Page 1

MANUAL DEL USUARIO
USER MANUAL
MANUEL D’ENTRETIEN
LIBRETTO D´USO
BETRIEBSANLEITUNG
enducross EC´08
enducross EC´08
enducross EC´08
Page 2

Page 3

ENGLISH
USER MANUAL
USER MANUAL
enducross EC´08
enducross EC´08
enducross EC´08
Page 4

Page 5

-3-
Foreword
GAS GAS thanks you for the trust you have placed in us.
By choosing the new GAS GAS EC / MC / SM 2008 you have become part of the great GAS GAS family and,
as a user of the number one manufacturer of off-road motorbikes, you deserve the distinguished treatment
that we wish to offer to you both in our after-sale relationship and in the explanations that we provide in this
manual.
Our EC / MC / SM 2008 is a motorcycle conceived for the practice of high-competition. It is actually the fruit
of many years of competition and experimentation in this demanding discipline, as well as the many great
successes achieved thanks to great trial riders who have contributed with their expertise to the basic data that
have allowed us to create motorcycles of the highest level, GAS GAS unique motorcycles which count on
important key factors: reliability, high features and a good stability.
Congratulations for making the right choice. With your skills at the command of this motorcycle, its adequate
preparation and the corresponding indispensable servicing, this motorcycle will prove to be highly reliable, and
you will be able to enjoy the most comfortable and rewarding practice of your favorite sport.
Thank you for your trust in us, and welcome to GAS GAS Motos, S.A.
Julyl 2007
Page 6

-4-
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
Read this Manual carefully. You will find it contains all the necessary
information for your safety, and that of other persons, as well as
guaranteeing the correct conservation and maintenance of the GAS
GAS motorcycle that you have just acquired.
You will find all the necessary instructions for the correct riding and
control of this vehicle are set out below. Each message is preceded
by a symbol with the following meaning: .
WARNING
This warning symbol identifies special instructions or procedures
which, if not correctly followed, could result in personal injury or even
death.
CAUTION
This symbol identifies instructions or procedures which, if not followed
strictly, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment.
NOTE
This note symbol indicates points of particular interest for more
efficient and convenient operation.
Motorcycle riding, if improverly conducted, has the potential to cause
environmental problems as well as conflicts with other people.
Responsible riding use of your motorcycle will ensure that these
problems and conflicts do not develop.
TO PROTECT THE FUTURE OF YOUR SPORT MAKE SURE YOU
USE YOUR MOTORCYCLE WHITHIN THE LAW, SHOW CONCERN
FOR THE ENVIRONMENT, AND RESPECT THE RIGHTS OF
OTHER PEOPLE.
Motorcycle riding is a wonderful sport, and we hope you will enjoy
it to the fullest.
RECOMMENDS THE USE OF OIL:
Page 7

-5-
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Foreword...........................................................................................3
How to use this manual.....................................................................4
Table of contents...............................................................................5
Specifications....................................................................................6
Location of components....................................................................8
Side Stand ......................................................................................12
Fuel.................................................................................................12
Serial Number.................................................................................14
Homologation Plate.........................................................................14
Starting the engine..........................................................................14
Shifting gears..................................................................................15
Stopping the motorcycle .................................................................16
Riding during the Break-In Period...................................................16
Maintenance Schedule ...................................................................17
Electronic Ignition............................................................................19
Cooling System...............................................................................19
Spark Plug ......................................................................................20
Transmission...................................................................................22
Air Cleaner......................................................................................24
Throttle Cable .................................................................................25
Carburetor.......................................................................................25
Clutch..............................................................................................26
Exhaust System..............................................................................26
Drive Chain Guide...........................................................................27
Handlebar .......................................................................................29
Brakes.............................................................................................30
Steering...........................................................................................31
Steering blockage ...........................................................................32
Front Fork .......................................................................................33
Rear suspension.............................................................................36
Wheels............................................................................................38
Cleaning..........................................................................................39
Bolts and nuts tightening.................................................................40
Lubrication ......................................................................................42
Tunning (Carburetor and Suspension)............................................43
Final recommendatios.....................................................................51
Homologation..................................................................................52
Preparation for competition.............................................................53
Storage ...........................................................................................54
GAS GAS Multifunction Instructions ..............................................55
Troubleshooting ..............................................................................63
Electric Schemas ............................................................................68
Warranty Manual.............................................................................69
Page 8

-6-
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE 2 cycles, single cylinder, crankcase intake, liquid cooled
125 cc Engine
Bore and stroke 54 x 54.5 mm
Displacement 124 cc
200 cc Engine (only EC)
Bore and stroke 62.5 x 65 mm
Displacement 199.4 cc
250 cc Engine
Bore and stroke 66.4 x 72 mm
Displacement 249.3 cc
300 cc Engine (only EC)
Bore and stroke 72 x 72 mm
Displacement 294.7 cc
Carburettor, diameter of diffusor 38
Lubrication system Mixture
100% Synthetic Oil 50:1 = 2%
Mineral Oil (Only USA) 32:1 = 3%
Starting system Starting lever
Ignition system CDI system
Ignition timing 1 mm BTDC
TRANSMISSION
Transmission type 6 speed in cascade
Clutch type Hydraulic operated multi-plate in oil bath
Secondary drive Chain driven
Gear ratio (200 cc, 250 cc, 300 cc) 1st 2.071 (29/14)
2nd 1.625 (26/16)
3rd 1.333 (24/18)
4th 1.100 (22/20)
5th 0.913 (21/23)
6th 0.791 (19/24)
Page 9

-7-
Primary reduction 2.85 (57/20) (250 cc, 300 cc)
Final reduction 3.692 (48/13) (250 cc, 300 cc)
Overall gear ratio 8.323 (6th gear)
Transmission oil Capacity 750 cc (125 cc)
900 cc (200 cc / 250 cc / 300 cc)
Type 10W30 API SF or SG
CHASSIS
Type Tubular, semi-double cradle
Tire size Front EC & MC - 90/90 x 21
SM - 120/60 ZR17
Rear EC - 140/80 x 18
MC - 120/80 x 19
SM - 150/60 ZR17
Suspension Front Inverted telescopic fork ø 45 mm (only EC, SM and MC 125)
Inverted telescopic fork ø 50 mm (only MC 250)
Rear Progressive system with single multi-adjustable shock
Suspension stroke Front 282 mm
Rear 320 mm
Front fork oil SAE 5 - 7.5
Front fork oil level 110 mm (compressed, without spring)
BRAKES
Type Front, Rear Disc brake
Effective disc diameter Front 260 mm (only EC and MC)
320 mm (only SM)
Rear 220 mm
DIMENSIONES
Overall height 1260 mm
Overall length 2135 mm
Overall width 810 mm
Seat height 940 mm
Minimum height 340 mm
Wheelbase 1475 mm
Fuel tank capacity 9 l
(Specifications are subject to change without notice and probably do not apply to all countries).
Page 10
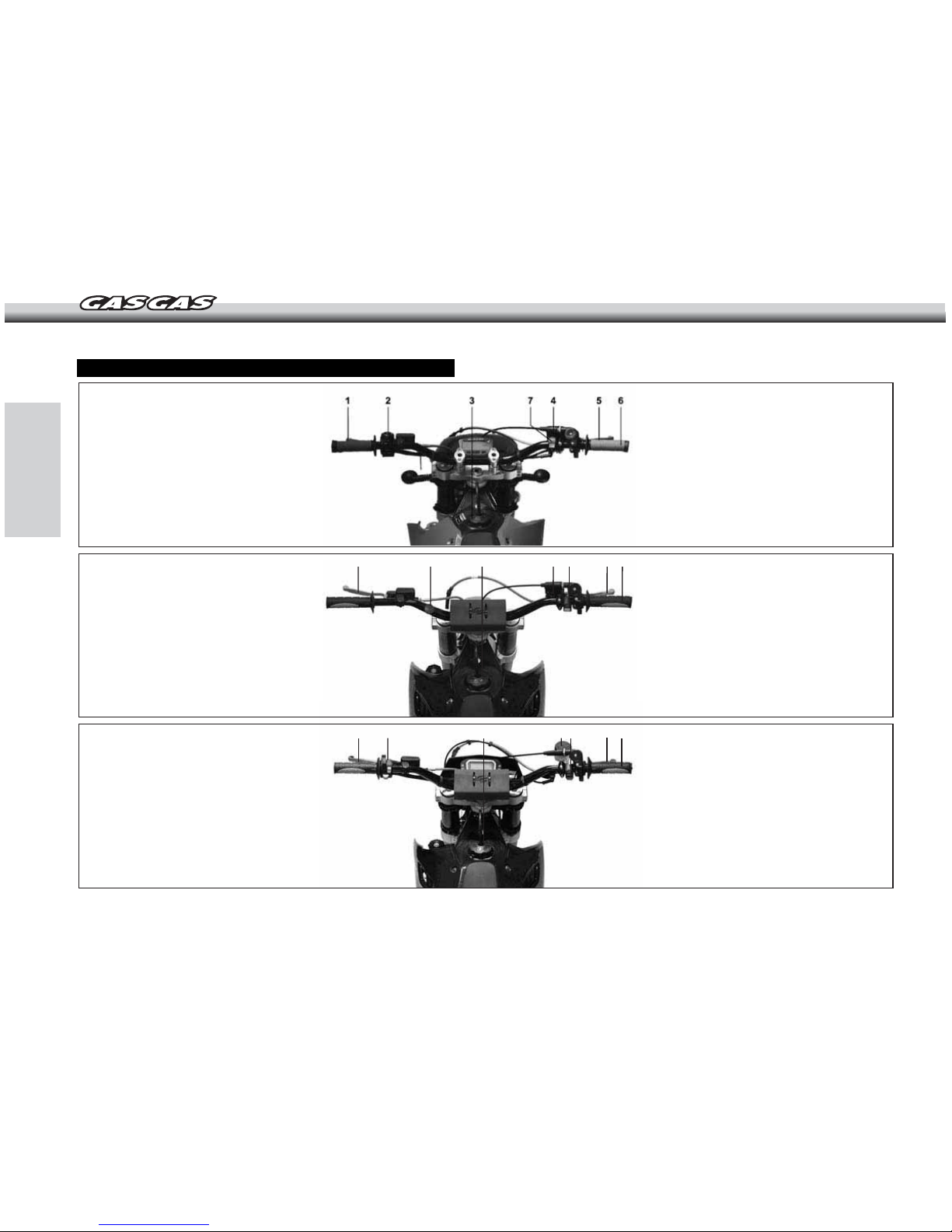
-8-
LOCATION OF COMPONENTS
GAS GAS EC 2008
1- Clutch lever
2- Steering, lights, horn and
headlamp controls
3- Fuel tank cap
4- Brake fluid reservoir
5- Front brake lever
6- Throttle grip
7- CDI Switch
GAS GAS MC 2008
1- Clutch lever
2- Engine stop button
3- Fuel tank cap
4- Brake fluid reservoir
5- Front brake lever
6- Throttle grip
7- CDI Switch
GAS GAS SM 2008
1- Clutch lever
2- Steering, lights, horn and
headlamp controls
3- Fuel tank cap
4- Brake fluid reservoir
5- Front brake lever
6- Throttle grip
7- CDI Switch
1
3
2
4
5
6
1 32 4 5 6
7
7
Page 11

-9-
7- Brake disc
8- Front suspension
9- Brake fluid reservoir
10- Fuel tank
11- Carburetor
12- Rear shock absorber
13- Brake caliper
14- Radiator
15- Gasoline cock
16- Shift pedal
17- Air cleaner
18- Muffler
19- Seat
20- Gas reservoir
21- Chain guide
22- Chain
23- Suspension linkage and swingarm
24- Rear brake pedal
25- Kick-start pedal
26- Exhaust
GAS GAS EC 2008
Page 12

-10-
7- Brake disc
8- Front suspension
9- Brake fluid reservoir
10- Fuel tank
13- Brake caliper
14- Radiator
18- Muffler
19- Seat
20- Gas reservoir & Rear shock absorber
21- Chain guide
22- Chain
23- Suspension linkage and swingarm
24- Rear brake pedal
25- Kick-start pedal
26- Exhaust
GAS GAS MC 2008
8
14
1019
7
13
21
18
24 25
92220
2623
Page 13

-11-
7- Brake disc
8- Front suspension
9- Brake fluid reservoir
10- Fuel tank
14- Radiator
18- Muffler
19- Seat
20- Gas reservoir & Rear shock absorber
21- Chain guide
22- Chain
23- Suspension linkage and swingarm
24- Rear brake pedal
25- Kick-start pedal
26- Exhaust
GAS GAS SM 2008
8
14
1019 7
13
21
18
24 25
9
22
20
2623
Page 14

