Page 1

SECURITY POLICY
FOR THE
M-RK I AND M-RK II SYSTEM/SCAN (AEGIS/DES)
HANDHELD PERSONAL PORTABLE
TWO-WAY FM RADIO
MRK I M-RK II
SYSTEM/SCAN
Page 2

Table of Contents
Table of Contents..............................................................................................................................................................2
1. Introduction...................................................................................................................................................................3
2. Scope...............................................................................................................................................................................3
3. Module Description......................................................................................................................................................4
3.1. Module Interfaces..................................................................................................................................................4
3.2. Module Components.............................................................................................................................................4
4. Software/Firmware Capabi lities...................................................................................................................................5
4.1. Radio Control Processor (RCP)............................................................................................................................5
4.2. Interrupt Control Processor (ICP)........................................................................................................................5
4.3. AEGIS DSP (ADI)..................................................................................................................................................5
4.4. Firmware ..................................................................................................................................................................5
5. Roles & Services ...........................................................................................................................................................5
5.1. Crypto-Officer Services.........................................................................................................................................6
5.2. User Services..........................................................................................................................................................6
5.3. Status Functions....................................................................................................................................................6
5.4. Key Management...................................................................................................................................................7
6. Secure Operation...........................................................................................................................................................7
6.1. AEGIS Clear, Digital, and DES Operation...........................................................................................................7
6.1.1. Clear Mode...................................................................................................................................................7
6.1.2. AEGIS Digital Mode...................................................................................................................................7
6.1.3. AEGIS Private Mode...................................................................................................................................8
6.1.4. Error Messages ..........................................................................................................................................8
Page 3

Ericsson Security Policy
1. Introduction
The M-RK II System/Scan (AEGIS) and M-RK I handheld personal portable two-way FM radio is a
high-quality, high performance FM radio. The radio is synthesized and operates in both trunked (Ericsson
EDACS™) and conventional communications systems. The trunked mode allows selection of either a
communications group or an individual radio within a system. Both the selected group and the individual
radio are secured through AEGIS digital signaling and DES encryption.
Trunked operation is where a set of radio frequency channels is used by multiple user groups. By using
high speed digital data, the radio goes to an unused channel when a call is initiated and will only respond to
calls in the same user group. In this way, conversation privacy between user groups is assured. This
operation is very similar to a cellular phone call.
A conventional mode of operation is communicating on radio channels allocated for conventional use.
Conventional use or operation is where a radio channel (transmit/receive) is allocated for conventional
(non-trunked) use and may be manually selected by the operator. The user selects a channel and directly
communicates on that channel. A channel is a transmit/receive radio frequency pair. Think of this mode as
“Walkie-Talkie” mode.
A trunked group consists of several users with a common group identification (GID). A radio may have
several groups but the selected group determines whom the unit can call at any specific time. In trunked
mode, a set of groups that communicate on a set of channels is called a system. In the conventional mode, a
system is a set of channels. A system may consist of all trunking groups and channels, all conventional
channels, or a mixture of both.
2. Scope
This document will define the security policy for the M-RK II System/Scan and M-RK I radio. This
policy will define the cryptographic module, cr ypto-officer roles, user roles, and key management functions.
M-RK (AEGIS/DES) Radio p. 3 of 3
Page 4

Ericsson Security Policy
3. Module Description
The M-RK DES radio can be divided into three main modules; User, Crypto-Officer, and Processing. These
are described in the following sections.
3.1. Module Interfaces
A
n
t
e
n
n
a
User
Interface
User Role
(Control Input, Status Output)
PC
Programmer
DES
Keyloader
Crypto-Officer Role
(Data Input, Control Input, Status Output)
LCD,
Tones
Keypad,
Switches
Personality
Key
Storage
Crypto-Processing
(Data Input, Data Output)
Battery Power
Microphone Speaker
DSP
(AEGIS/DES)
RF
MODEM
Figure 1 M -RK (AEGIS/DES) Radio Modules
3.2. Module Components
The User Role represents the user operating the radio. The user can input control data via the
keypad and associated keys and switches. Status Output information is provided to the user by viewing the
LCD, LED, and/or listening to the alert tones. This module is connected to the Processing module by the
microphone and speaker. The user speaks into the microphone and listens to received speech from the
speaker.
