Page 1

Programmable
Frequency Counter
PM6685 & PM6685R
Service Manual
Page 2

This is a complementary service manual covering instruments with manufacturing numbers exceeding 840684. The principal
differences are to be found in Chapter 7 and in Chapter 8 due to a major redesign of the main PCB.
Do not dispose of the previous edition, identified by the part number, 4822 872 25012, and the publishing date, June 1996.
You may have to refer to it for information on older instruments as well as options not mentioned here.
4822 872 20106
First Edition (May 2003)
No part of this manual may be copied without the express permission of the copyright owner.
All product names are trademarks of their respective companies.
Ó 2003 Pendulum Instruments AB
All rights reserved. Printed in Sweden.
Page 3

Contents
1 Safety Instructions
2 Performance Check
General Information .........................2-2
Recommended Test Equipment ................2-2
Front Panel Controls .........................2-2
Short Form Specification Test ..................2-3
Rear Input/Output ...........................2-4
Measuring Functions .........................2-4
Options ...................................2-5
3 Disassembly
Removing the Cover .........................3-2
Reinstalling the Cover ........................3-2
PM9624 (HF Input) ..........................3-2
PM9626B (GPIB Interface) ....................3-3
PM9691 or PM9692 (Oven Oscillator) ...........3-3
4 Circuit Descriptions
Block Diagram Description ....................4-2
General ..................................4-2
Hardware Functional Description ...............4-4
Front Unit .................................4-4
Main Board ................................4-5
Rear Panel Unit ............................4-13
Optional Units .............................4-14
Software Functional Description ..............4-15
Test Routines .............................4-16
5 Repair
Preventive Maintenance.......................5-2
Calibration .................................5-2
When to Replace the Fan
(PM6685R only ) ............................5-3
Troubleshooting .............................5-4
General ...................................5-4
Safety Inspection and Test After Repair .........5-9
General Directives...........................5-9
6 Calibration Adjustments
Introduction ................................6-2
Preparation ................................6-2
Power Supply ..............................6-2
Input Amplifier ..............................6-3
Reference Oscillators ........................6-4
Other Options ..............................6-6
7 Replacement Parts
Introduction ................................7-2
Mechanical Parts............................7-3
Main Board ................................7-6
Front Board ...............................7-12
GPIB Interface (PM9626B) ...................7-13
8 Drawings & Diagrams
How to read the diagrams.....................8-2
9 Appendix
How to Replace Surface Mounted Devices........9-2
Electrostatic discharge .......................9-3
Glossary ..................................9-4
Power Supply Switchmode Module .............9-5
Circuit Descriptions ..........................9-5
Repair ....................................9-6
Calibration Adjustments ......................9-7
Replacement Parts..........................9-8
PM6685R ..................................9-12
Introduction ...............................9-12
Performance Check ........................9-12
Functional Description.......................9-12
Calibration Adjustments .....................9-13
Replacement Parts .........................9-14
Page 4

This page is intentionally left blank.
Page 5

Chapter 1
Safety Instructions
Page 6

WARNING: These servicing instructions are for use
by qualified personnel only. To reduce the risk of
electric shock, do not perform any servicing other
than that specified in the Operating Manual unless
you are fully qualified to do so.
Authorized service and calibration of this instrument is available
through your Fluke representative. See address at the end of this
manual.
Read this chapter carefully before you check, adjust, or repair an in
strument.
The ground symbol on the rear panel indicates where the
protective ground lead is connected inside the instrument.
Never remove or loosen this screw.
When the instrument is brought from a cold to a warm environment,
condensation may cause hazardous conditions. Therefore, ensure
that the grounding requirements are strictly met.
Power extension cables must always have a protective ground con
ductor.
-
Indicates that the operator should consult the manual.
-
Caution and Warning Statements
You will find specific warning and caution statements where neces
sary throughout the manual.
CAUTION: Indicates where incorrect operating proce
dures can cause damage to, or destruction of,
equipment or other property.
WARNING: Indicates a potential danger that requires
correct procedures or practices in order to prevent
personal injury.
This Timer/Counter has been designed and tested in accordance with
safety class 1 requirements for Electronic Measuring Apparatus of
IEC (CENELEC) publication EN61010-1, and CSA 22.2
No. 1010-1, and has been supplied in a safe condition.
This manual contains information and warnings that should be fol
lowed by the user and the service technician to ensure safe operation
and repair in order to keep the instrument in a safe condition.
WARNING: Opening instrument covers or removing
parts, except those to which access can be gained
by hand, is likely to expose high voltages which
can cause death.
The instrument must be disconnected from all voltage sources before
it is opened. Remember that the capacitors inside the instrument re
tain their charge even if the instrument has been disconnected from
all voltage sources.
-
Grounding
This instrument is connected to ground via a sealed three-core power
cable, which must be plugged into socket outlets with protective
ground contacts. No other method of grounding is permitted for this
instrument.
WARNING: Any interruption of the protective ground
-
conductor inside or outside the instrument, or dis
connection of the protec- tive ground terminal, is
likely to make the instrument dangerous. Do not in
tentionally disrupt the protective grounding.
-
-
Disposal of Hazardous Materials
WARNING: Disposal of lithium batteries requires spe
cial attention. Do not expose the batteries to heat
or put them under extensive pressure. These mea
sures may cause the batteries to explode.
A lithium battery is used to power the nonvolatile RAM in this in
strument. Our world suffers from pollution, so don’t throw batteries
into your wastebasket. Return used batteries to your supplier or to the
Fluke representative in your country.
-
-
-
-
Line Voltage
The instrument can be powered by any voltage between 90 and
265 V
inal line voltages between 100 and 240 V.
n
Components that are important for the safety of this instrument may
-
only be replaced by components obtained from your local Fluke
representative. After exchange of the primary circuits, perform the
safety inspection and tests, as described in Chapter 5, “Repair”.
n
This instrument is protected by an ordinary 1.6 A slow blow fuse
mounted inside the instrument. NEVER replace this fuse without
first examining the Power Supply Unit.
without range switching. This makes it suitable for all nom
AC
Replacing Components in Primary Circuits
Fuses
-
1-2 Safety Instructions,
Page 7

Chapter 2
Performance Check
Page 8
General Information
Ω
WARNING: Before turning on the instrument, ensure
that it has been installed in accordance with the In
stallation Instructions outlined in Chapter 3 of the
Operators Manual.
This performance procedure is intended to:
Check the instrument’s specification.
–
Be used for incoming inspection to determine the acceptability
–
of newly purchased instruments and recently recalibrated in
struments.
Check the necessity of recalibration after the specified
–
recalibration intervals.
NOTE: The procedure does not check every facet of the in
strument’s calibration; rather, it is concerned primarily
with those parts of the instrument which are essential
for determining the function of the instrument.
It is not necessary to remove the cover of the instrument to perform
this procedure.
If the test is started less than 20 minutes after turning on the instru
ment, results may be out of specification, due to insufficient
warm-up time.
-
-
Preparations
Power up your instruments at least 20 minutes be
fore beginning the tests to let them reach normal
operating temperature. Failure to do so may result
in certain test steps not meeting equipment specifi
cations.
-
-
Front Panel Controls
Power-On Test
At power-on the counter performs an automatic self-test of the fol
-
-
lowing:
Microprocessor
–
–
RAM
ROM
–
Measuring circuits
–
Display
–
If a GPIB interface is installed, the GPIB address is displayed.
If there are any test failures, an error message is shown.
Turn on the counter and check that all segments light up on the
–
display and that no error message appears.
-
Recommended Test
Equipment
Type of instru
ment
LF Synthesizer Square;
Power Splitter 50 W PM9584/02
T-piece
Termination 50 W PM9585
Reference oscilla
tor
HF signal genera
tor
Pulse Generator 125 MHz
Oscilloscope with
probes
BNC cables 5 to 7 cables *
Table 2-1 Recommended Test Equipment.
*) Two of the cables must have 10 ns difference in delay, for ex
ample: 5 ns and 15 ns.
-
-
-
Required
Specifications
Sine up to 10 MHz
10 MHz ±0.1 Hz for
standard oscillator
10 MHz ±0.01 Hz for
PM9691 & PM9692
10 MHz ±0.0001 Hz
for PM6685R
0.5 GHz (no presc.)
3.3 GHz (option 10)
350 MHz
Suggested
Equipment
Fluke counter with
calibrated option
PM9691
Fluke PM6685R or
PM6681R
Fluke 910R or Ce
sium Standard
-
Fig. 2-1 Text on the display.
Internal Self-Tests
The different built-in test routines invoked by the power-on test can
also be activated from the front panel as follows:
Enter the Auxiliary Menu by pressing AUX MENU.
–
Select the test submenu by pressing DATA ENTRY up or
–
down.
Enter the test menu by pressing the ENTER key.
–
Selections for internal self-tests are:
1 TEST ALL (Test 2 to 5 in sequence)
2 TEST RO (ROM)
3 TEST RA (RAM)
4 TEST LOGIC (Measuring Logic)
5 TEST DISP (Display Test)
Use DATA ENTRY up/down to select TEST ALL, then press
–
ENTER.
If any fault is detected, an error message appears on the dis
–
play and the program halts.
If no faults are detected, the program returns to measuring
-
–
mode.
-
2-2 Performance Check, General Information
Page 9
Keyboard Test
The keyboard test verifies that the counter responds when you press
any key. To check the function behind the keys, see the tests further
on in this chapter.
Press the keys as described in the left column and look on the display
for the text, as described in the second column. Some keys change
more text on the display than described here. The display text men
tioned here is the text mainly associated with the selected key.
Key(s) Display Note Pass
STAND-BY Display Off Red LED
ON Backlight on
PRESET
ENTER
EXT REF EXT REF
Input A
FILTER FILTER
50 W
(2 times)
SENS
(2 times)
SENS
(2 times)
AUTO AUTO TRIG
PRESET
ENTER
MEAS TIME 200
DATA ENTRY 500
DATA ENTRY 200
ENTER NO SIGNAL
DISPLAY HOLD HOLD
DISPLAY HOLD
SINGLE SINGLE
FUNCTION DUTY F A
FUNCTION TOT A MAN
FUNCTION DUTY F A
FUNCTION FREQ A
AUX MENU RECALL
MEAS RESTART NO SIGNAL
PRESET
ENTER
CHECK 10.00000000
NULL NULL
NULL 10.00000000
BLANK DIGITS
(3 times)
MENU Displays all avail
DEFAULT?
NO SIGNAL
50 W
Bar graph:
zzzzzzzz
Bar graph:
zzzzzzzzzz
Other
DEFAULT?
NO SIGNAL
DEFAULT?
NO SIGNAL
10.00000___
able functions, pro
cesses and input
controls. Selected
items are blinking.
–3
s
–3
s
–3
s
6
Hz* Start
6
Hz*
6
Hz*
counting
-
-
Table 2-2 Keyboard Test.
beside
the key
On
Default
setting
Default
setting
Default
setting
/Fail
NOTE: For the instrument to respond correctly, this test must
be carried out in sequence and you must start with the
preset (power-on) setting.
* The LSD may vary.
** MENU is not disabled by setting DEFAULT; press menu again.
-
Short Form Specification
Test
Sensitivity and Frequency Range
Press the PRESET key to set the counter in the default setting.
–
Then confirm by pressing ENTER.
Turn off AUTO.
–
Select IMP A = 50 W and maximum sensitivity.
–
Connect a signal from a HF generator to a BNC power splitter.
–
Connect the power splitter to your counter and an oscilloscope.
–
Set input impedance to 50 W on the oscilloscope.
–
Adjust the amplitude according to the following table. Read
–
the level on the oscilloscope. The counter should display the
correct frequency.
Frequency Level Pass/Fail
MHz mV
1 30 10 –27
25 30 10 –27
50 30 10 –27
150 60 20 –21
200 90 30 –17
250 150 50 -13
300 150 50 -13
PP
mV
RMS
Table 2-3 Sensitivity of input A at various frequencies.
Reference Oscillators
X-tal oscillators are affected by a number of external conditions,
such as ambient temperature and supply voltage, but they are also af
fected by aging. Therefore, it is hard to give limits for the allowed
frequency deviation. You must decide the limits depending on your
application, and recalibrate the oscillator accordingly. See the Pre
ventive Maintenance in the Repair chapter, Chapter 5.
Oscillator Max. tempera
Standard ±100 Hz ±5 Hz ±50 Hz
PM9691 ±0.05 Hz ±0.1 Hz ±0.75 Hz
PM9692 ±0.025 Hz ±0.03 Hz ±0.2
Rubidium ±0.003 Hz ±0.0005 Hz ±0.002 Hz
ture dependence
Table 2-4 Deviation (for PM9691 and PM9692 after a
warm-up period of 48 hours).
To check the accuracy of the oscillator you must have a calibrated
reference signal that is at least five times as stable as the oscillator
that you are testing, see the following table.
Press the PRESET key, then press the ENTER key to set your
–
counter in the Default setting.
-
dBm Input A
Max. aging
per month
-
-
Max. aging
per year
Performance Check, Short Form Specification Test 2-3
Page 10
Connect the reference to input A.
–
Check the readout against the accuracy requirements of your
–
application.
Acceptance Test
n
As an acceptance test, the following table gives a worst case figure
after a 30 minute warm up time. All deviations that can occur in a
year are added together.
Oscillator Frequency readout Suitable refer
Standard 10.00000000 MHz
±120 Hz
PM9691 10.00000000 MHz
±1 Hz PM6685R
PM9692 10.00000000 MHz
±0.25 Hz
ence
PM9691
PM6681R
Pass
/Fail
Table 2-5 Acceptance test for oscillators.
Acceptance Test, PM6685R
n
To fully test the accuracy of the PM6685R, a reference signal of ex
tremely high stability is needed. Examples of such references are
Cesium Atomic references, or transmitted signals from a nationally
or internationally traceable source, like the GPS satellites.
EXT ARM INPUT
Press the PRESET key, then press the ENTER key to set your
–
counter in the Default setting.
Select 50 W input impedance.
–
Apply 10 MHz 500 mV
–
–
The counter measures and displays 10 MHz.
Press the AUX MENU key.
–
Press the DATA ENTRY UP/DOWN keys until the display
–
shows ‘Ar. Start’, confirm by pressing the ENTER key.
Press DATA ENTRY UP/DOWN keys until the display shows
–
‘POS’, confirm by pressing the ENTER key.
Press the ENTER key once more.
–
The counter does not measure.
–
Connect a pulse generator to Ext Arm input.
–
Settings for pulse generator: single shot pulse, amplitude TTL
–
=0-2V
Apply one single pulse to Ext Arm input.
–
-
The counter measures once and shows 10 MHz on the display.
–
, and duration = 10 ns.
PP
, (1.4 VPP) sine to input A
RMS
Recommended Test Equipment
Type Stability Model
10 MHz refer
ence
-
£ 1x10
-10
910R with satellite contact dur
ing the last 72 hours.
Test Procedure
Connect the counter to the line power.
–
Check that the UNLOCK indicator turns on, and then turns off
–
again within 6 minutes after connecting line power.
Connect the 10 MHz reference signal to input A of the counter.
–
Select FREQUENCY A measurement.
–
Select 2 s measuring time.
–
Check that the displayed frequency is 10.00000000 MHz
–
±0.05 Hz £ 10 minutes after connection to line power.
Rear Input/Output
INT REF Output
Connect an oscilloscope to the 10 MHz output on the rear of
–
the counter. Use coaxial cable and 50 W termination.
The output voltage is sinusoidal and should be above 2.8 VPP.
–
EXT REF Input
Press the PRESET key, then press the ENTER key to set your
–
counter in the Default setting.
Apply 10 MHz sine to input A equipped with a T-piece and to
–
Ext Ref input at the rear, terminated with 50 W. Amplitude on
10 MHz signal; 200 mV
–
Press the Ext Ref key.
The display should show 10.000000006Hz ± 5 LSD.
–
, (560 mVPP)
RMS
Measuring Functions
-
Preparation for Check of Measuring Function is as follows:
Connect a 10 MHz sine wave signal with 2.0 VPPamplitude
–
via a T-piece to Input A.
Connect a cable from the T-piece to Input E (Ext Arm) at the
–
rear.
Select the measuring function as in the ‘Selected Function’ col
–
umn and check that the counter performs the correct measure
ment by displaying the result as shown under the “Display”
column in the following table.
Selected Function Display Pass/ Fail
PRESET
ENTER
IMPA50W 10 MHz
Non AUTO 10 MHz
PER A 100 ns
RATIO A/E 1.0000000
PWIDTH A 50 ns
TOT A MAN
DISPLAY HOLD Start counting
DISPLAY HOLD Stop counting
DUTY FACT 0.500000
AUTO 0.500000
DEFAULT?
10 MHz
2)
1)
2)
2)
2)
1)
1)
Table 2-6 Measuring functions check.
1) Value depends on the symmetry of the signal.
2) Exact value depends on the input signal.
-
-
2-4 Performance Check, Rear Input/Output
Page 11

Options
Prescaler
This extra HF input (PM9624) is easily recognized by its front panel
connector (Input C, type N).
EX T
REF
Fig 2-2 Connect the output of the signal generator to the HF
Required Test Equipment Suggested Specification
HF signal generator 3.3 GHz
Table 2-8 Test equipment for 3.0 GHz HF input.
Connect the output of the signal generator to the HF input of
–
the counter.
Connect the 10 MHz REFERENCE OUT of the generator to
–
the REFERENCE IN at the rear panel of the counter.
Setting for the counter after Preset.
Function = FREQ C.
–
EXT REF.
–
Generate a sine wave in accordance with the following table.
Verify that the counter counts correctly. (The last digit will be
–
unstable).
Table 2-7 Sensitivity of the PM9624 HF input.
input of the counter.
Frequency Amplitude Pass/Fail
MHz mV
100-300 20 –21
-2500 10 –27
-2700 20 –21
-3000 100 –7
RMS
dBm
Performance Check, Options 2-5
Page 12

This page is intentionally left blank.
2-6 Performance Check, Options
Page 13

Chapter 3
Disassembly
Page 14
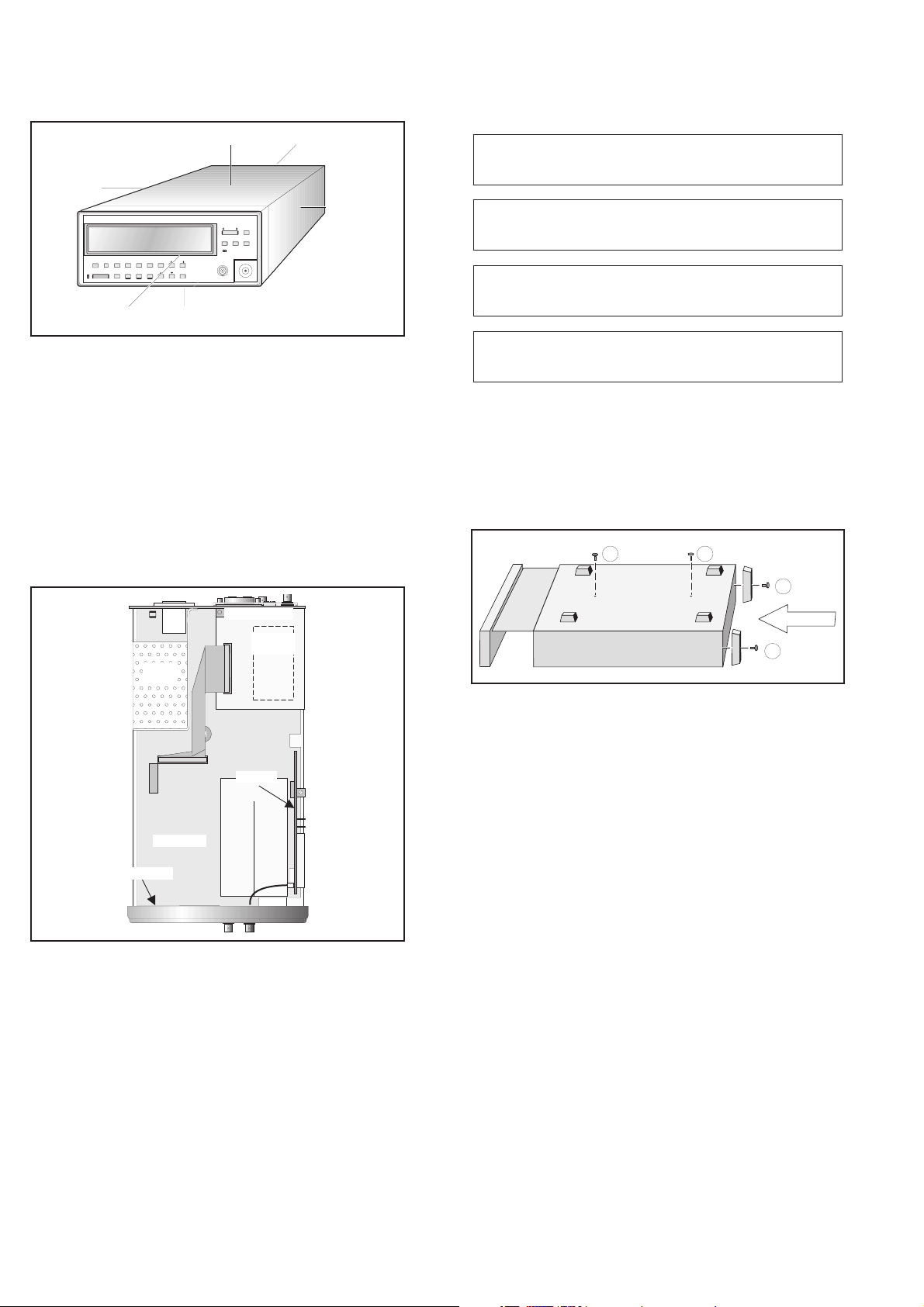
The terms in the following figure are used in all descriptions in this
manual.
To p
Left
Front Bottom
Fig. 3-1 Designations used in this manual.
The PM6685 is available with a number of options and accessories.
The labels on the rear panel of the counter identify the options and
accessories included. If there are no labels, the counter contains an
uncompensated crystal oscillator and no options. The following la
bels exist:
PM9624 3.0 GHz HF input
–
PM9691 High-Stability Oven Oscillator
–
PM9692 Ultra-High-Stability Oven Oscillator
–
PM9626B GPIB Interface
–
The location of these optional parts is illustrated in Fig.3-2.
GPIB interface
Power
Module
G1
Optional
oscillator
Rear
Right
Removing the Cover
WARNING: Do not perform any internal service or ad
justment of this instrument unless you are qualified
to do so.
WARNING: When you remove the cover you will ex
pose high voltage parts and accessible terminals
which can cause death.
WARNING: Although the power switch is in the off
position, line voltage is present on the printed cir
cuit board. Use extreme caution.
WARNING: Capacitors inside the instrument can hold
their charge even if the instrument has been sepa
rated from all voltage sources.
–
Make sure the power cord is disconnected from the counter.
Turn the counter upside down.
-
–
Loosen the two screws (A) at the bottom and the two screws
–
(B) in the rear feet.
Grip the front panel and gently push at the rear.
–
Pull the counter out of the cover.
–
A
Fig. 3-3 Remove the screws and push the counter out of
the cover.
A
B
B
-
-
-
-
HF input
Main board
Front panel
Fig. 3-2 Location of the boards in the counter.
Reinstalling the Cover
Gently push the counter back into the cover.
–
Turn it upside down.
–
Install the two screws (A) at the bottom.
–
Install the two rear feet with the screws (B) to the rear panel.
–
PM9624 (HF Input)
Disconnect the power cable.
–
Remove the cover from the counter.
–
Disconnect the cable from the mini-coax connector (A) on the
–
HF input.
Press the clips (B) apart and lift the HF input pca straight up
–
and out.
3-2 Disassembly, Removing the Cover
Page 15
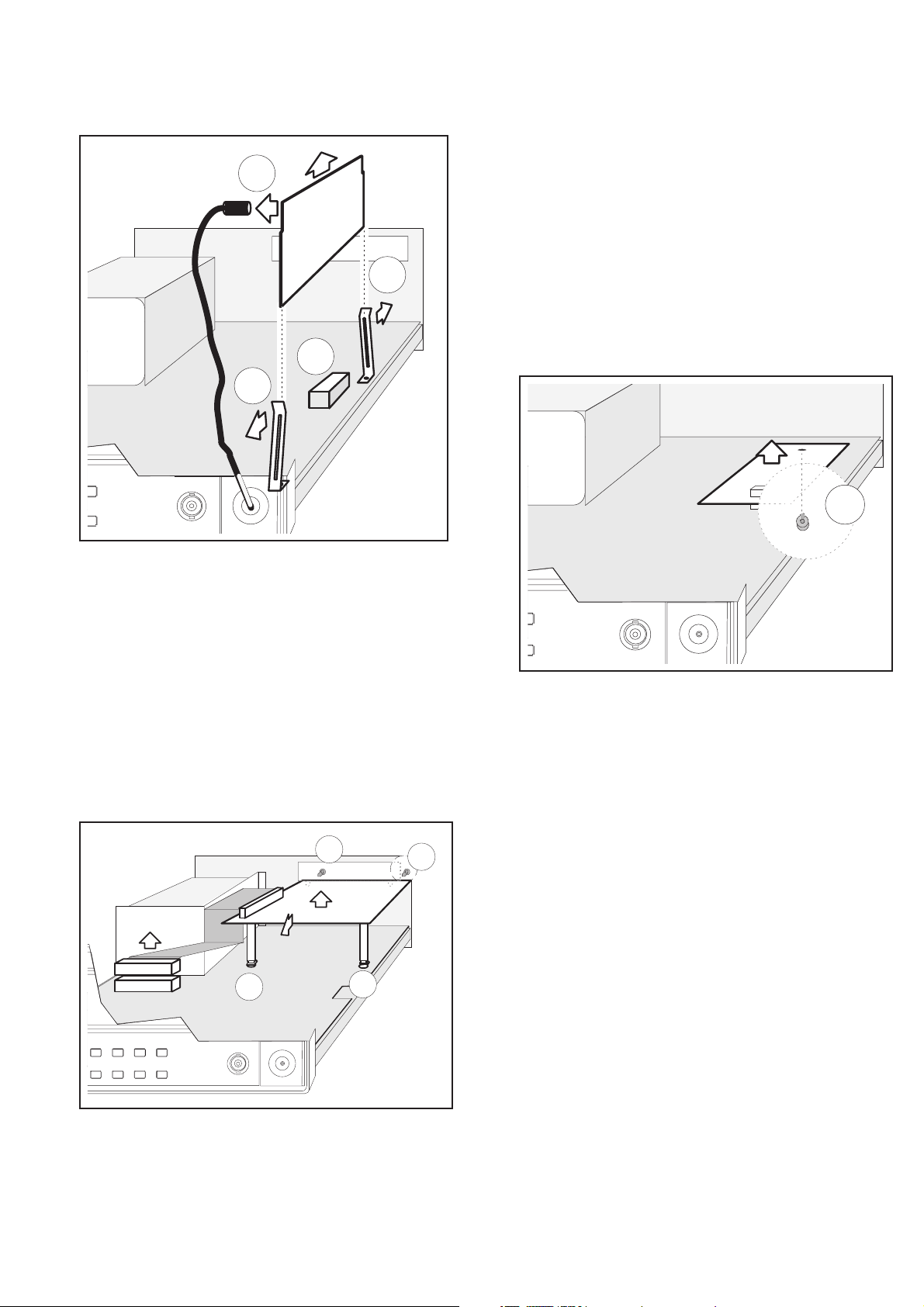
When installing the HF input, make sure that the connector
–
pins fit exactly in the holes in the connector housing (C).
A
B
C
B
PM9691 or PM9692 (Oven
Oscillator)
Disconnect the power cable.
–
Remove the cover of the counter.
–
Remove the two screws (A) holding the oscillator to the main
–
pca from underneath.
Press the clip (B) gently to the front of the counter and lift the
–
oscillator straight up.
Make sure that jumpers J14 and J15 are set in the correct posi
–
tion.
When fitting the oscillator, make sure that the connector pins
–
fit exactly in the holes in the connector housing.
A
-
Fig. 3-6 Removing the HF Input.
PM9626 (GPIB Interface)
Disconnect the power cable.
–
–
Remove the cover from the counter.
Loosen the two screws (A) holding the GPIB interface to the
–
rear panel.
Disconnect the interface cable from P103.
–
Move the GPIB interface pca toward the front of the counter
–
and lift the pca supports out from the “keyholes” (B) on the
main PCA.
A
B
B
Fig. 3-5 One of the two screws holding the oven oscillator
in place.
A
Fig. 3-4 Loosen the two screws in the rear panel and dis
engage the board from the keyholes.
-
Disassembly, PM9626 (GPIB Interface) 3-3
Page 16