FUEL
The GAS GAS EC / MC / SM models have 2-cycle engines that
require a mixture of gasoline and oil.
Gas Tank Capacity
9 L
The fuel tank cap is of the quick-release type.
To open the fuel tank cap, lift the plated latch and turn cap counterclockwise.
To close it, turn the cap clockwise and lower the latch.
NOTE
It is recommended that the rubber seal should be checked
thoroughly to insure it is airtight.
SIDE STAND (only EC and SM)
To set the side stand only turn it until it contacts the stopper, then
the side stand will be parallel to the ground and rest securely.
The side stand will return to its original position by means of the
double spring. The function of the double spring insures that, when
the side stand is down, the rest position is stable and above all
secure; moreover, it also returns the side stand to its original position.
EC 2008 and
SM 2008
(A). Side stand.
(B). Double
spring.
MC 2008
(A). Side stand.
NOTE
Do not start the engine or ride the motorcycle when the side
stand is down.
-12-
(A). Fuel tank cap.
(B). Vapor outlet tube.
(A)
Page 15
-13
-
RECOMMENDED FUEL
Use gasoline with an octane rating equal to or higher than that shown
in the table.
OCTANE RATING METHOD MINIUM
RATING
Antiknock Index (RON+MON)/2 90
Research Octane No. (RON) 98
NOTE
If knocking or pinging occurs, try a different brand of gasoline
or higher octane grade.
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain
conditions. Always stop the engine and do not smoke. Make sure
the area is well ventilated and free from any source of flame or
sparks; this includes any appliance with a pilot light.
Mixing oil inside the engine
Oil must be mixed with gasoline to lubricate the piston, cylinder,
crankshaft, and connecting rod bearings.
Recommended oil:
2-CYCLE SYNTHETIC
NOTE
If the recommended oil is not available, use only oil designed
for racing with 2-cycle engines.
Gasoline and engine oil mixing proportions:
Synthetic oil 100%: gasoline 50, engine oil 1 = 2%
Semi-synthetic oil: gasoline 50, engine oil 1 = 2%
Mineral oil: gasoline 32, engine oil 1 = 3%
CAUTION
Do not mix vegetable and mineral based oils.
Too much oil will cause excessive smoking and spark plug fouling.
Too little oil will cause engine damage or premature wear.
CAUTION
Below 0 ºC do not use 100% synthetic oil.
To prepare the mixture, first pour oil and half of the gasoline used
into a container and stir the mixture thoroughly. Then add the rest
of the gasoline and stir the mixture well.
NOTE
At low temperature, oil will not easily mix with gasoline. Take
time to ensure a well-blended mixture.
The lubrication quality of this mixture deteriorates rapidly; use
a fresh mixture for each day of operation.
Page 16

-14-
STARTING THE ENGINE
1. Make sure the motorcycle is in the neutral position.
2. Turn the gasoline cock (A) clockwise to the "ON" position.
3. If the engine is
cold, pull up the
choke knob (B).
SERIAL NUMBER (A)
It is stamped on the steering pipe. It indicates the frame number
registered for this motorcycle.
HOMOLOGATION PLATE (B)
This motorcycle carries its corresponding homologation plate where
it also shows the serial number, and this data must match the
information registered in the motorcycle documents.
ON
Open
OFF
Close
RES
Reserve
(A)
(B)
(A)
(B)
Page 17

Stopping the engine (MC model)
1. Shift the transmission into neutral.
SHIFTING GEARS
The transmission is a 6-speed, of the return shift type. A return shift
means that to go from first gear to third gear it must go first through
the second gear, that is to say that it upshifts gears one by one. To
engage first gear from neutral, pull the clutch lever in and push down
on the gearshift pedal, then release the gearshift pedal and gently
release the clutch lever.
CAUTION
When shifting gears, press firmly on the gearshift pedal to ensure
a positive shifting. Careless, incomplete shifts can cause the
transmission to jump out of gear and cause engine damage.
(A). Gearshift pedal.
-15-
NOTE
- When the engine is already warm or on hot days, open
the throttle instead of using the choke knob.
- If the engine is flooded, kick with the throttle fully open.
- If the clutch lever is pulled, the motorcycle can be
started while in any gear.
5. Even after the engine starts, keep the choke knob pulled up.
Stopping the engine (EC and SM models)
1. Shift the transmission into neutral.
4.
Start the
motorcycle with
kick-start pedal
(C).
2. After racing the
engine slightly,
close the throttle
completely and
depress the engine
stop button (D).
2. After racing the engine
slightly, close the throttle
completely and depress
the engine stop button
(A).
(A)
Page 18

STOPPING THE MOTORCYCLE
For maximum deceleration, close the throttle (A) and apply both
front and rear brakes. Disengage the clutch as the motorcycle comes
to a stop. Independent use of the front or rear brake may be
advantageous under certain conditions.
Downshift progressively as speed is reduced to ensure good engine
response when you want to accelerate.
RIDING DURING THE BREAK-IN PERIOD
A break-in period is necessary to ensure a smooth operation and
obtain an optimum engine and the transmission responses. During
the first hour or 20 km of operation, run the engine at low and
moderate speeds and revolutions per minute (RPM).
NOTE
The slow riding necessary during the break-in period may cause
carbon deposits to build up on the spark plug and foul it. If
inspection of the spark plug shows this to be the case, replace
the standard spark plug with another of a higher heat range.
Perform the break-in period following these steps:
1. Start the engine and let it run at idle until the engine is warm.
2. Stop and let the engine cool completely.
3. Start the engine and ride for 10 minutes at moderate speed -
NEVER ACCELERATE HARD.
4. Stop and let the engine cool completely. Be sure to check and
adjust chain slack and spoke tightness and cxarry out a general
inspection.
5. Start the engine and ride for 20 minutes at moderate speed. -
NEVER ACCELERATE HARD.
6. Stop and let the engine cool completely. Check and adjust as
needed (Refer to the table of adjustments).
7. Install the parts removed.
8. Fill the radiator with the recommended coolant. Before starting
the motorcycle, bleed the air from the cooling system.
9. Start the engine and ride for 30 minutes at moderate speed.
10. Stop and let the engine cool completely. Check and adjust.
11. After the break-in procedure has been properly carried out, the
motorcycle is ready for regular operation.
CAUTION
However, avoid accelerating recklessly that can lead to engine failure.
Be careful to use the necessary skills and techniques while operating
the motorcycle.
NOTE
After the break-in period, install a new set of standard spark
plugs.
-16-
Page 19
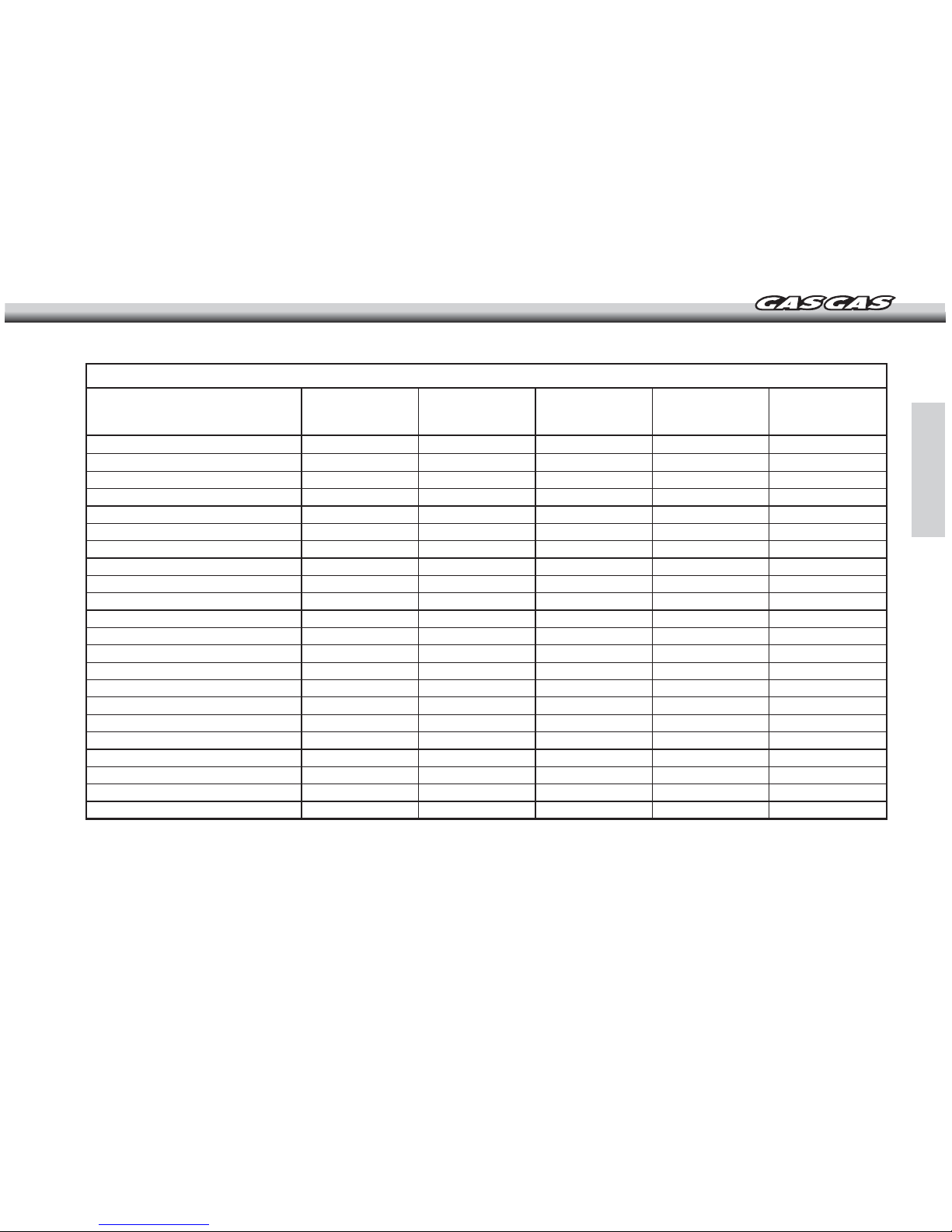
-17-
The maintenance and adjustments in this table are easy to follow and must be carried out to keep the motorcycle in good running condition.
NOTE: (*) Inspect and carry out these operations only if it is necessary.
Item
Clutch
Discs
Throttle cable
Spark plug
Air cleaner element
Carburetor
Transmission oil
Piston and piston ring
Cylinder head, cyl. & exhaust valves
Exhaust
Muffler gasket
Piston bearing
Kick-start pedal and gearshift pedal
Exhaust pipe o'ring
Engine bearings
Coolant
Radiator tube and connections
Brake adjustment
Brake pads wear
Brake fluid level
Brake fluid
Brake pump piston & dust cover
MANTENANCE SCHEDULE
Check / Inspect Change / Replace Apply grease /
Lubricate
Adjust
At each fill up
3 fill ups
-
-
-
1 fill up
3 fill ups
3 fill ups
1 fill up
3 fill ups
-
-
10 fill ups
3 fill ups
1 fill up
3 fill ups
5 fill ups
3 fill ups
-
-
At each fill up
3 fill ups*
1 fill up
-
-
1 fill up
3 fill ups*
3 fill ups*
1 fill up*
10 fill ups*
3 fill ups*
-
-
10 fill ups*
3 fill ups*
1 fill up*
3 fill ups*
5 fill ups*
3 fill ups*
-
-
At each fill up
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
3 fill ups
1 fill up
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Clean
At each fill up*
3 fill ups*
-
-
When damaged
-
3 fill ups
3 fill ups*
3 fill ups*
1 fill up*
10 fill ups
10 fill ups
-
3 fill ups
10 fill ups*
3 fill ups*
1 fill up*
3 fill ups*
5 fill ups*
3 fill ups*
Every 2 years
Every 2 years
-
-
1 fill up
1 fill up
-
-
3 fill ups
1 fill up
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 20
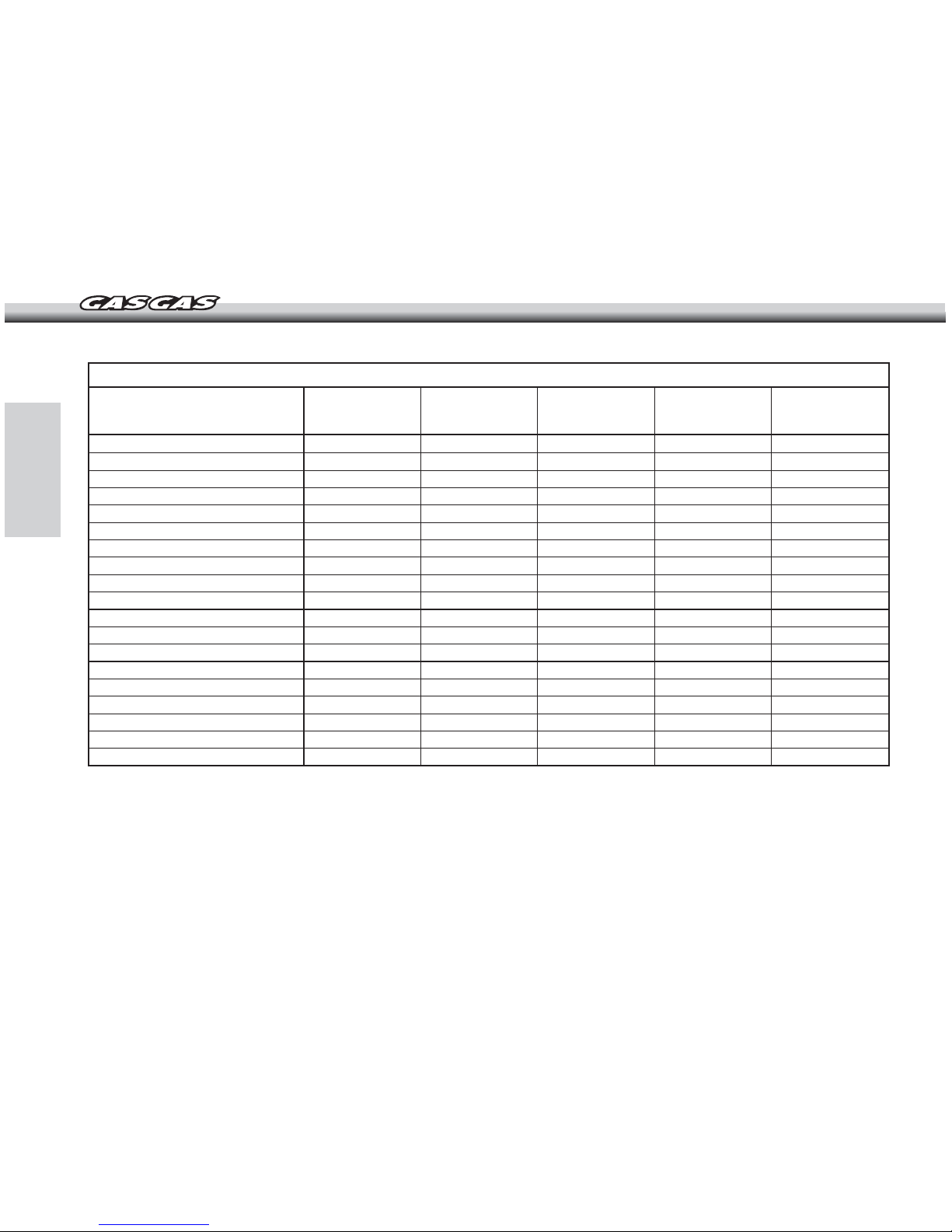
-18-
The maintenance and adjustments in this table are easy to follow and must be carried out to keep the motorcycle in good running condition.
NOTE: (*) Inspect and carry out these operations only if it is necessary.
Item
Brake caliper piston seal & dust seal
Brake hose and pipe
Spoke tightness and rim runout
Lubricate drive chain
Drive chain
Drive chain wear
Chain slider
Front fork
Front fork oil
Nuts, bolt, fasteners
Fuel hose
Fuel system
Steering play
Rear sprocket
General lubrication
Steering bearing
Wheel bearing
Swingarm and linkages
Rear shock absorber oil
MANTENANCE SCHEDULE
Check / Inspect Change / Replace Apply grease /
Lubricate
Adjust
-
-
1 fill up
-
1 fill up
-
5 fill ups
1 fill up
5 fill ups
7 fill ups
-
1 fill up
5 fill ups
5 fill ups
-
10 fill ups
5 fill ups
Every 2 years
-
-
1 fill up*
-
-
5 fill ups
5 fill ups*
When necessary
5 fill ups*
7 fill ups*
-
5 fill ups*
-
-
10 fill ups*
5 fill ups*
2 years*
-
-
-
1 fill up
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
5 fill ups
10 fill ups
-
5 fill ups
-
Clean
Every 2 years
Every 4 years
1 fill up*
-
-
5 fill ups
5 fill ups*
When damaged
Every year
5 fill ups*
7 fill ups
10 fill ups
-
5 fill ups*
-
-
10 fill ups*
5 fill ups*
2 years*
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
When necessary
-
-
-
When necessary
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 21
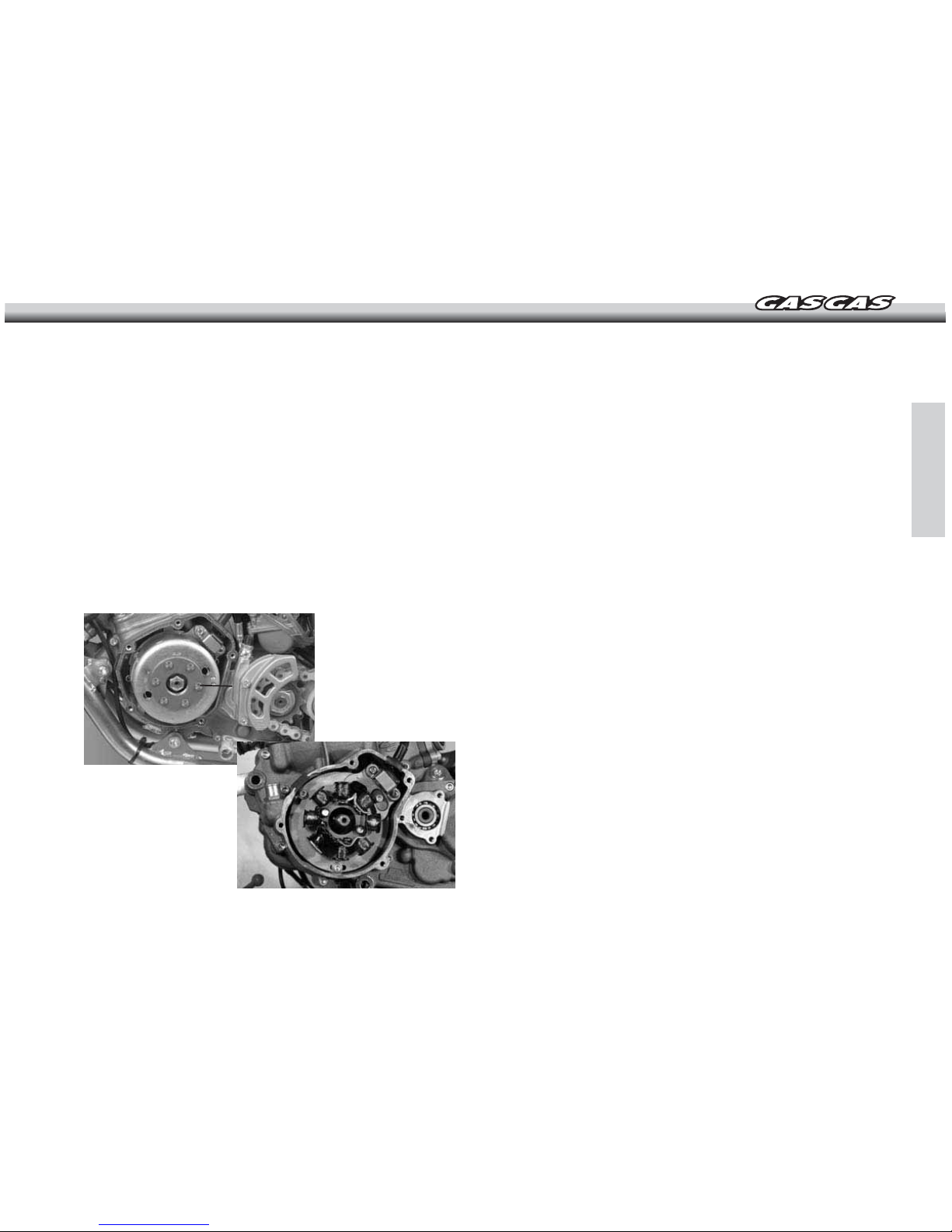
-19-
- If the marks are not aligned, loosen the magnetic inertia wheel
screws and turn it.
- Tighten the screws securely.
- Install the magnetic flywheel cover.
NOTE
Engine tune-up can be adjusted to match the rider´s preferences
and skills.
- Remove the magnetic flywheel cover.
- Loosen the stator screws.
- Adjust the engine tune-up by changing the position of the stator
within prudent limits
NOTE
For the best engine performance, it is very important to adjust
the engine tune-up within the set of limits described.
- Tighten the stator screws.
- Install the magnetic flywheel cover.
- Test ride the motorcycle and readjust the engine tune-up, if
necessary.
COOLING SYSTEM
Radiator Hoses
Check the radiator hoses for cuts or deterioration, and the connections
for looseness and leaks.
Radiator
Check the radiator fins for obstructions (insects or mud). Remove
any obstructions with a stream of low water pressure.
ELECTRONIC IGNITION
This motorcycle uses a capacitor discharge ignition system (CDI).
The ignition system should never require adjustment unless the
stator of the magnetic flywheel was incorrectly installed during engine
reassembly.
If necessary, inspect and adjust as follows:
Adjustment
- Remove the magnetic flywheel cover (A).
- Make sure that the mark on the stator plate is aligned with the
mark on the crankcase.
125 cc
200 / 250 / 300 cc
(A)
Page 22
-20-
CAUTION
If high water pressure is used the radiator fins could be damaged
and impair the radiator effectiveness.
Do not obstruct or deflect airflow through the radiator by installing
unauthorized accessories. Any interference with the radiator airflow
can lead to engine overheating and damage.
Coolant information
To protect the cooling system aluminum parts (engine and radiator)
from rust and corrosion, the use of corrosion and rust inhibitors
chemicals in the coolant is essential. If rust inhibitors were not used,
over a period of time the radiator will be corroded. This will clog the
tubes of the cooling system.
CAUTION
Use of incorrect coolant solutions will cause engine and cooling
system damage.
Use coolant containing corrosion inhibitors made specifically for
aluminum engines and radiators in accordance with the instructions
of the manufacturer
.
WARNING
Chemical liquids are harmful to the human body. Follow manufacturer
instructions.
CAUTION
Distilled water must be used with corrosion inhibitors and the
antifreeze in the cooling system. If tap water is used in the system,
the cooling tubes can be clogged and reduce the cooling system
efficiency.
If the lowest ambient temperature encountered falls below the freezing
point of water, protect the cooling system. Use a permanent type of
antifreeze in the cooling system (distilled water and ethylene glycol
and corrossion inhibitors for aluminium engines and radiators).
For the coolant mixture ratio under extreme conditions, choose the
mixture ratio listed on the container for the lowest ambient temperature.
CAUTION
Permantent types of antifreeze have anticorrosion and anti-rust
properties. When it is diluted excessively, it loses its antifreeze and
anticorrosion properties. Mix in accordance with the instructions of
manufacturer.
Liquid recommended
Permanent type of antifreeze (distilled water and ethylene glycol)
plus corrossion inhibitors for aluminium engines and radiators.
NOTE
Initially, at the factory a permanent type of antifreeze is installed
in the cooling system. It is colored green, it contains a 50%
solution of ethylene glycol, and has a freezing point of –35 ºC.
Coolant recommended
Coolant absorbs excessive heat from the engine and transfers it to
the air at the radiator. If the coolant level is low, the engine overheats
and may suffer severe damage. Check the coolant level each day
before riding the motorcycle. Add liquid recommended if the level is
low (see next page).
Page 23

