Page 1

REFERENCEGUIDE
®
®
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: About This Reference . . . . . . . . . . . 1
About this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Accessing your online User Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Gateway contact information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Chapter 2: Checking Out Your Computer. . . . . 5
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Digital media manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Media control panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Multimedia panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Back . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chapter 3: Setting Up and Getting Started . . 13
Working safely and comfortably . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Reducing eye strain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Setting up your computer desk and chair . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Sitting at your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Avoiding discomfort and injury from repetitive strain . .16
Preparing power connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Protecting from power source problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Connecting to a broadband modem or network . . . . . . . . . .17
Connecting a dial-up modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Starting your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Waking up your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Turning off your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Restarting (rebooting) your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Opening the hideaway port panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Using the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Using the mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Using optical drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Loading an optical disc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Identifying optical drive types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
i
Page 4

Contents
Playing discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Creating discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Using the digital media manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Memory card types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Using a memory card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Using the Copy button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Adjusting the volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuring the audio jacks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Installing a printer, scanner, or other device . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Chapter 4: Advanced Hardware Setup . . . . . . 35
Setting up multiple monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Using a removable hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Setting up RAID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
About RAID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
RAID 0 for performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
RAID 1 for security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
RAID 5 and 10 for both performance and security . . . . 38
Preparing your computer for RAID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Configuring RAID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Getting help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Chapter 5: Upgrading Your Computer. . . . . . . 43
Preventing static electricity discharge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Opening the case . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Removing the left side panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Removing the right side panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Removing the front bezel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Closing the case . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Replacing the front bezel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Replacing the side panels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Adding or replacing memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Adding or replacing an optical disc drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Adding or replacing a hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Adding or replacing an internal hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Adding a removable hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Replacing the power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
ii
Page 5

www.gateway.com
Adding or replacing an expansion card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Chapter 6: Maintaining Your Computer . . . . . 63
Setting up a maintenance schedule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Caring for your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Cleaning your computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Cleaning the exterior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Cleaning the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Cleaning the monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Cleaning the mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Cleaning optical discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Updating Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Using BigFix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Managing hard drive space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Checking hard drive space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Deleting unnecessary files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Checking the hard drive for errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Defragmenting the hard drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Backing up files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Backing up files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Scheduling maintenance tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Moving from your old computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Transferring files and settings automatically . . . . . . . . . .78
Transferring files and settings manually . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Chapter 7: Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Safety guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
Try these steps first . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Internet and networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Modem (cable or DSL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Modem (dial-up) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Optical discs 91
iii
Page 6

Contents
Memory card reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Audio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Expansion cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Media Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Checking for device problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Recovering your system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Creating recovery discs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Recovering pre-installed software and drivers . . . . . . . 104
Returning to a previous system condition . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Returning your system to its factory condition . . . . . . 106
Technical support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Before calling Gateway Customer Care . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Calling Customer Care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Appendix A: Legal Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
iv
Page 7

CHAPTER1
About This Reference
• About this guide
• Accessing your online User Guide
• Gateway contact information
• Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity
• For more information
1
Page 8

CHAPTER 1: About This Reference
About this guide
This guide includes information and maintenance instructions
that are specific to your model of Gateway computer. Some
illustrations in this guide may look different than your
computer because hardware options and port locations may
vary. For all other computer information, see your online User
Guide.
For more information
For more information about your computer, visit Gateway’s
Support page at www.gateway.com
on your computer’s label. The Support page also has links to
additional Gateway documentation and detailed specifications.
or the Web address shown
Accessing your online User
Guide
In addition to this guide, your User Guide has been included on
your hard drive. Your User Guide is an in-depth, easy-to-read
manual that includes information on the following topics:
• Using and customizing Windows and other software
• Controlling audio and video settings
• Using the Internet
• Protecting your files
• Playing and recording media
• Networking
To access your User Guide:
• Click (Start), All Programs, then click Gateway
Documentation.
2
Page 9

www.gateway.com
Gateway contact information
See your setup poster for Customer Care contact information.
The label on the back of your computer contains information
that identifies your computer model and serial number.
Customer Care will need this information if you call for
assistance.
Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity
The Microsoft Certificate of Authenticity label found on the
back or side of your computer includes the product key code
for your operating system. If you ever reinstall Windows from
the installation DVD, you will need to enter these numbers to
activate Windows.
3
Page 10

CHAPTER 1: About This Reference
4
Page 11

• Front
• Back
CHAPTER2
Checking Out Your
Computer
5
Page 12

Front
Media navigation interface
Optical disc drive
CHAPTER 2: Checking Out Your Computer
Digital media manager
USB ports
Optical disc drive
(optional)
Multimedia panel
Removable hard drive
carriers
Optical drive eject
buttons
Power button/
power indicator
Backup button
6
Page 13

www.gateway.com
Component Description
Media navigation
Press these buttons to control media playback.
interface
Optical disc drive Use this drive to listen to audio CDs, install games and
programs, watch DVDs, and store large files onto recordable
discs. For more information about your drive, see
“Identifying optical drive types” on page 26.
Multimedia panel Connect multimedia devices to these ports and jacks.
(available ports may vary)
■
R (red) RCA jack—Connect the RCA cable for the right
channel of two-channel (stereo) audio to this jack.
■
L (white) RCA jack—Connect the RCA cable for the left
channel of two-channel (stereo) audio to this jack.
■
V (yellow) RCA jack—Connect an RCA cable for analog
video to this jack.
■
USB ports—Connect USB devices to these ports.
■
IEEE 1394 (FireWire) port—Connect an IEEE 1394 device to
this port.
■
Microphone jack—Connect an external microphone to
this jack.
■
Headphone jack—Connect headphones or external
speakers to this jack.
Removable hard
drive carriers
Install a new hard drive to one of these carriers, then back
up important files to the hard drives for removable storage.
For more information, see “Adding a removable hard drive”
on page 55 and “Backing up files” on page 76.
Digital media
manager
Insert a memory card from a digital camera, MP3 player,
PDA, cellular telephone, or other devices into the digital
media manager (memory card reader). For more
information, see “Using the digital media manager” on
page 29.
USB ports Plug USB (Universal Serial Bus) devices (such as a USB
external drive, printer, scanner, camera, keyboard, or
mouse) into these ports. For more information, see
“Installing a printer, scanner, or other device” on page 34.
Optical drive eject
Press these buttons to open the optical drive disc tray.
buttons
Power
button/power
indicator
Press this button to turn the power on or off. You can also
configure the power button to operate in Standby/Resume
mode or Hibernate mode. The power indicator lights when
the computer is turned on.
Backup button Press this button to launch the Backup Status and
Configuration program.
7
Page 14
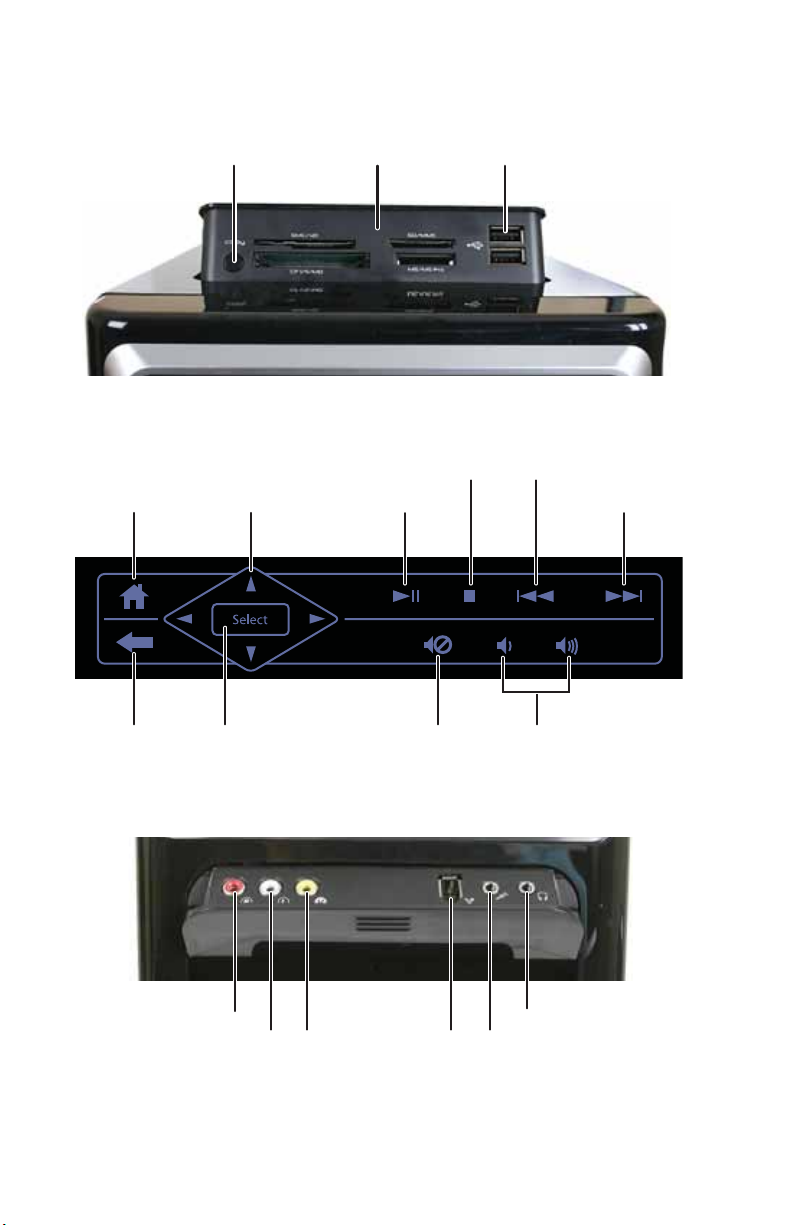
CHAPTER 2: Checking Out Your Computer
Digital media manager
Memory card reader USB portsCopy button
Media control panel
Home button
Stop button
Navigation buttons Play/Pause button
Select buttonBack button Mute button Volume control buttons
Rewind/Skip back button
Multimedia panel
Right-channel stereo RCA jack Headphone jack
Left-channel stereo RCA jack Analog video
RCA jack
FireWire jack
Microphone jackIEEE 1394/
Fast forward/Skip
forward button
8
Page 15

Back
Power connector
Voltage switch
www.gateway.com
Important
Your computer’s hardware options and port locations may vary from this
illustration.
Case cover Phillips screw
PS/2 keyboard port
HDMI port
Integrated monitor
(VGA) port
USB ports
Surround left/right jack
S/PDIF output jack
Microphone jack
Headphone/
Front speaker jack
Modem jack (optional)
PS/2 mouse port
IEEE 1394/FireWire port
Ethernet (network) jack
Center/Subwoofer jack
Audio in/side speaker jack
Add-in video card (optional)
Expansion slot cover
thumbscrew
Side panel Phillips screw
Telephone jack (optional)
9
Page 16

