Galaxy dx2547 Service Manual

DX 2547
CHAPTER 1
SPECIFICATIONS
1.0 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.1 Transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.2 Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
TABLE OF
CONTENTS
PAGE
CHAPTER 2
OPERATION
2.0 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1 Control and Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.1 Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.2 Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.3 Frequency Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 Microphone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3.1 Procedure to Receive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3.2 Procedure to Transmit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.4 Alternate Microphones and Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
CHAPTER 3
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
3.0 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.1 PLL Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.2 Receiver Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.3 Transmitter Modulation Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.4 Transmitter Amplifier Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
CHAPTER 4
ALIGNMENT
4.0 Required Test Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.1 Alignment Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.1.1 PLL Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.1.2 Transmitter Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.1.3 Receiver Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
CHAPTER 5
MAINTENANCE
5.0 Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.1 Periodic Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.2 Fuse Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
CHAPTER 6
DIAGRAMS AND PART LIST
6.0 PCB Layout and Part List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CHAPTER 1
- 1 -
DX 2547 SPECIFICATIONS
1.0 GENERAL
Model DX 2547
Frequency Range 26.965 – 27.405 MHz
Emission Modes AM/USB/LSB
Frequency Control Phase Lock Loop (PLL) synthesizer
Frequency Tolerance 0.005 %
Frequency Stability 0.001 %
Operating Temperature Range
Microphone Dynamic PTT, 500 Ω
Input Voltage (DC/AC Selectable) 13.8V DC / 110V AC 60Hz
Current Drain: Transmit (AM full mod.) < 3.5A
Current Drain : Receiver (Squelched)
(Max. audio output) < 1A
Antenna Connector UHF; SO239
1.1 TRANSMITTER
RF Power Output AM : 4W ; SSB : 12W PEP
RF Transmit Modes AM/SSB
Modulation High and Low level Class B, Amplitude Modulation :
Spurious Emissions - 60dB
Carrier Suppression - 60dB
Audio Frequency Response 300 to 2500 Hz
Antenna Impedance 50 Ohms
Output Indicators Meter shows relative signal strength, RF output
1.2 RECEIVER
Sensitivity For 10dB S/N (AM/ SSB)
IF Frequency AM: 10.695 MHz 1st IF, 455 KHz 2nd IF
Image Rejection - 50dB
Adjacent Channel Selectivity - 60dB
RF Gain Control 45dB adjustable for optimum signal reception
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Figure Of Merit 100mV for 10dB Change in Audio Output
Squelch
Noise Blanker RF type
Audio Output Power 2.5W @ 10% THD
Audio Frequency Response 300 to 2500 Hz
Built-in Speaker 8 Ohms, 4 Watts
External Speaker (Not Supplied) 8 Ohms, 4 Watts
(SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE)
DX 2547
-30°C to +50°C
≤ 0.5A
AM and SSB.
