Page 1

ADAC Ultra2 S466
Single Ended and Low-
Voltage Differential SCSI
PCI RAID Controller
Hardware Guide
8503624 A MAN US ADAC U2 S466 GDE R0
8/14/98
Page 2

© Copyright 1998 Gateway, Inc.
All rights reserved.
This publication contains proprietary information which is protected by copyright. No part of
this publication can be reproduced, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, translated into any
language or computer language, or transmitted in any form whatsoever without the prior written
consent of the publisher, Gateway, Inc. Gateway, Inc. acknowledges the following trademarks:
Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation
MS-DOS, and Microsoft are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Windows 95,
Microsoft Windows and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
SCO, UnixWare, and Unix are registered trademarks of the Santa Cruz Operation. Inc.
Novell NetWare is a regist ered trademark of Novell Corporation.
IBM, AT, VGA, PS/2, and OS/2 are registered trademarks and XT and CGA are trademarks of
International Business Machines Corporation.
NEC is a registered trademark of Nippon Electric Corporation.
Hewlett-Packard is a registered trademark of Hewlett-Packard Corporation.
Siemens is a registered tr ademark of Siemens Corpora tion.
AMP is a trademark of AMP Corporation.
.
Revision History
6/8/98 Initial release.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
ii
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 Overview...............................................................1
Single Ended and Differential SCSI Buses ..............................2
Maximum Cable Length for SCSI Standards ...........................2
Documentation.........................................................................3
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Block Diagram.........................................4
2 Introduction to RAID............................................5
RAID Benefits..........................................................................5
In This Chapter.........................................................................6
ADAC Ultra2 S466 – Host-Based RAID Solution...................7
RAID Overview.......................................................................8
Consistency Check...................................................................8
Fault Tolerance ........................................................................8
Disk Striping............................................................................9
Disk Spanning........................................................................10
Disk Mirroring .......................................................................11
Parity......................................................................................12
Hot Spares..............................................................................13
Disk Rebuild...........................................................................14
Logical Drive .........................................................................15
Hot Swap................................................................................15
SCSI Drive States...................................................................16
Logical Drive States...............................................................16
Disk Array Types...................................................................17
Enclosure Management..........................................................17
3 RAID Levels........................................................19
Selecting a RAID Level.........................................................20
RAID 0...................................................................................21
RAID 1...................................................................................22
RAID 3...................................................................................23
RAID 5...................................................................................25
RAID 10.................................................................................26
RAID 30.................................................................................27
RAID 50.................................................................................28
4 ADAC Ultra2 S466 Features ..............................29
Hardware Requirements.........................................................30
Configuration Features........................................................... 30
Hardware Architecture Features.............................................31
Array Performance Features...................................................31
RAID Management Features..................................................32
Fault Tolerance Features........................................................32
Contents
iii
Page 4

Software Utilities....................................................................33
Operating System Software Drivers.......................................33
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Specifications.........................................34
PCI Bridge/CPU.....................................................................35
Cache Memory.......................................................................35
ADAC Ultra2 S466 BIOS ......................................................35
Onboard Speaker.................................................................... 36
Serial Port...............................................................................36
SCSI Bus................................................................................36
SCSI Connectors....................................................................37
SCSI Termination...................................................................37
SCSI Firmware.......................................................................37
RAID Management ................................................................38
Fault-Tolerance Features........................................................39
Compatibility..........................................................................40
Summary................................................................................40
5 Configuring ADAC Ultra2 S466.........................41
Configuring SCSI Physical Drives.........................................41
Current Configuration ............................................................42
Logical Drive Configuration ..................................................42
Physical Device Layout ..........................................................43
Configuring Arrays.................................................................45
Configuration Strategies.........................................................46
Assigning RAID Levels..........................................................48
Configuring Logical Drives....................................................48
Optimizing Data Storage........................................................49
Planning the Array Configuration..........................................50
Array Configuration Planner..................................................51
6 Hardware Installation.........................................53
Checklist.................................................................................53
Installation Steps....................................................................54
Step 1 Unpack........................................................................55
Step 2 Power Down................................................................55
Step 3 Configure Motherboard...............................................55
Step 4 Install Cache Memory.................................................56
Step 5 Set Jumpers.................................................................58
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Card Layout...........................................58
Step 6 Set Termination........................................................... 61
SCSI Termination...................................................................62
Step 7 Install ADAC Ultra2 S466..........................................65
Step 8 Connect SCSI Cables..................................................66
Step 9 Set Target IDs .............................................................67
Device Identification on ADAC Ultra2 S466.........................68
Step 10 Power Up ..................................................................69
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
iv
Page 5

Step 11 Run ADAC BIOS Setup............................................70
Step 12 Install Operating System Driver................................70
Summary................................................................................72
7 Troubleshooting.................................................73
BIOS Boot Error Messages ....................................................75
Other BIOS Error Messages...................................................77
DOS ASPI Driver Error Messages.........................................78
Other Potential Problems .......................................................79
A SCSI Cables and Connectors............................83
SCSI Connectors....................................................................83
68-Pin High Density SCSI Internal Connector.......................83
High-Density 68-Pin SCSI Connector Pinout........................89
68-Pin Connector Pinout for LVD SCSI................................91
B Audible Warnings...............................................93
Index........................................................................95
Contents
v
Page 6

Page 7

Preface
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 PCI RAID Controller supports all single
ended and low-voltage differential (LVD) SCSI devices on an
Ultra and Wide SCSI channel with data transfer rates up to 80
MB/s (Megabytes per second). This manual describes ADAC
Ultra2 S466.
Limited Warranty The buyer agrees if this product proves to be defective, that
Gateway is only obligated to repair or repl ace this product at
Gateway’s discretion according to the terms and conditions of the
warranty registration card that accompani es t his product.
Gateway shall not be liable in tort or contract for any loss or
damage, direct, incidental or consequential resulting from the use
of this product. Please see the Warranty Registration Card
shipped with this product for full warranty details.
Limitations of Liability Gateway, Inc. shall in no event be held liable for any loss,
expenses, or damages of any kind whatsoever, whether direct,
indirect, incidental, or consequential (whether arising from the
design or use of this product or the support materials provided
with the product). No action or proceeding against Gateway may
be commenced more than two years after the delivery of product
to Licensee of Licensed Software.
Licensee agrees to defend and indemnify Gateway from any and
all claims, suits, and liabilities (including attorney’s fees) arising
out of or resulting from any actual or alleged act or omission on
the part of Licensee, its authorized third parties, employees, or
agents, in connection with the distribution of Licensed Software
to end-users, including, without limitation, claims, suits, and
liability for bodily or other injuries to end-users resulting from
use of Licensee’s product not caused solely by faults in Licensed
Software as provided by Gateway to Licensee.
Cont’d
Preface vii
Page 8
Preface, Continued
Package Contents You should have received:
• a ADAC Ultra2 S466 PCI RAID Controller,
• a ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide,
• a ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration Software Guide,
• a ADAC Ultra2 S466 Operating System Drivers
Guide,
• software license agreement,
• diskette(s) with the ADAC Ultra2 S466 software, and
• a warranty registration card.
Technical Support If you need help insta lling, configuring, or running the
ADAC Ultra2 S466 PCI RAID Controller, call your
Gateway OEM Technical Support representative. For the
current number, refer to the Assistance Resources
Brochure that was included with your system. Before you
call, please complete the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Problem
Report form on the next page.
Web Site We invite you to access the Gateway world wide web site
at:
http://www.gateway.com.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
viii
Page 9
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Problem Report Form
Customer Information ADAC Ultra2 S466 Information
Name Today’s Date
Company Date of Purchase
Address Invoice Number
City/State Serial Number
Country
email address Cache Memory
Phone Firmware Version
Fax BIOS Version
System Information
Motherboard: BIOS manufacturer:
Operating System: BIOS Date:
Op. Sys. Ver.: Video Adapter:
ADAC Ult ra2 S4 66
Driver Ver.:
Network Card: System Memory:
Other disk controllers
installed:
Description of problem:
Steps necessary to re-create problem:
1.
CPU Type/Speed:
Other adapter cards
installed:
2.
3.
4.
Logical Drive Configuration
Logical
Drive
RAID
Level
Stripe
Size
Logical Drive
LD1
LD2
LD3
LD4
LD5
LD6
LD7
LD8
Preface
Size
Cache
Policy
Read
Policy
Write
Policy
# of Physical
Drives
ix
Page 10
Physical Device Layout
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
x
Channel 1
Page 11
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Channel 1
Preface
xi
Page 12

Preface, Continued
Disclaimer This manual describes the operation of the Gateway ADAC
Ultra2 S466 Disk Array Controller. Although efforts have been
made to assure the accuracy of the information contained here,
Gateway expressly disclaims liability for any error in this
information, and for damages, whether direct, indirect, special,
exemplary, consequential or otherwise, that may result from such
error, including but not limited to the loss of profits resulting
from the use or misuse of the manual or information contained
therein (even if Gateway has been advised of the possibility of
such damages). Any questions or comments regarding this
document or its contents should be addressed to Gateway at the
address shown on the cover.
Gateway provides this publication “as is” without warranty of
any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited
to, the implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a
specific purpose.
Some states do not allow disclaimer of express or implied
warranties or the limitation or exclusion of liability for indirect,
special, exemplary, incident al or consequenti al damages in
certain transactions; therefore, this statement may not apply to
you. Also, you may have other rights which vary from
jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
This publication could include technical inaccuraci es or
typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein; these changes will be incorporated in new
editions of the publication. Gateway may make improvements
and/or revisions in the product(s) and/or the program(s)
described in this publication at any time.
Requests for technical information about Gateway products
should be made to your Gateway representative.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
xii
Page 13

FCC Regulatory Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Warning: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved
by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority
to operate the equipment.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a specific installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
1) Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2) Increase the separation between the equipment and
the receiver.
3) Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
4) Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician
for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used with this product to ensure
compliance with the Cla ss B FCC limits.
Gateway ADAC Ultra2 S466 PCI RAID Controller
Model Number: Series 466
FCC ID Number: IUESER466
Preface
xiii
Page 14
Disclaimer
Gateway only certifies that this product will work correctly when this
product is used with the same jumper settings, the same system
configuration, the same memory module parts, and the same
peripherals that were tested by Gateway with this product. The
complete list of tested jumper settings, system configurations,
peripheral devices, and memory modules are documented in the
Gateway Compatibility Report for this product. Call your Gateway
sales representative for a copy of the Compatibility Report for this
product.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
xiv
Page 15

1 Overview
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 PCI RAID controller is a high
performance intelligent PCI-to-SCSI host adapter with
RAID control capabilities. The ADAC Ultra2 S466
provides reliability, high performance, and fault-tolerant
disk subsystem management. The ADAC Ultra2 S466 is an
entry level-to mid-range RAID controller solution. ADAC
Ultra2 S466 offers a cost-effective way to implement
RAID in a server. The ADAC Ultra2 S466 has an Ultra
and Wide SCSI channel supporting data transfer rates up to
80 Megabytes per second (MB/s) per channel. The SCSI
channel supports up to fifteen non-Ultra SCSI devices.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Features ADAC Ultra2 S466 features:
• provides a high performance I/O migration path while
preserving existing PCI-SCSI software,
• Performs SCSI data transfers up to 80 MB/s,
• performs synchronous operation on a wide LVD SCSI bus,
• allows up to 15 LVD SCSI devices on the wide bus,
• includes an Intel® i960RP that performs RAID calculations
and routing and
• supports 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 MB of Fast Page Mode or
EDO DRAM cache memory in a SIMM socket used for read
and write-back caching and RAID 5 parity generation.
SCSI Channel The ADAC Ultra2 S466 upgrade card includes one Fast-20
SCSI channel. The channel is powered by a Symbios Logic
53C895 (Fast-40) SCSI processor.
NVRAM and Flash ROM A 32 KB x 8 NVRAM stores RAID system
configuration information. The ADAC Ultra2 S466
firmware is stored in flash ROM for easy upgrade.
SCSI Connectors ADAC Ultra2 S466 has one ultra high density 68-pin
external connector for external storage subsystem and one
high density 68-pin internal co nnector.
Chapter 1 Overview
1
Page 16
Single Ended and Differential SCSI Buses
The SCSI standard defines two electrical buses:
• a single ended bus and
• low-voltage differential bus.
Maximum Cable Length for SCSI Standards
Standard Single ended LVD Maximum Number
of Drives
SCSI I 6 m 12 m 7
Fast SCSI 6 m 12 m 7
Fast Wide SCSI 6 m 12 m 15
Ultra SCSI 1.5 m 12 m 7
Ultra SCSI 3 m 12 m 3
Wide Ultra SCSI 12 m 15
Wide Ultra SCSI 1.5 m 12 m 7
Wide Ultra SCSI 3 m 12 m 3
Ultra 2 SCSI 25 m 1
Ultra 2 SCSI 12 m 7
Wide Ultra 2 SCSI 25 m 1
Wide Ultra 2 SCSI 12 m 15
SCSI Bus Widths and Maximum Throughput
SCSI Standard SCSI B us Width SCSI Throughput
SCSI I 8 bits 5 MB/s
Fast SCSI 8 bits 10 MB/s
Fast Wide SCSI 16 bits 20 MB/s
Ultra SCSI 8 bits 20 MB/s
Wide Ultra SCSI 16 bits 40 MB/s
Ultra 2 SCSI 8 bits 40 MB/s
Wide Ultra 2 SCSI 16 bits 80 MB/s
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
2
Page 17

