Farallon Communications 412, 612 User Manual
F
arall
on
Netopia ISDN Modem
User’s Guide
Model 612 for PC Computers
Model 412 for Macintosh Computers
Farallon Communications, Inc.

Copyright notice
Copyright © 1996 Farallon Communications, Inc. v.1096
All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
This manual and any associated artwork, software, and product designs are
copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws this manual, artwork,
software, and product designs may not be copied, in whole or part, without the
written consent of Farallon Communications. Under the law, copying includes
translation to another language or format.
Farallon Communications, Inc.
2470 Mariner Square Loop
Alameda, CA 94501-1010
U.S.A.
Trademarks
Netopia, Farallon, and the Farallon logo design are trademarks of Farallon
Communications, Inc.
All other product names are the trademarks of their respective owners.
Credits
Portions of this user’s guide were written by Igal Dahari Levy and Robert Remillard.
Portions of this user’s guide were adapted by Igal Dahari Levy. Josie Cerrato edited
this user’s guide.
Part number
For additional copies of this user’s guide, order Farallon part number
6120264-00-03.
Printed on
Recycled Materials

Contents
iii
Chapter 1 — Introduction.......................................................1-1
Netopia ISDN Modem features................................................ 1-2
Farallon support.................................................................. 1-3
Netopia ISDN Modem package contents.................................. 1-3
Computer system requirements .............................................. 1-4
PC requirements ................................................................. 1-4
Macintosh computer requirements ....................................... 1-4
Cabling requirements .......................................................... 1-5
Chapter 2 — Setting Up ISDN Service ....................................2-1
About ISDN............................................................................ 2-2
ISDN and the Netopia ISDN Modem...................................... 2-2
Terms used in this user’s guide ........................................... 2-5
SPID formats ...................................................................... 2-6
Preparing for an ISDN line....................................................... 2-7
Find an ISDN service provider .............................................. 2-7
Decide on a type of ISDN line............................................... 2-8
Choose a phone line ........................................................... 2-8
Use your ISDN worksheet .................................................... 2-8
Ordering your ISDN line........................................................... 2-9
Contacting the telephone company..................................... 2-10
General ISDN line configuration.......................................... 2-14
Chapter 3 — Installing the Netopia ISDN Modem....................3-1
Connecting to a PC................................................................. 3-2
Connecting to a Macintosh computer....................................... 3-4
Connecting analog equipment................................................. 3-6

iv Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
Chapter 4 — Configuration using a PC....................................4-1
Configuration using Windows, Windows 95, and Windows NT..... 4-2
Placing calls with Windows................................................. 4-10
Installing the Windows 95 modem driver............................. 4-10
Placing calls with Windows 95............................................ 4-13
Installing the Windows NT modem driver............................. 4-16
Placing calls with Windows NT............................................ 4-18
Windows configuration options........................................... 4-19
Configuration using DOS....................................................... 4-23
Placing calls with DOS....................................................... 4-26
Chapter 5 — Configuration using a Macintosh computer.........5-1
Configuration using a Macintosh computer............................... 5-2
The ISDN Setup application .................................................... 5-5
The Easy Setup window ....................................................... 5-6
The Advanced window.......................................................... 5-9
The Utilities window........................................................... 5-14
The Modem View window................................................... 5-16
Saving and loading modem settings ................................... 5-18
Quitting the ISDN Setup application.................................... 5-20
Placing calls with a Macintosh computer................................ 5-20
Chapter 6 — Advanced Features............................................6-1
Placing calls using AT commands............................................ 6-2
Using data compression......................................................... 6-3
Using Multilink PPP ................................................................ 6-4
Storing Multilink Endpoint Identifiers in S registers ................ 6-5
Using PPP authentication protocols ...................................... 6-6
Using Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation........................................ 6-7
Placing a Toll Saver call .......................................................... 6-8
About QuickSelect.................................................................. 6-8
Optimizing serial port performance.......................................... 6-9
PC serial ports.................................................................... 6-9
Macintosh serial ports......................................................... 6-9

Contents v
About autobaud ................................................................... 6-10
Using the analog device ports............................................... 6-11
Receiving analog calls .......................................................... 6-12
Call routing to the analog device ports................................ 6-13
Receiving data calls ............................................................. 6-16
Chapter 7 — Troubleshooting.................................................7-1
Netopia ISDN Modem LEDs..................................................... 7-2
Troubleshooting tips............................................................... 7-4
Downloading firmware to your ISDN modem ............................. 7-8
From a PC .......................................................................... 7-8
From a Macintosh computer............................................... 7-10
Appendix A — Modem Operation............................................A-1
Modem basics....................................................................... A-2
Operating modes................................................................. A-2
The AT command set........................................................... A-3
Using the modem................................................................ A-5
Modem command summaries................................................. A-8
AT commands..................................................................... A-8
S registers........................................................................ A-11
ISDN modem result codes ................................................. A-17
Appendix B — ISDN Events....................................................B-1
ISDN event cause codes...................................................... B-2
Appendix C — Technical Specifications ..................................C-1
RS-232-D pin assignments................................................... C-3
PC serial cable pin assignments........................................... C-4
Macintosh DIN-8 pin assignments ........................................ C-5
Regulatory notices .............................................................. C-6
Appendix D — About the COM Port Accelerator......................D-1
Installation ............................................................................ D-2

