Page 1

GE
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
Transportation
1150 HP AC Drilling Motor,
Model 5GEB22
Document No. GEK-91696, Rev. D
Page 2

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
© {2009} Genera
General Electric Company and is disclosed in confidence. This publication is intended for use by GE customers solely
for purposes of operating and performing routine maintenance of purchased or licensed GE products, and it shall not
be reproduced
any form, in whole or in part, or used for any other purpose, or disclosed to third parties, without the express written
consent of GE.
GE and Customer agree that the information contained herein does not purport to cover all details or variations in GE
products or
mation be desired or should particular problems arise that are not covered sufficiently for the user’s purposes, the matter
should be referred to Gene ral Electric Company. Any applicable Federal, State or local regulations or company safety or
operating r
has no obliga tion to keep the material up to date after the original publication.
GENERAL ELECTRIC COMPANYEXPLICITLY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES OFACCURACY, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR
ANY PURPOSE IN CONNECTION WITH THIS PUBLICATION AND USE THEREOF.
If you are not an authorized recipient of this publication, you are hereby notified that any perusal, use, distribution, copy-
ing or dis
following address: GE Transportation, Technical Publications Department, Building 14, 2901 East Lake Rd., Erie, PA 16531.
closure is strictly prohibited. If you have received this publication in error, please immediately return to GE at the
l Electric Company. All rights reserved. The information contained in this publication is the property of
, redistributed, retransmitted, translated, abridged, adapted, condensed, revised or otherwise modified, in
to provide for ever y possible contingency with installation, operation or maintenance. Should further infor-
ules must take precedence over any information or instructions given in the Technical Documentation. GE
2
Page 3

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drilling Motor, Model 5GEB22
CONTENTS
Page
1. GENERAL INFORMATION.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.1. INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.2. SAFETY INFOR
1.3. ATEX CERTIFICATION.................................................................................................................................................................................................. 4
1.4. INSTALLATION AND OPERATIONAL INSTRUCTIONS..................................................................................................................................... 5
1.5. MODEL DIFFE
2. CONTROLS AND INDICATORS................................................................................................................................................................................ 13
3. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
4. SCHEDULED M
4.1. MONTHLY SCHEDULED MAINTENANCEPROCEDURE..................................................................................................... ............................ 14
4.2. CLEANING THE MOTOR ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 16
5. REMOVAL AN
5.1. MOTORPREPARATION FOR SHIPMENT.............................................................................................................................................................. 16
5.2. DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURES............................................................................................................................................ ...................................... 19
5.3. INSPECTI
5.4. STEAM CLEANING.......................................................................................................................................................................................................28
5.5. STATIC ELECTRICAL TESTING.................................................................................................................................................................................. 29
5.6. ROTOR SUB
5.7. ROTOR INSTALLATION INTO THE STATOR FRAME .........................................................................................................................................35
5.8. MOTORBEARING CHECKS AFTER ASSEMBLY.................................................................................................................................................37
5.9. FINAL AS
5.10.FINAL ASSEMBLY OF ROTOR CONNECTION END (CE) COMPONENTS.................................................................................................. 39
5.11. ELECTRICAL RUNNING TESTS.... .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. ........................................................................................ 39
5.12. HUB INS
6. SUMMARY DATA........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 44
6.1. DRILL MOTOR DATA....................................................................................................................................................................................................44
6.2. DRILL M
6.3. INSPECTIONDATA....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 47
6.4. SPECIAL TOOLS AND MATERIALS......................................................................................................................................................................... 47
MATION..............................................................................................................................................................................................
RENCES ...............................................................................................................................................................................................
AINTENANCE..................................................................................................................................................................................
D REPLACEMENT PROCEDURES ...............................................................................................................................................
ON AND REPAIR PROCEDURES ..........................................................................................................................................................
ASSEMBLY PROCEDURES...................... .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. .............. ......................................................
SEMBLY OF ROTOR DRIVE END (DE) COMPONENTS ................................................................................................................
TALLATION....................................................................................................................................................................................................
OTOR COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION................................................................................................................................................
4
13
13
16
25
30
39
40
46
3
Page 4
GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
1. GENERAL INFORM
1.1. INTRODUCTION
This publication provides basic instructions for inspection, maintenance, and overhaul procedures the drilling
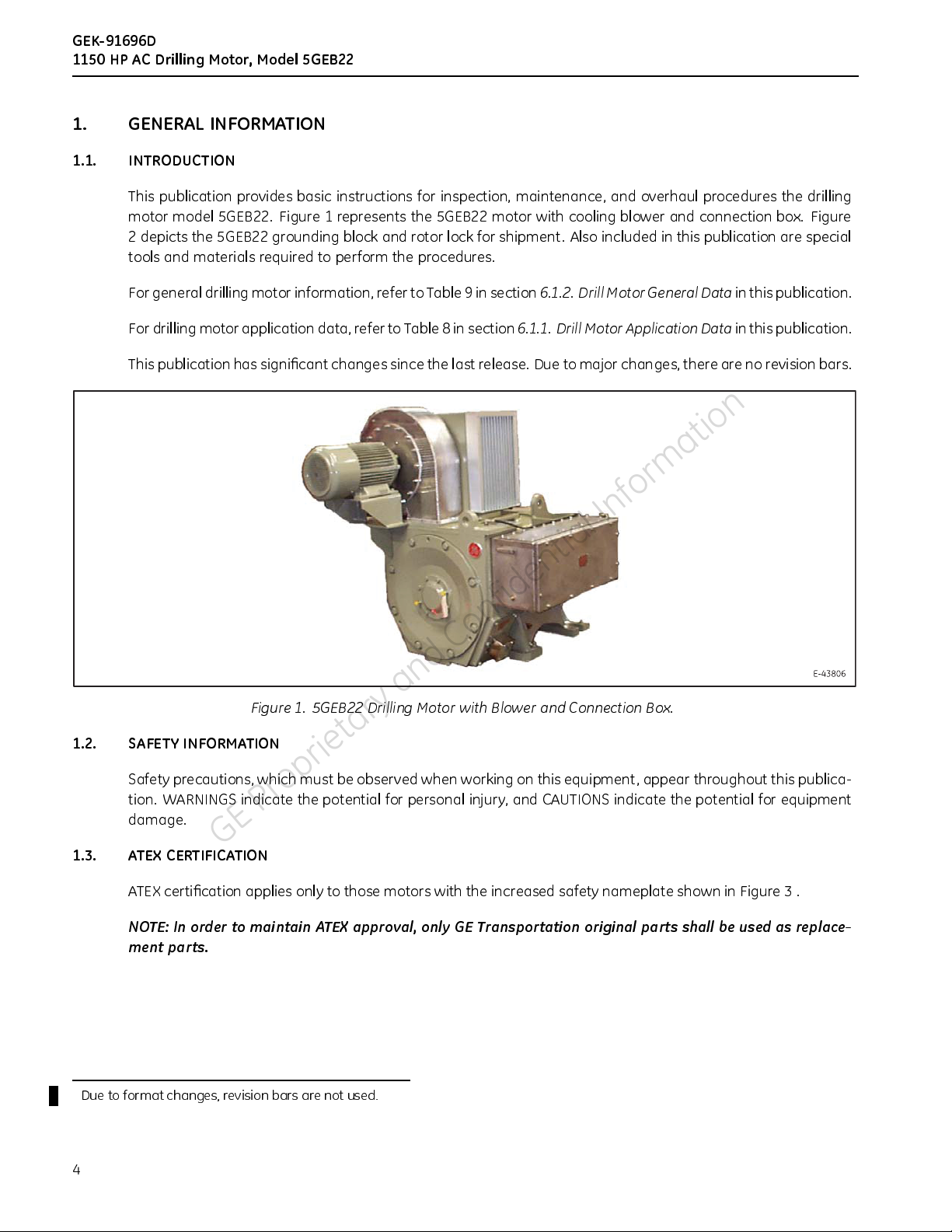
motor model 5GEB22. Figure 1 represents the 5GEB22 motor with cooling blower and connection box. Figure
2depictsthe
tools and materials required to perform the procedures.
For general
For drilling motor application da ta, refer to Table 8insection
This publication has significant changes since the last release. Due to major changes, there are no revision bars.
5GEB22 grounding block and rotor lock for shipment. Also included in this publication are special
drilling motor information, refer to Table 9 in section
ATION
6.1.2. Drill Motor General Data
6.1.1. Drill Motor Application Data
in this publication.
in this publication.
Figure 1. 5GEB22 Drilling Motor with Blower and Connection Box.
1.2. SAFETY INFORMATION
Safety precautions, which must be observed when working on this equipment, appear throughout this publica-
tion. WARNINGS indicate the potential for personal injury, and CAUTIONS indicate the potential for equipment
damage.
1.3. ATEX CERTIFICATION
ATEX certification applies only to those motors with the increased safety nameplate shown in Figure 3 .
NOTE: In order to maintain ATEX approval, only GE Transportation ori ginal parts shall be used as replace-
ment parts.
Due to format changes, revision bars are not used.
4
Page 5
1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
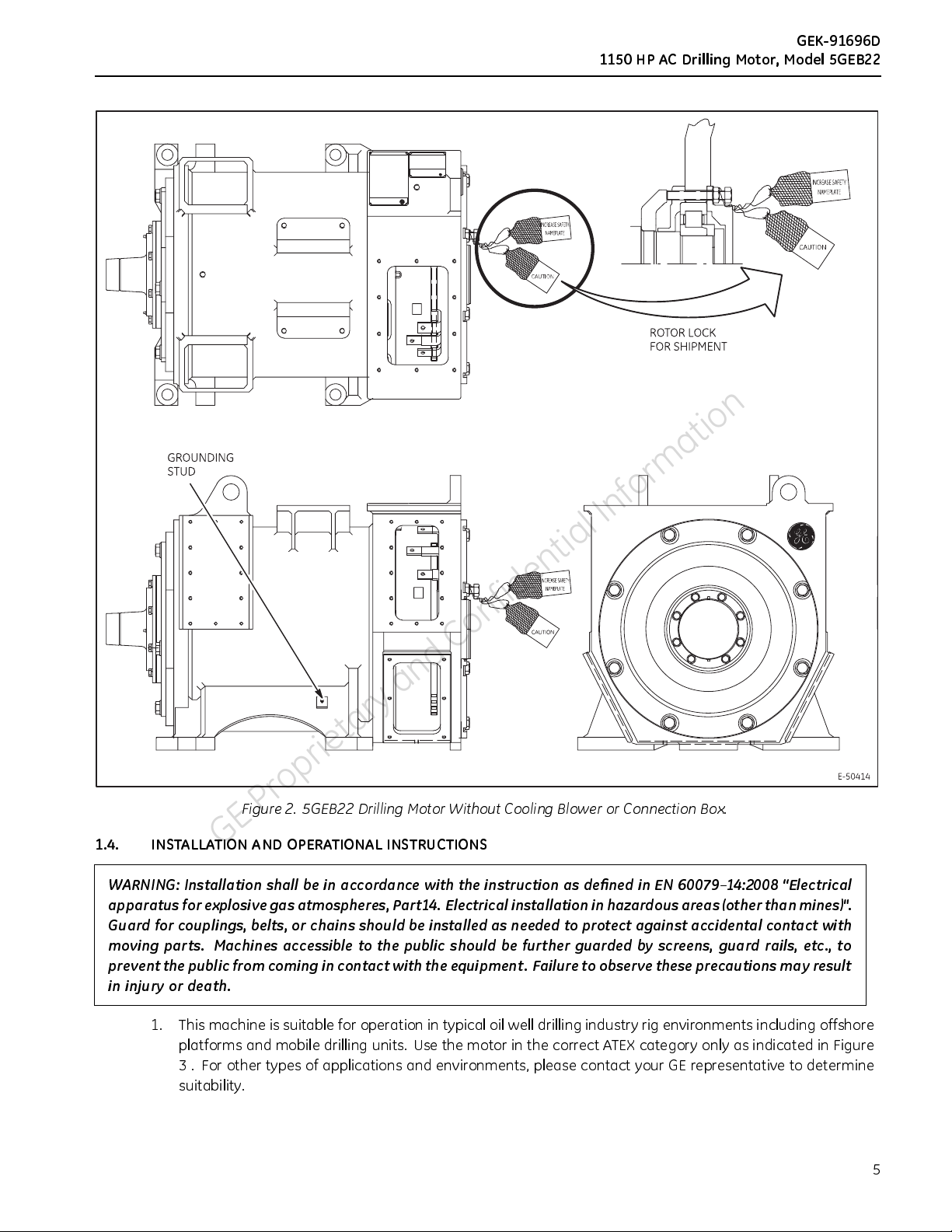
Figure 2. 5GEB22 Drilling Motor Without Cooling Blower or Connection Box.
1.4. INSTALLATION AND OPERATIONAL INSTRUCTIONS
ING: Installation shall be in accordance with the instruction as defined in E N 60079–14:2008 “Electrical
WARN
apparatus for explosive gas atmospheres,Part14. Electrical installation in hazardous areas(otherthanmines)".
Guard for couplings, belts, o r chains should be installed as needed to protect against accidental contact with
ing parts. Machines accessible to the public should be further guarded by screens, guard rails, etc., to
mov
prevent the public from coming in contact with the equipment. Failure to observe these precautions may result
in injury or death.
1. This machine is suitable for operation in typical oil well drilling industry rig environments including offshore
platforms and mobile drilling units. Use the motor in the correct ATEX categor y only as indicated in Figure
3 . For other types of applications and environments, please contact your GE representative to determine
suitability.
5
Page 6

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
DRILLING MOTOR MODEL NO. – 5GEB22
.ON LAIRES
COOLING–3000 SCFM AIR SUPPLIED
BY BLOWER UNIT
CLOSED COOLING SYSTEM, IP56, TO MAINTAIN MAX.
INTERNAL AIR TEMPERATURE OF 45 C
RATINGS S9 CONTINUOUS
PHASE 3
AC VOLTS (L-L) 587
AMPS AC 1380 1120 / 1048
RATER RPM 800
SHAFT HP 1400 1150 / 1075
MAX. FREQUENCY HERTZ 153
MAX OPERATING RPM 3000
CONSTANT HP 800–1800 RPM (600 VOLT L–LINE SUPPLY)
CONSTANT HP 800–2400 RPM (690 VOLT L–LINE SUPPLY)
INSULATING CLASS H
INGRESS PROTECTION
WITH 600 VOLTS MAINTAINED ABOVE 820 RPM
WITH 690 VOLTS MAINTAINED ABOVE 940 RPM
AMBIENT AIR MAX 45 C 45 C / 55 C
N WYEOITCENNOC
IP44 / 6424 LBS (2914 Kg)
IP56 / 7124 LBS (3238 Kg)
Figure 3. Safe Electrical Parameters for the 5GEB22 Motor.
2. It is the end user’s responsibility to ensure that the motor with steel components including shaft, stator
frame, stator core, and rotor core, along with the blower and variable speed drive are installed in the correct
gnated area and will not be subjected to existing (or foreseeable) aggressive destructive substances.
desi
3. Periodic lubrication is not required on model 5GEB22 drilling motor between scheduled overhaul intervals
ause the bearings are grease packed and permanently sealed. Motor bearings MUST be replaced after
bec
25,000 hours of operation, which is 90% of calculated bearing life. All maintenance must be carried out in
accordance with:
a.
EN 60079–17:2003
— Electrical apparatus for expl osive gas atmospheres, Part 17. Inspection and
maintenance of electrical installations in hazardous areas (other than mines).
6
E-
50984
Page 7