Documentation
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 documentation set includes:
Using ADAC Ultra2 S466 Manuals This manual contains the RAI D
overview, RAID planning, and RAID system configuration
information you will need first. Read the ADAC Ultra2
S466 Hardware Guide first.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration Software Guide This manual describes
the software configuration utilities that configure and
modify RAID systems.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Operating System Drivers Guide This manual provides
detailed information about installing the ADAC Ultra2
S466 operating system drivers.
Chapter 1 Overview
3
Page 18
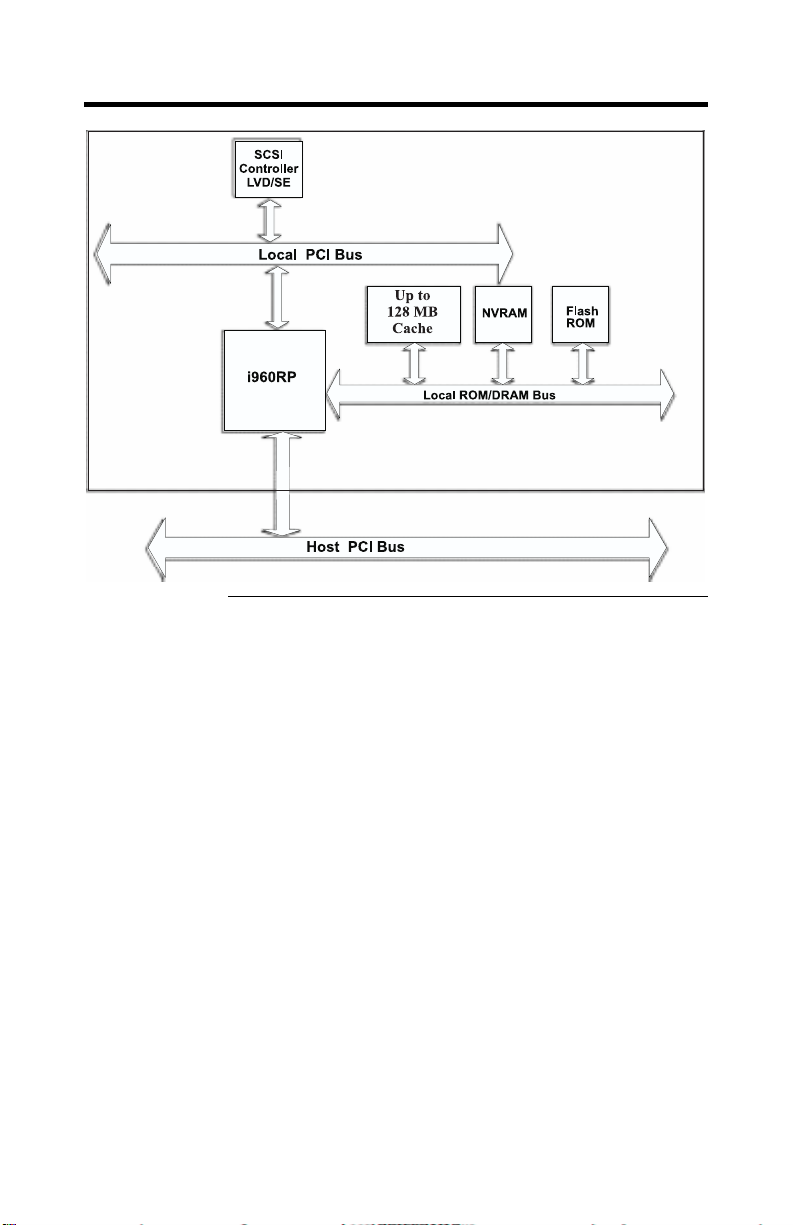
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Block Diagram
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
4
Page 19
2 Introduction to RAID
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is an array
of multiple independent hard disk drives that provide high
performance and fault tolerance. A RAID disk subsystem
improves I/O performance over a computer using only a
single drive. The RAID array appears to the host computer
as a single storage unit or as multiple logical units. I/O is
expedited because several disks can be accessed
simultaneously. RAID systems improve data storage
reliability and fault tolerance compared to single-drive
computers. Data loss because of a disk drive failure can be
recovered by reconstructing missing data from the
remaining data and parity drives.
RAID Benefits
RAID has gained popularity because it: improves I/O
performance, and increases storage subsystem reliability.
RAID provides data security through fault tolerance and
redundant data storage. The ADAC Ultra2 S466
management software configures and monitors RAID disk
arrays.
Improved I/O Although disk drive capabilities have improved drastically,
actual performance has improved only three to four times
in the last decade. Computing performance has improved
over 50 times during the same time period.
Increased Reliability The electromechanical components of a disk
subsystem operate more slowly, require more power, and
generate more noise and vibration than electronic devices.
These factors reduce the reliability of data stored on disks.
Chapter 2 Introduction to RAID
5
Page 20
In This Chapter
The following topics are discussed:
Major Topic Subtopic turn to
Host-based solution page 7
RAID overview page 8
Consistency check page 8
Fault tolerance page 8
Disk striping page 9
Disk spanning page 10
Disk mirroring page 11
Parity page 12
Hot spares page 13
Disk rebuilds page 14
RAID levels page 19
Selecting a RAID level page 20
RAID 0 page 2 1
RAID 1 page 2 2
RAID 3 page 2 3
RAID 5 page 2 5
RAID 10 page 26
RAID 30 page 27
RAID 50 page 28
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
6
Page 21

ADAC Ultra2 S466 – Host-Based RAID Solution
RAID products are either:
• host-based or
• SCSI-to-SCSI.
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller is a host-based RAID
solution. ADAC Ultra2 S466 is a PCI adapter card that is
installed in any available PCI expansion slot in a host
system.
Host-Based A host-based RAID product puts all of the RAID
intelligence on an adapter card that is installed in a network
server. A host-based RAID product provides the best
performance. ADAC Ultra2 S466 is part of the file server,
so it can transmit data directly across the computer’s buses
at data transfer speeds up to 132 MB/s.
The available sequential data transfer rate is determined by
the following factors:
the sustained data transfer rate on the motherboard
•
PCI bus,
the sustained data transfer rate on the i960RP PCI to
•
PCI bridge,
the sustained data transfer rate of the SCSI controller,
•
the sustained data transfer rate of the SCSI devices,
•
the number of SCSI channels, and
•
the number of SCSI disk drives.
•
Host-based solutions must provide operating systemspecific drivers.
SCSI-to-SCSI A SCSI-to-SCSI RAID product puts the RAID intelligence
inside the RAID chassis and uses a plain SCSI Host
Adapter installed in the network server. The data transfer
rate is limited to the bandwidth of the SCSI channel. A
SCSI-to-SCSI RAID product that has two wide SCSI
channels that operate at speeds up to 80 MB/s must
squeeze the data into a single wide SCSI (40 MB/s)
channel back to the host computer.
In SCSI-to-SCSI RAID products, the hard drive subsystem
uses only a single SCSI ID, which allows you to connect
multiple drive subsystems to a single SCSI controller.
Chapter 2 Introduction to RAID
7
Page 22
RAID Overview
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a
collection of specifications that describe a system for
ensuring the reliability and stability of data stored on large
disk subsystems. A RAID system can be implemented in a
number of different versions (or RAID Levels). The
standard RAID levels are 0, 1, 3, and 5. ADAC Ultra2
S466 supports all standard RAID levels and RAID levels
10, 30, and 50, special RAID versions supported by ADAC
Ultra2 S466.
Consistency Check
In RAID, check consistency verifies the correctness of
redundant data in an array. For example, in a system with
dedicated parity, checking consistency means computing
the parity of the data drives and comparing the results to
the contents of the dedicated parity drive.
Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is achieved through cooling fans, p ower
supplies, and the ability to hot swap drives. ADAC Ultra2
S466 provides hot swapping through the hot spare feature.
A hot spare drive is an unused online available drive that
ADAC Ultra2 S466 instantly plugs into the system when
an active drive fails.
After the hot spare is automatically moved into the RAID
subsystem, the failed drive is automatically rebuilt. The
RAID disk array continues to handle request while the
rebuild occurs.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
8
Page 23
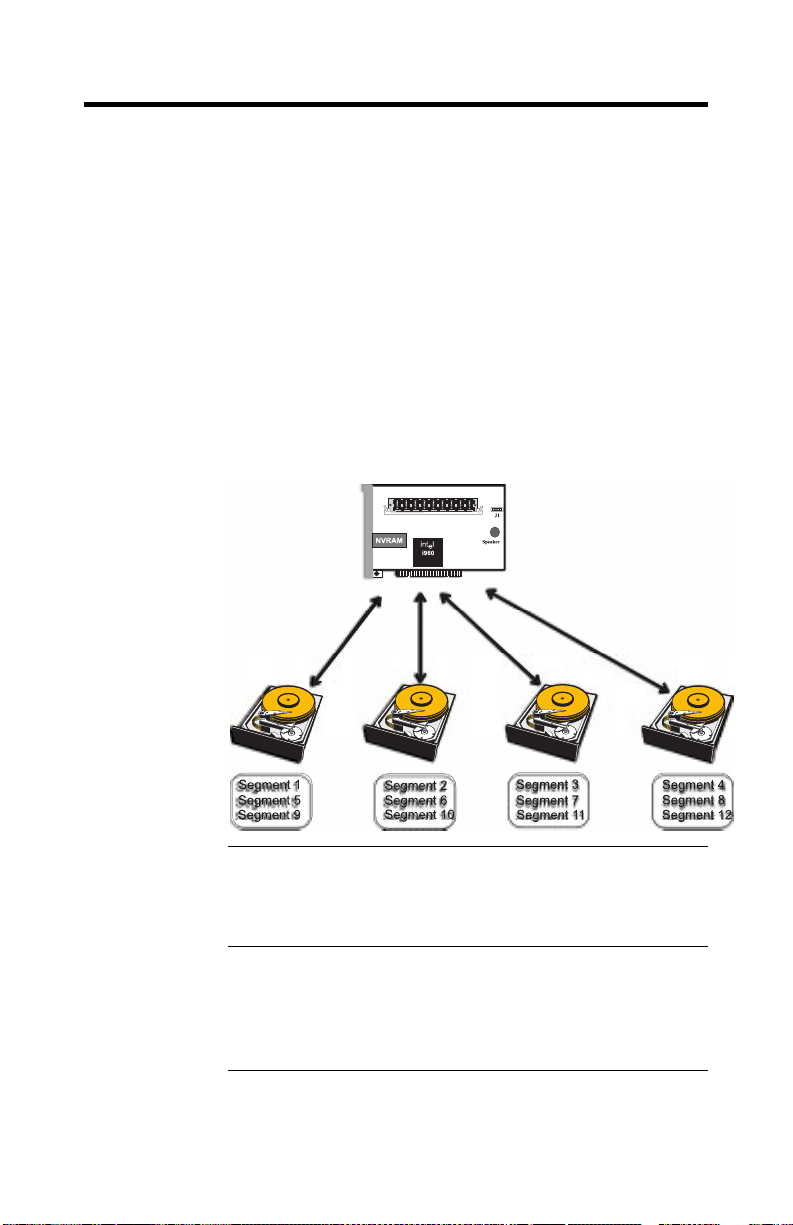
Disk Striping
Disk striping writes data across multiple disk drives instead
of just one disk drive. Disk striping involves pa rtitioning
each drive storage space into stripes that can vary in size
from 2 KB to 128 KB. These stripes are interleaved in a
repeated sequential manner. The combined storage space is
composed of stripes from each drive. ADAC Ultra2 S466
supports stripe sizes of 2 KB, 4 KB, 8 KB, 16 KB, 32 KB,
64 KB, or 128 KB.
For example, in a four-disk system using only disk striping
(as in RAID level 0), segment 1 is written to disk 1,
segment 2 is written to disk 2, and so on. Disk striping
enhances performance because multiple drives are
accessed simultaneously; but disk striping does not provide
data redundancy.
Stripe Width Stripe width is the number of disks involved in an array
where striping is implemented. For example, a four-disk
array with disk striping has a stripe width of four.
Stripe Size The stripe size is the length of the interleaved data
segments that ADAC Ultra2 S466 writes across multiple
drives. ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports stripe sizes of 2 KB, 4
KB, 8 KB, 16 KB, 32 KB, 64 KB, or 128 KB.
Chapter 2 Introduction to RAID
9
Page 24
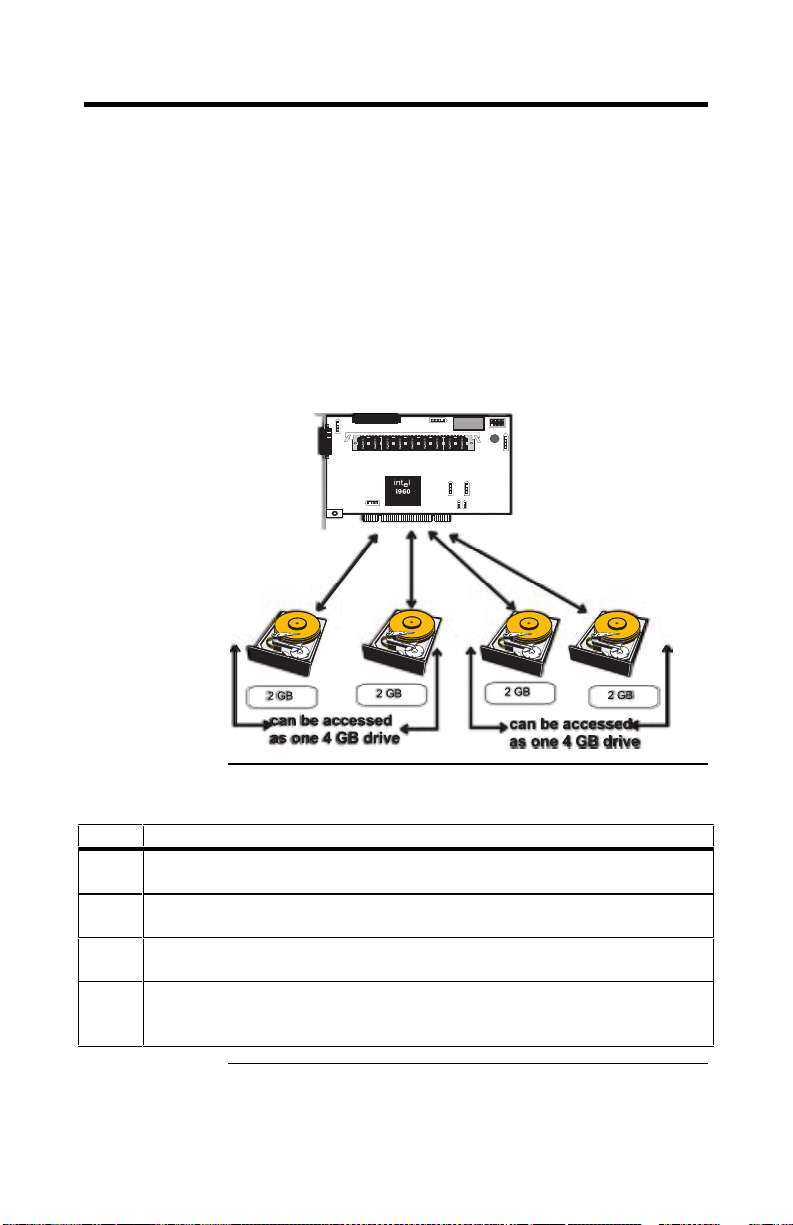
Disk Spanning
Disk spanning allows multiple disk drives to function like
one big drive. Spanning overcomes lack of disk space and
simplifies storage management by combining existing
resources or adding relatively inexpensive resources. For
example, four 400 MB disk drives can be combined to
appear to the operating system as one single 1600 MB
drive.
Spanning alone does not provide reliability or performance
enhancements. Spanned logical drives must have the same
stripe size and must be contiguous. In the following
graphic, RAID 1 array is turned into a RAID 10 array.
Spanning for RAID 10, RAID 30, or RAID 50
Level Description
10 Configure RAID 10 by spanning two contiguous RAID 1 logical drives.
The RAID 1 logical drives must have the same stripe size.
30 Configure RAID 30 by spanning two contiguous RAID 3 logical drives.
The RAID 3 logical drives must have the same stripe size.
50 Configure RAID 50 by spanning two contiguous RAID 5 logical drives.
The RAID 5 logical drives must have the same stripe size.
Note:
10
Spanning two contiguous RAID 0 logical drives does not produce a new
RAID level or add fault tolerance. It does increase the size of the lo gical
volume and improves performance by doubling the number of spindles.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
Page 25
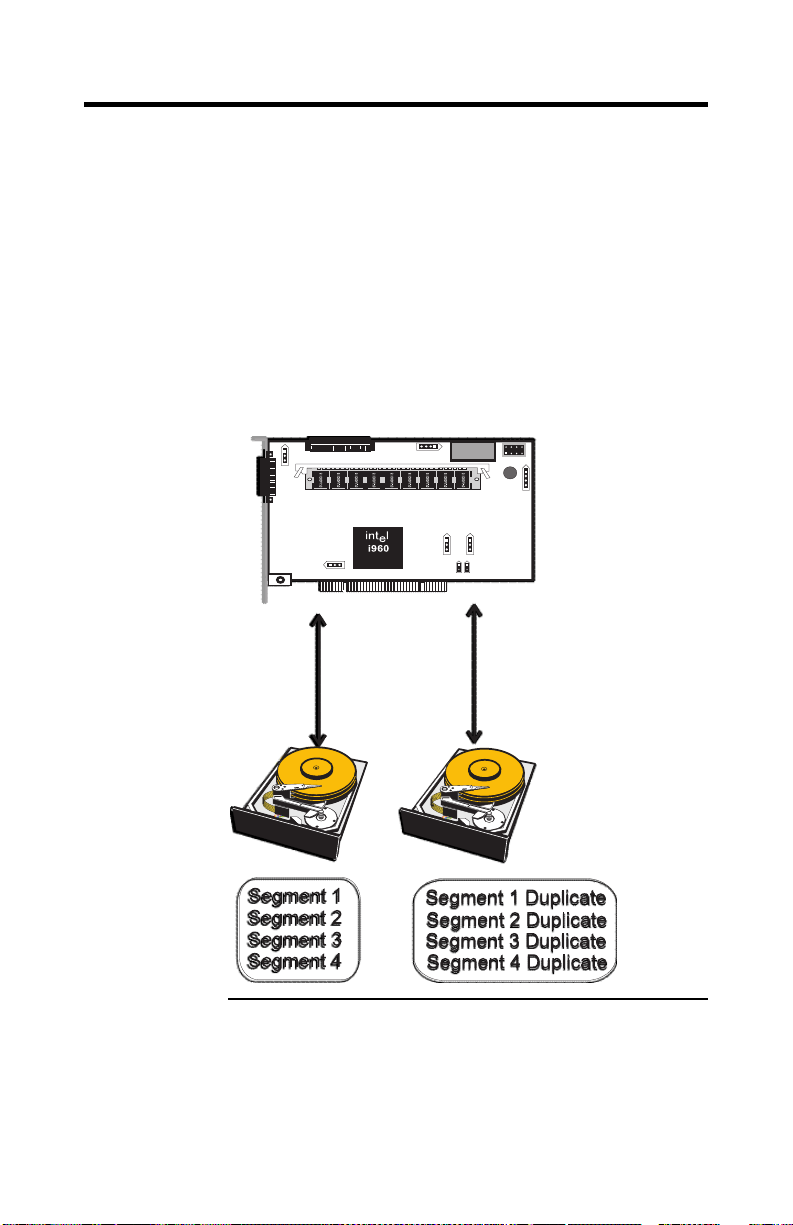
Disk Mirroring
With mirroring (used in RAID 1), data written to one disk
drive is simultaneously written to another disk drive. If one
disk drive fails, the contents of the other disk drive can be
used to run the system and reconstruct the failed drive. The
primary advantage of disk mirroring is that it provides
100% data redundancy. Since the contents of the disk drive
are completely written to a second drive, it does not matter
if one of the drives fails. Both drives contain the same data
at all times. Either drive can act as the operational drive.
Disk mirroring provides 100% redundancy, but is
expensive because each drive in the system must be
duplicated.
Chapter 2 Introduction to RAID
11
Page 26
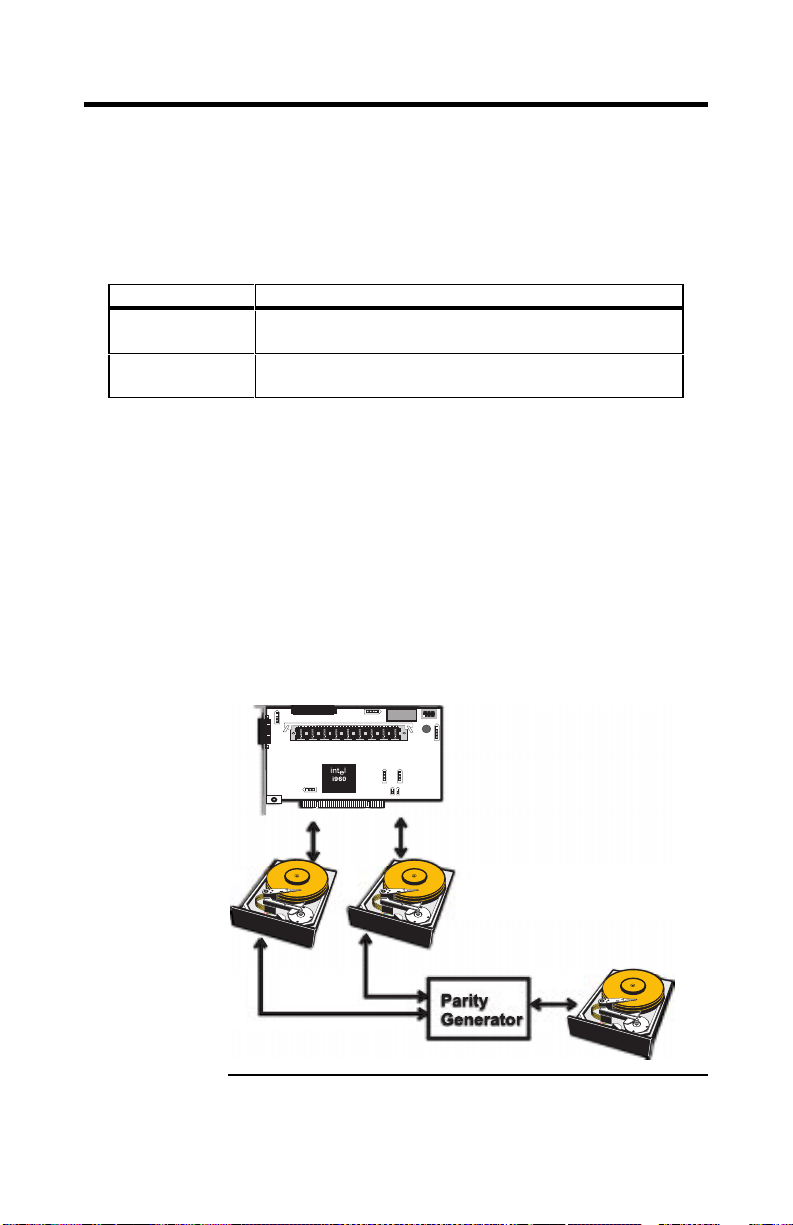
Parity
Parity generates a set of redundancy data from two or more
parent data sets. The redundancy data can be used to
reconstruct one of the parent data sets. Parity data does not
fully duplicate the parent data sets. In RAID, this method is
applied to entire drives or stripes across all disk d rives in
an array. The types of parity are:
Type Description
Dedicated Parity The parity of the data on two or more disk drives is
stored on an additional disk.
Distributed
Parity
The parity data is distributed across all drives in the
system.
If a single disk drive fails, it can be rebuilt from the parity
and the data on the remaining drives.
RAID level 3 combines dedicated parity with disk striping.
The parity disk in RAID 3 is the last logical drive in a
RAID set.
RAID level 5 combines distributed parity with disk
striping. Parity provides redundancy for one drive failure
without duplicating the contents of entire disk drives, but
parity generation can slow the write process. A dedicated
parity scheme during normal read/write operations is
shown below:
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
12
Page 27
Hot Spares
Hot spares are only employed in arrays with redundancy, for
A hot spare connected to a specific ADAC Ultra2 S466
controller can only be used to rebuild a drive that is
A hot spare is an extra, unused disk drive that is part of the
disk subsystem. It is usually in standby mode, ready for
service if a drive fails. Hot spares permit you to replace
failed drives without system shutdown or user intervention.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 implements automatic and transparent
rebuilds using hot spare drives, providing a high degree of
fault tolerance and zero downtime. The ADAC Ultra2
S466 RAID Management software allows you to specify
physical drives as hot spares. When a hot spare is needed,
the ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller assigns the hot spare that
has a capacity closest to and at least as great as that of the
failed drive to take the place of the failed drive.
Important
example, RAID levels 1, 3, 5, 10, 30, and 50.
connected to the same controller.
Chapter 2 Introduction to RAID
13
Page 28

