x00EF
08h Get Consumed connection size UINT 0x00EF
09h Get/Set Expected package rate UINT 0x0000
0Ch Get/Set Watchdog timeout action USINT 0 = transition to
0Dh Get Produced path length UINT 0x0000
0Eh Get Produced path BYTE [6] <null>
0Fh Get Consumed path length UINT 0x0000
10h Get Consumed path BYTE [6] <null>
11h Get Production inhibit timer UINT 0x0000
xxxxxx - MAC ID
xxxxxx - MAC ID
time-out
1 = auto delete
2 = auto reset
3 = deferred delete
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 59
Page 64

FIELDBUS INTERFACE COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Table 23: Connection Object, Class Code 05h, Instance 04h (Polled Input/Output Connection):
ATTRIBUTE ACCESS NAME/DESCRIPTION DATA TYPE VALUE
01h Get State BYTE 0x03
02h Get Instance type BYTE 0x01
03h Get Export class trigger BYTE 0x82
04h Get Produced connection ID UINT MAC ID
05h Get Consumed connection ID UINT MAC ID
06h Get Initial comm. characteristics USINT 0x01
07h Get Produced connection size UINT 0x0026
08h Get Consumed connection size UINT 0x0020
09h Get/Set Expected package rate UINT 0x0000
0Ch Get/Set Watchdog timeout action USINT 0x00
0Dh Get Produced path length UINT 0x0006
0Eh Get Produced path BYTE [6] variable
0Fh Get Consumed path length UINT 0x0006
10h Get Consumed path BYTE [6] variable
11h Get Production inhibit timer UINT 0x0000
DeviceNet Motor Data - Poll, Explicit Object (Class Code A0H)
Table 24: Motor Data Object, Class Code A0h, Services:
CODE SERVICES AVAILABLE TO THIS OBJECT
NAME DESCRIPTION
0x0E Get_Attribute_Single Returns the contents of the given attribute
Table 25: Motor Data Object, Class Code A0h, Attributes:
ATTRIBUTE ACCESS NAME/DESCRIPTION DATA TYPE VALUE
01H Get Revision of Motor Data Object UINT 1
Table 26: Motor Data Object, Class Code A0h, Instance 01h, Attributes, Get Access:
ATTRIBUTE NAME/DESCRIPTION SIZE IN BYTES FORMAT
01H Motor Data (Poll group 1) 38 See below
02H Digital Data 9 See below
03H Summary of Motor Data 7 See below
04H Reserved NA NA
05H Motor status 1 FC129 (low byte only)
06H Motor load (%) 2 F1
07H Cause of last trip 2 FC134
08H Thermal capacity used (%) 2 F1
09H Current metering 8 See below
0AH Average Line Voltage (V) 2 F1
0BH Power metering 6 See below
0CH Contact Input Status 8 BIT per input
0DH Contact Output Status 4 BIT per output
0EH RTD metering 3 See below
60 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 65

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE FIELDBUS INTERFACE
DATA FORM AT, DIG ITAL DATA
ITEM DESCRIPTION SIZE IN BYTES FORMAT
Motor status 1 FC129 (low byte only)
Contact Input Status 8 BIT per input
DATA FORMAT, SUMMARY OF MOTOR DATA
ITEM DESCRIPTION SIZE IN BYTES FORMAT
Motor status 1 FC129 (low byte only)
Motor load (%) 2 F1
Cause of last trip 2 FC134
Thermal capacity used (%) 2 F1
DATA FORMAT, MOTOR DATA
ITEM DESCRIPTION SIZE IN BYTES FORMAT
Motor status 1 FC129 (low byte only)
Motor load (%) 2 F1
Cause of last trip 2 FC134
Thermal capacity used (%) 2 F1
Average phase current (A) 4 F10
Ground current (A) 4 F10
Average Line Voltage (V) 2 F1
Real power (kW) 4 F13
Power factor 2 F21
Contact Input Status 8 BIT per input
Contact Output Status 4 BIT per output
Local hottest RTD number 1 Unsigned 8 bit integer
Local hottest RTD temperature 2 F4
DATA FORMAT, CURRENT METERING
ITEM DESCRIPTION SIZE IN BYTES FORMAT
Average phase current (A) 4 F10
Ground current (A) 4 F10
DATA FORMAT, POWER METERING
ITEM DESCRIPTION SIZE IN BYTES FORMAT
Real power (kW) 4 F13
Power factor 2 F21
DATA FORMAT, RTD METERING
ITEM DESCRIPTION SIZE IN BYTES FORMAT
Local hottest RTD number 1 Unsigned 8 bit integer
Local hottest RTD temperature 2 F4
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 61
Page 66