CHAPTER 2: Checking Out Your Computer
Component Icon Description
Power connector Plug the power cord into this connector.
Voltage switch Make sure this switch is set to the proper
local voltage.
PS/2 keyboard port Plug a PS/2 keyboard into this port.
Integrated monitor
(VGA) port
Connect a VGA monitor to this port if the
optional add-in video card is not installed.
HDMI port Connect an HDMI video device to this port.
USB ports Plug USB (Universal Serial Bus) devices (such
as a USB printer, scanner, camera, keyboard,
or mouse) into these ports. For more
information, see “Installing a printer,
scanner, or other device” on page 34.
Surround left/right
jack (black)
Plug your rear right and left speakers into
this jack . Thi s jack is disab led when an au dio
expansion card is installed.
For more information, see “Configuring the
audio jacks” on page 33.
S/PDIF output jack Plug an optical cable from an amplifier or
entertainment system into this jack for
digital sound.
Microphone jack
(pink)
Plug a microphone into this jack. This jack is
disabled when an audio expansion card is
installed.
Headphone/analog
speakers jack (green)
-ORFront speakers jack
This jack is user configurable for one of the
following:
■
Headphone: Plug headphones or
amplified speakers into this jack
(Default).
■
Stereo out: Plug your front left and right
speakers into this jack.
This jack is disabled when an audio
expansion card is installed. For more
information, see “Configuring the audio
jacks” on page 33.
Modem jack
(optional)
Case cover Phillips
screws
10
Plug a modem cable into this jack. For more
information, see “Connecting a dial-up
modem” on page 17.
Remove these screws to remove the left side
panel.
Page 17

www.gateway.com
Component Icon Description
PS/2 mouse port Plug a PS/2 mouse into this port.
IEEE 1394/FireWire
port
Plug IEEE 1394 (also known as Firewire
devices (such as a digital camcorder) into
this 6-pin IEEE 1394 port. For more
information, see “Installing a printer,
scanner, or other device” on page 34.
®
)
Ethernet (network)
jack
Plug an Ethernet network cable or a device
(such as a DSL or cable modem for a
broadband Internet connection) into this
jack. For more information, see “Learning
about the Internet” in your online User
Guide and “Connecting to a broadband
modem or network” on page 17.
Center/subwoofer
jack (orange)
Plug your center speaker and subwoofer
into this jack. This jack is disabled when an
audio expansion card is installed.
For more information, see “Configuring the
audio jacks” on page 33.
Audio in (Line in) jack
(blue)
-ORSide speaker jack
This jack is user configurable for one of the
following:
■
Stereo in: Plug an external audio input
source (such as a stereo) into this jack so
you can record sound on your computer
(Default).
■
Stereo out: Plug your side left and right
speakers into this jack.
This jack is disabled when an audio
expansion card is installed. For more
information, see “Configuring the audio
jacks” on page 33.
Video card Plug a monitor into a port on this card. If the
card is a high-performance video card, the
expansion slot opening above the card may
be occupied by the card’s ventilation fan.
Expansion slot cover
thumbscrew
Tel e phon e jack
(optional)
Remove this screw and open the expansion
slot cover to unlock the expansion cards.
Plug the cord from your telephone into this
jack.
Cable lock slot Attach a cable lock to this slot, then attach
the cable to a solid object like a desk or table
to prevent your computer from being
stolen.
11
Page 18

CHAPTER 2: Checking Out Your Computer
12
Page 19

CHAPTER3
Setting Up and Getting
Started
• Working safely and comfortably
• Preparing power connections
• Connecting to a broadband modem or
network
• Connecting a dial-up modem
• Starting your computer
• Turning off your computer
• Restarting (rebooting) your computer
• Opening the hideaway port panels
• Using the keyboard
• Using the mouse
• Using optical drives
• Using the digital media manager
• Adjusting the volume
• Configuring the audio jacks
• Installing a printer, scanner, or other device
13
Page 20

CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
Working safely and comfortably
Before using your computer, follow these general guidelines
for setting up a safe and comfortable work area and avoiding
discomfort and strain:
• Keep hands and arms parallel to the floor.
• Adjust the monitor so the screen is perpendicular to your
line of sight, and the top of the screen is no higher than
eye level.
• Place your feet flat on the floor or on a footrest.
• Keep ventilation openings clear of obstructions.
Hands and arms are
parallel to the floor
Top of screen is not
higher than eye level
Screen is perpendicular to
your line of sight
14
Feet are flat on the floor
Page 21

www.gateway.com
Reducing eye strain
Sunlight or bright indoor lighting should not reflect on the
screen or shine directly into your eyes.
• Position the computer desk and monitor so you can
avoid glare on your screen and light shining directly into
your eyes. Reduce glare by installing shades or curtains
on windows and by installing a glare screen filter.
• Use soft, indirect lighting in your work area. Do not use
your computer in a dark room.
• Set paper holders at the same height and distance as the
monitor.
• Avoid focusing your eyes on your computer screen for
long periods of time. Every 10 or 15 minutes, look around
the room, and try to focus on distant objects.
Setting up your computer desk and chair
When you are setting up your computer desk and chair, make
sure that the desk is the appropriate height and the chair helps
you maintain good posture.
• Select a flat surface for your computer desk.
• Adjust the height of the computer desk so your hands
and arms are positioned parallel to the floor when you
use the keyboard and touchpad. If the desk is not
adjustable or is too tall, consider using an adjustable
chair to control your arm’s height above the keyboard.
• Use an adjustable chair that is comfortable, distributes
your weight evenly, and keeps your body relaxed.
• Position your chair so the keyboard is at or slightly below
the level of your elbow. This position lets your shoulders
relax while you type.
• Adjust the chair height, adjust the forward tilt of the seat,
or use a footrest to distribute your weight evenly on the
chair and relieve pressure on the back of your thighs.
• Adjust the back of the chair so it supports the lower
curve of your spine. You can use a pillow or cushion to
provide extra back support.
15
Page 22

CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
Sitting at your computer
• Avoid bending, arching, or angling your wrists. Make
sure that they are in a relaxed position when you type.
• Do not slouch forward or lean far back. Sit with your back
straight so your knees, hips, and elbows form right
angles when you work.
• Take breaks to stand and stretch your legs.
• Avoid twisting your torso or neck.
Avoiding discomfort and injury from repetitive strain
• Vary your activities to avoid excessive repetition.
• Take breaks to change your position, stretch your
muscles, and relieve your eyes.
• Find ways to break up the work day, and schedule a
variety of tasks.
Preparing power connections
Protecting from power source problems
Warning
High voltages can enter your computer through both the power cord and
the modem connection. Protect your computer by using a surge protector. If you
have a telephone modem, use a surge protector that has a modem jack. If you
have a cable modem, use a surge protector that has an antenna/cableTV jack.
During an electrical storm, unplug both the surge protector and the modem.
During a power surge, the voltage level of electricity coming
into your computer can increase to far above normal levels and
cause data loss or system damage. Protect your computer and
peripheral devices by connecting them to a surge protector,
which absorbs voltage surges and prevents them from
reaching your computer.
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) supplies battery power
to your computer during a power failure. Although you cannot
run your computer for an extended period of time with a UPS,
a UPS lets you run your computer long enough to save your
work and shut down your computer normally.
16
Page 23

www.gateway.com
Connecting to a broadband modem or network
Important
Your computer has a built-in Ethernet (network) jack. For information
about setting up a wired or wireless Ethernet network, see your online User
Guide.
You can connect your computer to a broadband (cable or DSL)
modem or to a wired Ethernet network.
To connect to a broadband modem or to an Ethernet
network:
1 Insert one end of the network cable into the network
jack on the back of your computer.
2 Insert the other end of the network cable into a cable
modem, DSL modem, or network jack.
Connecting a dial-up modem
Warning
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger
telecommunications line cord.
Your computer may have a 56K modem that you can use with
a standard telephone line to connect to the Internet or to fax
documents.
To connect the modem:
1 Insert one end of the modem cable into the modem
jack on the modem at the back of your computer.
2 Insert the other end of the modem cable into a telephone
wall jack. (The modem will not work with digital or PBX
telephone lines.)
3 If you want, connect a telephone to the PHONE jack on
the modem at the back of your computer.
17
Page 24

CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
Starting your computer
To start your computer:
1 Connect the power, network, mouse, and keyboard
cables to your computer according to the setup poster.
2 Press the power button on the front of your computer.
If your computer does not turn on, check the power
cable connections.
Important
Your computer has a built-in, variable-speed fan. In addition, your
computer uses a powerful processor which produces heat and has its
own cooling fan. Both the system fan and processor fan can run at
different speeds at times to ensure correct system cooling. You may
notice an increase in the fan noise when the fan is running at high speed
and a decrease in the fan noise when it switches to normal speed.
Power button
18
3 If you are starting your computer for the first time,
follow the on-screen instructions to select the language
and time zone and to create your first user account.
4 Attach and turn on any USB or audio peripheral devices,
such as printers, scanners, and speakers. See the
documentation that came with each device for its setup
instructions.
5 To open your computer’s Start menu, click (Start).
From that menu, you can run programs and search for
files. For more information on using your computer’s
menus, see “Using Windows” and “Customizing
Windows” in your online User Guide.
Page 25

www.gateway.com
Waking up your computer
Tip
For more information about changing the power button mode, see the
“Customizing” chapter in your online User Gu ide.
When you have not used your computer for several minutes,
it may enter a power-saving mode called Sleep. While in Sleep
mode, the power indicator on the power button flashes.
If your computer is in Sleep mode, move the mouse, press a
key on the keyboard, or press the power button to “wake” it
up. If the computer remains in Sleep mode, press the power
button.
Turning off your computer
Warning
When you turn off your computer, certain components in the power
supply and system board remain energized. In order to remove all electrical
power from your computer, unplug the power cord and modem cable from the
wall outlets. We recommend disconnecting the power cord and modem cable
when your computer will not be used for long periods.
Important
If for some reason you cannot use the Shut Down option in Windows to
turn off your computer, press and hold the power button for about five seconds,
then release it.
Putting your computer into Sleep mode is the easiest way to
power down your computer. Although it does not turn your
computer completely off, it does turn off or slow down most
system operations to save power, and saves your desktop
layout so the next time you restore power, the programs are
laid out just as you left them. Waking your computer from a
Sleep state is much faster than turning on your computer after
it has been turned completely off.
To put your computer to sleep:
1 Click (Start), then click (power). The computer
saves your session and partially shuts down to save
power.
2 To “wake” your computer, press a key on the keyboard
or press the power button. If the computer remains in
Sleep mode, press the power button.
19
Page 26

CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
To turn off your computer:
1 Click (Start), click the arrow next to the lock icon, then
click Shut Down.
2 To completely disconnect all power (such as for servicing
internal components), also disconnect the power cord.
The computer turns off.
Restarting (rebooting) your computer
If your computer does not respond to keyboard or mouse
input, you may need to restart (reboot) your computer.
To restart yo ur compu te r:
1 Click (Start), click the arrow next to the lock icon, then
click Restart. Your computer turns off, then turns on
again.
20
2 If your computer does not turn off, press and hold the
power button until the computer turns off (about five
seconds), then press it again to turn the computer back
on.
Page 27

www.gateway.com
Opening the hideaway port panels
In addition to the many ports and jacks on the back, your
computer also has ports contained within panels that can be
retracted into the case. The retractable panels are the memory
card reader and the multimedia panel.
To open the hideaway port panels:
1 Press the front edge (marked with finger grip lines) of
the panel firmly against the case until it clicks, then
release the panel.
2 To close the panels, press them back into the case until
they click into place.
Using the keyboard
The keyboard has several different types of keys and buttons.
Your keyboard also has status indicators that show which
keyboard feature is active.
Media playback
controls
Function keys Audio playback keys
Status indicators
Windows key Application
Windows key
key
Navigation keys Numeric keypad
21
Page 28
CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
Feature Icon Description
Function keys Press these keys to start program actions. Each
Audio playback
keys
Windows key Press this key to open the Windows Start menu.
Fn key Press this key in combination with keys that have
Application key Press this key to access shortcut menus and help
Navigation keys Press these keys to move the cursor and to copy,
Numeric keypad Press these keys to type numbers when the
program uses different function keys for different
purposes. See the program documentation to
find out more about the function key actions.
Press these keys to play your audio files and to
adjust the volume.
This key can also be used in combination with
other keys to open utilities like F (Find/Search),
R (Run), and E (Computer).
alternate functions defined, such as the F9-F12
keys.
assistants in Windows.
cut, and paste objects.
numeric keypad (NUM LOCK) is turned on.
22
Page 29

