Page 1

XMap 7® GIS User Guide
This user guide is a printable version of the XMap Help system. When you are using
XMap, use the Help system to take advantage of links to related Help topics.
Note: Some content from the Help system is not available in the pr int version.
WARNING: Messaging, tracking and SOS functions require an active Iridium
satellite subscription. Always test your device before you go.
This manual is provided as a convenience.
GARMIN IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR THE ACCURACY OF THIS MANUAL AND
DISCLAIMS ANY LIABILITY ARISING FROM THE RELIANCE THEREON.
Page 2

Table of Contents
Getting Started ........................................................................................................ 1
Map Legend .......................................................................................................... 28
Using the Toolbar ................................................................................................... 32
Customizing the Map and Tab D isplay ....................................................................... 42
Using Keyboard Shortcuts ....................................................................................... 55
Using Projects/Map Data ......................................................................................... 61
Working With GIS .................................................................................................. 82
Printing ............................................................................................................... 199
Finding a Location on the Map ................................................................................. 211
Using Address Book Contacts .................................................................................. 227
Searching for Phone Book Listings ........................................................................... 233
Using the Draw Tools ............................................................................................. 241
Using XData ......................................................................................................... 291
Registering Images ............................................................................................... 300
Profiling Linear Objects .......................................................................................... 306
Viewing Your Map in 3-D ........................................................................................ 315
Routing ............................................................................................................... 321
Using GPS ............................................................................................................ 340
Using Voice Navigation and Speech Recognition ........................................................ 354
Using DeLorme PN-Series GPS Devices .................................................................... 364
Using Third-party GPS Devices ................................................................................ 392
Using Small-screen Devices .................................................................................... 397
Using NetLink and MapShare .................................................................................. 398
Using GeoTagger .................................................................................................. 408
Using the XMap API Command Window .................................................................... 412
Legal Information ................................................................................................. 417
Index .................................................................................................................. 429
ii
Page 3

Getting Started
Welcome to XMap 7
For more information about XMap, visit our website at www.xmap.com.
XMap 7 GIS Enterprise, XMap 7 GIS Editor, and XMap 7 Professional provide a three-tiered
GIS solution for efficiently creating, importing, editing, classifying, querying, and sharing
your GIS data in an enterprise environment. XMap 7 is equally suited as a standalone GIS
software solution or as a supplement component to your existing GIS infrastructure.
In addition to GIS, XMap includes powerful routing and in-vehicle navigation tools;
advanced GPS support for field tracking and navigation; interoperability with Earthmate PNSeries GPS devices for field data collection and exchange of map data, waypoints, and
tracks; 3-D terrain modeling with simulated fly-over functionality; advanced printing tools;
and much more.
XMap 7 GIS Enterprise
The upper tier of the XMap suite is designed to meet the specific needs of enterprise GIS
managers who need to efficiently manage and deploy GIS data throughout a company.
XMap GIS Enterprise also includes all of the features in XMap GIS Editor. Create and
distribute GPS data collection forms to XMap Editor and XMap Professional users and PNSeries GPS owners. XMap Professional users require an XMap Forms license.
• Quickly sync layers—increased sync speed for large databases.
• Establish database permissions for Windows security groups.
• Access your existing GIS databases with ArcSDE support. Supports Oracle and SQL
Server databases.
• Ensure data integrity with check-out/check-in tools.
• Share data across the enterprise with database synchronization tools.
• Use the API Command Window to perform basic mapping functions from a third-
party application.
• Automate the import and export of standard spatial data files with the bulk
importer/exporter.
• Supports Microsoft® SQL Server® 2008.
• XMap GIS Enterprise in conjunction with multiple copies of XMap Professional
provides a complete field force GIS data collection system.
XMap 7 GIS Editor
XMap 7 GIS Editor is a perfect choice for small GIS departments or for a company or
organization that is considering the development of a GIS to increase productivity. XMap
GIS Editor also includes all the features in XMap Professional.
• Create forms in databases synchronized from an XMap Enterprise database.
• Create zero and negative polygon buffers.
• Export KML files.
• Geocode by State Plane and UTM coordinate systems.
• Cut individual GIS layers to a PN-Series GPS device for field work.
1
Page 4

XMap User Guide
• Search for GIS objects using enhanced real-time proximity search for GIS objects
using GPS Radar on the Find tab.
• Import and work with a variety of GIS file formats including, ESRI .shp and .e00;
MapInfo .mif and .tab; AutoCAD .dwg and .dxf; and more.
• Geocode your existing data in .mdb, .xls, and other formats to create GIS layers.
• Create and edit points, lines, and polygons with freehand draw tools or with precise
coordinate geometry input tools.
• Ensure the spatial integrity of your line layers w ith topological editing and edge
matching.
• Access advanced classification, annotation, buffer, and geospatial query tools.
• Create your own raster data layers with multi-point image registration.
XMap 7 Professional
XMap 7 Professional is ideally suited for field crews and mobile professionals. By offering
access to GIS data that has been processed using the GIS Editor or GIS Enterprise editions
of XMap, it provides an affordable alternative to a full-fledged GIS for use on the road and
in the field.
XMap Professional offers essential and fundamental mapping functions that include data
visualization, access to aerial and satellite imagery, address-to-address routing, annotation
tools, document linking, advanced printing, GPS support, and more. In addition, you can
view and print GIS maps created using XMap GIS Editor and XMap 7 GIS Enterprise.
• Collect and edit data using forms synchronized from an XMap Enterprise database—
XMap Forms license required.
• Optimize response time with the latest in-vehicle, voice-controlled navigation tools.
• Perform country-wide searches of address locations and points of interest.
• Easily redline data corrections to Enterprise GIS data and efficiently share these edits
with your GIS administrator.
• View your data in stunning 3-D with the latest terrain modeling technology.
• Import ESRI shapefiles into the GIS tab and apply symbolization.
2
Page 5

Getting Started
What's New in XMap 7
XMap 7 facilitates GPS data collection for mobile field workers across all industries with tools
that create and work with data collection forms.
• Embedded document support
to let your organization collect data with a GPS component. Store images, rich text
documents, spreadsheets, and other files in your database and associate them with
your GIS records.
• XMap Forms
(sold separately)–Easily create, display, or change the attributes of
records in your GIS layer using a customized electronic form alongside your map.
• Affordably automate field data collection with customized forms that match
your business requirements.
• Sync collected data with XMap OpenSpace databases.
• Use forms created in XMap on an Earthmate® PN-40 GPS device to collect
data and sync with XMap.
Note Requires one license of XMap Enterprise to create Enterprise databases and additional Forms license
for XMap Professional users.
• Earthmate PN-40 Pro firmware update
• Send individual GIS layers to a PN-40
• GPX file format support for GIS point layers and XMap Forms.
• Export
XMap created GPS data collection forms to a PN-40 and sync
with XMap.
• Easily import
• Efficiently share data with a PN-40 with the enhanced XMap Handheld Export
tab.
• GPS Radar enhancements
based on you current GPS position—includes voice support.
• Improved GIS database synchronization
• Two-way syncing allows users with specific permissions to locally edit data
and synchronize the edits with the master server.
• Faster layer sync speed for large databases.
• Extends synchronization support out to the PN-40 through XMap Forms.
• Supports Oracle and Microsoft® SQL Server® 2008 databases.
• Permissions work for groups with admin rights.
• KML support
–Export XMap OpenSpace files to KML formats—supports points, lines,
and polygons (including polygons that are bitmaps).
• Create negative and zero polygon buffers
• Geocode by State Plane and UTM coordinate systems.
• Easily establish database permissions for Microsoft Windows® security groups
• Supports new XMap World Base Map Data—1:250,000 topographic, accurate, and
seamless map of the world that includes major transportation layers, inlan d and
shoreline hydrography, jurisdiction boundaries, and major geographic features.
–XMap works with your company’s existing documents
for field work.
collected GPS point data directly into the XMap GIS tab.
–Search in real time for GIS objects within a radius range
tools
.
.
3
Page 6

XMap User Guide
How do I?
Click a question to open the related Help topic. See also, Frequently Asked Questions.
Controlling the Map
How do I pan the map?
How do I zoom the map in and out?
How do I change the map view to show the left map view, right map view, or both?
Display Preferences
How do I change the map colors?
Draw Tools
How do I add a road or trail to my map?
Searching for a Location
How do I search for a location?
GIS
How do I import a layer into a database?
How do I manage the layers in my workspace?
What is a workspace?
How do I classify a layer?
How do I create a query?
How do I use XMap Forms?
GPS
How do I start tracking with my GPS device?
How do I switch from NavMode to GPS tab view?
See also, Routing
Handheld Export
How do I use my mapping application with my PN-Series GPS?
Map Data
What is a project?
How do I add or remove base data?
How do I add data and imagery?
How do I set data as routing data?
Phone
How do I install the phone data or use it from the DVD without inst alling it?
Routing
How do I create a route?
How do I track a route with my GPS receiver?
4
Page 7
Getting Started
How can I automatically recalculate my route when I'm off course?
How can I avoid a specific area when routing?
Printing
How do I print a map?
Profile
How do I view a profile of a route I've created?
1. Center the route you want to profile on the map.
2. Click the Profile tab.
3. Select a route on the map to generate its profile. When the object is selected, it is
highlighted and the Profile graph displays in the Profile dialog area.
3-D
How do I generate a 3-D map?
How can I expand my 3-D map to fit the entire screen?
Helpful Tips
These tips may help you use the features in your DeLorme mapping program. The Did You
Know? pop-up tutorials provide hints while you are working in the application.
Tips
• To disable a specific pop-up tutorial, select the Don't Show Again check box before
you close it.
• To disable all pop-up tutorials, click the Help button
Shut Off All Pop-up Tutorials.
• To enable all pop-tutorials after you have shut off one or more, click the Help button
on the toolbar and click Reset All Pop-up Tutorials.
Control Panel
If you want to... Use this tip...
Zoom the map out/in
quickly
Pan the map quickly • Position your cursor on the edge of the map; it
Drag the map cursor in an up-left direction to zoom the
map out or drag it in a down-right direction to zoom the
map in.
becomes a white hand that you can use to drag the
map to the new location.
• With your cursor anywhere on the map, press the
CTRL key on your keyboard—the cursor becomes a
white hand. Hold down your left mouse button to drag
the map to a new location.
on the toolbar and click
Update the coordinate
format that displays in the
Control Panel
View the last map center Press the middle button in the Compass Rose in the
Update your measurement preferences at any time using
the Display tab in the Options dialog box.
5
Page 8
XMap User Guide
Control Panel to center the map on the previous map view.
This button performs an undo function for the last pan or
zoom (up to 256 times).
Draw
If you want to... Use this tip...
Create a route using a
road or trail you have
added to the map with the
Draw tab
When drawing a routable road/trail, click each existing
road it crosses to ensure that you can route on the new
road/trail. When you open a track you've imported from
your GPS device, join the imported line with existing lines
by right-clicking each intersection and selecting Manage
Draw/Join.
Find
If you want to... Use this tip...
Modify a Find search result Right-click a result item in the Find tab to add it as a
MapNote, insert it as a stop in your route, copy the
information to your clipboard, and so on.
Find a custom point of
interest (such as a Chinese
You can use the Custom option to find other categories
besides those listed, or to find multiple categories at once.
restaurant) when
performing a GPS radar
search in Find
GPS
If you want to... Use this tip...
View a GPS log on the map Use the Draw tab to import a GPS log file and view it as a
line object on the map.
Handheld Export
If you want to... Use this tip...
Modify the export area in
Handheld Export
When you click Preview, the default export area for the
location you selected displays on the map as shaded
rectangles. Click Select to confirm the area. To edit the
area, click the Select/Edit tool and then click the map to
add or remove rectangles to/from the export area.
Info
If you want to... Use this tip...
Quickly view information
for a location on the map.
Hover your cursor over objects on the map to see
information (such as road names, city/town, details about
draw objects, etc.) in the status line that appears at the
bottom of the map, just above the tab area.
6
Page 9
Map Data
If you want to... Use this tip...
Getting Started
Learn how to add route
and/or draw layers to your
project
Add existing route and/or draw files to your project by
clicking the Add button and selecting the Draw File or
Route File option.
Measurement Tool
If you want to... Use this tip...
Measure the
area/perimeter of a
location on the map
Use the Measure tool
polygon on the map and determine its area and perimeter.
Just click point-by-point to draw the polygon on the map
and then double-click to close the polygon. The area and
perimeter display in the center of the polygon.
Phone
If you want to... Use this tip...
Get all of the phone
listings for a particular
You can right-click the map on a road to view phone
listings for that road.
road.
Print
If you want to... Use this tip...
on the toolbar to draw a
Stop a page in a multipage map from printing
If you do not want to print all the pages in a multi-page
map, on the Layout graphic, click each page you do not
want to print.
Route
If you want to... Use this tip...
Reorder inserted stops Reorder your inserted route stops using the Advanced
features in the Route tab.
Create a route quickly For quick route creation, right-click the map and select one
of the Create Route options or use the Route buttons on
the toolbar.
Reorder the columns in the
Route Directions list
Determine the difference
between adding and
inserting stops and vias
Click the Directions list column headers to change the
column order.
Added stops/vias are placed in the order you add them to
the route. Inserted stops/vias are placed in the order you
would approach them between the Start and Finish points
of the route.
View information about
your second turn
Click the Show Turns button when GPS tracking to view
information about the following turn.
7
Page 10
XMap User Guide
Tab Area
If you want to... Use this tip...
Adjust the size of the tab
area
Show, hide, or reorder
tabs
Import or export a tab
configuration file
Voice
If you want to... Use this tip...
Create new speech
recognition profiles
Learn how to make the
microphone more sensitive
to your commands in noisy
environments
XData
If you want to... Use this tip...
Adjust the size of the tab area by dragging the top or right
side of the tab area.
Use the Tab Manager option in the Help menu to show,
hide, or reorder tabs.
Use the Tab Manager option in the Help menu to import or
export a tab configuration file
You can create a new speech recognition profile for each of
your working environments (noisy, quiet) and users (your
spouse or child) by clicking the Speech settings in the
Windows Control Panel.
If there is background noise while you are speaking, it may
be helpful to precede all of your voice commands with a
special phrase (like Simon Says). See the Voice Settings
tab of the Options dialog box.
Geoplace XData records
that do not have complete
address information or
were not correctly located
during the import process
Add a blank record to your
XData database
You can drag a record from the Query list and place it at
the correct geo-location on the map.
To add a blank record to an XData database, you must
select All Records as the Table Display type.
Frequently Asked Questions
These questions are asked most frequently by our customers.
• Why doesn't map data display in all projects?
The procedure for adding data to XMap varies; it depends on if you want to add the
data to the current project or if you want to add it to all projects. If you added the
data to only the current project and you want to view it in all projects, you must add
the data as base data in the application.
Use the steps below to add a map dataset as base data.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
8
Page 11

Getting Started
2. Click Data and then click Base Data.
The Base Data Locations dialog box opens listing each of the data sources on
your system.
3. Click Add, select the hard drive location where you saved your data from the
Browse for Folder dialog box, and click OK.
The OK button is enabled when you select a folder containing a file that
contains the properties of the map data being added.
4. Click Done.
• What map data is included with XMap?
XMap includes a worldwide reference base map dataset that includes major roads,
cities, boundaries, and geographic features, which is visible between data zoom
levels 1 and 6. For more detailed map features or aerial imagery, you can purchase a
variety of base map datasets from DeLorme or integrate your own data using XMap's
import and data adding tools. Note that most of the maps used by DeLorme to
convey the capabilities of the software are created using an optional DeLorme base
map dataset and/or data or imagery from third-party sources.
• How do I add non-DeLorme imagery to my map?
Use the Map Data tab to add imagery in MrSID and GeoTIFF format to your map.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Click Data and then click Add.
The Add Data to Maps dialog box opens.
3. Browse to the file you want to add, select it, and then click Add.
The imagery is added to the current project.
Note Imagery will not display unless projection information is specified in the file.
• How do I import files from an earlier version of XMap into this version?
Use the Map Data tab to import projects, routes, draw files, and XData from many
other DeLorme mapping programs. For information about migrating data to XMap,
see Migrating Data to the New DeLorme Docs Location
.
To Open A Project
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Click File and then click Open.
3. Select the project you want to view and then click Open.
4. Click OK.
To Open a Route
5. Click the Map Data tab.
6. Click Data and then click Add.
The Add Data to Maps dialog box opens.
7. Browse to the file you want, select it, and then click Add.
The route is added to the current project.
To Open a Draw File
8. Click the Map Data tab.
9. Click Data and then click Add.
The Add Data to Maps dialog box opens.
9
Page 12

XMap User Guide
10. Browse to the file you want, select it, and then click Add.
The draw file is added to the current project.
To Open an XData File
11. Click the Map Data tab.
12. Click Data and then click Add.
The Add Data to Maps dialog box opens.
13. Browse to the file you want, select it, and then click Add.
The XData file is added to the current project.
• What is my server name?
XMap uses Microsoft SQL Server as its DeLorme OpenSpace database engine. Your
server name varies, depending on if you are connecting to or creating a DeLorme
database in Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express/Microsoft SQL Server 2008 or a
Microsoft Enterprise SQL Server at your company.
• To establish a local connection to SQL Server 2005 Express or SQL Server
2008, use <computer name>\XMAP7 for the server name.
To establish a connection to SQL Server 2005 Express on another computer in
your network, use <computer name>\XMAP7.
• To establish a connection to a Microsoft Enterprise Microsoft SQL Server, use
<Server Name> for the server name. You will need to ensure that you have
the proper server and database permissions and you are connected to the
network. Contact your IT department if you experience problems.
• Why doesn't my Workspace display any layers?
If there are no layers in your Workspace, you may have accidentally removed them.
To retrieve the layers, click the GIS tab, click the Workspace subtab (if it is not
currently selected), click the Layers button, and then click Manage. Select the
Source Database you want to pull layers from, highlight the Layers in the Database,
and then click the move or move all button to move the layers into your workspace.
If the database where your layers are present is not listed in the Source Database
drop-down list, you can connect to it by selecting the Other… option. If you have
not yet created a database, you can do so using Database Manager or by selecting
the New… option in the Target Database drop-down list in the Create Layer and
Import Wizard dialogs.
• Where do I find the map settings and other Options settings?
Click the Options button
on the toolbar to modify GPS, voice, GIS,
map feature, display, handheld, and keyboard shortcut, and 3-D preferences. For
more information, see To Open the Options Dialog Box
.
• Upgraders only: What happens to my projects when I upgrade?
In previous versions of XMap, your projects, draw files, route files, log files, XD ata
files, and other DeLorme files were stored by default in the DeLorme Docs folder on
the root of your computer's C drive unless you specified a different directory during
installation.
10
Page 13
Getting Started
In XMap 6 and later versions, the DeLorme Docs folder for all files except NetLink
downloads is located in the My Documents (Windows XP) or Documents (Windows
Vista or Windows 7) folder under your user name. For NetLink downloads, the
Downloads folder is located in the DeLorme Docs folder under Shared Documents
(Windows XP) or Public Documents (Windows Vista or Windows 7).
For information about migrating data to XMap, see Migrating Data to the New
DeLorme Docs Location.
• Upgraders only: Why doesn't XMap overwrite the older version?
XMap 5 and later versions do not overwrit e older versions of XMap, such as XMap 4.5
or earlier. This allows you to view both versions on the same computer.
• Upgraders only: Should I uninstall my previous version bef ore installing the new
version?
You are not required to uninstall XMap 4.5 or earlier versions before installing XMap
7.
• Can I see imagery and data from Topo USA or Street Atlas USA within XMap?
Yes. The location of the Downloads folder changed beginning with XMap 6. If you
stored your data in the DeLorme Docs Downloads folder in XMap 5 or earlier, it will
automatically migrate to the new location. If you stored it in a different location, you
can use the Map Data tab to browse to the location and add it.
For information about migrating data to XMap, see Migrating Data to the New
DeLorme Docs Location.
• How do I get data updates or fix the roads on my map?
If you find there is a local road that is missing, you can add it to the current draw
layer using the Routable Roads Draw tool. For more information, see Drawing
Routable Roads or Trails on the Map.
To report a correction to us:
1. Click the NetLink tab.
2. Click the Support subtab.
3. Click the Submit Correction link.
4. Use the Customer Revisions Wizard to submit the change.
• How do I initialize my GPS receiver?
Each time you use your GPS receiver, you initialize it, which means you set your
starting position on the map by obtaining the initial coordin a tes of your location. This
can be done automatically or manually.
For more information, see GPS Options/Initializing GPS
.
• What is the difference between NavMode and the GPS tab view when using GPS?
The default GPS view is NavMode—a hands free full-screen view that you can display
in 2-D or 3-D. By default, the Control Panel is hidden and the tabs are minimized;
however, you can customize your interface
. For more information, see the NavMode
tutorial.
11
Page 14