-21-
Total quantity
Mix antifreeze and distilled water 1:1 (distilled water 50%, antifreeze
50%).
Capacity: 1.1 L
Coolant Replacement
Coolant should be changed periodically to ensure long engine life.
- Wait for the engine to cool completely.
- Place the motorcycle in riding position.
- Remove the radiator cap.
- Place a container under the coolant drain screw, and drain the
coolant from the radiator and engine by removing the drain screw
(B) at the bottom of the water pump cover (A). Wash off immediately
any coolant spilled on the chassis, engine, or wheels.
WARNING
To prevent severe scalding do not remove the radiator cap or try to
change liquid, when the engine is still hot. Wait until it cools.
Coolant level
- Place the motorcycle in riding position.
- Turn the radiator cap (A) counterclockwise and wait a few seconds
until vapors inside are released. Then push and turn it further in
the same direction and remove the cap.
NOTE
Check the level when the engine is cold.
- Check the coolant level. The coolant level should be just at a level
below de cap rubber seal.
- If the coolant level is low, add the correct amount of coolant
through the filler opening.
(1). Coolant level.
(2). Filler opening.
125 cc.200 / 250 / 300 cc.
(B)
(A)
(A)
(B)
Page 24

Standard Spark Plug
125 cc 0.7-0.8 mm
200 / 250 / 300 cc 0.7-0.8 mm
The spark plug should be removed periodically to check its gap. If
the plug is oily or has carbon deposits, clean it with a sandblaster.
After removing the abrasive particles, the spark plug must be cleaned
using a wire brush or a similar tool. Measure the gap with a feeler
gauge, if incorrect adjust the gap by bending the side electrode. If
the spark plug electrodes are corroded or damaged, or if insulator
is cracked, replace the plug.
NOTE
Inspect every 30 hours and change every 60 hours.
To find out whether the right heat range plug is being used, remove
it and inspect the ceramic insulator around the center electrode. If
the ceramic is light brown, the spark plug is correctly matched to
engine temperature. If the ceramic is whie, the spark plug should
be replaced with the next colder plug. If the ceramic is black, the
spark plug should be replaced with the next hotter plug.
NOTE
If the engine performance drops, replace the spark plug first to
recover its output.
TRANSMISSION
For the transmission and clutch to function properly, maintain the
transmission oil level at the optimum level and change it periodically.
A motorcycle with insufficient transmission oil, deteriorated or
contaminated can accelerate wear and tear and cause transmission
damages.
WARNING
If coolant gets on the tires will make them very slippery and can
cause an accident.
- Visually inspect the old coolant. If whitish spots are observed in
the liquid is a clear indication that the aluminum parts in the cooling
system are corroded. If the coolant is brown, iron or steel parts
of the system are rusting. In both cases, flush the cooling system.
- Check the cooling system for damage, leaks or missing gaskets
in the cooling system.
- Install the water pump cover drain screw with the specified torque
values shown in the table. Always replace the gasket with a new
one.
Drain plug tightening torque (refer to torque table)
Water pump screw: 9 Nm
- Fill the radiator up to the edge of the cap with coolant, and install
the radiator cap.
- Inspoect the cooling system for leaks.
- Start and warm up the engine, then stop the engine.
- Check the coolant level after the engine cools down. Add coolant
up to the cap.
SPARK PLUG
The standard spark plug is a shown in the table and should be
tightened to 27 Nm.
-22-
Page 25

Oil change
NOTE
The engine must be completely cool and then warm up the
engine again for a few minutes to normal operating temperature,
to register the correct engine oil temperature and to obtain an
accurate oil level measurement.
- The transmission oil should be changed periodically to ensure
long engine life.
- Warm up the engine for 5 minutes so any oil sediment will float.
- Stop the engine, and place an oil pan under the engine.
- Remove the drain screw (see previous photo) and place the
motorcycle in riding position to allow the oil to drain out.
- Clean the drain screw magnet of any iron particles.
- Tighten the oil drain screw with its O-ring to 20-Nm.
- Remove the oil filler opening plug (C) and pour 900 cc of new
transmission oil for the models 200 / 250 / 300, and 750 cc for
model 125.
- Check the oil level, after kicking the kick-start pedal 3 or 4 times.
- Install the oil filler opening plug.
-23-
Oil level inspection
- Wait a few minutes if the motorcycle has been operating.
- If the level is low, add the necessary quantity of oil by opening the
plug (C). Use the same type and oil manufacturer used currently
with the engine.
Transmission Oil Viscosity: SAE 10W30
Capacity: 750 cc (EC 125)
900 cc (EC 200-250-300)
- Check the oil level
through the
inspection window
in the lower right
hand side of the
engine (A).
- Oil level must be
kept between the
maximum and
minimum marks.
-
If the lever is too
high, you have to
remove the excess
oil through the drain
plug
(B).
(A)
(B)
(C)
(C)
200/250/300 cc.125 cc.
Page 26

