Page 1

USER GUIDE
FortiGate
IPS User Guide
Version 3.0 MR7
www.fortinet.com
Page 2

FortiGate IPS User Guide
Version 3.0 MR7
September 16, 2008
01-30007-0080-20080916
© Copyright 2008 Fortinet, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this
publication including text, examples, diagrams or illustrations may be
reproduced, transmitted, or translated in any form or by any means,
electronic, mechanical, manual, optical or otherwise, for any purpose,
without prior written permission of Fortinet, Inc.
Trademarks
Dynamic Threat Prevention System (DTPS), APSecure, FortiASIC,
FortiBIOS, FortiBridge, FortiClient, FortiGate, FortiGate Unified Threat
Management System, FortiGuard, FortiGuard-Antispam, FortiGuardAntivirus, FortiGuard-Intrusion, FortiGuard-Web, FortiLog, FortiAnalyzer,
FortiManager, Fortinet, FortiOS, FortiPartner, FortiProtect, FortiReporter,
FortiResponse, FortiShield, FortiVoIP, and FortiWiFi are trademarks of
Fortinet, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. The names of
actual companies and products mentioned herein may be the trademarks
of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Introduction ........................................................................................ 5
The FortiGate IPS............................................................................................... 5
About this document......................................................................................... 6
Document conventions.................................................................................. 6
Fortinet documentation .................................................................................... 6
Fortinet Knowledge Center .......................................................................... 8
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation .......................................... 8
Customer service and technical support ........................................................ 8
IPS overview and general configuration.......................................... 9
The FortiGate IPS............................................................................................... 9
IPS settings and controls .............................................................................. 9
When to use IPS ......................................................................................... 10
Network performance...................................................................................... 10
Default signature and anomaly settings ...................................................... 10
Default fail open setting............................................................................... 10
Controlling sessions .................................................................................... 11
Setting the buffer size ................................................................................. 11
Monitoring the network and dealing with attacks ........................................ 11
Configuring logging and alert email............................................................. 11
Attack log messages ................................................................................... 12
The FortiGuard Center ................................................................................ 13
Using IPS sensors in a protection profile ..................................................... 14
Creating a protection profile that uses IPS sensors .................................... 14
Adding protection profiles to firewall policies .............................................. 14
Adding protection profiles to user groups.................................................... 15
Predefined signatures ..................................................................... 17
IPS predefined signatures .............................................................................. 17
Viewing the predefined signature list............................................................ 17
Fine tuning IPS predefined signatures for enhanced system performance 18
Custom signatures........................................................................... 21
IPS custom signatures.................................................................................... 21
Viewing the custom signature list.................................................................. 21
Custom signature configuration .................................................................... 22
Adding custom signatures using the web-based manager ......................... 22
Adding custom signatures using the CLI..................................................... 22
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 3
Page 4

Creating custom signatures........................................................................... 23
Custom signature fields .............................................................................. 23
Custom signature syntax ............................................................................ 24
Example custom signatures........................................................................ 33
Protocol decoders ........................................................................... 37
Protocol decoders........................................................................................... 37
Upgrading the IPS protocol decoder list....................................................... 37
Viewing the protocol decoder list.................................................................. 38
IPS sensors ...................................................................................... 39
Viewing the IPS sensor list............................................................................. 39
Adding an IPS sensor ................................................................................. 40
Configuring IPS sensors................................................................................. 40
Configuring filters ........................................................................................ 42
Configuring pre-defined and custom overrides ........................................... 43
DoS sensors..................................................................................... 45
Viewing the DoS sensor list ........................................................................... 46
Configuring DoS sensors ............................................................................... 46
Understanding the anomalies ........................................................................ 48
SYN flood attacks ............................................................................ 51
What is a SYN flood attack? ........................................................................... 51
How SYN floods work ..................................................................................... 51
The FortiGate IPS Response to SYN flood attacks ...................................... 52
What is SYN threshold?.............................................................................. 52
What is SYN proxy? ................................................................................... 52
How IPS works to prevent SYN floods........................................................ 52
Configuring SYN flood protection ................................................................. 54
Suggested settings for different network conditions .................................. 54
ICMP sweep attacks......................................................................... 55
What is an ICMP sweep? ................................................................................ 55
How ICMP sweep attacks work ...................................................................... 55
The FortiGate IPS response to ICMP sweep attacks.................................... 55
Predefined ICMP signatures ....................................................................... 56
ICMP sweep anomalies .............................................................................. 57
Configuring ICMP sweep protection.............................................................. 58
Suggested settings for different network conditions .................................. 58
Index.................................................................................................. 59
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
4 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 5

Introduction The FortiGate IPS
Introduction
This section introduces you to the FortiGate Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
and the following topics:
• The FortiGate IPS
• About this document
• Fortinet documentation
• Customer service and technical support
The FortiGate IPS
Spam and viruses are not the only threats facing enterprises and small
businesses. Sophisticated, automated attack tools are prevalent on the Internet
today, making intrusion detection and prevention vital to securing corporate
networks. An attack or intrusion can be launched to steal confidential information,
force a costly web site crash, or use network resources to launch other attacks.
The FortiGate IPS detects intrusions by using attack signatures for known
intrusion methods, and detects anomalies in network traffic to identify new or
unknown intrusions. Not only can the IPS detect and log attacks, but users can
choose actions to take on the session when an attack is detected. This guide
describes how to configure and use the IPS and the IPS response to some
common attacks.
This guide describes:
• IPS overview and general configuration
• Predefined signatures
• Custom signatures
• Protocol decoders
• IPS sensors
• DoS sensors
• SYN flood attacks
• ICMP sweep attacks
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 5
Page 6
About this document Introduction
!
About this document
Document conventions
The following document conventions are used in this guide:
• In the examples, private IP addresses are used for both private and public IP
addresses.
• Notes and Cautions are used to provide important information:
Note: Highlights useful additional information.
Caution: Warns you about commands or procedures that could have unexpected or
undesirable results including loss of data or damage to equipment.
Typographic conventions
FortiGate documentation uses the following typographical conventions:
Convention Example
Keyboard input In the Gateway Name field, type a name for the remote VPN
Code examples F-SBID (--protocol tcp; --flow
CLI command syntax config firewall policy
Document names FortiGate Administration Guide
File content <HTML><HEAD><TITLE>Firewall
Menu commands Go to VPN > IPSEC > Phase 1 and select Create New.
Program output Welcome!
Variables
Fortinet documentation
peer or client (for example, Central_Office_1).
established; --content "content here";
--no_case)
edit id_integer
set http_retry_count <retry_integer>
set natip <address_ipv4mask>
end
Authentication</TITLE></HEAD>
<BODY><H4>You must authenticate to use this
service.</H4>
<address_ipv4>
The most up-to-date publications and previous releases of Fortinet™ product
documentation are available from the Fortinet Technical Documentation web site
at http://docs.forticare.com.
The following FortiGate product documentation is available:
• FortiGate QuickStart Guide
Provides basic information about connecting and installing a FortiGate unit.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
6 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 7

Introduction Fortinet documentation
• FortiGate Installation Guide
Describes how to install a FortiGate unit. Includes a hardware reference,
default configuration information, installation procedures, connection
procedures, and basic configuration procedures. Choose the guide for your
product model number.
• FortiGate Administration Guide
Provides basic information about how to configure a FortiGate unit, including
how to define FortiGate protection profiles and firewall policies; how to apply
intrusion prevention, antivirus protection, web content filtering, and spam
filtering; and how to configure a VPN.
• FortiGate online help
Provides a context-sensitive and searchable version of the Administration
Guide in HTML format. You can access online help from the web-based
manager as you work.
• FortiGate CLI Reference
Describes how to use the FortiGate CLI and contains a reference to all
FortiGate CLI commands.
• FortiGate Log Message Reference
Describes the structure of FortiGate log messages and provides information
about the log messages that are generated by FortiGate units.
• FortiGate High Availability User Guide
Contains in-depth information about the FortiGate high availability feature and
the FortiGate clustering protocol.
• FortiGate IPS User Guide
Describes how to configure the FortiGate Intrusion Prevention System settings
and how the FortiGate IPS deals with some common attacks.
• FortiGate IPSec VPN User Guide
Provides step-by-step instructions for configuring IPSec VPNs using the webbased manager.
• FortiGate SSL VPN User Guide
Compares FortiGate IPSec VPN and FortiGate SSL VPN technology, and
describes how to configure web-only mode and tunnel-mode SSL VPN access
for remote users through the web-based manager.
• FortiGate PPTP VPN User Guide
Explains how to configure a PPTP VPN using the web-based manager.
• FortiGate Certificate Management Guide
Contains procedures for managing digital certificates including generating
certificate requests, installing signed certificates, importing CA root certificates
and certificate revocation lists, and backing up and restoring installed
certificates and private keys.
• FortiGate VLANs and VDOMs User Guide
Describes how to configure VLANs and VDOMS in both NAT/Route and
Transparent mode. Includes detailed examples.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 7
Page 8

Customer service and technical support Introduction
Fortinet Knowledge Center
Additional Fortinet technical documentation is available from the Fortinet
Knowledge Center. The knowledge center contains troubleshooting and how-to
articles, FAQs, technical notes, and more. Visit the Fortinet Knowledge Center at
http://kc.forticare.com.
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation
Please send information about any errors or omissions in this document, or any
Fortinet technical documentation, to techdoc@fortinet.com.
Customer service and technical support
Fortinet Technical Support provides services designed to make sure that your
Fortinet systems install quickly, configure easily, and operate reliably in your
network.
Please visit the Fortinet Technical Support web site at http://support.fortinet.com
to learn about the technical support services that Fortinet provides.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
8 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 9

IPS overview and general configuration The FortiGate IPS
IPS overview and general configuration
This section contains the following topics:
• The FortiGate IPS
• Network performance
• Monitoring the network and dealing with attacks
• Using IPS sensors in a protection profile
The FortiGate IPS
An IPS is an Intrusion Prevention System for networks. While early systems
focused on intrusion detection, the continuing rapid growth of the Internet, and the
potential for the theft of sensitive data, has resulted in the need for not only
detection, but prevention.
The FortiGate IPS detects intrusions by using attack signatures for known
intrusion methods, and detects anomalies in network traffic to identify new or
unknown intrusions. Not only can the IPS detect and log attacks, but users can
choose actions to take on the session when an attack is detected. This guide
describes how to configure and use the IPS and the IPS response to some
common attacks.
Both the IPS predefined signatures and the IPS engine are upgraded through the
FortiGuard Distribution Network (FDN). These upgrades provide the latest
protection against IM/P2P and other threats. Firmware upgrades will update
anomaly options. The FortiGate IPS default settings implement the recommended
settings for all signatures and anomalies. Signature settings and some anomaly
thresholds are pre-set to work best with the normal traffic on the protected
networks. You can create custom signatures for the FortiGate IPS in diverse
network environments.
Administrators are notified of intrusions and possible intrusions through log
messages and alert email.
Packet logging provides administrators with the ability to analyze packets for
forensics and false positive detection.
IPS settings and controls
Configure the Intrusion Protection system using either the web-based manager or
the CLI, then select IPS sensors in individual firewall protection profiles.
Note: If virtual domains are enabled on the FortiGate unit, the Intrusion Protection settings
are configured separately in each VDOM. All sensors and custom signatures will appear
only in the VDOM in which they were created.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 9
Page 10