This page is intentionally left blank.
3-4 Disassembly, PM9691 or PM9692 (Oven Oscillator)
Page 17

Chapter 4
Circuit Descriptions
Page 18

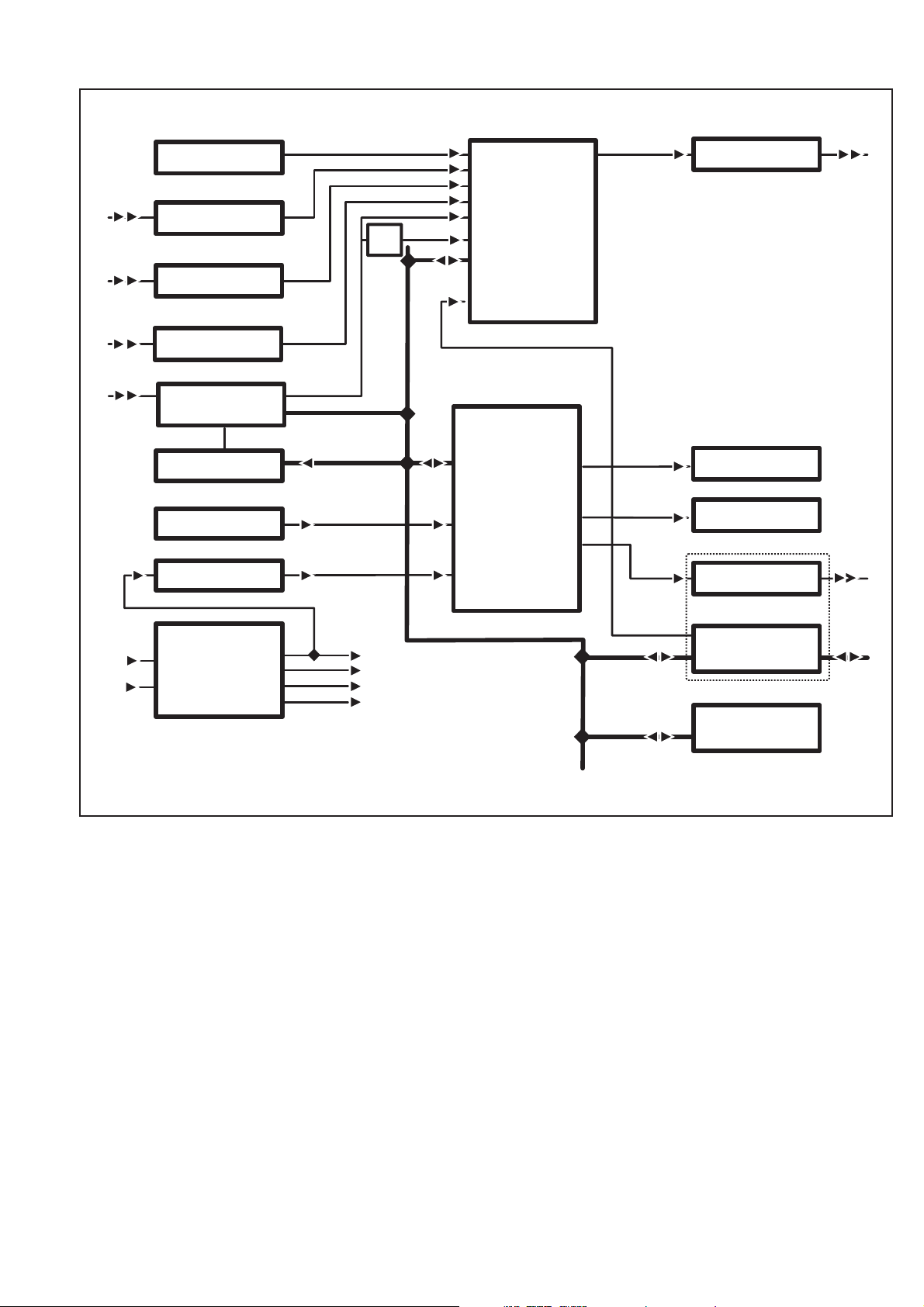
Block Diagram Description
General
The PM6685 Frequency Counter consists of three main units:
Front unit
–
Main board unit
–
Rear panel unit
–
The following options can be added:
GPIB interface including analog output (PM9626B)
–
–
Prescalers 1.3 GHz (PM9621), 3.0 GHz (PM9624)
Oven-controlled crystal oscillators (PM9691 or PM9692)
–
Rack mount adapter (PM9622/02)
–
Battery option (PM9623)
–
The chassis of the counter consists of a front piece molded in alumi
num, an aluminum rear panel, and two profiled aluminum rods that
hold the front and rear panels together. This unit can be slid into the
aluminum cover of the instrument.
The front unit contains all functions needed for the user communica
tion. It is connected to the main board unit with a flat cable, and the
molded front unit is fixed to the two profiled aluminum rods with
screws.
The main board unit consists of a PCB mounted on two profiled alu
minum rods. Most functions, such as the following, are placed on the
main board:
Input amplifiers with trigger level circuits
–
Power supply
–
–
Measurement logic
Microcomputer circuitry
–
Some outputs, such as the trigger levels and probe compensation
view outputs are directly mounted on the main board.
The rear panel unit is of aluminum with a number of mounted con
-
-
nectors. Most of the connectors are soldered directly to the main
board. The rear panel is fixed to the two profiled aluminum rods with
screws.
-
-
4-2 Block Diagram Description
Page 19
Optional oscillator
A
X2
EXTC
INTREF
10 MHz out
G
B2
E
External arming
÷2
EXTREF
A
A2
C
HF input
GET
D
A
External reference
Input Amplifier
U29
Counter
ASIC
Micro-
computer
Trigger DAC´s
Local preset
Reset circuit
HSI.0
RESET
U11
2
IC
PWM
Gate LED
Display
Analog output
Option 80
Power supply
C
90-265 V
+5V
+12V
GPIB option
+7V
-5.2V
Keyboard
Fig. 4-1 PM6685 block diagram.
Block Diagram Description 4-3
Page 20
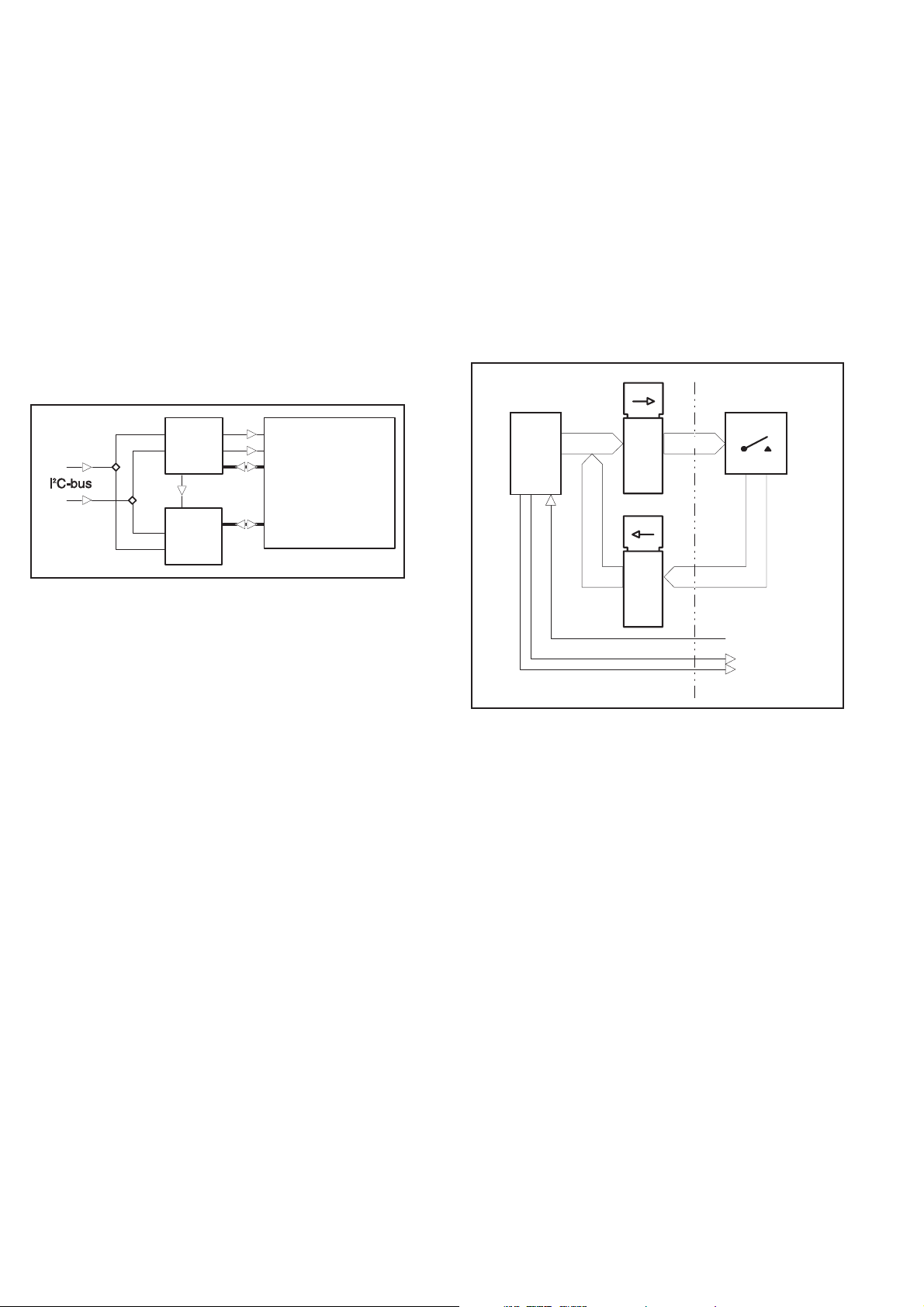
Hardware Functional Description
Front Unit
LCD Drivers
U201
Driver 1
SCL
SDA
PC F8 576
Sync.
U2 02
Driver 2
PC F8576
Fig. 4-2 Front panel LCD drivers.
An LCD and two LEDs are used as indicators. The LCD is used to
show both the measurement result and the state indicators of the in
strument setting. The LEDs show standby and gating.
The LCD has 158 segments that are multiplexed with a ratio of 2:1.
Two parallel and synchronized LCD drivers (U201 and U202) are
used. They are connected with a serial I
on the main board. The clock frequency of the drivers is approxi
mately 140 kHz, set by R201. The VLCD pin is connected to GND
on the main board.
The LCD is provided with a backlight, an LED array integrated into
one component. Its current consumption is set by the resistors
R204-R207. The backlight dissipates approximately 1.5 W .
Backpl. 0
Backpl. 1
LC D
1 58 segment s
2:1 Multiplex
2
C bus to the microcomputer
Keyboard
Main Board
U11
AD0-AD7 H0-H3
CPU
HS1.0
P1.1
P1.0
-
Fig. 3 Keyboard scanning.
-
The front panel pushbuttons are connected in a matrix. The scanning
signals H0 to H3 come from the main board. If a push button is
pressed and H0 to H3 is high, one of the output signals V0 to V7 will
be high. The STAND-BY/ON and LOCAL-PRESET buttons are not
part of the scanning but are connected directly to the main board.
The front unit is fixed to the main board unit with three screws. The
electrical connection is made with a 40-lead flat cable to the main
board.
U13A
Latch
U14A
Latch
AD0-AD7
Keyboard & Display
Board
V0-V7
LOCAL/PRESET
SCL
SDA
4-4 Hardware Functional Description
Page 21
Main Board
Introduction
Components not necessary for explaining the function are omitted
from the figures in this chapter. For the complete set of components,
see the circuit diagrams in Chapter 8, Drawings and Diagrams.
Input Amplifier
The input amplifier has 300 MHz bandwidth and is of the split-band
type. It contains four main stages: the signal adaptation stage, the im
pedance converter stage, the comparator stage, and the buffer stage.
Signal Adaptation
n
This part of the amplifier contains:
50 W/1 MW impedance selector
–
x1/x11 attenuator
–
Voltage limiter
–
50 W /1MW Impedance Selector
K2
C2
R6
J1
R1
K1
R7-R17
C1
R2 R3-R5
R22-R23
R18
K3
R19R20
R24R26
C3
To Voltage
li mi te r
R27R28
selected if the relay is open. Depending on selected attenuation, the
1MW input impedance is determined by different combinations of
resistors.
In x1 attenuation mode (K2 is closed and K3 is open) the impedance
is determined by resistor network R22 to R28.
In x11 attenuation mode (K2 is open and K3 is closed) the same net
work as in the x1 case is involved plus the resistors R3 to R5 and R18
to R20.
The input capacitance in parallel with 1 MW is 24 pF at x1 attenua
-
tion and 12 pF at x11 attenuation.
-
The series resistor R1 immediately after the selector serves both as
current limiter together with the voltage limiter (see below) and as
impedance matching resistor. The resistor also improves the Volt
age-Standing-Wave-Ratio (VSWR) of the amplifier input.
x1/x11 Attenuator
The x1 attenuator consists of a resistive low-frequency divider,
which reduces the input signal by a factor of 2, and a capacitive
high-frequency divider. The attenuator is formed by the resistors
R22-R23 andR24-R26 in parallel with R27-R28. The capacitive part
is formed by the variable capacitor C2 in parallel with R22-R23, and
the parasitic capacitance across R24-R26.
The capacitive attenuator is adjusted via variable capacitor C2 to the
same attenuation value as the resistive attenuator.
The x11 attenuator also consists of a resistive low-frequency divider
and a capacitive high-frequency divider. The resistive part is formed
by R1-R5, and R18-R20 in parallel with 1 MW (the x1 attenuator im
pedance). The capacitive divider is formed by the variable capacitor
C1 and the parasitic capacitance at the node where R5, R18 and R22
meet.
-
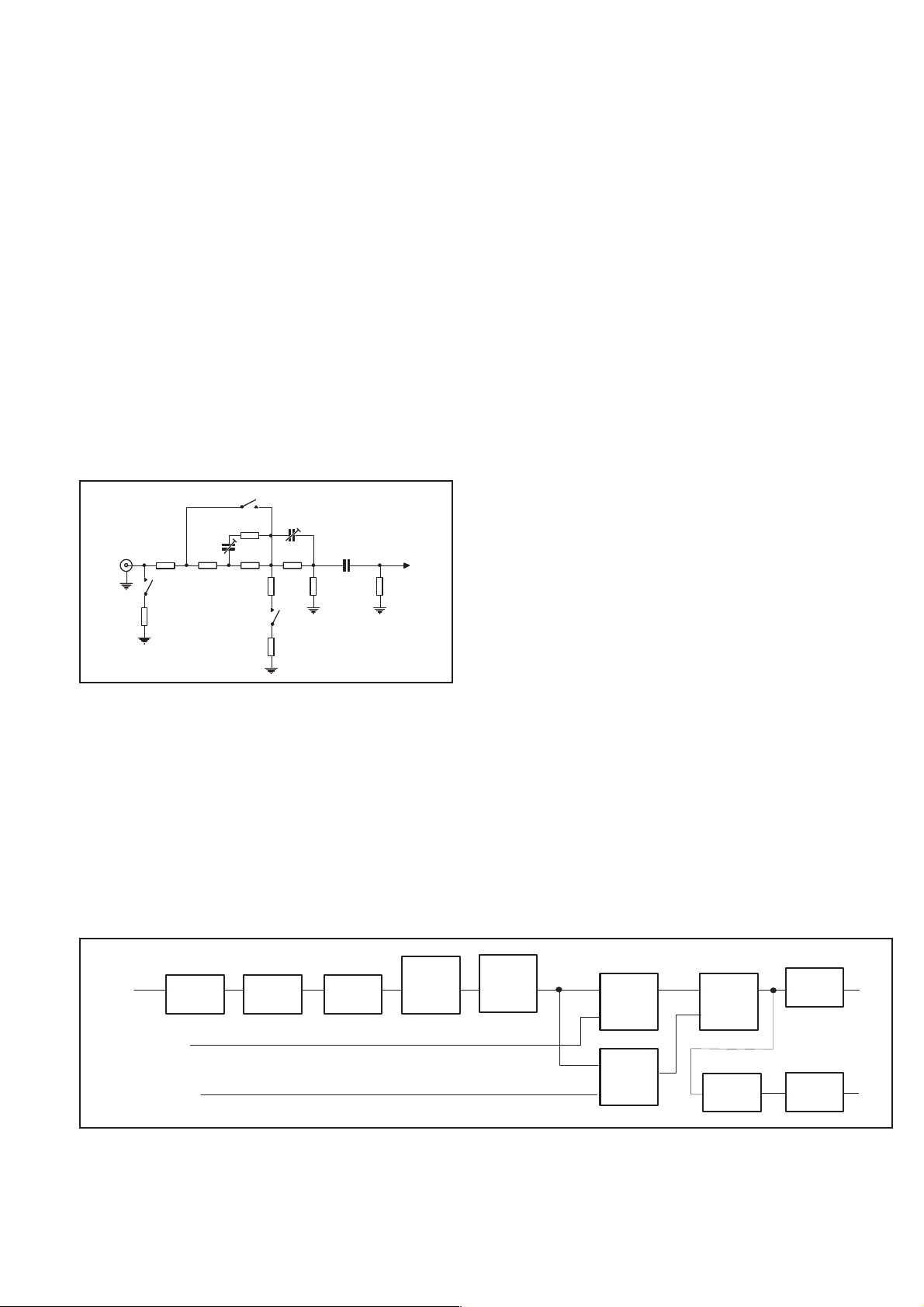
Fig. 4-4 Impedance selector and 1X/11X attenuator.
The 50 Wor1MW impedance modes are selected by relay K1. 50 W
is selected via the resistors R7 to R17, if the relay is closed. 1 MW is
Input A
Imp. Att. Limiter
Imp.
Conv.
Trigger
level Comp I
Trigger
level Comp II
Resistors R2 and R6 improve the frequency response.
LP
filter
Comp-
arator
FlipFlop
Comp-
arator
÷2
Buffer
Buffer
A
A2
Fig. 4-5 Input amplifier block diagram.
Hardware Functional Description 4-5
Page 22
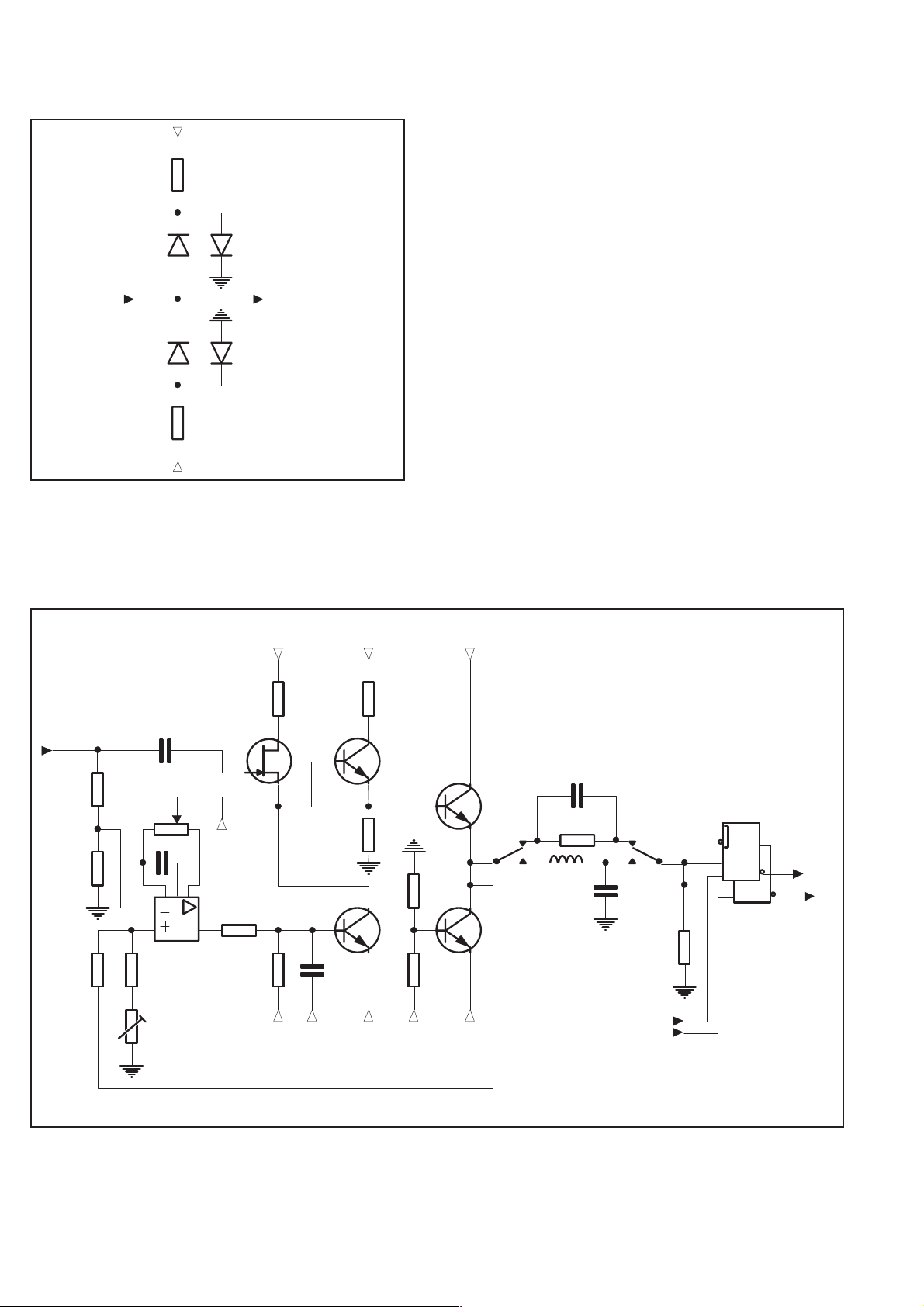
Voltage limiter
p
+5
and D3 to clamp positive voltage and resistor R36 plus the diodes D2
and D4 to clamp negative voltage. The clamp voltage is approxi
mately ±2.1 V for low frequency signals. At high frequency the
clamp voltage rises to approximately ±2.3 V.
-
R35
D3D1
From
Attenuator
D2
R36
-
To Impedance
converter stage
D4
Fig. 4-6 Voltage limiter.
A voltage limiter that protects the impedance converter against
overvoltage is placed between the attenuator and the impedance con
verter. The voltage limiter consists of resistor R35 and the diodes D1
Impedance Converter Stage
n
The analog signal from the input stage is fed to an amplifier stage
where split-band technique is used to get good frequency response
over a wide range. This means that the high-frequency contents of
the signal are fed to a high-impedance AC-coupled FET transistor
stage Q1. The low-frequency contents are fed to a DC-coupled oper
ational amplifier stage with negative feedback from the output of the
converter stage buffer. The low-frequency path handles frequencies
up to approximately 5 kHz.
The high-frequency signal is fed to the gate of Q1. The high imped
ance at the gate is converted to a low impedance at the source. The
source is connected to the base of HF transistor Q2, the summing
point for the two signal paths.
To make the FET work well in its active region within the whole dy
namic range, the FET drain is supplied with +7 V via resistor R42.
The low-frequency signal is divided by the two resistors R27 and
R28 before it is coupled to the input pin #2 of the operational ampli
fier U1. The resistors R37 and R38 at the operational amplifier out
-
put pin #6 center the output swing, and capacitor C6 stabilizes the
operational amplifier stage.
-
The low-frequency path goes from the operational amplifier to the
base of transistor Q3, the collector of which is connected to the base
Fr om Pr o t ec t io n
ci rcu its
R27
R28
R32
C13
R33
R29R30
R31
C5
+7 +5
R42 R43
Q1
-5.2
R37
R38
-5.2 -5.2 -5.2 -5.2 -5.2
Q3
C6
+5
Q2
R105
R46
R47
Q13
C20
R50
K4
L1
C18-
Q4U1
C19
K4
R106
U8
To
+
-
+
-
Flip-Flo
Trig
Level
Fig. 4-7 Impedance converter.
4-6 Hardware Functional Description
Page 23
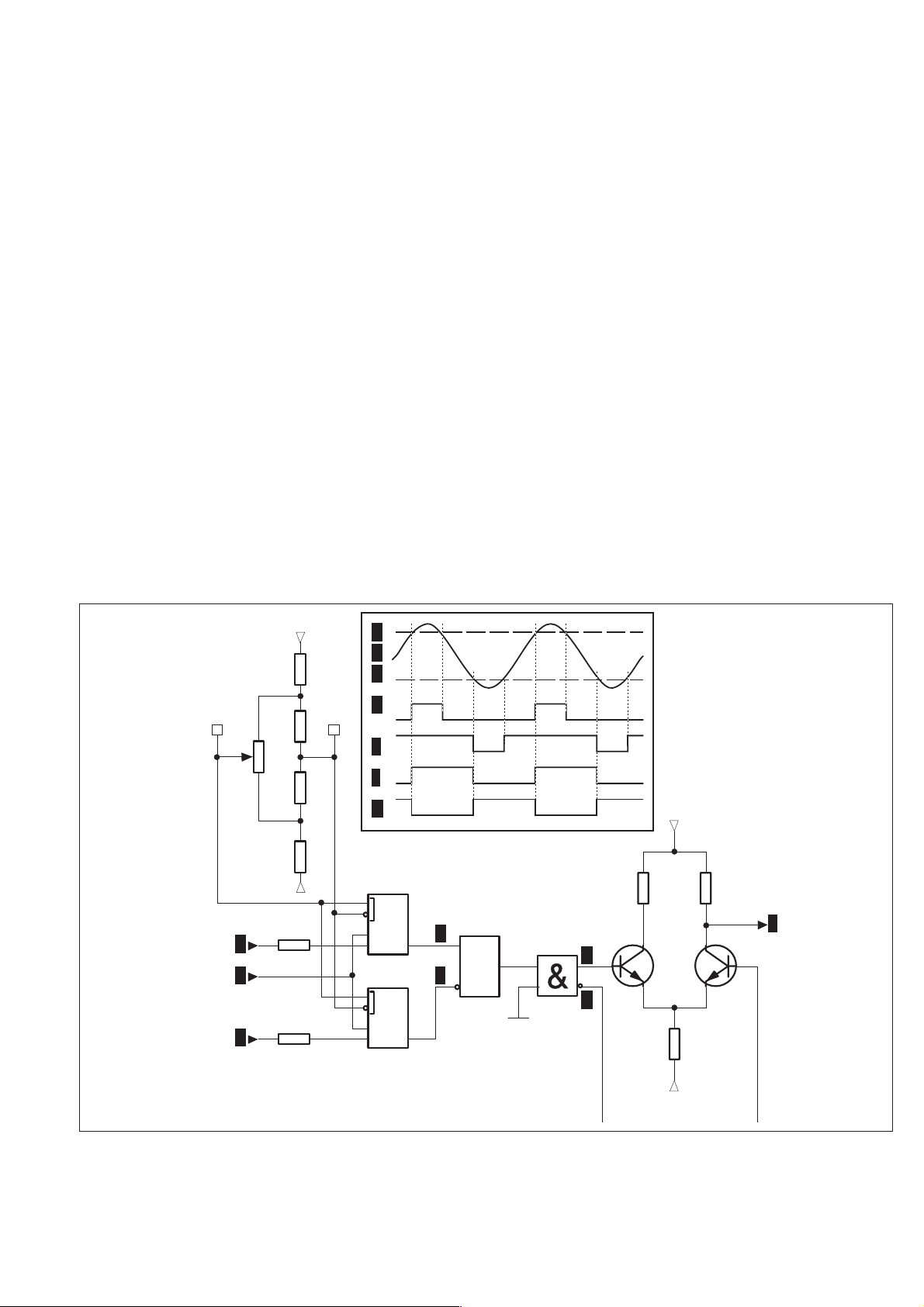
of transistor Q2. This point is common to the high and low frequency
paths.
A buffer amplifier with high driving capacity is used to get a linear
output in the 100 W load resistor R106 over a swing of 2 V. This am
plifier consists of a driver stage Q2, an output stage Q13, and a cur
rent generator Q4.
From the output of this second amplifier stage, the signal is fed back
to theop amppin 3via thedivider chainR29 toR32. Thetrimmer po
tentiometer R31 sets the gain of the low-frequency path equal to the
high-frequency gain of about 0.9. Capacitor C5 is connected to oper
ational amplifier pins #1 and #8 to achieve stable operation. The
trimmer potentiometer R33 between pins #1 and #5 on the opera
tional amplifier is used for adjusting the offset voltage of the opera
tional amplifier.
The channel A filter connected to the output of the second amplifier
stage isa 100kHz low-pass LC filter. It consists of the coil L1 and the
two capacitors C18 and C19 in parallel. The filter is controlled by the
relay K4. The filter output is connected to the input of the comparator
stage.
Comparator Stage
n
The comparator stage converts the analog signal from the impedance
converter stage to a square wave. This circuit consists mainly of the
high-speed integrated comparators U8A and U8B plus a separate
trigger level circuit connected to the comparators at pins 9 and 13 via
resistors R87 and R88.
The trigger level circuits, which are described later, generate a DC
level in the range of approximately æ1.6 V. This covers a dynamic
range of 6.4 V since the input signal is divided by a factor of 2 before
-
-
-
-
-
-
it reaches the comparator.
The counter is provided with adjustable hysteresis, i.e., it is control
lable via the front panel or GPIB. The circuitry for setting the hyster
esis consists of the resistor network R91 to R96, supplied with +5 V
and –5.2 V. It is connected to the latch enable inputs of the compara
tor, pin 5 and 7 for Comparator I and pin 17 and 15 for Comparator II.
The input signal is fed to both comparators, the outputs of which are
used for setting/resetting the Flip-Flop U9.
Buffer Stage
n
Before the signal is fed further into the ASIC U29, it has to be
level-shifted by a buffer stage. The negative ECL logic levels
(~ –0.9 V to ~ –1.7 V) from U9 pins 17 and 18, are converted to a
single-ended signal with CMOS logic levels ( ~ 5 V to~0V).
The buffer is a differential amplifier consisting of the two transistors
Q32 and Q33 whose bases are fed differentially from the two com
parator outputs. Resistor R304 serves as a current generator that is
switched alternately to the two collector resistors R296 and R297.
-
-
-
-
Trigger Level Circuits
The trigger level circuits generate the trigger voltage levels to the in
put comparators. The trigger level range is –3.2 V to + 3.2 V with a
maximum resolution of 0.6 mV. The input amplifier attenuation is
-
TP27 TP26
Trig ger Level I
Input signal
Tri gger Level II
+5
B
A
R92
C
D
R93
E
R91
F
R94
R96
-5.2
R87
B
A
G
U8A
+
-
U8B
+5
R296
U9
D
Flip Flop
E
U9
Q32
F
R297
Q33
F
To
Counter
circuits
G
R88
C
+
-
R304
Fig. 4-8 Comparator flip-flop and buffer stages.
-5.2
Hardware Functional Description 4-7
Page 24
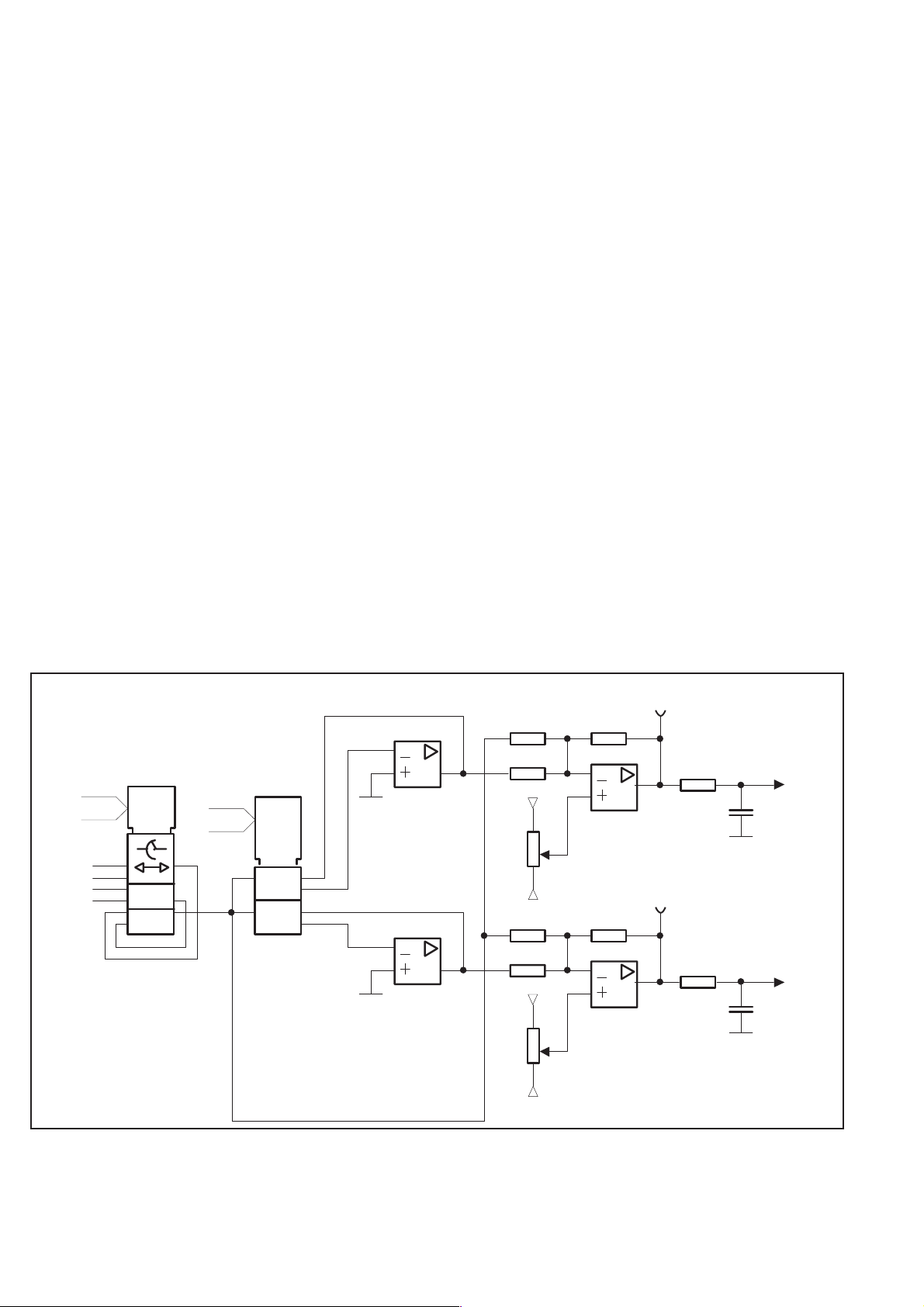
approximately 2 times. The trigger level circuits generate a DC level
that has the same attenuation. This means that the output of this cir
cuit has a range of –1.6 V to +1.6 V with a resolution of maximum
0.3 mV. Adual 8-bit DAC is used. The DACs only generate voltages
between 0 and +1.6 V, but by using a X2 amplifier and an offset shift
of 50%,the voltagerange of –1.6 Vto +1.6V is achieved. The supply
voltages to the trigger level circuits are filtered by R and C to prevent
noise originating in the digital circuitry from influencing the trigger
levels. The ground plane under the trigger level circuits is separated
from the rest of the ground plane, and the planes are connected only
at the front of the counter.
The trigger level circuits consist of the following:
Resistor network R57 to R68 for generating the reference volt
–
-
ages 0.04 V, 0.22 V, 0.59 V, and 1.6 V.
Three multiplexers (U3) to select one of the levels. With this
–
arrangement there is a total trigger level range of
–1.6 V to +1.6 V.
A double DAC (U4).
–
Two current-to-voltage converters U6. These circuits convert
–
the current at the IOUT pins of the DACs to a voltage. This
signal has a range of 0 V to approximately 1.6 V.
Two amplifiers, U7, with an amplification of X2, to generate a
–
signal with a range of 0 V to 3.2 V. Resistors R69 and R70 set
the reference voltage to the amplifier to get the 50 % offset
shift. To get exact voltages, 0.5 % precision resistors are used:
R73-R75, R78-R79 and R80-R82, R85-R86.
The zero adjust of the trigger levels is done with trimmer po
–
-
tentiometers R69 and R70 connected to the amplifiers in U7.
Two low-pass filters R87-C29 and R88-C30.
–
AD0-AD2
1.6V
0 .59V
0 .22V
0 .04V
U3
AD0- A D8
U4
D0- D7
+DACA
VREFR FB
IOUT
VREFR FB
IOUT
U6
U6
R73-R74
R75
R69
R80-R81
R82
R70
+5
-5.2
+5
-5.2
Trig ger lev el Comp I
R78-R79
U7
R87
C29
Trig ger l evel
Comp II
R85-R86
U7
R88
C30
Compar ator I
Comparator II
Fig. 4-9 Trigger level circuits.
4-8 Hardware Functional Description
Page 25
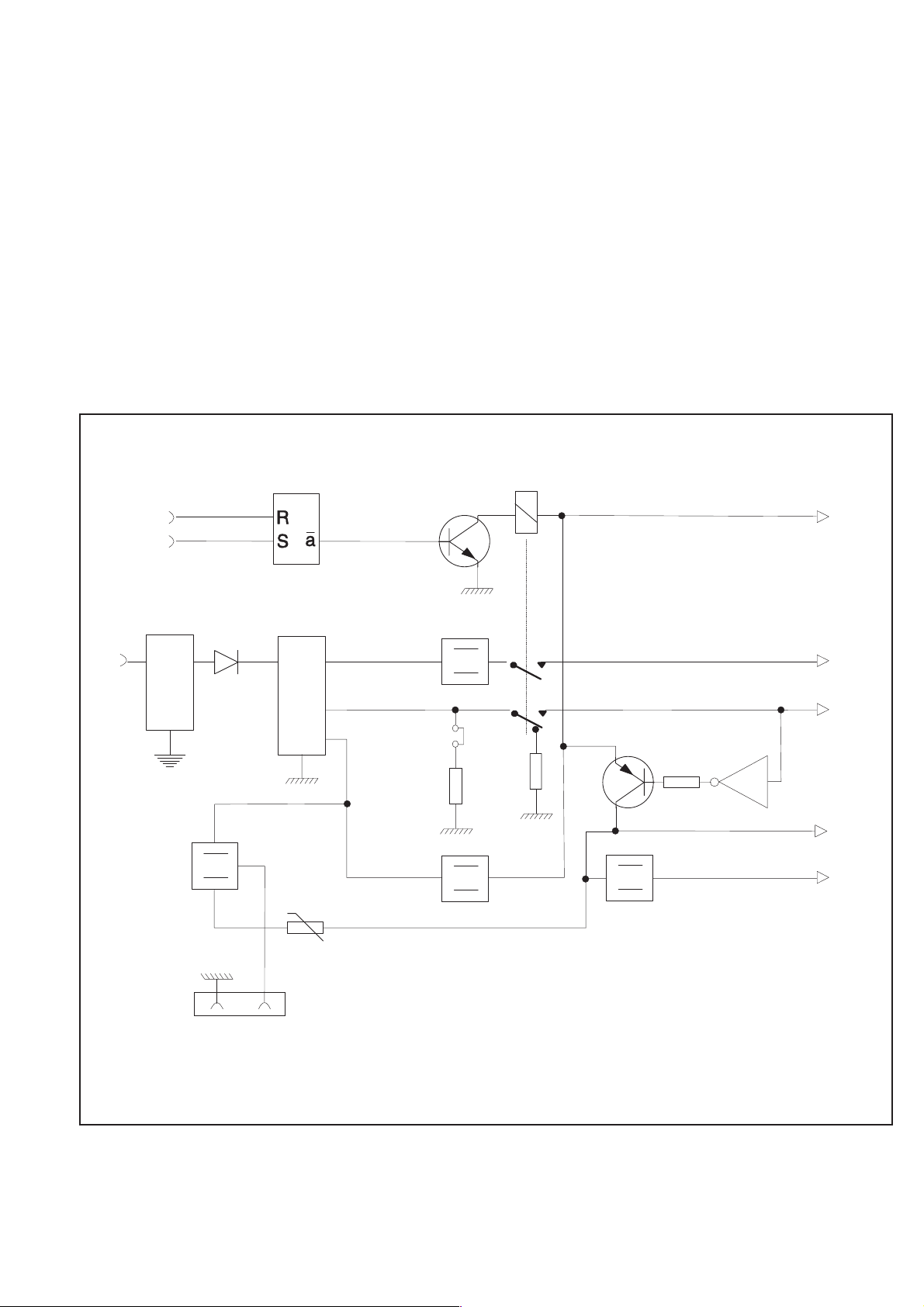
Power Supply
General survey
n
The power supply generates four regulated DC supply voltages to the
counter, as well as some other supply voltages for special purposes.
The power supply block also contains the ON/STANDBY logic.
The main building block of the power supply is a primary switch
mode power module (U39). The line power AC voltage (90 V to
265 V) is rectified to a DC voltage before it is fed to the power mod
ule.
After a line power filter in the power inlet, a fuse of 1.6 AT and an
NTC resistor protect the power supply. The fuse F1 should only blow
if a catastrophic error occurs on the primary side of the power supply.
A short-circuit on the secondary side should not affect the primary
side. To minimize the inrush current to the capacitors at the connec
tion of the power cord, an NTC resistor (R148) is used. The resis
tance is 15 Wwhen the resistor is cold but decreases to a few ohms as
it is warmed up by the steady-state current.
The AC voltage is rectified in the bridge rectifier D9 and filtered in
C64. C65 suppresses noise from D9. L6 and C82-C83 serve as a fil
ter at the input of U39.
All inputs and outputs of the power module have HF chokes. The
module is mounted with distance washers on the main board.
-
-
-
From the module there are three DC voltages outputs. One of those is
regulated (+ 5 V) and the others are unregulated. These voltages will
vary with input line voltage, the current at+5V,andattheunregu
lated voltages. The output marked +15 will be approximately +18 V,
and the output marked –7 will be approximately –8 V. The outputs
are filtered; HF is filtered by C70-C73, and LF is filtered by L7-L9
and C74-C76.
-
-
On
Stand by
ains Inlet
M
D9
Filter&Fuse
U42
U
U40B
U39
R156
-7
+5
+15
Power Module
Q14
U43
U
R149-R155
U
U41
J15
K5
R130-R145
K5
U
U21A&Q17
+12 V*
-5.2 V
+5 V
Q5-Q6
+12 V
+7 V
Fan
PM6685R
only
Fig. 4-10 Power Supply.
J31
+-
*) for ON/STBY control & OCXO
Hardware Functional Description 4-9
Page 26

