Page 1

MARS Motherboard
User’s Manual
Page 2
Statement:
This manual is the intellectual property of Foxconn, Inc. Although the information
in this manual may be changed or modied at any time, Foxconn does not obligate
itself to inform the user of these changes.
Trademark:
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Version:
User’s Manual V1.2 for MARS Series motherboard.
P/N: 3A2216E00-000-G
Symbol description:
Caution: refers to important information that can help you to use motherboard
better, and tells you how to avoid problems.
Warning: indicating a potential risk of hardware damage or physical injury may
exist.
WEEE:
The use of this symbol indicates that this product may not be treated as household
waste. By ensuring this product is disposed of correctly, you will help prevent potential
negative consequences for the environment and human health, which could otherwise
be caused by inappropriate waste handling of this product. For more detailed
information about recycling of this product, please contact your local city ofce, your
household waste disposal service or the shop where you purchased this product.
More information:
If you want more information about our products, please visit Foxconn’s
website: http://www.foxconnchannel.com
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
W
A
R
N
I
N
G
!
© All rights reserved.
All trade names are registered trademarks of respective manufacturers listed.
All images are for reference only, please refer to the physical motherboard for specic features.
Page 3
Declaration of conformity
HON HAI PRECISION INDUSTRY COMPANY LTD
66 , CHUNG SHAN RD., TU-CHENG INDUSTRIAL DISTRICT,
TAIPEI HSIEN, TAIWAN, R.O.C.
declares that the product
Motherboard MARS
is in conformity with
(reference to the specication under which conformity is declared in
accordance with 89/336 EEC-EMC Directive)
■ EN 55022: 1998/A2: 2003 Limits and methods of measurements of radio
disturbance characteristics of information technology
equipment
■ EN 61000-3-2/:2000 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Part 3: Limits
Section 2: Limits for harmonic current emissions
(equipment input current <= 16A per phase)
■ EN 61000-3-3/A1:2001 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Part 3: Limits
Section 2: Limits of voltage uctuations and icker in low
voltage supply systems for equipment with rated current <=
16A
■ EN 55024/A2:2003 Information technology equipment-Immunity characteristics
limits and methods of measurement
Signature : Place / Date : TAIPEI/2008
Printed Name : James Liang
Page 4

Declaration of conformity
Trade Name: FOXCONN
Model Name: MARS
Responsible Party: PCE Industry Inc.
Address: 458 E. Lambert Rd.
Fullerton, CA 92835
Telephone: 714-738-8868
Facsimile: 714-738-8838
Equipment Classication: FCC Class B Subassembly
Type of Product: Motherboard
Manufacturer: HON HAI PRECISION INDUSTRY
COMPANY LTD
Address: 66 , CHUNG SHAN RD., TU-CHENG
INDUSTRIAL DISTRICT, TAIPEI HSIEN,
TAIWAN, R.O.C.
Supplementary Information:
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions : (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device
must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Tested to comply with FCC standards.
Signature : Date : 2008
Page 5
Installation Precautions
Please carefully read the following procedures to install your computer :
■ It is suggested to select high-quality, certied fans in order to avoid damage
to the motherboard and CPU due to high temperature. Never turn on the
computer if the CPU fan is not properly installed.
■ We cannot guarantee that your system can operate normally when your
CPU is overclocked. Normal operation depends on the overclocking capacity of your device.
■ If there is any, when connecting USB, audio, 1394a, RS232 COM, IrDA or
S/PDIF cables to the internal connectors on the motherboard, make sure
their pinouts are matching with the connectors on the motherboard. Incorrect
connections might damage the motherboard.
■ When handling the motherboard, avoid touching any metal leads or connectors.
■ If there is a PCI Express x16 graphics card installed in your system, we
recommend using a 24-pin ATX power supply to get the best performance.
■ Before turning on the power, please make sure the power supply AC input
voltage setting has been congured to the local standard.
■ To prevent damage to the motherboard, do not allow screws to come in contact
with the motherboard circuit or its components. Also, make sure there are no
leftover screws or metal components placed on the motherboard or within the
computer casing.
■ If you are uncertain about any installation steps or have a problem related to
the use of the product, please consult a certied computer technician.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
■ Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden and momentary electric current
that ows between two objects at different electrical potentials. Normally it
comes out as a spark which will quickly damage your electronic equipment.
Please wear an electrostatic discharge (ESD) wrist strap when handling
components such as a motherboard, CPU or memory.
■ Ensure that the DC power supply is turned off before installing or removing
CPU, memory, expansion cards or other peripherals. It is recommended to
unplug the AC power cord from the power supply outlet. Failure to unplug
the power supply cord may result in serious damage to your system.
W
A
R
N
I
N
G
!
Page 6

TAble of CoNTeNTS
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
Package List......................................................................................2
Product Specications.......................................................................3
Layout ...............................................................................................5
Back Panel Connectors.....................................................................6
Chapter 2 Hardware Install
Install the CPU and CPU Cooler .......................................................9
Install the Memory ...........................................................................12
Install an Expansion Card ...............................................................14
Install other Internal Connectors .....................................................15
Jumpers ..........................................................................................19
Onboard Button ...............................................................................20
Onboard LED ..................................................................................20
Chapter 3 bIoS Setup
Enter BIOS Setup............................................................................22
Main Menu ......................................................................................22
Standard CMOS Features...............................................................24
Advanced BIOS Features ...............................................................26
Advanced Chipset Features ............................................................28
Integrated Peripherals .....................................................................29
Power Management Setup..............................................................33
PnP/PCI Congurations ..................................................................36
PC Health Status.............................................................................37
Gladiator BIOS ...............................................................................38
Load Fail-Safe Defaults...................................................................44
Load Optimized Defaults ................................................................44
Set Supervisor Password ................................................................44
Set User Password .........................................................................44
Save & Exit Setup ...........................................................................44
Exit Without Saving .........................................................................44
Chapter 4 CD Instruction
Utility CD Introduction .....................................................................46
AEGIS PANEL
Main Panel .................................................................................49
Page 7
Overclocking ...............................................................................50
HWM INFO. ................................................................................51
ALARM .......................................................................................52
CONFIG .....................................................................................53
FOX LiveUpdate
Local Update ..............................................................................
54
Online Update ............................................................................56
Congure ...................................................................................59
About & Help ..............................................................................61
Chapter 5 RAID Conguration
RAID Conguration Introduction .....................................................64
Intel® Matrix Storage Manager ........................................................66
Create a RAID Driver Diskette ........................................................67
BIOS Conguration .........................................................................69
Create RAID in BIOS ......................................................................69
Create RAID Volume ..................................................................70
Delete RAID Volume ..................................................................86
Reset Disks to Non-RAID ...........................................................88
Exit RAID BIOS ..........................................................................92
Install a New Windows XP ..............................................................93
Existing Windows XP with RAID built as data storage ....................97
Appendix - Crossfile
TM
Technology ................................................101
Technical Support :
Website :
http://www.foxconnchannel.com
Support Website :
http://www.foxconnsupport.com
Worldwide online contact Support :
http://www.foxconnchannel.com/support/online.aspx
CPU, Memory, VGA Compatibility Supporting Website :
http://www.foxconnchannel.com/product/Motherboards/compatibility.aspx
Support
Page 8
Thank you for buying Foxconn Quantum Force series motherboardMARS. Foxconn Quantum Force products are engineered to
maximize computing power, providing only what you need for
break-through performance.
With advanced overclocking capability and a range of connectivity
features for today multi-media computing requirements, MARS
enables you to unleash more power from your computer.
This chapter includes the following information:
■ Package List
■ Product Specications
■ Layout
■ Back Panel Connectors
Page 9
2
1
Package List
Check your product package for the following items:
Before your purchase, if any of the above items is damaged or missing, please contact
your retailer. Accessories are not in the warranty, only motherboard is.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Motherboard Foxconn MARS motherboard
I/O modules 1 x USB 2.0 x 2 ports and 1 x 1394a module
Cables 4 x SATA Power and Signal cables
2 x SATA Power and Signal cables right angle
1 x Ultra DMA 133/100/66 cable
1 x Floppy Disk Drive cable
Accessory I/O Shield
1 x Foxconn Optional Fan
Application CD Foxconn motherboard support CD
Documentation User’s Manual
Easy Guide
Registration Card
Quantum Force stickers
Quantum Force tattoos
Quantum Force Dogtags
Page 10

3
1
1-1 Product Specications
CPU Support LGA775 socket Intel® CPU:
CoreTM 2 Extreme / CoreTM 2 Quad / CoreTM 2 Duo
Pentium® 4 Extreme Edition / Pentium® D / Pentium® 4 processors
Future-proof supporting for 45nm processors
Support Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology
Front Side Bus 1333/1066/800 MHz FSB
Chipset North Bridge: Intel® P35 chipset
South Bridge: Intel® ICH9R
Memory 4 x 240-pin DDR2 DIMM sockets
Support up to 8GB of system memory
Dual channel DDR2 1066(oc*)/800/667MHz architecture
(oc*: Overclocking)
Audio Realtek ALC888 chip
High Denition Audio
2/4/5.1/7.1-channel
Support for S/PDIF out
Support Jack-Sensin function
LAN On board Realtek 8111B chip
Support 10/100/1000 Mb/s Ethernet
Expansion Slots 2 x PCI Express x16 slots(1 x PCI-E x16 mode, 1 x PCI-E x4 mode)
2 x PCI Express x1 slots
3 x PCI slots
Onboard Serial ATA 6 x SATA connectors
1 x External SATA connector
300MB/s data transfer rate
Support hot plug and NCQ (Native Command Queuing )
Support RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10
Support Intel® Matrix Storage Technology
USB Support hot plug
Support up to 12 USB 2.0 ports (6 rear panel ports, 3 onboard USB
connectors providing 6 extra ports)
Supports USB 2.0 protocol up to 480Mb/s
Internal Connectors 1 x 24-pin ATX main power connector
1 x 8-pin ATX 12V power connector
1 x AUX Power connector
1 x Floppy disk drive connector
1 x IDE connector
6 x SATA connectors
3 x USB 2.0 connectors (supporting 6 x USB devices)
1 x CPU fan header (4-pin)
1 x System fan header (3-pin)
1 x NB fan header (3-pin)
2 x Power fan headers (3-pin)(FAN1, FAN2)
1 x Front panel connector
Page 11

