Page 1

Statement:
This manual is the intellectual property of FOXCONN, Inc. Although the
information in this manual may be changed or modified at any time,
FOXCONN does not obligate itself to inform the user of these changes.
Trademark:
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Version:
User’s Manual V1.0 in English for 945P7AA series motherboard.
91-181-945-A1-0E
P/N:
Symbol description:
Note: refers to important information that can help you to use motherboard
better.
Attention: indicates that it may damage hardware or cause data loss,
and tells you how to avoid such problems.
Warning: means that a potential risk of property damage or physical
injury exists.
More information:
If you want more information about our products, please visit FOXCONN
website:
www.foxconnchannel.com
Page 2
Declaration of conformity
HON HAI PRECISION INDUSTRY COMPANY LTD
66 , CHUNG SHAN RD., TU-CHENG INDUSTRIAL DISTRICT,
TAIPEI HSIEN, TAIWAN, R.O.C.
declares that the product
Motherboard
945P7AA series
is in conformity with
(reference to the specification under which conformity is declared in
accordance with 89/336 EEC-EMC Directive)
EN 55022/A1: 2000 Limits and methods of measurements of radio disturbance
characteristics of information technology equipment
EN 61000-3-2/A14:2000 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Part 3: Limits
Section 2: Limits for harmonic current emissions
(equipment input current <= 16A per phase)
EN 61000-3-3/A1:2001 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
Part 3: Limits
Section 2: Limits of voltage fluctuations and flicker in low-voltage
supply systems for equipment with rated current <= 16A
EN 55024/A1:2001 Information technology equipment-Immunity characteristics limits
and methods of measurement
Signature : Place / Date : TAIPEI/2005
Printed Name : James Liang Position/ Title : Assistant President
Page 3

Declaration of conformity
Trade Name: FOXCONN
Model Name: 945P7AA
Responsible Party: PCE Industry Inc.
Address: 458 E. Lambert Rd.
Fullerton, CA 92835
Telephone: 714-738-8868
Facsimile: 714-738-8838
Equipment Classification: FCC Class B Subassembly
Type of Product: Motherboard
Manufacturer: HON HAI PRECISION INDUSTRY
COMPANY LTD
Address: 66 , CHUNG SHAN RD., TU-CHENG
INDUSTRIAL DISTRICT, TAIPEI HSIEN,
TAIWAN, R.O.C.
Supplementary Information:
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions : (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
Tested to comply with FCC standards.
Signature : Date : 2005
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter
Chapter
Supply ............................................................................................
Chapter
Standard CMOS Features .......................................................................... 31
BIOS Features ...........................................................................................
Advanced BIOS Features ..........................................................................
Advanced Chipset Features ......................................................................
Integrated Peripherals ................................................................................
Power Management Setup .........................................................................
PnP/PCI Configurations ...............................................................................
PC Health Status ........................................................................................
Load Fail-Safe Defaults .............................................................................
Load Optimized Defaults ............................................................................
Set Supervisor/User Password ................................................................. 54
Save & Exit Setup ......................................................................................
Exit Without Saving ....................................................................................
Product Introduction
Installation Instructions
BIOS Description
Page 5

Table of Contents
Chapter
Utility CD content ........................................................................................ 57
Start to install drivers ................................................................................. 58
Chapter
SuperStep ................................................................................................. 61
SuperUpdate ............................................................................................. 64
SuperLogo................................................................................................. 68
Directions for Bundled Software
Chapter
SuperBoot ................................................................................................. 71
SuperBIOS-Protect .................................................................................... 72
SuperRecovery ......................................................................................... 73
SuperSpeed .............................................................................................. 82
Driver CD Introduction
Special BIOS Functions
Appendix
Using 8-channel Audio (optional) ............................................................... 83
Page 6
Warning:
1. Attach the CPU and heatsink using silica gel to ensure full contact.
2. It is suggested to select high-quality, certified fans in order to avoid
damage to the motherboard and CPU due high temperatures.
3. Never turn on the machine if the CPU fan is not properly installed.
4. Ensure that the DC power supply is turned off before inserting or
removing expansion cards or other peripherals, especially when
you insert or remove a memory module. Failure to switch off the DC
power supply may result in serious damage to your system or
memory module.
Warning:
We cannot guarantee that your system will operate normally while
over-clocked. Normal operation depends on the over-clock capacity
of your device.
Attention:
Since BIOS programs are upgraded from time to time, the BIOS
description in this manual is just for reference. We do not guarantee
that the content of this manual will remain consistent with the actual
BIOS version at any given time in the future.
Attention:
The pictures of objects used in this manual are just for your reference.
Please refer to the physical motherboard.
Page 7

This manual is suitable for motherboard of 945P7AA series.
Each motherboard is carefully designed for the PC user who
wants diverse features.
-L with onboard 10Mb/100Mb LAN
-K with onboard 1Gb LAN
-6 with 6-Channel audio
-8 with 8-Channel audio
-E with 1394 function
-S with SATA function
-R with RAID function
You can find PPID label on the motherboard. It indicates
the functions that the motherboard has.
For example:
On the blue mark of the PPID label, it means the
motherboard supports 6-channel audio(-6), 1394 port(-E),
onboard 10Mb/100Mb LAN (-L), SATA function(-S).
Page 8
Chapter
1
1
Thank you for purchasing FOXCONN 945P7AA series
motherboard. This series of motherboard is one of our new
products, and offers superior performance, reliability and
quality, at a reasonable price. This motherboard adopts the
advanced Intel® 945P+ ICH7/ICH7R chipset, providing users
a computer platform with a high integration-compatibilityperformance price ratio.
This chapter includes the following information:
Main Features
Motherboard Layout
Page 9

Chapter 1 Product Introduction
Main Features
Size
ATX form factor of 12 inch x 9.6 inch
Microprocessor
Supports Intel® Pentium® 4 processor in an LGA775 package
Supports FSB at 533MHz/800MHz/1066 MHz
Supports Hyper-Threading technology
Supports FSB Dynamic Bus Inversion (DBI)
Chipset
Intel® 945P (North Bridge) + ICH7/ICH7R (South Bridge)
System Memory
Four 240-pin DDR2 DIMM slots
Supports Dual-Channel DDR2 533/667 DIMMs
Available bandwidth up to 5.3GB/s (DDR2 667) for Single-Channel mode
and 10.7 GB/s (DDR2 667) in Dual-Channel Interleaved mode
Supports 256 Mb, 512 Mb, and 1 Gb DDR2 technologies for x8 and x16
devices
Supports up to 4GB memory capacity
Supports non-ECC DIMMs only
USB 2.0 Ports
Supports hot plug
Eight USB 2.0 ports (four rear panel ports, two onboard USB connectors
providing four extra ports)
Supports wake-up from S1 and S3 mode
Supports USB 2.0 Protocol up to 480 Mbps transmission rate
Onboard Serial ATA (optional)
300 MBps transfer rate
Supports up to four S-ATA devices
Supports RAID 5, RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10, Matrix RAID (supported on ICH7R)
2
Page 10

Chapter 1 Product Introduction
Onboard IDE RAID Controller (IT8212)(optional)
Two Ultra DMA 133/100/66 IDE connectors
Supports RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1, and JBOD configuration
Onboard LAN (-L/-K) (optional)
Supports 10/100/1000 (-K optional) Mbit/sec Ethernet
LAN interface built-in on board
Onboard 1394 (-E ) (optional)
Support hot plug
With rate of transmission at 400Mbps
Self-configured addressing
Can connect with 2 independent 1394 units synchronously at most
Onboard Audio (-6) (optional)
AC’97 2.3 Specification Compliant
Supports SPDIF output
Onboard Line-in jack, Microphone jack, Line-out jack
Supports 6-channel audio (setting via software)
Onboard Audio (-8) (optional)
Supports 8-channel audio
Supports SPDIF output
Supports Intel High Definition Audio
Supports high quality differential CD input
PCI Express x16 Support
Supports 4 GB/sec (8 GB/sec concurrent) bandwidth
Low power consumption and power management features
Green Function
Supports ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
Supports S0 (normal), S1 (power on suspend), S3 (suspend to RAM), S4
(Suspend to disk - depends on OS), and S5 (soft - off).
3
Page 11

