Page 1

Contents
1 Checking Out Your Gateway Solo 3350. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Back . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Indicator light panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2Getting Started. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Connecting the AC adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Protecting from power source problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Starting your notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Waking up your notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Turning off your notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Using the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Function key combinations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Using the EZ Pad touchpad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Using the touchpad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Connecting the modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Connecting the network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Installing a printer, scanner, or other peripheral device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3 Windows Basics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
About the Windows environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Desktop items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Window items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Using the Start menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Working with files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
About drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
About folders and files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Copying and moving files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Deleting files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Browsing for files and folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Searching for files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Using the Windows Me or Windows 2000 Search utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Using the Windows 98 Find utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Working with documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
i
Page 2

Creating a new document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Saving a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Opening a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Printing a document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Shortcuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Transferring software and hardware from your old computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Transferring files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Transferring Internet settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Reinstalling your old printer or scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Reinstalling your old programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
4 Using the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Learning about the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Setting up an Internet account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Accessing your Internet account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Using the World Wide Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Connecting to a Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Downloading files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Using e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Sending e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Checking your e-mail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
5 Using Multimedia. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Adjusting the volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Connecting the external drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Using diskettes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Using the CD/DVD drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Inserting a CD/DVD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Listening to music CDs in Windows Me . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Listening to music CDs in Windows 98 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Recording and playing audio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Playing audio and video files with Windows Media Player . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Playing a DVD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
Using MusicMatch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Playing CDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Creating music files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Building a music library . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Changing the music library display settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Editing track information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Listening to Internet radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .91
Using advanced features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
ii
Page 3

6 Sending and Receiving Faxes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Setting up your cover page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Sending a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Faxing from programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Receiving and viewing a fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
7 Managing Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Monitoring the battery charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Changing batteries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Extending battery life . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Conserving battery power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Using alternate power sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Changing power modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Changing automatic p ower settings in Windo ws Me, Window s 98, or
Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Changing power settings in Windows NT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Changing SpeedStep settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
8 Travel Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
9 Customizing Your Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Adjusting the screen and desktop settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Adjusting the color depth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Adjusting the screen area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Applying a color scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Changing the desktop background . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Selecting a screen saver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
10 Upgrading Your Notebook . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Adding PC Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Preventing static electricity discharge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Replacing the hard drive kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Installing Memory and Replacing the Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Removing the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Replacing the memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Replacing the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
iii
Page 4

11 Using the Port Repl icator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .147
Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .148
Connecting to the port replicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .150
12 Networking Your Home . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .153
Using a home network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .154
Sharing a single Internet connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .154
Sharing MP3 audio and MPEG video files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .154
Sharing drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .155
Sharing a printer or scanner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .155
Playing multi-player games . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .155
Introducing the Gateway Connected Home . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
Components of a Gateway Connected Home . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .157
Selecting a connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158
What are HPNA and Ethernet? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158
Assessing your connection needs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .159
Comparing data transfer speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .160
Connected home shopping list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .162
HPNA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .162
Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .163
For more information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .164
13 Maintaining Your Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .165
Caring for your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .165
Creating an emergency startup diskette . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .167
Protecting your computer from viruses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .169
Managing hard drive space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .171
Checking hard drive space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .171
Using Disk Cleanup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .172
Scanning the hard drive for errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .173
Defragmenting the hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
Backing up files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .177
Using Maintenance Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .178
Recalibrating the battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .179
Cleaning your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .180
Cleaning the exterior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .180
Cleaning the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .181
Cleaning the screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .181
Cleaning the mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .181
14 Using Gateway GoBack. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .183
About Gateway GoBack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .184
iv
Page 5

Using Gateway GoBack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Recovering a file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Going back to an earlier hard drive state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Using Gateway GoBack if your computer will not start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Turning off Gateway GoBack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Clearing Gateway GoBack history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Starting your computer using a diskette . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Changing Gateway GoBack’s storage capacity and location . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Updating your Gateway GoBack software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Getting help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
15 Reinstalling Device Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Reinstalling device dr ivers in Windows 98, Windows Me, or Windows 2000 . . . . 206
Updating device driv ers in Windows 98, Windows Me, or Windo ws 2000 . . . . . . 208
Reinstalling Windows NT 4.0 device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Locating Windows NT 4.0 drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Reinstalling Windows NT 4.0 video device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Reinstalling Windows NT 4.0 audio device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Reinstalling Windows NT 4.0 modem device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
Reinstalling Windows NT 4.0 network device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Reinstalling the Windows NT Service Pack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
16 Restoring Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Reinstalling Windows 98, Windows Me, or Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Reinstalling Windows NT 4.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Reinstalling programs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
17 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
Safety guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
CD/DVD drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
Device installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Diskette drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
File management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
LCD panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
v
Page 6

Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .245
PC Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .246
Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .246
Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .247
ScanDisk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .248
Sound . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .248
Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .249
18 Getting Help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .251
HelpSpot™ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .252
HelpSpot videos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .254
Software support tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .255
Gateway Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .256
Online help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .259
Telephone support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .260
Before calling Gateway technical support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .260
Telephone numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .261
Tutoring and training . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .262
Self-help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .262
Tutoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .262
Training . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .263
A Safety, Regulatory, and Legal Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .265
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
vi
Page 7

Checking Out Your Gateway Solo 3350
Tips & Tricks To access the contents of this manual while you are
traveling, download the manual from
www.gateway.com/support/manlib/.
1
1
Page 8
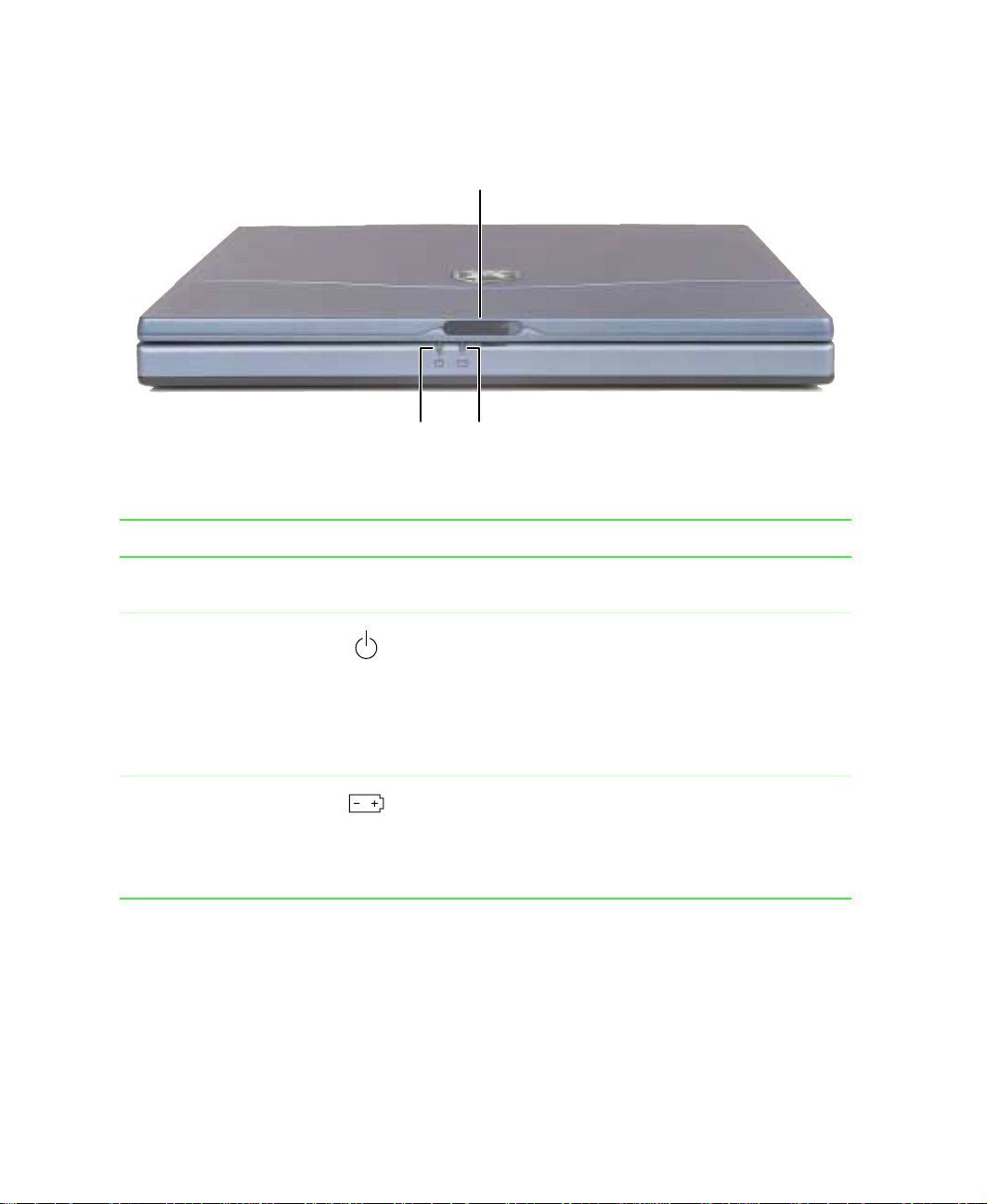
Front
Release latch
Power
indicator
light
Battery
indicator
light
Component Icon Description
Release latch Open the noteboo k cov er b y sliding the re lease latch to the
right.
Power indicator light Lights up when the notebook is turned on and shows
notebook power status:
■
Steady green light indicates that power is on and the
notebook is in operation.
■
Flashing green light indicates that the notebook is in
standby mode.
■
No light indicates that the notebook is off.
Battery indicator light Indicates the battery status while the AC power adapter is
plugged in:
■
Green light indicates that the battery is fully charged.
■
Orange light indicates that the battery is charging.
■
Red light indicates a battery error.
2 Checking Out Your Gateway Solo 3350
Page 9

Left
Ventilation fan
(do not block)
Microphone jack
USB port
Spea ker ja ck
Component Icon Description
Ventilation fan Helps cool system components. Do not block.
Microphone jack Plug a microphone into this jack. While the external
microphone is connected, the built-in microphone is
disabled.
Speaker jack Plug external speakers or headphones into this jack.
USB port Plug a USB (UniversalSerial Bus) device (such as a USB
Iomega™ Zip™ drive, scanner, or camera) into this port.
Left 3
Page 10