Network performance IPS overview and general configuration
To create an IPS sensor, go to Intrusion Protection > IPS Sensor. See “IPS
sensors” on page 39 for details. To access the protection profile IPS sensor
selection, go to Firewall > Protection Profile, select Edit or Create New, and
select IPS.
To create a DoS Sensor, go to Intrusion Protection > DoS Sensor. See “DoS
sensors” on page 45 for details.
When to use IPS
IPS is best for large networks or for networks protecting highly sensitive
information. Using IPS effectively requires monitoring and analysis of the attack
logs to determine the nature and threat level of an attack. An administrator can
adjust the threshold levels to ensure a balance between performance and
intrusion prevention. Small businesses and home offices without network
administrators may be overrun with attack log messages and not have the
networking background required to configure the thresholds and other IPS
settings. In addition, the other protection features in the FortiGate unit, such as
antivirus (including grayware), spam filters, and web filters offer excellent
protection for all networks.
Network performance
The FortiGate IPS is extremely accurate and reliable as an in-line network device.
Independent testing shows that the FortiGate IPS successfully detects and blocks
attacks even under high traffic loads, while keeping latency within expected limits.
This section describes:
• Default signature and anomaly settings
• Default fail open setting
• Controlling sessions
• Setting the buffer size
Default signature and anomaly settings
You can use IPS sensors to apply appropriate IPS signatures to different
protection profiles, then different firewall policies.
Default fail open setting
If for any reason the IPS should cease to function, it will fail open by default. This
means that crucial network traffic will not be blocked and the Firewall will continue
to operate while the problem is resolved.
Change the default fail open setting using the CLI:
config ips global
end
set fail-open [enable | disable]
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
10 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 11

IPS overview and general configuration Monitoring the network and dealing with attacks
Controlling sessions
Use this command to ignore sessions after a set amount of traffic has passed.
The default is 204800 bytes.
config ips global
set ignore-session-bytes <byte_integer>
end
Setting the buffer size
Set the size of the IPS buffer. The size of the buffer is model-dependent.
config ips global
set socket-size <ips_buffer_size>
end
Monitoring the network and dealing with attacks
After configuring IPS and enabling it in protection profiles, it is time to set up
tracking and notification of attacks. Enabling logging and alert email to maintain
user awareness of attacks on the network.
The next step is dealing with attacks if and when they occur. The FortiGuard
Center at http://www.fortinet.com/FortiGuardCenter/ provides a comprehensive
Attack Encyclopedia to help decide what actions to take to further protect the
network.
This section describes:
• Configuring logging and alert email
• Attack log messages
• The FortiGuard Center
Configuring logging and alert email
Whenever the IPS detects or prevents an attack, it generates an attack log
message that can be recorded or sent as an alert email.
The FortiGate unit categorizes attack log messages by signature or anomaly and
includes the attack name in the log message. Enable logging and alert email for
attack signatures and attack anomalies.
Note: Attack and intrusion attempts occur frequently on networks connected to the Internet.
Reduce the number of log messages and alert email by disabling signatures for attacks that the
system is not vulnerable to (for example, web attacks when not running a web server).
To configure logging and alert email for IPS events using the web-based
manager
1 Go to Log&Report > Log Config > Log Setting.
2 Select and configure the settings for any logging locations to use.
3 Select Apply.
4 Go to Log&Report > Log Config > Alert Email.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 11
Page 12

Monitoring the network and dealing with attacks IPS overview and general configuration
5 Select and configure authentication if required and enter the email addresses that
will receive the alert email.
6 Enter the time interval to wait before sending log messages for each logging
severity level.
Note: If more than one log message is collected before an interval is reached, the messages
are combined and sent out as one alert email.
7 Select Apply.
To access log messages from memory or on the local disk
View and download log messages stored in memory or on the FortiGate local disk
from the web-based manager. Go to Log&Report > Log Access and select the
log type to view.
See the FortiGate Administration Guide and the FortiGate Log Message
Reference Guide for more logging procedures.
Attack log messages
Signature
The following log message is generated when an attack signature is found:
Message ID: 70000
Severity: Alert
Message: attack_id=<value_attack_id> src=<ip_address> dst=<ip_address>
Example: 2004-07-07 16:21:18 log_id=0420073000 type=ips subtype=signature
Meaning: Attack signature message providing the source and destination
Action: Get more information about the attack and the steps to take from the
src_port=<port_num> dst_port=<port_num>
interface=<interface_name> src_int=<interface_name>
dst_int=<interface_name> status={clear_session | detected | dropped |
reset} proto=<protocol_num> service=<network_service>
msg="<string><[url]>"
pri=alert attack_id=101318674 src=8.8.120.254 dst=11.1.1.254
src_port=2217 dst_port=25 interface=internal src_int=n/a dst_int=n/a
status=reset proto=6 service=smtp msg="signature: Dagger.1.4.0.Drives
[Reference: http://www.fortinet.com/ids/ID101318674]"
addressing information and the attack name.
Fortinet Attack Encyclopedia in the FortiGuard Center. Copy and paste
the URL from the log message into your browser to go directly to the
signature description in the Attack Encyclopedia.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
12 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 13

IPS overview and general configuration Monitoring the network and dealing with attacks
Anomaly
The following log message is generated when an attack anomaly is detected:
Message ID: 73001
Severity: Alert
Message: attack_id=<value_attack_id> src=<ip_address> dst=<ip_address>
Example: 2004-04-07 13:58:53 log_id=0420073001 type=ips subtype=anomaly
Meaning: Attack anomaly message providing the source and destination
Action: Get more information about the attack and the steps to take from the
src_port=<port_num> dst_port=<port_num>
interface=<interface_name> src_int=<interface_name>
dst_int=<interface_name> status={clear_session | detected | dropped |
reset} proto=<protocol_num> service=<network_service>
msg="<string><[url]>"
pri=alert attack_id=100663396 src=8.8.120.254 dst=11.1.1.254
src_port=2217 dst_port=25 interface=internal src_int=n/a dst_int=n/a
status=reset proto=6 service=smtp msg="anomaly: syn_flood, 100 >
threshold 10.[Reference: http://www.fortinet.com/ids/ID100663396]"
addressing information and the attack name.
Fortinet Attack Encyclopedia in the FortiGuard Center. Copy and paste
the URL from the log message into your browser to go directly to the
signature description in the Attack Encyclopedia.
The FortiGuard Center
The FortiGuard Center combines the knowledge base of the Fortinet technical
team into an easily searchable database. FortiGuard Center includes both virus
and attack information. Go to http://www.fortinet.com/FortiGuardCenter/.
Search for attacks in the FortiGuard Attack Encyclopedia by any of the criteria
shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Searching the FortiGuard Attack Encyclopedia
Type in the name or ID of the attack, or copy and paste the URL from the log
message or alert email into a browser.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 13
Page 14

Using IPS sensors in a protection profile IPS overview and general configuration
Using IPS sensors in a protection profile
IPS can be combined with other FortiGate features – antivirus, spam filtering, web
filtering, and web category filtering – to create protection profiles. Protection
profiles are then added to individual user groups and then to firewall policies, or
added directly to firewall policies.
This section describes:
• Creating a protection profile that uses IPS sensors
• Adding protection profiles to firewall policies
• Adding protection profiles to user groups
Creating a protection profile that uses IPS sensors
To create a protection profile using the web-based manager
1 Go to Firewall > Protection Profile.
2 Select Create New.
Figure 2: New Protection Profile
3 Enter a name for the protection profile.
4 Expand the IPS option list.
5 Select an IPS sensor from the dropdown list. For information about IPS sensors,
see “IPS sensors” on page 39.
6 Configure any other required protection profile options.
7 Select OK.
The protection profile can now be added to any firewall policies that require it. The
protection profile can also be added to user groups and these user groups can be
used to apply authentication to firewall policies.
Adding protection profiles to firewall policies
Adding a protection profile to a firewall policy applies the profile settings, including
IPS, to traffic matching that policy.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
14 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 15

IPS overview and general configuration Using IPS sensors in a protection profile
Adding protection profiles to user groups
When creating a user group, select a protection profile that applies to that group.
Then, when configuring a firewall policy that includes user authentication, select
one or more user groups to authenticate. Each user group selected for
authentication in the firewall policy can have a different protection profile, and
therefore different IPS settings, applied to it.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 15
Page 16

Using IPS sensors in a protection profile IPS overview and general configuration
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
16 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 17

Predefined signatures IPS predefined signatures
Predefined signatures
This section describes:
• IPS predefined signatures
• Viewing the predefined signature list
IPS predefined signatures
Predefined signatures are arranged in alphabetical order. By default, some
signatures are disabled to prevent interference with common traffic, but logging is
enabled for all signatures.
Use the IPS sensor to customize the predefined signatures and apply appropriate
sensors to different protection profiles. For details, see “IPS sensors” on page 39.
Note: By allowing your IPS signature settings to run on default, you may be slowing down
the overall performance of the FortiGate unit. By fine tuning the predefined signature and
logging setting, you can ensure maximum performance as well as maximum protection.
See “Fine tuning IPS predefined signatures for enhanced system performance” on
page 18.
Viewing the predefined signature list
The predefined signature list displays the characteristics of each signature. Use
these characteristics to define which signatures are included in your IPS sensors.
The signature list also displays the default action, the default logging status, and
whether the signature is enabled by default.
Note: If virtual domains are enabled on the FortiGate unit, the Intrusion Protection settings
are configured separately in each VDOM. All sensors and custom signatures will appear
only in the VDOM in which they were created.
To view the predefined signature list, go to Intrusion Protection > Signature >
Predefined. You can also use filters to display the signatures you want to view.
Figure 3: Predefined signature list
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 17
Page 18