Chapter 1 Product Introduction
Expansion Slots
Three PCI slots
Two PCI Express x1 slots
One PCI Express x16 graphics slot
Advanced Features
PCI 2.3 specification compliant
Supports Windows 2000/XP soft-off
Supports Wake-on-LAN function (optional)
Supports PC Health function (capable of monitoring system voltage, CPU/
system temperature, and fan speed)
4
Page 12
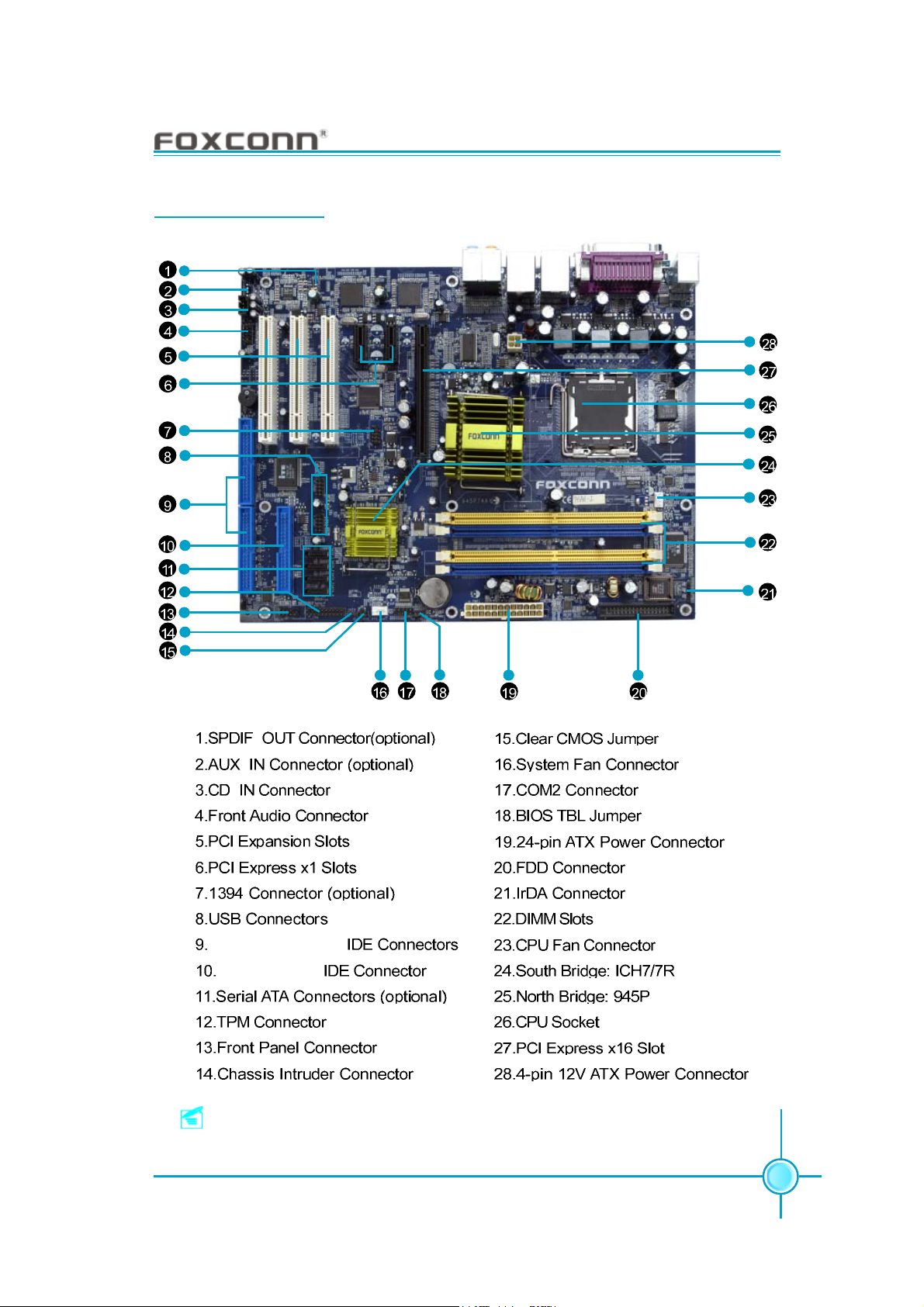
Motherboard Layout
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
ATA 133/100/66/33
ATA 100/66/33
Note: The above motherboard layout is provided for reference only;
please refer to the physical motherboard.
5
Page 13
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
Chapter
2
2
This chapter introduces the hardware installation process,
including the installation of the CPU, memory, power supply,
slots, rear panel and pin headers, and the mounting of
jumpers. Caution should be exercised during the installation
of these modules. Please refer to the motherboard layout
prior to any installation and read the contents in this chapter
carefully.
This chapter includes the following information:
CPU
Memory
Power supply
Rear Panel Connectors
Other Connectors
Expansion Slots
Jumpers
6
Page 14
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Attention:
Take note of the following precautions before you install components
or change settings.
1. Use a grounded wrist strap or touch a safely grounded object,
such as an attached power supply, before handling components
to avoid damaging them due to static electricity.
2. Unplug the power cord before opening your chassis or touching
any component.
3. Hold components by their edges to avoid touching any exposed
integrated circuits (ICs).
4. Whenever you uninstall a component, place it on a grounded
anti-static pad or into the anti-static bag that it came in.
7
Page 15
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
CPU
This motherboard supports Smithfield, Pentium® 4, Celeron® D Processor in
an LGA775 package.
Dynamic Bus Inversion (DBI).
Installation of CPU
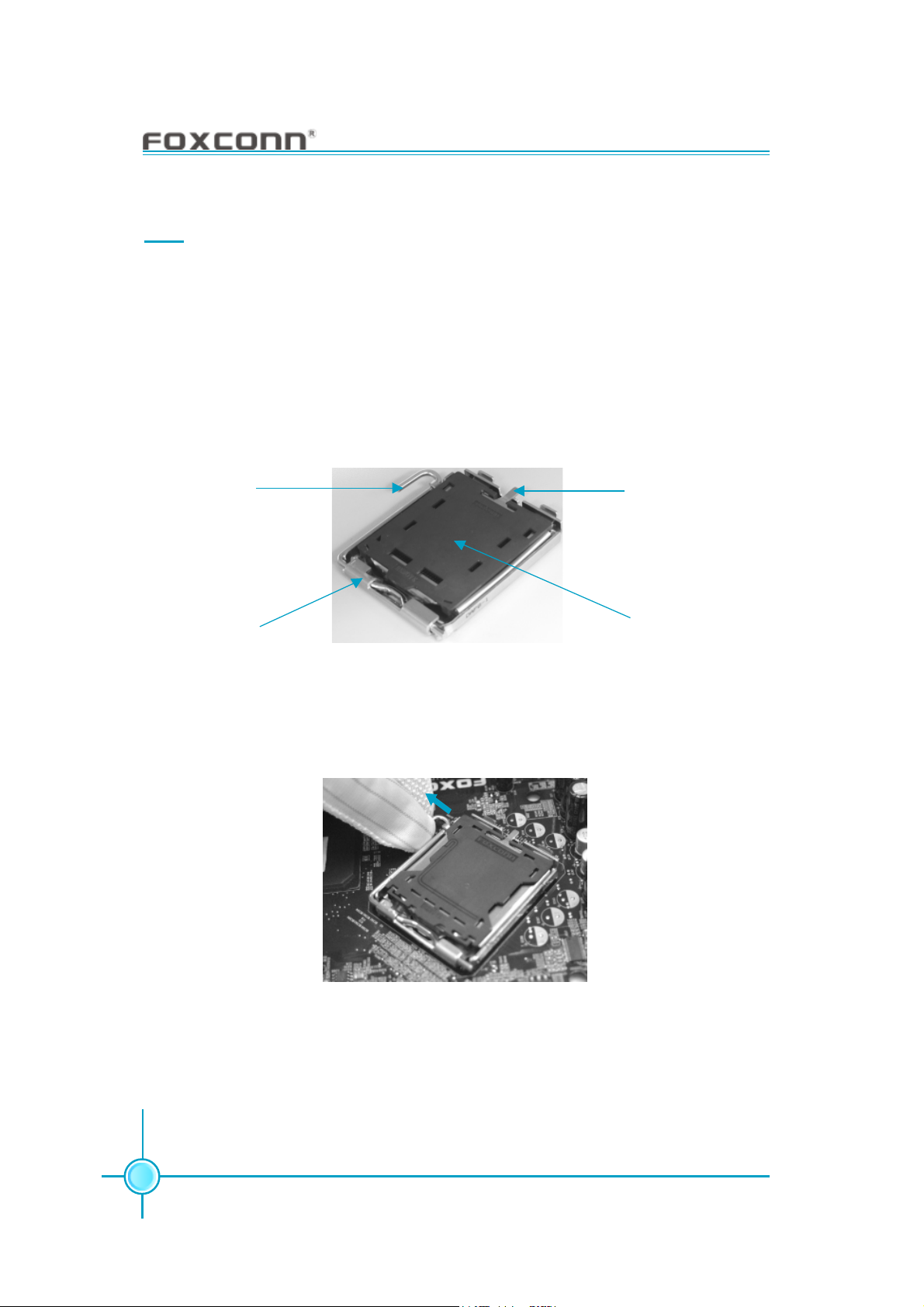
Below is the CPU socket illustration. Follow these procedures to install a CPU.
It also supports Hyper-Threading Technology and FSB
Load lever
Load plate
Protective cover
Load stiffener
1. Use thumb and forefinger to hold the hook of the load lever and pull the lever
down and away from socket to unlock it. Lift the load lever.
2. Push down the rear tab with your forefinger to bring the front end of the load
plate up slightly. Open the load plate with thumb. Be careful not to touch the
contacts.
8
Page 16
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
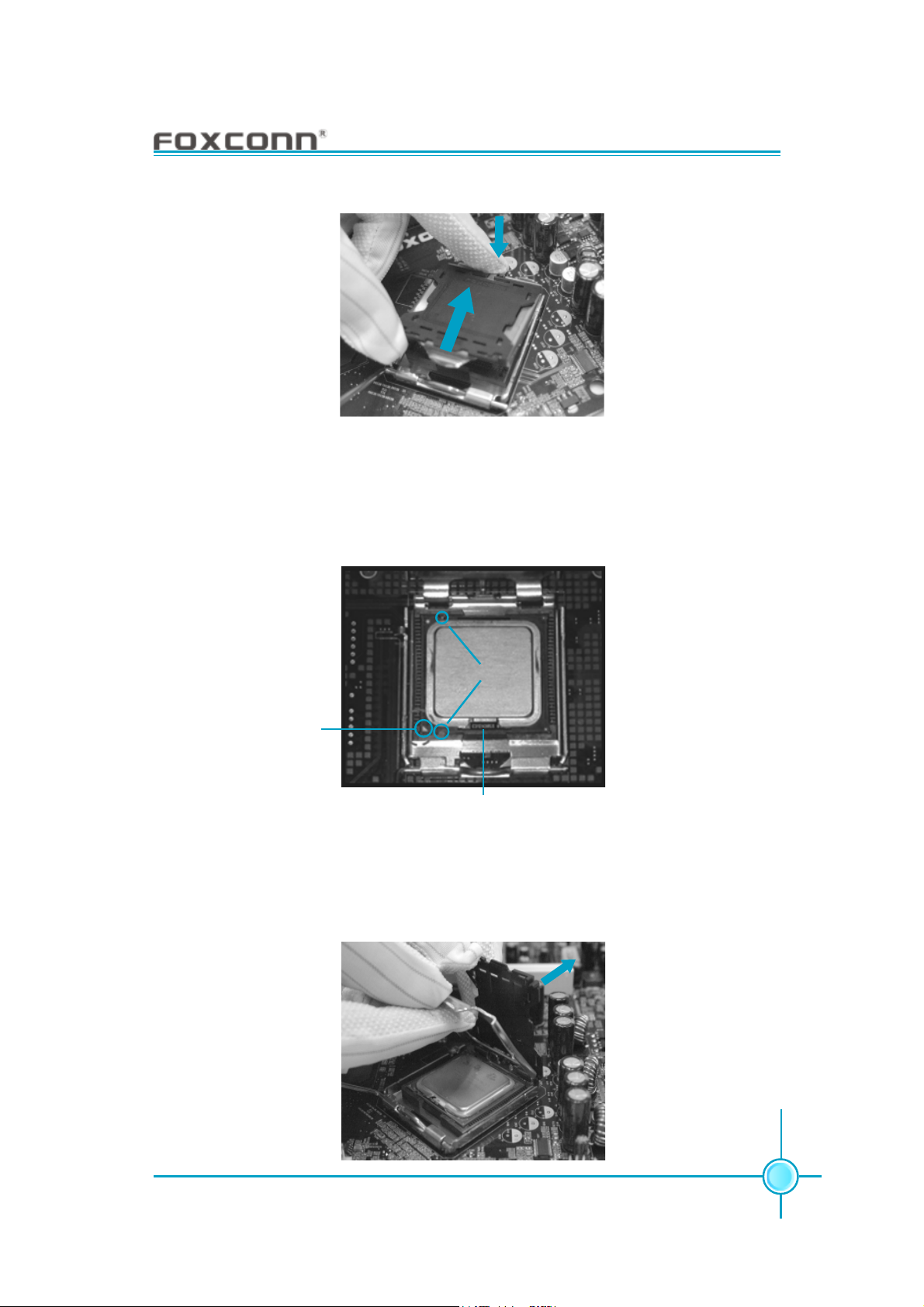
3. Hold CPU with thumb and forefinger. Ensure fingers align to socket cutouts.
Match the CPU triangle marker to Pin 1 position as shown below. The alignment
key also provides the orientation directed function. Lower the CPU straight down
without tilting or sliding the CPU in the socket.
Alignment Key
Pin 1 position
Socket Cutouts
4. After installing the CPU, remove the protective cover from load plate. The
protective cover is used to protect the contacts of the socket. Do not discard the
protective cover. Always replace the socket cover if the CPU is removed from the
socket.
9
Page 17

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
10
Warning:
Excessive temperatures will severely damage the CPU and
system. Therefore, you should install CPU cooling fan and make
sure that the cooling fan works normally at all times in order to
prevent overheating and damaging to the CPU. Please refer to your
CPU fan user guide to install it properly.
Page 18
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Qualified CPU Vendor List
The following table lists the CPUs that have been tested and qualified for use
with this motherboard.
Vendor
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Intel
Frequency
2.8G Prescott D0 533
3.0G Prescott D0 800
Celeron D2.93G Prescott E0 533
3.2G Prescott D0 800
3.4G Prescott D0 800
3.8G Prescott E0 800
3.73G Prescott 1066
3.6G Prescott E0 800
2.8G Prescott D0 800
2.66 Prescott E0 533
3.6G Prescott 3/ 800
3.0G Prescott 3/ 800
3.4G Prescott 3/ 800
3.2G Prescott 3/ 800
2.8G Prescott 4/ 800
3.0G Prescott 4/ 800
3.2G Prescott 4/ 800
Kernel
Stepping
FSB (MHz)
11
Page 19