XMap User Guide
The GPS tab view option allows you to use the GPS tab to control navigating and
tracking. By default, the tabs and Control Panel are visible, but you can opt to hide
them. It is available only in 2-D mode.
To turn NavMode on or off, click the NavMode button
button appears indented,
NavMode is on.
on the toolbar. When the
Note The button is grayed out unless you have a GPS device plugged in or are
playing back a GPS log file
You can also change your GPS view in the Options dialog box:
1. Click the Options button
You can also click the Options button
on the toolbar and click the GPS tab.
on the GPS tab.
2. Clear the Use NavMode check box to turn it off, or select the check box to
turn it on.
3. Click OK.
• What's the difference between a stop and a via?
When routing, you have the option of adding or inserting stops or vias in the route. A
stop is a location in the middle of a route where you want to stop and then proceed
from. A via is a road on the map that you want to specifically use when rout ing.
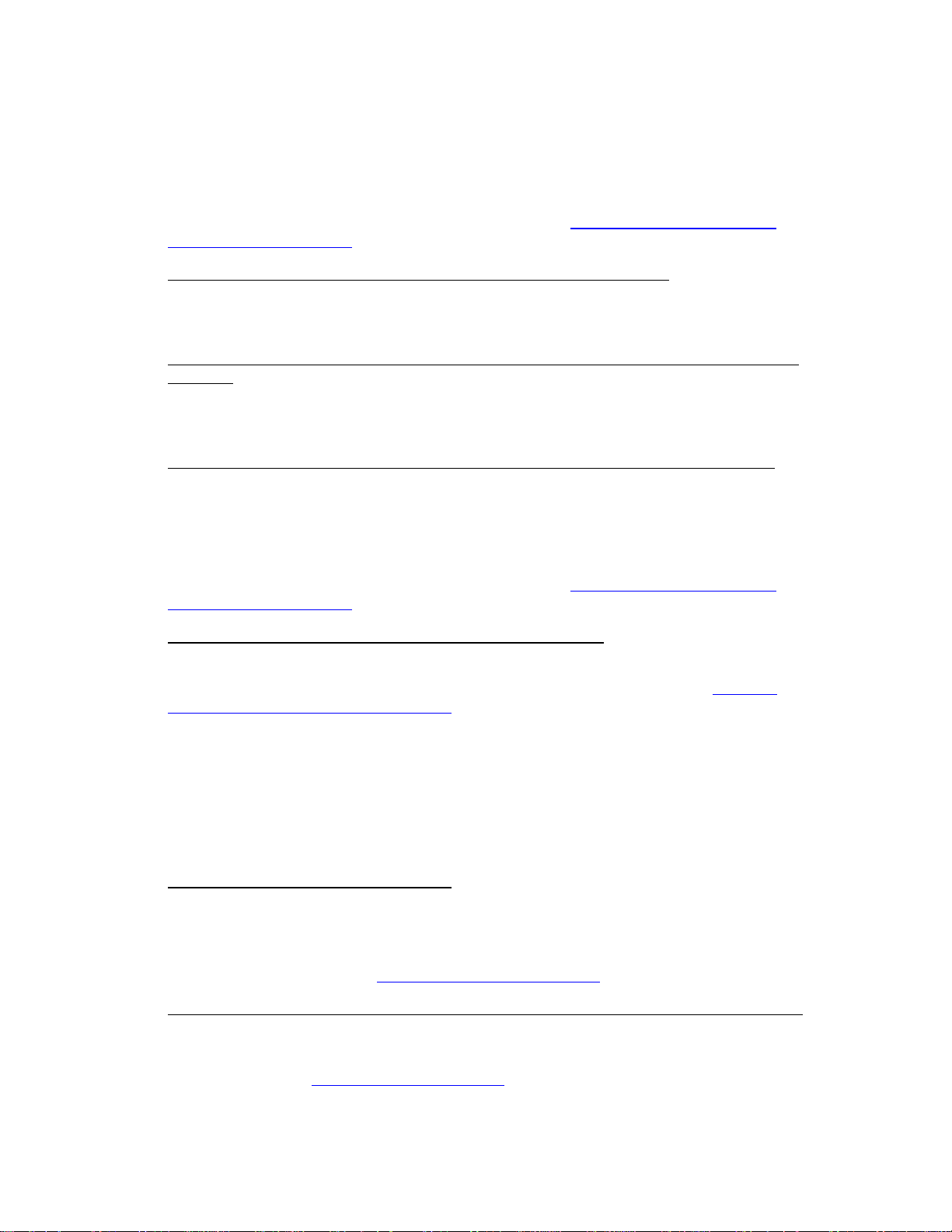
For example, if you create a route between Portland, Maine, and Yarmouth, Maine,
without any stops or vias, the route directions will tell y o u to take I-295. However, if
you want to take US Route 1 instead, you can place vias in the route on US Route 1
to force the route to go by way of US Route 1. If you plan on stopping in Falmouth
Foreside for lunch, you will want your route directions to reflect that stop. When you
add a stop, the route can be recalculated to include the stop in the middle of your
route.
The map below shows the area between Portland, Maine, and Yarmouth, Maine, with
two vias and one stop.
12
Page 15
Getting Started
• What's the difference between adding and inserting a stop or via?
The Insert Stop/Via function arranges stops/vias geographically in the route. The Add
Stop/Via function adds stops/vias in the order you add them to the route.
• Why did my route fail to calculate?
Your route will fail to calculate if you create a route:
• With a route start, stop, via, or finish point in an area that you have
designated as a Route Avoid
.
• That includes route points outside the United States, Mexico, or Canada.
• On an island without roads. In this case, XMap will look for the nearest road
to that island to place the route point. If the nearest road is not routable (for
example, it is the only road on the island and/or the island does not have
ferry access), you will get an error message saying "Route failed to calculate."
• Why do X marks display on the map when I calculate a route?
• When you place a route point in a location that isn't on a street, XMap finds
the closest street to that location, marks the space between the point you
clicked and the street with X marks, and starts the route at the street.
13
Page 16
XMap User Guide
• If you perform a Find for an address that is on a walkway and place a route
point on it, XMap finds the closest street to that location, marks the space
between the point you clicked and the street with X marks, and starts the
route at the street.
• Why are the tab area and control panel so narrow?
XMap was designed to accommodate resolutions of 1024 x 768 or higher. If you are
using a very high resolution (such as 1920 x 1200), the tab area and control panel in
XMap may appear to be very narrow. You can modify the size of the map and tab
area or use the Windows Control Panel to adjust your display settings.
• What's the best way to measure the distance of a road or trail?
The best way to determine the distance of a particular road or trail, is to create a
route. You can create a route using right-click functionality, the toolbar, or the Route
tab. For more information, see Creating a Route.
The best way to determine the distance of a particular road or trail, is to create a
route. You can create a route using right-click functionality, the toolbar, or the Route
tab. For more information, see Creating a Route.
The best way to determine the distance of a particular road or trail is to create a
route. You can create a route using right-click functionality, the toolbar, or the Route
tab. For more information, see Creating a Route
• What's the best way to measure a large area on the map?
.
The best way to measure a large area on the map is with the area tools in the Draw
tab, such as the polygon tool. When you draw an area object on the map, the area
displays next to the object on the map. If you click off of the object, you can view
the area again by clicking the Select tool in the Draw tab and then clicking the area
object on the map. For more information about drawing area objects, see Drawing a
Circle, Rectangle, or Polygon on the Map.
• What's the best way to measure a short distance on the map?
The best way to measure a short distance that is not made up of a road/trail on the
map is to use the Measure tool
on the toolbar. The measure tool allows you to
measure linear distance and area on the map based on the units chosen in the
Display tab of the Options dialog box. For instructions on how to use the measure
tool, see Measuring Distance and Area
• Why won't 3-D billboards display?
.
If you receive a message saying that 3-D billboards cannot be displayed, ensure that
you have a 32 MB video card with the latest drivers and that it supports DirectX and
transparencies. For more information, see the DeLorme Forums.
14
Page 17
Getting Started
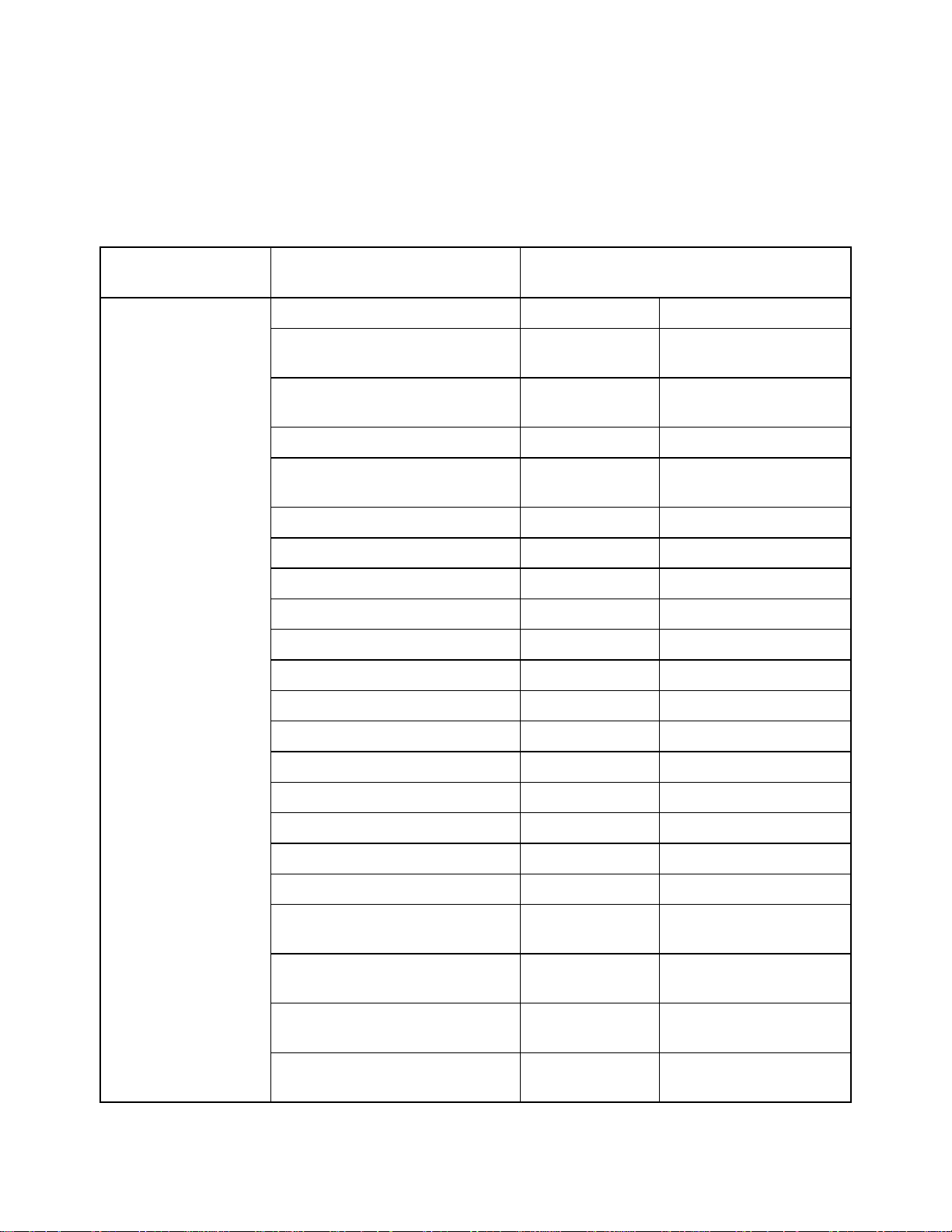
Chart of Supported Coordinate Formats
These are the supported search formats. Sample coordinates are for Yarmouth, Maine.
Tip Examples of search formats are listed in the Advanced search drop-down text boxes
along with a history of your most current search criteria.
Coordinate
Format
Latitude/Longitude N 43 48 30, W70 9 52 N 43 48 30 W70 9 52
QuickSearch Advanced Search
N 43 48.4910, W 070
09.8440
N434829.4600,
W0700950.6400
N43-48-30, W70-9-52 N43-48-30 W70-9-52
N 43:48:29.46, W
70:9:50.64
4348, -7009 4348 -7009
4348N, 7009W 4348N 7009W
N4348, W7009 N4348 W7009
4348n, 7009w 4348n 7009w
n4348, w7009 n4348 w7009
4348 N, 7009 W 4348 N 7009 W
N 4348, W 7009 N 4348 W 7009
N 43 48.4910 W 070 09.8440
N434829.4600 W0700950.6400
N 43:48:29.46 W 70:9:50.64
4348 n, 7009 w 4348 n 7009 w
n 4348 w 7009 n 4348 w 7009
434829, -700950 434829 -700950
4348.491, -7009.844 4348.491 -7009.844
4348.491, -7009.844 4348.491 -7009.844
434829.46, -700950.64 434829.46 -700950.64
43.80818333, -
70.16406667
43 48.4910 N, 70 09 50.64 W 43 48.4910 N 70 09 50.64 W
43 48.4910 n, 70 09 50.64
w
N 43 48.4910, W 70 09
50.64
43.80818333 -70.16406667
43 48.4910 n 70 09 50.64 w
N 43 48.4910 70 09 50.64 W
15
Page 18
XMap User Guide
434829.46 N, 700950.64 W 434829.46 N 700950.64 W
43, -70 43 -70
MGRS/USNG 19TDJ 06354 51187
19TDJ0635451187
(NAD27)*
19TDJ06355109
19TDJ064511
19TDJ0651
UTM/UPS 19T 0406311E 4850964N Zone 19T
19T 0406311 4850964 Zone 19T
19T / 0406311 / 4850964 Zone 19T
SPCS
ME-W 0500490 0355150 Zone ME-W
Same as QuickSearch
Easting 0406311E
Northing 4850964N
Easting 0406311
Northing 4850964
Easting 0406311
Northing 4850964
Easting 0500490
Northing 0355150
* Use this example for USNG with non-standard datum.
Migrating Data to the New DeLorme Docs Locations
In versions of XMap prior to XMap 6 and in other DeLorme products, your projects, draw
files, route files, log files, XData files, imagery, and other DeLorme files were stored by
default in the DeLorme Docs folder on the root of your computer's C drive unless you
specified a different directory during installation.
For XMap 6 and newer versions:
• The DeLorme Docs folder for all files except NetLink downloads is located in the My
Documents (Windows XP) or Documents (Windows Vista and Windows 7) folder
under your user name.
• The DeLorme Docs folder for NetLink downloads is located in the DeLorme Docs
folder under Shared Documents (Windows XP) or Public Documents (Windows Vista
and Windows 7). This allows all users on the computer to access NetLink downloads.
What is Migration?
The migration process does not move your files—it copies them to the new locations. When
you are sure your files are working correctly in th e new locations, you can delete them from
the old locations as long as you are not using them for another DeLorme program. For
example, if you have an imagery file you use in Topo USA or XMap (5.x or earlier), keep
both files.
16
Page 19

Getting Started
Because all new information you add to a project will be saved to the new file location—
even if you open it from the old location, we strongly recommend that you migrate your
files. If you do not, you could have project data in two DeLorme Docs locations; your
project will work correctly, but your data will not all be in th e same location.
Initial Migration
The initial migration process, which occurs when you open XM ap the first time after you
install it, copies the data in the existing Net Link Downloads, Symbols, and GPSLogs folders
to their new locations as indicated above.
Note The automatic migration process copies files from only one existing DeLorme Docs
location. If you have more than one DeLorme Docs location on your computer, only one
location will be recognized
New Users
When you installed XMap on your computer, you were asked if you had previously installed
a DeLorme program. If you had not, you clicked New User and the application opened. The
migration process does not apply to you if you have never installed a DeLorme program on
your computer.
Existing Users
When you opened XMap for the first time after installation, your computer was scanned for
an existing DeLorme Docs directory. If a DeLorme Docs directory was found, any data in the
existing NetLink Downloads, Symbols, and GPSLogs folders was copied to their new
locations as indicated above.
If an existing DeLorme Docs folder was not automatically detected on your computer, you
are asked if you had previously installed a DeLorme program. If you had, you clicked
Existing User which opened a dialog box for browsing to the existing DeLorme Docs location
and choosing one of the following migration options:
• Migrate–The data in the NetLink Downloads, Symbols, and GPSLogs folders was
migrated to their new DeLorme Docs locations.
• Don't Migrate–The migration was cancelled and any data in the NetLink Down loads,
Symbols, and GPSLogs folders was not migrated. You will not be prompted to
migrate again.
• Try Again Later–Cancels the migration, but you are prompted to migrate the next
time you open the program. You will be prompted each time you open the program
until you select Migrate or Don't Migrate.
Project Migration
When you migrate a project, all associated files (routes, draw layers, XData sets, and
connections to GIS layers in a database) are moved with it. When you open a project from
any location other than the new DeLorme Docs location, you are prompted to migrate it.
You can also directly migrate projects.
To Migrate a Project When You Open It
Use the following steps to migrate a project when you open it.
1. Open a project
2. When the Migrate Project dialog box opens, click Migrate.
The Migration Completed dialog box opens. Go to step 4.
OR
If a file with the same name already exists in the new DeLorme Docs location, the
Confirm Link to Existing File dialog box opens. Go to step 3.
.
17
Page 20

XMap User Guide
3. Click Link to replace the project link to the existing file in the new location and then
go to step 4.
OR
Click Link All to replace any project links to existing files in the new location and
then go to step 4.
OR
Click Save Copy to maintain the project link to the current file and save it with a
different name.
OR
Click Cancel to stop the migration process and roll back any file migration that has
occurred up to this point.
4. In the Migration Completed dialog box, click OK to open the migrated project.
Note If there is a problem with the migration, a message will notify you of any
corrective action you need to take.
To Manually Migrate a Project
Use the following steps to migrate a project at any time.
1. Click the arrow next to the Open button
Migrate Project.
OR
Click the Map Data tab, click File, and then click Migrate Project.
The Migrate Project dialog box opens.
2. Browse to the project you want to migrate, click the project, and then click Migrate.
3. The Migration Completed dialog box opens. Go to step 5.
OR
If a file with the same name already exists in the new DeLorme Docs location, the
Confirm Link to Existing File dialog box opens. Go to step 4.
4. Click Link to replace the project link to the existing file in the new location and then
go to step 5.
OR
Click Link All to replace any project links to existing files in the new location and
then go to step 5.
OR
Click Save Copy to maintain the project link to the current file and save it with a
different name.
OR
Click Cancel to stop the migration process and roll back any file migration that has
occurred up to this point.
5. In the Migration Completed dialog box, click Open to open the migrated project or
Close to close the dialog box and return to your last active project.
Note If there is a problem with the migration, a message will notify you of any
corrective action you need to take.
on the toolbar and then click
Basic Functions
Zooming In and Out
You can use the drag and zoom feature, zoom tools, or the data zoom level (Data zoom
level is the relationship between what you see in a map view and how it exists in reality. It
is the amount of geographic data displayed on a computer monitor. The data zoom level is
similar to the traditional fractional relationship expressed on paper maps. For example,
18
Page 21

Getting Started
1:24,000, 1:100,000, 1:500,000, and so on.) to quickly change the zoom level of the map
view.
Notes
• Increase the data zoom level number to show a smaller geographic area at greater
detail.
• Decrease the data zoom level number to show a larger geographic area at lesser
detail.
• If you view both the right (primary) and left (secondary) maps at different data
zoom levels, a box (or lines, depending on the current data zoom level) displays on
the map that is zoomed out the furthest. The box/lines indicate the area that is in
view on the other map. You can disable this feature by clearing the Show Ref check
box at the top of the secondary map window.
• If you view the right and left maps at the same data zoom level but they are not
equally represented on the screen (50/50), a box (or lines) displays on the map that
is covering the most screen area. The box/lines indicate the area that is in view on
the other map.
To Drag and Zoom In
Use the following steps to zoom in either the right or left map.
1. Click and hold down the left mouse button as you drag the mouse in a down-right
direction on the map to encompass the area you want to display. A view box displays
on the screen and changes dimension as you move the mouse. A label displays the
data zoom level at the current map center.
2. Once you reach the map area or data zoom level you want to display, release the
mouse button. The area you selected fills the map window, the map re-centers, and
the map view adjusts to show the appropriate level of detail.
Tip To move the view box to another location, press the SHIFT key at any time.
To Drag and Zoom Out
Use the following steps to zoom in either the right or left map.
1. Click and hold down the left mouse button as you drag the mouse in an up-left
direction on the map. A staircase with a small circle displays on the screen.
2. Continue dragging the mouse in an up-left direction. The small circle moves up the
steps, one step per data zoom level. A label displays the data zoom level to the
bottom-right of the staircase.
3. Once you reach the data zoom level you want to display, release the mouse button.
The map view adjusts to display the appropriate level of detail. The map center is
retained on your screen.
To Zoom In/Out Using the Zoom Tools
There are two sets of zoom tools. The zoom tools for the right map are located in the
Control Panel
. The zoom tools for the left map are located at the top of the left map view.
Click the up arrow to zoom out one minor data zoom level at
a time. Click the down arrow to zoom in one minor data
zoom level at a time.
Right
Map
Controls
Click the Zoom In 1 tool to increase the detail number to
the next full level.
Click the Zoom Out 1 tool to decrease the detail number to
the next full level.
19
Page 22

