Page 1
Instruction Manual
MICRO CONTROLLER X
COMMUNICATION
FUNCTIONS
(RS-485 MODBUS)
TYPE: PXR
INP-TN512642a-E
Page 2

NOTICE
1. Exemption items from responsibility
The contents of this document may be changed in the future without prior notice.
We paid the utmost care for the accuracy of the contents. However, we are not liable for direct and
indirect damages resulting from incorrect descriptions, omission of information, and use of
information in this document.
Page 3

CONTENTS
1. COMMUNICATION FUNCTIONS
1.1 General
2. SPECIFICATIONS
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
2.1 Communication Specifications
3. CONNECTION
3.1 Terminal Allocation
3.2 Wiring
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
4. SETTING OF COMMUNICATION CONDITION
4.1 Set Items
4.2 Setting Operation Method
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
5. MODBUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL
5.1 General
5.2 Composition of Message
5.3 Response of Slave Station
5.4 Function Code
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
5.5 Calculation of Error Check Code (CRC-16)
5.6 Transmission Control Procedure
5.7 FIX Processing (Cautions at write-in of data)
6. DETAILS OF MESSAGE
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
6.1 Read-out of Bit Data [Function code:01
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
]
H
6.2 Read-out of Read-out Only Bit Data [Function code:02
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
6.3 Read-out of Word Data [Function code:03
]
H
6.4 Read-out of Read-out Only Word Data [Function code:04
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
6.5 Write-in of Bit Data (1 bit) [Function code:05
]
H
6.6 Write-in of Word Data (1 word) [Function code:06
6.7 Write-in of Continuous Word Data [Function code:10
7. ADDRESS MAP AND DATA FORMAT
7.1 Data Format
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
7.2 Address Map of Internal Calculation Value Data
7.3 Address Map of Engineering Unit Data
7.4 Additional Explanation of Address Map
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
]
H
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
]
H
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
]
H
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
]
H
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
5
5
6
7
7
8
10
11
12
13
15
16
16
17
19
22
24
25
26
28
28
31
36
41
8. SAMPLE PROGRAM
9. TROUBLESHOOTING
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
-i-
44
49
Page 4
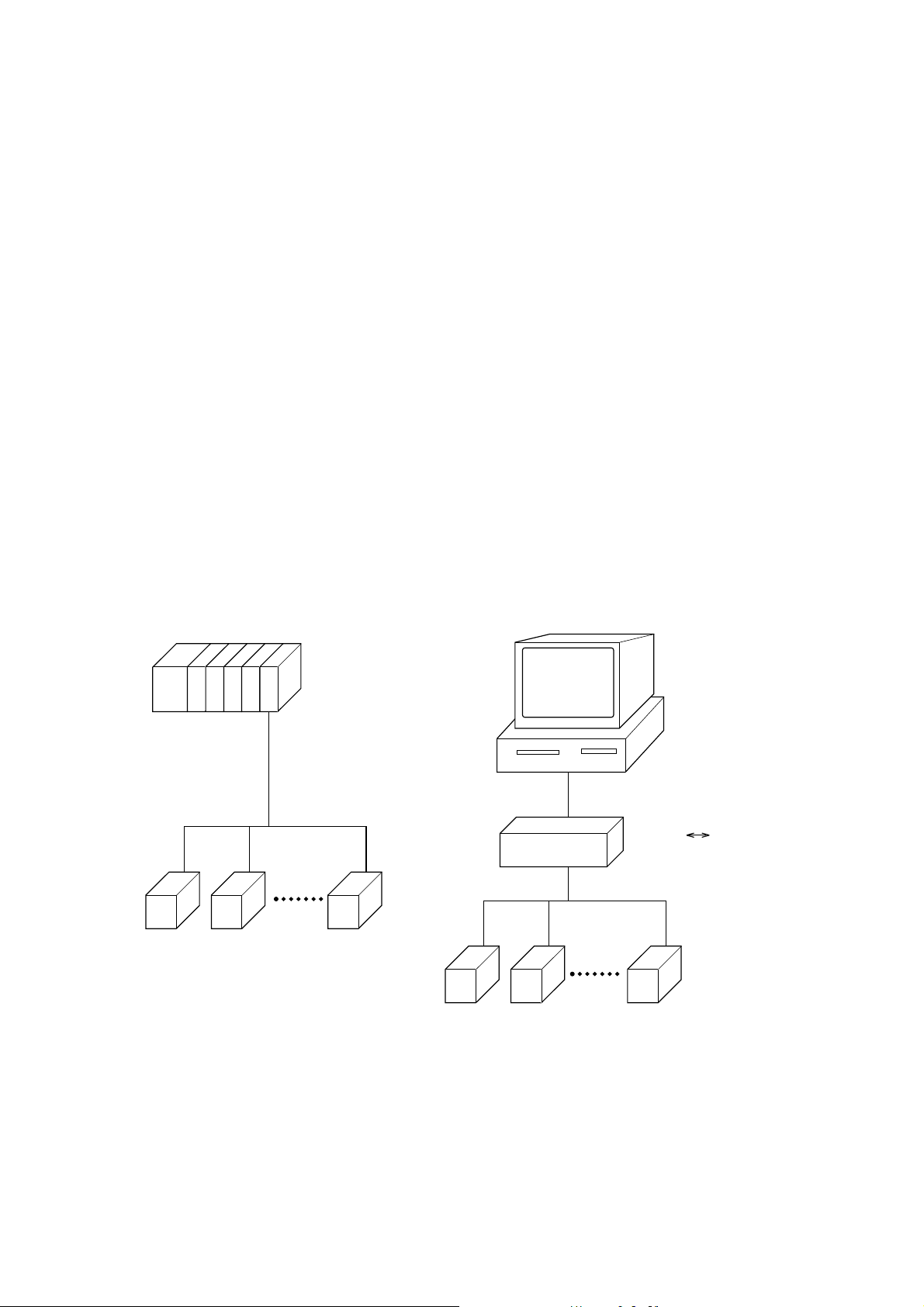
1. COMMUNICATION FUNCTIONS
1.1 General
• PXR provides a communication function by RS-485 interface, by which it can transmit and receive data to and
from host computer, programmable controller, graphic display panel, etc.
• The communication system consists of master station and slave stations. Up to 31 slave stations (PXR) can
be connected per master station.
Note that, because the master station can communicate with only one slave station at a time, a party to
communicate with must be specified by the "Station No." set at each slave station.
• In order that the master station and slave station can communicate, the format of the transmit/receive data must
coincide. For the PXR, the format of the communication data is determined by the MODBUS protocol.
• Please use an RS-232C↔RS-485 converter in case of designating a personal computer or other devices which
have an RS-232C interface as a master station.
[RS-232C↔RS-485 converter] (recommended article)
Type: KS-485 (non-isolated type)/SYSTEM SACOM Corp.
Type: SI-30A (isolated type)/SEKISUI ELECTRONICS Co., Ltd.
[Note] MODBUS
Programmable
controller
RS-485
®
is the registered trade mark of Gould Modicon.
Personal
computer
RS-232C
RS-232C RS-485 converter
RS-485
-1-
Page 5

2. SPECIFICATIONS
2.1 Communication Specifications
Item Specification
Electrical specification Based on EIA RS-485
Transmission system 2-wire, semi-duplicate
Synchronizing system Start-stop synchronous system
Connection format 1 : N
Number connectable units Up to 31 units
Transmission distance 500m max. (total extension distance)
Transmission speed 9600bps
Data format
Transmission code HEX value (MODBUS RTU mode)
Error detection CRC-16
Isolation Functional isolation between transmission circuit
Data length 8 bits
Stop bit 1 bit
Parity none, even, odd (selectable)
and others (withstand voltage : 500V AC)
-2-
Page 6

3. CONNECTION
WARNING
For avoiding electric shock and malfunctions, do not turn on the power supply untill all wiring
have been completed.
3.1 Terminal Allocation
Terminal number Signal name
7 +
8 -
-3-
Page 7
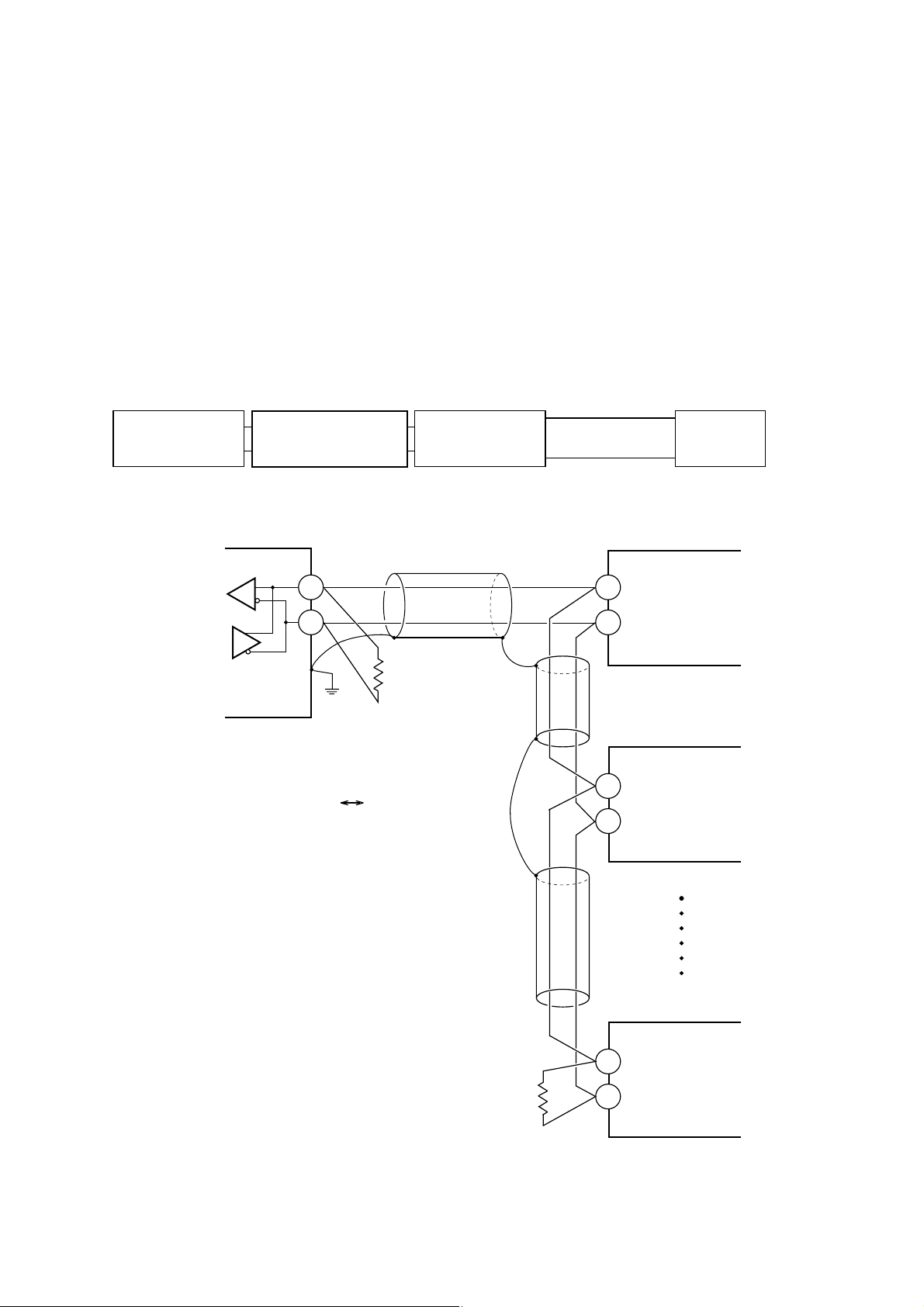
3.2 Wiring
• Use twisted pair cables with shield.
Recommended cable: UL2464, UL2448, etc.
• The total extension length of the cable is up to 500 m. A master station and up to 31 units of the PXR can be
connected per line.
• Both ends of the cable should be terminate with terminating resistors 100Ω1/2W.
• The shield wire of the cable should be grounded at one place on the master station unit side.
• If the PXR is to be installed where the level of noise applied to the PXR may exceed 1000 V, it is
recommended to install a noise filter in the master station side as below.
Recommended noise filter: ZRAC2203-11/TDK
Master station
(
PC, etc.
)
RS-232C⇔RS-485
Master station side
Noise filter PXR
Transmission
cable
Slave station (PXR)
Twisted pair cable with shield
−
FG
Terminating resistor
100Ω(1/2W)
RS-485 interface
or
RS-485 side of the RS-232C RS-485 converter
78+
−
Slave station (PXR)
78+
−
Slave station (PXR)
78+
−
Terminating resistor
100Ω(1/2W)
-4-
Page 8
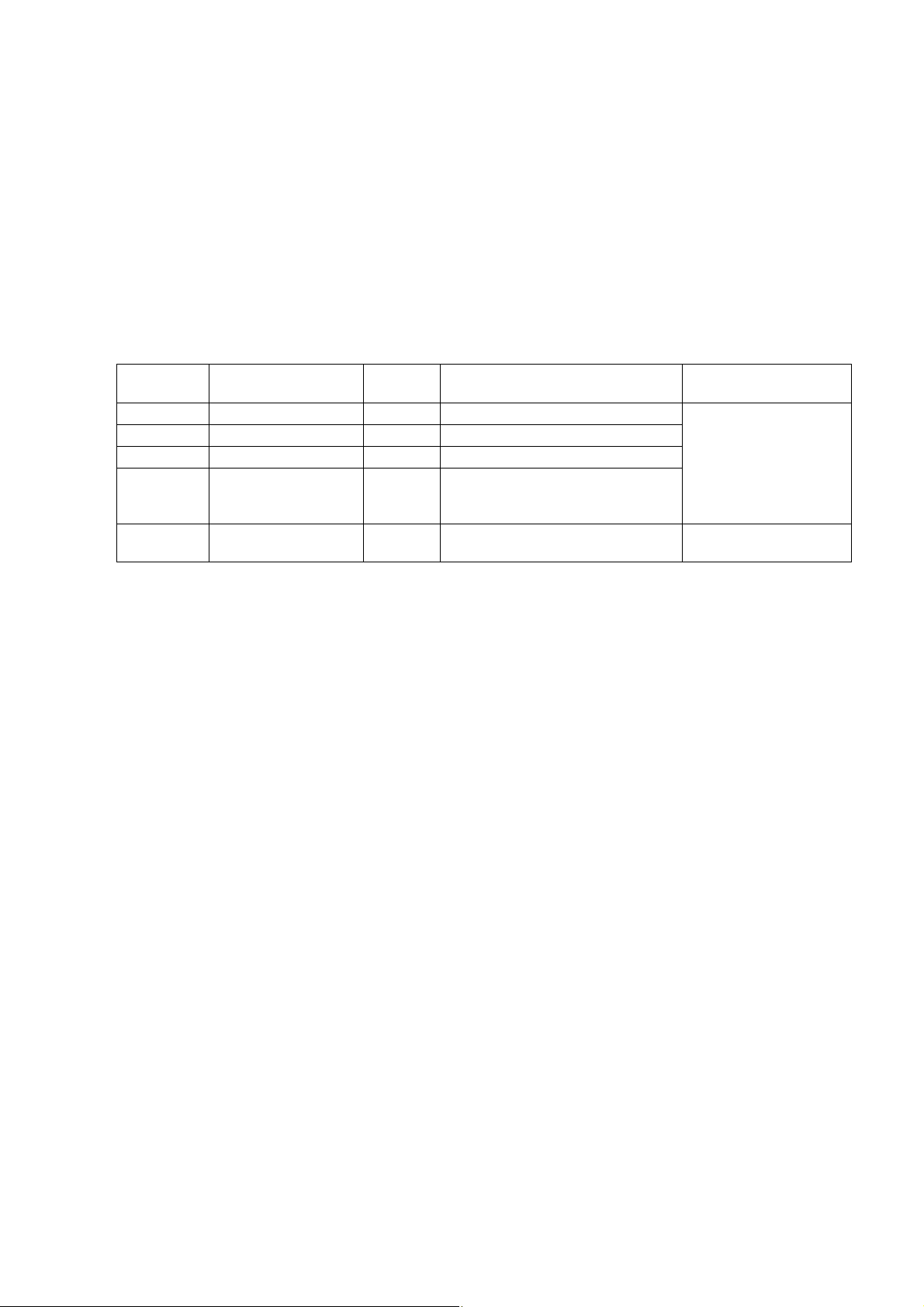
4.
In order that the master station and instrument (PXR) can correctly communicate, following settings are required.
SETTING OF COMMUNICATION CONDITION
• All communication condition settings of the master station are the same as those of instruments (PXR).
• All instruments (PXR) connected on a line are set to "Station Nos. (STno)" which are different from each other.
(Any "Station No." is not shared by more than one instrument.)
4.1 Set Items
The parameters to be set are shown in the following table. Set them by operating the front panel keys.
Parameter
symbol
―――
―――
―――
CoM Parity setting 0
STno Station No. 1
Transmission speed 9600bps Fixed (can not be changed)
Data length 8 bits Fixed (can not be changed)
Stop bit 1 bit Fixed (can not be changed)
Item
Value at
delivery
Setting range Remarks
0: odd parity
1: even parity
2: none parity
0 to 255
(0:communication function stop)
Set the same
communication
condition to the master
station and all slave
stations.
Set a different value to
each station.
-5-
Page 9