Viewing the predefined signature list Predefined signatures
By default, the signatures are sorted by name. To sort the table by another
column, select the required column header name.
Column
Settings
Clear All Filters If you have applied filtering to the predefined signature list display, select
Name The name of the signature, linked to the FortiGuard Center web page
Severity The severity rating of the signature. The severity levels, from lowest to
Tar get The target of the signature. Servers, clients, or both.
Protocols The protocol the signature applies to.
OS The operating system the signature applies to.
Applications The applications the signature applies to.
Enable The default status of the signature. A green circle indicates the signature
Action The default action for the signature. The available actions are pass and
ID A unique numeric identifier for the signature.
Logging The default logging behavior of the signature. A green circle indicates
Group A functional group that is assigned to the signature. This group is only
Packet Log The default packet log status of the signature. A green circle indicates
Revision The revision level of the signature. If the signature is updated, the
Select to customize the signature information displayed in the table. You
can also readjust the column order.
this option to clear all filters and display all the signatures.
about the signature.
highest, are Information, Low, Medium, High, and Critical.
is enabled. A gray circle indicates the signature is not enabled.
drop.
• Pass allows the traffic to continue without any modification. If you
want to determine what effect IPS protection would have on your
network traffic, you can enable the required signatures, set the action
to pass, and enable logging. Traffic will not be interrupted, but you
will be able to examine in detail which signatures were detected.
• Drop prevents the traffic with detected signatures from reaching its
destination.
If logging is enabled, the action appears in the status field of the log
message generated by the signature.
logging is enabled. A gray circle indicates logging is disabled.
for reference and cannot be used to define filters.
packet log is enabled. A gray circle indicates packet log is disabled.
revision number will be incremented.
Fine tuning IPS predefined signatures for enhanced system performance
In FortiOS the FortiGate unit will have most of the predefined signatures enabled
and will log all of them by default. To meet your specific network requirements, you
need to fine tune the signature settings.
By fine tuning the signatures and log settings you can provide the best protection
available but also free up valuable FortiGate resources. Fine tuning enables you
to turn off features that you are not using. By turning off signatures and logs that
you do not use, you allow the FortiGate unit to perform tasks faster thus improving
overall system performance.
Not all systems require you to scan for all signatures of the IPS suite all the time.
By configuring the FortiGate unit to not monitor for these signatures, you will
maintain a high level of security and increase overall performance.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
18 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 19

Predefined signatures Viewing the predefined signature list
You should also review exactly how you use the information provided by the
logging feature. If you find that you do not review the information, it is best to turn
off IPS logging. Logging is best used to provide actionable intelligence.
To create an IPS sensor
1 Go to Intrusion Protection > IPS Sensor.
2 Create a sensor and add IPS filters to it.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 19
Page 20

Viewing the predefined signature list Predefined signatures
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
20 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 21

Custom signatures IPS custom signatures
Custom signatures
Custom signatures provide the power and flexibility to customize the FortiGate
Intrusion Protection system for diverse network environments. The FortiGate
predefined signatures represent common attacks. If you use an unusual or
specialized application or an uncommon platform, you can add custom signatures
based on the security alerts released by the application and platform vendors.
You can also create custom signatures to help you block P2P protocols.
After creation, you need to specify custom signatures in IPS sensors created to
scan traffic.
This section describes:
• IPS custom signatures
• Viewing the custom signature list
• Custom signature configuration
• Creating custom signatures
IPS custom signatures
The FortiGate predefined signatures cover common attacks. If an unusual or
specialized application or an uncommon platform is being used, add custom
signatures based on the security alerts released by the application and platform
vendors.
Use custom signatures to block or allow specific traffic. For example, to block the
SMTP “vrfy” command, add custom signatures similar to the following:
F-SBID( --name "Block.SMTP.VRFY.CMD"; --protocol tcp;
--service SMTP; --pattern "vrfy"; --no_case;
--context header; )
Note: If virtual domains are enabled on the FortiGate unit, IPS is configured separately in
each VDOM. Sensors, filters, and custom signatures will only appear in the VDOM in which
they were created.
Viewing the custom signature list
To view the custom signature list, go to Intrusion Protection > Signature >
Custom.
Figure 4: The custom signature list
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 21
Page 22

Custom signature configuration Custom signatures
Create New Select to create a new custom signature.
Name The custom signature name.
Signature The signature syntax.
Delete icon Select to delete the custom signature.
Edit icon Select to edit the custom signature.
Custom signature configuration
Add custom signatures using the web-based manager or the CLI. For more
information about custom signature syntax, see “Creating custom signatures” on
page 23 and “Custom signature syntax” on page 24.
Adding custom signatures using the web-based manager
To add a custom signature
1 Go to Intrusion Protection > Signature > Custom.
2 Select Create New to add a new custom signature, or select the Edit icon to edit a
custom signature.
Figure 5: Edit Custom Signature
3 Enter a name for the custom signature.
4 Enter the Signature.
5 Select OK.
Adding custom signatures using the CLI
After adding the custom signature, configure the settings for it under the signature
group named custom.
Command syntax pattern
config ips custom
edit <name_str>
set signature <signature_str>
end
Keywords and variables Description Default
name_str The name of the custom signature.
signature
<signature_str>
Enter the custom signature. No default.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
22 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 23

Custom signatures Creating custom signatures
Creating custom signatures
Custom signatures are added separately to each VDOM. In each VDOM, there
can be a maximum of 255 custom signatures.
A custom signature definition is limited to a maximum length of 512 characters. A
definition can be a single line or span multiple lines connected by a backslash (\)
at the end of each line.
A custom signature definition begins with a header, followed by a set of
keyword/value pairs enclosed by parenthesis [( )]. The keyword and value pairs
are separated by a semi colon (;) and consist of a keyword and a value separated
by a space. The basic format of a definition is HEADER (KEYWORD VALUE;)
You can use as many keyword/value pairs as required within the 512 character
limit.
Custom signature fields
Ta bl e 1 shows the valid characters for custom signature fields.
Table 1: Valid characters for custom signature fields
Field Valid Characters Usage
HEADER F-SBID The header for an attack definition
KEYWORD Each keyword must start with
“--”, and be a string of 1 to 19
characters.
Normally, keywords are an
English word or English
words connected by “_”.
Keywords are case
insensitive.
VAL UE Double quotes must be used
around the value if it contains
a space and/or a semicolon.
If the value is NULL, the
space between the
KEYWORD and VALUE can
be omitted.
Values are case sensitive.
Note: if double quotes are
used for quoting the value,
the double quotes are not
considered as part of the
value string.
signature. Each custom signature must
begin with this header.
The keyword is used to identify a
parameter. See “Custom signature
syntax” on page 24 for tables of
supported keywords.
Set the value for a parameter identified
by a keyword.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 23
Page 24

Creating custom signatures Custom signatures
Custom signature syntax
Table 2: Information keywords
Keyword and value Description
--attack_id <id_int>; This optional value is used to identify the signature. It
--name <name_str>; Enter the name of the rule. A rule name must be unique
Table 3: Session keywords
cannot be the same value as any other custom rules within
the same VDOM. If an attack ID is not specified, the
FortiGate automatically assigns an attack ID to the
signature.
An attack ID you assign must be between 1000 and 9999.
Example:
--attack_id 1234;
within the same VDOM.
The name you assign must be a string greater than 0 and
less than 64 characters in length.
Example:
---name "Buffer_Overflow";
Keyword and value Description
--flow {from_client |
from_server |
bi_direction };
Specify the traffic direction and state to be inspected.
They can be used for all IP traffic.
Example:
--src_port 41523;
--flow bi_direction;
The signature checks traffic to and from port 41523.
Previous FortiOS versions used to_client and
to_server values. These are now deprecated, but
still function for backwards compatibility.
--service {HTTP | TELNET
| FTP | DNS | SMTP | POP3
| IMAP | SNMP | RADIUS |
LDAP | MSSQL | RPC | SIP
| H323 | NBSS | DCERPC |
SSH | SSL};
Specify the protocol type to be inspected.
This keyword allows you to specify the traffic type by
protocol rather than by port. If the decoder has the
capability to identify the protocol on any port, the
signature can be used to detect the attack no matter
what port the service is running on. Currently, HTTP,
SIP, SSL, and SSH protocols can be identified on any
port based on the content.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
24 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 25

Custom signatures Creating custom signatures
Table 4: Content keywords
Keyword and value Description
--byte_jump
<bytes_to_convert>,
<offset>[, relative]
[, big] [, little]
[, string] [, hex]
[, dec] [, oct]
[, align];
Use the byte_jump option to extract a number of
bytes from a packet, convert them to their numeric
representation, and jump the match reference up that
many bytes (for further pattern matching or byte
testing). This keyword allows relative pattern matches
to take into account numerical values found in network
data.
The available keyword options include:
• <bytes_to_convert>: The number of bytes to
examine from the packet.
• <offset>: The number of bytes into the payload to
start processing.
• relative: Use an offset relative to last pattern
match.
• big: Process the data as big endian (default).
• little: Process the data as little endian.
• string: The data is a string in the packet.
• hex: The converted string data is represented in
hexadecimal notation.
• dec: The converted string data is represented in
decimal notation.
• oct: The converted string data is represented in
octal notation.
• align: Round up the number of converted bytes to
the next 32-bit boundary.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 25
Page 26

Creating custom signatures Custom signatures
Table 4: Content keywords (Continued)
Keyword and value Description
--byte_test
<bytes_to_convert>,
<operator>, <value>,
<offset>[, relative]
[, big] [, little]
[, string] [, hex]
[, dec] [, oct];
--depth <depth_int>; The FortiGate unit looks for the contents within the
--distance <dist_int>; The FortiGate unit searches for the contents within the
--content
[!]"<content_str>";
The FortiGate unit compares a byte field against a
specific value (with operator). This keyword is capable
of testing binary values or converting representative
byte strings to their binary equivalent and testing them.
The available keyword options include:
• <bytes_to_convert>: The number of bytes to
compare.
• <operator>: The operation to perform when
comparing the value (<,>,=,!,&).
• <value>: The value to compare the converted
value against.
• <offset>: The number of bytes into the payload to
start processing.
• relative: Use an offset relative to last pattern
match.
• big: Process the data as big endian (default).
• little: Process the data as little endian.
• string: The data is a string in the packet.
• hex: The converted string data is represented in
hexadecimal notation.
• dec: The converted string data is represented in
decimal notation.
• oct: The converted string data is represented in
octal notation.
specified number of bytes after the starting point
defined by the offset keyword. If no offset is
specified, the offset is assumed to be equal to 0.
If the value of the depth keyword is smaller than the
length of the value of the content keyword, this
signature will never be matched.
The depth must be between 0 and 65535.
specified number of bytes relative to the end of the
previously matched contents. If the within keyword is
not specified, continue looking for a match until the end
of the payload.
The distance must be between 0 and 65535.
Deprecated, see pattern and context keywords.
The FortiGate unit will search for the content string in
the packet payload. The content string must be
enclosed in double quotes.
To have the FortiGate search for a packet that does not
contain the specified context string, add an exclamation
mark (!) before the content string.
Multiple content items can be specified in one rule. The
value can contain mixed text and binary data. The
binary data is generally enclosed within the pipe (|)
character.
The double quote ("), pipe sign(|) and colon(:)
characters must be escaped using a back slash if
specified in a content string.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
26 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 27