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Memory
This motherboard accomodates four 240-pin DDR2 DIMM slots. These slots
support 256 Mb, 512 Mb and 1 Gb DDR2 technologies for x8 and x16 devices.
The available bandwidth is up to 5.3GB/s (DDR2 667) for Single-Channel mode
and 10.7 GB/s (DDR2 667) in Dual-Channel Interleaved mode.
Before you install memory modules, please make sure that all DIMMs in one
system are of the same type. To ensure normal operation, you must install at
least one memory bank.
Memory Qualified Vendor List
The following table list is the memory modules that have been tested and
qualified for use with this motherboard.
Qualified DDR2 Memory Vendor List
Vendor
APACER 1G DDR2 533
APACER 512M DDR2 533
CORSAIR 256M DDR2 533
CORSAIR 256M DDR2 675
CORSAIR 512M DDR2 675
INFINEON 256M DDR2 533
INFINEON 512M DDR2 533
MT 128M DDR2 533
MT 512M DDR2 533
MT 512M DDR2 675
SAMSUNG 256M DDR2 533
SAMSUNG 512M DDR2 533
Size
Type
12
Page 20
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
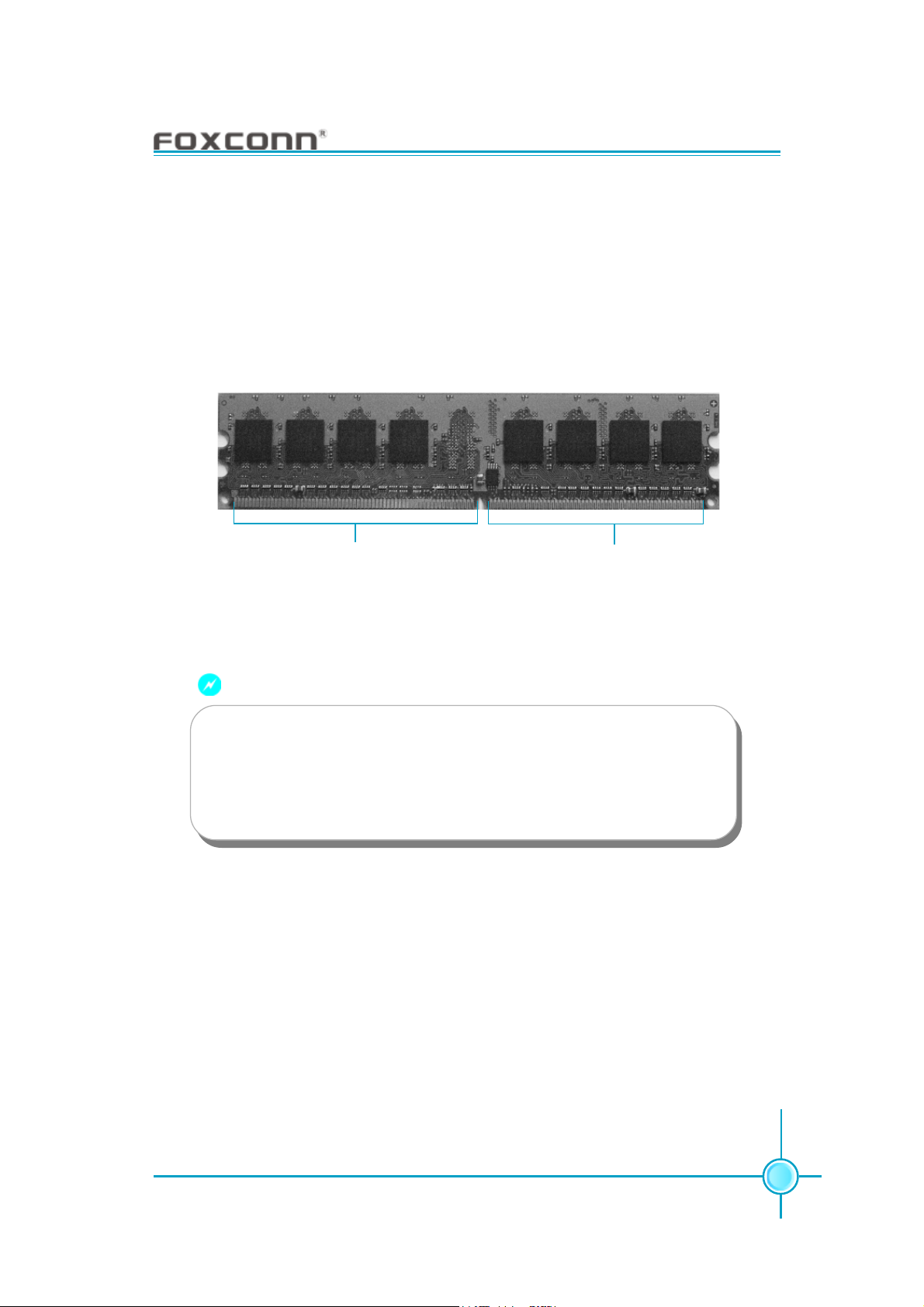
Installation of DDR2 Memory
1. There is only one gap in the middle of the DIMM slot, and the memory
module can be fixed in one direction only. Unlock a DIMM slot by pressing the
module clips outward.
2. Align the memory module to the DIMM slot, and insert the module vertically
into the DIMM slot.
128 Pins
3. The plastic clips at both sides of the DIMM slot will lock automatically.
112 Pins
Warning :
Be sure to unplug the AC power supply before adding or removing
expansion cards or other system peripherals, especially the
memory devices, otherwise your motherboard or the system
memory might be seriously damaged.
13
Page 21

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Power Supply
This motherboard uses an ATX power supply. In order to avoid damaging any
devices, make sure that they have been installed properly prior to connecting
the power supply.
4-pin ATX_12V Power Connector: PWR2
The ATX power supply connects to PWR2 and
provides power to the CPU.
(For detailed location, please refer to Item 28 on
the motherboard layout in Chapter 1)
24-pin ATX power connector: PWR1
PWR1 is the ATX power supply connector. Make
sure that the power supply cable and pins are
properly aligned with the connector on the
motherboard. Firmly plug the power supply cable
into the connector and make sure it is secure.
(For detailed location, please refer to Item 19 on
the motherboard layout in Chapter 1 )
4-pin ATX_12V power connector
4
12V
GND
2
24-pin ATX power connector
+5V_AUX +5V
1
13
+3.3V
-12V
GND
GND
GND
GND
PSON
GND
+5V
GND
PWROK
RSVD
+5V
3
1
+12V
+5V
12V
GND
+12V
+5V
+3.3V
12
24
GND GND
Note: We strongly recommended you use 24pin power supply. If you want to use 20-pin
power supply, you need to align the ATX power
connector according to the right picture.
14
align the connector
Page 22
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Rear Panel Connectors
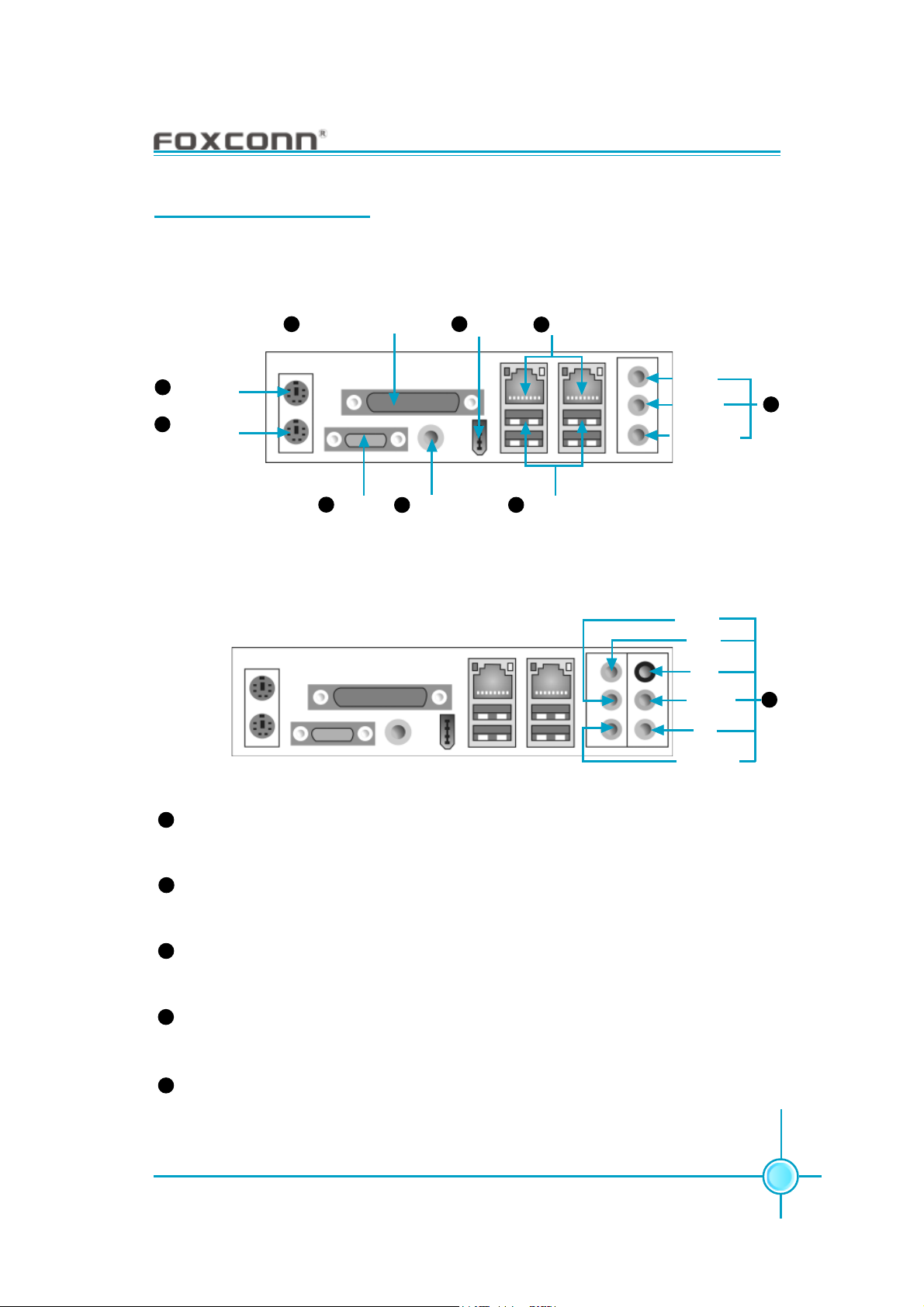
This motherboard provides the ports as below:
-6 models (optional)
4
Parallel Port (Printer Port)
PS/2 Mouse
1
Connector
2
PS/2 Keyboard
Connector
-8 models (optional)
Serial Port
3
3
(COM1)
S/PDIF Coaxial
5
Out Port
1394 Port
6
(optional)
8
LAN Ports (optional)
7
USB 2.0 Ports
Line-in
Line-out
Microphone
Line out
Line in
Rear
LFE/CEN
Side
Microphone
9
10
1
PS/2 Mouse Connector
This green 6-pin connector is for a PS/2 mouse.
2
PS/2 Keyboard Connector
This purple 6-pin connector is for a PS/2 keyboard.
3
Serial Port (COM1)
This 9-pin COM1 port is for pointing devices or other serial devices.
4
Parallel Port (Printer Port)
This 25-pin port connects a parallel printer, a scanner, or other devices.
5
S/PDIF Coaxial Out Port
This port connects to external audio output devices with coaxial cable connectors.
15
Page 23

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
6
1394 Port (optional)
This digital interface supports electronic devices such as digital cameras,
scanners, and printers.
7
USB 2.0 Ports
These four Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports are available for connecting USB
2.0/1.1 devices.
8
LAN Ports (optional)
These ports allow connection to a Local Area Network (LAN) through a network
hub.
9
Line in, Line out, Microphone Jacks (for -6 models)
When using a 2-channel sound source, the Line-out jack is used to connect to
speaker or headphone; the Line-in jack connects to an external CD player, tape
player or other audio device. The Microphone jack is used to connect to the
microphone.
When using a 6-channel sound source, connect the front speaker to the green
audio output; connect the surround sound speaker to the blue audio output;
connect the center speaker/subwoofer to the red Microphone output.
10
Line in, Line out, Microphone, Rear, LEF/CEN, Side Jacks (for -8 models)
When using an 8-channel sound source, connect the front speaker to the green
audio output; connect the rear sound speaker to the black audio output; connect the center speaker/subwoofer to the orange audio output; connect the side
sound speaker to the grey audio output.
16
Page 24
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Other Connectors
This motherboard includes connectors for floppy devices, IDE HDD devices,
Serial ATA devices, USB devices, IR module, and others.
FDD connector: FLOPPY (Refer to Item 20 on motherboard layout in Chapter 1
for detailed location)
This motherboard includes a standard FDD connector, supporting 360 K, 720
K, 1.2 M, 1.44 M, and 2.88 M FDDs.
HDD connectors: PIDE, SIDE1/SIDE2 (Refer to Item 10, 9 on motherboard
layout in Chapter 1 for detailed location respectively)
This motherboard includes one Ultra DMA 100/66/33 IDE connector (PIDE) and
two Ultra DMA 133/100/66/33 IDE connectors(SIDE1, SIDE2). These connectors support the provided Ultra DMA IDE ribbon cables. We suggest you connect the cable’s blue connector to the IDE connector, then connect the black
connector to the master device and connect the grey connector to the slave
device. The two Ultra DMA 133/100/66/33 IDE connectors support IDE RAID
(You can reference the RAID MANUAL to install the IDE RAID).
Attention:
Ribbon cables are directional, therefore, make sure to always connect with the cable on the same side as pin 1 of the PIDE/SIDE1/
SIDE2 or FDD connector on the motherboard.
17
Page 25