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
b.
IEC 60079–19:2006
haul for appara
1150HPACDrill
— Electrical apparatus for explosive gas atmospheres, Part 19. Repair and over-
tus used in explosive atmospheres (other than mines or explosive industry).
4. Safe electrical parameters are defined in Figure 3 and Figure 4 defines the safe environmental parameters
for the drilli
ng motor model 5GEB22. The drilling motor may be operated in the presence of typical vibrat ion
levels encountered on land and offshore rigs.
CERTIFIED Ex e II T3 (T
IEC 60034–1
SIRA 09ATEX3077X
Year of Construction
1180
II 2 G c T3
Motor Model Number: 5GEB22
Maximum Current: 1800 AMPS (RMS)
Ratio Max./Nom. (IA / IN) Current: 1.36
Safe Stall Time: 37 Seconds
Temperature Protection Devices Must Be
Set At 190
C (maximum)
DO NOT OPEN WHEN ENERGIZED
AMB
Figure 4. Safe Environmental Parameters for the 5GEB22 Motor.
1.4.1. Drilling Motor Model 5GEB22 Operational Requirements
The drilling motor requires:
–40 C to +55 C)
E-50985
1. The cable fitted to the equipment must be capable of withstanding maximum temperatures of 230°F (110°C)
at the cable entry point. No PVC type insulation is permitted.
2. The equipment must be supplied continuously with at least 3000 Standard Cubic Feet per Minute (SCFM)
(84930 SLPM) of cooling air. The cooling arrangements must be suitable for the area in which it is installed.
When fitted to the equipment, the cooling arrangements must ensure that the equipment satisfies a degree
of protection of at least IP44.
3. RTDs suppli ed with the motor are to be connected to intrinsically safe circuits to meet compliance of the Ex
certification for operation in a hazardous environment. The protective device must be suitably certified as
compliant with the European Directive 94/9/EC as a Safety Relate d Device. These circuits are to be manually
reset only and will trip (stop) the motor at 190 °C (374 °F).
7
Page 8
GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
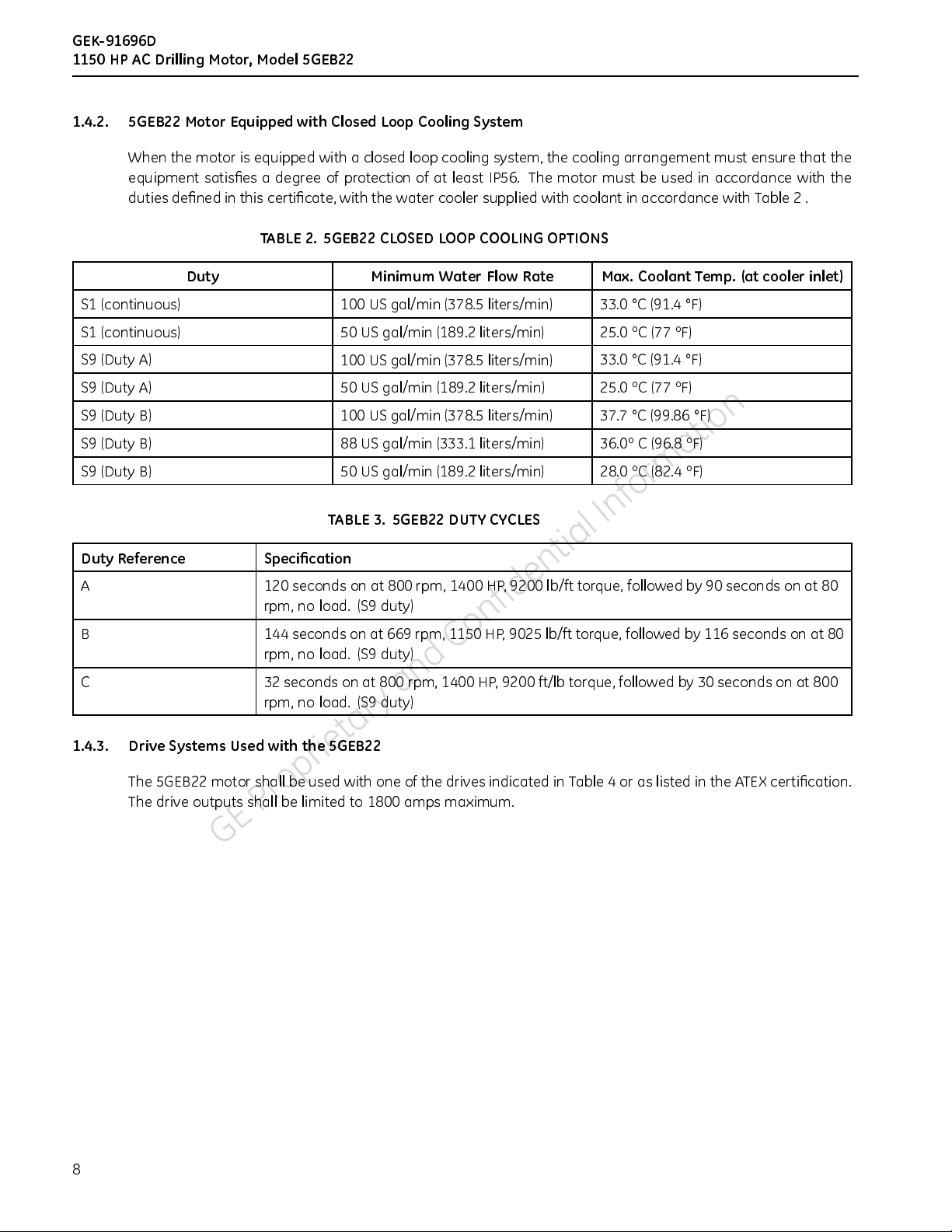
1.4.2. 5GEB22MotorEquippedwithClosedLoopCoolingSystem
When the motor is equippe d with a closed loop cooling system, the cooling arrangement must ensure that the
equipment satisfies a degree of protection of at least IP56. The motor must be used in accordance with the
duties defined in this certificate, with the water cooler supplied with coolant in accordance with Table 2 .
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
TABLE 2. 5GEB22 CLOSED LOOP COOLING OPTIONS
Duty Minimum Water Flow Rate Max. Coolant Temp. (at cooler inlet)
S1 (continuous)
S1 (continuous)
S9 (Duty A)
S9 (Duty A) 50 US gal/min (189.2 liters/min) 25.0 ºC (77
S9 (Duty B)
S9 (Duty B)
S9 (Duty B)
Duty Reference Specification
A
B
C
1.4.3. Drive Systems Used with the 5GEB22
120 seconds on at 800 rpm, 1400 HP, 9200 lb/ft torque, followed by 90 seconds on at 80
rpm, no load. (S9 duty)
144 se
rpm, no load. (S9 duty)
32 seconds on at 800 rpm, 1400 HP, 9200 ft/lb torque, followed by 30 seconds on at 800
rpm, no load. (S9 duty)
100 US gal/min (378.5 liters/min)
50 US gal/min (189. 2 liters/min)
100 US gal/min (378.5 liters/min)
100USgal/
88 US gal/min (333. 1 liters/min)
50 US gal/min (189. 2 liters/min)
TABLE 3. 5GEB22 DUTY CYCLES
conds on at 669 rpm, 1150 HP, 9025 lb/ft torque, followed by 116 seconds on at 80
min (378.5 liters/min) 37.7 °C (99.86 °F)
33.0 °C (91.4 °F)
25.0 ºC (77 ºF)
33.0 °C (91.4 °F)
36.0º C (96.8 ºF)
28.0 ºC (82.4 ºF)
ºF)
The 5GEB22 motor shall be used w ith one of the drives indicated in Table 4 or as listed in the ATEX certification.
The drive outputs shall be limited to 1800 amps maximum .
8
Page 9
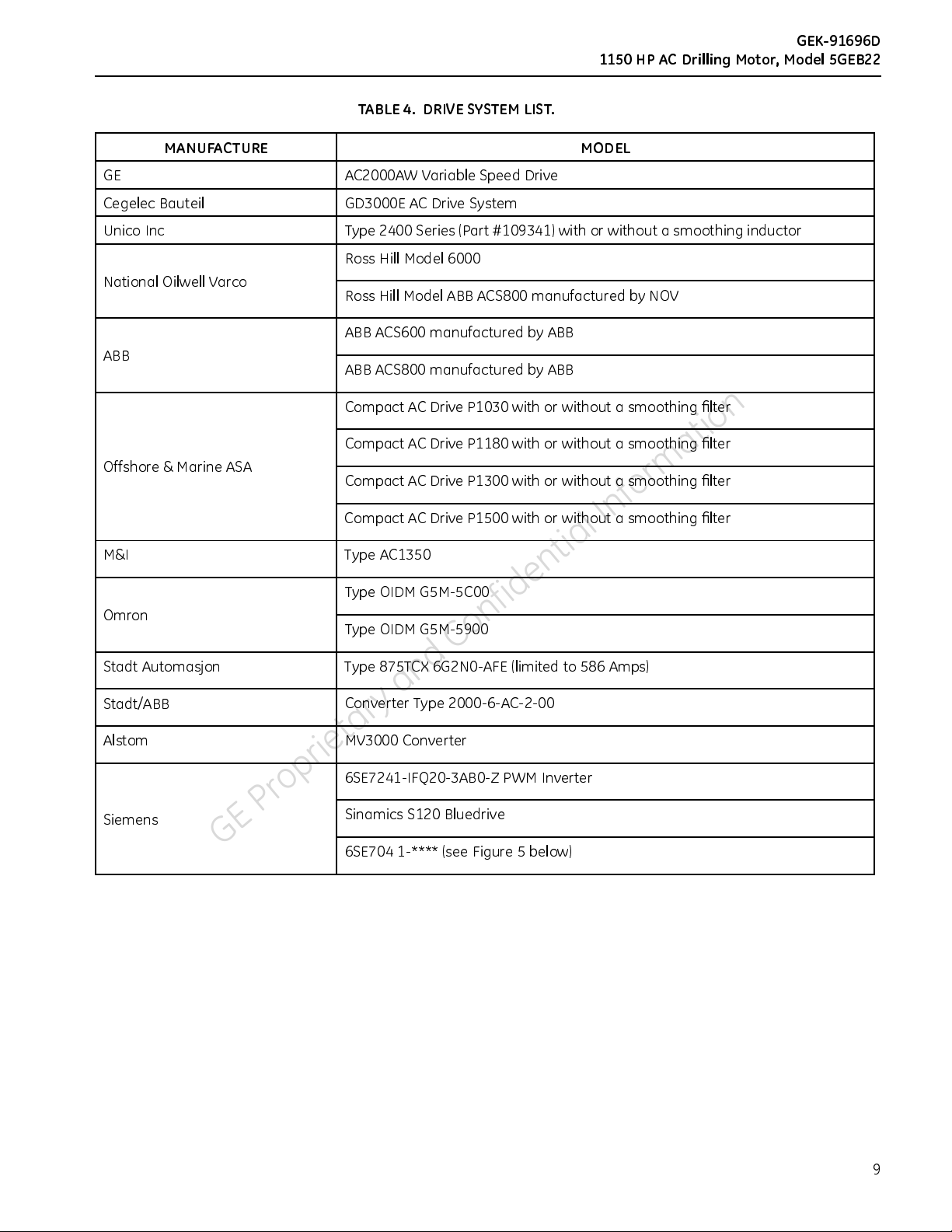
TABLE 4. DRIVE SYSTEM LIST.
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
MANUFACTURE MODEL
GE AC2000AW Variable Speed Drive
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Cegelec Baut
Unico Inc Type 2400 Series (Part #109341) with or w ithout a smoothing inductor
National Oilwell Varco
ABB
Offshore
M&I Type AC1350
Omron
eil
&MarineASA
GD3000E AC Dr
Ross Hill Model 6000
Ross Hill Model ABB ACS800 manufactured by NOV
ABB ACS600 manufactured by ABB
ABB ACS800 manufactured by ABB
Compact AC Dri ve P1030 with or without a smoothing filter
Compact AC Dri ve P1180 with or without a smoothing filter
Compact AC Dri ve P1300 with or without a smoothing filter
Compact AC Dri ve P1500 with or without a smoothing filter
Type OIDM G5M-5C00
Type OIDM G5M-5900
ive System
Stadt Automasjon Type 875TCX 6G2N0-AFE (limited to 586 Amps)
Stadt/ABB
Alstom MV3000 Converter
Siemens
Converter Type 2000-6-AC-2-00
6SE7241-IFQ20-3AB0-Z PWM Inverter
Sinamics S120 Bluedrive
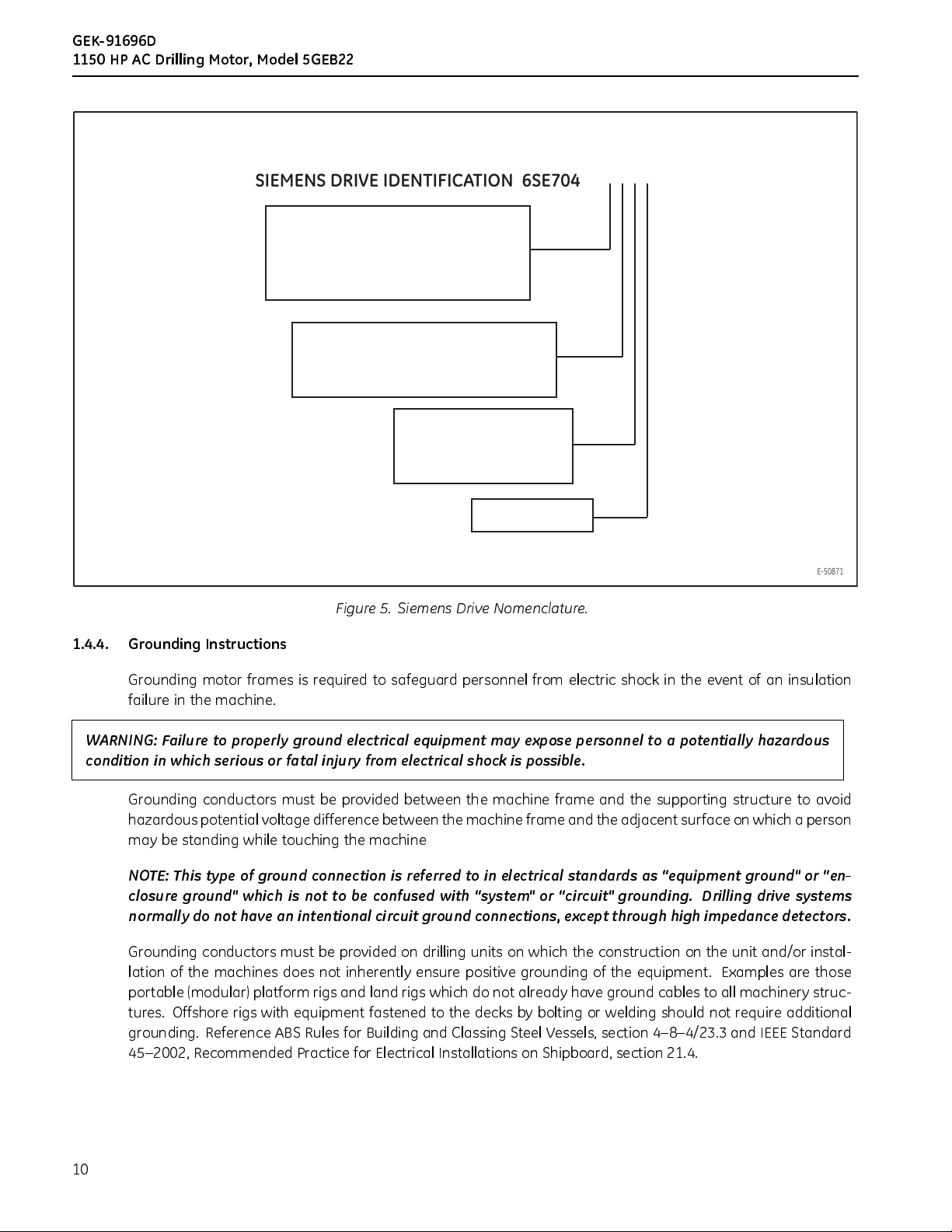
6SE704 1-**** (see Figure 5 below)
9
Page 10
GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
SIEMENS DRIVE IDENTIFICATION 6SE7041 - * * * *
RATED CURRENT INDICATOR:
0 = 1000A (M CHASSIS)
2 = 1200A (L OR M CHASSIS)
5 = 1500A (M CHASSIS)
DC LINK VOLTAGE INDICATOR:
V = 930V (690V LINE-LINE)
U = 780V (600V LINE-LINE)
CHASSIS INDICATOR:
M
L
DIGIT 2 OR 6
Figure 5. Siemens Drive Nomenclature.
1.4.4. Grounding Instructions
Ground
failure in the machine.
WARNI
condition in which serious or fatal injury from electrical shock is possible.
Grounding conductors must be provided between the machine frame a nd th e sup porting structure to avoid
hazardous potential voltage difference between the machine frame and the adjacent surface on which a person
may be standing while touching the machine
NOTE: This type of ground connection is referred to in electrical standards as “equipment ground" or “en-
closure ground" which is not to be confu sed with “system" or “circuit" grounding. Drilling drive systems
normally do not have an intentional circuit ground connections, except through high impedance detectors.
Grounding conductors must be provided on drilling units on which the construction on the unit and/or instal-
lation of the machines does not inherently ensure positive grounding of the equipment. Examples are those
portable (modular) platform rigs and land rigs which do not already have ground cables to all machinery struc-
tures. Offshore rigs with equipment fastened to the decks by bolting or welding should not require additional
grounding. Reference ABS Rules for Building and Classing Steel Vessels, section 4−8−4/23.3 and IEEE Standard
45−2002, Recommended Practice for El ectrical Installations on Shipboard, section 21.4.
ing motor frames is required to safeguard personnel from electric shock in the event of an insulation
NG: Failure to properly ground electrical equipment may expose personnel to a potentially hazardous
E-50871
10
Page 11