Disk Rebuild
You rebuild a disk drive by recreating the data that had
been stored on the drive before the drive failed.
Rebuilding can be done only in arrays with data
redundancy such as RAID level 1, 3, 5, 10, 30, and 50.
Standby (warm spare) rebuild is employed in a mirrored
(RAID 1) system. If a disk drive fails, an identical drive is
immediately available. The primary data source disk drive
is the original disk drive.
A hot spare can be used to rebuild disk drives in RAID 1,
3, 5, 10, 30, or 50 systems. If a hot spare is not available,
the failed disk drive must be replaced with a new disk drive
so that the data on the failed drive can be rebuilt.
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller automatically and
transparently rebuilds failed drives with user-definable
rebuild rates. If a hot spare is available, the rebuild starts
automatically when a drive fails. ADAC Ultra2 S466
automatically restarts the system and the rebuild if the
system goes down during a rebuild.
Rebuild Rate The rebuild rate is the fraction of the compute cycles
dedicated to rebuilding failed drives. A rebuild rate of 100
percent means the system is totally dedicated to rebuilding
the failed drive.
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 rebuild rate can be configured
between 0% and 100%. At 0%, the rebuild is only done if
the system is not doing anything else. At 100%, the rebuild
has a higher priority than any other system activity.
Physical Array A RAID array is a collection of physical disk drives
governed by the RAI D management software. A RAID
array appears to the host computer as one or more logical
drives.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
14
Page 29
Logical Drive
Hot Swap
A logical drive is a partition in a physical array of disks
that is made up of contiguous data segments on the
physical disks. A logical drive can consist of any of the
following:
• an entire physical array,
• more than one entire physical array,
• a part of an array,
• parts of more than one array, or
• a combination of any two of the above conditions.
A hot swap is the manual replacement of a defective
physical disk unit while the computer is still running. When
a new drive has been installed, you must issue a command
to rebuild the drive.
Chapter 2 Introduction to RAID
15
Page 30
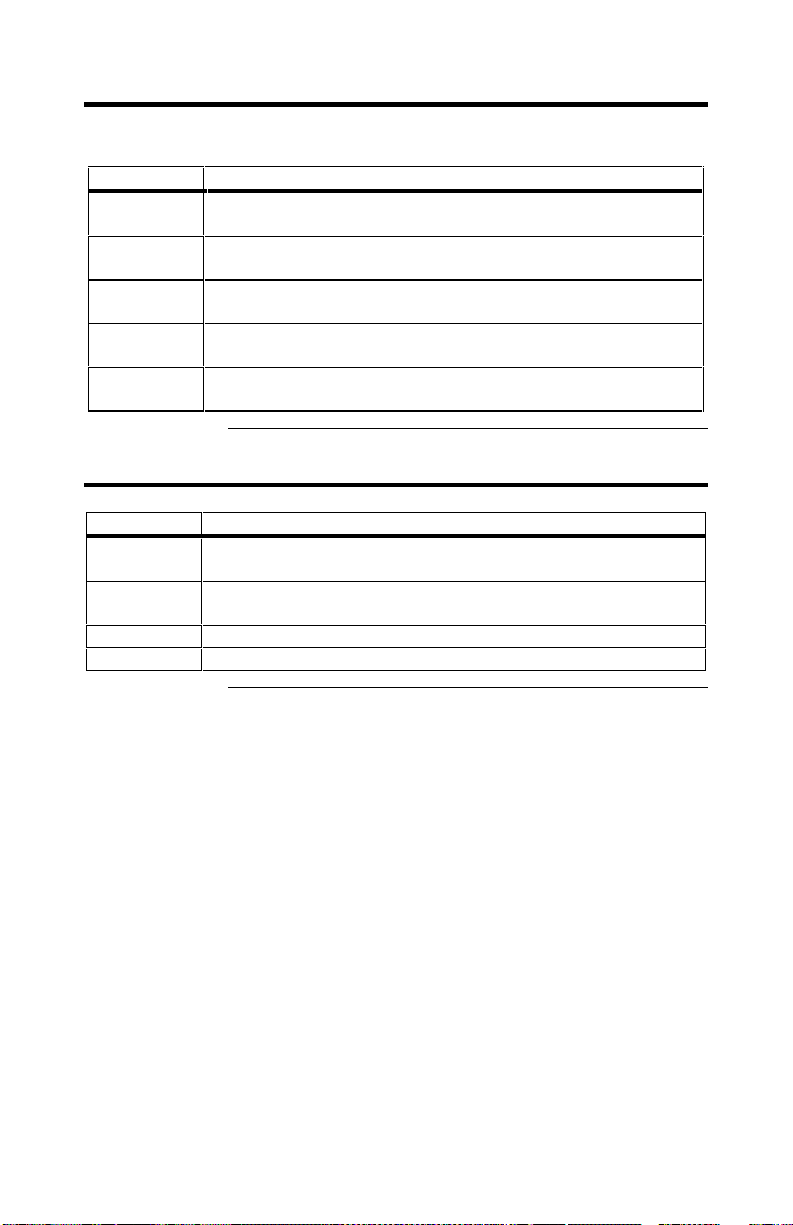
SCSI Drive States
A SCSI disk drive can be in one of these states:
State Description
Online
(ONLIN)
Ready
(READY)
Hot Spare
(HOTSP)
Fail
(FAIL)
Rebuild
(REB)
The drive is functioning normally and is a part of a configured
logical drive.
The drive is functioning normally but is not part of a configured
logical drive and i s not designated as a hot spare.
The drive is powered up and ready for use as a spare in case an
online drive fails.
A fault has occurred in the drive placing it out of service.
The drive is being rebuilt with data from a failed drive.
Logical Drive States
State Description
Optimal The drive operating condition is good. All configured drives are
online
Degraded The drive operating condition is not optimal. One of the
configured drives has failed or is offline.
Failed The drive has failed.
Offline The drive is not available to ADAC Ultra2 S466.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
16
Page 31