The Crypto-Officer Role allows the crypto-officer the ability to configure the radio’s operation.
The crypto-officer can input or output personality information using a PC. The personality configures the
radio by specifying items such as trunked channels, conventional channels, DES talkgroups, clear
M-RK (AEGIS/DES) Radio p. 4 of 4
Page 5

Ericsson Security Policy
talkgroups, etc. The crypto-officer can enter the DES encryption keys into the radio using a DES keyloader.
These keys are scrambled and hidden into the radio’s EEPROM memory. The crypto-officer can’t read the
keys out for security purposes. Status Output information is provided to the crypto-officer by viewing the
LCD, LED, and/or listening to the alert tones.
The Crypto-Processing module represents the crypto-processing portion of the radio. This module
samples speech from the microphone and digitizes it for processing. The DSP converts the speech to digital
using the AEGIS algorithm. It then encrypts the AEGIS speech using the DES algorithm. The digital data is
passed to the modem for transmission over an EDACS network or conventional system. Similarly, the
reverse process receives a data transmission and passes the digital data to the modem. The DSP decrypts
the DES speech into AEGIS speech and then converts it to an analog waveform to be played out the
speaker. All of the DSP processing is performed in software.
4. Software/Firmware Capabilities
The M-RK contains numerous firmware and softwar e components. All of the associated hardware
can be found on the schematics.
4.1. Radio Control Processor (RCP)
The RCP S/W is the main M-RK S/W that resides both in ROM and FLASH memory. This S/W
controls the entire operation of the radio. It is the master while all other S/W components are slaves. This
S/W controls the User Interface, Transmitting and Receiving, Keyloading, Private Mode, Zeroizing Keys,
and numerous other functions.
4.2. Interrupt Control Processor (ICP)
The ICP S/W is the slave S/W that responds to RCP commands. It controls such functions as
read/write digital and analog I/O, serial port control, keyboard scanning, synthesizer loading, channel guard
encode/decode, and UDC sc anning. It is very low-level hardware control that notifies the RCP via interrupts
whenever something happens. This S/W is not essential to the cryptographic module and its’ operation.
4.3. AEGIS DSP (ADI)
The ADI S/W resides in the ADI DSP ROM and RCP FLASH memory. The FLASH portion is
downloaded at power up to the ADI’s RAM memory. This S/W, under the control of the RCP, performs
A/D and D/A conversions on the user’s voice for transmit and receive operations. The A/D and D/A
conversion is performed using a proprietary algorithm known as AEGIS. Also, the ADI S/W executes the
DES algorithm on the digital voice to encrypt or decrypt. It receives the encryption key from the RCP. The
DES algorithm has already been certified and received FIPS approval.
4.4. Firmware
The ASIC (Modem), Audio Signal Processor (ASP), and Display Processor (DP) are considered
firmware. The S/W in these devices is very low -level hardware control that is performed via latch, relay, and
register reads and writes. This S/W is not essential to the cryptographic module and its’ operation.
5. Roles & Services
There are two separate roles in the operation of the M-RK DES radio: Crypto-Officer and User. The
M-RK DES radio can be used by anyone requiring secure two-way dispatch communications. This would
include police officers, firemen, utility workers, etc. The group purchasing the radios would be the users
and someone within the group would be designated as the technical liaison (Crypto-Officer). For example,
the local police department buys 500 M-RK DES radios. The police would have a Crypto-Officer program all
500 radios and load the appropriate DES encryption keys. The radios would then be handed out to 500
M-RK (AEGIS/DES) Radio p. 5 of 5
Page 6

Ericsson Security Policy
Users. The Crypto-Officer may setup DES talkgroups for Undercover work, Narcotics, Traffic Control as
well as a global DES talkgroup so everyone can communicate together.
5.1. Crypto-Officer Services
A Crypto-Officer can perform the following services:
Program Radio Personality
Program DES Encryption Keys
The M-RK DES Radio Personality is created on a PC using the program, EDACS4 or PC
Programmer. This personality contains numerous items including which talkgroups will be clear, AEGISclear, and AEGIS DES. It defines what encryption keys will be used on what systems and groups. Basically,
it defines everything from the contrast settings to protocol timeouts. The personality can be read or written
to the M-RK through the UDC connector.