4.2 Setting Operation Method
The following example shows how to set the communication conditions.
Example: Selecting an even parity and “STno=18” on a station.
Key
operation
SEL
(6 seconds)
∨
SEL
∧∨
SEL
∨
SEL
∧∨
SEL
SEL
(3 seconds)
Indication Description
200
200
P-n1
0
STno
0
STno
0
STno
18
STno
18
CoM
0
CoM
0
CoM
1
CoM
1
200
200
Running state (PV/SV indication)
Press the SEL key for approximately 6 seconds. P-n1 appears and
No. 3 block parameter is selected.
Operate the ∨ key repeatedly until STno parameter appears. (If
past over, operate the ∧ key to return.)
Press the SEL key. The numeric value on the lower indicator
blinks and the setting mode is selected.
Operate the ∧ or ∨ key to change the numeric value to 18.
Press the SEL key again. The numeric value stops blinking and
the setting is registered.
Press the ∨ key to display the CoM parameter.
Press the SEL key. The numeric value on the lower indicator
blinks and the setting mode is selected.
Operate the ∧ or ∨ key until the numeric value changes to 1 (even
parity).
Press the SEL key again. The numeric value stops blinking and
the setting is registered.
Press the SEL key for 3 seconds to resume the running indication
(PV/SV indication).
-6-
Page 10
5. MODBUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL
5.1 General
The communication system by the MODBUS protocol is that the communication is always started from the master
station and a slave station responds to the received message.
Transmission procedures is as shown below.
1) The master station sends a command message to a slave station.
2) The slave station checks that the station No. in the received message matches with the own station No. or
not.
3) If matched, the slave station executes the command and sends back the response message.
4) If mismatched, the slave station leaves the command message and wait for the next command message.
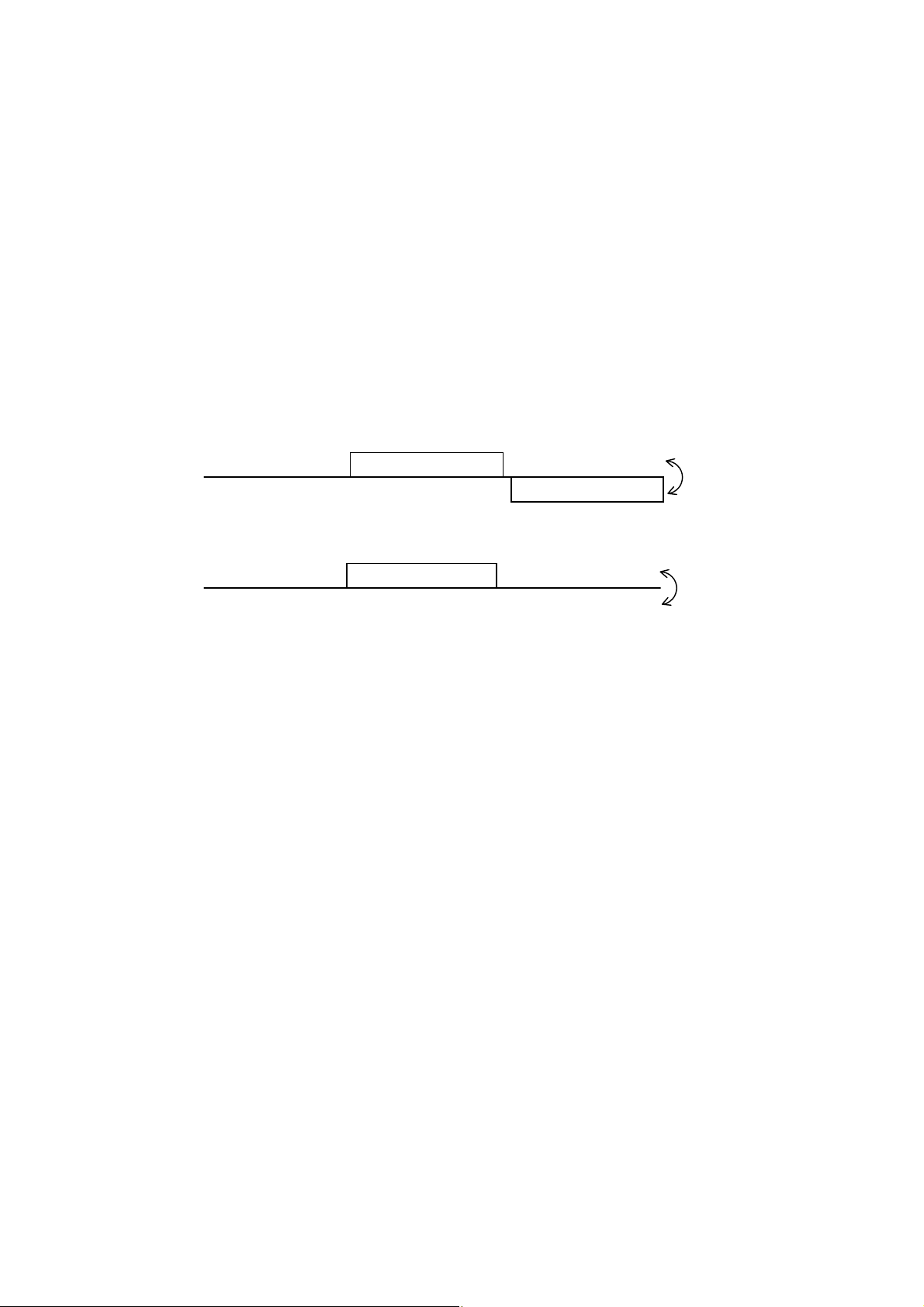
a) In case when the station No. in the received command message matches with the own slave station No.
Master to slave
Slave to master
b) In case when the station No. in the received command message mismatches with the own slave station
No.
Master to slave
Slave to master
The master station can individually communicate with any one of slave stations connected on the same line upon
setting the station No. in the command message.
Command message
Command message
Response message
(Not respond)
Data on
the line
Data on
the line
-7-
Page 11
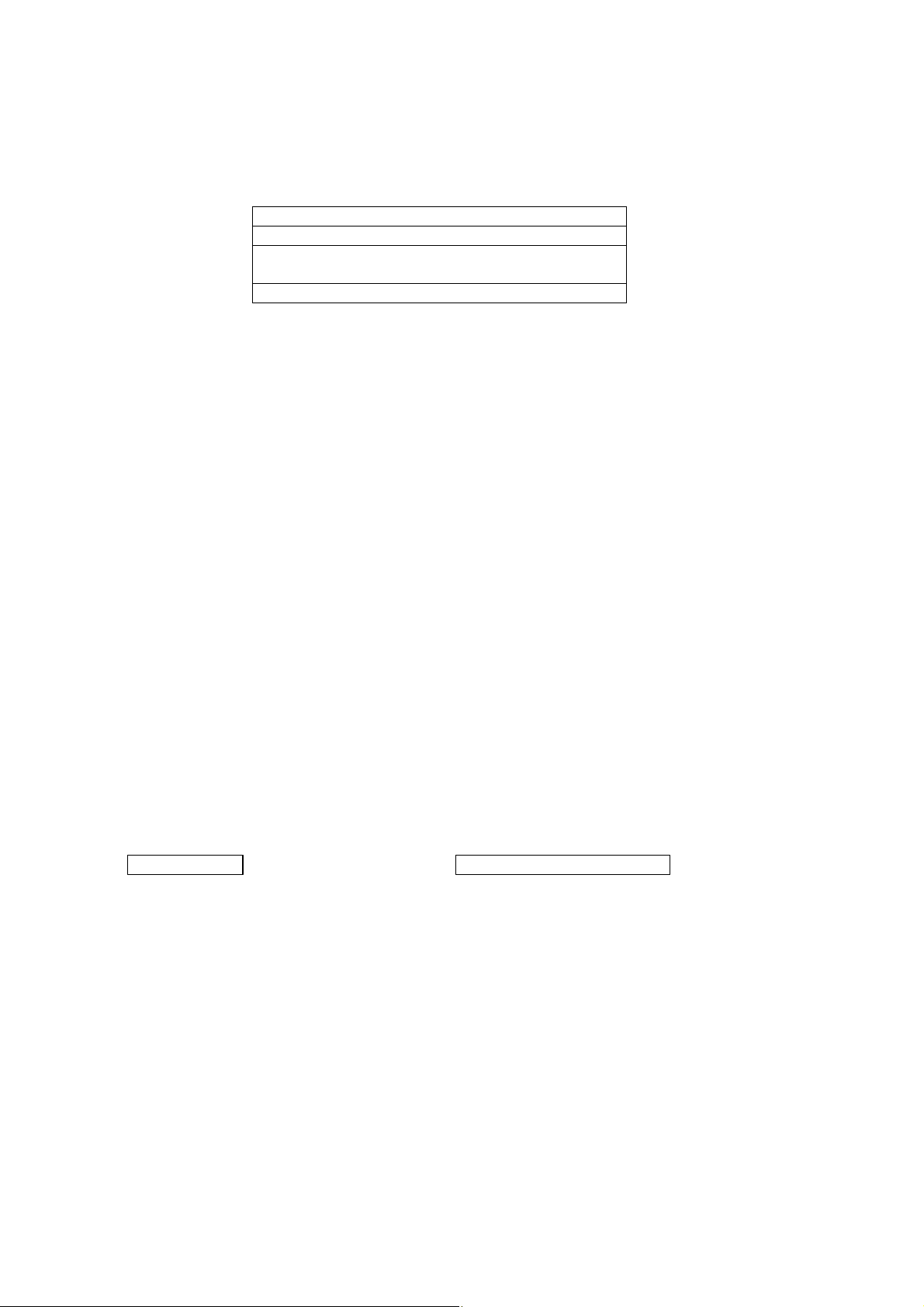
5.2 Composition of Message
Command message and response message consist of 4 fields ; Station No., Function code, Data and Error check
code. And these are send in this order.
Station No. (1 byte)
Function code (1 byte)
Data (2 to 125 bytes)
Error check code (CRC-16) (2 bytes)
Fig. 5-1 Composition of message
In the following, each field is explained.
(1) Station No.
Station No. is the number specifiing a slave station. The command message is received and operated only by
the slave station whose station No. matches with the No. set in the parameter "STno".
For details of setting the parameter "STno", refer to chapter 4.
(2) Function code
This is a code to designate the function executed at a slave station.
For details, refer to section 5.4.
(3) Data
Data are the data required for executing function codes. The composition of data varies with function codes.
For details, refer to chapter 6.
A coil number or a register number is assigned to each data in the temperature controller. For reading/writing
the data by communication, designate the coil number or register number.
Note that the coil number or register number transmitted on message is expressed as its relative address.
The relative address is calculated by the following expression.
The lower 4 digits of the
Relative address
For example, when the resister number designated by a function code is 40003,
Relative address = (lower 4 digits of 40003) – 1
= 0002
is used on the message.
=
Coil number or register number
– 1
-8-
Page 12