Disk Array Types
The RAID disk array types are:
Type Description
Software-
Based
SCSI to SCSI The array controller resides outside of the host computer and
Bus-Based The array controller resides on the bus (for example, a PCI or
The array is managed by software running in a host computer using
the host CPU bandwidth. The disadvantages associated with this
method are the load on the host CPU and the need for different
software for each operating system.
communicates with the host through a SCSI adapter in the host.
The array management software runs in the controller. It is
transparent to the host and independent of the host operating
system. The disadvantage is the limited data transfer rate of the
SCSI channel between the SCSI adapter and the array con troller.
EISA bus) in the host computer and has its own CPU to generate
the parity and handle other RAID functions. A bus-based controller
can transfer data at the speed of the host bus (PCI, ISA, EISA, VLBus) but is limited to the bus it is designed for. ADAC Ultra2 S466
resides on a PCI bus, which can handle data transfer at up to 132
MB/s. With ADAC Ultra2 S466, the channel can handle data
transfer rates up to 80 MB/s per SCSI channel.
Enclosure Management
Enclosure management is the intelligent monitoring of the
disk subsystem by software and/or hardware.
The disk subsystem can be part of the host computer or
separate from it. Enclosure management helps you stay
informed of events in the disk subsystem, such as a drive or
power supply failure. Enclosure management increases the
fault tolerance of the disk subsystem.
Chapter 2 Introduction to RAID
17
Page 32

ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
18
Page 33

3 RAID Levels
There are six official RAID levels (RAI D 0 through RAID
5). ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports RAID levels 0, 1, 3, and
5. Gateway has designed three additional RAID levels (10,
30, and 50) that provide additional benefits. The RAID
levels that ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports are:
RAID Level Type turn to
0 Standard page 21
1 Standard page 22
3 Standard page 23
5 Standard page 25
10 ADAC Ultra2 S466 only page 26
30 ADAC Ultra2 S466 only page 27
50 ADAC Ultra2 S466 only page 28
Select RAID Level To ensure the best performance, you should select the
optimal RAID level when you create a system drive. The
optimal RAID level for your disk array depends on a
number of factors:
the number of drives in the disk array,
•
the capacity of the drives in the array,
•
the need for data redundancy, and
•
the disk performance requirements.
•
Selecting a RAID Level The factors you need to consider when selecting a
RAID level are listed on the next page
Chapter 3 RAID Levels
19
Page 34

Selecting a RAID Level
Level Description and
Use
0 Data divided in
blocks and
distributed
sequentially (pure
striping). Use for
non-critical data
that requires high
performance.
1 Data duplicated on
another disk
(mirroring). Use
for read-intensive
fault-tolerant
systems
3 Disk striping with a
dedicated parity
drive. Use for noninteractive apps
that process large
files sequentially.
5 Disk striping and
parity data across
all drives. Use for
high read volume
but low write
volume, such as
transaction
processing.
10 Data striping and
mirrored drives.
30 Disk striping with a
dedicated parity
drive.
50 Disk striping and
parity data across
all drives.
Pros Cons M ax .
High data
throughput
for large
files
100% data
redundancy
Achieves
data
redundancy
at low cost
Achieves
data
redundancy
at low cost
High data
transfers,
complete
redundancy
High data
transfers,
redundancy
High data
transfers,
redundancy
No fault
tolerance. All
data lost if
any drive
fails.
Doubles disk
space.
Reduced
performance
during
rebuilds.
Performance
not as good as
RAID 1
Performance
not as good as
RAID 1
More
complicated
More
complicated
More
complicated
Drives
One to
32
2, 4, 6,
or 8
Three to
eight
Three to
eight
4, 6, or
8
Six to
32
Six to
32
Fault
Tolerant
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
20
Page 35

RAID 0
Uses
Strong Points
Weak Points
Drives
RAID 0 provides disk striping across all drives in the
RAID subsystem. RAID 0 does not provide any data
redundancy, but does offer the best performance of any
RAID level. RAID 0 breaks up data into smaller blocks
and then writes a block to each drive in the array. The size
of each block is determined by the stripe size parameter,
set during the creation of the RAID set. RAID 0 offers high
bandwidth. By breaking up a large file into smaller blocks,
ADAC Ultra2 S466 can use several drives to read or write
the file faster. RAID 0 involves no parity calculations to
complicate the write operation. This makes RAID 0 ideal
for applications that require high bandwidth but do not
require fault tolerance.
RAID 0 provides high data throughput, especially for large
files. Any environment hat does not require fault tolerance.
Provides increased data throughput for large files. No
capacity loss penalty for parity.
Does not provide fault tolerance. All data lost if any drive
fails.
One to 32
Chapter 3 RAID Levels
21
Page 36

RAID 1
Uses
Strong Points
Weak Points
Drives
In RAID 1, ADAC Ultra2 S466 duplicates all data from
one drive to a second drive. RAID 1 provides complete
data redundancy, but at the cost of doubling the required
data storage capacity.
Use RAID 1 for small databases or any other environment
that requires fault tolerance but small capacity.
RAID 1 provides complete data redundancy. RAID 1 is
ideal for any application that requires fault tolerance and
minimal capacity.
RAID 1 requires twice as many disk drives. Performance is
impaired during drive rebuilds.
2, 4, 6, or 8 drives.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
22
Page 37

RAID 3
Uses
Strong Points
Weak Points
Drives
RAID 3 provides disk striping and complete data
redundancy though a dedicated parity drive. The stripe size
must be 64 KB if RAID 3 is used. RAID 3 handles data at
the block level, not the byte level, so it is ideal for
networks that often handle very large files, such as graphic
images. RAID 3 breaks up data into smaller blocks,
calculates parity by performing an exclusive-or on the
blocks, and then writes the blocks to all but one drive in
the array. The parity data created during the exclusive-or is
then written to the last drive in the array. The size of each
block is determined by the stripe size parameter, which is
set during the creation of the RAID set. If a single drive
fails, a RAID 3 array continues to operate in degraded
mode. If the failed drive is a data drive, writes will
continue as normal, except no data is written to the failed
drive. Reads reconstruct the data on the failed drive by
performing an exclusive-or operation on the remaining data
in the stripe and the parity for that stripe. If the failed drive
is a parity drive, writes will occur as normal, except no
parity is written. Reads retrieve data from the disks.
Best suited for applications such as graphics, imaging, or
video that call for reading and writing huge, sequential
blocks of data.
Provides data redundancy and high data transfer rates.
The dedicated parity disk is a bottleneck with random I/O.
Three to eight
Chapter 3 RAID Levels
Cont’d
23
Page 38

RAID 3, Continued
RAID 5 vs RAID 3 You may find that RAID 5 is preferable to RAID 3 even
for applications characterized by sequential reads and
writes, because ADAC Ultra2 S466 has very robust
caching algorithms.
The benefits of RAID 3 disappear if there are many small
I/O operations scattered randomly and widely across the
disks in the logical drive. The RAID 3 fixed parity disk
becomes a bottleneck in such applications. For example:
The host attempts to make two small writes and the writes
are widely scattered, involving two different stripes and
different disk drives. Ideally both writes should take place
at the same time. But this is not possible in RAID 3, since
the writes must take turns accessing the fixed parity drive.
For this reason, RAID 5 is the clear choice in this scenario.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
24
Page 39

RAID 5
Uses
Strong Points
Weak Points
Drives
RAID 5 includes disk striping at the byte level and parity.
In RAID 5, the parity information is written to several
drives. RAID 5 is best suited for networks that perform a
lot of small I/O transactions simultaneously.
RAID 5 addresses the bottleneck issue for random I/O
operations. Since each drive contains both data and parity
numerous writes can take place concurrently. In addition,
robust caching algorithms and hardware based exclusive-or
assist make RAID 5 performance exceptional in many
different environments.
RAID 5 provides high data throughput, especially for large
files. Use RAID 5 for transaction processing applications
because each drive can read and write independently. If a
drive fails, ADAC Ultra2 S466 uses the parity drive to
recreate all missing information. Use also for o ffice
automation and online customer service that requires fault
tolerance. Use for any application that has high read req uest
rates but low write request rates.
Provides data redundancy and good performance in most
environments
Disk drive performance will be reduced if a drive is being
rebuilt. Environments with few processes do not perform as
well because the RAID overhead is not offset by the
performance gains in handling simultaneous processes.
Three to eight
Chapter 3 RAID Levels
25
Page 40

RAID 10
Uses
Strong Points
Weak Points
Drives
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. RAID
10 has mirrored drives. RAID 10 breaks up data into
smaller blocks, and then stripes the blocks of data to each
RAID 1 raid set. Each RAID 1 raid set then duplicates its
data to its other drive. The size of each block is determined
by the stripe size parameter, which is set during the
creation of the RAID set. RAID 10 can sustain one to four
drive failures while maintaining data integrity if each failed
disk is in a different RAID 1 array.
RAID 10 works best for data storage that must have 100%
redundancy of mirrored arrays and that also needs the
enhanced I/O performance of RAID 0 (striped arrays).
RAID 10 works well for medium-sized databases or any
environment that requires a higher degree of fault tolerance
and moderate to medium capacity.
RAID 10 provides both high data transfer rates and
complete data redundancy.
RAID 10 requires twice as many drives as all other RAID
levels except RAID 1.
2n, where n is greater than 1.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
26
Page 41

RAID 30
Uses
Strong Points
Weak Points
Drives
RAID 30 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 3. RAID
30 provides high data transfer speeds and high data
reliability. RAID 30 is best implemented on two RAID 3
disk arrays with data striped across both disk arrays. RAID
30 breaks up data into smaller blocks, and then stripes the
blocks of data to each RAID 3 raid set. RAID 3 breaks up
data into smaller blocks, calculates parity by performing an
exclusive-or on the blocks, and then writes the blocks to all
but one drive in the array. The parity data created during
the exclusive-or is then written to the last drive in each
RAID 3 array. The size of each block is determined by the
stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation of the
RAID set.
RAID 30 can sustain one to four drive failures while
maintaining data integrity if each failed disk is in a
different RAID 3 array.
Use RAID 30 for sequentially written and read data, prepress and video on demand that requires a higher degree of
fault tolerance and medium to large capacity.
Provides data reliability and high data transfer rates.
Requires 2 – 4 times as many parity drives as RAID 3.
Six to 32
Chapter 3 RAID Levels
27
Page 42

RAID 50
Uses
Strong Points
Weak Points
Drives
RAID 50 provides the features of both RAID 0 and RAID
5. RAID 50 includes both parity and disk striping across
multiple drives. RAID 50 is best implemented on two
RAID 5 disk arrays with data striped across both disk
arrays. RAID 50 breaks up data into smaller blocks, and
then stripes the blocks of data to each RAID 5 raid set.
RAID 5 breaks up data into smaller blocks, calculates
parity by performing an exclusive-or on the blocks, and
then writes the blocks of data and parity to each drive in
the array. The size of each block is determined by the
stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation of the
RAID set.
RAID 50 can sustain one to four drive failures while
maintaining data integrity if each failed disk is in a
different RAID 5 array.
RAID 50 works best when used with data that requires high
reliability, high request rates, and high data transfer and
medium to large capacity
RAID 50 provides high data throughput, data redundancy,
and very good performance.
Requires 2 to 4 times as many parity drives as RAID 5.
Six to 32
.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
28
Page 43

4 ADAC Ultra2 S466 Features
ADAC Ultra2 S466 is a family of high performance
intelligent PCI-to-SCSI host adapters with RAID control
capabilities. ADAC Ultra2 S466 has a SCSI channel that
supports Ultra and Wide SCSI at data transfer rates up to
80 MB/s. The SCSI channel supports up to 15 Wide
devices and up to seven non-Wide devices.
In This Chapter Topics described in this chapter include:
• new features,
• configuration features,
• hardware architecture features,
• array performance features,
• RAID management features,
• fault tolerance features,
• utility programs, and
• software drivers.
SMART Technology The ADAC Ultra2 S466 Self Monitoring Analysis
and Reporting Technology (SMART) detects up to 70% of
all predictable drive failures. SMART monitors the internal
performance of all motors, heads, and drive electronics.
Configuration on Disk Configuratio n on Disk (drive roaming) saves
configuration information both in NVRAM on ADAC
Ultra2 S466 and on the disk drives connected to ADAC
Ultra2 S466. If ADAC Ultra2 S466 is replaced, the new
ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller can detect the actual RAID
configuration, maintaining the integrity of the data on each
drive, even if the drives have changed channel and/or
target ID.
Chapter 4 Features
29
Page 44

Hardware Requirements
ADAC Ultra2 S466 can be installed in an IBM AT®compatible or EISA computer with a motherboard that has
5 volt PCI expansion slots. The computer must support
PCI version 2.0 or later. The computer should have an Intel
Pentium, Pentium Pro, or more powerful CPU, a floppy
drive, a color monitor and VGA adapter card, and a
keyboard. A mouse is recommended.
Configuration Features
Specification Feature
RAID Levels 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, 30, and 50.
SCSI Channels 1
Maximum number of drives per channel 15
Array interface to host PCI 2.1
Drive interface Fast and Wide Ultra SE and LVD
Upgradable cache size 4 MB, 8 MB, 16 MB, 32 MB, 64 MB,
or 128 MB
Cache Function Write-through, write-back, ARA,
NRA, RA
Multiple logical drives/arrays per
controller
Maximum number of ADAC Ultra2 S466
controller per system
Online capacity expansion Yes
Dedicated and pool hot spare Yes
Flashable firmware Yes
Hot swap devices supported Yes
Non-disk devices supported Yes
Mixed capacity hard disk drives Yes
Number of 16-bit internal connectors 1
Number of 16-bit external connectors 1
Support for hard disk drives with
capacities of more than 8 GB.
Clustering support (Failover control) No
Online RAID level migration Yes
RAID remapping Yes
No reboot necessary after expansion Yes
More than 200 Qtags per physical drive Yes
Hardware clustering support on the board Yes
User-specified rebuild rate Yes
Up to 8 logical drives per controller
12
Yes
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
30
Page 45