Function
n
The three DC voltages from the power module are used for
generating the following four supply voltages in the counter:
+5 V
Regulated +5 V from the power module is used directly.
–5.2 V
–7 V is used, with regulator U43.
+12 V
+15 V is used, with regulator U41.
+7 V
Stabilized +12 V is used, with regulator U21A and Q17.
temperature sensor, controls the speed by applying a variable refer
ence voltage to the fan voltage regulator U42.
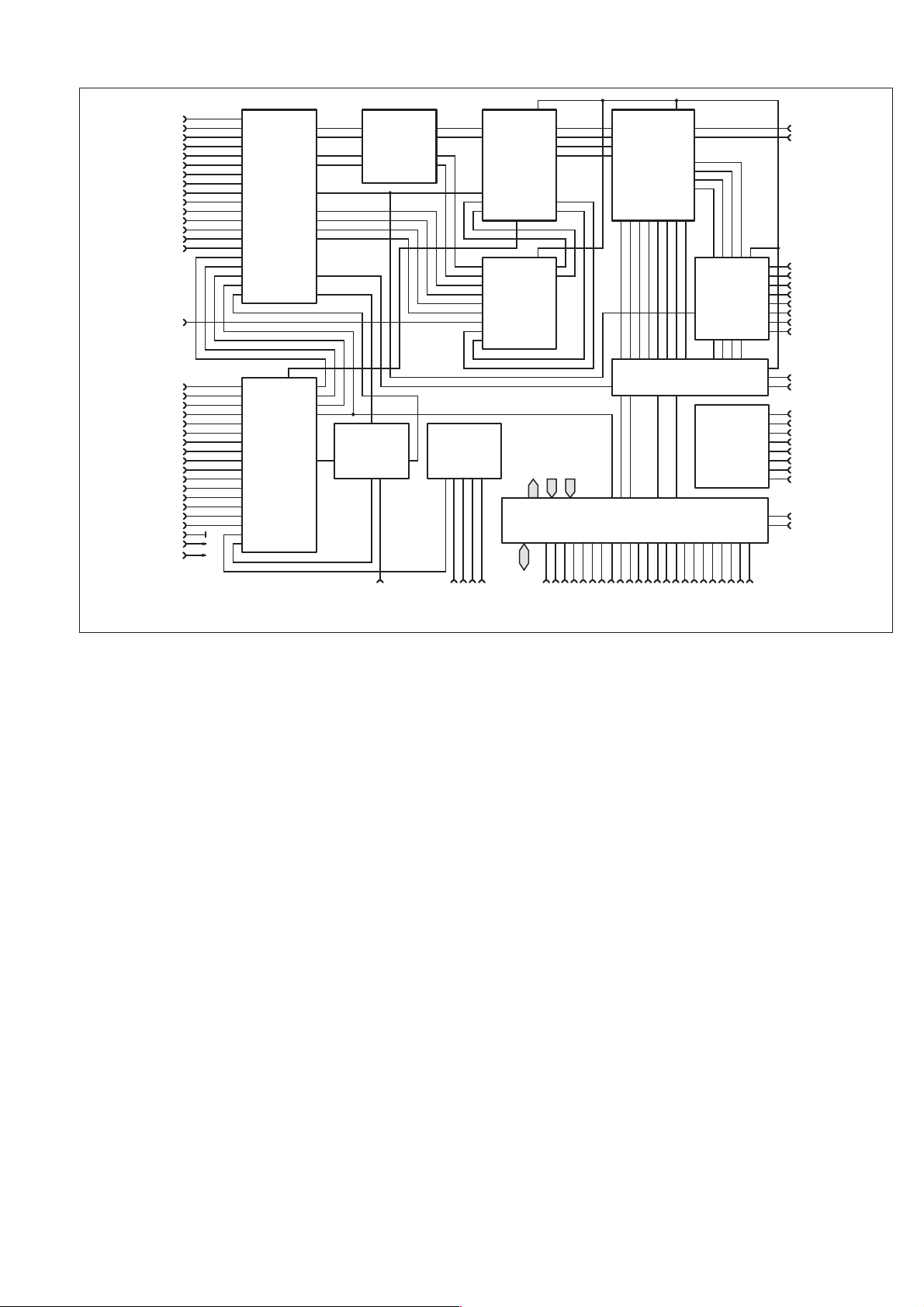
Counter ASIC
The main part of the counting logic is integrated in a CMOS ASIC
specially designedfor theFluke MultiFunctionCounter series.There
are also analog blocks included in the 100 pin QPF package.
MUX
The MUX block is a switchboard for incoming and internal signals
involved in the measuring process. Some signals are divided by 2 to
make it possible to measure higher frequencies. The trigger slope is
controlled by the MUX block as well. Atrigger edge detector senses
the presence or absence of comparator pulses and controls the trigger
level DAC’s in the TLDAC block. These functional units form an es
sential part of the Auto Trigger System.
-
-
The following supply voltage is used for a special purpose:
+12 V*
This voltage comes directly from the +12 V regulator U41and will be
present as soon as the power cord is connected, regardless of the po
sition ofthe ON/STANDBY switch. It is used for the ON/STANDBY
control logic and for supplying an optional OCXO in STANDBY to
avoid the long warm-up time otherwise needed to obtain maximum
accuracy.
At stand-by, the four main supply voltages are switched off, but as
described above, some parts of the instrument should not be
diconnected. Therefore the power module will never be switched off.
The PM6685 has consequently only a secondary power switch.
A relay (K5) disconnects the load on the +5 V and –5.2 V at stand-by.
Because the power module must always have a load on the regulated
voltage, seven bleeder resistors R149-R155 are always connected to
+5 V via J15. At stand-by the counter only needs +15 V, so a dummy
load consisting of R130-R145 is connected to the power module by
means of the relay K5 in order to stabilize the operation of the
switchmode converter.
+5 V controls the switching on/off of +12 V and +7 V. When +5 V is
on, Q6 and Q5 will conduct, i.e. +12 V will be on. If there is no +5 V,
Q6 and Q5 will be off, thus blocking the +12 V.
The ON/STANDBY logic controls relay K5, which operates as de
scribed above. It is also possible to open the relay by changing the
position of J16.
The ON/STANDBY logic consists of the RS (set-reset) flip-flop
U40B that is controlled by the ON/STANDBY button on the front
panel. Pressing STANDBY will apply a high voltage (+12 V) to the
set input. The inverting output of the flip-flop will be low, discon
necting K5 via Q14. Pressing ON will give a high voltage (+12 V) on
the reset input. The inverting output of the flip-flop will be high,
engaging K5. Inserting the power cord into the power inlet will cause
a pulse on the reset input, via C35. The microcomputer can disable
the ON/STAND-BY button via Q12 and Q7. This is done in remote
mode and during RAM-testing. A high level on the base of Q12 en
ables STAND-BY, a low level disables it.
The STAND-BY indicator on the front panel is controlled by the
+5 V via Q16. +5 V off lights the STAND-BY LED that is fed by the
uninterruptible +12 V*.
+5 V also indirectly controls the fan in the PM6685R. It is a 12 V DC
fan that operates only if +12 V is on. An NTC resistor, serving as a
OSC
The oscillator block generates, selects, and distributes the reference
clock for the circuit. The active semiconductors of the standard oscil
-
lator are included in this block. The crystal is connected to pins X1
and X2. A TCXO or OCXO is connected to X2 only. An external ref
erence clock is connected to EXTREF. The PWM signal generated at
OTRIM controls the frequency of the reference oscillator after exter
nal integration.
-
-
-
PG
A built-in pulse generator having the 10 MHz clock as a reference
can generate pulses with controllable duration and repetition rate at
the OUTPUT connector. The level is fixed TTL.
RTC
A real time clock not used at present.
TLDAC
This block contains two 10-bit DAC’s generating the trigger levels
for the input comparators, VOUTA for channel A and VOUTB for
channel B. An external reference voltage is connected to V+REFA
and V+REFB.
HO
The Hold Off block can manipulate the internal measuring signal X
-
-
-
in several ways. One operating mode simulates a low pass filter (nor
mal hold off), another mode is used in burst measurements.
The following blocks (SYNC, STST, CNTS and MCTRL) form the
actual measuring logic in the ASIC. Three types of measurements
can be made in this MEAS block:
Continuous measurements (frequency, ratio and period average).
Not used at present.
Controlled measurements (time interval, period single, pulse width,
frequency, totalize gated, totalize start-stop, and ratio).
Totalize manual.
SYNC
The SYNC block synchronizes the actual measurement with certain
internal or external events like measuring time and arming signals.
-
STST
The start and/or the stop of the measurements are controlled by this
block. External events can be used to define the exact moments.
4-10 Hardware Functional Description
Page 27
EXTC
BURST
TRA
TRB
VCCO
GNDD1
GNDD2
GNDD3
GNDD4
GET
SB
SA
OKD
CLOCK
RE S ET
Inter-
polator
FNb
FNa
I
I
CY 1
CY 2
VC CG
GNDG
VR EFA D
IR ES
IN TP1
IN TP2
IN TS1
OK a
OKb
IN TS2
A2
A
SR
B
B2
P
MUX HO SYNC CNTS
X
Y
HODLYX
HODLYY
CL O C K
S TAAR M
STO ARM
STAD LY
STO DL Y
TI ME
MREF
FREQC
MCLK
PGARM
PCL
PGT RIG
X
Y
HODLYX
HODLYY
HO S X
HO S Y
XH
YH
XH
YH
CLOCK
ST O P
ST AR T
HO S X
HO S Y
STA AR M
STO A RM
STA DLY
STO DL Y
GET
TOTSTA
STA
TOTSTA
GATEO
STOP
STAR T
STST
STA
R1
R2
L1
L2
R1
R2
L1
L2
I
INTB
INTA
NB
FND
F
OKA
FNC
OKB
FNA
I
OK C
I
I
X1
X2
V+R EFO
OTRIM
V- REF O
EXTREF
MTC XO
IN TR EF
OUTMUX
MPCL K
PH1
PH2
VCCB
GNDB
VCCC
GNDC
GNDA
VCCA
VCCX +5
OSC
RTC
+5
PGOUT
TI ME
MREF
FREQC
MCL K
PGR EF
PG
PGR EF
PGT RIG
PGA RM
PGOUT
PG
Fig. 4-11 Counter ASIC, block diagram.
CNTS
Two 32-bit binary counters count external events or keep track of the
time.
Interpolator
This block is not used at present.
MCTRL
The different events in the measurement cycle of the ASIC are timed
by this block.
MPI
This is the microprocessor interface block. The bus width is 16 bits,
AD0 toAD15. Interruptsto themicroprocessor are generated at INT.
GET
The GET signal from an optional GPIB interface can control the start
of a measurement.
External Interpolator
n
The X-POLATOR unit is connected directly to the internal
interpolator in the ASIC. It is used for increasing the time resolution
beyond the limits set by the reference clock period of 100 ns. An er
ror pulse is generated in the SYNC block. Its width is determined by
the difference between an external event on an input channel and the
next clock pulse. This pulse controls a current generator charging a
capacitor. When the pulse has expired the voltage across the capaci
tor is A/D converted and the value is added to the result. There are
two interpolators, one for the start event and one for the stop event.
RTC
RTC
RTCX1
-
-
MCTRL
FI N1
DMAR
TLDAC
DMABR
CS RS SS
PCL
OK
MCL K
MPI
C1
C3
CS
A16
A18
ALE
VBAT
RTCX2
LARMN
RDN
AD0-AD15
A17
WR L N
WRHN
INT
A19
S1N
HO L D N
S2N
HLDAN
QDM AN
C2
S4N
S5N
S3N
FIN
MTIM E
V+R EFA
VOU TA
V- REF A
V+R EFB
VOU TB
V- REF B
VC CE
GNDE
VC CF
GNDF
C4
They are calibrated over the possible error pulse range to allow for
any aberrations from the theoretical linear behavior.
Oscillator Circuits
CPU Oscillator
n
The microcontroller U11 is clocked at 12 MHz. The crystal B1 is
connected to the XTAL inputs of the microcontroller.
n
Reference Oscillators
A 10 MHz crystal oscillator is used as the reference for the measur
ing logic. If a stable external 10 MHz reference is available, it can be
connected to REF IN on the rear panel and selected by means of the
EXT REF button on the front panel.
In addition to the standard crystal oscillator there are two optional
oven-controlled crystal oscillators (OCXO) to choose from.
Standard
The uncompensated standard oscillator consists of the crystal B2,
C109, C113-C115, R209 and R211. C115 is used for manual adjust
ment of the frequency when the calibration tolerance has been ex
ceeded. Theactive circuitryis builtinto theASIC U29and is accessi
ble via the pins marked X1 and X2.
OCXO
If one of the OCXOs is mounted, the standard oscillator has to be in
activated by moving the jumpers J23 and J25 to their alternative po
sition. These oscillators are connected to J24 and are self-contained
-
-
-
-
-
-
Hardware Functional Description 4-11
Page 28
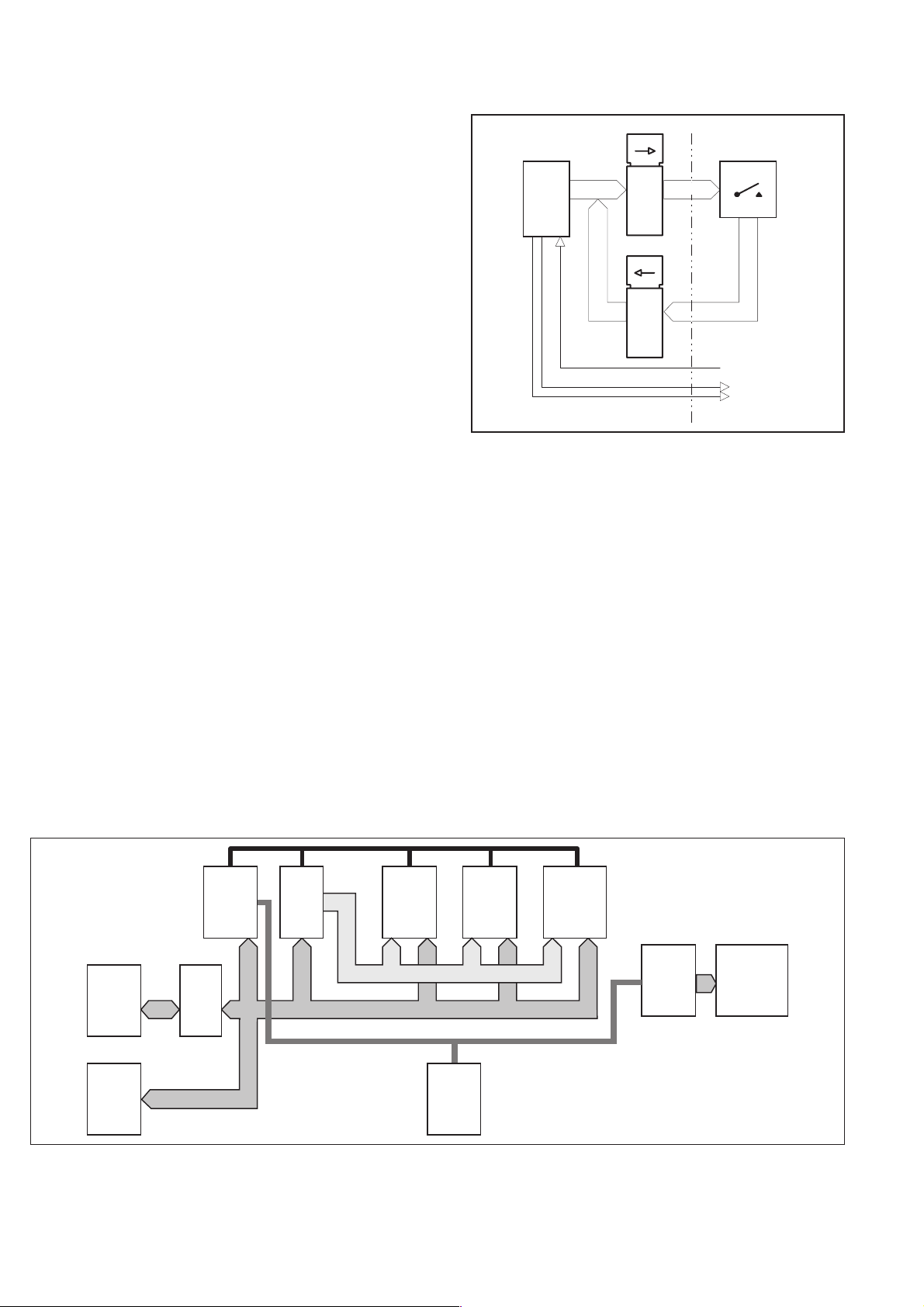
units with facilities for coarse and fine adjustment. They are fixed to
the main PCB with two screws. The output signal is AC-coupled to
the X2 pin on U29 via C107.
External
This input consists of an AC-coupled line receiver with Schmitt trig
ger function (U28) and is protected against excessive voltage
excursions by a resistor-diode network. The output signal from U28
has CMOS logic levels and is connected to the EXTREF pin on the
counter ASIC U29.
Logic
Microcomputer Circuits
n
Microcontroller
The microcomputer circuitry consists mainly of the microcontroller
U11, an Intel 16-bit CMOS 80C196, RAM (U22A), and EPROM
(U23A). The microcontroller is clocked at 12MHz. The data and ad
dress lines AD0 to AD15 are shared by means of multiplexing.
Therefore the addresses are stored in the latches U16A and U17A.
The ALE signal (Address Latch Enable) enables the latches.
UVEPROM
The main program is stored in U23A that is mounted in an IC socket,
making it easy to update and customize the instrument firmware by
changing the EPROM.
EEPROM
Front panel settings, GPIB address and certain other data that are not
changed frequently, e.g. information in the Protected User Data
Area, are stored in U12A which does not need battery backup.
Reset Circuit
A special reset circuit, the power supply supervisor U10, is included
in the design. If the +5 V supply line becomes lower than 4.5 V, the
reset output pin 5 goes low and the microcontroller will start over.
The length of the reset pulse is set by C88; 2.2 µF gives a pulse of ap
proximately 30 ms. U10 also controls the reset pulse during
power-up so that the microcontroller will be initiated correctly.
Keyboard Scanning
n
Main Board Keyboard & Display
U11
-
AD0-AD7 H0-H3
CPU
P1.0
HS1.0
P1.1
-
U13A
Latch
U14A
Latch
AD0-AD7
Board
V0-V7
LOCAL/PRESET
SCL
SDA
Fig. 4-13 Keyboard scanning.
The keyboard scanning is done in two modes. The first mode is ac
tive aslong asno buttonhas beendetected asdepressed. Then all out
-
puts of U13A are set high, and the latch U14A is read. If no button
has been depressed, all outputs are low. This check is done at every
timer interrupt in the microcontroller, every 25 ms. If a button is
depressed, one of the output bits is high. When this event is detected,
mode two is entered. The outputs of U13A must be set high one after
the other to find the specific button. When found, only this button
will be checked, so other simultaneously depressed buttons will not
be recognized. The depressed button must stay down for several
timer interrupts before action is taken. After the button has been rec
ognized, the timer interrupt SW will be waiting for the button to be
released. The button must be released for several timer interrupts be
-
fore the keyboard scanning returns to mode 1. Then the search for
-
other activated buttons can be resumed.
The following three buttons are not scanned in this way:
The ON button is connected to the ON/STANDBY logic in the
–
power supply.
CPU Latch
Key-
board
Latch
rd
GPIB
Fig. 4-12 Microcomputer circuits, block diagram.
4-12 Hardware Functional Description
RAM
Address Bus
UV
EPROM
OM
Address & Data Bus
2
ICBus
EE
PROM
Counter
ASIC
LCD
Drivers
LCD
Page 29