4
1
1 x 1394a connector
1 x CD_IN connector
1 x Front audio connector
1 x Speaker connector
1 x COM1 connector
1 x IrDA connector
Back Panel 1 x PS/2 Keyboard port
Connectors 1 x PS/2 Mouse port
1 x Optical S/PDIF out connector
1 x Coaxial S/PDIF out connector
6 x USB 2.0 ports
1 x RJ-45 LAN port
1 x 1394a port
1 x External SATA port
6 x Audio jacks
Hardware Monitor System voltage detection
CPU/System/NB temperature detection
CPU/System/NB fan speed detection
System voltage warning
CPU/System/NB overheating warning
CPU/System/NB fan speed control
Onboard 1394a Support hot plug
400Mb/s transmission rate
Support 2 independent 1394a units synchronously at most
PCI Express x1 Support 250MB/s (500MB/s concurrent) bandwidth
Low power consumption and power management features
PCI Express x16 Support 4GB/s (8GB/s concurrent) bandwidth
Low power consumption and power management features
PCI Express x4 Support 1GB/s (2GB/s concurrent) bandwidth
Low power consumption and power management features
Green Function Support ACPI (Advanced Conguration and Power Interface)
Support S0 (normal), S1 (power on suspend), S3 (suspend to RAM), S4
(suspend to disk), and S5 (soft - off)
Bundled Software AEGIS PANEL
FOX LiveUpdate
Operating System Support for Microsoft® Windows® Vista/XP/2000
Form Factor ATX Form Factor, 12 inches x 9.6 inches (30.5cm x 24.4cm)
Page 12
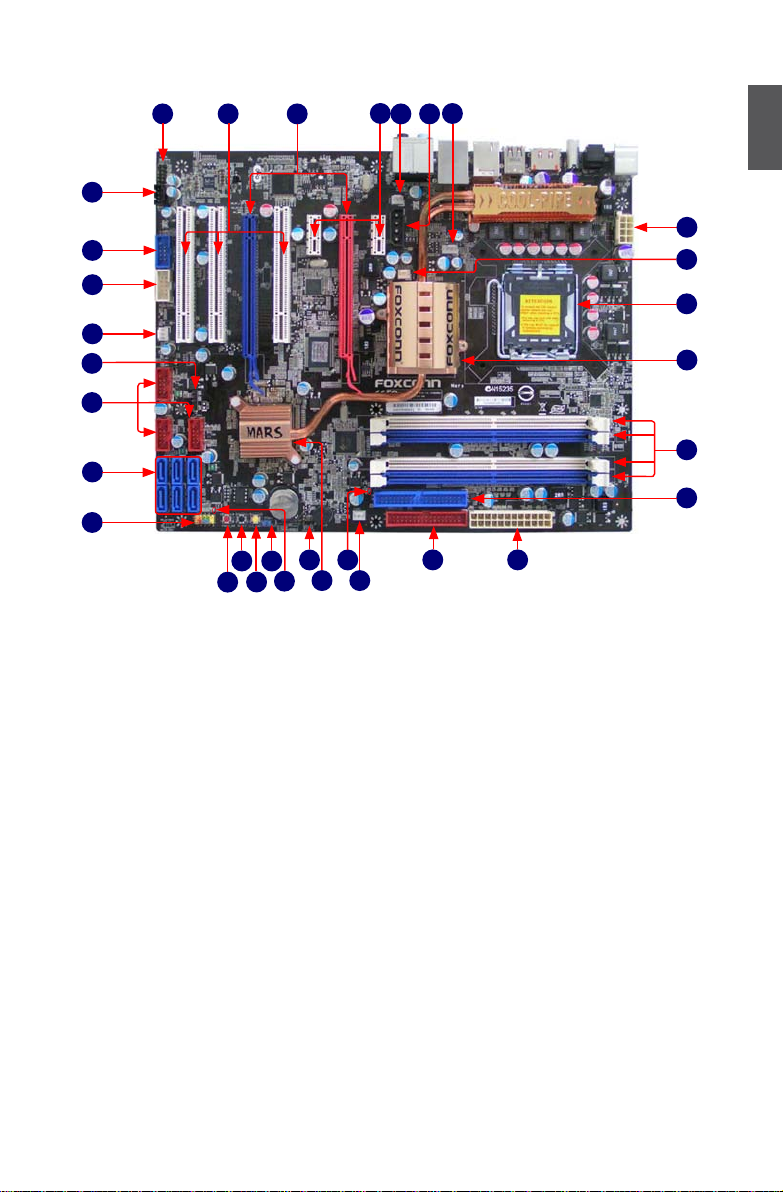
5
1
1-2 layout
1. CPU_FAN Header 17. Reset Button
2. AUX Power Connector: PWR3 18. Clear CMOS Button
3. FAN1 Header 19. Clear CMOS Jumper
4. PCI Express x1 Slots 20. +5V Standby LED
5. PCI Express x16 Slots 21. Speaker Connector
6. PCI Slots 22. South Bridge: Intel® ICH9R
7. Front Audio Connector 23. DRAM Power LED
8. CD_IN Connector 24. FAN2 Header
9. 1394a Connector 25. FLOPPY Connector
10. COM1 Connector 26. 24-pin ATX Power Connector
11. SYS_FAN Header 27. IDE Connector: PIDE
12. IrDA Connector 28. DDR2 DIMM Slots
13. Front USB Connectors 29. North Bridge: Intel® P35 Chipset
14. SATA Connectors 30. LGA 775 CPU Socket
15. Front Panel Connectors 31. NB_FAN Header
16. Power on Button 32. 8-pin ATX 12V Power Connector
10
1
2
11
13
14
15
16
171819
20
21 23
22
26
27
25
30
31
3
5
4
67
8
9
32
12
24
28
29
Note : The above motherboard layout is for reference only, please refer to the physical
motherboard for detail.
Page 13
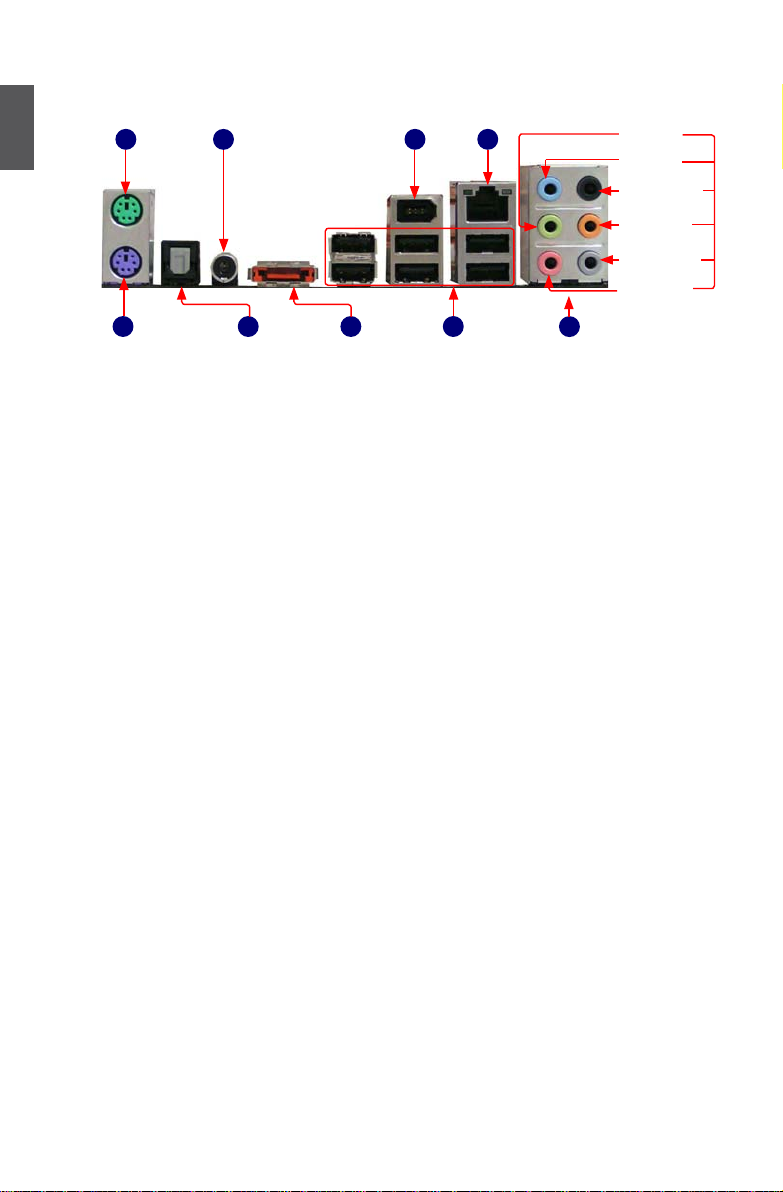
6
1
1-3 back Panel Connectors
1. PS/2 Mouse Port
Use the upper port (green) to connect a PS/2 mouse.
2. PS/2 Keyboard Port
Use the lower port (purple) to connect a PS/2 keyboard.
3. optical S/PDIf out Connector
This connector provides digital audio out to an external audio system that supports digital optical
audio.
4. Coaxial S/PDIf out Connector
This connector provides digital audio out to an external audio system that supports digital coaxial
audio. Before using this feature, ensure that your audio system provides a coaxial digital audio in
connector.
5. external SATA Port
To connect external SATA device(s) to your system by expanding the internal SATA port(s) to the
chassis back panel. External SATA device shall provide power by its own.
6. USb Ports
The USB port supports the USB 2.0/1.1 specication. Use this port for USB devices such as an
USB keyboard/mouse, USB printer, USB ash drive and etc.
External
SATA Port
USB Ports
LAN PortCoaxial S/PDIF Out
PS/2 Keyboard Port
PS/2 Mouse Port
Line Out
Microphone
Subwoofer
Rear Speaker
Side Speaker
Line In
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
Optical
S/PDIF Out
1394a Port
Audio Ports
Page 14
7
1
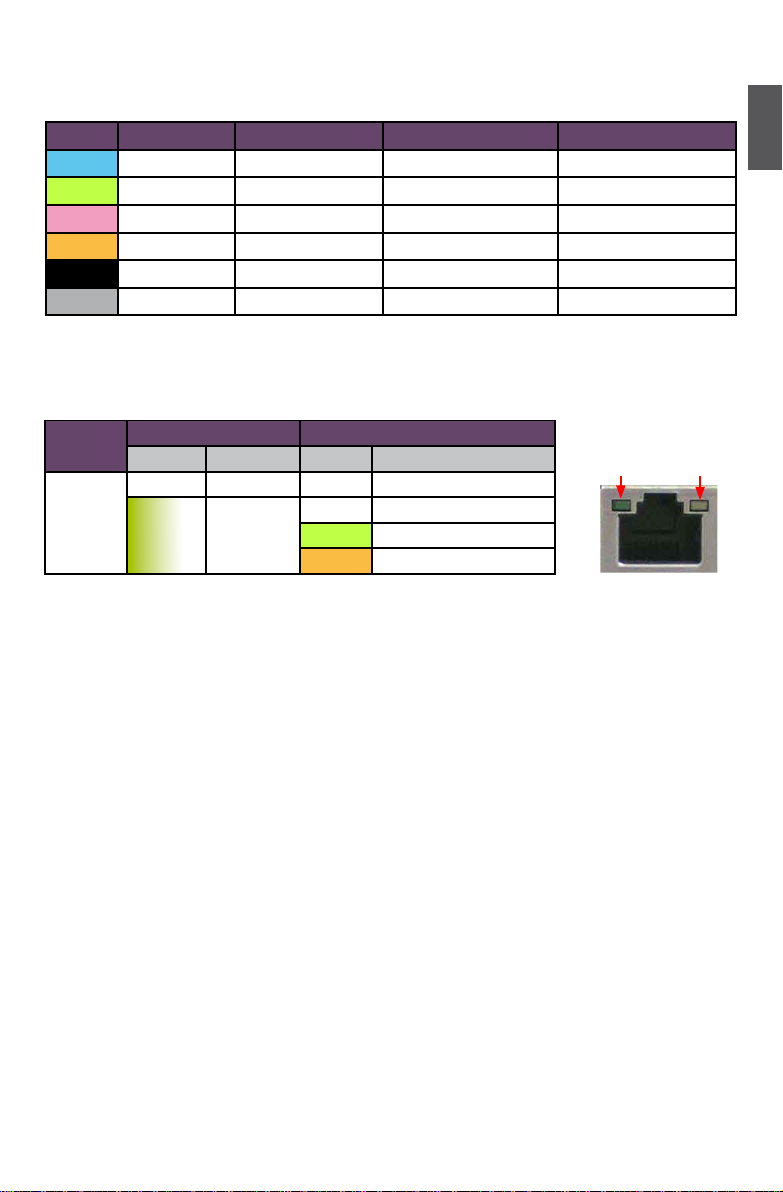
7. Audio Connectors
For the denition of each audio port, please refer to the table below :
8. RJ-45 lAN Port
The Gigabit Ethernet LAN port provides Internet connection at up to 1Gb/s data rate.
9. 1394a Port
This port is used to connect a 1394a device.
Port 2-channel 4-channel 5.1-channel 7.1-channel
Blue Line In Line In Line In Line In
Green Line Out Front Speaker Out Front Speaker Out Front Speaker Out
Pink Microphone In Microphone In Microphone In Microphone In
Orange - - Center/Subwoofer Out Center/Subwoofer Out
Black - Rear Speaker Out Rear Speaker Out Rear Speaker Out
Grey - - - Side Speaker Out
LAN Type
Left: Active Right: Link
Status Description Status Description
1000M
Off No Link Off No Link
Green
Blinking
Data
Activity
Off 10 Mb/s Connection
Green 100 Mb/s Connection
Orange 1000 Mb/s Connection
Active
LED
Link
LED
Page 15
This chapter introduces the hardware installation process, including
the installation of the CPU, memory, power supply, slots, pin
headers and the mounting of jumpers. Caution should be exercised
during the installation of these modules. Please refer to the
motherboard layout prior to any installation and read the contents in
this chapter carefully.
This chapter includes the following information :
■ Install the CPU and CPU Cooler
■ Install the Memory
■ Install an Expansion Card
■ Install other internal Connectors
■ Jumpers
■ Onboard Button
■ Onboard LED
Please visit this website for more supporting information about CPU, Memory and
VGA for your motherboard :
http://www.foxconnchannel.com/product/Motherboards/compatibility.aspx
Page 16
9
2
2-1 Install the CPU and CPU Cooler
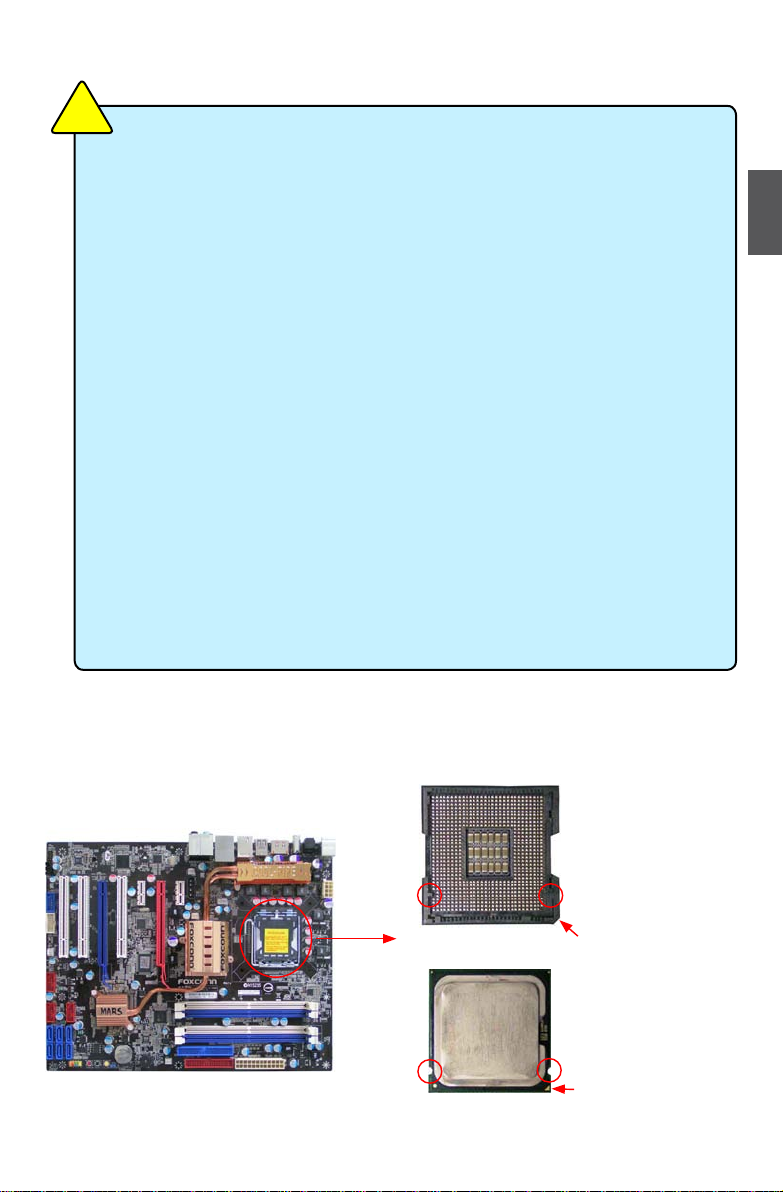
Install the CPU
Locate the alignment keys on the motherboard CPU socket and the notches on the CPU.
LGA775 CPU Socket
Alignment Key
Pin_1 Corner of the
CPU Socket
LGA775 CPU
Notch
Pin_1 triangle marking
of CPU
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install the CPU :
■ Make sure that the motherboard supports the CPU.
■ Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power supply before
installing the CPU to prevent hardware damage.
■ Locate the Pin_1 of the CPU. The CPU cannot be inserted if oriented incorrectly. (Or
you may locate the notches on both sides of the CPU and alignment keys on the CPU
socket.)
■ Apply an even and thin layer of thermal grease on the surface of the CPU.
■ Do not turn on the computer if the CPU cooler is not installed, otherwise overheating
and damage of the CPU may occur.
■ Set the CPU host frequency in accordance with the CPU specications. It is not
recommended that the system bus frequency be set beyond hardware specications
since it does not meet the standard requirements for the peripherals. If you wish to
set the frequency beyond the standard specications, please do so according to your
hardware specications including the CPU, graphics card, memory, hard drive, etc.
Hyper-Threading Technology System Requirements:
(Go to Intel's website for more information about the Hyper-Threading Technology)
■ An Intel® CPU that supports HT Technology
■ A chipset that supports HT Technology
■ An operating system that is optimized for HT Technology
■ A BIOS that supports HT Technology and has it enabled
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Page 17

10
2
Follow the steps to install the CPU onto the CPU socket :
1. Remove protective socket cover. 2. Release the CPU socket lever.
3. Lift the metal cover on the CPU
socket.
5. When CPU is properly seated,
replace the metal cover and push the
CPU socket lever back to its locked
position.
4. Check pin one marking (triangle)
with the pin one corner of the CPU
socket, align the CPU notches with
the socket alignment keys and gently
put the CPU onto the socket.
Before installing the CPU, make sure to turn off the computer and unplug the power
cord from the power outlet to prevent damage to the CPU.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Page 18