Hardware Architecture Features
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 hardware architecture features
include:
Specification Feature
Processor Intel i960RP3V 33
SCSI Controller Symbios Logic 53C895
Size of Flash ROM 1 MB
Amount of NVRAM 32 KB
Hardware XOR assistance No
Direct I/O Yes
Removable cache memory module Yes
SCSI bus termination Active, single-ended or LVD
Double-sided SIMMs Yes
Auxiliary TermPWR source No
Direct I/O bandwidth 132 MB/s
Array Performance Features
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 array performance features
include:
Specification Feature
Host data transfer rate 132 MB/s
Drive data transfer rate 80 MB/s
Maximum Scatter/Gathers 26 elements
Maximum size of I/O requests 6.4 MB in 64 KB stripes
Maximum Queue Tags per drive 211
Stripe Sizes 2 KB, 4 KB, 8 KB, 16 KB, 32 KB, 64
KB, or 128 KB
Maximum number of concurrent
commands
255
Chapter 4 Features
31
Page 46

RAID Management Features
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 RAID management features
include:
Specification Feature
Support for SNMP Yes
Performance Monitor provided Yes
Remote control and monitoring Yes
Event broadcast and event alert Yes
Hardware connector RS232C
Drive roaming Yes
Support for concurrent multiple stripe
sizes
Web-based management tools Not released yet
Windows NT and NetWare server
support via GUI client utility
SCO Unix, OS/2, and UnixWare
server support via GUI client utility
DMI support Yes
Management through an industry-
standard browser
Not released yet
Fault Tolerance Features
Yes
Yes
Yes
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 fault tolerance features include:
Specification Feature
Support for SMART Yes
Enclosure management SAF-TE compliant
Drive failure detection Automatic
Drive rebuild using hot spares Automatic
Parity Generation and checking Software
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
32
Page 47
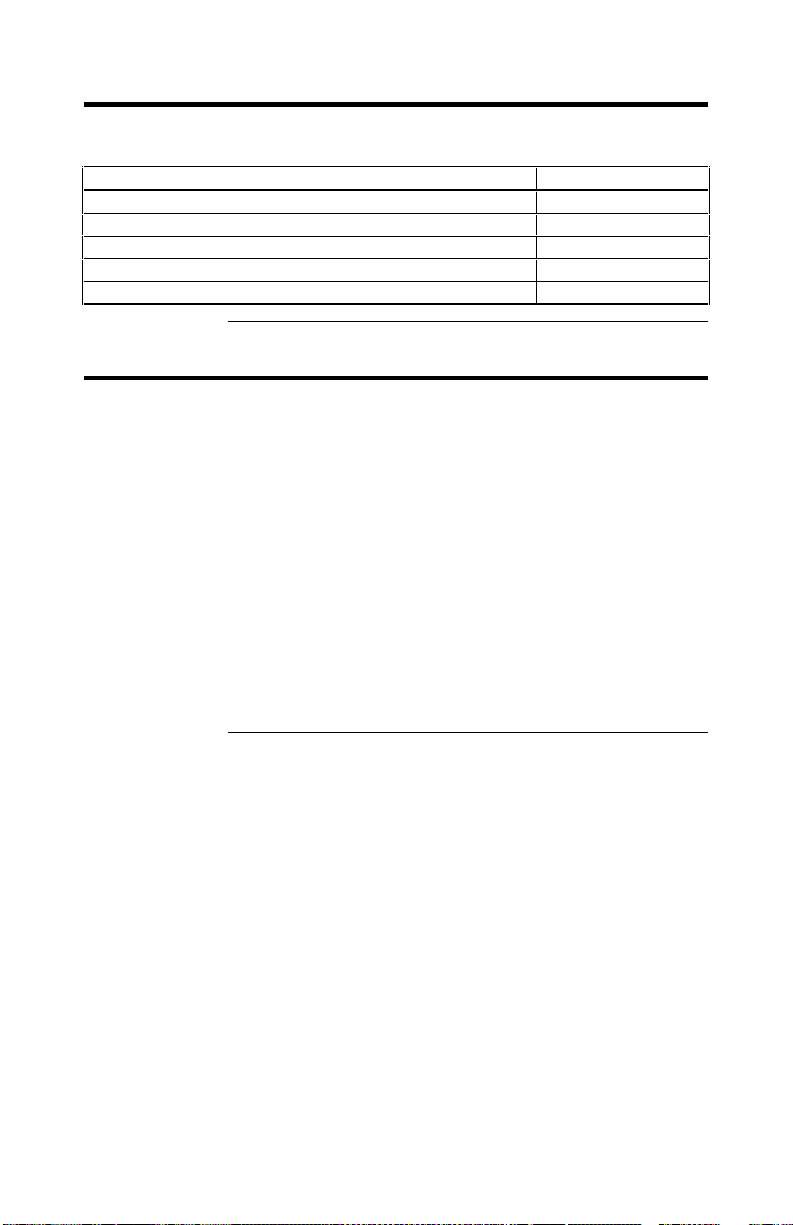
Software Utilities
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 software utility features include:
Specification Feature
Graphical user interface Yes
Management utility Yes
Bootup configuration via ADAC Configuration Manager Yes
Online Read, Write, and cache policy switching Yes
Internet and intranet support through TCP/IP Yes
Operating System Software Drivers
Operating System Drivers ADAC Ultra2 S466 includes a DOS software
configuration utility and drivers for:
Windows NT V4.0
•
Novell NetWare 4.x,
•
OS/2,
•
SCO UnixWare 2.1x, and
•
SCO Open Server R5.0x
•
The DOS drivers for ADAC Ultra2 S466 are contained in
the firmware on ADAC Ultra2 S466 except the DOS ASPI
and CD-ROM drivers. Call your Gateway OEM support
representative for information about drivers for other
operating systems.
Chapter 4 Features
33
Page 48

ADAC Ultra2 S466 Specifications
Parameter Specification
Card Size 7.375" x 4.2" (half length PCI)
Processor Intel i960RP™ 32-bit RISC processor @ 33 MHz
Bus Type P CI 2.1
PCI Controller Intel i960RP
Bus Data Transfer Rate Up to 132 MB/s
BIOS AMIBIOS ADAC Ultra2 S466 BIOS
Cache Configuration 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 MB through a 60 ns × 36
Fast Page Mode or EDO 72-pin SIMM.
Firmware 1 MB × 8 flash ROM
Nonvolatile RAM 32 KB × 8 for storing RAID configuration
Operating Voltage 5.00 V ± 0.25 V
SCSI Controller One SCSI controller for Ultra and Wide support.
SCSI Data Transfer
Rate
SCSI Bus LVD or single-ended
SCSI Termination Active
Termination Disable Automatic through cable and device detection
Devices per SCSI
Channel
SCSI Device Types
Supported
RAID Levels Supported 0, 1, 3, 5,10, 30, and 50
SCSI Connectors One 68-pin internal high-density connector for 16-
Serial Port 9-pin RS232C-compatible berg
Up to 80 MB/s
Up to 15 wide or seven non-wide SCSI devices. Up
to 6 non-disk SCSI drives per ADAC Ultra2 S466
controller.
Synchronous or Asynchronous. Disk and non-disk.
bit SCSI devices. One ultra-high density 68-pin
external connector for Ult r a and Wide SCSI.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
34
Page 49

PCI Bridge/CPU
ADAC Ultra2 S466 uses the Intel i960RP PCI bridge with
an embedded 80960JF RISC processor running at 33 MHz.
The RP bridge handles data transfers between the primary
(host) PCI bus, the secondary PCI bus, cache memory, and
the SCSI bus. The DMA controller supports chaining and
unaligned data transfers. The embedded 80960JF CPU
directs all controller functions, including co mmand
processing, SCSI bus transfers, RAID processing, drive
rebuilding, cache management, and error recovery.
Cache Memory
ADAC Ultra2 S466 cache memory resides in a memory
bank that uses 1 MB x 36, 4 MB x 36, 16 MB x 36, or 32
MB x 36 72-pin 60 or 70 ns Fast Page Mode or EDO
SIMMs. Possible configurations are 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128
MB.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports write-through or write-back
caching, selectable for each logical drive. To improve
performance in sequential disk accesses, the ADAC Ultra2
S466 controller uses read-ahead caching by default. You
can disable read-ahead caching.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 BIOS
The BIOS resides on a 1 MB × 8 flash ROM for easy
upgrade. The ADAC Ultra2 S466 BIOS supports INT 13h
calls to boot DOS without special software or device
drivers. The ADAC Ultra2 S466 BIOS provides an
extensive setup utility that can be accessed by pressing
<Ctrl> <M> at BIOS initialization. ADAC BIOS Setup is
described in the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration
Software Guide.
Chapter 4 Features
35
Page 50

Onboard Speaker
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller has an onboard tone
generator for audible warnings when system errors occur.
Audible warnings can be generated through this speaker.
The audible warnings are listed on page 93.
Serial Port
ADAC Ultra2 S466 includes a 9-pin RS232C-compatible
serial port berg connector, which can connect to
communications devices.
SCSI Bus
ADAC Ultra2 S466 has a Fast and Wide SCSI channel that
supports both LVD and single-ended devices with active
termination. Synchronous and asynchronous devices are
supported. ADAC Ultra2 S466 provides automatic
termination disable via cable detection. The SCSI channel
supports up to 15 wide or seven non-wide SCSI devices at
speeds up to 80 MB/s. ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports up to
six non-disk devices pe r controller.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
36
Page 51

SCSI Connectors
ADAC Ultra2 S466 has two types of SCSI connectors:
• a 68-pin high density internal connector and
• a 68-pin external ultra-high-density connector.
Both connector types can be used for the SCSI channel.
SCSI Termination
ADAC Ultra2 S466 uses active termination on the SCSI
bus conforming to Alternative 2 of the SCSI-2
specifications. Termination enable/disable is automatic
through cable dete ction.
SCSI Firmware
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 firmware handles all RAID and
SCSI command processing and also supports:
Feature Description
Disconnect/
Reconnect
Tagged Command
Queuing
Scatter/Gather Multiple address/count pairs
Multi-threading Up to 255 simultaneous commands with elevator sorting and
Stripe Size Variable for all logical drives: 2 KB, 4 KB, 8 KB, 16 KB, 32
Rebuild Multiple rebuilds and consistency checks with user-
Optimizes SCSI Bus seek.
Multiple tags to improve random access
concatenation of requests per SCSI channel
KB, 64 KB, or 128 KB.
definable priority.
Chapter 4 Features
37
Page 52

RAID Management
RAID management is provided by software utilities that
manage and configure the RAID system and ADAC Ultra2
S466, create and manage multiple disk arrays, control and
monitor multiple RAID servers, provide error statistics
logging, and provide online maintenance. They include:
• ADAC BIOS Setup,
• Power Console Plus,
• ADAC Man ager
• General Alert Module.
ADAC BIOS Setup BIOS Setup configures and maintains RAID arrays,
formats disk drives, and manages the RAID system. It is
independent of any operating system. See the ADAC
Ultra2 S466 Configuration Software Guide for additional
information.
Power Console Plus Power Console Plus runs in Windows NT. It
configures, monitors, and maintains multiple RAID servers
from any network node or a remote location. See the
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration Software Guide for
additional information.
ADAC Configuration Manager This is a character-based utility that works
in DOS, SCO Unix SVR3.2 R4.2, SCO UnixWare, OS/2
2.x, OS/2 Warp, and Novell NetWare 3.x and 4.x. See the
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration Software Guide for
additional information.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
38
Page 53

Fault-Tolerance Features
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 fault-tolerance features are:
• automatic failed drive detection,
• automatic failed drive rebuild with no user
intervention required,
• hot swap manual replacement without bringing the
system down, and
• SAF-TE compliant enclosure management.
Detect Failed Drive The ADAC Ultra2 S466 firmware automatically detects
and rebuilds failed drives. This can be done transparently
with hot spares.
Hot Swap ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports the manual replacement of a
disk unit in the RAID subsystem without system shutdown.
Chapter 4 Features
39
Page 54

Compatibility
ADAC Ultra2 S466 compatibility issues include:
• server management,
• SCSI device compatibility, and
• software compatibility
Server Management As an SNMP agent, ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports all
SNMP managers and RedAlert from Storage Dimensions.
SCSI Device Compatibility ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports SCSI hard disk
drives, CD-ROMs, tape drives, optical drives, DAT drives
and other SCSI peripheral devices.
Software All SCSI backup and utility software should work with
ADAC Ultra2 S466. Software that has been tested and
approved for use with ADAC Ultra2 S466 includes
Cheyenne®, CorelSCSI®, Arcserve®, and Novaback®.
This software is not provided with ADAC Ultra2 S466.
Summary
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Features were discussed in this
chapter.
Hardware installation is discussed in Chapter 6.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
40
Page 55

5 Configuring ADAC Ultra2
S466
Configuring SCSI Physical Drives
SCSI Channel Physical SCSI drives must be organized into logical drives.
The arrays and logical drives that you construct must be
able to support the RAID level that you select.
Your ADAC Ultra2 S466 adapter has one SCSI channel.
Basic Configuration Rules You should observe the following guidelines
when connecting and configuring SCSI devices in a RAID
array:
attach non-disk SCSI devices to a single SCSI channel
•
that does not have any disk drives,
you can place up to eight physical disk drives in an
•
array,
include all drives that have the same capacity to the
•
same array,
make sure any hot spare has a capacity that is at least
•
as large as the largest drive that may be replaced by
the hot spare, and
when replacing a failed drive, make sure that the
•
replacement drive has a capacity that is at least as
large as the drive being replaced.
Chapter 5 Configuring ADAC Ultra2 S466
41
Page 56