XMap User Guide
Click the Zoom Out 3 tool to decrease the detail number by
three full levels.
Click the plus button to increase the detail number to the
next full level.
Left
Map
Controls
Click the minus button to decrease the detail number to the
next full level.
The data zoom level of the left map displays in the text area
to the left of the buttons.
Tips
• Press ALT+PAGE UP on your keyboard to zoom out to the next full data zoom level.
Press ALT+PAGE DOWN on your keyboard to zoom in to the next full data zoom
level.
• Use the mouse wheel to zoom the map in and out. Rotate the mouse wheel to zoom
in by individual data zoom level steps or hold the SHIFT key while rotating the
mouse wheel to zoom to the next full data zoom level.
Panning/Centering the Map
Use any of the following methods to pan (move) or center the map.
• Click anywhere on the map. The point you click becomes the new map center.
• Double-click a layer name in the GIS workspace.
• When you point near the map edge, a white hand displays. Drag the hand to move
the map in that direction.
• With your cursor anywhere on the map, press the CTRL key on your keyboard—the
cursor becomes a white hand. Hold down your left mouse button to drag the map to
a new location.
• Click the Map Panning button
on the toolbar to drag/pan the 2-D or 3-D map
in any direction.
• Click anywhere on the overview map
. The point you click becomes the new map
center. This allows you to traverse greater distances with each mouse click than you
can within the main map.
• Point anywhere on the black view box in the overview map window. When the
pointer becomes a
, drag the view box to the new location.
• Use the search features on the Find tab to center the map on a particular location.
• Assign shortcut keys
to pan the map up, down, left, or right in small increments.
20
Page 23

Getting Started
Copying Your Map to the Clipboard
Click the Copy to Clipboard button on the Print tab to copy your map to the clipboard.
You can then paste it into another program.
You can also right-click anywhere on the map and click Copy Map to Clipboard.
Saving a Map as a Bitmap or JPEG Image
You can save the current map view as a bitmap (.bmp) or J PEG (.jpg) image in all page
layout formats: Single, 2 x 2, and 3 x 3. If you select a multi-page format, all the active
pages are saved as individual bitmaps or JPEGs. The file name is the specified file name
with an incremental page number at the end.
See Printing a Map
To Save a Map as a Bitmap or JPEG
Use the following steps to save a map as an image.
1. Locate the area on the map that you want to save as an image.
2. Click the Print tab and then click the Map subtab (if it is not already selected).
3. Under Map, select Left, Right, or Both.
4. Under Print Layout, select Page
specified in the Setup options) or Screen
size).
The print area for a Page map displays as a red box and the print area for a Screen
map displays as a blue box on the overview map.
5. If you selected Page in step 4, the following options are available.
• Under Print Layout, select a layout option (Single, 2 x 2, or 3 x 3). The
for information about printing a map without saving it as a file.
(the map print area is based on the paper size
(the map print area is based on the screen
print area displays on both the Map and the Overview Map. In the example
below, 2 x 2 is selected. This means the print area encompasses four
standard pages at whatever paper size you specified in the Setup options. You
can assemble a multipage map
into a large map.
• If you selected 2 x 2 or 3 x 3 and do not want to save all the pages in the
multipage map on the map layout graphic, click each page you do not want to
save. The page appears dimmed or gray. In the example below, page 4 will
not print.
• Verify this is the location and photo zoom you want to save. If not, pan the
map to the location and zoom to the level you want.
Note Changing the photo zoom enlarges/reduces the map features and
changes the map area that you save as an image. If you increase the photo
zoom level, map text, lines, symbols, etc. are larger and your map area is
reduced. If you decrease the photo zoom level, map text, lines, symbols, etc.
21
Page 24
XMap User Guide
are smaller and your map area is enlarged. The reduction/enlargement
percentages for your photo zoom level display under the Photo Zoom dropdown list.
• If you want to use other tabs and functions but not lose your current print
area, print photo zoom, or other settings, select the Lock Print Center check
box. This locks the print area and changes the tab label to red.
• Add text or graphics to your map
• Select the Print Preview check box to zoom the map and view the entire
area that will be saved as a bitmap image. Clear the check box to return to
your previous data zoom level.
.
6. Click the Save button
The Save 2D Map Image dialog box opens.
7. Type the file name in the File Name text box, select to save the file as a .bmp or
.jpg from the Save as Type drop-down list, select the DPI (dots per inch) value
(optional), and click Save.
.
Measuring Distance and Area
Use the Measure tool on the toolbar to measure linear distance and area on the map
based on the units chosen in the Display tab of the Options dialog box.
The snap function snaps (attaches) the point of a measurement line to a point on a road or
another measurement object. This ensures a more accurate measurement of distance or
area. To measure area, you must completely enclose the area by snapping your finish point
to your starting point.
Notes
• The Measure tool is the best way to measure short distances on the map. If you want to
measure the distance of a road, try creating a route
area on the map, use the area object tools
• To disable the auto-snap function, hold down the ALT key on your keyboard while using
the Measure tool.
• Measure objects (lines and areas) are saved with the current project. When you create
a new project, the measure objects do not display. If you want the same measure
objects on your new project, you must recreate them.
• To view information about a measurement line, right-click it and click Info. The
measurement information is automatically displayed in the Info tab.
in the Draw tab.
. If you want to measure a large
To Measure Distance or Area
Use the following steps to measure linear distance or area on the map.
1. Verify you have the correct units of measure selected in the Display tab of the
Options dialog box. For more information, see Setting Units of Measure Preferences
2. On the toolbar, click the Measure tool
3. Click point-by-point to draw a measurement line on the map. A text box displays
next to your pointer indicating the total distance of the measurement taken.
Note When you pass over a point in a road, measurement line, or measurement
area to which you can snap, a yellow circle
the point of the measure line to the road or measurement object's point coordinate.
22
. The pointer changes to .
defines the snap point. Click to snap
.
Page 25
Getting Started
4. To end a measurement line, double-click the last point of the measurement line.
OR
Click the last point of your measure line or area and then click the Measure tool on
the toolbar.
The measure line is a two-pixel wide yellow line and th e total length of the line is
displayed in a label at each endpoint of the line.
5. To end a measure area, hover over the starting point until the yellow snap circle
displays, and then double-click the last point to the starting point. The closure area
is transparently shaded, and the area and perimeter measurements display.
Searching Tips
When you use the Quick Search subtab on the Find tab or the Route tab to search for a
location, you must enter the information in a specif ic format.
Tips
• Use punctuation as in the examples in the table below.
• Do not use periods.
• Search with the minimum amount of information to increase the number of results.
For example, if you are searching for a road, and you are not sure of the spelling,
type in part of the name and then scroll through the list of resu lts until you find a
match.
This table shows formats for search types.
For this type of search... Use this format... Example
Address Street address, City, State 100 Baxter Blvd, Portland,
ME
Street address, ZIP Code 100 Congress St, 04101
Street address, City, State,
ZIP Code
City City, State Atlanta, Georgia
ZIP/Postal Code Within the U.S.: ##### (5-
digit ZIP Codes only)
Within Canada: ### (6-
digit Postal Codes only)
Minor Point of Interest POI name, City, State Subway, Columbus, OH
Major Point of Interest or
Landmark
Latitude/Longitude See Chart of Supported of Supported Coordinate Formats
For more information about the Find tab, see the Help topics under Finding a Location on
the Map.
POI/landmark name Mount Rushmore
POI/landmark name, State Space Needle, WA
100 Congress St, Portland,
ME 04101
04096
J8E756
23
Page 26

XMap User Guide
About the Interface
Tab Area
You can access most of the application's functions from the tab area at the bottom of the
screen. To access Help for a specific tab, click the Help button
reorder the tabs
• Map Data
• GIS
• Print
• Find
• Phone
• Info
• NetLink
• ImageReg
• Draw
• Profile
• 3-D
• Route
• GPS
• Voice
• Handheld Export
• XData
, show or hide individual tabs or show or hide the tab panel.
on the tab. You can also
24
Page 27

Getting Started
Control Panel
The Control Panel, located to the right of the map view, displays information pertinent to
the current map view and map cursor position. It also includes zoom and map pan buttons.
You can customize your interface to show or hide the Control Panel
Data Zoom Level—The current data zoom level of the map view;
ranges between 0-0 (maximum zoom out) and 20-0 (maximum zoom
in).
Zoom Tools—Buttons that quickly zoom out three levels, out one level,
or in one level. For more information, see Zooming In and Out
Compass Rose—A group of nine buttons on a globe. The outer buttons
have yellow arrows; click one of the arrow buttons to pan the map in
that direction. Click the middle button to center the map on the
previous map view. This button performs an undo function for the last
pan or zoom (up to 256 times).
Map Rotation Tool—The arrow in the graphic indicates True North in
relation to the rotated map. Use the Map Rotation Tool to rotate the
map in any direction. You can rotate the map by clicking or dragging
the square map graphic in the direction you want or by selecting/typing
the degree of map rotation from the drop-down list.
Map Coordinates—Coordinates for the current map cursor position
display based on the units of measurement preferences
Display tab of the Options dialog box.
Elevation and Interval—Display in the measurement chosen in the
Display tab of the Options dialog box. The data zoom level affects
interval display.
Scale Bar—Indicates the distance one scale bar unit equals in the
measurement chosen under in the Display tab of the Options dialog
box.
.
.
chosen in the
Overview Map
The overview map is a small map in the lower-right corner of the screen that offers a wideangle view of your current map view area. It is approximately three data zoom-levels out
from the current map view.
Tips
• Click anywhere on the overview map and that point becomes the new map center.
This allows you to travel greater distances with each mouse click than you can within
the larger, current map view.
25
Page 28

XMap User Guide
• Use the black view box in the overview map window to pan the map. Point anywhere
on the view box. When the pointer becomes a
location.
, drag the view box to the new
Toolbar
Use the toolbar to perform many functions in the application without navigating through the
tab area.
Tips
• Not all of the toolbar features are activated by default. To modify which toolbar items
you want to view, right-click the toolbar. Toolbar options with selected check box
next to them are currently displayed on the toolbar. Click the item to activate or
inactivate it on the toolbar.
• In addition to customizing which toolbar features are displayed, you can also
reposition the toolbar segments horizontally or vertically. Just drag the vertical
dotted bar that separates each segment to the new location (left, right, up, or
down). You cannot move a toolbar segment above the top-most line on the toolbar,
customize toolbar groups, or remove toolbar groups from the toolbar.
Exchange
• Exchange GIS layers, draw layers, maps, routes, waypoints, or tracks with an
Earthmate PN-Series GPS device.
• Export and import GIS points to and from an Earthmate PN-Series GPS device.
See the Help topics under Using Handheld Devices for more information.
GIS Layer Management
See To Use the GIS Tools.
GIS Tools
See To Use the GIS Tools.
GPS/Nav Mode
• Start or stop your GPS connection (also available on the GPS tab).
• Turn GPS NavMode
on or off.
GeoTagger
• Combine images and data with GPS information on the map.
26
Page 29

Getting Started
Info/Profile
• Get information about a location on the map. You can also right-click a location on
the map and click Info.
• Profile a linear object
linear object on the map and then click Profile.
on the map. You can also select the Profile tab, right- click the
Map Library/MapShare
• Open the NetLink tab to download or purchase data and imagery.
• Share maps, route directions, or profiles
MapShare using the Internet.
with friends, family, or associates with
Map Navigation
• Recenter the map and zoom it in and out.
• Grab and pan the map
in any direction.
Measure
• Measure linear distance and area on the map based on the units chosen in the
Display tab of the Options dialog box.
Options/Help
• Open the Options dialog box to set GIS, GPS, display, map feature, voice navigation,
3-D, search, handheld export, and keyboard shortcut preferences.
• Open the Help menu to access the XMap Help topics, Map Legend
, and more.
Print
• Print your current map screen. See the Print tab for more printing options.
• Quick print with the current Print tab settings.
Project
• Create, save, and/or open projects. You can also access these options on the Map
Data tab.
Redline/Synchronization Tools
Available when an active subscription exists.
See To Use the GIS Tools
.
Route
• Set route start, finish, and stop, and via points and calculate a route. You can also
access these options from the Route tab.
Undo/Redo
• Undo/redo your last GIS edit and measure tool actions.
27
Page 30
Map Legend
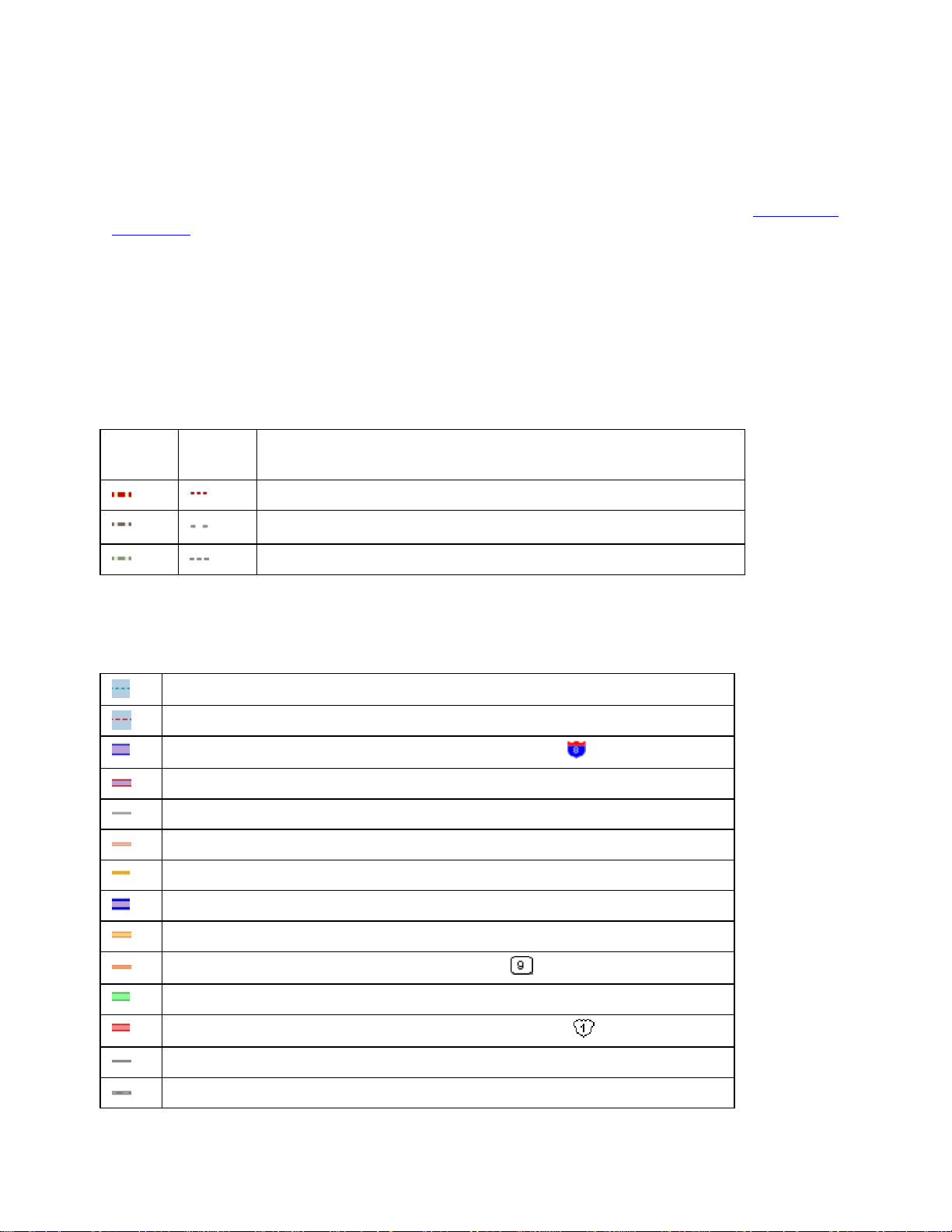
Map Legend
The features that display on the map may display differently depending on which map colors
you chose on the Display tab of the Options dialog box. The tables below show the
symbolization of each feature, by map color.
Notes
• Not all features are available at all zoom levels.
• Not all features are available in all datasets.
• High-contrast Color features display the same as Street Color features (except for land,
which displays as black).
Routable Trail Features
Topo
Colors
Street
Colors
Description
Major Trail (National Scenic, National Historic, etc.)
4-wheel Drive Trail
Trail/Walkway/Foot Trail
Important Some trails may cross private property. Contact the applicable trail department
to ensure you have the appropriate permissions before following a major trail.
For contact information, see Recreational Contacts.
Routable Road Features
Ferry Passenger
Ferry Vehicle
Interstate Highway (can also include this symbol: )
Limited Access Road
Local Road
Major Connector, Forest Road
Minor Connector
Non Limited Access Interstate
Primary State Route
State Route (can also include this symbol: )
Toll Road
U.S./National Route (can also include this symbol: )
Unclassified Road
Unimproved Road
28
Page 31

Land Cover
Map Legend
Topo
Colors
Street
Description
Colors
n/a Bare Rock or Sand
Bureau of Land Management Land
Bureau of Mine Reclamation Land
n/a Forest, evergreen
n/a Forest, mixed
Ice or Snowfield
Indian Reservation (at data zoom level 11)
Indian Reservation (at data zoom level 2 thru 10-7)
Intermittent Water
Land
Military Area (at data zoom level 11)
Military Area (at data zoom level 2 thru 10-7)
n/a Mine or Quarry
Parks
n/a Transitional Area, Lava, Salt Flats, or Mixed Barren
n/a Wetlands
Point Features
Topo
Colors
Street
Colors
River/Stream
Water
Description
Amusements
Airport (private)
Airport (commercial public)
Airport (general aviation public)
Business (Amusement, Recreation, Specialty or Dept.
Store)
Camping (at data zoom level 14)
Camping (at data zoom level 11 thru 13)
Cemetery
29
Page 32

XMap User Guide
Educational Facility
Exit, with services (at data zoom levels 10 thru 11-7)
Exit, without services (at data zoom levels 10 thru 11-7)
Exit, food (at data zoom levels 12 thru 17)
Exit, gas (at data zoom levels 12 thru 17)
Exit, lodging (at data zoom levels 12 thru 17)
Exit, other (at data zoom levels 12 thru 17)
Fast Food
Gas
Hospital
Lodging
Metropolitan City
National Capital (data zoom level 7 thru 10)
National Capital (data zoom levels 2 thru 6)
Point of Interest (smaller black square)
Population Center
Public Service
Religious (buildings)
Rest Area with Facilities (at data zoom levels 10 thru 11)
Rest Area with Facilities (at data zoom level 12)
Rest Area without Facilities (at data zoom levels 10 thru
11)
Rest Area without Facilities (at data zoom level 12)
Restaurants (general)
Restaurants (specialty)
Small City
State Capital
Unique Natural Feature (at data zoom level 8)
30
Page 33

Line Features
Map Legend
Topo
Colors
Street
Colors
Description
County Boundary
Dam
Game Management District
International Boundary
Park Boundary
Pipeline
Power Line
Railroad (Abandoned)
Railroad
Runway
State Boundary
DeLorme Atlas and Gazetteer Symbols
Symbol Description
Developed Boat Ramp (at data zoom levels 11 and 12)
Developed Boat Ramp (at data zoom level 13)
Freshwater Fishing (at data zoom levels 11 and 12)
Freshwater Fishing (at data zoom level 13)
Hunting (at data zoom levels 11 and 12)
Hunting (at data zoom level 13)
Saltwater Fishing (at data zoom levels 11 and 12)
Saltwater Fishing (at data zoom level 13)
Undeveloped Boat Ramp (at data zoom levels 11 and 12)
Undeveloped Boat Ramp (at data zoom level 13)
31
Page 34

Using the Toolbar
Showing/Hiding Toolbar Options
You can customize the toolbar to show the options you use most. You can also activate
toolbar options that are not turned on by default or hide or show the entire toolbar. Some
toolbar options are grouped—for these, you can show or hide the group of buttons.
To Modify the Toolbar
1. Right-click the toolbar.
Toolbar options with a selected check box next to them are displayed on the toolbar.
2. Click an item to activate or inactivate it in the toolbar.
Reordering the Toolbar Options
To reposition the toolbar groups horizontally or vertically, just drag the dotted vertical bar
that separates each group to the new location (left, right, up, or down).
32
Page 35