11
2
Install the CPU Cooler
Follow the steps below to correctly install the CPU cooler on the motherboard. (The following
procedures use Foxconn cooler as the example.)
1. Apply and spread an even thermal
grease on the surface of CPU.
2. Place the four bolts of the CPU
cooler to the holes of the motherboard,
push them straight down from the top,
and the bolts will be fastened on the
motherboard. That's it.
3. Check the solder side of the
motherboard, the push pin should be
xed as depicted in the picture.
3
2
1
4. Attach the 4-wire CPU cooler
connector to the CPU FAN socket on
the motherboard .
Release bolts of CPU cooler from
motherboard :
1. Turning the push pin (bolt)
along with the direction of arrow
(counterclockwise).
2. Pull the push pin straight up.
3. Turning push pin clockwise to its
default position.
Use extreme care when removing the CPU cooler because the thermal grease may
adhere to the CPU. Inadequately removing the CPU cooler may damage the CPU.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Page 19
12
2
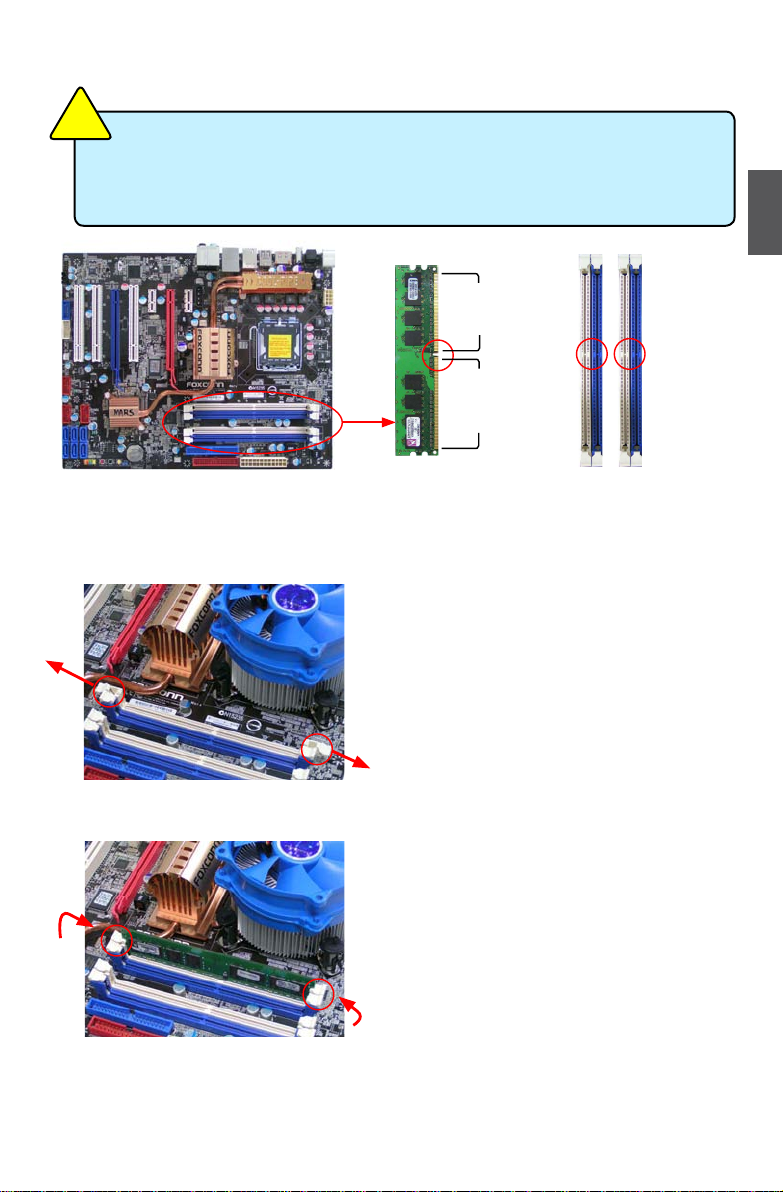
2-2 Install the Memory
Dual Channel Memory Conguration
This motherboard provides four DDR2 memory sockets and supports Dual Channel Technology.
When memory is installed, the BIOS will automatically check the memory in your system.
Four DDR2 memory sockets are divided into two channels and each channel has two memory
sockets as following:
Channel 0 : DIMM1, DIMM2
Channel 1 : DIMM3, DIMM4
The combinations of DIMM modules are :
DIMM1 DIMM2 DIMM3 DIMM4
Single Channel DS/SS - - Single Channel DS/SS DS/SS -
Single Channel - - DS/SS -
Single Channel - - DS/SS DS/SS
Double Channel DS/SS - DS/SS Double Channel - DS/SS - DS/SS
Double Channel DS/SS DS/SS DS/SS DS/SS
(DS : Double Side, SS : Single Side, - : No Memory)
It is recommended that memory of the same capacity, brand, speed, and chips be
used and please select dual channel rst to achieve optimum performance.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install the memory :
■ Make sure that the motherboard supports the memory. It is recommended that memory
of the same capacity, brand, speed, and chips be used.
■ Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before
installing the memory to prevent hardware damage.
■ Memory modules have a foolproof design. A memory module can be installed in only
one direction. If you are unable to insert the memory, switch the direction.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Page 20
13
2
Installing a Memory
If you take a look at front side of memory module, it has asymmetric pin counts on both sides separated
by a notch in the middle, so it can only t in one direction. Follow the steps below to correctly install
your memory modules into the sockets.
Step 1:
Spread the clips at both ends of the memory socket.
Place the memory module onto the socket, then put
your ngers on top edge of the module, and push
it down rmly and seat it vertically into the memory
socket.
Step 2:
The clips at both ends of the socket will snap into place
when the memory module is securely inserted.
Before installing a memory module, make sure to turn off the computer and unplug the
power cord from the power outlet to prevent damage to the memory module. Be sure
to install DDR2 DIMMs on this motherboard.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Notch
112-Pin128-Pin
Page 21
14
2
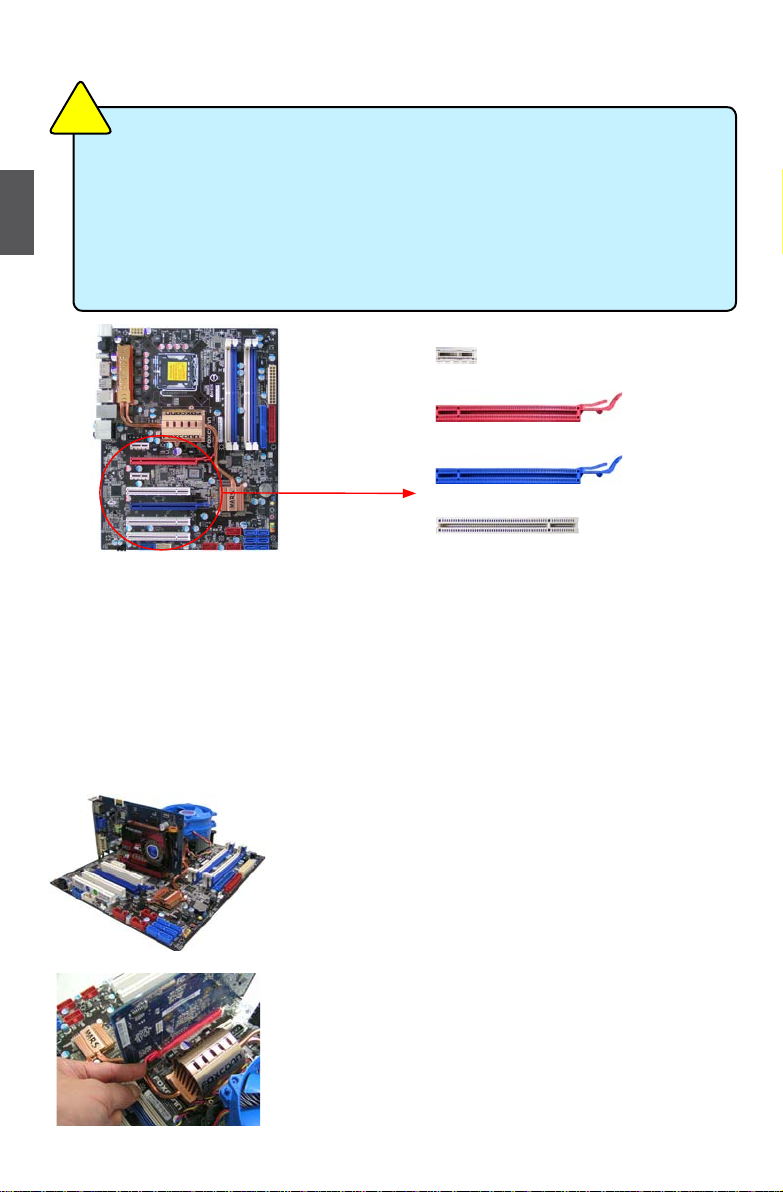
2-3 Install an expansion Card
Follow the steps below to correctly install your expansion card in the expansion slot.
1. Locate an expansion slot that supports your card. Remove the metal slot cover from the chassis
back panel.
2. Align the card with the slot, and press down on the card until it is fully seated in the slot.
3. Make sure the metal contacts on the card are completely inserted into the slot.
4. Secure the card's metal bracket to the chassis back panel with a screw.
5. After installing all expansion cards, replace the chassis cover.
6. Turn on your computer. If necessary, go to BIOS Setup to make any required BIOS changes for
your expansion card(s).
7. Install the driver provided with the expansion card in your
operating system.
Installing and Removing a PCI Express x16 Graphics Card :
• Installing a Graphics Card:
Gently insert the graphics card into the PCI Express x16 slot.
Make sure the graphics card is locked by the latch at the end of
the PCI Express x16 slot.
• Removing the Card:
Push the latch at the end of the PCI Express x16 slot to release
the card and then pull the card straight up from the slot.
PCI Express x1
PCI
■ Make sure the motherboard supports the expansion card. Carefully read the manual
that came with your expansion card.
■ Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before
installing an expansion card to prevent hardware damage.
■ The PCI-E2_16X slot and the two PCI-E x1 (PCI-E1_1X, PCI-E2_1X) slots are shared,
if an expansion card was installed into the PCI-E2_16X slot, the function of the other
two -PCI-E x1 slots would be turned off automatically.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
PCI Express x16 (PCI-E x16 mode)
PCI Express x16 (PCI-E x4 mode)
Page 22
15
2
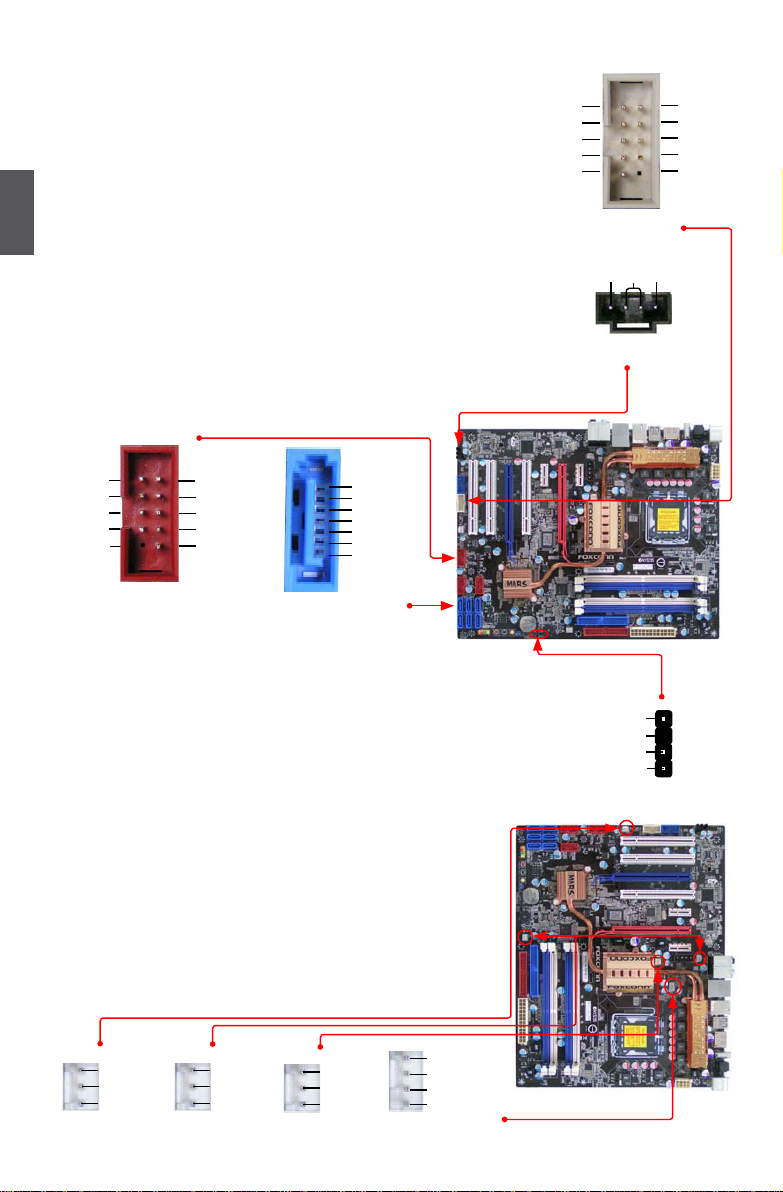
2-4 Install other Internal Connectors
Power Connectors
This motherboard uses an ATX power supply. In order not to damage any device, make sure all the
devices have been installed properly before applying the power supply.
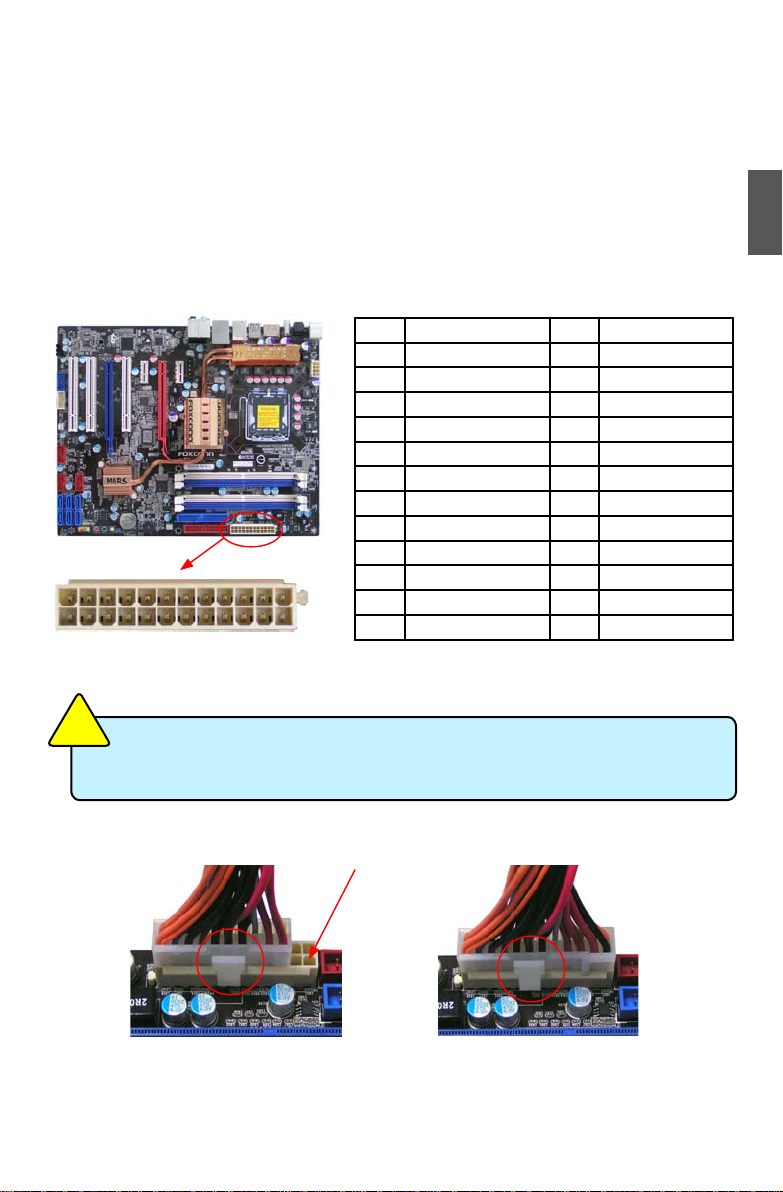
24-pin ATX power connector : PWR1
PWR1 is the ATX power supply connector. Make sure that the power supply cable and pins are
properly aligned with the connector on the motherboard. Firmly plug the power supply cable into the
connector and make sure it is secure.
Pin # Denition Pin # Denition
1 3.3V 13 3.3V
2 3.3V 14 -12V
3 GND 15 GND
4 +5V 16 PS_ON(Soft On/Off)
5 GND 17 GND
6 +5V 18 GND
7 GND 19 GND
8 Power Good 20 NC
9 +5V SB(Stand by +5V) 21 +5V
10 +12V 22 +5V
11 +12V 23 +5V
12 3.3V 24 GND
PWR1
24
13
12
1
We recommend you using a 24-pin power supply. If you are using a 20-pin power supply,
you need to align the ATX power connector according to the following picture.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
20-Pin Power 24-Pin Power
Pin No. 24
Page 23
16
2
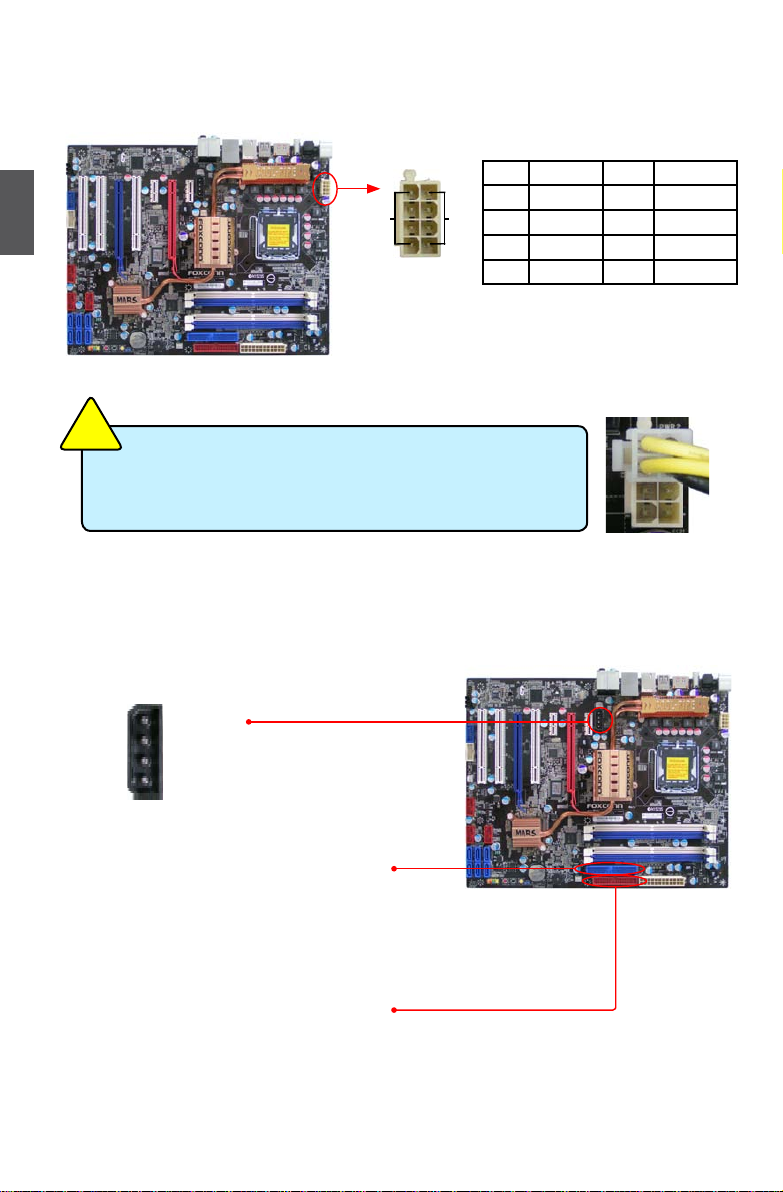
Exclusive Graphics power Connector : PWR3
This connector is an auxiliary power for graphics card.
Exclusive power for graphics card is for better graphics
performance and future upgrade usage.
IDe Connector : PIDe
With the provided Ultra DMA133/100/66 IDE ribbon cable,
you can connect to any IDE type of hard disk and CD/DVD
ROM/RW drive. You also can congure as a disk array
through the JMicron RAID controller.
Floppy Disk Drive Connector : FLOPPY
This motherboard includes a standard oppy disk drive(FDD)
connector, supporting 360KB, 720KB,1.2MB, 1.44MB, and
2.88MB FDDs.
Pin # Denition Pin # Denition
1 GND 5 +12V
2 GND 6 +12V
3 GND 7 +12V
4 GND 8 +12V
+5V
GND
GND
+12V
1
4
Connect a 4-pin
power plug
We recommend you using an 8-pin ATX 12V power supply. If
you are using a 4-pin power supply, you need to align the ATX
power connector according to the picture on the right.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
PWR3
8-pin ATX 12 V Power Connector : PWR2
The 8-pin ATX 12V power supply connects to PWR2 and provides power to the CPU.
145
8
PWR2
GND
+12V
Page 24