Right
Kensington
lock slot
Hard drive
PC Card
eject button
PC Card
slot
Component Icon Description
Kensington™ lock slot Secure your computer to an object by connecting a
Kensington cable l ock to this s lot.
Hard drive The hard drive is stored here.
PC C ard eject button Press the eject button to remove the PC Card from the
PC Card slot. For more information, see “Adding PC Cards”
on page 132.
PC C ard slot Inser t a Type I or II PC Card into this slot. For more
information, see “Adding PC Cards” on page 132.
4 Checking Out Your Gateway Solo 3350
Page 11

Back
Ethernet
jack
Modem
jack
Monitor
port
Parallel
port
External drive
connection
Power
connection
PS/2
port
Component Icon Description
Ethernet jack (optional) Plug an Ethernet 10/100 network cable into this jack.
Modem jack Plug a modem cable into this jack.
Monitor port Plug an external (VGA) monitor into this port.
Parallel port Plug a parallel device (such as a printer) into this port.
External drive connection Plug the external drive cable into this connection.
Power connection Plug the AC power adapter cable into this connection.
PS/2 port Plug a PS/2 (Personal System/2™) device (such as a
keyboard or mouse) into this port.
Back 5
Page 12
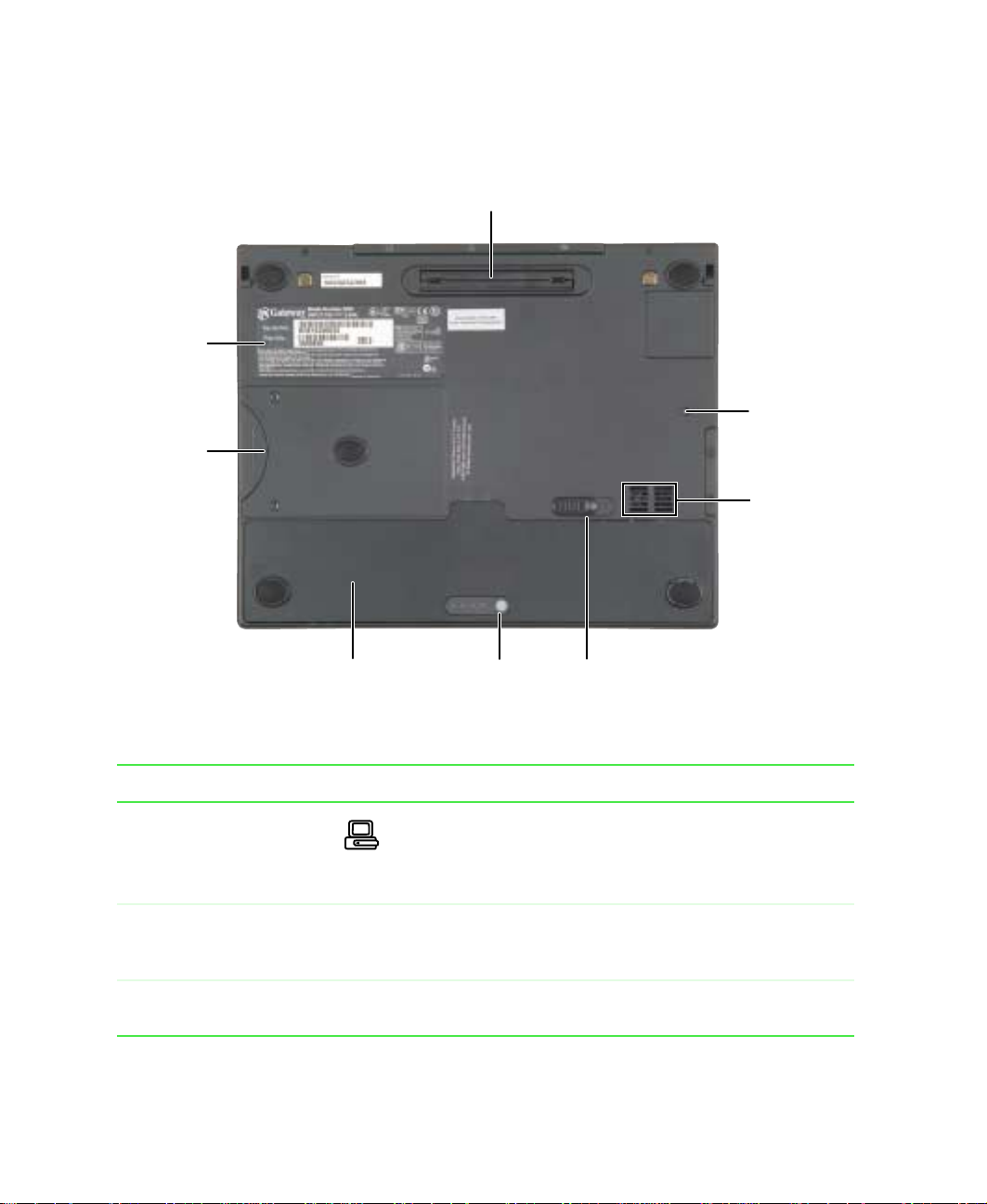
Bottom
System
label
Hard
drive
bay
Docking
port
Reset
hole
Speaker
Battery
bay
Battery
status
indicator
Battery
release
latch
Component Icon Description
Docking port Connect an optional port replicator to this port.
Warning! Power is passed through this connection. This
docking connection is UL certified for use only with Solo
3350 port replicator devices.
Reset hole If the system does not respond to input and you cannot use
the shut down pr ocedure, press a st raightened paper clip into
this hole to turn off the system.
Speaker Provides audio output. The speaker is turned off while
headphones are connected.
6 Checking Out Your Gateway Solo 3350
Page 13

Component Icon Description
Battery release latch Slide to release the battery.
Battery status indicator Press to see the charge level of the battery. A full charge is
indicated by four lights.
Battery bay The notebook uses power from this battery while not
connected to AC power.
Hard drive bay The hard drive is stored here.
System label Includes the product model number and serial number.
Bottom 7
Page 14

Indicator light panel
A
1
Power
button
Hard drive
Scroll lock
Pad lo ck
Caps lock
Microphone
Indicator Icon Description
Power button Press to turn the power on or off. You can also configure
the button to operate in Standby/Resume mode or
Hibernate mode. For more information on config uring the
power button mode, see “Changing power modes” on
page 105.
Hard drive Turns on when the hard drive is in use.
Pad Lock Turns on when the embedded numeric keypad is
1
Caps Lock Tur ns on when Caps Lock is activated.
Scroll Lock Tur ns on when Scroll Lock is activated.
activated.
Microphone Record audio through this microphone. The built-in
microphone is turned off while an e x ternal microphone is
connected.
8 Checking Out Your Gateway Solo 3350
Page 15

Accessories
Gateway offers accessories that can help you make the most of using your
notebook.
Batteries and automobile/airplane power adapt ers
If you run your notebook on battery power for extended periods, you may
want to buy an additional battery so that you can swap batteries when
necessary.
With an automobile/airplane power adapter, you can save battery power by
plugging your notebook into an automobile cigarette lighter or an airplane
in-flight power receptacle.
Carrying cases
Gateway has large-capacity carrying cases if you need additional space for
accessories or supplies.
External drive module
Y our notebook has an optional external drive bay tha t lets you use a removable
drive such as a diskette drive or CD /DVD drive. To change drives, you need
to replace the drive module in the drive bay.
Port replicator
Although you can attach external devices directly to your notebook, a port
replicator lets you make all of those connections at once. When you travel
with your notebook, you merely disconnect from the port replicator instead
of unplugging all the external devices.
A port replicator also provides additional ports and o ther expansion features
not included with your notebook. For more information, see “Using the Port
Replicator” on page 147
External devices
Y ou can attach external devices suc h as a keyboard, mouse, printer, o r monitor
to your notebook or docking station.
Memory
Large programs, such as multimedia games or graphics programs, use a lot of
memory. If your programs are running more slowly than you think they
should, try adding more memory. For more information, see “Replacing the
memory” on page 142.
Accessories 9
Page 16

Printers
You can attach almost any type of printer to your computer. The most
common types are inkjet and laser printers, which print in color or black and
white.
Inkjet printers and cartridges are relatively inexpensive, but usually they are
slower than laser printers. Using an inkjet color printer, you ca n print pictures,
banners, and greeting cards, as well as documents.
Laser printers and cartridges are more expensive, but usually they print much
faster than inkjet printers. Laser printers are better than inkjet printers when
you are printing large documents.
10 Checking Out Your Gateway Solo 3350
Page 17