power, SWR and AM Modulation level. Transmit
LED glows red when transmitter is in operation.
< 0.5µV / < 0.15µV
Adjustable; threshold less than 0.5µV
CHAPTER 2
OPERATION
- 2 -
POWER
TALKBACK
S
1
MOD
PWR
AM / SSB Base Station CB Radio
OFF
PHONES
RF POWER
MIC
MIC RF
3
20%
0
SWR
1
SWR
9
7
5
60%
40%
9
6
3
3
2
1.5
MOD
DIM TONE
+20
+40
80%
100%
12
15
MAX
DX 2547
PWR
dB
+60
R. B.
PA
RX / TX
GNF R.B. PA AM
CHANNEL
SWR ALERT
USB
USB
ANL
ANL
GNF
AM
LSB
LSB
NB
NB
CLARIFIER
CLARIFIER
NORMAL
9
SQUELCH
VOLUME
19
OFF
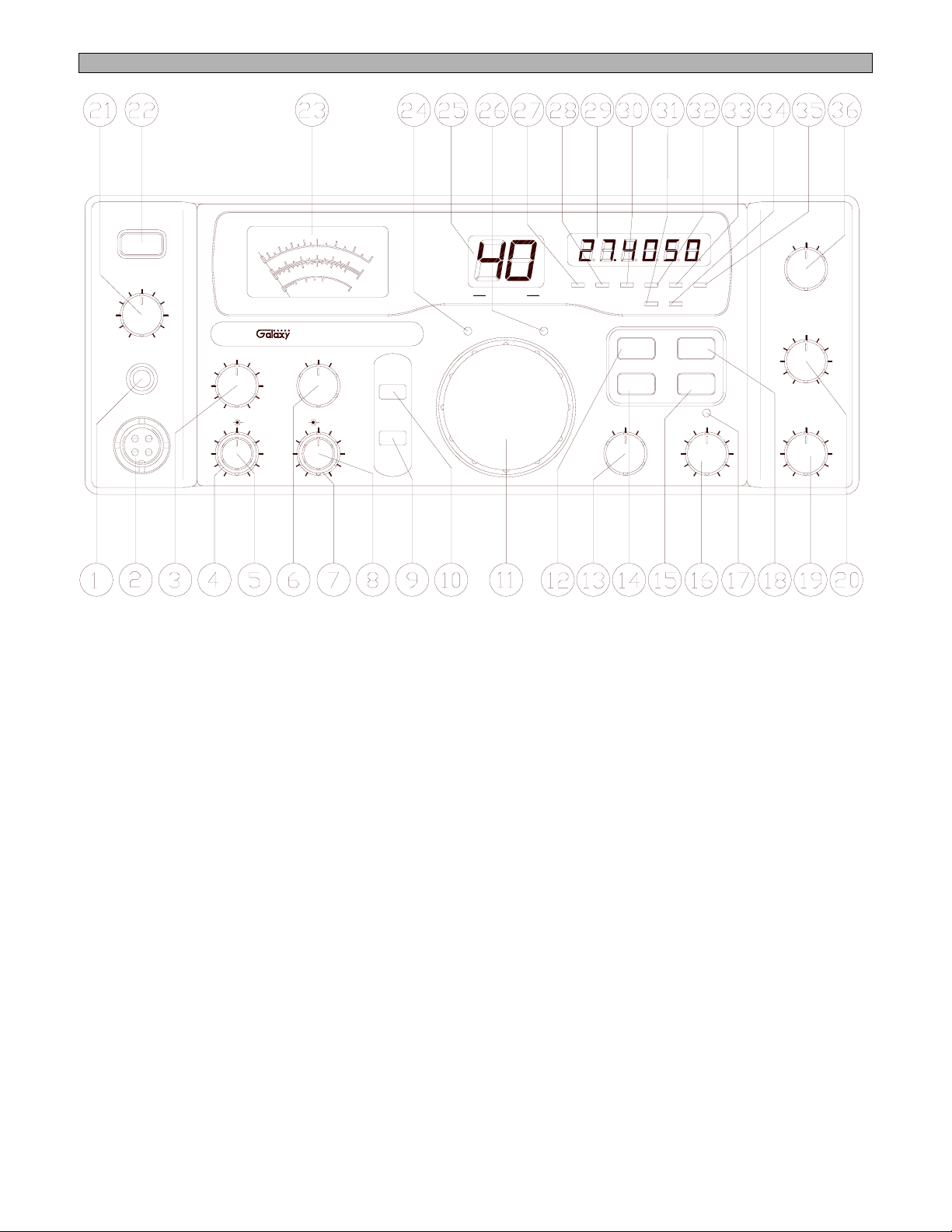
Figure 2-1 Front Panel
2.0 INTRODUCTION
This section explains the basic operating procedures for the Galaxy DX 2547 Base Station transceiver.
2.1 CONTROL AND CONNECTIONS
2.1.1 FRONT PANEL
Refer to the above Figure 2-1 for the location of the following controls:
1. PHONE JACK
Used to connect headphones.
2. MICROPHONE JACK
Used to connect microphone supplied with your radio.
3. RF POWER CONTROL
This control allows the user to adjust RF power output.
4. RF GAIN CONTROL
This control is used to reduce the gain of the RF amplifier under strong signal conditions.
5. MIC GAIN CONTROL
- 3 -

Adjusts the microphone gain in the transmit and PA mode. This controls the gain to the extent that full
talk power is available several inches away from the microphone. In the Public Address (PA) mode, the
control functions as the volume control.
6. SWR/MOD/PWR SWITCH
This switch controls the function of the meter during the transmit mode. In the “SWR” position, the
meter indicates the Standing Wave Ratio (SWR) of your antenna. There are no adjustments because the
SWR circuit in this radio calibrates itself automatically. When the switch is in the “MOD” position, the
green scale on the meter indicates your percentage of modulation. It is the most accurate when testing
at four watts output. This operates in AM only, not in SSB. When this switch is in “PWR” position, the
meter indicates your power output.
7. TONE CONTROL
This controls changes tone quality in receive only. Rotating the knob clockwise increases treble,
counter clockwise rotation increases bass.
8. DIMMER CONTROL
This knob controls the level of brightness for the meter lamp and the channel display.
9. PA SWITCH
When this switch is pressed in, your voice will be heard only if an external speaker has been plugged
into the “PA.” jack on the back of the radio. The radio does not operate when you are in the “PA”
mode.
10. ROGER BEEP SWITCH
When this switch is pressed in, the radio transmits an audio tone at the end of your transmission to
indicate that transmission has ended. As a courtesy to others, use the Roger Beep only when necessary.
11. CHANNEL SELECTOR
This control is used to select a desired transmit and receive channel.
12. ANL SWITCH
When this switch is pressed in, the Automatic Noise Limiter is activated.
13. MODE SWITCH
This control allows you to select one of the following operating modes: USB, AM or LSB.
14. GNF SWITCH
When this switch is pressed in, the radio is in CB operation but the Galaxy Noise Filter is engaged.
This is a special noise filter that de-emphasizes audio high frequency response in order to increase the
signal-to-noise ratio of weak signals. While you will notice a dramatic reduction in the “rushing” sound
when this filter is activated, it does not have much effect on the signal-to-noise ratio of strong signals.