Using the Toolbar
To Create New Projects
To create a new project, click the New button on the toolbar. If you made changes to
the open project, the Save Changes dialog box opens to ask you if you want to save your
changes.
For more information, see Creating and Deleting Projects
.
To Open a Project
To open an existing project:
1. Click the Open button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Open button, and then click Open Project.
If you made changes to a project that is already open, the Save Changes dialog box
opens. Note Projects have .xmp extensions and are saved by default in
C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Projects.
The Open File dialog box opens.
2. Select the project you want to view and click Open.
Note If the project has not been migrated to the new DeLorme Docs location, you
will be prompted to migrate it. Click Migrate to create a copy of the file in the new
DeLorme Docs location. Click No to cancel. For more information about migrating
projects, see Migrating Data to the New DeLorme Docs Location
For more options for opening files, see Opening a Project.
on the toolbar.
.
To Migrate a Project
To migrate an existing project from C:\DeLorme Docs\Projects to C:\...\DeLorme
Docs\Projects:
1. Click the arrow next to the Open button, and then click Migrate Project.
The Migrate Project dialog box opens.
2. Browse to the project you want to migrate and click Migrate.
After the migration is complete, a confirmation message appears.
3. Click Open to open the project or Close to close the message.
For more information about migrating projects, see Migrating Data to the New DeLorme
Docs Location.
33
Page 36

XMap User Guide
To Save a Project
To save the project that is currently open:
1. Click the Save button
The Save File dialog box opens.
2. Browse to the location where you want to save the project.
If you want to rename the project, type a new name in the File Name text box.
3. Click Save.
on the toolbar.
To Print
To print a map using the current settings in the Print t ab, click the Print button on the
toolbar.
The Print button is hidden by default
and click Print.
For more information, see Printing a Map
; to show it, right-click the toolbar to open the menu
.
To Print the Map Screen
To print the current view as it displays on the screen, click the Print Screen button on
the toolbar.
The Print Screen button is hidden by default
menu and click Print Screen.
; to show it, right-click the toolbar to open the
To Open the Map Library
To open the Map Library subtab on the NetLink tab, click the Map Library button.
To Share Maps
To share your current map view, a route map and directions, or a profile, click the
MapShare button
MapShare lets you share maps—even 3-D maps, routes, and profiles.
For information on e-mailing maps, routes, and profiles w ith the MapShare Wizard, click the
Help button in the MapShare Wizard.
on the toolbar to open the MapShare Wizard.
To Use the Map Navigation Tool
Click the Navigation tool on the toolbar to enable Navigation mode.
• To zoom in, click the map, hold down the left mouse button, and drag down and
right. (2-D maps only)
34
Page 37

Using the Toolbar
• To zoom out, click the map, hold down the left mouse button, and drag up and left.
(2-D maps only)
• To re-center the map, click the map where you want to center it.
To Grab and Pan the Map
To drag and pan the 2-D or 3-D map in any direction, click the Map Panning button
on the toolbar.
Tip With your cursor anywhere on the map, press the CTRL key on your keyboard—t he
cursor becomes a white hand. Hold down your left mouse button to drag the map to a new
location.
To Use the GIS Tools
There are many GIS tools available on the toolbar, including tools that allow you to edit
geometries, create redline layers, perform COGO editing, and more.
GIS Layer Management
• Import Layers menu — Import a layer (add, append, or replace) into a
database from a file or ArcSDE database.
• Manage Layers
from your workspace, delete layers from the source database, or remove a database
reference.
• Forms menu
topics for more information about the options that are available for your version of
XMap.
— Use the Manage Layers dialog box to add and remove layers
— Create, manage, and open forms. See the related Help
GIS Tools
• Active Layer — Use the Active Layer drop-down list to select a layer from your
workspace as the active layer.
• Selection
editing.
• Magic Wand
• Edit
• Edit Points
• Edge Matching
polygon/line.*
— Highlight geometries on the map without the risk of accidental
—Edit topological lines.*
—Move or change the size of a geometry.*
—Edit points in a polygon/line layer.*
— Match shape points in a polygon/line to those in another
• Rotate
— Rotate a geometry.*
35
Page 38

XMap User Guide
• Draw Geometries (
points, lines, or polygons to a layer.*
• COGO
measurements, or bearing/distance measurements.*
• Classification (
classification for a selected geometry.
• Commit Changes
layer.*
*These tools are available only in XMap Editor and XMap Enterprise.
— Place a polygon/line/point by coordinates, angle/distance
, , or depending on the active layer type) — Add
, , or depending on the active layer type) — Modify the
— Save all of the changes you have made to the active
Redlining/Synchronization Tools
These tools appear in the toolbar when an active subscription exists.
• Redlining
• Synchronizing
database, and send edits to the database.
• Add Synchronized Layers
subscription to your workspace.
—Mark up a GIS layer.
—Refresh subscription layers, send redline layers to the source
— Add all of the layers that are in the active
• Revert
layer with the database on the Enterprise database server.
— Discard changes made to a layer before synchronizing the active
Undo/Redo
• Undo and Redo — Use these tools to undo/redo your last action as long as
the action is not committed. The Undo button may not be available for XMap
Professional users as most actions are automatically committed.
To Create a Route
To set route points using the toolbar:
1. Type the location where you want to start your route in the Start text box (next to
the green Start button).
OR
Click the green Start button
want to start your route.
OR
Select an address book entry, a previous location, or your current GPS position from
the Start drop-down list.
2. Type the location where you want to end your route in the Finish text box (next to
the red Finish button).
OR
and then click the location on the map where you
36
Page 39

Using the Toolbar
Click the red Finish button
want to end your route.
OR
Select an address book entry or your current GPS position from the Finish drop-
down list.
3. Optional. If you want to add a stop or via to your route, click the Stop button
or the Via button
add or insert the stop or via. Repeat this step for each stop or via you want to add to
your route.
Note If the Add option is selected in the Route tab, stops and vias are added in the
order they are added to the route. If the Insert option is selected in the Route tab,
stops and vias are added in the order they are approached in the route. For more
information, see Adding and Inserting Stops and Vias
4. Click the Calculate button
Important If you have only the left map window open, the route Start, Finish, and Stop
buttons on the toolbar and on the Route tab are grayed out. To activate the options, use the
map resize tool
Note To use the current GPS location in a route, you must connect your device to your
to expose the right map window.
and then click the location on the map where you want to
and then click the location on the map where you
.
.
computer and click the GPS button
Tip Once a route is calculated, you can use the subtabs in the Route tab to view route
directions, edit a route, and more. Click the Directions subtab to view the route directions,
the Advanced subtab to display the advanced routing options, or click Back on Track to
add your current GPS position as a stop to the current route.
on the toolbar or on the GPS tab.
To Start/Stop Your GPS Connection
The GPS button on the toolbar lets you start your GPS connection if the device is not active
or stop the connection if it is active.
To start or stop your GPS connection, click the GPS button
• If you are using NavMode
but you can show them. For more information, see Customizing the Interface
• If you start a connection and you are not using NavMode, the GPS tab area opens so
you can monitor your GPS status
, the GPS tab is minimized and the Control Panel is hidden,
.
on the toolbar.
.
To Use GPS NavMode
NavMode offers a hands free, full-screen view that you can view in 2-D or 3-D.
The NavMode button is hidden by default
GPS/NavMode.
; to show it, right-click the toolbar and click
To Turn NavMode On/Off
37
Page 40

XMap User Guide
Click the NavMode button to turn it on or off. The button is grayed out
a GPS device plugged
indented
You can also change your GPS view in the Options dialog box:
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the Options button
2. Clear the Use NavMode check box if you do not want to use NavMode when you
start your GPS. Select the check box if you do want to start GPS in NavMode.
3. Click OK.
, NavMode is on.
in or are playing back a GPS log file. When the button appears
on the toolbar and click the GPS tab.
on the GPS tab.
unless you have
To Exchange Information with a Handheld GPS
Use the Exchange button on the toolbar (also on the GPS and Handheld Export tabs)
to exchange objects such as maps (Earthmate PN-Series GPS only), waypoints, tracks, and
routes with a handheld device.
You can also use the Send GIS Layer button
export
For more information on exchanging information, see Help topics listed under Using
DeLorme PN-Series GPS Devices or Exchanging Information with a Third-Party GPS Device.
and import GIS point layers, including forms, between XMap and your device.
and Import GIS Layer button to
To Add Images and Data to a GPS Location
To open the GeoTagger Wizard, where you can combine images and data with GPS
information on the map, click the GeoTagger button
The Geotagger button is hidden by default
menu and click Geotagger.
For more information, see Getting Started with GeoTagger
; to show it, right-click the toolbar to open the
on the toolbar.
.
To Measure Distance
Use the following steps to measure linear distances and perimeter/area on the map. For
more information, see Measuring Distance and Area
1. Click the Measure tool
2. Click point-by-point to draw a measurement line on the map. A text box displays
next to your pointer indicating the total distance of the measurement taken.
Note When you pass over a point in a road, measurement line, or measurement
area to which you can snap, a yellow circle
the point of the measure line to the road or measurement object's point coordinate.
Press and hold the ALT key on your keyboard to disable snapping.
on the toolbar.
.
defines the snap point. Click to snap
38
Page 41

Using the Toolbar
3. To end a measurement line, double-click the last point of the measurement line. The
measure line displays as a two-pixel wide yellow line and th e total length of the line
displays in a label at each endpoint of the line.
4. To end a measure area, hover over the starting point until the yellow snap circle
displays and then double-click the last point to the starting point. The perimeter
measurements display.
To Get Information About a Location
Use the Information button on the toolbar to click a point, symbol, feature,
measurement line, track, or area on the map to identify it and view detailed information
about it.
The Information button is hidden by default
menu and click Information.
Use the following steps to get information about a particu lar map feature.
1. Click the Information button.
2. Click the map feature you want information for, such as a road, town, measurement
line, waypoint, track, draw symbol, or point of interest.
The Info tab opens and displays a list of information categories.
Note Descriptive information may include a name or feature type, length/area,
ZIP/Postal Code, town name, county name, state/province, coordinates, and
Standard Industrial Classification categories.
3. Click the plus sign next to each of the information categories to expand the category
to view more detailed information.
OR
Right-click in the information box and click Expand All to expand all of the
information categories. Right-click in the information box again an d click Collapse
All to minimize all of the information categories.
4. Optional. Repeat steps 1–3 to get information about another location.
5. Optional. Right-click in the information box and click Print to print your map feature
information.
Notes
• You can also get information about a location using the right-click option. Just rightclick the location and click Info.
• The status bar (located above the tab area) displays draw object type, draw file
information, point of interest name (if applicable), street name/address, highway, city,
state/province, and ZIP/Postal Code information for the map location that your cursor is
positioned on.
• Some map features (such as campgrounds, national scenic/historic trail information
centers, and state parks) display with a blue outline at higher data zoom levels. The
blue outline indicates that the feature has a hyperlink to its website. To open the
hyperlink, right-click the feature and then click Open Hyperlink OR click the URL in the
Info tab.
; to show it, right-click the toolbar to open the
39
Page 42

XMap User Guide
To Create a Profile
To create a profile:
1. Center your 2-D map
OR
Center the route
you want to profile on the map.
on the area with the linear object you want to profile.
2. Click the Profile button
3. Move your pointer over the map. The pointer changes from
passes over an object that you can profile.
4. Select a linear object or route on the map to generate its profile.
When the object is selected, it is highlighted and the Profile graph displays in the
Profile tab area.
Note Move your pointer along the elevation profile in the Profile graph. The
intersection of the vertical and horizontal blue lines travels along the top of the
terrain profile. These lines indicate the height and distance of the particular location.
A small crosshair follows along the corresponding object on the map.
You can also right-click a linear object or route on the map and click Profile. For more
information about profiles, see the Help topics under Profiling Linear Objects.
on the toolbar.
to when it
To Choose Options
To open the Options dialog box, click the Options button on the toolbar. Use
the Options dialog box to set preferences for program options.
The Options dialog has the following tabs:
• GIS
• GPS
• Voice
• Find (GPS Radar)
• Map Features (Basic
• Display
• Handheld
• Keyboard Shortcuts
• 3-D
An Options button that opens the Options dialog box is also available on the 3-D, Handheld
Export, Find>GPS Radar, and GPS tabs.
and Custom)
To open the Options menu, click the arrow next to the Options button
toolbar. The following menu options are available:
• Options—Opens the Options dialog box.
• Tab Manager—Opens the Tab Manager dialog box where you can show or hide
individual tabs and reorder tabs.
40
on the
Page 43

Using the Toolbar
• Netbook Mode—Allows you to turn the Netbook Mode on or off. If the mode is
turned on, the check box next to it is selected. Click Netbook Mode to turn it on or
off. For more information, see Using Small-screen Devices
You can also customize your interface
• Show Tab Area Panel—Allows you to show or hide all the tabs. If Show All Tabs is
turned on, the check box next to it is selected. Click Show Tab Area Panel to show
or hide the tab area.
• Show Control Panel—Allows you to show or hide the Control Panel. If Show Control
Panel is turned on, the check box next to it is selected. Click Show Control Panel to
show or hide it.
:
.
41
Page 44

Customizing the Map and Tab Display
Customizing the Interface
You can customize the interface for your application by hiding the tab panel area and the
Control Panel.
To Customize the Interface
1. Click the arrow next to the Options button
2. To turn on an option when it is not selected, click it to select the check box.
OR
To turn off an option when it is selected, click it to clear th e check box.
• Use Tab Manager to show or hide individual tabs
• Use Show Tab Area Panel to show or hide the entire tab area.
• Use Show Control Panel to show or hide the Control Panel.
• Use Netbook Mode to turn the optimized small-screen device view on or off.
For more information, see Using Small-screen Devices
Notes
• You can also use keyboard shortcuts
• Your settings are saved until you change them.
• Click Options in the menu to open the Options dialog box.
to customize the interface.
on the toolbar.
or reorder tabs.
.
Displaying Basic Map Features
You can show or hide basic map features on your map.
You can also customize map features
Notes
• If you cannot make changes to the basic preference check boxes, verify the Use
Custom Map Features check box is not selected.
• Click Use Defaults to change the map feature settings to the default preferences.
• The options available depend on the datasets you are using.
• The map features available are based on the Map Colors option
To Select Basic Map Feature Preferences
Use the following steps to change the basic map feature preferences. Changes made to the
map view display almost immediately after selection.
and customize the interface.
you are using.
42
Page 45

Customizing the Map and Tab D isplay
1. Click the Options button
on the toolbar.
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Map Features tab.
3. Select the check box next to the map features you want to display on the map.
OR
Clear the check box next to the map features you want to hide on the map.
• Shaded Relief
Shaded relief becomes visible at data zoom level 6-0 or greater. It simulates
the effect of sun shining on terrain features and casting shadows, providing
greater depth perception of the image. Lighter shades of gray indicate gentle
terrain and darker shades indicate steep terrain. Using shaded relief may slow
down the draw time of the map screen as you pan.
• Contours
Contour lines are available at data zoom level 6-0 or greater. Co ntour lines
show the elevation of the land in feet or meters. The closer the contour lines,
the greater the slope. The distance between the lines is the contour interval,
which is indicated in the Control Panel (distance units
are controlled in the
Options dialog box).
• Land Cover
Land cover colors are available at all data zoom levels. Colors indicate
vegetation and land cover areas on the map such as rock and sand, forests,
transitional areas, and wetlands.
• Grids
The Grids option can be used to identify coordinate points on the map. Grid
lines automatically adjust for the data zoom level of your map.
• Parks or Reserves
Parks and Reserves are available at data zoom level 7-0 or greater and
include areas such as parks, preserves, recreational area and public forests.
• Publicly Managed Lands
Publicly Managed Lands are only available when the Bureau of Land
Management (BLM) dataset is downloaded and installed. The feature includes
areas such as lands managed through the Bureau of Land Management and
displays at all data zoom levels.
• Game Management Districts
Wildlife Management Units are only available when the Wildlife Management
Units (WMU) dataset is downloaded and installed. The feature includes areas
of managed wildlife and game and displays at data zoom level 6-0 or greater.
• USGS Quadrangle Coverage
The USGS 7.5 minute quadrangle coverage is indicated by red lines. These
display at data zoom level 8-0 or greater. Quadrangle names display at data
zoom level 9-0 and higher. To view quad info such as Orig Date and Quad
Order ID number (needed when purchasing quads), right-click a point within
the quad and then click Info. An information box displays in the lower-right
corner of the screen.
43
Page 46

XMap User Guide
• 3DTQ Region Coverage
Displays the DeLorme 3DTQ product CD volume label, which covers each map
area at data zoom level 10-0 or greater.
• Map Center Crosshair
The map center crosshair indicates the map center at any data zoom level.
• Exits
View exits on primary limited access roads, interstates, and toll roads.
Available at data zoom level 10-0 or greater.
• One Ways
One ways display as bright green triangles on roads, pointing toward the
direction of travel (most noticeable in large cities). They are available at data
zoom level 13-0 or greater.
• Places (Minor)
View smaller towns, suburbs, locales, and natural features. Zoom levels vary.
• Roads (Minor)
View secondary roads, local and rural routes, trails, and railroads. Zoom
levels vary.
• Points of Interest
• Major—View many different points of interest, including recreational
areas, public safety, rest areas, and more.
• Minor—View general points of interest including educational,
technology, government, and religious buildings/locations.
• Business (Major)—View many different travel-related points of
interest including hospitals, camping, restaurants, and more.
• Business (Minor)—View general points of interest including small
shops and food stores, laundromats, and golfing.
• ZIP-Postal Codes
ZIP/Postal Code boundaries display at data zoom level 8-0 and greater, with
ZIP/Postal Code labels displaying at data zoom level 10-0 and greater.
• Town Borders
• View town borders at data zoom level 10-0 and greater for the
following states:
44
Arkansas
Connecticu
t
Illinois
Indiana
Iowa
Kansas
County Borders
•
Louisiana
Maine
Maryland
Massachusett
s
Michigan
Minnesota
Mississipp
i
Missouri
Nebraska
New
Hampshir
e
New
Jersey
New York
North
Carolina
North
Dakota
Ohio
Pennsylvani
a
Rhode
Island
South
Dakota
Vermont
Virginia
Washingto
n DC
West
Virginia
Wisconsin
Page 47

Customizing the Map and Tab D isplay
View shaded outlines of U.S. counties at data zoom levels 7-0 or greater.
• International Labels
View country labels at data zoom levels 0-0 through 4-0.
• Urban Area Color
Displays a shaded map area in populated regions at data zoom levels 5-0.
4. Click OK to commit the change and exit the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Apply to commit the change and keep working in the Options dialog box.
Customizing the Map Feature Preferences
You can change the display of a wide variety of map features so you can customize your
map to meet your specific needs. You can even customize which POIs display.
To Set Custom Map Features
This is an advanced feature that lets you create a specific, custom set of map features for
your map display from hundreds of options. Note that changes are not visible until you click
the Done button.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Map Features tab.
3. Select the Use Custom Map Features check box and then click Customize
Features to display the custom options.
Note Custom map feature selections override selections in the basic features list.
4. To quickly search for a particular type of feature, type the name of the item in the
Search text box.
A list of matching keywords displays and corresponding feature types are listed in
the Search Results window. Results for the number of keywords and types found
also display.
A selected check box indicates the feature displays on the map.
• Select/clear the individual feature check box to show or hide that feature.
• Click the small None button to the right of the Search Results window to
show none of the features listed.
• Click the small All button to the right of the Search Results window to
display all of the features listed.
• Click Only to display only those features listed in th e Search Results
window.
• Click Exclude to display all features except those listed in the Search
Results window.
5. To use the map feature tree to select which POIs display on the map, click the plus
signs to expand the individual branches. A selected check box indicates the feature
type displays on the map.
Note Some branches expand further than others. Selecting/clearing a check box at
a certain branch of the tree shows/hides all the items below that level.
on the toolbar.
45
Page 48

XMap User Guide
• Select/clear the individual map feature check box to show or hide that
feature.
• Click All to select all map features in the program.
• Click None to select none of the types in the program.
Note A small number of features cannot be turned off. They are part of the
base map display and cannot be changed. This is why certain levels on the
tree remain unavailable (appear dimmed or gray).
6. Click OK to accept the change and exit the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Apply to accept the change and keep working in the Options dialog box.
Notes
• When you save the current project, the following feature preferences are saved in
reference to map features:
o Major map features preferences
o Individual custom feature preferences
o When you create a new project, the current map settings are used. Click Use Defaults
to return to the default settings.
Changing the Map Colors
When you use a laptop computer while traveling, it can be difficult to see the map display
on your screen. This can be especially true at night or on a bright sunny day. Changing your
default map colors to high-contrast map colors can make your map display easier to see.
To Change the Map Colors
Use the following steps to change the map display.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Display tab.
3. From the Map Colors drop-down list, select High-Contrast Colors to make the
map display darker for improved in-vehicle visibility, Stree t Colors to emphasize
streets and highways on the map, or Topo Colors to emphasize contours, parks and
public lands, land cover, and so on.
4. Click OK to accept the change and exit the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Apply to accept the change and keep working in the Options dialog box.
on the toolbar.
Changing the Map Magnification Level
If you want to change the size of the map image, but not change the degree of geographic
detail on the map, use the magnification settings in the Options dialog box.
To Change the Map Magnification
Use the following steps to change the map magnification.
46
Page 49