The STAND-BY button is connected to the ON/STANDBY
–
logic in the power supply.
The LOCAL/PRESET button is connected directly to input pin
–
24 on the microcontroller U11. Pressing this button sends an
interrupt to a special handler in the SW.
Rear Panel Unit
The rear panel contains the following connectors
INPUTS:
External reference input D - REF IN (BNC)
–
External arming input E - EXT ARM (BNC)
–
Power supply inlet including EMI filter
–
OUTPUTS:
Internal reference output G - 10 MHz OUT (BNC)
–
If a GPIB interface is installed in the device, it is mounted on the rear
panel and connected to the main board with a flat cable.
Besides the normal standard GPIB connector, this optional unit also
has a BNC connector capable of outputting an analog representation
of any three consecutive digits on the display.
There is also a 6 SPST DIP switch on this unit for setting the default
GPIB address.
ON
ANALOG OUT
P M962 1
P M962 3
P M962 4
P M962 5
OF F
168 421
A DDRE S S
I E E E 4 88 / I E C 62 5 IN T ER F A C E
SH 1, AH1, T 5, L4, SR1,
RL1, DC1, DT 1, E 2
PM9626
PM9678
PM9690
PM9691
10M Hz O UT RE F I N E XT AR M
GDE
PM9628 /85
P M9697
_______
_______
EXT SUPPLY
12-24V DC
-I NT -S T BY
BAT T ERY
-EX T /L I NE
POWE R
90 V - 26 5V
PRIMARY FUSE
1.6AT
INSIDE
Fig. 4-14 Rear panel.
Hardware Functional Description 4-13
Page 30

Optional Units
B
i
b
d
GPIB Interface Including Analog Output
GPIB, PM9626B
n
IC101/106/117
Analog Out
n
The result on the display can be converted to an analog signal by
means of a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) signal from the micro
processor. The signal is filtered, attenuated, offset-adjusted, inte
grated and buffered by IC103 and supporting passive components to
give an analog DC level between 0 and 4.98 V with a resolution of
20 mV. The analog output has a separate analog ground connected to
the cabinet.
-
-
oar
IC107/108
c
as
A0-15
AD0-15
IC111/
112
IC109/
110
IC113
IC114/115
GPIB
connector
IC116
+5V
Fig. 4-15 GPIB interface.
The GPIB interface controls the communication between the internal
microprocessor and the external GPIB bus. A 32K extension of the
ROM and RAM is placed on the interface board. An analog output is
also included. The PCB is connected to J18 on the main board with a
ribbon cable and fixed to the rear panel with two screws. Two metal
studs at the rear edge of the PCB are inserted in slots on the main
board in order to relieve mechanical stress.
The GPIB control circuit, IC113, communicates with the external
GPIB bus via the bidirectional bus drivers IC114 and IC115. IC113 is
controlled from the microprocessor by writing and reading in the in
ternal control registers. If IC113 has a message for the microproces
sor, it uses the GPIB interrupt signal. The address switch setting is
read by the microprocessor via IC116.
A 32K extension of both ROM (IC109 and IC110) and RAM (IC111
and IC112) is placed on the interface board. The circuit board is pre
pared for a 16-bit extension, but only 8 bits are used. IC110 (ROM),
IC112 (RAM) and R118 are not mounted. IC107, IC108 are address
latches andIC101, IC106and IC117 use the latched address to gener
ate chip select and chip enable signals for internal use on the GPIB
board.
HF Input
You can add an optional prescaler. This HF input is mounted on the
main board, to the right of the input amplifier. It is connected to J19
where there are three pins reserved for ID coding. Preparations have
thus beenmade forother prescalerswith different prescaling factors.
Prescaler 3.0 GHz, PM9624
n
This prescaler cannot be repaired at a local workshop. It must be sent
to the factory for repair.
The prescaler consists of the following parts:
Limiter
The limiter consists ofa6dBattenuator and a PIN diode at
–
tenuator to achieve constant input amplitude to the amplifiers.
Amplifier
–
Five amplifier stages are divided into three blocks. One block
consists of one amplifier. Two blocks consist of two amplifiers
each and an AGC control.
Automatic Gain Control (AGC)
Helps the amplifiers retain a constant output amplitude.
–
-
-
Dividers
Two dividers divide the input signal frequency by 16.
–
Detector
Detects whether the level of the input signal is high enough to
–
ensure correct measurement and, if not, blocks the output sig
-
nal from the prescaler.
Positive Voltage Regulator
–
-
Supplies a well-regulated voltage to the HF amplifiers.
-
-
-5.2V
Zero
IC103
PWM
Full scale
Fig. 4-16 Analog output.
4-14 Hardware Functional Description
IC103
+7V
Analog
Out
Page 31

Software Functional Description
General
The PM 6685 software is divided into two main modules: the GPIB
and DEVICE modules. The GPIB fully implements the Message Ex
change protocol as described in the IEEE 488.2 - 1987 standard.
The DEVICE module is a real-time measurement executive that can
be interrupted to do other tasks, such as handling the keyboard, per
forming bus commands etc.
The basic structure of the main module is as follows:
main PM6685()
{
Initialize();
while (TRUE)
{
if (BREAKFLAG_KEYBOARD)
{
HandleKeyboard();
}
if (BREAKFLAG_PRESET)
{
PresetDevice();
}
if (BREAKFLAG_GPIBCOMMAND)
{
ExecuteGpibCommands();
}
if (BREAKFLAG_RESTART)
{
RestartMeasurement();
}
while (not any BREAKFLAG)
{
Measure( );
}
}
}
All break flags are set by interrupt-driven events, either from exter
-
nal functions (the GPIB interface) or from internal functions (timers
-
etc.).
The Initialize procedure does all necessary initialization at power
up. It also does the power up tests. See Power-On test in chapter 2.
-
The Handlekeyboard procedure controls all user input/output via
the front panel, except displaying the measurement results.
The PresetDevice procedure reprograms the complete device when
the PRESET key has been pressed (in local mode). It aborts pending
measurements.
The ExecuteGpibCommands procedure executes GPIB commands
and, if a query is received, it starts the response formatter and sends
the requested data to the GPIB interface. If the display is switched
on, the results are also displayed.
The RestartMeasurement procedure aborts pending measure
ments; the measure loop will later continue to measure. This is
mainly used when the RESTART key is pressed.
The Measure procedure is the measurement control loop that is used
in local mode. It sends its result to the display.
The ParseGpibInputData procedure parses the GPIB messages
found in the input buffer and sends executable statements to the
ExeceuteGpibCommands procedure. The input of data to the input
buffer from the external GPIB interface is fully controlled in inter
rupts. These interrupts are always enabled so the new data bytes can
be stored in the input buffer while parsing commands. This
ParseGpibInputDat is also executed in interrupt.
Software Functional Description 4-15
Page 32

Test Routines
Test Routines via AUX MENU Key
The testroutines arethe routinesaccessible via the AUX MENU key.
Refer to the PM6685 Operators Manual.
Power-On Tests
At power-on some tests are automatically performed. If any of these
tests fails, an error message is displayed and the instrument is halted.
Pressing the LOCAL/PRESET key makes the device continue inde
pendently of the detected error, but without performing the next tests
in the start-up sequence.The following tests/actions are performed:
Write 001 to internal test pins
–
Pulse all microcomputer i/o ports twice
–
Write 0.1 on display
–
Write 0.1.2. on display and 010 on test pins
–
Test mC internal RAM ( error = Err mC & halt)
–
Write 0.1.2.3 to display and 011 on test pins
–
Test mC timer ( error = Err mC & halt)
–
Write 0.1.2.3.4. on display and 100 on test pins
–
Test main board RAM ( error = Err ra. & halt )
–
Write 0.1.2.3.4.5. to display and 101 to test pins
–
Test ASIC ( error = Err. 5xx & halt)
–
Write 110 on test pins
–
Check display (light all segments for 2 s)
–
Clear Display
–
Perform GPIB RAM test if GPIB is installed
–
(error = Err ra. & halt)
Write 111 on test pins ( final value)
–
Clear display and start normal measurement procedure
–
-
4-16 Software Functional Description
Page 33

Chapter 5
Repair
Page 34

Preventive Maintenance
Calibration
To maintain the performance of your counter we recommend that
you calibrate your instrument every year, or more often, if greater
time base accuracy is required. Calibration should be performed with
traceable references and instruments at a certified calibration labora
tory. Contact your local Fluke representative for calibration.
To know the present status of your instrument, test your timer/coun
ter from time to time. The test can be made according to the informa
tion in Chapter 2, Performance Check.
Oscillators
The frequency of the reference crystal oscillator is the main parame
ter affecting accuracy in a counter. The frequency is affected by ex
ternal conditions like the ambient temperature and supply voltage,
but also by aging. When recalibrating, the reference crystal oscillator
is compensated only for deviation in frequency due to aging.
Some important points:
n
The high stability oscillators have been built into an oven in
–
order to keep the oscillator temperature as stable as possible.
Continuous operation is also important for stability. After a
power interruption, the oscillator restarts at a slightly different
frequency. It will then, as time goes on, age at an equal rate.
The stability indicated for the oscillators is valid within a tem
–
perature range of 0 to +50 °C, with a reference temperature of
+23 °C. If the timer/counter is used in a room temperature of
20 to 30 °C, the temperature stability of an OCXO will be in
-
creased by a factor of 3.
-
-
-
The temperature stability indicated for the standard oscillator is
–
mainly dependent on the ambient temperature. When the coun
ter is operating there is always an internal temperature increase
that will influence the oscillator.
Recalibration intervals
n
-
The Mean Time Between ReCalibration, MTBRC, is defined as:
-
MTBRC
Acceptable error Temperature stability
=
-
−()( )
Agi
(
ng)
MTBRC can be calculated when the total acceptable error and the
oscillator specifications are known.
The total acceptable error is defined as:
()
()
Acceptable error
Deviation of reference frequency
=
(
Nominal reference frequency)
Model PM6685 PM6685R
Option:
Timebase type:
Total uncertainty,
0°Cto50°C,at2
- 1 month after calibration
- 3 months after calibration
- 1 year after calibration
- 2 years after calibration
Typical total uncertainty, for operating
temperature 20°C to 26°C, at 2
dence interval:
- 1 month after calibration
- 3 months after calibration
- 1 year after calibration
- 2 years after calibration
*
After 1styear of operation. For 1styear add: < 3x10
for operating temperature
s (95%) confidence interval:
s (95%) confi
Standard
UCXO
< 1.2 x 10
<1.2x10
<1.2x10
<1.5x10
-
<4x10
<4x10
<7x10
<1.2x10
Table 5-1 Stability of timebase oscillators.
5-2 Preventive Maintenance
PM9691
OCXO
-5
-5
-5
-5
-6
-6
-6
-5
-10
<3x10
<4x10
<1x10
<2x10
<3x10
<4x10
<1x10
<2x10
-8
-8
-7
-7
-8
-8
-7
-7
PM9692
OCXO Rubidium
-9
<8x10
<1.2x10
<2.5x10
-8
<5x10
-9
<8x10
<1.2x10
<2.5x10
-8
<5x10
-8
-8
-5
-8
<4x10
<4x10
<4x10
<6x10
<1x10
<2x10
<2.5x10
<5x10
-10
-10
-10 *
-10 *
-10
-10
-10 *
-10 *
Page 35

Example:
A user can accept a maximum of 3 Hz deviation on the
–
10 MHz frequency of the oscillator. This results in:
()Acceptable error =
3
×
10 10
6
=×
310
−
7
The aging and temperature factors can be selected from the table on
page 5-2.
The value of the aging factor is correctly selected from the table
when the calculation of MTBRC results in 1 to 30 days (use /24h), 1
to 12 months (use /month) or over 1 year (use /year) (not, e.g., 43
days or 17 months or 0.8 years).
Example:
The user has the same requirements as in the example above.
–
The counter has a PM9691 oscillator.
Look up information about PM9691 in the table on page 5-2.
–
The results will be the following:
Relative Frequency deviation caused by:
Ambient temperature deviation
–
(within 0 to 50 °C; reference point at 23 °C): Less than
–8
3*10
Aging/year: Less than 1.5 * 10
–
Use the MTBRC formula with the above values. This gives a
–
–7
MTBRC of maximum:
78
−−
310 310
×−×
−
15 10
×
.
18
=
7
. year
NOTE: When recalibrating, the reference crystal oscillator will be
compensated only for frequency deviation caused by aging.
When to Replace the Fan
(PM6685R only )
To maintain the high reliability of a counter used in
around-the-clock’ applications, you must replace the fan every sec
ond year. For part time and low ambient temperature use, you can ex
tend this service interval to 6-10 years or more. Additional informa
tion can be found in Chapter 9, Appendix.
-
-
-
Preventive Maintenance 5-3
Page 36

Troubleshooting
General
Quick Troubleshooting
The PM6685is ahighly integratedFrequency counterwith dedicated
LSI counter circuits and microcontrollers that control the complete
units. The microcontroller can help you locate faulty parts by run
ning test programs and generating stable signal patterns on t
he bus. If the microcontroller does not work or the fault is in a part of
the counter that cannot be accessed by the microcontroller, tradi
tional troubleshooting must be performed.
Where to Start
After reading the safety instructions, continue with this chapter for
troubleshooting and repair instructions. When you have fixed the in
strument, always do the Safety Inspection and Test after Repair, as
described later in this Chapter. Then do the checks in Chapter 2, Per
formance Check. Recalibrate if required by following the adjustment
instructions in chapter 6, Calibration Adjustments.
Logic Levels
The PM6685 contains logic of four families. The levels for these
families are listed in the following table.
Positive
ECL
Supply voltage +5 V -5.2 V +5 V +5 V
Signal ground 0 V 0 V 0 V 0 V
Input voltage
High, V
IH >+3.9 V >-1.1 V >+4 V >+2 V
Low, V
IL <+3.5 V <-1.5 V <+1 V <+0.8 V
Output voltage
High, V
OH >+4 V >-1 V >+4.9 V >+2.7 V
Low, V
OL <+3.3 V <-1.7 V <+0.05 V <+0.4 V
Bias ref. voltage, V
BB +3.7 V -1.3 V - -
Table 5-2 Logic levels.
Negative
ECL
CMOS TTL
Required Test Equipment
To test the instrument properly using this manual, you will need the
equipment listed below. The list contains specifications for the criti
-
cal parameters.
-
-
DMM
Oscilloscope 300 MHz 2-channel
Signal generator 3300 MHz
Power supply 12 V/2 A
BNC-BNC 50 W cables RG-58
Type Performance
3.5 digits
Table 5-3 Required test equipment.
-
-
PROM Identification
There are two different PROMs in the PM6685, one on the main
PCB containing the instrument firmware, the other on the optional
GPIB board, containing the interface bus firmware.
They have labels with version designation of the traditional form
Vx.yz, where x, y, and z are digits. The last digit can be followed by a
single letter. The version numbers do not have to coincide, except for
the last letter. So the combination Vr.stE and Vu.vwE is valid,
whereas Vr.stE and Vu.vwF is not.
Operating Conditions
Power voltage must be in the range of 90 to 260 VAC.
Introduction
GPIB(Level 10)
IN P U T A M P LIF I E R ( L ev el 9 )
D / A C O N VE R TE RS ( L ev el 8 )
MEASU RING LOG IC (Le vel7 )
KEY BOARD (L eve l6 )
INT E RN A L CONT R O L S IG NAL S & DIS P LA Y (L ev el 5 )
MICROCOMPUTER KERNEL (Level4)
MICROCONTROLLER (Level 3)
OSCILLATOR(Level2)
POWE RSU PPL Y ( Level 1)
Fig. 5-1 Functional levels.
5-4 Troubleshooting
The troubleshooting strategy for the PM6685 is an integrated part of
the overall service strategy for the instrument. This instrument is hi
-
Page 37

erarchically designed in different levels, and troubleshooting can be
performed in any design level if the lower levels are OK. It is, there
fore, important to disconnect all options at the beginning of the trou
bleshooting procedure.
Power Supply
J3
J4
Fuse
J9
1 5
J10
TP22, +7
Power
Module
6 14
TP17, -7
J15
TP16, +15
+5V adjust
TP15, +5
J16
TP20, -5.2
J21
Load
Disconnected
Connected
TP23, +5
TP21,+12V
To verify the Power Module proceed as follows:
-
-
If the primary fuse is broken, there is a short circuit in the
–
primary circuits. Use a DMM and try to locate the fault by
resistance measurements.
Disconnect L6 and check the resistance between pin 1 and
–
pins 4 and 5 on the power module. The DMM should not
show a short circuit. Put L6 back.
Check that the DC voltage between pin 1 and pins 4 and 5
–
on the power module is about Ö2 times the input
AC-voltage. If not, use traditional troubleshooting tech
-
niques to locate the fault.
–
Remove the power cable from the counter.
Measure the resistances according to the table below.
–
Test Pins Resistance
(GND) and TP15 (+5 V) » 10 W
(GND) and TP16 (+15 V) »1.5 kW
(GND) and TP17 (–7 V) »270 W
Table 5-5 Output resistances.
If one of the above-mentioned measurements shows 0 W,
–
remove L7, L8, and L9 and use conventional troubleshoot
ing techniques to isolate the fault.
Measure the resistances according to the table below.
–
Test Pins Resistance
10, 11 and 13, 14 »150 W
8 and 9 »1.5 kW
6 and 7 »270 W
Table 5-6 Output resistances.
Fig. 5-2 Test points and trimmers for the power supply.
Connect the counter to line power.
Set the counter to STAND-BY mode.
–
Check that the voltage between J9 and J10 is in the range of
–
90 to 260 VAC, (see Fig. 5-2).
Check that the input voltage to the power module, U39 be
–
tween pin 1 and pins 4 and 5 on the bottom side of the PCA, is
120 to 375 VDC.
Move the jumper J16 to the DISCONNECT position.
–
Check the “STAND BY” voltages after the power module,
–
U39. Use for instance the screen around the input amplifier as
ground connection. There are also a number of ground pads on
the PCB available for this purpose.
Test Points Voltage
TP15 +5.10V±10mV*
TP16 +14.8 V to +21 V
TP17 –12.5 V to –7.5 V
TP21 +12 V ± 0.5 V
Table 5-4 Standby voltages.
If the resistances deviate considerably from the values in the table,
the complete power module must be replaced.
Move jumper J16 to the CONNect position.
–
Connect the power cable to the counter.
–
Switch the counter ON.
–
Check the “POWER ON” voltages.
–
Test Points Voltage
TP23 +5.06V±30mV*
-
TP20 –5.2V±50mV
TP22 +7 V ± 100 mV
Table 5-7 Power-on voltages.
*NOTE: If the +5 V voltage is outside the specification, all
other levels will be wrong, since they are based on the
+5 V level.
If you find any fault, continue with traditional troubleshooting tech
-
niques and replace defective circuits. Also refer to Power Supply in
Chapter 4, Circuit Descriptions.
*NOTE: If this voltage does not meet the above-mentioned
spec, and if it is not possible to adjust it, the output
resistances of the module must be checked.
Troubleshooting 5-5
Page 38

Oscillator
d
1
Optio
1
U23
Check that the RESET circuit U10 works properly by moving
–
B2
Stan
C1
J27
1
U23
14
Optional OCXO
Coarse adjust
Fine adjust
r
J24
B1
U22
U17U16
44
61
U11
1
10
27
J13
J14
J11
J29J30
J12
U29
81
1
31
J23 J25
51
Fig. 5-3 Test points and jumpers for checking the
microcontroller.
U14
U13
Optional oscillator
Standard oscillator
B2
C115
the RESET jumper J29 temporarily to the ON position.
If the CPU is not running, check the state of the pins J11-J13. See ta
-
ble below.
Fig 5-4 Trimmers for the reference frequency oscillators.
Standard Oscillator
n
Be sure the jumpers J23 and J25 are in the STD position, (see
–
Fig. 5-4).
Check that 10 MHz is present at U29, pin 42.
–
Check that 10 MHz is present at the rear panel connector
–
10 MHz OUT (J27).
If you find any fault, continue with traditional troubleshooting tech
niques and replace defective circuits. Also refer to Chapter 4, Circuit
Descriptions, Oscillator Circuits.
OCXO, PM9691 or PM9692
n
This test can be carried out only if the counter is equipped with one of
the optional oscillators, PM9691 or PM9692.
Be sure the jumpers J23 and J25 are in the OPT position, (see
–
Fig. 5-4).
Check that 10 MHz is present at U29, pin 42.
–
Check that 10 MHz is present at the rear panel connector
–
10 MHz OUT (J27).
These oscillators cannot be repaired in a local workshop. They must
be sent to the factory for repair.
Microcontroller
Check that 6 MHz is present at U11, pin 65 (see Fig.5-3).
–
Display JP11, J12,
0.1 0, 0, 1 - mC I/O port
0.1.2 0, 1, 0 Err UC mC internal
0.1.2.3 0, 1, 1 Err UC mC timer er
0.1.2.3.4 1, 0, 0 Err rA RAM error Replace U22
0.1.2.3.4.5 1, 0, 1 Err ASIC ASIC error Replace U29
All seg
ments
-
J13
1, 1, 0
-
1, 1, 1 Err rA GPIB RAM
Message Error Action
error
RAM error
ror
error
Test OK
Replace U11
Replace U11
Replace U11
-
Replace U111 on
GPIB board
Table 5-8 Start-up test.
If you find any fault, continue with traditional troubleshooting tech
niques and replace defective circuits. Also refer to Chapter 4, Circuit
Descriptions.
NOTE: Check that activity is going on at U11 pin 62 (ALE), pin
61 (RD), pin 63 (INST), and pin 43 (READY). These
pins should not be stuck HIGH or LOW.
If one or more bits on the AD-bus are corrupt, the
–
microcontroller ( mC) often reads the same instructions re
-
peatedly. When the mC discovers an invalid OP code, it will
RESET itself and start from the beginning again. The mC
sets the RESET input low when it resets itself. This can be
discovered at the RESET input of U11, (pin 16). If +5 V to
U10 is OK, this could be the cause of trouble.
5-6 Troubleshooting
Page 39