This filter works best in SSB mode and may cause AM receive to sound distorted.
15. CLARIFIER SWITCH
Pushing this switch turns the Clarifier on for receive tracking.
16. CLARIFIER CONTROL
- 4 -

When activated, allows adjustment of the receive frequency above or below the channel frequency by
up to 800Hz. Although this control is intended primarily to tune in SSB signals, it may be used to
optimize AM signals as well.
17. CLARIFIER LED
This LED lights when the Clarifier control is activated.
18. NB SWITCH
When this switch is pressed in, the Noise Blanker is activated. The Noise Blanker is very effective in
eliminating repetitive impulse noise such as ignition interference.
19. VOLUME CONTROL
Turn clockwise to set the desired listening level.
20. SQUELCH CONTROL
This switch is used to eliminate background noise being heard through the receiver which can be
disturbing when no signal is being received. To use this feature of your radio, gently turn the switch
fully counterclockwise, and then turn clockwise until the background noise is just eliminated. Further
clockwise rotation will increase the threshold level so that only strong signals will be heard.
21. TALKBACK CONTROL
Adjust this knob for desired volume of Talkback. This is used to monitor your own voice. For example,
you could use this feature to compare different microphones.
22. POWER ON/OFF SWITCH
Push this switch to apply power to the unit.
23. FRONT PANEL METER
The Front Panel Meter allows the user to monitor incoming signal strength, RF output power, SWR
and AM Modulation level.
24. TX/RX LED
This LED lights red during transmit and green during receive.
25. CHANNEL DISPLAY
The channel display indicates the current selected channel.