Customizing the Map and Tab D isplay
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Display tab.
3. Select a magnification percentage (50%, 75%, 100%, 125%, 150%, 175%, or
200%) from the Magnification drop-down list.
Note Although the size of the image changes, the degree of geographic detail does
not.
4. Click OK to accept the change and exit the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Apply to accept the change and keep working in the Options dialog box.
on the toolbar.
Changing How POIs Display on the Map
You can change the data zoom level at which large POI symbols display on the map.
To Change the Data Zoom Level for Large POI Symbols
Use the following steps to change the data zoom level at which large POI symbols are
displayed on the map.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Display tab.
3. Select the data zoom level from the Large Symbols At drop-down list.
4. Click OK to accept the change and exit the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Apply to accept the change and keep working in the Options dialog box.
Notes
• The appearance of a POI many change at different data zoom levels.
• The number of points of interest that displays is dependent on the basic map
features you selected on the Map Features tab in the Options dialog box. For more
information, see Displaying Basic Map Features
This table shows the actions that may happen if you display major and minor POIs.
on the toolbar.
.
If you
view large
symbols
at data
zoom
level...
14 names and
15 small name of the name of the name of the name of the
You will see
the following
information
at data
zoom level
13-0
small square
symbols
You will see
the following
information
at data
zoom level
14-0
name of the
POI and the
large symbol
You will see
the following
information
at data
zoom level
15-0
name of the
POI and the
large symbol
You will see
the following
information
at data
zoom level
16-0
name of the
POI and the
large symbol
You will see
the following
information
at data
zoom level
17-0
name of the
POI and the
large symbol
47
Page 50

XMap User Guide
squares only POI and a
small square
symbol
16 N/A small square
symbols
only
17, 18,
19, or 20
N/A small square
symbols and
some names
of POIs
POI and the
large symbol
name of the
POI and a
small square
symbol
name of the
POI and a
small square
symbol
POI and the
large symbol
name of the
POI and the
large symbol
name of the
POI and a
small square
symbol
POI and the
large symbol
name of the
POI and the
large symbol
name of the
POI and the
large symbol
Setting Units of Measure Preferences
You can change the units of measure used to represent how coordinate formats, distance,
datum, and bearing listings display. Changing these preferences affects how units of
measure display in several areas of the program: such as on the map and in the Control
Panel.
As you change your unit of measure preferences, a description of each choice displays in the
information box (in the center of the Options dialog box) immediately after you select it.
To Change the Coordinate Preferences
Changing the coordinate preferences affects the:
• Coordinates display on the Control Panel.
• Coordinate MapNotes.
• Grid label display, if Grids are selected in Map Features.
• Any other place where coordinates display or print.
Use the following steps to change how coordinate measurement units display.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Display tab.
3. Select the coordinate display format from the Coordinates drop-down list.
• Degrees
• Degrees, Minutes
• Deg, Min, Sec
• UTM/UPS (Universal Transverse Mercator/Universal Polar Stereographic)
• MGRS (Military Grid Reference System)
• USNG (United States National Grid)
• SPCS (State Plane Coordinate System)
Note When you select SPCS, an additional drop-down box displays for Zone.
Select the zone from the list.
4. Select the datum from the Datum drop-down list.
on the toolbar.
48
Page 51

Customizing the Map and Tab D isplay
• WGS84 (World Geodetic System of 1984)
• NAD27 (North American Datum of 1927), which also includes OOH (Old
Hawaiian) Datum when in Hawaii
• NAD83 (North American Datum of 1983)
5. Click OK to commit the change and exit the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Apply to commit the change and keep working in the Options dialog box.
Notes
• UTM/UPS and MGRS coordinate systems are best used with NAD27 datum. 95% of
the USGS quads containing UTM grid lines uses the NAD27 datum, which is helpful if
you are comparing a map generated from your mapping application to a USGS map.
• If the USNG coordinate system is not matched with NAD83 datum, a warning
message displays (unless you selected the Do Not Show This Message Again option).
• If the UTM/UPS or MGRS coordinate system is mismatched to WGS84 datum, a
warning message displays (unless you selected the Do Not Show This Message Again
option).
• The State Plane Coordinate System originally used NAD27 datum and was measured
in statute miles. Some states have updated their systems to WGS84 datum and/or
kilometers. If you are working with a site map, verify the datum, distance measures,
and zone used and match them in your application.
To Change the Distance Preferences
Distance preferences affect how distance and areas display throughout the program.
Use the following steps to change the measurement units for distance and area.
1. Click the Options button
on the toolbar and then click Options.
2. Click the Display tab.
3. Select the measurement from the Measurements drop-down list.
• Statute Miles (statute feet are used for small distances)
• Kilometers (meters are used for small distances)
• Nautical Miles/Feet (statute feet are used for small distances)
• Nautical Miles/Meters (meters are used for small distances)
4. Click OK to commit the change and exit the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Apply to commit the change and keep working in the Options dialog box.
To Change the Bearing Preferences
Bearing listings are created as the result of creating route directions in the Route tab or
from an Advanced (Distance From) search in the Find tab. Bearing refers to the compass
direction of a given object measured clockwise in degrees (for example, 30°) or nearest
compass point (for example, NNE) and indicated from True North or Magnetic North.
Notes:
• Magnetic declination is the difference in degrees between True North and Magnetic
North at a specific location.
• The bearing setting does not affect map appearance.
Use the following steps to change the bearing.
1. Click the Options button
on the toolbar and then click Options.
49
Page 52

XMap User Guide
2. Click the Display tab.
3. Select the bearing from the Bearing drop-down list.
• True North—The direction to the north pole. This is the default setting.
• Magnetic North—The direction that a compass needle points.
4. Click OK to commit the change and exit the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Apply to commit the change and keep working in the Options dialog box.
Resizing the Map and Tab Areas
You can horizontally and vertically resize the primary (right) map, secondary (left) map, tab
area, and overview map with the map and tab area resize tools.
Notes
• The tab and overview map window size does not change when you choose another
tab.
• Some tab areas that provide search results automatically resize depending on the
number of results.
• You can also hide the tab area panel
To Resize the Map and Tab Area Using the Drag M ethod
.
Use the drag method to horizontally or vertically resize these areas.
1. Point to the frame area between the tab and overview map windows. The pointer
becomes a
OR
Point to the horizontal edge of the tab/main map window. The pointer becomes a
.
2. Drag to resize.
3. To cancel the resize while dragging, press the ESC key on your keyboard. The size
just prior to this resize is restored.
To Resize the Map Area Using the Resize Tools
The map resize tool runs perpendicular to the tab area. If the secondary and primary maps
are both displaying, the resize tool is the bar that separates them. When the bar is moved
all the way to the left of the map, only the primary map displays. When the bar is moved all
the way to the right of the map, only the secondary map displays.
There are several methods you can use to resize the map area:
• Drag the bar left to expose the area of the primary map you want to see.
• Drag the bar right to expose the area of the secondary map you want to see.
• Click the right arrow on the resize tool once to move the secondary map 1/4 of the
screen width. You can repeat this step until the primary map is no longer visible.
• Click the left arrow on the resize tool once to move the primary map 1/4 of the
screen width. You can repeat this step until the secondary map is no longer visible.
• Double-click the bar above the right arrow to show only the secondary map.
• Double-click the bar below the left arrow to show only th e primary map.
.
50
Page 53

Customizing the Map and Tab D isplay
• Double-click the bar between the right and left arrows to display an equal percentage
of both the secondary and primary maps.
To Resize the Tab and Map Area Using the Resize Tools
There are two tab area resize tools. The horizontal resize tool is located above the tab area
and lets you adjust the height of the tab area. The vertical resize tool is located between the
tab area and the overview map lets you resize the width of the tab area.
Using the Horizontal Resize Tool
• Drag the horizontal bar up/down to expose the tab area you want to see.
• Click the up arrow on the horizontal resize tool once to incrementally increase the
tab height. You can repeat this step until the top of the tab area is flush with the
bottom of the compass rose in the control panel.
• Click the down arrow on the horizontal resize tool once to incrementally decrease the
tab height. You can repeat this step until only t he tab names display.
• Double-click the bar to the right of the up arrow to expand the tab height to its
maximum percentage (if the tab height is at the default mode or higher).
Note If the tab area is below the default mode, double-click the bar to return the
tab height to its default percentage.
• Double-click the bar to the left of the down arrow to decrease the tab height to its
minimum percentage (if the tab height is at the default mode).
Note If the tab area is above the default mode, double-click the bar to return the
tab height to its default percentage.
• Double-click the bar between the up and down arrows to return the tab height to its
default view.
Using the Vertical Resize Tool
• Drag the vertical bar left to expose the area of the overview map you want to see.
• Drag the vertical bar right to expose the tab area you want to see.
• Click the right arrow on the vertical resize tool once to incrementally increase the tab
width. You can repeat this stop until the overview map is no longer exposed.
• Click the left arrow on the vertical resize tool on ce to incrementally increase the
width of the overview map. You can repeat this step until the tab area is no longer
exposed.
• Double-click the bar above the right arrow to show only the tab area.
• Double-click the bar below the left arrow to show only th e overview map.
• Double-click the bar between the right and left arrows to return the tab and overview
maps to their default views.
Viewing Two Maps at the Same Time
The split-window lets you view two maps at the same time.
The maps interact as follows:
• If you are viewing both the right and left maps at different data zoom levels, a box
(or lines, depending on the current data zoom level) display s on the map that is
zoomed out the furthest. The box/lines indicate the area that is in view on the
opposite map.
51
Page 54

XMap User Guide
• If you are viewing the right and left maps at the same data zoom level but they are
not equally represented on the screen (50/50), a box (or lines) displays on the map
that is covering the larger amount of screen area. The box/lines indicate the area
that is in view on the opposite map.
• Both windows are centered on the same coordinate position. Panning or rotating in
one map causes the same action on both maps.
• The left map window has its own zoom level controls. You can change t he zoom level
of the left map without affecting the zoom level in the right map window. However,
after you adjust the zoom level in the left map window, the zoom tools on the
Control Panel
level 6-0 and the right map at zoom level 8-0, and you click the Zoom Out 1 tool,
the left map displays at zoom level 5-0 and the right map at 7-0.
• The overview map in the tab area is always associated with the right map window.
• Other tab functionality may be affected by use of the split-screen function, as
follows:
Draw—The line and polygon draw tools work in either map window. The
incrementally adjust the map. For example, if the left map is at zoom
Select tool
then manipulate both objects at the same time. Draw files are created for
both windows in the same project.
Route—You can create routes only in the right window; routes display in both
windows.
GPS—You can log with GPS in the right map window; log playback displays in
both windows.
3-D—The 3-D map always displays in the left map window.
highlights the same draw object on both maps and you can
Showing or Hiding Tabs
The Tab Manager feature allows you to customize your program by showing or hiding
individual tabs. You can access Tab Manager:
• During installation
• After installation using the Tab Manager option in the Options menu
• From the Start menu
Notes
• If you use Tab Manager while the program is open, you must exit and restart the
program to view the tab changes.
• To show or hide the entire tab area panel, click the arrow next to the Options button
Show Tab Area Panel to clear the check box next to it. If the tab area is hidden
and you want to show it, click Show Tab Area Panel to select the check box.
on the toolbar. If the tab area is showing and you want to hide it, click
To Show Individual Tabs
Use the following steps to show tabs using Tab Manager.
1. Open XMap, click the arrow next to the Options button
toolbar, and select Tab Manager from the menu.
OR
From the Start menu, point to Programs> DeLorme>XMap...>Tools, and then
click Tab Manager.
52
on the
Page 55

Customizing the Map and Tab D isplay
2. Select the check box next to each tab you want to display in the program.
Note Click Default to show all the tabs in the program in the default order.
3. Click OK.
4. Exit XMap.
5. Open XMap.
To Hide Individual Tabs
Hiding tabs may significantly increase the startup speed of XMap.
Use the following steps to hide tabs using Tab Manager.
1. Open XMap, click the arrow next to the Options button
and select Tab Manager from the menu.
OR
From the Start menu, point to Programs> DeLorme>XMap...>Tools, and then
click Tab Manager.
2. Clear the check box next to each tab you want to hide in the program.
OR
Click Minimum. Only the required tabs will display in the program.
Note Find, Map Data, Info, GIS, and NetLink are required tabs and cannot be
hidden.
3. Click OK.
4. Exit XMap.
5. Open XMap.
on the toolbar,
Importing/Exporting Tab Manager Preferences
Tab Manager includes a feature that allows you to share your custom tab manager
preferences with other XMap users.
To Import Tab Manager Preferences
Use the following steps to import another user's Tab Manager preferences.
1. If your application is open, click the arrow next to the Options button
on the toolbar and click Tab Manager.
OR
From the Start menu, point to Programs > DeLorme > XMap... > Tools and then
click Tab Manager.
2. Click File and then click Import.
The Import Tab Configuration dialog box opens.
3. Browse to the location of the configuration (preferences) file, select it, and then click
Open.
Tab Manager displays with the preferences saved in the imported configuration file.
4. Click OK to close Tab Manager.
5. Exit your application.
6. Open your application.
To Export Tab Manager Preferences
Use the following steps to export your Tab Manager preferences as a configuration file.
53
Page 56

XMap User Guide
1. If your application is open, click the arrow next to the Options button
on the toolbar and click Tab Manager.
OR
From the Start menu, point to Programs > DeLorme > XMap... > Tools, and
then click Tab Manager.
2. Click File and then click Export.
The Export Tab Configuration dialog box opens.
3. Type a name for the configuration (preferences) file in the File Name text box and
then click Save. Configuration files are saved by default in C:\...\DeLorme
Docs\Configuration.
4. Click OK to close Tab Manager.
Reordering the Tabs
Use the Tab Manager feature to customize your program by reordering tabs. You can access
Tab Manager:
• During installation
• After installation using the Tab Manager option in the Options menu
• From your computer's Start menu
Note If you use Tab Manager to make changes while the program is open, you must exit
and restart the program to view the tab changes.
To Reorder the Tabs
Use the following steps to reorder the tabs with Tab Manager.
1. Open XMap, click the arrow next to the Options button
and click Tab Manager.XMap...
2. Click the tab you want to reorder to highlight it.
3. Click the up arrow
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each tab you want to reorder.
5. Optional. Click Default to cancel the reordering process and use the default tab
order (showing all available tabs).
6. Click OK.
7. Exit XMap.
8. Open XMap.
or the down arrow to move the tab to the new position.
on the toolbar
54
Page 57

Using Keyboard Shortcuts
Selecting a Keyboard Shortcut Scheme
Your application comes with the following DeLorme keyboard shortcut schemes:
• 3-D Navigation
• Desktop Mapping
• In-vehicle Navigation
You cannot edit DeLorme schemes, but you can create custom schemes that you can edit.
You can create as many additional custom schemes
To Select a Keyboard Shortcut Scheme
Use the following steps to select a keyboard shortcut scheme.
as you need.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Select a scheme from the Scheme drop-down list.
4. Click Apply to activate the selected scheme.
on the toolbar.
Creating a New Custom Scheme
You can create a custom keyboard shortcut scheme for different program uses.
To Create a Custom Scheme
Use the following steps to create a custom scheme.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Click File and then click New.
The Scheme drop-down list is completed with Custom Scheme# (where # indicates
the incremental number for the number of custom scheme files you have created).
Note If you want to rename the new scheme file, click File, click Rename, and then
type a new name in the Scheme text box. Press the ENTER key on your keyboard
when finished. The new name displays.
4. Assign keyboard shortcuts
for the commands that are listed.
on the toolbar.
Assigning Keyboard Shortcuts in a Custom Scheme
There are three DeLorme keyboard shortcut schemes that you cannot edit; however, you
can create a custom scheme that you can edit with Keyboard Shortcuts tab in the Options
dialog box.
To Assign Keyboard Shortcuts in a Custom Scheme
Use the following steps to edit a custom scheme.
55
Page 58

XMap User Guide
1. Click the Options button
on the toolbar.
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Select a custom scheme
from the Scheme drop-down list.
Note You cannot edit DeLorme schemes.
4. Select the List option.
5. From the Commands drop-down list, select the command grouping to which you
want to assign shortcuts. If you want assign shortcuts to several groupings, select
All Commands.
6. Click to select the command to which you want to assign a shortcut.
7. Click inside the Customize Shortcut text box.
8. Press the shortcut key combination on your keyboard that you want to assign for
that command.
9. Click Assign. The shortcut for that command changes to the combination you
assigned and displays as "pending."
10. Repeat the steps for each command you want to assign.
11. Click Apply to save the changes.
OR
Click OK to save the changes and close the Options dialog box.
OR
Click Cancel to cancel your pending changes and close the Options dialog box.
Notes
• To sort the command list view, click a heading (Group, Command, or Shortcut).
• You cannot change the following keyboard shortcut combinations:
o ALT+F4 (Close Window)
o F1 (Help)
o ALT+F1 (Help Menu)
o SHIFT+F10 (Context Menu)
o CTRL+C (Copy)
o CTRL+V (Paste)
o CTRL+X (Cut)
o CTRL+Y (Redo)
o CTRL+Z (Undo)
o ALT+M (Set Focus on Map)
You cannot use the following keys when assigning shortcuts:
o
o Windows Key
o Application Key
o Print Screen
o Scroll Lock
o Sleep
o Pause/Break
o Enter
56
Page 59

Using Keyboard Shortcuts
o Caps Lock
o Num Lock
o Spacebar
o Insert
o Backspace
o Multi-media Keys
o You cannot assign a letter or number on its own. For example, you cannot assign a
keyboard shortcut with the number 3; you must use a modifier (such as CTRL or ALT)
with letters and numbers.
Customizing a DeLorme Scheme
You cannot edit DeLorme schemes; however, you can create a copy of a DeLorme scheme
that you can modify to fit your needs.
To Customize a DeLorme Scheme
Use the following steps to customize a DeLorme scheme.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Select the DeLorme scheme you want to copy from the Scheme drop-down list.
4. Click File and then click Copy.
The active scheme changes to Copy of Desktop Mapping#, Copy of In-vehicle
Navigation#, Copy of 3-D Navigation#, etc. (depending on the DeLorme scheme you
chose to copy).
5. Assign keyboard shortcuts
6. Optional. Rename the scheme
for the copied scheme.
.
on the toolbar.
Renaming a Custom Scheme
Custom schemes can be renamed to whatever name you choose. You cannot rename
DeLorme schemes.
To Rename a Custom Scheme
Use the following steps to rename a custom scheme.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Select the custom scheme you want to rename from the Scheme drop-down list.
4. Click File and then click Rename.
The Scheme text box becomes active.
5. Type the name in the Scheme text box.
on the toolbar.
57
Page 60

XMap User Guide
6. Click Apply. The new name displays.
OR
Press the ENTER key on your keyboard. The new name displays.
OR
Press the ESC key on your keyboard to keep the old name.
Deleting a Custom Scheme
Once you have created a custom scheme, you can delete it at any time. You cannot delete
DeLorme schemes.
To Delete a Custom Scheme
Use the following steps to delete a custom keyboard shortcut scheme.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Select the custom scheme you want to delete from the Scheme drop-down list.
4. Click File and then click Delete.
5. Click Yes when asked if you are sure you want to delete the scheme.
on the toolbar.
Importing a Custom Scheme
You can share their keyboard shortcut schemes with other DeLorme users.
To Import a Custom Scheme
Use the following steps to import a custom scheme.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Click File and then click Import.
The Import Scheme File dialog box opens.
4. Browse to the location where you saved the .keyscheme file, select it, and then click
Open.
The imported file is now your active scheme.
on the toolbar.
Exporting a Custom Scheme
You can share their keyboard shortcut schemes with other DeLorme users.
To Export a Custom Scheme
Use the following steps to export a custom scheme.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
58
on the toolbar.
Page 61

Using Keyboard Shortcuts
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Select the scheme you want to export from the Scheme drop-down list.
4. Click File and then click Export.
The Export Scheme File dialog box opens.
5. Type a name in the File Name text box, browse to the location where you want to
save the .keyscheme file, and then click Save.
Searching For Commands
The Keyboard Shortcuts tab in the Options dialog box has a Search feature that lets you
search for a specific command or command group.
Note You can sort the command list view at any time by clicking the heading you want to
sort by (Group, Command, or Shortcut).
To Search For a Command or Command Group
Use the following steps to search for a command or command group.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Select the Search option.
4. In the Commands text box, begin typing the name of the command or command
group you are searching for. As you type, the list box under the Commands text box
displays word matches.
on the toolbar.
Viewing All of the Shortcut Keys for a Scheme
The Reference Card option in the Keyboard Shortcuts tab lets you view a complete list of all
of the scheme's shortcut keys.
To View a List of Shortcut Keys
Use the following steps to view a list of shortcut keys for a scheme.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the Keyboard Shortcuts tab.
3. Select the scheme that contains the shortcut keys you want to view from the
Scheme drop-down list.
4. Optional. To sort the list view, click the heading you want to sort by (Group,
Command, or Shortcut).
5. Click Reference Card.
The list displays in your default Web browser and is sorted by the same column you
selected in step 3.
6. Optional. Print the list from your Web browser.
on the toolbar.
59
Page 62

