Page 1
The hardware used in the AXE system has
been updated continuously. Initially, all
telephony-related hardware in AXE was analogue. Over the years, almost all hardware
has been redesigned to take advantage of the
formidable advances in electronics. This has
been a continuous, ongoing process. Digitalisation was gradually introduced in the
early 1980s, followed by applicationspecific integrated circuits (ASIC) in the
mid-1980s. A major breakthrough came in
19861. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the
evolution continued in small steps. A few
original products have remained, however.
Today, these last remaining products are
being replaced. At the same time, almost all
other hardware products that make up the
basic AXE system are being rationalised.
52
Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
AXE hardware evolution
Urban Hägg and Tomas Lundqvist
The AXE system is the most widely deployed switching system in the world.
It is used in public telephony-oriented applications of every type, including
traditional fixed network applications in local, transit, international and
combined networks. AXE is also deployed for all major mobile standards –
analogue as well as digital. AXE is very strong in intelligent networks and
other real-time database applications. Recent designs also enable data
communication capabilities to be added to the system.
From its inception, the AXE system was designed to accommodate continuous change. Throughout the years, new applications have been introduced, its array of functions has grown, and its hardware has been steadily
updated.
The authors describe how the latest advances in hardware technology have
been brought into the system, thereby dramatically improving such characteristics as floor space, power consumption, system handling, and cost of
ownership. As always, backwards compatibility has been maintained to the
greatest possible extent, in order to protect previous investments in AXE.
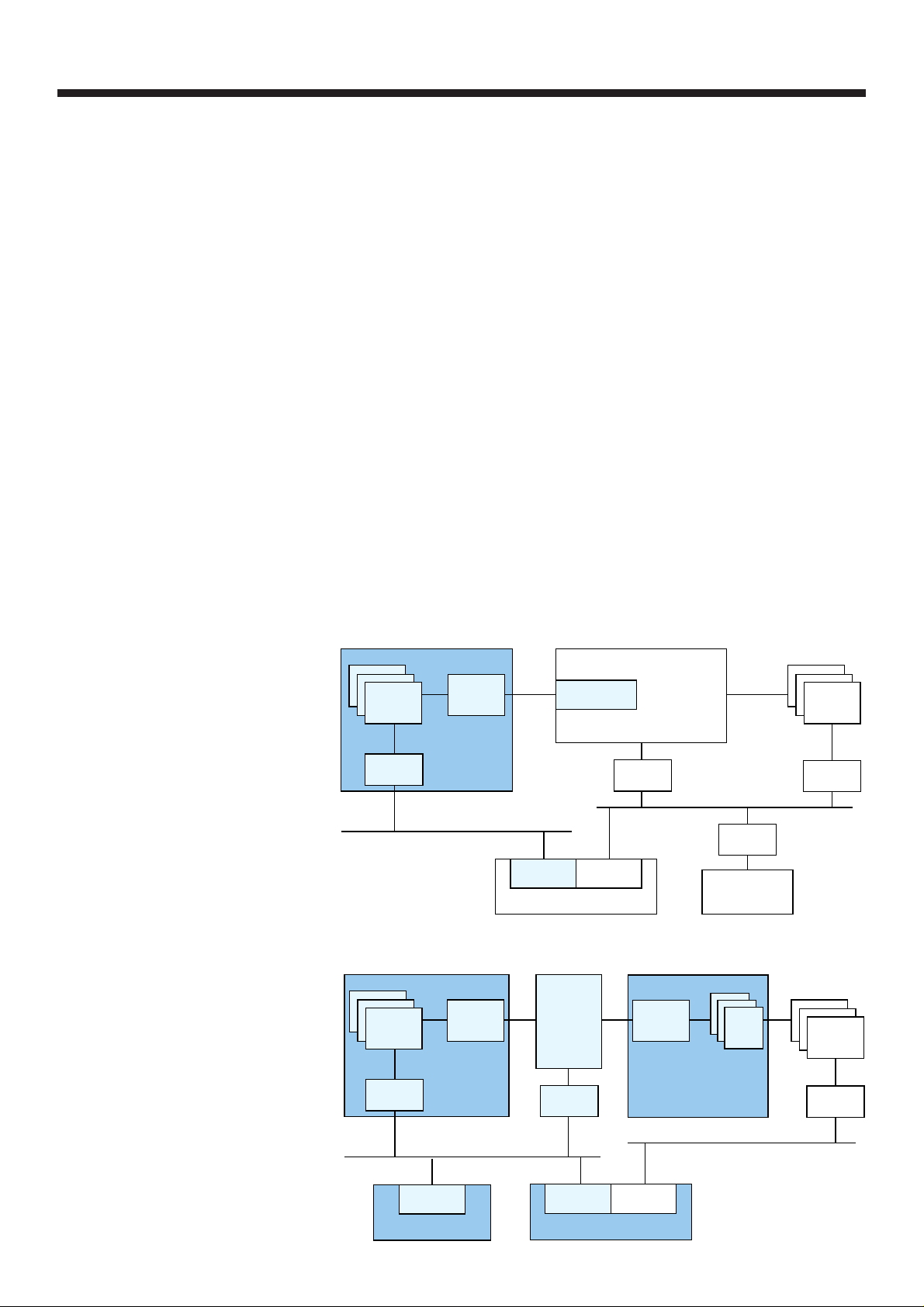
DL2
DLMUX
APT dev
TSM-DL3
DL3
DL1
DL2
APT dev
RP4
RP
RP
RP
RPB-S
RPH-S
RPH
IOG
CP
Generic device
magazine
AXE evolution
Extensions
GSS64K
RPB-P
DL2
DLMUX
APT dev
DL3 DL2
APT dev
RP4
RP4
RP
RPB-S
RPH-S
RPH-P
CP
Generic device
magazine
GSS64K
AXE evolution
New deliveries
DL3
DLMUX
DL_IO
DL2
Generic device
magazine or
BYB 202 equipment
RPV2
RPB-P
IOG20
Figure 1
The figures show how the new interfaces are
used for extensions and new deliveries.