17
2
front Panel Connector : fP1
This motherboard includes one connector for connecting the
front panel switch and LED Indicators.
Hard Disk leD Connector (HDD-leD)
Connect to the chassis front panel IDE indicator LED. It
indicates the active status of the hard disks. This 2-pin
connector is directional with +/- sign.
Reset Switch (ReSeT-SW)
Attach the connector to the Reset switch on the front
panel of the case; the system will restart when the switch
is pressed.
Power leD Connector (PWR-leD)
Connect to the power LED indicator on the front panel of
the chassis. The Power LED indicates the system’s status.
When the system is in operation (S0 status), the LED is
on. When the system gets into sleep mode (S1) , the LED
is blinking; When the system is in S3/S4 sleep state or
power off mode (S5), the LED is off. This 2-pin connector
is directional with +/- sign.
Power Switch Connector (PWR-SW)
Connect to the power button on the front panel of the
chassis. Push this switch allows the system to be turned
on and off rather than using the power supply button.
IrDA Connector : IR
This connector supports infrared wireless transmitting and
receiving device.
1394a Connector : f_1394
The 1394a expansion cable can be connected to either the front
(provided that the front panel of your chassis is equipped with
the appropriate interface) or real panel of the chassis.
Audio Connector : f_AUDIo
The audio connector supports HD Audio standard.
Front Audio supports re-tasking function.
GND
+12V
TPA-
TPB-
GND
TPB+
+12V
GND
TPA+
EMPTY
1
2
10
9
F_1394
HDD-LED
RESET-SW
NC
+
PWR-SW
+
-
PWR-LED
EMPTY
1
2
10
9
FP1
1
2
3
4
5
+5V
EMPTY
IRRX
GND
IRTX
IR
MIC_L
MIC_R
LINEOUT_L
SENSE_SEND
SENSE1_RETURN
PRESENCE_J
EMPTY
SENSE2_RETURN
AUD_GND
1
2
109
F_AUDIO
LINEOUT_R
Page 25
18
2
CoM Connector : CoM1
This motherboard supports one serial RS232 COM port for legacy
compatibility. User must purchase another RS232 cable with a 9-pin
D-sub connector at one end to connect with the external RS232
device and another end with 10-pin female connector to connect
with COM1 connector in the motherboard.
Audio Connector : CD_IN
CD_IN is a Sony standard audio connector, it can be connected to
a CD/DVD-ROM drive through a CD/DVD audio cable.
USb Connectors : f_USb1/2/3
In addition to the six USB ports on the rear panel, this product
also provides three 10-pin USB connectors on its motherboard.
By connecting through USB cables with them, user can quickly
expand another six USB ports on the front panel .
Serial ATA Connectors : SATA_1/2/3/4/5/6
The Serial ATA connector is used to connect with SATA Hard Disk
or CD devices which supporting this feature. The current Serial
ATA II interface allows up to 300MB/s data transfer rate.
Speaker Connector : SPeAKeR
The speaker connector is used to connect speaker of the
chassis.
Fan Connectors : CPU_FAN, SYS_FAN, NB_FAN,
fAN1/2
There are ve fan headers on this motherboard. The fan speed
can be controlled and monitored in “PC Health Status” section of
the BIOS Setup. These fans can be automatically turned off after
the system enters S3, S4 and S5 sleeping states.
NC
SPKJ
EMPTY
SPEAKER
SPKJ
RLSD
SOUT
RI
GND
RTS
DSR
DTR
CTS
EMPTY
SIN
1
2
10
9
COM1
NC
GND
5V_DUAL
D+
D-
D+
GND
D-
5V_DUAL
EMPTY
1
2
10
9
F_USB 1/2/3
SATA_1/2/3/4/5/6
GND
TX+
TXGND
RX-
RX+
GND
1
CD_IN
CD_L GND CD_R
CPU_FAN
NB_FAN
FAN_1/2 SYS FAN
GND
+12V
SENSE
GND
+12V
SENSE
GND
+12V
SENSE
GND
POWER
SENSE
CONTROL
1
2
3
4
Page 26
19
2
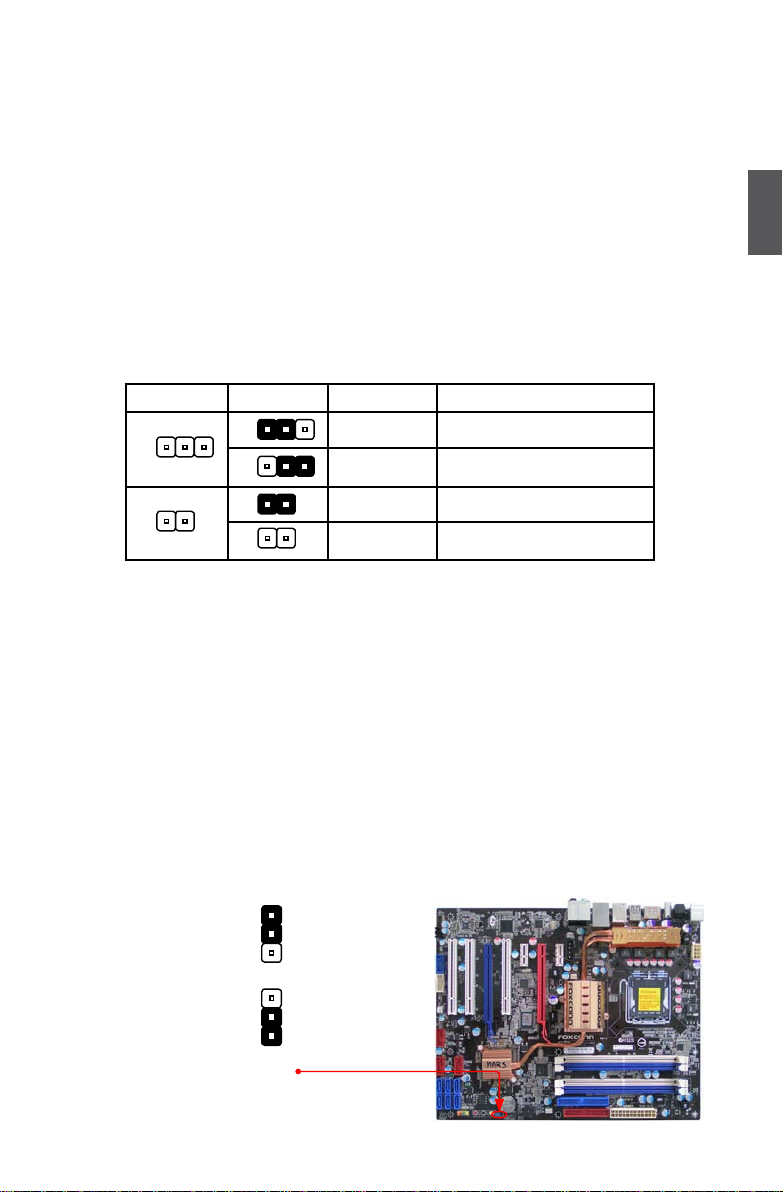
2-5 Jumpers
For some features needed, users can change the jumper settings on this motherboard to modify them.
This section explains how to use the various functions of this motherboard by changing the jumper
settings. Users should read the following content carefully prior to modifying any jumper setting.
Description of Jumpers
1. For any jumper on this motherboard, pin 1 can be identied by the bold silkscreen next to it.
However, in this manual, pin 1 is simply labeled as “1”.
2. The following table explains different types of the jumper settings. "Closed" means placing a jumper
cap on the two pins to temporarily short them. The shorting can also be done by touching two
pins by a screwdriver for a few seconds, but using jumper cap is recommended. It can prevent
hazardous ESD (Electrical Static Discharge) problem.
Clear CMoS Jumper: ClR_CMoS
The motherboard uses CMOS RAM to store the basic hardware information (such as BIOS data,
date, time information, hardware password...etc.). Clear CMOS data is the fast way to go back to
factory default when the BIOS settings were mistakenly modied.
The steps to clear CMOS data are :
1. Turn off the computer, unplug the power cord from the power outlet.
2. Remove jumper cap from pins 2 and 3, put it onto pins 1 and 2 to short them. This will clear
CMOS data.
3. Return the setting to its original with pins 2 and 3 closed.
4. Plug in the power cord to your computer and turn it on.
5. Go to BIOS Setup to congure new system as described in next chapter.
Jumper Diagram Denition Description
1-2 Set Pin 1 and Pin 2 closed
2-3 Set Pin 2 and Pin 3 closed
Closed Set two pins closed
Opened Set two pins opened
1
1
1
1
1
1
Clear
1
2
3
Normal
(Default)
1
2
3
CLR_CMOS
Page 27
20
2
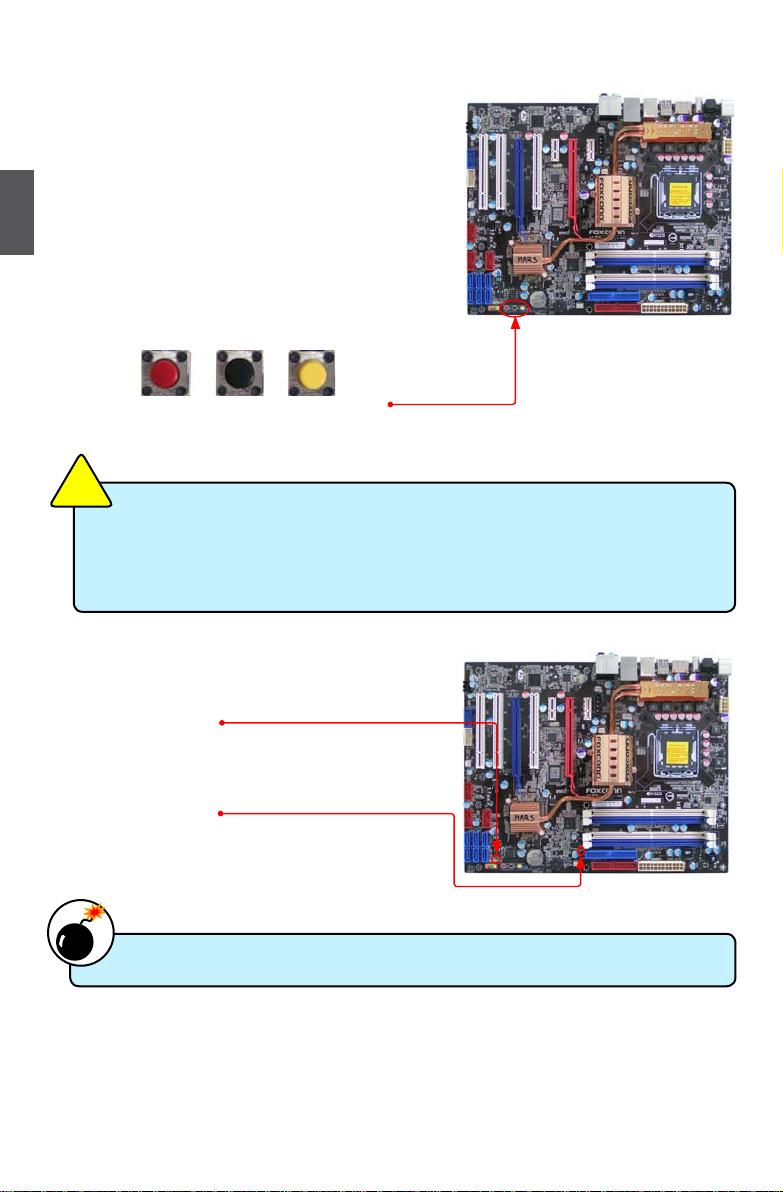
2-6 onboard button
Power on button: PoWeR_oN
Push the power on button to power on the system.
Reset button: ReSeT
Push the reset button to reboot the system.
Clear CMoS button: ClS_CMoS
Turn off the AC power supply, push the CLS_CMOS button
and hold there for a couple of seconds to clear CMOS.
2-7 onboard leD
+5V Standby leD:
It will light whenever the power supply that connected to
the motherboard is switched on.
DRAM Power leD:
The LED lights up indicating the system is on or the system
is staying at S1 or S3 sleeping state.
POWER_ON RESET CLS_CMOS
■ Make sure the power supply is turned off before pressing the CLS_CMOS button to
clear CMOS.
■ Push down the CLS_CMOS button and hold it there for a couple of seconds to clear
the CMOS completely, then release.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Do not remove or plug in any device when the onboard LED is lighting on.
W
A
R
N
I
N
G
!
Page 28
This chapter tells how to change system settings through
the BIOS Setup menus. Detailed descriptions of the BIOS
parameters are also provided.
You have to run the Setup Program when the following cases
occur :
1. An error message appears on the screen during the system
Power On Self Test (POST) process.
2. You want to change the default CMOS settings.
This chapter includes the following information :
■ Enter BIOS Setup
■ Main Menu
■ Standard CMOS Features
■ Advanced BIOS Features
■ Advanced Chipset Features
■ Integrated Peripherals
■ Power Management Setup
■ PnP/PCI Congurations
■ PC Health Status
■ Gladiator BIOS
■ Load Fail-Safe Defaults
■ Load Optimized Defaults
■ Set Supervisor Password
■ Set User Password
■ Save & Exit Setup
■ Exit Without Saving
Since BIOS could be updated some other times, the BIOS information described
in this manual is for reference only. We do not guarantee the content of this
manual will remain consistent with the newly released BIOS at any given time in
the future. Please visit our support website for updated manual if it is available.
Page 29
22
3
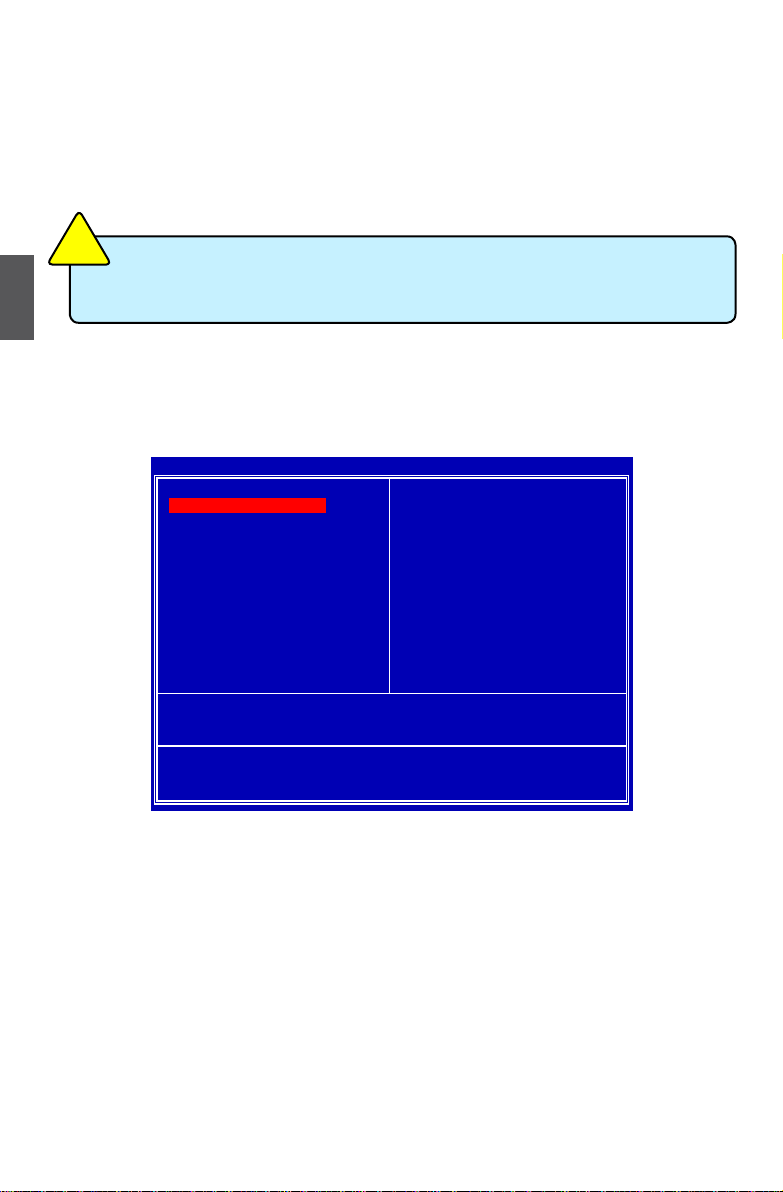
enter bIoS Setup
The BIOS is the communication bridge between hardware and software, correctly setting up the
BIOS parameters is critical to maintain optimal system performance. Power on the computer,
when the message "Press TAb to show PoST screen, Del to enter SeTUP" appears at the
bottom of the screen, you can press <Del> key to enter SETUP.
Main Menu
The main menu allows you to select from a list of setup functions together with two exit choices.
Use the arrow keys to select a specic item and press <Enter> to go to the submenu.
Each item in the main menu is explained below:
► Standard CMOS Features
It displays the basic system conguration, such as BIOS date code, ID, system date, time and
Floppy drive. They all can be set up through this menu.
► Advanced BIOS Features
The advanced system features can be set up through this menu.
► Advanced Chipset Features
The values for the chipset can be changed through this menu, and the system
performance can be optimized.
► Integrated Peripherals
All onboard peripherals can be set up through this menu. There are IDE devices, Super I/O
devices such as Serial I/O, Parallel port and other USB ports...etc.
► Power Management Features
All the items related with Green function features can be set up through this menu.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
► Standard CMOS Features
► Gladiator BIOS
► Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
► Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
► Integrated Peripherals Set Supervisor Password
► Power Management Setup Set User Password
► PnP/PCI Congurations Save & Exit Setup
► PC Health Status Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit ↑↓→← : Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type...
► Standard CMOS Features
We do not suggest that you change the default values in the BIOS Setup, and we shall
not be responsible for any damage which resulted from the change you made.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Page 30

23
3
► PnP/PCI Congurations
PCI/PnP features, such as O/S supporting, IRQ/DMA settings and bus master enabling/
disabling...etc. can be modied through this menu.
► PC Health Status
This setup enables you to read/change Fan speeds, and displays temperatures and voltages
of your CPU/System.
► Gladiator BIOS
Some special proprietary features (such as overclocking) can be set up through this menu.
► Load Fail-Safe Defaults
The Fail-safe default BIOS settings can be loaded through this menu. For normal operation, it
is more reliable than optimal setting. But if your system loading becomes heavy (such as more
I/O cards, memory...etc.), we will recommend you to adjust some BIOS settings instead of
using this default.
► Load Optimized Defaults
The optimal performance settings can be loaded through this menu. However, it may offer
better performance in some ways (such as less I/O cards, less memory ...etc.), still, it may
cause problem if you have more memory or I/O cards installed. It means, if your system
loading is heavy, set to optimal default may sometimes come out an unstable system. What
you need now is to adjust BIOS setting one by one, trial and error, to nd out the best setting
for your current system.
► Set Supervisor Password
The supervisor password can be set up through this menu.
► Set User Password
The user password can be set up through this menu.
► Save & Exit Setup
Save setting values to CMOS and exit.
► Exit Without Saving
Do not change anything and exit the setup.
When we talk about <+> and <-> keys in this manual, they are the single-keypad
keys of the numeric keypad which is located at the right hand side of your desktop
keyboard. They are not the combination keys made by pressing and holding down
<Shift> key rst, then press <+ => or <-_> key the next.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Page 31

24
3
Standard CMoS features
This submenu is used to set up the standard BIOS features, such as the date, time, oppy drive
and so on. Use the arrow up/down keys to select an item, then use the <+> or <-> keys to change
the setting.
► Date - <weekday><month><date> <year> format
Day—weekday from Sun. to Sat., automatically displayed by BIOS (Read Only).
Month—month from 1 to 12.
Date—date from 1st to 31st.
Year—year, set up by users.
Use <Enter>, <Tab> keys to select a eld. Use <+>, <->, <PageUp> or <PageDown> to select
a value.
► Time - <hour> : <minute> : <second> format
This item allows you to congure the desired time. Use <Enter>, <Tab> to move forward and
select a eld. Directly input a value or use <PageUp>, <PageDown>, <+> or <-> to select a
value.
► SATA Channel 1/2/3/4/5/6, IDE Channel Master/Slave, e-SATA Channel
These categories identify the hard disks connected to the Intel® ICH9R and JMicron controllers
in the system. In each channel’s display, you can press [Enter] to go to its submenu. You can
further congure specic drive settings.
[None], [Auto], and [Manual]. “None” means no HDD is installed or set; “Auto” means the
system can auto-detect the hard disk when booting up; by choosing “Manual” and changing
Access Mode to “CHS”, the related information should be entered manually.
In Access Mode setting, selections of [CHS], [LBA], [Lage] and [Auto] can help you to select
hard drive for legacy compatibility.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Standard CMOS Features
Date (mm:dd:yy) Wed, Nov 7 2007 ▲ Item Help
Time (hh:mm:ss) 17 : 44 : 13
█
█
Menu Level ►
► SATA Channel 1 WDC WD2500JS-60NCB1 █
► SATA Channel 2
None █ Press [Enter] to enter
► SATA Channel 3
Maxtor 6L250S0 █ next page for detail
► SATA Channel 4
None █ hard drive settings
► SATA Channel 5 ST3320620SV
█
► SATA Channel 6 ST3300831AS
█
► IDE Channel Master
None █
► IDE Channel Slave
None █
► e-SATA Channel
None █
█
Drive A
1.44M, 3.5 in. █
█
Video EGA/VGA █
Halt On All Errors ▒
BIOS ID P35A04.F1.P.09.MARS ▒
▼
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
WDC WD2500BB-22FTA0
Page 32

25
3
Award (Phoenix) BIOS can support 3 HDD modes: CHS, LBA and Large.
Note: Set to [Auto] , the system can detect the hard disk and select the HDD mode automati-
cally. Suggest you select this option.
The SATA Channel information will not be displayed if SATA mode is set to [AHCI] or [RAID]. In
these two modes, the hard disk information can be found by getting into Intel® Matrix Storage
Manager option ROM utility (or RAID BIOS). We will discuss RAID BIOS later.
► Drive A
This option allows you to select which kind of the Floppy Disk Drive is installed in your system.
It can be [360KB, 5.25"], [1.2MB, 5.25"], [720KB, 3.5"], [1.44MB, 3.5"] and [2.88 MB, 3.5"].
► Video
The following table is provided for your reference in setting the display mode for your system.
► Halt On
This category determines whether or not the computer will stop if an error is detected during
powering up.
► BIOS ID
This item shows the information of the BIOS ID.
► Base/Extended/Total Memory
These are Display-Only information of the system memory, determined by POST(Power On
Self Test) of the BIOS.
EGA/VGA Enhanced Graphics Adapter / Video Graphic Array. For
EGA, VGA, SEGA, SVGA, or PGA monitor adapters.
CGA 40 Color Graphic Adapter, powering up in 40 column mode.
CGA 80 Color Graphic Adapter, powering up in 80 column mode.
MONO Monochrome adapter, including high resolution monochrome
adapters.
All Errors Whenever the BIOS detects a nonfatal error, the system will stop
and you will be prompted.
No Errors The system boot will not stop for any errors that may be
detected.
All, But Keyboard The system boot will not stop for a keyboard error; but it will stop
for all other errors.
All, But Diskette The system boot will not stop for a diskette error; but it will stop
for all other errors.
All, But Disk/Key The system boot will not stop for a keyboard or disk error, but it
will stop for all other errors.
CHS For HDD <528MB
LBA For HDD >528MB & Supporting LBA (Logical Block Addressing)
Large For HDD>528MB but not supporting LBA
Page 33