-24-
AIR CLEANER
A clogged air cleaner restricts the engine air intake, increasing fuel
consumption, reducing engine power, and causing spark plug fouling.
WARNING
A clogged air cleaner may allow dirt and dust to enter the carburetor
and stick the throttle open. This could cause an accident.
A clogged air cleaner may allow dirt and dust to enter the engine
causing excessive wear and tear and other damages.
Do not omit checking the element, before and after each race or
practice session. Clean it if necessary.
Element Cleaning
WARNING
Clean the element in a well-ventilated area, and make sure that
there are no sparks or flame anywhere near the working area (this
includes any appliance with a pilot light). Do not use gasoline to
clean the element because could cause an explosion.
To access the air filter, remove the seat by removing the bolt that
secures it.
- Place a lint-free towel in the intake port of the carburetor so no
dirt is allowed to enter the carburetor.
CAUTION
Do not turn the filter since it can be easily damaged or torn.
- Wipe out inside the air cleaner hoousing with a clean damp towel.
- Pull the cage (B) out
of the air cleaner (A).
- Squeeze it dry with a
clean towel. Do not
wring the element or
blow it dry since it can
be damaged.
- Clean the filter using
a soft bristle brush in
a bath of filter cleaning
fluid.
- Remove the cover.
- Remove the screw
(A) and remove the
filter (B).
(B)
(A)
Page 27

-25-
- If the free play cannot be set by adjusting the cable, remove the
cable protector in the throttle body. Make the necessary free play
adjustments with the tensor at the end of the cable, tighten the
locknut, and reinstall the protector.
CARBURETOR
Idle speed adjustment
Is carried out using the air screw (A) and idle screw (B).
- First turn in the air screw until it is loose, then tighten it 1 1/2 turns.
- After thoroughly warming up the engine, turn the idle adjusting
screw to obtain the desired idle speed. If there are no idle
preferences, turn the screw until the engine stops.
- Tighten lightly the idle screw..
- Open and close the throttle a few times to make sure the idle
speed does not change. Readjust if necessary.
- With the engine idling, turn the handlebar to each side. If handlebar
movement changes the idle speed, the throttle cable may be
improperly adjusted or routed incorrectly, or it may be damaged.
Be sure to correct any of these conditions before riding.
- Inspect the filter for damage such as tears, hardening, or shrinkage.
If damaged, replace it or it will allow dirt into the carburetor.
- Apply grease to all connections and screws in the air cleaner and
intake ports.
- Install the air filter in the motorcycle and make sure it is correctly
secured.
THROTLE CABLE
- Check that the throttle grip turns smoothly.
- Check that the throttle grip has 2-3 mm of free play.
- If the free play is incorrect, loosen the locknut on the upper end
of the throttle cable, and turn the adjuster to obtain the correct
amount of free play.
- Tighten the locknut again.
- Install the filter in the
cage and pack the
filter lip with grease
(A), to ensure good
sealing and prevent
dirt entrance.
(A). Adjuster.
(B). Locknut.
(C). Throttle grip.
(A). Air screw.
(B). Idle screw.
Page 28

EXHAUST SYSTEM
The exhaust and the muffler reduce the noise and send gases away
from the rider.
If the exhaust is badly damaged, dented, cracked or rusted, replace
it with a new one. Replace the muffler fibre if the exhaust noise
becomes too loud or if the engine performance drops.
Muffler replacement
- Remove the retaining screws
(A) of the muffler (B) and
remove the muffler towards
the rear.
- Separate the silencer from
the joint -arrow-.
- Replace the muffler and reinstall the assembly.
WARNING
Riding with a damaged throttle cable could be dangerous.
CLUTCH
The clutch lever should have a maximum play of 3 mm. This margin
increases with the wear on the clutch plate.
To adjust, proceed as follows:
- Use bolt A to adjust the lever’s range of movement to the rider’s
convenience.
- Adjust the play of the lever using bolt B.
WARNING
- Maintain the clutch lever with the play shown, otherwise the
performance and useful life of the clutch may be adversely affected.
- The EC 2006 model uses mineral oil GRO ULTRA 5 for the clutch
hydraulic circuit.
- Tank C must not be filled with liquid from the models of previous
years.
-26-
- Remove the retaining screws of the right side number-posting cover .
(A)
(B)
Page 29

(A). Rivets.
(B). Cover.
Changing the silencer packing
- Remove all cover rivets with a drill.
- Remove the inside core of the muffler.
- Replace the muffler fibre by wraping it around the inner tube.
- Reinstall the assembly.
DRIVE CHAIN GUIDE
The drive chain must be checked, adjusted, and lubricated in
accordance with the Maintenance Schedule. If the chain is worn or
adjusted incorrectly (either too loose or too tight) the chain could
become loose or break. Replace the chain, if necessary.
WARNING
A chain that breaks or becomes loose could snag on the engine or
on the rear wheel, severely damaging the motorcycle and causing
it to go out of control
30-50 mm.
-
27-
EC Model
MC and SM Models
Drive Chain Slack Inspection
The space between the chain and the swingarm at the same height
of the chain slider should be 30-50 mm. Rotate the rear wheel to
find the place where the chain is tighter. Adjust the drive chain if it
has too much or too little slack.
In addition to checking the slack, rotate the rear wheel to inspect for
damaged rollers, loose pin and links, unevenly or excessively worn
teet, and damaged teeth.
Page 30

-28-
(A)
(B)
Drive Chain Slack Adjustment
- Loosen the rear axle nut (A).
- Turn the nuts on the chain adjusting tensors (B) until the drive
chain has a gap of 30-50 mm between the chain and the swing
arm. To keep the chain and wheel aligned, the left chain tensor
should aligned with the right chain tensor.
WARNING
Misalignment of the wheel will result in abnormal wear and may
cause an unsafe riding condition.
NOTE
Wheel alignment can also be checked using the string metod.
- Tighten the chain tensor nuts (B).
- Tighten rear axle nut to 98 Nm.
- Rotate the wheel, measure the chain slack again at the tightest
position, and readjust if necessary.
WARNING
If the axle nut is not securely tightened an unsafe riding condition
may result.
Drive chain, chain guide, chain slider, and rear sprocket teeth.
When the chain is worn so much that it is more than 2% longer than
when new, it is no longer safe for use and should be replaced.
Whenever the chain is replaced, inspect both the engine output
pinion and rear sprocket teeth, and replace them if necessary. Worn
sprocket teeth will cause a new chain to wear quickly.
NOTE
When a part ir worn, replace it with a genuine part for maximum
resistance and safety.
To minimize any chance of the master link coming apart, the m
aster
link clip must be installed with the closed end of the «U» facing in
the direction of the chain rotation.
(A). Clip.
(B). Direction of rotation
Page 31

Chain Guide Slider
Visually inspect the upper and lower chain slider at the location of
the swingarm. If damaged or worn, replace it with a new part.
(A). Chain Guide Slider.
(B). Swingarm.
Pinion Teeth, Pinion Sprocket and Sprocket Wear
Visually inspect the pinion teeth. If they are worn or damaged, replace
the the pinion or the sprocket.
Lubrication
Lubrication is necessary after riding through rain or in the mud, or
any time that the chain appears dry. A heavy oil is preferred to a
lighter ol because it will stay on the chain longer and provide better
lubrication.
Apply oil to the sides of the chain rollers for better oil penetration.
Wipe off any excess oil.
HANDLEBAR
To suit various riding positions, the handlebar position can be adjusted
front to rear.
Handlebar position adjustment
Loosen the handlebar holder (A) screws (B), turn the handlebar and
place it in the desired position.
-29-
(A)
(B)
(A). Apply oil.
Page 32

Rear brake pedal position
When the brake pedal is in rest position, there should be a free play
of 10 mm.
Check the brake for good braking power and no brake drag.
WARNING
If the brake pedal feels spongy when it is applied, there might be air
trapped in the brake pump or the brake may be defective. Since it
is dangerous to operate the motorcycle under such conditions, have
the brake checked inmediately.
-30-
Tighten the bolts, front first and then the rear, to 25 Nm of torque.
BRAKES
Disc and disc pad wear is automatically compensated for and has
no effect on the brake lever or pedal action. So there are no parts
that require adjustment on the brakes except brake lever free play
and brake pedal position
Front brake lever free play
Adjust the front brake lever (A) to match your requirements. To
adjust, loosen the nut (B). After adjustment, tighten it securely. Then
check that the brake response is correct.
If the handlebar is
installed correctly,
there will be an
even gap at the
front and rear after
tightening (A).
(B)
(A)
(A). Brake pedal.
(B). 10 mm free play.
(A)
(B)
Page 33

-31-
Brake fluid
Inspect the brake fluid level and change it periodically. The brake
fluid should also be changed if it becomes contaminated with dirt or
water
.
Liquid recommended
Use D.O.T 3 or D.O.T 4.
Brake fluid level inspection
The front (A) and rear (B) reservoirs must be kept more than half
full with brake fluid. If the brake fluid is insufficient, add brake fluid.
CAUTION
Do not spill brake fluid onto any painted surface. Do not use fluid
from a container that has been left open or that has been unsealed
for a long time. Check for fluid leakage around the fittings. Check
for brake hose damage.
WARNING
Do not mix different types of fluid. Change the brake fluid in the
reservoirs completely if the same type of brake fluid is not available.
Brake wear inspection
If the thickness of either pad, front and rear, is less than 1 mm,
replace both pads as a set. Pad replacement should be carried out
only by an authorized GAS GAS dealer.
STEERING
The steering should always be kept adjusted so that the handlebar
will turn freely but without free play.
EC and MC Models
SM Model
ALL Models
(B)
Page 34

-
32-
To check the steering adjustment use a stand under the chassis,
and lift the motorcycle off the ground. Move the handlebar lightly to
either side; if the handlebar continues moving under its own
momentum, the steering is not too tight. Squatting in front of the
motorcycle, grasp the lower end of the front fork (at the axle), and
push and pull the fork (as shown on the previous photo); if free play
is felt, the steering is too loose.
If the steering needs adjustment
- Use a stand or a special support to stabilize the motorcycle.
- Raise the front wheel off the ground.
- Remove the handlebar (A) by loosening the handlebar holder
screws and removing the upper holders.
- Loosen the steering stem nut (B).
- Loosen the screws of the suspension top bridge (C) and remove
it.
- Turn the steering adjustment nut with the special wrench to obtain
the proper adjustment.
- Install the suspension top bridge (D).
- Tighten the steering stem nut, and front fork washers and screws.
Steering nut: 44 Nm (4.5 Kgm).
Suspension top bridge: 22 Nm (2.25 Kgm).
- Check the steering again, and readjust if necessary.
- Install the removed parts.
STEERING BLOCKAGE
As indicated by its name, this mechanism allows us to lock the
handlebar. Is located in the steering pipe.
You have to turn the handlebar completely to the right, next insert
the key, turn left, press, turn right and remove the key.
(A). Steering lock.
(A)
Page 35

-33-
CAUTION
Never leave the key in the latch. If the steering is turned to the left
with the key inerted in the latch it will be severely damaged.
FRONT FORK
The front fork should always be adjusted for the rider´s weight and
road conditions. The adjustments must be performed in 4 steps:
- Air pressure: Air pressure affects the fork travel. The air pressure
increases as the fork heats up, in other words it varies as a function
of time of operation. We do not recommend using air pressure,
because the suspension has been designed to work without air
pressure.
- Rebound and compression dampening adjustment: This adjustment
affects how quickly it rebounds. The fork rebound dampening
adjuster has 18 positions. The tightest position is full hard. The
position 12 from close is the standard setting, and position 18 from
close is full soft.
- Oil level adjustment: The effects of higher or lower fork oil level
are only felt during the final 100 mm of fork travel. A higher oil level
will make the fork rebound faster. The lower the oil level is the fork
rebound will be slower.
- Fork spring: Optional springs are available that are softer and
stiffer than standard.
Air Pressure
The standard air pressure in the fork is atmospheric air pressure.
The air pressure increases as the fork heats up, because of this the
fork action becomes harder.
- Using a stand under the frame, and stabilize the motorcycle.
- Place a support under the engine so that the front wheel is raised
off the ground.
- Remove the purge screw at the top of the front fork to bleed the
air out.
Rebound Dampening Adjustment
- To adjust the rebound, turn and hand tighten the adjuster knob (A)
located at the top of the front fork.
- Adjust the rebound to suit the rider’s preference under determined
conditions.
(A). Air purge screw.
(A). Adjuster knob.
(A)
Page 36

-34-
Use the standard settings to adjust the rebound (turn it 6 positions
counterclockwise).
CAUTION
The left and right fork tubes must be at the same level and aligned
with the top bridge.
Compression dampening adjustment
- To adjust the compression, turn with your finger the adjusting knob
located at the top of the front fork.
- Adjust the compression to suit the rider’s preference under
determined conditions.
- Use the standard measures to adjust the compression (turn it 6
positions counterclockwise).
Oil level adjustment
- Place a stand under the motorcycle engine (to keep it in a straight
and stable position).
- Remove the handlebar screws and remove the handlebar.
- Remove the suspension caps from the tubes.
- Compress the front fork slowly all the way.
- Lift the fork springs.
- Hold the suspension tube cap with a spanner, the loosen the cap
locknut.
- Remove the suspension tube caps.
- Remove the suspension srping guide.
- Use a wrench to remove the fork springs.
- Put the oil level gauge on the upper portion of the fork tube, and
measure the distance from the top of the fork tube to the oil level.
Standard oil level
110 mm
Fill the oil.
Adjust the oil level as required within the adjustable range using the
following oil:
Oil recommended by the manufacturer.
Page 37