(4) Error check code
This is the code to detect message errors (change in bit) in the signal transmission.
On the MODUBUS protocol (RTU mode), CRC-16 (Cycric Redundancy Check) is applied.
For CRC calculation method, refer to section 5.5.
-9-
Page 13
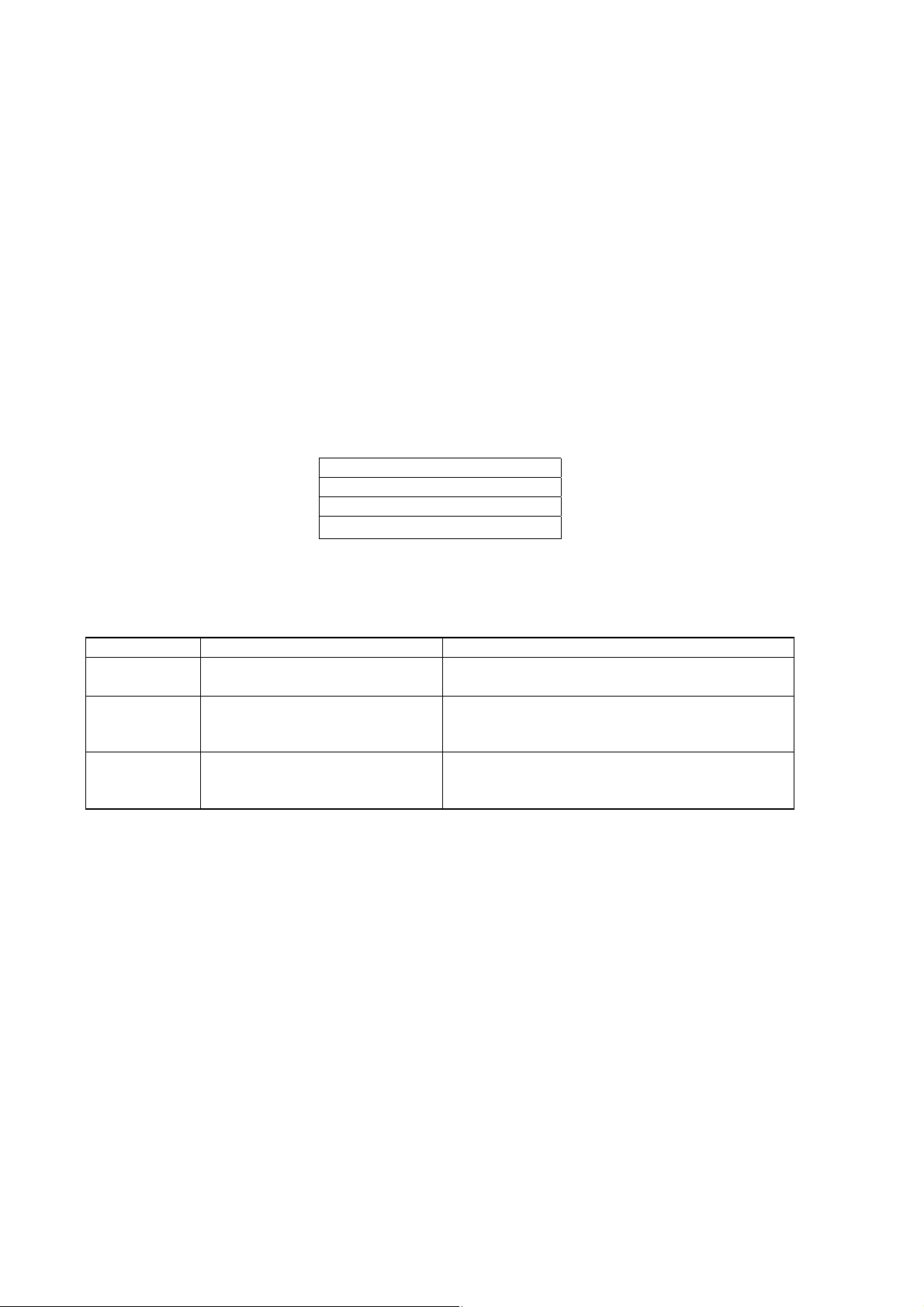
5.3 Response of Slave Station
(1) Response for normal command
To a relevant message, the slave station creates and sends back a response message which corresponds to the
command message. The composition of message in this case is the same as in section 5.2.
Contents of the data field depend on the function code. For details, refer to Chapter 6.
(2) Response for abnormal command
If contents of a command message have an abnormality (for example, non-actual function code is designated)
other than transmission error, the slave station does not execute that command but creates and sends back a
response message at error detection.
The composition of response message at error detection is as shown in Fig. 5-2 The value used for function
code field is function code of command message plus 80
Table 5-1 gives error codes.
Station No.
Function code + 80H
Error code
Error check(CRC-16)
Fig. 5-2 Response message at error detection
.
H
Table 5-1 Error code
Error code Contents Description
01H Illegal function Non-actual function code is designated.
Check for the function code.
02H Illegal data address A relative address of a coil number or resister
number to which the designated function code can
not be used.
03H Illegal data value Because the designation of number is too much,
the area where coil numbers or resister numbers do
not exist is designated.
(3) No response
Under any of the following items, the slave station takes no action of the command message and sends back no
response.
・A station number transmitted in the command message differs from the station number specified to the
slave station.
・ A error check code is not matched, or a transmission error (parity error, etc.) is detected.
・ The time interval between the composition data of the message becomes longer than the time
corresponding to 24 bits. (Refer to section 5.6 Transmission Control Procedure)
・While the data is being written in non-volatile memory after write via communication, the next write is
attempted.
-10-
Page 14
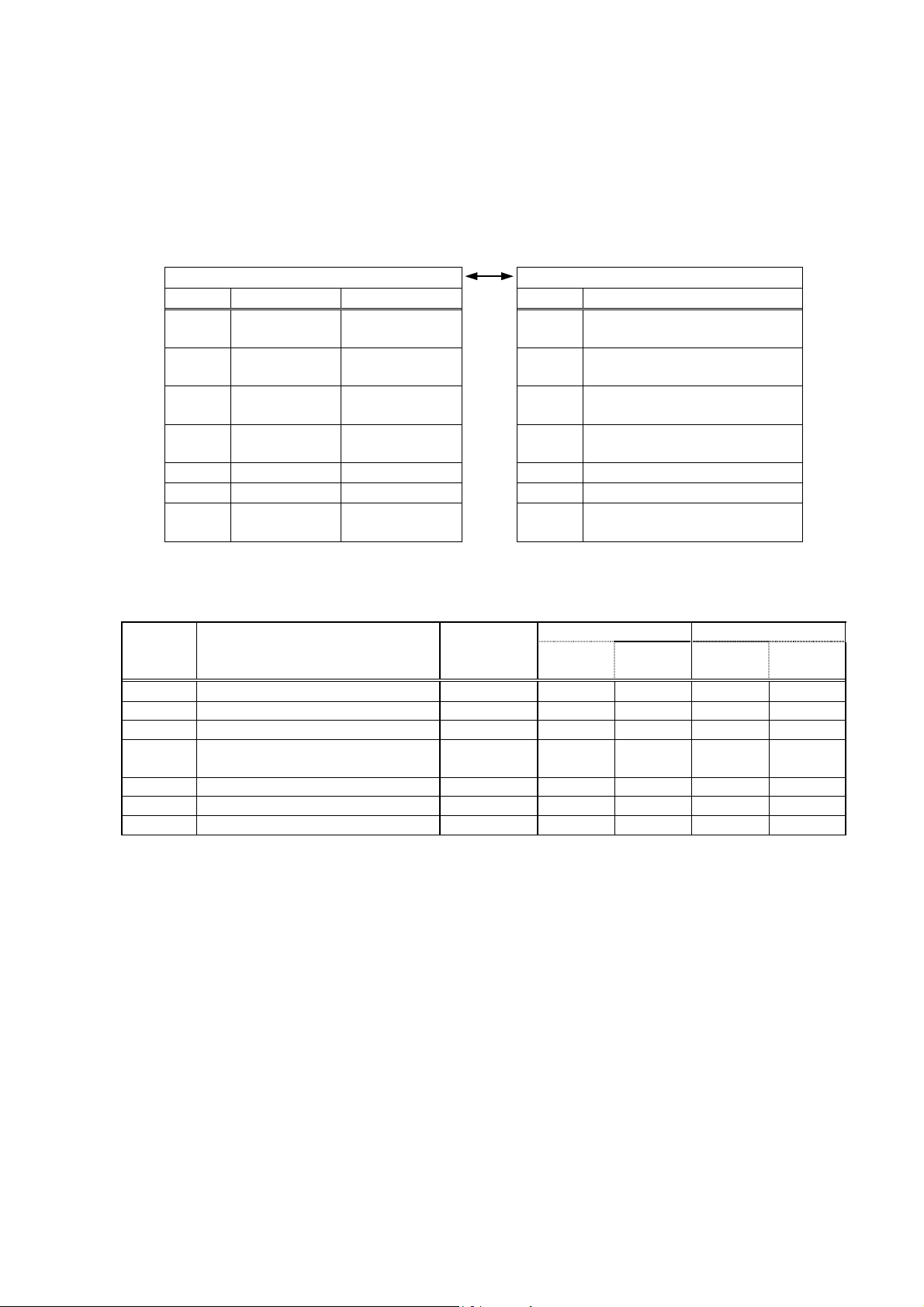
5.4 Function Code
According to MODBUS protocol, coil numbers and register numbers are assigned by function codes.
Each function code acts on specific coil number and register number.
This correspondence is shown in Table 5-2, and the message length by function is shown in Table 5-3.
Table 5-2 Correspondence between function codes and objective address
Function code
No. Function Object
01H Read-out
Coil
0xxxx Read-out/write-in bit data
Coil No. and resister No.
No. Contents
(continuously)
02H Read-out
Input relay
1xxxx Read-out bit data
(continuously)
03H Read-out
Holding register
4xxxx Read-out/write-in word data
(continuously)
04H Read-out
Input register
3xxxx Read-out word data
(continuously)
05H Write-in Coil
06H Write-in Holding register
10H Write-in
Holding register
0xxxx Read-out/write-in bit data
4xxxx Read-out/write-in word data
4xxxx Read-out/write-in word data
(continuously)
Table 5-3 Function code and message length
[Unit:byte]
Function
code
Contents Number of
designatable
Command message Response message
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
data
01H Read-out of bit data 1bit
02H Read-out of bit data (read-out only) 8 bits
03H Read-out of word data 60 words
04H Read-out of word data
*1
*1
15 words
*1
*1
8 8 6 6
8 8 6 6
8 8 7 125
8 8 7 35
(read-out only)
05H Write-in of bit data 1 bit 8 8 8 8
06H Write-in of word data 1 word 8 8 8 8
10H Write-in of continuous word data 60 words
*1
11 129 8 8
*1) The "Number of designatable data" given above is the limit due to the number of data which the instrument
assigns to coil number and register number (except function codes 05
, 06H).
H
-11-
Page 15
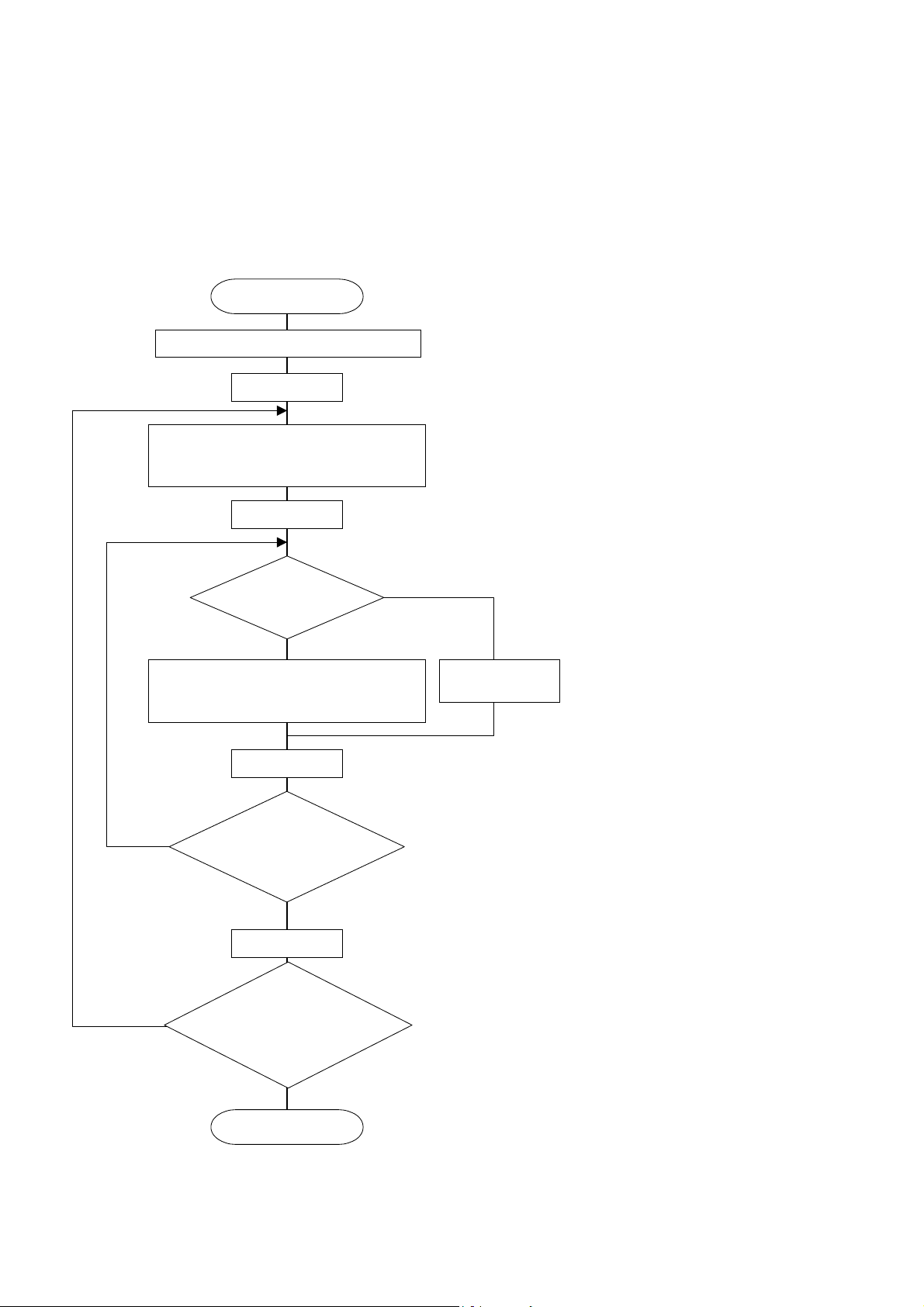
5.5 Calculation of Error Check Code (CRC-16)
t
CRC-16 is the 2-byte (16-bits) error check code. From the top of the message (station No.) to the end of the
data field are calculated.
The slave station calculates the CRC of the received message, and does not respond if the calculated CRC is
different from the contents of the received CRC code.
Fig. 5-3 shows the flow of the CRC-16 calculation system.
Start
Set FFFFH (hexadecimal number) in CR.
Set 1 in J.
Exclusive logical sum (XOR) is executed
with CR and one character (1 byte) of the I
characters, and its results is set in CR.
Set 1 in J.
Bit at right end
of CR is 1?
YES
Shift CR to right by 1 bit, and A001H and
exclusive logical sum (XOR) are executed
and its result is set in CR.
NO
Explanation of variables
CR:CRC error check data (2 bytes)
I:Digits of calculation characters
in command message
J:Check on the number of times
of CR calculation
Shift CR to righ
by 1 bit.
NO
NO
Add 1 to J.
Calculation (8 times) is
finished?
J>8
YES
Add 1 to J.
Calculation of all characters is
completed?
I>All characters
YES
End
Fig. 5-3 Flow of CRC-16 calculation
(Calculation is executed in the order of
command message station No., function
code and data.)
CR calculation result shall be added to
the last command message in the order
of LOW byte and HIGH byte.
-12-
Page 16