Getting Started
This chapter provides basic information about your Gateway notebook. Read
this chapter to find out:
■ How to connect the AC power adapter
■ How to start and turn off your notebook
■ How to use the keyboard
■ How to use the EZ Pa d™ touch pad
■ How to connect the modem
■ How to con nect to a networ k
■ How to insta ll peripheral d evices
2
11
Page 18
Connecting the A C adapter
Y ou can run y our notebook using an AC adapter or the notebook battery . The
battery was shipped to you partially charged. You should use the AC adapter
right away to fully charge the battery.
Important If the battery is not fully charged before you use your
notebook on battery pow er f or the first tim e, the battery lif e
may be much shorter than you expect. If the battery life
seems short even after being charged for 24 hours, the
battery may need to be recalibrated. For information on
recalibrating the b attery , se e “Recalibr ating the ba ttery” on
page 179.
To connect the AC adapter:
1 Connect the power cord to the AC adapter, then plug it in to a wall power
outlet.
Warning Replace the power cord if it becomes damaged. The
12 Getting Started
replacement cord must be of the same type and voltage
rating as the original cord or the notebook may be
damaged.
Page 19
2 Connect the AC ad apter to your notebook’s power connector.
The battery charging indicator light turns on. If the battery charging
indicator light does not turn on, disconnect the adapter from your
notebook and repeat Step 2.
3 When you finish using your notebook, turn the notebook off and leave
the notebook connected to AC power for at least 24 hours. The battery
charge meters may not show a charge for several hours. For more
information about battery meters, see “Monitoring the battery charge”
on page 102.
4 If the battery meters do not show a full charge after 24 hours, contact
technical support at www.gateway.com/support/contact.
Warning Do not attempt to disassemble the ACadapter. The
AC adapter has no user-replaceable or user-serviceable
parts inside. The A C adapter has dangerous v o ltages that
can cause serious injury or dea th. Contact G ate wa y about
returning defective AC adapters.
Connecting the AC adapter 13
Page 20
Protecting from power source problems
During a power surge, the voltage level of electricity coming into your
computer can increase to far above normal levels and cause data loss or system
damage. Protect your computer and peripherals by connecting them to a surge
protector, which will absorb voltage surges and prevent them from reaching
your computer.
Warning High voltages can enter your computer through both the
power cord and the modem connection. Protect your
computer by using a surge protector. If you have a
telephone modem, use a surge protector that has a
modem jack. If you have a cable modem, use a surge
protector that has an antenna/cable TV jack. During an
electrical storm, unplug both the surge protector and the
modem.
14 Getting Started
Page 21
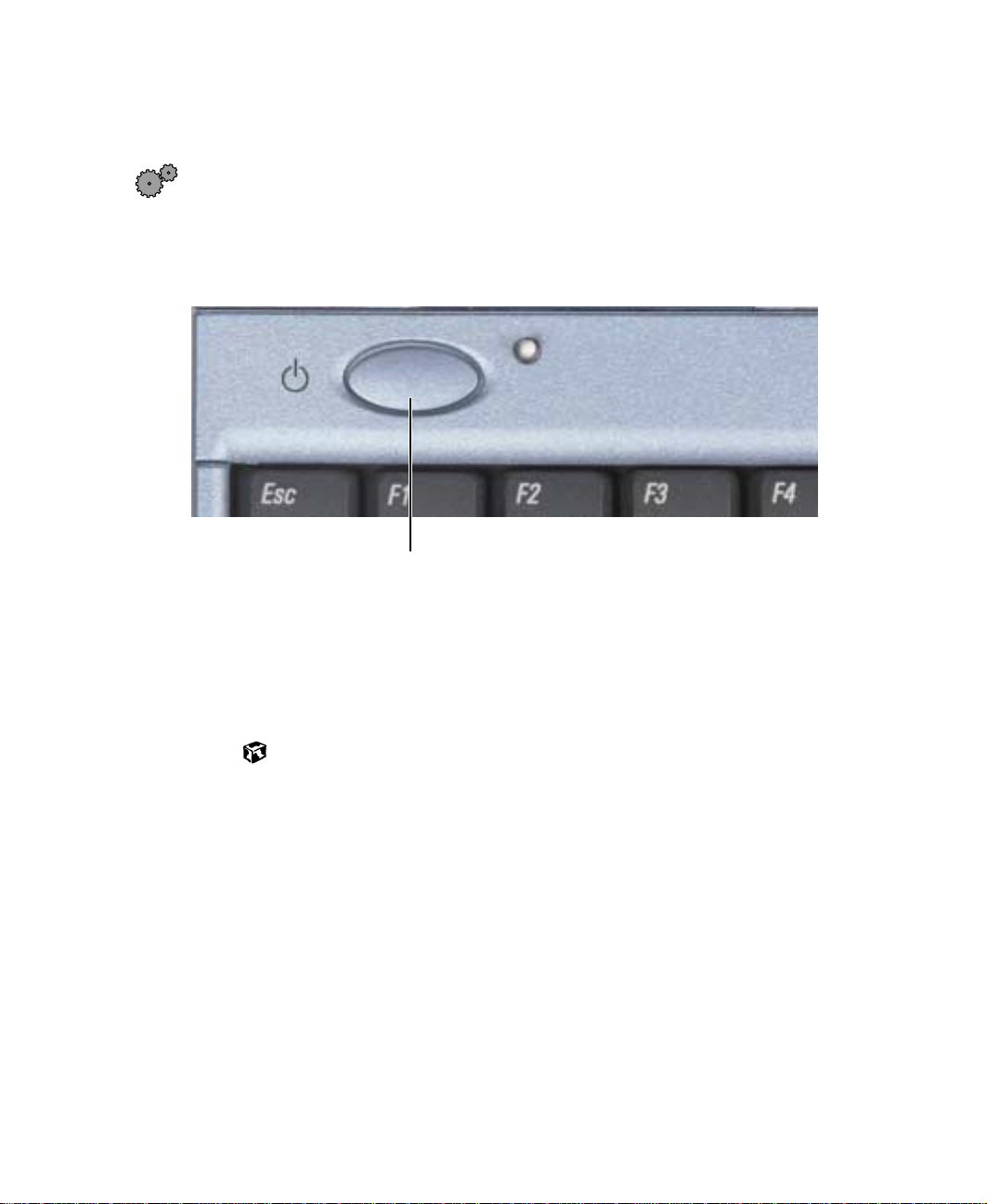
Starting your notebook
To start the notebook:
1 Open your notebook by sliding the latch on the front of your notebook
to the right and lifting the LCD panel.
2 Press the power button located above the keyboard.
Power button
The power button is preset to On/Off mode. However, you can also set
it to function in Standby/Resume mode. For instructions on changing
the power button mode, see “Changing p ower modes” on page 105.
3 If you are starting your computer for the first time, follow the on-screen
instructions to set up your computer.
Starting your notebook 15
Page 22

W aking up your notebook
When you have not used your notebook for several minutes, it may go into
a basic power-saving mode which turns off your LCD and hard drive. Two
advanced pow er-saving modes (call ed Standby and Hibernate) are also available
for the Solo 3350. While in Standby, the power indicator light flashes.
When you are ready to use your notebook after the screen has gone into basic
power-saving mod e, wake it up by pressing a button or key on the key board .
If your notebook has gone into Standby or Hibernate mode, wake it up by
briefly pressing the power button. For more information on changing
power-saving settings, see “Extending battery life” on page 104.
16 Getting Started
Page 23

Turning off y our notebook
To turn off your notebook:
1 Click Start, then select Shut Down. The Shut Down Windows dialog box
opens.
2 Select Shut down.
3 Click OK. Windows shuts down and turns off your notebook.
Important If for some reason you cannot use the Shut down option
in Windows to turn off your notebook, press and hold the
power button for about five seconds.
Turning off your notebook 17
Page 24

Using the keyboar d
Your notebook features a keyboard that has the same functionality as a
desktop computer keyboard. Many of the keys have been assign ed alternate
functions. The alternate function is printed on the key in green text.
F
N key
Windows
Key
Function keys
Numeric
keypad
Application
key
Navigation keys
Arrow keys/
Brightness
controls
18 Getting Started
Page 25

Keys
Keys Icons Description
Function keys Press these keys to perform actions in programs.
For example, pressing F1 may open help.
Each program uses different function keys for
different purposes. Refer to the program
documentation to find out more about the function
key actions.
N key Pre ss the FN key in combination w ith a Function key
F
(such as F4 or F10) to p erf orm a specifi c action. F or
more information, see “Function k ey combinations ”
on page 20.
Windows keys Press to open the Windows Start menu.
Numeric keypad Use these keys to type numbers when Pad Lock is
turned on. Press
keypad.
Applicatio n key Press for quick access to sh ortcut menu s an d hel p
assistants i n Windows.
FN+F9 to turn on the numeric
Arrow keys/
Brightness controls
Navigation keys Press these keys to move the cursor up or down a
Press these keys to move the cursor up, down, right,
or left. When used with the F
control the screen brightness.
page, or to the beginning or end of a document.
N key, these also
Using the keyboard 19
Page 26

Function key combin ations
When you press an FN key and a Function key at the same time, the notebook
performs the action identified by the green text on the key.
FN and this
Press
function key...
To...
Open the power st atus bo x in the upper left corner of y our scree n.
The menu shows the battery charge level, the BIOS version, and
whether the AC power adapter is being used.
Toggle the notebook screen between the LCD, an external
monitor, or both displays at the same time.
Enable Standby mode (Windows 98, Windows 2000, and
Windows Me) or Suspend mode (Window s NT) on your notebook.
Press the power button to exit Standby or Suspend mode.
Decrease volume.
Increase volume.
Mute the sound. Press the key combination again to restore the
sound.
20 Getting Started
Tur n on Pad Lock so you can use the numeric keypad. The
Pad Lock status indicator ap pears while th is functio n is turned on.
Press the key combination again to turn off Pad Lock.
Pause the text scrol lin g i n a D OS s creen . T he Scro ll Lo ck sta tus
indicator ap pears wh en this f unctio n is tur ned on. Press the key
combination again to continue scrolling. (This function is only
available in some programs.)
Pause text scrolling. Press any key to continue the text scrolling.
(This function is only available in some programs.)
Page 27