Page 2

Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
53
Architecture
As the AXE system continues to evolve, system designers ensure that the very solid and
proven system architecture is maintained.
The fundamental principle of a central processor (CP) that controls regional processors
(RP), which in turn control hardware services, has proved to be superior. Strict interfaces ensure that different system components can be developed independently. To
ensure non-stop operation, all vital traffic
and operation and maintenance (O&M) system products are built in duplicated structures.
In order to fully exploit the advantages of
modern electronics, some fundamental system hardware interfaces are now being improved and extended. It goes without saying that compatibility is maintained in
AXE.
Traditionally, a parallel bus, or a regional processor bus (RPB), has been used for
communication between the central and regional processors. Now, however, in order
to increase capacity (data transfer rate) and
to decrease the need for interface hardware,
a serial bus is being introduced alongside
the existing RPB (Figure 1). The new RPB
permits single-board regional processors to
be housed in the same subrack as the devices
they control, thus minimising hardware and
cable interconnections between hardware
devices.
In earlier generations of AXE, an extension module (EM) bus and cables were
used to connect regional processors to application hardware (extension modules). In
the new hardware design, however, most regional processors are located in the same
subrack as the extension modules they control. By locating the regional processors in
this way, designers have all but eliminated
the EM bus, except in the backplane. The
new location makes it much easier for
operators to install and extend equipment.
The traditional AXE interface (called the
digital link 2, DL2) between the group
switch (GS) and its connected devices was
at the 2 Mbit/s primary multiplexing pulse
code modulation (PCM) level.
Now, a new high-speed interface is being
ALI Alarm interface
ANSI American National Standards
Institute
ASIC Application-specific integrated
circuit
AST-DR-V3 Announcement service terminal
version 3
ATM Asynchronous transfer mode
BGA Ball grid array
BM Building module (1 BM=40.64
mm)
BSC Base station controller
CANS Code answer
CCD Conference call device
CMOS Complementary metal-oxide semi-
conductor
CP Central processor
CSFSK Code sender for FSK tones
CSK Code sender for DTMF tones
CSR Code sender/receiver
D-AMPS Digital AMPS
DL2 Digital link interface 2
DL3 Digital link interface 3
DSP Digital signal processor
DTMF Dual-tone multifrequency
E0 64 kbit/s digital link
E1 2 Mbit/s digital link
ECP 303 Echo canceller in pool
generation 3
ECP 404 Echo canceller in pool
generation 4
EM Extension module
EMB Extension module bus
EMC Electromagnetic compatibility
EMI Electromagnetic interference
ETC5 Exchange terminal circuit
generation 5
ETSI European Telecommunications
Standards Institute
FSK Frequency shift keying
GDM Generic device magazine (sub-
rack)