5.6 Transmission Control Procedure
(1) Transmission procedure of master station
The master station must proceed to a communication upon conforming to the following items.
(1-1) Before sending a command message, provide 48 bits time or more vacant status.
(1-2) For sending, the interval between bytes of a command message is below 24 bits time.
(1-3) Within 24 bits time after sending a command message, the receiving status is posted.
(1-4) Provide 48 bits time or more vacant status between the end of response message reception and
beginning of next command message sending [same as in (1-1)].
(1-5) For ensuring the safety, make a confirmation of the response message and make an arrangement so
as to provide 3 or more retries in case of no response, error occurrence, etc.
Note) The above definition is for most unfavorable value. For ensuring the safety, it’s recommended the
program of the master to work with safety factors of 2 to 3. Concretely, it is advised to arrange the
program for 9600 bps with 10 ms or more for vacant status (1-1), and within 1 ms for byte interval (1-2)
and changeover from sending to receiving (1-3).
(2) Description
1) Detection of the message frame
Since the communication system uses the 2-wire RS-485 interface, there may be 2 statuses on a line below.
(a) Vacant status (no data on line)
(b) Communication status (data is existing)
Instruments connected on the line are initially at a receiving status and monitoring the line. When 24 bits
time or more vacant status has appeared on the line, the end of preceding frame is assumed and, within
following 24 bits time, a receiving status is posted. When data appears on the line, instruments receive it
while 24 bits time or more vacant status is detected again, and the end of that frame is assumed. I.e., data
which appeared on the line from the first 24 bits time or more vacant status to the next 24 bits time or more
vacant status is fetched as one frame.
Therefore, one frame (command message) must be sent upon confirming the following.
(1-1) 48 bits time or more vacant status precedes the command message sending.
(1-2) Interval between bytes of 1 command message is smaller than 24 bits time.
2) Response of this instrument (PXR)
After a frame detection (24 bits time or more vacant status), this instrument carries out processing with that
frame as a command message. If the command message is destined to the own station, a response
message is returned. Its processing time is 1 to 30 ms (depends on contents of command message).
After sending a command message, therefore, the master station must observe the following.
(1-3) Receiving status is posted within 24 bits time after sending a command message.
-13-
Page 17

Master station → PXR
Master station ← PXR
Data on line
Space time of longer than 5ms is
needed
(longer than 10ms is recommended)
POL1 POL2
1 to 30msec
POL1 response data
POL1 POL2 POL1 response data
-14-
Page 18

5.7 FIX Processing (Cautions at write-in of data)
The instrument is provided inside with a non-volatile memory (EEPROM) for holding the setting parameters.
Data written in the non-volatile memory is not lost even if turning off the power. When setting parameter is
written via communication, the data is stored in the internal memory (RAM) and then written in the non-volatile
memory.
FIX execution writes the parameters stored in the internal memory into the non-volatile memory, but this
function is not required any more because the data is written in non-volatile memory when it is written in the
parameter.
Fig. 5-4 shows the FIX procedure.
Cautions:
・ Write in the non-volatile memory takes approximately 5 seconds at the longest approximately 5 seconds.
・ While writing, do not turn off the power of the PXR. Otherwise, the data in the non-volatile memory will
be destroyed, whereby the PXR could not be used any longer.
・ The non-volatile memory (EEPROM) is a device where the number of write-in times is limited. The
guaranteed number of write-in times of the non-volatile memory used on the instrument is 10,000 minimum.
Therefore, limit the times of change of parameter setting to absolute minimum. Refrain from carrying out
the FIX processing periodically for example or while such is not absolutely required.
Start FIX
Read the FIX bit
with function code : 01
relative address : 0000
No
FIX=0?
Yes
Write ‘1’ into FIX bit
with function code : 05
relative address : 0000
Read the FIX bit
with function code : 01
relative address : 0000
No
FIX=0?
H
H
H
H
H
Yes
End FIX
Fig. 5-4 FIX procedure
-15-
Page 19

6. DETAILS OF MESSAGE
6.1 Read-out of Bit Data [Function code:01
Function code Max. bit number read-out in one message Relative data address Coil number
01H 1 bit 0000H 00001
H
]
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
00H Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Read-out bit number
CRC data
* Arrangement of read-out bit data
MSB LSB
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
00H
00H State of the first 8 bits
01
Upper
Lower
H
CRC data
01
H
Upper
Lower
State of read-out bit
(2) Function explanations
The state of the bit of the coil No. 00001 is read-out.
(3) Message transmission (example)
The following shows an example of reading-out the FIX execution request data from No. 1 slave station.
FIX execution request bit Relative address:0000
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No.. 01
Function code 01H Function code 01H
Upper 00H Read-out byte number 01H Read-out start No.
(relative address)
bit number
CRC data
* Meaning of read data
MSB LSB
State of FIX execution request 00H= 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
No execution of FIX
Lower 00
Upper 00H Upper 51H Read-out
Lower 01
Upper FDH
Lower CA
Station No. 01H
H
State of the first 8 bits 00H
H
H
H
Number of data:01
H
CRC data
H
Lower 88H
↑
-16-
Page 20

6.2 Read-out of Read-out Only Bit Data [Function code:02H]
Function code Max. bit number read-out in one message Relative data address Coil number
02H 8 bits
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Upper Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Read-out bit number
CRC data
Lower
00H State of the read-out bit
Lower 01
Upper
to 08 H Upper
H
CRC data
Lower
* Arrangement of read-out bit data
MSB LSB
(2) Function explanations
01
H
-000F
0000
H
10001-10016
H
Lower
State of the first 1 bit
……
State of the last 1 bit
Bit information data of continuous read-out bit number from the read-out start number.
Read-out bit data are arranged in 8-bit unit and transmitted from the slave station.
When read-out bit data number is not multiple of 8, all the bits (MSB side) not related with the state of the last
8 bits will become "0".
-17-
Page 21

(3) Message transmission (example)
(
The following shows an example of reading-out the state of the alarm 1 and alarm 2 transmitted from No.31
slave station.
Alarm 1 detect data bit Relative address : 000C
Alarm 2 detect data bit Relative address : 000D
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 1F
H
Function code 02H Function code 02H
Upper 00H Read-out byte number 01H Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Lower 0C
H
Upper 00H Upper 66H Read-out
bit number
CRC data
Lower 02
H
Upper 3AH
Lower 76
H
* Meaning of read-out data
MSB LSB
State of alarm detection of 01
= 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
H
alarms 1 and 2
State of the first 2 bits)
Data number : 02H
H
H
Station No. 1FH
State of the first 8 bits 01H
CRC data
Lower 60H
Alarm 2 OFF state
Alarm 1 ON state
-18-
Page 22

6.3 Read-out of Word Data [Function code:03H]
(
Function code Max. word number read-out
in one message
03H 60 words
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Read-out start
No.
relative address)
Read-out word
number
CRC data
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
* Arrangement of read-out word data
MSB LSB
Upper byte of contents of the first word data
Lower byte of contents of the first word data
Upper byte of contents of the next word data
Lower byte of contents of the next word data
~ ~
Upper byte of contents of the last word data
Lower byte of contents of the last word data
(2) Function explanations
Relative data address Resister No. Kind of data
Internal calculation value
Engineering unit
Read-out word number×2
1 to 60
-0070
0000
03E8
H
-0458
H
40001-40113
H
41001-41113
H
Read-out byte number
Contents of the
first word data
Contents of the
next word data
~ ~
Contents of
Upper
the last word
data
CRC data
Lower
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
Word data of continuous word numbers from the read-out start No. can be read. Read-out word data are
transmitted from the slave station in the order of upper and lower bytes.
-19-
Page 23

(3) Message transmission
(a) In case of data of internal calculation value
The following shows an example of reading the low and high limits of set value from No. 2 slave station.
Relative address of low limit of set value : 001E
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 02
Function code 03H Function code 03H
Upper 00H Read-out byte number 04H Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Lower 1EH Upper 00H
Upper 00H
number
CRC data
Lower 02
Upper A4H
Lower 3E
* Meaning of read-out data
Low limit of set value 00 00
(contents of first word data)
High limit of set value 27 10
(contents of next word data)
When input range is 0 to 400℃
Station No. 02H
H
H
Upper D3H
H
Data number : 02H
H
Contents of the
first word data
Contents of the
next word data
CRC data
= 10000(=100.00%FS)
H
= 10000(=100.00%FS)
H
Lower 00H Read-out word
Upper 27H
Lower 10H
Lower 0FH
Low limit of set value =400℃(=100.00%FS)
High limit of set value =400℃(=100.00%FS)
Point
For handling of the internal calculation value, engineering unit and decimal point,
refer to section 7.1.
-20-
Page 24

(b) In case of data of engineering unit
The following shows an example of reading the low and high limits of set value from No. 2 slave station.
Relative address of low limit set value : 0406H Data number : 02H
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 02
Station No. 02H
H
Function code 03H Function code 03H
Upper 04H Read-out byte number 04H Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Lower 06H Upper 0H
Upper 00H
number
CRC data
Lower 02H
Upper 25H
Lower 09
Upper C8H
H
Contents of the
first word data
Contents of the
next word data
CRC data
Lower 0H Read-out word
Upper 01H
Lower 90H
Lower CFH
* Meaning of read-out data
Low limit of set value 00 00
= 100
H
(contents of first word data)
High limit of set value 01 90
= 400
H
(contents of next word data)
When the position of decimal point is 0 (Parameter P-dP=0),
Low limit of set value =400℃
High limit of set value =400℃
Point
For handling of the internal calculation value, engineering unit and decimal point,
refer to section 7.1.
-21-
Page 25

6.4 Read-out of Read-out Only Word Data [Function code:04H]
Function code Max. word number read-out
in one message
04H 15 words
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Upper
Lower Upper
Upper
number
CRC data
Lower
Upper
Lower
* Arrangement of read-out word data
MSB LSB
Upper byte of contents of the first word data
Lower byte of contents of the first word data
Upper byte of contents of the next word data
Lower byte of contents of the next word data
~ ~
Upper byte of contents of the last word data
Lower byte of contents of the last word data
(2) Function explanations
Relative data address Resister No. Kind of data
-000E
0000
H
-03F6
03E8
H
30001-30015
H
31001-31015
H
Read-out byte number
Internal calculation value
Engineering unit
Read-out word number×2
Contents of the
1 to 15
first word data
Contents of the
next word data
~
Lower Read-out word
Upper
Lower
~
Upper Contents of
the last word
data
CRC data
Lower
Upper
Lower
Word data of continuous word numbers from the read-out start No. can be read. Read-out word data are
transmitted from the slave station in the order of upper and lower bytes.
-22-
Page 26

(3) Message transmission
(a) In case of data of internal calculation value
The following shows an example of reading-out the PV from No. 1 slave station.
Relative address of PV:0000
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Function code 04H Function code 04H
Upper 00H Read-out byte number 02H Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Lower 00
Upper 00H
number
CRC data
Lower 01H
Upper 31H
Lower CA
* Meaning of read-out data
Contents of the first word data 03 46
When input range is 0-400℃,
Data number:01H
H
Station No. 01H
H
Upper 03H
H
H
Contents of the
first word data
CRC data
= 838(=8.38%FS)
H
Lower 46H Read-out word
Upper 38H
Lower 32H
PV=33.5℃(=8.38%FS×400
)
Input range
(b) In case of data of engineering unit
The following shows an example of reading-out the PV value from No. 1 slave station.
Relative address of PV value:03E8
Data number:01H
H
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Station No. 01H
H
Function code 04H Function code 04H
Upper 03H Read-out byte number 02H Read-out start No.
(relative address)
number
CRC data
Lower E8
Upper 01H
H
Upper 00H
Lower 01H
Upper B1H
Lower BA
H
Contents of the
first word data
CRC data
Lower 4FH Read-out word
Upper 38H
Lower 32H
* Meaning of read-out data
Contents of the first word data 01 4F
= 335
H
When the position of decimal point is 1 (Parameter P-dP=1),
PV=33.5℃(=33.5)
Point
For handling of the internal calculation value, engineering unit and decimal point,
refer to section 7.1.
-23-
Page 27