1.4.5. Grounding Procedures
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
The 5GEB22 has a ground blockattached totheframeasshowninFigure2 . The mounting stud is 3/8–16 thread.
To attach a ground cable to the ground block:
1. Obtain a 3/8–16 nut and a lockwasher. Also required is a cable lug to fit the ground cable and terminal hole
clearance for the 0.375 diameter stud.
2. Prepare a ground conductor (use appropriate size cable per National Electrical Code) long enough to run
from the motor frame to an existing ground conductor system or to a suitable equipment ground point as
defined by the National Electrical Code Article 250 or other applicable regulation. Check that the system
ground detector is a lso connected to the Common ground point for the rig and make connection if neces-
sary.
3. Install terminal lugs on cable. Remove paint, rust and oil from all surfaces to which the cables are to be
attached and bolt the lugs securely to t hese surfaces. Torque the nut to 25 lb-ft (34 Nm).
4. After installation, protect the ground stud, nut, and cable lug connection from corrosion by applying a rust
inhibitor on the exposed components.
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
1.4.6. Motor Coupling and Alignment
CAUTION: Be sure to align, or check alignment carefully on either motors or MG sets. Misalignment can cause
excessive vibration and damaging forces on shaft and bearings.
Time taken to assure good alignment will be returned in reduced downtime.
1
.4.6.1.Coupled
On coupled drives, when a motor and adriven unit together have fourormorebearings, flexible couplings should
be used
CAUTION: Careful alignment of machines, when using either solid (rigid) or flexible couplings, is essential to
nt excessive vibration, hot bearings, or shaft failures.
preve
Couplings must be properly sized to be capable of driving maximum machine t orque. Interference fits should be
used between motor shaft and coupling.
1
.4.6.2. V-Belt Drives
On V−beltdrives, thedrivinganddriven shafts shouldbelocated so that they areparallelandthe sheaves aligned.
If properly aligned, there is minimum wear on the belts and no excessive thrust on the machine bearings. The
sheave should be mounted as close as possible to the motor bearings. The following recommendations should
be followed concerning the minimum sheave pitch diameter which can be used for the particular motor. The
belt manufacturer should be consulted for the maximum speed ratio and belt for the particular application.
Drives
to facilitate alignment. Three−bearing construction requires a rigid coupling.
The following formula and dat a can be used to select the MINIMUM allowable sheave diameter from the stand-
point of bearing life and shaft stress. A larger s heave will further reduce the shaft stress and bearing loading.
This data is based upon the belts being tightened to a maximum total pull of 1.5 times the required transmission
load used in the sheave diameter calculation. Belts should never be tightened more than necessary to transmit
this torque.
D = HP/RPM X 189000/W
11
Page 12

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
Where D = Minimum sheave pitch diameter in inches for V-belt application.
HP/RPM = Maximum ratio of hors epower, including overloads, to the speed which that power occurs.
W = Maximum allowable radial load.
Belt−driven machines may be equipped with sliding rails. Proper and constant belt tension is easily maintained
and the replacement of belts is simplified. This reduces the operating cost a nd increases the efficiency. Sliding
rails are to be used for floor mounting only.
Belt idlers reduce the life of the belts and should not be used if any other method is available. The belts should
never be forced over the sheaves. W hen the drive is started and operating at full speed and full load, the take−up
should be adjusted until only a slight bow appears in the slack side. If slippage occu rs after the belt tension has
been correctly adjusted, the belts and p ulleys have not been chosen properly for the job.
CAUTION: Over−tightening to avoid this slippage may result in early failures of belts, shafts, and bearings.
Belt tension s hould be checked and adjusted following the belt manufacturer’s recommendations.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
There is n
belts seat themselves in the sheave grooves and initial stretch is removed. Belt tension should be rechecked
after a day or two of operation.
Matched belts run smoother,look better, and last longer. Longer belt life results if the belts and sheaves are kept
clean and the belts are prevented from rubbing against the belt guards or other obstructions.
1
.4.6.3. Grouting
On conc
A rich, non−shrink grout should be used. High− grade grout mixtures are available commercially. If the grout
is to be
to give a stiff mixture. The clean, but rough surface of the foundation should be wet and the grout rammed or
puddled under the base.
1
.4.6.4. Flexible Coupling Alignment Procedure
Leve
should be checked as follows :
1. Remo
2. Check the coupling hub spacing is in accordance with the outline dimensions with the units in the mechan-
ormally a drop in tension during the first 24 to 48 hours of operation. During this "run in" period, the
rete foundations, a minim um of one inch (25 mm) should be allowed for grouting.
prepared at the site, a cement−sand ratio of 1:2 is recommended. Just enough water should be used
l all mounting base supports before setting the base in position. Before grouting the base, the alignment
ve all coupling bolts a nd slide the shells back so the hub faces are exposed.
l center of their end play.
ica
3. Start with the coupling next to the largest unit (usually the motor) or near the middle of multiple units. Check
radial alignment by using a straightedge across the two hubs at vertical and hori zontal. Or, clamp a dial
the
indicator to one hub and use the outside diameter of the other member to give indication of the misalign-
ment. Be sure the dial indicator supports do not bend or sag, since this will give inaccurate readings. The
ximum variation should not exceed 0.002 inches (0.05 mm).
ma
4. Insert a feeler gage or use the dia l indicator at hub faces. Measure the gap between hub faces at 0, 90, 180
d 270 degrees and record. Rotate both shafts together 90 degrees and repeat the gap readings. Continue
an
rotation in 90 degree inc rem ents until five sets of readings are taken. The fifth set of readings is a check on
12
Page 13

the first set of readings to assure that data is reliable. The readings should not vary by more than 0.002
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
inches (0.05 mm
5. Correct the horizontal alignment by shifting frames on the base and the vertical alignment by shimming
between the ma
6. Repeat Steps 2, 3 and 4 on each coupling, working away from the motor or center unit.
7. Recheck the coupli ngs on long sets after completing the above checks, because shimming when checking
subsequent units may affect those already checked. After the set has been aligned within the specified
limits, the
1.5. MODEL DIFFERENCES
coupling shells may be bolted together.
TABLE 5. 5GEB22 MODEL DIFFERENCE INFORMATION
1150HPACDrill
) between the four readings taken at each coupling position.
chines and the base.
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
5GEB22A1 Original d
5GEB22A2 Same as 5GEB22A1 except new rotor shaft material.
5GEB22A3 Same as 5GEB22A2 except new CE bearing.
2D1
B22D4
4
Same as 5
Same a
Sam
5GEB22A
5GEB22A5 Same as 5GEB22A3 except stator t erminal alignment.
5GEB22C1 Same as 5GEB22A2 except shaft lengthened and CE insulated bearing.
5GEB2
5GEB22D2 Same as 5GEB22D1 except without ABS sha ft certification.
5GEB22D3 Same as 5GEB22D1 except stator terminal alignment.
5GE
esign 5GEB22.
GEB22A2 except stator t erminal alignment.
s 5GEB22A3 except rotor shaft diameter increase.
e as 5GEB22D2 except stator terminal alignment.
2. CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
t Appli cable to drill motor model 5GEB22. Refer to drive system instruction publications for controls and indi-
No
cators.
3. FU
NCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The Model 5GEB22 drilling motor is a force–ventilated, three–phase alternating–current induction motor de-
igned for use in the oil and gas industry to power offshore and land based drilling rigs. The normal function of
s
the horizontally mounted 5GEB22A motor is to provide power for the mud pumps and drawworks. The 5GEB22D
motor has an oversized shaft and is designed for belted horizontal applications such as mud pumps.
Motor speed is controlle d by varying the frequency of the alternating current in the motor stator windings. The
direction of rotation of the motor rotor is changed by reversing the phase rotation in the motor stator.
The motor is force ventilated by a blower assembly, meeting IP44. It can also be provided with a closed loop
cooling system meeting IP56.
4. SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE
Periodic mainten ance should be performed to ensure successful motor operation. The following procedures de-
tail the procedures for Scheduled Ma intenance. The motor bearings do not require lubrication between overhaul
intervals due to packed grease and permanently sealed bearings.
13
Page 14

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
NOTE: In order to maintain ATEX approval, only GE Transportation ori ginal parts shall be used as replace-
ment parts.
4.1. MONTHLY SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE PROCEDURE
4.1.1. Covers, Seals, and Latches
WARNING: Hazardous voltages are present in this equipment. Follow shutdown procedures to ensure power
is not applied to the machine before performing any maintenance procedures. Failure to do so may result in
injury or death.
1. Remove all power from the machine before attempting maintenance procedures.
2. Clean the outside of the mach ine and remove the inspection covers.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
WARNING: W
to personnel in the immediate area. Personnel should be provided with, and trained in the use of, protective
equipment as specified by applicable federal or state safety regulations. Failure to do so may result in injury or
death.
4.1.2. Power Cable Inspection
hen using compressed air for cleaning pu rposes, flying debris and particles may present a hazard
3. Use clean, dry compressed air and blow the dirt and dust from the interior of the machine.
4. Check exterior covers to ensure the felt seals are intact. Replace seals if missing, broken, deformed or hard-
ened.
5. Install the covers into position on the machine. Torque the cover bolts to 58 ±2 lb.–ft. (79 ±2,7 Nm).
During inspection of the power cables and associated hardware, replace any components that are damaged.
Inspect the power cables for:
1. Inspect the cable terminals for discoloration from heat, arc damage, cracks or fractures. Replace terminals
and/or cable if damage is found.
2. Ensure terminal connections are tight and arcing is not present.
3. Inspect cable insulation for cracked, worn, cut, bubbled or burnt insulation. Replace the cable if damage is
found.
4. Check cable connection bushings and mounting hardware (such as cable cleats). Replace damaged or miss-
ing hardware.
5. Check the ground cable connection to the motor frame. Ensure the connection is tight on the ground stud.
4.1.3. Megohmmeter Test
The insulation condition of the motor and cables can be determined by a megohmmeter test. When the high
voltage of the megohmmeter test instrument is applied to the power components of the motor circuit, a high
ohm reading i ndicates good insulation quality. Low ohm readings indicate insulation breakdown, moisture/de-
bris contamination, or carbon tracking. To test the power circuit insulation with a megohmmeter:
1. Ensure all the components in the power circuit are not affecte d by a megohmmeter test. Check the drive
system for megohmmeter test procedures or disconnect power cables from the drive system. If cables are
14
Page 15

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
disconnected for the megohmmeter, make sure the cables are insulated from touching any surrounding
surfaces.
2. Connect a le ad from the megohmmeter instr ument to th e motor TA lead.
3. Connect the second lead of the megohmmeter to a cleaned ground connection.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
4. Apply a 500 vo
5. If the reading is above 2 megohms, the power circuit insulation is satisfactory and proceed to Step 7.
6. If the reading is below 2 megohms, the power circuit insulation is degraded or bad. Perform the following
procedures to attempt to raise the ohm reading:
a. Check the power cables for cracks, scuffed or open insulation. Repair or replace the cables if dam-
b. Water or dirt/debris contamination may be adversel y affecting the ohm reading. Disconnect the
7. Connect o
8. Connect the second lead of the megohmm eter to one of the RTD leads (red, white, or white).
9. Apply a 500V megohmmeter test to the circuit.
10. If the re
the RTD cable for cracked, scuffed, or open insulation. Repair or replace the cable if damage is found. If no
cable damage is found, then the RTD is defective and should not be used.
ading is greater than 2 megohms, proceed to Step 11. If the reading is less than 2 megohms, check
lt megohmmeter test to the power circuit.
age is found.
power cables from themotorandretestjustthe stator leads. If the reading is still below 2 megohms,
the motor w
publication for cleaning instructions.
ne lead of the megohmmeter to the motor lead TA.
ill have to be removedfor cleaning or repair. Refer to
4.2. CLEANING THE MOTOR
in this
4.1
11. Move the first lead of the megohm meter from the motor TA lead to a cleaned motor frame ground while
leaving the second lead of the megohmmete r connected to one of the RTD leads (red, white, or white).
12. Apply a 500V megohmmeter test to the circuit.
13. If the
14. Repeat Steps 7 through 13 until all the RTD cables have been checked against the stator motor leads and
15. Remove the megohmmeter leads and return all components to operating condition.
.4.
Mot
Check the motor mounting bolts, nuts, and associated hardware. Ensure the hardware is not missing or loose.
Rep
reading is greater than 2 megohms, proceed to Step 14. If the reading is less than 2 megohms, check
the RTD cable for cracked, scuffed, or open insulation. Repair or replace the cable if damage is found. If no
cable damage is found, then the RTD is defective and should not be used.
the motor frame.
or Mounting Hardware
lace missing hardware and tighten loose bolts.
15
Page 16