Custom signatures Creating custom signatures
Table 4: Content keywords (Continued)
Keyword and value Description
--context {uri |
header | body | host};
Specify the protocol field that the pattern should be
looked for. If context is not specified for a pattern, the
FortiGate unit searches for the pattern anywhere in the
packet buffer. The available context variables are:
• uri: Search the pattern in HTTP URI line.
• header: Search the pattern in HTTP header lines
or SMTP/POP3/SMTP control messages.
• body: Search the pattern in HTTP body or
SMTP/POP3/SMTP email body.
• host: Search the pattern in HTTP HOST line.
Example:
--pattern "GET "
--context uri
--pattern "yahoo.com"
--context host
--no_case
--pcre "/DESCRIBE\s+\/\s+RTSP\//i"
--context header
--no_case; The no-case keyword forced the FortiGate unit to
--offset <offset_int>; The FortiGate unit starts looking for the contents the
--pattern
[!]"<pattern_str>";
perform a case-insensitive pattern match.
specified number of bytes into the payload. The
specified number of bytes is an absolute value in the
payload. Follow the offset keyword with the depth
keyword to stop looking for a match after a specified
number of bytes. If no depth is specified, the FortiGate
unit continues looking for a match until the end of the
payload.
The offset must be between 0 and 65535.
The FortiGate unit will search for the specified pattern.
A pattern keyword normally is followed by a
context keyword to define where to look for the
pattern in the packet. If a context keyword does not
present, the FortiGate unit looks for the pattern
anywhere in the packet buffer.
To have the FortiGate search for a packet that does not
contain the specified URI, add an exclamation mark (!)
before the URI.
Example:
--pattern "/level/"
--pattern "|E8 D9FF FFFF|/bin/sh"
--pattern !"|20|RTSP/"
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 27
Page 28

Creating custom signatures Custom signatures
Table 4: Content keywords (Continued)
Keyword and value Description
--pcre
[!]"(/<regex>/|m<delim><
regex><delim>)[ismxAEGRU
B]";
--uri [!]"<uri_str>"; Deprecated, see pattern and context keywords.
--within <within_int>; When used with the distance keyword, the FortiGate
Similar to the pattern keyword, pcre is used to
specify a pattern using Perl-compatible regular
expressions (PCRE). A pcre keyword can be followed
by a context keyword to define where to look for the
pattern in the packet. If no context keyword is
present, the FortiGate unit looks for the pattern
anywhere in the packet buffer.
For more information about PCRE syntax, go to
http://www.pcre.org.
The switches include:
• i: Case insensitive.
• s: Include newlines in the dot metacharacter.
• m: By default, the string is treated as one big line of
characters. ^ and $ match at the beginning and
ending of the string. When m is set, ^ and $ match
immediately following or immediately before any
newline in the buffer, as well as the very start and
very end of the buffer.
• x: White space data characters in the pattern are
ignored except when escaped or inside a character
class.
• A: The pattern must match only at the start of the
buffer (same as ^ ).
• E: Set $ to match only at the end of the subject
string. Without E, $ also matches immediately
before the final character if it is a newline (but not
before any other newlines).
• G: Invert the "greediness" of the quantifiers so that
they are not greedy by default, but become greedy if
followed by ?.
• R: Match relative to the end of the last pattern
match. (Similar to distance:0;).
• U: Deprecated, see the context keyword. Match
the decoded URI buffers.
The FortiGate unit will search for the URI in the packet
payload. The URI must be enclosed in double quotes.
To have the FortiGate search for a packet that does not
contain the specified URI, add an exclamation mark (!)
before the URI.
Multiple content items can be specified in one rule. The
value can contain mixed text and binary data. The
binary data is generally enclosed within the pipe (|)
character.
The double quote ("), pipe sign(|) and colon(:)
characters must be escaped using a back slash if
specified in a URI string.
unit searches for the contents within the specified
number of bytes of the payload.
The within value must be between 0 and 65535.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
28 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 29

Custom signatures Creating custom signatures
Table 5: IP header keywords
Keyword and Value Description
--dst_addr [!]<ipv4>; The destination IP address.
To have the FortiGate search for a packet that does
not contain the specified address, add an
exclamation mark (!) before the IP address.
You can define up to 28 IP addresses or CIDR
blocks. Enclose the comma separated list in square
brackets.
Example:
• dst_addr [172.20.0.0/16,10.1.0.0/16,
192.168.0.0/16]
--ip_id <field_int>; Check the IP ID field for the specified value.
--ip_option {rr | eol | nop
| ts | sec | lsrr | ssrr |
satid | any};
--ip_tos <field_int>; Check the IP TOS field for the specified value.
--ip_ttl [< | >] <ttl_int>; Check the IP time-to-live value against the
--protocol
{<protocol_int> | tcp |
udp | icmp};
--src_addr [!]<ipv4>; The source IP address.
Use the ip_option keyword to check various IP
option settings. The available options include:
• rr: Check if IP RR (record route) option is
present.
• eol: Check if IP EOL (end of list) option is
present.
• nop: Check if IP NOP (no op) option is present.
• ts: Check if IP TS (time stamp) option is
present.
• sec: Check if IP SEC (IP security) option is
present.
• lsrr: Check if IP LSRR (loose source routing)
option is present.
• ssrr: Check if IP SSRR (strict source routing)
option is present.
• satid: Check if IP SATID (stream identifier)
option is present.
• any: Check if IP any option is present.
specified value. Optionally, you can check for an IP
time-to-live greater-than (>) or less-than (<) the
specified value with the appropriate symbol.
Check the IP protocol header.
Example:
--protocol tcp;
To have the FortiGate search for a packet that does
not contain the specified address, add an
exclamation mark (!) before the IP address.
You can define up to 28 IP addresses or CIDR
blocks. Enclose the comma separated list in square
brackets.
Example:
• src_addr 192.168.13.0/24
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 29
Page 30

Creating custom signatures Custom signatures
Table 6: TCP header keywords
Keyword and Value Description
--ack <ack_int>; Check for the specified TCP acknowledge
--dst_port [!]{<port_int> |
:<port_int> | <port_int>: |
<port_int>:<port_int>};
--seq <seq_int>; Check for the specified TCP sequence number.
--src_port [!]{<port_int> |
:<port_int> | <port_int>: |
<port_int>:<port_int>};
number.
The destination port number.
You can specify a single port or port range:
• <port_int> is a single port.
• :<port_int> includes the specified port and
all lower numbered ports.
• <port_int>: includes the specified port and
all higher numbered ports.
• <port_int>:<port_int> includes the two
specified ports and all ports in between.
The source port number.
You can specify a single port or port range:
• <port_int> is a single port.
• :<port_int> includes the specified port and
all lower numbered ports.
• <port_int>: includes the specified port and
all higher numbered ports.
• <port_int>:<port_int> includes the two
specified ports and all ports in between.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
30 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 31

Custom signatures Creating custom signatures
Table 6: TCP header keywords (Continued)
Keyword and Value Description
--tcp_flags
<FSRPAU120>[!|*|+]
[,<FSRPAU120>];
Specify the TCP flags to match in a packet.
• S: Match the SYN flag.
• A: Match the ACK flag.
• F: Match the FIN flag.
• R: Match the RST flag.
• U: Match the URG flag.
• P: Match the PSH flag.
• 1: Match Reserved bit 1.
• 2: Match Reserved bit 2.
• 0: Match No TCP flags set.
• +: Match on the specified bits, plus any
others.
• *: Match if any of the specified bits are set.
• !: Match if the specified bits are not set.
The first part if the value (<FSRPAU120>) defines
the bits that must present for a successful match.
For example:
--tcp_flags AP
only matches the case where both A and P bits
are set.
The second part ([,<FSRPAU120>]) is optional,
and defines the additional bits that can present
for a match. For example:
tcp_flags S,12
matches the following combinations of flags: S, S
and 1, S and 2, S and 1 and 2.
The modifiers !, * and + can not be used in the
second part.
--window_size
[!]<window_int>;
Check for the specified TCP window size.
You can specify the window size as a
hexadecimal or decimal integer. A hexadecimal
value must be preceded by 0x.
To have the FortiGate search for the absence of
the specified window size, add an exclamation
mark (!) before the window size.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 31
Page 32

Creating custom signatures Custom signatures
Table 7: UDP header keywords
Keyword and Value Description
--dst_port [!]{<port_int> |
:<port_int> | <port_int>: |
<port_int>:<port_int>};
--src_port [!]{<port_int> |
:<port_int> | <port_int>: |
<port_int>:<port_int>};
The destination port number.
You can specify a single port or port range:
• <port_int> is a single port.
• :<port_int> includes the specified port and
all lower numbered ports.
• <port_int>: includes the specified port and
all higher numbered ports.
• <port_int>:<port_int> includes the two
specified ports and all ports in between.
The source port number.
You can specify a single port or port range:
• <port_int> is a single port.
• :<port_int> includes the specified port and
all lower numbered ports.
• <port_int>: includes the specified port and
all higher numbered ports.
• <port_int>:<port_int> includes the two
specified ports and all ports in between.
Table 8: ICMP keywords
Keyword and Value Usage
--icmp_code <code_int>; Specify the ICMP code to match.
--icmp_id <id_int>; Check for the specified ICMP ID value.
--icmp_seq <seq_int>; Check for the specified ICMP sequence value.
--icmp_type <type_int>; Specify the ICMP type to match.
Table 9: Other keywords
Keyword and Value Description
--data_size {<size_int> |
<<size_int> | ><size_int> |
<port_int><><port_int>};
--data_at <offset_int>[,
relative];
Test the packet payload size. With data_size
specified, packet reassembly is turned off
automatically. So a signature with data_size
and only_stream values set is wrong.
• <size_int> is a particular packet size.
• <<size_int> is a packet smaller than the
specified size.
• ><size_int> is a packet larger than the
specified size.
• <size_int><><size_int> within the
range between the specified sizes.
Verify that the payload has data at a specified
offset, optionally looking for data relative to the
end of the previous content match.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
32 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 33