26
3
Advanced BIOS Features
► Hard Disk Boot Priority
This option is used to select the Priority for HDD startup. After pressing <Enter>, you can
select the HDD using the Up/Down arrow keys, and change the HDD priority using <PageUp>/
<PageDown>; you can exit this menu by pressing <Esc>.
► Virus warning
This item is used to set up the virus warning message for the IDE HDD boot sector. When set
to enabled, a warning message will appear on the screen if any program wants to write any
information to this sector, and will give out a warning sound.
Note: Such function provides protection to the startup sector only; it dose not protect the entire
hard disk.
► First/Second/Third Boot Device
These three options allow you to select the priority of boot sequence from different devices.
► Boot Other Device
With this function set to enable, the system will boot from some other devices provided that the
rst/second/third boot devices failed. The setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
► Boot Up Floppy Seek
This item controls whether the BIOS will be checking for a oppy drive while booting up. If it
cannot detect one (either due to improper conguration or physical unavailability), it will appear
an error message. Disabling this function, then POST will not detect the oppy.
► Boot Up NumLock Status
This item denes if the keyboard Num Lock key is active when your system is started. The
available settings are: On (default) and Off.
► Gate A20 Option
This feature determines how Gate A20 is used to address memory above 1MB. When this
option is set to Fast, the motherboard chipset controls the operation of Gate A20. But when
set to Normal, a pin in the keyboard controller controls Gate A20. Setting Gate A20 to Fast
improves memory access speed and thus, overall system speed, especially with OS/2 and
Windows. This is because OS/2 and Windows enter and leave protected mode via the BIOS
a lot so Gate A20 needs to switch often from enabled to disabled and back again. Setting this
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Advanced BIOS Features
► Hard Disk Boot Priority Press Enter ▲ Item Help
Virus Warning
Disabled █
First Boot Device
Hard Disk █ Menu Level ►
Second Boot Device
CDROM █
Third Boot Device
USB-ZIP █ Select Hard Disk Boot
Boot Other Device
Enabled █ Device Priority
Boot Up Floppy Seek
Disabled █
Boot Up NumLock Status
on █
Gate A20 Option
Fast █
Typematic Rate Setting
Disabled █
x Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) 6 █
x Typematic Delay (Msec) 250 █
Security Option
Setup █
APIC Mode
Enabled █
MPS Version Control for OS
1.4 █
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB
Non-OS2 █
Report No FDD For WIN 95
No ▒
Full Screen Logo Show
Enabled ▒
Small Logo(EPA) Show
Disabled ▼
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Press Enter
Page 34

27
3
feature to Fast improves memory access performance above 1MB because the chipset is
much faster in switching Gate A20 than the keyboard controller. It is recommended that you
set it to Fast for faster memory accesses.
► Typematic Rate Setting
If this item is enabled, you can use the following two items to see the typematic rate and the
typematic delay settings for your keyboard.
► Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
This item is used to dene how many characters per second a hold-down key generated.
► Typematic Delay (Msec)
This item is used to dene how many delayed milliseconds before a hold-down key begins
generating repeat characters.
► Security Option
When it is set to “Setup”, a password is required to enter the CMOS Setup screen; When it
is set to “System”, a password is required not only to enter CMOS Setup, but also to start up
your PC.
► APIC Mode (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller)
This item is used to enable or disable APIC function.
APIC interrupt subsystems can have as many IRQs as are required in a specic machine.
APICs are benecial for the following reasons :
• APICs can contribute to resolving resource conicts in the PC platform.
• Windows operating systems have been designed with APICs in mind.
• APICs are necessary for enabling new features in the PCI specication.
► MPS Version Control For OS (Multi-Processor Specication)
This feature is only applicable to multiprocessor motherboards as it species the version of the
MPS that the motherboard will use. The MPS is a specication by which PC manufacturers
design and build Intel architecture systems with two or more processors. MPS 1.1 was the
original specication. MPS version 1.4 adds extended conguration tables for improved
support of multiple PCI bus congurations and greater expandability in the future. In addition,
MPS 1.4 introduces support for a secondary PCI bus without requiring a PCI bridge.
If your operating system comes with support for MPS 1.4, you should keep the setting as
the default 1.4. You also need to enable MPS 1.4 support if you need to make use of the
secondary PCI bus on a motherboard that doesn't come with a PCI bridge.
You should only leave it as 1.1 only if you are running an older operating system that only
supports MPS 1.1.
► OS Select For DRAM>64MB
This item is only required if you have installed more that 64MB of memory and you are running
the OS/2 operating system.
► Report No FDD For WIN 95
If you are using the Windows 95 and running a system with no oppy drive, select “Yes” for
this item to ensure compatibility with Windows 95 logo certication.
► Full Screen Logo Show
This item allows you to enable or disable full screen logo show.
► Small Logo(EPA) Show
This item allows you to enable or disable the EPA logo.
► Summary Screen Show
This item allows you to enable or disable the summary screen show.
Page 35

28
3
Advanced Chipset Features
► System BIOS Cacheable
Select “Enabled” to allow caching of the system BIOS which may improve performance. If any
other program writes to this memory area, a system error may result.
► Memory Hole At 15M-16M
This item is used to set the memory hole. The available values are [Disabled] and [Enabled].
Some special ISA cards require this area of memory for them to work properly. Enabling this
function reserves the memory area for the card's use. In some cases, it may also prevent the
system from accessing memory above 15MB. If you enable this function, 1MB of RAM (the
15th MB) will be reserved and is therefore not available for the OS' use. Since ISA cards are a
thing of the past, you should always disable this feature.
► PCI Express Port 1/2/3/4/5/6
This option is used to enable or disable the PCI Express port. Setting to [Auto] allows the
system to detect the PCI Express devices automatically. If detected, the PCI Express Port is
enabled, or the PCI Express Port is disabled.
► PCI-E Compliancy Mode
This item is used to set the PCI-E compliancy mode. Setting options: [v1.0a]; [v1.0].
► PEG Force X1 (PCI Express Graphics)
This item is used to force PCI Express slot to work at X1 specication instead of X16..
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Advanced Chipset Features
System BIOS Cacheable Enabled Item Help
Memory Halt At 15M-16M Disabled
PCI Express Port 1
Auto Menu Level ►
PCI Express Port 2
Auto
PCI Express Port 3
Auto
PCI Express Port 4
Auto
PCI Express Port 5
Auto
PCI Express Port 6
Auto
PCI-E Compliancy Mode
v1.0a
PEG Force X1
Disabled
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Enabled
Page 36

29
3
Integrated Peripherals
► OnChip IDE Device/Onboard Device Control /USB Device Setting
Press <Enter> to go to relative submenu, please refer to the next sections.
► Onboard Lan Boot ROM
This item is used to enable or disable the onboard LAN boot optional ROM. A LAN boot ROM
lets you set up a diskless workstation on the network. By installing a boot ROM in the network
board, you can enable a client PC system on the network to be booted remotely.
► Onboard FDC Controller
This item is used to enable or disable the onboard FDC controller.
► Onboard Serial Port 1
This item is used to assign the I/O address and interrupt request (IRQ) for the onboard serial
port 1.
► Onboard IrDA Device
This item is used to assign the I/O address and interrupt request (IRQ) for the onboard IrDA
device.
► UR2 Duplex Mode
This item enables you to determine the infrared function of the onboard infrared chip.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Integrated Peripherals
► OnChip IDE Device Press Enter Item Help
► Onboard Device Control
Press Enter
► USB Device Setting
Press Enter Menu Level ►
Onboard Lan Boot ROM
Disabled
Onboard FDC Controller
Enabled
Onboard Serial Port 1
3F8/IRQ4
Onboard IrDA Device
2F8/IRQ3
UR2 Duplex Mode
Half
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Press Enter
Page 37

30
3
onchip IDe Control
► SATA Mode
This item is used to set the Serial ATA Mode. Setting options: [IDE]; [RAID]; [AHCI].
The SATA interface is controlled by Intel® south bridge chip ICH9R.
► LEGACY Mode Support
There are Native IDE and Legacy (or compatible) IDE modes. Legacy mode supports OS
through legacy IDE driver. Most SATA functions are not supported in Legacy mode, like SATA
II 3G, NCQ, HotPlug and etc, and Native mode supports SATA II 3G, NCQ, and Hotplug.
This item is used to enable/disable the Legacy IDE mode support for the SATA ports. Certain
OS is not supported under Native mode, and must choose Legacy mode.
► Turbo Memory (Robson Technology) Support
Turbo Memory (Robson Technology) features an integrated disk cache using ash memory
in order to speed up disk access and also save energy. It uses non-volatile memory (Flash
memory) to increase system responsiveness, make multi-tasking faster, and extend battery
life.
This item is used for supporting the Turbo Memory.
► Onboard IDE/SATA Chip
You may set your PATA and e-SATA to IDE mode or RAID Mode or AHCI+IDE mode(AHCI for
e-SATA, IDE for PATA). We are using JMicron chip to control PATA and e-SATA devices.
► Delay For HDD (Secs)
You can select the delay for HDD while booting. It allows you to use your system with old
fashion type IDE devices which run slowly.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
OnChip IDE Device
SATA Mode IDE Item Help
LEGACY Mode Support Disabled
x Turbo Memory Support Disabled
Menu Level ►
Onboard IDE/SATA Chip IDE Mode
Delay For HDD (Secs)
0
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
IDE
Page 38

31
3
Onboard Device Control
► HD Audio Controller
This item is used to set whether the HD Audio controller is enabled.
► Onboard 1394 Controller
This item is used to set whether the onboard 1394 controller is enabled.
► Onboard LAN Controller
This item is used to set whether the onboard LAN controller is enabled.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Onboard Device Control
HD Audio Controller Enabled Item Help
Onboard 1394 Controller
Enabled
Onboard LAN Controller Enabled Menu Level ►
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Enabled
Page 39

32
3
USB Device Setting
► USB 1.1 Controller
This item is used to enable or disable the Universal Host Controller Interface for USB.
► USB 2.0 Controller
This item is used to enable or disable the Enhanced Host Controller Interface for USB.
► USB Operation Mode
This item is used to set the USB operation mode. If you select the [High Speed], then the USB
operation mode is determined by the USB device; select [Full/Low Speed], the USB device
operates on full/low speed.
► USB Storage Function
This option is used to set whether the USB Mass Storage controller is enabled in a legacy
operating system (such as DOS).
***USB Mass Storage Device Boot Setting***
BIOS auto detects the presence of USB Mass Storage Devices, you can congure the Boot
setting mode for the detected USB MSD. Setting Options: [Auto]; [FDD Mode]; [HDD Mode].
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
USB Device Setting
USB 1.1 Controller Enabled Item Help
USB 2.0 Controller
Enabled
USB Operation Mode High Speed Menu Level ►
USB Storage Function Enabled
[Enable] or [Disable]
*** USB Mass Storage Device Boot Setting *** Universal Host
Controller
Interface for Universal
Serial Bus
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Enabled
Page 40

33
3
Power Management Setup
ACPI (Advanced Conguration and Power Interface) is an open industry standard that denes
power and conguration management interfaces between an operating system and the BIOS.
In other words, it is a standard that describes how computer components work together
to manage system hardware. In order to use this function the ACPI specication must be
supported by the OS (for example, Windows2000 or WindowsXP).
ACPI denes ve sleeping states, they are :
S1 - The S1 sleeping state is a low wake latency sleeping state. In this state, no system
context is lost (CPU or chip set) and hardware maintains all system context. (also called
Power on Suspend)
S2 - The S2 sleeping state is a low wake latency sleeping state. This state is similar to
the S1 sleeping state except that the CPU and system cache context is lost (the OS
is responsible for maintaining the caches and CPU context). Control starts from the
processor’s reset vector after the wake event.
S3 - The S3 sleeping state is a low wake latency sleeping state where all system context is lost
except system memory. CPU, cache, and chip set context are lost in this state. Hardware
maintains memory context and restores some CPU and L2 conguration context. Control
starts from the processor’s reset vector after the wake event. (also called Suspend to
RAM)
S4 - The S4 sleeping state is the lowest power, longest wake latency sleeping state supported
by ACPI. In order to reduce power to a minimum, it is assumed that the hardware platform
has powered off all devices. Platform context is maintained. (also called Suspend to
Disk)
S5 - The S5 state is similar to the S4 state except that the OS does not save any context. The
system is in the “soft” off state and requires a complete boot when it wakes. Software
uses a different state value to distinguish between the S5 state and the S4 state to allow
for initial boot operations within the BIOS to distinguish whether or not the boot is going to
wake from a saved memory image.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Power Management Setup
► Power On Function
Press Enter Item Help
ACPI Function
Enabled
ACPI Suspend Type
S3(STR) Menu Level ►
Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume
Auto
Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN
Instant-off
Resume by Alarm
Disabled
x Date(of Month) Alarm 0
x Time(hh:mm:ss) Alarm 0 : 0 : 0
HPET Support
Enabled
HPET Mode
32-bit mode
PWRON After PWR-Fail
Off
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Press Enter
Page 41

34
3
► Power On Function
Press <Enter> to select the submenus of these two settings.
► ACPI Function
This item is used to enable or disable the ACPI function.
► ACPI Suspend Type
This item is used to set the energy saving mode of the ACPI function. When you select “S1
(POS)” mode, the power is always on and computer can be resumed at any time. When
you select “S3 (STR)” mode, the power will be down after a period of time. The status of the
computer before it entering STR will be saved in memory, and the computer can quickly return
to previous state when the STR function wakes.
When you select "S1&S3", it means OS will automatically take care and assign which mode is
the most suitable now.
► Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume
This item allows the system to initialize the VGABIOS from S3 (Suspend to RAM) sleep state.
The available setting values are: Auto, Yes and No.
► Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN
This item is used to set the power down method. This function is only valid for systems using
an ATX power supply. When set to [Delay 4 Sec.], the power button will put the system in
Suspend mode if you push the power button in less than 4 Second then release. If set to
[Instant-Off], the PC powers off immediately when the power button is pressed.
► Resume by Alarm
This item is used to set the timing of the start-up function. In order to use this function, the
start-up password function must be disabled. Also, the PC power source must not be turned
off.
► Date (of Month) Alarm
When Resume by Alarm is set to “Enabled”, this item can be modied. It is used to set the
timing for the start-up date.
► Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm
When Resume by Alarm is set to “Enabled”, this item can be modied. It is used to set the
timing for the start-up time.
► HPET Support
HPET stands for High Precision Even Timer. If you have the HPET disabled, then windows
does not have access to it and therefore falls back to less accurate timing methods. This item
is used to enable or disable the HPET Support.
► HPET Mode
This item is used to set the HPET Mode. Conguration options: [32-bit mode]; [64-bit mode].
It can be available only when the HPET Support is enabled.
► PWRON After PWR-Fail
This item is used to set which state the PC will take with when it resumes after an AC power
loss.
Page 42

35
3
Power on function Menu
► Wake- Up by PCI card
This item is used to set the system to wake up by PCI card.
► Power On by Ring
If this item is enabled, it allows the system to resume from a software power down or power
saving mode whenever there is an incoming call to an installed fax. This function needs to be
supported by the relevant hardware and software.
► USB KB WakeUp From S3
This item is used to set the system to wake up by USB equipment when it is in S3(Suspend to
RAM) mode.
► Power On by Mouse
When enabled, it allows you to use the PS/2 mouse to wake up the system from soft off and
green mode. This feature requires an ATX power supply.
► Power On by Keyboard
This item allows you to use the PS/2 keyboard to wake up the system from soft off and green
mode. This feature requires an ATX power supply. The setting values: [Disabled]; [Ctrl+ESC];
[Ctrl+F1]; [Ctrl+Space]; [Any Key].
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Power On Function
Wake-Up by PCI card Disabled Item Help
Power On by Ring
Disabled
USB KB Wakeup From S3
Disabled Menu Level ►
Power On by Mouse
Disabled
Power On by Keyboard
Disabled
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Disabled
Page 43

36
3
PnP/PCI Congurations
► Init Display First
This item is used to choose the initial display device which will be used rst when your PC
starts up. Options are : [PCI Slot] and [PCIEx].
► Resources Controlled By
This item is used to dene the system resource control scheme. If all cards you use support
PnP, then select [Auto] and the BIOS will automatically distribute interruption resources. If
the PCI cards you installed need special IRQ resources, you will need to select [Manual] and
manually adjust interruption resources in the event of hardware conicts.
► IRQ Resources
Press the <Enter> key, then manually set IRQ resources.
► PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
This option is only useful if you use an MPEG card or an add-on card that makes use of the
graphics card's Feature Connector. It corrects incorrect color reproduction by "snooping"
into the graphics card's frame buffer memory and modifying (synchronizing) the information
delivered from the graphics card's Feature Connector to the MPEG or add-on card. It will also
solve the problem of display inversion to a black screen after using the MPEG card. Feature
Connector normally stays at top edge of the graphics card.
► INT Pin 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8 Assignment
This item is used to assign IRQ resources for INT Pin 1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8. Default INT Pin
assignments can be found from the help menu.
***PCI Express relative items***
► Maximum Payload Size
This item is used to set maximum Transaction Layer Packets (TLP) payload size for PCI
Express devices. The unit is byte.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
PnP/PCI Congurations
Init Display First PCI Slot Item Help
Resources Controlled By
Auto Menu Level ►
x IRQ Resources Press Enter
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
Disabled
INT Pin 1 Assignment
Auto
INT Pin 2 Assignment
Auto
INT Pin 3 Assignment
Auto
INT Pin 4 Assignment
Auto
INT Pin 5 Assignment
Auto
INT Pin 6 Assignment
Auto
INT Pin 7 Assignment
Auto
INT Pin 8 Assignment
Auto
** PCI Express relative items **
Maximum Payload Size
128
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
PCI Slot
Page 44

37
3
PC Health Status
► Shutdown Temperature
This item is used to set the system temperature upper limit. When the temperature exceeds
the set value, the system will shut down automatically.
► Current CPU/System/North Bridge Temperature
These items show the current CPU/System/NB temperature detected automatically by the
system.
► Smart CPUFan Function
This item is used to set the Smart CPU Fan function. Conguration options:
[Full Speed]; [By Duty-Cycle]; [Smart FAN].
► Smart CPUFan Duty Cycle
It allows you to control the fan by the Duty-Cycle directly. You can input the value between 0
and 99.
► Current CPUFan Speed
This item shows the Current CPU Fan speed detected automatically by the system.
► Smart SYSFan Function
It allows you to set the smart System Fan function. Conguration options:
[Full Speed]; [By Duty-Cycle]; [Smart FAN].
► Smart SYSFan Duty Cycle
This item is used to control the fan by the Duty-Cycle directly. You can input the value between
0 and 99.
► Current SYSFan Speed
This item shows the Current System Fan speed detected automatically by the system.
►Smart NBFan Function
This item is used to set the Smart NBFan Function. Conguration options:
[Full Speed]; [By Duty-Cycle]; [Smart FAN].
► Smart NBFan Duty Cycle
It allows you to control the fan by the Duty-Cycle directly. You can input the value between 0
and 99.
► Current NBFan Speed
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
PC Health Status
Shutdown Temperature Disabled ▲ Item Help
Current CPU Temperature 38○C █
Current System Temperature 39○C █ Menu Level ►
Current NB Temperature 37○C █
Smart CPUFan Function
Smart FAN █
Smart CPUFan Duty Cycle 90% █
Smart CPU Fan Speed 2035 RPM █
Smart SYSFan Function
Smart FAN █
Smart SYSFan Duty Cycle 90% █
Current System Fan Speed 0 RPM █
Smart NBFan Function
Smart FAN █
Smart NB Fan Duty Cycle 90% █
Current NB Fan Speed 6726 RPM █
Current CPU Voltage 1.33V
█
Current DRAM Voltage 1.90V
█
Current NB Voltage 1.27V █
Current +5 Voltage 5.07V █
Current +12 Voltage 12.14V ▒
Current +3.3 Voltage 3.31V ▼
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Disabled
Page 45