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
4.2. CLEANING THE MOTOR
Cleaning the motor is essential to long–term motor life. When the drilling motor is removed from its machinery,
accumulated dirt a nd oil buildup can be removed. The external motor surfaces can be cleaned by steam clean-
ing. The i nternal motor components should not be sprayed with a steam cleaner. To clean the motor:
1. Clean the motor only when the drilling motor is removed from its machinery and power is removed from the
WARNING: Personnel performing cleaning procedures must wear protective clothing, gloves and eye protec-
tion. Follow local practices and procedures for cleaning. Failure to do so may result in injury or death.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
motor.
CAUTION: Al
due to theadverseaffects on motor insulation. Use of thesesolutionsmaycause motor failure or reducedmotor
life.
CAUTION: Do not spray the internal components of the motor with a steam cleaner. Moisture contamination
may cause motor failure or reduced motor life.
WARNIN
to personnel in the immediate area. Personnel should be provided with, and trained in the use of, protective
equipment as specified by applicable federal or state regulators. Failure to do so may result in injury or death.
kali and chlorinated hydrocarbon cleaning solutions arenot recommended forcleaningdrillmotors
2. Cover the motor air inlet and outlet with heavy plastic and tape. Ensure the interior motor components are
protect
3. Steam clean the external surfaces of the motor. Do not direct the spray at mot or openings or the plastic
covers.
4. When steam cleaning is complete, let excess fluid drain from the motor.
5. Remove the plastic covers or protecti ve covers and tape from the motor.
G: When using compressed air for cleaning purposes, flying debris and particles may present a hazard
6. Using compressed air, blow out the interior of the motor to remove all dirt, dust and moi sture. If necessary,
apply heat to dry the motor thoroughly.
ed from spray during cleaning
Recommended cleaning solutions are: CHEMICAL METHODS, INC., 809 or GE BETZ KLEEN SBC120.
5. REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT PROCEDURES
The following procedures outl ine the overhaul process. All procedures may not be required even though all are
described. Inspection of the components will determine the procedures necessary to return the motor to oper-
ation.
Do not order replacement parts from this publication. Refer to the PARTS CATALOG for the motor for the correct
replacement part number.
5.1. MOTOR PREPARATION FOR SHIPMENT
The drill motor must be prepared for shipment to prevent damage to components during shipping. The following
sections detail rotor locking procedures and packaging for shipment.
16
Page 17
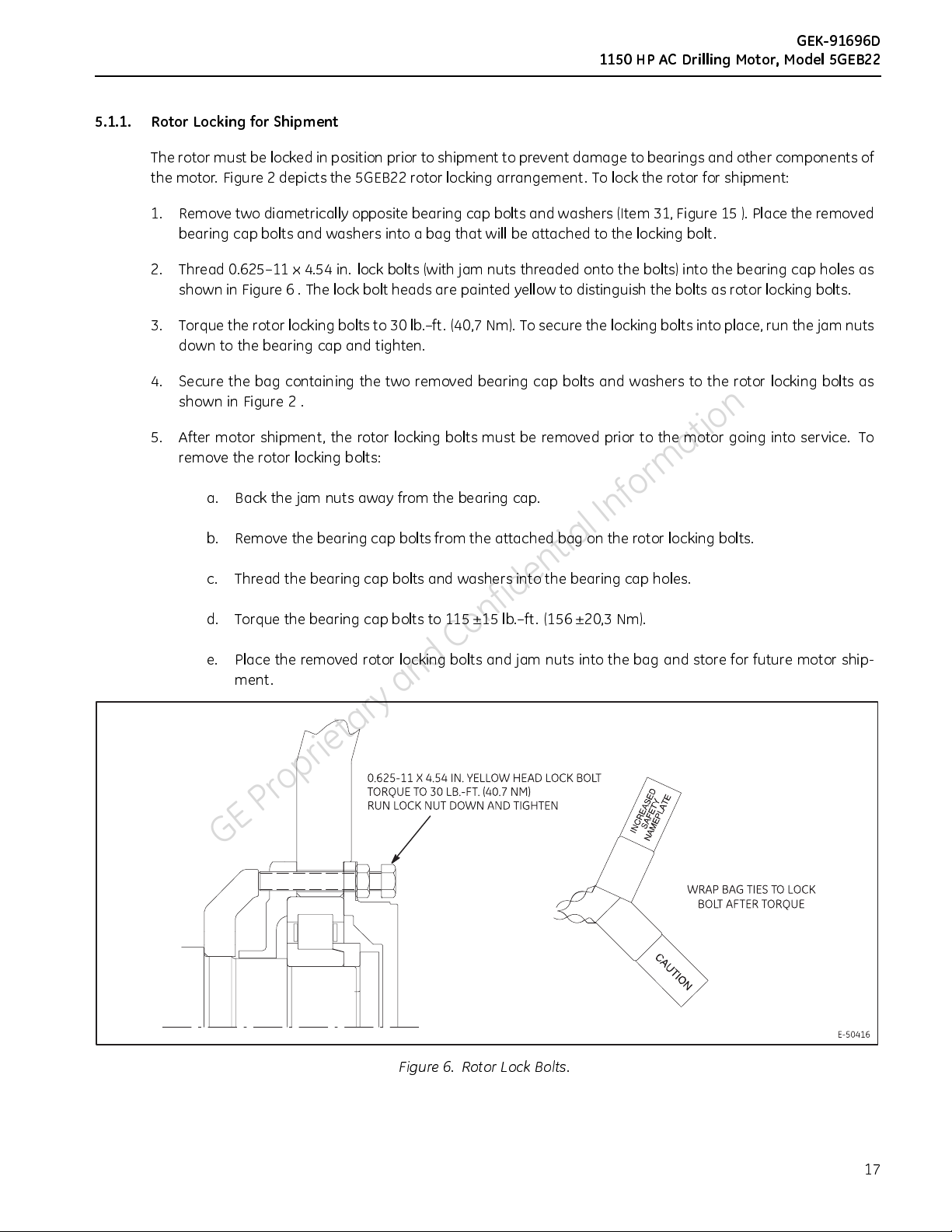
5.1.1. Rotor Locking for Shipment
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
The rotor must be locked in position prior to shipm ent to prevent damage to bearings and othe r components of
the motor. Figure 2 depicts the 5GEB22 rotor locking arrangement. To lock the rotor for shipment:
1. Remove two diametrically opposite bearing cap b olts and washers (Item 31, Figure 15 ). Place the rem oved
bearing cap bolts and washers into a bag that will be attached to the locking bolt.
2. Thread 0.625–11 x 4.54 in. lock bolts (with jam nuts threaded onto the bolts) into the bearing cap holes as
shown in Figure 6 . The lock bolt heads are painted yellow to distinguish the bolts as rotor locking bolts.
3. Torque the rotor locking bolts to 30 lb.–ft. (40,7 Nm). To secure the locking bolts into place, run the jam nuts
down to the bearing cap and tighten.
4. Secure the bag containing the two removed bearing cap bolts and washers to the rotor locking bolts as
showninFigure2.
5. After motor shipment, the rotor locking bolts m ust be removed prior to the motor going into service. To
remove the rotor locking bolts:
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
a. Back the jam nuts away from the bea ring cap.
b. Remove the bearing cap bolts from the attached bag on the rotor locking bolts.
c. Thread the bearing cap bolts and washers into the bearing cap holes.
d. Torque the bearing cap bolts to 115 ±15 lb.–ft. (156 ±20,3 Nm).
e. Place the removed rotor locking bolts and jam nuts into the bag and store for future motor ship-
ment.
gure 6. Rotor Lock Bolts.
Fi
17
Page 18

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
5.1.2. Motor Packaging for Shipment
After locking the rotor for shipment, the motor should be securely packaged to avoid damage during s hipment.
To package the motor for shipment:
1. Prepare wood stock of sufficient length to skid the motor as shown in Figure 7 . The yellow pine wood stock
2. Drill 1.62 in. (41,2 mm) clearance holes in the wood stock to fit the holes in the motor mounting feet (four
WARNING: The drill motor weighs approximately 5689 lbs. (2580 kg). Use appropriat e lifting devices when lifting
the motor. Failure to do so may result in injury or death.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
must be able to support the approximate 5700 lbs. (2585 kg) weight of the motor (not including the blower
and connection box).
holes).
3. To avoid da
a. Do not lift the motor by the rotor shaft.
b. Do not allow the motor to impact another object when lifted.
c. Do not wra
be wrapped around the motor frame.
4. Lift the
5. Install four 1.5–6 in. bolts and washers through the motor mounting feet an d wood stock frame. Tighten the
bolt int
6. Slush the machined surfaces with a rust inhibitor before enclosing the motor for shipment.
5.1.3. Motor Storage
The mo
1. When preparing the motor for storage:
motor onto the wood frame and align the motor foot holes with the wood frame holes.
o position.
tor should be prepared for storage to prevent damage.
a. Construct a platform to secure the motor as described in section
ment
mage to the motor during handling:
p the rotor with straps or banding for shipment. Any securing straps or banding should
5.1.2. Motor Packaging for Ship-
in this publication.
b. Slush the exposed machined surfaces with a rust inhibitor.
c. Inst
d. Ins
e. Apply power to the anti−condensation heater while motor is stored.
18
all wire leads to the anti−condensation heater that allow the heater leads to be connected to
an external power source.
tall cover and side panel to crate the motor.
Page 19
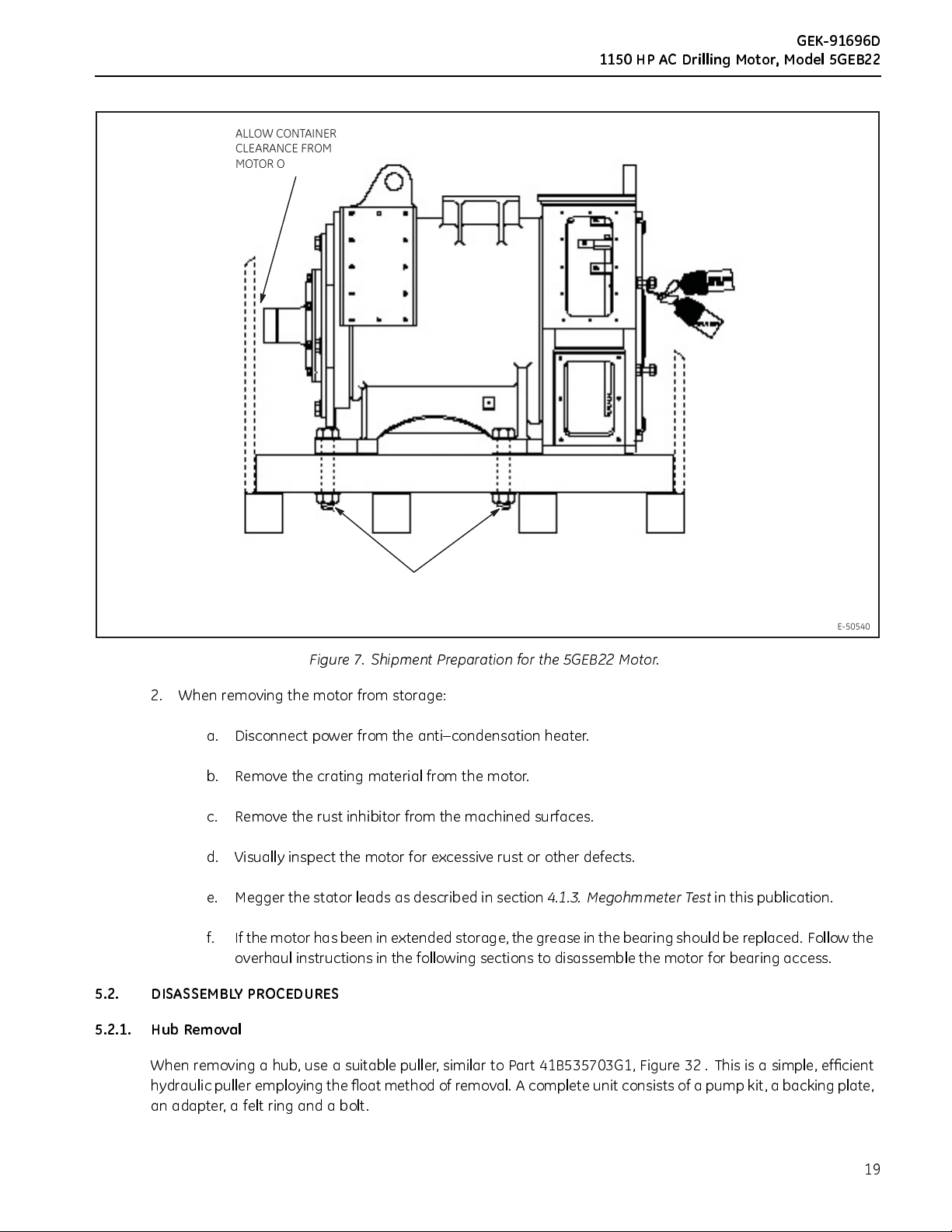
ALLOW CONTAINER
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
CLEARANCE FROM
MOTOR ON BOTH ENDS
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 7. Shipment Preparation for the 5GEB22 Motor.
2. When removing the motor from storage:
a. Disco
nnect power from the anti−condensation heater.
b. Remove the crating material from the motor.
c. Remove the rust inhibitor from the machined surfaces.
d. Visu
ally inspect the motor for excessive rust or other defects.
e. Megger the stator lea ds as described in section
f. If the motor has been in extended storage, the grease in the bearing should be replaced. Follow the
overhaul instructions in the following sections to disassemble the motor for bearing access.
5.2. DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURES
5.2
.1.
Hub
Removal
1.5-6 BOLTS, NUTS, AND
WASHERS, 4 PLACES
APPROXIMATE WEIGHT OF MOTOR 5689 LBS (2580 KG)
4.1.3. Megohmmeter Test
in this publication.
E-50540
When removing a hub, use a suitable puller, similar to Part 41B535703G1, Figure 32 . This is a simple, efficient
draulic puller employing the float method of removal. A complete unit consists of a pump kit, a backing pla te,
hy
anadapter,afeltringandabolt.
19
Page 20

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
NOTE: Do not heat the hub before pulling it, and do not use steel wedges between the hub and bearing cap.
1. Remove the set−screw plug from the tapped hole in the end of the shaft.
2. Screw the backing plate, with felt ring in place, to the end of the shaft as tight as possible by hand. Back off
the backing plate to line up the slot with the tapped hole in the end of the shaft. This is to provide sufficient
clearance for the hub to pop off.
3. Screw the pressure−fitting adapter into the hole in the shaft until it seats at the bottom.
4. Attach the pump by screwing the connector on one end of the pressure tube into the adapter, and the other
end into the pump.
5. Close the hand relief valve and work the pump handle to force oil into thegrooveinthearmatureshaftunder
the hub. When sufficient pressure has been built up, the hub will pop off the shaft and be stopped by the
felt washer and backing plate.
NOTE: Capacity of the pump is 40,000 psi (275800 kPa). It holds sufficient oil to remove eight to ten hubs;
check at each use. Periodically, remove the filling plug and refill with SAE−10 lubricating oil.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
6. Open the relief valve, disconnect the pump from adapter, remove the adapter and backin g plate from the
shaft, and lift off the hub. Rein sert the plug to prevent clogging the hole.
5.2.2. Rotor Removal
To remove the rotor from the motor assembly:
CAUTION: Special precautions should be taken to avoid damage to the rotor, bearings, or bearing fits when
lifting the rotor in the vertical position or turning the rotor to a horizontal position.
NOTE: N
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
1. Place
2. Remove the eight bolts and flat washers (31) securing the connection−end bearing housing to the connec-
3. Screw two long guide studs (.625–11 X 10) through the frame head and into the connection−end bearing
4. Plac
umbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
the motor in a horizontal positi on.
end frame head. Remove the connection−end bearing cap
tion−
r cap (35) in opposite holes of the six just emptied. These studs will help to guide the rotor out of the
inne
motor frame.
e the motor on a heavy−duty stand with the drive−end up. Level the mot or so that the rotor can be lifted
vertically with a hoist without damaging the bearing or bus rings.
5. Rem
6. Screw a 1 in.−8 steel lifting eyebolt into the threaded hole in the drive−end of the rotor shaft (5).
7. Align the hoist cable with the center line of the rotor and attach the hoist hook to the lifting eye.
NO
removed with the rotor as an assembly.
20
ove the eight bolts (10) and flat washers holding the drive−end frame head to the motor frame.
TE: The connection−end bearing and housing and the drive−end frame head, bearing and housing are
Page 21