6.5 Write-in of Bit Data (1 bit) [Function code:05H]
(
(
(
(
Function code Max. bit number written-in one message Relative data address Coil No.
05H 1 bit 0000H 00001
This function has become unnecessary. (The customer can continue using the controller without changing the
program.)
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Write-in designate
00
No.
relative address)
00
Upper Upper State of write-in
designation
CRC data
Lower
Upper Upper
Lower
(2) Function explanations
H
H
0000H=0
FF00
H
=1
Write-in
designate No.
relative address)
State of write-in
designation
CRC data
00
H
00
H
Lower
Lower
0000H=0
FF00
=1
H
Data of "0" or "1" is written in a bit of write-in designation No. bit. When "0" is written-in data of 0000H is
transmitted, and when "1" is written-in, data of FF00H is transmitted.
(3) Message transmission (example:This is the method of FIX execution)
The following shows an example of FIX execution request to No. 1 slave station.
FIX execution request bit Relative address:0000
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Station No. 01H
H
Function code 05H Function code 05H
Write-in
Upper 00H
designate No.
relative address)
Lower 00
H
Upper FFH Upper FFH State of write-in
designation
CRC data
Lower 00
Upper 8CH Upper 8CH
Lower 3A
H
H
After receiving above command, it takes approximately 100ms to 5s seconds that PXR saves memory data
from RAM to EEPROM.
Caution
If you turn off the PXR during above saving (approximately 100ms to 5s), memory data are broken
and can not be used.
H
Write-in
designate No.
relative address)
State of write-in
designation
CRC data
Upper 00H
Lower 00
H
Lower 00H
Lower 3A
H
Point
For details of FIX processing, refer to section 5.7.
-24-
Page 28

6.6 Write-in of Word Data (1 word) [Function code:06H]
(
(
Function code Max. word number write-in
in one message
06H 1 words
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Write-in
designate No.
relative address)
data
CRC data
Upper
Lower
Upper Upper Write-in word
Lower
Upper Upper
Lower
(2) Function explanation
Designated word data is written in write-in designate No. Write-in data are transmitted from master station in
the order of upper and lower bytes.
(3) Message transmission (example)
Relative data address Resister No. Kind of data
0000
03E8
-0070
H
-0458
H
40001-40113
H
41001-41113
H
Write-in
designate No.
relative address)
Upper
Lower
Internal calculation value
Engineering unit
Write-in word
data
CRC data
Lower
Lower
The following shows an example of setting 100.0 (10000=C3E8H) to the parameter "P" of No.1 slave station.
Parameter "P" Relative address: 0005
(table of internal calculation unit)
H
(or 03ED
(table of engineering value))
H
* Parameter "P" is not in the engineering unit setting, the same value is
written in both tables.
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Station No. 01H
H
Function code 06H Function code 06H
H
H
In case of
interval
calculation
Write-in
designate No.
(relative address)
State of write-in
designation
CRC data
Lower 05
H
Lower E8H
Lower 75
H
Write-in
designate No.
(relative address)
designation
CRC data
Upper 00H Upper 00H
Lower 05
Upper 03H Upper 03H State of write-in
Lower E8H
Upper 99H Upper 99H
Lower 75
Point
Note!
For handling of internal calculation value, engineering unit and decimal point, refer
to section 7.1.
1)While setting is being locked, response is returned normally, but the command is
not executed.
2)While the data is written in non-volatile memory, response is not returned.
-25-
Page 29

6.7 Write-in of Continuous Word Data [Function code:10H]
Function code Max. word number write-in
in one message
10H 60 words
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Upper Upper Write-in start No.
(relative address)
number
Write-in byte number
Lower
Upper Upper Write-in word
Lower
Upper First write-in
word data
Lower
Upper Next write-in
word data
~ ~
Lower
Upper Last write-in
word data
CRC data
Lower
Upper
Lower
* Arrangement of write-in word data
MSB LSB
Upper byte of contents of the first word data
Lower byte of contents of the first word data
Upper byte of contents of the next word data
Lower byte of contents of the next word data
~ ~
Upper byte of contents of the last word data
Lower byte of contents of the last word data
(2) Function explanation
Relative data address Resister No. Kind of data
0000
03E8
-0070
H
-0458
H
40001-40113
H
41001-41113
H
Internal calculation value
Engineering unit
Write-in start No.
1 to 60
Write-in word number×2
(relative address)
Write-in word
number
CRC data
Lower
Lower
Upper
Lower
Word data of continuous word number is written from write-in start address. Write-in word data are
transmitted from master station in the order of upper and lower bytes.
-26-
Page 30

(3) Message transmission (example)
The following shows an example of writing-in P=100.0, I=10, and D=5.0 to No. 1 slave station.
P=03E8
I=0064
D=0032
Parameter "P" Relative address:0005
(=1000D)
H
(=100D)
H
(=50D)
H
Data number:03
H
H
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Station No. 01H
H
Function code 10H Function code 10H
Write-in start No.
Upper 00H Upper 00H
Lower 05
H
Upper 00H Upper 00H Write-in word
number
Lower 03H
Write-in byte number 06H Upper 90H
Upper 03H
word data
Lower E8
H
Write-in start No.
Write-in word
number
CRC data
Lower 05H
Lower 03H
Lower 09H First write-in
Upper 00H Next write-in
word data
Lower 64
H
Upper 00H Last write-in
word data
CRC data
Lower 32H
Upper 56H
Lower BE
H
Point
Since the transmission data can not include a decimal point, data of 100.0 is transmitted as
"1000".
For transmission format of each data, refer to the address map (Chapter 7).
-27-
Page 31

7. ADDRESS MAP AND DATA FORMAT
7.1 Data Format
7.1.1 Transmission data format
The MODBUS protocol used in this instrument (PXR) is RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) mode.
Transmitted data is "numeric value" and not "ASCII code".
7.1.2 Internal calculation value and engineering unit
This instrument can handle 2 kinds of set value data or other data which are affected by input range as follows.
1) Internal calculation value : In % with respect to input range (0.00 to 100.00, without decimal point)
2) Engineering unit : Subjected to scaling to actual value according to input range
"Engineering unit" data can be handled with "Internal calculation value" address (register No.) plus 1,000
[Example] The value of "PV = 150" (input range: 0 to 400°C)
Register No. Data (HEX)
Internal
calculation value
Engineering unit 31001 0096H 150
In case of "Internal calculation value" here,
37.50 (%) × 400 (full scale) = 150 (°C) is obtained.
Note that the same data is handled at both addresses if it is not affected by input range.
This handling does not apply to bit data. (Address increased by 1,000 is invalid.)
For data affected by input range, refer to address maps in Sections 7.2 and 7.3.
Note : After changing the input range by communication write-in, pay attention to the decimal point position.
After changing the decimal point position by communication write-in, simultaneously change the lower
limit and upper limit of input range.
Example: Input range 0 to 400 changed into 0.0 to 400.0
a) Face panel operation:
b) Communication write-in:
30001 0EA6H
P-dP=0→1 suffices
P-dP=0→1
P-SL=0→0
P-SU=400→4000
Data (decimal)
3750(37.50%)
must be performed.
-28-
Page 32

7.1.3 Handling of decimal point
Some internally stored data have more digits below decimal point than displayed on the face panel.
No decimal point is added to transmission data.
For data given in the following table, carry out an alignment of decimal point.
(a) Internal calculation value data (address map shown in Section 7.2)
Digits below point Kind Resister No.
Parameter [ P-SL ] 40018 Designate by
parameter [P-dP]
Parameter [ P-SU ] 40019
(0 to 2)
1 digit below point
Parameter [ P ] 40006
Parameter [ i ] 40007
Parameter [ d ] 40008
Parameter [ CooL ] 40010
Parameter [ P-dF ] 40022
Parameter [ HB ] 40039
Parameter [ CT ] 30010
2 digits below point
Data affected by input range See address map (Section 7.2)
Parameter [ dB ] 40011
Parameter [ bAL ] 40013
Parameter [ PLC1 ] 40025
Parameter [ PHC1 ] 40026
Parameter [ PLC2 ] 40027
Parameter [ PHC2 ] 40028
Parameter [ OUT1 ] 30004
Parameter [ OUT2 ] 30005
(b) Engineering unit (address map shown in Section 7.3)
Digits below point Kind Resister No.
Designate by
parameter [P-dP]
(0 to 2)
1 digit below point
Parameter [ P-SL ] 41018
Parameter [ P-SU ] 41019
Data affected by input range See address map (Section 7.3)
Parameter [ P ] 41006
Parameter [ i ] 41007
Parameter [ d ] 41008
Parameter [ CooL ] 41010
Parameter [ P-dF ] 41022
Parameter [ HB ] 41039
Parameter [ CT ] 31010
2 digits below point
Parameter [ dB ] 41011
Parameter [ bAL ] 41013
Parameter [ PLC1 ] 41025
Parameter [ PHC1 ] 41026
Parameter [ PLC2 ] 41027
Parameter [ PHC2 ] 41028
Parameter [ OUT1 ] 31004
Parameter [ OUT2 ] 31005
-29-
Page 33

7.1.4 Data when input is abnormal
When "UUUU" or "LLLL" is displayed on the face panel on account of over-range, under-range or input open-
circuit for example, PV read-out value is 105% or -5% of input range.
Presence of any input abnormality via communication can be detected by:
"Register No. 30008 (or 31008): Input/main unit abnormal status"
-30-
Page 34

7.2 Address Map of Internal Calculation Value Data
Data affected by input range is handled in terms of internal value (0.00 to 100.00% value) before
scaling.
For detailed contents about individual parameter function or setting range, refer to the operation manual
(ECNO: 406).
H
, 05H]
H
0:Not writing-in
1:Writing in memory
]
0:Alarm 1 OFF,1: Alarm 1 ON
0: Alarm 2 OFF,1: Alarm 2 ON
0: Relay output of alarm 1 OFF
1: Relay output of alarm 1 ON
0: Relay output of alarm 2 OFF
1: Relay output of alarm 2 ON
0: HB alarm output OFF
1: HB alarm output ON
0: Alarm 1 OFF,1: Alarm 1 ON
0: Alarm 2 OFF,1: Alarm 2 ON
0:HB alarm output OFF
1:HB alarm output ON
Write-in data
setting range
0:No request
1:Request to write in
Affected by
input range
Affected by
input range
(Same as 10001)
(Same as 10002)
(Same as 10012)
Bit data [read-out/write-in] : Function code [01
Relative
address
0000H 00001 Bit
Coil No. Type Memory contents Read-out data
Write in non-volatile memory
(FIX execution)
Bit data [read-out only] : Function code [02
Relative
address
0000H 10001 Bit Alarm 1 ON/OFF
0001H 10002 (Reserve)
0002H 10003 (Reserve)
0003H 10004 (Reserve)
0004H 10005 Bit Alarm 2 ON/OFF
0005H 10006 (Reserve)
0006H 10007 (Reserve)
0007H 10008 (Reserve)
0008H 10009 Bit
0009H 10010 Bit
000AH 10011 (Reserve)
000BH 10012 Bit HB alarm relay output
000CH 10013 Bit Alarm 1 ON/OFF
000DH 10014 Bit Alarm 2 ON/OFF
000EH 10015 (Reserve)
000FH 10016 Bit HB alarm relay output
Coil No. Type Memory contents Read-out data
Alarm 1 output
(Calculation result of nonexciting alarm)
Alarm 2 output
(Calculation result of nonexciting alarm)
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
(the same
function as
40001)
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
-31-
Page 35

Word data [read-out/write-in] : Function code [03
Relative
address
0000H 40001 Word Non-volatile memory write-in
0001H 40002 Word PID/FUZZY/SELF selection
0002H 40003 Word SV value set on face panel
0003H 40004 Word Control RUN/standby
0004H 40005 Word Auto tuning command
0005H 40006 Word P
0006H 40007 Word I
0007H 40008 Word D
0008H 40009 Word
0009H 40010 Word COOL
000AH 40011 Word Dead band
000BH 40012 Word Anti-reset windup
000CH 40013 Word Output convergence value
000DH 40014 Word PV shift
000EH 40015 Word SV offset
000FH 40016 Word Input type code 0 to 16
0010H 40017 Word Temperature unit
0011H 40018 Word Input scale lower limit -1999 to 9999
0012H 40019 Word Input scale upper limit -1999 to 9999
0013H 40020 Word Decimal point place 0 to 2
0014H 40021 (Do not use)
0015H 40022 Word Input filter time constant
0016H 40023 Word RCJ yes/no
0017H 40024 Word MV limit kind 0 to 15
0018H 40025 Word Output 1 lower limit
0019H 40026 Word Output 1 upper limit
001AH 40027 Word Output 2 lower limit
001BH 40028 Word Output 2 upper limit
001CH 40029 (Do not use)
001DH 40030 (Do not use)
001EH 40031 Word Set value (SV) lower limit
001FH 40032 Word Set value (SV) upper limit
0020H 40033 (Do not use)
0021H 40034 (Do not use)
0022H 40035 (Do not use)
0023H 40036 (Do not use)
0024H 40037 (Do not use)
0025H 40038 (Do not use)
0026H 40039 Word Heater burnout alarm set value
0027H 40040 Word Setting lock 0 to 5
Resister
No.
Type Memory contents Read-out data
Hysteresis range at
two-position control
, 06H, 10H]
H
0: Not writing-in
1: Writing in memory
0:PID control
1:FUZZYcontrol
2:SELF tuning control
0 to 10000
(within 0.00 to 100.00% FS within set
value limits)
0: Invalidate standby (RUN)
1:Validate standby
0: Auto tuning
disabled
1: While executing
standard type AT
executed
2: While executing
low PV type AT
executed
0 to 9999(0.0 to 999.9%)
0 to 32000(0 to 3200.0 sec)
0 to 9999(0.0 to 999.9 sec)
0 to 5000(0.00 to 50.00%FS) *
0 to 1000(0.0 to 100.0)
-5000 to 5000(-50.00 to +50.00)
0 to 10000(0.00 to 100.00%) *
-10000 to 10000
(-100.00 to 100.00%)
-1000 to 1000(-10.00 to 10.00%FS) *
-5000 to 5000(-50.00 to 50.00%FS) *
0:℃ 1:°F
0 to 9000(0.0 to 900.0 sec)
0: Disable RCJ compensation
(do not perform reference cold junction
compensation)
1: Enable RCJ compensation (perform
reference cold junction compensation)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
0 to 10000(0.00 to 100.00%FS) *
0 to 10000(0.00 to 100.00%FS) *
0 to 500(0.0 to 50.0A)
Write-in data
setting range
0:No request
1:Request to write in
0: Disable auto
tuning
1: Request
execution of
standard type
2: Request
execution of low
PV type AT
Affected by
input range
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
(Same function
as 00001)
CTrL
* Inhibit change
while
controlling
STby
AT
P
i
D
HyS
CooL
db
Ar
bAL
PVOF
SVOF
P-n2
P-F
P-SL
P-SU
P-dP
P-dF
rCJ
PCUT
PLC1
PHC1
PLC2
PHC2
SV-L
SV-H
Hb
LoC
-32-
Page 36