Press FN a nd this
function key...
To...
Stop the cur rently r unning D OS program. (This func tion is on ly
available in some pr ograms.)
Increase the brightness of the screen.
Decrease the brightness of the screen.
Using the keyboard 21
Page 28
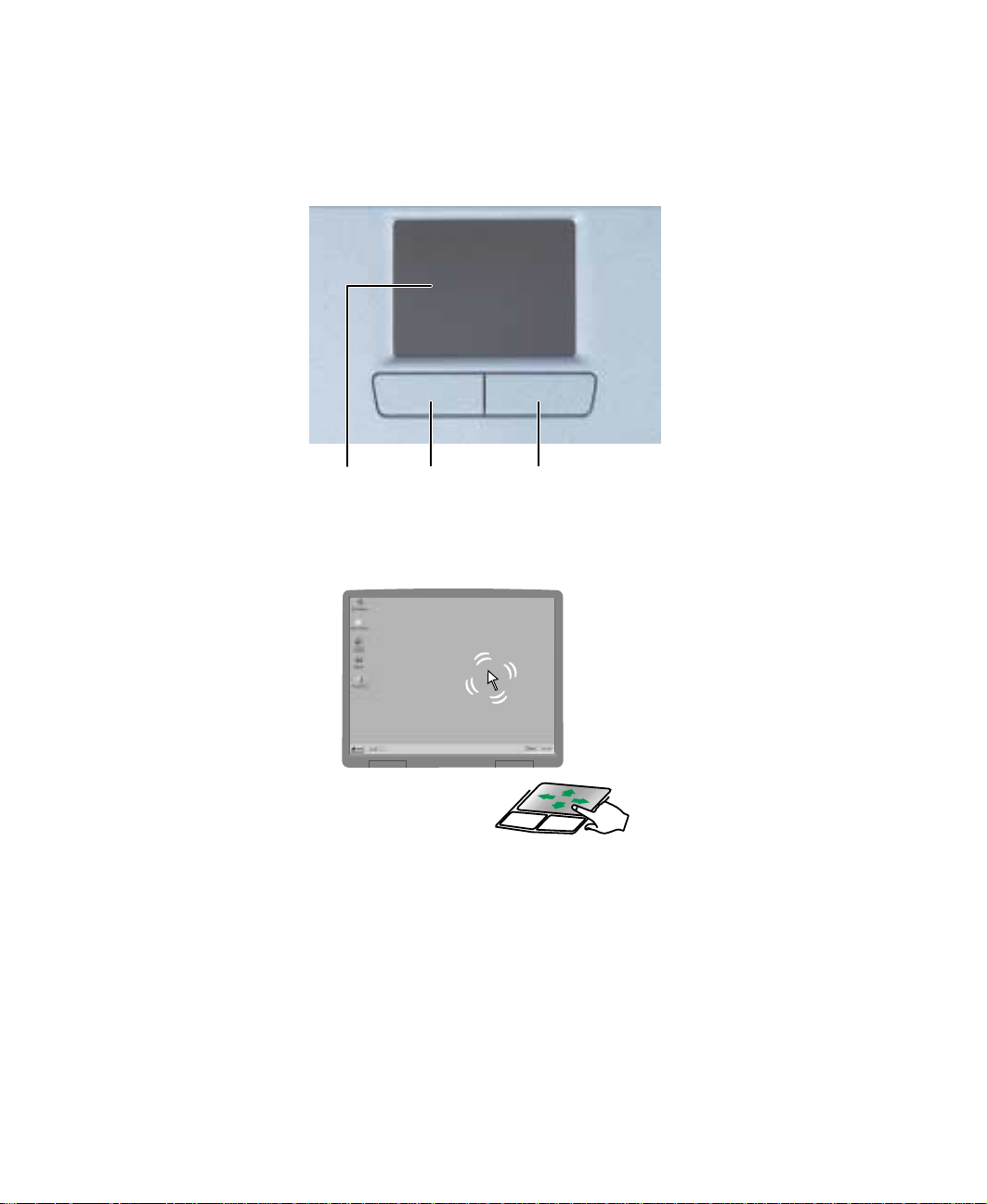
Using the EZ P ad touchpad
The EZ Pad™ consists of a touchpad and two buttons.
Touchpad Pad buttons
When you move your finger on the touchpad, the pointer (arrow) on the screen
moves in the sam e directi on.
You can use the EZ-Pad left and right buttons below the touchpad to select
objects.
22 Getting Started
Page 29
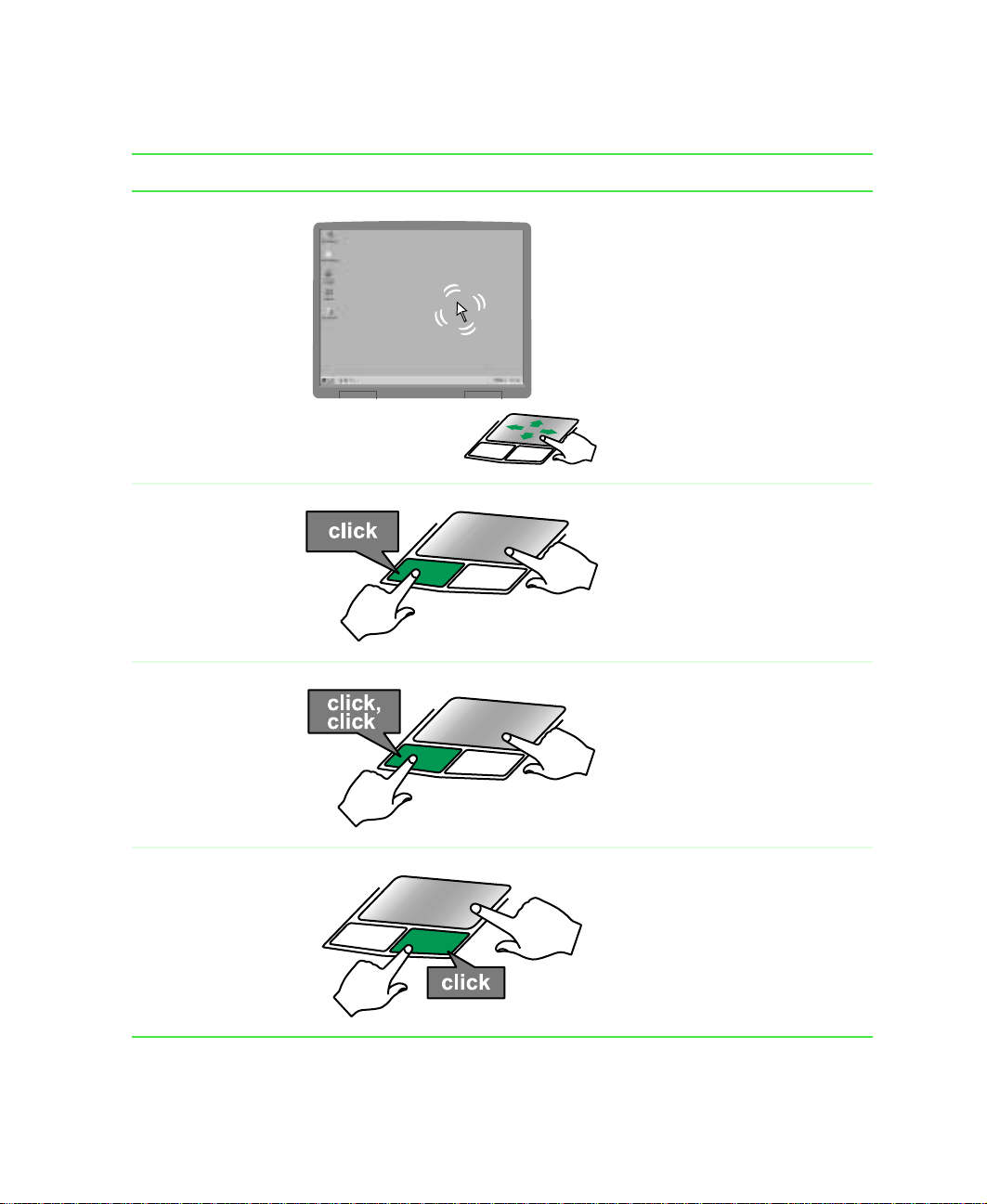
Using the touchpad
To... Do this...
Move the poin ter
on the screen.
Select an object
on the screen.
Start a program
or open a file or
folder.
Move y our finger around on the
touchpad. If you run out of
space on your t ouchpad an d
need to move the pointer
farther, lift your finger, move it
to the middle of the touchpad,
then continue moving your
finger.
Position the point er over the
object. Press the left button
below the touc hpad o nce . This
action is called clicking.
Position the point er over the
object. Press the left button
below the touchpad twice in
rapid succession. This action is
called double-clicking.
Access a
shortcut menu or
find more
information
about an object
on the screen.
Position the point er over the
object. Quickly press and
release the right button once.
This action is called
right-clicking.
Using the EZ Pad touchpad 23
Page 30
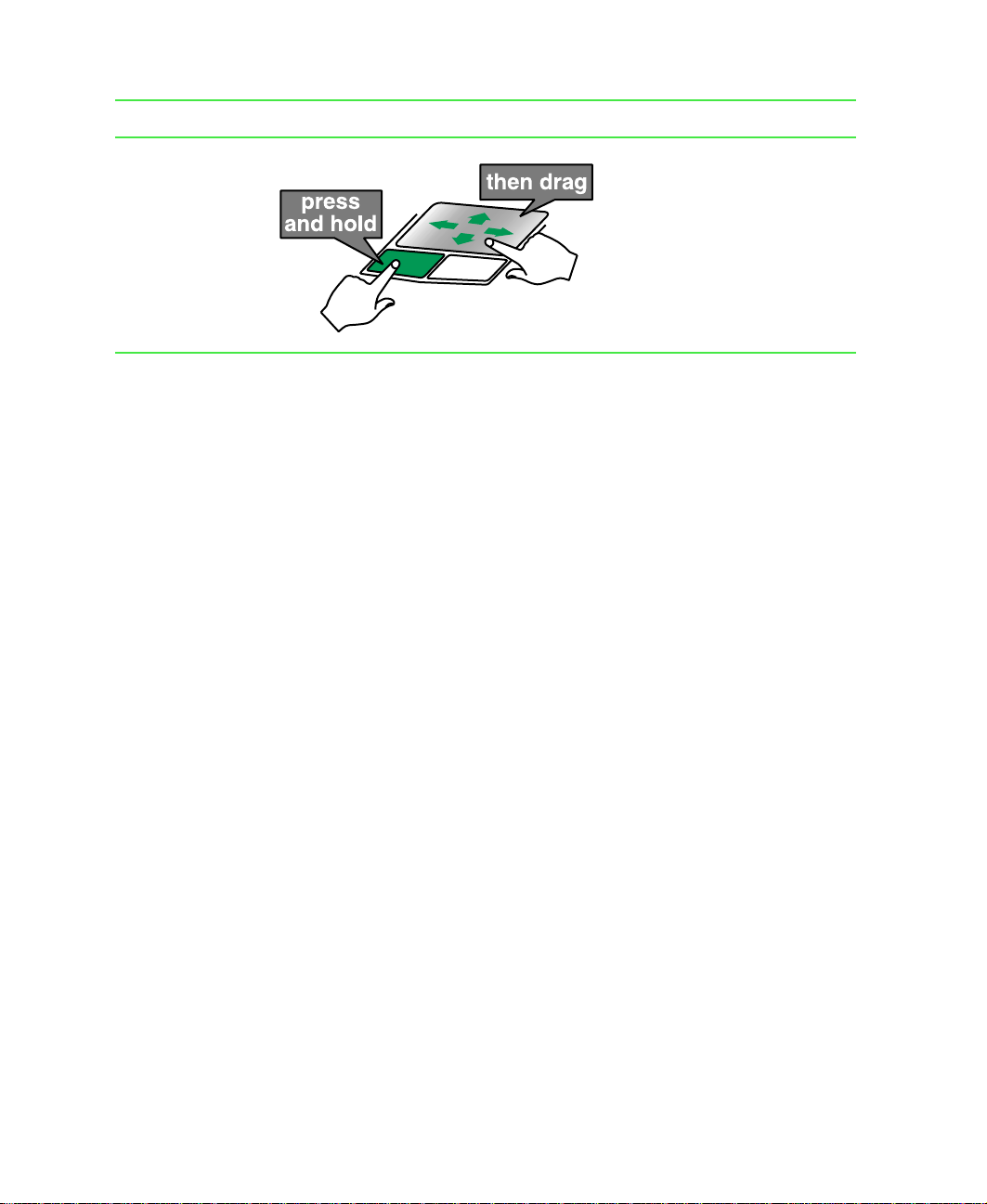
To... Do this...
Move an object
on the screen.
Position the point er over the
object. Press the left button
and hold it down, then use the
touchpad to move (drag) the
object to the appropriate part of
the screen. Release the b utton
to drop the object where you
want it.
24 Getting Started
Page 31