vi Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
Farallon Technical Support....................................................TS-1
Before calling Farallon....................................................... TS-1
Environment profile ........................................................... TS-2
How to reach us................................................................ TS-2
Glossary...............................................................................GL-1
Index ........................................................................................1
Limited Warranty and Limitation of Remedies
Chapter 1
Introduction
1-1
The Netopia ISDN Modem is an external, stand-alone, ISDN
terminal adapter. Using Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
technology, the Netopia ISDN Modem provides high-speed access to
analog and digital services. With the Netopia ISDN Modem, you can
access the Internet, your corporate local area network (LAN), or
another individual computer.
This chapter introduces the Netopia ISDN Modem and its features.
It also explains the requirements for using the Netopia ISDN
Modem.
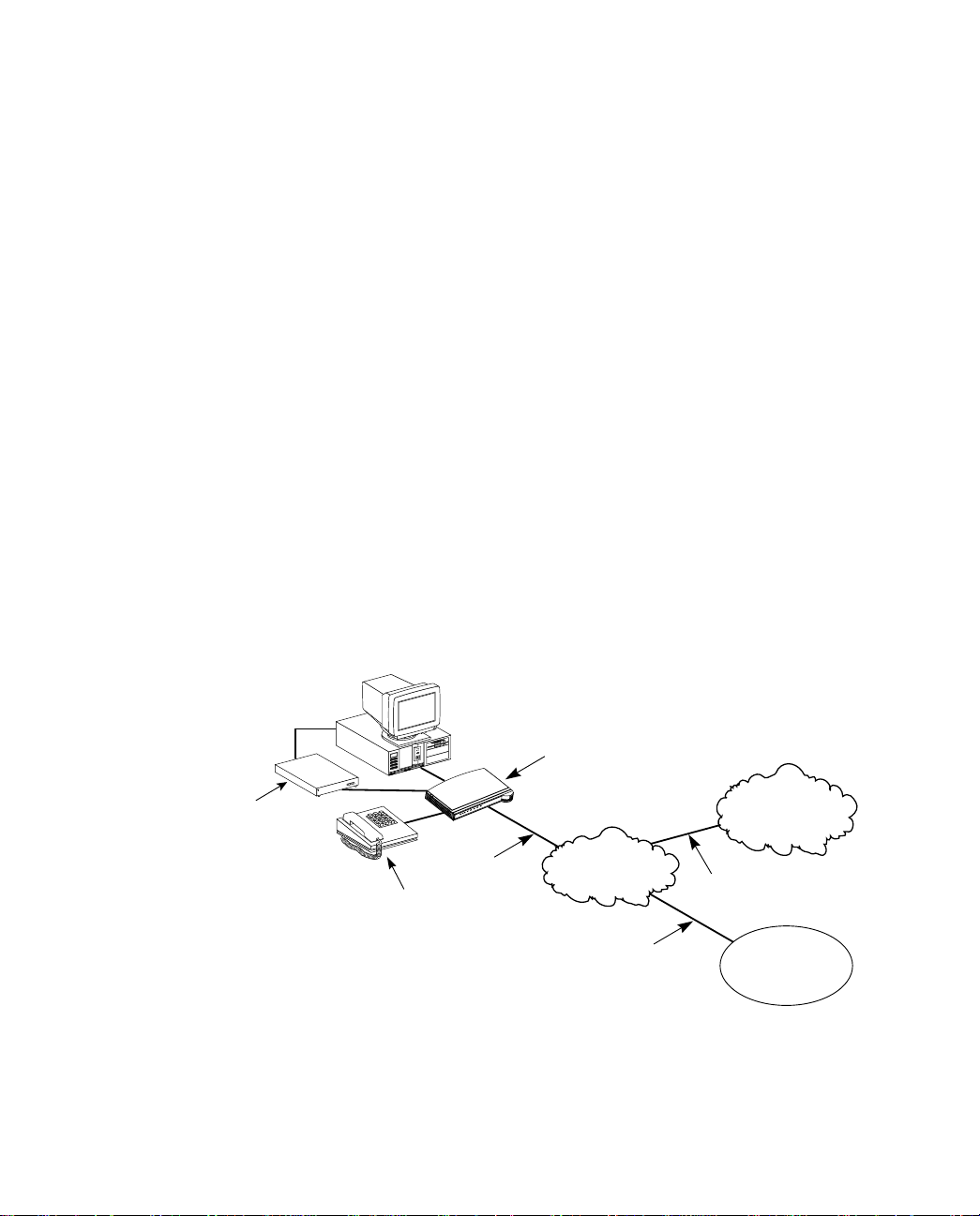
Analog Modem
Netopia
ISDN Modem
P
D
o
-C
w
T
h
e
a
e
r
n
s
t
n
e
B
l
-1
B
-2
n
o
ll
a
r
a
F
ISDN line
M
3 Com
T
Impact
R
T
D
D
R
D
S
2
B
1
DB
T
S
E
T
R
W
P
Public telephone
network
Analog or ISDN line
Analog telephone
Analog or ISDN line
Analog and digital network access with the Netopia ISDN Modem
Internet
or
on-line service
Corporate
LAN

1-2 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
Netopia ISDN Modem features
You can use the Netopia ISDN Modem to dial into any
ISDN-compliant terminal adapter or router that supports the Point-to
Point (PPP) protocol over ISDN.
The Netopia ISDN Modem comes in two models:
■
Model 612 for use with PC computers
Model 412 for use with Macintosh computers
■
The Netopia ISDN Modem’s features include:
■
Support high-speed digital access using Multilink PPP, Stac
compression, and a high-speed serial port.
■
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA).
■
A complete digital network termination (Basic Rate ISDN NT1).
■
Two analog device ports for using analog telephone devices
with the ISDN line and flexible call routing to the two analog
ports.
■
QuickSelect feature to automatically convert asynchronous
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) into synchronous (HDLC-based)
PPP.
■
Support for the Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) and the
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP).
■
Automatic detection and adaptation to the baud rate of your
computer’s serial port (autobaud).
■
Toll Saver 56K permissive dialing, which allows you to place a
data call over an ISDN line set up for voice connections.
■
A comprehensive diagnostic test and LED status display.
■
Netopia ISDN Assistant to configure the switch type and SPID
parameters.

Introduction 1-3
Farallon support
Netopia Care Service Program that includes 30 days of
■
toll-free telephone technical support, lifetime technical support
via e-mail, the World Wide Web, fax, and the Farallon bulletin
board service (BBS). This program also includes a 1-year
warranty that allows you to receive a replacement unit with a
5-day turnaround.
Keep it Running, Guaranteed!
■
support plan that provides toll-free telephone support and a
next-day product-replacement warranty.
Up & Running, Guaranteed!
■
which Farallon helps you obtain ISDN and Internet services and
guarantees a successful connection.
Netopia ISDN Modem package contents
The Netopia ISDN Modem package includes:
A Netopia ISDN Modem unit (model 612 connects to a PC;
■
model 412 connects to a Macintosh computer)
A power cable with an AC wall transformer
■
A DB-25–to–DB-9 serial cable (model 612 only)
■
A DB-25–to–mini-DIN-8 serial cable (model 412 only)
■
An RJ-11–to–RJ-11 ISDN telephone cable
■
A 3.5" installation diskette with configuration software
■
A Netopia ISDN Modem user’s guide
■
A Getting Started card with an attached phone card
■
, an optional 3-year premium
, an optional service program in
Internet access software
■
1-4 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
Computer system requirements
Refer to the appropriate section below for information on PC and
Macintosh computer requirements.
PC requirements
Your PC should have the following:
A 386, 486, or Pentium processor
■
640 KB of conventional memory
■
■
MS-DOS 5.0 or later operating system
■
Microsoft Windows 3.1 or later, Windows 95, or Windows NT
■
A hard disk drive with 2 MB of free space
■
An available serial (COM) port equipped with a 16550 universal
asynchronous transmitter. (See the “Optimizing serial port
performance” section on page 6-9 for more information.)
Macintosh computer requirements
Your Macintosh computer must be a Macintosh Plus or later model.
It must have the following:
■
System 7 or later operating system
■
A hard disk drive with 2 MB of free space
■
An available serial port (see the “Optimizing serial port
performance” section on page 6-9 for more information).

Introduction 1-5
Your communications software, such as a PPP client application,
may additionally require:
■
System 7.1 or later
■
A Macintosh computer equipped with a 68020 or later CPU
Cabling requirements
Your package contains a PC or Macintosh serial cable to connect
the Netopia ISDN Modem to your computer.
If your PC computer has a 25-pin serial port, you will need a
DB-9–to–DB-25 adapter. See “RS-232-D pin assignments” on
page C-3 for a description of the pins on the ISDN modem’s
RS-232-D port.