Input Amplifier
A Input Check
n
DC levels
Switch on the counter.
–
Press LOCAL/PRESET and ENTER.
–
Deselect AUTO and set the sensitivity to 1 Vrms.
–
Measure the DC voltages according to Fig. 5-5. Use the DMM
–
with a 10 kW resistor in series with the test cable.
AC levels
Connect a 1000 Hz sine wave signal with an amplitude of
–
1V
to Input A.
pp
Measure the AC-levels according to Fig. 5-5. Use the oscillo
–
scope and a 10 MW probe.
If you find any fault, continue with traditional troubleshooting tech
niques and replace defective circuits. Also refer to Input Amplifiers
A and B in Chapter 4, Circuit Descriptions.
-
-1.7V -0.9V
U9
TP27, -1.4V
TP10
7V
TP26, -1.4V
TP11
-3V
-2.3V
Q2
D4
2V
R91
Q13
Q1
U8
Q4
0.8V
4.3V
0.8V
0.4V
-
R31R33
0V
0.6Vpp
U1
0V
0.3Vpp
1.5V
0.6Vpp
Q3
D3
-2V
0.6Vpp
D1
1Vpp
R23
R22
D2
C2
C1
Fig. 5-5 Typical voltages, input amplifier.
Troubleshooting 5-7
Page 40

Prescaler 3.0 GHz, PM9624
n
See Chapter 2, Performance Check, for verification.
Sensitivity
-10 dBm
-20 dBm
-30 dBm
-40 dBm
-50 dBm
0
Fig. 5-6 Specified and typical sensitivity of input C
(PM9624).
This prescalercannot be repaired in a local workshop. It must be sent
to your Fluke representative for repair.
1GHz 2GHz
2.5 GHz
Frequency
GPIB Interface and Analog Output
Setup
Connect the counter to line power.
–
Switch on the counter.
–
–
Press PRESET and then ENTER.
Connect a DMM to the BNC output BU102.
–
Activate the analog output.
–
Select AUX MENU.
–
–
Press DATA ENTRY p /q until the display reads ANA
LOG OUT.
Press ENTER
–
Press DATA ENTRY p/q to select ON.
–
Press ENTER.
–
Press DATA ENTRY p/q until the display reads 1.0-3V.
–
Press ENTER.
–
Connect a LF synthesizer to Input A on the counter.
–
Set the synthesizer to 500 Hz, 1 V
–
Read the DMM result. The voltage should be 2.49 V ± 35 mV.
–
Minor deviations can depend on the settings of the trimmer potenti
ometers for ZERO and FULL SCALE. See Chapter 6, Calibration
Adjustments, for a decription of the procedure to follow.
PP
-
-
BU103
U114 U115
U113
Zero
U116
BU102
U103
Full Scale
GPIB
U108
U109
BU101
U107
U117
Fig. 5-7 Component layout, GPIB interface.
General Remark
n
If the GPIB board is suspected to be faulty, be sure the basic instru
ment is OK by performing a few functional checks after the ribbon
cable has been disconnected from J18.
Analog Output
n
The microcontroller generates a PWM signal that is applied to pin 1
on U101.The frequencyis approximately 20 Hz, but the duty cycle is
dependent on several factors like the frequency of the measured sig
nal, the measurement time, and the selected scaling factor.
U106
U111
U101
Large deviations indicate a fault. Trace the signal through the inte
gration chain with traditional troubleshooting techniques and replace
defective circuits. The duty cycle at U101:1 should be 50 %. Also re
fer to GPIB Interface Including Analog Output in Chapter 4, Circuit
Descriptions.
Bus Interface
n
A simple method to check the most fundamental functions of the in
terface is to send the standardized query message*IDN? and check
the response string.
-
-
-
Setup
Make sure you have access to a PC with GPIB capability.
–
Check that there is a program installed that can send simple
–
commands entered via the keyboard and that can receive and
display the response strings.
Connect the GPIB connectors of the counter and the PC by
–
means of a standard GPIB cable.
Set the address switches on the counter (the five rightmost
–
ones seen from the rear) so that their binary weight corre
sponds to the wanted decimal value between 0 and 30.
Send the command*IDN? to the counter and observe the re
–
sponse string. See the programming manual for more
information on the response format and contents.
You can also try the command*OPT? to get a listing of in
–
stalled options (except OCXO).
-
-
If you find a fault, continue with traditional troubleshooting tech
niques and replace defective circuits. Try to exercise the address/data
bus by writing small program loops. Look for stuck nodes with an
oscilloscope.
-
-
-
-
The PWM signal is converted to a DC voltage between 0 V and
4.98 V by integration, first in a passive RC network (R101, C103,
R102, C102 and then in an active integrator U103.
5-8 Troubleshooting
Page 41

Safety Inspection and Test After Repair
General Directives
After repair in the primary circuits, make sure that you have not re
duced the creepage distances and clearances.
Before soldering, bend component pins on the solder side of the
board. Replace insulating guards and plates.
Safety Components
Components in the primary circuits are important to the safety of the
instrument and may be replaced only by components obtained from
your local Fluke representative.
Checking the Protective Ground
Connection
Visually Check the correct connection and condition and measure
the resistance between the protective lead at the plug and the cabinet.
The resistance must not be more than 0.5 W. During measurement,
the power cord should be moved. Any variations in resistance show a
defect.
Safety Inspection and Test After Repair 5-9
Page 42

This page is intentionally left blank.
5-10 Safety Inspection and Test After Repair
Page 43

Chapter 6
Calibration
Adjustments
Page 44

Introduction
Required Test Equipment
Type Performance
DMM Acc. 0.02% / Res. 1mV
HF synthesizer 3300 MHz
Pulse generator 125 MHz/2nsrise/fall time
LF synthesizer 50 MHz / 20 Vpp
Oscilloscope 300 MHz / 2-channel
Passive probe 10:1, preferably 500 W (or well
FET probe 300 MHz
Power supply 12V/2A
Power splitter 50 W /4W
Feed-through termination 50 W
10 MHz reference 1x10
10 MHz reference 1x10-9*
BNC-BNC cables Different lengths
Screwdrivers Torx 10 & 20
Table 6-1 Required test equipment.
* For adjustment of PM9691 and PM9692 Oven Oscillators only.
Note: Only calibrated instruments should be used.
compensated 10 MW)
-7
J3
J4
J9
1 5
Power
Module
6 14
TP17, -7
J15
TP16, +15
Fuse
J10
+5V adjust
TP15, +5
J16
TP20, -5.2
J21
Load
Disconnected
Connected
TP22, +7
TP23, +5
TP21,+12V
Preparation
WARNING: Live parts and accessible terminals which
can be dangerous to life are always exposed inside
the unit when it is connected to line power. Use ex
treme caution when handling, testing, or adjusting
the counter.
Before beginning the calibration adjustments, power up the instru
ment andleave iton forat least30 minutesto letit reachnormal oper
ating temperature.
Power Supply
CAUTION: If you adjust the +5 V trimmer you have to
adjust the complete instrument.
Setup
n
Remove the protective cover above the power module.
–
WARNING: The heat sink inside the power module is
connected to line power.
Connect the counter to line power.
–
Switch on the counter.
–
Press PRESET, then press ENTER.
–
NOTE: The backlight must be switched on during the adjust
ment of the power module.
Fig. 6-1 Test points and trimmer for the Power Supply.
Adjustment
n
-
-
-
-
Connect the DMM to test point TP15 = +5V and GND, (see
–
Fig. 6-2).
Adjust the +5V trim potentiometer inside the power module
–
until the DMM reads +5.10 ± 0.01 V.
Check that the voltage between the test point TP23 = +5 V and
–
GND is +5.06 ± 0.03 V.
Check that the unregulated voltage from the power module at
–
test point TP16 = +15 V is about +18 V.
Check that the unregulated voltage from the power module at
–
test point TP17 = –7 V is about –8 V.
Reinstall the protective cover onto the power module.
–
6-2 Introduction
Page 45

Input Amplifier
P
Connect the other output from the power splitter to channel A
–
of the oscilloscope.
The instructions in this section are consecutive. Do not change a set
ting until you are told to do so, either in the text or in the tables.
Setup
n
Remove the screen shield before performing any adjustments
–
in the input amplifier.
Connect the counter to line power.
–
Switch on the counter.
–
Press PRESET, then press ENTER.
–
TP27
,SENSE
TP10, T R IG L E V E L COM P I
ZERO ADJ. COMP I
ZERO ADJ.COMP II
Sense Adj.
1
J2 U8
13
Li n A (R31)
Offset A (R33)
TP26, SENSE
TP11, TRIG LEVEL COM
-
PM6685
Pulse generator
Oscilloscope
Input A 50 W
Sensitivity Any level below 1 V
Amplitude 5Vppin 50 W
Period 2 ms, symmetrical
Time 200 ms/div
Setting: A 0.5 V/div, 50 W,DC
Setting: B 20 mV/div, 10:1 probe, DC
rms
Table 6-2
NOTE: The Pulse Generator with 50 ohm output impedance
should be set to 5 V
level recorded at the CRO A channel (equal to the in
put to the DUT) is 2.5 V
when loaded in 50 W, so that the
pp
, after going through the split
pp
-
-
ter.
NOTE: If you are using a 10 MW x10 CRO probe, ensure that
its compensation has been correctly adjusted, so that
incorrect observations of undershoots/overshoots are
not made.
Use the probe to connect channel B of the oscilloscope to
–
Pin 10 of U8 .
Adjust R31 = LIN A until both signals look as alike as possi
–
-
ble.
NOTE: The AC coupling will give the curve a slight tilt.
X1(C2)
X11 (C1)
Fig. 6-2 Test points and trimmers for the Input amplifiers.
Offset
–
Connect the DMM to Pin 10 of U8 and GND = screen, see
Fig. 6-2. Pin 1 is marked in the figure and is the middle pin on
the side closest to the rear of the unit. Alternatively you can
use one of the soldering pads of resistor R114 as a test pad, as
it is connected to Pin 10. This resistor is normally not
mounted.
Adjust R33 = OFFSET A until the DMM reads 0.0 ±0.2 mV.
–
Linearity
Setup
n
Press the Waveform Key once. (This step puts the instrument
–
into the correct mode so that it switches from x1 Attenuator to
x11 Attenuator when the sensitivity is adjusted above 2.8V.)
Connect the pulse generator to the A input of the counter via
–
the power splitter.
x1 Attenuator
Setup
n
PM6685
Pulse generator
Oscilloscope
Impedance 50 W
Sensitivity Any level below 1 V
Amplitude 5Vppin 50 W
Period 100 ms, symmetrical
Time 10 ms/div
Setting: A 0.5 V/div, 50 W,DC
Setting: B 20 mV/div, 10:1 probe, DC
rms
Table 6-3
Adjust C2 = X1 until both signals on the screen look as alike
–
as possible, without any overshoots or undershoots. The level
displayed on the CRO B channel for Pin 10 of U8 is approxi
mately 1.2 V
.
pp
x11 Attenuator
Setup
n
PM6685
Pulse generator
Oscilloscope
Table 6-4
Adjust C1 = X11 until both signals on the screen look as alike
–
as possible, without any overshoots or undershoots.
Impedance 50 W
Sensitivity Any level above 2.8 V
Amplitude 5V
Period
Time 10 ms/div
Setting: A 0.5 V/div, 50 W,DC
Setting: B 5 mV/div, 10:1 probe, DC
pp
100 ms, symmetrical
rms
-
Input Amplifier 6-3
Page 46

Observe that the level displayed on the CRO B channel for
1
U23
–
Pin 10 of U8 is now approximately 120 mV
the x11 Attenuator has been selected.
, indicating that
pp
Reference Oscillators
Trigger Levels
Setup
n
PM6685
Table 6-6
Disconnect all input signals to the counter.
–
Zero levels
n
Channel A
Connect the DMM to test points TP10 = TRIG LEVEL
–
COMP I and GND = screen.
Adjust R69 = ZERO ADJ COMP. I until the DMM reads
–
+0.95 ± 0.05 mV.
Connect the DMM to test points TP11 = TRIG LEVEL
–
COMP II and GND=screen.
Adjust R70 = ZERO ADJ COMP. II until the DMM reads
–
–0.95 ± 0.05 mV.
Impedance 50 W
Sensitivity 10 mV
rms
Sensitivity
Setup
n
Measure the DC voltage between test points TP26="–" and
–
TP27="+", (see Fig. 6-2).
Adjust R91 = SENSE until the DMM reads 10 ± 0.2 mV.
–
Offset
Setup
n
J27
Optional OCXO
Coarse adjust
Fine adjust
J24
U29
81
1
31
51
J23 J25
Optional oscillator
Standard oscillator
B2
Fig. 6-3 Trimmers for the reference oscillator frequency.
NOTE: The standard oscillator is always mounted in the unit,
even if an optional oscillator is installed. You set the
jumpers J23 and J25 to select the timebase source
that you want to use.
C115
PM6685
Signal generator
Table 6-5
Connect the Signal generator to the A input of the counter.
–
–
Press NULL on the counter.
Decrease the amlitude from the signal generator to
–
–28 dBm.
Adjust R33 = OFFSET A until the counter reads < ±100 Hz.
–
If this is not possible, adjust R91= SENSE until the counter
–
reads < ±100 Hz.
NOTE: Reinstall the screen shield after making these adjust
ments.
Impedance 50 W
Sensitivity 10 mV
Amplitude –18 dBm
Frequency 50 MHz
rms
Standard Oscillator
Setup
n
Connect the counter to line power.
–
Switch on the counter.
–
Press PRESET, then press ENTER.
–
Connect the 10 MHz reference to the A input of the counter.
–
Press CHECK, NULL, and CHECK again.
–
The adjustment should preferably be made at an ambient tempera
ture of +23 °C.
Adjustment
n
Adjust C115 = STD OSC ADJ, until the counter reads
-
–
10 MHz ± 5 Hz.
NOTE: Move the two jumpers J23 and J25 back to position
OPT if an optional oscillator is installed.
-
6-4 Reference Oscillators
Page 47

Oven-Controlled Oscillators (OCXO),
PM9691 & PM9692
PM9691 is adjusted to 10 MHz ± 0.2 Hz when manufactured,
PM9692 to 10 MHz ± 0.05 Hz, so there is no need to adjust the fre
quency directly after installation.
These oscillators, like any oscillator, change frequency because of
aging. Use the table in the User’s Handbook, Chapter 11, to calculate
when calibration is due. The complete specifications can be found in
the same manual, Chapter 12.
Required test equipment
Instrument Required specification Model
Counter with Rubidium
Reference
Table 6-7
Setup
n
Connect the counter to the line power.
–
Switch on the counter.
–
Set the counter to default settings (preset).
–
Make the adjustment at an ambient temperature of +23 °C, if possi
ble. The oscillator must have been operating continuously for 48
hours before an adjustment.
Connect the 10 MHz OUT socket of the counter to be adjusted
–
(rear panel) to the Input A of the PM6681R/PM6685R.
Set up the PM6681R/PM6685R:
–
Measuring time = 0.5 s
–
50 W input impedance
–
Frequency A measurements
–
10 MHz ± 0.01 Hz (Uncer
tainty £ 1x10
-9
)
-
PM6681R or
PM6685R
Coarse adjustment
Make this adjustment only if the trimmer range is insufficient to ad
just the oscillator.
–
-
-
Remove the tape from the DIP-switch.
Adjust the trimmer to its mid position (about 12 turns from ei
–
ther end position).
Read the frequency on the PM6681R/PM6685R.
(Nominal 10.000000 MHz).
If the frequency is too low, set the DIP-switches to the next
–
higher voltage range.
If the frequency is too high, set the DIP-switches to the
–
next lower voltage range.
Trimmer range (V) DIP switch number (1 = on, 0 = off)
12345678
2.6-3.4 00 01 00 00
3.2-3.9 01 01 10 00
3.5-4.3 10 01 10 00
4.0-4.7 10 11 11 00
4.1-5.0 10 10 11 10
Table 6-8
NOTE: There are also oscillators that do not have DIP
switches. If this is the case, then the trimmer potenti
ometer alone covers the whole adjustment range.
-
-
-
Adjustment
n
The oscillator has a voltage controlled adjustment range. This range
is divided into five fixed steps set via DIP switches, and a trimmer to
fine tune the control voltage.
Trimmer for fine tuning
Connector
Switches for coarse adj.
Fig. 6-4 Adjusting the optional oscillator frequency.
Normally the range of the trimmer should be sufficient to compen
sate for the aging that occurs during at least two years of operation.
Fine adjustment
Adjust the trimmer to better than 10 MHz ± 0.2 Hz (PM9691)
–
or 10 MHz ± 0.05 Hz (PM9692), i.e. ±20 resp. ±5 in the last
two digits on the PM6681R/PM6685R display.
If this adjustment is OK, reassemble the counter.
–
-
Reference Oscillators 6-5
Page 48

Other Options
HF Input 3.0 GHz , PM9624
J19
HF input
R61
TP1
TP9
GPIB Interface, PM9626B
BU103
U114
U115
U113
GPIB
U108
U109
BU101
U107
U106
Fig. 6-6 Trimmers for the GPIB interface.
Setup
n
Zero
U116
U111
U101
BU102
U103
Full Scale
Fig. 6-5 Test points and trimmers for the 3.0 GHz HF
NOTE: Before beginning any adjustments, the HF input must
Setup
n
PM6685
Signal gener
ator
Table 6-9
Connect the counter to line power.
–
Switch on the counter.
–
Press PRESET, then press ENTER.
–
Connect the signal generator to the HF input.
–
n
Adjustment
–
Turn the potentiometer R61, (see Fig. 6-5) fully counterclockwise.
Check that the GATE indicator stops blinking.
–
Turn R61 slowly clockwise until the GATE indicator starts
–
blinking.
The input frequency, 800 ± 25 MHz, will now be displayed.
To verify the 3.0 GHz HF input, a sweep frequency synthesizer is
needed. Also refer to Chapter 2 - Performance Check: Options,
Prescaler.
input.
have been in operation for at least one minute to let it
reach normal operating temperature.
Function FREQ C
Frequency 800 ± 25 MHz
-
Amplitude 5.9 ± 0.5 mV
rms
PM6685
LF synthe
sizer
Table 6-10
Connect the counter to line power.
–
Switch on the counter.
–
Press PRESET, then press ENTER.
–
Connect the DMM to the BNC output of the analog output.
–
Activate the analog output.
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Connect the LF synthesizer to the A input of the counter.
–
The counter should read 1000.0xxxxx Hz.
n
Adjust the trimmer ZERO (see Fig. 6-6) until the output volt
–
ageis0V±1mV.
Set the LF synthesizer to 999.90 Hz/1Vppsquare wave.
–
The counter should read 999.9xxxxx Hz.
Adjust the trimmer FULL SCALE (see figure 6-6) until the
–
output voltage is 4.980 V±3mV.
–
Set the LF synthesizr to 100.01 Hz/1Vppsquare wave.
The counter should read 100.0xxxxxx Hz.
Check that the output voltage is 500 mV±5mV.
–
-
Select AUX MENU.
Press DATA ENTRY UP/DOWN keys until the display
reads ANALOG OUT.
Press ENTER.
Press DATA ENTRY UP/DOWN keys to select ON.
Press ENTER.
Press DATA ENTRY UP/DOWN keys to until the display
reads 1.0
Press ENTER.
-3
V.
Adjustment
Input A 50 W / AC / Manual trigger levels
Amplitude 1V
Period 1000.01 Hz square wave
pp
-
6-6 Other Options
Page 49

Chapter 7
Replacement Parts
Page 50

Introduction
Standard Parts
Electrical and mechanical replacement parts can be obtained through
your local Fluke organization or representative. However, many of the
standard components can be obtained from other local suppliers. Before
purchasing or ordering replacement parts, check the parts list for part
number, value, tolerance, rating, and description.
If the value of the physical component differs from what is described in
the parts list, you should always replace the part with the same value as
originally mounted.
Standard parts are unmarked or marked with an ‘S’ in the P column of
the parts lists.
Special Parts
In addition to standard electronic components, the following special
components are used:
Components that are manufactured or selected by the manufac
–
turer to meet specific performance requirements.
Components that are important for the safety of the instrument.
–
Both types of components may be replaced only by components ob
tained through your local Fluke organization.
NOTE: Physical size and shape of a component may af
fect the performance of the instrument, particularly at
high frequencies. Always use direct replacements un
less it is known that a substitute will not degrade the
performance of the instrument.
These parts are ‘Recommended Replacement Parts’ and are marked
with an ‘R’ in the P column of the parts lists.
Components marked with a ‘P’ in the P column are ‘Production items’
not kept in replacement parts stock. These items can be ordered, but the
delivery time is longer than for normal replacement parts.
-
-
-
-
7.2 Replacement Parts, Introduction
Page 51

Mechanical Parts
Pos Description Part Number P
PCA 1, Main board 4031 100 65420 P
PCA 2, Front board 4031 100 48250 P
13 Stand-off, plastic 5322 532 12746 R
18 Textplate kit 4031 100 62430 R
20 Rubber keypad 4031 100 62720 R
22 Cover and Front panel 4031 100 49570 R
25 Rear panel 5322 447 31085 P
34 Profile-support 5322 460 60542 P
35 Profile-support 4031 100 53210 P
38 Shield cover 5322 447 91931 P
39 Shield cover 5322 462 50459 P
50 Rearfoot, cabinet, m-90 5322 462 41719 R
52 Bottom foot, cabinet, m-90 5322 462 41554 R
53 Bracket, cabinet 5322 401 11422 R
54 Spring, cabinet 5322 492 63808 R
Pos Description Part Number P
56 Rubber foot, sj-5018 black 5322 462 44434 R
58 Tilting support 5322 401 11471 R
62 Coax connector 5322 267 10004 S
63 Coax connector 5322 265 10264 R
64 Soldering tag, 9.6X15/15 ms fs 5322 290 30318 S
67 Toroid core 30nh rcc9/6/3 4c65 violet 5322 526 10545 P
68 Bottom shield 5322 447 91829 P
70 BNC holder 4031 100 48830 P
84 Mains filter 1a fs3514-1/07 5322 121 42352 R
90 PCA guide for prescaler 5322 401 11347 P
92 Stand-off nut M3x14 4031 100 48800 P
100 Washer, 4.0X10x2 pa6-6 5322 532 52364 P
102 Washer, 9.5X13x2.3 4822 532 10222 P
104 BNC plate, 25.4X25.4 5322 466 82868 P
110 Insulate plate 5322 466 61932 P
122 Shielding strip 610mm 99-210
self-adhesive
150 Screw, mrt-kombi 3x06, stfz 4822 502 11658 P
152 Screw, mrt-kombi 3x08, stfz 5322 502 21489 P
156 Screw, mrt-kombi 4x16, stfz 5322 502 21491 P
160 Screw, mft-tt 3x08 stfzb tx 4822 502 11713 P
5322 466 62077 P
Replacement Parts, Mechanical Parts 7-3
Page 52

Pos Description Part Number P
161 Screw, mfx-tt 3x08 st fz poz 4822 502 11713 P
164 Screw, mft-tt 4x12 stfzb tx 5322 502 13553 P
166 Screw, mrt-tt 3x08 stfzb tx 4822 502 11691 P
168 Screw, mrt-tt 4x16 stfzb tx 5322 502 13552 P
172 Screw, mft 4x10 st fzb, tx 5322 502 13641 P
176 Screw, rtk-ko st3.5X10 stfz 5322 502 30703 P
180 Spring washer, kba 3.2 St fz din137 4822 530 80173 P
Pos Description Part Number P
182 Spring washer, kba 4.3 St fz din137 4822 530 80076 P
184 Lock washer, yt4.3 St fz din6798a 4822 530 80083 P
190 Nut, m6m 04 st fzb 4822 505 10326 P
200 Receptacle, 140825-2, 2.8X0.8 5322 268 10275 P
201 Protect sleeve 2.8mm N 94610 transppa5322 321 40117 P
202 Cable clip, reel srb-2.5T-m4 5322 358 50107 P
7-4 Replacement Parts, Mechanical Parts
Page 53

80
Lug bent 15° to lock
Replacement Parts, Mechanical Parts 7-5
Page 54

Main Board
Pos Description Part No. P
227 CHOKE 4S2 3.5X6MM BANDAD 80ohm at 100MHz 5322 157 61928 S
B1 CRYSTAL 12.000 MHz SMD MA-406 2422 543 01353 P
B2 CRYSTAL 10 MHz HC-49U/13 5322 242 82118 P
C1 CAPACITOR-TRIM 0.5-2 pF 300V 5322 124 80335 S
C10 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C100 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C101 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C102 CAPACITOR 33 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15339 S
C103 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C104 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C105 CAPACITOR 6.80 UF 20% 16V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 10687 R
C106 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C107 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C108 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C109 CAPACITOR 22 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 5322 122 32658 S
C11 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C110 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C111 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20%6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C112 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C113 CAPACITOR 82 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15829 S
C114 CAPACITOR 100 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15101 S
C115 CAPACITOR-TRIM 3-10 pF TZBX4Z100BB110 5322 125 50306 R
C116 CAPACITOR 47 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15479 S
C117 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C118 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C119 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C12 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C120 CAPACITOR 10 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15109 S
C121 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C122 CAPACITOR 680 pF 20% 63V NP0 1206 4822 126 12075 S
C123 CAPACITOR 47 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15479 S
C124 CAPACITOR 100nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C125 CAPACITOR 2.20 UF 20% 6.3V 3.2X1.6 MOLD 5322 124 10685 S
C126 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C127 CAPACITOR 1 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34123 S
C128 CAPACITOR 82 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15829 S
C129 CAPACITOR 6.8 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15688 S
C13 CAPACITOR 47 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15479 S
C130 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C131 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C132 CAPACITOR 2.20 UF 20% 6.3V 3.2X1.6 MOLD 5322 124 10685 S
C133 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C134 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C135 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C136 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C138 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C139 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C14 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C140 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C141 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C142 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C143 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C145 CAPACITOR 390 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 4822 122 32636 S
C146 CAPACITOR 10 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15109 S
C148 CAPACITOR 470 pF 1% 63V NP0 0805 5322 126 14051 S
C149 CAPACITOR 22 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 5322 122 32658 S
C15 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C150 CAPACITOR 390 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 4822 122 32636 S
C151 CAPACITOR 10 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15109 S
C153 CAPACITOR 470 pF 1% 63V NP0 0805 5322 126 14051 S
C154 CAPACITOR 22 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 5322 122 32658 S
Pos Description Part No. P
C155 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C156 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C157 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C158 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C159 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C16 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C160 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C161 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C162 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C163 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C164 CAPACITOR 2.20 UF 20%6.3V 3.2X1.6 MOLD 5322 124 10685 S
C165 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C166 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C167 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C168 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C169 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C17 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C170 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C171 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C172 CAPACITOR 2.20 UF 20% 6.3V 3.2X1.6 MOLD 5322 124 10685 S
C173 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C174 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C175 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C176 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C177 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C178 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C179 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C18 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C180 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C181 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C182 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C183 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C184 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C185 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C186 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C19 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C2 CAPACITOR-TRIM 2.0-18 pF 300V 2222 809 05217 R
C20 CAPACITOR 1 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34123 S
C21 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C22 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C23 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C24 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C25 CAPACITOR 10 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15109 S
C26 CAPACITOR 10 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15109 S
C27 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C28 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C29 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C3 CAPACITOR 22 nF 10% 200V X7R 1206 5322 126 14081 R
C30 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C31 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C32 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C33 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C34 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C35 CAPACITOR 470 nF 10% 25V X7R 1210 4822 126 12549 S
C36 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C37 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C38 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C39 CAPACITOR 6.80 UF 20% 16V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 10687 R
C4 CAPACITOR 3.3 pF ±0.25pF 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15338 S
C40 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C41 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
7-6 Replacement Parts, Main Board
Page 55