26. SWR ALERT LED
This LED lights red when your SWR is higher than about 3:1. This is not an exact indicator of 3:1
SWR, but it is an indication that you should check your SWR reading.
27. GNF LED
This LED lights red when the GNF is on.
28. R.B. LED
This LED lights red when the Roger Beep is on.
29. FREQUENCY COUNTER
This display indicates the frequency of the selected channel.
30. PA LED
This LED lights red when the radio is in the PA mode.
- 5 -

31. ANL LED
This LED lights red when the ANL is on.
32. USB LED
This LED lights red when the radio is in the USB mode.
33. AM LED
This LED lights red when the radio is in the AM mode.
34. NB LED
This LED lights red when the NB is on.
35. LSB LED
This LED lights red when the radio is in the LSB mode.
36. CH9/NORMAL/CH19 SWITCH
This control allows you to select channel 9 or channel 19 instantly. When the switch is placed in the
“NORMAL” position, the user is able to select a desired transmit and receive channel with the channel
selector switch.
2.1.2 REAR PANEL
Figure 2-2 represents the location of the following connections:
- 6 -
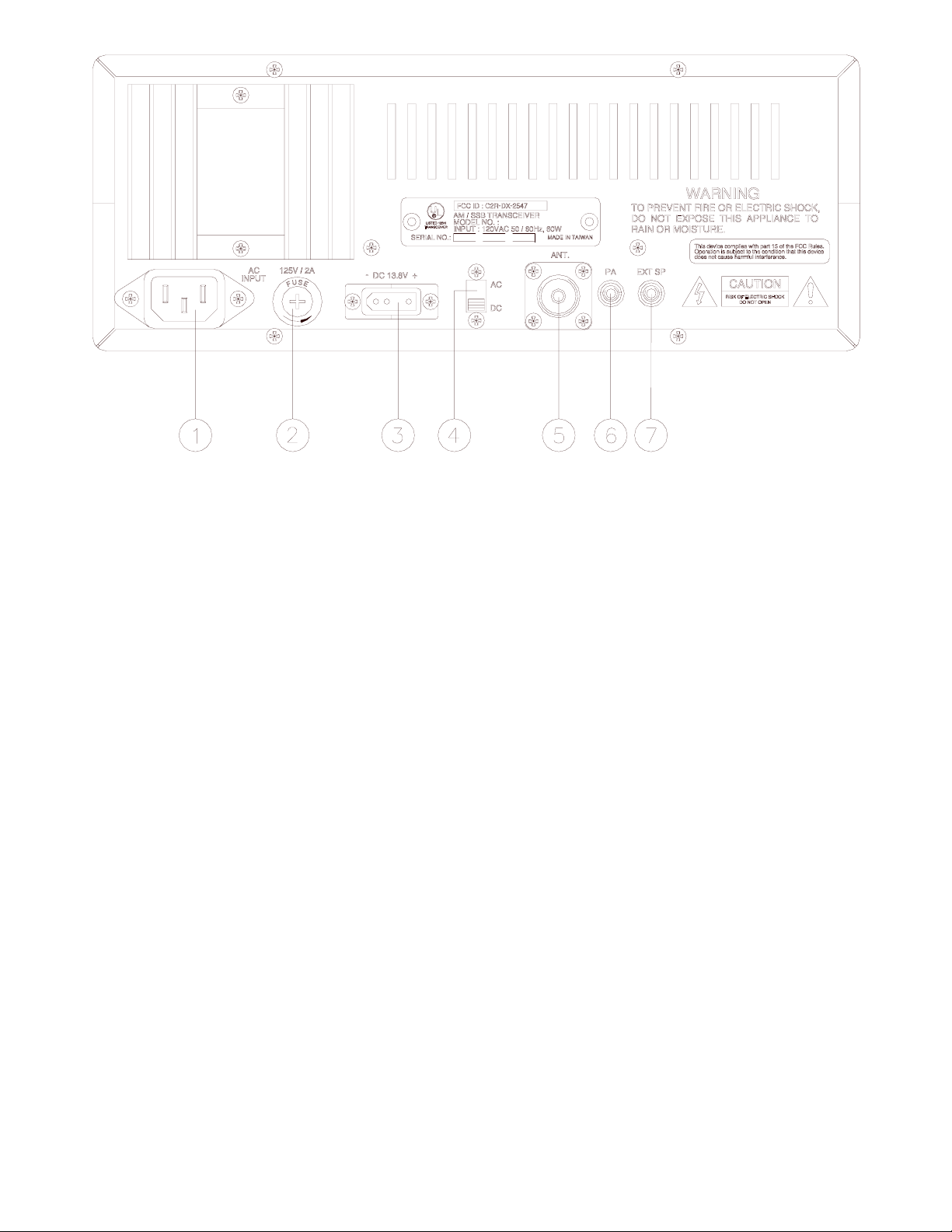
Figure 2-2 Rear Panel
1. AC POWER CORD
Connect to AC power outlet for AC main supply.
2. FUSE
Accommodates a fuse for AC input circuit protection. Use a 125V 2A fuse for replacement.
3. DC POWER
This accepts a 13.8V DC power cable with built-in 7A fuse. The power cord provided with the radio
has a black and red wire. The black goes to negative and the red goes to positive.
4. AC/DC POWER SELECTOR
This control is used to select a desired power supply of AC power or DC power.
5. ANTENNA
This jack accepts 50 ohms coaxial cable with a PL-259 type connector.
6. PA