Chapter 2
Setting Up ISDN Service
This chapter shows you how to set up ISDN service. You will learn
about what ISDN is, how to prepare for setting up an ISDN line, and
how to work with an ISDN service provider. If you already have an
ISDN line, you may still want to read the rest of this chapter to find
the ISDN information needed to properly configure your Netopia
ISDN Modem.
2-1
If you opted for the
will set up ISDN service for you. However, you may still want to read
this chapter to become familiar with basic ISDN concepts.
This chapter is divided into three main sections:
■
A short description of ISDN and definitions of some common
ISDN terms
■
Preparing to order your ISDN line
■
Ordering your ISDN line
Up & Running, Guaranteed!
program, Farallon

2-2 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
About ISDN
ISDN uses digital technology to connect to the public telephone
network. Using the existing copper wire and public telephone
network infrastructure, ISDN provides for existing voice services
and high-speed, dial-up data service.
Networks using ISDN communicate more efficiently than those
using analog lines. This is due to the relatively low cost of ISDN, the
fact that digital lines are relatively free of the random noise
associated with analog lines, and the high communication speeds
that can be achieved. ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI) lines can
reach speeds of up to 128 thousand bits per second (Kbps). A
typical high-speed modem can only send data over an analog line at
up to 28.8 Kbps.
You can convert almost any existing regular telephone line to ISDN
by ordering ISDN service for that line. In most cases, no rewiring is
necessary for the conversion and no special equipment is needed
to use the converted line with your Netopia ISDN Modem. (Keep in
mind that if you convert an analog line to an ISDN line, you will not
be able to directly connect analog devices to the ISDN line in most
cases.)
ISDN and the Netopia ISDN Modem
If you’ve been using an ordinary modem to dial into analog data
services, such as a corporate LAN or online service, you can
continue to do so with your digital ISDN line. Simply connect your
analog modem to one of the analog device ports on the Netopia
ISDN Modem and continue to use your analog devices in the same
fashion as before.
The Netopia ISDN Modem will convert the analog signal to a digital
signal for transmission over the ISDN line in such a way that it can
be retransmitted by the public switched network to an analog
device.
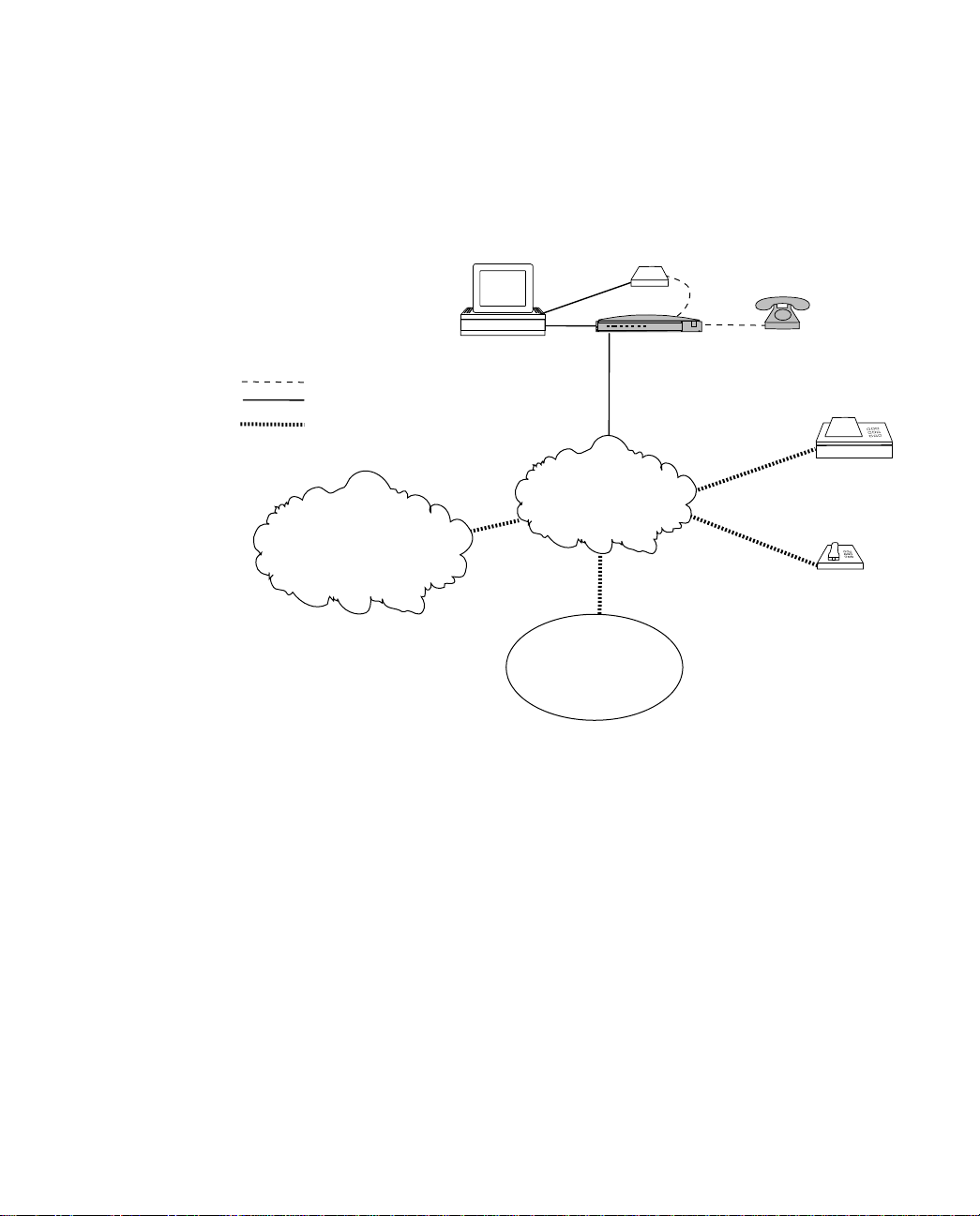
Setting Up ISDN Service 2-3
Analog connection
Digital connection
Analog or digital connection
Internet Service Provider
or online service
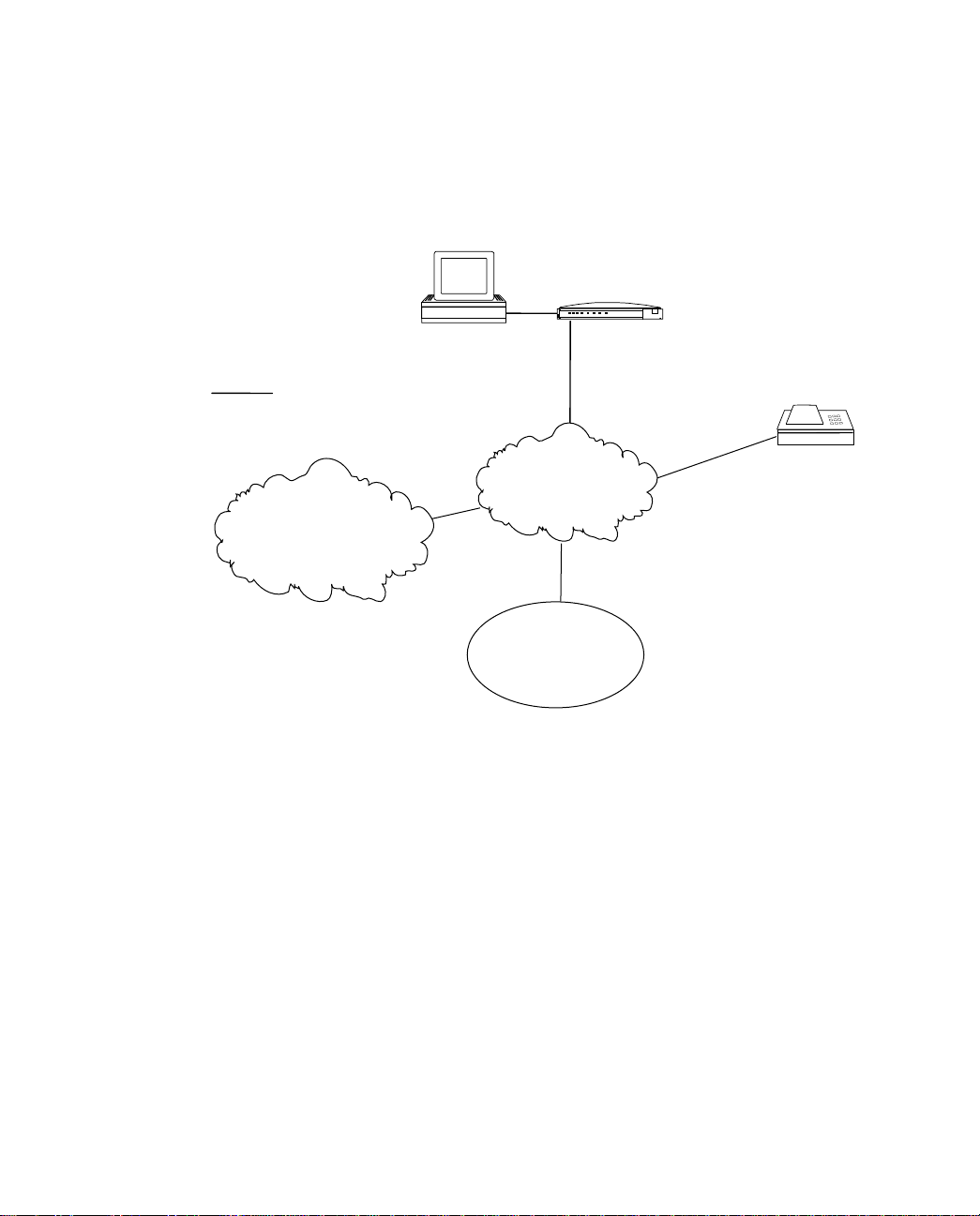
Using analog devices with the Netopia ISDN Modem to communicate with
analog voice and data services
Your computer
Analog modem
PWR TESTD B1 B2 SD RD DTR
Netopia
ISDN Modem
Public telephone
network
Corporate
LAN
Netopia
Analog phone
Fax services
Telephone voice
services
2-4 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
Your computer
Digital connection
Internet Service Provider
or online service