www.gateway.com
Using the mouse
Scroll wheel
Left button
The mouse is a device that controls the pointer movement on
the screen. This illustration shows the standard mouse.
As you move the mouse, the pointer (arrow) on the screen
moves in the same direction.
Right button
You can use the left and right buttons on the mouse to select
objects on the screen.
23
Page 30
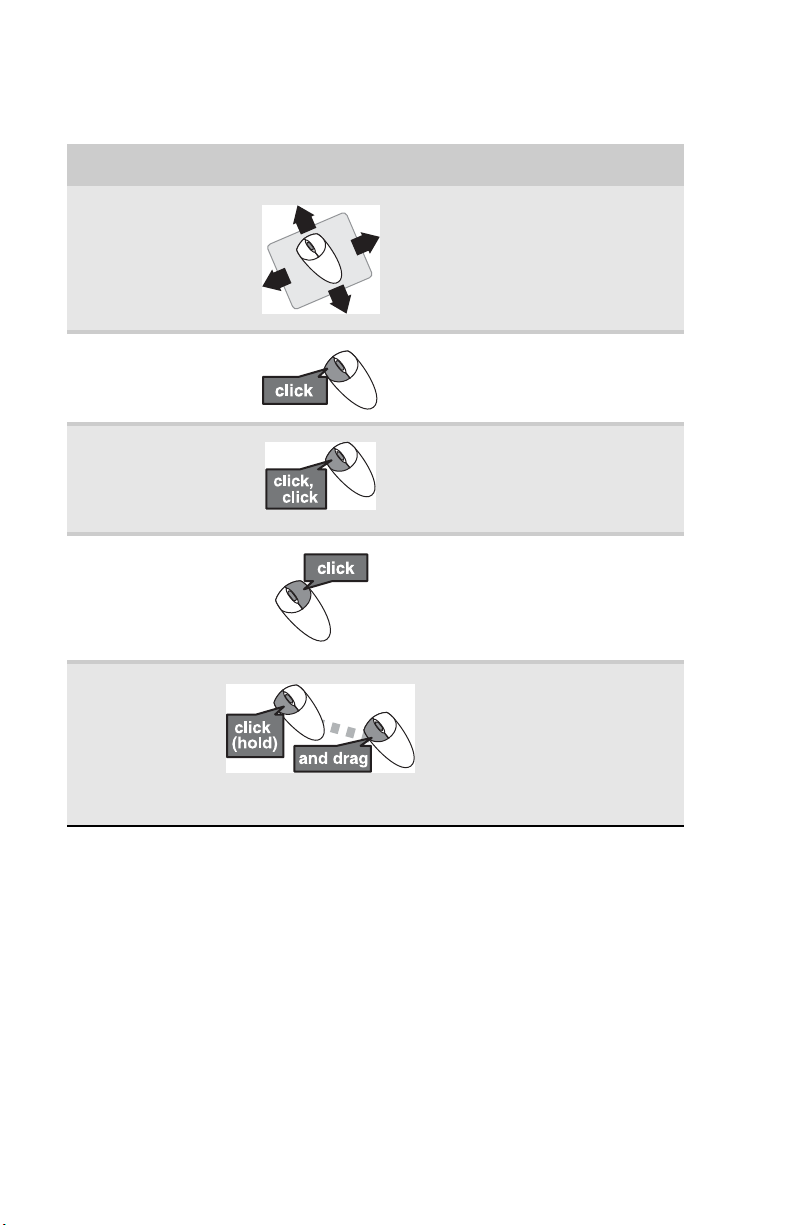
CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
You can use the scroll wheel on the mouse to move through a
document. This feature is not available in all programs.
To... Do this...
Move the pointer
on the screen
Select an object
on the screen
Start a program
or open a file or
folder
Access a
shortcut menu
or find more
information
about an object
on the screen.
Move an object
on the screen.
Move the mouse around. If you
reach the edge of your mouse
pad and need to move the
mouse farther, lift the mouse
and place it in the middle of the
mouse pad, then continue
moving the mouse.
Position the pointer over the
object. Quickly press and
release the left mouse button.
This is called clicking.
Position the pointer over the
object. Quickly press and
release the left mouse button
twice. This is called
double-clicking.
Position the pointer over the
object. Quickly press and
release the right mouse button
once. This is called
right-clicking.
Position the pointer over the
object. Press the left mouse
button and hold it down. Move
(drag) the object to the
appropriate part of the screen.
Release the button to drop the
object where you want it. This is
called clicking and dragging.
24
For more information about how to adjust the double-click
speed, pointer speed, right-hand or left-hand configuration,
and other mouse settings, see the “Customizing” chapter in
your online User Guide. For instructions on how to clean the
mouse, see “Cleaning the mouse” on page 67.
Page 31

www.gateway.com
Using optical drives
Features
Your optical drive has the following basic components:
Flip-down drive
tray cover
Eject button
Loading an optical disc
To insert an optical disc:
1 Press the eject button on the optical disc drive.
Important
When you place a single-sided disc in the tray, make sure that the
label side is facing up. If the disc has two playable sides, place the disc
so the name of the side you want to play is facing up.
2 Place the disc in the tray with the label facing up.
3 Press the eject button to close the tray.
25
Page 32

CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
Identifying optical drive types
Your computer may contain one of the following drive types.
Eject the drive tray, then look on the front of the tray for these
logos:
If your optical drive has
this logo...
Your drive type
is...
CD-RW
DVD/CD-RW
DVD
DVD+RW
DVD R/RW
Double layer
DVD+RW
Use your drive for...
Installing programs, playing
audio CDs, accessing data, and
creating CDs.
Installing programs, playing
audio CDs, accessing data,
creating CDs, and playing DVDs.
Installing programs, playing
audio CDs, playing DVDs, and
accessing data.
Installing programs, playing
audio CDs, playing DVDs,
accessing data, and recording
video and data to CDs and
DVD+R or DVD+RW discs.
Installing programs, playing
audio CDs, playing DVDs,
accessing data, and recording
video and data to CDs and
DVD+R, DVD+RW, DVD-R, and
DVD-RW discs.
Installing programs, playing
audio CDs, playing DVDs,
accessing data, and recording
video and data to CDs and
double layer DVD+R discs.
Note: To use the double layer
capability of the double layer
recordable DVD drive, the blan k
DVDs you purchase must state
Double Layer, Dual Layer, or DL.
Using other types of blank
media will result in less
capacity.
26
Page 33

www.gateway.com
If your optical drive has
this logo...
RECORDER
Playing discs
Playing a CD
Important
Some music CDs have copy protection software. You may not be able to
play these CDs on your computer.
A standard compact disc (CD) can hold an entire album of
digital songs and can be played on a CD player or your
computer’s CD drive.
Use a music program or Windows Media Player on your
computer to:
• Play music CDs
• Create MP3 music files from your music CDs
• Edit music track information
• Use your music files to build a music library
For more information about playing CDs, see your online User
Guide.
Your drive type
is...
DVD-RAM/-RW
Blu-ray Disc
Use your drive for...
Installing programs, playing
audio CDs, playing DVDs,
accessing data, and recording
video and data to CDs and
DVD-RAM, DVD-R, or DVD-RW
discs.
Installing programs, playing
audio CDs, playing DVDs,
playing Blu-ray Discs, accessing
data, and recording video and
data to CDs, DVD-RAM, DVD-R,
DVD-RW, and Blu-ray discs.
Playing a DVD
A Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) is similar to a standard CD but has
greater data capacity. Because of this increased capacity,
full-length movies, several albums of music, or several
gigabytes of data can fit on a single disc. DVDs can be played
on a DVD player or a DVD drive-equipped computer. For more
information about playing DVDs, see your online User Guide.
27
Page 34

Playing a Blu-ray Disc
Blu-ray Disc is a high-capacity optical disc that can store much
more data than a DVD. A dual-layer Blu-ray Disc can hold 50 GB
of files, about 23 hours of standard-definition video, or about
nine hours of high-definition video. Blu-ray Discs can be played
on a Blu-ray-compatible player or a Blu-ray drive-equipped
computer. For more information about playing Blu-ray Discs,
see your online User Guide.
Creating discs
Recording to optical discs
You can use the disc burning program on your computer to
copy tracks from a music CD to your hard drive, copy or create
data discs, create music CDs, create video DVDs, and more. For
more information about creating CDs and DVDs, see your
online User Guide.
Creating audio and video files
You can create audio and music files, either from scratch or
from music CDs. You can also create video files from home
video. For more information, see your online User Guide.
CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
28
Copying optical discs
You can copy optical discs to make backups of your data. For
more information, see your online User Guide.
Page 35

www.gateway.com
Using the digital media manager
You can use the digital media manager to transfer pictures
from a digital camera to your computer. You can also use the
digital media manager to transfer data between your
computer and a device that uses memory cards, such as a PDA,
MP3 player, or cellular telephone.
Memory card reader USB portsCopy button
Memory card types
The digital media manager supports several memory card
types. To determine which types are supported by your card
reader and the slots to use for each type of card, examine the
face plate of the digital media manager. Each slot is assigned
a different drive letter (for example, the E: and F: drives) so data
can be transferred from one memory card type to another.
Using a memory card
Caution
Before inserting a memory card into a slot, make sure that the slot is
empty, or you could damage the card reader.
To insert a memory card:
1 Insert the memory card into the appropriate memory
card slot.
2 To access a file on the memory card, click (Start),
then click Computer. Double-click the drive letter (for
example, the
E: drive), then double-click the file name.
29
Page 36

CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
To remove a memory card:
• Make sure that the card is not being read from or written
to, then pull the memory card out of the slot.
Important
Do not use the remove hardware icon in the taskbar to remove
the memory card, or you will have to restart the computer to re-enable
the digital media manager.
Using the Copy button
Your digital media manager includes a Copy button that makes
it easy to copy pictures, movies, and data files from a memory
card to your computer.
To use t he Copy button:
1 Insert the memory card into the appropriate slot in the
digital media manager.
2 Press and hold the Copy button until the Smart Copy
dialog box opens indicating that the files are being
copied to your computer. It may take a few seconds for
the Smart Copy dialog box to open.
30
3 Release the Copy button.
By default, if you are copying picture files, Smart Copy
creates a folder using the date the picture was taken as
its name and places it in the Pictures\SmartCopy folde r
on your computer’s hard drive. Smart Copy then copies
the picture files into that folder.
Also by default, if you are copying other types of files,
Smart Copy copies them into the Pictures\SmartCopy
folder on your computer’s hard drive.
Important
During this copy process, no files are deleted from the memory
card.
If a file name already exists in the folder, the new file will have a number
added to the file name. The first number will be 1, the next number will
be 2, and so on.
Page 37

www.gateway.com
4 When the Smart Copy dialog box closes, remove the
memory card.
Adjusting the volume
You can adjust volume using your speakers’ controls or the
Windows volume controls. You can also adjust the volume of
specific sound devices in your computer.
To adjust the overall volume using hardware controls:
• If you are using external speakers, turn the knob on the
front of the speakers.
-OR-
Use the mute and volume control buttons on the
keyboard. For more information, see “Using the
keyboard” on page 21.
To adjust the volume from Windows:
1 Click (Volume) on the taskbar. The volume control
slider opens.
2 Click and drag the slider up to increase volume and down
to decrease volume.
3 To mute the volume, click (Mute). To restore volume,
click it again.
31
Page 38

CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
4 To adjust device volume levels, click Mixer. The Volume
Mixer dialog box opens, where you can click and drag
sliders for individual devices.
Tip
Adjust the Windows Sounds slider to change system sounds
volume independently of general volume (such as the volume used for
music and game sounds).
5 Click × in the top-right corner of the window to close it.
32
Help
For more information about adjusting the volume, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type adjusting volume in the Search Help
box, then press E
NTER.
Page 39

www.gateway.com
Configuring the audio jacks
If the back of your computer has five audio jacks, they are
universal jacks. This means that they can be used for more than
one purpose. For example, the blue jack on the computer can
be a stereo in jack or a stereo out jack. To use the audio jacks
for something other than the default audio device, you need
to configure the audio jacks. For a description of the default
audio jack setup, see “Back” on page 9.
Important
If an audio expansion card is installed in your computer, then the
computer’s built-in audio jacks are disabled.
To configure the audio jacks:
Shortcut
Start Ö Control Panel Ö Hardware and Sound Ö Advanced
1 Connect your audio device(s) to the computer audio
jack(s).
2 Click (Start), then click Control Panel. The Control
Panel window opens.
3 Click Hardware and Sound, Sound, the Playback tab,
then click Configure.
-OR-
If your computer has the Realtek Sound Effect Manager
installed, double-click the Sound Effect Manager
icon on the taskbar. The Realtek dialog box opens.
4 Follow the on-screen instructions to configure the audio
jacks for your speaker setup.
33
Page 40

CHAPTER 3: Setting Up and Getting Started
Installing a printer, scanner, or other device
Important
Before you install a printer, scanner, or other peripheral device, see the
device documentation and installation instructions.
Your computer has IEEE 1394 (also known as Firewire®) ports
and Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports. You use these ports to
connect peripheral devices such as printers, scanners, and
digital cameras to your computer. For more information about
port locations, see “Checking Out Your Computer” on page 5.
IEEE 1394 and USB ports support plug-and-play and
hot-swapping, which means that your computer will usually
recognize such a device whenever you plug it into the
appropriate port. When you use an IEEE 1394 or USB device for
the first time, your computer will prompt you to install any
software the device needs. After doing this, you can disconnect
and reconnect the device at any time.
Help
For more information about installing peripheral devices, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type installing devices in the Search Help box,
then press E
NTER.
34
Page 41

CHAPTER4
Advanced Hardware Setup
• Setting up multiple monitors
• Using a removable hard drive
• Setting up RAID
35
Page 42

CHAPTER 4: Advanced Hardware Setup
Setting up multiple monitors
If your computer came with a dual-DVI port graphics card
installed, you can connect up to two monitors for a
multi-screen panel array. To set up multiple monitors, see the
“Customizing Windows” chapter in your online User Guide.
Using a removable hard drive
You can use your computer’s removable hard drive carriers for
high-volume backups and convenient backup storage.
To use a removable hard drive for backups:
1 Make sure that a removable hard drive is installed into
one of the carriers and is formatted for use. For
instructions on installing a removable hard drive, see
“Adding a removable hard drive” on page 55.
2 Copy files to the hard drive using Windows Explorer or
a backup utility. For more information, see “Backing up
files” on page 76.
3 Turn off your computer, then remove the hard drive and
store it in a secure location.
Setting up RAID
About RAID
Your computer can use multiple hard drives (if installed) to
increase performance or reliability. RAID (Redundant Array of
Inexpensive/Independent Disks) lets your computer use
multiple hard drives more efficiently. Your computer supports
RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10.
RAID 0 for performance
RAID 0 lets your computer see multiple hard drives as a single
drive. This type of RAID can increase file access speeds, which
is important if you work with video editing, sound editing, and
high-performance games. RAID 0 is also an affordable way to
increase your total file storage capacity.
36
Page 43

www.gateway.com
How it increases performance
The more drives you have in your RAID 0 array, the faster the
potential drive reading performance. All hard drives have
limitations on how fast they can read and write files. If half a
file is stored on one RAID 0 drive and the other half on another
RAID 0 drive, each drive only has to read half of the file. So, the
entire file is accessed by the computer up to twice as fast (using
a two-drive RAID 0 array). In a three-drive RAID 0 array, if the
file is evenly distributed among the drives, each drive must
read only a third of the file, and so on. If the entire file happens
to be stored on only one of the drives, the file is accessed at
the same speed as if it were on a standard hard drive setup.
Dividing up files between multiple hard drives is called striping.
In the following graphic, each letter represents a unique block
of data, and each column represents a separate hard drive.
RAID 0
A
C
E
B
D
F
How it makes file storage cheaper
Because RAID 0 lets your computer see multiple hard drives as
a single drive, you can install several lower capacity (less
expensive) drives and have the same single-drive storage
simplicity and capacity as a larger, more expensive hard drive.
Drawbacks
Unfortunately, RAID 0 lets multiple drives behave as one in
another way. If part of the array fails (such as a hard drive
crashing), the entire array fails. Because the drives are treated
like a single drive, parts of files (including operating system
files) can be spread across several drives, leaving the computer
with only file fragments if one drive fails. Regular and frequent
backups are critical.
Another drawback is that RAID 0 treats each hard drive as if it
has the storage capacity of the smallest drive in the array. So
if you have three drives (300 GB, 250 GB, and 200 GB) in a
RAID 0 array, your computer only recognizes 600 GB total
capacity.
37
Page 44

CHAPTER 4: Advanced Hardware Setup
RAID 1 for security
RAID 1 maintains a complete copy of all files on each physical
hard drive in the array. Maintaining simultaneous, complete
copies of files across multiple hard drives is called mirroring.
If a drive fails, the mirrored drive takes over and acts as the
primary drive.
In the following graphic, each letter represents a unique block
of data, and each column represents a separate hard drive.
RAID 1
A
B
C
File reading performance (seek time) is increased using the
same methods that RAID 0 uses, although writing speed is the
same as if writing to a single hard drive.
Drawback
RAID 1 treats the entire array as a single drive with the storage
capacity of the smallest physical drive in the array. So if you
have two drives (300 GB and 250 GB) in a RAID 1 array, your
computer only recognizes a single drive with 250 GB total
capacity.
A
B
C
RAID 5 and 10 for both performance and security
Understanding RAID 5
RAID 5 uses striping (at the file level) with on-the-fly error
correction across all drives. Because of this error correction,
small file read/write errors can be quickly and automatically
fixed without a significant drop in system performance. RAID 5
offers good performance and data redundancy. This array
preserves your files if a drive fails.
RAID 5 stripes both data and parity information (error-checking
information) across multiple drives. Striping across drives
improves overall performance, and the parity information
provides data protection. Because of the error-correction
capabilities, if a drive fails, the data can be quickly and
automatically fixed.
38
Page 45

www.gateway.com
In the following graphic, each letter represents a unique block
of data, and the number next to each letter represents which
copy of the data files are stored on that drive. The “P” next to
a letter represents parity (error-checking) information, and
each column represents a separate hard drive.
RAID 5
A1
B1
CP
A2
BP
C1
AP
B2
C2
Understanding RAID 10
RAID 10 (also called RAID 1+0 or RAID 1&0) contains sets of
RAID 1 mirrors acting as drives within a RAID 0 striping array.
With this setup, the array could survive one drive failure in each
mirrored array.
In the following graphic, each letter represents a unique block
of data, and each column represents a separate hard drive.
RAID 0
RAID 1
A
C
E
Drawback
A RAID 5 array is treated as one drive with the capacity of all
but one of the drives added together.
RAID 10 treats the entire array as a single drive with twice the
storage capacity of the smallest drive. So if you have four drives
(350GB, 300GB, 250GB, and 200GB) in a RAID10 array, your
computer recognizes a single drive with 400 GB total capacity.
A
C
E
RAID 1
B
D
F
B
D
F
39
Page 46

CHAPTER 4: Advanced Hardware Setup
Preparing your computer for RAID
Setting up RAID on your computer can involve two major steps,
depending on how your computer has been configured.
To prepare your computer for RAID:
1 Configure the RAID arrays. See the Array Manager User
Guide or “Configuring RAID” on page 40.
2 Install the operating system from the Windows disc that
came with your computer.
Configuring RAID
Creating a RAID volume
Because RAID can be configured so many ways, this procedure
covers only the basics. This procedure assumes that no RAID
has been defined yet.
To cre ate a RAID volume:
1 Install additional hard drives as needed for your RAID
plan. For instructions on installing hard drives, see
“Adding or replacing a hard drive” on page 52.
2 Start (or restart) your computer, then press F9 during
startup. The MediaShield Utility (RAID setup) screen
opens.
3 To create a new array, set RAID Mode to Striping (for
RAID 0), then select drives on the left and click Add to
add the drives to the array.
4 Press F7, then press Y. The new array is created.
5 Press CTRL+X to exit the utility. Your computer restarts.
6 Install the operating system from the Windows disc that
came with your computer.
40
Page 47

Deleting a RAID volume
Deleting a RAID volume deletes all files on that volume,
including operating system files. Before deleting a RAID
volume, make sure that all important files have been
backed up.
To delete a RAID volume:
1 Start (or restart) your computer, then press F9 during
2 Press the arrow keys to highlight the RAID volume you
3 Press D to delete the array. In this screen, you can also
Getting help
www.gateway.com
startup. The MediaShield Utility (RAID setup) screen
opens.
want to delete, then press E
opens.
Caution
If your computer has the operating system installed on a RAID,
deleting the RAID will remove the operating system, and you will not be
able to start your computer into Windows.
press C to clear (delete all data from) the array.
NTER. The Array Detail screen
For more information on RAID concepts, configuration, and
maintenance, search for RAID FAQ information on the Gateway
Technical Support Web site (www.gateway.com
Internet search engine to search for:
) or use an
• RAID
• configuring RAID
• RAID tutorials
• RAID levels
41
Page 48

CHAPTER 4: Advanced Hardware Setup
42
Page 49

CHAPTER5
Upgrading Your Computer
• Preventing static electricity discharge
• Opening the case
• Closing the case
• Adding or replacing memory
• Adding or replacing an optical disc drive
• Adding or replacing a hard drive
• Replacing the power supply
• Adding or replacing an expansion card
43
Page 50

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
Preventing static electricity discharge
Warning
To avoid exposure to dangerous electrical voltages and moving parts, turn
off your computer and unplug the power cord and modem and network cables
before opening the case.
To prevent risk of electric shock, do not insert any object into the vent holes of
the power supply.
The components inside your computer are extremely sensitive
to static electricity, also known as electrostatic discharge (ESD).
Before opening the computer case, follow these guidelines:
• Wear a grounding wrist strap (available at most
electronics stores) and attach it to a bare metal part of
your computer.
• Turn off your computer.
• Touch a bare metal surface on the back of the computer.
• Unplug the power cord and the modem and network
cables.
Caution
ESD can permanently damage electrostatic discharge-sensitive
components in your computer. Prevent ESD damage by following ESD guidelines
every time you open the computer case.
44
Before working with computer components, follow these
guidelines:
• Avoid static-causing surfaces such as carpeted floors,
plastic, and packing foam.
• Remove components from their antistatic bags only
when you are ready to use them. Do not lay components
on the outside of antistatic bags because only the inside
of the bags provide electrostatic protection.
• Always hold expansion cards by their edges or their
metal mounting brackets. Avoid touching the edge
connectors and components on the cards. Never slide
expansion cards or components over any surface.
Page 51

www.gateway.com
Opening the case
Your computer case provides easy access to internal
components.
Removing the left side panel
Warning
To avoid exposure to dangerous electrical voltages and moving parts, turn
off your computer, then unplug the power cord and modem cable before opening
the case.
To remove the left side panel:
1 Follow the instructions in “Preventing static electricity
discharge” on page 44.
2 Shut down your computer, then disconnect the power
cord and modem, network, and all peripheral device
cables.
3 Press the power button for ten seconds to drain any
residual power from your computer.
4 Remove the security tape (if any) on the rear edge of the
side panel.
5 Remove the two Phillips hex screws on the back edge of
the left side panel. For their location, see “Back” on
page 9.
6 Slide the side panel toward the back of your computer,
then pull the panel away from your computer.
45
Page 52