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Front Panel Connector: FP1 (Refer to Item 13 on motherboard layout in Chap-
ter 1 for detailed location)
This motherboard includes one connector for connecting the front panel switch
and LED indicators.
PWRLED PWRSW
+ -
FP1
1
+ -
HD-LED
IDE LED Connector (HD-LED)
The connector connects to the case’s IDE indicator LED indicating the activity
status of hard disks.
Reset Switch (RESET)
Attach the connector to the Reset switch on the front panel of the case; the
system will restart when the switch is pressed.
RESET
NC
Power LED Connector (PWRLED)
Attach the connector to the power LED on the front panel of the case. The Power
LED indicates the system’s status. When the system is in S0 status, the LED is
on. When the system is in S1 status, the LED is blink; When the system is in S3,
S4, S5 status, the LED is off.
Power Switch Connector (PWRSW)
Attach the connector to the power button of the case. Pushing this switch allows
the system to be turned on and off rather than using the power supply button.
18
Page 26
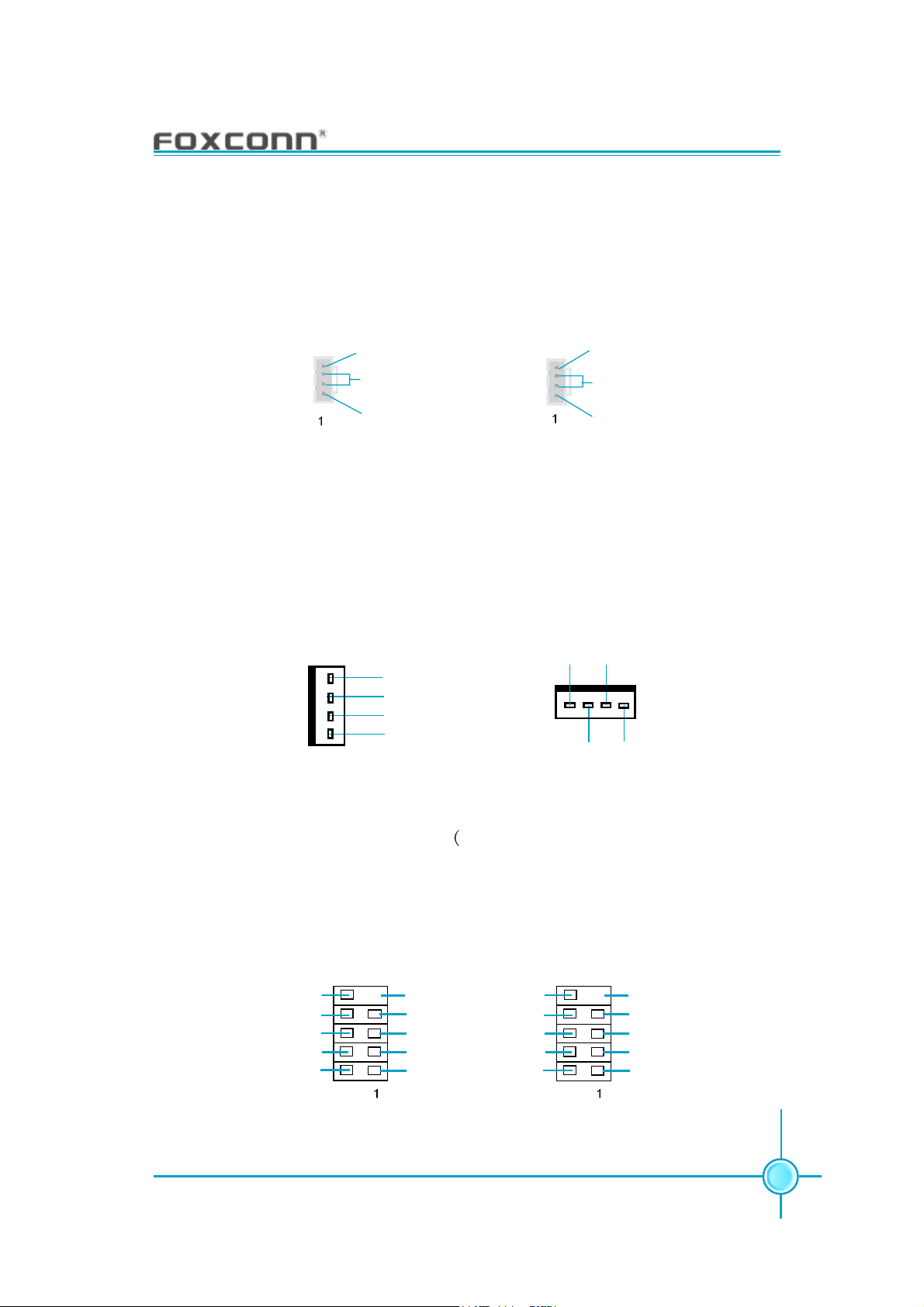
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Audio Connectors: AUX_IN (optional), CD_IN (Refer to Item 2, 3 on motherboard
layout in Chapter 1 for detailed location respectively)
CD_IN, AUX_IN are Sony standard CD audio connectors, they can be connected
to a CD-ROM drive through a CD audio cable.
AUX_L
GND
AUX_R
AUX_IN (optional)
CD_R
GND
CD_L
CD_IN
Fan Connectors: SYS_FAN1, CPU_FAN (Refer to Item 16, 23 on motherboard
layout in Chapter 1 for detailed location respectively)
The fan speed of CPU_FAN and SYS_FAN can be detected and viewed in “PC
Health Status” section of the CMOS Setup. Connect the CPU fan/ system fan
power cable to the CPU_FAN and SYS_FAN1 connectors respectively.
1
CPU_FAN
CONTROL
GND
POWER
SENSE
CONTROL
POWER
SENSE
GND
SYS_FAN1
1
USB Connectors: F_USB1, F_USB2 Refer to Item 8 on motherboard layout
in Chapter 1 for detailed location)
Besides four USB ports on the rear panel, the series of motherboards also
have two 10-pin connectors on board which may connect to front panel USB
cable(optional) to provide additional four USB ports.
NC
GND
D5+
D5-
VCC
F_USB 1
Empty
GND
D4+
D4-
VCC
NC
GND
D7+
D7-
VCC
F_USB 2
Empty
GND
D6+
D6-
VCC
19
Page 27
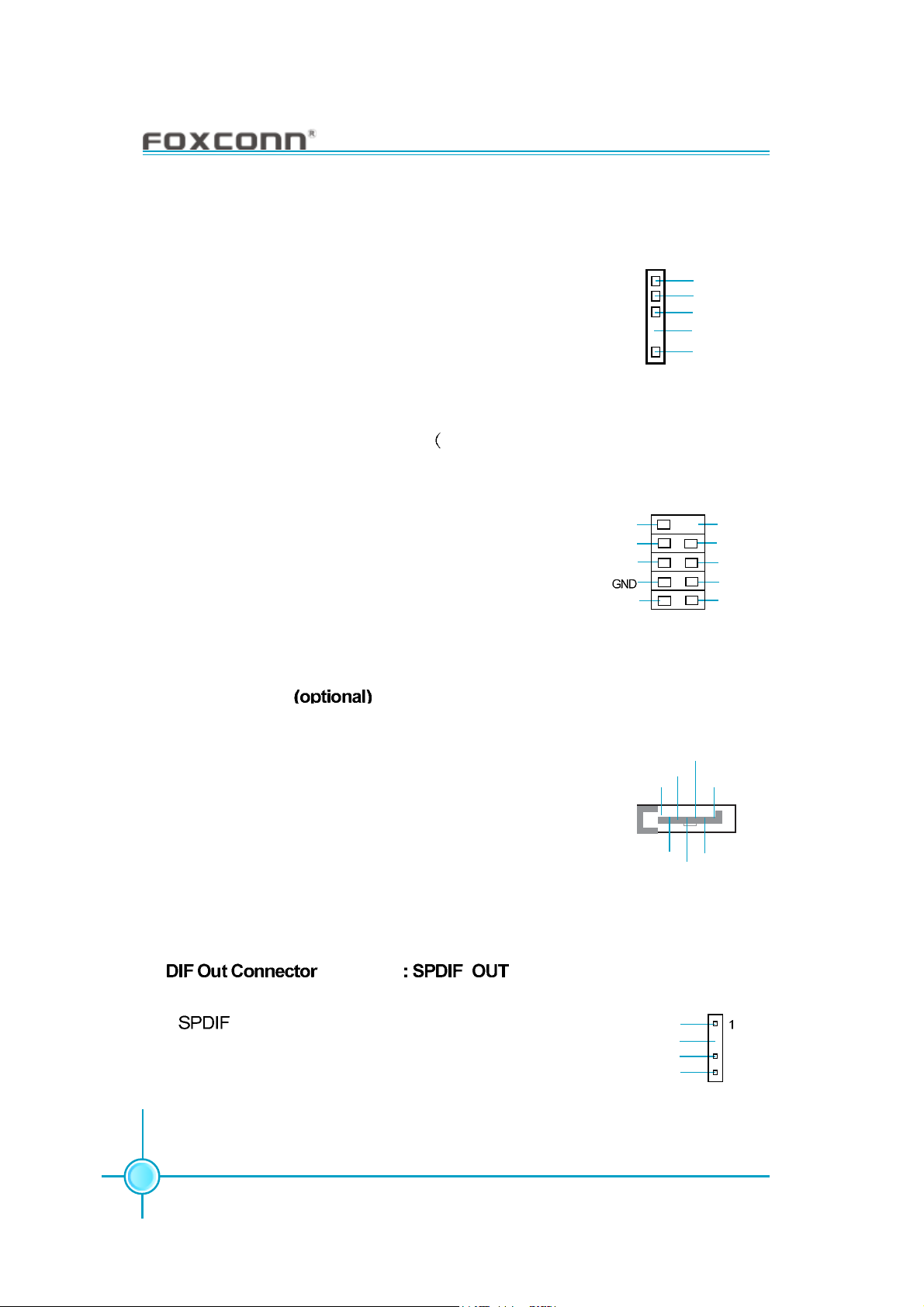
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
IrDA Connector: IR (Refer to Item 21 on motherboard layout in Chapter 1 for
detailed location)
This connector supports wireless transmitting and receiving device. Before using this function, configure the
settings of IR Mode from the “Integrated Peripherals”
section of the CMOS Setup.
1394 Connector (optional) : F_1394
Refer to Item 7 on motherboard layout in
Chapter 1 for detailed location)
The 1394 expansion cable can be connected to either
the front (provided that the front panel of your chassis
is equipped with the appropriate interface) or rear
panel of the chassis.
S-ATA Connectors
: SATA_1, SATA_2, SATA_3, SATA_4 (Refer to Item
GND
+12V
TPB -
TPA -
11 on motherboard layout in Chapter 1 for detailed location)
1
IR
2
F_1394
IRTX
GND
IRRX
Empty
+5V
910
Empty
+12V
TPB +
GND
TPA +
1
GND
RX-
TX-
GND
The S-ATA connector is used to connect the S-ATA device to the motherboard. These connectors support the
thin Serial ATA cables for primary internal storage
1
devices. The current Serial ATA interface allows up to
TX+
150MB/s data transfer rate.
SATA _1/SATA _2/
SATA _3/SATA _4
GND
RX+
SP (optional) (Refer to Item 1 on motherboard
layout in Chapter 1 for detailed location)
The out connector is capable of providing digital
audio to external speak-ers or compressed AC3 data to
an external Dolby digital decoder.
Note:The empty pin of SPDIF cable should be aligned
+5V
Empty
SPDIF_OUT
GND
SPDIF_OUT
to empty pin of S/PDIF out connector.
20
Page 28
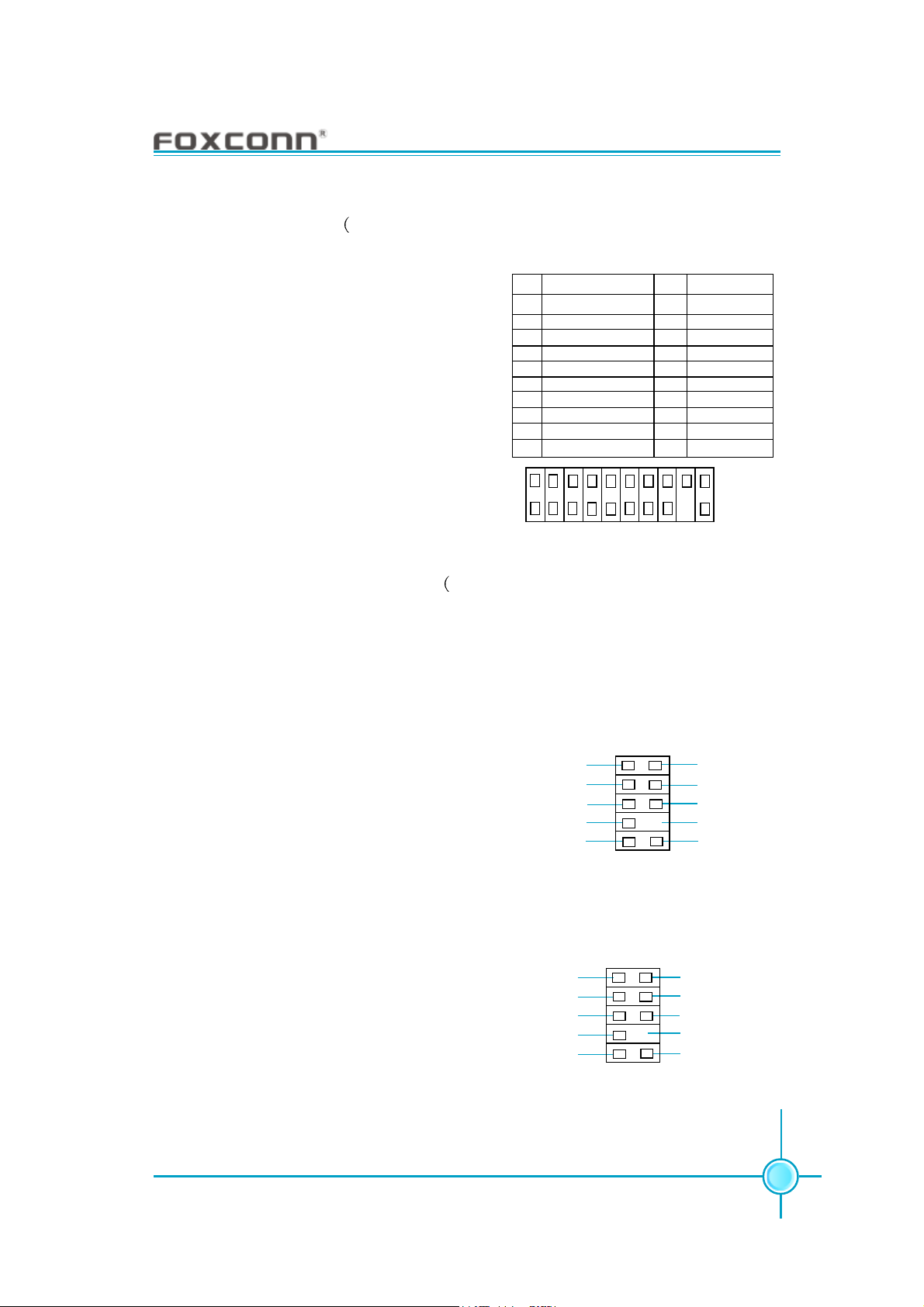
Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
TPM Connector: TPM Refer to Item 12 on motherboard layout in Chapter
1 for detailed location)
The TPM (Trusted Platform Module )
provides the ability to the PC to run
applications more secure and to make
transactions and communication more
trustworthy. To utilize this function, you
should purchase addtional devices and
install the driver.
Pin Pin Definition
1 CK_33M_TPM
2 GND
3 L_FRAMEJ
4 Empty
5 ICH_P_PCIRSTJ
6NC
7 L_AD3
8 L_AD2
9 3D3V_SYS
10 L_AD1
1
2
Pin Pin Definition
11 L_AD0
12 GND
13 NC
14 NC
15 NC
16 SERIRQ
17 GND
18 GND
19 LPCPDJ
20 NC
19
TPM
20
Front Audio Connector: F_AUDIO Refer to Item 4 on motherboard layout in
Chapter 1 for detailed location)
For -6 models (optional)
The audio connector provides two kinds of audio output choices: the Front Audio,
the Rear Audio. Their priority is sequenced from high to low (Front Audio to Rear
Audio). If headphones are plugged into the front panel of the chassis (using the
Front Audio), then the Line-out (Rear Audio)
on the rear panel will not work. If you do
not want to use the Front Audio, pin 5 and
6, pin9 and 10 must be SHORT, and then
the signal will be sent to the rear audio
port.
For -8 models (optional)
The audio connector provides two kinds
of audio output choices: the Front Audio,
the Rear Audio. Front Audio supports retasking function. Their priority is the same.
MIC_IN
MIC_PWR
AUD_OUT-R
NA
AUD_OUT-L
PORT1_L
PORT1_R
PORT2_R
SENSE_SEND
PORT2_L
1
MIC_GND
+5VA
AUD_RET-R
Empty
AUD_RET-L
F_AUDIO
1
AUD_GND
PRESENCEJ
SENSE1_RETURN
Empty
SENSE2_RETURN
F_AUDIO
21
Page 29

