Page 1

Instruction Manual
CC-Link Interface Option "OPC-E1-CCL"
Thank you for purchasing our CC-Link Interface Card OPC-E1-CCL.
• This product is designed to connect the FRENIC-Multi series of inverters to CC-Link network.
Read through this instruction manual in conjunction with the FRENIC-Multi User's Manual and
be familiar with the handling procedure for correct use.
• Improper handling blocks correct operation or causes a short life or failure.
• Deliver this manual to the end user of the product. The end user should keep this manual in a
safe place until the CC-Link Interface Option is discarded.
• For the usage of inverters, refer to the instruction manual prepared for the FRENIC-Multi
series of inverters.
Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd. INR-SI47-1175-EU Rev 052010
Page 2

Copyright © 2006 Fuji Electric FA Components & Systems Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or copied without prior written permission from Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd.
All products and company names mentioned in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
The information contained herein is subject to change without prior notice for improvement.
Page 3

Preface
Thank you very much for purchasing our CC-Link Interface Option "OPC-E1-CCL."
This manual has been prepared to help you connect your FRENIC-Multi to a CC-Link master (Mitsubishi Electric
sequencer, etc.) via CC-Link.
Mounting this option on your FRENIC-Multi allows you to connect the FRENIC-Multi to a CC-Link master and
control it as a slave using run command, speed command, and access to inverter's function codes.
This option has the following features:
•
CC-Link Version: Complies with CC-Link versions 1. 10 and 2.00
• Applicable Profile: Inverter (1 station occupied)
• Monitoring the status of the FRENIC-Multi (running status, frequency, output torque, output current, output
voltage and etc.)
•
Reading and writing from/to function codes applicable to the FRENIC-Multi
Logo
mark:
Th
is option is a CC-Link version 2.00 compliant remote device unit and supports the following:
- Extended cyclic transmission
- Easing restrictions on inter-station cable length
This instruction manual does not contain inverter handling instructions
conjunction with the FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1204-E) and be familiar with proper handling
and operation of this product. Improper handling might result in incorrect operation, a short life, or even a failure
of this product.
Keep this manual in a safe place.
.
Read through this instruction manual in
Related Publications
Listed below are the other materials related to the use of the CC-Link Interface Option "OPC-E1-CCL." Read
them in conjunction with this manual as necessary.
• RS-485 Communication User's Manual
• FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manual
The materials are subject to change without notice
Safety precautions
Read this manual thoroughly before proceeding with installation, connections (wiring), operation, or
maintenance and inspection
safety information and precautions before proceeding to operate the inverter.
fety precautions are classified into the following two categories in this manual.
Sa
. Ensure you have sound knowledge of the device and familiarize yourself with all
(MEH448)
(INR-SI47-1204-E)
.
Be sure to obtain the latest editio ns for us e.
Failure to heed the information indicated by this symbol may lead to
dangerous conditions, possibly resulting in death or serious bodily
injur
ies.
Failure to heed the information indicated by this symbol may lead to
dangerous conditions, possibly resulting in minor or light bodily injuries
and
/or substantial property damage.
Failure to heed the information contained under the CAUTION title can also result in serious consequences.
These safety precautions ar e of utm ost impor tance and must be observed at all times.
1
Page 4
Installation and w iring
• Turn the inverter's power OFF and wait for at least five minutes. Further, check that the DC link bus
voltage between the P (+) and N (-) terminals is lower than 25 VDC.
• Qualified electricians should carry out wiring.
Otherwise, electric shock could occur.
• Do not use the products th at ar e da mag e d or lacking p arts.
Doing so could cause a fire, accident, or injury.
•
Prevent lint, paper fibers, sawdust, dust, metallic chips, or other foreign materials from getting into
the inverter and the option.
Otherwise, a fire or an accident might result.
• Incorrect handling in installation/removal jobs could cause a failure.
A failure might result.
• Noise may be emitted from the inverter, motor and wires. Implement appropriate measure to prevent
the nearby sensors and devices from malfunctioning due to such noise.
Otherwise, an accident could occur.
Operation
• Be sure to mount the inv erter's and option's terminal covers before turning the inverter's power ON.
Do not remove the cov ers wh ile power is applied.
Otherwise electric shock could occur.
• Do not operate switches with wet hands.
Doing so could cause electric shock.
•
If you configure the function codes wrongly or without completely understanding FRENIC-Multi
Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1204-E) and the FRENIC-Multi User's Manual (MEH457), the motor
may rotate with a torque or at a speed not permitted for the machine. Confirm and adjust the setting
of the function codes before running the inverter.
Otherwise, an accident could occur.
Maintenance and inspection, and parts replacement
•
Turn the inverter's power OFF and wait for at least five minutes before starting inspection.
check that the DC link bus voltage between the P (+) and N (-) terminals is lower than 25 VDC.
Otherwise, electric shock could occur.
Further,
• Maintenance, inspection, and parts replacement should be made only by qualified persons.
• Take off the watch, rings and other metallic objects before starting work.
• Use insulated tools.
Otherwise, electric shock or injuries could occur.
2
Page 5

Disposal
•
Treat the product as an industrial waste when disposing of it.
Otherwise injuries could occur.
Others
• Never attempt to modify the product.
Doing so could cause electric shock or injuries.
How this manual is organized
This manual is made up of chapters 1 through 12.
Chapter 1 BEFORE USING THE CC-Link INTERFACE OPTION
Lists points to be checked upon delivery of this option and describes the applicable inverters.
Chapter 2 NAMES AND FUNCTIONS
Shows the inside view of this option an d describes t he termi nating r esistor switch and LED status indicators.
Chapter 3 MOUNTING THE CC-Link INTERFACE OPTION
Provides instructions and precautions for mounting this option.
Chapter 4 WIRING AND CABLING
Provides wiring instructions around the terminal blocks on this option and the cable specifications.
Chapter 5 CONFIGURING INVERTER'S FUNCTION CODES FOR CC-Link COMMUNICATION
Describes the inverter's function codes to be set for the C C-Link commu nications link. Also this chapter lists the
related function codes.
Chapter 6
Guides you to establish a CC-Link c ommu nication s link.
Chapter 7
Provides the details of remote I/O signals a vailable for CC -Link co mmuni cation.
SETTING-UP PROCEDURE
LIST OF I/O SIGNALS
Chapter 8 INVERTER REACTION TO CC-Link COMMUNICATIONS ERRORS
Describes on how the inverter operat es if a
Chap
ter 9
Lists and describes inverter’s alarm codes.
Chapter 10
Provides program examples that control the inverter by a sequencer.
ALAR
M CODE LIST
APPLICATION PROGRAM EXAMPLES
CC-Link
communications error occurs.
Chapter 11 TROUBLESHOOTING
Provides troubleshooting instructions for certain problems, e.g., when the inverter does not operate as ordered
or when an alarm condition has been recognized.
Chapter 12 SPECIFICATIONS
Lists the general specifications and communications specifications.
3
Page 6