Pos Description Part No. P
C42 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C43 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C44 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C45 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C46 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C47 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C48 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C49 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C5 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C50 CAPACITOR 2.20 UF 20% 6.3V 3.2X1.6 MOLD 5322 124 10685 S
C51 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C52 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C53 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C54 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C55 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C56 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C57 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C58 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C59 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C6 CAPACITOR 1 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34123 S
C60 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C61 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C62 CAPACITOR 2.20 nF PME289MA4220MR04 5322 121 43756 S
C63 CAPACITOR 2.20 nF PME289MA4220MR04 5322 121 43756 S
C64 CAPACITOR 270 µF 20% SMG 400V 25X45 5322 124 80334 S
C65 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 250V 2222 336 20104 S
C66 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C67 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C68 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C69 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C7 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C70 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C71 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C72 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C73 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C74 CAPACITOR 68 µF 20% 6.3V SOLID AL 5322 124 10455 S
C75 CAPACITOR 33 µF 20% 63V RADIAL 2M 6.3x11 2222 037 90074 S
C76 CAPACITOR 33 µF 20% 63V RADIAL 2M 6.3x11 2222 037 90074 S
C77 CAPACITOR 10 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15109 S
C78 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C79 CAPACITOR 33 µF 20% 63V RADIAL 2M 6.3x11 2222 037 90074 S
C8 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C80 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C81 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C82 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C83 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C85 CAPACITOR 22 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 5322 122 32658 S
C86 CAPACITOR 22 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 5322 122 32658 S
C87 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C88 CAPACITOR 2.20 UF 20% 6.3V 3.2X1.6 MOLD 5322 124 10685 S
C89 CAPACITOR 100 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15101 S
C9 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C90 CAPACITOR 100 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 2222 861 15101 S
C91 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C92 CAPACITOR 15 UF 20% 6.3V 6.0X3.2 MOLD 5322 124 11418 S
C93 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C94 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C95 CAPACITOR 100 nF 20% 25V X7R 0805 5322 126 13638 S
C96 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C97 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C98 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C99 CAPACITOR 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
D1 DIODE 0.10A BAT18 35V 1PF SOT23 5322 130 32076 S
D10 DIODE 1A SB140 40V DO41 5322 130 81917 S
Pos Description Part No. P
D12 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D13 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D14 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D15 DIODE BYD17G 400V 1.5A SOD87 9338 122 40701 R
D16 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D17 DIODE BYD17G 400V 1.5A SOD87 9338 122 40701 R
D18 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D19 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D2 DIODE 0.10A BAT18 35V 1PF SOT23 5322 130 32076 S
D21 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D22 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D23 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D24 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D25 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D26 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D3 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D4 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D5 DIODE 0.10A BAV99 SOT23 5322 130 34337 S
D6 DIODE 1A 1N4003/200 DO41 4822 130 31878 S
D7 DIODE 1A SB140 40V DO41 5322 130 81917 S
D8 DIODE 1A SB140 40V DO41 5322 130 81917 S
D9 BRIDGE RECTIFIER 2KBP08 2A 800V 5322 130 50474 S
F1 FUSE HOLDER 011 656 5X20mm 4822 256 30139 S
F1 FUSE 1.6A 5X20 T FST034.3119 4822 253 30024 S
J1 SOLDERING LUG 10.0X15/21 CU SN 4031 100 58390 P
J1 CONNECTOR-COAX BNC 5322 267 10004 S
J10 FLAT PIN 2.8mm E184/8 LESA SN BAND 5322 290 34064 S
J15 CONNECTOR 2 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 265 44074 S
J15 CONNECTOR 2POL F095 JUMPER GREY 5322 263 50101 S
J16 CONNECTOR 2POL F095 JUMPER GREY 5322 263 50101 S
J16 CONNECTOR 3 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 290 60445 S
J17 CABLE ASSY 5322 321 60669 R
J18 CONNECTOR 40 POL LOW PROFILE HEADER 5322 265 41051 S
J19 CONNECTOR 16 POL TMH-108-01-L-DW 5322 265 41013 S
J21 CONNECTOR 2POL F095 JUMPER GREY 5322 263 50101 S
J21 CONNECTOR 3 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 290 60445 S
J22 CONNECTOR 2POL F095 JUMPER GREY 5322 263 50101 S
J22 CONNECTOR 3 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 290 60445 S
J23 CONNECTOR 2POL F095 JUMPER GREY 5322 263 50101 S
J23 CONNECTOR 3 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 290 60445 S
J24 CONNECTOR 10 POL 22-03-2101 4030-10A 5322 265 64028 S
J25 CONNECTOR 2POL F095 JUMPER GREY 5322 263 50101 S
J25 CONNECTOR 3 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 290 60445 S
J29 CONNECTOR 2POL F095 JUMPER GREY 5322 263 50101 S
J29 CONNECTOR 3 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 290 60445 S
J3 FLAT PIN 2.8mm E184/8 LESA SN BAND 5322 290 34064 S
J30 CONNECTOR 2POL F095 JUMPER GREY 5322 263 50101 S
J30 CONNECTOR 3 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 290 60445 S
J32 CONNECTOR 20 POL LOW PROFILE HEADER 5322 265 51296 S
J4 FLAT PIN 2.8mm E184/8 LESA SN BAND 5322 290 34064 S
J5 FLAT PIN 2.8mm E184/8 LESA SN BAND 5322 290 34064 S
J6 FLAT PIN 2.8mm E184/8 LESA SN BAND 5322 290 34064 S
J7 CONNECTOR 2 POL F095 SINGLE ROW 5322 265 44074 S
J9 FLAT PIN 2.8mm E184/8 LESA SN BAND 5322 290 34064 S
K1 RELAY REED 5V PRMA-15157-3790 5322 280 20489 R
K2 RELAY REED 5V PRMA-15157-3790 5322 280 20489 R
K3 RELAY REED 5V PRMA-15157-3790 5322 280 20489 R
K4 RELAY TQ2-5 SV/1A 2pol vx 14X9X5m 5322 280 20514 R
K5 RELAY 2p vx V23042-A1003-B101 (alt.A2303) 5322 280 60557 R
L1 CHOKE 220 UH 10% NL453232T-221K 5322 157 61918 S
L10 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L11 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
Replacement Parts, Main Board 7-7
Page 56

Pos Description Part No. P
L12 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L13 CHOKE 4.70µH 5% LQH1N4R7J 2422 535 94048 P
L14 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L15 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L16 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L17 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L18 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L19 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L2 CHOKE 4S2 3.5X6MM BANDAD 80ohm at 100MHz 5322 157 61928 P
L20 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L21 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L22 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L23 CHOKE 4S2 3.5X6MM BANDAD 80ohm at 100MHz 5322 157 61928 P
L24 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L25 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L3 CHOKE 4S2 3.5X6MM BANDAD 80ohm at 100MHz 5322 157 61928 S
L4 FILTER-EMI BLM21A102SPT Z=1Kohm 0.2A
R=0.6ohm
L5 CHOKE 4S2 3.5X6MM BANDAD 80ohm at 100MHz 5322 157 61928 S
L6 CHOKE 10mH B82722-J2102-N1 1A 5322 157 70143 S
L7 CHOKE 10.00µH NEWPORT 18R103 2422 536 00061 P
L8 CHOKE 10.00µH NEWPORT 18R103 2422 536 00061 P
L9 CHOKE 33µH TSL0809-330K1R2 5322 157 53568 S
Q1 TRANSISTOR BF513 .03A20V SOT23 4822 130 60686 S
Q10 TRANSISTOR 0.5A BC807-25 45V SOT23 5322 130 60845 S
Q11 TRANSISTOR 0.5A BC817-25 45V SOT23 4822 130 42804 S
Q12 TRANSISTOR BC847B .1A45V SOT23 4822 130 60511 S
Q13 TRANSISTOR BFG97 0.1A 15V SO223 4822 130 63069 S
Q14 TRANSISTOR BC847B .1A45V SOT23 4822 130 60511 S
Q15 TRANSISTOR BC857B .1A45V SOT23 5322 130 60508 S
Q16 TRANSISTOR BC847B .1A45V SOT23 4822 130 60511 S
Q17 TRANSISTOR 0.5A BC817-25 45V SOT23 4822 130 42804 S
Q2 TRANSISTOR 25 MA BFR92A 20V SOT23 5322 130 60647 S
Q24 TRANSI-NPN SMD BFG16A SOT223 1.5GHz 1W 9340 022 10701 R
Q27 TRANSI-NPN SMD BFG16A SOT223 1.5GHz 1W 9340 022 10701 R
Q28 TRANSISTOR BFT92 25MA 15V SOT23 5322 130 44711 S
Q29 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q3 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q30 TRANSISTOR BFT92 25MA 15V SOT23 5322 130 44711 S
Q31 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q32 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q33 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q34 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q35 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q36 TRANSISTOR BSR12 0.1A 15V SOT23 5322 130 44743 S
Q37 TRANSISTOR BSR12 0.1A 15V SOT23 5322 130 44743 S
Q38 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q39 TRANSISTOR BFS17 .05A 15V SOT23 5322 130 40781 S
Q4 TRANSI-HF N SMD BFR93A 35mA 12V SOT23 5322 130 60705 S
Q5 TRANSISTOR BCP51 1.5A 45V SOT223 5322 130 62639 S
Q6 TRANSISTOR BC847B .1A45V SOT23 4822 130 60511 S
Q7 TRANSISTOR 0.5A BC807-25 45V SOT23 5322 130 60845 S
R1 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80448 S
R10 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R100 RESISTOR 27 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 4031 002 27090 S
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
2422 549 43133 P
Pos Description Part No. P
R101 RESISTOR 4.7 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 54702 S
R105 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R106 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R107 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R108 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R109 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R11 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R110 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R111 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R112 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R113 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R115 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R116 RESISTOR 15.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 82261 S
R117 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R118 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R119 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R12 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R121 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R122 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R123 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R124 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R125 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R126 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R127 RESISTOR 1.00 Mohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10105 S
R128 RESISTOR 1.50 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51502 S
R129 RESISTOR 470 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 54701 S
R13 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R130 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R131 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R132 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R133 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R134 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R135 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R136 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R137 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R138 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R139 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R14 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R140 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R141 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R142 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R143 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R144 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R145 RESISTOR 330 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53301 S
R146 RESISTOR 15.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 82261 S
R147 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R148 THERMISTOR 16.0 W 20% 3.5A S236/16 5322 116 30457 S
R149 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R15 RESISTOR 150 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51501 S
R150 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R151 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R152 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R153 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R154 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R155 RESISTOR 330 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53301 S
R158 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12506 S
R159 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R16 RESISTOR 150 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51501 S
R160 RESISTOR 390 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53901 S
R161 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R162 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R163 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R164 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R165 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
7-8 Replacement Parts, Main Board
Page 57

Pos Description Part No. P
R166 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R167 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R168 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R169 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R17 RESISTOR 27.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 82262 S
R170 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R171 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R172 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R173 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R174 RESISTOR 330 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53301 S
R175 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R176 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R177 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R178 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R179 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R18 RESISTOR 68.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 56803 S
R180 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R181 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R182 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R183 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R184 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R185 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R186 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R187 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R188 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R189 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R19 RESISTOR 22.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52203 S
R190 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R191 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R193 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R194 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R195 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R196 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12506 S
R197 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12506 S
R198 RESISTOR 4.70 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 54702 S
R199 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R2 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51001 S
R20 RESISTOR 8.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10822 S
R200 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R201 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R202 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R203 RESISTOR 560 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10561 S
R204 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R205 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R206 RESISTOR 5.60 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10562 S
R207 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R209 RESISTOR 560 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10561 S
R21 RESISTOR 15.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10159 S
R211 RESISTOR 1.00 Mohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10105 S
R217 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R218 RESISTOR 680 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 56801 S
R219 RESISTOR 330 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 117 10969 S
R22 RESISTOR 220 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52204 S
R220 SENSOR-TEMP KTY82/120 5322 130 10682 S
R222 RESISTOR 180 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51804 S
R23 RESISTOR 220 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52204 S
R230 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R233 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R235 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12506 S
R24 RESISTOR 470 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80447 S
R241 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R242 RESISTOR 680 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 56801 S
R243 RESISTOR 18.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 117 10034 S
R244 RESISTOR 82 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10829 S
Pos Description Part No. P
R245 RESISTOR 3.90 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53902 S
R247 RESISTOR 820 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 82264 S
R248 RESISTOR 680 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 56801 S
R249 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R25 RESISTOR 470 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80447 S
R251 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R252 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51001 S
R253 RESISTOR 560 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10561 S
R254 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R255 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R258 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R259 RESISTOR 680 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 56801 S
R26 RESISTOR 470 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80447 S
R260 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R261 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R262 RESISTOR 10.0 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10109 S
R263 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R264 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R265 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R266 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R267 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R268 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R269 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R27 RESISTOR 470 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80447 S
R270 RESISTOR 8.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10822 S
R271 RESISTOR 820 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 82264 S
R272 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R273 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R274 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R275 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R276 RESISTOR 33.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53303 S
R277 RESISTOR 33.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53303 S
R278 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R279 RESISTOR 8.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10822 S
R28 RESISTOR 470 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80447 S
R280 RESISTOR 820 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 82264 S
R281 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R282 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R283 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R284 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R285 RESISTOR 33.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53303 S
R286 RESISTOR 33.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53303 S
R287 RESISTOR 0 ohm JUMPER RC-01 1206 4822 051 10008 S
R288 RESISTOR 68 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10689 S
R288 RESISTOR 33.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10339 S
R289 RESISTOR 220 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 4031 002 22010 S
R29 RESISTOR 22.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52203 S
R290 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R291 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R292 RESISTOR 0 ohm JUMPER RC-01 1206 4822 051 10008 S
R293 RESISTOR 330 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53301 S
R294 RESISTOR 27 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 4031 002 27090 S
R295 RESISTOR 270 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10271 S
R296 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R297 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R298 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R3 RESISTOR 470 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80447 S
R30 RESISTOR 470 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80447 S
R300 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R301 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R302 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R303 RESISTOR 27 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 4031 002 27090 S
R304 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12506 S
R305 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
Replacement Parts, Main Board 7-9
Page 58

Pos Description Part No. P
R306 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R307 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R309 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R31 POTENTIOMETER 100 kohm 3304X-1-104 5322 101 10841 S
R310 RESISTOR 27 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 4031 002 27090 S
R311 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R312 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R313 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R314 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12506 S
R315 RESISTOR 820 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 82264 S
R316 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R317 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R318 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R319 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R32 RESISTOR 470 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80447 S
R320 RESISTOR 56 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10569 S
R321 RESISTOR 10.0 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10109 S
R322 RESISTOR 10.0 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10109 S
R323 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R325 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R326 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R327 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R328 RESISTOR 27 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 4031 002 27090 S
R329 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12506 S
R33 POTENTIOMETER 10 kohm 3304X-1-103 5322 100 11143 S
R330 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R331 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R34 RESISTOR 18.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 117 10034 S
R35 RESISTOR 470 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 54701 S
R36 RESISTOR 470 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 54701 S
R37 RESISTOR 1.50 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51502 S
R38 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R39 RESISTOR 10 MOHM 10% 0.25W RC-01 1206 4822 051 10106 S
R4 RESISTOR 220 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52204 S
R40 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R41 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R42 RESISTOR 15.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10159 S
R43 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R44 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80448 S
R45 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R46 RESISTOR 150 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51501 S
R47 RESISTOR 150 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51501 S
R48 RESISTOR 82 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10829 S
R49 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R5 RESISTOR 220 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52204 S
R50 RESISTOR 8.2 ohm 10% 0.25W RC-01 1206 4822 051 10828 S
R51 RESISTOR 2.70 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52702 S
R53 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R54 RESISTOR 560 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10561 S
R55 RESISTOR 560 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10561 S
R56 RESISTOR 390 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53901 S
R57 RESISTOR 15.0 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 82261 S
R58 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R6 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80448 S
R60 RESISTOR 4.70 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 54702 S
R61 RESISTOR 220.0 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52201 S
R63 RESISTOR 6.80 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10682 S
R64 RESISTOR 1.00 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R65 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R66 RESISTOR 4.70 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 54702 S
R67 RESISTOR 2.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 52202 S
R69 POTENTIOMETER 100 kohm 3304X-1-104 5322 101 10841 S
R7 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R70 POTENTIOMETER 100 kohm 3304X-1-104 5322 101 10841 S
Pos Description Part No. P
R71 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R72 RESISTOR 100 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R73 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R74 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R75 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R76 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R77 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R78 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R79 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R8 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R80 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R81 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R82 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R83 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R84 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R85 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R86 RESISTOR 10.0 kohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R87 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R88 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R89 RESISTOR 68 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10689 S
R9 RESISTOR 120 ohm 1% 0.125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10121 S
R90 RESISTOR 68 ohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10689 S
R91 POTENTIOMETER 100ohm CVR-4A-101 5322 101 10989 S
R92 RESISTOR 8.20 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10822 S
R93 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R94 RESISTOR 47 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12505 S
R95 RESISTOR 3.30 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53302 S
R96 RESISTOR 1.80 kohm 1% .125W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 10182 S
R98 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
R99 RESISTOR 100 ohm 1% 0.1W 100PPM 0805 5322 117 12497 S
U1 IC-OP AMP CA3140AM CA3140 AM BIMOS SO8 9322 114 39682 R
U10 IC-ANA TL7705BCD SMD LOW VOLT DETECT 5322 209 90426 R
U11 IC MICROP N80C196KB10 5322 209 52203 R
U12 IC-PROM 24LC16B 16kBIT I2C SMD SO8 9322 186 14682 P
U13 IC PC74HC574T SO20 4822 209 60451 S
U14 IC PC74HC573T SO20 5322 209 60424 S
U15 IC PC74HC02T SO-14 5322 209 71563 S
U16 IC PC74HC573T SO20 5322 209 60424 S
U17 IC PC74HC573T SO20 5322 209 60424 S
U18 IC PC74HC21T SO14 5322 209 60437 S
U19 IC PC74HC00T SO14 5322 209 71802 S
U2 IC PC74HC574T SO20 4822 209 60451 S
U20 IC PC74HC138T SO16 5322 209 73178 S
U21 IC NE532D DUAL SO-8 5322 209 71553 R
U22 IC-SRAM TC55257DFL-85L SOP28 32Kx8 9322 106 65682 R
U23 IC-PROM PM6685 27C512 5322 209 31776 P
U23 IC SOCKET 32 POL P/N 213-032-602 5322 255 41141 S
U24 IC PC74HC32T SO14 4822 209 63475 S
U25 IC PC74HC32T SO14 4822 209 63475 S
U26 IC-CMOS 74HC10 SO14 SO-14 9337 142 80653 S
U27 IC-DIG ECL 100331QC 3XDFLIP-FLOP PCC28 5322 209 33604 S
U28 IC-BUS TRANSCEIV 75ALS176D SO-8 SMD 5322 209 33171 R
U29 IC-ASIC 5322 209 90513 R
U3 IC PC74HC4353T SO20 4822 209 62805 S
U30 IC PC74HC00T SO14 5322 209 71802 S
U31 IC-OMV ADC 10BIT ADC1061C1WM SO20 9322 187 55682 R
U32 IC PC74HC573T SO20 5322 209 60424 S
U34 IC PC74HC00T SO14 5322 209 71802 S
U35 IC-OMV ADC 10BIT ADC1061C1WM SO20 9322 187 55682 R
U36 IC PC74HC573T SO20 5322 209 60424 S
U38 IC NE532D DUAL SO-8 5322 209 71553 S
U39 POWER MODULE 5322 693 22828 R
U4 IC 8 BIT PM7528HPC PLCC20 4822 209 62803 S
U40 IC HEF4013BT SO14 5322 209 14477 S
7-10 Replacement Parts, Main Board
Page 59

Pos Description Part No. P
U41 INSULAT.PLATEP TO220 CLIP Sil-Pad 400AC 5322 466 61813 P
U41 CLAMP TO220 5322 401 11257 P
U41 IC 12V LM2940CT-12 TO220 4822 209 62085 S
U43 INSULAT.PLATEP TO220 CLIP Sil-Pad 400AC 5322 466 61813 S
U43 CLAMP TO220 5322 401 11257 P
U43 IC 1.50 A LM337T TO-220 5322 209 81236 S
U44 IC-CMOS 74HC125 SMD SO14 9337 569 90701 S
U5 IC NE532D DUAL SO-8 5322 209 71553 S
U50 IC-COMP MAX961 SO8 4.5ns 9322 194 34682 R
U6 IC NE532D DUAL SO-8 5322 209 71553 S
U7 IC NE532D DUAL SO-8 5322 209 71553 S
U8 IC-COMP AD96687BP PLCC20 4822 201 62795 R
U9 IC-DIG ECLIPS MC10E104 4822 209 31775 R
Replacement Parts, Main Board 7-11
Page 60

Front Board
Pos Description Part Number P
5 Connector row, SG0.25x100x6.0x3.0 5322 267 70294 R
7 LCD Display 5322 214 91033 R
10 LCD bezel 4031 100 62820 R
11 Backlight-LED 5322 130 82201 R
14 Window LCD 5322 381 11136 P
16 LED spacer, LEDS1E-3-01 for led 5322 255 41228 P
20 Rubber keypad 4031 100 62720 R
32 Screw, RX-PT Z 2-28X8 FZB 4822 502 30081 P
C201 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R, 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C202 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R, 0805 5322 122 34098 S
D201 LED 3 mm HLMP-1300 red 5322 130 81921 R
Pos Description Part Number P
D202 LED 3mm Yellow 590nm
4-8MCD/10mA
P204 Connector 40 POL TMH-120-01-L-DW 5322 265 51295 P
R201 Resistor 220 k 1% .125W 100PPM
1206
R204 Resistor, 10.0 W 1% 0.125W 1206 4822 051 10109 S
R205 Resistor, 10.0 W 1% 0.125W 1206 4822 051 10109 S
R206 Resistor, 10.0 W 1% 0.125W 1206 4822 051 10109 S
R207 Resistor, 10.0 W 1% 0.125W 1206 4822 051 10109 S
U201 IC, PCF8576T, VSO56 5322 209 11129 R
U202 IC, PCF8576T, VSO56 5322 209 11129 R
TORQU E 3 Nc m
TIGHTEN THIS SCREW FIRST TO GUIDE LCD HOLDER
4822 130 30953 R
4822 051 52204 S
ORIENTATION MARK FOR LCD
7-12 Replacement Parts, Front Board
Page 61

GPIB Interface (PM9626B)
Pos Description Part Number P
Connector, KC-79-35 5322 267 10004 S
IC-Socket, 40pin, DIL 5322 255 44217 S
Lock Washer, YT3.2 ST FZ DIN6798A 4822 530 80082 P
Screw, MRT-KOMBI 3X08, STFZ 5322 502 21489 P
Screw, MRT-KOMBI 3X10, STFZ 5322 502 21644 P
Spring Washer, KBA 3.2 ST FZ
DIN137
BU101 Cable Assy 5322 321 61341 P
BU103 Connector 24pin
57LE-20240-77OOD35G
C101 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C102 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C103 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C104 Capacitor 220 pF 5% 50V NP0 0805 4822 122 33575 S
C105 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V X7R 1206 4822 122 33496 S
C106 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C107 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C108 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C109 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C110 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C111 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C112 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C113 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C114 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C115 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C116 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C117 Capacitor 10 nF 20% 50V X7R 0805 5322 122 34098 S
C118 Capacitor 68 mF 20% 6.3V SOLID AL 5322 124 10455 S
IC101 IC PC74HC32T SO14 4822 209 63475 S
IC103 IC NE532D DUAL SO-8 5322 209 71553 R
IC106 IC PC74HC00T SO14 5322 209 71802 S
IC107 IC PC74HC573T SO20 5322 209 60424 S
IC108 IC PC74HC573T SO20 5322 209 60424 S
IC109 IC socket 32pin P/N 213-032-602 5322 255 41141 S
IC109 IC-PROM PM9626B 5322 209 51853 R
IC111 IC-SRAM TC55257DFL-85L SOP28
32Kx8
IC113 IC-DIG UPD7210D IEC BUS GPIB
CONTROLLER
IC114 IC SN75160AN 5322 209 81807 R
IC115 IC SN75161AN 5322 209 81842 R
IC116 IC PC74HC573T SO20 5322 209 60424 S
IC117 IC PC74HC86T SO-14 5322 209 71562 S
R101 Resistor 47 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80446 S
R102 Resistor 47 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 5322 116 80446 S
R103 Resistor 4.7 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 54702 S
R104 Potentiometer 1k 3304X-1-102E 5322 101 11095 S
R105 Resistor 10 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51003 S
R106 Resistor 330 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53301 S
R107 Potentiometer 10 k 25% 0.1W
3304X-1-103
R108 Resistor 3.3 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 53302 S
R109 Resistor 100 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51001 S
R110 Resistor 100 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51001 S
R111 Resistor1k1%1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51002 S
R112 Resistor 100 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R113 Resistor 100 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
4822 530 80173 P
5322 267 60148 P
9322 106 65682 R
9322 023 60682 R
5322 100 11143 S
Pos Description Part Number P
R114 Resistor 100 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R115 Resistor 100 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R116 Resistor 100 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
R117 Resistor 100 k 1% 1/8W 100PPM 1206 4822 051 51004 S
SK101 DIP switch 6-p 206-6 RAST 5322 277 21125 R
Replacement Parts, GPIB Interface (PM9626B) 7-13
Page 62

This page is intentionally left blank.
7-14 Replacement Parts, GPIB Interface (PM9626B)
Page 63

Chapter 8
Drawings & Diagrams
Page 64

How to read the diagrams
Inside the symbol, at the top is an abbreviated description of the cir
cuit’s function.
-
This chapter contains circuit diagrams and component layout.
Each diagram has been completed with lists of the ICs used in the
unit. This list indicates the connections that are not shown in the dia
gram, such as GND and supply voltages.
Signals
The signals in these units are named after what they do, e.g.,
LEAD-EDGE isused ascontrol currentto the leading edge circuits.
Two different types of arrows are used to mark references for contin
ued connection somewhere else in the diagram.
This arrowis usedif thereference isdirected toa point
located on the same page.
A1
This arrowis usedif thereference isdirected toa point
/1.A1
located on another page. The example means that the
point is on sheet 1, coordinate A1.
Circuit symbols
The circuit diagrams are computer drawn. The symbols conform to
the IEC standards. These symbols are designed to be logical and easy
to read.
Pin numbers are written outside the symbol and, if it is a complex cir
cuit, the pin functions are written inside.
-
A small circle on a pin indicates that the input/output inverts the sig
nal.
The component name is written below the symbol.
The signal flow through the circuit is always from left to right.
-
-
Resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors
-
and other components.
These components are similar to the old fashioned, hand-drawn sym
bols.
They have their component number above and their value or compo
nent name below.
A resistor contained in a resistor network has a frame drawn around it
and one of the pin numbers is written to the left or below it.
-
-
Component numbers
“R305" is a typical component number. The ”R" indicates that it is a
resistor,"3" that it is positioned on the “unit 3", and 05 that it is the
fifth resistor in the component list for that unit.
The component number is written above the symbol.
Drawings & Diagrams 8-2
Page 65