38
3
This item shows the Current NBFan Speed auto-detected by the system.
► Current CPU/DRAM/NB Voltage
These items show the Current CPU/DRAM/NB Voltage detected automatically by the system.
► Current + 5.0V / + 12V / + 3.3V / VBAT
These items show the + 5.0V / + 12V / + 3.3V / VBAT Voltage detected automatically by the
system.
Gladiator bIoS
► CPU Feature/Memory Timing Cong/All Voltage Control/OC Gear
Press <Enter> to go to each Submenu.
► Over Clock (O.C.) Phase Select
It allows you to select the over clock phase. Setting values: [O.C. Disabled]; [Manual O.C.];
[Instant O.C.].
► Instant OverClocking
This item is used for instant OverClocking, you may choose over clock instantly by 5%,
10%,15%.....etc.
***Ratio and Clock Setting***
► CPU Clock Ratio Unlock
This item is used to enable or disable the CPU Clock Ratio Unlock.
► CPU Clock Ratio
This item is used to set the ratio of an unlocked CPU. Using different CPU, the setting values
are different.
► CPU Clock
This item allows you to adjust the CPU clock.
► CPU Clock vs Memory Speed
This item allows you to set the ratio between CPU Clock and Memory Speed.
► System Memory Frequency
This item shows the System Memory Speed.
► PCI Express Clock
This item allows you to adjust the PCI Express bus clock.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Gladiator BIOS
► CPU Feature Press Enter Item Help
► Memory Timing Config
Press Enter
► All Voltage Control
Press Enter Menu Level ►
► OC Gear
Press Enter
Over Clock Phase Select
O.C. Disabled
Instant OverClocking Default
******* Ratio and Clock Setting *******
CPU Clock Ratio Unlock Disabled
x CPU Clock Ratio 9 X
Target CPU Core Speed
1800MHz
CPU Clock 200MHz
CPU Clock vs Memory Speed Auto
System Memory Speed
800MHz
PCI Express Clock 100MHz
PCI Clock 33.6MHz
************ Miscellaneous ************
Auto Detect PCI Clock
Enabled
Spread Spectrum
Enabled
Over Clock Recovery
Disabled
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Press Enter
Page 46

39
3
► PCI Clock
This item allows you to adjust the PCI bus clock. Conguration options:
[Synchronous] (Synchronous with PCI Express bus clock); [33.6 MHz]; [37.3 MHz]; [42.0
MHz].
***Miscellaneous***
► Auto Detect PCI Clock
This item is used to allow the system to supply the PCI slot bus clock if system detected a PCI
add-on card on the slot.
► Spread Spectrum
If you enabled this function, it can signicantly reduce the EMI (ElectroMagnetic Interference)
generated by the system, so to comply with FCC regulation. But if overclocking is activated,
you better disable it.
► Over Clock Recovery
When this feature is enabled, once system failed after overclocking, it will load the previous
CMOS settings (before overclocking) back, so the system can always work.
CPU feature
► EIST function
You can select the EIST (Processor Power Management, PPM) through this item. Setting
values: [Native Mode] (For fully support ACPI OS, e.g. Windows XP, Vista); [SMM Mode] (For
legacy OS, e.g. Windows2000);
► Limit CPUID MaxVal
This item is used to enable or disable CPUID maximum value limit conguration. Set Limit
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
CPU Feature
EIST Function Native Mode Item Help
Limit CPUID MaxVal
Disabled
C1E Function Auto
Execute Disable Bit Enabled
Frequency Unlimit
Disabled
Core Multi-Processing
Enabled
Virtualization Technology
Enabled
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Native Mode
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® technology (EIST) allows the system to dynamically
adjust processor voltage and core frequency, which can result in decreased average
power consumption and decreased average heat production. There are some system
requirements must be met, including CPU, chipset, motherboard, BIOS and operation
system. Please refer to Intel website for more information.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Page 47

40
3
CPUID MaxVal to 3. Should be [Disabled] for WinXP.
► C1E Function
C1E represents Enhanced HALT State. It is a feature which Intel CPU uses to reduce power
consumption when in halt state. C1E drops the CPU's multiplier and voltage to lower levels
when a HLT (halt) command is issued. This item is used to enable/disable the C1E support.
► Execute Disable Bit
This item is used to enable/disable the Execute Disable Bit feature.
Intel's Execute Disable Bit functionality can help prevent certain classes of malicious buffer
overow attacks when combined with a supporting operating system.
Execute Disable Bit allows the processor to classify areas in memory by where application
code can execute and where it cannot. When a malicious worm attempts to insert code in the
buffer, the processor disables code execution, preventing damage and worm propagation.
Replacing older computers with Execute Disable Bit-enabled systems can halt worm attacks,
reducing the need for virus-related repairs. By combining Execute Disable Bit with anti-virus,
rewall, spyware removal, e-mail ltering software, and other network security measures, IT
managers can free IT resources for other initiatives.
► Frequency Unlimit
It means the processor is not ratio locked and has no factory congured maximum ratio limit
on the Smitheld XE multi-processing CPU core.
► Core Multi-Processing
When disabled, it will disable one execution core of each CPU die. It is going to provide
backward compatibility, any way, keep it enabled.
► Virtualization Technology
Virtualization (i.e. Intel® Vanderpool Technology) allows a platform to run multiple operating
systems and applications in independent partitions or “containers.” One physical compute
system can function as multiple “virtual” systems. Vanderpool Technology can help improve
future virtualization solutions. This item will be displayed only when the CPU is supporting this
feature and the setting is used to enable/disable it.
Memory Timing Cong
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Memory Timing Cong
DRAM Timing Selectable By SPD Item Help
CAS Latency Time (tCL) Auto
RAS# to CAS# Delay (tRCD) Auto
Menu Level ►
RAS# Precharge (tRP) Auto
Prechange delay (tRAS) Auto
Write to Precharge(tWR) Auto
Row Refresh Cycle(tRFC) Auto
Write to Read Delay(tWTR) Auto
Row to Row Delay(tRRD) Auto
Read to Precharge(tRPT) Auto
Fast Chip Select
Auto
Clock Per Command
Auto
Memory Channel0 DLL Adjust Auto
Memory Channel1 DLL Adjust Auto
Refresh Count Adjust Auto
Performance Level Auto
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
By SPD
Page 48

41
3
► DRAM Timing Selectable
This item is used to enable/disable provision of DRAM timing by SPD device. The Serial
Presence Detect (SPD) device is a small EEPROM chip, mounted on a DDR2 memory
module. It contains important information about the module's speed, size, addressing mode
and various other parameters, so that the motherboard memory controller (chipset) can better
access the memory.
► CAS Latency Time (tCL)
This item controls the CAS latency, which determines the timing delay (in clock cycles) before
SDRAM starts a read command after receiving it.
► RAS# to CAS# Delay (tRCD)
This item allows you to select a delay time (in clock cycles) between the CAS and RAS strobe
signals.
► RAS# Precharge (tRP)
This item allows you to select the DRAM RAS precharge time (in clock cycles).
► Precharge Delay (tRAS)
This item allows you to set the precharge delay time (in clock cycles).
► Write to Precharge (tWR)
This item allows you to set Write to Precharge delay (in clock cycles).
► Row Refresh Cycle (tRFC)
This item allows you to set Row Refresh Cycle (in clock cycles).
► Write to Read Delay (tWTR)
This item allows you to set minimum Write-to-read delay (in clock cycles).
► Row to Row Delay (tRRD)
This item allows you to set Row to Row Delay (in clock cycles).
► Read to Precharge (tRPT)
This item is used to set the read CAS to precharge time (in clock cycles).
► Fast Chip Select
This item used to enable or disable the fast chip select signal of the DDR RAM.
► Clock Per Command
This item is used to set the Clock Per Command for your memory. (in clock cycles).
► Memory Channel0 DLL Adjust
The DLL stand for Delay Lock Loop, and it uses a symmetrical delay line for tight locking on
both the rising and falling edges of DRAM. This is to adjust Channel 0 DDR2 timing.
► Memory Channel1 DLL Adjust
This is to adjust Channel 1 DDR2 timing.
► Refresh Count Adjust
In merged DRAM circuit, the DRAM could suffer from shorter data retention time because of
heat and noise caused by the logic portion. Frequent refreshes increase power consumption.
Also, they disturb normal DRAM accesses leading to performance degradation. In order to
overcome this problem, we propose several DRAM refresh architectures.
► Performance Level
User can run freeware program such as Memset to nd out the performance level of your
motherboard. For example, if the performance level tested and read is 5, then user can set
this level setting to 4 to over drive the memory or set the level to 6 to slow down the memory
access. Lower value in this setting means faster speed.
Page 49

42
3
All Voltage Control
********All Voltage Control********
► CPU Voltage Multiplier
This item is used to set CPU Voltage Multiplier.
► CPU Voltage Setting
This item is used to set CPU Voltage.
► Target/Current/Default CPU Voltage
These items show the Target/Current/Default CPU Voltage.
NOTE: The Target CPU Voltage equal to “CPU Voltage Multiplier” multiply “CPU Voltage
Setting” .
► DRAM Voltage Setting
This item is used to set DRAM Voltage. The default voltage is 1.890V.
► NB Voltage Setting
This item is used to set NB Voltage. The default voltage is 1.250V.
► CPU VTT Voltage Setting
This item is used to set CPU VTT Voltage. The default voltage is 1.200V.
► SB Voltage Setting
This item is used to set SB Voltage. The default voltage is 1.500V.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
All Voltage Control
******** All Voltage Control ******** Item Help
x CPU Voltage Multiplier x 1.000
x CPU Voltage Setting 1.3250V
Menu Level ►
Target CPU Voltage
1.3250V
Current CPU Voltage 1.3360V
Default CPU Voltage
1.3250V
x DRAM Voltage Setting 1.890V
x NB Voltage Setting 1.250V
x CPU VTT Voltage Setting 1.200V
x SB Voltage Setting 1.500V
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Page 50

43
3
oC Gear
*************oC Gear**************
► Current Storage Gear
We have more spaces in CMOS to allow you to store up to 4 sets of BIOS conguration data.
You can change any setting of BIOS, including the overclocking information, and save the
whole BIOS settings to one of four storage area. Later, you can retrieve BIOS settings by
restore it. This item is used to choose storage section to store your BIOS settings. Setting
values: [Not Use It]; [Storage Gear 1]; [Storage Gear 2]; [Storage Gear 3]; [Storage Gear 4].
► Store/Restore/Clear My Setting
This item allows you to Store/Restore/Clear the BIOS settings. See the help string in “Item
Help” table for detail.
********foxconn function********
► Smart Boot menu
This item is used to enable or disable the smart boot menu.
► Smart Power LED
Smart Power LED is a feature built on your motherboard to indicate different states during
Power On Self Test (POST). The LED is located at the front panel, which can display POST
state by using different long-short blinking intervals. You can always leave this state enabled.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
OC Gear
*************** OC Gear *************** Item Help
Current Storage Gear Not Use It
x Storage My Setting Store Menu Level ►
x Restore My Setting Restore
x Clear My Setting Clear Choose storage section
1 or 2 or 3 or 4 to
********** Foxconn Function ********** store your over clock
Smart Boot Menu
Disabled setting. If you store
Smart Power LED
Enabled your setting to
Current Storage Gear
successfully, then the
Storage Gear will
turn to Green color
If you clear the
Current Storage Gear
successfully, then the
color will turn back
to normal.
↑↓→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Not Use It
Page 51

44
3
load fail-Safe Defaults
If you encounter any system unstable problem, you may try to
load Fail-Safe defaults, which are the safest and most stable BIOS
settings for the motherboard.
Select this option and press <Enter>. A dialogue box pops out, press <Y> then press <Enter> to
load the defaults; press <N> and press <Enter> to skip.
The BIOS have set the basic and safest default functions to ensure the stability of your system. If
your computer fails to run properly, then you may load this default to recover the system back to
normal, and carry out failure analysis in next steps.
Load Optimized Defaults
Select this option and press <Enter>. A dialogue pops out, select
<Y> then press <Enter> to load the defaults; press <N> to skip.
By this default, BIOS have set the optimized performance
parameters of system to improve the performances of system components. But if the optimized
performance parameters to be set cannot be supported by your hardware devices, the system
may fail to work. It may happen on when you installed too many add-on cards on your system, or
overloaded the hardware until it can not afford.
Set Supervisor Password
The supervisor password can be set up through this menu.
Press <Enter>, and key in a password, save the change and
exit. The next time, when you enter the BIOS, it will ask you to
conrm the password to maintain your access right. After you
have the right to access the BIOS, you then can select this
setting again, and press <Enter> to disable this function or to change it to another password.
Set User Password
The user password can be set up through this menu. Only when there exists a Supervisor
password, then this setting can be active.
Save & Exit Setup
When you select this option and press <Enter>,
Select <Y> to save your changes to CMOS and exit the program;
Select <N> or <ESC> to return to the main menu.
Exit Without Saving
If you select this option and press <Enter>,
Select <Y> to exit CMOS without saving your modications;
Select <N> or <ESC> to return to the main menu.
Load Fail-Safe Defaults (Y/N)? N
Load Optimized Defaults (Y/N)? N
SAVE to CMOS and EXIT (Y/N)? Y
Quit Without Saving (Y/N)? N
Enter Password:
PASSWORD DISABLED !!!
Press any key to continue...
Page 52

The utility CD that came with the motherboard contains
useful software and several utility drivers that enhance
the motherboard features.
This chapter includes the following information :
■ Utility CD Introduction
■ AEGIS PANEL
■ FOX LiveUpdate
Note : Because each module is independent, so the
section number will be reorganized and unique to each
module, please understand.
Page 53

46
4
Utility CD introduction
This motherboard comes with one Utility CD. To begin with, simply insert the CD into your CD drive.
The CD will automatically run and display the main menu on the screen.
1. Install Driver
Click on "Install Driver", then use these options to install all the necessary drivers for your
motherboard. You need to restart your computer after nishing all the installations of drivers.
Intel chipset driver
Use it to install Intel chipset driver.
Realtek Audio drivers
Use it to install Realtek Audio driver.
Realtek 8111 LAN driver
Use it to install Realtek 8111 LAN driver.
JMicron Raid drivers
Use it to install JMicron RAID driver. JMircon provides one external SATA port together with two
Page 54

47
4
IDE PATA ports (Master/Slave). Due to limitation of RAID interface on JMircon, we recommend
you building RAID system by using onboard SATA ports (controlled by Intel ICH9R) instead of
JMicron.
Microsoft DirectX 9.0C
Use it to install Microsoft DirectX 9.0C driver.
Intel Matrix Storage Manager
Install this driver needs BIOS SATA Mode being set to [AHCI] or [RAID]. This restriction forces us
to nd out another way to install this driver. Please go to "5-5 Existing Windows XP with RAID
built as data storage." for more detail.
2. Software
Use these options to install additional software programs.
AeGIS PANel
Foxconn new utility software for monitoring system information. See “AEGIS PANEL” for details.
Fox LiveUpdate
The Fox LiveUpdate allows you to backup or update the system BIOS, drivers and utilities in
Windows® environment. See “Fox LiveUpdate” for details.
Adobe Reader
Installs Adobe® Acrobat® Reader that is used for viewing and printing the PDF document.
Norton Internet Security
Installs Norton® Internet Security to protect your PC from being affected by viruses.
Page 55

48
4
3. Create RAID Driver Floppy
When you are establishing a brand new Windows XP operating system on a new RAID system,
during installation, Windows XP needs a RAID driver in oppy drive to help the installation. Vista
has included this driver in itself, so you do not need this oppy.
This section is helping you to create a oppy diskette with RAID driver. You need to create this
diskette from another PC.
Depending on different 32-bit/64-bit Windows platforms you are using, you can choose
appropriate driver for the diskette.
Create (32bit/64bit) JMicron SATA RAID floppy
Allows you to create (32bit/64bit) JMicron SATA RAID Floppy.
Create (32bit/64bit) Intel MSM SATA RAID floppy
Allows you to create (32bit/64bit) Intel MSM SATA RAID Floppy.
Please go to Chapter 5, "Installing a New Windows XP on a Brand New RAID System" for
more detail.
4. browse CD
Click it to browse the CD content.
Page 56

49
4
AeGIS PANel
This is Foxconn’s new utility software. Aegis Panel, is a Windows innovation tool to provide
fan control, alarm function and system monitoring information such as fan speed, temperature,
voltage and CPU clock etc..
The powerful features are:
Overclocking (OC)
HWM INFO. (Hardware Monitor Information)
ALARM
CONFIG
Supported Operating Systems :
-Windows 2000
-Windows XP (32-bit and 64-bit)
-Windows 2003 (32-bit and 64-bit)
-Windows Vista (32-bit and 64-bit)
Using AEGIS PANEL:
1. Main Panel
Hazard Light
Open/Close main
panel to view
CPU clock
Open/Close
control panel for
detail operation
Open/Close the
left panel
Open/Close the
right panel
Minimize Aegis Panel to
taskbar
Visit Foxconn
website
Get help
Hide Aegis Panel
and put it in the
notication area of
taskbar ( or System
Tray)
Page 57

50
4
Aegis is a very important system monitoring program, so when
you click cross icon on it, Aegis only goes to notication area
of the taskbar, but does not stop running. If you really want to
close it, you must right click on it on the notication area, and
select exit to make it.
Open : Open Aegis Panel main panel on the screen.
Congure : Open Aegis Panel and directly enter congure mode.
Exit : Close Aegis program.
2. Overclocking
Click on "Foxconn" button to open/close the display screen. The information of CPU, memory,
and PCIE clocks are displayed.
Click on green button to go to Control Panel. Click on OC icon to visit Overclocking menu which
allows you to overclock your CPU and PCI bus manually.
Open/Close
screen
Page 58