XMap User Guide
Print a reference card from your web browser
• Use the Print Preview functionality in y our web browser to see if the list will
display as you want it to. If you do not like the way the list looks in the preview
(for example, the list prints without grid lines in the table or does not print in
color), change the advanced print settings in your Web browser.
• If you want to remove the header and footer text from the printout, from the File
menu, select Page Setup. Remove the text and the header and footer text boxes
and then click OK.
• Changes made to the browser's advanced print settings and page setup affect the
printing of all web pages.
60
Page 63

Using Projects/Map Data
Map Data Overview
XMap lets you save all of the work that you have done as a single project file so y o u can
open it again later. You can create different map views and save each in a different project.
What is a Project?
A project includes the current GIS workspace, map center coordinates, the current data
zoom level, the current magnification, rotation, preferences, and links to routes or draw
layers you have added to it.
As you create routes, draw, and GIS layers, they are added to the currently selected
project. Projects are saved by default in C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Projects.
Each associated file is saved in its respective folder in the DeLorme Docs directory. For
example, a draw layer is saved in C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Draw.
Can I Reuse Draw Layers and Routes in Other Projec ts?
After you create routes or add your own roads, you may not want to do all of the work
again in another project. You can share routes and draw layers between projects using the
Add button on the Map Data tab.
Can I Send Routes or Draw Layers to Another XMap User?
You can package projects, including their routes and draw layers, into one transfer file for
convenience. The transfer file facilitates e-mailing, copying project information to other
computers, and copying projects between DeLorme programs.
You can use MapShare to share maps, routes, or profil e s with non-XMap users. For more
information, see To Share Maps
.
Migrating Data to the New DeLorme Docs Locations
In versions of XMap prior to XMap 6 and in other DeLorme products, your projects, draw
files, route files, log files, XData files, imagery, and other DeLorme files were stored by
default in the DeLorme Docs folder on the root of your computer's C drive unless you
specified a different directory during installation.
For XMap 6 and newer versions:
• The DeLorme Docs folder for all files except NetLink downloads is located in the My
Documents (Windows XP) or Documents (Windows Vista and Windows 7) folder
under your user name.
• The DeLorme Docs folder for NetLink downloads is located in the DeLorme Docs
folder under Shared Documents (Windows XP) or Public Documents (Windows Vista
and Windows 7). This allows all users on the computer to access NetLink downloads.
What is Migration?
The migration process does not move your files—it copies them to the new locations. When
you are sure your files are working correctly in th e new locations, you can delete them from
the old locations as long as you are not using them for another DeLorme program. For
example, if you have an imagery file you use in Topo USA or XMap (5.x or earlier), keep
both files.
61
Page 64

XMap User Guide
Because all new information you add to a project will be saved to the new file location—
even if you open it from the old location, we strongly recommend that you migrate your
files. If you do not, you could have project data in two DeLorme Docs locations; your
project will work correctly, but your data will not all be in th e same location.
Initial Migration
The initial migration process, which occurs when you open XM ap the first time after you
install it, copies the data in the existing Net Link Downloads, Symbols, and GPSLogs folders
to their new locations as indicated above.
Note The automatic migration process copies files from only one existing DeLorme Docs
location. If you have more than one DeLorme Docs location on your computer, only one
location will be recognized
New Users
When you installed XMap on your computer, you were asked if you had previously installed
a DeLorme program. If you had not, you clicked New User and the application opened. The
migration process does not apply to you if you have never installed a DeLorme program on
your computer.
Existing Users
When you opened XMap for the first time after installation, your computer was scanned for
an existing DeLorme Docs directory. If a DeLorme Docs directory was found, any data in the
existing NetLink Downloads, Symbols, and GPSLogs folders was copied to their new
locations as indicated above.
If an existing DeLorme Docs folder was not automatically detected on your computer, you
are asked if you had previously installed a DeLorme program. If you had, you clicked
Existing User which opened a dialog box for browsing to the existing DeLorme Docs location
and choosing one of the following migration options:
• Migrate–The data in the NetLink Downloads, Symbols, and GPSLogs folders was
migrated to their new DeLorme Docs locations.
• Don't Migrate–The migration was cancelled and any data in the NetLink Down loads,
Symbols, and GPSLogs folders was not migrated. You will not be prompted to
migrate again.
• Try Again Later–Cancels the migration, but you are prompted to migrate the next
time you open the program. You will be prompted each time you open the program
until you select Migrate or Don't Migrate.
Project Migration
When you migrate a project, all associated files (routes, draw layers, XData sets, and
connections to GIS layers in a database) are moved with it. When you open a project from
any location other than the new DeLorme Docs location, you are prompted to migrate it.
You can also directly migrate projects.
To Migrate a Project When You Open It
Use the following steps to migrate a project when you open it.
1. Open a project
2. When the Migrate Project dialog box opens, click Migrate.
The Migration Completed dialog box opens. Go to step 4.
OR
If a file with the same name already exists in the new DeLorme Docs location, the
Confirm Link to Existing File dialog box opens. Go to step 3.
62
.
Page 65

Using Projects/Map Data
3. Click Link to replace the project link to the existing file in the new location and then
go to step 4.
OR
Click Link All to replace any project links to existing files in the new location and
then go to step 4.
OR
Click Save Copy to maintain the project link to the current file and save it with a
different name.
OR
Click Cancel to stop the migration process and roll back any file migration that has
occurred up to this point.
4. In the Migration Completed dialog box, click OK to open the migrated project.
Note If there is a problem with the migration, a message will notify you of any
corrective action you need to take.
To Manually Migrate a Project
Use the following steps to migrate a project at any time.
1. Click the arrow next to the Open button
on the toolbar and then click
Migrate Project.
OR
Click the Map Data tab, click File, and then click Migrate Project.
The Migrate Project dialog box opens.
2. Browse to the project you want to migrate, click the project, and then click Migrate.
3. The Migration Completed dialog box opens. Go to step 5.
OR
If a file with the same name already exists in the new DeLorme Docs location, the
Confirm Link to Existing File dialog box opens. Go to step 4.
4. Click Link to replace the project link to the existing file in the new location and then
go to step 5.
OR
Click Link All to replace any project links to existing files in the new location and
then go to step 5.
OR
Click Save Copy to maintain the project link to the current file and save it with a
different name.
OR
Click Cancel to stop the migration process and roll back any file migration that has
occurred up to this point.
5. In the Migration Completed dialog box, click Open to open the migrated project or
Close to close the dialog box and return to your last active project.
Note If there is a problem with the migration, a message will notify you of any
corrective action you need to take.
63
Page 66

XMap User Guide
Managing Data
Adding Data and Imagery to XMap
XMap is compatible with a variety of DeLorme datasets and imagery formats. You may have
some of these datasets installed on your hard drive, or you may access the data on a DVD.
Whether the data is on a DVD or saved on your hard drive, you can choose to add the data
to current and future projects or only the current project.
Notes
• When adding third-party imagery formats, such as MrSID (.sid) and GeoTIFF (.tif), a
DeLorme .adc file is automatically created in the directory where the data resides.
This file is a connection between the original data and t he DeLorme application.
• When you add MrSID or GeoTIFF to future projects, you can select the .adc file to
automatically add the data. If you select the .sid or .t if extension, an .adc file with
the same name is created and you are prompted to overwrite the file name if it
exists.
Adding Data to Current and Future Projects
Data that is in current and future projects is considered "base data." If your data is saved
on your hard drive, you must update the Base Data settings in the Map Data tab to include
that data in your current and future projects.
Note If you are accessing data from a DVD, your data is added to every project you create
while the DVD is in the DVD drive and it is not necessary for you to follow the steps below.
Use the following steps to add data to current and future projects.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
Create a new
2.
3. Click Data and then click Base Data.
The Data Locations dialog box opens listing each of the data sources on your system.
4. Click Add, select the hard drive location where your saved your data from the
Browse for Folder dialog box, and click OK. The OK button is enabled when you
select a folder containing a file that contains the .adc file of the map data being
added.
Note Your hard drive location may already be listed in the Data Location dialog box,
but the check box for that location might not be selected. Ensure all of the data
locations you want to display in your current and future projects have selected check
boxes.
5. Click Done.
or open an existing project.
Adding Data to the Current Project
You can choose to add data to only the current project if the data is saved on your hard
drive. Any data on a DVD in your DVD drive displays in your projects as long as the DVD is
in the drive.
Use the following steps to add data to the current project.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. If the project you want to add data to is not displaying, open
Note To verify the project you want is displaying, check the title bar. The project
name displays directly after the product name.
3. Click Data and then click Add.
The Add Data to Maps dialog box opens.
64
the project.
Page 67

Using Projects/Map Data
4. Browse to the folder where the file you want to add is located and click the file to
select it.
5. Select the map you want to add the file to (primary, secondary, or both) from the
Add To drop-down list.
6. Click Add. The file is added to the current project under the selected map.
Note If you add a file to a project and later update the file, the file is updated in
every project you have added to.
7. Save your project
C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Projects.
Notes
• For information about migrating data to XMap, see Migrating Data to the New DeLorme
Docs Location.
• Select the check box next to a file to display it. Clear the check box to hide it.
. Projects have .xmp extensions and are saved by default in
• Use the Move to Primary Map
datasets from one map to the other.
and Move to Secondary Map buttons to move
Adding/Removing Base Data
Use the Base Data function in the Map Data tab to modify the default map data source(s)
for your current and future projects.
To Add Base Data
Use the following steps to add base data to your current and future projects.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Create a new
3. Click Data and then click Base Data.
The Data Locations dialog box opens and lists each of the data sources on your
system.
4. Select the check box next to the data source you want to use as a data source for
your current and future projects.
AND/OR
Click Add, select a data folder from the Browse for Folder dialog box, and click OK.
5. Click Done.
To Remove Base Data
Use the following steps to remove base data from your current and future projects.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Create a new
3. Click Data and then click Base Data.
The Data Locations dialog box opens and lists each of the data sources on your
system.
4. Click to select the data source you want to remove from your current and future
projects. Click Remove. Click OK when the confirmation message displays. The base
data is removed from the list.
OR
Clear the check box next to the base data you want to remove. The base data is kept
in the list, but is removed from the current and future projects.
5. Click Done.
or open an existing project.
or open an existing project.
65
Page 68

XMap User Guide
Setting Data as Routing Data
The first dataset added to your project is the default routing dataset; however, not all
datasets support road and direct routing. If you are using more than one dataset in XMap,
you can determine which dataset to use for routing.
To Set Data to be Used as Routing Data
Use the following steps to assign a dataset for routing.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
In the Primary Map window, the dataset that is currently set to be used for routing
displays the routing icon
2. Under Primary Map, highlight the dataset you want to assign as your routing
dataset.
3. Click Data and then click Set as Routing Data.
The routing data is updated and the routing icon
highlighted in step 2.
OR
Right-click the selected dataset and click Set as Routing Data.
The routing data is updated and the routing icon
highlighted in step 2.
to the left of the dataset name.
displays next to the dataset
displays next to the dataset
Viewing Data from NetLink
When you use NetLink to download imagery and data, the dataset is automatically listed as
base data. Downloaded imagery is saved by default in saved in C:\...\DeLorme
Docs\Downloads. If you purchased a DVD, you can add your imagery and data to your
current and future projects by adding it as base data
Note Not all data displays at all data zoom levels.
To View Imagery
Use the following steps to view imagery.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Primary Map and/or Secondary Map (depending on the map window you
want to use to view the dataset), click the plus sign next to the dataset.
3. Double-click the file name.
The imagery displays on the map(s).
ADP Data
If you have an ADP (Aerial Data Packet) dataset from a previous version of a DeLorme
application, you still have access to it.
To Designate Which ADP Layer Displays on the Map
Once the dataset is listed in the Map Data tab, you can designate which layer you want to
display on the map. For example, an ADP dataset may consist of DOQQ data and Sat 10
data. If you select both of these, the last check box you select is the data that displays on
the map.
Use the following steps to designate which data layer to display on the map.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Primary Map and/or Secondary Map (depending on the map window you
want to use to view the dataset), click the plus sign next to ADP Dataset.
Each of your ADP datasets display.
.
66
Page 69

Using Projects/Map Data
3. Click the plus sign next to the ADP location.
The contents of the dataset display.
4. If the check box next to the data layer you want to display on the map is selected,
clear the check box and then select it again. The data layer displays on the map.
OR
If the check box next to the data layer you want to display is cleared, select the
check box. The data layer displays on the map.
Managing Projects
Creating and Deleting Projects
You can create different data configurations and save them in separate projects.
To Create a New Project
When you create a new project, all of the data selected as your base data is available in the
new project. For more information, see Adding/Removing Base Data
Use the following steps to create a new project.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Click File and then click New.
A new untitled project opens, using the last map view as the default view. Untitled #
displays in the title bar after the product name.
OR
To name the file and save it, click File and then click Save As. Type the name in the
File Name text box and then click Save.
Note Projects have .xmp extensions and are saved by default in C:\...\DeLorme
Docs\Projects.
.
To Delete a Project
Use the following steps to delete a project.
1. On your computer, browse to the location of the project you want to delete.
Note Projects have .xmp extensions and are saved by default in C:\...\DeLorme
Docs\Projects. Projects created in XMap 5.x or earlier are stored in the DeLorme
Docs folder on the root of your C drive. For more information, see Migrating Data to
the New DeLorme Docs Location.
2. Select the file from the file list and then click the Delete button on the toolbar or
press the DELETE key on your keyboard.
OR
Right-click the file in the file list and click Delete.
Tip You can open a project to verify it is the one you want to delete. For more information,
see Opening a Project
.
Opening a Project
You can open projects created in all versions of XMap.
To Open a Project
Use the following steps to open a project.
1. Open a project from the toolbar
OR
Click the Map Data tab, click File, and then click Open.
The Open File dialog box opens.
.
67
Page 70

XMap User Guide
Note If you made changes to a project that is already open, the Save Changes
dialog box opens. Note Projects have .xmp extensions and are saved by default in
C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Projects.
2. Click the project and then click Open.
The last saved map view for that project displays.
OR
Double-click the project. The last saved map view for that project displays.
Note If the project has not been migrated to the new DeLorme Docs location, you
will be prompted to migrate it. Click Migrate to create a copy of the file in the new
DeLorme Docs location. Click No to cancel. For more information about migrating
projects, see Migrating Data to the New DeLorme Docs Location
.
Saving a Project
Use the Map Data tab to save each of your projects quickly and easily using one of the
following methods:
• Click File and then click Save or click the Save button
o If you have not saved the project before, the Save File dialog box opens.
Type a file name in the File Name text box and click Save.
o If you have saved the project before, the Save dialog box opens. All of the
changes made to the current project display as a check list. Select the check
box next to each change you want to save and clear the check box next to
each change you do not want to save. Click Yes to save the selected changes,
click No to save the file without the changes, or click Cancel to cancel the
saving process.
• Click File and then click Save As.
The Save File dialog box opens. Type a file name in the File Name text box and click
Save.
You can also click the Save button
on the toolbar.
.
Adding/Removing Files in a Project
As you create new GIS layers, routes, draw layers, XData datasets, and so on, or need to
add more datasets to the Map Data tab, they are added to the current project.
To Add Files to a Project
Use the following steps to add specific files to a particular project.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. If the project you want to add files to is not displaying, open
The contents of the current project display in the primary map window on the right
side of the dialog area.
Note To verify the correct project is displaying, check the title bar. The project
name displays directly after the product name.
3. To add a new route or draw file, click Data, click New, and then click Draw File or
Route File.
A new draw or route file is added to your project.
OR
To add an existing route, draw, .adc, .dcf, .tif, .sid, .txt, or .dds file:
a. Click Data and then click Add.
The Add Data to Maps dialog box opens.
the project.
68
Page 71

Using Projects/Map Data
b. Browse to the folder where the file you want to add is located and click to
select it.
c. Select the map you want to add the file to (primary, secondary, or both) from
the Add To drop-down list.Notes
• .adc, .txt, .tif, and .sid files are the only files you can add to both the
primary and secondary maps.
• .sid and .tiff/.tif files must contain spatial reference information to add
them. If they do not, an error message displays and you must use a
third-party application to specify the spatial reference information.
d. Click Add.
The file is added to the current project under the selected map.
Note If you add a file to a project and then edit and save it later, the file is
updated in every project you have added it to. This does not apply to raster
property settings for .sid and .tiff/.tif data.
4. Save the project
C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Projects.
To Remove Files in a Project
Use the following steps to add or delete specific files in a particular project.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. If the project you want to remove files from is not displaying, open
The contents of the current project display in the primary map window on the right
side of the dialog area.
Note To verify the correct project is displaying, check the title bar. The project
name displays directly after the product name.
3. To remove a file, select that file from the project list on the Map Data tab and then
. Projects have .xmp extensions and are saved by default in
the project.
click the Remove button
Note This does not delete the file; it removes it from the selected project.
4. Save the project
C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Projects.
Notes
• Projects created in XMap 5.x or earlier are stored in the DeLorme Docs folder on the
root of your C drive. For more information, see Migrating Data to the New DeLorme
Docs Location.
• Select the check box next to a file to display it. Clear the check box to hide it.
• Use the Move to Primary Map
datasets from one map to the other.
. Projects have .xmp extensions and are saved by default in
.
and Move to Secondary Map buttons to move
Renaming a Project
Projects are untitled when you first add them to XMap. When you save the map, you can
accept the default name or give it a specific name. When you have many different projects
and are trying to locate a specific map view, you may find it more helpful to rename the
project.
To Rename a Project
Use the following steps to rename a project.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
69
Page 72

XMap User Guide
2. If the project you want to add/delete files for is not displaying, open
The contents of the current project display in the Primary Map window on the right
side of the dialog area.
Note To verify the correct project is displaying, check the title bar. The project
name displays directly after the product name.
3. Click File and then click Save As.
The Save File dialog box opens.
4. Type the name in the text box and then click Save.
You now have two files; one with the original name and one with the new name.
the project.
Using Transfer Files
Using Transfer Files Overview
This section describes how to create, import, and e-mail a transfer file. You can package
projects, including their routes, draw layers, and other contents, into one transf er file for
convenience. The transfer file facilitates e-mailing, copying project information to other
computers, and copying projects between DeLorme programs. Transfer files do not include
map data or GIS data.
Creating Transfer Files
A project and its contents can be packaged into a single file, called a transfer file, to
facilitate e-mailing or copying.
You can create a transfer file with or without hyperlinked file attachments. When you create
a transfer file with hyperlinked files, you have the option of saving the common directory
structure of the hyperlinked files. Saving the directory structure of common files can be
helpful when you are sharing and updating transfer files. Transfer files do not include map
data or GIS data.
To Create a Transfer File
Use the following steps to create a transfer file.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Open the project
3. Click File, click Transfer, and then click Create.
The Create Transfer File dialog box opens.
4. In the File Name text box, type the file name.
Transfer files have .dmt extensions and are saved by default in C:\...\DeLorme
Docs\Projects.
5. Click Create.
Your file is created and saved in the specified location.
To Maintain the Directory Structure When Creating a Transfer File with
Hyperlinked Files
When you create a transfer file containing hyperlinked files, you can select to maintain part
of the directory structure for files with at least a common drive location.
Use the following steps to create a transfer file with hyperlinked files.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Open the project
3. Click File, click Transfer, and then click Create. The following dialog box opens.
you want to create as a transfer file.
you want to create as a transfer file.
70
Page 73

Using Projects/Map Data
4. Verify the Include Hyperlink Files for Transfer check box is selected.
If you do not want to include hyperlink files in you r transfer file, clear this check box
and go to step 8.
5. Under File Options, select Maintain Directory Info to save the directory structure
of the hyperlinked files.
If you do not want to include the directory information for the hyperlinked files in the
transfer file, select Do Not Include Directory Info and go to step 7.
6. Type the common base directory location of the hyperlinked files (up to the folder
location that you want to maintain) in the text box.
OR
Click the Browse button
and browse to the common base directory location.
7. Under Select Files to Be Included, clear the check box next to each file you do not
want to include in your transfer file.
8. Click OK.
The Create Transfer File dialog box opens.
9. In the File Name text box, type the file name.
Transfer files have .dmt extensions and are saved by default in C:\...\DeLorme
Docs\Projects.
10. Click Create.
Your file is created and saved in the specified location. The default location for
imported transfer file attachments is C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Transfer Files.
71
Page 74