This page is intentionally left blank.
Drawings & Diagrams 8-3
Page 66

Main PCB, Component layout
8-4 Drawings & Diagrams
Top View
Page 67

Control Logic, PCB 1, sheet 1(5)
+5CPU
R160
390
TMH-108- 01-L-DW
TO PRESCALER
LO BATT
BACKLIGHT
TO DISPLAY/
KEYBOARD
+12VREG /BATT
R179
Con40
U+12V
10K
J19
J17
-5.2V
+7V
8
7
2
C88
2.2uF-6.3V
J30
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
+5V
R172
10K
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
R159
10K
U10
RESET
VCC
SENSE
RESET
RESIN
CT3GND
TL7705B
3
2
TEST
R201
10K
+5V
C
+12V
BURST
-5.2V
R199
10K
+5V
R170
R171
2.2K
2.2K
+5V
+5V
U+12V
ON
STANDBY
+5V
5
6
1
REF
4
+5V
R200
10K
R169
100K
-5.2V
+7V
U+12V
+12VREG /BATT
R173
10K
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
J18
Con40
12MHZ
GET
TO GPI B
AR[0-7]
AD[0-15]
ALE
RD
WRL
DISABLE STANDBY
ENA-EXT-REF
A8
CSRLY
DACMUX
CSIB
CSIA
CSDAC
CSASIC
+5V
R195
C89
U15D
HC02
R205
56
100p
9
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
+5V
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
U26A
12
&
HC10
L10
BLM21A102S
15uF-6.3V
10
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
25
24
21
23
2
26
1
22
27
20
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
29
28
24
27
3
30
31
2
23
25
1
2
13
C92
13
1
C101
100nF
R191
B1
+5CPU
1
R164
100K
VCC
U11
CPU
ADR
DATA
80C196KB
1
A0
2
A1
A23WP
5
SDA
6
SCL
R165
100K
C85
22p
U12A
24LC16B
EEPROM
C86
22p
C87100nF
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
FIN
+5V
Q15
BC857B
R175
10K
67
16
2
3
12
13
37
43
64
6
5
7
4
11
10
8
9
19
20
21
22
23
30
31
32
18
17
15
44
42
39
33
38
68
36
12MHz
XTAL1
RESET
EA
NMI
AGND
VREF
VPP
READY
BUSWIDTH
ACH0/P0.0
ACH1/P0.1
ACH2/P0.2
ACH3/P0.3
ACH4/P0.4
ACH5/P0.5
ACH6/P0.6
ACH7/P0.7
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
TDX/P2.0
RDX/P2.1
EXTINT/P2.2
T2CLK/P2.3
T2RST/P2.4
PWM/P2.5
P2.6
P2.7
VSS
VSS
GATE IND.
R174
330
R162
100K
R163
100K
R161
100K
+5V
R158
120
XTAL2
CLKOUT
WR/WRL
BHE/WRH
ALE/ADV
AD0/P3.0
AD1/P3.1
AD2/P3.2
AD3/P3.3
AD4/P3.4
AD5/P3.5
AD6/P3.6
AD7/P3.7
AD8/P4.0
AD9/P4.1
AD10/P4.2
AD11/P4.3
AD12/P4.4
AD13/P4.5
AD14/P4.6
AD15/P4.7
HSI.0
HSI.1
HSO.4/HSI.2
HSO.5/HSI.3
HSO.0
HSO.1
HSO.2
HSO.3
R166
100K
INST
7
56
66
65
40
41
61
RD
62
63
AD0
60
AD1
59
AD2
58
AD3
57
AD4
56
AD5
55
AD6
54
AD7
53
AD8
52
AD9
51
AD10
50
AD11
49
AD12
48
AD13
47
AD14
46
AD15
45
24
25
26
27
28
29
34
35
14
VSS
R167
R168
100K
100K
2
AD0
AR0
CARRY 2
J11
J12
TEST SIGN ALS
Q16
BC847B
+5V
C91
15uF-6.3V
1
J29
RESET
3
R182
56
J13
+12VREG/BATT
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
11
R181
56
AD1
R183
56
AR1
AD[0-15]
CARRY1
J14
STAND BY IND.
+5V
R202
10K
U13A
OE
C1
Q0
D0
Q1
D1
Q2
D2
Q3
D3
Q4
D4
Q5
D5
Q6
D6
Q7
D7
HC574
U14A
D0
Q0
D1
Q1
Q217D2
D3
Q3
D4
Q4
D5
Q5
Q6
D6
Q712D7
OE
C1
HC573
VCC20GND
10
R203
560
U16B
HC573
AD2
AR2
R204
2.2K
6MHz
R180
R178
56
R177
56
56
AD4
AD3
R185
AR3
AR0
AR1
AR2
AR3
C94
100nF
R186
56
56
AR4
AR[0-7]
AR0
AR1
AR2
AR3
AR4
AR5
AR6
AR7
CSKEYBO
U17B
HC573
VCC20GND
10
R184
56
1
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
19
18
16
15
14
13
WRL
RD
ALE
R176
INST
56
AD7
AD6
AD5
R187
R188
56
AR6
R193
56
CSKEYBOARDIN
28
GND14VCC
8
14
U22B
55257
R189
56
AR7
2
D0
3
D1
4
5
D3
6
D4
7
D5
8
D6
9
1
OE
11
C1
HC573
2
D0
3
D1
4
5
D3
6
D4
7
D5
8
D6
9
1
OE
11
C1
HC573
U12B
24LC16B
VCC
GND
4
U19E
HC00
VCC
GND
7
56
AR5
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
AD8 A8
AD9
AD10
AD11
AD12
AD13
AD14
AD15
WAITSTATE
+5V
20
U14B
HC573
VCC
GND
10
ARDOUT
C95
100nF
8
U16A
U17A
+5V
U15C
U19C
&
HC00
U19D
&
HC00
1
2
3
4
5
6
C99
10n
A[0-15]
U20A
A0
A1
A2
E1A
E2A
E3
HC138
8
1
9
HC02
CSROM
8
CSRAM
11
15
Y0
14
Y1
13
Y2
12
Y3
11
Y4
10
Y5
9
Y6
7
Y7
U15E
HC02
VCC14GND
7
U15A
2
1
3
HC02
AR[0-7]
A0
19
Q0
Q1
Q217D2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q712D7
Q0
Q1
Q217D2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q712D7
U18B
&
HC21
C96
10n
A1
18
A2
A3
16
A4
15
A5
14
A6
13
A7
19
A9
18
A10
A11
16
A12
15
A13
14
A14
13
A15
+5V
9
10
12
13
20
U13B
HC574
VCC
GND
10
14
U24E
HC32
VCC
GND
7
U23B
27C51
2-90
VCC32GND
16
R190
1
56
RAM/ROM
U19A
1
A14
+5V
A15
A14
A15
+5V
A13
A9
A10
A11
A13
U20B
C97
HC138
VCC16GND
10n
8
3
&
2
HC00
U19B
4
&
5
HC00
U18A
1
2
&
4
5
HC21
C98
10n
9
10
6
6
12
13
+5V
U18C
HC21
VCC14GND
7
10
BUSWIDTH
C100
100nF
11
12
CSGPIB
U26D
HC10
VCC14GND
7
R194
10K
U26C
&
HC10
U22A
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
OE
R/W
CE
55257
U23A
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
CE
OE/VPP
27C512-90JC
C93
100nF
8
11
I/O1
12
I/O2
13
I/O3
15
I/O4
16
I/O5
17
I/O6
18
I/O7
19
I/O8
13
O0
14
O1
15
O2
18
O3
19
O4
20
O5
21
O6
22
O7
CSKEYBOARD
C90
100p
+5CPU
RD
10K
+5V
-5.2V
+7V
AD15
AD14
AD13
AD12
AD11
AD10
AD9
AD8
AR7
AR6
AR5
AR4
AR3
AR2
AR1
AR0
+5V
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
A8
U24A
WRL
1
3
1
2
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
HC32
U15B
5
4
1
6
HC02
U24B
4
6
1
5
HC32
U24C
9
8
1
10
HC32
U24D
12
11
1
13
HC32
U25A
1
3
1
2
HC32
U26B
3
4
6
&
5
HC10
Drawings & Diagrams 8-5
Page 68

Main PCB, Component layout
K1
K2
K3
K4
+
--
8-6 Drawings & Diagrams
Bottom View
Page 69

Counter Circuits, PCB 1, sheet 2(5)
C
External
control
input
(rear panel)
ENA-EXT-REF
External
referenc e
input
(rear panel)
R330
47
R235
120
C123
47p
J26
BNC-Coax
J28
BNC-Coax
A
AN
-2ECL
C178
100nF
Q36
BSR12
R319
56
R321
10
R247
R252
100
C138
10n
-5ECL
820
+5ECL
R313
56
BSR12
C182
100nF
R261
100
C107
10n
Q24
BFG16A
Q27
BFG16A
+12VREG/BATT
R262
10
+5V
R52
Not used
R97
Not used
D15
BYD17G
R255
100
R258
100
D17
BYD17G
C124
100n
C133
J24
OPTIONAL OSCILLATOR
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
4030-10A
PXB
PXA
SXB
SXA
FIN
CARRY 1
CARRY2
AR[0-7]
AD[0-15]
2.2uF-6.3V
C125
J27
C130
100nF
100n
BNC-Coax
2.2uF-6.3V
C132
Internal
reference
output
(rear panel)
STD
ALE
WRL
RD
-5.2V
-2.1V
C141
10n
Oscillator
selection
C131
100nF
+5ECL
C142
100nF
C117
100nF
OPT
3
4
5
9
10
BLM21A102S
BLM21A102S
2
+5M
R208
Not used
U25B
HC32
U25C
HC32
L22
L21
C143
100nF
J23
-5.2V
1
R209
560
C113
82p
R51
2.7K
6
1
8
1
C109
C115
3-10pF
R218
680
22p
R220
1K
R233
47
C186
15uF-6.3V
C185
15uF-6.3V
B2
10MHz
C122
680pF
+5M
Oscillator
selection
R217
100
C120
10p
12
13
C121
100nF
C184
100nF
C116
47p
U25D
HC32
C114
100p
R230
100
1
1
C119
10n
-5ECL
-2ECL
1
VCC
VEES8VEES15VEES
STD
OPT
J25
3
2
R211
-5.2V
21
25
24
23
18
1
VCC
COUNTER CIRCUIT
GND
R244
82
L13
4.7uH
C102
33pF
U27C
S
Q
Q
1D
C1
R
100331
C110
100 nF
26
27
1M
+5M
83
RTCX2
82
VBAT
46
X2
52
PH2
43
MTCXO
48
EXTREF
12MHZ
+5M
R219
330K
R222
+5M
180K
GET
BURST
11
2
12
MS
16
MR
VCCA
U27D
100331
VEE
22
14
-5ECL
29
MPCLK
41
V+REFO
39
V-RE FO
54
V+REFA
56
V-RE FA
58
V+REFB
60
V-RE FB
88
VREFAD
87
IRES
36
VCCN
47
VCCB
50
VCCC
57
VCCE
71
VCCD
85
VCCG
93
VCCA
38
GNDA
44
GNDB
53
GNDC
61
GNDE
67
GNDD3
69
GNDD2
73
GNDD1
75
GNDD4
86
GNDG
37
GET
72
A
74
A2
68
B2
70
B
66
SR
76
EXTC
65
P
64
BURST
27
CS
26
ALE
23
WRL
24
WRH
25
RD
99
HLDA
28
+5M
-5ECL
QDMA
-5ECL
U29
57370
+5V
L16
BLM21A102S
C128
82p
L11
BLM21A102S
C111
15uF-6.3V
OUTMUX
INTREF
RTCX1
ALARM
X1
PH1
OTRIM
VOUTA
VOUTB
INTP1
INTP2
INTS1
INTS2
FIN
MTIME
CY1
CY2
TRA
TRB
PG
C1
C2
C3
C4
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
INT
HOLD
A16
A17
A18
A19
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
AD8
AD9
AD10
AD11
AD12
AD13
AD14
AD15
L12
BLM21A102S
R250
Not used
C127
1n
+5V
84
81
45
51
49
42
40
55
59
89
90
91
92
94
96
97
98
62
63
30
80
79
78
77
31
32
33
34
35
95
100
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
R245
3.9K
R259
680
C134
10n
AR0
AR1
AR2
AR3
AR4
AR5
AR6
AR7
AD8
AD9
AD10
AD11
AD12
AD13
AD14
AD15
R254
10K
R251
1K
D18
BAV99
TP28
R249
47
R260
47
+5ECL
C175
100nF
R296
220
R298
47
R300
47
R302
R301
100
100
C177
100nF
BFS17
R314
120
R310
27
R327
100
-2ECL -2ECL
R306
220
Q35
+5ECL
C180
100nF
R317
220
R323
47
R325
47
C36
100nF
BLM21A102S
R264
220
R267
100
Q38
BFS17
BFS17
R329
120
R328
27
C183
100nF
-5ECL
L14
C144
Not Used
R307
R309
U27B
+5ECL
R305
220
Q34
47
47
U28
BFS17
C179
100nF
-5ECL
3
Q
4
Q
R326
100
-2ECL-2ECL
U50
1
2
3
4
8
EN
EN
+IN
-IN
SHDN
LE
3
4
2
1
MAX961
C77
10p
8
VCC
7
QN
6
Q
5
GND
R243
18K
U27A
11
6
S
Q
5
7
Q
1D
9
C1
10
R
100331
R312
R311
100
100
R315
820
D19
BAV99
D14
BAV99
R316
2.2K
D16
BAV99
-2ECL -2ECL
-5ECL
R268
1K
17
S
18
1D
19
C1
20
R
100331
+5V
R241
10K
R242
680
C135
10n
6
7
5
75ALS176D
+5ECL
+5ECL
R101
4.7k
R263
1K
R265
1K
C129
R331
47
C181
10n
R320
56
R322
10
R248
680
R253
560
6.8p
R266
1K
Q37
Q32
BFS17
C176
100nF
R318
220
Q39
+5V
BLM21A102S
-5ECL
R297
220
Q33
BFS17
R304
120
R303
27
CSASIC
+5V
L15
BLM21A102S
U25E
VCC14GND
HC32
7
L17
C139
15uF-6.3V
C140
10n
C136
15uF-6.3V
Drawings & Diagrams 8-7
Page 70

This page is intentionally left blank.
8-8 Drawings & Diagrams
Page 71
Input Amplifier & Trigger Level DACs, PCB 1, Sheet 3(5)
CSRLY
CSDAC
AR[0-7]
DACMUX
WRL
A8
J1
MiniCoax-3
DACMUX
J8
Not used
100K
Q11
BC817-25
U6C
NE532D
470K
+5
C7
R35
10n
470
C4
3.3pF
R36
470
-5.2
C5
R33
10K
10n
185
U1A
2
-
6
+
3
3140
R32
C25
10p
U6A
2
-
3
+
NE532D
C26
10p
U6B
6
-
5
+
NE532D
8
U7C
V+
NE532D
V-
4
D3
BAV99
C810n
D1
BAT18
C13
47p
D2
BAT18
C9
10n
D4
BAV99
R34
18K
-5.2
R37
1.5K
C6
R38
1K
1n
-5.2
+5
R69
100K
1
7
+5V
-5.2
R70
100K
20
U2B
VCC
HC574
GND
10
C2710n
+5
-5.2
C28
10n
R73
10K
R71
100K
R80
10K
R72
100K
C10
10n
R39
10M
R40
47
+7 +5
R42
15
Q1
BF513
R100
27
Q3
BFS17
R41
220
-5.2
R74
10K
R75
10K
R76
10K
R77
10K
R89
68
R81
10K
R82
10K
R83
10K
R84
10K
R90
68
+5
R43
C11
100
10n
Q2
BFR92A
C80
10n
R44
47
R105
1K
-5.2
R46
150
R45
47
D5
BAV99
C14
R47
10n
150
-5.2
R78
R79
10K
10K
U7A
2
-
1
3
+
NE532D
R85
R86
10K
10K
U7B
6
-
7
5
+
NE532D
11
VCC
-5.2L
Q13
BFG97
Q4
BFR93A
R87
100
R88
100
U9F
16
21
20
F1
VCC0
VCC0
19
F2
VEE
10E104
1
C16
C12
15uF-6.3V
10n
C20
1n
9
7
U8C
AD96687BP
-5.2
R50
8.2
L1
220uH
R49
100
C17
C18
10n
10n
25
26 15
10E104
C49
U9D
TP10
10n
14
&
+7V
K4B
8
R48
C15
82
10n
C29
100nF
C30
100nF
+5
14
VCC
GND
VEE8GND
4
18
2
4
C19
10n
TP11
R115
10K
R116
15K
L2
4S2 3.5X6MM
C37
100nF
TP26
TP27
U8A
5
LE
7
LE
10
2
+
OUT
3
9
-
OUT
AD96687BP
K4A
3
C31
10n
C32
10n
17
LE
15
LE
12
+
13
-
AD96687BP
R114
R106
100
J2
+5V
C55
100nF
U5B
6
-
7
5
+
NE532D
R117
47
-5.2
-5.2V
100nF
C38
10n
U8B
C40
OUT
OUT
C44
10n
R91
100
20
19
R107
100
L5
4S2 3.5X6MM
Q10
BC807-25
R118
47
L3
4S2 3.5X6MM
6.8u-16V
+5
R92
8.2K
R93
47
R94
47
R95
3.3K
R96
1.8K
-5.2
-2.1
C56
10n
C51
10n
+7
C39
-2.1
C33
10n
C34
10n
R109
R110
C41
10n
100
100
R108
100
27
28 13
10E104
-2.1
-2.1 -2.1-2.1
C59
10n
C52
10n
U9C
12
&
-2.1
R98
Not used
R111
C43
10n
100
R112
100
C53
10n
-2.1
2
3 10
4
5 8
C60
100nF
U9B
&
10E104
U9A
&
10E104
C54
10n
BLM21A102S
BLM21A102S
C46
10n
9
7
C61
15uF-6.3V
4S2 3.5X6MM
L4
L25
C45
100nF
U9E
23
24 18
&
10E104
R113
100
L24
BLM21A102S
L23
C126
10n
17
-2.1
BACKLIGHT
+5
+5D
-2.1V
-2.1
C50
2.2uF-6.3V
-5.2L
(U16)
C48
10n
-5.2D
-5.2
C47
15uF-6.3V
A
AN
R99
Not used
K2A
81
714
REED
C1
0.5-2pF
R13
120
R14
120
2613
R3
470K
R15
150
R16
150
C23
K1B
10n
REED
C24
10n
U2A
1
OE
11
C1
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
HC574
LE
S0
S1
S2
E2
E1
A0
A1
B0
B1
C0
C1
HC4353T
U3
VCC
GND
ACOM
BCOM
CCOM
19
Q0
18
Q1
17
Q2
16
Q3
15
Q4
14
Q5
13
Q6
12
Q7
AR[0:7]
20
9
VEE
10
18
19
5
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
15
13
12
8
7
16
17
2
1
6
4
R1
47
817
K1A
REED
14
R7
R9
120
120
R8
R10
120
120
CSRLY
AR0
AR1
AR2
R2
100
R11
120
R12
120
R1727
C21
10n
C22
10n
AR0
AR1
AR2
AR3
AR4
AR5
AR6
AR7
+5D
R4
220K
2613
K2B
REED
R6
47
R5
220K
+5
-5.2D
C42
10n
2
3
R21
15
R22
220K
R18
68K
817
REED
K3A
14
R19
22K
R20
8.2K
2613
C66
10n
C67
10n
+5D
C58
10n
U5A
-
1
+
NE532D
K3B
REED
C2
2-18pF
R23
220K
C68
10n
WRL
A8
AR0
AR1
AR2
AR3
AR4
AR5
AR6
AR7
1
10
15
16
6
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
4
18
R24
470K
R25
470K
R26
470K
K4C
C69
10n
R119
1K
Not used
CS
WR
DACA/DACB
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
VREF A
VREF B
C3
22nF
R120
U4
PM7258
470K
AGND
RFB A
OUT A
RFB B
OUT B
R29
22K
R30
GND
R27
470K
R28
470K
R31
+5D
17
VCC
5
1
3
2
19
20
TRIG LEVEL DAC'S
DAC RANGE REFERENCE
+5
0.22V
R60
4.7K
R61
220
R57
15K
0.04V
R58
R59
120
R62
Not used
0.59V
R63
6.8K
1.6V
R65
R64
10K
1K
C57
R66
10n
4.7K
+5
7
8
U1B
V+
R68
R67
Not used
2.2K
V+
3140
V-
4
4
V-
U5C
NE532D
8
V+
V-
4
-5.2
Drawings & Diagrams 8-9
Page 72

This page is intentionally left blank.
8-10 Drawings & Diagrams
Page 73

Power Supply, PCB 1, sheet 4(5)
STAND BY
DISABLE STANDBY
EXT. DC
ON REAR
PAN EL
To Rubidium
Power
To Rubidium
Power
U+12V
TP23
+12V
J32
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TO BATT
11
UNIT
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Con20
LO BATT
+12VREG/BATT
U+12V
+12V
+5V
+5V
Q7
BC807-25
R121
10K
ON
R122
100K
J5
J6
J3
J9
J10
J4
F1
1.6AT
D9
C65
100n
2KBP08
R123
100K
Q12
BC847B
R148
16
R124
J22
100K
1
3
2
R125
100K
-+
C64
270uF
R126
1K
D12
BAV99
L6
10mH
2.2nF
C35
470n
SB140
SB140
SB140
C62
U40B
8
S
9
13
1D
11
12
C1
10
R
HEF4013BT
J16
1
U+12V
R127
1M
D7
D8
D10
U39
+
9
-
+
99
C63
2.2nF
1
4
5
POWER MODULE
+DCIN
-DCIN
-DCIN
-
+
+
-
-
PF
3
2
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
14
12
C70
10n
PF
SAFETY EARTH
R146
15K
U+12V
1
16
R1472.2K
C71
10n
K5C
Q14BC847B
D13
BAV99
D6
1N4003/200
C79
33uF-63V
TP17
L9
33uH
TP16
L7
10uH
TP15
L8
10uH
C72
C73
10n
10n
-7V
+15V
+5V
C74
68uF-6.3V
U+12V
C75
33uF-63V
U41
+
12V
U__
2
-
LM2940CT-12
13
C76
33uF-63V
3 2
J15
R155
330
OPTIONAL
FAN
U42
_
+
1.25V
_
U
-
LM317T
1
BZX79-B5V6
R154
220
D20
R153
DISCONNECT IF
BATTERY OPTION
INSTALLED
J21
1
3
2
C84
220uF-50V
R152
220
J31
Q5
BCP51
R156
R157
2.2K
6.81K
K5A
4
R149
R150
R151
220
220
220
220
R53
2.2K
8
6
SIGNAL GROUND
J7
TP21
+12V
R56
390
R55
560
R54
560
Q6
BC847B
C83
15uF-6.3V
-5.2V
+5V
6
5
3
4
U40A
S
1D
C1
R
HEF4013BT
R131
R130
220
+12V
R198
4.7K
U+12V
1
2
VCC14GND
7
U40C
HEF4013BT
+12V
R206
5.6K
8
U21C
V+
NE532D
V-
4
U21B
6
-
7
5
+
NE532D
C104
R207
10n
1K
U21A
2
-
3
+
NE532D
R197
1
120
C10310n
R196
120
Q17
BC817-25
C105
6.8u-16V
TP22
+7V
+7V
C106
10n
R132
220
R133
220
220
R134
220
R135
220
R136
220
U43
REG
In2Out
LM337T
R137
220
Adj
1.25V
R139
R140
R138220
220
R128
1.5K
R129
470
1
3
220
C82
15uF-6.3V
R141
220
13
R143
R144
-5.2V
R145
330
220
-5.2V
+7V
R142
220
220
TP20
K5B
11
9
Drawings & Diagrams 8-11
Page 74

This page is intentionally left blank.
8-12 Drawings & Diagrams
Page 75

Interpolators, PCB 1, sheet 5(5)
SXB
PXB
CSIA
SXA
PXA
CSIB
+12V
+5V
8
L18
BLM21A102S
U30A
1
3
&
R269
220
R278
220
2
HC00
C145
390pF
U30B
4
6
&
5
HC00
U34A
1
3
&
2
HC00
C150
390pF
U34B
4
6
&
5
HC00
+12J
C174
100nF
1
6
C157
15uF-6.3V
U34E
HC00
VCC14GND
7
U31B
VCC
ADC1061
+VCC
GND
10
U32B
C81
VCC20GND
10n
10
C158
100nF
+5ADC
C108
10n
R272
2.2K
R281
2.2K
VCC20GND
C159
100nF
10
U36B
HC573HC573
+12J
R270
R271
8.2K
820
R275
2.2K
R284
2.2K
C168
100nF
R273
47
R282
47
+5J
BFT92
Q28
C148
+12J
R279
8.2K
U35B
ADC1061
C112
10n
D23
BAV99
D25
BAV99
470pF
R280
820
BFT92
Q30
C153
470pF
C160
100nF
U44E
HC125
VCC14GND
7
D22
BAV99
+5J
D24
BAV99
+5J
1
6
VCC
+VCC
GND
10
C161
100nF
BFS17
BFS17
C118
10n
Q29
Q31
L19
BLM21A102S
R274
100
R283
100
R277
33K
R286
33K
C166
15uF-6.3V
C149
22p
C154
22p
R276
33K
R285
33K
C167
100nF
C147
Not Used
8
11
C152
Not Used
8
11
VREF-
VREF-
U30C
&
HC00
U30D
&
HC00
U34C
&
HC00
U34D
&
HC00
VREF+
9
10
12
13
VREF+
9
10
12
13
+5V
D21
BAV99
C146
10p
+5V
D26
BAV99
C151
10p
L20
BLM21A102S
U38C
V+
NE532D
V-
4
C156
15uF-6.3V
C78
U30E
VCC14GND
10n
HC00
7
U31A
20
DB0
19
DB1
8
9
7
4
3
5
8
9
7
4
3
5
VIN
VREF+
VREF-
RD
S/H
CS
VIN
VREF+
VREF-
RD
S/H
CS
ADC1061
U35A
ADC1061
18
DB2
17
DB3
16
DB4
15
DB5
14
DB6
13
DB7
12
DB8
11
DB9
2
INT
20
DB0
19
DB1
18
DB2
17
DB3
16
DB4
15
DB5
14
DB6
13
DB7
12
DB8
11
DB9
2
INT
C165
10n
C173
10n
+5V
+5V
+5J
R287
0
R288
33
R289
220
R291
47
R292
0
R293
330
R295
270
U32A
2
D0
3
D1
4
5
D3
6
D4
7
D5
8
D6
9
1
OE
11
C1
HC573
12 11
9 8
2 3
1
5 6
4
U36A
2
D0
3
D1
4
5
D3
6
D4
7
D5
8
D6
9
1
OE
11
C1
HC573
2
-
3
+
6
-
5
+
Q0
Q1
Q217D2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q712D7
U44D
HC125
13
U44C
HC125
10
U44A
HC125
U44B
HC125
Q0
Q1
Q217D2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q712D7
U38A
NE532D
U38B
NE532D
19
18
16
15
14
13
19
18
16
15
14
13
C155
10n
R290
1
100
C169
10n
R294
7
AR2
AR3
AR4
AR5
AR6
AR7
AD8
AD9
AD[0-15]
AR0
AR1
AR0
AR1
AR2
AR3
AR4
AR5
AR6
AR7
AD8
AD9
AD[0-15]
VREF+
C164
C163
C162
100nF
27
C170 C171
100nF 100nF
100nF
VREF-
2.2uF-6.3V
C172
2.2uF-6.3V
AR[0-7]
AD[0-15]
Drawings & Diagrams 8-13
Page 76