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Addtional COM
: COM2 (Refer to Item 17 on motherboard layout in
Chapter 1 for detailed location)
9
10
Empty
RI
RTS
DSR
CTS
COM2
GND
SOUT
1
2
SIN
DTR
This motherboard provides an additional serial COM
header for your machine.
Connect one side of a switching cable to the header,
then attach the serial COM device to the other side of
the cable.
Chassis Intruder Connector: INTR Refer to Item 14 on motherboard layout
in Chapter 1 for detailed location)
The connector connects to the chassis security switch
on the case. The system can detect the chassis intru-
INTRUDERJ
sion through the status of this connector. If the connector has been closed once, the system will send a
12
message. To utilize this function, set “Case Open Warning” to “Enabled” in the “PC Health Status” section of
the CMOS Setup. Save and exit, then boot the operating
GND
INTR
system once to make sure this function takes effect.
22
Page 30

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Expansion Slots
This motherboard includes three 32-bit Master PCI bus slots, two PCI Express
x1 slots, and one PCI Express x16 slot.
PCI Slots (Refer to Item 5 on motherboard layout in Chapter 1 for detailed
location)
The expansion card can be installed in the PCI slot. When you install or take out
such card, you must make sure that the power plug has been pulled out.
Please carefully read the instructions provided for such card, and install and set
the necessary hardware and software for such card, such as the jumper or
BIOS setup.
PCI Express Slots (Refer to Item 6&27 on motherboard layout in Chapter 1 for
detailed locations)
PCI Express will offer the following design advantages over the PCI and AGP
interface:
-Compatible with existing PCI drivers and software and Operating Systems.
-High Bandwidth per Pin. Low overhead. Low latency.
-PCI Express supports a raw bit-rate of 2.5 Gb/s on the data pins. This
results in a real bandwidth per pair of 250 MB/s.
-A point to point connection, allows each device to have a dedicated connection without sharing bandwidth.
-Ability to comprehend different data structure.
-Low power consumption and power management features.
PCI Express will take two forms, x16 and x1 PCI Express slots. Whereas the x16
slot is reserved for graphic/video cards, the x1 slots are designed to accommodate less bandwidth-intensive cards, such as a modem or LAN card.
The difference in bandwidth between the x16 and x1 slots are notable to be
sure, with the x16 slot pushing 4GB/sec (8GB/sec concurrent) of bandwidth,
and the x1 PCI Express slot offering 250 MB/sec.
Note:
If a performance graphics card was installed into x16 PCI
Express slot, 2X12 pin power supply was strongly recommended since that card may be drawn 75W power.
23
Page 31

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Installing an expansion card
1. Before installing the expansion card, please make sure that the power supply is switched off or the power cord is unplugged. Please read the documentation that came with it and make the necessary hardware settings for
the card.
2. Remove the bracket facing the slot that you intend to use. Keep the screws
for later use.
3. Align the card connector with the slot and press firmly until the card is
completely seated on the slot.
4. Secure the card to the chassis with the screw you removed earlier.
Qualified PCI Express x16 Graphics Cards Vendor List
The following table lists the PCI Express x16 graphics cards that have been
tested and qualified for use with this motherboard.
PCI-E VGA Card
ASD II 6600 Geforce 6600 128MB
ASD II 6200(EVGA) Geforce 6200 128MB
ASUS RADEON X300 128MB
ASUS EN6600GT/TD128M/A Geforce 6600GT 128MB
ASUS EAX600XT-A1814TD RADEON X600 XT 128MB
ASUS EAX600Pro 128 RADEON X600Pro 128MB
ASUS EN5750/A Geforce PCX5750 128MB
ATI X800 RADEON X800SE 128MB
DOOM3 Geforce 6600GT 128MB
MSI RX600XT-VTD128E RADEON X600XT 128MB
NVIDIAGeForce PCX5750 Geforce PCX5750 256MB
WinFast PX6600TD Geforce 6600 128MB
WinFast PX6600GT TDH Geforce 6600GT 128MB
WinFast PX6800GT Geforce 6800GT 256MB
WinFast PX68000 Ultra Geforce 6800 Ultra 256MB
MemoryVGA Chip
24
Page 32

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
Jumpers
The users can change the jumper settings on this motherboard if needed. This
section explains how to use the various functions of this motherboard by changing the jumper settings. Users should read the following contents carefully prior
to modifying any jumper settings.
Description of Jumpers
1. For the jumpers on this motherboard, pin 1 can be identified by the silkscreen printed “
labeled as “1”.
2. The following table provides some explanation of the jumper pin settings.
User should refer to this when adjusting jumper settings.
Jumper Diagram Definition Description
1
1
1
1
1
” next to it. However, in this manual, pin 1 is simply
1-2 Set pin1 and pin2 closed
2-3 Set pin2 and pin3 closed
Closed Set the pin closed
Open Set the pin opened
Clear CMOS Jumper: CLR_CMOS (Refer to Item 15 on motherboard layout in
Chapter 1 for detailed locations)
This motherboard uses the CMOS RAM to store all the set
parameters. The CMOS can be cleared by removing the CMOS
jumper.
How to clear CMOS?
1 3 2
Normal
(Default)
1.Turn off the AC power supply and connect pins 1 and 2
together using the jumper cap.
2.Return the jumper setting to the default setting (pins 2 and 3
1 3 2
Clear CMOS
together with the jumper cap).
3.Turn the AC power supply back on.
CLR_CMOS
Warning:
1. Disconnect the power cable before adjusting the jumper settings.
2. Do not clear the CMOS while the system is turned on.
25
Page 33

Chapter 2 Installation Instructions
BIOS TBL Jumper: TBL_EN Refer to Item 18 on motherboard layout in
Chapter 1 for detailed locations)
The system cannot boot, if the BIOS failed to be flashed
in conventional flash BIOS process. But you will have
no such worry when using the BIOS TBL function, which
is used to protect BIOS “Top Boot Block”. By using this
function, the system still can boot even if the BIOS fails
to flash. To utilize this function, you can short pin 2 and
3 with the jumper cap.
BIOS TBL
Enable
BIOS TBL
Disable
TBL_EN
26
Page 34

Appendix
Chapter
This chapter tells how to change system settings through
the BIOS Setup menus. Detailed descriptions of the BIOS
parameters are also provided.
You have to run the Setup Program when the following cases
occur:
1. An error message appears on the screen during the system
2. You want to change the default CMOS settings.
This chapter includes the following information:
3
3
POST process.
Enter BIOS Setup
Main Menu
Standard CMOS Features
BIOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Advanced Chipset Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PnP/PCI Configurations
PC Health Status
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor/User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
28
Page 35

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Enter BIOS Setup
The BIOS is the communication bridge between hardware and software,
correctly setting up the BIOS parameters is critical to maintain optimal system
performance. Power on the computer, when the following message briefly
appears at the bottom of the screen during the POST (Power On Self Test),
press <Del> key to enter the AWARD BIOS CMOS Setup Utility.
Press TAB to show POST screen, DEL to enter SETUP.
Note:
We do not suggest that you change the default parameters in the
BIOS Setup, and we shall not be responsible for any damage that
result from any changes that you make.
Main Menu
The main menu allows you to select from the list of setup functions and two exit
choices. Use the arrow keys to select among the items and press <Enter> to
accept or go to the sub-menu.
Main Menu
The items in the main menu are explained below:
Standard CMOS Features
The basic system configuration can be set up through this menu.
BIOS Features
The special features can be set up through this menu.
29
Page 36

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Advanced BIOS Features
The advanced system features can be set up through this menu.
Advanced Chipset Features
The values for the chipset can be changed through this menu, and the
system performance can be optimized.
Integrated Peripherals
Onboard peripherals can be set up through this menu.
Power Management Setup
All the items of Green function features can be set up through this menu.
PnP/PCI Configurations
The system’s PnP/PCI settings and parameters can be modified through
this menu.
PC Health Status
This will display the current status of your PC.
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
The fail-safe default BIOS settings can be loaded through this menu.
Load Optimized Defaults
The optimal performance settings can be loaded through this menu,
however, the stable default values may be affected.
Set Supervisor/User Password
The supervisor/user password can be set up through this menu.
Save & Exit Setup
Save CMOS value settings to CMOS and exit setup.
Exit Without Saving
Abandon all CMOS value changes and exit setup.
30
Page 37

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Standard CMOS Features
This sub-menu is used to set up the standard CMOS features, such as the date,
time, HDD model and so on. Use the arrow keys to select the item and set up,
and then use the <PgUp> or <PgDn> keys to choose the setting values.
Standard CMOS Features Menu
Date
This option allows you to set the desired date (usually as the current date)
with the <day><month><date><year> format.
Day—weekday from Sun. to Sat., defined by BIOS (read-only).
Month—month from Jan. to Dec..
st
Date—date from 1
to 31st, can be changed using the keyboard.
Year—year, set up by users.
Time
This option allows you to set up the desired time (usually as the current time)
with <hour><minute><second> format.
IDE Channel 0/1/2 Master/Slave
These categories identify the HDD types of 1 IDE channel installed in the computer system. There are three choices provided for the Enhanced IDE BIOS:
None, Auto, and Manual. “None” means no HDD is installed or set; “Auto” means
the system can auto-detect the hard disk when booting up; by choosing “Manual”
and changing Access Mode to “CHS”, the related information should be entered
manually. Enter the information directly from the keyboard and press < Enter>:
Cylinder number of cylinders Head number of heads
Precomp write pre-compensation Landing Zone landing zone
Sector number of sectors
31
Page 38

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Award (Phoenix) BIOS can support 3 HDD modes: CHS, LBA and Large or read
Auto mode.
CHS For HDD<528MB
LBA For HDD>528MB & supporting LBA (Logical Block Addressing)
Large For HDD>528MB but not supporting LBA
Auto Recommended mode
Drive A/B
This option allows you to select the kind of FDD to be installed, including [None],
[360K, 5.25 in], [1.2M, 5.25 in], [720K, 3.5 in], [1.44M, 3.5 in] and [2.88 M, 3.5 in].
Video
The following table is provided for your reference in setting the display mode for
your system.
EGA/VGA Enhanced Graphics Adapter / Video Graphic Array. For EGA,
VGA, SEGA, SVGA, or PGA monitor adapters.
CGA 40 Color Graphic Adapter, powering up in 40 column mode.
CGA 80 Color Graphic Adapter, powering up in 80 column mode.
MONO Monochrome adapter, including high resolution monochrome adapters.
Halt On
This category determines whether or not the computer will stop if an error is
detected during powering up.
All Errors Whenever the BIOS detects a nonfatal error, the system
will stop and you will be prompted.
No Errors The system boot will not stop for any errors that may
be detected.
All, But Keyboard The system boot will not stop for a keyboard error; but
it will stop for all other errors.
All, But Diskette The system boot will not stop for a diskette error; but it will
stop for all other errors.
All, But Disk/Key The system boot will not stop for a keyboard or disk
error, but it will stop for all other errors.
32
Page 39

