Fairchild Semiconductor DM9368N Datasheet
October 1988
Revised March 2000
DM9368
7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch
with Constant Current Source Outputs
General Description
The DM9368 is a 7-se gment decoder driv er incorporating
input latches and constant c urrent output circuits to drive
common cathode type LED displays directly.
Ordering Code:
Order Number Package Number Package Description
DM9638N N16E 16-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide
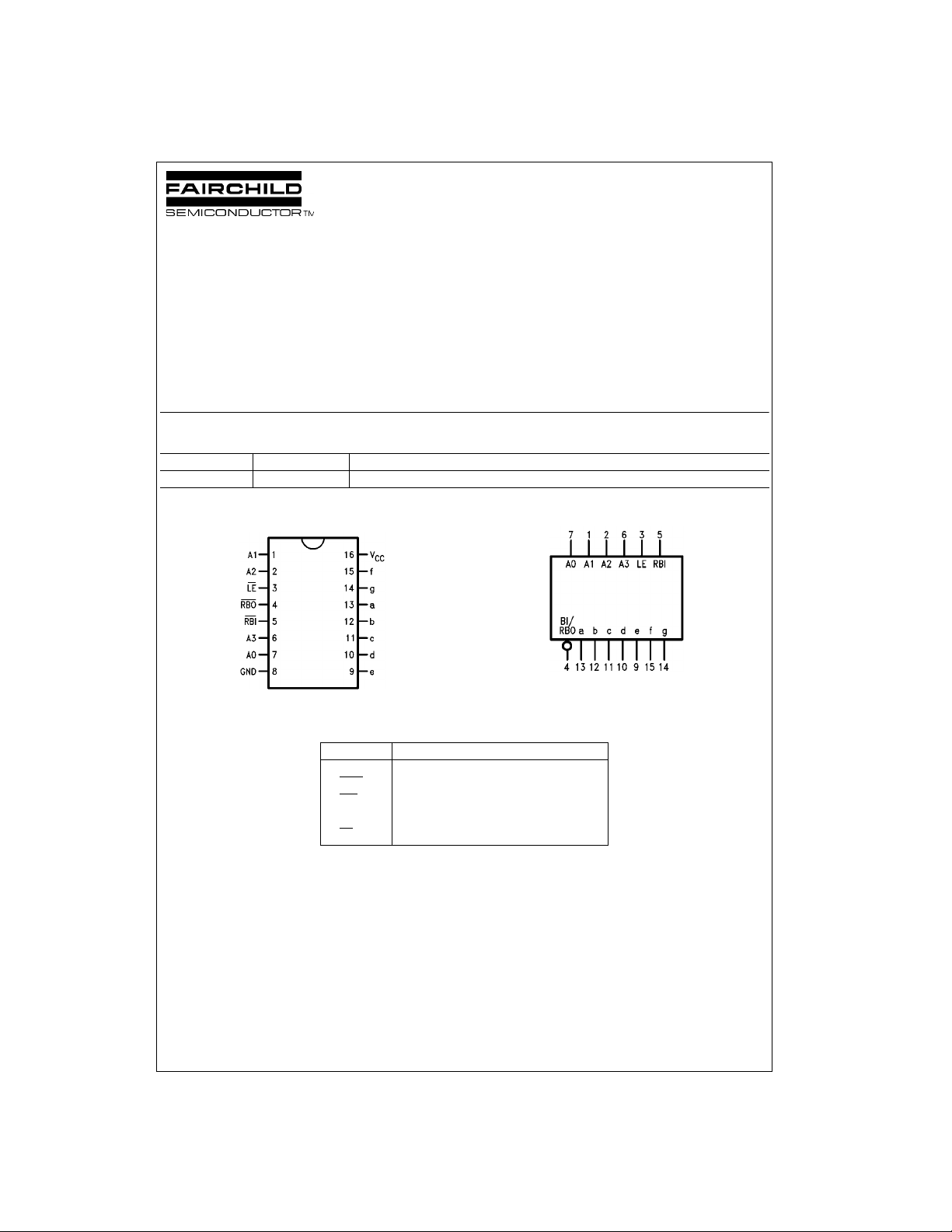
Connection Diagram Logic Symbol
DM9368 7-Segment Decoder/Driver/Latch with Constant Current Source Outputs
VCC = Pin 16
GND = PIN 8
Pin Descriptions
Pin Name Description
A0–A3 Address (Data) Inputs
RBO
RBI
a–g Segment Drivers-Outputs
LE
© 2000 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation DS009796 www.fairchildsemi.com
Ripple Blanking Output (Active LOW)
Ripple Blanking Input (Active LOW)
Latch Enable Input (Active LOW)
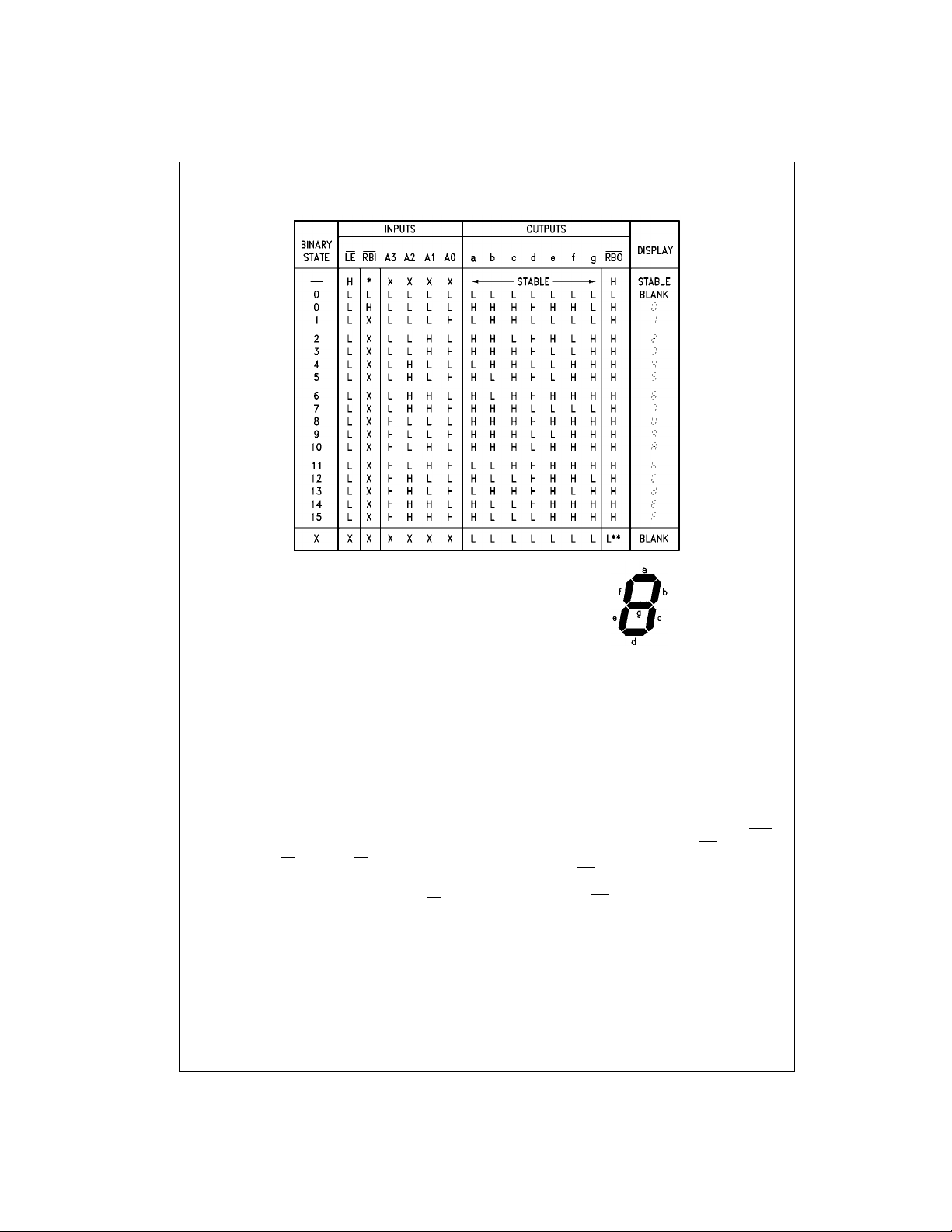
Truth Table
DM9368
*The RBI will blank the display on ly if a binary zero is stored in the lat c hes.
used as an input overr ides all other input condit ions.
*The RBO
H = HIGH Voltage Level
L = LOW Voltage Level
X = Immaterial
Functional Description
The DM9368 is a 7-segme nt decoder driver designed to
drive 7-segment common cathode LED displays. The
DM9368 drives a ny com mo n cath ode LED display rated at
a nominal 20 mA at 1.7V per segment without need for current limiting resistors.
This device accepts a 4-bit bina ry code and p roduces ou tput drive to the appropriate segments of the 7-segment display. It has a hexadecimal decode for mat which produces
numeric codes “0” thru “9” and alpha codes “A” through “F”
using upper and lower case fonts.
Latches on the fo ur dat a input s are c ontr olled b y an ac tive
LOW latch enable LE
the outputs is determin ed by the input dat a. When the LE