The DES Encryption Keys are created and loaded into the radio using the DES Keyloader. This is a
separate device that programs the keys into the M-RK’s EEPROM through the UDC connector. The keys
are 8 bytes long and must contain the correct parity. They can’t be read out of the radio once they are
programmed.
5.2. User Services
A User can perform the following services:
Transmit Conventional Clear/Private Receive Conventional Clear/Private
Transmit EDACS Clear/Private Receive EDACS Clear/Private
Zeroize Encryption Keys Display Encryption Key Index
Bypass Private Mode
The User must first select the system they will be communicating on; conventional or EDACS
trunked. Next, they select the talkgr oup they will be communicating with. When a call on that group is
received it will automatically be heard in the speaker. To transmit a call, the user presses PTT and speaks
into the microphone. The communication will be in clear mode if the talkgroup is programmed for clear and
the radio is in private mode. The communication will be in DES private mode if the talkgroup is programmed
for private, the system is programmed for private, valid encryption keys for the system have been loaded,
and the radio is in private mode.
Bypass Private Mode can be accomplished by the User by pressing the PVT button while in
private mode. The PVT icon\LED will be turned off and an alert tone sounded. The radio personality has a
lot to do with how this function works. Private Mode can be forced on which would negate bypass mode.
The user can Zeroize the encryption keys at anytime by pressing the two buttons on the side of the
radio simultaneously. The user first hears a warning tone indicating the keys are about to be zeroized and
then a solid tone is heard indicating the keys are now zero.
The user can Display the current encryption key index in use by the talkgroup and system on the
M-RK II. The M-RK I assumes bank 1. The M-RK stores the DES encryption keys in banks. There are 8
banks possible with 7 keys per bank for a total of 56 DES keys that can be stored in the radio. The bank and
key index are set via personality. For M-RK II, the user can display the current key index, 1-7, but not the
actual key data.
5.3. Status Functions
Status information is displayed to both the Crypto-Officer and User via the LCD, LEDs, icons, and
alert tones. The M-RK I has no display so it communicates status via LEDs and alert tones. The M-RK II
M-RK (AEGIS/DES) Radio p. 6 of 6
Page 7

Ericsson Security Policy
communicates status via the LCD, which contains a 2x8 screen and icons along the border, and alert tones.
Refer to the M-RK I and M-RK II User Manuals for details.
5.4. Key Management
As stated under the Crypto-Officer Role, the DES keys are loaded into the radio using a DES
keyloader by the Crypto-Officer. The Crypto-Officer performs the following steps to load DES encryption
keys:
• Connect the keyloader to the radio via the UDC connector and turn the radio on.
• The M-RK II will display KEYLOAD, BANK=1 on the LCD. Use the arrows keys to select bank 1-8.
The M-RK I will assume BANK=1.
• The keyloader can transfer 1 key or all 7 keys to the selected bank.
• After the keys are loaded, disconnect the keyloader and radio will resume normal operation.
The keybanks provide additional security to the users. For example, the M-RK might be programmed with
two EDACS trunked systems; EA and EB. EA could use bank 1 and EB could use bank 2. EA and EB are
actually the same system on the same frequencies. The users could alternate between the two systems on a
daily basis or permanently switch to EB if they felt EA was no longer secure.
The DES keys are 8 bytes long and are stored in EEPROM with a 2 byte CRC for a total length of 10 bytes
per key. The keys are scrambled with a random pattern every time the keyloader is attached. This technique
makes it very difficult to determine the exact location of the keys in EEPROM.
6. Secure Operation
6.1. AEGIS Clear, Digital, and DES Operation
Each system (trunked or conventional) is programmed for either AEGIS or Voice Guard (VG)
communications. VG is an earlier generation algorithm that was replaced by AEGIS and will not be
discussed in this document. AEGI S programmed systems have three different voice modes: clear (analog),
digital and private (DES encrypted). The voice modes are programmed on a per-group basis within each
trunked system and on a per -channel basis within each conventional system.