Icons
The following icons are used throughout this manual.
This icon indicates information which, if not heeded, can result in the product not operating to full
fficienc
e
y, as well as information concerning incorrect operations and settings which can result in
accidents.
This icon indicates information that can prove handy when performing certain settings or operations.
T
his icon indicates
a reference to more detailed information.
Table of Contents
Preface
How this manual is organized .............................................. 3
Chapter 1 BEFORE USING THE CC-Link INTERFACE Chapter 9 LIS T OF INVERTER A LARM CODES .............
1.1 Acceptance Inspection ............................................
Chapter 2 NAMES AND FUNCTIONS ...............................
2.1 Parts Names ...........................................................
2.2 Terminating Resistor Switch ....................................
2.3 LED Status Indicators..............................................
2.4 RJ-45 Connector .....................................................
2.5 Power Supply Terminal Block and CC-Link
Chapter 3 MOUNTING THE CC-Link INTERFACE
Chapter 4 WIRING AND CABLING..................................
4.1 Basic Connection Diagram....................................
4.2 Wiring for Power Supply Terminal Block................
4.3 Wiring for CC-Link Terminal Block.........................
4.4 ON/OFF Timing of the Option and the Inverter......
Chapter 5 CONFIGURING INVERTER'S FUNCTION
Chapter 6 SETTING-UP PROCEDURE...........................
Chapter 7 LIST OF I/O SIGNALS.....................................
7.1 Remote I/O Signals ...............................................
7.2 Remote Registers .................................................
7.3
7.4 Command Codes and Response Codes...............
..........................................................................
OPTION................................................ .............
Terminal Block.........................................................
OPTION................................................ .............
CODES FOR CC-Link COMMUNICATION
List of Monitor Item Codes ....................................
13
13
14
15
17
..... 18
19
20
20
22
26
27
1
5
5
6
6
6
7
8
8
9
Chapter 10 APPLICATION PROGRAM EXAMPLES..........
10.1 System Configuration...........................................
10.2 Network Parameter Settings ................................
10.3 Relationship between Master Statio n Dev ic e
10.4 CC-Link Startup Program.....................................
10.5 Program Example Using the Inverter Running
10.6 Program Example for Changing the Oper ation
10.7 Program Example for Specifying R un Comm an d. 34
10.8 Program Example for Monitoring the Output
10.9 Program Example for Reading fr om the
10.10 Program Example for Writing to Inverter's
10.11 Program Example for Settin g up the Refer enc e
10.12 Program Example for Rea ding out Alarm Codes . 38
10.13 Program Example for Resetting a Inverter Trip.... 38
Chapter 11 TROUBLESHOOTING.....................................
Chapter 12 SPECIFICATIONS ...........................................
12.1 General Specifications ......................................... 40
12.2
Chapter 8 ..INVERTER REACTION TO CC-Link
COMMUNICATIONS ERRORS .......................
and Remote I/O and Remote Register.................
Status Read .........................................................
Mode.................. ..................................................
Frequency ............................................................
Inverter's Function Code Data .............................
Function Code Data
Frequency ............................................................
CC-Link Specifications.........................................
.............................................
29
30
31
31
31
32
33
33
34
35
35
36
37
39
40
40
4
Page 7
Chapter 1 BEFORE USING THE CC-Link INTERFACE OPTION
1.1 Acceptance Inspection
Unpack the package and check the following:
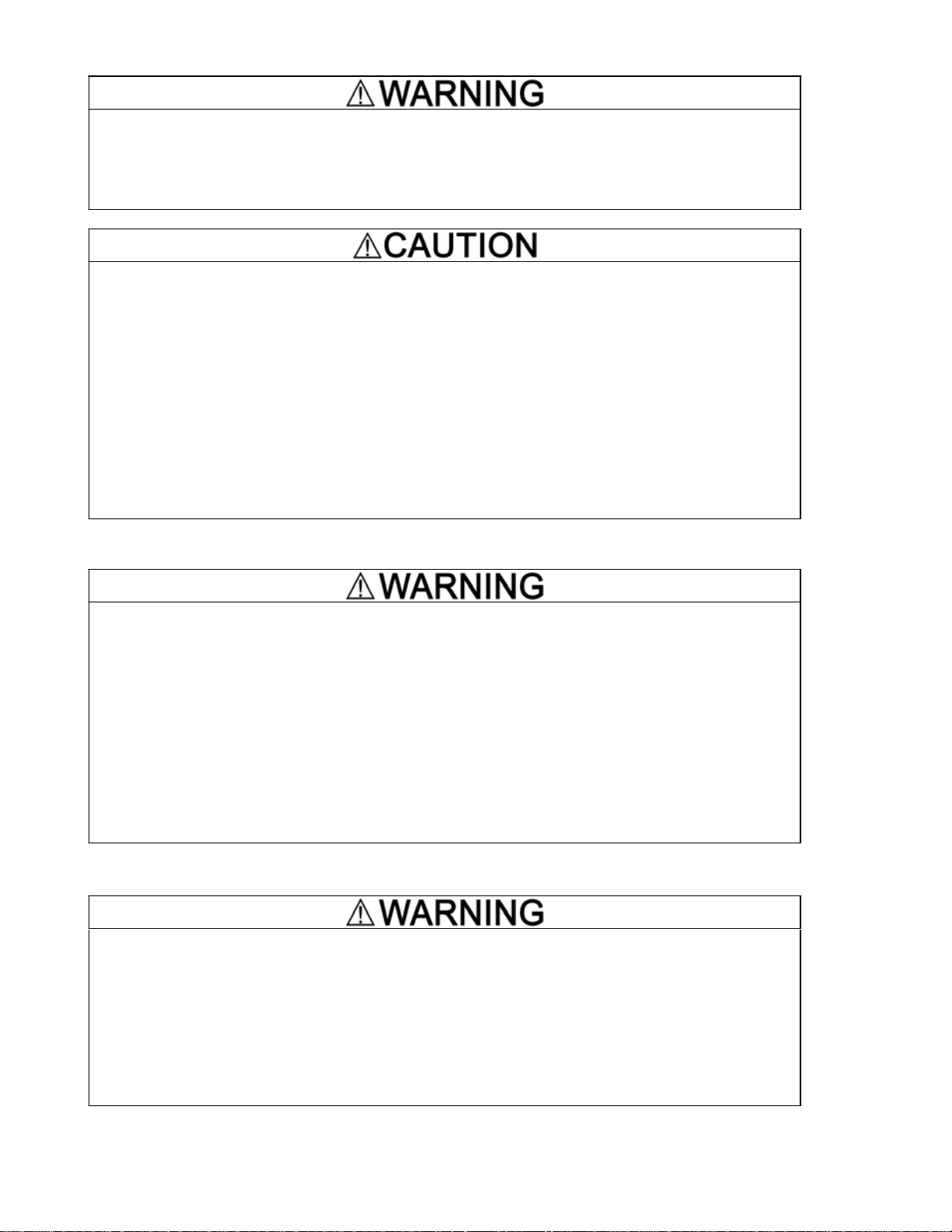
(1) A CC-Link interface option and the following accessories are contained in the package. (See Figure 1.1.)
-Two option connection cables (A short one for inverters with a capacity of 5 HP or below and a long one for inverters
with a capacity of 7.5 HP or above)
-One option fixing screw
-CC-Link Interface Option Instruction Manual (this manual)
(2) The option and accessories have not been damaged during transportation—there should be no dents or parts missing.
(3) The model name "OPC-E1-CCL" is printed on the nameplate attached to the right side of the option. (See Figure 1.1.)
If you suspect the product is not working properly or if you have any questions about your product, contact your Fuji Electric
representative.
Figure 1.1 CC-Link Interface Option and Accessories
Figure 1.1 CC-Link Interface Option and Accessories
5
Page 8
Chapter 2 NAMES AND FUNCTIONS
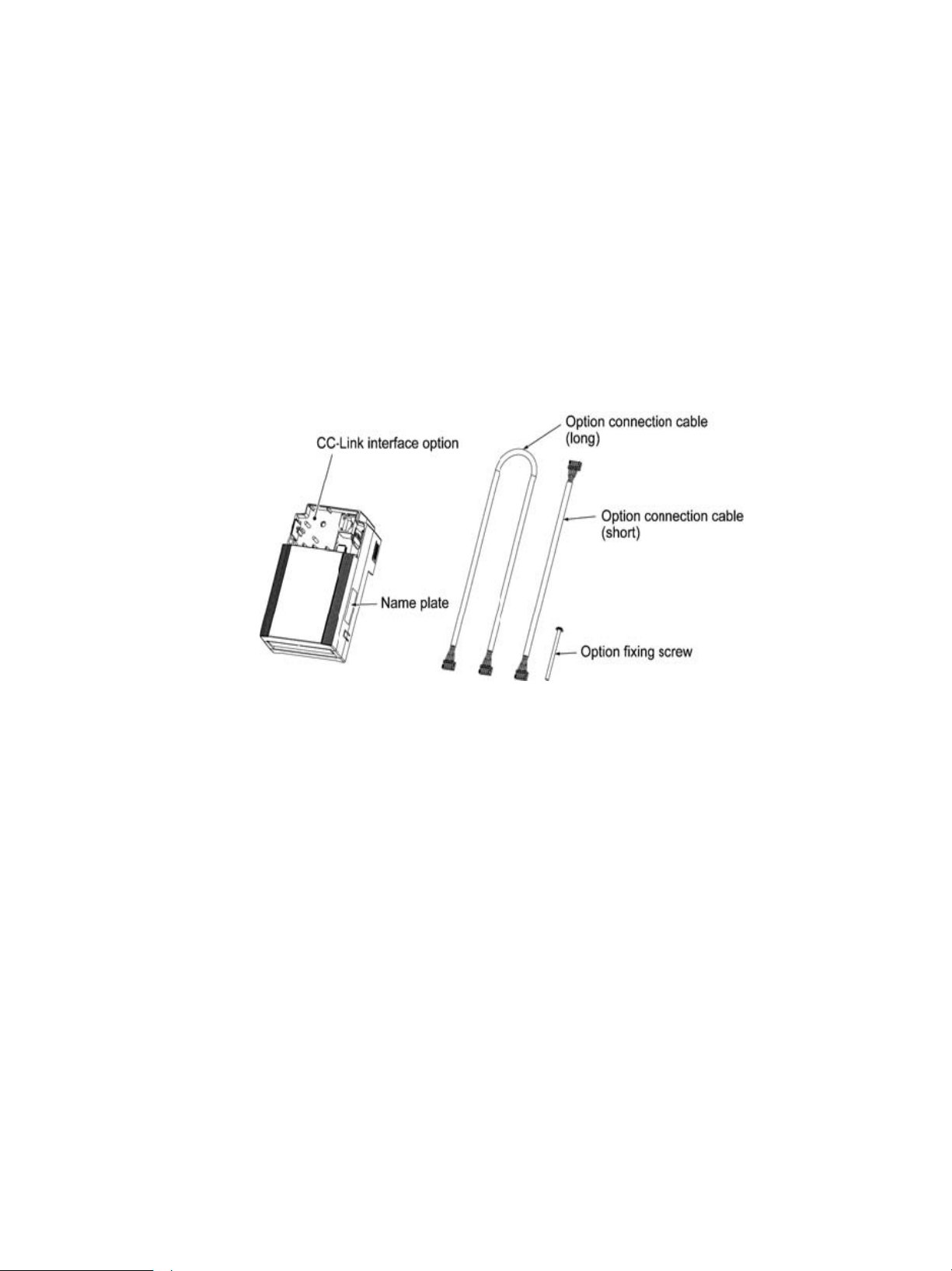
2.1 Parts Names
Figure 2.1 shows the inside view of the CC-Link interface option with its terminal cover (See Figure 3.3)
removed.
Figure 2.1 Parts Names of CC-Link Interface Option
2.2 Terminating Resistor Sw itch
The CC-Link communications network requires insertion of line terminating resistors at its both ends. When this
option is mounted on the inverter at either end of the network, turn this switch ON to insert the terminating
resistor.
ON
OFF
OFF: No insertion of terminating resistor ON: Insertion of terminating resistor
Figure
2.2 Terminating Resistor Switch Settings
ON
OFF
6
Page 9
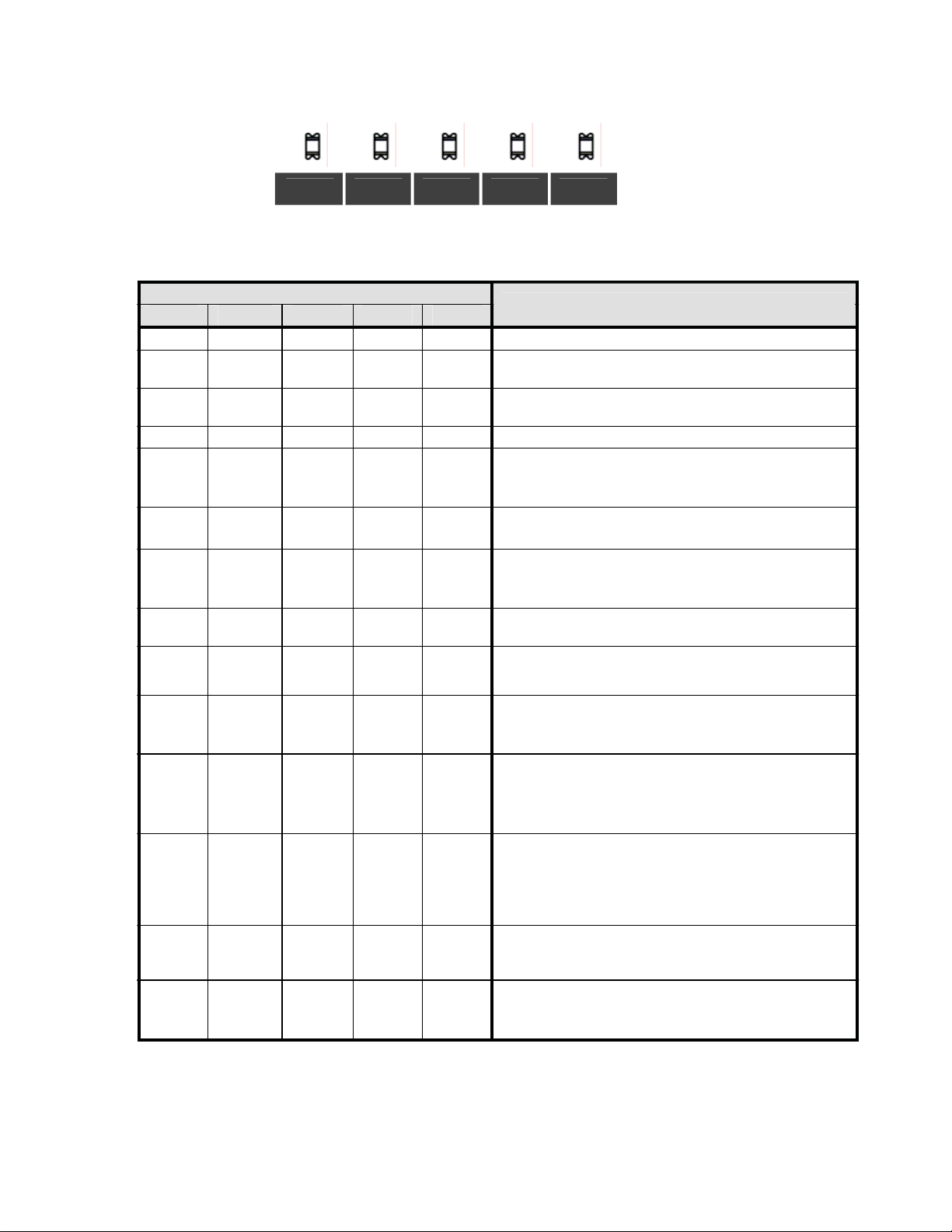
2.3 LED Status Indicators
This option has five LED status indicators show n b elow. They indicate the operation status of the option as listed
in Table 2.1.
L.RUN
L.RUN RUN L.ERR
Figure 2.3 LED Status Indicators
Table 2.1 LED Indications and Operation Status
LED States
RUN
L.ERR
SD
RD
SD
mally communicating.
Nor
Normally communic ating. But sometimes a CRC error
occurs due to electrical noise.
Received data contains a CRC error, so t his option
cannot respond.
Data destined for this station does not come.
Responding to polling
contains a CRC error.
The inverter trips with alarm
Data destined for this station contains a CRC error.
The inverter trips with alarm
Station address incorrectly specified.
Data destined for this station cannot be received due
to electrical noise.
Transmission speed (Baud rate) and/or station
address out of the allowable range.
RD
Operation Status
.
But refresh data received
isplayed
d
isplayed
d
. *1
. *1
(at 0.8-second
intervals)
(at 0.4-second
intervals)
(at 0.2-second
intervals)
(at 50 ms
intervals)
: ON, : O Blinking (It may seem to be ON depending on the current transmission speed.)
1
*
Alarm
established once.
It is possible to change the
Chapter 8 "INVERTER REACTION TO CC-Link COMMUNICATIONS ERRORS."
FF,
occurs when a communications error is detected after a normal communications link has been
occurrence conditions with inverter's function codes
Transmission speed (Baud rate) or station address
changed
This option cannot receive data due to broken wires,
etc.
Th
The master station is compliant with CC-Link version
1.xx and this slave station, with CC-Link ver sion 2.xx.
Or the inverter's function code o30 is set to "5 to 255."
The inverter trips with alarm
Du
cable has been broken or the power to the inverter has
been cut OFF.
If the cable has been broken, the inverter trips with
alarm
When this option is turned ON, the inverter has been
OFF or the option connection cable has been
disconnected.
This option is OFF or broken.
If the inverter power is ON, it trips with alarm
displayed.
during CC-Link communication.
isplayed
e inverter trips with alarm
ring normal communication, the option connection
displayed.
d
isplayed. d
. For details, refer to
. *1
7
Page 10