Relative
address
0028H 40041 Word Alarm 1 type 0 to 34
0029H 40042 Word Alarm 2 type 0 to 34
002AH 40043 (Do not use)
002BH 40044 Word
002CH 40045 Word
002DH 40046 (Do not use)
002EH 40047 Word Alarm 1 upper limit set value
002FH 40048 Word Alarm 2 upper limit set value
0030H 40049 (Do not use)
0031H 40050 Word Alarm 1 hysteresis
0032H 40051 Word Alarm 2 hysteresis
0033H 40052 (Do not use)
0034H 40053 Word Alarm 1 ON-delay set value
0035H 40054 Word Alarm 2 ON-delay set value
0036H 40055 (Do not use)
0037H 40056 (Do not use)
0038H 40057 Word Ramp/soak No. 1 target value
0039H 40058 Word Ramp/soak No. 2 target value
003AH 40059 Word Ramp/soak No. 3 target value
003BH 40060 Word Ramp/soak No. 4 target value
003CH 40061 Word Ramp/soak No. 5 target value
003DH 40062 Word Ramp/soak No. 6 target value
003EH 40063 Word Ramp/soak No. 7 target value
003FH 40064 Word Ramp/soak No. 8 target value
0040H 40065 Word Ramp/soak No. 1 ramp time
0041H 40066 Word Ramp/soak No. 1 soak time
0042H 40067 Word Ramp/soak No. 2 ramp time
0043H 40068 Word Ramp/soak No. 2 soak time
0044H 40069 Word Ramp/soak No. 3 ramp time
0045H 40070 Word Ramp/soak No. 3 soak time
0046H 40071 Word Ramp/soak No. 4 ramp time
0047H 40072 Word Ramp/soak No. 4 soak time
0048H 40073 Word Ramp/soak No. 5 ramp time
0049H 40074 Word Ramp/soak No. 5 soak time
004AH 40075 Word Ramp/soak No. 6 ramp time
004BH 40076 Word Ramp/soak No. 6 soak time
004CH 40077 Word Ramp/soak No. 7 ramp time
004DH 40078 Word Ramp/soak No. 7 soak time
004EH 40079 Word Ramp/soak No. 8 ramp time
004FH 40080 Word Ramp/soak No. 8 soak time
0050H 40081 Word Ramp/soak mode 0 to 15
0051H 40082 Word Ramp/soak command
Resister
No.
Type Memory contents Read-out data
Alarm 1 set value or
alarm 1 lower limit set value
Alarm 2 set value or
alarm 2 lower limit set value
For absolute value alarm
For deviation alarm
For absolute value alarm
For deviation alarm
0 to 5000(0.00 to 50.00%FS) *
0 to 5000(0.00 to 50.00%FS) *
0 to 9999(0 to 9999 sec)
0 to 9999(0 to 9999 sec)
0 to 10000
(0.00 to 100.00%FS,
within set value limit)
0 to 5999(0 to 5999 min)
* With main unit parameter,
0: oFF
1: rUn
2: HLd
3: End
Write-in data
setting range
0 to 10000(0.00 to 100.00%FS)
-10000 to 10000
(-100.00 to 100.00%FS)
0 to 10000(0.00 to 100.00%FS)
-10000 to 10000
(-100.00 to 100.00%FS)
Hour Minute
is displayed and set.
Therefore, correspondence occurs as:
3601:Data via communication
∥
6001:Display/setting on main unit
Ramp/soak stopped
Ramp/soak operated
Ramp/soak halted
Ramp/soak ended
0:oFF
Stop ramp/soak
1:rUn
Start ramp/soak
2:HLd
Halt ramp/soak
3: End ランプ
ソーク終了
Affected by
input range
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
ALM1
ALM2
AL1 or A1-L
AL2 or A2-L
A1-H
A2-H
A1hy
A2hy
dLy1
dLy2
Sv-1
Sv-2
Sv-3
Sv-4
Sv-5
Sv-6
Sv-7
Sv-8
TM1r
TM1S
TM2r
TM2S
TM3r
TM3S
TM4r
TM4S
TM5r
TM5S
TM6r
TM6S
TM7r
TM7S
TM8r
TM8S
MOD
ProG
-33-
Page 37

Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
PTn
SLFb
P-n1
TC
TC2
A1op
A2op
di-1
ONOF
ADJ0
ADJS
dSP1
dSP2
dSP3
dSP4
dSP5
dSP6
dSP7
dSP8
dSP9
dSP10
dSP11
dSP12
dSP13
Note
Relative
address
0052H 40083 Word Ramp/soak pattern selection
0053H 40084 (Do not use)
0054H 40085 Word PV stable range
0055H 40086 (Do not use)
0056H 40087 Word
0057H 40088 Word Control action type code 0 to 19
0058H 40089 Word
0059H 40090 Word
005AH 40091 (Do not use)
005BH 40092 Word Alarm 1 option function
005CH 40093 Word Alarm 2 option function
005DH 40094 (Do not use)
005EH 40095 Word DI1 action setting 0 to 12
005FH 40096 (Do not use)
0060H 40097 Word Hysteresis mode setting
0061H 40098 Word (Do not use)
0062H 40099 Word User zero adjustment
0063H 40100 Word User span adjustment
0064H 40101 Word
0065H 40102 Word
0066H 40103 Word
0067H 40104 Word
0068H 40105 Word
0069H 40106 Word
006AH 40107 Word
006BH 40108 Word
006CH 40109 Word
006DH 40110 Word
006EH 40111 Word
006FH 40112 Word
0070H 40113 Word
Resister
No.
Type Memory contents Read-out data
0: Execute No. 1 to 4 ramp/soak
1: Execute No. 5 to 8 ramp/soak
2: Execute No. 1 to 8 ramp/soak
0 to 10000(0.00 to 100.00%FS) *
Communication DI action
request
Output proportional cycle
(output 1)
Output proportional cycle
(output 2)
DSP1
(parameter mask designation)
DSP2
(parameter mask designation)
DSP3
(parameter mask designation)
DSP4
(parameter mask designation)
DSP5
(parameter mask designation)
DSP6
(parameter mask designation)
DSP7
(parameter mask designation)
DSP8
(parameter mask designation)
DSP9
(parameter mask designation)
DSP10
(parameter mask designation)
DSP11
(parameter mask designation)
DSP12
(parameter mask designation)
DSP13
(parameter mask designation)
*② (refer to section 7.4.)
0: Current output type
1 to 150(1 to 150 sec):
Relay, SSR drive output type
1 to 150(1 to 150 sec)
0 to 7(binary data 000B to 111
0 to 7(binary data 000B to 111
0: off (main unit parameter setting)
1: on (main unit parameter setting)
-5000 to 5000
(-50.00 to 50.00%FS)
-5000 to 5000
(-50.00 to 50.00%FS)
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
(PTn=1)
(PTn=2)
(PTn=3)
Write-in data
setting range
B
B
Affected by
input range
)
)
*
*
Note) Read-out/write-in data from Resister No. 40083 (ramp/soak pattern selection) correspond to parameter “PTn”
to be displayed as shown below:
Read-out/write-in data Parameter PTn Contents
0 1 1 to 4 ramp/soak executed
1 2 5 to 8 ramp/soak executed
2 3 1 to 8 ramp/soak executed
-34-
Page 38

Word data (read-out only) : Function code [04
Relative
address
0000H 30001 Word Process value (PV)
0001H 30002 Word Currently used set value (SV)
0002H 30003 Word Currently used deviation (DV)
0003H 30004 Word MV (output 1)
0004H 30005 Word MV (output 2)
0005H 30006 Word Station No. 0 to 255
0006H 30007 Word Alarm status
0007H 30008 Word Input/main unit abnormal status
0008H 30009 Word
0009H 30010 Word Heater current
000AH 30011 Word Timer 1 current count
000BH 30012 Word Timer 2 current count
000CH 30013 (Reserve)
000DH 30014 (Reserve)
000EH 30015 Word DI action status
Resister
No.
Type Memory contents
Ramp/soak current running
position
]
H
0 to 10000(0.00 to 100.00%FS) *
0 to 10000(0.00 to 100.00%FS) *
-10000 to 10000
(-100.00 to 100.00%FS)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
*③ (refer to Section 7.4.)
*④ (refer to Section 7.4.)
0 to 17
*⑥ (refer to Section 7.4.)
0 to 500(0.0 to 50.0A)
0 to 9999(0 to 9999 sec)
0 to 9999(0 to 9999 sec)
*⑤ (refer to Section 7.4.)
Notes)
• For details of *
to * ⑥ in the table, refer to Section 7.4.
②
• The area marked (Do not use) is a reserve area. Do not write in there.
• Register numbers 30002 (currently used SV) and 40003 (face panel set SV) do not become the same
value while switching-SV is active or ramp/soak is under way. (Example: While SV-1 is selected, the
value of SV-1 is read out of register number 30002.) For reading out SV for monitoring, use SV in
register number 30002.
Read-out data
Affected by
input range
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
(Displayed PV
value)
(Displayed SV
value)
OUT1
OUT2
STno
STAT
CT
TM-1
TM-2
-35-
Page 39

7.3 Address Map of Engineering Unit Data
Data affected by input range is handled in terms of a value (engineering unit) after scaling.
For detailed contents about individual parameter function or setting range, refer to the operation manual
(ECNO: 406).
H
, 05H]
H
0:Not Writing-in
1:Writing in memory
]
0:Alarm 1 OFF,1: Alarm 1 ON
0: Alarm 2 OFF,1: Alarm 2 ON
0: Relay output of alarm 1 OFF
1: Relay output of alarm 1 ON
0: Relay output of alarm 2 OFF
1: Relay output of alarm 2 ON
0: HB alarm output OFF
1: HB alarm output ON
0: Alarm 1 OFF,1: Alarm 1 ON
0: Alarm 2 OFF,1: Alarm 2 ON
0:HB alarm output OFF
1:HB alarm output ON
Write-in data
setting range
0:No request
1:Write-in request
Affected by
input range
(the same
Affected by
input range
(Same as 10001)
(Same as 10002)
(Same as 10012)
function as
40001)
Bit data [read-out/write-in] : Function code [01
Relative
address
0000H 00001 Bit
Coil No. Type Memory contents Read-out data
Write in non-volatile memory
(FIX execution)
Bit data [read-out only] : Function code [02
Relative
address
0000H 10001 Bit Alarm 1 ON/OFF
0001H 10002 (Reserve)
0002H 10003 (Reserve)
0003H 10004 (Reserve)
0004H 10005 Bit Alarm 2 ON/OFF
0005H 10006 (Reserve)
0006H 10007 (Reserve)
0007H 10008 (Reserve)
0008H 10009 Bit
0009H 10010 Bit
000AH 10011 (Reserve)
000BH 10012 Bit HB alarm relay output
000CH 10013 Bit Alarm 1 ON/OFF
000DH 10014 Bit Alarm 2 ON/OFF
000EH 10015 (Reserve)
000FH 10016 Bit HB alarm relay output
Coil No. Type Memory contents Read-out data
Alarm 1 output
(Calculation result of nonexciting alarm)
Alarm 2 output
(Calculation result of nonexciting alarm)
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
-36-
Page 40