*
Using the Netopia ISDN Modem to connect to digital voice and data services
PWR TESTD B1 B2 SD RD DTR
Netopia
ISDN Modem
Public telephone
network
Corporate
LAN
Netopia
ISDN fax service
* If you choose not to connect any analog devices to the Netopia
ISDN ModemÕs analog device ports, you will be able to connect to
other ISDN devices, but not to analog devices. See the diagrams
above.
Setting Up ISDN Service 2-5
Terms used in this user’s guide
The following ISDN-related terms are used in this user’s guide:
Basic Rate Interface (BRI):
order from the ISDN service provider. A BRI ISDN line has two
B channels and a D channel. The B channels carry data at 56 Kbps
or 64 Kbps, and can be used by the applications you use to access
the Internet. The D channel is reserved for call setup and signalling.
D channel
Switch:
from the telephone company’s local central office. You must know
the type of switch—sometimes referred to as
configuration
Directory number (DN):
the ISDN line you order (the directory number is also referred to as
the “telephone number” in this user’s guide). Depending on the type
of switch on your line, there may be one directory number for both
B channels, or one for each B channel.
The massive computer that controls your telephone line
—on your line to properly configure the ISDN modem.
BRI is the type of ISDN service you will
B channels
ISDN BRI
switch
The actual phone number associated with
SPID:
The Service Profile ID generally looks like the directory
number with some extra digits (the TID) appended to it. The number
of SPIDs received with BRI service can vary from none to two.
TID (Terminal ID): This one- or two-digit number is associated with
the SPID. It’s usually 1 or 01 for the first SPID and 2 or 02 for the
second SPID, but it can vary in form.
If you encounter other unfamiliar terms, check the glossary.
2-6 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
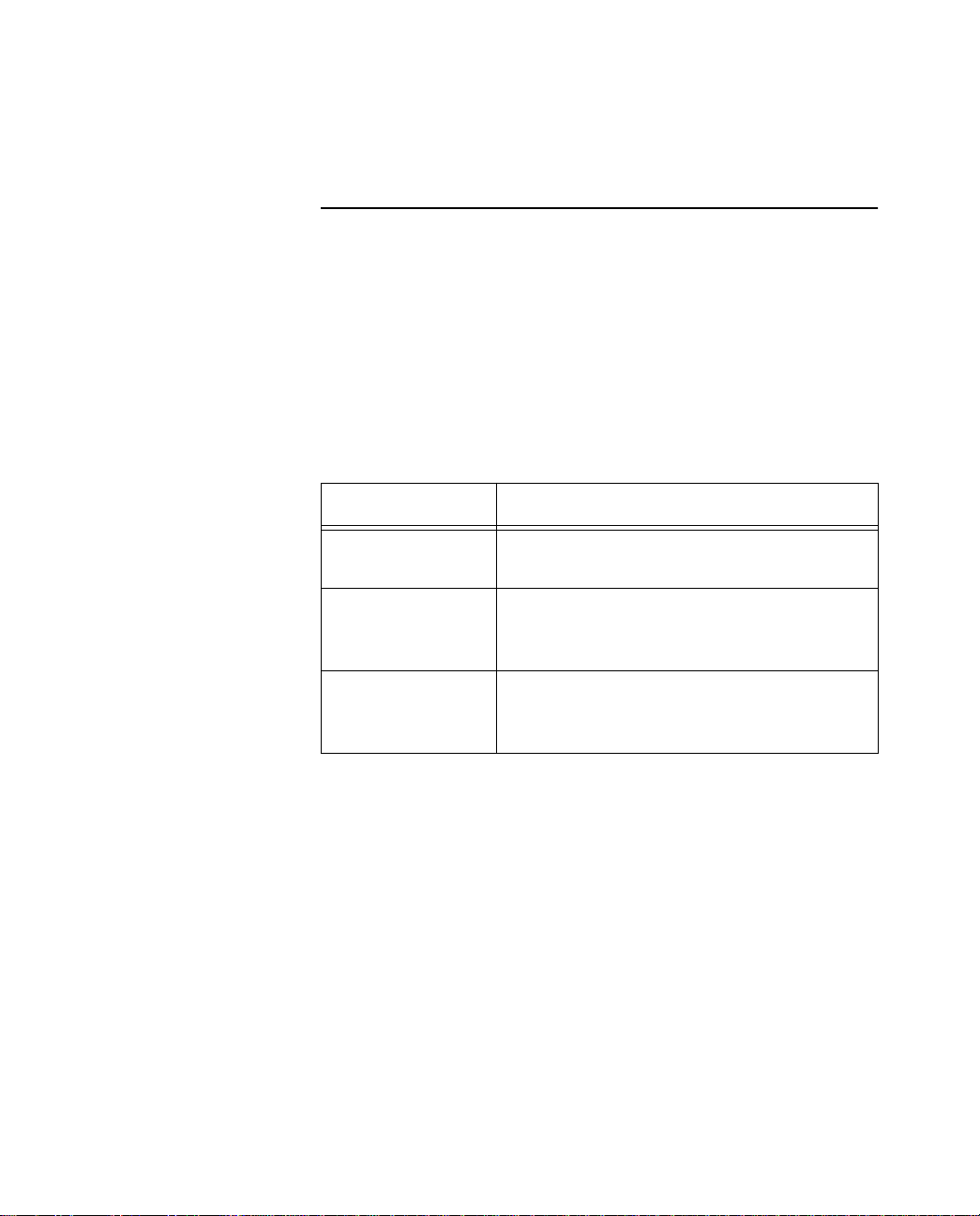
SPID formats
The exact format of ISDN SPIDs is sometimes a point of confusion.
This is because several formats exist, and some formats allow
variations.
The table below displays the general SPID formats for some of the
types of ISDN switch configurations supported by the Netopia ISDN
Modem. The formats shown are a subset of possible SPID formats,
but in most cases they should work.
In the following table, xxxxxxx represents the directory number
assigned to your ISDN line, and yyy represents your area code.
Switch SPID format
AT&T 5ESS custom (multipoint)
National ISDN-1
on AT&T 5ESS
(multipoint)
National ISDN-1
on Northern
Telecom DMS-100
Note: AT&T 5ESS custom point-to-point switches have no SPIDs
and are not represented in the table above. However, this type of
switch configuration is supported by the Netopia ISDN Modem.
Example SPIDs If your ISDN line is controlled by a DMS-100 using National ISDN-1,
and your directory numbers are given as (415)234-5678 and
(415)234-5679, your SPIDs are 4152345678100 and
4152345679200. Alternately, your SPIDs can be
41523456780100 and 41523456790200.
yyyxxxxxxx100 and yyyxxxxxxx200
yyyxxxxxxx0100 and yyyxxxxxxx0200
01xxxxxxx0
01xxxxxxx00
or