2.4 RJ-45 Connector
The RJ-45 connector is used to co nnect the ke ypad of the FRENIC- Multi to this option.
The keypad can be detached from the option and mounted on a panel. For details, refer to the
FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1204-E), Chapter 2, Section 2.4 "Mounting and Connecting a
Keypad."
2.5 Power Supply Terminal Block and CC-Link Term inal Block
The power supply terminal block and CC-Link terminal block are used to connect the 24V power cable and
CC-Link cable, respectively, in order to operate this option.
For details, refer to Chapter 4 "WIRING AND CABLING."
8
Page 11

Chapter 3 MOUNTING THE CC-Link INTERFACE OPTION
Turn the inverter's power OFF and wait for at least five minutes. Further, check that the DC link bus voltage
between the P (+) and N (-) terminals is lower than 25 VDC.
Otherwise, electric shock could occur.
•
Do not use the products that ar e d ama ge d or lack ing pa rts.
Doing so could cause a fire, accident, or injury.
• Prevent lint, paper fibers, sawdust, dust, metallic chips, or other foreign materials from getting into
the inverter and the option.
Otherwise, a fire or an accident might result.
• Incorrect handling in installation/removal jobs could cause a failure.
• When handling this option, take any antistatic measure or hold the plastic parts taking care not to
directly touch the circuit board; otherw ise, the st atic electricity charg ed in your body may da mag e it.
A failure might result.
9
Page 12
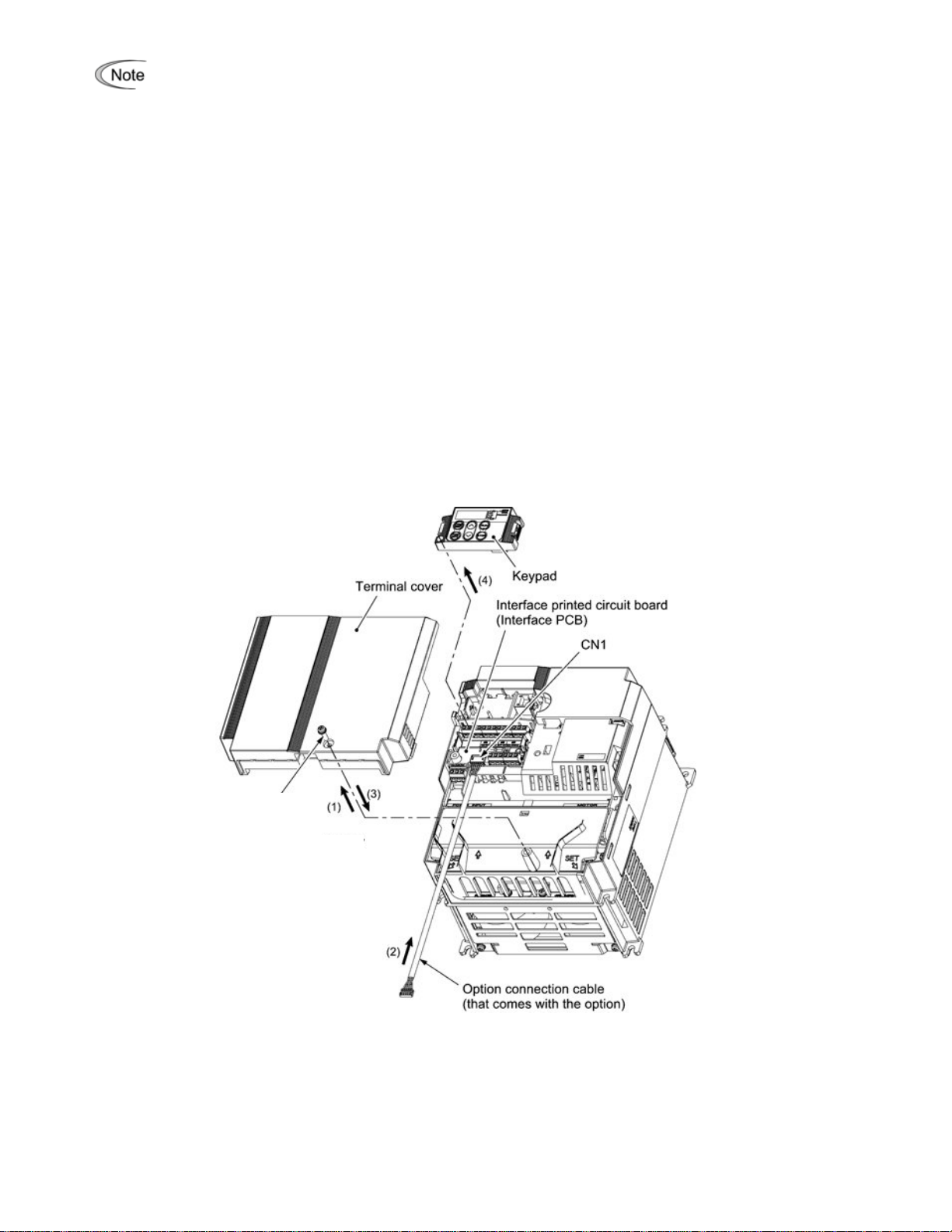
Before mounting the option, perform the wiring for the main circuit terminals and control circuit
terminals.
(1) Remove the terminal cover from the inverter.
Note:
For inverters with a capacity of 7.5 to 20 HP, you need to remove the terminal cover fixing screw to
remove the terminal cover.
For details on how to remove the terminal cover, refer to the FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manual
(INR-SI47-1204-E), Chapter 2, Section 2.3 "Wiring."
(2) Connect the option connection cable to the CN1 connector on the interface printed circuit board (interface
PCB) on the inverter.
Use the short cable for inverters w ith a capacity of 5 HP or below, and the lon g cable for the ones with a
capacity of 7.5 HP or above.
(3) Mount the terminal cover.
or details on how to mount the terminal cover, refer to the FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manual
F
(INR-SI47-1204-E), Chapter 2, Section 2.3 "Wiring."
(4) Push the hooks provided on both sides of the keypad and pull the keypad up and out of the inverter.
For details
(INR-SI47-1204-E), EChapter 2, Section 2.4 "Mounting and Connecting a Keypad."
on how to remove the keypad, refer to the FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manual
Terminal cover
fixing screw
(for inverters with a
capacity of 7.5 to 20 HP)
Figure 3.1 Connecting the Option Connection Cable to the Interface PCB and Removing the Keypad
(For inverters with a capacity of 15 and 20 HP)
10
Page 13
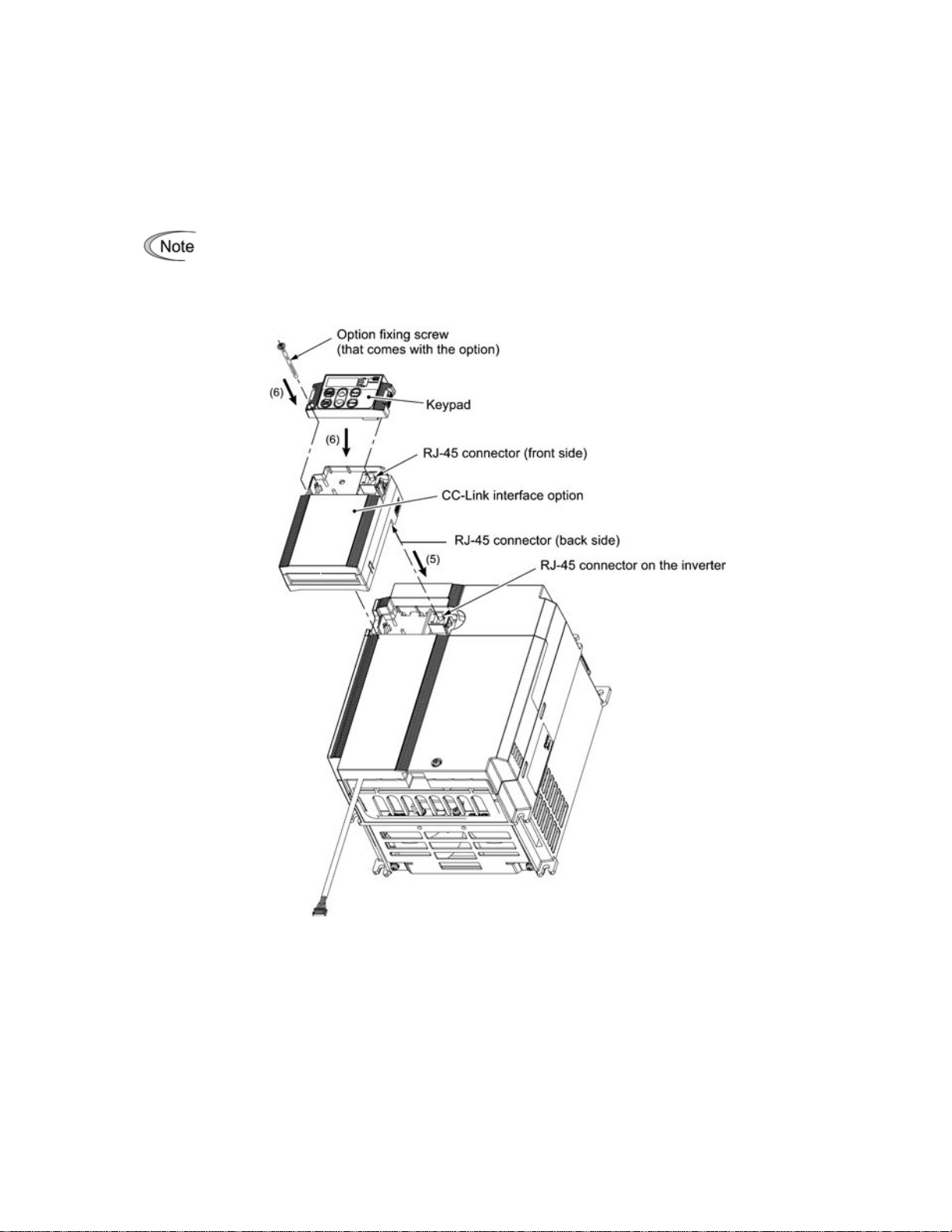
(5) Mount the option on the inverter, making the RJ-45 connector on the back side of the option engage with
the RJ-45 connector on the inverter (to which the keypad had been connected).
(6) Connect the keypad to the RJ-45 connector on the front side of the option, then secure the keypad and
option to the inverter with the option fixing screw (that comes with the option).
When using the keypad at a remote site, secure the option without the keypad to the inverter with the
screw.
Tightening torque: 0.6 N·m(0.44 lbf·ft)
Take care not to tighten the option fixing screw too much
.
Doing so could make the screw defective.
Figure 3.2 Mounting the CC-Link Interface Option and the Ke ypad
11
Page 14
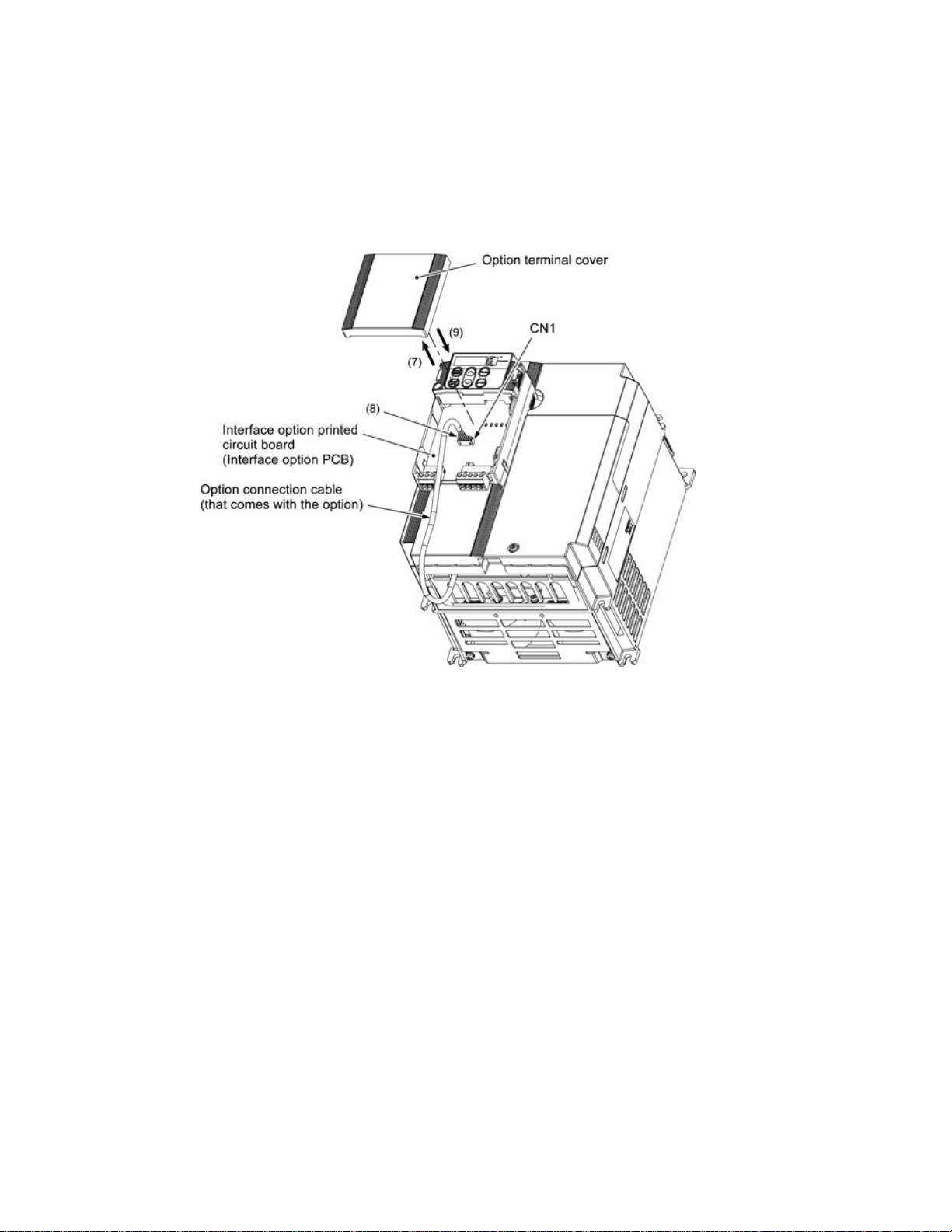
(7) Slightly pull the bottom of the option terminal cover towards you and remove it downward.
(8) Connect the other end of the option connection cable (whose end has been connected to the interface PCB
on the inverter in step (2) above) to the CN1 connector on the interface option printed circuit board
(interface option PCB).
(9) Mount the option terminal cover.
First fit the bosses on the top of the cover into the square holes provided in the option, and then push the
bottom of the cover until it snaps into place.
Figure 3.3 Connecting the Option Conne ction Cable to the Interface Option PCB
12
Page 15