This jack is for PA operation. Before operating, you must first connect a PA speaker (8 ohms, 4W) to
this jack.
7. EXT SP
This jack accepts a 4 to 8 ohm, 4 watt external speaker. When the external speaker is connected to this
jack, the built-in speaker will be disabled.
2.1.3 FREQUENCY CHART
- 7 -
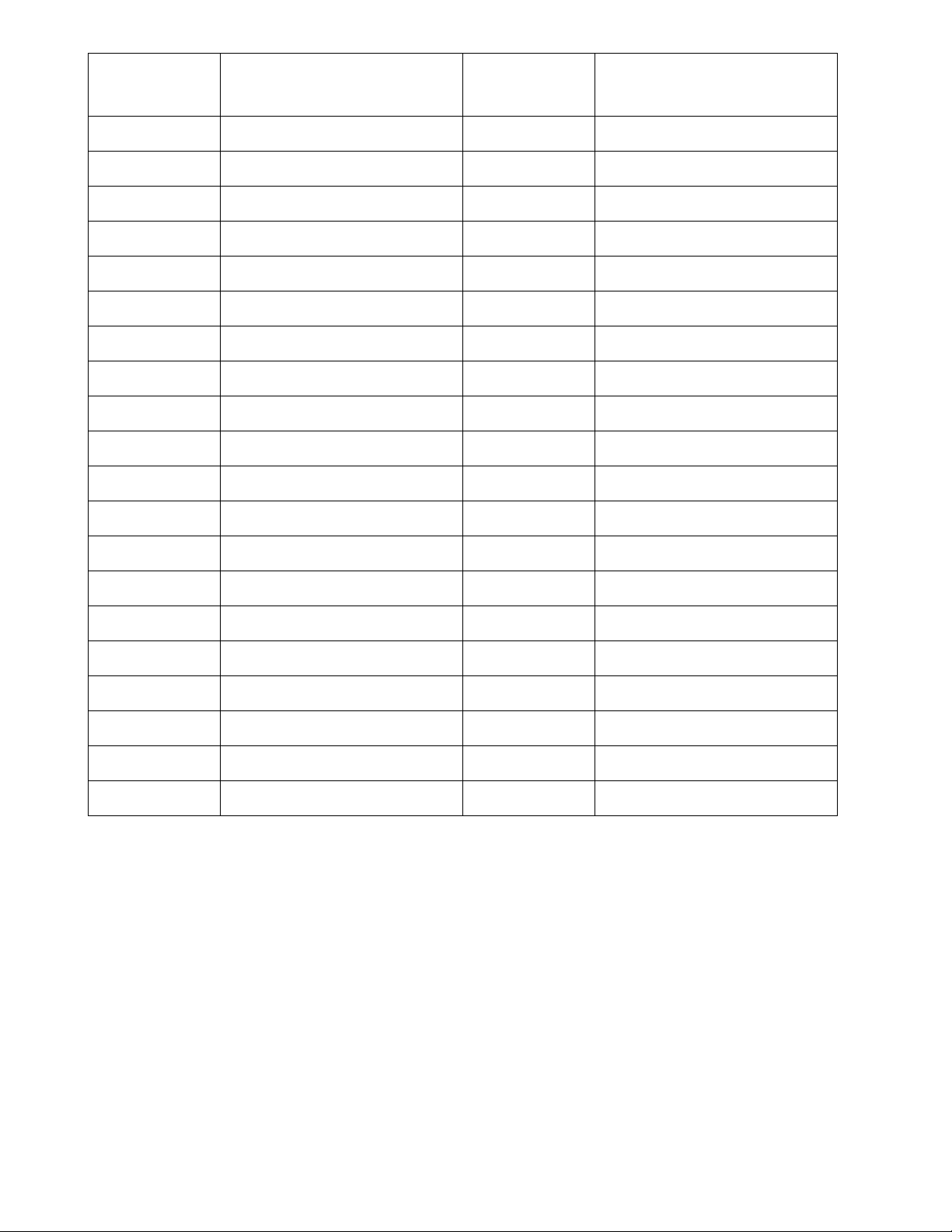
CHANNEL CHANNEL FREQUENCY
(MHz)
CHANNEL CHANNEL FREQUENCY
(MHz)
1 26.965 21 27.215
2 26.975 22 27.225
3 26.985 23 27.255
4 27.005 24 27.235
5 27.015 25 27.245
6 27.025 26 27.265
7 27.035 27 27.275
8 27.055 28 27.285
9 27.065 29 27.295
10 27.075 30 27.305
11 27.085 31 27.315
12 27.105 32 27.325
13 27.115 33 27.335
14 27.125 34 27.345
15 27.135 35 27.355
16 27.155 36 27.365
17 27.165 37 27.375
18 27.175 38 27.385
19 27.185 39 27.395
20 27.205 40 27.405
2.2 MICROPHONE
The receiver and transmitter are controlled by the push-to-talk switch on the microphone. Press the
switch and the transmitter is activated, release the switch to receive. When transmitting, hold the
- 8 -

microphone two inches from your mouth and speak clearly in a normal voice. The radio comes
complete with a low impedance (500 ohm) dynamic microphone.
2.3 OPERATION
2.3.1 PROCEDURE TO RECEIVE
1. Be sure that the power source, microphone and antenna are connected to the proper connectors
before going to the next step.
2. Press the POWER switch to apply power to the radio.
3. Set the VOL to a comfortable listening level.
4. Set the MODE switch to the desired mode.
5. Listen to the background noise from the speaker. Turn the SQUELCH knob slowly clockwise until
the noise just disappears. The SQUELCH is now properly adjusted. The receiver will remain quiet
until a signal is actually received. Do not advance the control too far or some of weaker signals will