GS Group switch
GSM Global system for mobile commu-
nication
GSS Group switch subsystem
HLR Home location register
IN Intelligent network
I/O Input/output
IOG11 I/O system 11
IOG20 I/O system 20
IP Internet protocol
ISDN Integrated services digital network
ITU-T International Telecommunication
Union - Telecommunications Stan-
dardization Sector
IWU Interworking unit
KRD Keyset receiver device
LED Light-emitting diode
LUM Line unit module
MSC Mobile switching centre
MTBF Mean time between failures
MW Megaword
O&M Operation and maintenance
PCM Pulse code modulation
PDC Pacific digital cellular
PROM Programmable read-only memory
PSTN Public switched telephone network
RAM Random access memory
RMS Remote measurement subsystem
ROM Read-only memory
RP Regional processor
RP4 Regional processor generation 4
RPB Regional processor bus
RPD Regional processor device
RPG Regional processor with group
switch interface
RPV Regional processor connected to
VME
SCP Service control point
SCSI Small computer system interface
SNT Switching network terminal
SPM Space switch module
STC Signalling terminal central
STM Synchronous transfer mode
STP Signalling transfer point
T1 1.5 Mbit/s digital link
TCD Trunk continuity check device
TSM Time switch module
TSM-1 155 Mbit/s time switch module
VME Versa Module Eurocard
Box A Abbreviations
Page 3
introduced at the third level in the basic
PCM hierarchy. The interface, which is
called DL3 (digital link 3), works at the
32 Mbit/s level (overhead excluded).
The introduction of the DL3 interface dramatically decreases group switch and device
hardware. Equally important, it removes
massive amounts of internal system cabling.
The DL2 interface has been retained to ensure compatibility.
Each DL3 interface contains 16 multiplexed DL2 interfaces. In fact, the DL2s run
in the backplane of the new device subracks,
which means that only one sixteenth of the
cabling is needed between the group switch
and the devices that are connected to it.
Basic technology
In general, designers taking part in the AXE
hardware evolution programme have used
ASICs, high-performance microprocessors,
digital signal processors (DSP) and faster interfaces to improve AXE hardware. ASICs
were chosen where volumes of circuits are
very high or where performance is critical.
Commercial microprocessors, which are becoming commonplace for more and more
applications, have also been integrated into
the hardware. These changes allow designers to integrate commercial operating systems and software – especially at the regional processor level.
Also, inasmuch as the processing capacity of regional processors has kept pace with
developments in general-purpose processor
technology, the new AXE hardware requires
fewer processors than were used before. This
was another important factor in reducing
the size of the exchange.
The most common type of processor in
AXE systems today is the digital signal processor. DSPs, which are used in many kinds
of application, are flexible platforms that
may easily be programmed to provide new
functions. Moreover, software at the DSP
level may be sourced from other manufacturers, which allows designers to introduce
new functionality with shorter time to market.
Today almost all AXE hardware uses a