Chapter 4 WIRING AND CABLING
• Before starting installation, turn the inverter's power OFF and wait for at least five minutes.
check that the DC link bus voltage between the P (+) and N (-) terminals is lower than 25 VDC.
• Qualif
Otherwise, electric shock could occur.
ied electricians should carry out wiring.
Further,
The inverter, motor, and wiring emit electrical noise. Take appropriate measures to prevent the nearby
sensors and devices from malfunctioning due to such noise.
Otherwise, an accident could occur.
4.1 Basic Connection Diagram
FRENIC-Multi
L1/R
L2/S
L3/T
U
V
W
Motor
M
G
24 VDC
power
supply
OPC-E1-CCL
Terminating
resistor switch
Power supply
terminal block
24V
0V
E
G
CC-Link
terminal bl ock
DA
DB
DG
SLD
FG
Blue
White
Yellow
CC-Link cable
G
Figure 4.1 Basic C onnection Diagram
To CC-Link network
For the 24 VDC power supply to be connected to the power supply terminal block, be sure to use an
external 24 V power supply with a capacity of at least 150 mA. Never use the PLC terminal o n the inverter;
doing so flows a current exceeding the capacity of the PLC terminal, resulting in a damaged inverter.
A failure might result.
13
Page 16

4.2 Wiring for Power Suppl y Terminal Block
A
A
This terminal block is used to supply this option with 24 V power to operate it. Perform wiring for the terminal
block as described blow.
For the 24 VDC power supply to be connected to the power supply terminal block, be sure to use an
.
external 24 V power supply with a capacity of at least 150 mA
doing so flows a current exceeding the capacity of the PLC terminal, resulting in a damaged inverter.
A failure might result.
(1) Wiring for the power supply terminal block (TERM3)
The terminal block uses a pluggable 3-pin connector as shown in Figure 4.2. Table 4.1 shows the pin
assignment.
A typical connector that matches this terminal block is Phoenix Contact MSTB 2.5/3-ST-5.08.
Never use the PLC terminal on th e inverter;
Table 4.1 Pin Assignment o n Po wer Su pply Terminal Block
Pin #
Terminal
name
Description
Remarks
1
2 3
1
24 V
2
0 V
3
E
Power supply
(24 VDC, + side)
Power supply
(24 VDC, - side)
Grounding
terminal
Never use the PLC termin al
on the inverter for 24 V
power.
Connect the ground
terminal of the inverter
(
G) to this terminal.
Figure 4.2 Connectors on the Power
Supply Terminal Block
For protection against external noise and prevention of failures, be sure to connect a grounding
wire.
Table 4.2 lists the recommended w ire size, terminal screw size and its tightening torque.
Table 4.2 Recommended W ire Size, Terminal Screw Size, and Its T ightening T orque
for the Power Supply Terminal Block
WG20 to AWG16 (0.5 to 1.5 mm2 ), wire with rated
temperature 105
Wire size
C(221 F) (UL) recommended
Cable wire
Terminal screw size
M3
pprox.
6.0 mm(0.23 in)
Tightening torque
0.5 to 0.6 N·m
(0.37 to 0.44 lbf·ft)
Figure 4.3 Recommended Strip Length of the Cable W ire End
for Terminal Connection
14
Page 17

(2) Input power requirements
Select the 24 V input power supply that meets the specifications listed in Table 4.3.
Table 4.3 Input Power Requirements
Item
Specifications
Input power voltage range
Power consumption
21.6 to 27.0 V
Maximum 150 mA
4.3 Wiring for CC-Link Terminal Block
(1) To connect this option to a CC-Link network, use a CC-Link dedicated cable complying with the CC-Link
specifications
performance. Also observe the wiring lengths specified in the CC-Link version 1.10 specifications.
. Using a cable other than a CC-Link dedicated cable does not assure the CC-Link system
The recommended CC-Link cable is FANC-110SBH made by Kuramo Electric Co., Ltd.
For details about wiring for CC-Link, refer to the CC-Link Master Use's Manual or CC-Link Cable Wiring
Manual published by the CC-Link Partner Association. The CC-Link Cable Wiring Manu al is available as a
free download from the CC-Link Partner Association's website at:
http://www.cc-link.org/eng/t_html/siryo.html
(2) Wiring around the CC-Link terminal block
The terminal block uses a pluggable 5-pin connector as shown in Figure 4.4. Table 4.4 shows the
correspondence between the pin numbers and the ID colors.
A typical connector that matches this terminal block is Phoenix Contact MSTB 2.5/5-ST-5.08 AU.
The Phoenix Contact TMSTBP 2.5/5-ST-5.08 AU and TFKC 2.5/5-STF-5.08 AU (spring-cage
conn
ection type) connectors for multidrop connection are also usable. Note that, however, the
former can be used only for FREN IC - Multi wi th a ca pacity of 5 H P or below.
Table 4.4 Layout of Terminal Pins
Terminal ID Color of
Pin Name
DA
DB
DG
SLD
FG
Wire Sheath
Blue
White
Yellow
Metallic
---
Description
For
communication
data
For shielded
wire
For grounding
Remarks
This is internally
connected with
terminal FG.
Connect the ground
terminal of the inverter
( G) to this terminal.
Figure 4.4 Connectors on the
CC-Link Terminal Block
15
Page 18

Table 4.5 lists the recommended terminal screw size and its tightening torque, and Figure 4.5 shows the
A
recommended strip length of the cable wire end.
Table 4.5 Recommended T ightening Torque of the
Terminal Screws on the CC-Link Terminal Block
Terminal screw size
M3
Tightening torque
0.5 to 0.6 N·m(0.37 to 0.44 lbf· ft)
(3) When two or more inverters are connected
Master
A DA DA
D
Term inating
res ist o r
DB DB DB
DG DG DG
FG FG
cable
Figure 4.6 Connection Diagram of T wo or More Inverters
pprox.
Cable wire
6.0 mm(0.23 in)
Figure 4.5 Recommended Strip Length of the
Cable Wire End for Terminal
Connection
*1
SLDSLD CC-Link
CC-Link
cable
OPC-E1-CCL OPC-E1-CCL
Terminating resistor
(SW 5 = ON)
SLD
FG
1
On CC-Link interface options connected in the middle of the network, set their terminating resistor
*
switches (SW5) to OFF (No insertion of terminating resistor).
16
Page 19