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Memory
This is a Display-Only Category, determined by POST (Power On Self Test) of
the BIOS.
Base Memory The BIOS POST will determine the amount of base (or
conventional) memory installed in the system.
Extended Memory The BIOS determines how much extended memory is
present during the POST.
Total Memory Total memory of the system.
33
Page 40

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
BIOS Features
BIOS Features Menu
[SuperBoot] SuperBoot (Default: Disabled)
SuperBoot allows system-relevant information to be stored in CMOS upon the
first normal start-up of your PC, and the relevant parameters will be restored
to help the system start up more quickly on each subsequent start-up. The
available setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
[SuperBIOS-Protect] SuperBIOS-Protect (Default: Disabled)
SuperBIOS-Protect function protects your PC from viruses, e.g. CIH. The
available setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
[SuperRecovery] SuperRecovery Hotkey (Default: LSHIFT+F12)
SuperRecovery provides the users with an excellent data protection and HDD
recovery function. There are 12 optional hotkeys and the default hotkey is
LSHIFT+F12.
[SuperSpeed] SuperSpeed
Press <Enter> to set the items of SuperSpeed. Setting these items are good
for overclocking. Please refer to the next page.
Warning:
Be sure your selection is right. Overclocking will be dangerous!
We will not be responsible for any damage caused.
34
Page 41

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
SuperSpeed Menu
Ratio Free (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to limit CPU ratio to minimum if CPU supports, then user
can furthest overclock external frequency to improve performance.
CPU Clock Ratio (Default: Depend on CPU )
This option is used to set the ratio of an unlocked CPU.
Auto Detect PCI Clk (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to set whether the clock of an unused PCI slot will be
disabled to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Spread Spectrum (Default: Disabled)
If you enable spread spectrum, it can significantly reduce the EMI (ElectroMagnetic Interference) generated by the system.
Overclock (Default: Default)
This option is used to configure the overclocking and performance setting.
The available setting value are: Default, Manual, Optimal Reference.
1). “Default” indicates non-overclocking.
2). If “Manual” is selected, the following options will be activated and user can
set it personally;
System Memory Frequency (Default: Auto)
This option is used to set system memory frequency.
CPU Clock (Default: Depend on CPU)
This option is used to set CPU clock.
PCI Express Clock (Default: 100)
This option is used to set PCI Express clock.
35
Page 42

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
PCI Bus Clock (Default: 33.33Mhz)
This option is used to set PCI Bus clock.
CPU Voltage Regulator (Default: Default)
The option is used to adjust the CPU voltage.
Memory Voltage (Default: Default)
This option is used to set memory voltage.
System Core Voltage (Default: Default)
This option is used to set system core voltage.
3). If it is set as “Optimal Reference”, Super Level will be enabled and shown.
Super Level (Default: L1)
This option is used to set the overclock level. Frequency setting varies with the
level. The higher the level goes up, the higher frequency increases.
36
Page 43

Advanced BIOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features Menu
CPU Feature
Press <Enter> to enter the following screen.
Chapter 3 BIOS Description
CPU Feature Menu
Delay Prior to Thermal (Default: 16Min)
This option is used to set the delay time before the CPU enters auto thermal
mode. The setting values are: 4 Min, 8 Min, 16 Min, 32 Min.
Thermal Management (Default: Thermal Monitor 1)
This option is used to manage Prescott CPU thermal.
Limit CPUID MaxVal (Default: Disabled)
The option is used to set limit CPUID MaxVal. The available setting values are:
Disabled and Enabled.
37
Page 44

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Hard Disk Boot Priority
This option is used to select the priority for HDD startup. After pressing <Enter>,
you can select the HDD using the <PageUp>/<PageDn> or Up/Down arrow
keys, and change the HDD priority using <+> or <->; you can exit this menu by
pressing <Esc>.
Virus Warning (Default: Disabled)
Allows you to choose the VIRUS warning feature for IDE hard disk boot sector
protection. If this function is enabled and someone attempts to write data into
this area, BIOS will show a warning message on screen and an alarm will
beep. The setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Note: Such function provides protection to the start-up sector only; it does
CPU L1 & L2 Cache (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to turn on or off the CPU L1 and L2 cache. The available
setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
not protect the entire hard disk.
CPU L3 Cache (Default: Enabled) (optional)
This option is used to turn on or off the CPU L3 cache. The available setting
values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Hyper-Threading Technology (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to turn on or off the Hyper-Threading function of the CPU.
The available setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Note: This function will not be displayed until a CPU that supports Hyper-
Threading has been installed.
First/Second/Third Boot Device (Default: Floppy/Hard Disk/CDROM)
This option allows you to set the boot device sequence. The available setting
values are: Floppy, LS120, Hard Disk, CDROM, ZIP100, USB-FDD, USB-ZIP,
USB-CDROM, LAN and Disabled.
Boot Other Device (Default: Enabled)
With this function set to Enabled, the system will boot from some other
devices if the first/second/third boot devices failed. The available setting
values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Swap Floppy Drive (Default: Disabled)
If you have two floppy diskette drives in your system, this item allows you to
swap the assigned drive letters. The available setting values are: Disabled
and Enabled.
38
Page 45

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Boot Up Floppy Seek (Default: Disabled)
This option controls whether the BIOS checks for a floppy drive while booting
up. If it cannot detect one (either due to improper configuration or physical
unavailability), it will appear an error message. The available setting values
are: Disabled and Enabled.
Boot Up NumLock Status (Default: On)
This item defines if the keyboard Num Lock key is active when your system is
started. The available setting values are: On and Off.
Gate A20 Option (Default: Fast)
This option is used to set up the A20 signal control necessary for access to
the 1MB memory. The available setting values are: Normal and Fast.
Typematic Rate Setting (Default: Disabled)
If this item is enabled, you can use the following two items to see the typematic
rate and the typematic delay settings for your keyboard. The available setting
values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) (Default: 6)
Use this item to define how many characters per second a held-down key
generated.
Typematic Delay (Msec) (Default: 250)
Use this item to define how many milliseconds must elapse before a helddown key begins generating repeated characters.
Security Option (Default: Setup)
When it is set to “Setup”, a password is required to enter the CMOS Setup
screen; When it is set to “System”, a password is required not only to enter
CMOS Setup, but also to startup your PC.
APIC Mode (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to enable or disable APIC function.
MPS Version Control For OS (Default: 1.4)
This option is used to set up the version of MPS Table used in NT4.0 OS.
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB (Default: Non-OS2)
This item is only required if you have installed more than 64 MB of memory
and you are running the OS/2 operating system. Otherwise, leave this item at
the default.
39
Page 46

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Advanced Chipset Features
Advanced Chipset Features Menu
DRAM Timing Selectable (Default: By SPD)
This item determines DRAM clock/ timing using SPD or manual configuration.
The available setting values are: By SPD and Manual.
CAS Latency Time (Default: depend on memory)
This item determines CAS Latency. The available setting values are: 3, 2.5, 2
and Auto.
DRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay (Default: depend on memory)
This item allows you to select a delay time between the CAS and RAS strobe
signals. The available setting values are: 5, 4, 3, 2, and Auto.
DRAM RAS# Precharge (Default: depend on memory)
This item allows you to select the DRAM RAS# precharge time. The available
setting values are: 5, 4, 3, 2, and Auto.
Precharge delay(tRAS) (Default: depend on memory)
This item allows you to set the precharge delay time. The available setting
values are: Auto, 4 - 15.
System BIOS Cacheable (Default: Enabled)
Select “Enabled” to allow caching of the system BIOS which may improve
performance. If any other program writes to this memory area, a system error
may result. The available setting values are: Enabled and Disabled.
40
Page 47

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Video BIOS Cacheable (Default: Disabled)
Select “Enabled” to allow caching of the Video BIOS which may improve
performance. If any other program writes to this memory area, a system error
may result. The available setting values are: Enabled and Disabled.
Memory Hole At 15M-16M (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to determine whether the 15M-16M address field of memory
is reserved for the ISA expansion card. The available setting values are:
Enabled and Disbled.
PCI Express Root Port Func
Press <Enter> to enter the following screen.
PCI Express Root Port Func Menu
PCI Express Port 1/ 2 (Default: Auto)
This option is used to enable or disable PCI Express port 1/2. The available
setting values are: Auto, Enabled, Disabled.
PCI-E Compliancy Mode (Default: v1.0a)
This option is used to select the PCI Express compliancy mode version. The
available setting values are: v1.0a, v1.0.
41
Page 48

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Integrated Peripherals
Integrated Peripherals Menu
Use the arrow keys to select your options; press the <Enter> key to enter the
setup sub-menu. The options and setting methods are discussed below:
Onchip IDE Device Menu
IDE HDD Block Mode (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to set whether the IDE HDD block mode is allowed. The
available setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
IDE DMA transfer access (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to set the IDE transfer access—with it set to Enabled, the
IDE Transfer Access uses the DMA mode; with it set to Disabled, the IDE
Transfer Access uses the PIO mode.
On-Chip Primary/Secondary PCI IDE (Default: Enabled)
Use this item to enable or disable the Primary/Secondary PCI IDE channel
that is integrated on the motherboard.
42
Page 49

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO (Default: Auto)
These four items let you assign which kind of PIO (Programmed Input/Output)
is used by IDE devices. Choose Auto to let the system auto detect which PIO
mode is best or select a PIO mode from 0-4.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA (Default: Auto)
UltraDMA technology provides faster access to IDE devices. If you install a
device that supports UltraDMA, change the appropriate item on this list to
Auto. The available setting values are: Disabled and Auto.
SATA Mode (Default: IDE)
This option is used to set the Serial ATA Mode. The available setting values
are: IDE, RAID, AHCI.
On-Chip Serial ATA (Default: Enhanced Mode)
This option is used to set the On-chip Serial ATA function. When it is set to
“Disabled”, the function will be disabled; when it is set to “Combined Mode”,
four HDDs at most will be supported; with it set to “Enhanced Mode”, six HDDs
at most will be supported (for those under Windows 2000 and Windows XP
only); with it set to “SATA Only”, only the S-ATA HDD can be used.
PATA IDE Mode (Default: Primary)
When On-Chip Serial ATA set as “Combined Mode”, this option will be modified.
It is used to set the PATA IDE Mode. The available setting values are: Primary,
Secondary.
SATA Port (Default: P2, P4 is Secondary)
This option is used to set the Serial ATA Port.
43
Page 50

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Onboard Device Menu
USB Controller (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to set whether the USB Controller is enabled. The
available setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
USB 2.0 Controller (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to set whether the USB 2.0 Controller is enabled. The
available setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
USB Keyboard Support (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set whether the USB keyboard controller is enabled in a
legacy operating system (such as DOS). The available setting values are:
Disabled and Enabled.
USB Mouse Support (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set whether the USB mouse controller is enabled in a
legacy operating system (such as DOS). The available setting values are:
Disabled and Enabled.
Azalia/AC97 Audio Select (Default: Auto)
This option is used to set whether onboard Azalia/AC97 Audio is enabled. The
available setting values are: Disabled and Auto.
PCI LAN Controller (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to set whether the PCI LAN controller is enabled. The
available setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Onboard Lan Boot ROM (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to decide whether to invoke the boot ROM of the onboard
LAN chip. The available setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
44
Page 51

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Super IO Device Menu
Onboard Serial Port 1/2 (Default: 3F8/IRQ4 / 2F8/IRQ3)
This option is used to assign the I/O address and interrupt request (IRQ) for
the onboard serial port 1/2. The onboard serial port 2 I/O address and IRQ is
for IrDA using.
UART Mode Select (Default: Normal)
Use this option to select the UART mode. Setting values include Normal,
IrDA, ASKIR. The setting value is determined by the infrared module installed
on the board.
UR2 Duplex Mode (Default:Half)
This option is available when UART 2 mode is set to either ASKIR or IrDA. This
item enables you to determine the infrared function of the onboard infrared chip.
Onboad Parallel Port (Default: 378/IRQ7)
This item allows you to determine onboard parallel port controller I/O address
and interrupt request (IRQ). Setting values include Disabled, 378/IRQ7, 278/
IRQ5, and 3BC/IRQ7.
Parallel Port Mode (Default: SPP)
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the onboard parallel port.
Setting values include SPP, EPP, ECP, ECP+EPP.
45
Page 52