3.3 V power supply. This change and the
use of submicron technology (0.25-0.5 µm)
have reduced power consumption to levels
far below that of previous hardware generations.
Equipment practice
Owing to the introduction of high-speed interfaces and tougher requirements for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), AXE
hardware designers constructed a new
equipment practice, called the BYB 5012.
The BYB 501 has excellent EMC characteristics and fulfils Class B requirements with
good margin. Compared with the BYB 202,
whose cabinet shields against electromagnetic interference (EMI), the new equipment practice provides shielding at the subrack level. Note: the standard on which the
BYB 501 is based uses the term subrack.
However, in AXE terminology, the word
magazine is often used.
The equipment practice supports multipoint and single-point earthing. The multi-
54
Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
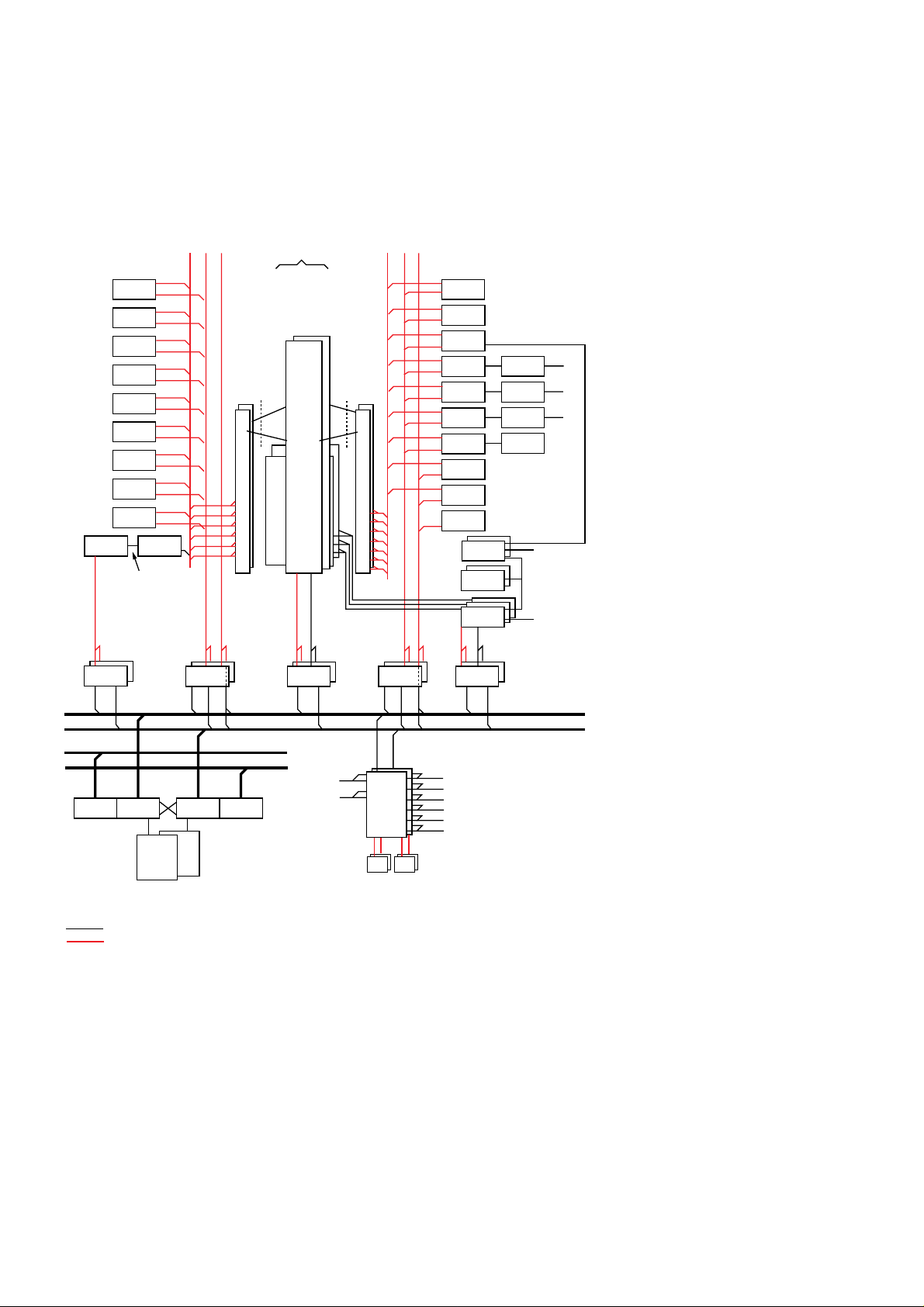
D
L
M
U
L
T
I
P
L
E
X
E
R
D
L
M
U
L
T
I
P
L
E
X
E
R
CAT
CSKD
KRDD
CCD
CSR
TCD
CSFSK
ECP404
TRA
ASTV3
ETCJ32
ETC24
ETC5
ETC5
DL2_IO
DL2_IO
DL2_IO
STC
SS7
AUTH
DL2_IO
ICM
RCM
CLM
RP4
RP4 RP4 RP4 RP4
external
sync.
external
sync.
ETC5 sync.
test
phone
test
instr.
test
instr.
RSM
PCD-D
PCD
TRU
RPHP RPHS RPHS RPHP
CP
CP
Terminal V24
Terminal V24
Billing X.25
OMC X.25
Alarm V.24
Alarm
printer V.24
OD
HD
IOG20
RPB-P
RPB-P
TSM
DL3
DL3
D
L
M
U
L
T
I
P
L
E
X
E
R
D
L
M
U
L
T
I
P
L
E
X
E
R
SPM
RPB-S
RPB-S
DL2
DL2
EMB
RPB-S
DL2
EMB
RPB-S
GS
EMB
EMB
Cable
Backplane
Figure 2
AXE hardware architecture using new hardware.
Page 4

Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
55
point earthing concept will be used in all
new AXE deliveries. The equipment practice also supports several different sizes of
board and cabinet. However, for use with
AXE, two main board sizes are used: 115 x
175 mm, and 265 x 175 mm. The standard
dimensions of the cabinet are as follows:
Height: 1800 mm
Width: 600 mm
Depth : 400 mm
Normally, no backplane cabling is needed
on the subracks. Consequently, the cabinets
may be placed back-to-back, giving the exchange a very small footprint and allowing
a flexible cabinet arrangement against walls.
The cabinets will also be delivered fully
equipped, their hardware tested and cabled
at the factory – a feature that greatly reduces
installation time and other time-tocustomer-related activities.
Group switch
The group switch3has been the subject of
far-reaching rationalisation. For example,
a configuration for 65,536 group switch
ports is now contained in two cabinets
(Figure 3). What is more, the new group
switch consumes 95% less power than its
predecessor. Nevertheless, the basic structure of the switch – that is, the time-spacetime (T-S-T) switching architecture, the
time switch, the space switch, the clock
module, and system concepts such as the
switching network terminal maintenance
(SNT) and DL2 hardware interface – has
been maintained, which facilitates hardware and software design and preserves
compatibility.
In improving the group switch, designers
made the following changes:
• A 32 Mbit/s DL3 interface replaces sixteen 2 Mbit/s DL2 switch interfaces.
• Four time switch module (TSM) functions
are grouped onto one board, yielding
2,048 ports per board (Figure 4).