not be heard.
6. Set the CHANNEL selector switch to the desired channel.
7. Set the RF GAIN control fully clockwise for maximum RF gain.
8. Adjust the CLARIFIER control to clarify the SSB signals or to optimize AM signals.
2.3.2 PROCEDURE TO TRANSMIT
1. Select the desired channel of transmission
2. Set the MIC GAIN control fully clockwise.
3. If the channel is clear, depress the push-to-talk switch on the microphone and speak in a normal
voice.
2.4 ALTERNATE MICROPHONES AND INSTALLATION
For best results, the user should select a low impedance dynamic type microphone or a transistorized
microphone. Transistorized type microphones have a low output impedance characteristic. The
microphones must be provided with a four-lead cable. The audio conductor and its shielded lead
- 9 -
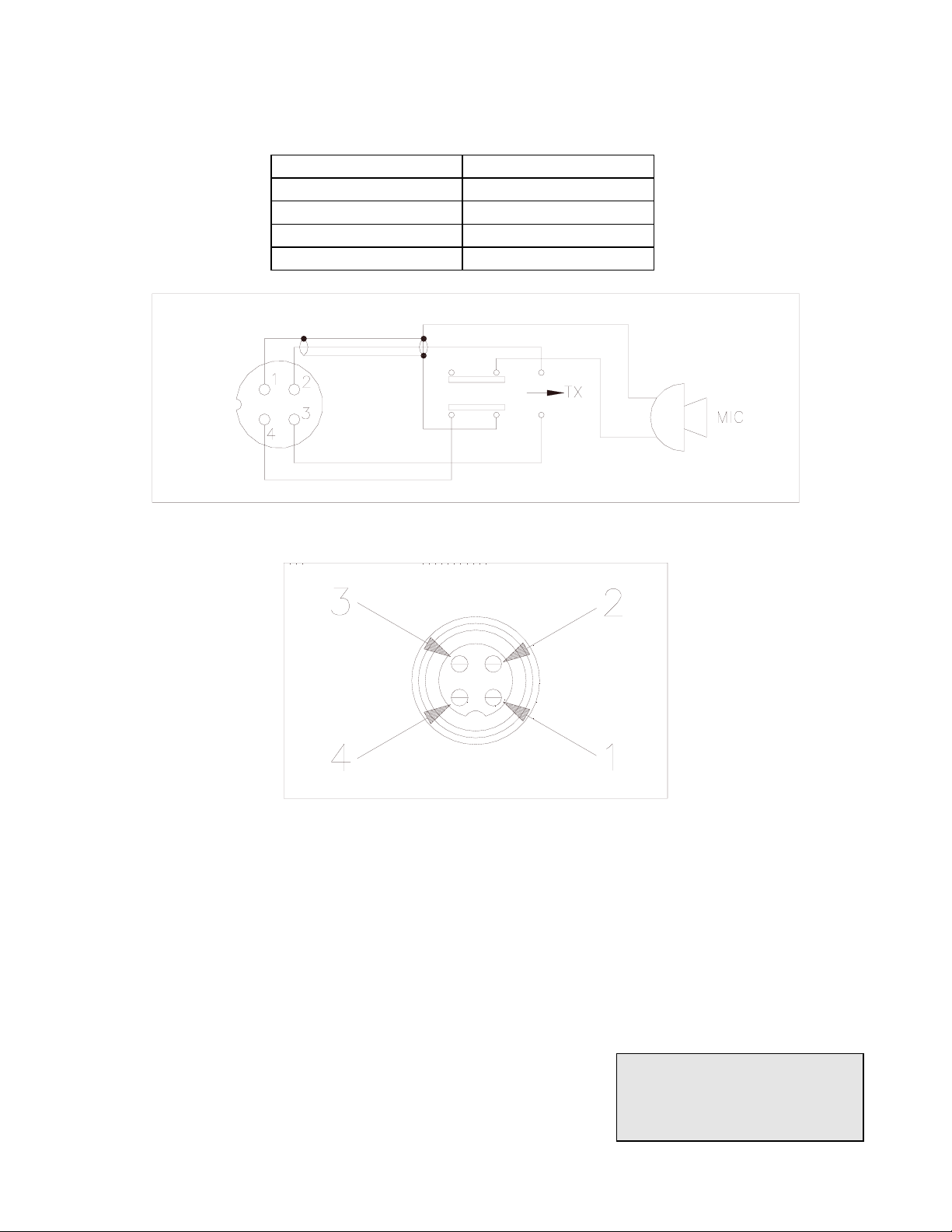
comprise two of the leads. The third lead is for transmit control and the fourth is for receiving control.
The microphone should provide the functions shown in the schematic below (Figure 2-3).
4 WIRE MIC CABLE
Pin Number Mic Cable Lead
1 Audio Shield
2 Audio Lead
3 Transmit Control
4 Receive Control
Figure 2-3 Your Transceiver Microphone Schematic
Figure 2-4 Microphone plug an pin numbers viewed from rear of pin receptacle.
CHAPTER 3
CIRCUIT
DX 2547
DESCRIPTION
- 10 -

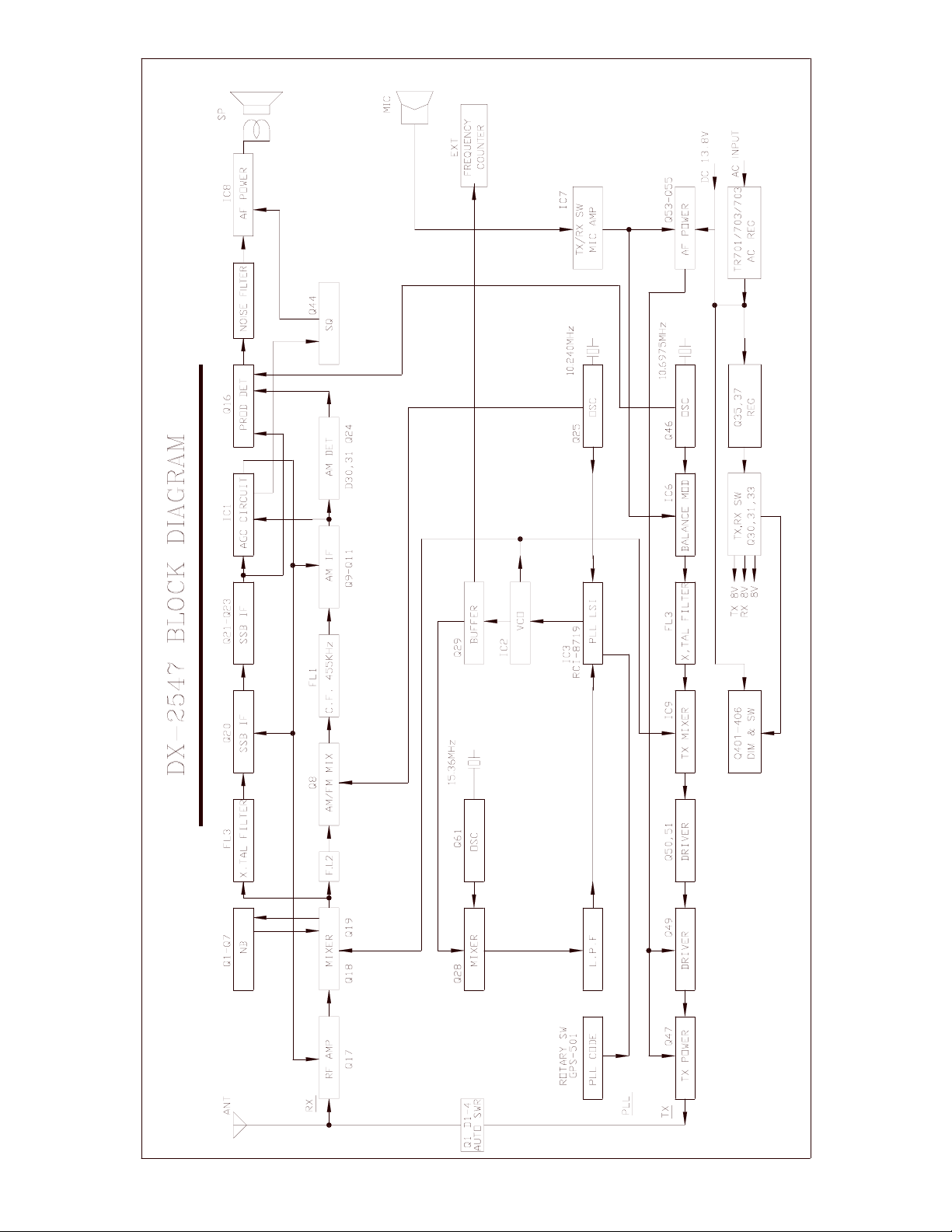
3.0 INTRODUCTION
This section explains the technical theory of operation for the Galaxy DX 2547 Base Station
transceiver.
3.1 PLL CIRCUIT
The Phase Lock Loop (PLL) circuit is responsible for developing the receiver’s first local oscillator
signal and the transmitter’s exciter signal. The PLL circuit consists primarily of IC2, IC3, Q25, Q29