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
CAUTION: Use extreme care when turning the rotor to the horizontal position to avoid damage to the core and
the bearing and
8. Carefully lift the rotor assembly out of the motor stator and p lace the rotor in a horizontal position on a
9. With the rotor in t he horizontal position, remove the two long guide studs (.625–11 X 10) from the connec-
frame head fits. Use two hoists when positioning the rotor horizontally.
wooden cradle supporting the core assembly.
tion−end bearing housing.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
10. Remove and service the rotor bearings according to instruction in section
Assembly Removal
5.2.3. Connection End (CE) Bearing Assembly Removal
There are two Connection End (CE) bearing assemblies used for the 5GEB22 models. Models of the 5GEB22 man-
ufactured prior to October, 2001 use the original design CE bearing assembly as shown in Figure 8 . 5GEB22
models manufactured after September, 2001 ( Figure 9 ) use an enhanced p erformance CE bearing assembly.
Refer to section
the CE bearing designs. The following sections describe the CE bearing removal for both designs of CE bearings.
Select the removal procedure appropriate for the bearing design on the drill motor.
5
.2.3.1. Connection End Bearing Assembly Removal Procedure for 5GEB22 Models Manufactured Prior to October,
2001
The following procedure details the removal procedure for 5GEB22 drill motor models manufactured prior to
October, 2001. To remove the CE bearing assembly:
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
1. Remove the twosetscrews(40) from the rotorbearingnut(33). Attach the spanner wrench (GE Tool9945228)
to the rotor beari ng nut. Using a dead blow hammer, tap the wrench handle in a counter clockwise (CCW)
direction t o loosen the nut. Remove the spanner wrench, and remove the bearing nut from the rotor.
of this publication.
6.2. DRILL MOTOR COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION
in this publication for details of differences in
5.2.3. Connection End (CE) Bearing
2. Assemble the bearing puller (GE Tool 41D736059G3), and use the hydraulic jack to pull the connection–end
bearing housing (35) and bearing (34) from the rotor shaft.
3. Position the bearing housing – with the bearing down – on a flat surface. Reassemble the be aring puller (to
GE Tool 41D736059G4), and use the hydraulic jack to push the bearing from the bearing housing.
21
Page 22

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
± ±
± ±
Figure 8. Connection End (CE) Bearing Assembly for Models Manufactured Prior to September 2001.
22
Page 23

1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
±
±
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
± ±
Figure 9. Connection End (CE) Bearing Assembly for Models Manufactured After September 2001.
5
.2.3.2. Connection End Bearing Assembly Removal Procedure for 5GEB22 Models Manufactured After September,
2001
The following procedure details the removal procedure for 5GEB22 drill motor models manufactured after to
September, 2001. To remove the CE bearing assembly:
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
1. Remove the four bearing clamp (41) retaining bolts and hardened washers (42).
2. Thr
3. Assemble the bearing puller (GE Tool 41D736059G3), and use the hydraulic jack to pull the connection–end
4. Position the bearing housing – with the bearing down – on a flat surface. Reassemble the be aring puller (to
ead two bolts into the bearing clamp (41) jack out holes. Tighten the bolts alternately until the bearing
clamp (41) is free of the rotor shaft fit. Remove the bearing clamp and remove the jack out bolts from the
bearing clamp.
bearing housing (35) and bearing (34) from the rotor shaft.
GE Tool 41D736059G4), and use the hydraulic jack to push the bearing from the bearing housing.
23
Page 24

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
5.2.4. Drive End Bearing Assembly Removal
The following procedures details the drive end (DE) bearing assembly ( Figure 10 ) removal. To remove the DE
bearing assembly:
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
1. Remove the eight bolts and the flat washers (8) from the outer bearing cap (7).
2. Support the weight of the DE frame head (11) with a hoist, taking care not to lift the rotor off its support.
3. Use an arbor press and fixtures to separate the bearing assembly (3) from the DE frame head (11).
4. Remove the inner shaft collar (1) only if damaged, if outside of inspection limits, or if the shaft must be re-
5.2.5. Connection End Frame Head Removal
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Assemble the bearing puller and use the hydraulic jack to pull the frame head (11), roller bearing (3), and
inner bearing cap (12) from the rotor.
moved from the rotor. If necessary, use a pulle r to remove the sleeve.
Removal of the connection end frame head may be required to gai n acce ss t o the bus rings and stator coil
connections. To remove the CE frame head:
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
1. Remove the eight bolts and flat washers (28) holding the frame head (27) to the stator fram e (21).
2. Thread three 1–8x3 jack out bolts into the threaded holes of the CE frame head (27). Evenly tighten the jack
out bolts until the frame head is free of the stator frame (21) fit.
WARNING: The CE frame head weighs approximately 220 lbs. (100 kg). Use appropriate lifting devices for this
weith. Failure to do so may result in injury or death.
3. Lift the frame head (27) from the stator frame (21).
24
Page 25

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
±
±
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 10. 5GEB22 Drive End (DE) Bearing Assembly.
5.3. INSPECTION AND REPAIR PROCEDURES
1.
5.3.
5.3.2. Stator Coils and Bus Rings Connection Inspection
r Shaft Inspection
Roto
Check dime nsions as shown in Figure 16 located in section
pect the stator coils and bus rings as follows:
Ins
1. Examine the bus rings for damaged or loose connections.
2. Observe the condition of the coil insulation and varnish. Evidence of burned or charred insulation or varnish
may indicate an overheating condition from a defective connection or defective coils.
6.3.1. Rotor Shaft Inspection Data
in this publication.
25
Page 26

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
5.3.2.1. Repairing Stator Coils to Bus Ring Connection, Cleaning and Breaking the Connection
The connection of the stator coils to the bus ring can be repaired when the connection shows signs of overheat-
ing. The connections are exposed by cutting and stripping the insulation around the connection requiring the
use of a hammer, knife, chisel, screwdriver, pry bar, and slip joint pliers. To expose the connections for repair:
NOTE: Read this entire procedure first to become familiar with these steps.
1. Position the stator frame to obtain the best working position for the connections to be cleaned.
2. Remove any mount ing hardware (bolts, nuts, insulating blocks, etc.) from the area of the brazed connection.
3. Use the knife, chisel, and hammer to cut the insulation. Cut the insulation down to the copper the full length
4. After cutting the insulation the full le ngth, pry the i nsulation away from the connection using the slip joint
5. Brazing tool heat can be used to soften the insulation for final cleaning. Alternately heat the insulation, and
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
of the connection.
pliers, pry bar, screwdriver, or knife.
scrape off all material until reaching bare copper.
NOTE: Use the resistance brazing machine (GE Tool 41D780746–1 or equivalent) and tongs (GE Tool
41D780746–11 or equivalent) to produce the heat necessary to separate the connection. Passing current
through the brazing tongs carbons and the metal to be separated produces heat.
6. The area of the joint to be disconnected must be clean and free of dirt, oil and insulating material such as
varnish and tape.
WARNING: Observe all government and shop safety regulations when using compressed air. Failure to do so
may result in injury.
7. Position the brazing tong on the connection that is to be opened. Keep an air supply nozzle on hand to cool
parts after separation occurs. The air supply also is used to cool the surrounding area by dissi pating heat
he area being heated.
from t
CAUTION: Power is to be applied in pulses ONLY. This enables the heat to spread out gradually, providing a more
eating of the connection area, and eliminating any intense hot spots that may damage the ring or coil
even h
material.
8. Apply power to the brazin g tongs in pulses ONLY until the heat melts the brazing material in the joint, then
shut off the power.
9. Quickly remove the brazing tongs, and using the screwdriver or pry bar, spread the connection joints before
the solder cools and resolidifies.
10. When the bus ring and stator coil connections are sepa rated, repair or replace damaged bus rings, straps,
or stator coil leads prior to brazing the connection together.
11. Before brazing together, ensure the material is clean, parts being brazed are flat against each other to pre-
vent voids.
5
.3.2.2. Repairing Stator Coils to Bus Ring Connection, Brazing and Insulating
To braze and insulate the connection after repairs have been made:
26
Page 27

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
NOTE: The brazing median can be used in strip form (GE Part 41A231281P46) or rod form (GE P art
41A330300P2). It is recommended that strips 0.010 in (0.25 mm) thick cut into squares or rectangles 0.06 in.
(1.6 mm) larger than the conductors, beused for the initial connection. Use the brazing rod to fill voids after
the initial co nnection. Use of this m aterial eliminates the need for flux.
1. The connection area of the material to be brazed must be clean and free of dirt, oil, and insulating materials.
2. If necessary, bend the soft copper connecting straps to align the connection.
NOTE: When using brazing material in strip form, the strip should be sandwiched between the two pieces
being brazed, which must be flat along the entire length of the joint.
3. Insert a brazing strip between the two c onnecting straps being brazed.
4. Position the b razing tongs on the area to be brazed, and clamp in place.
WARNING: Observe all government and shop safety regulations when using compressed air. Failure to do so
may result in injury.
CAUTION: Power is to be applied in pulses ONLY. This enables the heat to spread out gradually, providing a more
even heating of the connection area, and eliminating any intense hot spots that may damage the ring or coil
material
.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
5. Apply p owe r to the brazing tongs in pulses ONLY, and heat until t he brazing solder flows freely. Using an air
nozzle, blow air on the surrounding area while heating to dissipate heat from the area being brazed.
NOTE: When brazing,silver solder in rod form will be required to fill areaswhere the strip may have dripped
outortofillvoids.
6. Remove power from the tongs, but do NOT release the tongs until the silver solder has cooled enough to
hold the connection. Blowing compressed air on the brazed area will speed the cooling.
7. Insulate the connection area using Micamat (part number 41A239176P215) and half lap insulating tape (part
number 41A239176P15) or other appropriate insulation material specific to the connection area.
8. Varnish application over the new insulation is required either by P5D-EP25 VPI process or hand application.
5.3.3. Stator / Rotor Reconditioning
The stator and rotor must be reconditioned during the overhaul procedures before bein g returned to service.
These process help ensure long operating life for the components.
The stator assembly should be treated by Vacuum Pressure Impregnation (VPI) with an approved varnish. VPI
will seal and secure the stator coils. VPI only after cleaning, inspection and testing of the stator assembly. The
VPI process is GE Process P5D–EP25.
The rotor assembly should be treated by a powder coating process. Powder coat the rotor after cleaning and
inspecting. The powder coat treating is GE Process P6C– EP45.
Due to changing technology, contact your local GE representative or Drill Product Service Center for current
instruction processes at time of overhaul. Drill product Service Center contact information as follows:
27
Page 28

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
GE Transportation
Attention Drill Product Service
2901 East Lake Road
Erie, PA 16531
www.GEtransportation.com
5.4. STEAM CLEANING
5.4.1. Steam Cleaning Introduction
WARNING: Cleanin g agents may be toxic and/or flammable. Cleaning agents can cause serous or fatal injury
if used without proper precautions. For safety; do not inhale fumes, use only in adequately ventilated areas,
avoid contact of cleaning agents with the skin, do not expose cleaning agent to flame or sparks, and observe
cautions and warnings issued by the manufacture of the cleaning agent.
Care must betakeninthe selection and strength of cleaning agents ordetergents usedinconjunctionwithsteam
cleaning. Typical cleaning agents pH (alkalinity) are alkaline and not chemically neutral. Check the pH level with
a pH monit
is used, Table 6 depicts the pH test paper color and corresponding alkalinity level.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
or or pH test paper strips to ensure of the cleaning solution is in an acceptable range. If pH test paper
TABLE 6.
Acid Neutral Base−Alkaline
5 — 6 7 8 9 10 11
Orange Yellow Green Ivy—Green Blue Purple
Cleaning processes in which heavy, dirty, greasy mechanical equipment is cleaned should not be used to clean
rical eq uipment. Due to chemical make up and high concentrations of cleaning agents in solution, utilizing
elect
the mechanical equipment cleaning processes on electrical equipment can have a significant impact on the life
of the electrical insulation systems used in motors
A suggested cleaning agent for use in steam cleaning processes for electrical equipment is CM−809−S (or equiv-
alent). This cleaning agent is available at Chem Methods, Inc., 12703 Trisket Road, Cleveland, OH 44111. Chem
ods, Inc. telephone number is (216) 476−8400. This cleaning agent is Potassium Phosphate based and does
Meth
not contain caustic materials or silicate.
mixed steam cleaning solution should be heated to 158 °F to 194 °F (70 °C to 90 °C) and have a pH of 10.5
The
to 11.0. Approximately a 10% solution of the cleaning agent and heated water should achievethe pH level. The
10% solution should be used on the rotor and stator of the motor. If needed, a 50% solution of the cleaning
ent and heated water can be used on the motor frame externally. Do not allow the stronger solution to leak
ag
internally to the motor.
control the cleaning agent in solution, a steam cleaner with an adjustable soap (cleaning agent) valve should
To
be used.
CLEANING AGENT PH DATA.
28
Page 29

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
To clean the motor:
1. Using the 50% solution, spray the external motor frame with the cleaning solution. Let the cleaning solution
soak the motor frame five to t w enty minutes (depending on the contaminant) to penetrate the accumulated
contaminants.
2. If deposits of contaminants are too heavy to be steam cleaned off, manually scrap the debris off and steam
clean.
3. Rinse the cleaning solution off motor with steam and hot water.
4. Blow the motor frame dry with clean, dry compressed air.
5. After motor disassembly during the overhaul process, clean the internal motor components using a 10%
cleaning solution.
6. Rinse of the cleaning solution off with hot water heated to a minimum 194ºF (90ºC).
NOTE: The internalmotor componentsmust be thoroughly rinsed. Cleaningsolutions mayform a crystalline
compound if left on the motor components. The motor insulation systems may be affected by the crystalline
deposits which may shorten the insulation life.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
WARNING: When using compressed air, loosened debris may make the surrounding area dangerous for per-
sonnel. Ensure all personnel are clear and wear appropriate safety equipment. Follow all local regulations and
procedures for compressed air use. Failure to d o may result in injury or death.
7. Using clean, dry compressed air, blow excess water off internal motor components.
8. Bake th
9. Allow parts to cool to room temperature and visually inspect for defects.
10. Perform the Megohmmet er and High−Potential tests described in section
troduction
11. If the stator assembly does not meet specifications in tests, bake an additional two hours in the oven and
retest.
5.5. STATIC ELECTRICAL TESTING
5.5.
1.
ic Electrical Testing Introduction
Stat
Static electrical tests include a Megohmmeter tes t and High−Potential (Hi−Pot) test. Both tests check motor insu-
on systems. Always perform the Megohmmeter test prior to the Hi−Pot test. High voltage used in the Hi−Pot
lati
test may be destructive to insulation if water or debris is present. If the Megohmmeter test indicates moisture or
debris is present, clean the stator as described in section
e th e Megohmmeter test specification is met, proceed to the Hi−Pot test.
Onc
e motor electrical parts in a ventilated oven at 257ºF to 320ºF (125ºC to 160ºC) for 8 to 12 hours.
5.5.1. Static Electrical Testing In-
of this publication.
5.4.1. Steam Cleaning Introduction
of this publication.
5
.5.1.1. Megohmmeter Test
Perform the Megohmmeter test as described in section
4.1.3. Megohmmeter Test
in this publication.
29
Page 30