6.1.1. Clear Mode
AEGIS clear mode is when the radio transmits and receives only clear (analog) voice signals. These
analog signals are non-digitized and non-encrypted. Clear mode transmissions can be easily monitored by
unauthorized persons. Groups or channels programmed for clear operation cannot transmit or receive AEGIS
digital or private messages.
6.1.2. AEGIS Digital Mode
AEGIS Digital mode allows the radio to transmit and receive digitized voice signals. AEGIS digital
signals provide improved weak signal performance and cannot be easily monitored with a standard receiver.
Groups and channels programmed for AEGIS digital operation transmit only digital signals. Private calls
cannot be received or transmitted when the radio is in the AEGIS digital mode because the radio does not
know the cryptographic key used. Message trunked group calls and individual calls will be answered back
on the mode they were received, assuming the call or hang time is still active. Individual, phone, broadcast,
and emergency calls will be transmitted clear if digital mode is disabled or inoperative.
1. If receiving an analog message trunked call, the radio will respond in the analog mode during the
hang time on the working channel.
2. If receiving an analog individual call (I-Call), the radio will respond in the analog mode during the
hang time.
M-RK (AEGIS/DES) Radio p. 7 of 7
Page 8

Ericsson Security Policy
3. When using the “WHC” feature to respond to an I-Call (after the hang time has timed out), the call
will be transmitted in the mode defined by the system mode as programmed for the current system
if the ID being called is not in the I-Call list. If the ID is in the I-Call list, then the call will be
transmitted as defined by the I-Call mode programmed in the list for that ID.
6.1.3. AEGIS Private Mode
AEGIS private mode allows the radio to transmit DES encrypted messages and receive clear or private
transmissions. The radio will transmit private if the group/channel is programmed for private operation and
forced operation is pre -programmed. If auto select operation was pre-programmed and the radio is in private
mode, the radio will transmit in the mode of the received call if the hang time is active. If no hang time is
active, the radio will transmit private.
DES Cryptographic keys are transferred to the radio using a DES Keyloader. Up to seven different
cryptographic keys, numbered 1-7 can be transferred from a DES Keyloader and stored in the radio. An
individual key is automatically selected on a per-group/channel basis according to the radio’s programming.
Groups and channels within an AEGIS system can be programmed for keys 1-7. Up to 8 banks of 7 keys can
be stored for Aegis DES systems and the bank is specified per system.
DES radios require a DES Keyloader (Option V4025 with software version 3.N or later). Keyloader cable
19B801971P18 is also required.
When operating on a group or channel programmed for private mode, all transmissions will be private
transmissions and the radio will receive clear and private signals. For M-RK II, the PVT status flag in the
display turns on when the private mode is enabled. For M-RK I, the OPT LED flashes Red. If the selected
group or channel is programmed for autoselect capability, the mode may be toggled between private and
clear with the PVT key. Radios programmed for forced private operation do not allow a change of the
transmit mode.
6.1.4. Error Messages
The M-RK can generate errors at anytime. At radio power up, numerous tests are executed which can
generate errors. During normal radio operation, error conditions are constantly checked. There are 2 types
of error codes:
• Fatal errors - these errors will cause the radio to continuously reset and no operation is possible.
• Non-Fatal errors - these errors are indicated to the user but the radio will not reset. It will continue to
operate.
The M-RK indicates to the user when an error has occurred by using the output device. For the M-RK
II, an error message and code are displayed on the LCD. For the M-RK I, an error is indicated by the color of
the OPT LED.