goes HIGH, the last data present at the inputs is stored in
the latches and the out puts remain stable. The LE
width necessary to accept and store data is typically 30 ns
which allows data to be strobed into the DM9368 at normal
TTL speeds. This fea ture means that data can be routed
directly from hig h speed counters and freque ncy dividers
into the display without slowing d own the system clock or
providing intermediate data storage.
Another feature of the DM 9368 is that the unit loading on
the data inputs i s very low (−100 µA Max) wh en the latch
enable is HIGH. This allows DM9368s to be driven from an
www.fairchildsemi.com 2
. When the LE is LOW, the state of
pulse
MOS device in multiplex mode with out the nee d for driv ers
on the data lines.
The DM9368 also has p rovision for automa tic blanking of
the leading and/or trailing edge zeros in a multidigit decimal
number, resulting in an easily readable decimal display
conforming to normal writing practice. In an eight digit
mixed integer fraction decimal representation, using the
automatic blanking capability, 0060.0300 would be displayed as 60.03. Leading edge zero suppression is
obtained by connecting the Ripple Bl anking Output (RBO
of a decoder to t he Ri pple Bl anking Input (RBI
lower stage device. The most significant decoder stage
should have the RBI
sion of the least significa nt intege r zero in a n umber is not
usually desired, the RBI
be left open. A similar procedure f or the fractional part of a
display will provide automatic suppression of trailing edge
zeros. The RBO
with a modulating signal via an isolating buffer to achieve
pulse duration intens ity modulation. A suitable signal can
be generated for this pur pose by forming a variable frequency multivibrator with a cross coupled pair of TTL or
DTL gates.
input grounded; an d since suppres-
input of this decoder stage sho uld
terminal of the decode r can be OR-tied
) of the next
)
 Loading...
Loading...