FIELDBUS INTERFACE COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
DeviceNet - Explicit Motor Analog Data Object, Class Code B0H, Services
Table 27: Explicit Motor Analog Data Object, Class Code B0h, Services:
CODE SERVICES AVAILABLE TO THIS OBJECT
NAME DESCRIPTION
0x0E Get_Attribute_Single Returns the contents of the given attribute
Table 28: Explicit Motor Analog Data Object, Class Code B0h, Attributes:
ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION SIZE IN BYTES
01H Currents Currents 20
02H Reserved 6
03H Motor load 4
04H Line voltages 8
05H Phase voltages 8
06H Phase voltage angles 6
07H Frequency 2
08H Power 14
09H Energy 12
0AH Local hottest stator RTD and temperature 3
0BH Local RTD temperatures 12
0CH Learned data 10
0DH Motor statistics 8
0EH Cause of trip 2
0FH Last trip date and time 8
10H Currents Last pre-trip currents 16
11H Last pre-trip motor load 4
12H Last pre-trip line voltages 6
13H Last pre-trip phase voltages 6
14H Last pre-trip frequency 2
15H Last pre-trip power 12
16H Trip diagnostic data 12
17H Alarm diagnostic data 12
18H Start block status data 18
19H All actual values 211
62 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 67

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE FIELDBUS INTERFACE
Table 29: Data Formats, Explicit Motor Analog Data Object
ATTRIBUTE ITEM DESCRIPTION SIZE IN
01H Currents Ia 4 F10
Ib 4 F10
Ic 4 F10
Iavg 4 F10
Igrd 4 F10
03H Motor load Motor Load 2 F1
I Unb 2 F1
04H Line voltages Vab 2 F1
Vbc 2 F1
Vca 2 F1
Average Line Voltage 2 F1
05H Phase voltages Van 2 F1
Vbn 2 F1
Vcn 2 F1
Reserved 2 NA
06H Phase voltage angles Va Angle 2 F1
Vb Angle 2 F1
Vc Angle 2 F1
07H Frequency Frequency 2 F3
08H Power Power Factor 2 F21
Real Power 4 F13
Reserved 2 NA
Reactive Power 4 F13
Apparent Power 2 F2
09H Energy MWh Consumption 4 F17
Mvarh Consumption 4 F17
Reserved 2 NA
Reserved 2 NA
0AH Local hottest stator RTD and
temperature
Hottest Stator RTD 1 Unsigned 8 bit
BYTES
FORMAT
integer
Hottest Stator RTD Temp 2 F4
0BH Local RTD Temperatures RTD 1 Temp 2 F4
RTD 2 Temp 2 F4
RTD 3 Temp 2 F4
RTD 4 Temp 2 F4
RTD 5 Temp 2 F4
RTD 6 Temp 2 F4
0CH Learned data Learned Acceleration Time 2 F2
Learned Starting Current 4 F10
Learned Starting Capacity 2 F1
Average Motor Load Learned 2 F3
0DH Motor Statistics Number of Motor Starts 2 F1
Number of UV Restarts 2 F1
Motor Running Hours 4 F9
0EH Cause of Trip Cause of Last Trip 2 FC134
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 63
Page 68

FIELDBUS INTERFACE COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
ATTRIBUTE ITEM DESCRIPTION SIZE IN
BYTES
0FH Last trip date and time Time of Last Trip 4 F19
Date of Last Trip 4 F18
10H Last pre-trip currents Pre Trip Ia 4 F10
Pre Trip Ib 4 F10
Pre Trip Ic 4 F10
Pre Trip Igrd 4 F10
11H Last pre-trip motor load Pre Trip Motor Load 2 F3
Pre Trip Current Unbalance 2 F1
12H Last pre-trip line voltages Pre Trip Vab 2 F1
Pre Trip Vbc 2 F1
Pre Trip Vca 2 F1
13H Last pre-trip phase voltages Pre Trip Van 2 F1
Pre Trip Vbn 2 F1
Pre Trip Vcn 2 F1
14H Last pre-trip frequency Pre Trip System Frequency 2 F3
15H Last pre-trip power Pre Trip Real Power 4 F13
Pre Trip Reactive Power 4 F13
Pre Trip Apparent Power 2 F2
Pre Trip Power Factor 2 F21
16H Trip diagnostic data Trip Status 3 4 FC185
Trip Status 2 4 FC184
Trip Status 1 4 FC183
17H Alarm diagnostic data Alarm Status 3 4 FC181
Alarm Status 2 4 FC180
Alarm Status 1 4 FC179
18H Start block status data Reserved 2 F1
Start Timer 1 2 F1
Start Timer 2 2 F1
Start Timer 3 2 F1
Start Timer 4 2 F1
Start Timer 5 2 F1
Time Between Starts Lockout 2 F1B
Restart Block Lockout 2 F1
Starts/Hour Block 2 F1
19H All of the above items from attributes 01H-18H
FORMAT
64 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
Page 69

COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE FIELDBUS INTERFACE
DeviceNet - Explicit Motor Object, Class Code B1H
Table 30: Explicit Motor Control Object, Class Code B1h, Services:
CODE SERVICES AVAILABLE TO THIS OBJECT
NAME DESCRIPTION
0x10 Set_Attribute_Single Sets the contents of the given attribute
Table 31: Explicit Motor Control Object, Class Code B1h, Attributes:
ATTRIBUTE ACCESS DESCRIPTION DATA TYPE VALUE
01H Set Control Command BYTE See below
Table 32: Data Value, Class B1h
VALUE DESCRIPT IO N
1 Reset
2Lockout Reset
3Stop
4Start A
5Start B
Commands are actioned on rising edge (0 to 1 transition).
MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE 65
Page 70

FIELDBUS INTERFACE COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
66 MM300 MOTOR MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – COMMUNICATIONS GUIDE
 Loading...
Loading...