4.4 ON/OFF Timing of the Option and the Inverter
Observe the following instructions about the ON/OFF timing of this option and the inverter.
(1) Power ON
It is recommended that this option be turned ON at the same time as or before the inverter.
inverter ON first may detect no operation of the option, causing a trip with
be reset after this option is turned ON.
(2) Power OFF
It is recommended that this option be turned OFF at the same time as or after the inverter.
option OFF first may cause the inverter to detect no operation of the option, causing a trip with
Turning the inverter OFF resets the
alarm.
alarm
. The
Turning the
alarm can
Turning the
alarm.
The inverter issues an alarm if the option's power stays OFF for approximately 1 second when the
in ver
ter power is ON.
17
Page 20

Chapter 5 CONFIGURING INVERTER'S FUNCTION CODES FOR CC-Li nk
A
COMMUNICATION
Before starting CC-Link communication between the inverter equipped with this option and the CC-Link master
device, configure the inverter's function co d es listed in Ta ble 5. 1.
Table 5.2 lists other related function codes to be configured if necessary.
Table 5.1 Inverter's Function Codes for CC-Link Communication
Function
code
*1
o27
Respo
when a CC-Link
Function
nse mode to apply
communications error occurs
Operation timer to apply whe n
*1
o28
a CC-Link communications
error occurs
*2
o30
o31
o32
*1
For details about the function codes o27 and o28, refer to Chapter 8 "INVERTER REACTION TO CC-Link
COMMUNICATIONS ERRORS."
*2
OFF and then ON) validates the new setting. However, resetting the option causes an inverter trip with an alarm
if Version 1.xx is specified on the master station and Version 2.xx on the opti on.
*3 Changing the o31 or o32 d ata causes the L.ERR LED to star
and turns the L.ERR LED OFF.
CC-Link extension
*3
Station address
*3
Transmission speed
fter changing the o30 data, resetting the option (by turning the terminal RST ON or by turning the option's power
The underlined values
(
Setting range
are factory defaults.)
Se
to 15
0
communications link error or an option failure is
detected.
Specify the timer period during w hic h t he
to 60.0 sec.
0.0
inverter keeps running even if a communications
link error is detected.
0, 1
2
3
4
5 to 255
1 to 64
0, 65 to 255
0
1
2
3
4
5 to 255
Table 5.2 Other Related Function Codes
1 station occupied (CC-Link version 1.10)
1 station occupied, 2X setting
(CC-Link version 2.00)
1 station occupied, 4X setting
(CC-Link version 2.00)
1 station occupied, 8X setting
(CC-Link version 2.00)
No operation
Set a station address.
Invalid
156 kbps
625 kbps
2.5 Mbps
5 Mbps
10 Mbps
Invalid
t blinking. Resetting the option validates the new setting
Description
lect a response mode to apply when a
Function
code
*1
y98
*1
In addition to y98, there are some func tion codes that specify run/frequency command sources. Using those function
codes enables more flexible settings of run/frequency command sources . For details, refer to the description for the
function codes H30 and y98 in the FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manual (INR-SI47-1204-E), Chapter 5 "FUNCTION
CODES."
Function
Run
/frequency
command sources
Factory default
0
Function code data
Select from the following choices:
Frequency
command
0
1
2
3
Inverter
CC-Link
Inverter
CC-Link
18
Run
command
Inverter
Inverter
CC-Link
CC-Link
Remarks
If there is no
special problem
with your system,
setting y98 = 3 is
recommended.
Page 21

Chapter 6 SETTING-UP PROCEDURE
The following flow shows the initial setting-up procedure for the CC-Link interface option.
Start
Ac
ceptance inspection
Mount the option
Connect the power cable and CC-Link cable
Configure the terminating resi stor switch (SW 5)
Turn ON the power to the option and inverter
Configure function codes y98 and o27 to o32
to match the settings in the master
See Chapter 1 "BEFORE USING THE
CC-Link INTERFACE OPTION."
See Chapter 3 "MOUNTING TH E
CC- Link INTERFACE OPTION."
See Chapter 4 "WIRING AND
CABLING."
See Chapter 2, Section 2.2
"Terminating Resistor Switch."
See Chapter 4, Section 4.4 "ON/ OFF
Timing of the Option and the Inverter."
See Chapter 5 "CONFIGURING
INVERTER'S FUNCTION CODES
FOR CC-Link COMMUNICATION."
Preparation completed
Now the inverter is ready to run via CC-Link.
After confirming that the CC-Link master has been set up, check that the communications link is established
according to the ON/OFF states of the LED status indicators (see Chapter 2, Section 2.3 "LED Status
Indicators").
After the CC-Link master becomes ready, run the sequencer to operate the inverter via CC-Link.
19
Page 22

Chapter 7 LIST OF I/O SIGNALS
A
7.1 Remote I/O Signals
(1) Remote outputs (Master Inverter)
Device No
0
RY
RY1
RY2
RY3
RY4
RY5
RY6
RY7
RY8
RY9
RYA
RYB
RYC
RYD
RYE
RYF
RY1A
.
Signal name
Run forward comman d
Run reverse command
minal X1 function
Ter
Terminal X2 function
Terminal X3 function
Terminal X4 function
Terminal X5 function
Not used.
Not used.
Secondary side output
cut off (BX)
Description
OFF: Stop command
ON: Run forward comman d
OFF: Stop command
ON: Run reverse command
Terminal command assigned by inverter's
function code E01
Terminal command assigned by inverter's
function code E02
Terminal command assigned by inverter's
function code E03
Terminal command assigned by inverter's
function code E04
Terminal command assigned by inverter's
function code E05
--
--
ON:
Coast to a stop
S
turning RY0 and RY1
ON results in 0 Hz of
frequency.
Factory default:
1
*
Factory default:
1
*
Factory default:
1
*
Factory default:
1
*
Factory default:
1
*
Effective only when
the run command
source is CC-Link.
Not used.
Not used.
2
Monitor command
*
Turning this signal ON causes the inverter to store monit ored values
emote registers RWr0, 1, 4 to 7 an d then turns th e "Monit oring"
into r
--
--
signal (RXC) ON.
3
Frequency command
*
(RAM)
Turning this signal ON writes the reference frequency (RWw1) to the
.
inverter's RAM
Upon completion of writing, the "Frequency setting
completed" signal (RXD) is turned ON.
Not used.
4
Command code
*
execution request
Turning this signal ON executes proc essing corr espondi ng to
command codes specified in RWw2, 10, 12, 14, 16, and 18
--
execution of those command codes, the "Command code execution
completed" signal (RXF) is turned ON.
If
a command code execution error occurs, the error factor will be set
to the response code (RWr2).
5
larm reset request flag Turning this signal ON and then OFF when a trip has occurred
*
resets the trip state and turns this flag (RX1A) OFF.
Remarks
imultaneously
--
--
--
--
.
After
SS1
SS2
SS4
BX
RST
RR*1
For details about inverter's function codes E01 to E05, refer to the FRENIC-Multi Instruction Manu al
(INR-SI47-1204-E), Chapter 5 "FUNCTION CODES." Depending upon terminal commands assigned to
terminals X1 through X5, these signals may not be operated via CC-Link. For details, refer to the RS-485
Communication User's Manual (MEH448), Chapter 5, Section 5.1.2 [ 3 ] "Operation command data."
*2
While the "Monitor command" (RYC) is ON, the monitored values are constantly updated.
*3
While the "Frequency command" (RYD) is ON, the current reference frequency (RWw1) is constantly
reflected on the speed.
*4
Each time the "Command code execution request" (RYF) is turned ON, the command specified by the
.
command code executes once
To execute it again, it is necessary to turn the "Command code execution
request" (RYF) ON again.
*5
The "Alarm reset request flag" (RY1A) should be turned ON and then OFF.
20
Page 23

(2
N
) Remote inputs (Inverter
Master)
Device No.
RX0
RX1
RX2
RX3
RX4
RX5
RX6
RX7
RXC
Signal name
ing forward
Runn
OFF: Exce pt running in forw ard direction
Description
(Stopped or Rotating in reverse
direction)
ON: Rotating in forward direction
Running reverse
OFF: Except running in rever se direction
(Stopped or Rotating in forward
direction
ON: Rotating in reverse direction
Terminal Y1 function Terminal status assigned by inverter's
function code E20
Terminal Y2 function Terminal status assigned by inverter's
-- --
--
--
Not used
Not used
Not used
.
.
.
Terminal 30A/B/C
function
Monitoring
function code E21
Terminal command assigned by inverter's
function code E27
This signal is turned ON when turning the "Monitor command" (RYC)
ON has caused the inverter to st ore m onitored v alues into re mote
registers RWr0, 1, 4 to 7.
Factory default:
1
*
Factory default:
1
*
Factory default:
1
*
Remarks
--
--
RU
OL
--
--
ALML
Turning the "Monitor command" (RYC) OFF turns this signal OFF.
RXD
Frequency setting
completed
This signal is turned ON when turning the "Frequency command"
(RYD) ON has written the reference frequency into the inverter.
Turning the "Frequency command" (RYD) OFF turns this signal OFF.
RXE
RXF
Not used.
Command code
execution completed
--
This signal is turned ON when turning the "Command code execution
request" (RYF) ON has completed the execution of processing
corresponding to command codes (specified in RWw2, 10, 12, 14, 16,
and 18).
Turning the "Command execution request" (RYF) OFF turns this signal
OFF.
RX1A
RX1B
Alarm state flag
Remote station
ready
This signal is turned ON when the inverter has tripped.
This signal is turned ON when powering on the inverter or resetting the
hardware has readied the inverter. (This signal is used for interlocking
with reading or writing from/to the master unit.)
This signal is turned OFF concurr ently wh en the " Alar m state fla g"
(
RX1A) is turned ON if the inverter trips.
*1
For details about inverter's function codes E20, E21 and E27, refer to the FRENIC-Multi Instruction
Manual (INR-SI47-1204-E), Chapter 5 "FUNCTION CODES."
21
Page 24