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
Removing the right side panel
Warning
To avoid exposure to dangerous electrical voltages and moving parts, turn
off your computer, then unplug the power cord and modem cable before opening
the case.
To help keep the case interior free from cable clutter, many
cables (such as hard drive and optical drive data cables) are
routed between the system board and the right side panel.
Removing the right side panel may be necessary to replace
some types of components.
To remove the right side panel:
1 Make sure that the left side panel has already been
removed by following the instructions in “Removing the
left side panel” on page 45.
2 Remove the two Phillips hex screws on the back edge of
the right side panel.
3 Slide the side panel toward the back of your computer,
then pull the panel away from your computer.
46
Page 53

www.gateway.com
Removing the front bezel
Tip
The bezel is the front “face” piece of your computer that has the optical
drive faces and the brand logo. It must be removed for some upgrading tasks.
To remove the front bezel:
1 Remove the left side panel by following the instructions
in “Removing the left side panel” on page 45.
2 Press the three bezel release tabs on the left side of the
computer, then swing the left side of the bezel away
from the computer until the bezel is completely
removed.
Bezel release
tabs
47
Page 54

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
Closing the case
Replacing the front bezel
To replace the front bezel:
1 Slide the hinge tabs on the right side of the bezel into
the slots on the front of the computer, then press the left
side of the bezel against the computer until its tabs snap
into place.
2 Replace the side panels that you removed previously by
following the instructions in “Replacing the side panels”
on page 48.
Replacing the side panels
To replace the side panels:
1 Make sure that all internal cables are arranged inside the
computer so they will not be pinched when you close the
computer.
2 Slide the side panels toward the front of the computer
until the backs of the side panels are flush with the back
of the computer.
3 Secure each side panel with the two Phillips screws you
removed previously.
4 Reconnect the cables and power cord.
Adding or replacing memory
When you upgrade the computer memory, make sure that you
install the correct type of memory module for your computer.
Your computer uses DIMM memory.
To install or replace DIMM memory:
1 Remove the side panel by following the instructions in
“Removing the left side panel” on page 45.
2 For more stability, place your computer on its side. To
avoid scratching the case, place it on a towel or other
non-abrasive surface.
3 Find the memory module banks on your system board.
48
Page 55
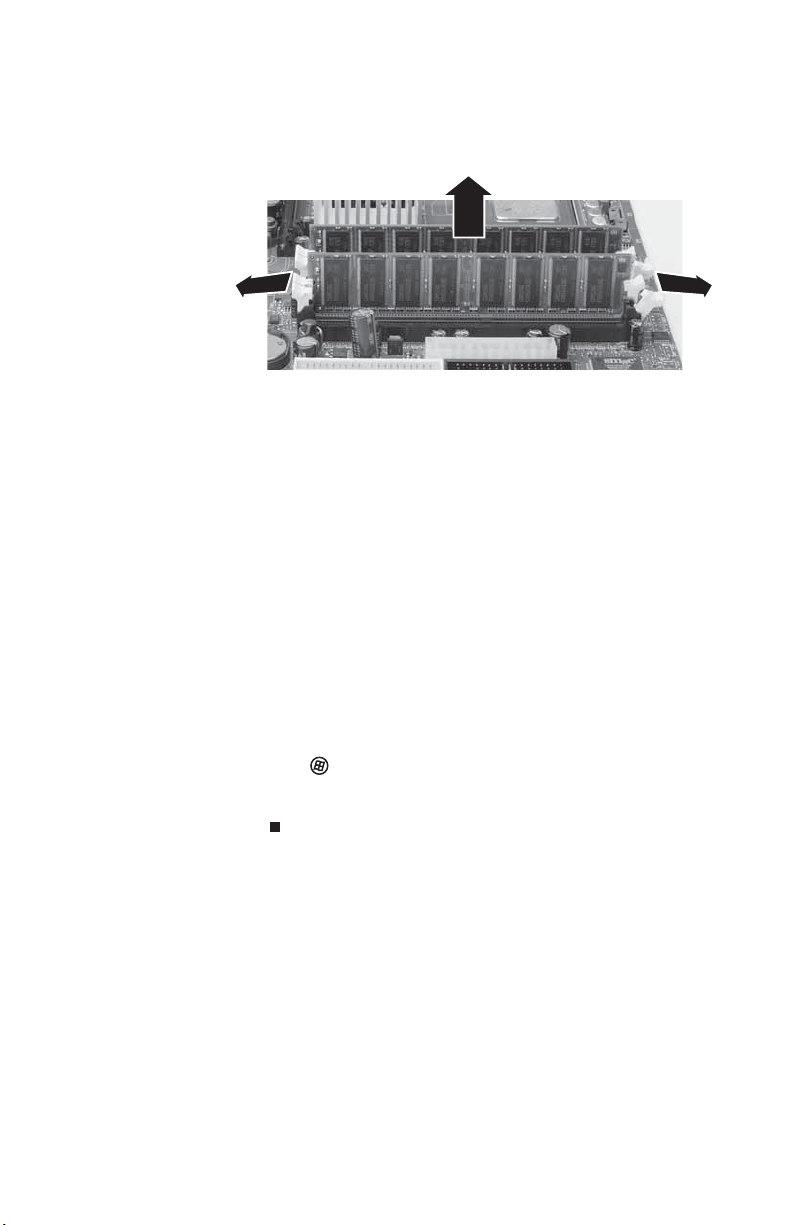
www.gateway.com
4 If you are removing a DIMM from the memory module
bank, gently pull the plastic tabs away from the sides of
the memory module and remove it.
- OR -
If you are adding a DIMM to an empty memory module
bank, gently pull the plastic tabs away from the sides of
the memory module bank.
5 Align the notches on the new DIMM with the notches on
the memory module bank, then press the module firmly
into the bank. The tabs on the sides of the memory
module should snap into place to secure the memory
module.
6 Return your computer to its upright position.
7 Replace the side panel by following the instructions in
“Replacing the side panels” on page 48.
8 Reconnect the cables and the power cord.
9 Turn on your computer. Windows starts and the
Windows desktop appears.
10 Click (Start), right-click Computer, then click
Properties. The amount of memory in your computer
is displayed.
49
Page 56

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
Adding or replacing an optical disc drive
Tools
You need a Phillips screwdriver to add or replace an optical drive.
To add replace an optical drive:
1 Remove the front bezel by following the instructions in
“Removing the front bezel” on page 47.
2 If you are installing a new drive (not replacing an old
one), remove the two drive retention screws in the drive
bay, then go to Step 7. For the location of the screws, see
the photo in Step 5.
Important
The color and shape of your replacement drive’s front cover may
vary from your original drive.
3 If you are replacing an existing drive, disconnect the
cables from the drive, noting their locations and
orientation. You will reconnect the cables after you
install the new drive.
50
Drive data cable Drive power cable
4 Note any jumper settings on the old drive (if any) and set
the jumper on the new drive to be the same.
Page 57

www.gateway.com
5 Remove the two drive retention screws.
Drive retention screws
6 Slide the drive forward and out of the drive bay.
7 Slide the new drive into the drive bay, line up the screw
holes on the drive bay with the screw holes on the drive,
then replace the two drive retention screws.
Important
Make su re that the optical d rive’s screw ho les are lin ed up wi th the
correct holes in the drive bay. If the drive screws are mounted through
the wrong holes, the front of the drive will protrude too far out the front
of the case for the front bezel to be reinstalled.
8 Reconnect the drive cables using your notes from Step 3,
or according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
9 Replace the front bezel by following the instructions in
“Replacing the front bezel” on page 48.
10 Replace the side panels by following the instructions in
“Replacing the side panels” on page 48.
51
Page 58
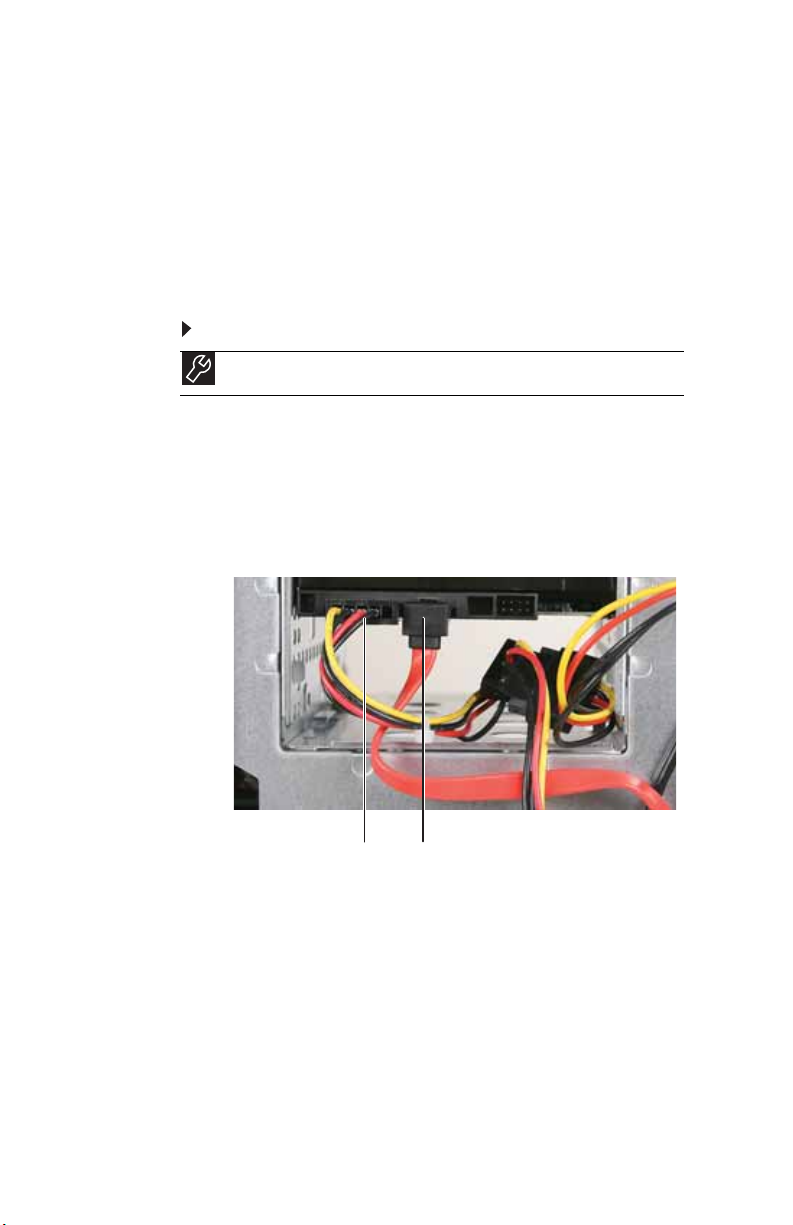
CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
Adding or replacing a hard drive
You can add hard drives to internal and external hard drive
bays.
Adding or replacing an internal hard drive
To add or replace an internal hard drive:
Tools
You need a Phillips screwdriver to add or replace a hard drive.
1 Remove the left and right side panels by following the
instructions in “Removing the left side panel” on page 45
and “Removing the right side panel” on page 46.
2 On the right side of the computer, label and disconnect
the cables for all internal hard drives, noting their
locations and orientation. (You will reconnect the cables
after you install the new drive.)
52
Data cablePower cable
Page 59

www.gateway.com
3 Remove the thumbscrew that secures the hard drive
cage to the computer, then slide the hard drive cage out
of the computer.
Hard drive cage thumbscrew
4 If you are replacing a drive, remove the screws that
secure the hard drive to the hard drive cage, then slide
the old hard drive out of the cage.
Hard drive screws
53
Page 60