Connecting the modem
If your notebook has a modem jack, the notebook has a built-in V.90 56K
modem and a telephone cable.
To connect the modem:
1 Insert one end of the telephone cable into the modem jack on the
back of the notebook.
2 Insert the o ther end of the telephone cable into a telephone wall jack.
The modem will not work with digital or PBX telephone lines.
3 Start your notebook, then start your communications software.
Connecting the modem 25
Page 32

Connecting the network
If your notebook has a network jack, the notebook can connect to an Ethernet
10/100 network.
To connect to a network:
1 Insert one end of the network cable into the network jack on the
back of the notebook.
2 Insert the other end of the network cable into a network wall jack. Ask
your network administrator to help you select the correct network jack.
Your notebook is now physically connected to the network. Your network
administrator can help you log on to your network.
26 Getting Started
Page 33

Installing a printer , scanner , or other peripheral device
Your computer has one or more of the following ports: Universal Serial Bus
(USB) and parallel. These ports are used for connecting peripheral devices such
as printers, scanners, and digital cameras to your computer. For more
information about port locations, see “Checking Out Your Gateway Solo
3350” on page 1
USB ports supp ort plug-and-play and hot swapping, which means that your
computer will usually recognize such a device whenever you plug it into the
appropriate port. When you use a USB device for the first time, your computer
will prompt you to install any software the device needs. After doing this,
you can disconnect and reconnect the device at any time.
Parallel port devices a re not plug-and -play . R efer to the devic e documentation
for detailed information and installation instructions.
Installing a printer, scanner, or other peripheral device 27
Page 34

28 Getting Started
Page 35

Windows Basics
Read this chapter to get basic information on how to:
■ Work on the Windows desktop
■ Manage files and folders
■ Wo r k w i t h d ocu men ts
■ Use shortcuts
■ Move data from your old computer to your new computer
HelpSpot For more information on using Windows, double-click the
3
HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
29
Page 36

About the Windows en viro nment
After your computer starts, the first screen you see is the Windows desktop.
The desktop is like the top of a real desk. Think of the desktop as your
personalized work space where you open programs and perform other tasks.
Y our deskto p may be different from the example shown below , depending on
how your computer is set up.
30 Windows Basics
Page 37

Desktop item s
Icons are graphic representations of objects on the desktop that you select and
open, such as a drive, folder, file, or program. Buttons are graphic
representations of controls that you use to open windows or apply changes.
Desktop icons, buttons, and elements Description
The My Computer icon provides access to drives
and other computer co ntrols. Doub le-click the My
Computer icon to vie w th e dri ves and fo lde rs on
your computer.
My Documents is a folder where you store your
personal f iles. You can create other folders to
save files in, but My Docum ents is easy t o find
because it is on the desktop. Double-click My
Documents to view your personal files and
folders.
The Recycle Bin is where files, folders, and
programs that you discarded are stored. You
must empty the Recycle Bin to permanently
delete them from y ou r comp uter. Fo r instruc tions
on how to use the Rec ycle Bin, see “Deletin g files
and folders” on page 41.
Microsoft Internet Explorer is a program called a
browser that lets you view Web sites and Web
pages on the Internet. Double-click this icon to
open the brow ser. For instructio ns on how to
access the Internet, see “Learning about the
Internet” on page 62.
The Gateway .net and America Online Included
icons let you connect to the Gateway.net or
America Online ISP (Internet Service Provider).
Double-click either the Gateway.net or America
Online Included icon to dial one of the services.
For instructi ons on how to set up an ISP, see
“Setting up an Internet account” on page 63.
About the Windows environment 31
Page 38

Desktop icons, buttons, and elements Description
Gateway has provided an easily accessible
interactive guide called HelpSpot for use with
Windows Me. Th is guide is desi gned to provide
help information and let y ou qui c kly di sco v er an d
use the features of your computer. Double-click
the HelpSpot icon to begin.
The Star t button provides access t o programs,
files, help for Windows and other programs, and
computer tools and utilities.
Click the Start button, then op en a file or prog ram
by cli cki ng ( selecting) an item on t he menu t hat
opens.
The taskbar is the bar at the bottom of the screen containing the Start button on the left and a
clock on the right. Other buttons on the taskbar represent programs that are running.
Click a program’s button on the taskbar to activate the program’s window.
32 Windows Basics
Page 39

Window items
When you double-click the icon for a drive, folder, files, or program, a window
opens on the desktop. This example shows the
opens after double-clicking the
window.
Local Disk (C:) window , which
Local Disk (C:) icon in the My Computer
Title bar
Menu bar
Close
button
Maximize
button
Minimize
button
About the Windows environment 33
Page 40

Every program window looks a little different because each has its own menus,
icons, and controls. Most windows include these items:
Window item Description
The title ba r is the horizontal bar at the top of
a window that shows the name of the program.
Clicking t he minimize button reduces the active
window to a but ton on the ta skbar. Clicking the
program button in the taskbar opens the
window again .
Clicking the maximize button expands the
active window to fit the entire screen. Clicking
the maximize button agai n restores t he windo w
to its former s ize.
Clicking the close button closes the active
window or pr ogram.
Clicking an item on the menu bar starts an
action such as Print or Save.
34 Windows Basics
Page 41

Using the Start menu
You can sta rt progra ms, open files, c ustomize your sys tem, get h elp, sea rch
for files and folders, and more using the
To open the Start menu:
■ Click the Start but ton on t he lower left of t he Win dows des ktop. Th e Start
menu opens showing you the first level of menu items.
When you move the pointer over any menu item that has an arrow next to
it, anothe r menu, or submenu, opens and reveals related files, programs, or
commands. Click a file or program to open it.
Start menu.
Using the Start menu 35
Page 42

W orking with files and f olders
You can organize your files and programs to suit your preferences much like
you would store information in a file cabinet. You can store these files in
folders and copy, move, and delete the information just as you would
reorganize and throw away information in a file cabinet.
HelpSpot For more information on working with files and folders,
double-click the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
About drives
Drives are like file cabinets because they hold files and folders. A computer
almost always has more than one drive. Each drive has a letter, usually
Disk (C:)
also have more drives such as a CD/DVD drive.
To view the drives on your computer:
■ Double-click the My Computer icon on your desktop.
for the hard drive and 3½ Floppy (A:) for the diskette drive. You may
Local
Drives
36 Windows Basics
Page 43

To see the files and folders on a drive:
■ Double-click the drive icon. If you do not see the contents of a drive after
you double-click its icon, click
View the entire contents of this drive.
Working with files and folders 37
Page 44

About folders and files
Folders are much like the folders in a file cabinet. They contain files and other
folders.
Files are much like pa per documents—letters, spreadsheets, and pictures—that
you keep on your computer. In fact, all information on a computer is stored
in files.
Folders
Files
To create a folder:
1 Doubl e-click the My Compute r icon on the desktop. The My Computer
window opens.
2 Double-click the drive or folder, for example 3½ Floppy (A:) or Local
Disk (C:)
The drive or folder window opens. If you do not see the contents of the
drive or folder, click
, where you want to p ut the new folder.
3 Select File, then New, then Folder. The new folder is created.
4 Type a name for the folder, then press ENTER. The new folder nam e
appears under the folder.
38 Windows Basics
View the entire contents of [this drive or this folder].
Page 45

Copying and moving files and f olders
The skills you need to copy and move files are copying, cutting, and pasting.
When you copy and paste a selection, you place a copy of the file you selected
on the Windows clipboard, which stores it. Then, when you decide what folder
you want the copy to go in (the destination folder), you paste it there.
When you cut and paste a selection, you remove the file from its folder and
place the file on the Windows clipboard. When you decide where you want
the file to go, you paste it there.
Important The clipboard stores whatever you cut or copy until you
cut or copy again. Then the clipboard contains the new
information only. Therefore, you can paste copies of a file
into more than one place, but as soon as you copy or cut
a file again, the old file is deleted from the clipboard.
To copy a file or folder to another folder:
1 Right-click the file or folder that you want to copy. A menu opens on
the desktop.
2 Select Copy from the menu.
3 Open the destination folder.
4 With the pointer inside the destination folder, press the right touchpad
button.
5 Select Paste. A copy of the file or folder appears in the new location.
Working with files and folders 39
Page 46

To move a file or folder to another folder:
1 Right-click the file or folder that you want to move. A menu opens on
the desktop.
2 Select Cut from the menu.
3 Open the destination folder.
4 With the pointer inside the destination folder, press the right touchpad
button.
5 Select Paste. The file or folder you moved appears in its new location and
is removed from its old location.
40 Windows Basics
Page 47

Deleting files and f olders
When you throw away paper files and folders, you take them from the file
cabinet and put them in a trash can. Eventually the trash can is emptied.
In Windows, you throw away files and folders by first moving them to the
Windows trash can, the Recycle Bin, where they remain until you decide to
empty the bin.
You can recover any file in the Recy cle Bin as long as the bin has not been
emptied.
To delete files or folders:
1 In My Computer or Windows Explorer, select the files or folders that you
want to delete. For instructions on how to select multiple files and folders,
see “Shortcuts” on page 54.
2 Select File, then select Delete. Windows moves the files and folders to the
Recycle Bin.
To recover files or folders from the Recycle Bin:
1 Doubl e-click the Recycle Bin icon. The Recycle Bin window opens listing
the files and folders you have thrown away since you last emptied it.
2 Select the files or folders that you want to restore. For instructions on
how to select multiple files and folders, see “Shortcuts” on page 54.
3 Click File, then Restore. Windows returns the deleted files and folders to
their original locations.
If the Recycle Bin was emptied before you decided that you want to restore
a file, use Gateway GoBack (if available on your notebook).
Working with files and folders 41
Page 48

To empty the Recycle Bin:
Caution Emptying the Recycle Bin permanently erases any files or
folders in the bin. These files cannot be restored.
1 Double-click the Recycle Bin icon on the desktop. The Recycle Bin window
opens.
2 Select File, then select Empt y Recycle Bin. Windows asks you if you are
sure that you want to empty the bin.
3 Click Yes. Windows permanently deletes all the files in the Recycle Bin.
42 Windows Basics
Page 49

Bro wsing for fil es and folder s
A file or folder that you need is rarely right on top of your Windows desktop.
It is usually on a drive inside a folder that may be inside yet another folder,
and so on.
Windows drives, folders, and files are organized in the same way as a real file
cabinet in that they may have many levels (usually many more levels than
a file cabinet, in fact). So you usually will have to search through levels of
folders to find the file or folder that you need. This is called browsing.
To browse for a file:
1 Doubl e-click the My Compute r icon on the desktop.
2 Double-click the drive or folder that you think contains the file or folder
that you want to find.
3 Continue double-clicking folders and their subfolders until you find the
file or folder you want. (If you do not see the contents of a folder, click
View the entire contents of this folder.)
Working with files and folders 43
Page 50