Custom signatures Creating custom signatures
Table 9: Other keywords (Continued)
Keyword and Value Description
--rpc_num <app_int>[,
<ver_int> | *][,
<proc_int> | *>];
--same_ip; The source and the destination have the same
Check for RPC application, version, and
procedure numbers in SUNRPC CALL
requests. The * wildcard can be used for
version and procedure numbers.
IP addresses.
Example custom signatures
Custom signature fields and syntax are fully described in this chapter, though
using them to build a custom signature can be complex. It’s best to start with a
simpler signature.
Example 1: signature to block access to example.com
In this first example, we will create a custom signature to block access to the
example.com URL.
1 Custom signature basic format
All custom signatures have a header, and at least one keyword/value pair. The
header is always the same:
F-SBID( )
The keyword/value pairs appear within the parentheses and each pair is followed
by a semicolon.
2 Choosing a name for the custom signature
Every custom signature requires a name, so it is good practice to assign a name
before any other keywords are added.
Use the --name keyword to assign the custom signature a name. The name
value follows the keyword after a space. Enclose the name value in doublequotes:
F-SBID( --name "Block.example.com"; )
The signature, as it appears here, will not do anything if used. It has a name, but
doesn’t look for any patterns in network traffic. You must specify a pattern for the
FortiGate unit to search for.
3 Adding a signature pattern
Use the --pattern keyword to specify what the FortiGate unit will search for:
F-SBID( --name "Block.example.com"; --pattern
"example.com"; )
The signature will now detect the example.com URL appearing in network traffic.
The custom signature should only detect the URL in HTTP traffic, however. Any
other traffic with the URL should be allowed to pass. For example, an Email
message to or from example.com should not be stopped.
4 Specifying the service
Use the --service keyword to limit the effect of the custom signature to only the
HTTP protocol.
F-SBID( --name "Block.example.com"; --pattern
"example.com"; --service HTTP; )
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 33
Page 34

Creating custom signatures Custom signatures
The FortiGate unit will limit its search for the pattern to the HTTP protocol. Even
though the HTTP protocol uses only TCP traffic, the FortiGate will search for
HTTP protocol communication in TCP, UDP, and ICMP traffic. This is a needless
waste of system resources.
5 Specifying the traffic type.
Use the --protocol tcp keyword to limit the effect of the custom signature to
only TCP traffic. This will save system resources by not unnecessarily scanning
UDP and ICMP traffic.
F-SBID( --name "Block.example.com"; --pattern
"example.com"; --service HTTP; --protocol tcp; )
The FortiGate unit will limit its search for the pattern to TCP traffic and ignore UDP
and ICMP network traffic.
6 Ignoring case sensitivity
By default, patterns are case sensitive. If a user directed his or her browser to
Example.com, the custom signature would not recognize the URL as a match.
Use the --no_case keyword to make the pattern matching case insensitive.
F-SBID( --name "Block.example.com"; --pattern
"example.com"; --service HTTP; --no_case; )
Unlike all of the other keywords in this example, the --no_case keyword has no
value. Only the keyword is required.
7 Limiting pattern scans to only traffic sent from the client
The --flow command can be used to further limit the network traffic being
scanned to only that send by the client or by the server.
F-SBID( --name "Block.example.com";
--pattern "example.com"; --service HTTP; --no_case;
--flow from_client; )
Web servers don’t contact clients until clients first open a communication session.
Therefore, using the --flow from_client command will force the FortiGate
until to ignore all traffic originating from the server. Since the majority of HTTP
traffic flows from the server to the client, this will save considerable system
resources and still maintain protection.
8 Specifying the context
When the client browser tries to contact example.com, a DNS is first consulted to
get the example.com server IP address. The IP address is then specified in the
URL field of the HTTP communication. The domain name will still appear in the
host field so this custom signature will not function without the --context host
keyword/value pair.
F-SBID( --name "Block.example.com";
--pattern "example.com"; --service HTTP; --no_case;
--flow from_client; --context host; )
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
34 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 35

Custom signatures Creating custom signatures
Example 2: signature to block the SMTP ‘vrfy’ command
The SMTP vrfy command can be used to verify the existence of a single email
address, or it can be used to list all of the valid email accounts on an email server.
A spammer could potentially use this command to obtain a list of all valid email
users and direct spam to their inboxes.
In this example, we will create a custom signature to block the use of the vrfy
command. Since the custom signature blocks the vrfy command from coming
through the FortiGate unit, the administrator can still use the command on the
internal network.
1 Custom signature basic format
All custom signatures have a header, and at least one keyword/value pair. The
header is always the same:
F-SBID( )
The keyword/value pairs appear within the parentheses and each pair is followed
by a semicolon.
2 Choosing a name for the custom signature
Every custom signature requires a name, so it is good practice to assign a name
before any other keywords are added.
Use the --name keyword to assign the custom signature a name. The name
value follows the keyword after a space. Enclose the name value in doublequotes:
F-SBID( --name "Block.SMTP.VRFY.CMD"; )
The signature, as it appears here, will not do anything if used. It has a name, but
doesn’t look for any patterns in network traffic. You must specify a pattern for the
FortiGate unit to search for.
3 Adding a signature pattern
Use the --pattern keyword to specify what the FortiGate unit will search for:
F-SBID( --name "Block.SMTP.VRFY.CMD"; --pattern "vrfy"; )
The signature will now detect the vrfy command appearing in network traffic. The
custom signature should only detect the command in SMTP traffic, however. Any
other traffic with the pattern should be allowed to pass. For example, an Email
message discussing the vrfy command should not be stopped.
4 Specifying the service
Use the --service keyword to limit the effect of the custom signature to only the
HTTP protocol.
F-SBID( --name "Block.SMTP.VRFY.CMD"; --pattern "vrfy";
--service SMTP; )
The FortiGate unit will limit its search for the pattern to the SMTP protocol.
Even though the SMTP protocol uses only TCP traffic, the FortiGate will search
for SMTP protocol communication in TCP, UDP, and ICMP traffic. This is a
needless waste of system resources.
5 Specifying the traffic type.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 35
Page 36

Creating custom signatures Custom signatures
Use the --protocol tcp keyword to limit the effect of the custom signature to
only TCP traffic. This will save system resources by not unnecessarily scanning
UDP and ICMP traffic.
F-SBID( --name "Block.SMTP.VRFY.CMD"; --pattern "vrfy";
--service SMTP; --protocol tcp; )
The FortiGate unit will limit its search for the pattern to TCP traffic and ignore the
pattern in UDP and ICMP network traffic.
6 Ignoring case sensitivity
By default, patterns are case sensitive. If a user directed his or her browser to
Example.com, the custom signature would not recognize the URL as a match.
Use the --no_case keyword to make the pattern matching case insensitive.
F-SBID( --name "Block.SMTP.VRFY.CMD"; --pattern "vrfy";
--service SMTP; --no_case; )
Unlike all of the other keywords in this example, the --no_case keyword has no
value. Only the keyword is required.
7 Specifying the context
The SMTP vrfy command will appear in the SMTP header. The
--context host keyword/value pair allows you to limit the pattern search to
only the header.
F-SBID( --name "Block.SMTP.VRFY.CMD"; --pattern "vrfy";
--service SMTP; --no_case; --context header; )
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
36 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 37

Protocol decoders Protocol decoders
Protocol decoders
This section describes:
• Protocol decoders
• Upgrading the IPS protocol decoder list
• Viewing the protocol decoder list
Protocol decoders
The FortiGate IPS uses protocol decoders to identify the abnormal traffic patterns
that do not meet the protocol requirements and standards. For example, the
HTTP decoder monitors the HTTP traffic to identify any HTTP packets that do not
meet the HTTP protocol standards.
On the Intrusion Protection > Signature > Protocol Decoder page, you can
view the decoders and the port numbers the protocol decoders monitor.
Upgrading the IPS protocol decoder list
The Intrusion Protection system protocol decoders are upgraded automatically
through the FortiGuard Distribution Network (FDN) if existing decoders are
modified or new decoders added. The FDN keeps the protocol decoder list up-todate with protection against new threats such as the latest versions of existing
IM/P2P as well as against new applications.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 37
Page 38

Viewing the protocol decoder list Protocol decoders
Viewing the protocol decoder list
To view the decoder list, go to Intrusion Protection > Signature > Protocol
Decoder.
Figure 6: The protocol decoder list
Protocols The protocol decoder names.
Port The port number or numbers that the protocol decoder monitors.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
38 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 39

IPS sensors Viewing the IPS sensor list
IPS sensors
You can group signatures into IPS sensors for easy selection in protection
profiles. You can define signatures for specific types of traffic in separate IPS
sensors, and then select those sensors in profiles designed to handle that type of
traffic. For example, you can specify all of the web-server related signatures in an
IPS sensor, and the sensor can then be used by a protection profile in a policy
that controls all of the traffic to and from a web server protected by the FortiGate
unit.
The FortiGuard Service periodically updates the pre-defined signatures, with
signatures added to counter new threats. Because the signatures included in
filters are defined by specifying signature attributes, new signatures matching
existing filter specifications will automatically be included in those filters. For
example, if you have a filter that includes all signatures for the Windows operating
system, your filter will automatically incorporate new Windows signatures as they
are added.
This section describes:
• Viewing the IPS sensor list
• Configuring IPS sensors
Viewing the IPS sensor list
To view the IPS sensors, go to Intrusion Protection > IPS Sensor.
Figure 7: IPS Sensor list showing the default sensors
The IPS sensor list displays the following information.
Create New Add a new IPS sensor. For more information, see “Adding an
Name The name of each IPS sensor.
Comments An optional description of the IPS sensor.
Delete and Edit icons Delete or edit an IPS sensor.
IPS sensor” on page 40.
Five default IPS sensors are provided with the default configuration.
all_default Includes all signatures. The sensor is set to use the default
all_default_pass Includes all signatures. The sensor is set to use the default
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 39
enable status and action of each signature.
enable status of each signature, but the action is set to pass.
Page 40

Configuring IPS sensors IPS sensors
protect_client Includes only the signatures designed to detect attacks
protect_email_server Includes only the signatures designed to detect attacks
protect_http_server Includes only the signatures designed to detect attacks
Adding an IPS sensor
An IPS sensor must be created before it can be configured by adding filters and
overrides. To create an IPS sensor, go to Intrusion Protection > IPS Sensor and
select Create New.
Figure 8: New IPS sensor
Name Enter the name of the new IPS sensor.
Comment Enter an optional comment to display in the IPS sensor list.
against clients; uses the default enable status and action of
each signature.
against servers and the SMTP, POP3, or IMAP protocols;
uses the default enable status and action of each signature.
against servers and the HTTP protocol; uses the default
enable status and action of each signature.
Configuring IPS sensors
Each IPS sensor consists of two parts: filters and overrides. Overrides are always
checked before filters.
Each filter consists of a number of signatures attributes. All of the signatures with
those attributes, and only those attributes, are checked against traffic when the
filter is run. If multiple filters are defined in an IPS Sensor, they are checked
against the traffic one at a time, from top to bottom. If a match is found, the
FortiGate unit takes the appropriate action and stops further checking.
A signature override can modify the behavior of a signature specified in a filter. A
signature override can also add a signature not specified in the sensor’s filters.
Custom signatures are included in an IPS sensor using overrides.
The signatures in the overrides are first compared to network traffic. If the IPS
sensor does not find any matches, it then compares the signatures in each filter to
network traffic, one filter at a time, from top to bottom. If no signature matches are
found, the IPS sensor allows the network traffic.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
40 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 41