51
4
3. HWM INfo. (Hardware Monitor Information)
Click "HWM INFO." button in the opening CONTROL PANEL to show the sensor's information.
Within this display, you can view the fan's speeds, temperatures and voltages.
Click on the rotating-fan button to control each fan function.
Fan control has 4 operating modes :
full Speed :
No control at all, running at full speed.
by Duty-Cycle :
The fan speed is controlled by setting the percentage
to the fan duty (between 0% ~ 100%).
by Temperature:
The Temperature and Duty elds can be manually adjustable if you select them. The relationships
between temperature and duty eld are dened as following :
SEC1SPEED1 : If temperature is over 60°C, fan will be running at its 100% duty. (Range 100%)
SEC2SPEED1 : If temperature is over 50°C, fan will be running at 75% duty. (Range 75% ~ 99%)
SEC3SPEED1 : If temperature is over 30°C, fan will be running at 50% duty. (Range 50% ~ 74%)
SEC4SPEED1 : If temperature is over 20°C, fan will be running at 25% duty. (Range 25% ~ 49%)
If current temperature is below any level, fan will be
running at its lowest 20% duty.
by Smartfan:
Fan speed is controlled by the system automatically,
and user does not have to know about how it is
controlled.
Click to go to
Fan Control menu
Click to view HW
Monitor menu
Close this page
Page 59

52
4
4. AlARM
Click "ALARM" button to trigger the warning events. It allows you to set the low/high limits of the
monitoring sensors. You can select a particular sensor to be watched carefully, or choose them
all.
If the monitoring value is lower than the low limit or higher than the high limit, and the Action
setting in CONFIG menu was set to "Ask Me", then you can hear buzzer sounds and the hazard
light is blinking. Click OK/Cancel button in the popped out HMW Alarm screen to acknowledge/
cancel the warning. If OK is pressed, the relative item will be displayed by red characters on the
"HWM INFO" screen.
Hazard light
Page 60

53
4
5. CoNfIG
Click "CONFIG" button to congure Aegis function. (Recommend using default values if possible).
fahrenheit / Celsius scales :
You can select temperature scales between them.
external / onboard Speaker :
It allows you to choose the warning tone devices.
Refresh Interval :
It is used to select the interval of refreshing the current monitoring information such as the CPU
clock, temperature, voltage etc.. (Unit: second per times)
Action when exceed the limitations :
It provides you four action items to handle events.
Ask Me : Default. Pop out HWM Alarm screen, and red mark item on HWM INFO. display.
Ignore : Just red mark current item, no HMW Alarm screen is displayed.
Disable : No HMW Alarm screen and no red mark.
Shutdown : The computer will be shut down after 10 seconds if selected.
Launch "Aegis Panel" on startup :
The Aegis Panel will be automatically started after the Windows operating system is activated.
Hidden tray icon :
Hide Aegis from the system tray display.
Go to System Tray
Page 61

54
4
FOX LiveUpdate
FOX LiveUpdate is a useful utility to backup and update your system BIOS, drivers and utilities by
local or online.
Supporting Operating Systems :
■ Windows 2000
■ Windows XP (32-bit and 64-bit)
■ Windows 2003 (32-bit and 64-bit)
■ Windows Vista (32-bit and 64-bit)
Using FOX LiveUpdate :
1. local Update
1-1 local Update - bIoS Information
This page lets you know your system BIOS information.
*** : please refer to the physical motherbard for detail.
Exit
Toolbar
Minimum
Show current
BIOS information
Link to website
Page 62

55
4
1-2 local Update - backup
This page can backup your system BIOS. You can click “Backup”, and key in a le name, then
click “Save” to nish the backup operation. The extension of this backup le is ".BIN" for Award
BIOS and ".ROM" for AMI BIOS. Default directory is "C:\Desktop\My Documents" in Windows XP
and "Documents" in Vista. Make sure you can remember the le name together with the directory
which it is stored, prevented that you may need them to recover your BIOS later.
1-3 local Update - Update
This page helps you to update your BIOS from a local le. After click “Update”, An alert message
will be displayed to ensure if you really want to continue, click “Yes” to conrm. A setup wizard
will guide you to load a local BIOS le to nish the operation. You must remember from which
directory to load your new BIOS le (with an extension of ".BIN" for Award BIOS, ".ROM" for AMI
BIOS) before the setup wizard starts.
Key in a BIOS name
Click here
FOX LiveUpdate can automatically backup old BIOS before update. This feature can be
enabled in the "Congure-System" setup. Please refer to "Congure-System" section
for more detail. The default backup directory is C:\LiveUpdate_Temp, but the backup
le name will be automatically generated. It is hard to nd it out from a backup directory,
and we recommend you using Explorer to check date/time message of this backup le
to nd it out and write its name down to remember it.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
Page 63

56
4
2. online Update
2-1 online Update - Update bIoS
This page lets you update your system BIOS from Internet. Click “start”, it will search the new
BIOS from Internet. Then follow the wizard to nish the update operation.
2-2 Online Update - Update Driver
This page lets you update your system drivers from Internet. Click “start”, it will search the new
drivers from Internet. Then follow the wizard to nish the update operation.
Click here
Current information
Search new BIOS
from Internet
Browse detailed
information
Update BIOS
Close the window
Select BIOS to update
Click here
Current information
Search new drivers
from Internet
Page 64

57
4
2-3 online Update - Update Utility
This page lets you update utilities from Internet. Click “start”, it will search the new utilities from
Internet. Then follow the wizard to nish the update operation.
Browse detailed
information
Install the selected
driver
Close the window
Select the driver to update
Click here
Current information
Search new utilities
from Internet
Browse detailed
information
Install the selected
utility
Close the window
Select the utility to update
Page 65

58
4
2-4 online Update - Update All
This page lets you update your system drivers from Internet. Click “start”, it will search all new
BIOS/drivers/utilities from Internet. Then follow the wizard to nish the update operation.
Click here
Current information
Search all new BIOS/
drivers/utilities from
Internet
Browse detailed
BIOS information
Close the window
Browse detailed
driver information
Browse detailed
utility information
Page 66

59
4
3. Congure
3-1 Congure - option
This page lets you set auto search options. After you enable the auto search function, Fox
LiveUpdate will start its searching from Internet and if any qualied item found, it will pop out a
message on the task bar to inform you to do the next step.
Double click on the icon as show below, you can see the detailed information.
Double click here
Apply the changes
Reset to default value
Click here
Set auto
search options
Select search
which kind of
versions
Set auto search
the latest
FOX LiveUpdate
Page 67

60
4
When you enable "Auto Search FOX LiveUpdate", if your FOX LiveUpdate version is older, it will
auto search from internet and prompt you to install the new version.
3-2 Congure - System
This page lets you set the backup BIOS location and change different skin of the Fox LiveUpdate
utility.
Click here
Set the location of
download les or
auto backup BIOS
Determine if the FOX LiveUpdate can
auto run when the system starts up
Select different skin
of the software
Apply the changes
Reset to default value
Prompt you to
install the new
FOX LiveUpdate
Page 68

61
4
3-3 Congure - Advance
This page lets you select to ash BIOS / Boot Block and clear CMOS. If you choose Flash Boot
Block, it means BIOS is not protective, and you must make sure the ash process is continuous
and without any interruption.
4. About & Help
This page shows some information about FOX LiveUpdate.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
We recommend that you should better keep the default setting unchanged to avoid any
damage.
Click here
Select which BIOS ROM
to ash(Only available to
motherboard with backup
BIOS ROM )
Apply the changes
Reset to default value
Select to ash Boot Block
Select to clear CMOS
Click here
Show information about
FOX LiveUpdate
Page 69

This chapter will cover two topics :
■ Installing a new Windows XP (Vista) in a brand new RAID
system.
■ Existing Windows XP (Vista) system with new RAID built as
data storage.
It includes the following information :
■ RAID Conguration Introduction
■ Intel® Matrix Storage Manager
■ Create a RAID Driver Diskette
■ BIOS Conguration
■ Create RAID in BIOS
■ Install a New Windows XP
■ Existing Windows XP with RAID built as data storage.
The RAID BIOS Setup pictures shown in this chapter are for
reference only, please refer to the practical screen.
Page 70

63
5
Installing a new Windows XP (Vista) in a brand new RAID
system.
1. Follow 5-1 to create a RAID driver diskette.
(Windows Vista has in-box driver by its own and can skip this step).
2. Follow 5-2 to set BIOS setting SATA mode to RAID or AHCI.
3. Follow 5-3 to create RAID in BIOS.
4. Follow 5-4 to Install Windows Operating System.
What kinds of hardware and software you need here :
1. A oppy drive.
2. A CD-ROM drive.
3. Several SATA hard disks.
4. A RAID driver diskette.
5. MARS CD. (To create RAID driver diskette if it is not bundled.)
6. Windows XP or Vista Install CD.
Existing Windows XP (Vista) system with new RAID built as
data storage.
Follow 5-5 to go through the processes to build a new RAID data storage in your
existing Windows XP system, it includes :
1. Copy RAID driver setup program to your hard disk. (Vista can skip)
2. Follow 5-2 to set BIOS setting SATA mode to RAID or AHCI.
3. Follow 5-3 to create RAID in BIOS.
4. Run setup program to install Intel® Matrix Storage Manager driver into your current
Windows XP system. (Vista can skip this step)
5. Format new RAID partitions.
What kinds of hardware and software you need here :
1. A CD-ROM drive.
2. Several SATA hard disks.
3. A MARS driver CD.
Page 71

64
5
RAID Conguration Introduction
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a method for computer data storage
schemes that divide and/or replicate data among multiple hard drives. RAID can be
designed to provide increased data reliability (fault tolerance) or increased I/O (input/
output) performance, or both. The motherboard comes with the Intel ICH9R. The
following RAID congurations are provided for users.
There are three major key concepts in RAID:
1. Mirroring : The copying of data to more than one disk;
2. Striping : The splitting of data across more than one disk;
3. Error correction : Where redundant data is stored to allow problems to be detected
and possibly xed (known as fault tolerance).
Different RAID levels use one or more of these techniques, depending on the system
requirements. The main aims of using RAID are to improve reliability, important for
protecting information that is critical to a business, for example a database of customer
orders; or where speed is important, for example a system that delivers video on
demand TV programs to many viewers.
The conguration affects reliability and performance in different ways. The problem
with using more disks is that it is more likely that one will go wrong, but by using
error checking the total system can be made more reliable by being able to survive
and repair the failure. Basic mirroring can speed up reading data as a system can
read different data from both the disks, but it may be slow for writing if it insists that
both disks must conrm that the data is correctly written. Striping is often used for
performance, where it allows sequences of data to be read off multiple disks at the
same time. Error checking typically will slow the system down as data needs to be
read from several places and compared. The design of RAID systems is therefore a
compromise and understanding the requirements of a system is important. Modern
disk arrays typically provide the facility to select the appropriate RAID conguration.
RAID is often used in high availability systems, where it is important that the system
keeps running as much of the time as possible.
Page 72

65
5
RAID 0 (Stripe)
RAID 0 reads and writes sectors of data interleaved among multiple drives. If any disk
member fails, it affects the entire array. The disk array data capacity is equal to the
number of drive members times the capacity of the smallest member. The striping
block size can be set from 4KB to 128KB. RAID 0 does not support fault tolerance.
RAID 1 (Mirror)
RAID 1 writes duplicate data onto a pair of drives and reads both sets of data in
parallel. If one of the mirrored drives suffers a mechanical failure or does not respond,
the remaining drive will continue to function. Due to redundancy, the drive capacity of
the array is the capacity of the smallest drive. Under a RAID 1 setup, an extra drive
called the “spare drive” can be attached. Such a drive will be activated to replace a
failed drive that is part of a mirrored array. Due to the fault tolerance, if any RAID 1
drive fails, data access will not be affected as long as there are other working drives in
the array.
RAID 5 (Parity)
RAID 5 provides data striping at the byte level and also stripes error correction
information. This results in excellent performance and good fault tolerance. Level 5 is
one of the most popular implementations of RAID.
RAID 10 (0+1)
RAID 10 is a combination of striping and mirroring. This conguration provides optimal
speed and reliability, but you need four SATA hard disks.
Comparison Table :
Solution Hard Disks No. Capacity Performance Reliability Application
RAID0 >=2 All Highest Dangerous Look for speed
RAID1 2 50% Read faster Excellent 100% Data backup
RAID5 >=3 N-1 Read faster
Write slower
Good Limited budget
RAID10 >=4
(Even number)
Smallest
*2
High Excellent Unlimited budget
Page 73

66
5
Intel
®
Matrix Storage Manager
The Intel® Matrix Storage technology supports RAID 0 ,RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10
(0+1) functions. It allows you to get high performance with fault tolerance, big capacity,
or data safety provided by different RAID functions.
In this section, we will use four SATA hard disks as an example to guide you how
to congure your RAID system. There are two 232.9GBs, one 298.1GB, and one
279.5GB. A creation of second volume will also be well described.
In each screen, there is also a message bar about each key’s function, such as <Tab>,
<Enter>, <Del>...etc. it is to help making your selection easier.
Two topics will be introduced :
1). Installing a new Windows XP in a brand new RAID system.
2). Existing Windows XP system with new RAID built as data storage.
Steps to Install Serial ATA Hard Disks :
1. Install SATA hard disks into the drive bays.
2. Connect one end of the SATA cable to motherboard’s SATA connector, and the
other end to SATA hard disk.
3. Connect SATA power cable to the power connector of SATA hard disk.
Before installing the SATA hard disks, make sure to turn off the computer
and unplug the power cord from the power outlet to prevent damage to the
hardware.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
■ Both AHCI and RAID modes need to install Intel
®
Matrix Storage driver.
■ Set SATA mode in BIOS to AHCI, you can skip RAID BIOS creation steps,
but the software driver installation of Intel® Matrix Storage Manager shall
follow the same rule as described for RAID.
W
A
R
N
I
N
G
!
Page 74

67
5
1. Find another PC, put a diskette into its
oppy drive, this diskette will be formatted
later. Put the MARS driver CD into CDROM drive, the screen will come out.
Click on "Create RAID Driver Floppy" icon.
2. Depending on each platform of your XP
system, normally, it is a 32-bit system.
Click on "Create(32-bit) Intel MSM SATA
RAID floppy" to create the diskette.
3. Click "GO" to start.
4. Select the desired destination FDD drive.
It can be the default drive A: or any USB
FDD. Click "OK" to continue.
5. Insert a diskette, click "OK" to continue.
5-1 Create a RAID driver diskette
If you want to install a brand new Windows XP on a AHCI or RAID system, you need to
congure the SATA Mode in BIOS to either AHCI or RAID rst. You also need to create
a RAID driver diskette for use in installing your Windows XP system.
Windows Vista has native RAID driver in itself, you can skip these steps.
Page 75

68
5
6. You can input a volume label for this diskette, click
on "Start" to format.
7. Click on "OK" to go through this warning
message.
8. Format nished. Click "OK" to continue copying of
RAID driver into this diskette.
9. Check if the diskette contains the driver les.
Later, when in the process of installing Windows
XP in your RAID system, it will ask you to use this oppy diskette to provide driver for
additional specic devices, for example, a RAID device.
10. Install Serial ATA Hard Disks :
10-1. Shut down your computer.
10-2. Install SATA hard disks into the drive bays, connect all power and SATA
cables.
Page 76

69
5
5-2 BIOS Conguration
1. Enter the BIOS setup by pressing <DEL> key during the POST(Power On Self Test).
2. Select the “Integrated Peripherals” from the “Main menu”, then select the “OnChip
IDE Device” item and press <Enter> to go to the conguration items.
3. Select and Set the “SATA Mode” option to [RAID].
4. Press <F10> to save the setting then PC will reboot itself.
5-3 Create RAID in bIoS
enter RAID bIoS Setup
When BIOS is restarted, it will display a message asking you to press <Ctrl>+<I> keys
simultaneously to enter the main menu of Intel® Matrix Storage Manager Option ROM
Utility. Press the <Ctrl>+<I> to enter Conguration Utility.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
None Dened.
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
1. Create RAID Volume
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
OnChip IDE Device
SATA Mode RAID Item Help
LEGACY Mode Support
Disabled
x Robson Support Disabled Menu Level ►
Onboard IDE/SATA Chip IDE Mode
Delay For HDD (Secs)
0
↑↓←→:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Page 77

70
5
Create RAID Volume
Create RAID 0 (1st Volume)
1. Select “1. Create RAID Volume” from the menu and press <Enter>.
The menu appears :
2. In "Name" item, you can input a device name for the RAID0 system and press <Enter>
to apply it. Here, we name it as TryRAID0 to replace the default Volume0.
3. In “RAID Level” item, you can use Up or Down arrow key to make a selection from
one of RAID0, 1, 5, 10 items. Select RAID0 (Stripe) and press <Enter>.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Choose the RAID level:
RAID 0: Stripes data (performance).
RAID1: Mirrors data (redundancy).
RAID 10: Mirrors data and stripes the mirror.
RAID 5: Stripes data and parity.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
RAID0(Stripe)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Enter a unique volume name that has no special characters and is
16 characters or less.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
Volume0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
Volume0
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Page 78

71
5
4. It then goes to “Disks” item. Press <Enter> to choose the hard disks for this RAID0
system.
5. From the hard drive list, use Up or Down arrow key to reach the hard disks you want
to combine them as RAID0, then press <Space> key to select them. A triangle sign
will appear to indicate the drive selected. Here, we select two 232.9GB hard disks as
an example. Press <Enter> key to nish the selection.
Creating RAID 1
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
TryRAID0
RAID0(Stripe)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 disks to use in creating the volume
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [Enter]-Done
[ SELECT DISKS ]
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Creating RAID 1
Name:
RAID Level:
Volume0
RAID0(Stripe)
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
►0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
►2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 disks to use in creating the volume
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [Enter]-Done
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
[ SELECT DISKS ]
Page 79

72
5
6. It is now entering “Strip Size” menu. Use Up or Down arrow key to select the desired
strip size. The available values range from 4KB to 128KB. The strip value should be
selected based on different applications. Some suggested choices are :
16K - Best for sequential transfer.
64K - Good general purpose strip size.
128K - Best performance for most desktops and workstations .
The default value is 128K for RAID0. Press <Enter>.
7. In “Capacity” line, it displays there are maximum 232.9GB * 2 = 465.8GB available.
As we want to introduce how to create two disk volumes (like logical devices C: and
D:) in a RAID0 system, so we only key in 200GB here to build the rst volume. Later,
we will also describe how the second volume is generated. Input 200GB, and press
<Enter>.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
The default value indicates the maximum capacity using the selected
disks. Entering a lower capacity allows you to create a second
volume on these disks
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
465.8 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ HELP ]
465.8
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
The following are typical values:
RAID0 - 128KB
RAID10 - 64KB
RAID5 - 64KB
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
465.8 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ HELP ]
128KB
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 80