Searc hing for files
If you are looking for a particular file or folder or a set of files or folders that
have characteristics in common, but you do not remember where they are
stored on your hard drive, you can use the Search utility in Windows Me or
Windows 2000, or the Find utility in Windows 98 to search by:
■ Name or part of a name
■ Creation date
■ Modification date
■ File type
■ Text contained in the file
■ Time period in which it was created or modified
You can also combine sea rch criteria to refine se arches.
Files and folders found using these utilities can be opened, copied, cut,
renamed, or deleted directly from the list in the results window.
44 Windows Basics
Page 51

Using the Windows Me or Windows 2000
Search utility
To find files and folders using the Search utility:
1 Click Start, then select Search, then For Files or F olde r s. The search dialog
box opens.
2 If you want to search by file or folder name, type in all or part of the
file or fo lder na me in t he
pane of the window.
■ If you type all of the name, Search will list all files and folders of
that name.
■ If you type part of the name, Search will list all of the file and folder
names containing the letters you typed.
Search for files or folders named box in the left
Searching for files 45
Page 52

3 Click Search Now. When the search is completed, Windows lists the files
and folders whose names contain the text that you searched for.
4 Open a file, folder, or program by double-clicking the name in the list.
Using advanced search options
Search can find files meeting more criteria than file name. You can select
options to narrow your search by clicking
options t hat you w ant:
Search Options and selecting the
■ Date searches for files that were created or modified on a specific date or
during a specific period.
■ Size searches for files of a specific size.
■ Type searches for files of a specific type, such as a program or a text
document.
■ Advanced Options give you access to further search options.
46 Windows Basics
Page 53

Using the Windows 98 Find utility
To find files and folders using the Find utility:
1 Click Start, then select Find, then Files or Folders. The Find: All Files dialog
box opens.
2 If you want to search by file or folder name, click the Name & Location
tab, then type in all or part of the file or folder name in the
box.
■ If you type all of the name, Find will list all files and folders of
that name.
Named text
■ If you type part of the name, Find will list all of the file and folder
names containing the letters you typed.
Searching for files 47
Page 54

3 Click Find Now. When the search is completed, Windows lists the files
and folders whose names contain the text that you searched for.
4 Open a file, folder, or program by double-clicking the name in the list.
Using advanced search options
Y ou can fin d files meeting more crit eria than file name. You can select options
to narrow your search by clicking the
options t hat you w ant:
■ Date searches for files that were created or modified on a specific date or
during a specific period.
■ Size searches for files of a specific size.
■ Type searches for files of a specific type, such as a program or a text
document.
48 Windows Basics
Date or Advanced tabs and selecting the
Page 55

W orking with documents
Documents are commonly word processing files, spreadsheet files, or other
similar files. The basic methods of creating, saving, opening, and printing a
document apply to most of these types of files.
The following examples illustrate the concepts for creating, saving, opening,
and printing a document in Microsoft
Microsoft W ord, similar procedures apply to other programs such as Microsoft
Excel, Microsoft Works, and Microsoft Publisher.
For more information about using a program, select
®
Word. Though these examples use
Help on the menu bar.
Working with documents 49
Page 56

Creating a ne w document
HelpSpot For more information on creating a document, d ouble-c lick
the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To create a new document:
1 Click Start, then select Programs, then Microsoft Word. Microsoft Word
starts and a blank docu ment opens.
2 Select File, then select New. The New dialog box opens.
3 Click a tab for the type of document you want to create, select a
documen t templ ate styl e, then click
4 Begin composing your document. Use the me nu s and toolbar buttons at
the top of the window to format the document.
50 Windows Basics
OK. The document template opens.
Page 57

Saving a document
After you create a document, you need to save it if you want to use it later.
HelpSpot For more information on saving a document, double-click
the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To save a document in Microsoft Word:
1 Select File, then Save. The Save As dialog box opens.
2 In the Save in list, find the folder in which you plan to save the file.
3 Type the new file name.
File
folder
File
name
4 Click Save.
Working with documents 51
Page 58

Opening a document
To view, revise, or print an existing document, yo u need to open it. Open
the document in the program it was created in.
HelpSpot For more information on opening a document, d ouble-c lick
the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To open a document in Microsoft Word:
1 Click Start, then select Programs, then Microsoft Word. Microsoft Word
starts and a blank docu ment opens.
2 Select File, then Open.
3 In the Look in list, find the folder you want to open.
File
folder
File
name
4 Double-click the document file name. The document opens.
52 Windows Basics
Page 59

Printing a document
To print a document, you must have a printer connected to your computer
or have access to a network printer. For more information about installing or
using you r printe r, refer to the printer documen tation.
HelpSpot For more inf ormat ion on p rinting a docum ent, do ub le-cl ic k
the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To print a document in Microsoft Word:
1 Make sure that the printer is turned on and loaded with paper.
2 Star t Microsoft Word and open a document.
3 Select File, then Print. The Print dialog box opens.
4 Select the print options, then click OK. The document prints.
Working with documents 53
Page 60

Shortcuts
The following table shows a fe w shortc uts tha t yo u ca n use in Windows and
almost all programs that run in W indows. For more information on W indows
shortcuts, see your Windows or program documentation.
To... Do this...
Copy a file, folder, text, or graphic Select the item, then press CTRL + C.
Cut a file, folder, text, or graphic Select the item, then press C
Paste a file, folder, text, or graphic Select the item, then press C
Select multiple icons on the desktop Click the first icon, press and hold down the C
TRL + X.
TRL + V.
TRL key,
then click ea ch of t he r emaini ng ic ons tha t you want to
select.
Select multiple items in a list or in an
Explorer window
Click the first item, press and hold down the C
then click each of the remaining items.
TRL key,
Select multiple adjacent items in a list Click the first item in the list, press and hold down the
S
HIFT key, then click the last item in the list.
Permanently delete a file or folder Click the file or folder, then press S
HIFT + DELETE. The
file is permanently deleted and is not stored in the
Recycle Bin.
Rename a file or folder Select the file or folder, press F2, type the new name,
then press E
Close the active window o r program Pre ss A
Switch to a different file, folder, or
Press A
NTER.
LT + F4.
LT + TAB.
running program
54 Windows Basics
Page 61

T ransf erring software and hard ware from y our old computer
If your new computer is replacing an old computer, you may have personal
data files, Internet settings, a printer or other peripheral devices, and other
unique computer settings that you want to move from your old computer to
your new one.
Gateway Data Move r Plus kit
If both your old and new computers have USB ports, you can use the
Gateway Data Mover Plus kit to automatically transfer customized computer
settings, such as Desktop settings, sound schemes, Internet and e-mail
settings, as well as personal data files, such as documents, spreadsheets, and
photographs. This program, with its special USB cable, helps you do this
quickly and efficiently. To order the Gateway Data Mov er Plus kit, visit the
Gateway Accessory Store at www.gateway.com.
T ransf erring files
You can manually transfer your personal data files by
copying them to removable media, such as a diskette, CD,
or Zip disk, or by using a home network. For more
information about using a home network, see
“Networking Your Home” on page 153.
Finding your files
Many programs automatically save your personal data files in the
My Documents folder. Look in your old computer’s My Documents folder for
personal data files. Use Windows Find or Search to locate other personal data
files.
Transferring software and hardware from your old computer 55
Page 62

To find files in the My Documents folder:
1 Doubl e-click the My Computer icon on your desktop. The My Computer
window opens.
2 Doubl e-click the C:\ drive icon. The C:\ window o pens.
3 Double-click the My Documents folder . The My Documents window opens
and displays many of your saved personal da ta files.
Y ou can often identify different data file type s by looking at the file’s extension
(the part of the file name following the last period). For example, a document
file might have a .DOC extension and a spreadsheet file might have an .XLS
extension.
File type File usually ends in...
Documents .doc, .txt, .rtf, .htm, .html, .dot
Spreadsheets .xls, .xlt, .txt
Pictures .jpg, .bmp, .gif, .pdf, .pct, .tif, .png
Movies .mpeg, .mpg, .avi, .gif, .mov
Sound and Music .wav, .cda, .mp3, .mid, .midi
To find files using Find or Search:
1 Click Start, then select Find or Search, then Files or Folders or For Files or
Folders
. The Search Results window opens.
2 Use Windows Search to locate data files by file name or file type. For help
on findin g files , click
56 Windows Basics
Help, then select Help Topics.
Page 63

T ransf erring Internet settings
You can use different methods to transfer your Internet
account from your old computer to your new one.
Setting up your ISP
■ If your current Internet Service Provider (ISP) software came preinstalled
on your new computer, run that setup program. If it asks to set up a new
account or an existing one, choose to reconnect to an existing account.
■ If your current ISP software is not preinstalled on your new computer,
locate the original Internet setup program provided by your local ISP, or
contact your ISP to see if they have an updated version of their software,
and install it on your new computer.
■ If you use MSN as your ISP, or if you know your ISP settings, use the
Windows Internet Connection Wizard.
To use the Internet Connection Wizard:
1 Click Start, then select Programs, Accessories, Communications, then
Internet Connection Wizard. The Internet Connection Wizard window
opens.
2 Configure your Internet settings by following the on-screen instructions.
T ransferring y our e-mail and address book
Refer to your old e-mail progra m’s online help for information on exporting
and importing e-mail messages and the address book. You can often export all
of your old e-mail messages or address book to a disket te, then import them
from the diskette into your new computer’s e-mail progra m. Alternatively , you
may want to consider simply printing the old information or e-mailing it to
yourself.
T ransferring y our Internet shortcuts
You can export and import your old bookmarks (Netscape Navigator) or
favorites (Microsoft Internet Explorer). Fo r more information, refer to your
Internet browser program’s online help.
Transferring software and hardware from your old computer 57
Page 64

Reinstalling your old printer or scanner
Older printers, scanners, or other peripheral devices may
have Windows support integrated (built in), which means
you do not need any additional software. Newer devices,
however, usually require your original software
installation CDs or disks.
Reinstalling a USB printer or scanner
USB devices may have special installation instructions. Refer to your USB
device’s installation guide.
Reinstalling a parallel port printer
You can usually install parallel port printers by following these steps.
To reinstall your old printer:
1 Exit Windows and turn off your computer.
2 Connect your parallel port printer.
3 Turn on your printer, then your computer.
4 If Windows detects your printer, install your printer by following the
on-screen instructions. You are finished.
- OR If Windows does not detect the printer, go to the next step.
5 Click Start, then select Settings, then Printers. The Printers window opens.
6 Double-click the Add Printer icon. The Add Printer Wizard window opens.
7 Install your printer by following the on-screen instructions.
Refer to your peripheral device’s user guide for installation information and
tips. Because most installation software is periodically updated, you should
also check the manufacturers’ Web s i t e f or driver updates.
58 Windows Basics
Page 65