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Power Management Setup
Power Management Setup Menu
ACPI Function (Default: Enabled)
ACPI stands for “Advanced Configuration and Power Interface”. ACPI is a
standard that defines power and configuration management interfaces
between an operating system and the BIOS. In other words, it is a standard
that describes how computer components work together to manage
system hardware. In order to use this function the ACPI specification must be
supported by the OS (for example, Windows2000 or WindowsXP). The
available setting values are: Enabled and Disabled.
ACPI Suspend Type (Default: S1 (POS))
This option is used to set the energy saving mode of the ACPI function.
When you select “S1 (POS)” mode, the power will not shut off and the power
supply status will remain as it is. In S1 mode the computer can be resumed
at any time. When you select “S3 (STR)” mode, the power will be cut off after
a delay period. The status of the computer before it enters STR will be saved in
memory, and the computer can quickly return to previous status when the STR
function wakes. When you select “S1 & S3” mode, the system will automatically
select the delay time.
Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume (Default: Auto)
This option allows the system to initialize the VGABIOS from S3 (Suspend to
RAM) sleep state when you select “S3 (STR)” mode in the above option. The
available setting values are: Auto, Yes and No.
Power Management (Default: User Define)
This option is used to set the power management scheme. The available
setting values are: User Define, Min Saving, and Max Saving.
46
Page 53

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Vdieo Off Method (Default: DPMS)
This option is used to define the video off method. “Blank Screen” mode
means that after the computer enters power saving mode, only the monitor
will close, however, the vertical and horizontal scanning movement of the screen
continues. When you select the “V/H SYNC + Blank” mode the vertical and
horizontal scanning movement of screen stops when the computer enters
power saving mode. “DPMS” mode is a new screen power management system,
and it needs to be supported by the monitor you’re using.
Video Off In Suspend (Default: Yes)
This option is used to determine whether the video is turned off when the
system enters sleep mode. The setting values are: No and Yes.
Suspend Type (Default: Stop Grant)
This option is used to set sleep mode. The setting values are Stop Grant
(saves the status of the whole system and then turns off power), and PwrOn
Suspend (CPU and core system go to low power mode, keeps power supply).
MODEM Use IRQ (Default: 3)
This option is used to set the IRQ in which the modem can use. The system
will automatically wake up when the modem receives an incoming call.
Suspend Mode (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set the idle time before the system enters into sleep
status. The setting values are Disabled and 1 Min-1 hour.
HDD Power Down (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to turn off hard disk power if the hard disk is idle for a given
period of time. The setting values are: Disabled and 1 Min-15 Min.
Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN (Default: Instant-Off)
This option is used to set the power down method. This function is only valid
for systems using an ATX power supply.
When “Instant-Off” is selected, press the power switch to immediately turn off
power. When “Delay 4 Sec.” is selected, press and hold the power button for
four seconds to turn off power.
CPU THRM-Throttling (Default: 50.0%)
This option is used to specify the CPU speed (at percentage) to slow down
the CPU when it reaches the predetermined overheat temperature. The
setting values are 75.0%, 50.0%, 25.0%.
47
Page 54

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
PWRON After PWR-Fail (Default: Off)
This option is used to set what action the PC will take with the power supply
when it resumes after a sudden power failure. The available options are: Off
(remain in turn off status),On (auto power on) and Former-Sts (resume with
the previous status).
Power Management Events
Press <Enter> to set the items of power management events. Please
refer to page 49.
Primary IDE 0/1, Secondary IDE 0/1 (Default: Disabled)
When these items are enabled, the system will restart the power saving timeout
counters when any activity is detected on any of the drives or devices on the
primary or secondary IDE channels. The setting values are Disabled and Enabled.
FDD, COM, LPT Port (Default: Disabled)
When this item is enabled, the system will restart the power saving timeout
counters when any activity is detected on the floppy disk drive, serial port, or
the parallel port.
PCI PIRQ[A-D]# (Default: Disabled)
When this option is disabled, any PCI device set as the Master will not power
on the system.
48
Page 55

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Power Management Events Menu
Wake-Up by PCI card (Default: Enabled)
This option is used to set the system to wake up by PCI card. The setting
values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Power On by Ring (Default: Enabled)
If this item is enabled, it allows the system to resume from a software
power down or power saving mode whenever there is an incoming call to
an installed fax. This function needs to be supported by the relevant
hardware and software. The setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
USB KB Wake-Up From S3 (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set the system to wake up by USB equipment when it is
in S3 (Suspend to RAM) mode. The setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Resume by Alarm (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set the timing of the start-up function. In order to use this
function, the start-up password function must be cancelled. Also, the PC power
source must not be turned off. The setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Date (of Month) Alarm
When the Resume by Alarm set as “Enabled”, this option will be modified. It is
used to set the timing for the start-up date. The setting values contain 0 - 31.
Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm
When the Resume by Alarm set as “Enabled”, this option will be modified. It is
used to set the timing for the start-up time. The setting values contain hh:0 –
23; mm:0 – 59; ss:0 – 59.
Power on By Mouse (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set the power-on method of your PC. The available
setting values are: Disabled, Mouse Move, Mouse Click.
49
Page 56

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Power On By Keyboard (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set the power-on method of your PC. The available
setting values are: Disabled, Password, Hot KEY, Any Key, Keyboard 98.
KB Power On Password (Default: Enter)
When the “Power On By Keyboard” is set as “Password”, use this item to set
the keyboard password that powers on the system.
Hot Key Power On (Default: Ctrl - F1)
When the “Power On By Keyboard” is set as “Hot KEY”, use this item to set the
hot key combination that awakes the system. The available setting values are:
Ctrl+F1-F12.
50
Page 57

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
PnP/PCI Configurations
PnP/PCI Configurations Menu
Reset Configuration Data (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set whether the system is permitted to automatically
distribute IRQ DMA and I/O addresses when each time the machine is turned
on. The setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Resources Controlled By (Default: Auto (ESCD))
This option is used to define the system resource control scheme. If all cards
you use support PnP, then select Auto (ESCD) and the BIOS will automatically
distribute interruption resources. If the ISA cards you installed do not support
PnP, you will need to select “Manual” and manually adjust interruption
resources in the event of hardware conflicts. However, since this motherboard
has no ISA slot, this option does not apply.
IRQ Resources
Only when the “Resoureces Controlled By” is set as “Manual” can this option
be modified. Press the <Enter> key, then manually set IRQ resources.
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop (Default: Disabled)
If you use a nonstandard VGA card, use this option to solve graphic
acceleration card or MPEG audio card problems (e.g., colors not accurately
displayed). The setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
INT Pin 1-8 Assignment (Default: Auto)
This option is used to name the interrupt request (IRQ) line assigned to a
device connected to the PCI interface on your system.
51
Page 58

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Maximum Payload Size (Default: 4096)
This option is used to set maximum TLP payload size for PCI Express devices.
The unit is byte. The available setting values are: 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048,
4096.
PC Health Status
PC Health Status Menu
Case Open Warning (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to enable or disable case open warning function. The
setting values are: Disabled and Enabled.
Shutdown Temperature (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set the system temperature upper limit. When the
temperature exceeds the setting value, the motherboard will automatically cut
off power to the computer.
Warning Temperature (Default: Disabled)
This option is used to set the warning temperature for the system. When the
temperature of CPU is higher than setting value, the motherboard will send off
warning information.
CPU Vcore/Vddr/+3.3 V/+12 V/5.0V (optional)
The current voltages will be automatically detected by the system.
Voltage Battery (optional)
This option is used to show the voltage of battery.
52
Page 59

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
CPU Temperature
The current CPU temperature will be automatically detected by the system.
System Temperature
The current system temperature will be automatically detected by the system.
CPU Fan Speed
The current speed of the CPU fan will be automatically detected by the system.
System Fan Speed
The current speed of the system fan will be automatically detected by the
system.
53
Page 60

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Press <Enter> to select this option. A dialogue box will pop up that allows you to
load the default BIOS settings. Select <Y> and then press <Enter> to load the
defaults. Select <N> and press <Enter> to exit without loading. The defaults set
by BIOS set the basic system functions in order to ensure system stability. But if
your computer cannot POST properly, you should load the fail-safe defaults to
restore the original settings, then carry out failure testing. If you only want to load
the defaults for a specific option, you can select the desired option and press
the <F6> key.
Load Optimized Defaults
Select this option and press <Enter>, and a dialogue box will pop up to let you
load the optimized BIOS default settings. Select <Y> and then press <Enter> to
load the optimized defaults. Select <N> and press <Enter> to exit without loading.
The defaults set by BIOS are the optimized performance parameters for the
system, to improve the performance of your system components. However, if
the optimized performance parameters are not supported by your hardware
devices, it will likely cause system reliability and stability issues. If you only want
to load the optimized default for a specific option, select the desired option and
press the <F7> key.
Set Supervisor/User Password
The access rights and permissions associated with the Supervisor password are
higher than those of a regular User password. The Supervisor password can be
used to start the system or modify the CMOS settings. The User password can
also start the system. While the User password can be used to view the current
CMOS settings, these settings cannot be modified using the User password.
When you select the Set Supervisor/User Password option, the following message
will appear in the center of the screen, which will help you to set the password:
Enter Password:
Enter your password, not exceeding 8 characters, then press <Enter>. The
password you enter will replace any previous password. When prompted, key in
the new password and press <Enter>.
54
Page 61

Chapter 3 BIOS Description
If you do not want to set a password, just press <Enter> when prompted to enter
a password, and in the screen the following message will appear. If no password
is keyed in, any user can enter the system and view/modify the CMOS settings.
PASSWORD DISABLED!!!
Press any key to continue …
Under the menu “Advanced BIOS Features Setup”, if you select “System” from
the Security Option, you will be prompted to enter a password once the system
is started or whenever you want to enter the CMOS setting program. If the
incorrect password is entered, you will not be permitted to continue.
Under the menu “Advanced BIOS Features Setup”, if you select “Setup” from the
Security Option, you will be prompted to enter a password only when you enter
the CMOS setting program.
Save & Exit Setup
When you select this option and press <Enter>, the following message will
appear in the center of the screen:
SAVE to CMOS and EXIT (Y/N)?Y
Press <Y> to save your changes in CMOS and exit the program; press <N> or
<ESC> to return to the main menu.
Exit Without Saving
If you select this option and press <Enter>, the following message will appear
in the center of the screen:
Quit Without Saving (Y/N)?N
Press <Y> to exit CMOS without saving your modifications; press <N> or <ESC>
to return to the main menu.
55
Page 62

Chapter
4
4
The utility CD that came with the motherboard contains
useful software and several utility drivers that enhance the
motherboard features.
This chapter includes the following information:
Utility CD content
Start to install drivers
Page 63

Chapter 4 Driver CD Introduction
Utility CD content
This motherboard comes with one Utility CD. To begin using the CD, simply insert
the CD into your CD-ROM drive. The CD will automatically displays the main
menu screen.
1. Install Drivers
Using this choice, you can install all the drivers for your motherboard. You should
install the drivers in order, and you need to restart your computer after the drivers are all installed.
A. Chipset Software B. IMSM Driver (optional)
C. ITE RAID Driver (optional) D. DirectX 9.0c
E. Audio Driver F. LAN 1000M Driver (optional)
G. LAN 100M Driver (optional) H. USB2.0 Driver
2. Accessories
Use this option to install additional software programs.
A. SuperUtility B. Adobe Reader
C. Norton Internet Security D. Word Perfect Office 12
3. Browse CD
Click here to browse CD content.
4. Manual
Click here to view multilingual user manual & RAID manual content.
5. Homepage
Click here to visit Foxconn motherboard homepage.
57
Page 64

Chapter 4 Driver CD Introduction
Note:
1. Install the latest patch first if your OS is Windows XP or Win-
dows 2000.
2. Follow the CD screen order to install your motherboard drivers.
Start to install drivers
Install Drivers
Select <Install Driver>, and click to enter the install driver screen. You can
select the driver that you want to install and begin the setup steps.
58
Follow the
screen order
to install
the drivers
Page 65

Chapter 4 Driver CD Introduction
Install Accessories
From the main menu screen, select <Accessories> (shown as below), then
follow the screen sequence to install the accessry software.
Click to
install the
accessory
software
59
Page 66

Chapter
Chapter 4 Driver CD Introduction
This chapter will introduce how to use attached software.
This chapter includes the following information:
SuperStep
SuperUpdate
SuperLogo
60
Page 67

Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
SuperStep
SuperStep is a utility that allows users to change the frequency of the CPU. It also
displays system health introduction including CPU temperature, CPU voltage,
and PCI/PCI Express clock.
SuperStep features:
1. Supports Win2000 and WinXP.
2. Automatic alarm mechanism when system runs irregularly
3. Adjusts the CPU frequency to speed up your system and achieve better system
performance.
4. Simple and easy to operate, with a user-friendly graphics interface.
Using SuperStep:
CPU Fan
speed
Adjust System
Fan1 warning
criteria
Adjust CPU
Fan warning
criteria
Go to Fan
page
Reset the
warning criteria
to default
settings
System Fan1
speed
System Fan2
speed
Minimize Window
Exit Program
About SuperStep
SuperStep Help
Link to FOXCONN
Website
Adjust System Fan2
warning criteria
Apply the
adjustments
61
Page 68