Preparing for an ISDN line
When you order an ISDN line, you will exchange information with the
ISDN service provider about the kind of service you need. The
provider, in turn, will give you some information about your line that
will be useful when you configure your Netopia ISDN Modem.
There are a few things to do before you can order an ISDN line:
■ Find an ISDN service provider
■ Decide on a type of ISDN line
■ Choose a phone line
■ Use your ISDN worksheet
These are explained in the corresponding sections below.
Setting Up ISDN Service 2-7
Find an ISDN service provider
ISDN service is typically provided by local telephone companies. In
certain regions, there may be other types of companies providing
ISDN service, such as long distance telephone companies. In this
user’s guide, we’ll refer to the ISDN service providers as telephone
companies.
If you are unsure of who provides ISDN service in your area, start by
contacting your local telephone company (refer to the list of contact
numbers for telephone companies that appears later in this
chapter). Ask for the ISDN service representative or for someone in
the company’s marketing or business services office.
Regardless of who you choose for ISDN service, the basic process
of setting up an ISDN line should be the same.
2-8 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
Decide on a type of ISDN line
An ISDN line can be configured to carry data only, or both data and
voice.
Choose a phone line
To order an ISDN line, you must either designate an existing
telephone line to be converted, or order a new line to be installed.
There will probably be an additional charge if you add a new ISDN
line. However, if you convert an analog line to an ISDN line, you will
not be able to directly connect analog devices to the ISDN line in
most cases.
Regardless of your choice, make sure there is a wall jack for the line
you choose near where you intend to install your Netopia ISDN
Modem.
Use your ISDN worksheet
The ISDN Worksheet at the end of this chapter (see page 2-18)
contains sections where you can note important information about
your ISDN account. You may want to photocopy the ISDN Worksheet
and fill in the copy.
Note: The ISDN Worksheet is for your convenience only. You may
receive forms containing similar information from your telephone
company. In any case, the ISDN Worksheet is not an application for
an ISDN line nor a substitute for the forms your telephone company
uses.
Fill in section 1 of the worksheet once you find out exactly who you’ll
order your ISDN line from. Fill in as much of section 2 as you can
before calling your telephone company. The information in section 3
can only be filled in after you order your ISDN line.

Be sure to check the accuracy of the information you enter on the
worksheet. Some of it will be needed later when you configure your
Netopia ISDN Modem.
It’s also a good idea to have the worksheet available if you call
Farallon technical support. The information on the sheet may help a
Farallon technician answer your questions more quickly.
Ordering your ISDN line
This section contains the information you’ll need to successfully
order an ISDN line.
Read this section through before contacting your telephone
company. Then refer to it when you actually order your line.
The first step in ordering your ISDN line is to prepare for the
questions your telephone company may ask, such as:
Setting Up ISDN Service 2-9
■ Will you be using an existing telephone line or need a new one?
■ Where is the line located?
■ Who is the contact person at that location?
■ Who will be billed for the line or should this line be added to an
existing account?
■ Should the service (or number) be listed?
Use section 2 of the ISDN Worksheet to record the answers to
these questions before calling your telephone company. Your
telephone company may also ask other questions about the type of
service you want.