-35-
- Pull the hydraulic rod out slowly.
- At this time, the fork oil pours out of the hydraulic rod hole, keep
it raised to let it drain until it stops.
- Install the fork spring (1) inside the fork tube.
- Tighten the suspension spring and insert the wrench (5) in the
locknut (2) to lock the cap (3).
- Install the suspension cap (3) in the fork tube and tighten it to 29
Nm.
- Mount the other fork.
- Install the parts removed.
(1). Spring.
(2). Locknut.
(3). Suspension cap.
(4). Cap wrench.
(5). Locknut wrench.
Suspension tube spring
Different springs are available in accordance with the rider´s weight
or the road conditions.
- Harder springs make the fork stiffer, and rebound action quicker.
- Softer springs make the fork softer, and rebound action slower.
Suspension top bridge position adjustment
Make sure the front tire does not rub against the fender when the
fork tubes are compressed fully. Make this adjustment to a minimum
of 5 mm.
CAUTION
The suspension tubes, both right and left, must be adjusted evenly.
Page 38

(1). Suspension top bridge position.
REAR SUSPENSION
The rear suspension is composed of the shock absorber, swingarm,
linkages and torque rod.
Generally speaking, the operating characteristics are similar to the
front fork. But its unique characteristic is that it has, besides the
shock absorber, an articulated quadrilateral composed of the linkages
and torque rod.
To match various riding condition types, the shock absorber spring
can be adjusted or replaced with an optional one. Also the dampening
force can be easily adjusted, this feature makes it unnecessary to
change oil viscosity.
-36-
(A). Extension adjuster.
Shock absorber extension adjustment
To adjust, turn by hand the extension adjuster in the lower part of
the shock absorber until a “CLICK” is heard.
Total number of adjustments possible is: 40 "CLICKS".
Rebound adjustment standard measures:25 “CLICKS”.
(Counterclockwise from fully closed position).
High compression adjustment
Use a screwdriver for adjustments. The control has 4 complete turns.
As the control is closed the compression will be harder, on the other
hand as it is opened it will be softer. Normally, the standard
measurement would be 1,5 turns from the completely closed position.
(1)
(A). Extension adjustment.
(A)
Page 39

Suspension spring
The standard spring is 5.2 (250 cc, 300 cc) - 5.0 (125 cc, 200 cc) -
5.6 (MC). The spring length preloaded with the shock absorber at
rest is 258 mm.
- Tighten the locknut securely.
- After adjustment, move the spring up and down to make sure that
the spring is fully seated.
- Install the parts removed.
Rear shock absorber spring replacement
Harder and softer springs are available. If the standard spring is not
adequate for your purpose, select a proper one according to the
rider´s weight and the road conditions.
- Using the harder spring:The rebound is quicker.
- Using the softer spring:The rebound is slower.
NOTE
Refer to the suspension adjustments on page 47.
-37-
(A). Nut.
(B). Spring.
(C). Locknut.
Spring adjustment
- Remove the seat and side covers.
- Loosen the air cleaner duct clamp screw.
- Remove the muffler.
- Remove the subframe with the air cleaner box.
(C)
(A)
(B)
(A). High and low
compression
adjustment.
(A)
Page 40

-38-
WARNING
Improper installation of the rear shock absorber spring may cause
the spring and any of its related parts to be ejected at high velocity.
Always wear eye and face protection. The installation of these parts
should be performed by an authorized dealer.
WHEELS
Tires
- Tire pressure affects traction, and tire life.
- Adjust the tire pressure to match road conditions and rider’s
preference, but do not stray too far from the recommended pressure.
NOTE
Tire pressure should be checked when the tires are cold before
riding.
Road conditions
- When the road is wet, muddy, sandy or slippery, reduce the tire
pressure.
- On gravel roads or hard terrain, increase the tire pressure.
Spokes and wheel rims
The spokes on both wheels must be tightened evenly and should
not be allowed to have free play. Unevenly tightened or loose spokes
will cause wheel rim runout, the other spokes will be stressed and
might break.
Wheel rim runout
Place a dial indicator at the rim side, and spin the wheel by hand
to measure the axial runout.
Place the dial indicator at the inner circumference of the wheel and
spin the wheel, the difference between the highest and lowest
quantities is the runout.
If the runout is not excesive it can be corrected tightening or loosening
some spokes with the spoke adjusting wrench (B). If the wheel rim
is curved or bent it must be replaced.
NOTE
A welded area on the rim may indicate excessive runout.
Disregard this when measuring rim runout.
(A). Spoke adjusting wrench.
Page 41

-39-
CLEANING
1- Preparation for washing
Before washing the motorcycle, precautions must be taken to prevent
water from entering the following parts of the motorcycle.
Exhaust: Cover it with a plastic bag tightened with rubber bands.
Clutch and brake levers, hand grips, and engine stop button:
Cover these parts with plastic bags.
Air cleaner intake: Cover the opening with tape or with a rag.
2- Where to be careful
Avoid spraying water with any great force near the following
areas:
- Brake calipers and brake pump piston.
- Ignition coil or into the spark plug cap.
- Front and rear wheel hubs.
- Steering bearings.
- Rear suspension system.
- Swingarm bearings.
CAUTION
To avoid excessive ageing of the plastic parts and other washable
pieces of the motorcycle, it is suggested that these items must be
washed carefully. If the washer applies water at high pressure and/or
temperature, take the precaution of maintaining the washer outlet
gun at a distance of 30 centimeters minimum, this will ensure the
correct gloss of the plastics and maintain adherence of the selfadhesive labels that decorate the motorcycle.
3- After washing
- Remove the plastic bags, and clean the air cleaner intake.
- Lubricate the points listed in the lubrication section (see pag. 40).
- Start the engine and let it run for 5 minutes.
- Check the brakes before operating the motorcycle.
WARNING
Never wax or lubricate the brake disc. Loss of braking and an accident
could result. Clean the disc with trichloroethylene or acetone.
Page 42

-40-
BOLTS AND NUTS TIGHTENING
Every day before riding, check the tighteness of the bolts and nuts described here. Also check that all other fasteners are in place and in good
condition.
1- Front and rear wheel.
2-
Front fork.
3- Handlebar.
4- Clutch lever holder screw.
5- Cylinder head bolt.
6- Spark plug.
7- Cylinder nuts.
8- Air cleaner box holder bolts.
9- Trailing plate bolts.
19- Seat mounting bolts.
20- Subframe bolts.
21- Rear shock absorber bolts.
22- Exhaust mounting bolts.
23- Suspension top bridge bolts.
24- Steering stem nut.
25- Brake lever bracket screw.
26- Rear axle nut.
27- Linkage mounting bolt.
10- Spokes.
11- Front axle bolt.
12- Brake hose screw.
13- Radiator bracket bolts.
14- Engine holder bolts and nuts.
15- Gearshift pedal bolt.
16- Subframe bracket bolt.
17- Chain guide bolts.
18- Chain adjuster nut.
28- Rear brake pedal bolt.
29- Torque rod mounting bolt.
30- Swingarm shaft nut.
31- Kick-start pedal bolt.
32- Kick-start pedal nut.
33- Front brake hose fastening screw.
26 27 28 29
31,32
10
11
12
13 14 15 16 17 18
1
2
3,4 5,6,7 8 9 1
23,24,25
19 20 22 21
30
33
Page 43

-41-
Torque Values Table
Tighten all bolts and nuts to the proper torque using an adequate wrench. A bolt or nut loose might damage the motorcycle or even cause an
accident.
F
R
A
M
E
PART NAME
Brake caliper mounting bolt
Disc mounting screw
Engine mounting bolt
Front axle bolt
Front brake hose mounting bolt
Suspension clamp bolt
Steering nut
Rear axle nut
Rear brake pedal bolt
Subframe bracket bolt
Rear shock absorber bolt
Rear drive plate nut
Spokes
Steering stem nut
Torque rod bolt
Rear linkage bolt
Nm
25
10
36
51
6
29
98
98
9
26
39
29
1.5
4
81
81
E
N
G
I
N
E
PART NAME
Cylinder head screws
Cylinder nut
Engine drain plug
Kick-start pedal bolt
Kick-start pedal nut
Gearshift pedal bolt
Spark plug
Water pump cover drain plug
Crankcase screws
Starter pedal plate screw
Ignition motor stator screws
Ignition motor coil nut
Selector spring fixing screw
Primary nut
Clutch spring screws
Valve control support screws
Valve control nuts
Reed valve screws
Thermostat housing screws
Clutch housing screws
Valve housing screws
Ignition housing screws
Nm
25
25
20
20
25
15
27
9
10
8
8
40
15
40
10
10
8
10
10
10
8
10
Page 44

(D) (C)
-42-
LUBRICATION
Lubricate the points shown here, apply either engine oil or grease,
periodically or whenever the vehicle has been operated under wet
or rainy conditions, and especially after using high water pressure.
Before lubricating each part, remove any rusty spots with rust remover
and wipe off any grease, oil, or dirt.
General lubrication
- Clutch lever (A).
- Front brake lever (B).
- Rear brake pedal (C).
- Rear brake bearing (D).
- Gearshift pedal (E).
Use an aerosol with a tube for pressure lubrication:
Apply grease inside
the gas cable (A).
Page 45

Drive Chain Lubrication
Lubricate the drive chain after driving on wet terrein or when the
chain looks dry. A high viscosity oil is preferred rather than a lower
viscosity because it will stick to the chain longer and lubricate the
chain better.
Apply oil to the sides of the chain rollers (A) for better oil penetration.
Wipe off any excess oil.
(A). Apply grease.
TUNE-UP
1. CARBURETOR TUNE-UP
Mixture
First step is to establish a basic knowledge on the identification and
operation of carburetor components. Change settings in accordance
with the temperature:
-43-
NOTE
The main jet should be increased or decreased 1 to 5 sizes and
tested until the engine gives maximum power.
Main jet
It has a great overall effect. The number stamped on lower part of
the main jet indicates the size of the hole metering fuel. A greater
number corresponds to a bigger hole which supplies more fuel.
WARNING
Gasoline is extremely flammable and can be explosive under certain
conditions. Always stop the engine and do not smoke. Make sure
the area is well ventilated and free from any source of flame or
sparks (this includes any appliance with a pilot light).
(A)
Condition Mixture Change setting
Cold air Lean Rich
Warm air Rich Lean
Dry air Lean Rich
Low altitude Standard Standard
High altitude Rich Lean
(A). Main jet.
(A)
Page 46

-44-
Idling nozzle and mixture adjustment screw
Controls the mixture from the closed position to an opening of 1/8
of throttle range, but has little effect on full throttle. To adjust the
mixture in this range, the air screw can be turned to change the air
flow through the circuit, or the slow jet can be changed to provide
more or less fuel. Start by turning the air screw. Screwing it in richens
the mixture. The air screw must be turned from a lightly seated
position. Make changes in 1/2 turn increments. If turning the screw
between 1 and 2.5 turns does not give the desired results, change
the slow jet (B) one step and tune up with the air screw (A).
Carburetor jet needle
The jet needle and jet needle hole together have their greatest effect
in the one-half throttle range. The needle moves in and out of the
jet needle hole; since the needle is tapered, its position in the jet
determines the amount of fuel allowed to flow.
There are five grooves in the upper section of the needle where a
circlip fits. This clip locates the needle in the throttle valve and
determines its relative position in the jet needle hole, and provides
a rich mixture. Moving the clip to the top will provide a lean mixture.
Change the clip position one step at a time. The straight area of the
needle affects throttle valve response in the small openings range.
Test runs with the motorcycle
- Warm up the engine with the carburetor at the standard setting,
and inspect the operating conditions of the spark plug.
- Test-ride the motorcycle with the throttle opened.
Symptoms of improper settings
If your motorcycle exhibits one of the following symptoms the changes
must be adjusted. Before attempting any changes, make sure that
everything else is in good operating condition.
(B)
Clip position
Jet needle
number
Right section
(A)
Page 47

Check the condition of the spark plug, make sure the ingnition timing
is correct, service the air cleaner element, decarbonize the exhaust
tube
If you machine has run properly up to this point, it is possible that
the problem is elsewhere; changing the carburetor settings in such
a case would probably be a waste of time.
- Set the carburetor so that the engine delivers satisfactory power
with the throttle valve opened.
- If the air-fuel mixture is too lean, the engine tends to overheat and
may be seized. On the other hand, if it is too rich, the spark plug
easily gets wet and causes misfires. The proper mixture varies
depending on atmospheric conditions. Taking these conditions into
consideration, adjust the carburetor settings properly.
NOTE
Keep in mind that the carburetor components that regulate fuel
flow and the screw that control the flow of air must be tight.
The standard competition measurements EC 250 are an example.
-45-
Correction factors:
(For altitude or temperature changes).
1. Find the correction factor to adjust the carburetor.
Example: 1000 meters altitude with an air temperature of 35°C. The
correction factor is 0.94.
2. Using the correction factor, select the correct slow jet and main
jet.
Example: For a correction factor of 0.94 multiply the jet size by that
number.
Main jet: # 180 x 0.94 = # 170.
3. Find the correction factor on the Jet Needle / Air Screw chart and
change the jet needle clip position and air screw opening as indicated.
- Jet needle clip setting: from the 3rd groove to the 2nd groove.
- Air screw opening: 1 1/2 + 1 turn = 2 1/2 turns out.
NOTE
For the following recommendations to be accurate, you must
use the standard settings as a base-line. Also do not change
any of the settings until you have determined what changes are
necessary. All specifications are based on the use of the fuel
and oil specified.
FUEL
Throttle valve
Idle jet
Needle
Main Jet
UNLEADED
7
h2
N1EF
180
Correct
Too lean
Too rich
Insulator is dry & light tan color
White color insulator
Insulator is wet & black color
Replace the main jet to one
step larger
Replace the main jet to one
step smaller
Spark plug condition
Page 48