and Q28. The PLL circuit is programmed by the rotary channel switch GPS-0501. The GPS-0501
communicates the correct binary data information to the programmable divider inside of IC3. IC3 then
controls the VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) to oscillate on the correct frequency. This signal is
fed either into the receiver’s first mixer (for receive operation) or the transmitter’s mixer (for transmit
operation).
3.2 RECEIVER CIRCUIT
The incoming RF signal comes into the radio via the antenna and into the front-end pre-amp, Q17. The
RF signal is fed into the dual mosfet mixer circuit of Q18/Q19 and then into the AM/SSB IF section of
the receiver (depending on the mode of operation). The signal is then detected by either the AM
detector or product detector and then fed to the audio amplifier section of the receiver and finally out to
the speaker.
3.3 TRANSMITTER MODULATION CIRCUIT
(i) The transmitter modulation circuit modulates the low-level RF signal from the PLL exciter circuit
with the user’s audio voice signal from the microphone. The audio from the microphone is then
amplified and fed into the transmit amplifier circuit.
(ii) If the transceiver is in the AM mode, the AF Power amplifier modulates the last RF amplifier,
which produces a true amplitude modulated RF signal.
(iii) If the transceiver is in the SSB mode, the audio signal is mixed with the 10.6975MHz oscillator in
IC6.
3.4 TRANSMITTER AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
The transmitter takes the basic exciter signal from the TX mixer and amplifies it through a series of
amplifiers consisting of Q52, Q51, Q49 and Q47 where it is then sent out to the antenna connector.