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
5.5.1.2. High–Potential (Hi–Pot) Test
WARNING: High−Potential (Hi−Pot) testing is performed with high voltage electrical power. Follow safety regu-
lations and local practices for high voltage testing. Failure to do so may result in injury or death.
Hi−Pot te sts evaluate the insulation dielectric strength (ability to insulate) of the motor insulation systems. High
voltage is ap
CAUTION: Always perform the Megohmmet er test before Hi−Pot test. Damage may occur to insulation during
Hi−Pot test
damage to the stator windings requi ring replacement of the stator.
1. Ground one lead of the RTD temperature sensor for sensor protection. Do not Hi−Pot the RTD during testing.
2. Apply the specified high voltage at 60 Hz to each motor lead for one minute with the other lead of the Hi−Pot
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
plied to each motor phase to test insulation to ground during the test. To perform the Hi−Pot test:
ing if moisture or debris is present in the coils of the stator. Failure to do so may result in permanen t
connected to ground. There should not be any significant current (amperage) leakage to ground during
testing. The voltage applied should be:
a. New or recoiled stator − apply 3500 VAC rms.
b. Reconditioned stator − apply 2500 VAC rms.
c. In−service or used stator − apply 2250 VAC rms.
3. If the stator windings show significant current leakage to ground, clean the stator as described in section
5.4.1. Steam Cleaning Introduction
5.6. ROTOR SUBASSEMBLY PROCEDURES
5.6.1. Rotor Balancing
Dynamic balance of the rotor assembly is required for smooth operation and low vibration. If not corrected, an
out−of−balance rotor will lead to complete motor failure.
The rotor must be balanced to within 50 gram−in. at both ends of the rotor.
These instructions pertain only to the location and method of attaching the balance weights. The set−up, fixtures
to hold components in the balance machine, and the procedures required to obtain a balance within specified
limits is dependent on the type of balance machine. Therefore, follow the operating procedures for the balance
machine used.
CAUTION: Use ONLY the specified welding rod. Use of other types may result in poor welds leading to motor
failure.
in this publication. After cleaning, retest the stator windings.
E: Keep weld splatter out of the rotor core vent holes when welding balance weights to the end pla te.
NOT
Attach the balance weights as needed by welding to the rotor end plates at a diameter of 13.75 in. (276,9 mm).
e welding rod GE Spec. G50E37, BRON ZE (AWS−E−Cu−Sn−C). Weld the balance weights using GE weld process
Us
P8B−EP35.
30
Page 31

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
5.6.2. Connection–End (CE) Frame Head Installation
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
WARNING: The CE frame head weighs approximately 220 lbs. (100 kg). Use appropriate lifting devices for this
weith. Failure to do so may result in injury or death.
To assemble the connection–end frame head (27), align the frame head on the motor frame. Install and
hand–tighten the eight bolts and hardened flat washers (28) holding the frame head (27) to the motor frame
(21). Then t
5.6.3. Connection−End (CE) Bearing Assembly
To assemble the CE bearing onto the 5GEB22 rotor:
orque the bolts evenly in a diametrically opposite sequence to 468 ±28 lb–ft (634 ±38 Nm).
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
NOTE: Numb
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
WARNING:
sonnel. Ensure all personnel are clear and wear appropriate safety equipment. Follow all local regulations and
procedures for compressed air use. Failure to d o may result in injury or death.
WARNING: Components heat in ovens may be hot enough to cause injury. Use appropriate safety equipment
and follow shop procedures for handling heat ed compon ents. Failure to do so may result in injury.
When using compressed air, loosened debris may make the surrounding area dangerous for per-
1. Using clean, dr y, com pressed a ir, blow debris from CE bearing mounting area on the rotor shaft (5).
2. Inspect all CE bearing assembly components to ensure parts are clean and free of damage or burrs.
3. The rotor assembly must be in the horizontal position and blocked to prevent rotation or movement during
the assembly procedure.
4. If removed, install the rotor locking collar (36). To install the collar:
ers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
a. Heat the rotor locking collar (36) to 212°F (100°C) in an oven.
b. Remo
ve the locking collar (36) from the oven and place onto the rotor shaft. Press the collar into
position against the shoulder of the rotor shaft (5).
c. Sec
5. Fill th e cavity of the CE inner bearing cap (35) with 2.2 oz. (62.4 g) of GE specification D6A2C10 grease.
6. Pack the CE bearing (34) with 5 oz. (142 g) of GE specification D6A2C10 grease.
enly heat the CE inner bearing cap (35) to 212°F (100°C) in an oven to expand the cap’s bearing fit for the
7. Ev
CE bearing (34). Remove the inner bearing cap (35) from the oven and place onto a flat surface. Press the
CE bearing (34) (rotor side of the bearing as shown in Figure 15 ) into the inner bearing cap (35) bearing fit.
8. Cover or coat the CE rotor shaft (5) running surfaces with 0.25 oz. (7 g) of GE specification D6A2C10 grease.
ure the collar into position until it cools.
31
Page 32

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
9. Heat the CEinnerbearingcap,withthe CE bearing, to 212°F (100°C) inanove n. Remove the heated assembly
from the oven and immediately slide the assembly onto the CE end of the rotor shaft. Press the assembly
tightly against the shaft shoulder. Secure the assembly in position until cool.
10. Securing the CE bearing assembly on the rotor shaft (5) depends on the 5GEB22 model. Select the app ro-
priate process for the 5GEB22 model.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
a. For 5GEB22 models manufactured prior to September, 2001, the CE bearing assembly is secured
on the rotor shaft with a bearing retaining nut (33). Refer to Figure 8 for grease application during
assembly process. To secure thebearing assembly ontherotor shaft, thread the nut into thetapped
end of the rotor shaft until hand tight. Insert a spanner wrench (tool number 9945228) into the
holes on the outside flat of the bearing nut. Using a brass sledgehammer, strike two or three sharp
blows, driving the n ut clockwise, approximately one quarter turn from hand tightened. Thread the
two locking set screws (40) into the bearing retaining nut (33) and torque the set screws to 40 ±2
lb—ft (54 ±3Nm). Using a heavy center punch, stake or peen each set screw intwoplaces to prevent
loosing.
b. For 5GEB22 models manufactured after September, 2001, the CE bear ing assembly is secured on
the rotor shaft with a bearing clamp (41). Refer to Figure 9 for grease applications during assembly
process. To secure the bearing assembly on the rotor shaft, Inspect the rotor shaft bore (5) and
clamp (41) to ensure the components are free of damage and burrs. Lightly coat the rotor shaft
bore with GE specification D6A2C10 grease to facilitate assembly. Insert the bearing clamp into the
rotor shaft b ore. Thread the clamp bolts (42) through the clamp into the tapped holes of the rotor
shaft. Tighten the clamp bolts alternately to evenly to draw the clamp into the rotor shaft bore.
When the clamp is fully seated in the rotor shaft, torque the clamp bolts to 58 ±2 lb—ft (78 ±3 Nm).
11. Apply the gasket and assemble the dummy CE bearing cap 41C689896 ( Figure 36 ) with four bearing cap
bolts and hardened washers (31). Thread the bolts through the dummy bearing cap into the inner bearing
cap (35) to secure the bearing assembly.
5.6.4. Drive End (DE) Bearing Assembly
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
ToassembletheDEbearing:
WARNING: When using compressed air, loosened debris may make the surrounding area dangerous for per-
sonnel. Ensure allpersonnel are clearand wear appropriate safety equipment. Follow alllocal regulations and
procedures for compressed air use. Failure to do may result in injury or death.
1. Using clean, dry compressed air, blow any loose debris clear of the DE rotor shaft (5).
2. Inspect the DE bearing assembly and rotor shaft to ensure parts are free of damage and burrs.
3. The
WARNING: Componentsheated in ovens maybehot enough to cause injury. Use appropriate safety equipment
d follow shop procedures for handling heated components. Failure to do so may result in injury.
an
rotor should be in the horizontal position and blocked to prevent movement and rotation.
4. If removed, install th e inboard DE shaft collar (1) onto the rotor shaft (5). to install the rotor shaft:
32
Page 33

a. Heat the shaft collar (1) to 212°F (100°C) in an oven.
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
b. With the rotor in a horizontal position, remove the collar from the oven and press onto the rotor
shaft (5) drive end until seated against the rotor shaft shoulder. Secure the collar in place until cool.
c. After the collar has cooled, coat the rotor shaft collar’s running surfaces with GE specification
D6A2C10 grease as shown in Figure 10 .
d. Pack approximately 8 oz. (227 g) with GE specification D6A2C10 grease into the DE inner bearing
cap (12) as shown in Figure 10 . Coat the inner bearing cap running surfaces with the same grease.
5. Place the inner bearing cap in position over the DE shaft collar (1).
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
6. Install the
7. Install
8. Fill the DE bearing (rollers and outer race) with 16 oz. (454 g) with GE specification D6A2C 10 grease as shown
inFigure10.
flinger (2) onto the rotor shaft drive end. To install the flinger:
a. Heat the flinger to 212°F (100°C) in an oven.
b. Ensure the inner bearing cap (12) is in position on the rotor shaft drive end.
c. With the r
shaft drive end until the flinger is seated against the shaft collar (1). Secure the flinger in position
until cool.
d. When the flinger has cooled, coat the flinger with GE specification D6A2C10 grease.
the DE bearing (3) inner race onto the rotor shaft (5) drive end. To install the bearing inner race:
a. Heat the inner race to 212°F (100°C) in an oven.
b. With the rotor in a horizontal position, remove the inner race from the oven and press onto the rotor
shaft drive end until the inner race is seated against the flinger (2). Secure the inner race in position
until c
c. When the inner race has cooled, coat the race with GE specification D6A2C10 grease.
otor in a horizontal position, remove the flinger from the oven and press onto the rotor
ool.
9. Assemble the DE frame head (11), the DE i nner bearing cap (12), and DE bearing (3) (outer race and rollers)
together. To assembly these components:
a. Cold press the DE bearing (3) (outer race and rollers) into the DE frame head (11). Refer to Figure 10
for approximate position of the bearing in the fr ame head.
b. Install t he DE bearing pilot tool (8849499P7), Figure 37 , on the rotor shaft as shown in Figure 11 .
E: Without the use of a rotor drive–end bearing pilot, the upper–most rollers will drop toward the center,
NOT
making the assembly of rollers over the inner race diffi cult. Refer section 6.4. SPECIAL TOOLS AND MATERI-
ALS in this publication for the bearing pilot, guide stud and dummy bearing cap part numbers.
c. Thread a guide stud (.625–11 X 10) in the inner bear cap (12) as shown in Figure 11 .
33
Page 34

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
d. Align the inner bearing cap gasket (9) over the guide stud onto the inner bearing cap (12) as shown
in Figure 10 .
WARNING: The DE frame head weighs approximately 75 lbs. (34 kg). use appropriate lifting devices for this
weight. Failu
re to do so may result in injury.
e. Lift the DE frame head (11) with a hoist, align on the guide stud, and install ont o the rotor shaft over
the DE bearing as shown in Fi gure 12 . The DE frame head should remain supported by the hoist
until the inner bearing cap (12), the DE frame head (11), and the outer dummy bearing cap (7) are
bolted together.
f. Remove the DE bearing pilot tool (8849499P7) from the rotor shaft.
g. Install and align the outer gasket (9) over the guide stud onto the DE fram e head.
h. Align the dummy bear cap, Figure 38 , (6796493P3, used for assembly purposes) on the guide stud
and position against the DE frame head (11).
i. Thread four bearing cap bolts with washers (8) through the dummy bearing cap and DE frame head
(11) into the inner bearing cap (12). Remove the guide stud and thread the last bearing ca p bolt into
position. Tighten the bolts to secure the assembly together.
NOTE: Do not assemble the remaining DE bearing assembly components until the rotor is installed in the
stator frame.
GUIDE STUD FOR
ASSEMBLING FRAMEHEAD
BOLTS IN INNER BEARING CAP
BEARING PILOT USED
TO GUIDE FRAMEHEAD
(WITH OUTER RACE AND
ROLLERS) OVER THE INNER RACE.
E-50559
Figure 11. DE Bearing pilot and Guide Studs Installed.
34
Page 35

GUIDE STUD
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
BEARING PLOT
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
5.7. ROTOR IN
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONE
The rotor assembly is installed by lowering the rotor into the vertical stator frame. The rotor assembly consists
of the C
bearing assembly (3) with the DE dummy bearing cap. To install the rotor assembly into the stator frame:
1. The CE
E bearing with inner bearing cap (35), the rotor shaft (5) and core (23), the DE frame head (11), and the DE
head is not installed, install the CE frame head as follows:
E-50560
Figure 12. DE Frame Head Installed Over DE Bearing on Rotor Shaft.
STALLATION INTO THE STATOR FRAME
NT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
frame head (27) must be mounted on the stator frame (21) prior to rotor installation. If the CE frame
a. Ensur
b. Ensure the CE frame head (27) stator frame fit is free of damage and burrs.
c. Align the CE frame head (27) on the stator frame (21) so that the largest gap on the CE frame head
d. Thread the CE frame head eight mounting bolts and hardened flat washers (28) through the CE
e the stator frame (21) CE frame head fit is free of damage and burrs.
bearing cap mounting holes is toward the stator frame feet as shown in Figure 13 .
frame head into the tapped holes of the stator frame (21).
e. Tighten the bolts to dra w the CE frame head into t he stator frame fit evenly.
f. Whe
n the CE frame head is fully seated against the stator frame, torque the mounting bolts to 468
±27 lb—ft (634 ±36 Nm).
35
Page 36

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
LARGEST BEARING CAP
BOLT SPACE TO BE AT
6 O’CLOCK POSITION
WHEN FRAME HEAD (27)
IS ASSEMBLED TO FRAME (21)
E-50831
Figure 13. CE Frame Head and CE Bearing Cap Alignment.
2. Mount the stator frame in a heavy–duty stand with the Drive End (DE) up. Level the stator frame so that
the rotor can be lowered vertically into the frame with a hoist without damaging the bearings or bus rings.
w enough clearance for the guide studs on the rotor assembly to extend approximately 8 in ches (203
Allo
mm) beyond the CE frame head (27)
3. Ens
4. Ensure the DE frame head (11), mounted on the rotor shaft, is free of damage and burrs.
5. Remove the CE outer dummy bearing ca p from the end of the rotor shaft. The inboard CE gasket must
ure the DE of the stator frame (21) is free of damage and burrs in the frame head fit.
remain aligned on the inner bearing cap (35).
36
Page 37

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
6. Thread two long guide studs (.625–11 X 10) into opposite holes of the inner bearing cap (35). Do not thread
the guide studs into the rotor locking ring (36). The studs must move freely to align with the CE frame head
(27) mounted on the stator frame (21).
7. Screw a 1 in.– 8 X 2.62 steel lifting eyebolt (GE Tool N672P39) into the threaded hole in the Drive End (DE) of
the rotor shaft.
WARNING: The partial rotor assembly weighs approximately 1887 lbs. (856 kg). Use appropriate lifting devices
for this weight. Failure to do so may result in injury or death.
CAUTION: Exercise extreme care when turning the rotor from the horizontal position to avoid damage to the
core and the bearing and frame head fits. A suitable turning fixture or two hoists should be used to position
the rotor ve
rtically.
8. Carefully lift the rotor assembly from the horizontal position, attaching a hoist hook to the lifting eye. Align
the hoist cable with the center line of the stator frame (21), and slowly lower the rotor into the motor frame,
guiding the long studs through the appropriate connection–end frame head (31) holes.
9. Install and hand–tighten the eight bolts and hardened flat washers (10) holding the DE frame head (11) to
the stator frame (21). If the DE frame head (11) does not seat into the frame fit then tighten the bolts evenly
in a diametrically opposite sequence until the DE frame head is mated to the stator frame. Following the
same diametrically opposite sequence, torque the bolts to the value of 472 ±24 lb—ft (640 ±32 Nm).
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
10. Rotate the motor to the rotor shaft horizontal position.
11. Align the dummy bearing cap, Figure 36,onthe CE frame head using the two guide studsprotruding through
the CE frame head. Thread two bearing cap bolts and hardened washers (31) into the open holes of the
dummy bearing cap. Remove the two guide studs and thread two bearing cap bolts and hardened washers
(31) into the open holes. Torque the bolts to 115 ± 5 lb—ft (155 ±7 Nm).
5.8. MOTOR BEARING CHECKS AFTER ASSEMBLY
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
5.8.1. Connection End (CE) Bearing Runout Check
To check the CE bearing (34) runout:
1. Raise the CE end of the motor 4 to 6 in. (102 to 152 mm), and force the rotor toward the Drive End (DE).
2. Clamp a dial in dicator on the face of the Connection End (CE) of the rotor shaft (5).
3. Zero the dial indicator reading on the face of the CE rotor bearing (34) outer race.
4. Rotate the rotor to determine the bearing runout.
a. If runout i s within allowable limits for runout as shown in section
this publication, proceed to the next bearing check procedure.
6.1.2. Drill Motor General Data
in
b. If runout is outside allowable limits, retighten the CE bearing cap bolts (31) and CE frame he ad bolts
(28). Repeat the runout check.
37
Page 38