7.2 Remote Registers
A
A
(1) Remote registers RWw (Master Inverter)
Device No.
RWw0
RWw1
RWw2
RWw3
Signal name
itor code 2/
Mon
Monitor code 1
Reference
frequency
Command code
Write data
Description
Write the codes (listed in Table 7.1) of monitor
tems to be referred to, into RWw0. After that,
i
turning the RYC ON stores t he v alue of thos e
monitor items into RWr0 and RWr1.
Write the reference frequency into RWw1
that, turning the RYD ON sets up that frequency
.
to the inverter
After completion of frequency
setting, the RXD is turned ON.
Write one of command codes (listed in Table 7.2)
into RWw2, which are required for execution of
the following: writing/reading of operation
methods (run command sources) and inverter's
function codes, referring to the alarm history,
alarm resetting, etc.
After writing of a command code, turning the RYF
ON executes that command.
Upon completion of the execution, the RXF is
turned ON.
Write object data specified in RWw2, into
RWw3, if necessary.
After writing into RWw2 and RWw3, turn the
RYF ON.
If no write data is required, zero (0) should be
written into RWw3.
.
After
Remarks
lower and upper
The
bytes correspond to
monitor codes 1 and
2, respectively.
Unit: 0.01 Hz
The command code
format for specifying
inverter's function
codes is shown in
Table 7.4.
RWw4
RWw5
RWw6
RWw7
RWw8
RWw9
RWwA
RWwB
RWw10
RWw12
RWw14
RWw16
RWw18
Monitor code 3
Monitor code 4
Monitor code 5
Monitor code 6
larm history
PID set value
(SV)
t used
No
Not used
.
.
Command code 2
Command code 3
Command code 4
Command code 5
Command code 6
Write the code (listed in Table 7.1) of monitor
item to be referred to, into the corresponding
n).
register (RWw
After that, turning the RYC ON
stores the data of the monitor item into the
RWrn.
("n" denotes any of the corresponding register
numbers 4 to 7.)
Write 0000, 0100, 0200, or 0300 into RWw8 to
specify which alarm code--latest, last, 2nd last, or
3rd last--should be read out, r es pe c tively.
(The lower 8 bits are fixed to 00
.)
H
The content of the specified alarm code and its
related information are stored in RWr8, 9, A, B,
and C.
Write the PID set value into RWw9.
The setting range is from -150.00% to 150.00%.
--
--
se these registers in the same way as RWw2.
U
fter writing into these registers, turning the RYF
ON executes these com man d co des in the or der
of RWw2, 10, 12, 14, 16, and 18.
Upon completion of execution of R Ww 18 , the RXF
is turned ON.
To nullify the execut ion of RWw10 to 18, FFFF
H
should be written into these registers.
Latest:
Last:
0000
0100
2nd last: 0200
3rd last: 0300
Unit: 0.01%
22
Page 25

A
Device No
RWw11
RWw13
RWw15
RWw17
RWw19
.
Signal name
Write data 2
Write data 3
Write data 4
Write data 5
Write data 6
Write
object data specified in RWw10, 12, 14, 16,
Description
and 18, if necessary, into RWw11, 13, 15, 17, and
19, respectively.
fter writing into RWw10, 12, 14, 16, and 18 an d
their respective registers RWw11, 13, 15, 17, and
19, the RYF should be turned ON.
If no write data is required, zero (0) should be
written into each of RWw11, 13, 15, 17, and 19.
CC-Link extension
In CC-Link version 1.10, R W w0 t o RW w 3 a re av ailable.
In CC-Link version 2.00,
with 2X setting, RWw0 to RWw7 are available
with 4X setting, RWw0 to RWwF (RWw9 for this option) are availa ble
with 8X setting, RWw0 to RWw1F (RWw19 for this option) are available.
Remarks
23
Page 26

(2) Remote registers RWr (Inverter
Master)
Device No.
r0
RW
RWr1
RWr2
RWr3
RWr4
RWr5
RWr6
RWr7
RWr8
RWr9
RWrA
RWrB
RWrC
Signal name
M
onitored value 1
Monitored value 2
Response code
Read data
Monitored value 3
Monitored value 4
Monitored value 5
Monitored value 6
Alarm code
Output frequency
at an alarm
occurrence
Output current at an
alarm occurrence
Output voltage at
an alarm
occurrence
Cumulative
power-ON time at
an alarm
elapsed until t he occurrence time of the alarm
occurrence
Description
Turning the RYC ON stores th e v alue of t he mo nitor
ite
m specified by "Monitor code 1" (RWw 0), into
RWr0.
Turning the RYC ON stores th e v alue of t he mo nitor
item specified by "Monitor code 2" (RW w0), into
RWr1.
Turning the RYF ON stores the res pons e c ode for
the command code specified in RWw2, into RWr2.
If the command code has norm ally executed, zer o
(0) is automatically written into RWr2; if any error
has occurred during proces sing of the co mman d
code, any value other than zero is written.
If the command code has nor mally execute d, the
response data for that command (specified by the
command code) is automatically written into RWr3.
Turning the RYC ON stores the valu e of the
n
monitor item specified by RWw
, into the
corresponding RWrn.
("
n
" denotes any of the register numbers 4 to 7.)
The content of the alarm code s pecified in RWw 8
is automatically written into the lower 8 bits of
RWr8. The upper 8 bits of RWw8 will be echoed
back into the upper 8 bits of RWr8.
This register stores the output frequency applied
at the occurrence time of the alar m specified in
RWw8.
This register stores the output current applied at
the occurrence time of the alar m specified in
RWw8.
This register stores the output voltage applied at
the occurrence time of the alar m specified in
RWw8.
This register stores the cumulative power-ON time
specified in RWw8.
Remarks
See Table 7.1 for
monitor item codes.
See Table 7.3 for
response codes.
See Chapter 9 for
alarm codes.
Unit: 0.01 Hz
Unit: 0.01 A
Unit: 0.1 V
Unit: 1h
RWr10
RWr12
RWr14
RWr16
RWr18
RWr11
RWr13
RWr15
RWr17
RWr19
Respo
nse code 2
Response code 3
Response code 4
Response code 5
Response code 6
Read data 2
Read data 3
Read data 4
Read data 5
Read data 6
Turning the RYF ON stores the response code to
the
command code specified in RWw10, 12, 14,
16, and 18, into RWr10, 12, 14, 16, and 18,
respectively.
If the command code has norm ally executed, zer o
(0) is automatically written into the corresponding
register (RWr10, 12,14, 16, or 18); if any error has
occurred during processing o f the comman d code,
any value other than zero is written.
If the command code specifie d in RW w10, 1 2, 14,
16, or 18 has normally executed, the response
data for that command code is automatically
written into RWr11, 13, 15, 17, or 19, respectively.
24
See Table 7.3 for
response codes.
Page 27

CC-Link extension
In CC-Link version 1.10, R W w0 t o RW w 3 a re av ailable.
In CC-Link version 2.00,
with 2X setting, RWw0 to RWw7 are available
with 4X setting, RWw0 to RWwF (RWw9 for this option) are availa ble
with 8X setting, RWw0 to RWw1F (RWw19 for this option) are available.
25
Page 28

7.3 List of Monitor I tem Codes
A
A
Table 7.1 lists the monitor item codes available in RW w0, 4 to 7.
Monitor Item Codes
--
0.01 Hz
0.01 A
0.1 V
--
0.01 Hz
1 r/min
0.1%
--
0.01 kW
0.01 kW
--
--
0.
--
Code
00
H
01
H
02
H
03
H
04
H
05
H
06
H
07
H
08
H
09H to 0C
0D
H
0E
H
0F
H
10
H
11
H
12H to 13
Monitor item
No monitoring (Fixed to 0)
Output frequency
Output current
Output voltage
No monitoring (Fixed to 0)
Reference frequency
Motor speed
Calculated torque
DC link bus voltage
No monitoring (Fixed to 0)
H
Input power
Motor power consumption
Input terminal status
Output terminate status
Load factor
No monitoring (Fixed to 0)
H
Table 7.1
0.1 V
1%
Unit
Remarks
In units of 1 V
*1
*2
ssuming the motor rated
torque as 100%
14
H
15H to 16
17
H
18
H
19
H
1AH to 33
34
H
35
H
36
H
37H
Cumulative run time
No monitoring (Fixed to 0)
H
Cumu
lative motor run time
Current output from t he inv erter in R MS
(based on the inverter rating)
Input watt-hour
No monitoring (Fixed to 0)
H
PID command
PID feedback
PID deviation
No monitoring (Fixed to 0)
1 hr
-1 hr
0.1%
1 kWhr
--
0.1%
0.1%
0.1%
--
ssuming the inverter rated
current as 100%
*1 The format of the input terminal status signal is show n below. Individual bits denote the ON/OFF states of
input terminals on the actual control circuit terminal board
b
y remote outputs RY2 to 6, the change of the ON/OFF states cannot be reflected on this monitor.
b15
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
b8 b7
.
If terminals X1 through X5 are turned ON or OFF
-
- X5 X4 X3 X2 X1 REV FWD
- Empty (Fixed to 0)
Figure 7.1 Input Terminal Status Signal Format
.
*2 The format of the output terminal status sign al is show n bel ow
output terminals on the actual control circuit terminal board
remo
te inputs RX2, 3, and 7.
Individual bits denote the ON/OFF states of
.
Their states are changed in synchronization with
b0
b15
-
-
-
-
-
-
b8 b7
- 30
-
-
-
-
-
-
Y2 Y1
b0
- Empty (Fixed to 0)
Figure 7.2 Output Terminal Status Signal Format
26
Page 29

7.4 Command Codes and Response Codes
Table 7.2 lists the command codes available in remote registers RWw2, 10, 12, 14, and 16. The response codes
(to be stored in RWr2, 10, 12, 14, and 16) to those command codes are listed in Table 7.3.
The format of command codes in reading or writing from/to the inverter's function codes is shown in Table 7.4.
Table 7.2 Command Codes
Item
Read from function
code
Write to function
code
Read from operation
method (run
command source)
Write to operation
method (run
command source)
Read from the latest
and last alarm codes
Read from the 2nd
and 3rd last alarm
codes
Read reference
frequency
Write reference
frequency
Clear alarm history
Reset alarm
Code number
0000H to 1163
0080H to 11E3
007B
00FB
0074
0075
006D
00ED
00F4
00FD
Reads or writes data from/to
H
inverter's function codes
H
0000H: Link operation (CC-
H
Description
Inverter's function codes should be
.
specified in the format shown in
Remarks
Table 7.4.
Link)
: and for
000
Terminal comm
1
H
external drive
0002H: Keypad
: Others
0003
H
H
: Link operation (CC-
0000
H
Link)
0001H: Terminal command
external drive
H
Reads the content of the latest
and last alarm codes.
H
Reads the
and 3rd last alarm codes.
H
Reads out the reference
H
frequency via CC-Link.
Writes the reference frequency.
(This frequency is ef
when the frequency comman
H
H
cesour is CC- Link.)
9696
: Clears alarm history.
H
9696
: Resets tripped state.
H
operation
tion 0002H: Keypad opera
content of the 2nd
fective only
Change
to y98=3
Change to y98=0 and F02=1
Change to y98=0, F02=0, and
for
F01=0
Lower byte: Latest alarm code
Higher byte: Last alarm code
(The contents of alarm cod es are
detailed in Chapter 9.)
Lower byte: 2nd last alarm c ode
Higher byte: 3rd last alarm code
(The contents of alarm codes are
detailed in Chapter 9.)
The allowable setting range is from 0
.
to +/-20000
Specify the ratio of the
frequency relative to the maximum
frequency (defined by F03 in Hz)
being assumed as 20000.
d
Code number
0000
H
0001
H
Item
Normal (No error)
Not allowed to write
Invalid command code
Out of setting range
Description
Execution of command code has been normally completed.
- Attempted to write to function code whose data cannot be
changed while the inverter is running.
- Attempted to write to function code whose data is being
edited from the keypad.
An invalid command code has been specified.
Write data is out of the allowable setting range.
27
Page 30