Word data [read-out/write-in]: Function code [03
Relative
address
03E8H 41001 Word
03E9 H 41002 Word PID/FUZZY/SELF selection
03EA H 41003 Word SV value controlled on face panel -1999 to 9999 (within set value limits)
03EB H 41004 Word Control RUN/standby
03EC H 41005 Word Auto tuning command
03ED H 41006 Word P
03EE H 41007 Word I
03EF H 41008 Word D
03F0 H 41009 Word
03F1H 41010 Word COOL
03F2H 41011 Word Dead band
03F3H 41012 Word Anti-reset windup
03F4H 41013 Word Output convergence value
03F5H 41014 Word PV shift
03F6H 41015 Word SV offset
03F7H 41016 Word Input type code 0 to 16
03F8H 41017 Word Temperature unit
03F9H 41018 Word Input scale lower limit -1999 to 9999
03FAH 41019 Word Input scale upper limit -1999 to 9999
03FBH 41020 Word Decimal point place 0 to 2
03FCH 41021 (Do not use)
03FDH 41022 Word Input filter time constant
03FEH 41023 Word RCJ yes/no
03FFH 41024 Word MV limit kind 0 to 15
0400H 41025 Word Output 1 lower limit
0401H 41026 Word Output 1 upper limit
0402H 41027 Word Output 2 lower limit
0403H 41028 Word Output 2 upper limit
0404H 41029 (Do not use)
0405H 41030 (Do not use)
0406H 41031 Word Set value (SV) lower limit
0407H 41032 Word Set value (SV) upper limit
0408H 41033 (Do not use)
0409H 41034 (Do not use)
040AH 41035 (Do not use)
040BH 41036 (Do not use)
040CH 41037 (Do not use)
040DH 41038 (Do not use)
040EH 41039 Word Heater burnout alarm set value
Resister
No.
Type Memory contents Read-out data
Non-volatile memory write-in
(FIX execution)
Hysteresis range at
two-position control
, 06H, 10H]
H
Write-in data
setting range
0: Not writing in
1: Write in memory
0:PID control
1:FUZZYcontrol
2:SELF tuning control
0: Invalidate standby (RUN)
1:Validate standby
0: Auto tuning
disabled
1: While executing
standard type AT
executed
2: While executing
low PV type AT
executed
0 to 9999(0.0 to 999.9%)
0 to 32000(0 to 3200.0 sec)
0 to 9999(0.0 to 999.9 sec)
0 to 9999 (0 to 50% value of input scale) *
0 to 1000(0.0 to 100.0)
-5000 to 5000
(-50.00 to +50.00%)
-1999 to 9999
(0 to 100% value of input scale)
-10000 to 10000
(-100.00 to 100.00%)
-1999 to 9999
(-10 to 10% value of input scale)
-1999 to 9999
(-50 to 50% value of input scale)
0:℃ 1:°F
0 to 9000(0.0 to 900.0 sec)
0: Disable RCJ compensation
(do not perform reference cold junction
compensation)
1: Enable RCJ compensation (perform
reference cold junction compensation)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-1999 to 9999(within input scale) *
-1999 to 9999(within input scale) *
0 to 500(0.0 to 50.0A)
0:No request
1:Request to write in
0: Disable auto
tuning
1: Request
execution of
standard type
2: Request
execution of low
PV type AT
Affected by
input range
*
*
*
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
(Same function
as 00001)
CTrL
* Inhibit change
while
controlling
STby
AT
P
i
D
HyS
CooL
db
Ar
bAL
PVOF
SVOF
P-n2
P-F
P-SL
P-SU
P-dP
P-dF
rCJ
PCUT
PLC1
PHC1
PLC2
PHC2
SV-L
SV-H
Hb
-37-
Page 41

Relative
address
040FH 41040 Word Setting lock 0 to 5
0410H 41041 Word Alarm 1 type 0 to 34
0411H 41042 Word Alarm 2 type 0 to 34
0412H 41043 (Do not use)
0413H 41044 Word
0414H 41045 Word
0415H 41046 (Do not use)
0416H 41047 Word Alarm 1 upper limit set value
0417H 41048 Word Alarm 2 upper limit set value
0418H 41049 (Do not use)
0419H 41050 Word Alarm 1 hysteresis
041AH 41051 Word Alarm 2 hysteresis
041BH 41052 (Do not use)
041CH 41053 Word Alarm 1 ON-delay set value
041DH 41054 Word Alarm 2 ON-delay set value
041EH 41055 (Do not use)
041FH 41056 (Do not use)
0420H 41057 Word Ramp/soak No. 1 target value
0421H 41058 Word Ramp/soak No. 2 target value
0422H 41059 Word Ramp/soak No. 3 target value
0423H 41060 Word Ramp/soak No. 4 target value
0424H 41061 Word Ramp/soak No. 5 target value
0425H 41062 Word Ramp/soak No. 6 target value
0426H 41063 Word Ramp/soak No. 7 target value
0427H 41064 Word Ramp/soak No. 8 target value
0428H 41065 Word Ramp/soak No. 1 ramp time
0429H 41066 Word Ramp/soak No. 1 soak time
042AH 41067 Word Ramp/soak No. 2 ramp time
042BH 41068 Word Ramp/soak No. 2 soak time
042CH 41069 Word Ramp/soak No. 3 ramp time
042DH 41070 Word Ramp/soak No. 3 soak time
042EH 41071 Word Ramp/soak No. 4 ramp time
042FH 41072 Word Ramp/soak No. 4 soak time
0430H 41073 Word Ramp/soak No. 5 ramp time
0431H 41074 Word Ramp/soak No. 5 soak time
0432H 41075 Word Ramp/soak No. 6 ramp time
0433H 41076 Word Ramp/soak No. 6 soak time
0434H 41077 Word Ramp/soak No. 7 ramp time
0435H 41078 Word Ramp/soak No. 7 soak time
0436H 41079 Word Ramp/soak No. 8 ramp time
0437H 41080 Word Ramp/soak No. 8 soak time
0438H 41081 Word Ramp/soak mode 0 to 15
0439H 41082 Word Ramp/soak command
Resister
No.
Type Memory contents Read-out data
Alarm 1 set value or
alarm 1 lower limit set value
Alarm 2 set value or
alarm 2 lower limit set value
-1999 to 9999
For absolute value alarm:
For deviation alarm:
-1999 to 9999
For absolute value alarm:
For deviation alarm:
0 to 9999
(0 to 50% value of input scale)
0 to 9999
(0 to 50% value of input scale)
0 to 9999(0 to 9999 sec)
0 to 9999(0 to 9999 sec)
-1999 to 9999
(within set value limit)
0 to 5999(0 to 5999 min)
* With main unit parameter,
0: oFF
1: rUn
2: HLd
3: End
Write-in data
setting range
0 to 100% value of input scale
–100 to 100% value of input scale
0 to 100% value of input scale
–100 to 100% value of input scale
Hour Minute
is displayed and set.
Therefore, correspondence occurs as:
3601:Data via communication
∥
6001:Display/setting on main unit
Ramp/soak stopped
Ramp/soak operated
Ramp/soak halted
Ramp/soak ended
0:oFF
Stop ramp/soak
1:rUn
Start ramp/soak
2:HLd
Halt ramp/soak
3: End ランプ
ソーク終了
Affected by
input range
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
LoC
ALM1
ALM2
AL1 or A1-L
AL2 or A2-L
A1-H
A2-H
A1hy
A2hy
dLy1
dLy2
Sv-1
Sv-2
Sv-3
Sv-4
Sv-5
Sv-6
Sv-7
Sv-8
TM1r
TM1S
TM2r
TM2S
TM3r
TM3S
TM4r
TM4S
TM5r
TM5S
TM6r
TM6S
TM7r
TM7S
TM8r
TM8S
MOD
ProG
-38-
Page 42

Note
Relative
address
043AH 41083 Word Ramp/soak pattern selection
043BH 41084 (Do not use)
043CH 41085 Word PV stable range -1999 to 9999 (Within input scale)
043DH 41086 (Do not use)
043EH 41087 Word
043FH 41088 Word Control action type code 0 to 19
0440H 41089 Word
0441H 41090 Word
0442H 41091 (Do not use)
0443H 41092 Word Alarm 1 option function
0444H 41093 Word Alarm 2 option function
0445H 41094 (Do not use)
0446H 41095 Word DI1 action setting 0 to 12
0447H 41096 (Do not use)
0448H 41097 Word Hysteresis mode setting
0449H 41098 Word (Do not use)
044AH 41099 Word User zero adjustment
044BH 41100 Word User span adjustment
044CH 41101 Word
044DH 41102 Word
044EH 41103 Word
044FH 41104 Word
0450H 41105 Word
0451H 41106 Word
0452H 41107 Word
0453H 41108 Word
0454H 41109 Word
0455H 41110 Word
0456H 41111 Word
0457H 41112 Word
0458H 41113 Word
Resister
No.
Type Memory contents Read-out data
0: Execute No. 1 to 4 ramp/soak
1: Execute No. 5 to 8 ramp/soak
2: Execute No. 1 to 8 ramp/soak
Communication DI action
request
Output proportional cycle
(output 1)
Output proportional cycle
(output 2)
DSP1
(parameter mask designation)
DSP2
(parameter mask designation)
DSP3
(parameter mask designation)
DSP4
(parameter mask designation)
DSP5
(parameter mask designation)
DSP6
(parameter mask designation)
DSP7
(parameter mask designation)
DSP8
(parameter mask designation)
DSP9
(parameter mask designation)
DSP10
(parameter mask designation)
DSP11
(parameter mask designation)
DSP12
(parameter mask designation)
DSP13
(parameter mask designation)
*② (refer to section 7.4.)
0: Current output type
1 to 150(1 to 150 sec):
Relay, SSR drive output type
1 to 150(1 to 150 sec)
0 to 7(binary data 000B to 111
0 to 7(binary data 000B to 111
0: off (main unit parameter setting)
1: on (main unit parameter setting)
-1999 to 9999
(-50 to 50% value of input scale)
-1999 to 9999
(-50 to 50% value of input scale)
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
0 to 255
Write-in data
setting range
)
B
)
B
Affected by
input range
*
*
*
corresponding
PTn
SLFb
P-n1
TC
TC2
A1op
A2op
di-1
ONOF
ADJ0
ADJS
dSP1
dSP2
dSP3
dSP4
dSP5
dSP6
dSP7
dSP8
dSP9
dSP10
dSP11
dSP12
dSP13
Note) Read-out/write-in data from Resister No. 41083 (ramp/soak pattern selection) correspond to parameter “PTn”
to be displayed as shown below:
Read-out/write-in data Parameter PTn Contents
0 1 1 to 4 ramp/soak executed
1 2 5 to 8 ramp/soak executed
2 3 1 to 8 ramp/soak executed
Remarks or
parameter
-39-
Page 43

Word data (read-out only) : Function code [04
Relative
address
03E8H 31001 Word Process value (PV)
03E9H 31002 Word Currently used set value (SV)
03EAH 31003 Word Currently used deviation (DV)
03EBH 31004 Word MV (output 1)
03ECH 31005 Word MV (output 2)
03EDH 31006 Word Station No. 0 to 255
03EEH 31007 Word Alarm status
03EFH 31008 Word Input/main unit abnormal status
03F0H 31009 Word
03F1H 31010 Word Heater current
03F2H 31011 Word Timer 1 current count
03F3H 31012 Word Timer 2 current count
03F4H 31013 (Reserve)
03F5H 31014 (Reserve)
03F6H 31015 Word DI action status
Resister
No.
Type Memory contents
Ramp/soak current running
position
]
H
-1999 to 9999 (within input scale) *
-1999 to 9999 (within set value limit) *
-1999 to 9999
(-100 to 100% value of input scale)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
-300 to 10300(-3.00 to 103.00%)
*③ (refer to Section 7.4.)
*④ (refer to Section 7.4.)
0 to 17
*⑥ (refer to Section 7.4.)
0 to 500(0.0 to 50.0A)
0 to 9999(0 to 9999 sec)
0 to 9999(0 to 9999 sec)
*⑤ (refer to Section 7.4.)
Notes)
• For details of * ② to * ⑥ in the table, refer to Section 7.4.
• The area marked (Do not use) is a reserve area. Do not write in there.
• Register numbers 31002 (currently used SV) and 41003 (face panel set SV) do not become the same
value while switching-SV is active or ramp/soak is under way. (Example: While SV-1 is selected, the
value of SV-1 is read out of register number 31002.) For reading out SV for monitoring, use SV in
register number 31002.
Read-out data
Affected by
input range
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
(Displayed PV
value)
(Dsiplayed SV
value)
OUT1
OUT2
STno
STAT
CT
TM-1
TM-2
-40-
Page 44

7.4 Additional Explanation of Address Map
*② Register number 40087, 41087 (read-out/write-in area)
Contents of the communication DI action
Used for requesting a DI action via communication. Once written in, the contents remain held unless
the power is turned off or another value is written in. Pay attention to this point particularly when
canceling the alarm latching.
Read-out data is the data which was written in via communication and is different from hardware DI
action request data (see * ⑤). Do not doubly request the action of the same function as hardware DI.
Bit Contents Read-out Write-in
0 1 Switching-SV selection
2 (Reserve)
3 (Reserve)
4 (Reserve)
5 Canceling the alarm 1
latching
6 Canceling the alarm 2
latching
7 (Reserve)
8 ALM1 relay timer action 0:Timer action not requested
9 ALM2 relay timer action 0:Timer action not requested
10 (Reserve)
11 (Reserve)
12 (Reserve)
13 (Reserve)
14 (Reserve)
15 (Reserve)
Bit 1 0 Bit 1 0
0 0 While selecting
face panel set SV
0 1 While selecting
SV-1
0:Not requested to cancel the
latching
1:Requested to cancel the latching
0:Not requested to cancel the
latching
1:Requested to cancel the latching
1:Timer action requested
1:Timer action requested
0 0 While selecting
face panel set SV
0 1 While selecting
SV-1
0:Not request to cancel the
latching
1:Request to cancel the latching
0:Not request to cancel the
latching
1:Request to cancel the latching
0:Request to reset timer
1:Request to start timer
0:Request to reset timer
1:Request to start timer
*③ Register numbers 30007, 31007 (read-out only area)
Alarm status contents (bit data, Coil numbers 10009 to 10016 grouped in 1 byte.)
Bit Contents Read-out
0 Alarm 1 output
(calculation result of de-energizing alarm)
1 Alarm 2 output
(calculation result of de-energizing alarm)
2 (Reserve)
3 HB alarm relay output 0:HB alarm output OFF
4 Alarm 1 ON/OFF
5 Alarm 2 ON/OFF
6 (Reserve)
7 HB alarm relay output 0:HB alarm output OFF
-41-
0:Alarm 1 relay output OFF
1:Alarm 1 relay output ON
0:Alarm 2 relay output OFF
1:Alarm 2 relay output ON
1:HB alarm output ON
0:Alarm 1 OFF,1:Alarm 1 ON
0:Alarm 2 OFF,1:Alarm 2 ON
1:HB alarm output ON
Page 45