Display & Keyboard PCB, Component layout
8-14 Drawings & Diagrams
Page 77

MAIN BOARD
STAND-
BY IND
GATE
IND
SCL
SDA
U+12V
STAND-
BY
LOCAL/
PRESET
BACKLIGHT
TEMP
COMP
+5V
GND
H0
H1
H2
ON
NC
3
P204
5
P204
7
P204
28
P204
32
P204
36
P204
35
P204
22
P204
24
P204
26
P204
38
P204
18
P204
20
P204
37
P204
21039
P204
1 4 6 12 14 16 30
P204
89111315173034
P204
V0
19 P204
EXT REF
LOCAL/PRESET
S201
ON
S222
STAND-BY
S223
S224
MAIN BOARD
V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 V7
21 P204
CHECK
S202
MEAS RESTART
23 P204 25 P204
S209
FILTER
S203
DISP HOLD
S210
<FUNCTION
S216
NULL/OFFSET
FUNCTION>
27 P204 29 P204
IMP
S204
S211
S217
TRIG LVL
S205
BLANK DIGITS
S212
MEAS TIME
S218
D201
HLMP-K150
D202
CQV13-6
AUTO
S206
DATA ENTRYUP
S213
MENU
S219
RED
YELLOW
31 P204
<SENS
S207
DATAENTRY DN
AUX MENU
S220
S214
+5V
R204
10
R20510R206
R207
10
10
BACKLIGHT
D203
DL100
+5V
IC TYPE
U201 PCF8576
PCF8576
U202
11,7,8,9 5,10
GND
+5V
511,7,8,9,10
33 P204
SENS>
S208
ENTER
S215
SINGLE
S221
+5V +5V
C202
10n
C201
10n
+5V
+5V
R201
220k
Display & Keyboard, PCB 2
U201
DISPDR
12
VLCD
4
CLK
3
SYNC
6
OSC
2
SCL
1
SDA
10
SA0
7
A0
8
A1
9
A2
PCF8576
DISPDR
12
VLCD
4
CLK
3
SYNC
6
OSC
2
SCL
1
SDA
10
SA0
7
A0
8
A1
9
A2
PCF8576
U202
13
BP0
15
BP1
14
BP2
16
BP3
17
S0
18
S1
19
S2
20
S3
21
S4
22
S5
23
S6
24
S7
25
S8
26
S9
27
S10
28
S11
29
S12
30
S13
31
S14
32
S15
33
S16
34
S17
35
S18
36
S19
37
S20
38
S21
39
S22
40
S23
41
S24
42
S25
43
S26
44
S27
45
S28
46
S29
47
S30
48
S31
49
S32
50
S33
51
S34
52
S35
53
S36
54
S37
55
S38
56
S39
82 78 74 70 66 60 58 55 52 49 46 4443
454748505153545657596162636465676869717273757677798081
E201
71013141822 27 323639403837353433313029282625242321201917161512119865432141 42
13
BP0
15
BP1
14
BP2
16
BP3
17
S0
18
S1
19
S2
20
S3
21
S4
22
S5
23
S6
24
S7
25
S8
26
S9
27
S10
28
S11
29
S12
30
S13
31
S14
32
S15
33
S16
34
S17
35
S18
36
S19
37
S20
38
S21
39
S22
40
S23
41
S24
42
S25
43
S26
44
S27
45
S28
46
S29
47
S30
48
S31
49
S32
50
S33
51
S34
52
S35
53
S36
54
S37
55
S38
56
S39
Drawings & Diagrams 8-15
Page 78

GPIB Unit, PM9626B, Component layout
8-16 Drawings & Diagrams
Page 79

GPIB Unit, PM9626B
Drawings & Diagrams 8-17
Page 80

This page is intentionally left blank.
8-18 Drawings & Diagrams
Page 81

Chapter 9
Appendix
Page 82

How to Replace Surface
Mounted Devices
Most of the components in this instrument are mounted on the sur
face of the board instead of through holes in the board. These compo
nents are not hard to replace but they require another technique. If
you do not have special SMD desoldering equipment, follow the in
structions below:
Fig. 9-1 Heat the leads and push a thin aluminum sheet
between the leads and the PC-board.
-
-
-
Fig 9-4 Attach the IC to the pad with the solder.
Fig. 9-5 Solder all leads with plenty of solder; don’t worry
about short-circuits at this stage.
Fig. 9-2 When removed, clean the pads with desoldering
braid.
Fig. 9-3 Place solder on the pad.
9-2 How to Replace Surface Mounted Devices
Fig. 9-6 Remove excessive solder with desoldering braid.
Fig. 9-7 Use a strong magnifying glass to make sure there
are no short-circuits or unsoldered leads.
Page 83

Electrostatic discharge
Almost all modern components have extremely thin conductors and
metal oxide layers. If these layers are exposed to electrostatic dis
charge they will break down or perhaps even worse, be damaged in a
way that inevitably will cause a breakdown later on. The lectro-tatic
Discharge, (ESD) sensitivity of MOS and CMOS semiconductors
have been known quite a while, but nowadays bipolar semiconduc
tors and even precision resistors are ESD sensitive. Consider
therefoe all components, pc boards and sub assemblies as sensi
tive toelectrostatic discharge. The text below explains how you can
minimize the risk of damage or destroying these devices by being
aware of the problems, and learning how to handle these compo
nents.
ESD sensitive options are packed in conductive containers
marked with the symbol to the leftl.
Never open the container unless you are at an ESD protected
work station.
Use a wrist strap grounded via a high resistance.
Use a grounded work mat on your work-bench.
Never let your clothes come in contact with ESD sensitive
equipment even when you are wearing a grounded
wrist strap.
Never touch the component leads.
-
-
-
Never touch open connectors.
Use ESD-safe packing materials.
Use the packing material only once.
Keep paper and non conductive plastics etc. away from your
work-bench. These may block the discharge path to
ground.
-
Electrostatic discharge 9-3
Page 84

Glossary
A
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
C
Calibration Adjust
ments
CSA Canadian Standards Association safety stan
G
GaAs A technique to make very fast IC’s using
GPIB General Purpose Instrumentation Bus used for
I
I2C-bus An internal address- and data bus for communi
IEC 1010-1 International Electrical Commission safety
How to restore an instrument to perform in
agreement with its specifications
dard.
Gallium Arsenide substrate.
interconnecting several measuring instruments
to a common controller.
cation between microcontroller, measuring
logic, and options.
standard.
-
-
L
LSI Large Scale Integrated circuit
O
OCXO Oven-Controlled X-tal Oscillator
P
PCA Printed Circuit Assembly
PCB Printed Circuit Board
Performance Check A procedure to check that the instrument is
functionally operational and performs to its
specification. Must not require opening of cabi
net. If the instrument passes the check it is con
sidered as calibrate.
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
T
TCXO Temperature-Controlled X-tal Oscillator
-
-
9-4 Glossary
Page 85

Power Supply Switchmode Module
Circuit Descriptions
Primary Circuits
n
For primary circuits outside the power supply module, see Chapter 4,
Circuit Descriptions, Power Supply.
The power supply module generates three DC voltages to the sec
ondary circuits.
R24-R27, R31, and R32 give the start-up voltage to the control cir
cuit U03.U03 outputs a frequency of 120 kHz on OUT (pin 10) to the
switch transistor V01. When the switch transistor has started, U03
will besupplied fromthe transformerT01 pin 3 via the diodes D09.
Every switch pulse causes a voltage drop over the resistors R35-R37
and R55. This voltage feeds the SENSE input (pin 5) of the control
circuit U03. When the voltage has reached the internal reference
level in U03, the switch transistor V01 is turned off.
P01 pin 1
P01
pin 4 & 5
-
-
T01
V05 is a blanking transistor that will compensate for high transients
generated by the transformer T01.
The internal sawtooth generator RC (pin 7) in U03 is connected to
the SENSE input via V03, to compensate for low load.
The regulated +5 V is sensed by U01 and adjusted by R50. The out
put of U03 is connected to the VF input (pin 3) of U03 via the
optocoupler U02.
The VREF pin (pin 14) outputs a reference voltage of 5 V DC.
Secondary circuits
n
For secondary circuits see Chapter 4, Circuit Descriptions, Power
Supply.
P02 pin 2
D01
P02 pin 7
D04
-
R24-R27,
R31-R32
SENSE
RC
VF
V05
Fig. 9-8 Power supply module primary circuits.
D09
OUT
U0 3
V03
V01
VR EF
U02
T0 1
D02
P02pin5&6
U01
R50
P02
pin1,4,8,& 9
P02 pin 3
D03
Circuit Descriptions 9-5
Page 86

Repair
Troubleshooting
n
Primary circuits
CAUTION: If you adjust the +5 V trimmer you have to
adjust the complete instrument.
Required Test Equipment
n
To be able to test the instrument properly using this manual you will
need the equipment listed in Table 9-1. The list contains specifica
tions for the critical parameters.
Type Performance
DMM 3.5 digits
Oscilloscope 50 MHz 2-channel
Table 9-1 Required test equipment.
Operating Conditions
n
Power voltage must be in the range of 90 to 260 VAC.
WARNING: Live parts and accessible terminals which
can be dangerous to life are always exposed inside
the unit when it is connected to the line power. Use
extreme caution when handling, testing or adjusting
the counter.
1
P0 1
»+5.0V
U03
+10 to 13.5V
C
E
D
»+10mV
A
V0 1
B
J16
16
U02
T01
127
»+8.2V
+5Vadjust
»+4.4V
U01
P0 2
1
TP17
TP15
TP16
To verify the power supply proceed as follows:
If the primary fuse is broken, there is a short circuit in the pri
–
-
mary circuits. Use a DMM and try to locate the fault by resis
tance measurements.
Remove the cover from the power supply.
–
Disconnect the power module from the main PCA and check
–
the resistance between pin 1 and 4 on the transformer T01, see
Fig. 9-9. If the DMM shows a short circuit, the fault is
proabably a broken transistor V01. Put the power module back.
Connect the counter to the line power via an insulating trans
–
former with separate windings.
Set the counter to STAND-BY mode.
–
Check that the voltage between J9 and J10 is in the range of
–
90 to 260 V
Check that the DC voltage between pin 1 and 4 on T01 is
–
about Ö2 times the input AC voltage. If not, use traditional
faultfinding techniques to locate the fault.
Disconnect the secondary load by moving the jumper J16 to its
–
alternative position.
Check the “STAND BY” voltages according to Table 9-2.
–
Test points Ground Voltage
U03 pin 11 & 12 U03 pin 8 +10 to +13.5 V
U03 pin 14 U03 pin 8 +5.0 V
V01 source U03 pin 8 +10 mV
U02 pin 1 Amplifier Screen +8.2 V
U01 pin 1 Amplifier Screen +4.4 V
TP15 Amplifier Screen +5.1 V
TP16 Amplifier Screen +14.8 V to +21 V
TP17 Amplifier Screen –12.5 V to –7.5 V
TP21 Amplifier Screen +12 V ±0.5 V
Table 9-2 Stand-by voltages.
Restore the jumper J16 to its normal position.
–
Check the waveforms in Fig. 9-10 at the corresponding
–
testpoints in Fig. 9-9 to verify the primary circuits. Use the
heat-sink of V01 as ground.
NOTE: U01 and U03 are located at the bottom side of the
PCA.
Secondary circuits
n
For secondary circuits see Chapter 5, Repair, Power Supply.
AC
.
-
-
-
Safety Inspection and Test After Repair
Fig. 9-9 Test points and voltages for the power supply.
9-6 Repair
General Directives
n
After repair in the primary circuits, make sure that you have not re
duced the creepage distances and clearances.
Before soldering, component pins must be bent on the solder side of
the board. Replace insulating guards and plates.
-
Page 87

V
V01 Sourc e ( curre nt )
1.2
1.1
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
024 8610uS
V
12
10
8
6
4
2
V
3
2
1
U03 pin 10 OUT
U0 3 p in 7 R C
A
C
E
V0 1 G a te
024 8610uS
V01 dra in
024 8610uS024 8610uS
500
400
300
200
100
V
12
10
8
6
4
2
V
Switch on the counter.
B
–
Press PRESET, then press ENTER.
–
Power
D
Modu le
TP23
+5V adjust
024 8610uS
Fig. 9-10 Typical curves of the power supply.
Safety Components
Components in the primary circuits are important to the safety of the
instrument and may be replaced only by components obtained from
your local Fluke organization.
Check the Protective Ground Connection
Visually check the correct connection and condition and measure the
resistance between the protective lead at the plug and the cabinet.
The resistance must not be more than 0.5 W. During measurement,
the power cord should be moved. Any variations in resistance shows
a defect.
Calibration Adjustments
Required Test Equipment
Type Performance
DMM 3.5 digits
Table 9-3 Required Test Equipment.
TP17
TP16
J1 8
Fig. 9-11 Test points and trimmer for the power supply.
Adjustment
n
CAUTION: If you adjust the +5 V trimmer you have to
adjust the complete instrument.
Connect the DMM between TP23 and ground, see Fig. 9-11.
–
Adjust the +5 V trimmer potentiometer R50 in the power sup
–
ply through the nearest vent in the protective cover, until the
DMM reads +5.00 ± 0.01 V.
Check that the unregulated voltage from the power supply at
–
test point TP16=+15 is about +18 V.
Check that the unregulated voltage from the power supply at
–
test points TP17=–7 is about –8 V.
-
Preparation
WARNING: Live parts and accessible terminals which
can be dangerous to life are always exposed inside
the unit when it is connected to the line power. Use
extreme caution when handling, testing, or adjust
ing the counter.
Before beginning the calibration adjustments, power up the instru
ment andleave iton forat least60 minutesto letit reachnormal oper
ating temperature.
Setup
n
Connect the counter to the line power.
–
-
-
-
Calibration Adjustments 9-7
Page 88

Replacement Parts
Pos Description Part Number P
Heat Sink 16°K/W TO220 5322 255 41313 P
Heat Sink 13.5°K/W TO220 5322 255 41314 P
C01 Capacitor 1 nF 5% 63V 4822 122 31746
C02 Capacitor 1 nF 5% 63V 4822 122 31746
C03 Capacitor 220 pF 20% 200V 5322 126 13129
C04 Capacitor 33 nF 10% 50V 4822 122 31981
C05 Capacitor 33 nF 10% 50V 4822 122 31981
C06 Capacitor 33 nF 10% 50V 4822 122 31981
C07 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V 4822 122 33496
C08 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V 4822 122 33496
C09 Capacitor 47 nF 10% 250V 4822 121 41676
C10 Capacitor 330 nF 20% 250V 5322 121 44222
C12 Capacitor 100 mF 20% 35V 5322 124 40852
C13 Capacitor 220 pF 20% 200V 5322 126 13129
C14 Capacitor 100 pF 5% 63V 4822 122 31765
C15 Capacitor 22 pF 5% 63V 4822 122 32482
C16 Capacitor 4.7nF 10% 63V 4822 122 31784
C17 Capacitor 4.7nF 10% 63V 4822 122 31784
C18 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V 4822 122 33496
C19 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V 4822 122 33496
C20 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V 4822 122 33496
C21 Capacitor 470 mF 20% 35V 2M 5322 126 13131
C22 Capacitor 470 mF 20% 35V 2M 5322 126 13131
C23 Capacitor 10000 mF 20% 6.3V 5322 124 80821
C24 Capacitor 1 nF 5% 63V 4822 122 31746
C25 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V 4822 122 33496
C26 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V 4822 122 33496
C27 Capacitor 100 nF 10% 63V 4822 122 33496
C28 Capacitor 220 pF 20% 200V 5322 126 13129
D01 Diode 7A BYW29/200 5322 130 32328
D02 Diode 7.5A MBR760 60V 5322 130 83602
D03 Diode 7A BYW29/200 5322 130 32328
D04 Diode 0.2A BAV23 200V 5322 130 33764
D06 Diode 0.35 W BZX84-C8V2 5322 130 80255
D07 Diode BYV26E DOD57 4822 130 60815
D08 Diode 0.35 W BZX84-C18 5322 130 80212
D09 Diode 0.2A BAV23 200V 5322 130 33764
D11 Diode 0.35 W BZX84-C18 5322 130 80212
D12 Diode 0.35 W BZX84-C18 5322 130 80212
D13 Diode 0.35 W BZX84-C8V2 5322 130 80255
D14 Diode 0.2A BAV23 200V 5322 130 33764
R01 Resistor 82 kW 1% .125W 4822 051 10829
R02 Resistor 82 kW 1% .125W 4822 051 10829
R03 Resistor 270 kW 1% .125W 4822 051 10271
R04 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R06 Resistor 2.20 kW 1% .125W 5322 116 80434
R07 Resistor 1.00 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51002
R08 Resistor 1.80 kW 1% .125W 4822 051 10182
R09 Resistor 3.90 kW 1% .125W 5322 116 80443
R10 Resistor 47 kW 1% .125W 5322 116 80446
R11 Resistor 220 kW 1% .125W 5322 116 80436
R12 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R13 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R14 Resistor 10.0 W 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R15 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R16 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
Pos Description Part Number P
R17 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R18 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R19 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R20 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R24 Resistor 100 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51004
R25 Resistor 100 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51004
R26 Resistor 100 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51004
R27 Resistor 100 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51004
R28 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R29 Resistor 4.7 W 10% 0.25W 4833 051 10478
R30 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R31 Resistor 100 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51004
R32 Resistor 100 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51004
R33 Resistor 10.0 W 1% 0.125W 4822 051 10109
R34 Resistor 1.00 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51002
R35 Resistor 2.7 W 5% 0.25W 4822 051 10278
R36 Resistor 2.7 W 5% 0.25W 4822 051 10278
R37 Resistor 2.7 W 5% 0.25W 4822 051 10278
R38 Resistor 1.00 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51002
R39 Resistor 10.0 W 1% 0.125W 4822 051 10109
R40 Resistor 100 W 1% 0.125W 5322 116 80426
R41 Resistor 100 W 1% 0.125W 5322 116 80426
R42 Resistor 1.00 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51002
R43 Resistor 100 W 1% 0.125W 5322 116 80426
R44 Resistor 100 W 1% 0.125W 5322 116 80426
R45 Resistor 1.00 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51002
R46 Varistor 95V 95VRMS4.1J 5322 116 21222 P
R47 Resistor 4.70 kW 1% .125W 5322 116 80445
R48 Resistor 10.0 kW 1% 0.125W 4822 051 51003
R49 Resistor 22.0 kW 1% .125W 5322 116 80435
R50 Potentiometer 1 kW 20% 4822 101 10792
R51 Resistor 3.30 kW 1% .125W 4822 051 53302
R52 Resistor 8.20 kW 1% .125W 4822 051 10822
R53 Resistor 470 kW 1% .125W 5322 116 80447
R54 Resistor 470 kW 1% .125W 5322 116 80447
R55 Resistor 2.7 W 5% 0.25W 4822 051 10278
R56 Resistor 100 W 1% 0.125W 5322 116 80426
R57
Resistor 47 W 1% .125W
R58 Resistor 270 W 1% .125W 4822 051 10271
T01 Transformer 5322 148 20035 P
U01 IC-ref 2.5V TL431I-D SO8 5322 209 62422
U02 Optocoupler CNX82A 4822 130 10025
V02 Transistor 0.50 A BC807-25 5322 130 60845
V03 Transistor 0.50 A BC817-25 4822 130 42804
V04 Transistor 0.50 A BC817-25 4822 130 42804
V05 Transistor 0.50 A BC817-25 4822 130 42804
V06 Transistor 0.50 A BC817-25 4822 130 42804
V07 Transistor 0.50 A BC817-25 4822 130 42804
V08 Transistor 0.50 A BC807-25 5322 130 60845
5322 116 80448
9-8 Replacement Parts
Page 89

This page is intentionally left blank.
Replacement Parts 9-9
Page 90

Power Supply, Component layout
TOP SIDE
BOTTOM SIDE
9-10 Replacement Parts
Page 91

Power Supply
2
3
4
5
C1 9
R5 8
C28
D03
BYW2 9F -20 0
27 0
R0 3
220P
C03
163
10 0N
C22
470U-35V
D02
R0 2
27 0
C02
220P
12109
11
4
C13
C0 9
4 7N- 250 V
R4 6
R1 7
10K
R1 8
10K
R16
10K
R19
10K
R15
10K
R20
10K
R53
470 K
R54
R2 4
100K
R2 5
C2 0
10 0N
C21
470U-35V
D01
BYW2 9F -20 0
82
R0 1
C01
1N
8
7
T0 1
P02
6
MBR760
82
1N
R33
22 0P
R1 2
R13
R14
470 K
100K
8
9
7
C1 8
10 0N
R05
C23
C06
33 N
10 000 U-6 . 3V
R04
10K
C0 5
33N
D04
BAV2 3
C0 4
33N
D04
BAV2 3
D09
BAV2 3
D09
10
BAV2 3
D07
BYV2 6E
10K
V01
10K
BUK446
10K
R3 2
100K
10K
6
A
U0 1
K
REF
1
R09
3.9K
R06
2. 2K
D0 6
C0 7
V08
BC807
R57
100
R29
4.7
C26
R55
10
R3 5
2.7
R3 6
2. 7
R37
2.7
R28
10 K
D08
BZX84C18
C25
V0 6
D11
BZX8 4C18
C12
R3 0
10K
8
C0 8
BZX84C 8V2
10 0N
C2 4
R49
100 N
100N
BC8 17
100 U-3 5V
R1 0
R0 8
1. 8K
R07
1K
1
2
U02
CNX82A
5
4
1N
1K
R3 4
22 K
1473
11, 12
VRE F
U03
OUT
10
R5 6
100
R38
R3 9
V07
BC81 7
R51
TL43 1I
10 0N
47K
VF
RC
5
R44
1K
10
3. 3K
13
2
1K
R5 0
R1 1
220 K
R52
8. 2K
R4 8
10 K
1
8, 9
CO MP
SENSE
100
V03
BC81 7
UC38 42 A
R47
4. 7K
R43
100
C1 4
1 00P
V02
BC80 7
R4 1
C27
10 0N
1K
R4 5
C17
4. 7N
C1 6
4.7N
V05
BC8 17
R42
1K
D1 4
BAV23
C15
22 P
10 0
D14
R31
R26
100K
R27
4 1
5
1
C10
33 0N
P01
100K
100K
D12
D13
BZX84 C18
BZX84C8 V2
V04
BAV2 3
BC81 7
R40
100
Replacement Parts 9-11
Page 92

PM6685R
Introduction
A Rubidium timebase is now available for the PM6685 Frequency
counter. This oscillator cannot be retrofitted in the standard version
of the PM6685. Due to the size of the timebase and its power require
ments, a larger cabinet must be used.
A fan is needed to keep the temperature to an acceptable level.
This version is called PM6685R, where “R” stands for Rubidium.
J3
J4
Supply
Main
Powe r
J31
J24
1
Aux Power
P3
Rubidium
Timebase
1
P1
Supply
P2
1
Fan
Performance Check
Required Test Equipment
-
Type Performance Model
10 MHz reference £1x10
Table 9-4 Required test equipment
NOTE: To fully test the accuracy of the PM6685R, access to
an extremely high stability reference signal is needed,
for example a Cesium atomic reference or a transmit
ted signal from a nationally or internationally traceable
source. Additionally the instrument has to be stabilized
for a period of one month.
The PM6685R is equipped with an LED labelled “UNLOCKED”.
When the LED is lit the Rubidium time base is still in its warm-up
phase and is not yet stabilized.
-10
Calibrated Rubidium
oscillator or Cesium
atomic standard
Test procedure
Connect the counter to the line power.
–
Check that the UNLOCK LED is lit.
–
Check that the UNLOCK LED is switched off within £ 6
–
minutes after connection to line power.
Connect a 10 MHz reference signal to input A of the counter.
–
Select FREQUENCY A measurement.
–
Select 1 s measuring time.
–
Check that the displayed frequency is 10.00000000 MHz
–
±1 LSD < 6 minutes after connection to line power.
-
Freq. Adj .
Fig. 9-12 Location of the Rubidium Timebase and its power
supply.
9-12 Introduction
Functional Description
The oscillator is supplied with 24 V from the extra power supply.
The oscillator generates a stable 10 MHz output frequency from a
20 MHz Voltage Controlled Crystal Oscillator (VCXO), whose fre
-
Page 93

quency is locked to the atomic-standard “resonance frequency” of
9
2
the rubidium atom, see Fig. 9-14.
Frequency multiplier/
Sy nt hesi zer
20 MH z Volt age t una ble
Quartz Oscillator
(VCXO)
6.8 GHz
DC correction
voltage
Rub idium
lamp
Detector
R ubi dium
cell
DC-error
si gn a l
Feedback
electronics
(Servo)
por to an increased extent causing a decrease in the photo detector
current. This “darkening” effect is used to generate an error signal
which permits continuous regulation of the quartz crystal oscillator
output frequency, thereby locking it to the frequency of the atomic
standard .
Calibration Adjustments
NOTE: Before Calibration Adjustment, the Rubidium time
base must have been in operation for more than 24
hours.
Required Test Equipment
10 MHz output
Fig. 9-14 Block diagram showing the principle of a Rubidium
Atomic Standard.
Type Performance Model
10 MHz reference £1x10
-10
Calibrated Rubidium
oscillator or Cesium
atomic standard
Table 9-5 Required test equipment.
A microwave signal that is derived from the VCXO tunable oscillator
is applied to rubidium vapor contained within a heated glass cell.
Light from a rubidium lamp is passed through the cell and
illluminates a photo detector causing current to flow in the detector.
As the applied microwave signal approaches the frequency that cor
responds tothe ultrastable rubidiumatomic resonancefrequency,the
rubidium light entering the glass cell is absorbed by the rubidium va
-
-
Setup
Connect the counter to the line power.
–
Press PRESET, then ENTER.
–
Press AUX.
–
UNIT 1J9
0to
60v
LINE
FILTER
CNT-85R REAR
PM6685R REAR
PA NEL
PANEL
SUPPLY
P1
L
31N
J3
J10
J4
REAR VIEW
OF P3
2
1
SAFETYEARTH
A1AUXPOWER
P2
0V
2
3
0V
4
+24V
5
+24V
10
J24
5
10 MHz
3
L1- L3
9
P3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
RUBIDIUM
OSCILLA TO R
TYPE LPRO
A2
D1 UNLOCKED
FREQ.
1
ADJ US T
R1
2
1k
2
3
R2
3.83k
1
3
Fig. 9-13 Wiring diagram showing the interconnections between the Rubidium timebase, its power supply, and the main PCA.
Calibration Adjustments 9-13
Page 94

Select NULL by pressing s or t.
–
Press ENTER twice.
–
Set the measuring time to 10 s.
–
Connect the 10 MHz reference to the input A of the counter.
–
Adjustment procedure
Remove the seal from the front panel.
–
Adjust the potentiometer beyond the seal until the display
–
reads 0.5
Check that the value is stable over time, (more than 30 min
–
utes).
Cover the “CALIBRATION ADJUSTMENT” hole on the front
–
panel with a relevant seal if necessary.
-3
Hz or less.
-
Replacement Parts
Pos Description Part Number P
Cover, (incl. front part). 5322 447 92194 P
Fan 2822 031 01327 R
Text plate kit 4031 100 62440 R
Rear plate 4031 100 53930 P
A1 Power supply 5322 214 91268 P
D1 LED, HLMP-1300, red 5322 130 81921
L1 Toroid 5322 526 10545
L2 Toroid 5322 526 10545
L3 Toroid 5322 526 10545
P1-P3 Cable kit 4031 100 61530 P
R1 Potentiometer, 1 kW 5322 101 11298
R2 Resistor 3.83 kW, 1% 0.5 W MRS25 4822 050 23832
NOTE: The rubidium time base (unit A2) must be sent to a
Fluke service center for repair. Follow the exchange
procedure.
9-14 Replacement Parts
 Loading...
Loading...