IPS sensors Configuring IPS sensors
To view an IPS sensor, go to Intrusion Protection > IPS Sensor and select the
Edit icon of any IPS sensor. The Edit IPS Sensor window is divided into three
parts: the sensor attributes, the filters, and the overrides.
Figure 9: Edit IPS sensor
IPS sensor attributes:
Name The name of the IPS sensor. You can change it at any time.
Comments An optional comment describing the IPS sensor. You can change it at
OK Select to save changes to Name or Comments.
any time.
IPS sensor filters:
Add Filter Add a new filter to the end of the filter list. For more information, see
# Current position of each filter in the list.
Name The name of the filter.
Signature
attributes
Enable The status of the signatures included in the filter. The signatures can be
Logging The logging status of the signatures included in the filter. Logging can
Action The action of the signatures included in the filter. The action can be set
Count The number of signatures included in the filter. Overrides are not
Delete icon Delete the filter.
Edit icon Edit the filter.
Insert icon Create a new filter and insert it above the current filter.
“Configuring filters” on page 42.
Signature attributes specify the type of network traffic the signature
applies to.
Severity The severity of the included signatures.
Tar get The type of system targeted by the attack. The targets
are client and server.
Protocol The protocols to which the signatures apply. Examples
include HTTP, POP3, H323, and DNS.
OS The operating systems to which the signatures apply.
Application The applications to which the signatures apply.
set to enabled, disabled, or default. The default setting uses the default
status of each individual signature as displayed in the signature list.
be set to enabled, disabled, or default. The default setting uses the
default status of each individual signature as displayed in the signature
list.
to pass all, block all, reset all, or default. The default setting uses the
action of each individual signature as displayed in the signature list.
included in this total.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 41
Page 42

Configuring IPS sensors IPS sensors
Move to icon After selecting this icon, enter the destination position in the window
View Rules icon Open a window listing all of the signatures included in the filter.
IPS sensor overrides:
Add Pre-defined
Override
Add Custom
Override
# Current position of each override in the list.
Name The name of the signature.
Enable The status of the override. A green circle indicates the override is
Logging The logging status of the override. A green circle indicates logging is
Action The action set for the override. The action can be set to pass, block, or
Delete and Edit
icons
Configuring filters
To configure a filter, go to Intrusion Protection > IPS Sensor. Select the Edit icon
of the IPS sensor containing the filter you want to edit. When the sensor window
opens, select the Edit icon of the filter you want to change, or select Add Filter to
create a new filter. Enter the information as described below and select OK.
that appears, and select OK.
Select to create an override based on a pre-defined signature.
Select to create an override based on a custom signature.
enabled. A gray circle indicates the override is not enabled.
enabled. A gray circle indicates logging is not enabled.
reset.
Delete or edit the filter.
Figure 10: Edit IPS Filter
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
42 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 43

IPS sensors Configuring IPS sensors
Name Enter or change the name of the IPS filter.
Severity Select All, or select Specify and then one or more severity ratings.
Target Select All, or select Specify and then the type of systems targeted by the
OS Select All, or Select Specify and then select one or more operating
Protocol Select All, or select Specify to list what network protocols are used by
Application Select All, or select Specify to list the applications or application suites
Enable Select from the options to specify what the FortiGate unit will do with the
Logging Select from the options to specify whether the FortiGate unit will create
Action Select from the options to specify what the FortiGate unit will do with
Severity defines the relative importance of each signature. Signatures
rated critical detect the most dangerous attacks while those rated as
info pose a much smaller threat.
attack. The choices are server or client.
systems that are vulnerable to the attack.
Signatures with an OS attribute of All affect all operating systems.
These signatures will be automatically included in any filter regardless
of whether a single, multiple, or all operating systems are specified.
the attack. Use the Right Arrow to move the ones you want to include in
the filter from the Available to the Selected list, or the Left Arrow to
remove previously selected protocols from the filter.
vulnerable to the attack. Use the Right Arrow to move the ones you
want to include in the filter from the Available to the Selected list, or the
Left Arrow to remove previously selected protocols from the filter.
signatures included in the filter: enable all, disable all, or enable or
disable each according to the individual default values shown in the
signature list.
log entries for the signatures included in the filter: enable all, disable all,
or enable or disable logging for each according to the individual default
values shown in the signature list.
traffic containing a signature match: pass all, block all, reset all, or block
or pass traffic according to the individual default values shown in the
signature list.
The signatures included in the filter are only those matching every attribute
specified. When created, a new filter has every attribute set to “all” which causes
every signature to be included in the filter. If the severity is changed to high, and
the target is changed to server, the filter includes only signatures checking for high
priority attacks targeted at servers.
Configuring pre-defined and custom overrides
Pre-defined and custom overrides are configured and work mainly in the same
way as filters. Unlike filters, each override defines the behavior of one signature.
Overrides can be used in two ways:
• To change the behavior of a signature already included in a filter. For example,
to protect a web server, you could create a filter that includes and enables all
signatures related to servers. If you wanted to disable one of those signatures,
the simplest way would be to create an override and mark the signature as
disabled.
• To add an individual signature, not included in any filters, to an IPS sensor.
This is the only way to add custom signatures to IPS sensors.
When a pre-defined signature is specified in an override, the default status and
action attributes have no effect. These settings must be explicitly set when
creating the override.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 43
Page 44

Configuring IPS sensors IPS sensors
Note: Before an override can affect network traffic, you must add it to a filter, and you must
select the filter in a protection profile applied to a policy. An override does not have the
ability to affect network traffic until these steps are taken.
To edit a pre-defined or custom override, go to Intrusion Protection >
IPS Sensor and select the Edit icon of the IPS sensor containing the override you
want to edit. When the sensor window opens, select the Edit icon of the override
you want to change.
Figure 11: Configure IPS override
Signature Select the browse icon to view the list of available signatures. From this
Enable Select to enable the signature override.
Action Select one of Pass, Block or Reset. When the override is enabled, the
Logging Select to enable creation of a log entry if the signature is discovered in
Packet Log Select to save packets that trigger the override to the FortiGate hard
Exempt IP: Enter IP addresses to exclude from the override. The override will then
list, select a signature the override will apply to and then select OK.
action determines what the FortiGate will do with traffic containing the
specified signature.
network traffic.
drive for later examination. This option is only valid on FortiGate units
with an internal hard drive.
apply to all IP addresses except those defined as exempt. The exempt
IP addresses are defined in pairs, with a source and destination, and
traffic moving from the source to the destination is exempt from the
override.
Source The exempt source IP address. Enter 0.0.0.0/0 to
include all source IP addresses.
Destination: The exempt destination IP address. Enter 0.0.0.0/0 to
include all destination IP addresses.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
44 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 45

DoS sensors
DoS sensors
The FortiGate IPS uses a traffic anomaly detection feature to identify network
traffic that does not fit known or common traffic patterns and behavior. For
example, one type of flooding is the denial of service (DoS) attack that occurs
when an attacking system starts an abnormally high number of sessions with a
target system. The high number of sessions slows down or disables the target
system so legitimate users can no longer use it. This type of attack gives the DoS
sensor its name, although it is capable of detecting and protecting against a
number of anomaly attacks.
You can enable or disable logging for each traffic anomaly, and configure the
detection threshold and action to take when the detection threshold is exceeded.
You can create multiple DoS sensors. Each sensor consists of 12 anomaly types
that you can configure. Each sensor examines the network traffic in sequence,
from top to bottom. When a sensor detects an anomaly, it applies the configured
action. Multiple sensors allow great granularity in detecting anomalies because
each sensor can be configured to examine traffic from a specific address, to a
specific address, on a specific port, in any combination.
When arranging the DoS sensors, place the most specific sensors at the top and
the most general at the bottom. For example, a sensor with one protected address
table entry that includes all source addresses, all destination addresses, and all
ports will match all traffic. If this sensor is at the top of the list, no subsequent
sensors will ever execute.
The traffic anomaly detection list can be updated only when the FortiGate
firmware image is upgraded.
Note: If virtual domains are enabled on the FortiGate unit, the Intrusion Protection settings
must be configured separately in each VDOM. All sensors and custom signatures will
appear only in the VDOM in which they were created.
This section describes:
• Viewing the DoS sensor list
• Configuring DoS sensors
• Understanding the anomalies
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 45
Page 46

Viewing the DoS sensor list DoS sensors
Viewing the DoS sensor list
To view the anomaly list, go to Intrusion Protection > DoS Sensor.
Figure 12: The DoS sensor list
Create New Add a new DoS sensor to the bottom of the list.
ID A unique identifier for each DoS sensor. The ID does not indicate the
Status Select to enable the DoS sensor.
Name The DoS sensor name.
Comments An optional description of the DoS sensor.
Delete Delete the DoS sensor.
Edit icon Edit the following information: Action, Severity, and Threshold.
Insert DoS
Sensor before
icon
Move To icon Move the current DoS sensor to another position in the list. After
sequence in which the sensors examine network traffic.
Create a new DoS sensor before the current sensor.
selecting this icon, enter the destination position in the window that
appears, and select OK.
Configuring DoS sensors
Because an improperly configured DoS sensor can interfere with network traffic,
no DoS sensors are present on a factory default FortiGate unit. You must create
your own and then enable them before they will take effect. Thresholds for newly
created sensors are preset with recommended values that you can adjust to meet
the needs of your network.
Note: It is important to know normal and expected network traffic before changing the
default anomaly thresholds. Setting the thresholds too low could cause false positives, and
setting the thresholds too high could allow otherwise avoidable attacks.
To configure DoS sensors, go to Intrusion Protection > DoS Sensor. Select the
Edit icon of an existing DoS sensor, or select Create New to create a new DoS
sensor.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
46 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 47

DoS sensors Configuring DoS sensors
Figure 13: Edit DoS Sensor
DoS sensor attributes:
Name Enter or change the DoS sensor name.
Comments Enter or change an optional description of the DoS sensor. This description
will appear in the DoS sensor list.
Anomaly configuration:
Name The name of the anomaly.
Enable Select the check box to enable the DoS sensor to detect when the
Logging Select the check box to enable the DoS sensor to log when the anomaly
Action Select Pass to allow anomalous traffic to pass when the FortiGate unit
Threshold Displays the number of sessions/packets that must show the anomalous
specified anomaly occurs. Selecting the check box in the header row will
enable sensing of all anomalies.
occurs. Selecting the check box in the header row will enable logging for all
anomalies. Anomalies that are not enabled are not logged.
detects it, or set Block to prevent the traffic from passing.
behavior before the FortiGate unit triggers the anomaly action (pass or
block). If required, change the number. For more information about how
these settings affect specific anomalies, see Table 10 on page 48.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 47
Page 48