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
5 If you are replacing a drive, note any jumper settings on
the old drive (if any) and set the jumpers on the new
drive to be the same.
- OR -
If you are adding a new drive, set the jumpers as
instructed by the drive’s user guide.
6 Secure the new hard drive into the cage using the screws
that you removed previously or that were provided with
the drive.
7 Install the hard drive cage back into the computer by
aligning the rails on the top of the cage with the slots
on the bottom of the optical drive cage.
Hard drive cage mounting rail Hard drive cage mounting rail
54
8 Secure the hard drive cage to your computer with the
thumbscrew you removed previously.
9 Connect the drive cables on the right side of the
computer. If you are replacing a drive, use your notes
from Step 2.
10 Replace the side panels by following the instructions in
“Replacing the side panels” on page 48.
11 Reconnect all external cables and the power cord.
12 Tu r n o n your compute r.
Page 61

www.gateway.com
13 If you are using the new hard drive as your primary
drive, install Windows using the operating system DVD
that came with your computer. For more information on
restoring your system, see “Recovering your system” on
page 101.
Adding a removable hard drive
You can use your computer’s removable hard drive carriers for
high-volume backups and convenient backup storage.
To install a removable hard drive:
1 Turn off your computer.
2 Slide open the removable hard drive cover.
55
Page 62

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
3 Pull the handle of one of the carriers to remove it from
the computer.
The empty carrier looks like this:
56
4 Align your new hard drive with the carrier so the end
with the connectors is at the opposite end as the carrier’s
handle.
5 Align the hard drive’s screw holes with the small metal
prongs on the inside of the carrier.
Page 63

www.gateway.com
6 Carefully pry the sides of the carrier away from each
other, slide the hard drive inside the carrier, then release
the sides. Make sure that the prongs on the inside of the
carrier are securely inserted into the screw holes on the
hard drive.
7 Slide the hard drive and carrier fully into the hard drive
slot on the front of your computer.
8 Turn your computer on. Your new drive is recognized by
your computer. Depending on the hard drive you
installed, it may need to be formatted before use.
57
Page 64

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
Replacing the power supply
Tools
You need a Phillips screwdriver to replace the power supply.
Warning
To avoid exposure to dangerous electrical voltages and moving parts, turn
off your computer, then unplug the power cord and modem cable before opening
the case.
To replace the power supply:
1 Follow the instructions in “Preventing static electricity
discharge” on page 44.
2 Remove the two side panels by following the instructions
in “Removing the left side panel” on page 45 and
“Removing the right side panel” on page 46. Make sure
that you unplug the computer’s external power cable.
3 Disconnect the power supply cables from all
components (such as hard drives, optical and diskette
drives, and the system board), noting their locations and
orientation. (You will reconnect the cables after you
install the new power supply.)
4 Remove the four Phillips screws that secure the power
supply to the case.
58
Phillips screws
Phillips screws
Page 65

www.gateway.com
5 Slide the power supply and cables out of the computer.
6 Insert the new power supply and cables into the case,
then secure it to the case using the four Phillips screws
you removed previously.
7 Reconnect the power supply cables using your notes
from Step 3.
8 Replace the side panels by following the instructions in
“Replacing the side panels” on page 48.
59
Page 66

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
Adding or replacing an expansion card
To add or replace an expansion card:
1 Remove the side panel by following the instructions in
“Removing the left side panel” on page 45.
Important
Your computer hardware options and port locations may vary
from the illustrations below.
2 Loosen the thumbscrew on the expansion card cover.
60
Page 67

www.gateway.com
3 Open the expansion card cover.
4 For more stability, place your computer on its side. To
avoid scratching the case, place it on a towel or other
non-abrasive surface.
5 If you are replacing a card, disconnect any cables that
are attached to the card, noting their locations and
orientation. (You may have to reconnect the cables after
you install the new card.)
6 Remove the old expansion card (if necessary). You can
slightly seesaw the card end-to-end to loosen it, but do
not bend the card sideways.
To remove a card (such as a video card) from the PCI
Express slot, press the card release lever before trying
to remove the card.
Caution
Do not touch the contacts on the bottom part of the expansion
card. Touching the contacts can cause electrostatic damage to the card.
7 Install the new card into the expansion slot. You can
slightly seesaw the card end-to-end to help insert the
card, but do not bend the card sideways.
8 Reconnect the expansion card cables (if any) using your
notes from Step 5, or, if you are adding a new card,
follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
61
Page 68

CHAPTER 5: Upgrading Your Computer
9 Tighten the thumbscrew on the expansion card cover.
10 Return your computer to its upright position.
11 Replace the side panels by following the instructions in
“Replacing the side panels” on page 48.
62
Page 69

CHAPTER6
Maintaining Your
Computer
• Setting up a maintenance schedule
• Caring for your computer
• Cleaning your computer
• Updating Windows
• Using BigFix
• Managing hard drive space
• Backing up files
• Scheduling maintenance tasks
• Moving from your old computer
63
Page 70

CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
Setting up a maintenance schedule
Use the following table to set up a regular maintenance
schedule.
Maintenance task Weekly Monthly When
Check for viruses X X X
Run Windows Update X X
Manage hard drive space X
Clean up hard drives X X
Scan hard drive for errors X X
Defragment hard drive X X
Back up files X X X
Clean computer case and
peripheral devices
needed
X
64
Page 71

www.gateway.com
Caring for your computer
To extend the life of your computer:
• Be careful not to bump or drop your computer, and do
not put any objects on top of it. The case, although
strong, is not made to support extra weight.
• When transporting your computer, we recommend that
you put it in the original packaging materials.
• Keep your computer away from magnetic fields.
Magnetic fields can erase data on hard drives.
• Never turn off your computer when the drive indicator
is on because data on the hard drive could be lost or
corrupted.
• Avoid subjecting your computer to extreme temperature
changes. The case can become brittle and easy to break
in cold temperatures and can melt or warp in high
temperatures. Damage due to either extreme is not
covered by your warranty. As a general rule, your
computer is safest at temperatures that are comfortable
for you.
• Keep all liquids away from your computer. When spilled
onto computer components, almost any liquid can result
in expensive repairs that are not covered under a
standard warranty.
• Avoid dusty or dirty work environments. Dust and dirt
can clog the internal mechanisms and can lead to
permanent damage to the computer.
• Do not block the ventilation fan slots. If these slots are
blocked, your computer may overheat, resulting in
unexpected shutdown or permanent damage to the
computer.
• When storing your computer for an extended period of
time, unplug AC power.
65
Page 72
CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
Cleaning your computer
Keeping your computer clean and the vents free from dust
helps keep your computer performing at its best. You may
want to gather these items and put together a computer
cleaning kit:
• A soft, lint-free cloth
• An aerosol can of air that has a narrow, straw-like
extension
• Cotton swabs
• An optical disc drive cleaning kit
Cleaning the exterior
Warning
When you shut down your computer, the power turns off, but some
electrical current still flows through it. To avoid possible injury from electrical
shock, unplug the power cord, modem cable, and network cable from the wall
outlets.
• Always turn off your computer and other peripheral
devices before cleaning any components.
• Use a damp, lint-free cloth to clean your computer and
other parts of your system. Do not use household
abrasive or solvent cleaners because they can damage
the finish on components.
• Your computer is cooled by air circulated through the
vents on the case, so keep the vents free of dust. With
your computer turned off and unplugged, brush the
dust away from the vents with a damp cloth. Be careful
not to drip any water into the vents.
66
Page 73

www.gateway.com
Cleaning the keyboard
You should occasionally clean the keyboard to remove dust and
lint trapped under the keys.
To clean the keyboard:
1 Use an aerosol can of air with a narrow, straw-like
extension to remove dust and lint trapped under the
keys.
2 If you spill liquid on the keyboard, turn off your
computer and turn the keyboard upside down. Let the
liquid drain, then let the keyboard dry before trying to
use it again. If the keyboard does not work after it dries,
you may need to replace it.
Cleaning the monitor
Caution
A flat-panel screen is made of specially coated glass and can be scratched
or damaged by abrasive or ammonia-based glass cleaners.
To clean the monitor:
• To clean an LCD flat panel monitor, use a soft cloth and
water to clean the screen. Dampen the cloth (never apply
liquid directly to the screen), then wipe the screen with
the cloth.
• To clean a CRT monitor, use a soft cloth and glass cleaner
to clean the monitor screen. Squirt a little cleaner on the
cloth (never directly on the screen), then wipe the screen
with the cloth.
Cleaning the mouse
If the mouse pointer begins moving erratically across the
computer screen or becomes difficult to control precisely,
cleaning the mouse will likely improve its accuracy.
To clean the mouse:
• Wipe the bottom of the mouse with a damp, lint-free
cloth.
67
Page 74

CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
Cleaning optical discs
Optical discs (CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray Discs) get dirty from
frequent handling.
To clean an optical disc:
1 Wipe from the center to the edge, not around in a circle,
using a product made especially for the purpose.
Updating Windows
Windows Update helps you keep your computer up-to-date.
Use Windows Update to choose updates for your computer’s
operating system, software, and hardware. New content is
added to the site regularly, so you can always get the most
recent updates and fixes to protect your computer and keep
it running smoothly. Windows Update scans your computer
and provides you with a tailored selection of updates that
apply only to the software and hardware on your computer.
For information on running Windows Update, see “Windows
Update” in your online User Guide. Windows Update can also
be controlled through the Windows Security Center. For more
information, see “Protecting Your Computer” in your online
User Guide.
68
Help
For more information about Windows Update, click Start, then click Help
and Support. Type windows update in the Search Help box, then press
E
NTER.
Page 75

Using BigFix
BigFix may be installed on your computer. BigFix monitors your
computer for problems and conflicts. It automatically gathers
information about the latest bugs, security alerts, and updates
from BigFix sites on the Internet. Whenever BigFix detects a
problem, it alerts you by flashing the blue taskbar icon. To fix
the problem, click on that icon to open BigFix.
To start BigFix:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, Accessories, System
Tools, then click BigFix.
2 To learn more about BigFix, click Help, then click
Tutorial.
www.gateway.com
69
Page 76

CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
Managing hard drive space
Windows provides several utilities you can use to check hard
drive space, delete unnecessary files, defragment files, and
back up files.
Checking hard drive space
To check hard drive space:
Shortcut
Start Ö Computer Ö right-click drive Ö Properties
1 Click (Start), then click Computer. The Computer
window opens.
70
Page 77

www.gateway.com
2 Right-click the drive that you want to check for available
file space, then click Properties. Drive space information
appears.
Deleting unnecessary files
Delete unnecessary files, such as temporary files and files in the
Recycle Bin, to free hard drive space.
To delete unnecessary files:
Shortcut
Start Ö Computer Ö right-click drive Ö Properties Ö
Disk Cleanup
1 Click (Start), All Programs, Accessories, System
Tools, then click Disk Cleanup. The Disk Cleanup Options
dialog box opens.
71
Page 78

CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
2 Click one of the options:
• My files only cleans only the folders for the
currently logged in user.
• Files from all users on this computer cleans all
folders.
The Disk Cleanup Options dialog box opens.
3 Click to select the types of files you want to delete, then
click OK. The types of files you indicated are deleted.
Help
For more information about keeping the hard drive free of
unnecessary files, click Start, then click Help and Support. Type disk
cleanup in the Search Help box, then press E
Checking the hard drive for errors
The Error-checking program examines the hard drive for
physical flaws and file and folder problems. This program
corrects file and folder problems and marks flawed areas on
the hard drive so Windows does not use them.
If you use your computer several hours every day, you
probably want to run Error-checking once a week. If you use
your computer less frequently, once a month may be adequate.
Also use Error-checking if you encounter hard drive problems.
To check the hard drive for errors:
1 Click (Start), then click Computer. The Computer
window opens.
2 Right-click the drive that you want to check for errors,
click Properties, then click the Tools tab.
NTER.
72
Page 79

www.gateway.com
3 Click Check Now, then click Start. Your drive is checked
for errors. This process may take several minutes.
Important
Error checking cannot scan a drive while the drive is being used,
so if you try to check your hard drive for errors, you see a prompt asking
you if you want to scan the hard drive later (the next time you restart
your computer). If you see this prompt, click Schedule disc check.
After Windows has finished checking the drive for errors,
it provides a summary of the problems that it found.
4 Correct any problems that are found by following the
on-screen instructions.
5 Click OK.
Help
For more information about checking the hard drive for errors,
click Start, then click Help and Support. Type checking for disk
errors in the Search Help box, then press E
Defragmenting the hard drive
When working with files, sometimes Windows divides the file
information into pieces and stores them in different places on
the hard drive. This is called fragmentation, and it is normal.
In order for your computer to use a file, Windows must search
for the pieces of the file and put them back together. This
process slows the hard drive performance.
Disk Defragmenter organizes the data on the drive so each file
is stored as one unit rather than as multiple pieces scattered
across different areas of the drive. Defragmenting the
information stored on the drive can improve hard drive
performance.
While Disk Defragmenter is running, do not use your keyboard
or mouse because using them may continuously stop and
restart the defragmenting process. Also, if you are connected
to a network, log off before starting Disk Defragmenter.
Network communication may stop the defragmentation
process and cause it to start over.
NTER.
Tip
Because defragmenting a drive may take hours to complete (depending
on the size of the drive being defragmented), consider starting the process when
you will not need the computer for several hours.
73
Page 80

CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
To defragment the hard drive:
1 Disconnect your computer from the network.
2 Click (Start), All Programs, Accessories, System
Tools, then click Disk Defragmenter. The Disk
Defragmenter dialog box opens.
3 Click Defragment now. This process may take hours to
complete, depending on the size of the drive being
defragmented.
Help
For more information about defragmenting the hard drive, click
Start, then click Help and Support. Type defragmenting in the
Search Help box, then press E
NTER.
Backing up files
Backing up files and removing them from the hard drive frees
space for new files on the hard drive. It also protects you from
losing important information if the hard drive fails or you
accidentally delete files.
You should back up your files regularly to a writable optical
disc (if you have a recordable drive). Use a backup device, such
as a recordable disc drive, to do a complete hard drive backup.
74
Page 81

www.gateway.com
To back up files:
1 Click (Start), then click Computer. The Computer
window opens.
2 Right-click the drive that you want to back up, click
Properties, then click the Tools tab.
3 Click Backup Now, then click Run a file backup now.
4 Follow the on-screen instructions to select a backup
storage location and the files and folders to back up.
Help
For more information about backing up files, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type backup in the Search Help box, then press
E
NTER.
75
Page 82

CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
Backing up files
Your Gateway computer makes backing up files as easy as
pressing a button.
To back up files:
Tip
If you are using a removable hard drive for your backup, see “Using
a removable hard drive” on page 36 for more information.
1 Press the Backup button near the power button on the
front of your computer.
Windows’ Backup and Restore Center opens.
Backup button
76
2 Click Back up files, then follow the on-screen
instructions to complete your backup.
Page 83

www.gateway.com
Scheduling maintenance tasks
Task Scheduler lets you schedule maintenance tasks such as
running Disk Defragmenter and checking your drives for
errors.
Important
Your computer must be o n during scheduled tasks. If your computer is off,
scheduled tasks will not run.
To start the Task Scheduler:
1 Click (Start), All Programs, Accessories, System
Tools, then click Task Scheduler. The Task Schedu ler
dialog box opens.
2 Click Create Basic Task for basic tasks or click Create
Task for more complex tasks, then follow the on-screen
instructions to finish setting up and scheduling the task.
Help
For more information about scheduling tasks, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type task scheduler in the Search Help box,
then press E
NTER.
77
Page 84

CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
Moving from your old computer
Transferring files and settings automatically
You can move your files, folders, software settings, and user
account settings (such as display, Internet, and e-mail settings)
from your old computer to your new one using Windows Easy
Transfer, providing your old computer uses Windows XP or
Windows Vista.
While using Windows Easy Transfer, you will not be able to run
other tasks on the computers.
Important
If your old computer does not use Windows XP or WindowsVista, you
must manually move your data by using a writeable disc, flash drive, or external
hard drive.
To move files and settings from your old computer:
1 If you want to transfer program settings to your new
computer, install those programs on the new computer
before running Windows Easy Transfer. Windows Easy
Transfer copies only the software’s settings, not the
software itself, to the new computer.
2 Click (Start), All Programs, Accessories, System
Tools, then click Windows Easy Transfer. The Windows
Easy Transfer dialog box opens.
3 Click Next, click Start a new transfer, then follow the
on-screen instructions to complete the transfer.
78
Help
For more information about transferring files, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type transferring files in the Search Help
box, then press E
NTER.
Page 85

www.gateway.com
Transferring files and settings manually
You can manually transfer your personal data files by copying
them to removable media, such as a writable disc, an external
hard drive, a network location, or a flash drive.
Finding your documents
Ma ny pro gra ms save your pers onal da ta f iles in the Documents
or My Documents folder. Look in your old computer’s
documents folder for personal data files.
To find files in the documents folder:
1 In Windows Vista, click (Start), then click
Documents. The Documents folder opens and displays
many of your saved personal data files. Go to 4.
- OR -
In Windows XP, click Start, then click My Documents.
The My Documents window opens and displays many of
your saved personal data files. Go to 4.
- OR -
In Windows 98, Windows Me, or Windows 2000,
double-click the My Computer icon on the desktop. Go
to the next step.
2 Double-click the C:\ drive icon.
3 Double-click the Documents or My Documents folder.
The My Documents window opens and displays many of
your saved personal data files.
4 Copy your personal data files to removable media or to
another computer on your network.
79
Page 86

CHAPTER 6: Maintaining Your Computer
Finding other files
Use Windows Find or Search to locate other personal data files.
For more information, see your online User Guide.
You can often identify different data file types by looking at
the file’s extension (the part of the file name following the last
period). For example, a document file might have a .DOC
extension and a spreadsheet file might have an .XLS extension.
File type File usually ends in...
Documents .DOC, .TXT, .RTF, .HTM, .HTML, .DOT
Spreadsheets .XLS, .XLT, .TXT
Pictures .JPG, .BMP, .GIF, .PDF, .PCT, .TIF, .PNG, .EPS
Movies .MPEG, .MPG, .AVI, .GIF, .MOV
Sound and music .WAV, .CDA, .MP3, .MID, .MIDI, .WMA
To find files using Find or Search:
1 In Windows Vista, click (Start), then click Search. The
Search Results window opens.
- OR -
In Windows XP, click Start, then click Search. The Search
Results window opens.
- OR -
In Windows 98, Windows Me, or Windows 2000, click
Start, Find or Search, then click For Files or Folders.
The Search Results window opens.
2 Type the filename you want to search for, then press
E
NTER. The search results are displayed.
3 To learn about more search options, click Help.
80
Page 87

CHAPTER7
Troubleshooting
• Safety guidelines
• Try these steps first
• Error messages
• Internet and networking
• Power
• Display
• Printing
• Optical discs
• Memory card reader
• Mouse
• Keyboard
• Files
• Memory
• Audio
• Passwords
• Expansion cards
• Media Center
• Checking for device problems
• Recovering your system
• Technical support
81
Page 88

CHAPTER 7: Troubleshooting
Safety guidelines
While troubleshooting your computer, follow these safety
guidelines:
Warning
To avoid bodily injury, do not attempt to troubleshoot your computer
problem if:
• Power cords or plugs are damaged
• Liquid has been spilled into your computer
• Your computer was dropped
• The case was damaged
Instead, unplug your computer and contact a qualified computer technician.
Warning
Never open your computer case while your computer is turned on and
while the modem cable, network cable, and power cord are connected.
Warning
Make sure that you are correctly grounded before accessing internal
components. For more information about preventing damage from static
electricity, see “Preventing static electricity discharge” on page 44.
Try these steps first
82
If you have problems with your computer, try these things first:
Warning
To avoid bodily injury, do not attempt to troubleshoot your
computer problem if:
• Power cords or plugs are damaged
• Liquid has been spilled into your computer
• Your computer was dropped
•The case was damaged
Instead, unplug your computer and contact a qualified computer
technician.
• Check all cable connections, including power.
• If an error message appears on the screen, write down
the exact message. The message may help Customer
Care in diagnosing and fixing the problem.
• If you added or removed peripheral devices, review the
installation procedures you performed and make sure
that you followed each instruction.
• If an error occurs in a program, see the program’s
printed documentation or the online help.
Help
For more information about troubleshooting, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type troubleshooting in the Search Help box,
then press E
NTER.
Page 89

www.gateway.com
Error messages
Error message Action
“Insufficient disk
space”
“Data error” See “You get a “Data error” message” on
“General failure
reading drive C”
“Operating system
not found”
“Unable to locate
host”
“Download Error” See “You get a “Download Error” message
“Memory error” See “You see a “Memory error” message”
“Not enough
memory”
See “You get an “Insufficient disk space”
error message” on page 93.
page 94.
See “The hard drive cannot be accessed,
or you see a “General failure reading drive
C” error message” on page 94.
See “You get an “Operating system not
found” error message” on page 94.
See “You see an “Unable to locate host”
message and are unable to browse the
Internet” on page 84.
when Media Center tries to update the
Program Guide” on page 99.
on page 96.
See “You see a “Not enough memory”
error message” on page 96.
83
Page 90

CHAPTER 7: Troubleshooting
Internet and networking
Internet
If you do not find a solution to your problem in this section,
the issue may be networking related. See “Networking” on
page 88 for more information.
You cannot connect to the Internet
• If you are using a cable or DSL modem, make sure that
the modem cable is securely plugged into the Ethernet
network jack. See more troubleshooting at “Modem
(cable or DSL)” on page 85.
- OR -
If you are using a dial-up modem, make sure that the
modem cable is plugged into the modem jack and not
the Ethernet network jack. See more troubleshooting at
“Modem (dial-up)” on page 86.
• Make sure that your account with your Internet service
provider (ISP) is set up correctly. For help, contact your
ISP technical support.
• Your ISP may be having connection problems. Contact
your ISP technical support to determine whether the
Internet outage is widespread (a problem they are trying
to solve).
Help
For more information about troubleshooting Internet
connections, click Start, then click Help and Support. Type
troubleshooting connections in the Search Help box, then press
E
NTER.
84
You see an “Unable to locate host” message and are unable to browse the Internet
• You may have typed the URL (Web address) incorrectly.
Check the URL, then enter it again, or try a different URL.
• Your Web browser may be experiencing problems. Close
your Web browser, then restart it. If that does not allow
you to connect, restart your computer.
• The problem may be with your network, not the Internet
itself. Check your network cables and network devices
(such as switches, routers, and hubs).
• Your ISP may be having connection problems. Contact
your ISP technical support to determine whether the
Internet outage is widespread (a problem they are trying
to solve).
Page 91

www.gateway.com
People are sending you e-mails, but you have not received them
• Click the Receive or Send and Receive button in your
e-mail program. This checks your mail server for
incoming e-mail.
• Make sure that your account with your Internet service
provider (ISP) is set up correctly. Contact your ISP for
technical support.
E-mails you send are returned as undeliverable
• Check the spelling of the e-mail address you are sending
e-mail to. A valid e-mail address consists of a user name,
the @ symbol, and the Internet domain name of the
Internet service provider (ISP) or company that “hosts”
that user. E-mail addresses never contain spaces and are
not case-sensitive.
• If possible, contact the intended recipient by using
another method, then ask them to verify their e-mail
address.
Modem (cable or DSL)
My computer cannot connect to the Internet.
• Make sure that your modem is connected to the network
jack.
• See the documentation that came with your modem for
additional troubleshooting information.
• Contact your modem manufacturer for technical
support.
85
Page 92