• A space switch module (SPM) function for
16,384 ports now fits on a single board
(Figure 5).
• Switching equipment and the RPs that
control the equipment are co-located in
the same subrack.
These design changes gave rise to a switch
subrack that contains eight TSM boards,
providing a total of 16,384 switch ports; one
SPM board; and four RP boards. Since the
switch is duplicated, another plane is located in a second subrack with exactly the same
configuration.
Some mobile systems employ subrate
switching to handle bit rates below 64 kbit/s
(8 kbit/s; 16 kbit/s; 24 kbit/s ... 64 kbit/s).
In its maximum configuration, which has
4,096 ports, the subrate switch is housed in
two small subracks: the A-plane is located
in one subrack and the B-plane is located in
the other.
As in earlier versions of the group switch
subsystem (GSS), wideband (n x 64 kbit/s)
is supported up to 2 Mbit/s.
The synchronisation equipment, which
occupies another two small subracks, consists of:
16K plane A
16K plane A
16K plane B
16K plane B
16K plane A
16K plane A
16K plane B
16K plane B
CLM, RCM
The 64K group switch
Figure 3
The new group switch in a 64K configuration,
including synchronisation equipment.
Figure 4
The new time switch module board, which
contains 2,048 ports, replaces four BYB 202
subracks.
Figure 5
The space switch module board, which handles 16,384 ports, replaces one subrack in
the BYB 202.
Page 5

• three clock modules;
• two highly accurate reference clock modules;
• two incoming clock reference boards (for
connecting additional clock references);
• regional processors for controlling the
synchronisation equipment.
Designers have also constructed a compact
switch subrack for switching applications
that require less than 4,096 ports. This subrack contains a 4,096-port switch, three
clock boards for synchronisation, 1,024
ports for subrate data transfer, and regional
processors for controlling the equipment.
The two switch planes are co-located in one
subrack.
The new group switch was designed to
provide backward compatibility. Accordingly, a DL3-to-DL2 converter subrack has
been developed. The converter connects
hardware that uses a DL2 cable interface to
a new switch that uses the DL3 interface.
Another way of connecting an old switch to
hardware that uses the new DL3 interface is
to add an interface board (which supports a
DL3 cable interface) in existing TSM64C
subracks.
The new design concept also allows the
GSS switch to be extended to up to
131,072 ports.
Central processor
Designers of the AXE central processor have
always emphasised high processing capacity. This holds true even today. Nonetheless,
while developing the next generation highcapacity central processor (APZ 212 30),
AXE designers also produced a smaller,
power-efficient processor (APZ 212 25) for
switching applications that require moderate processing capacity.
The APZ 212 25 has a very small foot-
print (Figure 6) and consumes only 75 W of
power. Designers reduced power consumption by replacing the 5 V supply voltage
with 3.3 V, and by using 0.5 µm complementary metal-oxide semiconductor
(CMOS) ASIC technology with ball grid
array (BGA) packaging. The maximum
memory capacity of the APZ 212 25 is
64 Megawords (MW), program store; and
256 MW, data store. Despite its small size,
this computer processor is 1.5 to 1.7 times
more powerful than its much larger predecessor, the APZ 212 11.
Although it was designed for use in the
BYB 501, where it uses the serial RP bus,
the APZ 212 25 is fully compatible with the
parallel bus used in earlier versions of AXE
switching equipment. In a minimum configuration, the APZ 212 25 may connect
four of the new serial RP buses, controlling
up to 128 regional processors. If more regional processors are required, or if parallel
and serial RP buses must be used simultaneously, then extension subracks may be
added that allow up to 512 regional processors to be connected.
Regional processors
A new regional processor, called the RPG
(regional processor with group switch interface, Figure 7) has been introduced for applications that require high processing capacity. Most applications that previously
ran on the regional processor device (RPD
– Motorola 68020) have been transferred to
the RPG, which has at least four times as
much processing capacity as the RPD. The
RPG is a single-board processor based on
the general-purpose Motorola 68060 running at 50 MHz. On the same board is a
communications processor (a Motorola
68360) for handling the switch interface and
a 10 Mbit/s Ethernet interface. Although it
may be used for any application that requires
high processing power, the RPG will initially be used with the following applications:
• signalling system no. 7 – signalling terminal according to ANSI;
• signalling system no. 7 – signalling terminal according to ITU-T;
• signalling terminal central (STC) – signalling terminal for base stations and remote subscriber switches;
• transceiver handler – base station signalling in GSM;
• authentication in all mobile systems;
• integrated services digital network
(ISDN) Internet access server (IP routing
function).
In AXE, the RPG is the platform for handling packet switched data communication.
With respect to traffic handling, these types
of regional processor have a more independent role, relative to the CP, than traditional
AXE regional processors.