Current voltage
readings
Go to Voltage
page
Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
Adjust voltages warning
criteria (upper limit)
Current CPU
Temperature
Current system
Temperature
Reset the warning
criteria to default
settings
Apply the
adjustments
Adjust voltages
warning criteria
(Lower limit)
Adjust CPU temperature warning
criteria
Adjust system
temperature
warning criteria
62
Reset the warning criteria to
default settings
Apply the adjustments
Go to
Temperature
page
Page 69

Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
Current CPU
Clock
Current CPU
Ratio
Reset to the default
settings
Go to
Clock page
Current PCI
Express clock
Current PCI clock
Adjust the CPU
External Frequency
Apply the
adjustments
Check for the
system to automatically provide
warning messages
Adjust the
monitoring
Interval
Reset to the
default settings
Go to Alarm page
Apply the
changes
63
Page 70

Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
SuperUpdate
SuperUpdate is a Windows utility that allows users to backup and upgrade the
system BIOS.
SuperUpdate features:
1.Supports Win2000 and WinXP.
2.Supports 4Mb size flash parts; flash write method is independent of flash
type.
3.Simple and easy to operate, with a user-friendly graphics interface.
Using SuperUpdate:
Browse BIOS bin file
from local HDD
Current
BIOS
Information
Perform the BIOS update
from local image
Minimize Window
Exit Program
BIOS Update Setting
About SuperUpdate
SuperUpdate Help
Link to Foxconn
Website
64
Show the latest
BIOS version
Backup system
BIOS to an image
file
Page 71

Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
Backup BIOS to local image:
1. Click <Backup> and name your BIOS binary file to backup current BIOS.
2. Click <OK> to finish the backup process.
Update BIOS from local image:
1. Click <Load> to load the BIOS file.
65
Page 72

Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
2. Click <Update>, the following message will appear.
3. Click <Yes> to backup the current BIOS, then the following picture will
appear.
4. Click <OK >, then click <Update>.
66
Page 73

5. Now is updating.
6. Click <Restart>.
Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
67
Page 74

Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
SuperLogo
SuperLogo is a Windows utility that allows users to change the BIOS sign on
logo. The utility is able to replace and backup the BIOS logo, and update and
backup the BIOS image within the Windows environment.
SuperLogo features:
1. Supports Win2000 and WinXP.
2. Supports 4Mb size flash parts, flash write method is independent with flash
type.
3. Simple and easy to operate, with a user-friendly graphics interface.
4. Supports BMP and JPEG graphic format files. The best color is 16 or 256
colors. The best resolution is 136 x 84 for top-right logo and 640 x 480 or 800
x 600 for full screen logo.
Using SuperLogo:
Display the Flash Information
Minimize Window
BIOS Write
Protect Status
Exit Program
About SuperLogo
BIOS Flash
Rom Free Space
Go to ROM Info. page
68
SuperLogo Help
Link to Foxconn
website
Page 75

Full screen mode
Top-Right mode
Chapter 5 Directions for Bundled Software
Boot without logo
Backup whole
BIOS image
Follow the
Wizard to
complete the
logo update
Go to Change Logo page
Backup Logo
Follow the Wizard
to complete the
backup function
BIOS image
file location
Go to Backup page
Browse a BIN file
for updating BIOS
Go to Update BIOS page
69
Page 76

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
Chapter
6
6
This chapter will introduce special functions of BIOS and how
to use them in detail. It can further exert the max potential
of motherboard to bring you super-value enjoyment.
This chapter introduces the following special functions of BIOS:
SuperBoot
SuperBIOS-Protect
SuperRecovery
SuperSpeed
70
Page 77

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
SuperBoot
SuperBoot technology greatly reduces the long boot process time of computers.
A BIOS without SuperBoot has to perform many routines every time when the
system starts, such as checking the system core and initializing system
peripherals. Now with SuperBoot, a PC can bootup without any unnecessary.
SuperBoot is quite easy to use: choose the right option in CMOS setup (refer to
BIOS features), SuperBoot saves the information when the PC boots up the first
time, and restores the parameters for the system, thus letting the PC boot freely
and rapidly.
Notes:
1. If the previous boot was not completed then the BIOS will perform a normal
POST, even if SuperBoot is enabled.
2. No matter whether SuperBoot is enabled or not, the BIOS will perform a
normal POST if the CMOS fails.
71
Page 78

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
SuperBIOS-Protect
The BIOS of the motherboard is contained inside the Flash ROM. Severe viruses,
such as the CIH virus, are so dangerous that they may overwrite the BIOS. If the
BIOS has been damaged, the system will be unable to boot. We provide the
following solution which protects the system BIOS from being attacked by such
viruses.
The way to implement this function:
Set “SuperBIOS-Protect” as “Enabled”, the BIOS will be protected.
72
Page 79

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
SuperRecovery
SuperRecovery is an easy-to-operate tool for backing up or recovering your hard
disk data. It offers simplified user interfaces with hotkey access and allows you
to experience unprecedented high security and reliability with extra functions,
such as hotkey launch, and powerful anti-virus protection.
Features:
1. Password Protection:
You can set a password for each HDD.
2. Data Protection:
Hidden partitions can only be accessed during data back up or recovery. Even
reformatting the disk using FDISK or PQMAGIC will not allow access to the
disk. This means that data backed up in a hidden partition is very secure.
3. Intelligent Menu:
Unavailable items will be displayed in gray. For example, if you haven’t divided
a hidden partition, items like “Release Hidden Partition”, “Back up” and “Recovery” will be displayed in gray and can’t be selected. And, when you select an
item, the related information will appear on the bottom of the screen.
Disclaimer:
Please study this software program’s specification carefully before using it.
The vendor should not be liable for any damage arising out of or in connection
with the use of this program, including liability for lost profit or data, or any
other damage whatsoever.
System Requirements:
1. ATA5 or above compliant IDE HDD.
2. FAT16, FAT32, NTFS files system.
3. PS/2 keyboard or USB keyboard.
Hotkey Selection:
You should enter the CMOS setup interface first by pressing <DEL> during
POST (Power On Self Test). Then select the “SuperRecovery Hotkey” option to
adjust the hotkey settings in the “BIOS Features” menu.
There are 12 options: LSHIFT (Left Shift)+F1~F12. LSHIFT+F12 is the default.
73
Page 80

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
Hard Disk Selection:
The hard disk selection menu will be displayed after you press the hotkey,
listing all the IDE HDDs installed in your system. You can switch the highlight
bar to make a selection and press <Enter> to confirm it.
Attention:
1. Make sure that you have selected a HDD before entering the main menu.
2. Make sure that the HDD you selected is ATA5 or higher. For HDDs lower
than ATA5, there will be a “No Support” message in the HDD list menu
listing beside the name of it.
3. Only one HDD can be operated at a time.
Note: If you have assigned a password to the selected HDD, you will be
prompted to provide it before proceeding.
74
Page 81

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
Main Menu:
Select a HDD to enter main menu. There are five function items, “Divide Hidden
Partition”, “Release Hidden Partition”, “Backup”, “Recovery” and “Change
Password”. You can switch the highlight bar to make a selection on the operation which should be performed on the HDD and confirm your selection by
pressing <Enter>. The following operation will be performed on the disk you
selected.
On-line help
message
Divide Hidden Partition:
1. What is a Hidden Partition?
SuperRecovery can be used to divide a hidden partition, which is to be
reserved for backing up HDD data. The partitioning will erase all the old data
saved in the HDD, to make sure that the following operations can be
continued. Once the division is done, any future variation to the HDD will
never affect the hidden partition, such as virus, causing turbulence, windows
system breaking down or data loss. SuperRecovery can recover all the data
backed up in hidden partition, letting you easily get your computer on track
again.
2. Divide Hidden Partition:
A. Enter a percentage of the HDD total capacity or an actual size in MB as the
size of the hidden partition, such as “30%” or “3000”. Press <Enter> to
confirm your input. As the average rate of compression is 50% or so, you
are suggested to divide 30% of the total as the capacity of the hidden
partition.
B. The system will then prompt you to Enter <Y> or <N> for confirmation.
Press <Y> to restart the computer, and the division for hidden partition
will go into effect after the system is restarted.
75
Page 82

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
Attention :
1. All the HDD data will be cleared by the partitioning process, so it is better
to do the division on an empty HDD.
2. At the same time, the overall HDD capacity will decrease in order to make
space for the hidden partition, which will be come unavailable for normal
use.
Release Hidden Partition:
This is used to release the hidden partition. If you choose this item and press
<Y> to confirm, the system will be restarted to release the hidden partition. But
the released partition is still unavailable for you after the system is restarted. It’s
necessary for you to enable it by using FDISK, PQMAGIC, or some other tools.
76
Page 83

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
Backup:
Select BACKUP to enter the Backup interface, where you can find the following
three sub-function items: “BACKUP CMOS SETUP”, “BACKUP PARTITION TABLE”
and “BACKUP HARDDISK DATA”. Switch the highlight bar by pressing the arrow
keys to make a selection and then press <Enter> to confirm your choice.
1. Backup CMOS Setup:
A. Support backing up of the CMOS data.
B. The backing up or recovery of CMOS data should be done on a motherboard
of the same type.
2. Backup Partition Table:
This function can help to backup all partition tables including extended
partitions.
77
Page 84

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
3. Backup Hard disk Data:
A. If there are active partitions (system partition), you can choose to backup
an active partition or the whole disk. But only one can be taken between
the two choices. Old data will be replaced by the newly backed up data.
B. Backing up with the progress bar showing.
78
Page 85

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
C. A report with all the critical data on this operation will be displayed after the
backup is completed.
Original Size: The data size loaded in selected partition;
Valid Size: The size of valid data.
Elapsed Time: How long the procession cost.
Compressed Size: The size of data after compression.
Compressed Rate: Compressed Size/Valid Size.
4. Back to Main:
This item is used to exit the Backup interface.
Recovery:
Select RECOVERY to enter the Recovery interface. You will see the following
sub-function items: RECOVER CMOS SETUP, RECOVER PARTITION TABLE
and RECOVER HARDDISK DATA. You can switch the highlight bar by pressing
the arrow keys to make a selection and press <Enter> to confirm your selection.
79
Page 86

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
1. Recover CMOS Setup:
This function is used to restore the latest backup of CMOS settings you made.
2. Recover Partition Table:
This function is used to recover all partition tables including extended partitions.
80
Page 87

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
3. Recover Hard disk Data:
This item is used to restore the backed up data from the hidden partition.
4. Back to Main:
This item is used to exit the Recovery interface.
CHANGE PASSWORD Introduction:
Select CHANGE PASSWORD to enter the Change Password interface.
A. Enter the old password first. Press <Enter> if password is null.
B. Enter the new password. Then enter the same again to confirm it.
C. Press <Enter> for null password.
D. The password will be saved in the hidden partition.
81
Page 88

Chapter 6 Special BIOS Functions
SuperSpeed
SuperSpeed is a powerful and efficient easy technology for PC DIY fans. It offers
a friendly interface. Users can set the CPU Clock easily in the BIOS setup.
Procedures:
1. Correctly install your CPU.
2. Plug in other configurations and restore the system.
3. Switch on power to the system and press the <Del> key to enter BIOS Setup.
4. Enter the <BIOS Features> menu to set the CPU clock.
5. Save and exit BIOS Setup; your system will now boot successfully.
BIOS provides you with a set of basic values for your processor selection instead of the jumper settings. The processor speed can be manually set from
the <BIOS Features> menu screen.
Warning:
Be sure your selection is right. CPU overclock can be dangerous!
We will not be responsible for any damage caused.
82
Page 89

Appendix
Using 8-channel Audio (optional)
1. Introduction
8-channel audio is the highest surround sound standard available adding two
speakers over existing 6-channel audio set-ups. 8-channel surround sound is
already a standard feature for premium consumer audio devices, so it only makes
sense that as users increasingly use their PCs to listen to the latest multimedia
content that 8-channel support makes the migration as a standard PC feature.
In the 8-channel surround sound configuration there are the standard front, center,
LFE (bass) speakers but also two surround speakers are placed at the sides of a
listener, and two speakers directly behind the listener. Some formats also support
a 6-channel audio configuration wherein there is only one speaker behind the
listener. However, since audio connections always come in stereo pairs most PC
hardware will automatically support the 8-channel configuration. It is also fully supported in the Windows XP operating system.
2. Using 8-channel Audio
STEP 1. Connect the front channels to green jack, the rear channels to orange
jack, the Center/Subwoofer channels to black jack and Side channels to grey
jack. Please refer to below figure.
83
Page 90

Appendix
Blue
Green
Red
Black
Orange
Grey
STEP 2. You need to install the driver for the audio chip before you can use
the 8-channel audio function.
84
Click here
Page 91

Appendix
STEP 3. After installation of the audio driver, you’ll find an icon on the taskbar’s
status area. Double click the icon, you will see the following picture.
STEP 4. Click “Speaker Configuration”. The following picture will appear.
STEP 5. Make sure you select “8CH Speaker” from the above picture. Now
you can enjoy the 8-channel audio function.
85
 Loading...
Loading...