XMap User Guide
Importing Transfer Files
You can package a project and its contents into a single file, called a transfer file, to
facilitate e-mailing or copying. You can also import transfer f iles, allowing you to share your
projects with other DeLorme users.
You can import a transfer file with or without attached hyperlink files. When you create a
transfer file with hyperlinked files, you can choose to maintain the directory information of
common files. By doing this, the recipient of the transfer file can keep a similar directory
structure as the creator. This is helpful when a transfer file is shared and updated between
users. Transfer files do not include map data or GIS data.
To Import a Transfer File
Use the following steps to import a transfer file, including transfer files that have been emailed to you by other DeLorme users.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Click File, click Transfer, and then click Import.
The Import Transfer File dialog box opens. The default location is C:\...\DeLorme
Docs\Projects. Browse to another location to change it. Transfer files have .dmt
extensions.
3. Click a file to select it.
The name displays in the File Name text box.
4. Click Import to finish the import process.
The imported project opens and displays in the map view.
To Import a Transfer File with Hyperlinked Files
Use the following steps to import a transfer file that includes hyperlinked file attachments.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Click File, click Transfer, and then click Import.
The Import Transfer File dialog box opens. The C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Projects
directory displays by default. Browse to another location to change it. Transfer files
have .dmt extensions.
3. Click a file to select it. The name displays in the File Name text box.
4. Click Import. The Browse for Folder dialog box opens.
5. Select the folder where you want to save the hyperlinked files. Th e default location is
C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Transfer Files. Transfer files have .dmt extensions.
6. Click OK.
The imported project opens in the map view.
E-mailing a Transfer File
You can package a project and its contents into a single file, called a transfer file, to
facilitate e-mailing or copying. Transfer files do not include map data or GIS data.
To E-mail a Transfer File
This procedure creates an attachment file but does not permanently save a file to
C:\...\DeLorme Docs\Projects.
Use the following steps to e-mail a transfer file.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Open the project
you want to e-mail as a transfer file.
72
Page 75

Using Projects/Map Data
3. Click File, click Transfer, and then click E-mail.
A transfer file is created and your computer's default operating system e-mail
program opens with the transfer file included as an attachment.
4. Complete the e-mail in accordance with your e-mail program.
Changing the Properties of Your Data
Changing the Properties in Your Data Overview
You can adjust the properties of some data categories to accommodate your needs. For
example, you can adjust the shaded relief properties to account for the sun shining in a
different direction, have contours display at varying densities at parti c ular zoom levels, etc.
Each dataset contains its own sub-categories of data (raster, vector, contours, etc.).
Because of this, not all of the property information in t his section of the Help will pertain to
every dataset.
Note It is important to remember that any changes made to the dataset properties are
permanent only when saved in a project.
Changing Imagery Display
When you use the Map Data tab to add imagery files, such as GeoTIFF, imagery, and
ImageReg data, or data and imagery downloads from NetLink, to a map—by default, the
image appears on top of any DeLorme vector base map by default. However, you can
customize the layering sequence so that selected vector map features (roads, contours,
etc.) appear on top of the image. Any added imagery files are listed in the Map Data tree
view under the appropriate series.
To Change the Properties of an Imagery File
Use the following steps to change the properties of an imagery file.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the imagery
series you want to modify.
3. Click the plus sign next to the specific imagery file you want to modify.
The types of imagery in the file display.
4. Right-click the imagery file and click Properties.
The Raster Properties dialog box opens.
5. Optional. For MrSID and some types of GeoTIFF data, you may be able to select a
color to display as transparent (for example, black). To do so, select the
Transparent Color check box, select a color, and click OK. Note that doing so
makes the default transparent color (bright pink) show around the imagery.
OR
If you do not want to select a color to display as transparent, click Next.
6. Type the minimum and maximum data zoom range for your custom raster properties
in the text boxes.
7. Select the raster data position for that data zoom range from the drop-down list.
Note The raster data position you select includes all of the options above it in the
list.
8. Click Add Change to update your data positioning selections to the map. You must
perform this step to apply any change.
9. Click Next.
73
Page 76

XMap User Guide
10. Drag the gray tab markers to the minimum and maximum data zoom levels at which
you want to see the imagery file on the map.
11. Click Next.
12. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
raster properties.
13. Click Finish.
Changing Point Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, etc.
Note You must use the Map Features tab of the Options dialog box to set the options for
viewing any changes made to the point properties on the map. See Displaying Basic Map
Features for information on showing/hiding points of interest.
To Change Point Properties
Use the following steps to change the properties of point data.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Highlight Map Points, click Data, and then click Properties.
The Point Properties dialog box opens.
OR
Right-click Map Points and click Properties.
The Point Properties dialog box opens.
5. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab markers to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
The minimum and maximum zoom range displays above the Set Zoom Range For
Display area.
Note The Show URLs check box is enabled if your dataset supports showing points
as hyperlinks on the map.
6. Click Next.
7. Review the dataset information and click Next, if applicable.
8. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
point properties.
9. Click Finish.
The Point Properties for that dataset are modified and are visible on the map.
Note The point property changes are made only in the current project. You must
save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing Vector Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, etc.
Note You must select to show land thoroughfares in the Display tab of the Options dialog
box to view any changes made to the vector properties on the map. See Customizing the
Map Features Preferences for information on showing/hiding land thoroughfares.
To Change Vector Properties
74
Page 77

Using Projects/Map Data
Use the following steps to change the properties of vector data.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Highlight Vectors, click Data, and then click Properties.
The Vector Properties dialog box opens.
OR
Right-click Vectors and click Properties.
The Vector Properties dialog box opens.
5. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab markers to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
The minimum and maximum zoom range displays above the Set Zoom Range For
Display area.
6. Click Next.
7. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
vector properties.
8. Review the dataset information and click Next, if applicable.
9. Click Finish.
The vector properties for that dataset are modified and are visible on the map.
Note The vector property changes are made only in the current project. You must
save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing the Contour Properties
Use the Properties option in the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, DEM properties, etc.
Notes
• You must select to show contours in the Map Features tab of the Options dialog box to
view any changes made to the contour properties on the map. See Displaying Basic Map
Features for information on showing/hiding contours.
• XMap remembers the last customized contour values. For example, if you customize
your contour settings and then change the settings to the default, the next time you try
to customize your contour settings the last saved customized values display.
To Change the Contour Properties
Use the following steps to change the properties of contours.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Right-click Contours and click Properties.
The Contour Properties dialog box opens (for Contours).
5. Select a contour option (Default, High Density, Low Density, or Custom) from the
drop-down list.
• Default—Uses the default values for displaying contours and labels.
• High Density—Approximately doubles the default values for displaying
contours and labels.
75
Page 78

XMap User Guide
• Low Density—Approximately halves the default values for displaying
contours and labels.
• Custom—Allows you to customize how contours and labels display on the
map.
6. For Contours, select the data zoom level at which you want labels to begin to
display.
7. Click Next.
8. If you selected Default, High Density, or Low Density in step 5, go to step 9.
OR
If you selected Custom in step 5, you can customize the contour display by choosing
the distance (in feet or meters) between contours and how many minor (unlabeled)
contour lines for every major (labeled) contour line.
• For a given range of data zoom levels, type the distance (in feet or meters)
between contour lines for those data zoom levels.
• Type the number of minor lines for each major line. For example, type 0 to
label every contour line or type 2 to label every th ird contour line.
Note Labels display only on major lines beginning at the zoom level that you
specified step 6.
• Click Add/Change to update the contour rules list.
OR
Click Reset to reset the settings to what displayed when you first launched
the dialog box.
OR
Click Use Defaults to use the default values to display contours and labels.
9. Click Next.
10. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab marker to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
The minimum and maximum zoom range displays above the Set Zoom Range For
Display area.
11. Click Next.
12. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
point properties.
13. Click Finish.
The Contour Properties for that dataset are modified and are visible on the map.
Notes
• The contour property changes are only made in the current project. You must
save your project
• Selecting Custom changes the Interval section in th e Control Panel to read,
"Custom."
to retain the property changes.
Changing Coordinate Grid Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features, such as coordinate grids, rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, and so
on.
You must select to show grids in the Display tab of the Options dialog box to view any
changes made to the coordinate grid properties on the map. See Displaying Basic Map
Features for information on showing/hiding grids.
To Change Coordinate Grid Properties
76
Page 79

Using Projects/Map Data
Use the following steps to change the properties of coordinate grids.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Highlight Grid Lines, click Data, and then click Properties.
The Coordinate Grid Properties dialog box opens.
OR
Right-click Grid Lines and click Properties.
The Coordinate Grid Properties dialog box opens.
5. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab markers to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
The minimum and maximum zoom range displays above the Set Zoom Range For
Display area.
6. Click Next.
7. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
coordinate grid properties.
8. Click Finish.
The Coordinate Grid Properties for that dataset are modified and are visible on the
map.
Note The coordinate grid property changes are made only in the current project.
You must
save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing USGS Quad Line Connection Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as USGS quad line connections, rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours,
points, etc.
Note You must select to show USGS quadrangle coverage in the Display tab of the Options
dialog box to view any changes made to the USGS quad line connection properties on the
map. See Displaying Basic Map Features
quadrangle coverage.
To Change USGS Quad Line Connection Properties
Use the following steps to change the properties of USGS quad line connections.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Highlight USGS Quad Lines, click Data, and then click Properties.
The USGS Quad Line Connection Properties dialog box opens.
OR
Right-click USGS Quad Lines and click Properties.
The USGS Quad Line Connection Properties dialog box opens.
5. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab markers to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
The minimum and maximum zoom range displays above the Set Zoom Range For
Display area.
6. Click Next.
for information on showing/hiding USGS
77
Page 80

XMap User Guide
7. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
USGS quad line connection properties.
8. Click Finish.
The USGS quad line connection properties for that dataset are modified and are
visible on the map.
Note The USGS quad line connection property changes are only made in the current
project. You must save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing Draw Connection Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features, such as draw objects, rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, and so on.
To Change Draw Connection Properties
Use the following steps to change the properties of draw objects.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the draw file for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Right-click the draw file and click Properties.
The Draw Connection Properties dialog box opens.
4. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab markers to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
The minimum and maximum zoom range displays above the Set Zoom Range For
Display area.
5. Click Next.
6. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
draw connection properties.
7. Click Finish.
The Draw Connection Properties are modified and are visible on the map.
Note The draw connection property changes are made only in the current project.
You must save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing the Raster Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, DEM properties, etc.
Note You must select to show images in the Display tab of the Options dialog box to view
any changes made to the raster properties on the map. See Customizing the Map Features
Preferences for information on showing/hiding images.
To Change Raster Properties
Use the following steps to change the raster properties.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Right-click Quad Rasters and click Properties.
The Raster Properties dialog box opens.
5. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab marker to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
78
Page 81

Using Projects/Map Data
The minimum and maximum data zoom range displays above the Set Data Zoom
Range For Display area.
6. Click Next.
7. Type the minimum and maximum data zoom range for your custom raster properties
in the text boxes.
8. Select the raster data positions from the drop-down list for that data zoom range.
Note The raster data position you select also includes all of the options above it in
the list.
9. Continue to enter data zoom ranges and choose a position for each range.
10. Click Add Change to update your data positioning selections to the map.
Note You must perform this step to apply any change.
11. Optional. Click Use Default to use the default zoom range and data positioning
options.
12. Click Next.
13. Review the dataset information and click Next, if applicable.
14. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
raster properties.
15. Click Finish.
The Raster Properties for that dataset are modified and are visible on the map.
Note The raster property changes are only made in the current project. You must
save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing the Shaded Relief Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, etc.
Note You must select to show shaded relief in the Display tab of the Options dialog box to
view any changes made to the shaded relief properties on the map. See Displaying Basic
Map Features for information on showing/hiding shaded relief.
To Change the Shaded Relief Properties
Use the following steps to change the properties of shaded relief.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Right-click Shaded Relief and click Properties.
The Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Properties dialog box opens (for Shaded Relief).
5. Select the direction from which you want the sun to shine for displaying the shaded
relief from the Sun Bearing drop-down list.
6. Select how many degrees you want the sun to be above the horizon from the Sun
Inclination drop-down list.
7. Under Brightness Range, drag the gray tab markers to the minimum and
maximum levels you want.
8. Optional. Click Reset if you have previously changed your shaded relief properties
and want to return to the settings which were in effect before you opened the
Properties dialog.
9. Optional. Click Use Defaults to change to the product defaults.
79
Page 82

XMap User Guide
10. Click Next.
11. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab markers to the
desired minimum and maximum levels.
The minimum and maximum zoom range displays above the Set Zoom Range For
Display area.
12. Click Next.
13. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
shaded relief properties.
14. Click Finish.
The Shaded Relief Properties for that dataset are modified and are visible on the
map.
Note The shaded relief property changes are made only in the current project. You
must save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing the Radio Coverage Ellipses Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as radio ellipses, rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, etc.
To Change the Radio Coverage Ellipses Properties
Use the following steps to change the properties of radio coverage ellipses.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Highlight Radio Coverage Ellipses, click Data, and then click Properties.
The Ellipse Connection Properties dialog box opens.
OR
Right-click Radio Coverage Ellipses and click Properties.
The Ellipse Connection Properties dialog box opens.
5. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab markers to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
6. Click Next.
7. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
properties.
8. Click Finish.
The Radio Coverage Ellipse Connection Properties for that dataset are modified and
are visible on the map.
Note The radio coverage ellipse property changes are made only in the current
project. You must
save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing the Elevation Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as elevations, rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours, points, DEM
properties, etc.
To Change the Elevation Properties
Use the following steps to change the properties of elevation.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
80
Page 83

Using Projects/Map Data
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the dataset for
which you want to modify the properties.
3. Click the plus sign next to the sub-data category.
4. Right-click Elevation and click Properties.
The Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Properties dialog box opens (for Elevation).
5. Select a priority (1-100) from the Priority scroll list.
Note When the program has more than one elevation connection, the connection
with the highest priority takes precedence in areas where there is coincident data.
6. Select the data zoom level at which you want elevations to begin to display.
7. Click Next.
8. Under Connection Usages, select or clear the appropriate check boxes to show or
hide elevation data.
9. Click Finish.
The Elevation Properties for that dataset are modified and are visible on the map.
Note The elevation property changes are made only in the current project. You
must save your project
to retain the property changes.
Changing XData Dataset Properties
Use the Properties option on the Map Data tab to change the properties of various map
features such as XData datasets, radio ellipses, rasters, vectors, shaded relief, contours,
points, etc.
To Change the XData Dataset Properties
Use the following steps to change the properties of XData datasets.
1. Click the Map Data tab.
2. Under Secondary Map or Primary Map, click the plus sign next to the XData
dataset for which you want to modify the properties.
3. Highlight the dataset name, click Data, and then click Properties.
The User Database Connection Properties dialog box opens.
OR
Right-click the XData dataset and click Properties.
The User Database Connection Properties dialog box opens.
4. Under Set Data Zoom Range For Display, drag the gray tab markers to the
minimum and maximum level you want.
The minimum and maximum zoom range displays above the Set Zoom Range For
Display area.
5. Click Next.
6. Select the check box next to each connection usage you want to include with your
properties.
Note Select the Include in Name Search check box to search for the contents of
your XData dataset using the Find tab (additional address information is required). If
you select the Add to World Placename Dictionary check box in addition to the
Include in Name Search check box, you can use the Find tab to search the contents
of your XData dataset without providing additional address information.
7. Click Finish.
The properties for that XData dataset are modified and are visible on the map.
Note The property changes are made only in the current project. You must
your project to retain the property changes.
save
81
Page 84

Working With GIS
GIS Overview
The topics that are in the Working with GIS Help section cover
functionality that is included in XMap Professional, XMap GIS Editor,
and XMap GIS Enterprise. Check the important note at the top of
each topic to see if it pertains to your version of XMap.
With the GIS tab, you can view and analyze the data in your ESRI files (.shp, .e00),
MapInfo (.mif, .tab), AutoCAD (.dxf, .dwf, dwg), Geocode Type files (.asc, .csv, .dbf, .txt,
.tab, .mdb, .xls), XData datasets (.dds), Draw files (.an1), or DeLorme OpenSpace transfer
files (.openspace) on the map. Once the data is imported as a layer, you can choose to
classify, symbolize, and label the data in the layers to your specifications. You can also:
• Create a database on a network server
• Create attribute queries
• Embed documents
• Use XMap Forms
• Create spatial queries
• Add fields to your layer
• Create a new layer
query results, or map selections.
• Use XMap Web to publish your newly analyzed data
view the information.
• Send GIS layers
• Create default option settings for layers
• And much more!
The GIS tab has five subtabs:
to easily collect data.
to an Earthmate® PN-Series GPS device.
using the fields in your layer.
and link URLs to attribute records.
between layers.
.
—a new empty layer or a new layer based on an existing layer,
to share data among group members.
and let other registered users
and queries.
Subtab
Name
Workspace The Workspace subtab is the primary area for using the GIS tab. You can
Attributes The Attributes subtab has two different views, the Datasheet View and the
Query The Query subtab lets you create custom attribute and spatial queries to
Layering The Layering subtab lets you move the layers in your workspace above,
Description
use the tools in the Workspace subtab to manage and analyze layers in
your databases as well as manage the databases themselves. See also,
Handling Disconnected or Deleted Layers
Design View. The Datasheet View displays the fields that are selected to
be "visible" in the Design View and lets you edit the attribute values. The
Design View lets you edit properties of the fields, view field metadata,
create fields, and import and link additional fields to your layer.
perform analysis on your layers. You can also rename, save, copy, delete,
and symbolize custom queries in the selected layer.
below, or equal to other layers and/or the standard DeLorme data layers.
.
82
Page 85

Working With GIS
Moving a layer up in the list helps to ensure the layer will be visible on the
map.
Checkout/in
Registration The Registration tab appears when you import a CAD layer that has no
Note If a shared layer in a single database is being manipulated by more than one user at
the same time, any analysis of that layer may produce unpredictable results.
The Check-out/in tab lets you check out/reserve portions of layers for
editing outside of the source database and then check them back in,
updating the source layer.
spatial reference to the Earth’s surface. The tab functions the same as the
ImageReg tab by allowing you to place control points between the
unregistered layer (in the left map) and the corresponding location on the
ground (in the right map).
Handling Disconnected or Deleted Layers
When a layer is disconnected or deleted, a red exclamation point (disconnected) or a red X
(deleted) displays next to the layer name in the Workspace.
This happens if the database the layer was connected to has been moved or deleted or if
the local source is unavailable. For example, if the database is on a laptop computer th at is
turned off, the connection will be broken.
You can try to refresh the connection, establish a new connection, or remove the
disconnected or deleted layer from the Workspace.
• To refresh the connection for all layers, click the Layers button and click Refresh
All Layers.
OR
To refresh the connection for specific layers; highlight the layers, right-click the
highlighted area, and click Refresh Selected Layers.
• To reconnect all layers to the original database or to connect them to a new
database, click the Layers button and click Reconnect. The Connect Layers dialog
box opens.
OR
To reconnect/connect specific layers, highlight the layers, right-click the highlighted
area, and click Reconnect. The Connect Layers dialog box
• To remove the active layer, click the Layers button and click Remove.
OR
To remove specific layers, highlight the layers, right-click the highlighted area, and
click Remove.
opens.
GIS Options
GIS Layer Options
You can customize the default settings for managing GIS layers.
To Set GIS Layer Options
83
Page 86

XMap User Guide
Use the following steps to create default settings for GIS layers.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the GIS tab, and then click the Layers subtab .
3. Set the following options:
• Add imported layers to Workspace–Select this check box to automatically
add imported layers to the Workspace subtab.
• Show imported layers on map–If you selected the above check box,
select this check box to show layers on the map after they are
imported to the Workspace subtab.
• Zoom to full layer extent–Select this check box to automatically
zoom the map to show the full extent of hte layer after import.
• Show layers added from Manage Layers on map–Select this check box to
show layers on the map when you add them using the Manage Layers dialog
box.
• Zoom map when centering on points–Use the drop-down list to select the
zoom level to use when you double-click a point geometry to center it on the
map in the Attributes subtab Datasheet View.
• Default List method–Use the drop-down list to select the default setting for
the List filter on the Attributes subtab for layers added to the Workspace. You
can manually change the filter after a layer is added to Workspace. Options
are Map Region (default), All, and Toolbar Select.
• Refresh attribute records for Map Region filter–Select this check box to
automatically refresh the Attributes subtab Datasheet View when the map
extent changes and Map Region is selected in the Show drop-down list. The
Map Region filter hides all attribute records whose map bounding region
(MBR) is not currently within the map window.
• Switch the List method to Toolbar Select–Select this check box to
automatically switch the method used by the List filter to Toolbar Select when
you are selecting an object that is not in the curren t list.
• Large layer definition (# of geometries)–Type the minimum number of
geometries a layer must include to define it as a large layer. When a layer
includes at least that number of geometries, XMap will hand le the layer
differently to improve processing speed. For example, the map will not zoom
to the location of the geometries and the count function for query results is
suppressed. The default number of geometries for a large layer is 50,000.
• Geometry selection color–Click the button to open the Color dialog box and
click the color for selection highlights on the map. Select geometries with th e
on the toolbar.
84
Selection Tool
subtab in datasheet view.
• Limit geometries from database to–If you want to limit the number of
geometries that the database is allowed to return, type the number in the
box. The database will return up to that number and then return no more
results. A zero in the box indicates that there is no limit.
in the toolbar or by selecting records on the Attributes
Page 87