Reinstalling your old programs
You probably use some programs that did not come
installed on your new computer, such as personal finance
software, graphics programs, or games.
Spend some time going through your old computer’s
menus, making note of any programs you want to install on your new
computer. Locate your original program installation CDs and installation
guides. Your original CDs and guides should contain any serial numbers or
product ID keys that may be required for program installation and
registration. Remember to check the manufacturers’ Web site for important
program upda tes.
Tips & Tricks If your new computer comes with a newer version of a
program, it is usually best to use the newer version than
to reinstall the old one.
Start and Programs
Transferring software and hardware from your old computer 59
Page 66

60 Windows Basics
Page 67

Using the Internet
This chapter provides information about the Internet and the World Wide
W eb, a nd tells you how to set up Gateway.net
services so that you can send and receive e-mail and ac cess other Internet
resources.
4
SM
or America Online® Internet
61
Page 68

Learning about the Internet
The Internet is a worldwide network of computers linked together to provide
information to people everywhere. The two most popular services on the
Internet are e-mail and the World Wide Web. You can access this network by
connecting your computer to a telephone, DSL, or cable line and signing up
with an Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Internet Servers
store infor mation so other
computers can access it
from the Internet.
Yo u r computer
connects to the
Internet through
an ISP.
ISP Servers
let you connect to
the Internet and
access your e-mail
messages.
If you want to access the Internet you need:
■ A modem – a device that connects your computer, using a telephone,
DSL, or cable line, to other computers or servers.
■ An I nternet Service Provider – a company that provides access to the
Internet through an ISP server. When you connect to an ISP, the ISP server
lets you access the Internet and yo ur e-mail messages.
■ A Web browser – a program that displays information from the World
Wide Web .
■ An e-mail program – a program that lets you create, send, and receive
e-mail messages over the Internet.
62 Using the Internet
Page 69

Setting up an Internet account
Before you can view the information on the World Wide Web, you need to
set up an Internet account with an Internet Service Provider (ISP). If you have
chosen Gateway.net or America Online as an ISP, follow these instructions to
set up and connect to your account. To establish a different ISP service, or to
transfer an existing account to this computer, contact the ISP directly.
If you set up an account with Gateway.net or America Online, an Internet
e-mail address is created for you. After completing the setup you are ready to
access the Internet.
HelpSpot For more information on setting up an Internet account,
double-click the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To set up an Internet account with Gateway.net or America Online:
1 Doubl e-click the Register with Gateway.net or the America Online Included
icon. If you do not find the service you want on the Windows desktop,
then look for the
the Online Services folder on the Windows desktop.
2 Follow the on-screen instructions. After setting up your account, you can
connect to the Internet and access your e-mail services.
Gateway.net or America Online Included icon located in
Setting up an Internet account 63
Page 70

Accessing your Internet account
HelpSpot For more information on accessing your Internet account,
double-click the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To connect to your Gateway.net or America Online Internet account:
1 Doubl e-click the Connect to Gateway.net or America Online Included icon.
The Connect dialog box open s.
2 Complete the member name and password information, then click
Connect. The computer dials the Internet account phone number.
If you are using a service other than Gateway.net or America Online,
check with your ISP for the correct proced ure for connecting.
After connecting, the W eb browser window opens. For information about the
Web and the Web browser, see “Using the World Wide Web” on page 65.
To disconnect from your Gateway.net or America Online Internet account:
■ Click X in the top right corner of the Gateway.net or America Online
program. Your computer disconnects from the Internet.
If you are using a service other than Gateway.net or America Online,
check with your ISP for the correct procedure for disconnecting.
Important Make sure that your computer disconnects properly from
64 Using the Internet
your Internet account. If you do not have an “unlimited
hours” ISP account, you may have to pay for the time that
you are connected, even if you are not at the computer.
Page 71

Using the W orld Wide W eb
The World Wide Web is a multimedia window to the Internet that gives you
access to millions of information sources.
Information on the Web c omes to you on Web pages, w hich are electronic
documents that you view using a Web page display program called a browser.
You can use any of the commercially available Web browsers, like Microsoft
Internet Explorer, which comes installed on your new computer.
Web pages can contain not only text, but animations, music, and other
multimedia features.
A group of related Web pages is called a Web si te. You can access Web sites to
shop, track investments, read the news, download programs, and much more.
You can explore a Web site or visit other Web sites by clicking areas on the
W eb page called links, or hyperlinks. A link may be colored or underlined text,
a picture, or an animated image. Y ou can identify a link by moving the pointer
over it. If the pointer changes to a hand, the item is a link.
To learn more about using the Web browser features, select
bar.
Link
Web
page
Linked W eb page
Help in the menu
Using the WorldWideWeb 65
Page 72

Connecting to a Web site
After you set up an account with an Internet Service Provider (ISP) such as
Gateway .net or America Online , you can access the many info rmation sources
on the World Wide Web.
HelpSpot For more information on connecting to a Web site,
double-click the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To connect to a Web site:
1 Connect to your Internet account. After the computer connects, a default
opening page or welcome screen opens.
2 To go to a different Web site, type the address (called a URL for “Universal
Resource Loca tor”) in the browser address bar (for example
www.gateway.com) then click
- OR On the current Web page, click a link to a Web site.
GO on the browser address bar.
The Web browser locates the server computer on the Internet, downloads
(transfers) data to your computer, and displays the page on the site that
you requested.
Sometimes Web pages display slowly. The speed that a Web page displays on
your screen depends on the complexity of the Web page and other Internet
conditions. Additionally, the speed of your connection will determine how
fast Web pages display.
66 Using the Internet
Page 73

Downloading files
Downloading is the process of transferring files from a computer on the
Internet to your computer.
To protect your computer against viruses, make sure that you scan the files
you download. For more information, see “Protecting your computer from
viruses” on page 169.
HelpSpot For more inf ormation on downloading fil es, double-cli ck the
HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To download files or programs from a Web site:
1 Connect to your Internet account.
2 In the address bar, type the address of the Web site that contains the file
or program you want to download, then click
bar.
- OR Click on links on a Web page to navigate to the Web site containing the
file that you want to download.
GO on the browser address
3 Create or locate the folder where you want to store the file on your
computer.
4 Click the link on the Web page for the file that you want to download.
5 Follow the on-screen instructions for saving the file in the folder that
you created.
A copy of the file is downloaded to your comp uter. The time that it takes
to transfer the file to your computer depends on file size and Internet
conditions.
6 Open the folder that you created.
7 Install or view the downloaded file by double-clicking it. If applicable,
follow the instructions provided on the Web site to run or install the
program.
Using the WorldWideWeb 67
Page 74

Using e-mail
E-mail (electronic mail) lets you send messages to anyone who has an Internet
connection and e-mail address. E-mail is usually a free service of your Intern et
account.
The Internet never closes, so you can send e-mail messages at any time. Your
e-mail messages arrive at most e-mail addresses in minutes.
An e-mail address consists of a user name, the @ symbol, and the Internet
domain name of the Internet Service Provider (ISP) or company that “hosts”
that user. Your e-mail address is assigned when you sign up for an account
with an ISP. For example, a person with an account with the Gateway.net ISP
might have an e-mail address that is similar to this one:
User name Internet do main name
Sending e-mail
jdoe@gateway.net
HelpSpot For more information on sending e-mail, double-click the
HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To send e-mail using Gateway.net or America Online:
1 Connect to your Gateway.net or America Online account.
2 Click Create Mail.
- OR -
Write.
Click
3 Type the e-mail address of the recipient you want to send e-mail to in
the
Send To box.
4 Type the subject of your e-mail in the Subject box.
68 Using the Internet
Page 75

5 Type the e-mail message.
6 When finished, click Send Now. Your e-mail is sent over the Internet to
the e-mail address you specified.
Checking y our e-mail
HelpSpot For more in formation on checking your e-mail , double-cli ck
the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To check your e-mail using Gateway.net or America Online:
1 Connect to your Gateway.net or America Online account.
2 Click Read Mail.
- OR Click
Read.
For more information about managing and organizing your e-mail messag es,
see the online help in your e-mail program.
Using e-mail 69
Page 76

70 Using the Internet
Page 77

Using Multimedia
This chapter provides information on using the multimedia capabilities of
your notebook. Read this chapter to learn how to:
■ Adjust the volume
■ Connect the external drive
■ Use the diskette drive
■ Use the CD/DVD drive
■ Play CDs and DVDs
■ Record and play audio files
■ Use Media Player
■ Use MusicMatch
5
71
Page 78

Adjusting the volume
Y ou c an use the volume controls to adjust the overall volume and the volume
of specific sound devices in your computer.
HelpSpot For more in formation on adjusting vo lume, doub le-clic k the
HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To adjust overall volume level:
■ Click the speaker icon on the taskbar, then drag the slider to change the
volume or click to select the
Mute check box.
- OR On the keyboard, press the volume buttons to change the volume,
or press the mute button to turn off all sound. For m ore information,
see “Using the keyboard” on page 18.
72 Using Multimedia
Page 79

To adjust specific volume levels:
1 Double-click the speaker icon on the taskbar . Th e Volume Control dialog
box opens.
If the device you want to adjust does not appear in the Volume Control
dialog box, select
to adjust, then click
Options, Properties, select the audio device you want
OK.
2 Drag the volume level and balance sliders for the device you want to
adjust, then close the window. For more information about the volume
controls, select
Help in the Volume Con trol dial og box.
Adjusting the volume 73
Page 80

Connecting the external drive
Y our notebook has an optional external drive bay tha t lets you use a removable
drive such as a diskette drive or CD/DVD drive. To change drives, you need
to replace the drive module in the drive bay.
To connect the external drive:
1 Turn off your notebook.
2 Plug the external drive cable into the connector on the back of the
external drive bay. Make sure the cable plug’s icons are facing up.
74 Using Multimedia
Page 81

3 Plug the other end of the external drive cable into the connector on the
back of the notebook. Make sure the cable plug’s icons are facing up.
4 Turn on your notebook.
5 To access files on the drive, use a program to open drive A: (for a diskette
drive) or drive D: (for a CD/DVD drive).
Connecting the external drive 75
Page 82