Modem (dial-up)
See also “Internet and networking” on page 84.
Your modem does not dial or does not connect
• Make sure that the modem cable is plugged into the
modem jack and not the Ethernet or the PHONE network
jack.
• Make sure that your computer is connected to the
telephone line and the telephone line has a dial tone.
• Remove any line splitters or surge protectors from your
telephone line, then check for a dial tone by plugging a
working telephone into the telephone wall jack.
• Make sure that call waiting is disabled before using the
modem. Contact your telephone service provider to get
the correct code to temporarily disable the service.
• Make sure that the modem dialing properties are set
correctly.
To check the dialing properties:
1 Click (Start), type modem, then press ENTER.
2 If the Location Information dialog box opens, enter
the information for your area, then click OK.
3 Click the Dialing Rules tab, click the location from
which you are dialing, then click Edit.
4 Make sure that all settings are correct.
CHAPTER 7: Troubleshooting
86
Help
For more information about dialing properties, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type dialing in the Search Help box, then
press E
NTER.
• Check for line noise (scratchy, crackling, or popping
sounds), which is a common problem that can cause the
modem to connect at a slower rate, interrupt downloads,
or even disconnect. You can also call your telephone
service and have the telephone line checked for noise or
low line levels.
• Try another telephone line (either a different telephone
number in your house or a telephone line at a different
location). If you can connect on this line, call your
telephone service.
Page 93

www.gateway.com
You cannot connect to the Internet
• The ISP may be having technical difficulties. Contact your
ISP for technical support.
• Review the troubleshooting information under “Internet
and networking” on page 84.
Your 56K modem does not connect at 56K
Current FCC regulations restrict actual data transfer rates over
public telephone lines to 53K. Other factors, such as line noise,
telephone service provider equipment, or ISP limitations, may
lower the speed even further.
The modem is not recognized by your computer
• Use the modem cable that came with your computer.
Some telephone cables do not meet required cable
standards and may cause problems with the modem
connection.
• Restart your computer.
• Run Windows modem diagnostics.
To run modem diagnostics:
1 Click (Start), type modem, then press ENTER.
2 Click the Modems tab, then click Properties.
3 Click the Diagnostics tab, then click Query Modem.
If information about the modem appears, the
modem passed diagnostics. If no modem
information is available, a white screen appears with
no data, or if you get an error such as port already
open or the modem has failed to respond, the modem
did not pass diagnostics.
Help
For more information about modem troubleshooting, click Start,
then click Help and Support. Type modem troubleshooting in the
Search Help box, then press E
The modem is noisy when it dials and connects
To turn down the modem volume:
NTER.
1 Click (Start), type modem, then press ENTER.
2 Click the Modems tab, then click Properties.
87
Page 94

Networking
For more information, see the Networking chapter in your
User Guide.
You cannot see the other computers on your network
• If a network cable is connected to your computer, make
• Make sure that the other computers are turned on.
• If you are using a router, make sure that it is turned on.
• If you are using a router, restart it by unplugging it from
• Make sure that all computers on your network have the
• If you assigned IP addresses to the computers, make sure
CHAPTER 7: Troubleshooting
3 Click the Modem tab, then adjust the Speaker
volume control.
4 Click OK twice to close the dialog boxes.
sure that the other end is plugged into a network router,
switch, hub, or other network device.
Most routers have lights that indicate they are working.
For more information, see your router’s documentation.
power for five seconds.
same workgroup name and Subnet Mask.
that all computers have different IP addresses. For home
networks, IP addresses should be 192.168.N.N where N
is a number you assign between 0 and 254. The first N
should be the same for all computers on your network,
and the second N should be different for all computers
on your network.
88
Your wired network is running slower than you expect
• If your network is running slower than you expect, check
the speed of each component. For best results, all
components should be standard Ethernet (10 Mbps),
Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps), or Gigabit Ethernet
(1000 Mbps). Components comprising a mixture of those
speeds will result in your network running at the speed
of the slowest component.
• For more troubleshooting help, see the documentation
for your network components.
Help
For more information about network troubleshooting, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type network troubleshooting in the Search
Help box, then press E
NTER.
Page 95

Power
Your computer will not turn on
Display
The screen resolution is not correct
The computer is on, but there is no picture
www.gateway.com
• Make sure that the power cord is connected to an
AC power source and to your computer, and that your
computer is turned on. If your power cables are
connected to a power strip, make sure it is turned on.
• Test the outlet by plugging in a working device, such as
a lamp.
• Make sure that the power cord is free from cuts or
damage, and replace any damaged cables.
• Change the screen resolution in Windows. For
instructions, see your online User Guide.
• Make sure that the computer is not in Standby
(power-saving) mode.
• Make sure that the monitor is connected to a power
outlet and to a video port on your computer, then make
sure that the monitor is turned on. If the monitor is on,
its power LED should be on.
• Adjust the monitor’s brightness and contrast controls.
For more information, see the monitor’s documentation.
• Check the video cable for bent or damaged pins.
• Connect a display that you know works (such as a
monitor from another computer) to your computer. If the
display still works, the original monitor is faulty. If the
display does not work, either the computer’s video card
(if installed) is faulty or the on-board video is faulty.
89
Page 96

The color is not uniform
• Make sure that the display warms up for at least
The text on the display is dim or difficult to read
• Adjust the brightness and contrast controls.
• Change the display settings. For instructions, see your
• For more information about display types, see your
then click Help and Support. Type screen resolution in the Search Help
box, then press E
Printing
The printer will not turn on
• Make sure that the power cable is plugged into an
CHAPTER 7: Troubleshooting
30 minutes before making a final judgment about color
uniformity.
online User Guide.
display and video card documentation.
Help
For more information about changing the screen resolution, click Start,
NTER.
AC power source.
90
The printer is on but will not print
• Make sure that the Print to file box is not checked in
the Print dialog box.
• If the printer you want to print to is not the default
printer, make sure that you have selected it in the printer
setup.
To set a default p rinte r:
1 Click (Start), type printer, then press ENTER.
Control Panel opens and lists available printers.
2 Right-click the printer you want to be the default
printer, then click Set as Default Printer.
Page 97

• Reinstall the printer driver. See your printer’s user guide
for instructions.
• Wait until files have been printed before sending
additional files to the printer.
• If you print large files or many files at one time, you may
want to add additional memory to the printer. See the
printer documentation for instructions on adding
additional memory.
• Contact your printer manufacturer’s technical support.
Help
For more information about printer troubleshooting, click Start, then click
Help and Support. Type printer troubleshooter in the Search Help box,
then press E
NTER.
Optical discs
Optical discs include CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs.
The computer does not recognize a disc or the disc drive
• Make sure that the disc label is facing up, and make sure
that the disc is clean and free from large scratches. For
information on cleaning the disc, see “Cleaning optical
discs” on page 68.
• Update the device driver. For instructions, see “Checking
for device problems” on page 100.
• Your computer may be experiencing some temporary
memory problems. Restart your computer.
www.gateway.com
An audio disc does not produce sound
• Make sure that the Windows volume controls are turned
up (and mute is turned off) and that any attached
speakers are turned on and connected correctly.
• Make sure that the disc is label side up, and make sure
that the disc is clean and free from large scratches. For
information on cleaning the disc, see “Cleaning optical
discs” on page 68.
A movie disc will not play
• Make sure that the disc is label side up, and make sure
that the disc is clean and free from large scratches. For
information on cleaning the disc, see “Cleaning optical
discs” on page 68.
91
Page 98

CHAPTER 7: Troubleshooting
• The regional code of the movie disc may not match your
drive’s regional code. Play only discs with a regional code
for your region. The DVD regional code for the United
States and Canada is 1, and the regional code for Mexico
is 4. The Blu-ray regional code for North and South
America is A, although many (if not most) Blu-ray movies
are region-free.
• Update the device driver. For instructions, see “Checking
for device problems” on page 100.
• Your computer may be experiencing some temporary
memory problems. Restart your computer.
Memory card reader
Drive letters for the memory card slots do not appear in the Computer window
• The memory card reader may have been temporarily
uninstalled using the Remove Hardware icon in the
system tray. Restart your computer, and it will recognize
the card reader again.
Mouse
The mouse does not work
The mouse works erratically
92
• Make sure that the mouse cable is plugged in correctly.
• Restart your computer.
• Try a mouse you know is working to make sure that the
mouse port works.
• Clean the mouse by wiping the bottom with a clean,
damp cloth. Make sure that the optical sensor is clean
and free of debris.
• You may be using the mouse on a transparent, reflective,
metallic, or glossy surface. Your mouse uses optical
sensors that do not work correctly on these surfaces. Use
a mouse pad or a surface with a non-glossy texture, such
as fabric.
• The mouse pad may have a printed or fabric pattern on
it that interferes with your mouse. Use a different mouse
pad.
Page 99

Keyboard
The keyboard does not work
• Make sure that the keyboard cable is plugged in
correctly.
• Clean the keyboard by using an aerosol can of air with
a narrow, straw-like extension to remove dust and lint
trapped under the keys.
• Try a keyboard that you know works to make sure that
the keyboard port works.
Liquid spilled in the keyboard
• Turn off your computer and unplug the keyboard. Wipe
off the keyboard, turn the keyboard upside down to
drain any remaining liquid, then blow the inside dry with
a can of compressed air. Let the keyboard dry for several
hours before using it again. If the keyboard does not
work after it dries, you may need to replace it.
Files
www.gateway.com
You get an “Insufficient disk space” error message
• Delete unnecessary files from the hard drive using Disk
Cleanup. For instructions, see “Deleting unnecessary
files” on page 71.
Help
For more information about file management, click Start, then
click Help and Support. Type file management in the Search Help
box, then press E
NTER.
• Empty the Recycle Bin by right-clicking the Recycle Bin
icon, then clicking Empty Recycle Bin.
Caution
All deleted files will be lost when you empty the Recycle Bin.
• Save your files to another drive. If the hard drive is full,
copy any files not regularly used to backup media, then
delete them from the hard drive.
93
Page 100

CHAPTER 7: Troubleshooting
A file was accidentally deleted
• If a file was deleted while holding down the SHIFT key,
or if the Recycle Bin has been emptied since the file was
deleted, the file cannot be restored.
To restore deleted files:
1 Double-click the Recycle Bin icon.
2 Right-click the file you want to restore, then click
Restore. The file is restored to the place where it was
originally deleted from.
Help
For more information about restoring deleted files, click Start,
then click Help and Support. Type System Restore in the Search
Help box, then press E
You get a “Data error” message
NTER.
• This may be the result of a defective area on the hard
drive. To fix hard drive problems, run the error checking
program. For instructions on fixing hard drive problems,
see “Checking the hard drive for errors” on page 95.
The hard drive cannot be accessed, or you see a “General failure reading drive C” error message
• If your computer has been subjected to static electricity
or physical shock, you may need to reinstall the
operating system. See “Recovering your system” on
page 101.
94
You get an “Operating system not found” error message
• Your computer is unable to detect the hard drive. Check
cable connections. For instructions on opening your
computer case, see “Opening the case” on page 45.
• A USB flash drive or a USB portable music player is
connected to one of your computer’s USB ports. Unplug
the USB device, then restart your computer.
• Your hard drive has no operating system installed on it,
or the operating system files cannot be recognized
because they have become corrupted or erased. See
“Recovering your system” on page 101.
You need to restore your computer to a working condition
• See “Recovering your system” on page 101.
 Loading...
Loading...