*④ Register numbers 30008, 31008 (read-out only area)
B
Input/main unit abnormal status
Bit Contents Read-out
0 Input Lower open-circuit 0:Lower open-circuit absent
1:Lower open -circuit present
1 Input Upper open-circuit 0:Upper open-circuit absent
1:Upper open-circuit present
2 Input under-range 0:Under-range absent
1:Under-range present
3 Input over-range 0:Over-range absent
1:Over-range present
4 (Reserve)
5 (Reserve)
6 Setting range error 0:Setting range normal
1:Setting range abnormal
7 EEPROM error 0:EEPROM normal
1:EEPROM abnormal
*⑤ Register numbers 30015, 31015 (read-out only area)
Contents of DI action status
Hardware DI (DI input terminal) action request information
Bit Contents Read-out
0 1 Switching-SV selection
2 Control RUN/standby 0:Control RUN requested
3 Auto tuning (standard) 0:AT not requested
4 Auto tuning (low PV type) 0:AT not requested
5 Canceling the alarm 1 latching 0:Not requested to cancel the latching
6 Canceling the alarm 2 latching 0:Not requested to cancel the latching
7 (Reserve)
8 ALM1 relay timer action 0:Timer action not requested
9 ALM2 relay timer action 0:Timer action not requested
10 (Reserve)
11 RUN/RESET selection of
ramp/soak
12 (Reserve)
13 (Reserve)
14 (Reserve)
15 (Reserve)
it 1 0
0 0 Face panel set SV selected
0 1 SV-1 selected
1:Control standby requested
1:AT (standard) action requested
1:AT (low PV type) action requested
1:Requested to cancel the latching
1:Requested to cancel the latching
(timer reset)
1:Timer action requested
(timer reset)
1:Timer action requested
0:Not requested RUN
(RESET)
1:Requested RUN
-42-
Page 46

*⑥ Register numbers 30009, 31009 (read-out only area)
Ramp/soak current running position
Read-
out data
Indication of parameter
“STAT”
0 oFF Stop status of ramp/soak
1 1-rP No. 1 ramp time
2 1-Sk No. 1 soak time
3 2-rP No. 2 ramp time
4 2-Sk No. 2 soak time
5 3-rP No. 3 ramp time
6 3-Sk No. 3 soak time
7 4-rP No. 4 ramp time
8 4-Sk No. 4 soak time
9 5-rP No. 5 ramp time
10 5-Sk No. 5 soak time
11 6-rP No. 6 ramp time
12 6-Sk No. 6 soak time
13 7-rP No. 7 ramp time
14 7-Sk No. 7 soak time
15 8-rP No. 8 ramp time
16 8-Sk No. 8 soak time
17 End End status of ramp/soak
Running position (status)
-43-
Page 47

8. SAMPLE PROGRAM
This section concerns data read-out/write-in sample program by GW-BASIC*1 which operated on Windows 95*1
1
MS-DOS*
Note that the program shown here is for reference for you to create a program and not for guaranteeing all actions.
Before executing the program, make sure of the communication conditions in the following procedure.
・ Communication speed (baud rate), data length, stop bits and parity bit
Set in this program. Match the conditions with this instrument.
Note) Cautions on using SEKISUI’s RS232C and RS485 converter unit (SI-30A)
*1: GW-BASIC, Windows 95 and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
PROMPT.
In SI-30A, send data are received, added to start of the answer data from the slave station. After
cleared data corresponding to the number of sending bytes, treat the remaining data as the answer data
in the data receiving process.
-44-
Page 48

(a) Example of data read-out
Operation:Read-out PV, SV (currently used), DV and MV (control output 1) at a time.
(Continuous word read-out from read-out only area)
Used function code :04H
Read-out start register No. :31001 (Engineering unit data)
Read-out word number :4
1000 '------------------------------------------------------1010 ' WRITE CONTINUOUS WORDS SAMPLE PROGRAM
1020 '------------------------------------------------------1030 '
1040 '
1050 '
1060 CLS
1070 DIM CC(255)
1080 '
1100 '-------------- Send data setting ----------------------1110 CC(1)=&H01 'Station No. = 1
1120 CC(2)=&H06 'Function code = 06H
1130 CC(3)=&H04 'Upper byte of relative address(0439H) of resister No.41082
1140 CC(4)=&H39 'Lower byte of relative address(0439H) of resister No.41082
1150 CC(5)=&H00 'Upper byte of write-in word data(0001H)
1160 CC(6)=&H01 'Lower byte of write-in word data(0001H)
1170 COUNT=6
1200 '
1210 '------------- CRC code calculation of send data -------------1220 GOSUB 3020 'GOSUB CRC.CALC
1230 CC(7)=CRC.L 'Lower byte of CRC calculation result -> Upper byte in message
1240 CC(8)=CRC.H 'Upper byte of CRC calculation result -> Lower byte in message
1250 COUNT=COUNT+2
1300 '
1310 '------------- Send data ----------------------------1320 PRINT "Sending data > ";
1330 OPEN "COM1:9600,o,8,1" AS #1 '9600bps, Odd Parity, Data Length=8, Stop bit=1
1340 FOR I=1 TO COUNT
1350 PRINT #1,CHR$(CC(I)); 'Writing in transmission port
1360 PRINT RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CC(I)),2);" "; 'Displaying on screen
1370 NEXT I
1380 '
1390 FOR I=O TO 30000 :NEXT I 'Interval time
1500 '
1510 '------------- Data receive ---------------------------1520 PRINT
1530 LENGTH=LOC(1) 'Number of data in receiving buffer
1540 IF LENGTH=0 THEN PRINT "No answer" :END
1550 PRINT "Receiving data < ";
1560 FOR I=1 TO LENGTH
1570 X$=INPUT$(1,#1) 'Taking data from receiving buffer
1580 CC(I)=ASC(X$) 'Digitizing and storing
1590 PRINT RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CC(I)),2);" "; 'Displaying on screen
1600 NEXT I
1610 CLOSE #1
1620 COUNT=LENGTH-2
1630 GOSUB 3020 'GOSUB CRC.CALC
1700 '
1710 '------------- Transmission error check ----------------------1720 PRINT
-45-
Page 49

1730 CRC.L$=RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CRC.L),2)
1740 CRC.H$=RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CRC.H),2)
1750 PRINT "CRC calculation = ";CRC.L$;" ";CRC.H$
1760 IF CC(LENGTH-1)<>CRC.L THEN GOTO 1790 'GOTO ER.MESSAGE
1770 IF CC(LENGTH)<>CRC.H THEN GOTO 1790 'GOTO ER.MESSAGE
1780 GOTO 1920 'GOTO PRT.RESULT
1790 'ER.MESSAGE
1800 PRINT "Communication error"
1810 END
1900 '
1910 '------------- Display of result --------------------------1920 'PRT.RESULT
1930 PRINT
1940 PRINT "Completion of ramp/soak start-up"
1950 END
3000 '
3010 '------------ CRC calculation -----------------------------3020 'CRC.CALC 'For contents, refer to CRC calculation flow chart
3030 CR=&HFFFF
3040 FOR I=1 TO COUNT
3050 CR=CR XOR CC(I)
3060 FOR J=1 TO 8
3070 CT=CR AND &H1
3080 IF CR<0 THEN CH=1 ELSE CH=0:GOTO 3100 'GOTO CRC.CALC.10
3090 CR=CR AND &H7FFF
3100 'CRC.CALC.10
3110 CR=INT(CR/2)
3120 IF CH=1 THEN CR=CR OR &H4000
3130 IF CT=1 THEN CR=CR XOR &HA001
3140 NEXT J
3150 NEXT I
3160 CRC.L=CR AND &HFF 'Lower byte of CRC calculation
3170 CRC.H=((CR AND &HFF00)/256 AND &HFF) 'Upper byte of CRC calculation
3180 RETURN
-46-
Page 50

(b) Data write-in example
Operation : Start ramp/soak of No. 1 station via communication
(Single word write-in)
Used function code :06H
Write-in register No. :41082 (Table of engineering unit data)
Write-in data :11082 (Ramp/soak start)
1000 '------------------------------------------------------1010 ' READ CONTINUOUS WORDS SAMPLE PROGRAM
1020 '------------------------------------------------------1030 '
1040 '
1050 '
1060 CLS
1070 DIM CC(255)
1080 '
1100 '-------------- Send data setting ----------------------1110 CC(1)=&H01 'Station No. = 1
1120 CC(2)=&H04 'Function code = 04H
1130 CC(3)=&H03 'Upper byte of relative address(03E8H) of resister No.31001
1140 CC(4)=&HE8 'Lower byte of relative address(03E8H) of resister No.31001
1150 CC(5)=&H00 'Upper byte of read-out word number(0004H)
1160 CC(6)=&H04 'Lower byte of read-out word number(0004H)
1170 COUNT=6
1200 '
1210 '------------- CRC code calculation of send data -------------1220 GOSUB 3020 'GOSUB CRC.CALC
1230 CC(7)=CRC.L 'Lower byte of CRC calculation result -> Upper byte in message
1240 CC(8)=CRC.H 'Upper byte of CRC calculation result -> Lower byte in message
1250 COUNT=COUNT+2
1300 '
1310 '------------- Send data -------------------------------1320 PRINT "Sending data > ";
1330 OPEN "COM1:9600,o,8,1" AS #1 '9600bps, Odd Parity, Data Length=8, Stop bit=1
1340 FOR I=1 TO COUNT
1350 PRINT #1,CHR$(CC(I)); 'Writing in transmission port
1360 PRINT RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CC(I)),2);" "; 'Displaying on screen
1370 NEXT I
1380 '
1390 FOR I=0 TO 30000 :NEXT I 'Interval time
1500 '
1510 '------------- Data receive ----------------------------1520 PRINT
1530 LENGTH=LOC(1) 'Number of data in receiving buffer
1540 IF LENGTH=0 THEN PRINT "No answer" :END
1550 PRINT "Receiving data < ";
1560 FOR I=1 TO LENGTH
1570 X$=INPUT$(1,#1) 'Taking data from receiving buffer
1580 CC(I)=ASC(X$) 'Digitizing and storing
1590 PRINT RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CC(I)),2);" "; 'Displaying on screen
1600 NEXT I
1610 CLOSE #1
1620 COUNT=LENGTH-2
1630 GOSUB 3020 'GOSUB CRC.CALC
1700 '
1710 '------------- Transmission error check ----------------------1720 PRINT
-47-
Page 51

1730 CRC.L$=RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CRC.L),2)
1740 CRC.H$=RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CRC.H),2)
1750 PRINT "CRC calculation = ";CRC.L$;" ";CRC.H$
1760 IF CC(LENGTH-1)<>CRC.L THEN GOTO 1790 'GOTO ER.MESSAGE
1770 IF CC(LENGTH)<>CRC.H THEN GOTO 1790 'GOTO ER.MESSAGE
1780 GOTO 1920 'GOTO PRT.RESULT
1790 'ER.MESSAGE
1800 PRINT "Communication error"
1810 END
1900 '
1910 '------------- Display of result --------------------------1920 'PRT.RESULT
1930 ' In case of decimal point position(P-dP)=1
1940 PRINT
1950 PV$=HEX$(CC(4))+RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CC(5)),2) '2 bytes -> 1 word
1960 SV$=HEX$(CC(6))+RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CC(7)),2) '2 bytes -> 1 word
1970 DV$=HEX$(CC(8))+RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CC(9)),2) '2 bytes -> 1 word
1980 MV$=HEX$(CC(10))+RIGHT$("0"+HEX$(CC(11)),2) '2 bytes -> 1 word
1990 PRINT "PV =";VAL("&H"+PV$)/10;"degree C" '1 place of decimal
2000 PRINT "SV =";VAL("&H"+SV$)/10;"degree C" '1 place of decimal
2010 PRINT "DV =";VAL("&H"+DV$)/10;"degree C" '1 place of decimal
2020 PRINT "MV1=";VAL("&H"+MV$)/100;"%" 'MV is data of 2 places of decimal
2030 END
3000 '
3010 '------------ CRC calculation -----------------------------3020 'CRC.CALC 'For contents, refer to CRC calculation flow chart
3030 CR=&HFFFF
3040 FOR I=1 TO COUNT
3050 CR=CR XOR CC(I)
3060 FOR J=1 TO 8
3070 CT=CR AND &H1
3080 IF CR<0 THEN CH=1 ELSE CH=0:GOTO 3100 'GOTO CRC.CALC.10
3090 CR=CR AND &H7FFF
3100 'CRC.CALC.10
3110 CR=INT(CR/2)
3120 IF CH=1 THEN CR=CR OR &H4000
3130 IF CT=1 THEN CR=CR XOR &HA001
3140 NEXT J
3150 NEXT I
3160 CRC.L=CR AND &HFF 'Lower byte of CRC calculation
3170 CRC.H=((CR AND &HFF00)/256 AND &HFF) 'Upper byte of CRC calculation
3180 RETURN
-48-
Page 52

9. TROUBLESHOOTING
If the communication is unavailable, check the following items.
□ Whether all devices related to communication are turned on.
□ Whether connections are correct.
□ Whether the number of connected instruments and connection distance are as specified
□ Whether communication conditions coincide between the master station (host computer) and slave stations
(PXR)
□ Transmission speed : 9600bps
□ Data length : 8 bits
□ Stop bit : 1 bit
□ Parity : □odd
□even
□none
□ Whether send/receive signal timing conforms to Section 5.4 in this manual.
□ Whether the station No. designated as send destination by the master station coincides with the station No. of
the connected PXR
□ Whether more than one instrument connected on the same transmission line shares the same station No.
□ Whether the station No. of instruments is set at other than 0.
If it’s 0, the communication function does not work.
□ Whether the 11th digit of type cord of this controller is M or V?.
(PXR4□□□□-□□
M
□□-□)
V
-49-
 Loading...
Loading...