2-10 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
Contacting the telephone company
Below is a list of items that can help you order your ISDN line more
easily. These items correlate with items in section 3 of the ISDN
Worksheet (see page 2-18).
Depending on your situation, some of these items may not apply to
your order, and all of the items may not be dealt with by your
telephone company at the same time. In addition, there may be
other issues you will need to ask the telephone company about.
When an item in this list generates information that should be
entered in your worksheet, be sure to do so.
First, read through this list and become familiar with its contents.
Then call your telephone company and refer to the items in the list
during the ordering process.
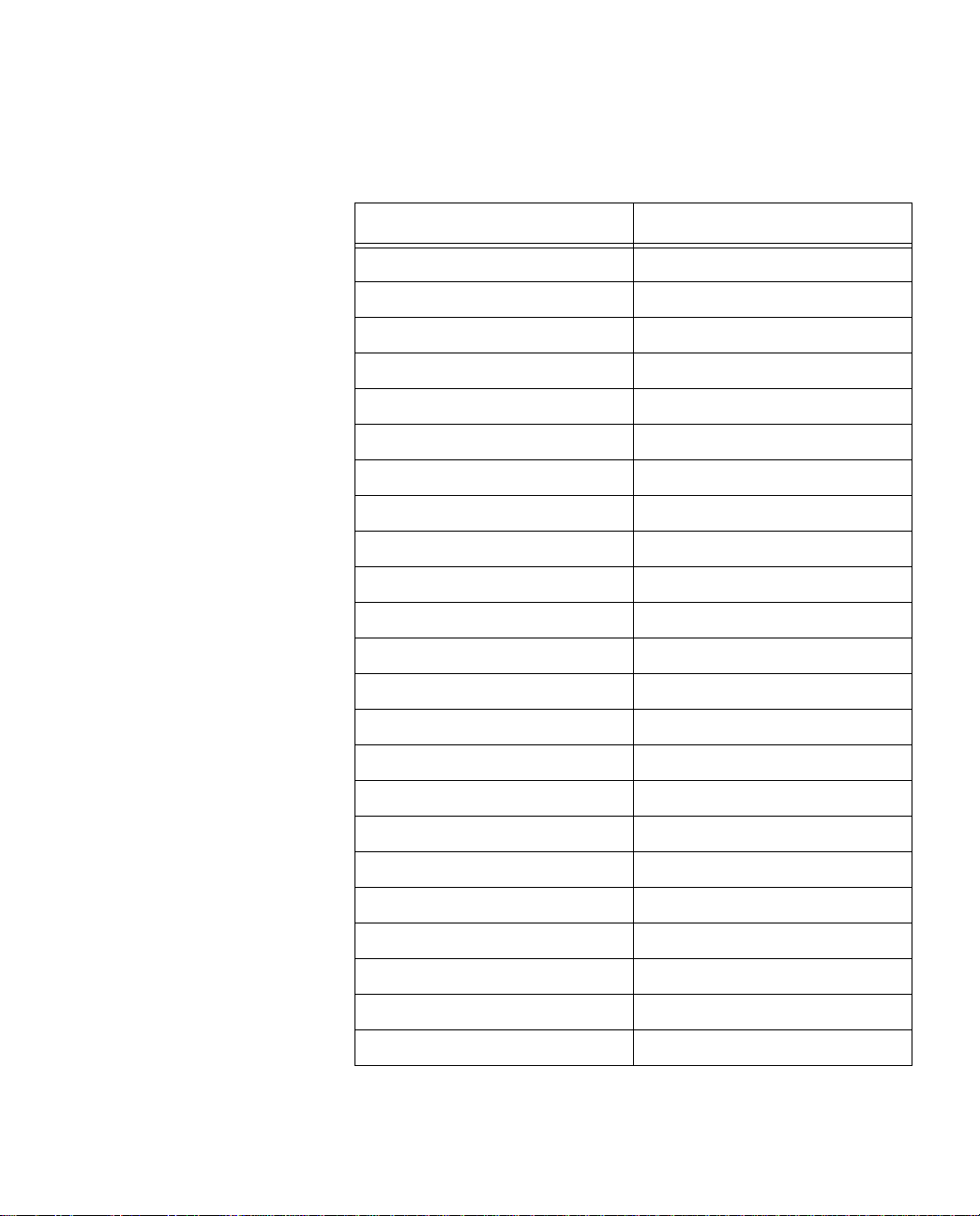
1. Call your telephone company. Refer to the table below for your
telephone company’s phone number.
State Telephone Number
Alabama 800-858--9413
Alaska 907-561-1221
Arizona 800-898-WORK
Arkansas 800-SWB-ISDN
California 800-4PB-ISDN
Colorado 800-898-WORK
Connecticut 800-430-ISDN
Delaware 800-570-ISDN
Florida 800-858--9413
Georgia 800-858--9413
Hawaii 808-586-3000
Setting Up ISDN Service 2-11
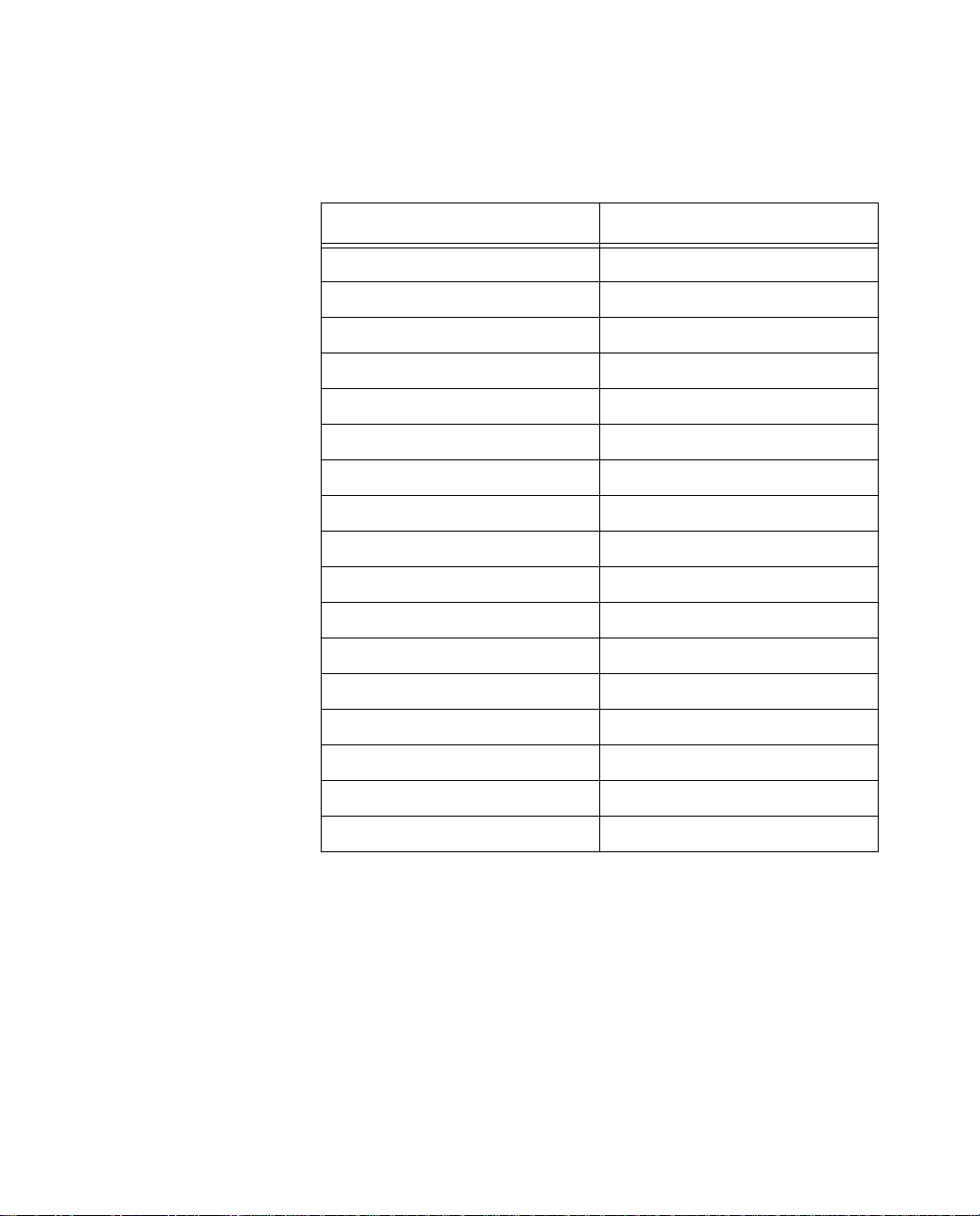
State Telephone Number
Idaho 800-898-WORK
Iowa 800-898-WORK
Illinois 800-TEAM-DATA
Indiana 800-TEAM-DATA
Kansas 800-SWB-ISDN
Kentucky 800-858--9413; 513-566--9413
Louisiana 800-858--9413
Maine 800-GET-ISDN
Maryland 800-570-ISDN
Massachusetts 800-GET-ISDN
Michigan 800-TEAM-DATA
Minnesota 800-898-WORK
Mississippi 800-858--9413
Missouri 800-SWB-ISDN
Montana 800-898-WORK
Nebraska 800-898-WORK
Nevada 702-333-4811
New Jersey 800-570-ISDN
New Hampshire 800-GET-ISDN
New Mexico 800-898-WORK
New York 800-GET-ISDN; 716-777-1234
North Carolina 800-858--9413
North Dakota 800-898-WORK
2-12 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
Ohio 800-TEAM-DATA; 513-566--9413
Oklahoma 800-SWB-ISDN
Oregon 800-898-WORK
Pennsylvania 800-570-ISDN
Rhode Island 800-GET-ISDN
South Carolina 800-858--9413
South Dakota 800-898-WORK
Tennessee 800-858--9413
Texas 800-SWB-ISDN
Utah 800-898-WORK
State Telephone Number
Vermont 800-GET-ISDN
Virginia 800-570-ISDN
Washington 800-898-WORK
Washington DC 800-570-ISDN
West Virginia 800-570-ISDN
Wisconsin 800-TEAM-DATA
Wyoming 800-898-WORK
2. ISDN line configuration. Your telephone company may have the
Netopia ISDN Modem on a list of supported products that have
been tested with a particular ISDN line configuration. If your
telephone company confirms that the Netopia ISDN Modem is
on that list, then it will know how to set up your line.
Note: If your telephone company does not recognize the
Netopia ISDN Modem, you should read “General ISDN line
configuration” on page 2-14.