To change the drive module:
1 Turn off your notebook.
2 Remove the external drive cable from the external drive by pressing in
both clips on the plug and pulling it away from the module.
3 Turn over the external drive bay.
4 Remove the drive module by pressing and holding the module release
latch and pulling out the module with the other hand.
76 Using Multimedia
Page 83

5 Slide the new module into the bay until it clicks into place.
6 Turn the external drive over, then reconnect the external drive cable.
Make sure the cable plug’s icons are facing up.
Connecting the external drive 77
Page 84

Using diskettes
The diskette drive uses 3.5-inch diskettes (sometimes called floppy disks).
Diskettes are useful for storing files or transferring files to another computer.
Warning Do not expose diskettes to water or magnetic fields.
Exposure could damage the data on the diskette.
Diskette slot Eject button
To use a diskette:
1 Attach the external diskette drive. For more information on attaching the
external drive, see “Connecting the external drive” on page 74.
2 Insert the diskette into the diskette drive with the label facing up.
3 To access a file on the diskette, double-click the My Computer icon, the
drive letter (drive
the file.
4 To remove the diskette, make sure the drive activity light is off, then press
the diskette eject button.
78 Using Multimedia
A: for the standard 1.44 MB diskette drive module), then
Page 85

Using the CD/D VD drive
You can use your computer to enjoy a wide variety of multimedia features,
such as making recordings, listening to audio CDs, and watching DVD movies.
Inserting a CD/DVD
Activity indicator
Eject button
Manual eject hole
To insert a CD/DVD:
1 Attach the external CD/DVD drive . For more information on attaching
the external drive, see “Connecting the external drive” on page 74.
2 Press the eject button on the CD/DVD drive, then pull the disc tray
completely open.
3 Place the CD/DVD in the tray with the label facing up, then press down
carefully on the disc until it snaps into place.
Important When you place a singl e-s ide d dis c i n the tray, make sure
that the label side is f ac ing u p . If the di sc has two pla y ab le
sides, place the disc so that the n ame of th e side y ou w ant
to play is facing up.
4 Push the tray in until it is closed.
Using the CD/DVD drive 79
Page 86

Listening to m usic CDs in Windo ws Me
The Windows Media Player turns your computer into a multimedia center.
Use the player to listen to Internet radio stations, play and copy your CDs,
look for Internet movies, and create lists of all media on your computer. For
more information about using the Windows Media Play er, select
To listen to a CD in the Windows Media Player:
■ Insert a CD into the CD/DVD drive. The Windows Media Player opens
and the CD plays.
If the Windows Media Player does not open aut omatically when you
insert the CD, open it from the Start menu by clicking
Programs, then Windows Media Player . When the media player opens, click
(play).
Start, then selecting
Help.
Play/
Pause
80 Using Multimedia
Stop
Sound
Controls
Track
Controls
Page 87

Listening to m usic CDs in Windo ws 98
Use the CD/DVD drive and th e Windows CD Player to play an a udio CD.
To play a CD:
■ Insert a CD into the CD/DVD drive. The CD Player opens and the CD
plays.
If the CD Player does n ot open automatically when you insert the CD,
open it from the Start menu by clicking
Accessories, Entertainment, then CD Player. When th e CD Player opens,
click (play).
Start, then selecting Programs,
Pause
Play
Stop
Rewind
Previous
Track
Next
Track
Skip
Forward
Eject
CD
If you do not hear audio or you want to change the volume, see “Adjusting
the volume” on page 72.
Using the CD/DVD drive 81
Page 88

Recording and pla ying audio
Use the instructions below to make an audio recording by speaking into the
microphone.
HelpSpot For more information on recording and playing audio,
double-click the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To make an audio recording:
1 Click Start, then s elec t Programs, Accessories, Entertainment, then Sound
Recorder
. The Sound Recorder opens.
Rewind Fast
2 Click (record), then speak into the microphone.
3 When you finish recording, click (stop).
4 Select File, then Save As. The Save As dialog box opens.
5 Name the recording, specify the path, then click Save. The recording is
saved.
82 Using Multimedia
Forward
Play Stop
Record
Page 89

To play an audio recording in Sound Recorder:
1 Open the S ound Recorder.
2 Select File, then Open. The Open dialog box open s.
3 Select the file you want to play back, then click Open.
4 Play the file by clicking (play), then stop playing the file by clicking
(stop).
Recording and playing audio 83
Page 90

Playing audio and video files with Windo ws Media Player
The Windows Media Player can pl ay several types of audio and video files,
including WAV, MIDI, MP3, AU, AVI, and MPEG formats. For more
information about the using the Windows Media Player, select
To play a file using the Media Player:
1 Click Start, then select Programs, Accessories, Entertainment, then
Windows Media Player. The Windows Media Player opens.
Help.
Video file
information
Video
screen
Play/Pause
2 Select File, then Open. The Open dialog box ope ns.
3 Select the file you want to play, then click Open.
4 Play the file by clicking (play), then stop playing the file by clicking
(stop).
For more information about the Windows Media Player, select
84 Using Multimedia
Stop
Help.
Page 91

Playing a D VD
A Digital Versatile Di sc (DVD) is similar to a standard CD but has greater data
capacity. Because of this increased capacity, full-length movies, several albums
of music, or several gigabytes of data can fit on a single disc. If your computer
has a DVD drive, you can play DVDs with the DVD Player program. See the
DVD help for more information about using the DVD player.
To play a DVD:
1 Make sure that the speakers are turned on or headphones are plugged in
and that the volume is turned up.
2 Turn off your system screen saver and standby timers.
3 Click Start, then select Programs, DVD Player, then DVD Player. The
DVD Player vid eo screen and control panel open.
4 Insert a DVD into the DVD drive, then click ( play). The DVD plays.
5 To control the DVD or adjust the volume, use the controls in the
DVD player. For more information on using the DVD player, see its
online help.
Recording and playing audio 85
Page 92

Using MusicMatch
Using the MusicMatch™ program, you can:
■ Play music CDs
■ Build a music library
■ Create MP3 music files from your music CDs and add them to your music
library
■ Enter music track information
■ Listen to Internet Radio
HelpSpot For more information on using MusicMatch, double-click
the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
Playing CDs
You can use the MusicMatch program to play mus ic CDs.
To play a music CD:
1 Doubl e-c lick th e MusicMatch Jukebox icon on your desktop. MusicMatch
opens.
2 Place the music CD into the CD/DVD drive on your computer . The names
of the music tracks appear in the playlist area.
3 Click Play.
86 Using Multimedia
Page 93

Creating music files
Using the MusicMatch program, you can copy the tracks from a music CD
to your computer hard drive as MP3 files.
Here are some terms that you need to know before you get started:
■ Bit rate is the number of bits required to store one second of music. CD
quality is 128 kilobits per second. A high bit rate gives you better sound
quality but the file size is also larger. For information about changing the
sound quality settings, see the online help in MusicMatch.
■ MP3 (MPEG Layer 3) is a standard for digitally compressing high-fidelity
music into compact files without noticeably sacrificing qua lity. MP3 files
end in the file extension .mp3.
■ Ripping is the process of copying a music track from a music CD and
storing it on your hard drive.
To create (rip) MP3 files:
1 Double-click the MusicMatch Jukebox icon.
2 Place a CD into the CD/DVD drive on your computer. The CD tracks
appear in the playlist with checkmarks next to them.
3 If you do not want to record a track, remove the checkmark.
4 Click REC. The recorder window opens.
5 Click REC in the Recorde r window. The tracks are copied as MP3 files to
your music library on the hard drive.
Using MusicMatch 87
Page 94

Building a m usic library
Use MusicMatch to build a music library. You can organize your music tracks
by categories, find a track quickly by using the sort features, and add
information to a song file.
You can add music tracks to your music library by:
■ Creating MP3 files – When yo u create MP3 files from the tracks on your
music CD, MusicMatch automatically adds these files to your music
library.
■ Dragging and Droppin g – Dra g and drop files from Windows Explorer
or your desktop to the music library.
■ Downloading files from the Internet – When you are connected to the
Internet, MP3 files that you download are automatically added to your
music library.
88 Using Multimedia
Page 95

Changing the music library display settings
To change the music library display settings:
1 Doubl e-click the Musi cMatch Jukebox icon.
2 Select Options, then Settings. The Settings window opens.
3 Click the Music Library tab.
4 Select the categories that you want to display in the columns.
5 Click OK.
Using MusicMatch 89
Page 96

Editing track in formation
If you are connected to the Internet and listening to a music CD, MusicMatch
downloads and displays information such as the artist, album, and track titles
from a database on the Internet called CD DataBase (CDDB).
After you add a CD track as an MP3 file to your music library, you can edit
track information.
To edit track information:
1 Doubl e-click the Musi cMatch Jukebox icon.
2 Create an MP3 file.
3 Right-click the file, then select E d i t Tr a c k Ta g.
4 Enter information such as track title, lead artist, album, or genre.
5 Click OK.
After you enter this track information, it is displayed in the MusicMatch
playlist, music library, and recorder.
90 Using Multimedia
Page 97

Listening to Internet radio
Use the Radio feature in MusicMatch to listen to Internet Radio stations.
To listen to an Internet radio station:
1 Doubl e-click the M usicM atch Juk ebox icon, then connect to the Internet.
2 Click Radio.
Click the
Radio icon .
The Radio window opens.
Using MusicMatch 91
Page 98

3 Click Station Selector. A window opens that lists radio stations by
music format, city, or country.
4 Select a radio station, then click Play. MusicMatch connects to the station.
Using advanced features
Y ou can a lso use MusicMatch to create your own music CDs and to download
MP3 files to your portable MP3 player. See the online help that came with
MusicMatch.
92 Using Multimedia
Page 99

Sending and Receiving Faxes
PhoneTools lets you send and receive faxes using the modem in your
computer.
After you have created a document using a spreadsheet, word processor, or
graphics program, you can send it as a fax. You can also receive faxes on your
notebook. This chapter shows you how to:
■ Set up a fax co ver page
■ Create and send a new fax
■ Fax a document you created in another program
■ Receive a fax
■ View and prin t a f ax
6
93
Page 100

Setting up y our cover page
Before you send your first fax, you need to s et up your user information. Your
fax cover sheets and fax headers will contain this information, which is
required by law.
HelpSpot For more information on setting up a fax cover page,
double-click the HelpSpot icon on your desktop.
To set up your fax cover page:
1 Click Start, then select Programs, PhoneTools, then PhoneTools.
PhoneTools opens.
2 Click Configure, then select General Configuration from the pop-up menu.
The General Configuration dialog box opens.
3 Click the Customize tab, then type your personal information in the User
boxes.
94 Sending and Receiving Faxes
 Loading...
Loading...