-46-
40
(104)
30
(86)
20
(68)
10
(50)
0
(32)
-10
(14)
0.86 0.88 0.90 0.92 0.94 0.96 0.98 1.00 1.02 1.04 1.06
Sea Level
1000 m (3200 ft)
2000 m (6400 ft)
3000 m (9600 ft)
T
E
M
P
E
R
A
T
U
R
A
(ºC)
(ºF)
FACTOR DE CORRECCIÓN
ALTITUD
NEEDLE POSITION / AIR SCREW OPENING
CORRECTION
FACTOR
NEEDLE
POSITION
AIR SCREW
OPENING
1.06 or HIGHER
LOWER CLIP 1
POSITION
TIGHTEN 1 TURN
1.06 - 1.02
SAME
TIGHTEN 1/2
TURN
1.02 - 0.98
SAME
SAME
0.98 - 0.94
SAME
LOOSEN
1/2 TURN
0.94 or LOWER
RAISE CLIP
1 POSITION
LOOSEN
1 TURN
ALTITUDE
CORRECTION FACTOR
T
E
M
P
E
R
A
T
U
R
E
°C
(°F)
TT
Page 49

-47-
Final del
recorrido
Recorrido suspensión
Nivel alto
Nivel estándar
aceite
Nivel bajo
Fuerza
2. SUSPENSION TUNE-UP
This adjustment is very critical because if an improperly tuned
suspension will keep even the best rider from attaining the full benefit
of his machine´s ability. Check the suspension in accordance to the
rider and the terrain conditions.
- If the motorcycle is new, break-in the suspension with at least one
hour of riding before making any setting evaluations or changes.
- The three factors which must be considered are rider’s weight,
rider’s ability, and terrain conditions (additional influences include
the rider´s style and position on the motorcycle).
- If you have a problem, test by changing your riding posture or
position so it can be deduced.
- Adjust the suspension to match the rider´s strong points. If he is
fast through the corners, adjust the suspension to allow fast cornering.
- Make setting changes in small increments; a little bit goes a long
way, and it is very easy to overadjust a setting.
- The front and rear suspension should be balanced; when one is
changed, the other might need to be changed similarly.
- When evaluating suspension performance the rider must make
every effort to ride consistently and recognizing the effects of his
input; such things as changes in rider position and increasing fatigue
may lead to incorrect judgments about necessary setting adjustments.
- When the proper settings have been determined for a particular
terrain, the settings should be written down for later reference when
returning to the same type of terrain.
- Before making any changes and also every 5 fill-ups, lubricate the
swingarm bearings, torque rod, linkages and O-rings, this precaution
will prevent excesive friction that can affect the suspension
performance.
Front fork
The oil level is adjustable. A change in the oil level will not affect the
lower part of travel, but it will have an affect on the upper part of
travel:
Force
Suspension travel
End of
travel
High level
Low level
Standard oil
level
- When the oil level is raised:
The spring effects become more progressive, and the front fork
action feels harder at the end of travel.
If the front suspension is making jounce stops, raise the oil level 10
mm. This increase will provoke a change in upper part of travel of
the spring.
- When the oil level is lowered:
The spring effects are less progressive, and the front fork action
does not become hard at the end of travel.
- Change the oil level correctly and the fork will work more at the
end of fork travel.
Oil level adjustment
Adjust the front fork oil level (refer to the maintenance chart).
Page 50

-
48
-
Troubleshooting Improper Settings
Listed below are some symptoms of improper suspension settings
and the most likely means of correcting them.
The proper settings can be achieved by applying the information in
this chapter in a scientific manner. Take time to think about the
changes you believe necessary, check them against the symptoms
and cures described here, and make the changes in small increments,
and take notes on the changes and their effects.
Symptoms of the front fork
- The front fork is too stiff:
1. Incorrect rebound adjustment.
2. The springs are too hard.
3. Too much oil.
4. Oil too dense.
- The fork becomnes hard at the end of travel:
1. The oil level is too high.
- The fork operates but slides hard:
1. Oil too dense.
2. Degraded fork oil.
- Too soft:
The fork shakes excessively when slowing down or applying brakes
1. Fork oil level is low.
2. Springs are too soft.
3. Oil too light.
4. Degraded fork oil.
5. Incorrect rebound or compression.
Symptoms of the rear shock absorber:
- Too hard:
1. The suspension is too stiff
• Compression damping is too high.
• Spring is too hard.
2. Is hard to ride
• Unbalanced condition between the spring and rebound
(too low).
3. The spring is hard or preloaded too much
- Too soft:
On landing after a big jump, the suspension makes jounce stops.
1. Soft spring or compression damping is too soft.
2. Degraded shock absorber oil
Determining the proper settings:
- Standard Settings
From the factory, the machine is set up for an average-weight rider
with average riding abilities. Hence, if the actual rider’s weight or if
his riding experience and abilities are considerably superior or below
the average, ii is necessary to make adjustments to the suspension.
- Readjustment of the suspension:
Ground surface
Smooth Soft spring
Rough Hard spring
Page 51

-49-
Riding experience
Beginner: Soft spring with rebound.
Experienced: Harder spring.
Rider's weight
Heavy: Hard spring.
Light: Soft spring.
Type of racing circuit
- Many corners:
Lower the front end slightly (Raise the fork tubes 5 mm).This increases
agility.
- Fast course with many jumps:
Raise the fornt end slightly (Lower the fork tubes 5 mm).
-
Deep potholes or sandy ground:
Raise the front end slightly to gain stability.
After making such preliminary adjustments, begin the actual on-track
testing and evaluation.
CAUTION
1- Make changes one step at a time.
2- Make sure the rider is consistent in this evaluation.
3- A change in the front suspension requires a change in the rear,
and vice versa.
Front and rear compatibility:
Use this procedure to determine if the suspension is balanced. Place
the motorcycle upright. While standing next to the right side of the
motorcycle, hold the front brake and press the rear brake pedal firmly.
If the motorcycle maintains its level attitude as the suspension is
compressed, the spring rates are well balanced. Sit astride the
motorcycle and take a riding posture. Next check to see that the
motorcycle is in a horizontal position. If one end drops noticeably
more than the other, the front and rear are not compatible and must
be readjusted to achieve a better balance.
This is one of the most effective adjustment procedures but suspension
settings will vary depending on the conditions at the terrain and the
rider´s preferences.
Does the motorcycle skids when driving down hill or when
accelerating out of a curve?
Front fork is too soft.
1. Increase the compression or rebound damping.
2. Increase the oil level 10 mm.
3. Use a harder spring, or increase spring preload.
Does the front end tends to turn inward?
Front fork is too soft.
1. Increase the compression or rebound damping.
2. Increase the oil level 10 mm.
Does the front end slips when entering in a curve?
1. Decrease the compression or rebound damping.
2. Bleed air trapped in the fork.
3. Decrease the oil level 10-20 mm.
4. Use a softer spring.
Page 52

-50-
Does the front fork fails to respond to small potholes while
managing wide turns?
Front Fork is hard:
1. Decrease the compression or rebound damping.
2. Decrease the oil level 10 mm.
3. Use softer duty spring.
Does the rear end jumps when braking over potholes?:
The shock absorber probably has too little rebound damping.
- Increase the rebound damping.
Does the rear tire lacks traction when coming out of corners?:
- The shock absorber is too hard:
1. Decrease the rear shock absorber spring.
2. Decrease the compression damping.
3. Use a softer spring.
Does it land on the front wheel in high speed jumps?:
(there may be a problem with the driver’s posture)
Rebound damping too soft or hard spring.
1. Increase the rebound damping.
2. Decrease the shock absorber spring preload.
3. Decrease the compression damping.
Does the suspension jounce stops at front and rear of the
motorcycle in high speed jumps?:
(If this occurs 1 or 2 times in the same lap of the race)
Front and rear suspension system are too soft:
1. Front: Increase the oil lever and / or use a harder spring.
2. Rear: Increase compression damping or use a harder spring.
NOTE
After any adjustment, check front and rear compatibility.
Adjustments that depend on the conditions of the jounce stops
(rear shock absorber).
- Suspension jounce stops at low speed, increase the spring preload
to the maximum setting.
- Jounce stops after 3 or 4 successive jumps, decrease the rebound
damping.
NOTE
The rear shock absorber due to its setting possibilities may
mislead some riders.
a) The rear shock absorber does not jounce stop when the spring
is correct for the total weight of the machine and rider.
b) A jounce stop sensation of the shock absorber may be caused
by the rider’s inexperience in riding a machine with a harder
spring.
Observe the rear end while it jumps; if it does not approach the
stopper, try lowering the sping preload.
Gearshift
Select the ratio development. Preconditions:
Race conditions: vary the transmission replacing the rear pinion.
Fast race: use pinions with less teeths.
Winding road or soft or sandy uphill surface: use pinions with more
teeths.
- If the straight portion of the course is long, the ratio development
can be extended and due to this the speed increases.
- When the course has many corners or uphills or is wet, the ratio
development will be reduced so that gear shifting is possible at
low speed.
Page 53

-51-
- Actually, the speed can be changed depending on the terrain
conditions on the day of the race and therefore, be sure to run
through the racing circuit prior to a race and set the machine
suitable for the entire course.
- If the straight portion of a course on which the machine can be run
at maximum speed is long, the motorcycle should be set so that
the maximum machine speed can be developed towards the end
of the straight course, but care should be taken not to over-rev the
engine.
- It is very difficult to adjust the motorcycle to be best setting for all
portions of the circuit. Therefore, determine which circuit portions
will have the greatest effect on lap time and set the motorcycle for
these portions. In this manner the motorcycle will deliver best
performance for the entire circuit.
Special care according to the terrain conditions.
1. In dry, dusty conditions special care must be given to keep the
air cleaner element clean since it accumulates dirt and the engine
operates too “rich”.
2. When riding on wet heavy clay the mud adheres to the tires and
other parts of the vehicle. The mud can add significantly to the
weight of the vehicle and therefore reduce performance. Take
care so that the engine is not overheated. The same applies
when driving in deep sand.
3. In muddy or sandy conditions loosen the drive chain slack to
release its tension.
4. Check chain and sprocket - pinion wear frequently when riding
in mud or sand since wear is increased under these conditions.
SPARE PARTS AVAILABLE
Refer to the sparts parts catalogue.
FINAL RECOMMENDATIONS
PREVENTIVE ADVICE
Before you ride the motorcycle, take all the time you may require
to check your motorcycle, carry out the periodical upkeep and check
all functions. In different sections of this manual you will find data
and work specifications that must be done at an autorized GAS GAS
dealer, because of this and to extend the useful life of the motorcycle,
all periodical inspections must be carried out by specially trained
professionals at a GAS GAS Post-Sale Service Shop.
Poor maintenance work of the motorcycle or not taking proper care
of any problem, even if its is a small concern, can cause severe
personal injury and may lead to death.
SAFE RIDING OF YOUR MOTORCYCLE
Safe riding of a motorcycle does not only depend on the vehicle.
The driver’s intelligence and common sense are key factors to be
taken into consideration. It is recommended that you practice your
favorite sport wearing all the necessary safety equipment (helmet,
protection gear, boots, etc.).
LEGAL ADVICE
In the interest of technical development we reserve the right to
modify the construction, the equipment and accesories of the
motorcycle. It is understood that all measurements, weights and
power data must include their respective tolerances. The photographs
included in this manual may not match the model you have purchased.
The descriptions and the illustrations may vary depending on the
volume of equipment and accesories of your motorcycle and also
of the versions exported. Because of this, there can be no liability
except in case of errors, misprint or omission.
GAS GAS MOTOS, S.A. reserves the right to make changes and/or
modifications at any time without notice.
Page 54

-52-
HOMOLOGATION (SM y EC):
The vehicle you have just acquired has been homologated under the directives of the EU and complies with all the homologation requirements
demanded.
Compulsory homologation elements required, among others, when travelling on a public road and to meet periodical vehicle inspection
approval at state controlled plants are listed below.
Among other requirements, all homologation components are identified with a determined and registered mark.
Each one of the homologation components must form part of the vehicle and in case of loss, breakage or malfunction it is recommended that
the owner contact his official dealer to correct this problem.
List of elements required: Quantity / motorcycle
- Manufacture identification plate 1
- Catalyzed exhaust 1
- Muffler 1
- Carburettor jets 1
- Front and rear turn signals 4
- License plate holder 1
- Speedometer 1
- Electrical installation, homologated lights 1
- Horn 1
- Rearview mirror 2
- Antitheft system 1
- Antimanipulation plate (125 cc version) 1
- Secondary air valve 1
- Air filter restiction 1
-
Throttle limiter (EC 200, 250, 300) 1
Page 55

PREPARATION FOR COMPETITION
(1). Check:
1. Front axle and bridges nuts tightness.
2. Front fork clamp bolts tightness.
3. Handlebar clamp bolts tightness.
4. Throttle grip screws tightness.
5. Throttle grip operation and apply grease.
6. Front and rear brake hose inspection.
7. Front and rear brake fluid level.
8. Front and rear brake disc and caliper inspection.
9. Front and rear brake operation test.
10. Fuel tank inspection.
11. Verify the installation of all cables.
12. Engine mounting bolts tightness.
13. Verify output pinion.
14. Gearshift pedal bolts tightness.
15. Transmission oil level.
16. Battery charge.
17. Throttle body.
18. Linkage tie rod mounting bolts tightness.
19. Linkages mounting bolts tightness.
20. Rear shock absorber bolts tightness.
21. Swingarm shaft nut tightness.
22. Rear axle nut tightness.
23. Rear sprocket bolts and nuts tightness.
24. Rear brake pedal operation.
25. Seat inspection.
26. Wheel spokes tightness.
27. Front and rear tire air pressure.
28. Drive chain slack.
29. Coolant level.
(2). After 1 day of racing competition:
1. Clean the air cleaner element.
2. Adjust drive chain slack.
3. Tighten rear sprocket nuts.
4. Tighten all spokes.
5. Check the tires air pressure.
6. Tighten front and rear axle nuts.
7. Tighten swingarm shaft nut.
8. Tighten muffler and exhaust bolts and nuts.
9. Tighten front and rear fender mounting bolts and nuts.
10. Tighten fuel tank and seat mounting bolts and nuts.
11. Check brakes.
12. Check steering free play.
13. Fill fuel tank .
14. Check coolant level .
(3). Maintenance after riding on dusty course:
If dirt or dust gets into the engine, the crankshaft will wear out
excessively. After riding, inspect the crankshaft. If the crankshaft is
worn beyond the service limit, change it
(4). Maintenance after riding in rain or muddy course:
1. Apply grease to swingarm pivot and the suspension system.
2. Inspect the drive chain and rear sprocket and pinion wear.
3. Clean the sprocket and pinion.
4. Check the cylinder–piston and crankshaft bearings.
5. Grease the throttle grip and cable.
-53-
Page 56