Current Configuration
SCSI ID Device Description Termination?
SCSI Channel 1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Logical Drive Configuration
Logical
Drive
RAID
Level
Stripe
Size
LD1
LD2
LD3
LD4
LD5
LD6
LD7
LD8
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
42
Logical Drive
Size
Cache
Policy
Read
Policy
Write
Policy
# of
Physical
Drives
Cont’d
Page 57

Physical Device Layout
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Chapter 5 Configuring ADAC Ultra2 S466
Channel 1
43
Page 58

Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Target ID
Device Type
Logical Drive Number/ Drive Number
Manufacturer/Model Number
Firmware level
Channel 1
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
44
Page 59

Configuring Arrays
Organize the physical disk drives in arrays after the drives
are connected to ADAC Ultra2 S466, formatted, and
initialized. Each array can consist of one to eight physical
disk drives.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports up to eight arrays. The
number of drives in a array determines the RAID levels
that can be supported.
Arranging Arrays You must arrange the arrays to provide additional
organization for the drive array. You must arrange arrays
so that you can create system drives that can function as
boot devices.
You can sequentially arrange arrays with an identical
number of drives so that the drives in the group are
spanned. Spanned drives can be treated as one large drive.
Data can be striped across multiple arrays as one logical
drive.
You can create spanned drives by using the ADAC BIOS
Setup utility or the ADAC Configuration Manager.
Creating Hot Spares Any drive that is present, formatted, and initialized
but is not included in a array or logical drive is
automatically designated as a hot spare.
You can also designate drives as hot spares via ADAC
BIOS Setup, the ADAC Configuration Manager , or Power
Console Plus.
Creating Logical Drives Logical drives are arrays or spanned arrays that
are presented to the operating system. You must create one
or more logical drives.
The logical drive capacity can include all or any portion of
a array. The logical drive capacity can also be larger than
an array by using spanning. ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports
up to 8 logical drives.
Chapter 5 Configuring ADAC Ultra2 S466
45
Page 60

Configuration Strategies
The most important factors in RAID array configuration
are: drive capacity, drive availability (fault tolerance), and
drive performance. You cannot configure a logical drive
that optimizes all three factors, but it is easy to choose a
logical drive configuration that maximizes one factor at the
expense of the other two fac t ors, although needs are
seldom that simple.
Maximize Capacity RAID 0 achieves maximum drive capacity, but does
not provide data redundancy. Maximum drive capacity for
each RAID level is shown below. OEM level firmware that
can span up to 4 logical drives is assumed.
RAID
Level
10 Mirroring and
30 RAID 3 and
50 RAID 5 and
Description Drives
Required
0 Striping
without parity
1 Mirroring 2 (Capacity of smallest disk) X (1)
3 Striping with
fixed parity
drive
5 Striping with
floating parity
drive
Striping
Striping
Striping
1 – 32 (Number of disks) X capacity of
3 – 8 (Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) - (capacity of 1 disk)
3 – 8 (Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) - (capacity of 1 disk)
4 – 8 (Must
be a multiple
of 2)
6 – 32 (Must
be a multiple
of arrays)
6 – 32 (Must
be a multiple
of arrays)
(Number of disks) X (capacity of
(Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) – (capacity of 1 disk X
(Number of disks) X (capacity of
smallest disk) – (capacity of 1 disk X
Capacity
smallest disk
smallest disk) / (2)
number of Arrays)
number of Arrays)
Cont’d
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
46
Page 61

Configuration Strategies, Continued
Maximizing Drive Availability You can maximize the availability of data
on the physical disk drive in the logical array by
maximizing the level of fault tolerance. The levels of fault
tolerance provided by the RAID levels are:
RAID Level Fault Tolerance Protection
0 No fault tolerance.
1 Disk mirroring, which provides 100% data redundancy.
3 100% protection through a dedicated parity drive.
5 100% protection through striping and parity. The data is
striped and parity data is written across a number of physical
disk drives.
10 100% protection through data mirroring.
30 100% protection through data striping. All data is striped
across all drives in two or more arrays.
50 100% protection through data striping and parity. All data is
striped and parity data is written across all drives in two or
more arrays.
Maximizing Drive Performance You can configure an array for optimal
performance. But optimal drive configuration for one type
of application will probably not be optimal for any other
application. A basic guideline of the performance
characteristics for RAID drive arrays at each RAID level
is:
RAID Level Performance Characteristics
0 Excellent for all types of I/O activity, but provides no data
security.
1 Provides data redundancy and good performance.
3 Provides data redundancy.
5 Provides data redundancy and good performance in most
environments.
10 Provides data redundancy and excellent performance.
30 Provides data redundancy and good performance in most
environments.
50 Provides data redundancy and very good performance.
Chapter 5 Configuring ADAC Ultra2 S466
47
Page 62

Assigning RAID Levels
Only one RAID level can be assigned to each logical drive.
The drives required per RAID level is:
RAID
Level
0 One 32
1Two Two
3 Three Eight
5 Three Eight
10 four Eight
30 Six 32
50 Six 32
Minimum Number of
Physical Drives
Ma ximum Number of Phys ical
Drives
Configuring Logical Drives
After you have installed the ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller
in the server and have attached all physical disk drives,
perform the following actions to prepare a RAID disk
array:
Step Action
1 Optimize the ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller options for your system. See
Chapter 6 for additional information.
2 Perform a low-level format the SCSI drives that will be included in the
array and the drives to be used for hot spares.
3 Press <Ctrl> <M> to run the ADAC Configuration Manager.
4 Define and configure one or more logical drives. Select Easy Configuration
in ADAC Configuration Manager or select New Configuration to
customize the RAID array.
5 Create and configure one or more system drives (logical drives). Sel ect the
RAID level, cache policy, read policy, and write policy.
6 Save the configuration.
7 Initialize the system drives. After initialization, you can install the
operating system.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
48
Page 63

Optimizing Data Storage
Data Access Requirements Each type of data stored in the disk subsystem
has a different frequency of read and write activity. If you
know the data access requirements, you can more
successfully determine a strategy for optimizing the disk
subsystem capacity, availability, and performance.
Servers that support Video on Demand typically read the
data often, but write data infrequently. Both the read and
write operations tend to be long. Data stored on a generalpurpose file server involves relatively short read and write
operations with relatively small files.
Array Functions You must first define the major purpose of the disk array.
Will this disk array increase the system storage capacity for
general-purpose file and print servers? Does this disk array
support any software system that must be available 24
hours per day? Will the information stored in this disk
array contains large audio or video files that must be
available on demand? Will this disk array contain data
from an imaging system?
You must identify the purpose of the data to be stored in
the disk subsystem before you can confidently choose a
RAID level and a RAID configuration.
Chapter 5 Configuring ADAC Ultra2 S466
49
Page 64

Planning the Array Configuration
Answer the following questions about this array:
Question Answer
Number of physical disk drives in th e array
Purpose of this array. Rank the following factors:
Maximize drive capacity
Maximize the safety of the data (fault tolerance)
Maximize hard drive performance and throughput
How many hot spares?
Amount of cache memory installed on ADAC Ultra2 S466
Are all of the disk drives and the server protected by a UP S?
Using the Array Configuration Planner The following table lists the
possible RAID levels, fault tolerance, and effective
capacity for all possible drive configurations for an array
consisting of one to eight drives. This table does not take
into account any hot spare (standby) drives. You should
always have a hot spare drive in case of drive failure.
RAID 1 and RAID 10 require 2, 4, 6, or 8 drives. RAID 30
and RAID 50 require at least 6 drives.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
50
Page 65

Array Configuration Planner
Number of
Drives
1 None Excellent No 100%
1 RAID 0 Excellent No 100%
2 None Excellent No 100%
2 RAID 0 Excellent No 100%
2 RAID 1 Good Yes 50%
3 None Excellent No 100%
3 RAID 0 Excellent No 100%
3 RAID 3 Good Yes 67%
3 RAID 5 Good Yes 67%
4 None Excellent No 100%
4 RAID 0 Excellent No 100%
4 RAID 1 Good Yes 50%
4 RAID 3 Good Yes 75%
4 RAID 5 Good Yes 75%
4 RAID 10 Good Yes 50%
5 None Excellent No 100%
5 RAID 0 Excellent No 100%
5 RAID 3 Good Yes 80%
5 RAID 5 Good Yes 80%
6 None Excellent No 100%
6 RAID 0 Excellent No 100%
6 RAID 1 Good Yes 50%
6 RAID 3 Good Yes 83%
6 RAID 5 Good Yes 83%
6 RAID 10 Good Yes 50%
6 RAID 30 Good Yes 67%
6 RAID 50 Good Yes 67%
7 None Excellent No 100%
7 RAID 0 Excellent No 100%
7 RAID 3 Good Yes 86%
7 RAID 5 Good Yes 86%
Possible
RAID Levels
Relative
Performance
Fault
Tolerance
Effective
Capacity
Chapter 5 Configuring ADAC Ultra2 S466
51
Page 66

ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
52
Page 67

6 Hardware Installation
Requirements You must have the following:
a ADAC Ultra2 S466 Controller,
•
• a host computer with an available PCI expansion slot,
• the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Installation diskettes,
• the necessary SCSI cables and terminators (this depends on
the number and type of SCSI devices to be attached),
• an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) for the entire
system, and
• Fast SCSI 2 or Wide SCSI hard disk drives and other SCSI
devices, as desired.
Optional Equipment You may also want to install SCSI cables that connect
ADAC Ultra2 S466 to external SCSI devices.
Checklist
Check Step Action
q
q
q
q
q
q
q
q
q
q
q
1 Turn all power off to the server and all hard disk drives,
enclosures, and system, components.
2 Prepare the host system. See the host system technical
documentation.
3 Determine the SCSI ID and SCSI termination requirements.
4 Make sure the jumper settings on the ADAC Ultra2 S466
controller are correct. Install t he cache memory.
5 Install the ADAC Ultra2 S466 card in the server and attach the
SCSI cables and terminator s as needed. Make sure Pin 1 on the
cable matches Pin 1 on the connector. Make sure that the SCSI
cables you use conform to all SCSI specifications.
6 Perform a safety check. Make sure all cables are properly
attached. Make sure the ADAC card is pr operly installed. Turn
power on after completing the safety check.
7 Install and configure the ADAC software utilities and drivers.
8 Format the hard disk drives as needed.
9 Configure system drives (logical drives).
10 Initialize the logical drives.
11 Install the network operating system drivers as needed.
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
53
Page 68

Installation Steps
ADAC Ultra2 S466 provides extensive customization
options. If you need only basic ADAC Ultra2 S466
features and your computer does not use other adapter
cards with resource settings that may conflict with ADAC
Ultra2 S466 settings, even custom installation can be quick
and easy.
Step Action Additional Information
1 Unpack the ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller
and inspect for damage. Make sure all
items are in the package.
2 Turn the computer off and remove the
cover.
3 Make sure the motherboard jumper settings
are correct.
4 Install cache memory on the ADAC Ultra2
S466 card.
5 Check the jumper settings on the ADAC
Ultra2 S466 controller.
6 Set SCSI termination.
7 Install the ADAC Ultra2 S466 card.
8 Connect the SCS I cables to SCSI devices.
9 Set the target IDs for the SCSI d evi ces.
10 Replace the computer cover and turn the
power on.
11 Run ADAC BIOS Setup. Optional.
12 Install software drivers for the desired
operating systems.
If damaged, call your
Gateway OEM support
representative.
4 MB minimum cache
memory is required.
See page 57 for the ADAC
Ultra2 S466 jumper
settings.
Be sure the SCSI devices
are powered up before or at
the same time as the host
computer.
Each step is described in detail below.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
54
Cont’d
Page 69

Step 1 Unpack
Unpack and install the hardware in a static-free
environment. The ADAC Ultra2 S466 controller card is
packed inside an anti-static bag between two sponge
sheets. Remove the controller card and inspect it for
damage. If the card appears damaged, or if any item listed
below is missing, contact your OEM support
representative. The ADAC Ultra2 S466 Controller is also
shipped with:
• the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration Software Guide,
• the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Operating System Drivers
Guide,
the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide,
•
• the so
the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration Utilities
•
diskette for DOS, and
the warranty registration card.
•
Step 2 Power Down
Turn off the computer and remove the cover. Make sure
the computer is turned off and disconnected from any
networks before installing the controller card.
ftware license agreement,
Step 3 Configure Motherboard
Make sure the motherboard is configured correctly for
ADAC Ultra2 S466. ADAC Ultra2 S466 is essentially a
SCSI Controller. Each ADAC Ultra2 S466 card you install
will require an available PCI IRQ; make sure an IRQ is
available for each controller you install.
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
55
Page 70

Step 4 Install Cache Memory
Important
A minimum of 4 MB of cache memory is required. The cache
memory must be installed before ADAC Ultra2 S466 is operational.
Bank0 must be populated by a SIMM.
Fast Page Mode SIMM FPM SIMMs are specified below. The DRAM
technology in the SIMM must have equal row and column
size.
Memory
Type
FPM 5 V 60ns Yes Single-sided No 1M x 36 4MB
FPM 5 V 60ns Yes Double-sided No 2M x 36 8MB
FPM 5 V 60ns Yes Single-sided No 4M x 36 16MB
FPM 5 V 60ns Yes Double-sided No 8M x 36 32 MB
FPM 5 V 60ns Yes Single-sided No 16M x 36 64 MB
FPM 5 V 60ns Yes Double-sided No 32M x36 128 MB
EDO SIMM EDO SIMMs are specified below. The DRAM technology
Memory
Type
EDO 5 V 50ns Yes Single-sided No 1M x 36 4MB
EDO 5 V 50ns Yes Double-sided No 2M x 36 8MB
EDO 5 V 50ns Yes Single-sided No 4M x 36 16MB
EDO 5 V 50ns Yes Double-sided No 8M x 36 32 MB
EDO 5 V 50ns Yes Single-sided No 16M x 36 64 MB
EDO 5 V 50ns Yes Double-sided No 32M x36 128 MB
Volt Speed Parity Type BBU
Support
Bank I Total Memory
in the SIMM must have equal row and column size.
Volt Speed Parity Type BBU
Support
Bank I Total Memory
Important
If the SIMM DRAM is not installed when you receive your ADAC Ultra2
S466 RAID controller, you must call the manufacturer for a list of approved
SIMM vendors. You must only use an approved SIMM.
Cont’d
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
56
Page 71