The errors are displayed on the radio as follows:
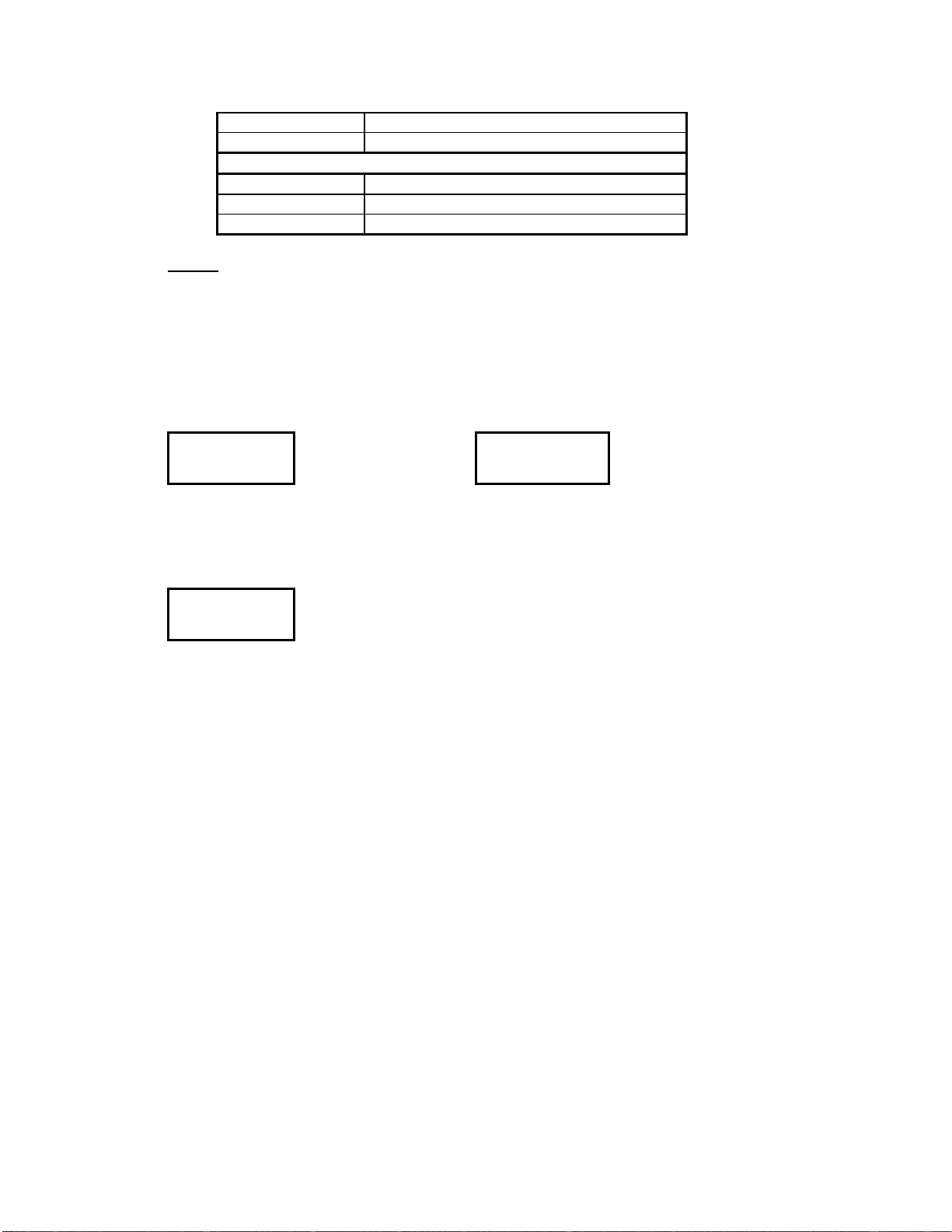
M-RK II:
message
ERR=xxxx
Error message Description
HARDWARE ROM errors
SOFTWARE General software failure
TRACKING Tracking data fatal error
NO LOCK Synthesizer not locking
where xxx is the error code and message is one of
the messages listed below
M-RK (AEGIS/DES) Radio p. 8 of 8
Page 9
Ericsson Security Policy
FREQDATA Frequency data fatal error
PERSDATA Personality errors
Non Fatal Errors
UNKNOWN
FEAT ERR Feature encryption error
DSP ERR DSP error
M-RK I:
• OPT LED is solid RED for fatal errors
• OPT LED flashes GREEN for non-fatal errors. It will flash the error code category. For example;
Error Code = 550, OPT LED flashes green 5 times to indicate a personality error code.
If either of the following error messages is indicated, the radio was either programmed incorrectly or
needs servicing:
DSP ERR
ERR=XXXX
Power up only Run-Time
If the DSP H/W circuit is not responding, the following error message will be indicated and the radio
needs servicing:
HARDWARE
ERR= 30
DSP ERR
M-RK (AEGIS/DES) Radio p. 9 of 9
 Loading...
Loading...