Setting Up ISDN Service 2-13
3. Type of switch configuration used on your line. You must
receive this information from your telephone company to properly configure the Netopia ISDN Modem. The switch should be
one of the types supported by the Netopia ISDN Modem:
■ AT&T 5ESS custom
■ Northern Telecom DMS-100 or Siemens EWSD
■ AT&T 5ESS
4. Directory numbers and SPID (service profile identifier) numbers. This information may be provided to you at a later time,
after your line has been set up. There may be one or two directory numbers, and one or two SPIDs. If the switch on your line
is an AT&T 5ESS custom point-to-point, you will receive no
SPIDs. It’s very important that you record this information accurately.
Note: Regardless of the number of directory numbers and
SPIDs you receive, your line should be configured to allow the
Netopia ISDN Modem to use both B channels at once.
5. Circuit ID number. Your line has a unique physical address
called a circuit ID. Y ou should obtain this number from your telephone company and record it on the worksheet. The circuit
number can be useful for locating your line and its associated
circuit in case of a problem.
6. Long-distance company to be used on your ISDN line. When
the Netopia ISDN Modem makes long distance calls on your
ISDN line, you will be billed by a long distance telephone company. Make sure that you have the long distance company of
your choice.

2-14 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
General ISDN line configuration
What if your telephone company does not recognize the Netopia
ISDN Modem? You can still use the ISDN Worksheet, but follow
these steps:
1. Ask for a standard Basic Rate Interface (BRI).
2. Ask the telephone company representative what type of switch
the company will use for your line: AT&T 5ESS custom, Northern Telecom DMS-100/Siemens EWSD, or AT&T 5ESS. Note
this information on your ISDN Worksheet for later use.
Note: NI-1 can appear on an AT&T 5ESS or a Northern Telecom
DMS-100.
3. Locate your telephone company’s ISDN switch type in the table
below. Provide the switch parameters to the representative.
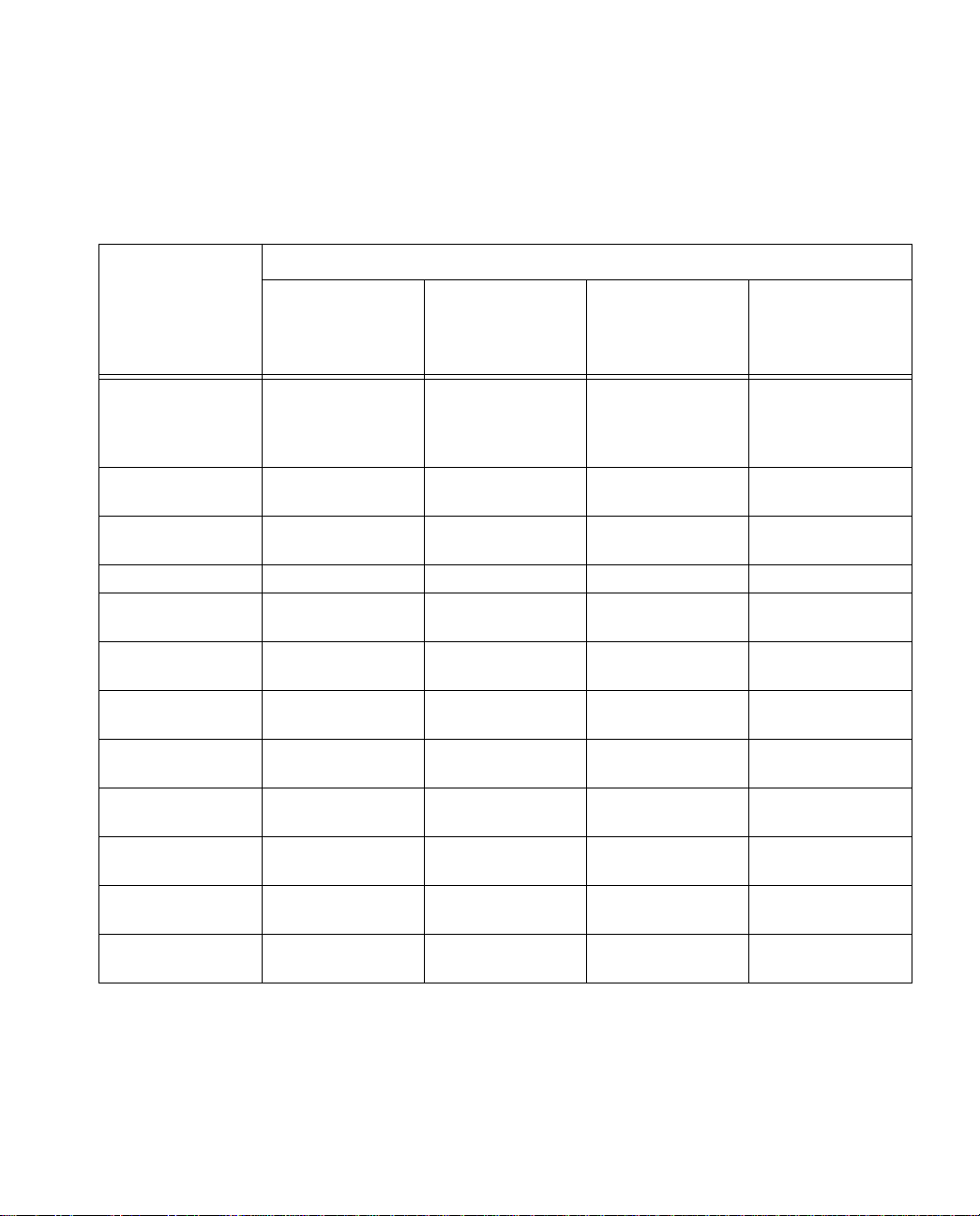
ISDN switch type
Setting Up ISDN Service 2-15
ISDN Line
Configuration
Parameter
AT&T
Custom
5ESS
AT&T 5ESS
National ISDN-1
Northern
Telecom
DMS-100
Siemens EWSD
National ISDN-1
National ISDN-1
Standard (2B+D)
Line type
line with
point-to-point
configuration
Line code
Interface type
2B1Q (no NT1
required)
U interface with an
RJ-45 jack
Directory numbers 2
Maximum
terminals
Maximum B
channels
Circuit-switched
voice
Circuit-switched
voice limit
Circuit-switched
voice channel
Circuit-switched
data
Circuit-switched
data and voice
Circuit-switched
data channel
*
1 1 NA NA
2222
*
2
*
2
Any Any NA NA
*
2
NA NA NA Yes
Any Any NA NA
Standard (2B+D)
National ISDN-1
line
2B1Q (no NT1
required)
U interface with an
RJ-45 jack
*
2
*
2
*
2
*
2
Standard (2B+D)
National ISDN-1
line
2B1Q (no NT1
required)
U interface with an
RJ-45 jack
22
NA NA
NA Dynamic
NA NA
Standard (2B+D)
National ISDN-1
line
2B1Q (no NT1
required)
U interface with an
RJ-45 jack