STORAGE
For extended storage of the motorcycle, you must do the following:
- Clean the motorcycle thoroughly.
- Start the engine for about 5 minutes to warm up the transmission oil and then
drain it (refer to the transmission section).
- Fill with new transmission oil.
- Empty the fuel tank (gasoline will deteriorate if left too long).
- Disconnect the battery.
- Lubricate the drive chain and all cables.
- Cover all unpainted metal surfaces with a coat of oil to prevent rust, do not
apply oil to the brakes and rubber parts.
- Cover the exhaust pipe with a plastic bag to prevent corrosion.
- Place the motorcycle in such a position so that the wheels do not touch the
ground (if this is not possible, place cardboards under the wheels).
- Cover the motorcycle to protect it from dust and dirt.
When starting off after an extended storage:
- Remove the plastic bag from the exhaust pipe.
- Tighten the spark plug.
- Fill the fuel tank.
- Check all points marked in the section “Daily Inspection Before Riding”.
- General lubrication.
- Connect the battery.
-54-
Page 57

-55
-
GAS GAS MULTIFUNCTION INSTRUCTIONS
The multifunction apparatus, which is waterproof, has 2 LED indicators
on a central indicator screen.
This central indicator screen, made of liquid crystal and with
illumination, gives information about the rpm, speed, distance
travelled, total kilometres travelled, time, average speed, maximum
speed, ambient temperature, length of time with motor running and
total time. The odometer and the control for the total time with motor
running save the data to the memory, even when the device is
switched off. When the multifunction apparatus is not activated, it
displays a clock. The value of the wheel circumference can be altered,
as well as the system of measurement (metric or British).
The ambient temperature is displayed on the upper left-hand part of the
screen.
The screen can display the engine temperature from an optional
temperature sensor. If this is too high, a warning LED lights up in yellow.
If the rpm are too high, the second warning LED lights up in red.
1. Yellow warning LED
2. Red warning LED
3. Right-hand button
4. MODE button
5. Left-hand button
6. Central display screen
Page 58

Initial voltage: 9 - 400 V AC/DC..
Speed sensor: Non-contact magnetic sensor.
Tachometer input: Electrical pulse sensor.
Wheel circumference adjustment: 1 mm – 3.999 mm (1 mm increments).
Operating / storage temperature: from 0 ºC to 60 ºC (from 32 ºF to 140 ºF) / from -20 ºC to 80 ºC (from -4 ºF to 176 ºF).
Battery / life: 3V CR2032 / Approx. 1 year
-56
-
Technical characteristics
FUNCTIONS SYMBOL TECHNICAL INCREMENTS PRECISION
CHARACTERISTICS
CURRENT SPEED SPD: 4 - 399.9 kmph or mph 0.1 kmph or mph +/- 0,1%
TACHOMETER RPM 0 -19999 rpm 10 rpm +/- 0,1%
TACHOMETER BAR 0 -12000 rpm. Variable +/- 0,1%
MAXIMUM SPEED MS 4 - 399.9 kmph or mph 0.1 kmph or mph +/- 0,1%
DISTANCE TRAVELLED DST 0.0 - 19999 km or mi. 0.1 kmph or mph +/- 0,1%
TIME RUNNING TT 0 - 9999 hours 59 minutes 1 second +/- 0.1%
ODOMETER ODO 0.0 – 999999 1 +/- 0,1%
OPERATION TIME RT 0 - 999 hours 59 minutes 1 minute +/- 0.1%
OPERATION TIME ART 0 - 9999 hours 59 minutes 1 minute +/- 0,1%
ACCUMULATED
CLOCK 00:00:00 12:59:59 or 23:59:59 +/- 0,1%
BATTERY LOW LO Approximately 1 year life +/- 0,1%
TYRE SIZE 0 - 3999 mm
Page 59

-57-
Functions
RPM: Bar
Tachometer with bar graph. The bar graph of the tachometer displays
up to 12,000 rpm.
RPM: Digital Tachometer
The rpm are shown on the right side, second row. The digital
tachometer displays up to 12,000 rpm. The tachometer signal can
be captured from the sparkplug cable.
Gear change indicator according to rpm
This function permits setting an indicator for changing gears at a
specific rpm level. The red LED warning light flashes when the rpm
reaches the specific level and stops flashing when the gear is
changed.
SPD: Speedometer
The speedometer information appears in the centre of the screen.
It shows up to 399.9 kmph or mph.
MS: Maximum speed gauge
It shows the highest speed reached since the last resetting of the
data.
DST: Distance travelled
This appears on the right side, in the second line of the screen. The
TRIP function contains the vehicle’s accumulated mileage since the
last RESET operation.
ODO: Odometer
It shows the total mileage accumulated by the vehicle. The data is
stored in the memory, even when the device is not running.
ART: Time of use controller
Calculates the total time in operation. It starts counting from the
moment the motor is turned on.
RT: Total time of use controller
It calculates the vehicle’s operation time since the last RESET
operation. It starts counting from the moment that movement begins.
The data is stored in the memory, even when the device is not
running.
12/24 hour clock
It shows the time in either 12 or 24 hour formats.
Ambient temperature / engine temperature gauge
The ambient temperature is displayed on the upper left-hand part of the
screen.
The screen can display the engine temperature from an optional
temperature sensor. If this is too high, a warning LED lights up in yellow.
High rpm gauge / Gear change warning according to rpm
If the rpm are too high, the second warning LED lights up in red.
This function permits setting an indicator for changing gear at a
specific rpm level The red LED warning light flashes when the rpm
reaches the specific level and stops flashing when the gear is
changed.
Page 60

-58-
Setting the multifunction display parameters
After confirming each value, the display goes from one screen to the next until all have been displayed. If no button is pressed, the display
returns to the home screen after 15 seconds.
Activating adjustment mode
To start setting mode for the
multifunction display, press
buttons 1, 2, and 3
simultaneously for 3 seconds,
and then release.
Selecting the values for the
wheel circumference
Enter the value for the wheel
circumference by pressing button
1 in succession. To go on to the
next digit, press button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Note:
If you do not know the value of
the wheel circumference, see
the section on "Measuring the
wheel circumference"
Selecting the speed unit
To change between kmph and
mph, press button 1.
Confirm the selection by pressing
button 2.
Selecting the time format
To change between the 12 and
24 hour clock, press button 1.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Page 61

-59-
Setting the time
Enter the value for the time by
pressing button 1 in succession.
To go on to the next digit, press
button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Setting the pulse per
revolution (PPR)
Note:
This step is only to be taken on
vehicles that change the type of
PPR pulse at a specific number
of rpm.
If you do not know this value,
press button 2 to go on to the
next screen.
Enter the value by pressing
button 1 in succession. To go on
to the next digit, press button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Setting the pulse per
revolution (PPR)
The gauge receives one
electrical pulse for each
revolution on the engine (PPR).
Default value for 2 and 4 stroke
engines: 1 PPR.
Enter the value by pressing
button 1 in succession. To go on
to the next digit, press button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Setting the pulse per revolution
(PPR)
Note:
This step is only to be taken if a
value of 0 was entered in the
previous step.
Default value: 1.0
If you do not know this value,
press button 2 to go on to the
next screen.
Enter the value by pressing button
1 in succession. To go on to the
next digit, press button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Page 62

-60-
Selecting the temperature unit
To change the temperature
display between ºC and ºF, press
button 1.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Selecting the danger
temperature
Note:
This step can only be taken on
vehicles fitted with the optional
temperature sensor.
When the engine temperature
exceeds the set value, the
warning LED on the right lights
up.
Default value: 110 °C (230ºF)
Enter the value by pressing
button 1 in succession. To go on
to the next digit, press button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Selecting the warning
temperature
Note:
This step can only be taken on
vehicles fitted with the optional
temperature sensor.
When the engine temperature
exceeds the set value, the
warning LED on the left lights up.
Default value: 90 °C (190ºF)
Enter the value by pressing
button 1 in succession. To go on
to the next digit, press button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Selecting the rpm for a gear
change
When the set rpm is reached,
the left-hand warning LED
flashes to show that the gear
must be changed.
Default value: 6000 rpm
Enter the value by pressing
button 1 in succession. To go on
to the next digit, press button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Page 63

Selecting the danger rpm
When the set rpm is reached,
the right-hand warning LED
flashes to show that the rpm on
the engine are too high.
Default value: 10000 rpm
Enter the value by pressing
button 1 in succession. To go on
to the next digit, press button 3.
Confirm by pressing button 2.
Resetting the display functions after each use of the vehicle.
After each use of the vehicle, the following functions can be reset
simultaneously:
- Maximum speed
- Distance
- Chronometer
- Maximum temperature
- Maximum rpm
Confirm the reset by pressing buttons 1 and 2 simultaneously.
Total reset of the display
Press the RESET button, using a suitable object. The display will
start from zero, except for the data for total accumulated distance
and time.
Internal battery
The display is powered by an internal 3 V battery, type CR2032.
When the voltage in the internal battery drops below 2.45V, the
screen displays LO.
To change the battery, open the cover behind the display, and use
a coin to unscrew it counter-clockwise. Make sure that the positive
terminal on the battery is facing upward.
-61-
Page 64

-62-
Screen options
The multifunction display shows all the information on three different
screens.
While in motion, screens 1 and 2 are on display. Screen 3 is displayed
for 3 seconds, and then returns to screen 1.
To change from one screen to another, press button 2 ("Mode") in
succession.
To edit the distance travelled (DST), keep button 3 pressed down.
Screen 1:
Screen 1 shows the following information:
- Speed, distance travelled, time, ambient temperature, tachometer (bar).
Screen 2:
Screen 2 shows the following information:
- Speed, digital tachometer, time in motion, time in operation, engine
temperature*, tachometer (bar).
Screen 3:
Screen 3 shows the following information:
- Maximum speed, danger rpm, accumulated time in operation,
odometer, maximum temperature*.
*Optional
Lighting
The display is powered by an internal 3 V battery, type CR2032.
To change the battery, open the cover behind the display, and use
a coin to unscrew it counter-clockwise. Make sure that the positive
terminal on the battery is facing upward.
When the display is powered by the internal battery only, the screen
lights up partially for 3 seconds when the button is pressed.
If the lighting is connected to the 12V system on the vehicle, it will
be brighter and stay on for up to 20 minutes after the vehicle has
come to a full halt.
Sleep Mode
If the multifunction display does not receive any information for 20
minutes (signal from wheels turning or a button pressed), the screen
goes off, showing only the time. When the vehicle starts or a button
is pressed, it will start up again.
Measuring the wheel circumference
Method 1
Measures the diameter of the front wheel. Multiply the diameter by
3.14 and, if necessary, convert the measurement into mm by
multiplying the figure obtained by 25.4. The measurement obtained
is the size of the wheel circumference.
Method 2
On a smooth, flat surface, make a mark on the side of the tyre where
it touches the ground. Move the vehicle forward until the tyre has
made a complete turn, and the mark is back at the lowest point.
Make a new mark on the ground at this point.
Measure the distance between the marks on the ground and, if
necessary, convert the measurement into mm by multiplying the
figure obtained by 25.4. The measurement obtained is the size of
the wheel circumference.
To obtain a more precise measurement, the driver must remain on
the vehicle while taking measurements.
Page 65

TROUBLESHOOTING
NOTE
This is not an exhaustive list of malfunctions, it only shows the most common problems.
MALFUNCTION
POSSIBLE CAUSE
REMEDY
Engine does not crank
Engine cranks but then stops
Engine overheating
The engine operates irregularly
- Seized crankshaft.
- Seized cylinder / piston / jornal bearing.
- Seized transmission assembly.
- Motorcycle inactive too long.
- Wet or fouled spark plug.
- Flooded engine.
- Incorrect air/fuel mixture.
- Exhaust valve stuck open
- Incorrect air supply.
- No fuel.
- Insufficient cooling liquid in the circuit.
- Radiator is dirty or partially restricted.
- Spark plug dirty, or misadjusted.
- Poor contact with the spark plug cap or
cable loose in cap.
- Go to a specialized workshop.
- Go to a specialized workshop.
- Go to a specialized workshop.
Drain old fuel out of the tank. With the fuel tank filled with
new fuel, the engine will start immediately.
- Clean and dry or replace the spark plug.
- In order to "relieve the engine", accelerate to max. speed,
press the starter pedal 5 or 10 times. Then, start the engine
as described above. If the engine fails to start, remove the
spark plug and dry it.
- Clean the fuel tank air vent. Adjust the air cleaner duct.
- Verify the exhaust valve and repair as necessary.
- Close the starter. Clean fuel tank air vent. Adjust the air
cleaner duct.
- Fill up the fuel tank.
- Fill up cooling liquid, verify the refrigeration system
watertightness.
- Clean radiator fins or replace it.
- Verify the spark plug condition and clean it accordingly,
tighten or replace it.
- Verify the spark plug cap condition. Replace if deteriorated.
1
2
3
4
-63-
Page 66