73
5
8. In “Create Volume” item, press <Enter>.
A warning message will appear :
9. Press <Y> to create the volume and return to the main menu, a 200GB RAID0 system
is normally congured.
WARNING: ALL DATA ON SELECTED DISKS WILL BE LOST.
Are you sure you want to create this volume ? (Y/N) :
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID0 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 200.0GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
1. Create RAID Volume
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Press ENTER to create the specified volume.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
200 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ HELP ]
Create Volume
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 81

74
5
Create RAID0 (2nd Volume)
1. Select “1. Create RAID Volume” from the menu and press <Enter>.
The menu appears :
2. In "Name" item, we name it as TryRAID0-1 for second volume.
3. In “RAID Level” item, you can use Up or Down arrow key to make a selection, only
RAID0, 1 can be selected. Select RAID0 (Stripe) and press <Enter>.
(Note : You also can try to select RAID1 for the second volume as an experiment here)
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Enter a unique volume name that has no special characters and is
16 characters or less.
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
Volume0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
Volume0
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Choose the RAID level:
RAID 0: Stripes data (performance).
RAID1: Mirrors data (redundancy).
RAID 10: Mirrors data and stripes the mirror.
RAID 5: Stripes data and parity.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID0-1
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
RAID0(Stripe)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 82

75
5
4. It then goes to “Disks” item. Press <Enter> to choose the hard disks for this RAID0
second volume system.
5. From the hard disk list, select the previously congured RAID0 hard disks, and press
<Space> key to select them. Two triangle signs will appear to indicate the selections.
Press <Enter> to continue.
Creating RAID 1
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
TryRAID0-1
RAID0(Stripe)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Member Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 disks to use in creating the volume
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [Enter]-Done
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Member Disk
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
[ SELECT DISKS ]
Creating RAID 1
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
TryRAID0-1
RAID0(Stripe)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
► 0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Member Disk
►2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Member Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 disks to use in creating the volume
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [Enter]-Done
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Member Disk
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
[ SELECT DISKS ]
Page 83

76
5
6. It goes to “Strip Size” menu directly. Capacity automatically displays 265.8GB, and
at this time, you can not input any value in capacity as there is no additional volume
available.
The available values of Strip Size range from 4KB to 128KB. The strip value should be
selected based on different applications. Some suggested choices are :
16K - Best for sequential transfer.
64K - Good general purpose strip size.
128K - Best performance for most desktops and workstations .
The default value is 128K. Press <Enter>.
7. Select “Create Volume” and press <Enter>.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
The following are typical values:
RAID0 - 128KB
RAID10 - 64KB
RAID5 - 64KB
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID0-1
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
265.8 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ HELP ]
128KB
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Press ENTER to create the specified volume.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID0-1
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
265.8 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ HELP ]
Create Volume
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 84

77
5
A message will appear :
Press <Y> to create the volume and return to the main menu. Two RAID0 volumes
were congured.
Are you sure you want to create this volume ? (Y/N) :
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID0 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 200.0GB
Normal Yes
1 TryRAID0-1 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 265.8GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Member Disk(0,1)
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0,1)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
1. Create RAID Volume
Page 85

78
5
Create RAID 1
1. Select “1.Create RAID Volume” from the main menu and press <Enter>.
2. In "Name" item, you can input a device name for the RAID1 system and press
<Enter> to apply it. Here, we name it as TryRAID1 to replace the default Volume0.
3. In “RAID Level” item, you can use Up or Down arrow key to make a selection from
one of RAID0, 1, 5, 10 items. Select RAID1 (Mirror) and press <Enter>.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Enter a unique volume name that has no special characters and is
16 characters or less.
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
Volume0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
TryRAID1
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Choose the RAID level:
RAID 0: Stripes data (performance).
RAID1: Mirrors data (redundancy).
RAID 10: Mirrors data and stripes the mirror.
RAID 5: Stripes data and parity.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID1
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
RAID1(Mirror)
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 86

79
5
4. It then goes to “Disks” item. Press <Enter> to choose the hard disks for this RAID1
system.
5. From the hard drive list, use Up or Down arrow key to reach the hard disks you want
to combine them as RAID1, then press <Space> key to select them. A triangle sign
will appear to indicate the drive selection. Here, we select one 232.9GB and one
298.1GB hard disks. Press <Enter> key to nish the selection.
Creating RAID 1
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
TryRAID1
RAID1(Mirror)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 disks to use in creating the volume
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [Enter]-Done
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
[ SELECT DISKS ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Volume0
RAID0(Stripe)
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Creating RAID 1
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
►2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
►4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 disks to use in creating the volume
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [Enter]-Done
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
[ SELECT DISKS ]
Page 87

80
5
6. It will skip “Strip Size” menu for RAID1.
7. In “Capacity” item, use the default value, and press <Enter>. The size of the smaller
hard disk 232.9GB is becoming the default value, and it indicates the maximum
capacity.
8. Select “Create Volume” and press <Enter>. A warning message will appear :
Press <Y> to create the volume and return to the main menu.
WARNING: ALL DATA ON SELECTED DISKS WILL BE LOST.
Are you sure you want to create this volume ? (Y/N) :
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID1 RAID1(Mirror) N/A 232.9GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Member Disk(0)
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
1. Create RAID Volume
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
The default value indicates the maximum capacity using the selected
disks. Entering a lower capacity allows you to create a second
volume on these disks
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
N/A
465.8 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ HELP ]
232.9
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 88

81
5
Create RAID 10 (0+1)
1. Select “1.Create RAID Volume” from the main menu and press <Enter>.
2. In "Name" item, you can input a device name for the RAID10 system and press
<Enter> to apply it. Here, we name it as TryRAID10 to replace the default Volume0.
3. In “RAID Level” item, you can use Up or Down arrow key to make a selection from
one of RAID0, 1, 5, 10 items. Select RAID10(RAID0+1) and press <Enter>.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Enter a unique volume name that has no special characters and is
16 characters or less.
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
Volume0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
TryRAID10
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Choose the RAID level:
RAID 0: Stripes data (performance).
RAID1: Mirrors data (redundancy).
RAID 10: Mirrors data and stripes the mirror.
RAID 5: Stripes data and parity.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID10
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
64KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
RAID10(RAID0+1)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 89

82
5
4. After exiting from "RAID Level", it goes directly to "Stripe Size" item. Because all
four disks are selected for RAID10, so there is no need to go to Disks option.
5. Use Up or Down arrow key to select the desired strip size when entering “Strip
Size” menu. The default value is 64K.
6. In “Capacity” item, use the default value, and press <Enter>. The default value is
twice the smallest hard disk size, that is, 232.9GB * 2 = 465.8GB.
7. Select “Create Volume” and press <Enter>. A warning message will appear :
Press <Y> to create the volume and return to the main menu.
WARNING: ALL DATA ON SELECTED DISKS WILL BE LOST.
Are you sure you want to create this volume ? (Y/N) :
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID10 RAID10(RAID0+1) N/A 232.9GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Member Disk(0)
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Member Disk(0)
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
1. Create RAID Volume
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
The following are typical values:
RAID0 - 128KB
RAID10 - 64KB
RAID5 - 64KB
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID10
RAID10(RAID0+1)
Select Disks
64KB
465.8 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ HELP ]
64KB
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 90

83
5
Create RAID5 (Parity)
1. Select “1.Create RAID Volume” from the main menu and press <Enter>.
2. In "Name" item, you can input a device name for the RAID5 system and press
<Enter> to apply it. Here, we name it as TryRAID5 to replace the default Volume0.
3. In “RAID Level” item, you can use Up or Down arrow key to make a selection from
one of RAID0, 1, 5, 10 items. Select RAID5(Parity) and press <Enter>.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Enter a unique volume name that has no special characters and is
16 characters or less.
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
Volume0
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
128KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
TryRAID5
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Choose the RAID level:
RAID 0: Stripes data (performance).
RAID1: Mirrors data (redundancy).
RAID 10: Mirrors data and stripes the mirror.
RAID 5: Stripes data and parity.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID5
RAID0(Stripe)
Select Disks
64KB
0.0 GB
Create Volume
RAID5(Parity)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 91

84
5
4. It then goes to “Disks” item. Press <Enter> to choose the hard disks for this RAID5
system.
5. From the hard drive list, use Up or Down arrow key to reach the hard disks you want
to combine them as RAID5, then press <Space> key to select them. A triangle sign
will appear to indicate the drive selection. Here, we select 232.9GB, 298.1GB and
279.5GB hard disks for an example. Press <Enter> key to nish the selection.
Creating RAID 1
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
TryRAID5
RAID5(Parity)
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 disks to use in creating the volume
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [Enter]-Done
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
[ SELECT DISKS ]
Name:
RAID Level:
Volume0
RAID0(Stripe)
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Creating RAID 1
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
►2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Non-RAID Disk
►4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Non-RAID Disk
►5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Select 2 to 6 disks to use in creating the volume
[↑↓]-Prev/Next [SPACE]-SelectDisk [Enter]-Done
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB Non-RAID Disk
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
[ SELECT DISKS ]
Page 92

85
5
6. Use Up or Down arrow key to select the desired strip size when entering “Strip
Size” menu. The default value is 64K. Press <Enter>.
7. In “Capacity” item, use the default value, and press <Enter>. The default value is
twice that of the smallest hard disk size, that is, 232.9GB * 2 = 465.8GB.
8. Select “Create Volume” and press <Enter>. A warning message will appear :
Press <Y> to create the volume and return to the main menu.
WARNING: ALL DATA ON SELECTED DISKS WILL BE LOST.
Are you sure you want to create this volume ? (Y/N) :
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID5 RAID5(Parity) 64KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Member Disk(0)
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Member Disk(0)
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
1. Create RAID Volume
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
The following are typical values:
RAID0 - 128KB
RAID10 - 64KB
RAID5 - 64KB
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Name:
RAID Level:
Disks:
Strip Size:
Capacity:
TryRAID5
RAID5(Parity)
Select Disks
64KB
465.8 GB
Create Volume
[↑↓]-Change [TAB]-Next [ESC]-Previous Menu [Enter]-Select
[ HELP ]
64KB
[ CREATE VOLUME MENU ]
Page 93

86
5
Delete RAID Volume
1. Take TryRAID5 for example. Select “2. Delete RAID Volume” in main menu and
press <Enter>.
2. Use Up or Down arrow key to select the RAID set you want to delete. Here only one
RAID5 is seen, so press <DEL> key to continue.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Name Level Drives Capacity Status Bootable
TryRAID0 ID0(Stripe) 2 465.8GB Normal Yes
Deleting a volume will reset the disks to non-RAID.
WARNING: ALL DISK DATA WILL BE DELETED.
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Previous Menu [DEL]-Delete Volume
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
[ DELETE VOLUME MENU ]
TryRAID5 RAID5(Parity) 3 465.8GB Normal Yes
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID5 RAID5(Parity) 64KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Member Disk(0)
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Member Disk(0)
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
2. Delete RAID Volume
Page 94

87
5
3. After <DEL> key is pressed, the screen appears as below:
Press <Y> key to conrm the volume deletion.
4. Return to Main Menu.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
Name Level Drives Capacity Status Bootable
TryRAID5 RAID5(Parity) 3 465.8GB Normal Yes
Deleting a volume will reset the disks to non-RAID.
WARNING: ALL DISK DATA WILL BE DELETED.
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Previous Menu [DEL]-Delete Volume
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ HELP ]
[ DELETE VOLUME MENU ]
ALL DATA ON SELECTED DISKS WILL BE LOST!
Are you sure you want to delete "TryRAID5"? (Y/N) :
[ DELETE VOLUME VERIFICATION ]
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
None Dened.
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
2. Delete RAID Volume
Page 95

88
5
Reset Disks to Non-RAID
Reset RAID volume allows you to replace a failed disk with a new one, and the
operating system will rebuild the data later. For RAID0, reset a hard disk would totally
crash the system, but for RAID1, RAID10 and RAID5, they all can be rebuilt.
When rebuild is needed, you must rst install a new hard disk in your system before
getting into Intel® Matrix Storage Manager utility, because the utility will ask you which
hard disk the new rebuild will be performed.
example 1. Reset a RAID0 system.
1. A TryRAID0 volume was built with two 232.9GB hard disks, we want to reset one of
them. Select “3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID” in main menu and press <Enter>.
2. A warning message is displayed.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID0 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
3. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID0 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Phiysical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Ststus(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
Resetting RAID disk will remove its RAID structures
and revert it to a non-RAID disk.
WARNING: Resetting a disk causes all data on the disk to be lost.
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Member Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Member Disk
Select the disks that should be reset
[↑↓]-Previous/Next [SPACE]-Selects [Enter]-Selection Complete
[ RESET RAID DATD ]
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Member Disk
Page 96

89
5
3. Select WDC hard disk as the one to be reset. Press <Enter>. A double conrmation
message pops out, press <Y> to conrm.
4. It goes back to Main menu with a "Failed" status of RAID0 volume.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
3. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID0 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Phiysical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Ststus(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
Resetting RAID disk will remove its RAID structures
and revert it to a non-RAID disk.
WARNING: Resetting a disk causes all data on the disk to be lost.
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
► 0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Member Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Member Disk
Are you sure you want to reset RAID data on selected disks? (Y/N):
[↑↓]-Previous/Next [SPACE]-Selects [Enter]-Selection Complete
[ RESET RAID DATD ]
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB Member Disk
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID0 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 465.8GB
Failed Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
Page 97

90
5
example 2. Reset a RAID5 system
1. A TryRAID5 volume was built with three hard disks, we want to reset one of them.
Select “3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID” in main menu and press <Enter>.
2. A warning message is displayed.
3. Select "Port 4 - ST3320620SV" hard disk as the one to be reset. Press <Enter>.
A double conrmation message pops out, press <Y> to conrm.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID5 RAID5(Parity) 64KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Member Disk(0)
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Member Disk(0)
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
3. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID0 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Phiysical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Ststus(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Non-RAID Disk
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
Resetting RAID disk will remove its RAID structures
and revert it to a non-RAID disk.
WARNING: Resetting a disk causes all data on the disk to be lost.
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Status
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB Member Disk
►4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Member Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Member Disk
Are you sure you want to reset RAID data on selected disks? (Y/N):
[↑↓]-Previous/Next [SPACE]-Selects [Enter]-Selection Complete
[ RESET RAID DATD ]
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB Member Disk
Page 98

91
5
4. A "DeGRADeD VolUMe DeTeCTeD" screen pops out asking you to select a new
hard disk for rebuilding. Here, we select WDC 232.9GB. Press <Enter> to select it.
5. It goes back to Main menu with a "Rebuild" status of RAID5 volume. Eventually,
a replacement hard disk has to join in and it always keeps three hard disks in the
RAID5 system.
6. Operating System will perform the rebuilding later.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
3. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID0 RAID0(Stripe) 128KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Member Disk(0)
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
"Degraded" volume and disk available for rebuilding detected. Selecting
a disk initiates a rebuild. rebuild completes in the operating system.
Select the port of the destination disk for rebuilding (ESC to exit):
Port Drive Model Serial # Size
0 WDC WD2500JS-60NCB1 WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
[↑↓]-Previous/Next [Enter]-Select [ESC]-Exit
[ DEGRADED VOLUME DETECTED ]
0 WDC WD2500JS-60NCB1 WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID5 RAID5(Parity) 64KB 465.8GB
Rebuild Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Non-RAID Disk
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Member Disk(0)
Volume with "Rebuild" status will be rebuilt within the operating system.
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
Page 99

92
5
exit RAID bIoS
1. Take TryRAID5 as an example, select “4. exit” in main menu and press <Enter>.
The screen displays :
2. Press <Y> to exit Intel® Matrix Storage Manager program. The system will reboot.
3. Shut down the computer, remove WD hard disk, and we will continue for Windows
OS installation. If you do not remove irrelevant WD hard disk, Windows may detect
it during the installation, and you could be confused.
4. Remove any diskette from oppy drive.
5. Restart computer to start Windows installation.
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v5.0.0.1011 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-04 Intel Corporation All Rights Reserved.
1. Create RAID Volume 3. Reset Disks to Non-RAID
2. Delete RAID Volume 4. Exit
RAID Volume :
ID Name Level Stripe Size Status Bootable
0 TryRAID5 RAID5(Parity) 64KB 465.8GB
Normal Yes
Physical Disks:
Port Drive Model Serial # Size Type/Status(Vol ID)
0 WDC WD2500JS-60N WD-WCANKC865380 232.9GB
Non-RAID Disk
2 Maxtor 6L250S0 L50SKP4G 232.9GB
Member Disk(0)
4 ST3320620SV 9QF4YJGQ 298.1GB
Member Disk(0)
5 ST3300831AS 3NF02XH2 279.5GB
Member Disk(0)
[↑↓]-Select [ESC]-Exit [Enter]-Select Menu
Intel(R) Matrix Storage Manager option ROM v7.6.0.1006 ICH9R wRAID5
Copyright(C) 2003-07 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
[ DISC/VOLUME INFORMATION ]
[ Main Menu ]
Are you sure you want to exit? (Y/N):
[ CONFIRM EXIT ]
Page 100

93
5
5-4 Install a New Windows XP
1. Press <DEL> to enter BIOS Setup during POST.
2. Insert the Windows installation CD into the optical drive.
3. Set the “First Boot Device” to “CDROM”, save changes and exit the BIOS setup.
4. The computer will reboot, and it will start installing Windows Operating System.
Watch the screen carefully, when the following picture appears, press <F6> key
immediately. If you forgot to do this, PC will go to an fatal blue screen, and you
may need to reboot the system again. PC may not respond to your <F6> input
immediately, and it keeps loading les until the next screen displays.
Phoenix - AwardBIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Advanced BIOS Features
► Hard Disk Boot Priority Press Enter ▲ Item Help
Virus Warning
Enabled █
First Boot Device
CDROM █ Menu Level ►
Second Boot Device
Hard Disk █
Third Boot Device
USB-ZIP █ Select Hard Disk Boot
Boot Other Device
Enabled █ Device Priority
Boot Up Floppy Seek
Disabled █
Boot Up NumLock Status
on █
Gate A20 Option
Fast █
Typematic Rate Setting
Disabled █
x Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) 6 █
x Typematic Delay (Msec) 250
█
Security Option
Setup █
APIC Mode
Enabled █
MPS Version Control for OS
1.4 █
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB
Non-OS2 █
Report No FDD For WIN 95
No ▒
Full Screen LOGO Show
Enabled ▒
Small LOGO(EPA) Show
Disabled ▼
↑↓←→:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
CDROM
Windows Setup
Press F6 if you need to install a 3rd party SCSI or RAID driver.
When you set the SATA Mode in BIOS to either AHCI or RAID, you need
to follow these steps to install your Windows XP system.
C
A
U
T
I
O
N
!
 Loading...
Loading...