* The directory number, circuit-switched voice, and circuit-switched voice limit parameters should be
set to 2 to allow both analog device ports to be used simultaneously. If these parameters are set
to 1, the ISDN line can only place or receive one call at a time.
*
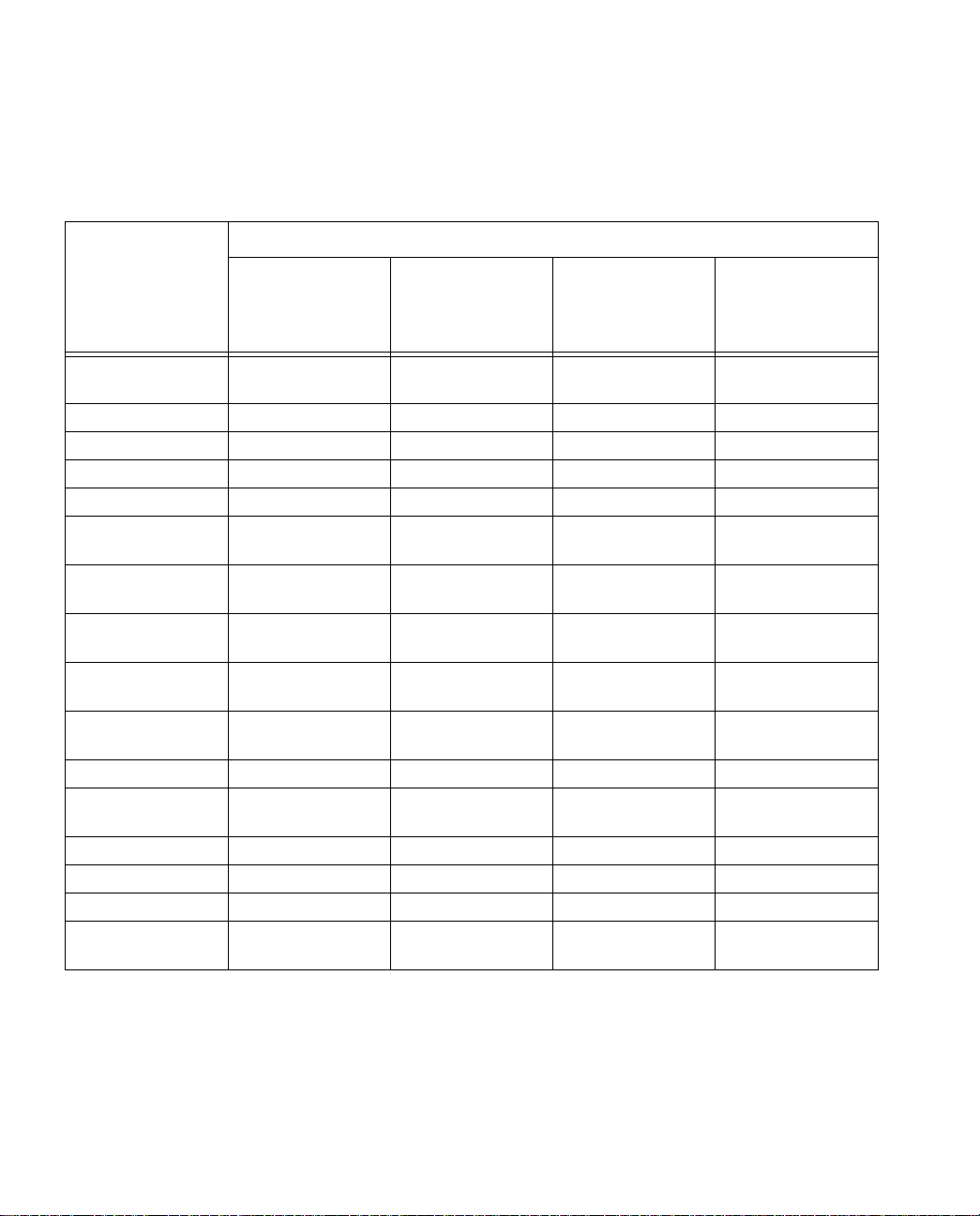
2-16 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
ISDN switch type
ISDN Line
Configuration
Parameter
AT&T
Custom
5ESS
AT&T 5ESS
National ISDN-1
Northern
Telecom
DMS-100
Siemens EWSD
National ISDN-1
National ISDN-1
Circuit-switched
data limit
2 2 NA None
Terminal type A (basic terminal) A (basic terminal) Functional PVC 2 Functional
Display Yes Yes NA NA
Actual user Yes Yes NA NA
Voice or data Both Both Both No
Data option NA NA
Call appearance
preference
Circuit-switched
option
Bearer restriction
option
Idle Idle NA NA
NA NA Yes NA
NA NA
Protocol NA NA
Lower layer
compatibility
No packet mode
data (NOPMD)
Functional version
2 (PVC 2)
NA
No packet mode
data (NOPMD)
Functional
SPID suffix NA NA 1 1
Terminal Endpoint
Identifier
NA NA Dynamic Dynamic
Maximum keys NA NA 64 NA
Ring NA NA No NA
Key system (EKTS) NA NA No No
Flexible Call
Offering (FCO)
Yes
*
Yes
*
Yes
*
Yes
*
* FCO (also referred to as “Additional Call Offering”) allows you to receive an incoming call while a
Multilink PPP call is active. If you do not want this feature, which might cost extra, notify your telephone service provider. Note that FCO is not required.

Setting Up ISDN Service 2-17
4. Ask the telephone company representative to provide the information you need to fill out section 3 of the worksheet.
5. Present the ordering information you receive from the telephone company representative to the ISDN line installer or telephone company service representative in your area. Also, make
sure that your local telephone company installer installs a new
or rewires an existing RJ-11 or RJ-45 jack for your ISDN line.
Y ou will connect the Netopia ISDN Modem to this jack using the
RJ-11–to–RJ-11 ISDN telephone cable.
6. Once your Netopia ISDN Modem is installed and configured, try
to place a call. If the line does not function properly with the
ISDN modem, contact your telephone company and ask them to
reconfigure the line until it works properly.

2-18 Netopia ISDN Modem User’s Guide
ISDN Worksheet
1. Telephone company contact information
Name and address:
_____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
Telephone/Fax numbers: _______________________________________
E-mail address: _______________________________________________
2. Your information
Street address where your ISDN line is located:
_____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
Contact person at this location, including phone number:
_____________________________________________________________
Is this an existing line or a new line (to be installed)?
__ existing
__ new
Should the number for this line be listed in the telephone company’s directory?
__ no
__ yes
Billing address for your ISDN line:
_____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________
 Loading...
Loading...