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
c. If run out remains excessive, disassemble the motor to check the CE frame head (27) bearing fit, and
the CE bearing h
to determine cause of excessive bearing runout. Reassemble the motor and repeat runout check.
ousing (35) bearing fit, and inspect all parts for burrs, debris, or component wear
5.8.2. Drive End (DE)
To check the DE bearing (3) runout:
1. Raise the DE end of the motor 4 to 6 i n. (102 to 152 mm), and force the rotor toward the Connection End (CE).
2. Clamp a dial
3. Zero the dial indicator reading on the face of the DE rotor bearing (3) outer race.
4. Rotate the rotor to determine the bearing runout.
5.8.3. Drive End (DE) Bearing Radial Clearance Check
Bearing Runout Check
indicatoronthefaceoftheDriveEnd(DE)oftherotorshaft(5).
a. If ru nout i
this publication, proceed to the next bearing check procedure.
b. If runout i
(10). Repeat the runout check.
c. If runout
the DE inner bearing cap (12) bearing fit, and inspect all parts for burrs, debris, or component wear
to determine cause of excessive bearing runout. Replace any worn components. Reassemble the
motor an
s within allowable limits for runout as shown in section
s outsid e allowable limits, retighten the DE bearing cap bolts (8) and DE frame head bolts
remains excessive, disassemble the motor to check the DE frame head (11) bearing fit,and
d repeat runout check.
6.1.2. Drill Motor General Data
in
To check the DE bearing (3) radial clearance:
1. With Dr
End (CE).
2. Selec
eral Data
3. Place
of the uppermost bearing roller. Hand–turn the rotor shaft just enough to roll the top bearing roller over the
minimum radial clearance feeler gage.
4. Repeat the minimum clearance check for each bearing roller in the drive–end rotor bearing. Reject the bear-
ing if one or more bearing rollers will n ot roll over the minimum radial clearance feeler gage.
5. Select a feeler gage thickness equal to the maximum radial clearance given in se ction
GeneralData
sur
the bearing rollers will roll over the maximum radial clearance feeler gage. Reject the bearing if one or more
bearing rollers will roll over the maximum radial clearance feeler gage.
5.8.4. Rotor Shaft End–Play Check
check rotor shaft (5) end—play:
To
ive End (DE) of the motor raised 4 to 6 in. (102 to 152 mm), force the rotor toward the Connection
t a feeler gage thickness equal to the minimum radial clearance given in section
of this publication for the drive–end rotor bearing.
the feeler gage flat against the rolling surface of the inner race of the DE rotor bearing (3), just in front
of this publication for the drive–end rotor bearing. Place the feeler gage flat against the rolling
face of the inner race of the dr ive–end rotor bear ing. Hand–turn the rotor shaft to check that none of
6.1.2. Drill Motor Gen-
6.1.2. Drill Motor
1. With the motor horizontal, force the rotor to seat at the Drive End (DE).
38
Page 39

2. Clamp a dial indicator to the motor frame at the Connection End (CE) of the motor or the dummy CE bear-
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
ing cap. Zero the indicator ball on the face of the rotor bearing nut (33) for m odels manufactured prior to
September 2001 or the rotor bearing clamp (41) for models manufactured after September 2001.
3. Force the rotor back to seat at the Connection End (CE). The amount of rotor shaft end–play indicated must
not exceed the end–play given in section
5.9. FINAL ASSEMBLY OF ROTOR DRIVE END (DE) COMPONENTS
If the rotor bearings pass the bearing runout and radial clearance checks, install the remaining DE component
parts as follows:
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
1. Remove the dummy DE bearing cap.
2. Pack the DE outer bearing cap (7) with 8.0 oz. (227 g) of GE Specification D6A2C10 greas e. Ensure the gasket
(9)isinplacebetweenthebearingcapandframehead.
6.1.2. Drill Motor General Data
1150HPACDrill
of this publication.
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
3. Assemble the bearing cap (7) insert to the DE frame head (11) and inner beari ng cap (12) with eight bolts and
hardened flat washers (8), and torque the bolts to 115 ±5 lb–ft (155 ±7 Nm).
4. Install the DE oute r sleeve (4) onto the rotor shaft (5). To install the sleeve:
a. Heat the DE outer sleeve (4) to 110°C (230°F) in an oven.
b. Remove the sleeve from the oven and press it onto the DE rotor s haft until seated against the inner
race of the DE bearing (3).
c. Secure the sleeve in place until cool.
5.10. FINAL ASSEMBLY OF ROTOR CONNECTION END (CE) COMPONENTS
Install the remaining CE component parts as follows:
NOTE: Numbers in parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
1. Remove the dummy CE bearing cap.
2. Apply 2.8 oz. (79.4 g) of GE Specification D6A2C10 grease to the CE bearing cap (32).
3. Align the CE bearing cap (32) with the largest gap between holes toward the mounting feet as shown in
Figure 13 . Assemble the bearing cap (32) to the CE frame head (27) and inner bearing housing (35) with
eight bolts and hardened flat washers (31), and torque the bolts to 115 ±5 lb–ft (155 ±7 Nm).
5.11. ELECTRICAL RUNNING TESTS
After the motor has been reconditioned and reassembled, perform the following tests to ensure that the motor
will operate satisfactorily:
WARNING: Electrical tests are performed at high voltage. Electrical shock can cause serious or fatal injury.
Proper precautions should be taken and observed by personnel performing testing to avoid injury
39
Page 40

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
NOTE: Numbers i
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION of this publication, unless otherwise noted.
1. Using stiff pu
The thermometers should be in physical contact with the bearing cap for a valid test.
2. Runthemotor
temperature should not exceed 100°F (55°C) rise above room temperature during or at the end of the tests.
a. Run the moto
b. Run the motor for two minutes on 82 Hz 572 volts rms line−to−line. The average amperage of the
c. Run the motor for forty minutes on 61 Hz 572 volts rms line−to−line. The average amperag e of the
3. Run motor
should be b etween 3080 and 3090. Observe for any unusual noise or vibration.
n parenthesis () refer to item numbers in Figure 15 located in section 6.2. DRILL MOTOR
tty, secure thermometers to the Drive End (DE) (7) and Connection End (CE) (32) bearing caps.
unloaded in the following sequence. Applied waveforms should be sinusoidal. The measured
r for two minutes on 41 Hz 572 volts rms line−to−line. The average amperage of the
three phases should be between 368 and 453 rms amperes. Motor rpm should be approximately
820 during the test.
three phases should be between 130 and 150 rms amperes. Motor rpm should be approximately
1640 durin
three pha
1220 during the test.
overspeed test. Run the motor for two minutes on 155 Hz 540 volts rms line−to−line. Motor rpm
gthetest.
ses should be between 145 and 183 rms amperes. Motor rpm should be approximately
4. Run moto
and DE bearings. Vibration should not exceed 0.44 peak in/sec (11,2 peak mm/sec). If vibration is excessive,
rebalance the rotor or consult the GE Transportation Representative.
5. Check for bearing noise. Run the motor on 60 Hz 572 volts rms line−to−line. Motor rpm should be approxi-
mately 1200. C heck the DE bearing with a demodulation meter. The demodulation meter should not register
in exce
6. Check for bearing noise. Run the motor on 70 Hz 572 volts rms line−to−line. Motor rpm should be approxi-
matel
in excess of 1.49g.
7. Perfo
5.12.HUB I
5.12.1. Hub Fitting
To prevent a hub from slipping, it should have at least 75 percent fit on th e shaft; i.e., at least 75 percent of the
tapered bore of the hub should be in contact with the tapered fit on the shaft. Before mounting a hub, check
and
1. Lightly cover the bore of the hub with a blueing compound such as Prussian Blue.
rm Dielectric Test. Hi−Pot any stator terminal to ground at 3500 VAC rms 60 Hz for one minute. Ground
one lead of the RTD during the test.
NSTALLATION
correct the fit as follows:
r vibration test. Run the motor on 150 Hz until the motor rpm is 3000. Measure vibration at t he CE
ss of 1.49g.
y 1400. Check the CE bearing with a demodulation meter. The demodulation meter should not register
2. Snap the cold hub forcefully onto the shaft.
3. Ma
40
rk the relative angular position of hub with respect to the shaft.
Page 41

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
4. Remove the hub from the shaft. A convenient method of removal is by the use of two finely tapered steel
wedges (hardened and ground), which are carefully driven between the hub and the bearing outer sleeve
on the shaft.
5. IMPORTANT! Inspect the taper fit of the shaft; blueing of the hub bore should now show on the shaft. If at
least 75 percent of shaft surface shows traces of blueing, the fit is satisfactor y. If, however, only a few spots
of blueing show on the shaft, the fit is not sa tisfactory.
6. Dress down the blue spots on the shaft very lightly with a fine emery cloth such as No. 400A Triemite.
7. Blue the hub bore again (refer to Step 1) and repeat Steps 2, 4, 5 and 6. Be sure to place the hub onto the
shaft in the same position as marked.
8. Generally, the fit will be improved, but the foregoin g procedure may have to be repeated several times to
obtain a 75 percent fit.
9. Under no circumstances use a lapping compound since lapping will produce a shoulder at the large end of
the tapered fit. A shoulder will prevent a perfect fit when the hub is mounted hot; i.e., when it is mounted in
the advanced position.
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
10. After a good fit has been obtained, thoroughly clean the shaft and th e hub bore to remove all blueing, oil or
grease. Then mount the hub.
5.12.2. Hub Mounting
1. Thoroughly clean the hub fit ontheshaftand bore of the hub (refertothe procedure insection
THE MOTOR
2. Spot the cold hub on the shaft by hand and check for at least 75 percent fit. Refer to section
Fitting
in this publication. If necessary, dress the shaft to obtain this fit.
3. Trial mount the cold hub onto the shaft. Measure and record the position of the hub with respect to the end
of the shaft. Take measurements with a micrometer advance gaug e (similar to that shown in Figure 14 ).
Zero the gauge. Refer to Figure 39 in section
advance gage information.
in this publication). Remove any scoring on the shaft or hub bore.
6.4.3.6. Hub Installation Advance Gage
4.2. CLEANING
5.12.1. Hub
in this publication for
41
Page 42

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
ADVANCE GAGE
ROTOR
SHAFT
4. Mark points of measurement, and mark across the end of shaft and hub face so that the hub, when heated,
can be mounted in exactly the s ame angular position, and so the advance measurement can be made from
the sam
CAUTION: Zero settings of advance gauge must not be disturbed until all readings on the hub are completed.
5. Mount the hub hot onto the shaft so as t o secure an advance from the cold position to the hot position along
the axis of the shaft as indicated in this section. The ESTIMATED difference between shaft temperature and
hub temperature(temperature rise) that will provide thisadvance is also given. The temperature difference
is only an estimate and should be adjusted (if necessary) to provide the advance within prescribed limits.
Refer to Table 7 .
e point.
HUB
Figure 14. Using Advance Gage for Hub Installation.
E-50962
CAUTION: The temperature of the hub must no t exceed 250°C (482°F); otherwise the hub may become annealed.
E: For rise or change in temperature from ambien t (room or part), only compare the ratio of change
NOT
between Celsius and Fahrenheit. Every 5 degrees of change in Celsius, Fahrenheit change will be 9 degrees.
The opposite would be true for Fahrenheit to Celsius change comparison; every 9°F change represents 5°C
nge. Do not add or subtract the offset (32 degrees).
cha
42
Page 43

1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
TABLE 7. HUB RISE TEMPERATURE IN DEGREES ABOVE SHAFT TEMPERATURE
PART NUMBER OF HUB ADVANCE, INCH (MM) TEMPERATURE RISE
493A471 .120 — .130 (3.048 — 3.302) 387°F (215°C)
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
GEK-91696D
41A237799 .120 — .130 (3
84B519250P1 .110 — .120 (2.794 — 3.048) 387°F (215°C)
6. Heat the hub in an oven until it has reached a uniform temperature (the desired number of degrees above
shaft temp
(25°C) + (heat rise) 387°F (215°C) = 464°F (240°C) hub temperature, which is maximum allowable hub tem-
perature.
7. Measure the temperature of the shaft and the hub with the same instrument. An accurate method must
be provided for measuring hub and shaft temperatures quickly before mounti ng the hub. T his can best be
done with
obtain the fit temperature.
8. Insure th
Then, using adequate hand protection, quickly mount the hot hub on the shaft in the same angular position
as when cold. When the hub is nearly in engagement with the taper fit (not in actual contact), snap it forcibly
into pla
cooled; otherwise, it will freeze to the shaft and cannot be adjusted further.
9. Check t
axis of the shaft must be held within the limits indicated. Check the actual advance with an indicator gauge,
located in the sam e relative position as used to measure the cold position in Step 3 (as shown in Figure 14 ).
erature). For example, if the shaft temperature is 77°F (25°C), the hub is heated to (ambient) 77°F
a hand pyrometer. In using the py rom eter, place point of the gauge inside the bore of the hub to
at the hub bore and the shaft taper are clean prior to assemb ling the heated hub to the rotor shaft.
ce with a quick push. It is important that the hot hub be instantly snapped into position before it has
he hot or shrunk−on position of thehubontheshaft. The advance from coldtohotposition along the
.048 — 3.302)
387°F (215°C
)
10. If the advance is not within specified limits, remove the hub and repeat the assembly procedure.
43
Page 44

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
6. SUMMARY DATA
6.1. DRILL MOTOR DATA
6.1.1. Drill Motor Application Da ta
TABLE 8. 5GEB22 APPLICATION DATA
SPEED (RPM) TORQUE, LB-FT (NM) HORSE-
POWER
0 10600 (14372) 0 3000 1470 15 seconds
669 9025 (12236) 1150 3000 1270 144 seconds load,
800 7550 (10236) 1150 3000 1120 Continuous
800 9200 (12474) 1400 3000 1380 120 seconds load,
800 9200 (12474) 1400 3000 1380 32 seconds load,
1600 3773 (5116) 1150 3000 1095 Continuous
1800 3351 (4543) 1150 3000 1125 Continuous
6.1.2. Drill Motor General Dat a
TABLE 9. 5GEB22 GENERAL DATA
Weight, complete motor (less connection box and blower), lbs. (kg) 5693 (2582)
Weight, rotor only, lbs. (kg) 1623 (736)
VENTILATION
(SCFM)
I
AMPS TIME
PH
116 seconds no load
90 seconds no load
30 seconds no load
Maximum permissible speed, RPM 3000
Maximum permissible vibration, peak in/sec (mm/sec)
Stator field resis tance each pair of terminals at 25 °C (77 °F), ohms 0.0088 — 0.0108
tator field megger value (any terminal to ground)
S
RTDs, ohms/material 100/platinum
Drive end (DE) bearing diametrical clearance range, assembled, in. (mm) 0.005 (0.127) — 0.009 (0.229)
Connection end (CE) bearing diametrical clearance range, assembled, in. (mm) 0.0005 (0.0127) — 0.0035 (0.089)
Rotor balance, each end, gram—inches 50
Runout measured from shaft to outer race, each end, in. (mm) 0.001 (0.0254)
Rotor drive end bearing grease lubrication capacity, ounce (gram) 32.5 (921.37)
Rotor connection end bearing grease lubrication capacity, ounce (gram) 10.25 (29.06)
Bearing lubricant (for additional information, refer to section
Lubricant D6A2C10 Data
44
in this publication)
6.1.3. Drill Motor
0.44 (0.01118)
2Megohms
≥
GE Spec D6A2C10
Page 45