Table 7.4 Command Code Format for Specifying Inverter's Function Codes
(bit 15) (bit 0)
15 14 13 12
Empty (Fixed to 0) Function code group
00H (=0):
01H (=1):
02H (=2):
03H (=3):
04H (=4):
11 10 9
F codes (F00 to F99)
E codes (E00 to E99)
C codes (C00 to C99)
P codes (P00 to P99)
H codes (H00 to H99)
8
7
6 5 4
0: Read
1: Write
Function code number
00 to 99 (00H to 63H)
3
2
1
0
06H (=6): o codes (o00 to o99)
07H (=7):
S codes (S00 to S99)
08H (=8): M codes (M00 to M99)
0DH (=13): J codes (J00 to J99)
0EH (=14): y codes (y00 to y99)
0FH (=15): W codes (W00 to W99)
10H (=16): X codes (X00 to X99)
11H (=17): Z codes (Z00 to Z99)
Inverter's communication dedicated function codes S01, S05, and S06 are read-only. Attempting to
w
rite to those function codes will result in a "Not allowed to write" error (Response code: 0001
).
H
These function codes are functionally equivalent to certain remote outputs and remote registers.
(Examples)
(1) Reading from H95
Function code group: 04H, Function code number: 95 (=5FH), bit 7 = 0 (Read)
Set "045FH" to the command code
(2) Writing "10" to E20
Function code group: 01
Set "0194H" to the command code
Write data: 10 (000A
Set "000AH" to the write data
The data of inverter's function codes should be specified in the individual data formats.
, Function code number: 20 (=14H), bit 7 = 1 (Write)
H
)
H
For details about
the data formats, refer to the RS-485 Communication User's Manual, Chapter 5, Section 5.2, "Data
Formats."
28
Page 31

Chapter 8 INVERTER REACTION TO CC-Link COMMUNICATIONS ERRORS
If the inverter detects a CC-Link communications error such as broken wires, it trips with an alarm
factory default
function codes o27 and o28 as listed in Table 8.1.
Table 8.1 Inverter Reaction to CC-Link Communications Errors, Specified with Function Codes o27 and o28
o27
0,
4 to
1
2
3
10
11
. The inverter reaction to be taken when it detects an error can be changed with the inverter's
9
o28
--
0.0 s to 60.0 s
0.0 s to 60.0 s
--
--
0.0 s to 60.0 s
Inverter reaction to CC-Link communications error
Immediately coast to a stop and trip with
After the time specified by o28, coast to a stop and
trip with
If the communications link is restored within the
time specified by o28, ignore the communications
.
error
.
Keep the current operation, ignoring the
communications error
Immediately decelerate to a stop.
Issue
After the time specified by o28, decelerate to a
stop
. Issue
.
After the timeout, coast to a stop and trip with
. (No
trip)
after stopping.
after stopping.
.
Factory default
The inverter's function
code F08 specifies the
deceleration time.
Same as above.
Remarks
by
If the communications link is restored within the
12
13
14
15
0.0 s to 60.0 s
--
--
--
In any of the following cases, the invert er does not t ake re actions sp ecified in Table 8. 1 when it detects
C-Link communications er r or, ignor i ng t h e occurrence of the error.
a
C
1) The CC-Link communications link has not been established once after the option was turned ON.
2) Both run command and frequency command sources specified are not CC-Link (that is, any of the
following three).
- Inverter's function code y98 = 0
- Terminal command
- Inverter's function code y99 = 3 or y99 data = y98 data.
time specified by o28, ignore the communications
error
.
After the timeout, decelerate to a stop and
trip with
Immediately turn run command OFF
Force to rotate the motor in forward direction.
(No
Force to rotate the motor in reverse direction.
(No
LE
.
. (No
trip)
trip)
trip)
is assigned to a terminal X and the LE is OFF.
Same as above.
29
Page 32

Chapter 9 LIST OF INVERTER ALARM CODES
Through CC-Link, the master can monitor the information on alarms (in Table 9.1) that have occurred in the
inverter, by using the following procedure.
(1) Specify which alarm code--latest, last, 2nd last, or 3rd last--should be read out, into the remote register
RWw8. (The alarm code will be stored in RWr8.)
(2) Specify command codes 0074
alarm codes.
(3) Use inverter's communication dedicated function codes M16 to M19 to read out the latest, last, 2nd last, and
3rd last alarm codes, respectively.
and 0075H (in remote registers RWw2, 10, 12, 14, 16, or 18) to read out
H
Table 9.1 List of Inverter Alarm Codes
Alarm
code
0 (00H)
1 (01H)
2 (02H)
No alarm --- 22 (16
Overcurrent
(during acceleration)
Overcurrent
(during deceleration)
Overcurrent
3 (03H)
(During running at constant
speed)
5 (05H) Ground fault
6 (06H)
7 (07H)
Overvoltage
(during acceleration)
Overvoltage
(during deceleration)
Overvoltage
8 (08H)
(during running at constant
speed or being stopped)
10 (0AH) Undervoltage
11 ( 0 BH) Input phase loss
Description
E
E
E
GH
W
W
W
NW
N+P
Alarm
code
) Braking resistor overheated
H
23 (17H) Motor 1 overload
24 (18H) Motor 2 overload
25 (19H) Inverter overload
31 (1FH) Memory error
32 (20H) Keypad communications error
33 (21H) CPU error
34 (22H)
35 (23H) CC-Link communications error
36 (24H) Operation protection
Interface option
communications error
Description
FDJ
N
N
NW
GT
GT
GT
GT
GT
GT
14 (0EH) Fuse blown
16 (10H) Charger circuit fault
17 (11H) Heat sink overheat
18 (12H)
19 (13H) Inverter overheat
20 (14H)
Alarm issued by an external
device
Motor protection
(PTC thermistor)
HWU
RDH
J
J
J
J
37 (25H) Tuning error
38 (26H) RS-485 communications error
46 (2EH) Output phase loss
51 (33H)
53 (35H)
54 (36H)
30
Data saving error due to
undervoltage
RS-485 communications error
(option)
LSI error
(Power printed circuit board)
GT
GT
RN
GTH
GTR
GTJ
Page 33

Chapter 10 APPLICATION PROGRAM EXAMPLES
(
r
g
)
10.1 System Configuration
Station #1 Station #2
Sequencer
Power
supply
Q61P-A1
Insert the terminating resistor that comes
with the master unit between DA and DB.
CPU CC-Link
Q02CPU
master
QJ61BT11N
unit
Input
unit
QX40
X20
CC-Link
FRENIC-Multi FRENIC-Multi
OPC-E1-CCL OPC-E1-CCL
Setthe
ti
mina n
te
resistor switch
ON.
o31=1 o31=2
Figure 10.1 System Configuration
10.2 Network Parameter Settings
In program examples given in this chapter, the network parameters of the master unit are set as listed in Table
10.1
Table 10.1 Network Parameter Settings of the Master Unit
Parameter Settings
Start I/O No.
For units where a data link
Operation settings
error is detected
At the time of CPU stop Refresh
pe
Ty
Mode Remote Net Ver.1 mode
T
otal number of slaves connected
Remote input (RX) X1000
Remote
Remote
output (RY)
register (RWr)
Remote register (RWw) W100
pecial relay (SB)
S
Special register (SW) SW0
Re
try count
Automatic reconnection station count
For CPU down Stop
Scan mode
0000
Clear input
Master unit
2
Y1000
W0
SB0
3
1
Asynchronous
31
Page 34

10.3 Relationship between Master Station Device and Remote I/O and Remote Register
(1) Remote I/Os
Figure 10.2 shows the relationship between the master station devices and remote I/Os (RX and RY) in the
program examples given on the following pages.
Master station Remote station Rem ote station
(Station #1) (Station #2)
X100F to X1000
X101F to X1010
X102F to X1020
X103F to X1030
X104F to X1040
X105F to X1050
Y100F to Y1000
Y101F to Y1010
Y102F to Y1020
Y103F to Y1030
Y104F to Y1040
Y105F to Y1050
RX F to RX 0
RX 1F to RX 10
RX F to RX 0
RX 1F to RX 10
RY F to RY 0
RY 1F to RY 10
RY F to RY 0
RY 1F to RY 10
Figure 10.2 Relationship between Master Station Devices and Remote I/Os
(2) Remote registers
Figure 10.3 shows the relationship between the master station devices and remote registers (RWw and RWr) in
the program examples given on the following pages.
Master station Remote station Rem ote station
(Station #1) (Station #2)
W 10 0
W 10 1
W 10 2
W 10 3
W 10 4
W 10 5
W 10 6
W 10 7
W 10 8
W 10 9
W 10 A
W 10 B
RW w0
RW w1
RW w2
RW w3
RW w0
RW w1
RW w2
RW w3
W 00 0
W 00 1
W 00 2
W 00 3
W 00 4
W 00 5
W 00 6
W 00 7
W 00 8
W 00 9
W 00 A
W 00 B
RW r0
RW r1
RW r2
RW r3
Figure 10.3 Relationship between Master Station Devices and Remote Registers
32
RW r0
RW r1
RW r2
RW r3
Page 35

10.4 CC-Link Startup Program
Shown below is a CC-Link startup program example to run for ACPU.
No startup program is required for QCPU which starts up CC-Link communication with the network parameter
settings made in the master unit.
X00 X0F
Unit fai lure Uni t ready
One scan ON
Unit fai lure Uni t ready
ʳ
M300
M
301
M9038
after RUN
ʳʳ
X00 X0F
ʳ
M302
303
M
PLS M300
SET
H0 H1 K2
TO
H0
TO
TO H0 H21 H1102 K1
H20 H1101
M301
K1
K1
RST M301
SET Y00
M302
PLS
SET M303
Y06
SE
T
Permission to write settings
Request to write settings
Number of units connected = 2
St
ation info on inverter (Station #1)
Station info on inverter (Station #2)
Writi ng of se tti ngs co mpleted
Permission to bit outp ut (If OFF, no RY
output yet.)
ermission to write settings
P
Request to write settings
Link start request
ʳ
ʳ
X0
6
Li
nk startup
normall y
completed
X07
Li
nk startup
abnormally
terminated
RST
RST
FROM
H0
ʳʳ
H668 D315 K1
RST
RST
Y06
M303
Y06
M303
Cancel of link start request
Link startup com
R
ead link special device
Can
cel of link start request
Link startup completed
pleted
ʳʳ
Figure 10.4 CC-Link Startup Program Example (for ACPU only)
10.5 Program Example Using the Inverter Running Status Read
The program example shown below turns ON the auxiliary relay M100 when FRENIC-Multi station #1 starts
running.
X0 X0F X1
Unit
Unit
failure
M0
Inverter running (RX02)
Host station
X1002
BMOV SW80 K4MO K4
edready being link
M100
Read out data link status of slave
stations
Tu
rn ON the auxiliary relay M100
Figure 10.5 Program Example
33
Page 36

10.6 Program Example for Changing the Operation Mode
The program example shown below switches the operation mode of FRENIC-Multi station #1 to network
operation (specifying CC-Link as both run command and frequency command sources).
X0 X0F X1
t failure Unit Host sta tion
Uni
M0
M300
Command code
execution
completed
ready being linked
X20
Writing
ON
BMOV SW80 K4M0 K4
PLS M300
SET M301
MOV H0FB W102
MOV H0 W 103
Read out data link s tatus of slave
stations
Write the “Operation mode”
command code (HFB) into RWw2 ,
and object data (H0000) into RW w3
M302
Command code
exec
completed
X100F
ution
SET Y100F
RST M301
SET M302
MOV W2 D2
RST Y100F
RST M302
END
Turn command code execution
request (R YF) ON
W
hen the comma nd code execution
completed signa l (RXF) is turned ON,
the response code (RWr2) is read
out into D2. (0: Reading out has
normally finis hed.)
Turn command code execution
request (RYF) OFF
Figure 10.6 Program Example
10.7 Program Example for Specifying Run Command
The program example shown below writes the run forward command (FWD) into FRENIC-Multi station #1
X0 X0F X01
t failure Unit Host stati on
Uni
ready being li nked
M0
Run ON
BMOV SW80 K4M0
K4
Y1000
Read out data link status of slave
stations
Run forward comma nd (RY0)
Figure 10.7 Program Example
34
EN
D
Page 37