- 11 -
- 12 -
- 13 -
CHAPTER 4
DX 2547
ALIGNMENT
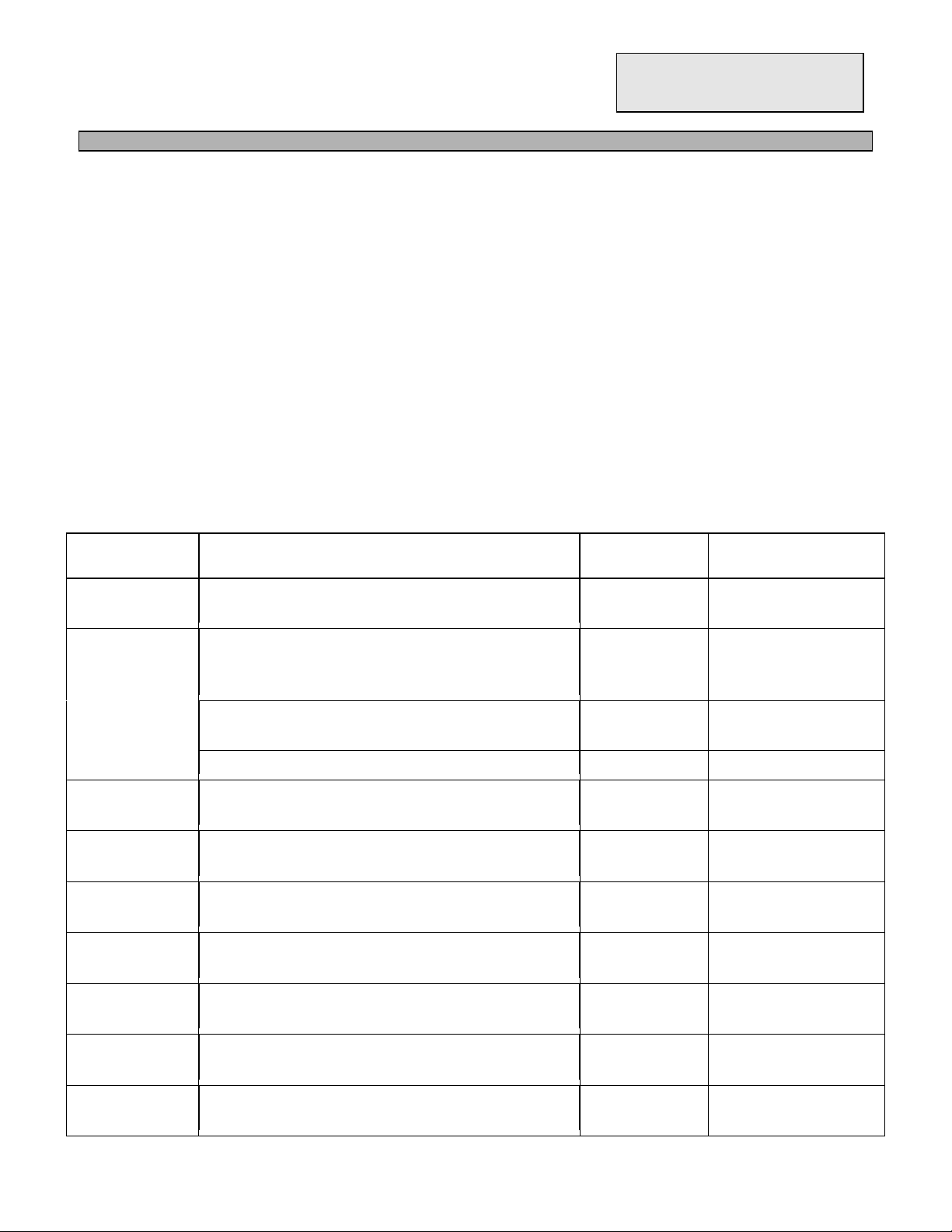
4.0 REQUIRED TEST EQUIPMENT
DC Power Supply (13.8VDC, 10A)
c
RF Wattmeter (100 MHz, 50W)
d
Multimeter (Digital)
e
Automatic Modulation Meter
f
Audio Signal Generator
g
Frequency Counter (100 MHz)
h
RF Signal Generator (100 MHz)
i
Automatic Distortion Meter
j
Oscilloscope (50 MHz)
k
Sinad Meter
l
4.1 ALIGNMENT PROCEDURES
This transceiver has been aligned at the factory and does not require any adjustments at installation.
The required test equipment listed is used for the test setup or alignment shown in Figure 4-1
Transmitter Test Setup and Figure 4-2 Receiver Test Setup. This test setup is used in part or total
during the following adjustments. Refer to Page 43 for adjustment location.
4.1.1 PLL ALIGNMENT
ITEM U.U.T. SETTING ADJUST
MEASUREMENT
POINT
Regulator
Voltage
VCO Disconnect ‘short PCB’ from TP7, TP8 and TP9.
Set CLARIFIER Control to 12 o’clock.
Connect Frequency Counter to IC3 Pin 8. VC1
AM Frequency Set radio to CH 1 AM RX mode.
USB Frequency Set radio to CH 1 USB RX mode.
LSB Frequency Set radio to CH 1 LSB RX mode.
TX Offset
Frequency
AM OSC Set radio to CH 1 AM TX mode.
USB OSC Set radio to CH 1 USB TX mode.
LSB OSC Set radio to CH 1 LSB TX mode.
Connect Voltmeter positive lead to power switch.
Connect Voltmeter negative lead to PCB ground. VR701
Set radio to CH 1 AM RX mode.
Connect Voltmeter to TP2.
L14
Connect Oscilloscope to TP3.
L15
Connect Frequency Counter to TP3.
L20
Connect Frequency Counter to TP3.
L21
Connect Frequency Counter to TP3.
Set radio to CH 1 AM TX mode.
Connect Frequency Counter to TP3.
L22
VR7
Connect Frequency Counter to TP5.
L23
Connect Frequency Counter to TP6.
L24
Connect Frequency Counter to TP6.
L25
13.8 VDC
2.5 VDC ± 0.1
Adjust for max.
10.2400MHz ± 20Hz
16.2700MHz ± 20Hz
16.2725MHz ± 20Hz
16.2675MHz ± 20Hz
16.2675MHz ± 20Hz
10.6950MHz ± 10Hz
10.6925MHz ± 10Hz
10.6975MHz ± 10Hz
4.1.2 TRANSMITTER ALIGNMENT
- 14 -
 Loading...
Loading...