A new version of the traditional regional
processor, called RP4 (regional processor
generation 4), is used for controlling extension modules. The RP4 is compatible with
earlier versions of the regional processor. A
prime benefit of the RP4 is that it is colocated in a subrack with the extension modules it controls. This design does away with
56
Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
Figure 6
The APZ 212 25 occupies only half a subrack
in the BYB 501.
Figure 7
The RPG consists of two boards mounted
together into one plug-in unit. Every interface
is to the backplane.
Page 6

Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
57
a large amount of cable, reduces size, and
simplifies equipment handling considerably.
Earlier versions of the central processor
may not be connected to new hardware without first modifying their side of the RP bus
interface.
The regional processor bus interface VME
(RPV) is a conversion product for the connection from the CP to the Versa Module
Eurocard-based IOG20, through the RP
bus. There are two RPVs: the first, known
simply as RPV, is used for the parallel bus
connection; the second, called the RPV2, is
used for the serial bus connection.
IOG20, the AXE I/O
system
A duplicated input/output (I/O) system,
known as the IOG20, handles data transport
to and from an AXE exchange. Communication to and from the AXE I/O system may
be broken down into customer administration and element handling.
The IOG20 is much smaller than the
IOG11 – the previous generation I/O system. For example, whereas the IOG11 fills
a whole cabinet in the BYB 202 equipment
practice, the IOG20 fits into a single sub-
rack. Moreover, the IOG20 outperforms the
IOG11 by as much as four to five times but
consumes only one third as much power.
The new I/O system, whose design is characterised by modern technology and greater
integration, contains relatively few printed
circuit board types (seven instead of 25). In
taking steps to make the system open to
commercially available components, designers used the industry standards Versa
Module Eurocard (VME) bus, Ethernet, and
small computer system interface (SCSI).
Similarly, they implemented Ethernet for
connections between nodes and as a line interface. The IOG20 is currently available in
three configurations:
• IOG20 – a fully compatible version of the
twin-subrack configuration with an in-
terface to a parallel RP bus;
• IOG20B – a twin-subrack version with
one node in each subrack (maximum con-
figuration);
• IOG20C – a single-subrack version with
two nodes (minimum configuration).
The IOG20B and the IOG20C are designed
to operate with the new serial RP bus.
The IOG20C is probably the most compact
and powerful I/O system ever produced
for telecommunications applications
(Figure 8).
Figure 8
The IOG20C with A- and B-sides in one subrack. With its daughter boards, the line unit
module can handle four different interfaces.
Page 7

In its maximum configuration, the
IOG20 stores data on three duplicated
3.5 inch/4 Gbyte hard disks and one duplicated 3.5 inch/640 Mbyte magneto-optical
disk. In the compact version, the IOG20
stores data on one duplicated 3.5 inch/
4 Gbyte hard disk and one duplicated
3.5 inch/640 Mbyte magneto-optical disk.
To connect data communication inter-
faces to the I/O system, the twin-subrack
version may contain up to four duplicated
line unit module (LUM) boards. Likewise,
the compact version may contain up to three
duplicated LUM boards. A LUM board consists of a main board and as many as four independent line module daughter boards for
almost any type of line interface, including
V.24, V.28, V.35, V.36, X.21, G.703 E0,
G.703 E1, and Ethernet.
An alarm interface (ALI) function consists
of two boards: one for supervising fans and
external alarm input/output, and another for
displaying alarms.
In terms of software and applications, the
IOG20 is fully compatible with its predecessor, the IOG11.
Connecting hardware to
the group switch
Hardware is connected to the switch either
by a trunk (for example, exchange terminals)
or by means of pooling (for example, of echo
cancellers). In AXE, only exchange terminals
and some signalling terminals are connected
by trunks. All other equipment is connected
in pool, which heightens reliability, flexibility, economy, and maintainability.
Announcement machines
Designers have also developed a new generation of system-integrated announcement
machines – AST-DR-V3. The new machines are substantially smaller than their
predecessors, but have more capacity for
speech storage and for a larger number of
dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) receivers. The announcement machines are
available in different sizes (configurations).
The largest machine has capacity for
256 DTMF receivers, up to eight hours of
stored speech, and provisions for backing up
speech on the hard disk.
The smallest configuration has capacity
for 32 DTMF receivers and two hours of
stored speech. Depending on how often
stored phrases are changed, speech may be
stored in either random access memory
(RAM) or in read-only memory (ROM) on
memory boards that support up to one hour
of speech per board. The high-capacity announcement machine occupies one and a
half subracks: one subrack for the control
subrack that contains the DTMF receivers,
and half a subrack for the memory boards
and hard disk. The smallest machine occupies only half a subrack. As many as 20 systems may be run in parallel, providing a
total of 5,120 ports. The systems may also
be used in large intelligent network (IN)
nodes or in other service-providing functions. The AST-DR-V3 forms a powerful
voice-response system that may be used as a
base product for the future development of
such applications as voice or fax mail, cashless calling, and the virtual telephone.