Understanding the anomalies DoS sensors
Protected addresses:
Each entry in the protected address table includes a source and destination IP
address as well as a destination port. The DoS sensor will be applied to traffic
matching the three attributes in any table entry.
Note: A new DoS sensor has no protected address table entries. If no addresses are
entered, the DoS sensor cannot match any traffic and will not function.
Destination The IP address of the traffic destination. 0.0.0.0/0 matches all addresses. If
Destination
Port
Source The IP address of the traffic source. 0.0.0.0/0 matches all addresses.
Add After entering the required destination address, destination port, and
the FortiGate unit is running in transparent mode, 0.0.0.0/0 also includes
the management IP address.
The destination port of the traffic. 0 matches any port.
source address, select Add to add protected address to the Protected
Addresses list. The DoS sensor will be invoked only on traffic matching all
three of the entered values. If no addresses appear in the list, the sensor
will not be applied to any traffic.
Understanding the anomalies
Each DoS sensor offers four configurable statistical anomaly types for each of the
TCP, UDP, and ICMP protocols.
Table 10: The four statistical anomaly types.
Flooding If the number of sessions targeting a single destination in one second is
Scan If the number of sessions from a single source in one second is over a
Source session
limit
Destination
session limit
over a specified threshold, the destination is experiencing flooding.
specified threshold, the source is scanning.
If the number of concurrent sessions from a single source is over a
specified threshold, the source session limit is reached.
If the number of concurrent sessions to a single destination is over a
specified threshold, the destination session limit is reached.
For each of the TCP, UDP, and ICMP protocols, DoS sensors offer four statistical
anomaly types. The result is twelve configurable anomalies.
Figure 14: The twelve individually configurable anomalies
Anomaly Description
tcp_syn_flood If the SYN packet rate, including retransmission, to one destination
tcp_port_scan If the SYN packets rate, including retransmission, from one source
tcp_src_session If the number of concurrent TCP connections from one source IP
48 01-30007-0080-20080916
IP address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed. The threshold is expressed in packets per second.
IP address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed. The threshold is expressed in packets per second.
address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
Page 49

DoS sensors Understanding the anomalies
Anomaly Description
tcp_dst_session If the number of concurrent TCP connections to one destination IP
udp_flood If the UDP traffic to one destination IP address exceeds the
udp_scan If the number of UDP sessions originating from one source IP
udp_src_session If the number of concurrent UDP connections from one source IP
udp_dst_session If the number of concurrent UDP connections to one destination IP
icmp_flood If the number of ICMP packets sent to one destination IP address
icmp_sweep If the number of ICMP packets originating from one source IP
icmp_src_session If the number of concurrent ICMP connections from one source IP
icmp_dst_session If the number of concurrent ICMP connections to one destination
address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed.
configured threshold value, the action is executed. The threshold is
expressed in packets per second.
address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed. The threshold is expressed in packets per second.
address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed.
address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed.
exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is executed.
The threshold is expressed in packets per second.
address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed. The threshold is expressed in packets per second.
address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed.
IP address exceeds the configured threshold value, the action is
executed.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 49
Page 50

Understanding the anomalies DoS sensors
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
50 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 51

SYN flood attacks What is a SYN flood attack?
SYN flood attacks
This section describes:
• What is a SYN flood attack?
• How SYN floods work
• The FortiGate IPS Response to SYN flood attacks
• Configuring SYN flood protection
• Suggested settings for different network conditions
What is a SYN flood attack?
A SYN flood is a type of Denial of Service (DoS) attack. DoS is a class of attacks
in which an attacker attempts to prevent legitimate users from accessing an
internet service, for example, a web server. Using SYN floods, an attacker
attempts to disable an Internet service by flooding a server with TCP/IP
connection requests which consume all the available slots in the server’s TCP
connection table. When the connection table is full, it is not possible to establish
any new connections, and the web site on the server becomes inaccessible.
This section provides information about SYN flood attacks and the FortiGate IPS
methods of preventing such attacks.
How SYN floods work
SYN floods work by exploiting the structure of the TCP/IP protocol. An attacker
floods a server with connection attempts but never acknowledges the server’s
replies to open the TCP/IP connection.
The TCP/IP protocol uses a three-step process to establish a network connection.
Figure 15: Establishing a TCP/IP connection
1 The originator of the connection sends a SYN packet (a packet with the SYN flag
set in the TCP header) to initiate the connection.
2 The receiver sends a SYN/ACK packet (a packet with the SYN and ACK flags set
in the TCP header) back to the originator to acknowledge the connection attempt.
3 The originator then sends an ACK packet (a packet with the ACK flag set in the
TCP header) back to the receiver to open the connection.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 51
Page 52

The FortiGate IPS Response to SYN flood attacks SYN flood attacks
After the handshaking process is complete the connection is open and data
exchange can begin between the originator and the receiver, in this case the web
browser and the web server.
Between steps 2 and 3 however, the web server keeps a record of any incomplete
connections until it receives the ACK packet. A SYN flood attacker sends many
SYN packets but never replies with the final ACK packet.
Since most systems have only a limited amount of space for TCP/IP connection
records, a flood of incomplete connections will quickly block legitimate users from
accessing the server. Most TCP/IP implementations use a fairly long timeout
before incomplete connections are cleared from the connection table and traffic
caused by a SYN flood is much higher than normal network traffic.
The FortiGate IPS Response to SYN flood attacks
The FortiGate unit uses a defense method that combines the SYN Threshold and
SYN Proxy methods to prevent SYN flood attacks.
What is SYN threshold?
An IPS device establishes a limit on the number of incomplete TCP connections,
and discards SYN packets if the number of incomplete connections reaches the
limit.
What is SYN proxy?
An IPS proxy device synthesizes and sends the SYN/ACK packet back to the
originator, and waits for the final ACK packet. After the proxy device receives the
ACK packet from the originator, the IPS device then "replays" the three-step
sequence of establishing a TCP connection (SYN, SYN/ACK and ACK) to the
receiver.
How IPS works to prevent SYN floods
The FortiGate IPS uses a pseudo SYN proxy to prevent SYN flood attack. The
pseudo SYN proxy is an incomplete SYN proxy that reduces resource usage and
provides better performance than a full SYN proxy approach.
The IPS allows users to set a limit or threshold on the number of incomplete TCP
connections. The threshold can be set either from the CLI or the web-based
manager.
When the IPS detects that the total number of incomplete TCP connections to a
particular target exceeds the threshold, the pseudo SYN proxy is triggered to
operate for all subsequent TCP connections. The pseudo SYN proxy will
determine whether a new TCP connection is a legitimate request or another SYN
flood attack based on a “best-effect” algorithm. If a subsequent connection
attempt is detected to be a normal TCP connection, the IPS will allow a TCP
connection from the source to the target. If a subsequent TCP connection is
detected to be a new incomplete TCP connection request, one of the following
actions will be taken: Drop, Reset, Reset Client, Reset Server, Drop Session,
Pass Session, Clear Session, depending upon the user configuration for SYN
Flood anomaly in the IPS.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
52 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 53
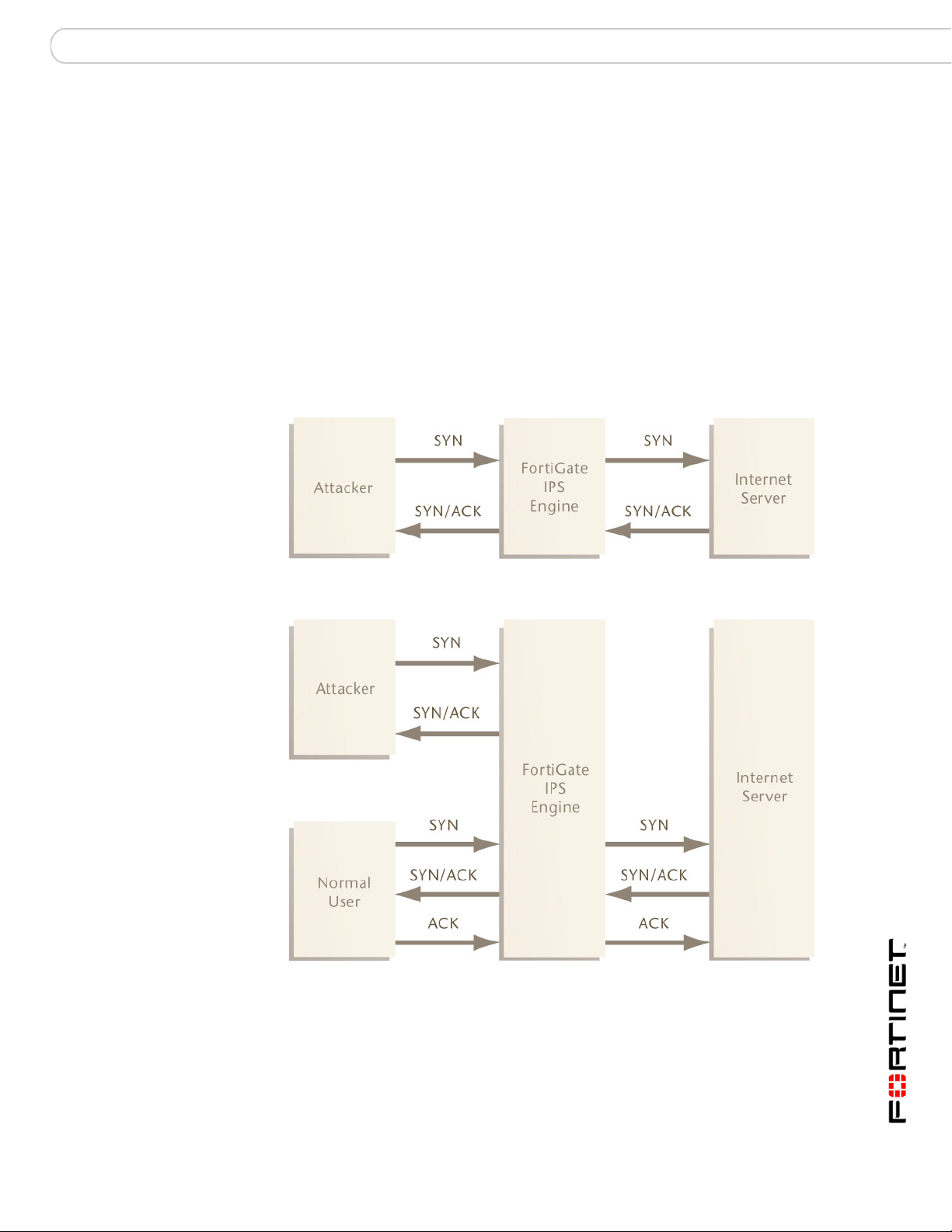
SYN flood attacks The FortiGate IPS Response to SYN flood attacks
A true SYN proxy approach requires that all three packets (SYN, SYN/ACK, and
ACK) are cached and replayed even before it is known if a TCP connection
request is legitimate. The FortiGate IPS pseudo SYN proxy retransmits every TCP
packet immediately from the packet source to the packet destination as soon as it
records the necessary information for SYN flood detection.
Since the pseudo SYN proxy in the IPS uses a “best effect” algorithm to determine
whether a TCP connection is legitimate or not, some legitimate connections may
be falsely detected as incomplete TCP connection requests and dropped.
However, the ratio of the pseudo SYN proxy dropping legitimate TCP connection
is quite small.
Figure 16 illustrates the operational behavior of the FortiGate IPS Engine before
the SYN Flood threshold is reached. Figure 17 illustrates the operation behavior
of the FortiGate IPS Engine after the SYN Flood threshold is reached.
Figure 16: IPS operation before syn_flood threshold is reached
Figure 17: IPS operation after syn_flood threshold is reached
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 53
Page 54