10.8 Program Example for Monitoring the Output Frequency
The program example shown below reads out the output frequency from FRENIC-Multi station #1 into data
register D1.
X00
X0F
X01
Unit Unit
failure
ready being linked
M0
X20
Writing
ON
Host station
BMOV
SW80
K4M0 K4
MOV H1 W100
Y100C
Read out data link status of slave
stations
the monitor item code (H01) of
Write
output frequency into RWw0
Turn mo nitor comma nd (RYC ) ON
X100C
Monitoring
MOV W0 D1
ND
E
Turning RYC ON reads out the output
frequency from the remote register
(RWw0) into D1. ʳʳ
Figure 10.8 Program Example
10.9 Program Example for Reading from the Inverter's Function Code Data
The program example shown below reads out the F07 data (Acceleration time 1) from FRENIC-Multi station #1
X0 X0F X1
Un
it failure
M300
M
Unit
ready being linked
M0
301
X20
Writing
ON
X100F
and code
Comm
execution
completed
Host station
BMOV SW80 K4M0
PLS M300
SET
MOV
H7
SET
RST
K4
M301
W102
Y100F
M301
Read out data link status of slave
stations
Write the “Read F07” command code
(H07) into RW w2
Turn command code execution
request (RYF) ON
M302
X100F
mmand code
Co
execution
comple ted
SET
MOV
MOV
W3
W2
RST
RST
Figure 10.9 Program Example
35
M302
D1
D2
Y100F
M302
END
When the command code execution
completed signa l (RXF ) is t urned ON,
the acce leration time 1 (RW r3) and
response code (RWr2) are read out
into D1 and D2, respectively
ʳʳ
Turn command code execution
request (RYF) OFF
Page 38

10.10 Program Example for Writing to Inverter's Function Code Data
The program example shown below writes 3.0 s to the F07 data (Acceleration time 1) of FRENIC-Multi station
#1.
X0 X0F X1
Unit failure Unit
M0
M300
01
M3
Command code
M302 X100F
Command code
ready
X20
Writing
ON
X100F
execution
completed
execution
completed
Host station
being linked
OV SW80 K4M0 K4
BM
PLS
SET M301
MOV H87 W102
MOV H12C W103
SET Y100F
RST M301
SET M302
MOV W2 D2
RST Y100F
RST M302
M300
Read out data li nk status of s lave
stations
Write the “W rite F07” comma nd code
(H87) into RWw2, and the
acceleration time (H12C) i nto RWw3
Turn comma nd code e xecutio n
request (RYF) ON
hen the comma nd code execution
W
completed signa l (RXF) is turned ON,
the response code is read out from
the remote register (RWr2) into D2.
(0: Writing normally comp leted.)
Turn comma nd code executio n
request (R YF) OFF
Figure 10.10 Program Example
END
36
Page 39

10.11 Program Example for Setting up the Reference Frequency
The program example shown below writes the reference frequency 50.00 Hz to FRENIC-Multi station #1.
X0 X0F X1
Unit failure
M0
M300
01
M3
Frequency setti ng
completed
Unit
Host station
re
ady being linked
X20
Writing
ON
X100D
BMOV SW80
K4M0 K4
PLS M300
T M301
SE
MOV K5 000 W101
SET Y100D
RST M301
SET M302
d out data link status of slave
Rea
stations
Write refe rence freq uenc y into RWw1
Turn the frequency command RAM
(RYD) ON
M302
X100D
Frequency setti ng
completed
W2
MOV
D2
RST
Y100D
RST M302
Figure 10.11 Program Example
END
W
hen the freque ncy setti ng
completed signal (RXD) is turned
ON, read out the response code
(RWr2) into D2
T
urn the freque ncy co mma nd RAM
(RYD) OFF
37
Page 40

10.12 Program Example for Reading out Alarm Codes
The program example shown below reads out alarm codes stored in FRENIC-Multi station #1 into data register
D1.
X0F X1
X0
Unit failure
M300
M3
M302
Unit
ady being linked
re
M0
01
mmand code
Co
execution
com
mmand code
Co
execution
completed
X20
Writing
ON
X100F
pleted
X100F
Host station
BMOV SW80 K4M0 K4
PLS M300
M301
SET
MOV H74
SET
MOV
MOV
W102
Y100F
RS
T M301
SET M302
W3
D1
W2
D2
Read out data link status of slave
stations
Write the “Read from the latest and
last alarm codes” command code
(H74) i nto RW w2
Turn command code execution
r
equest (RYF) ON
hen the command code execution
W
complete d signa l (RXF ) is t urned ON,
read out alarm code (RWr3) and
res
ponse code (RWr2) into D1 and
D2, respecti vely
RS
T Y100F
T M302
RS
END
Turn command code execution
request (RYF) OFF
Figure 10.12 Program Example
10.13 Program Example for Resetting a Inverter Trip
The program example shown below resets a trip that has occurred in FRENIC-Multi station #1.
X0 X0F X01
Unit fai lure Unit
M0
stat us flag reset request ON
Host station
ready being linked
X101A X20
Alarm
Alarm
BMOV
SW80 K4M0 K4
Figure 10.13 Program Example
Y1
END
01A
Read out data link status of slave
ns
statio
Turn
X20 from ON to OFF to reset
the trip
38
Page 41

Chapter 11 TROUBLESHOOTING
(1) Option error ( ) (2)
If a
has occurred
.
cause of the error referring to the RAS information in
the sequencer CPU. For the access
information and its contents, see the Sequencer User s
Do the CC-Link
versions of the slave
and master sta tions
match with each other ?
(master station version
1.xx, slave station
version 2.xx)
YES
Is the option m ounted
on the inverter
correctly?
NO
Mount the op tion i nto
place refe rring to th is
manual
.
Match the versions of
NO
the mast er stat ion and
the slave station with
each other
YES
The option or in verter
unit may be defective.
Con tact F uji El ectric.
.
Manual
(3) Commands via CC-Link not reflected
Comm ands rec eived
via CC-Link are not
reflected
.
Is the data of f un cti on
code y98 set to any
value other than
0 ?
YES
Is [LE] assi gned to X
function?
NO
Is the L. ERR LED on
the option lit or
blinking?
NO
Is the settin g of the
function code o30
"CC-Link extension"
correct?
YES
Is the comm and code
format for specifying
function code(s)
correct?
NO
Corre c t y98 data
YES
Tur n ON the
appropr ia te c onta ct
YES
Check the CC-Link
wiring and the
sequenc er CPU
settings
NO
Match the setting of
o30 with that of the
master
NO
Correct the format,
referring to the RS-485
Com m unicat i on Us er
Manual, Chapter 5
.
.
.
.
s
.
Network error (
)
network error (CC-Link error) occurs, analyze the
to
the RAS
.
has occurred
Is the pow er to t h e
sequencer shut down?
Or is the master uni t
detached?
Does the detailed RAS
information in the CPU
module indicate that
an error has occurred?
Is the station address
setting (o31) correct?
Any of the fol lowing
wiring problems?
Wire(s) broken
Wrong connection
to the te rminal blo ck
Signal lines wired in
parallel with power line
Terminating resistor
setting
CC-Link cable not
used
Maximum cable
length, inter-station
cable length, and the
number of units
connec t
ed, out of
speci fications
The option or inverter
unit may be defective.
Contact Fuji Electric.
NO
NO
YES
No
.
Turn ON the power to
YES
the sequencer, reset
the CPU, and reset
the inverter.
can be resumed
YES
Remove the error
factor from the station
concerned and reset
the inverter.
Make the station
NO
addre ss of o31 match
that in the system
configurati on
definition
.
Operation
.
Yes
Correct the wiring.
YES
Is data w ritten into the
buffer memory areas
(RX, RY, RWw, RW r)
as assi gn ed to
addresses?
YES
The option or in vert er
unit ma y be de f ec ti ve
Contact Fuji Electric.
NO
Check wri ting to the
I/O memory areas.
.
39
Page 42

Chapter 12 SPECIFICATIONS
12.1 General Specifications
For items not contained in the following table, the specifications of the inverter apply.
Item Specifications
Input power voltage 21.6 to 27.0 V
Power consumption Max. 150 mA, 24 VDC
Operating ambient temperature -10 to +50 C(14 to + 122 F)
Operating ambient humidity 5 to 95% RH (There shall be no condensation.)
External dimensions 79.6 x 127 x 47.5 mm(3.13 x 5 x 1.87 in)
12.2 CC-Link Specifications
For the items not contained in the following table, the CC-Link specifications apply.
Specifications
Name CC-Link interface option
Station type Remote device station
Number of units
connectable
Number of stations
occupied
CC-Link version The option complies with CC-Link versions 1.10 and 2.00. It can be configured with the
Terminal block for
connection
Communications cable CC-Link dedicated cable -Use the CC-Link dedicated cable in CC-Link system. -Using a
Station address 1 to 64. The station address can be specified with the inverter's function code o31.
Transmission speed
(Baud rate)
LED status indicators
Max. 42 units (one station occupied/unit), compatible with other options
1
function code o30 as follows: 1 station occupied (CC-Link version 1.10): o30 = 0 or 1 1
station occupied with 2X setting (CC-Link version 2.00): o30 = 2 1 station occupied with
4X setting (CC-Link version 2.00): o30 = 3 1 station occupied with 8X setting (CC-Link
version 2.00): o30 = 4 Setting invalid: o30 = Other than the above data
5-pin terminal block (M3×5 screws)
cable other than a CC-Link dedicated cable does not assure the CC-Link system
performance. -For further information about the CC-Link dedicated cable specifications
and inquiries, visit the CC-Link Partner Association's website at:
http://www.cc-link.org/eng/t_html/top.html
10 Mbps (o32 = 4), 5 Mbps (o32 = 3), 2.5 Mbps (o32 = 2), 625 kbps (o32 = 1), 156 kbps
(o32 = 0) The transmission speed can be specified with the inverter's function code o32.
L.RUN: Lights when the option is normally receiving refresh data. It goes off if data
transmission is interrupted for a certain period of time. L.ERR: Lights when a
communications error has occurred . It blinks if the station address (o31) or the
transmission speed (o32) is changed when the power is on. RUN: Lights during
normal communication . It blinks when mismatch in CC-Link version settings is found
or the connection between the inverter and the option is cut. SD: Lights during data
transmission. RD: Lights during data reception.
40
Page 43

CC-Link Interface Option "OPC-E1-CCL"
Instruction Manual
First Edition, December 2006
Fuji Electric FA Components & Systems Co., Ltd.
The purpose of this manual is to provide accurate information in the handling, setting up and operating of CC-Link Interface Option "OPC-E1-CCL" for the
FRENIC-Multi series of inverters. Please feel free to send your comments regarding any errors or omissions you may have found, or any suggestions you
may have for generally improving the manual.
In no event will Fuji Electric FA Components & Systems Co., Ltd. be liable for any direct or indirect damages resulting from the application of the information
in this manual.
Page 44

MEMO
Page 45

Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd.
Fuji Electric Corp. of America
47520 Westinghouse Drive Fremont, CA 94539, U.S.A.
Tel.+1-510-440-1060 Fax.+1-510-440-1063
Toll-free support 1-888-900-FUJI(3854)
INR-SI47
-1175-EU Rev 052010 Information subject to change without notice.
http://www.fujielectric.com/fecoa/
 Loading...
Loading...