Exchange terminals
AXE supports every kind of trunk interface
that has been incorporated into the new
equipment practice. By integrating all functionality into one ASIC, designers were able
to fit the 32-channel E1 (2 Mbit/s digital
link) interface onto one small board
(Figure 9). New versions of the 24-channel
T1 and the Japanese 32-channel interface
have also been designed.
In time, STM-1 (155 Mbit/s synchronous
transfer mode) terminations will be designed in AXE for each relevant standard.
Once they become available, the terminations will greatly reduce (possibly completely eliminating) operator requirements
for transmission equipment and generally
simplify system handling.
DSP platform
To date, much of the telephony devices in
AXE – conference call device (CCD); trunk
continuity check device (TCD); code
sender/receiver (CSR) for R1, R2, and no. 5
code; code sender for DTMF (CSK); code
sender for FSK tones (CSFSK); code answer
(CANS); keyset receiver device (KRD); and
several maintenance functions – is delivered
from separate subracks that range in size
from 3 to 12 building modules (BM) in the
BYB 202 equipment practice. Nonetheless,
designers have developed a new digital signal processor platform board that can be programmed to provide the functionality of any
one of these applications. Initially the boards
will be programmed at the factory. In a second step, operators will be able to change
the onboard software from the AXE system,
giving them tremendous flexibility and excellent means with which to handle redundancy and spare parts. Should a fault occur
58
Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
Figure 9
The 32-channel E1 interface is now made on
one small board.
Page 8

Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
59
on a board that provides the functions described above, then an operator can remotely activate an unprogrammed standby board
by command, taking it into operation. This
feature will simplify maintenance and reduce operating costs.
Echo cancellers
The ECP 3034has been replaced with a new
echo canceller, called the ECP 404. The ECP
404 has a capacity of 512 channels per subrack, which is twice the capacity of the ECP
303. As with its predecessor, the ECP 404
is connected to the group switch by means
of pooling.
Transcoders
Transcoders, which are included in all digital mobile telephony systems, are used for
speech compression – from 64 kbit/s to bit
rates below 16 kbit/s in the downlink direction, and from bit rates below 16 kbit/s
to 64 kbit/s in the uplink direction. Limited bandwidth in the air interface, which is
a major challenge of mobile telephony systems, requires that speech be compressed before it can be sent over the interface.
As with all other devices, the transcoders
are connected to the switch and supervised
by AXE. The capacity of each board differs
depending on the mobile standard for which
it has been deployed (for example, D-AMPS,
GSM or PDC). Each standard uses unique
algorithms that require different processing
capacity.
By employing the latest techniques in digital signal processing, designers have been
able to more than double the capacity of the
transcoder boards. This represents a significant achievement since the transcoders make
up a large part of mobile exchanges.
Data transmission interworking unit
Interworking functions are needed to provide
the digital transmission of data services within mobile networks as well as between them
and other networks. This is because protocols
for the standard network use analogue tones,
which are not suitable for transmission over
the radio interface to mobile terminals.
An interworking unit (IWU) extracts
analogue information received from a public switched telephone network (PSTN)
modem and sends it to the mobile terminal
by means of a digital protocol. The opposite
function is performed for signals from the
mobile terminal to the PSTN modem. The
interworking function is implemented in a
7.5 BM subrack, which can handle up to 32
simultaneous data or fax calls. The subrack
fits in the new equipment practice.
This function was previously used as a
stand-alone product in the Ericsson GSM
system, but it will now be integrated into
the system and supervised by AXE.
Remote measurement subsystem
The AXE remote measurement subsystem
(RMS) measures characteristics and transmission quality between telephony exchanges. It performs digital, analogue and
signalling tests. To date, this function –
which occupies one subrack in the BYB 202
equipment practice – has been used solely
in transit exchanges. In the new rationalised
version of the RMS, the function will be constructed from powerful DSPs on a single
board.
Subracks for switchconnected hardware
Nearly all telephony devices in AXE are now
single-board applications, giving rise to the
development of a new concept for generic
device magazines (subracks). The concept is
based on a subrack with 16 slots for device
boards. From the backplane, the boards are
connected to a duplicated group-switch interface, a duplicated RP bus interface, a duplicated EM bus interface, and a maintenance bus. Moreover, each board is given an
EM bus address and supplied with duplicated –48 V (Figure 10).
Besides the 16 device boards, two multiplexers on the front of the board are connect-
Group
switch
A
B
A
B
A
B
DL3
DL2
DL
multiplexer
Maintenance
bus
Generic device
magazine
EM bus
RPB-S
-48V-A
-48V-B
Maintenance
bus
RP4
RPB-S
-48V
CP
A
B
1
0
15
Device
-48V
Figure 10
Hardware architecture of the generic device
magazine (subrack).