-64-
MALFUNCTION POSSIBLE CAUSE REMEDY
The engine operates irregularly
Engine lacks power or poor
acceleration
Abnormal engine noise
Detonations from the exhaust
pipe
White smoke coming out of the
exhaust pipe
Brown smoke coming out of the
exhaust pipe
- Ignition rotor damaged.
- Water in fuel.
- Fuel supply defective.
- Dirty air cleaner.
- Leaking or deteriorated exhaust system.
- Dirty carburetor jets.
- Worn or damaged crankshaft bearings.
- Clutch slips.
- Ignition problem.
- Overheating.
- Carbon build up in combustion chamber.
- Incorrect octane or poor quality gasoline.
- Damaged spark plug or incorrect
specifications.
- Deteriorated exhaust system gaskets.
- Deteriorated cylinder head gasket (water
leakage into the cylinder).
- Incorrect throttle valve cable adjustment.
- Restricted air cleaner.
- Main jet set too high.
- Replace the rotor.
- Drain the fuel tank and fill up with new fuel.
- Clean the fuel system and verify its operation.
- Clean or replace the air cleaner. Verify its operation.
- Verify if the exhaust system is damaged. Replace the
muffler fiberglass packing, if necessary.
- Disassembly the carburetor and clean all jets.
- Replace the crankshaft bearings.
- Verify the clutch operation. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Go to a specialized workshop.
- Refer to section 5.
- Clean the combustion chamber.
- Drain all gasoline and fill up with a higher octane fuel.
- Replace the spark plug with a new one of the correct type.
- Verify if the exhaust system is damaged. All gaskets must
be in perfect conditions, otherwise replace them with new
ones if necessary.
- Replace the cylinder head gasket. Go to a
specialized workshop.
- Readjust the throttle valve cable.
- Clean or replace the air cleaner. Go to a specialized
workshop.
- Verify main jet operation. Go to a specialized workshop.
4
5
6
7
8
9
Page 67

-65-
MALFUNCTION POSSIBLE CAUSE REMEDY
Gears do not engage correctly
Jumps out of gear
Clutch slips
The motorcycle is unstable
- Clutch does not disengage.
- Bent or seized shift fork.
- Gear seized at the transmission.
- Damaged gearshift lever.
- Broken or loose selector position spring.
- Broken spring in the reverse selector
mechanism.
- Broken spring in the reverse selector
mechanism.
- Broken gear drum.
- Broken spring in the gear selector ratchet.
- Shift fork worn at the gears.
- Worn gear grooves.
- Worn gear dogs.
- Worn shift drum groove.
- Worn shift fork shaft.
- Broken selector drum position spring.
- Broken gears.
- No clutch lever free play.
- Worn clutch friction plate.
- Worn clutch center hub.
- Broken or weak clutch spring.
- Unevenly worn clutch discs.
- Cable interferes with the handlebar turns.
- Steering stem locknut too tight.
- Damaged or worn steering bearings.
- Bent steering stem.
- Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace the shift fork.
- Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace the gearshift lever.
- Adjust or replace the selector position spring.
- Replace the spring in the reverse selector
mechanism.
- Replace the spring in the reverse selector
mechanism.
- Replace the gear drum.
- Replace the spring in the gear selector ratchet.
- Replace the shift fork.
- Replace. Go to a specialized workshop
- Replace. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace shaft. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace the spring. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Go to a specialized workshop.
- Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace the clutch friction plate.
Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace the clutch center hub.
- Adjust or replace the clutch spring.
- Replace the clutch discs. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Move or loosen the cable just a little.
- Loosen the steering stem locknut.
- Replace the steering bearings.
- Replace the steering stem. Go to a specialized workshop.
10
11
12
13
Page 68

-66-
- Excessive front fork oil.
- Front fork oil viscosity too high.
- Bent front fork.
- Tire air pressure set too high.
- Incorrect rear shock absorber adjustment.
- Insufficient front fork oil.
- Front fork oil viscosity too low.
- Bent front fork.
- Tire air pressure too low.
- Incorrect rear shock absorber adjustment.
- Incorrect drive chain adjustment .
- Worn drive chain.
- Worn rear sprocket teeth.
- Insufficient drive chain lubrication .
- Incorrect rear wheel alignment.
- Insufficient front fork oil.
- Weak or broken front fork spring.
- Worn disc brake.
- Pad installed incorrectly or surface glazed.
- Damaged cylinder.
- Improperly tightened brackets, nuts, bolts.
- Worn tire, and worn swingarm or its
needle bearings.
- Wheel rim off-centre.
- Incorrect wheel alignment.
MALFUNCTION POSSIBLE CAUSE REMEDY
Shock absorber set too hard
Shock absorber set too soft
Abnormal motorcycle noises
Handlebar vibration
- Pour excess oil until reaching the correct oil level.
- Drain fork oil and fill with correct fork oil viscosity.
- Replace the front fork. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Check tire air pressure.
- Adjust rear shock absorber.
- Fill with fork oil until reaching the correct oil level.
- Drain fork oil and fill with correct fork oil viscosity.
- Replace the front fork. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Check tire air pressure.
- Adjust the rear shock absorber.
- Adjust the drive chain.
- Replace the drive chain, rear sprocket and the secondary
transmission pinion.
- Replace the rear sprocket.
- Lubricate with appropriate chain oil.
- Align the rear wheel. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Add front fork oil until reaching the correct level.
- Replace the front fork spring.
- Change the disc brake.
- Reinstall or replace pad.
- Replace the damaged cylinder.
- Verify and adjust to the correct torque values.
- Replace worn parts with new ones.
- Centre rim.
- Verify wheel spokes tension. Readjust if necessary.
14
15
16
17
Page 69

-67-
MALFUNCTION POSSIBLE CAUSE REMEDY
Handlebar vibration
Motorcycle pull to one side
Brakes do not operate correctly
Blown light bulbs
Lighting system does not
operate
- Excessive steering axles tolerances.
- Loose handlebar bracket, and loose
handlebar stem locknut.
- Bent chassis.
- Incorrect steering adjustment.
- Bent steering stem.
- Bent front fork.
- Incorrect wheel alignment.
- Worn discs.
- Leaking brake fluid.
- Deteriorated brake fluid.
- Broken pump piston.
- Incorrect brake adjustment.
-
Voltage regulator faulty.
- Blown lighting relay fuse.
- Tighten steering bracket and steering stem locknut to the
correct torque values.
- Tighten steering bracket and steering stem locknut to the
correct torque values.
- Replace the chassis. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Adjust the steering. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace the steering stem. Go to a specialized workshop.
- Replace the front fork.
- Align the wheels.
- Replace the discs.
- Verify the brake circuits. Replace the damaged or broken
parts.
- Drain the brake fluid and fill with the new fluid recommended
by the manufacturer.
- Replace the pump piston.
- Adjust brakes.
- Remove the seat and the fuel tank, and check all
connections, check the voltage regulator and the fuses in
the fuse box .
- Remove the seat, the fuse box cover, and replace the
fuse.
17
18
19
20
21
Page 70

-68-
Front right
indicator
Front brake
sensor
Front
sidelight
Dipped/
Full beam
Headlights
Front left
indicator
Speed
sensor
Ignition coil
Magnetic
flywheel
Indicator relay
Horn
Power
controller
Magnetic
flywheel
Rear brake
sensor
Rear right
indicator
Rear
sidelight/
brake light
Rear left
indicator
ELECTRIC SCHEMAS
Bl Black
Bu Blue
Gr Grey
Br Brown
W White
R Red
G Green
P Pink
O Orange
Y Yellow
V Violet
GL Bright green
Page 71

-69-
WARRANTY TERMS AND CONDITIONS
(According to Law decree 23/2003 on the 10th of July, covering Warranties on Consumer Item Sales)
Warranty terms of the manufacturer GASGAS Motos, S.A.
The company GAS GAS MOTOS, S.A. (hereafter referred to as “GG”), with this present document guarantees the consumer,
the purchaser of a vehicle manufactured by GG, that both the materials and the manufacturing are free of defects in
accordance with the highest standards of quality. Consequently, GG with this document guarantees the consumer (hereafter
referred to as the “purchaser”), in accordance with the conditions set out below, the repair, free of charge, of any defect in
materials or that might result from faulty manufacture that is detected in a new motorcycle within the period covered by
this Warranty and with no limit on the number of kilometres covered or hours of use.
Warranty Period
The period covered by this Warranty will begin on the day of delivery of the vehicle to the purchaser by a GG authorised
dealer, or in the case of demonstration models, on the date in which the vehicle is used for the first time.
The seller will be responsible for any unwarranted faults that become apparent within the period established in the Law
decree 23/2003 on the 10th of July covering Warranties on Consumer Goods Sold from the time of delivery and in accordance
with the Directive 1999/44/EC for other members of the European Community. For countries outside the European Community,
the Warranty Period will be determined by the existing regulations in those countries. Nevertheless, should the fault appear
during the first six months after the delivery of the motorcycle, it will be presumed that the said fault existed at the time of
delivery; from the end of the sixth month onwards, the purchaser must demonstrate that the unwarranted fault existed at
the moment of delivery. During the first six months subsequent to the delivery of the repaired vehicle, the seller will be
responsible for any unwarranted faults arising out of the repair.
Any defects detected in the product must be brought to the attention of a GG authorised dealer within the Warranty Period.
If the last day of this period is a Sunday or an official holiday, the Warranty period will be extended such that the last day
of the period covered will be the first working day after the Sunday or official holiday.
Those claims under Warranty for defects not brought to the attention of a GG authorised dealer before the end of
the Warranty Period will be excluded.
Page 72

Obligation of the purchaser
GG will have the right to reject any claims under Warranty in the event that:
a) The purchaser has failed to submit the vehicle to any of the inspections and/or maintenance work required in the Users’
Manual, or has exceeded the date set for such inspections or maintenance work. Also excluded from guarantee are those
faults that appeared prior to the dates established for an inspection or maintenance work where the latter was not carried
out, or was carried out later than the date established.
b) An inspection, maintenance or repair has been performed on the vehicle by third parties not recognised or authorised
by GG.
c) Any maintenance or repair has been carried out on the vehicle that violates the technical requirements, specifications
and/or instructions indicated by the manufacturer.
d) Spare parts whose use has not been authorised by GG have been used during the course of maintenance work or repairs
to the vehicle, or in the event that the vehicle has been used with fuels, lubricants or other liquids (including, amongst others,
cleaning products) that have not been expressly mentioned in the specifications set out in the User’s Manual.
e) The vehicle has been altered or modified in any way or fitted with components other than those expressly authorised by
GG as accepted components of the vehicle.
f) The vehicle has been stored or transported in a way that is not in accordance to the corresponding technical requirements.
g) The vehicle has been used for special purposes other than ordinary use, such as competition, races or record breaking
attempts.
h) The vehicle has been directly or indirectly damaged as a result of a fall or an accident.
Warranty exclusions
The following items are not covered by this Warranty:
a) Worn parts, including, without any limitation, spark plugs, batteries, petrol filters, oil filter elements, (secondary) chains,
engine output pinions, rear sprockets, air filters, brake discs, brake pads, clutch plates and discs, bulbs, fuses, carbon
brushes, footrest rubbers, tyres, inner tubes, cables and other rubber components
b) Lubricants (for example, oil, grease, etc.) and working fluids (for example, battery liquid, coolant, etc.)
c) Inspection, adjustments and other maintenance tasks, as well as all kinds of cleaning work
d) Damage to the paint-work and consequent corrosion due to external causes, such as stones, salt, industrial fumes and
other environmental impact, or inadequate cleaning with inappropriate products
-70-
Page 73

e) Any damages caused as a result of the defects, as well as any expenses incurred either directly or indirectly as a consequence
of the defects (for example, communication costs, accommodation expenses, car hire costs, public transport costs, breakdown
truck fees,
, courier costs, etc.), as well as other financial losses (for example, those caused by the loss of the use of the
vehicle, loss of income, time lost, etc.)
f) Any acoustic or aesthetic phenomenon that does not significantly affect the condition or use of the motorcycle (for example,
small or hidden imperfections, noise or vibrations that are normal in use, etc.)
g) Phenomena that are the result of the ageing of the vehicle (for example, discolouring of painted or metallic coated surfaces).
Various
1.- GG shall have the prerogative to decide, at its own discretion, whether to repair or replace defective parts. Where parts
are replaced, ownership of the parts removed shall pass to GG without any other consideration. The GG authorised dealer,
to whom the making good of the defects has been entrusted, is not authorised to make any declarations that are binding on
GG.
2.- In case of doubt regarding the existence of a defect, or a visual or material inspection is required, GG reserves the right
to demand the return of the parts which are the object of a claim under Warranty, or to arrange an inspection of the defect
by an expert from GG. Any additional obligations arising out of guarantees on parts replaced free of charge, or any other
service rendered free of charge, are excluded from the effects of this present warranty. The Warranty on parts replaced within
the Warranty Period will end at the expiry date for the Warranty Period of the product concerned.
3.- Should it prove to be the case that a defect can not be repaired, the purchaser guaranteed shall have the right to the
cancellation of the contract (payment of compensation) or a partial refund of the purchase price (discount), instead of repairing
the motorcycle.
4.- Any claims against Warranty by the purchaser under the terms of the sale contract with the corresponding authorised
dealer shall not be affected by the terms of this present Warranty. Neither will this present Warranty affect those additional
contractual rights acquired by the purchaser under the general commercial terms and conditions of the authorised dealer.
However, such additional rights may only be exercised through claims against the authorised dealer.
5.- Should the purchaser resell the product within the Warranty Period, the duration and conditions of the present Warranty
will remain unaltered, in such a way as that the rights to make claims under the present Warranty in accordance with the
terms and conditions set out in this present document shall be transferred to the new owner of the motorcycle.
-71-
Page 74

RECOMIENDA EL USO DE ACEITE:
RECOMMENDS THE USE OF OIL:
RECOMMANDE L’USAGE DE L’HUILE:
CONSIGLIA L’USO D’OLIO:
EMPFIEHLT DEN GEBRAUCH VON ÖL:
C/ UNICEF nº 17 · Poligon Industrial Torremirona · 17190 Salt (Girona) SPAIN · Tel: +34 902 47 62 54 Fax: +34 902 47 61 60
E-mail: officegg@gasgasmotos.es / partsgg@gasgasmotos.es
AGOSTO / AUGUST / AOÛT / AGOSTO / AUGUST 2007
PU010838019
 Loading...
Loading...