Step 4 Install Cache Memory, Continued
Supported Cache Memory Configurations
Cache Bank0 (Even)
4 MB Single-sided 1 MB x 36 Fast Page Mode
8 MB Double-sided 1 MB x 36 Fast Page Mode
16 MB Single-sided 4 MB x 36 Fast Page Mode
32 MB Double-sided 4 MB x 36 Fast Page Mode
64 MB Single-sided 16 MB x 36 Fast Page Mode
128 MB Double-sided 32 MB x 36 Fast Page Mode
Install cache memory on the ADAC Ultra2 S466 card in
the SIMM socket. This socket accepts a 72-pin × 36 Fast
Page Mode or EDO SIMM as specified on the previous
page.
Lay the controller card component-side up on a clean
static-free surface and install the SIMM. The SIMM clicks
into place, indicating proper seating in the socket, as shown
below.
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
57
Page 72

Step 5 Set Jumpers
Make sure the jumper settings on the ADAC Ultra2 S466
card are correct. The jumpers and connectors are:
Connector Description Type
J2 Internal SCSI Wide (16-bit) connector 68-pin connector
J6 External SCSI 2 Wide (16-bit)
connector
J5 Disk Activity LED four-pin connector
J1 Termination Enable Control 3-pin header
J3 I2C connector 4-pin header
J7 Cache memory SIMM socket 72-pin connector
J4 Serial port connector 9-pin connector
J8
J9
J10 Short Pins 1-2 3-pin header
J11 i960RP configuration 2-pin header
J12 i960RP configuration 2-pin header
Short Pins 1-2. 3-pin header
68-pin connector
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Card Layout
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
58
Cont’d
Page 73

Step 5 Set Jumpers, Continued
J1 Termination Enable J1 is a three-pin header that specifies hardware or
software control of SCSI termination.
Type of SCSI Termination J1 Setting
Software control of SCSI termination via drive
detection.
Permanently disable all onboard SCSI termination. Short Pins 2-3
Permanently enable all onboard SCSI termination. OPEN
J3 I2C Interface Connector J3 is a four-pin header that allows the i960JX
core processor to serve as a master and slave device that
resided on the I2C bus when used with the I2C Bus
Interface Unit. Attach a four-wire cable from J3 to the I2C
Bus Interface Unit.
J4 Serial Port J4 is a 9-pin berg that attaches to a serial cable. The pinout:
Pin Signal Description Pin Signal Description
1 Carrier Detect 2 Data Set Ready
3 Receive Data 4 Req uest to Send
5 Transmit Data 6 Clear to Send
7 Data Terminal Ready 8 Ring Indicator
9 Ground
Short Pins 1-2
J5 Hard Disk LED J5 is a four-pin connector that attaches to a cable that
connects to the hard disk LED mounted on the computer
enclosure. The LED indicates data transfers.
Pin Description
1High
2 SCSI Activity Signal
3 SCSI Activity Signal
4High
Cont’d
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
59
Page 74

Step 5 Set Jumpers, Continued
J8, J9 J8 and J9 are 3-pin jumpers. The factory setting is Pins 1-2
shorted. Pins 1-2 should always be shorted for J8 and J9.
J10 J10 is a 3-pin jumper. Make sure Pins 1-2 of J10 are
always shorted. This is the factory setting.
J11, J12 i960RP Initialization J11 and J12 are 2-pin bergs that specify the
i960RP mode when initially powered up. Mode 3 is used
for normal operation (J11 and J12 OPEN). All other modes
are used for test purposes only.
I960RP Initialization Mode J19 Setting J22 Setting
0 Short Pins 1-2 Short Pins 1-2
1 Short Pins 1-2 OPEN
2 OPEN Short Pins 1-2
3 OPEN OPEN
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
60
Page 75

Step 6 Set Termination
You must terminate the SCSI bus properly. Set termination
at both ends of the SCSI cable. The SCSI bus is an
electrical transmission line and must be terminated
properly to minimize reflections and losses. Termination
should be set at each end of the SCSI cable(s), as shown
below. Termination is always enabled, regardless of the
configuration. However, you can override this setting by
setting another state.
For a disk array, set SCSI bus termination so that removing
or adding a SCSI device does not disturb termination. An
easy way to do this is to connect the ADAC Ultra2 S466
card to one end of the SCSI cable and to connect an
external terminator module at the other end of the cable.
The connectors between the two ends can connect SCSI
devices. Disable termination on the SCSI devices. See the
manual for each SCSI device to disable termination.
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
61
Page 76

SCSI Termination
The SCSI bus is an electrical transmission line and it must
be terminated properly to minimize reflections and losses.
You complete the SCSI bus by setting termination at both
ends.
You can let ADAC Ultra2 S466 automatically provide
SCSI termination at one end of the SCSI bus. You can
terminate the other end of the SCSI bus by attaching an
external SCSI terminator module to the end of the cable or
by attaching a SCSI device that internally terminates the
SCSI bus at the end of the SCSI channel.
Selecting a Terminator Use standard external SCSI terminators on a SCSI
channel operating at 10 MB/s or higher synchro nous data
transfer.
Terminating Internal SCSI Disk Arrays Set the termination so that SCSI
termination and termination power are intact when any disk
drive is removed from a SCSI channel, as shown below:
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
62
Cont’d
Page 77

SCSI Termination, Continued
Terminating External Disk Arrays In most array enclosures, the end of the
SCSI cable has an independent SCSI terminator module
that is not part of any SCSI drive. In this way, SCSI
termination is not disturbed when any drive is removed, as
shown below:
Terminating Internal and External Disk Arrays You can use both
internal and external drives with ADAC Ultra2 S466. You
still must make sure that the proper SCSI termination and
termination power is preserved, as shown below:
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
Cont’d
63
Page 78

SCSI Termination, Continued
Connecting Non-Disk SCSI Devices SCSI Tape drives, scanners, CD-
ROM drives, and other non-disk drive devices must each
have a unique SCSI ID re gardless of the SCSI channel they
are attached to. The general rule for Unix systems is:
• tape drive set to SCSI ID 2, and
• CD-ROM drive set to SCSI ID 5.
Make sure that no hard disk drives are attached to the same
SCSI channel as the non-disk SCSI devices. Drive
performance will be significantly degraded if SCSI hard
disk drives are attached to this channel.
Warning
Since all non-disk SCSI devices are single ended, it is not
advisable to attach a non-disk device to a ADAC Ultra2 S466
RAID controller if LVD disk drives are also attached because the
SCSI bus will then operate in single ended mode.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
64
Page 79

Step 7 Install ADAC Ultra2 S466
Choose a 5 V PCI slot and align the ADAC Ultra2 S466
controller card bus connector to the slot. Press down gently
but firmly to make sure that the card is properly seated in
the slot. The bottom edge of the controller card should be
flush with the slot.
Insert the ADAC Ultra2 S466 card in a PCI slot as shown
below:
Screw the bracket to the computer frame.
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
65
Page 80

Step 8 Connect SCSI Cables
Connect SCSI cables to SCSI devices. ADAC Ultra2 S466
provides two SCSI connectors: J2, the SCSI channel
internal high-density 68-pin connector for Wide (16-bit)
SCSI and J6, the SCSI channel external ultra high-density
68-pin connector for Wide (16-bit) SCSI.
Connect SCSI Devices When connecting SCSI devices:
Step Action
1 Disable termination on any SCSI device that does not sit at the end of the
SCSI bus.
2 Configure all SCSI devices to supply TermPWR.
3 Set proper target IDs (TIDs) for all SCSI devices.
4 The cable length should not exceed three meters for Fast SCSI (10 MB/s)
devices or single ended 1.5 meters for Ultra SCSI devices. The cable length
can be up to 12 meters for LVD devices.
5 The cable length should not exceed six meters for non-Fast SCSI devices.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
66
Cont’d
Page 81

Step 8 Connect SCSI Cables, Continued
Cable Suggestions System throughput probl ems can occur if SCSI cable use
is not maximized. You should:
• you can use cables up to 12 meters for LVD devices.
• for single ended SCSI devices, use the shortest SCSI cables
(no more than 3 meters for Fast SCSI, no more than 1.5
meters for an 8-drive Ultra SCSI system and no more than 3
meters for a 6-drive Ultra SCSI system),
• use active termination,
• avoid clustering the cable nodes,
• cable stub length should be no more than 0.1 meter (4
inches),
• route SCSI cables careful l y,
• use high impedance cables,
• do not mix cable types (choose either flat or rounded and
shielded or non-shielded), and
• ribbon cables have fairly good cross-talk rejection
characteristics.
Step 9 Set Target IDs
Set target identifiers (TIDs) on the SCSI devices. Each
device in a specific SCSI channel must have a unique TID
in that channel. Non-disk devices (CD-ROM or tapes)
should have unique SCSI IDs regardless of the channel
where they are connected. See the documentation for each
SCSI device to set the TIDs. The ADAC Ultra2 S466
controller automatically occupies TID 7 in the SCSI
channel. Eight-bit SCSI devices can only use the TIDs
from 0 to 6. 16-bit devices can use the TIDs from 0 to 15.
The arbitration priority for a SCSI device depends on its
TID.
Priority
TID
Highest Lowest
765
2101514
…
Important
Non-disk devices (CD-ROM or tapes) should have unique SCSI
IDs regardless of the channel they are connected to.
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
…
98
67
Page 82

Device Identification on ADAC Ultra2 S466
All logical drives on each SCSI bus are identified to the
host as ID 0. Differentiate the drives with Logical Unit
Identifiers (LUNs). ID 0 cannot be used for non-disk
devices because they are limited to IDs 1 through 6. The
ADAC Ultra2 S466 is limited to eight logical drives
because LUNs are used to present logical drives. The
SCSI-2 ANSI specification has a limit of eight LUNs per
ID. The SCSI-3 specification increased the number of
LUNs to 16. An example of ID mapping follows.
Example of ADAC Ultra2 S466 ID Mapping
ID Channel 1
0A1-1
1A2-1
2CD
3A2-5
4CD
5A4-1
6 Optical
7 Reserved
8A5-2
9A5-6
10 A6-1
11 A6-4
12 A6-7
13 A7-2
14 A7-5
15 A7-8
As Presented to the Operating System
ID LUN Device ID LUN Device
0 0 Disk (A1-X) 1 0 Scanner
0 1 Disk (A2-X) 2 0 CD
0 2 Disk (A3-X) 3 0 Tape
0 3 Disk (A4-X) 4 0 CD
0 4 Disk (A5-X) 5 0 Tape
0 5 Disk (A6-X) 6 0 Optical
0 6 Disk (A7-X)
0 7 Disk (A8-X)
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
68
Page 83

Step 10 Power Up
Replace the computer cover and reconnect the AC power
cords. Turn power on to the host computer. Set up the
power supplies so that the SCSI devices are powered up at
the same time as or before the host computer. If the
computer is powered up before a SCSI device, the device
might not be recognized.
During boot, the ADAC Ultra2 S466 BIOS message
appears:
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Disk Array Adapter BIOS Version x
Firmware Initializing... [ Scanning SCSI Device ...(etc.)... ]
The firmware takes several seconds to initialize. During
this time the adapter will scan the SCSI channel. When
ready, the following appears:
Host Adapter-1 Firmware Version
0 Logical Drives found on the Host Adapter
0 Logical Drives handled by BIOS
Press <Ctrl><M> to run ADAC Ultra2 S466 BIOS Configuration Utility
x.xx
DRAM Size 4 MB
The <Ctrl> <M> utility prompt times out after several
seconds. The ADAC Ultra2 S466 host adapter (controller)
number, firmware version, and cache DRAM size are
displayed in the second portion of the BIOS message. The
numbering of the controllers follows the PCI slot scanning
order used by the host motherboard.
.xx date
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
69
Page 84

Step 11 Run ADAC BIOS Setup
Press <Ctrl> <M> to run the ADAC BIOS Setup utility.
See the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration Software Guide
for information about r unning BIOS Setup.
Step 12 Install Operating System Driver
The ADAC Ultra2 S466 ASPI driver can be used in the
DOS and Windows 95 environments. The DOS ASPI
driver supports:
• up to six non-disk SCSI devices (each SCSI device
must use a unique SCSI ID regardless of the SCSI
channel it resides on. SCSI ID s 1 through 6 are valid,
up to 12 ADAC Ultra2 S466 adapters, and
•
virtual DMA services (VDS) for up to eight lo gical
•
drives.
ASPI Driver CorelSCSI, Novaback, and PC Tools are not provided with
ADAC Ultra2 S466.
Drivers Devices Supported Applic ation Software Features
ADACASPI.SYS CD-ROM, tape,
optical drives, etc.
CorelSCSI, Novaback, PC
Tools.
VDS
Copy ADACASPI.SYS to your hard disk drive. Add the
following line to CONFIG.SYS:
device=<path>\ADACASPI.SYS
/v
Parameters The ADACASPI. SYS parameters are:
Parameter Description
/h INT 13h support is not provided.
/v Verbose mode. All message are displayed on the screen.
/a Physical drive ccess mode. Direct access to physical drives is
permitted.
/q Quiet mode. All message except error message are suppressed.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
70
Cont’d
Page 85

Step 12 Install Operating System Driver, Continued
CD-ROM Driver A device driver is provided with ADAC Ultra2 S466 for
CD-ROM drives operating under DOS, Windows 3.x, and
Windows 95. The driver filename is ADACDROM.SYS.
The ADACASPI.SYS ASPI manager must b e added to the
CONFIG.SYS file before you can install the CD-ROM
device driver. See the instructions on the previous page for
adding the ADACASPI.SYS driver. Copy
ADACDROM.SYS to the root directory of the C: drive.
Add the following line to CONFIG.SYS, making sure it is
preceded by the line for ADACASPI.SYS:
DEVICE=C:\ADACDROM.SYS
Add the following to AUTOEXEC.BAT. Make sure it
precedes the SMARTDRV.EXE line.
MSCDEX /D:MSCD001
MSCDEX is the CD-ROM drive extension file that is
supplied with MS-DOS® and PC-DOS® Version 5.0 or
later. See your DOS manual for the command line
parameters for MSCDEX.
Chapter 6 Hardware Installation
71
Page 86

Summary
This chapter discussed hardware installation. Configure the
RAID system via software configuration utilities. See the
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Configuration Software Guide for all
information about ADAC Ultra2 S466 software utilities.
The utility programs for configuring ADAC Ultra2 S466
are:
Configuration Utility Operating System
ADAC BIOS Setup independent of the operating system
ADAC Configuration
Manager
Novell NetWare 3.x, 4.x
Power Console Plus Microsoft Windows NT,
DOS
SCO UNIX SVR3.2
SCO UnixWare
Windows 95
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
72
Page 87