Working With GIS
GIS Query Options
Use the Query subtab on the GIS tab in the Options dialog box to create default settings for
managing queries.
Note Changes to query options apply only to the queries you create after you make the
changes.
To Set GIS Query Options
Use the following steps to create default settings for GIS queries.
1. Click the Options button
OR
Click the arrow next to the Options toolbar button to open the menu. Then, click
Options to open the dialog box.
2. Click the GIS tab, and then click the Queries subtab.
3. Set the following options:
• Zoom map to query results–Select this check box to zoom the map to
show the results of a query.
• Count results when running query–Select this check box to show a count
of the results in the Query Results area on the Query subtab when you run a
query.
• Attribute effect–Use the drop-down list to select the default attribute effect
of a new query for any layer. Options are Highlight, Filter, and None.
• Map effect–Use the drop-down list to control the default map effect of a new
query for any layer. Options are Highlight, Filter, and None.
on the toolbar.
Using Database Manager
Database Manager Overview
Database Manager delivers essential tools for DeLorme OpenSpace database management.
Its easy-to-use interface allows database administrators to add new SQL server
connections, add server account users, create databases and add users, modify database
permissions, create database subscriptions, and more. You can open the Database Manager
from the GIS tab or from the XMap GIS install directory.
Connecting to a Server
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
You can use Database Manager to connect to single or multiple SQL servers.
To Connect to a Server
Use the following steps to connect to a server with Database Manager.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
85
Page 88

XMap User Guide
4. From the Server menu, click New Connection.
The Connect dialog box opens.
5. Type the name of the server in the Server text box.
Note If the server was created on your local machine, type <computer
name>\xmap7. If you are connecting to an external server, see your Database
Administrator to obtain the server name information.
6. Select the authentication method; Windows Authentication or SQL Server
Authentication.
7. If you selected SQL Server Authentication, type the appropriate login name and
password in the applicable text boxes.
8. Click Connect.
Adding a User to a Server
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Once you connect to a SQL server, you can give users access to the databases on the
server. The Server Administrator can modify a user's role on that server to be Server User
(default), Database Creator, or Server Administrator.
To Add a User to a Server
Use the following steps to add a user to a server.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), click the server to which you want add a
new user.
5. From the Server menu, click New User.
The Add Server Account dialog box opens.
6. Type the individual's network user name in the User Name text box.
7. If you are using Windows Authentication, select that option and then type the user's
network domain.
OR
If you are using SQL Server Authentication, select that option and then type and
confirm a password for that user in the applicable text boxes.
8. Click OK.
9. On the left side of the window (tree view), expand the server menu and click Server
Users.
A list of all of the users who have access to the server displays on the right side of
the window.
10. To change a user's role for that server, find the name in the list and click the
System Role. Double-click to select a role (Server User, Database Creator, or
Server Administrator) from the drop-down list.
• Server Users have limited access to the server. They can log in and access
any databases that they have been granted access to, but they cannot create
or delete (drop) databases. Their permissions on each OpenSpace database
are governed by the database role they have been assigned.
86
Page 89

Working With GIS
• Database Creators can log in to the server and create databases. Database
creators have full access to the databases that they create, including deleting
the databases. Their database role on their own OpenSpace databases is
automatically XMap Owner. Their permissions on OpenSpace databases that
they did not create are governed by the database role they have been
assigned.
• Server Administrators have full access to the server and any database on
the server regardless of their database roles. They can add and remove
server users and assign server roles to users.
Tip Users can modify their SQL Server Authentication passwords at any time using the
Change Password feature in Database Manager
.
Disconnecting from/Reconnecting to a Server
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Use Database Manager to disconnect a server or completely remove the connection.
Connected servers display in Database Manager with a green arrow next to the server icon.
Disconnected servers display with a red arrow next to the server icon. Once a server is
disconnected, XMap cannot connect to it.
For information on removing a server, see Removing a Server
.
To Disconnect a Server
Use the following steps to disconnect from a server with Database Manager.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), click the server that you want disconnect.
5. From the Server menu, click Disconnect.
To Reconnect a Server
Use the following steps to reconnect to a server with Database Manager.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not currently selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), click the server that you want reconnect.
5. From the Server menu, click Connect.
Removing a Server
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Use Database Manager to completely remove a server connection or simply disconnect it.
For information on disconnecting a server, see Disconnecting from/Reconnecting to a
Server.
87
Page 90

XMap User Guide
To Remove a Server
Use the following steps to remove a server and the databases it contains with Database
Manager.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), click the server that you want remove.
5. From the Server menu, click Remove.
Creating a New Database
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
There are two ways to create a new database in XMap. You can use the Create Database
dialog box within XMap, which is accessed from the Import Layer wizard or Create Layer
dialog box, or use the Database Manager utility to create a new database.
To Create a New Database with the Create Database Dialog Box
Use the following steps to create a new database.
1. Click the GIS tab, click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
2. Click the Layers button, point to Create, and then click Empty Layer.
The Create Empty Layer dialog box opens.
OR
Click the Import Layer menu button
on the toolbar, and then click Import -
New Layer.
The Import Layer Wizard opens.
3. At the bottom of the dialog box, select New from the Target Database drop-down
list.
The Create Database dialog box opens.
4. Select the server you want the database to be created on from the Server dropdown list.
If the server you want to use does not display in the list, type the server name in the
text box.
Note If the server was created on your local machine, type <computer
name>\xmap7. If you are connecting to an external server, see your Database
Administrator to obtain the server name information.
5. Select the authentication method; Windows authentication or SQL Server
authentication (Windows Authentication (NTLM) is an authentication process used by
all members of the Windows NT family of products. It uses a challenge/response
process to prove the client’s identity without requiring that either a password or a
hashed password be sent across the network. If Use Windows Authentication is
selected, the user does not need to provide login name or password information to
create a new database on the specified server machine. This is because SQL Server
revalidates the Windows user account name and password. SQL Server
Authentication uses credentials stored in a SQL Server database to get access to the
server. When this choice is selected, the Login and Password text boxes are
88
Page 91

Working With GIS
enabled.)
.
6. If you selected to use SQL Server Authentication, type a login name in the Login
text box and a password in the Password text box.
7. Type a name for the new database in the Database Name text box. The name
should be alphanumeric (not case sensitive), may include underscores, has a 128
character limit, and cannot include spaces or start with a number.
8. From the Compatibility drop-down list, select the version of XMap that has the
features you want the layers you import into this database to have access to: XMap
7, XMap 6, or XMap 5.
9. Click OK.
The database is added to the server.
To Create a New Database with Database Manager
Use the following steps to create a new database.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. Connect to the server
where your new database will be stored.
5. Use the tree view on the left to select the server where you will store t he new
database.
6. From the Database menu, click New.
7. Type a name for the new database in the Database Name text box. The name
should be alphanumeric (not case sensitive), may include underscores, has a 128
character limit, and cannot include spaces.
8. Select a schema type (XMap 7, XMap 6, or XMap 5) from the Schema drop-down
list.
9. Click OK.
The database is added to the server.
Attaching/Connecting a Database
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Attach Database: When importing a layer with the Import Layer or Manage Layers dialog
box, the Attach Database dialog opens if you Other as the database.
Connect Database: If you are attempting to reconnect to a database for a disconnected or
deleted layer, the Connect Database dialog opens.
To Attach/Connect a Database
Use the following steps to attach a database.
1. Select the server you want the database to be connected to from the Server dropdown list.
If the server you want to use does not display in the list, type the server name in the
text box.
Note If the server was created on your local machine, type <computer
89
Page 92

XMap User Guide
name>\xmap7. If you are connecting to an external server, see your Database
Administrator to obtain the server name information.
2. Select the authentication method; Windows Authentication or SQL Server
Authentication. (Windows Authentication (NTLM) is an authentication process used
by all members of the Windows NT family of products. It uses a challenge/response
process to prove the client’s identity without requiring that either a password or a
hashed password be sent across the network. If Use Windows Authentication is
selected, the user does not need to provide login name or password information to
create a new database on the specified server machine. This is because SQL Server
revalidates the Windows user account name and password. SQL Server
Authentication uses credentials stored in a SQL Server database to get access to the
server. When this choice is selected, the Login and Password text boxes are
enabled.)
3. If you selected to use SQL Server Authentication, type a login name in the Login
text box and a password in the Password text box.
4. Type a name for the new database in the Database Name text box.
5. Click OK.
The database is added.
Adding/Removing a Database User
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Once you add users to a server, you can give them access to the databases that are on that
server. Once a user is added to a database, an administrator can assign the user's role
using the database (for example, XMap User, XMap Edit, XMap Checkout Creator, XMap
Administrator, or XMap Owner). You can add or remove individual users or a Windows
Group.
To Add a Database User
Use the following steps to give a user access to a particular database.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), expand the server and databases menus.
5. To add a user to an individual database, click a database in the tree view or in the
working view (right side).
OR
To add a user to multiple databases, in the working view (right side of th e win d ow),
hold the CTRL key on your keyboard while you click each of the databases to which
you want to add a user.
6. From the Database menu, click Add User.
The Add Users dialog box opens all of the users who have access to the database's
server.
7. Click to select a user from the Add Users dialog box. If you want to add multiple
users at once, press the CTRL key on your keyboard and click each user.
8. Click OK.
for
90
Page 93

Working With GIS
9. On the left side of the window (tree view), expand the database's menu and then
click the Database Users option underneath it.
A list of all of the users who have access to the database displays on the right side of
the window.
10. To change a user's role for that database, find the name in the list, click the role, and
then select a new role (XMap User, XMap Edit, XMap Checkout Creator, XMap
Administrator, or XMap Owner) from the available drop-down list. For definitions of
each role, see Database User Roles
.
To Remove a Database User
Use the following steps to remove a user's database privileges.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not currently selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), expand the server and database menus to
view the database to which you want to remove a user.
5. Expand the database and then click the Database Users option underneath it.
A list of all of the users who have access to the database displays on the right side of
the window.
6. Click to select the user that you want to remove.
7. From the Database menu, click Remove User.
Activating/Deactivating a Database
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
You can deactivate and then reactivate a database using Database Manager. In Database
Manager, active databases have a green arrow next to the database icon. Inactive
databases have a red arrow next to the database icon.
Deactivating a database removes it from the list of databases in the Manage Layers and
Import Layer dialog boxes. The application will not try to connect to an inactive database.
You can also use the remove connection feature in the Manage Layers dialog box to
deactivate a database.
To Activate/Deactivate a Database with Database Manage r
Use the following steps to deactivate a database with Database Manager.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), expand the server and database menus to
find the database you want to activate/deactivate.
5. To deactivate a database
menu, click Deactivate.
OR
To activate a database
Database menu, click Activate.
, click the database to deactivate. Then, from the Database
, click the database you want to activate. Then, from the
91
Page 94

XMap User Guide
To Deactivate a Database with the Manage Layers Dialog Box
Use the following steps to remove a database using the Manage Layers dialog box.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not currently selected.
3. Click the Layers button and then click Manage.
The Manage Layers dialog box opens.
OR
Click the Manage Layers tool
The Manage Layers dialog box opens.
4. From the Source Database drop-down, select the database that you want to
deactivate.
5. Click the Remove Database Connection button
6. Click Yes to confirm that you want to deactivate (remove) the database connection.
on the toolbar.
.
Deleting a Database
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Once you create a database, you can use Database Manager to delete (drop) it from the
server.
Notes
• You can delete a database only if you are the database owner or if you are a SQL
System Administrator.
• You cannot delete a database that is currently in use. If the database is currently in
use, you will receive the following error, "A database error occurred while dropping the
database..."
• The process of deleting a database may take over a minute.
To Delete a Database
Use the following steps to delete a database.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), click the database that you want to
delete.
5. From the Database menu, click Delete.
A confirmation message displays.
6. Click Yes to delete the database.
Deleted databases and their contents cannot be retrieved unless you created a
backup using Backup/Restore.
OR
Click No to cancel the deletion process.
92
Page 95

Working With GIS
Database User Roles
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
A Server Administrator can give multiple users access to one or all of the databases that are
stored on a server. Each user must be assigned a role for using a particular database; the
default role is XMap User. The table below shows the functionality that is available for each
of the role types; XMap User, XMap Edit, XMap Checkout Creator, XMap Administrator, or
XMap Owner.
Feature XMap
User
XMap
Edit
XMap
Checkout
XMap
Administrator
XMap
Owner
Creator
View GIS layers and
X X X X X
associated
information
(attributes,
classifications, layer
properties, etc.)
Run queries X X X X X
Export layers X X X X X
Subscribe to an
X X X X X
Enterprise database
Create redlines X X X X X
Synchronize to an
X X X X X
Enterprise database
Create queries X X X X
Edit geometries and
X X X X
attributes
Create check-outs
X X X
from an Enterprise
database
Save check-outs on
X X X
an existing database
Import layers X X
Delete layers X X
Add/delete attribute
X X
fields
Import/link attribute
X X
sets
Edit layer properties X X
93
Page 96

XMap User Guide
Create classifications X X
Save classification
X X
templates
Enable subscriptions
X X
on an Enterprise
database*
Create subscriptions
X X
on an Enterprise
database*
Enable/disable a layer
X X
for check-outs
Add users to a
X
database
Change database
X
user roles
Drop (delete)
X
databases
* Requires XMap GIS Enterprise.
Creating User Subscriptions
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap GIS
Enterprise.
A subscription is a read-only copy of a layer in an Enterprise database. A subscription must
be created by an administrator and activated on a user’s computer. When a user clicks the
Synchronize button on the toolbar, a copy of the Enterprise database that contains readonly copies of all layers they are subscribed to is created on the user's local machine. Layer
copies are updated to include changes to each original layer every time the Synchronize
button is clicked. This allows XMap users to quickly ensure they have the most up-t o-date
versions of the layers they need for reference in the field or office.
Note Enterprise databases can be created only with XMap GIS Enterprise.
To Create a User Subscription
Use the following steps to create a user subscription.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), expand the server menu that includes the
database where your layers are stored.
5. Expand the Database menu and click Subscriptions. If subscriptions are disabled
for that database (if the sync arrows next to the option are red and not green), rightclick Subscriptions and click Enable Subscriptions or select Enable
Subscriptions from the Database menu.
94
Page 97

Working With GIS
6. In the middle section of the Database Manager window, click to select each database
user whose subscription you will create. You can select multiple users at on ce by
holding the CTRL key on your keyboard while you click t o select each user.
Note Only server users are available in this list. See Adding a User to a Server
for
more information.
7. On the right side of the window (working view), select the check box next to each
layer you want to include in the subscription.
8. Click Create Subscription File.
9. Browse to the location where you want to save the subscription file and name the
file. When you are finished, click Save.
10. Outside of XMap, send the subscription file to each user you selected in step 6.
Changing Your SQL Server Authentication Password
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
If you have been given rights to access a server with SQL Server Authentication, you can
change your password at any time using Database Manager.
To Change Your Password
Use the following steps to change your SQL Server Authentication password.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open the Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), expand the server for which you want to
change the password.
5. On the left side of the window (tree view), click Server Users.
6. Select your account from the working view on the right side of the screen.
7. From the Server menu, click Change Password.
The Change Password dialog box opens.
8. Type your current password in the Old Password text box.
Note This option is unavailable when the system administrator is changing a user's
password.
9. Type the new password in the Password text box.
10. Re-type the password in the Confirm Password text box.
11. Click OK.
The password is changed.
Backing Up a Database
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Use the Backup/Restore feature in Database Manager to create backups (duplicates) of
databases in case of a computer crash or database corruption. You can restore the backups
95
Page 98

XMap User Guide
if such an event occurs, preserving the user’s layers in the database. You can create
multiple backup databases for a single source database.
In case of computer failure, it is strongly recommended that you store database backups on
separate media (CD, DVD, remote server, etc.).
To Back up a Database
Use the following steps to backup a database.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), click Databases or expand the Databases
menu and select an individual database.
5. From the Database menu, click Backup/Restore.
The Backup/Restore dialog box opens.
6. Select the database you want to backup from the Source Database drop-down list.
7. Click Backup.
The Backup dialog box opens.
8. Type the name for your backup database in the Name text box.
9. Type the location where you want to save the backup database or click the browse
button to browse to the location.
10. Optional. Type any related information about the backup database in the
Description text box.
11. Click OK.
The new backup database (as well as any other backup databases) that have been
created for the selected Source Database display in the Backup History table. The
backup database consists of two files; a file that contains the data and a file that
contains metadata about the backup.
Note To remove a backup database from the Backup History table, select the backup
database and click Remove From History. The backup database is removed from the table
but not deleted from the location where you saved it.
To permanently delete a backup database, browse to the location on your computer where
you saved the backup files and delete the files. The backup database displays in the Backup
History table until you select it and click Remove From History.
Restoring a Backed Up Database
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Once you create a backup database, you can restore it as the source database using the
Backup/Restore functionality in Database Manager.
To Restore a Database
Use the following steps to restore a backed up database.
1. Click the GIS tab.
2. Click the Workspace subtab if it is not selected.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
96
Page 99

Working With GIS
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), click Databases or expand the Databases
menu and select an individual database.
5. From the Database menu, click Backup/Restore.
The Backup/Restore dialog box opens.
6. Select the database that was originally backed up from the Source Database dropdown list.
Note Select Select All from the Source Database drop-down list to view a list of
all of the databases that are currently backed up.
7. Select the backup database you want to restore from the Backup History table and
click Restore.
The Restore dialog box opens.
OR
If the backup database that you want to restore does not display in the Backup
History table, click Restore from File, browse to the location where you saved the
backup database, and then click Open.
8. If you want to overwrite the original source database with the backup database
,
leave the Restore dialog box as is and click OK. Then, click Yes to confirm that you
want to replace the existing database with the backup database.
OR
If you want to restore the backup database but not overwrite the original database
,
type a new name for the restored database in the Database text box and then click
OK.
Forms Licenses
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap GIS
Enterprise.
A database created with XMap GIS Enterprise is required to create or use XMap
Forms. XMap Professional users must also obtain a Forms license to enable
viewing or editing data in a form. The fun ctions available in a form depend on the
permissions set by the database and Forms administrator.
To use XMap Forms with XMap Editor or XMap Professional, an administrator is required to
own one license of XMap 7 GIS Enterprise, which includes the form builder and enables
database synchronization across the network. An additional Forms license is also required
for XMap Professional users to access forms in an Enterprise database. For more information
and for sample OpenSpace files with form examples, visit www.xmap.com/forms
To Activate a Forms License
Once you purchase a Forms license for XMap Professional users, you will receive an e-mail
with the license file. Use the following steps to activate a Forms license. You must have
administrator rights to the server.
1. From the e-mail, save the license file to your computer.
2. In XMap, click the GIS tab and click the Workspace subtab.
3. Click DB Manager to open Database Manager.
4. On the left side of the window (tree view), click the server for which you want to
activate XMap Forms.
5. From the Server menu, click Forms Licensing.
The Forms Licensing dialog box opens.
.
97
Page 100

XMap User Guide
6. Click Activate.
Note If you have a previously activated license, the information appears in the
dialog box. Activating a new license overwrites any existing information.
7. Browse to the location on your computer where you saved the license file (the file
extension is .dfl).
8. Double-click the license to activate it. The licen se information appears in the dialog
and is also saved as a text file in the same location as the license file.
9. In Database Manager, Forms License is available in the menu tree.
10. Click Close to close the dialog.
Note To deactivate a Forms License, right-click the server and click Deactivate Forms
Licensing.
To Add a User to a Forms License
Once the Forms license is activated, you can add XMap Professional users to the license
using Database Manager. You must have added users to the server
Forms license for them.
1. In Database Manager, on the left side of the window (tree view), click the server that
has the Forms license.
2. In the menu tree, right-click Forms License and click Add User to open the Add
Users dialog box.
3. Select the user or users to add the license to. You can add a license to a group. The
license must have enough seats to cover all the selected users and all users in any
group.
4. Click OK.
Note To remove a user or users, double-click Forms License, select the user or users,
right-click Forms License, and click Remove User.
before you can enable a
XMap Database Limitations
You can import layers created in an older version of XMap into an XMap 5.0 or latercompatible database using the Import Wizard
New/Duplicate Layer feature
the XMap GIS Bulk Importer/Exporter.
in the GIS tab. Advanced users can convert multiple files usin g
in the GIS Workspace subtab or the
Using Layers in a Subscription
Opening a Subscription File
This Help topic describes features that are available in XMap
Professional, XMap GIS Editor, and XMap GIS Enterprise.
Once a database administrator sends you a subscription file, you must open it in XMap to
activate the subscription. A subscription to an Enterprise database allows you to synchronize
your local copy of the layers with the Enterprise database on the server. You can edit a
layer and then synchronize your edits with the Enterprise database. You can also use the
redlining feature
to make edits to the layer in a draw file.
98
 Loading...
Loading...