1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
6.1.3. Drill Motor Lu
D6A2C10greaseisalithiumsoapbasegreasewithaddedantioxidant.Itcontainsanoilofheavyviscosityand
is especially
grease specifications are liste d in Table 10 .
Worked Consistency, 77 °F (25 °C), MM/10
Dropping Point, Minimum Degrees °F (°C) 380 (193.14)
Mineral Oil Viscosity at 100 °F (,37.74 °C), SSU 475 — 525
Free Alkali, Percent (Max) 0.50
Free Acid, Percent (Max) 0.000
Color Amber
Base (with Antioxidant) Lithium
Oxidation Resistance Time to Reach 20 psi Drop at 210 °F, Hr. (Min) 1000
Corrosion Must pass
Approved Vender Shell Oil
Brand Name Cyprina RA
bricant D6A2C10 Data
suitable for high speed, high temperature open or shielded bearings in drilling motors. D6A2C10
TABLE 10. 5GE
B22LUBRICANTDATA
220 — 240
45
Page 46

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
6.2. DRILL MOTOR CO
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
MPONENT IDENTIFICATION
13 14
12
15
23
17
16
1
5
18
19
20
21
18
22
42
41
23
19
38
17
37
36
25
2624
35
27
28
29
30
39
31
32
33
34640
REF. DESCRIPTION
1 D.E. SHAFT COLLAR
2 FLINGER
3 ROLLER BEARING
4 SLEEVE
5 ROTOR SHAFT
6 PIPE PLUG
7 BEARING CAP (OUTER)
8 BOLT AND HARD WASHER
9 GASKET
10 BOLT AND HARD WASHER
11 D.E. FRAME HEAD
12 BEARING CAP (INNER)
13 STATOR AIR BAFFLE
14 FELT (AIR DAM)
15 TIE RING
16 STATOR COIL
17 ROTOR END RING
18 BALANCE WEIGHT
19 ROTOR BAR
20 ROTOR CAGE STOP RING
21 STATOR FRAME
VIEW OF PRODUCTION
NOTE: ALL PARTS SAME EXCEPT THOSE SHOWN
AFTER SEPTEMBER 2001
REF. DESCRIPTION
22 STATOR CORE
23 ROTOR CORE
24 BUS RING SUPPORT
25 TAP BLOCK
26 BUS RINGS
27 C. E. FRAME HEAD
28 BOLT AND HARD WASHER
29 BUS RING CLAMPS
30 BOLT AND INSULATING SLEEVE
31 BOLT AND HARD WASHER
32 C. E. BEARING CAP
33 BEARING RETAINING NUT
34 ROLLER BEARING
35 C. E. BEARING HOUSING
36 COLLAR (ROTOR LOCKING)
37 SHAFT NUT
38 SHAFT WASHER
39 GASKET
40 SET SCREW
41 BEARING CLAMP
42 BOLT AND HARD WASHER
E-50557
Figure 15. 5GEB22 Drill Motor Component Identification.
46
Page 47

6.3. INSPECTION DATA
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
6.3.1. Rotor Shaft Inspection Data
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 16. Rotor Shaft Dimensional Checks.
6.4. SPECIAL
The foll owing s ection detail special tools and materials recommended for 5GEB22 overhaul.
6.4.1. Standard Removal Tool Assemblies
The fo
scriptive figures follow Table 11 . The tool assemblies consists of various individual components that are detailed
in the section following t his.
TOOL
6751547G1 CE BEARING INNER RACE REMOVAL TOOL Figure 17
6751547G4 DE OUTER SLEEVE REMOVAL TOOL ASSEMBLY Figure 18
1547G5
675
6751547G6 DE INNER BE ARING CAP REMOVAL TOOL ASSEMBLY Figure 20
6751547G7 DE INN ER SLEEVE REMOVAL TOOL ASSEMBLY Figure 21
751547GX
6
TOOLS AND MATERIALS
llowing tool assemblies listed in Table 11 are used to aid disassembling the 5GEB22. Tool assemblies de-
TABLE 11. TOOL ASSEMBLIES
ASSEMBLY
EARING INNER RACE REMOVAL TOOL ASSEMBLY
DE B
E INBOARD ROTOR LOCK SLEEVE REMOVAL TOOL ASSEMBLY
C
DESC
RIPTION
FIGU
ure 19
Fig
igure 22
F
RE REFERENCE
47
Page 48

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 17. CE Bearing Inner Race Removal Tool 6751547G1.
48
Page 49

1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
18. DE Outer Sleeve Removal Tool Assembly 6751547G4.
Figure
49
Page 50

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 19. DE Bearing Inner Race Removal Tool Assembly 6751547G5.
50
Page 51

1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 2
0. DE Inner Bearing Cap Removal Tool Assembly 6751547G6.
51
Page 52

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 21. DE Inner Sleeve Removal Tool Assembly 6751547G7.
Figure 22. CE Inboard Rotor Lock Sleeve Removal Tool Assembly 6751547GX.
52
Page 53

1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
6.4.2. Individual Components of Tool Assemblies
The following list of components in Table 12 are used to create the tool assemblies listed in the previous section.
Detail figures for significant individual components follow Table 12 in this section. Item numbers within the fig-
ures of tool assemblies identify individual components in Table 12 .
TABLE 12. TOOL ASSEMBLIES INDIVIDUAL COMPONENT LISTING.
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QUANTITY FIGURE REFERENCE
1 6733347G1 CLAMP PLATE 1 Figure 23
2 8806566P1 BOLT, 2-8X6.25 (SPECIAL) 1 Figure 24
3 8806567P1 PRESS CAP 1 Figure 25
4 6734764P2 CLAMP 2 Figure 26
5 6727124G1 RING 1 Figure 27
6 41A235078P1 STUD, .625-11X4.75 (GRADE 8) 4 —
7 N203P33 NUT, .625-1 1 (GRADE 5) 4 —
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
GEK-91696D
8 6734765P2 CLAMP 2 Figure 28
9 6727110G1 RING 1 Figure 29
10 6733346P6 CLAMP 2 Figure 30
11 6717242P1 STUD, .4375-14X11 (GRADE 5) 4 —
12 8806337P1 STUD, .625-11X12.5 (GRADE 5) 4 —
13 6717243P1 STUD, .625-11X16.75 (GRADE 5) 4 —
14 N203P27B13 NUT, .4375-14 (GRADE 5) 4 —
15 UNASSIGNED CLAMP PLATE 1 Figure 31
16 UNASSIGNED STUD, .5-13X8.75 (GRADE 5) 3 —
17 UNASSIGNED NUT, .5-13 (GRADE 5) 3 —
53
Page 54

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
°
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
°
°
°
°
°
°
°
°
°
°
°
°
°
Figure 23. Clamp Plate 6733347G1 (Item 1, Table 12).
54
Page 55

1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
Figure 24. Bolt 8806566P1 (Item 2, Table 12).
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
°
°
°
Figure 25. Press Cap 8806567P1 (Item 3, Table 12).
55
Page 56

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
°
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
°
°
°
Figure 26. Clamp 6734764P2 (Item 4, Table 12).
56
Page 57

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
°
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 27. Ring 6727124G1 (Item 5, Table 12).
57
Page 58

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
°
°
°
Figure 28. Clamp 6734765P2 (Item 8, Table 12).
58
Page 59

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
°
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 29. Ring 6727110G1 (Item 9, Table 12).
59
Page 60

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
°
°°
Figure 30. Clamp 6733346P6 (Item 10, Table 12).
°
60
Page 61

1150HPACDrill
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 3
6.4.3. Other Special Tools and Materials
6
.4.3.1. DE Hub Removal Tool Assembly
The Tab
ures in thi s section depict the assembly and significant components.
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QUANTITY FIGURE REFERENCE
1 88439
2 8864170P1 HYDRAULIC FITTING ADAPTER 1 Figure 34
3 41B535119G1 BACKING PLATE 1 Figure 33
4 41A
5 N22P39040 BOLT, 1-8 X 2.5 1 —
le 13 de scribes the components that make up the 41B535703G1 Hub Removal Tool Assembly. The fig-
TABLE 1
47P20
230939P14
MANUA
T RING, 0.125 (THICK) X 3.9 (ID) X 5.5 (OD)
FEL
1. Clamp Plate (Item 15, Table 12).
3. HUB REMOVAL TOOL 41B535703G1.
L HYDRAULIC PUMP (10000 PSI)
1—
1—
61
Page 62

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
1
4
3
2
HUB
5
41B535703G1 HUB REMOVAL TOOL ASSEMBLY
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QNTY
1 8843947P20 MANUAL HYDRAULIC PUMP 1
2 8864170P1 HYDRAULIC FITTING ADAPTER 1
3 41B535119G1 BACKING PLATE 1
4 41A230939P14 FELT 1
5 N22P39040 BOLT, 1-8X2.5 1
ROTOR
SHAFT
Figure 32. 41B535703G1 Hub Removal Tool Assembly.
E-50541
62
Page 63

1.0625 (26.9875) DIA THRU
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
.40 (10.16)
1.75 (44.45)1.60 (40.64)
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
1.00
(25.4)
CEMENT FELT RING HERE
WITH 497A806P12
.4375 (11.1125) DRILL
THRU 2 HOLES
MAKE FROM B4C1B
250 FINSH ALL SURFACES
MEASUREMENT IN INCHES (MILLIMETERS IN PARENTHESES)
Figure 33. Hub Removal Tool Backing Plate 41B535119G1.
3.85 (97.79) DIA
3.85 (97.79) DIA
E-50832
63
Page 64

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
3.125
(79.375)
0.5625
(14.287)
0.50
(12.7)
0.180 +/- 0.005 DIA
(4.572 +/- 0.127)
0.285 +/- 0.002 DIA
(7.239 +/- 0.0508)
30°
0.875
(22.225)
0.375-24
UNF-2A
0.25 RAD
(6.35)
0.125 DRILL
(31.75)
0.375 DIA
(9.525)
0.625
(15.875)
0.4375
(11.1125)
30°
0.0625 CHAM
(1.5875)
0.900 +/- 0.005 DIA
(22.86 +/- 0.127)
0.2187 DIA
(5.555)
MAKE FROM B5F4M STEEL
ALTERNATE MATERIAL B4C1A
125 FINISH ALL SURFACES
MEASUREMENTS IN INCHES (MILLIMETERS IN PARENTHESES)
0.5625-18 UNF-2B
BOTTOM TAP
0.750
(19.05)
E-50542
Figure 3
6
.4.3.2. Bearing Nut Spanner Wrench
Bearing nut s panner w rench 9945258 ( Figure 35 )is used to remove and tighten the CE bearin g nut.
4. 8864170P1 Hydraulic Fitting Adapter.
64
Page 65

1150HPACDrill
1 HANDLE (4140)
2 PLATE (4140)
3PIN (T.S)
4 SOCKET HEAD SCREW (.5-13X1.25)
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
4.000 + .007 DIA
(101.600 + .1778)
BOLT CIRCLE
1.105 + .005
1.0 (25.4)
BLANCHARD
3.125 (79.375) DIA
BOLT CIRCLE
PART DESCRIPTION
1.105 + .005
(28.067 + .127)
1.105 + .005
(28.067 + .127)
(28.067 + .127)
PART 4
BOLT
.8125 (20.6375) C’BORE,
.125 (3.175) DEEP, C’SINK
.031 (794), 2 OPP. HOLES
GRIND
5.5 (139.7) DIA
9945228 SPANNER WRENCH
PART 3 PIN
0
45
1.105 + .005
(28.067 + .127)
+ 1.5 (38.1) RAD
17.0 (431.8)
20.75 (527.05)
DRILL FOR .625 (15.875) REAMER, PART 1 & 2,
2 OPPOSITE HOLES, REAM ASSEMBLED
.53125 (13.4938) DRILL THRU, .8125 (20.6375), 2 OPPOSITE
HOLES, C’BORE HANDLE .8125 (20.6375), .1875 (4.7625) DEEP
.5-13 TAP THRU
2 OPPOSITE HOLES
DRILL .5625 (14.287)
C’BORE .8125 (20.638) .5625 DEEP
2 OPPOSITE HOLES
2.3125 (58.7375) DIA
THRU, PARTS 1 & 2
PART 2 PLATE
NITRIDE HARDEN
RC 52-54
PART 1 HANDLE
NITRIDE HARDEN
RC 52-54
.1094
(2.7788)
2.25 (57.15)
.625 (15.875)
1.4375 (36.5125)
0
3
0
3
PART 3 PIN
ROCKWELL ‘C’ 45-50
PIN ENLARGED FOR DETAIL
1 (25.4)
RAD
.75 (19.05)
BLANCHARD GRIND
.75 (19.05) DIA
.6255 +.000/-.001 DIA
(15.8877 +.0000/-.0254)
.03125 RAD
(.79375)
.6255 +.000/-.001 DIA
(15.887 +.0000/-.0254)
.0625 RAD
(1.5875)
.0312 (.7925) RAD
.46875 (11.90.63) DIA
MEASUREMENTS IN INCHES (MILLIMETERS IN PARENTHESES)
Figure 35. Bearing Nut Spanner Wrench 9945228
E-50833
65
Page 66

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
6.4.3.3. CE Dummy Bearing Cap
.50 (12.70)
1.125 (28.575)
.180 +.000/-.010
(4.572 +.000/-.254)
.5625 (14.287) DRILL THRU
4 HOLES ON 9.5 (241.3) BC
7.890 +.001/-.000 DIA
(200.4060 +.0254/-.0000)
0
27
250 FINISH ALL SURFACES
MEASUREMENT IN INCHES (MILLIMETERS IN PARENTHESES)
8.465 +.004/-.000 DIA
10.5 (266.7) DIA
(215.011 +.1016/-.0000)
Figure 36. CE Dummy Bearing Cap 41C689896.
E-50834
66
Page 67

6.4.3.4. DE Bearing Guide
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
.5 RAD
(12.70)
250 FINISH ALL SURFACES
BREAK ALL SHARP CORNERS WITH .062 (1.575) RAD
CARBURIZE, HARDEN, AND GRIND (G) SURFACES AS SHOWN
MEASUREMENT IN INCHES (MILLIMETERS IN PARENTHESES)
.25
(6.35)
6.25 DIA
(158.750)
5.781 DIA
6
(146.837)
0
2.75
(69.85)
.375
(9.525)
.75
(19.05)
1.0 FLAT
(25.4)
6.00 DIA
(152.400)
5.758 +.001/-.000 DIA
7.474 +.000/-.001 DIA
(146.2530 +.0254/-.0000)
(189.8400 +.0000/-.0254)
Figure 37. DE Bearing Guide.
E-50835
67
Page 68

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
6.4.3.5. DE Dummy Bearing Cap
3.0
(76.20)
.625-11 NUT
3.0 (76.20)
.6875 (17.4625) DRILL THRU
4 HOLES ON 13.5 (342.9) BC
WELD
.0625 (1.5875) RELIEF
.031 (.7874) CHAMFER
.140 (3.556)
12.5625 (319.0880) DIA
11.50 (292.10) DIA
14.75 (374.65) DIA
1.125 (28.575)
68
250 FINISH ALL SURFACES
MEASUREMENT IN INCHES (MILLIMETER IN PARENTHESES)
E-50836
Figure 38. DE Dummy Bearing Cap 6796493P3.
Page 69

6.4.3.6. Hub Installation Advance Gage
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150HPACDrill
GEK-91696D
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
Figure 39. Hub Installation Advance Gage, GE 41D790941G1.
E-50961
69
Page 70

GEK-91696D
GE Proprietary and Confidential Information
1150 HP AC Drill
ing Motor, Model 5GEB22
NEW 06–98, GAS
REV 09–98, MGC/DGK
REV 12–01, GMD
REV 10–02, GMD
REV 03–09, PAB
70
 Loading...
Loading...