7 Troubleshooting
Problem Suggested Solution
The system hangs during the boot
process after installation.
The system hangs during the boot
process after installation.
Some operating systems do not load
in a computer with a ADAC Ultra2
S466 adapter.
One of the hard drive in the array
fails often
Pressed <Ctrl> <M>. Ran
ADAConf.exe and tried to make a
new configuration. The system
hangs when scanning devices.
Make sure the SCSI BIOS on the motherboard
has been disabled.
Make sure the ADAC Ultra2 S466 adapter
card is installed in the proper PCI expansion
slot. It must be installed in the RAID Upgrade
PCI slot..
Check the system BIOS configuration for PCI
interrupt assignments. Make sure some
Interrupts are assigned for PCI.
Initialize the logical drive before installing the
operating system.
Check the drive error counts using Power
Console Plus.
Format the drive.
Rebuild the drive
If the drive continues to fail, replace the drive
with another drive with the same capacity.
Check the drives IDs on each channel to make
sure each device has a different ID.
Check the termination. The device at the end
of the channel must be terminated .
Multiple drives connected to
ADAC Ultra2 S466 using the same
power supply. There is a problem
spinning the drives all at once.
Pressing <Ctrl> <M> or running
ADAConf.exe does not display the
Management Menu.
At system power-up with the
ADAC Ultra2 S466 installed, the
screen display is garbled or does
not appear at all.
Cannot flash or update the
EEPROM.
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
Replace the drive cable.
Set the drives to spin on command. This will
allow ADAC Ultra2 S466 to spin two devices
simultaneously.
These utilities require a color monitor.
For proper cache memory operation, you
should install at least 4 MB of memory in
ADAC Ultra2 S466.
You may need a new EEPROM.
73
Page 88

Firmware Initializing...
Problem Suggested Solution
appears and remains on the screen.
What SCSI IDs can a non-hard disk
device have and what is maximum
number allowed per adapter?
Why does a failed logical array still
get a drive assignment?
Make sure that TERMPWR is being properly
provided to each peripheral device populated
channel.
Make sure that each end of the channel chain
is properly terminated using the recommended
terminator type for the peripheral device. The
channel is automatically terminated at the
ADAC Ultra2 S466 card if only one cable is
connected to a channel.
Make sure (on a channel basis) only two type
of cables are connected at any one time.
If using an FPM SIMM, make sure the RAS
Access Time parameter is 70 ns.
Make sure that the ADAC Ultra2 S466
controller is properly seated in the PCI slot.
Non-hard disk d evices can only accommodate
SCSI IDs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6, regardless of the
channel used. A maximum of six non-hard
disk devices are supported per ADAC Ultra2
S466 adapter.
To maintain the DOS Path statement integrity.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
74
Page 89

BIOS Boot Error Messages
Message Problem Suggested Solution
Adapter BIOS Disabled.
No Logical Drives
Handled by BIOS
Host Adapter at Baseport
xxxx Not Responding
No ADAC U ltra2 S466
Adapter
Configuration of
NVRAM and drives
mismatch.
Run View/Add
Configuration option of
Configuration Utility.
Press any key to r un the
Configuration Utility.
1 Logical Drive Failed A logical drive failed to
The ADAC Ultra2 S466
BIOS is disabled.
Sometimes the BIOS is
disabled to prevent
booting from the BIOS.
The BIOS cannot
communicate with the
adapter firmware.
The BIOS cannot
communicate with the
adapter firmware.
The configuration stored
in the ADAC Ultra2 S466
adapter does not match
the configuration stored in
the drives.
sign on.
Enable the BIOS via the
ADAC Ultra2 S466 BIOS
Setup utility.
Make sure ADAC Ultra2
S466 is properly installed.
Make sure ADAC Ultra2
S466 is properly installed.
Press a key to run ADAC
Configuration Manager.
Choose View/Add
Configuration from the
Configure menu.
Use View/Add
Configuration to examine
both the configuration in
NVRAM and the
configuration stored on the
disk drives. Resolve the
problem by selecting one
of the configurations.
Make sure all physical
drives are properly
connected and are p owered
on.
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
Run ADAC Configuration
Manager to find out if any
physical drives are not
responding. Reconnect,
replace, or rebuild any
drive that is not
responding.
75
Page 90

Message Problem Suggested Solution
X Logical Drives
Degraded
x number of logical drives
signed on in a degraded
state.
1 Logical Drive Degraded A logical d rive signed on
in a degraded state.
Insufficient memory to
run BIOS. Press any key
to continue…
Not enough ADAC Ultra2
S466 memory to run
BIOS.
Insufficient Memory Not enough memory on
the ADAC adapter to
support the current
configuration.
The following SCSI IDs
are not responding:
Channel x:a.b.c
The physical drives with
SCSIO IDs a, b, and c are
not responding on SCSI
channel x.
Make sure all physical
drives are properly
connected and are p owered
on.
Run ADAC Configuration
Manager to find if any
physical drives are not
responding. Reconnect,
replace, or rebuild any
drive that is not
responding.
Make sure all physical
drives are properly
connected and are p owered
on.
Run ADAC Configuration
Manager to find out if any
physical drives are not
responding. Reconnect,
replace, or rebuild any
drive that is not
responding.
Make sure ADAC Ultra2
S466 memory has been
properly installed.
Make ADAC memory has
been properly installed.
Make sure the physical
drives are properly
connected and are p owered
on.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
76
Page 91

Other BIOS Error Messages
Message Problem Suggested Solution
Following SCSI
disk not found
and no empty
slot available for
mapping it
Following SCSI
IDs have the
same data y, z
Channel x: a, b,
c
Unresolved
configuration
mismatch
between disks
and NVRAM on
the adapter
The physical disk roaming
feature did not find the physical
disk with the displayed SCSI
ID. No slot is available to map
the physical drive. ADAC
cannot resolve the physical
drives into the current
configuration.
The physical drive roaming
feature found the same data on
two or more physical drive on
channel x with SCSI IDs a, b,
and c. ADAC cannot determine
the drive that has t he duplicate
information.
The configuration stored in the
ADAC NVRAM does not match
the configuration stored on the
drives.
Reconfigure the array.
Remove the drive or drives
that should not be used.
Press a key to run ADAC
Configuration Manager.
Choose View/Add
Configuration from the
Configure menu.
Use View/Add Configuration
to examine both t he
configuration in NVRAM and
the configuration stored on the
disk drives. Resolve the
problem by selecting one of
the configurations.
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
77
Page 92

DOS ASPI Driver Error Messages
Message Corrective Action
Gateway Inc. ASPI Man ager
has NOT been loaded.
Controller setup FAILED
error code=[0xab]
No non-disk devices were
located
’ERROR: VDS support is
*INACTIVE* for logical
drives
The ASPI manager is not loaded. One of the failure
codes listed below is displayed next.
Correct the conditi on that caused the failure. Th e failure
codes are:
0x40 No ADAC adapters found
0x80 Timed out waiting for interrupt to be posted
0x81 Timed out waiting for Response command.
0x82 Invalid command completion count.
0x83 Invalid completion status received.
0x84 Invalid command ID received.
0x85 No adapters found or no PCI BIOS support.
0x90 Unknown Setup completion error
The driver did not find any non-hard drive devices
during scanning. A SCSI device that is not a hard disk
drive, such as a tape drive o r CD-ROM drive, must be
attached to this SC SI channel. The SCSI ID must be
unique for each adapter and cannot be SCSI ID 0. The
supported SCSI IDs are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6.
The /h option is appended to driver in
CONFIG.SYS or this driver is used with a BIOS that is
earlier than v1.10, or no logical drives are configured.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
78
Page 93

Other Potential Problems
Topic Information
DOS ASPI AD ACASPI.SYS, the DOS ASPI manager, uses 6 KB of
system memory once it is loaded.
CD-ROM drives
under DOS
Physical Drive Errors To display the ADAC Configuration Manager Media Error
Virtual Sizing The Virtual Sizing option enables RAID expansion. Virtual
BSD Unix We do not provide a driver for BSDI Unix. ADAC Ultra2
Multiple LUNs ADAC Ultra2 S466 supports one LUN per each target ID.
Power Requirements The maximum ADAC Ultra2 S466 power requirements are
At this time, copied CDs are not accessi ble from DOS even
after loading ADACASPI.SYS and ADAC DROM.SYS.
and Other Error options, press <F2> after selecting a
physical drive under the Physical Drive menu, selected
from the Objects menu. A Media Error is an error that
occurred while actually transferring data. An Other Error is
an error that occurs at the hardware level because of a
device failure, poor cabling, bad termination, signal loss,
etc.
Sizing must be enabled to increase the size of a logi cal
drive or add a ph ysical drive to an existing logical drive.
Run ADAC Configuration Manager by pressing <Ctrl>
<M> to enable Virtual Sizing. Select the Objects menu,
then select the Logical Drive menu. Select View/Update
Parameters. Set Virtual Sizing to Enabled.
S466 does not support BSDI Unix.
No multiple LUN devices are supported.
15 watts at 5V and 3 Amps.
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
79
Page 94

Topic Information
SCSI Bus
The ANSI specification dictates the following:
Requirements
The maximum signal path length between terminators is 3
meters when using up to 4 maximum capacitance (25 pF)
devices and 1.5 meters when using more than 4 devices.
SCSI devices should be uniformly spaced between
terminators, with the en d devices located as close as
possible to the terminators.
The characteristic impedance of the cable should be 90 +/6 ohms for the /REQ and /ACK signals and 90 +/- 10 ohms
for all other signals.
The stub length(the distance from the controller’s external
connector to t he mainline SCSI bus) shall not exceed.1m
(approximately 4 inches).
The spacing of devices on the mainline SCSI bus should be
at least three times the stub length.
All signal lines shall be terminat ed once at both end s of the
bus powered by the TERMPWR line.
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
80
Page 95

Topic Information
Windows NT
Installation
When Windows NT is installed via a bootable CD, the
devices on the ADAC Ultra2 S466 will not be recognized
until after the initial reboot. The Microsoft documented
workaround is in SETUP.TXT:
SETUP.TXT is on diskette 2 or the CD
To install drivers when Setup recogni zes one of the
supported SCSI host adapters without making the devices
attached to it available for use:
1 Restart Windows NT Setup.
2 When Windows NT Setup displays
Setup is inspecting your computer ’s hardware
configuration...,
press <F6> to prevents Windows NT Setup from
performing disk controller detection. This allows
you to install the driver from the Dri ver s disk you
created. All SCSI adapters must be instal led
manually.
3. When Windows NT Setup displays
Setup could not determine the type of one or more
mass storage devices installed in your system, or
you have chosen to manually specify an adapter,
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
press S to display a list of suppor ted SCSI host
adapters.
4 Select Other from the bottom of the list.
5 Insert the Drivers Disk you made when prompted
to do so and select ADAC Ultra2 S466 from this
list. In some cases, Windows NT Setup repeatedly
prompts to swap disks. Windows NT will now
recognize any devices attached to this adapter.
Repeat this step for each host adapter not already
recognized by Windows NT Setup.
81
Page 96

ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
82
Page 97

A SCSI Cables and
Connectors
SCSI Connectors
ADAC Ultra2 S466 provides several different types of
SCSI connectors. The connectors are:
• one 68-pin high density internal connector, and
• one 68-pin ultra high density external connector.
68-Pin High Density SCSI Internal Connector
The SCSI channel on the ADAC Ultra2 S466 Controller
has a 68-pin high density 0.050 inch pitch unshielded
connector.
This connector provides all signals needed to connect
ADAC Ultra2 S466 to wide SCSI devices. The following
connector pinouts are provided for both single-ended and
differebtial primary bus (P-CABLE) as specified in SCSI-3
Parallel Interface X3T9.2, Project 885-D, revision 12b,
date July 2, 1993.
The cable assemblies that interface with the 68-pin
connector is:
flat ribbon or twisted pair cable for connecting internal
•
wide SCSI devices,
flat ribbon or twisted pair cable for connecting internal
•
and external wide SCSI devices,
cable assembly for converting from internal wide SCSI
•
connectors to internal non-wide (Type 2) connectors,
cable assembly for converting from internal wide to
•
internal non-wide SCSI connectors (Type 30), and
cable assembly for converting from internal wide to
•
internal non-wide SCSI connectors.
Appendix A SCSI Cables and Connectors
Cont’d
83
Page 98

68-Pin High Density Connectors, Continued
Cable Assembly for Internal Wide SCSI Devices The cable assembly for
connecting internal wide SCSI devices is shown below:
pin 1
pin 1
pin 1
Connectors: 68 position plug (male)
AMP - 786090-7
Cable: Flat Ribbon or Twisted-Pair Flat Cable
68 Conductor 0.025 Centerline
30 AWG
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
84
Cont’d
Page 99

68-Pin High Density Connectors, Continued
Connecting Internal and External Wide Devices The cable assembly for
connecting internal wide and external wide SCSI devices is
shown below:
A
pin 1
pin 1
B
pin 1
B
Connector A:68 position panel mount receptacle
with 4-40 holes (female)
AMP - 786096-7
NOTE: To convert to 2-56 holes, use screwlock
kit 749087-1, 749087-2, or 750644-1
from AMP
Connector B:68 position plug (male)
AMP - 786090-7
Cable: Flat Ribbon or Twisted-Pair Flat Cable
68 Conductor 0.025 Centerline
30 AWG
Appendix A SCSI Cables and Connectors
Cont’d
85
Page 100

68-Pin High Density Connectors, Continued
Converting Internal Wide to Internal Non-Wide (Type 2) The cable
assembly for converting internal wide SCSI connectors to
internal non-wide SCSI connec t ors is shown below:
68 POSITION
CONNECTOR
CONTACT NUMBER
*
*
*
OPEN
OPEN
OPEN
*
*
*
TABLE 1: CONNECTOR CONTACT
CONNECTION FOR WIDE
TO NON-WIDE CONVERSION
50 POSITION
CONNECTOR
CONTACT NUMBER
16
240
37
441
2049
2116
2250
2317
2451
2518
2652
2719
4729
4863
4930
5064
pin 1
pin 1
pin 1
Connector A:68 position plug (male)
Connector B:50 position IDC receptacle (female)
Wire: Twisted-Pair Flat Cable or
AMP - 749925-5
AMP - 499252-4, 1-746285-0, 1-746288-0
Laminated Discrete Wire Cable
25 pair 0.050 centerline
28 AWG
A
B
B
Cont’d
ADAC Ultra2 S466 Hardware Guide
86
 Loading...
Loading...