Configuring SYN flood protection SYN flood attacks
Configuring SYN flood protection
To configure the SYN flood protection
1 Go to Intrusion Protection > DoS Sensor.
2 Select Create New.
3 Configure the options for tcp_syn_flood.
4 Select OK.
Figure 18: Configuring the syn_flood anomaly
Suggested settings for different network conditions
The main setting that impacts the efficiency of the pseudo SYN proxy in detecting
SYN floods is the threshold value. The default threshold is 2000. Select an
appropriate value based on network conditions. Normally, if the servers being
protected by the FortiGate unit need to handle heavier requests, such as a busy
web server, the threshold should be set to a higher value. If the network carries
lighter traffic, the threshold should be set to a lower value.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
54 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 55

ICMP sweep attacks What is an ICMP sweep?
ICMP sweep attacks
This section describes:
• What is an ICMP sweep?
• How ICMP sweep attacks work
• The FortiGate IPS response to ICMP sweep attacks
• Configuring ICMP sweep protection
• Suggested settings for different network conditions
What is an ICMP sweep?
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is a part of the IP protocol and is
generally used to send error messages describing packet routing problems. ICMP
sweeps are not really considered attacks but are used to scan a target network to
discover vulnerable hosts for further probing and possible attacks.
Attackers use automated tools that scan all possible IP addresses in the range of
the target network to create a map which they can use to plan an attack.
How ICMP sweep attacks work
An ICMP sweep is performed by sending ICMP echo requests - or other ICMP
messages that require a reply - to multiple addresses on the target network. Live
hosts will reply with an ICMP echo or other reply message. An ICMP sweep
basically works the same as sending multiple pings. Live hosts accessible on the
network must send a reply. This enables the attacker to determine which hosts are
live and connected to the target network so further attacks and probing can be
planned.
There are several ways of doing an ICMP sweep depending on the source
operating system, and there are many automated tools for network scanning that
attackers use to probe target networks.
The FortiGate IPS response to ICMP sweep attacks
The FortiGate IPS provides predefined signatures to detect a variety of ICMP
sweep methods. Each signature can be configured to pass, drop, or clear the
session. Each signature can be configured to log when the signature is triggered.
Create custom signatures to block attacks specific to the network that are not
included in the predefined signature list.
The FortiGate IPS also has an ICMP sweep anomaly setting with a configurable
threshold.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 55
Page 56

The FortiGate IPS response to ICMP sweep attacks ICMP sweep attacks
Predefined ICMP signatures
Table 11 describes all the ICMP-related predefined signatures and the default
settings for each.
Note: The predefined signature descriptions in Table 11 are accurate as of the IPS Guide
publication date. Predefined signatures may be added or changed with each Attack Definition
update.
Table 11: Predefined ICMP sweep signatures
Signature Description Default settings
AddressMask.
Request
Broadscan.Smurf.
Echo.Request
Communication.
Administratively.
Prohibited.Reply
CyberKit.2.2.
Echo.Request
DigitalIsland.
Bandwidth.Query
Echo.Reply This signature detects ICMP echo reply
ISS.Pinger.Echo.
Request
Nemesis.V1.1.
Echo.Request
Oversized.Echo.
Request.Packet
AddressMask detects broadcast address mask
request messages from a host pretending to be
part of the network. The default action is to
pass but log this traffic because it could be
legitimate network traffic on some networks.
Broadscan is a hacking tool used to generate
and broadcast ICMP requests in a smurf
attack. In a smurf attack, an attacker
broadcasts ICMP requests on Network A using
a spoofed source IP address belonging to
Network B. All hosts on Network A send
multiple replies to Network B, which becomes
flooded.
This signature detects network packets that
have been blocked by some kind of filter. The
host that blocked the packet sends an ICMP
(code 13) Destination Unreachable message
notifying the source or apparent source of the
filtered packet. Since this signature may be
triggered by legitimate traffic, the default action
is to pass but log the traffic, so it can be
monitored.
CyberKit 2.2 is Windows-based software used
to scan networks. ICMP echo request
messages sent using this software contain
special characters that identify Cyberkit as the
source.
Digital Island is a provider of content delivery
networks. This company sends ICMP pings so
they can better map routes for their customers.
Use this signature to block their probes.
messages responding to ICMP echo request
messages.
ISS is Internet Security Scanner software that
can be used to send ICMP echo request
messages and other network probes. While
this software can be legitimately used to scan
for security holes, use the signature to block
unwanted scans.
Nemesis v1.1 is a Windows- or Unix-based
scanning tool. ICMP echo request messages
sent using this software contain special
characters that identify Nemesis as the source.
This signature detects ICMP packets larger
than 32 000 bytes, which can crash a server or
cause it to hang.
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Pass
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Drop
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Pass
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Pass
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Drop
Signature disabled
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Drop
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Drop
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Pass
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
56 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 57

ICMP sweep attacks The FortiGate IPS response to ICMP sweep attacks
Table 11: Predefined ICMP sweep signatures
Signature Description Default settings
NMAP.Echo.
Request
Redirect.Code4.
Echo.Request
Sniffer.Pro.
NetXRay.Echo.
Request
Superscan.Echo.
Request
TimeStamp.
Request
TJPingPro1.1.
Echo.Request
Traceroute.Traffic Traceroute is a very common network tool
Whatsup.Echo.
Request
NMAP is a free open source network
mapping/security tool that is available for most
operating systems. NMAP could be used
maliciously to perform an ICMP sweep. ICMP
echo request messages sent using this
software contain special characters that identify
NMAP as the source.
This signature detects ICMP type 5 code 4
redirect messages. An ICMP redirect message
describes an alternate route for traffic to take.
An attacker may use ICMP redirect messages
to alter the routing table or cause traffic to
follow an unintended route.
Sniffer Pro and NetXRay are scanning tools.
ICMP echo request messages sent using this
software contain special characters that identify
them as the source.
Superscan is a free network scanning tool for
Windows from Foundstone Inc. Superscan
could be used maliciously to perform an ICMP
sweep. ICMP echo request messages sent
using this software contain special characters
that identify Superscan as the source.
TimeStamp detects timestamp request
messages from a host pretending to be part of
the network.
TJPingPro1.1 is a widely-used network tool for
older versions of Windows. TJPingPro could be
used maliciously to perform an ICMP sweep.
ICMP echo request messages sent using this
software contain special characters that identify
TJPingPro as the source.
available on almost any operating system. This
tool could be sued maliciously to perform an
ICMP sweep. ICMP echo request messages
sent using this software contain special
characters that identify traceroute as the
source.
WhatsUp Gold is a network scanning tool for
Windows from IPswitch. WhatsUp could be
used maliciously to perform an ICMP sweep.
ICMP echo request messages sent using this
software contain special characters that identify
WhatsUpGold as the source.
Signature disabled
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Pass
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Drop
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Drop
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Pass
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Drop
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Pass
Signature enabled
Logging enabled
Action: Drop
ICMP sweep anomalies
The FortiGate unit also detects ICMP sweeps that do not have a predefined
signature to block them. The FortiGate IPS monitors traffic to ensure that ICMP
messages do not exceed the default or user-defined threshold.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
01-30007-0080-20080916 57
Page 58

Configuring ICMP sweep protection ICMP sweep attacks
Configuring ICMP sweep protection
To configure the ICMP sweep anomaly protection settings
1 Go to Intrusion Protection > DoS Sensor.
2 Select Create New.
3 Configure the options for icmp_sweep, icmp_src_session, and icmp_dst_session.
4 Select OK.
Suggested settings for different network conditions
Enable or disable the ICMP predefined signatures depending on current network
traffic and the network scanning tools being used.
To use the icmp_sweep anomaly, monitor the network to find out the normal ICMP
traffic patterns. Configure the icmp_sweep anomaly threshold to be triggered
when an unusual volume of ICMP requests occurs.
FortiGate IPS User Guide Version 3.0 MR7
58 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 59

Index
Index
A
alert email
configuring 11
anomalies
log messages 13
anomaly
destination session limit 48
flooding 48
scan 48
source session limit 48
attack log messages 12
anomalies 13
signature 12
C
comments, documentation 8
Create New
firewall policy 39
custom signature
adding 22
customer service 8
D
default settings 10
destination session limit
anomaly type 48
documentation
commenting on 8
Fortinet 6
DoS sensor
list 46
F
fail open 10
firewall policy
create new 39
firewall profiles 14
flooding
anomaly type 48
FortiGate documentation
commenting on 8
Fortinet customer service 8
Fortinet documentation 6
Fortinet Knowledge Center 8
FortiProtect Attack Encyclopedia 13
FortiProtect center 13
I
ICMP attack signatures 56
ICMP sweep
anomalies 57
configuring protection 58
introduction
Fortinet documentation 6
intrusion protection
DoS sensor list 46
IPS sensor list 39
IPS
adding custom signatures 22
predefined signature list 17
IPS sensor
list 39
L
logging
attack messages 12
configuring 11
M
messages
attack log 12
N
network performance 10
P
performance 10
policy
create new 39
predefined signature
action 18
list 17
protection profiles 14
creating 14
S
scan
anomaly type 48
signature 22
adding custom IPS signatures 22
signature attack log messages 12
source session limit
anomaly type 48
SYN flood 51
configuring protection 53, 54
diagrams 53
FortiGate response to 52
prevention 52
SYN proxy 52
SYN threshold 52
FortiGate Version 3.0 MR7 IPS User Guide
01-30007-0080-20080916 59
Page 60

T
technical support 8
Index
FortiGate Version 3.0 MR7 IPS User Guide
60 01-30007-0080-20080916
Page 61

www.fortinet.com
Page 62

www.fortinet.com
 Loading...
Loading...