Page 9

ed to the switch by means of a DL3 interface.
The multiplexers split the DL3 interface into
16 DL2 connections in the backplane, one
connection per board. The other interfaces are
connected to a pair of regional processors, one
at each end of the subrack. Moreover, since
the RP bus is also distributed in the backplane, it is possible to mix – in the same subrack – boards that use the EM bus with boards
that use the RP bus. Because some applica-
tions require a large board size while others
require a small one, two versions of the generic subrack have been constructed.
Product identification
A new function has been introduced for
checking the hardware of an AXE exchange.
Each board contains a small programmable
read-only memory (PROM) that stores the
unique serial number, product number, revision state and manufacturing date of that
board. Operators may fetch and read this information by command (on site or remotely), which enables them to check:
• hardware when replacing faulty units;
• revision states when upgrading hardware;
• for compatibility when introducing new
software.
Visual indication
Most boards in the new AXE system contain a light-emitting diode (LED) on their
front. The LEDs help operators in various
maintenance situations; for example, when
locating boards that need to be removed for
repair or for upgrade.
The indicator does not necessarily indi-
cate that a board is faulty. Instead, it indicates whether or not a board may be removed
without disturbing traffic.
Power supply
An optional battery backup and modular
power supply are offered for exchanges
whose power consumption is below 6 kW.
The batteries and rectifiers are housed together with the switching equipment. A
60
Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
T
R
H
T
R
H
S
S
7
S
S
7
FAN
CP
IOG20C
TRA
ETC
ETC
GS16
GS16
SYNC
SUBRATE
TRA
TRA
TRH
AC/DC
AC/DC
Battery
Battery
ETC
ETC
Top view
or
2400 mm
400 mm
600 mm
800 mm
1200 mm
Total area = 0.96 m
2
Figure 12
A complete AXE exchange in one cabinet.
This configuration can be used for any of the
following applications: HLR, STP, SCP, or
BSC (more than 120 transceivers).
Figure 11
A powerful BSC with capacity for more than
300 transceivers including power supply and
batteries. The configuration is similar to a
small local exchange (subscriber stage
excluded) or to a small MSC.
Page 10

Ericsson Review No. 2, 1997
61
single cabinet with battery backup can provide a 3 kW power supply for nearly two
hours. A 6 kW power supply is sufficient to
operate approximately 15 AXE cabinets,
which more or less corresponds to a highend mobile switching centre (MSC) in a mobile telephony system.
Most hardware in the BYB 501 equipment practice is fed with a redundant power
supply to each subrack through two branches of –48 V. Each branch of power is filtered
and distributed to the subrack backplane,
from which each board is supplied through
a double-diode configuration. This arrangement increases reliability, since the subrack
continues to work even if one branch of the
power supply is lost.
The power distribution system also allows
boards to be inserted into a subrack that is
in service, which greatly simplifies procedures when boards in the subracks must be
replaced.
Results
At the system level, recent developments
in the AXE hardware evolution programme have reduced the number of board
types used in AXE and made them smaller and much more power-efficient. For example, it was possible to reduce the size of
a base station controller (BSC) for a GSM
configuration that supports approximately 300 transceivers by nearly 90% – including power supply, battery backup
(Figure 11) and transcoders. Today, power
consumption for a complete base station
controller of this type is less than 1500 W.
Moreover, when the BSC is delivered for
installation, very little additional work is
required, since the cabinets are equipped
with subracks and internal system cables at
the factory.
For the first time, a complete AXE exchange fits into a single cabinet (Figure 12).
This configuration can be used for a home
location register (HLR), signalling transfer
point (STP), service control point (SCP), or
for a base station controller application.
Conclusion
The AXE hardware evolution programme
has successfully reduced the size of hardware
by between 70% and 90%; cabling in the
exchange has been reduced by 90%, and
power has been reduced by 75%. Therefore,
operators can expect that the time and re-
sources needed for installing the hardware
will also decrease by between 70% and 90%.
The delivery of fully equipped and tested exchanges will further simplify installation.
The following aspects contribute towards
reducing operator costs for running the new
exchanges:
• smaller footprints require less floor space
(reduced overhead);
• costs of power (batteries, rectifiers and
kW) and cooling are reduced (reduced
overhead);
• fewer spare parts are needed (smaller
facilities, smaller stores);
• operations have been simplified (less staff,
less training);
• less hardware implies that the mean time
between failures (MTBF) increases, while
the repair time decreases – in that way,
the total down time, due to hardware fail-
ures, will decrease;
• pooled devices;
• programmable platforms.
The hardware evolution described in this article represents only a first step in Ericsson’s
AXE hardware evolution programme. In
subsequent phases of the programme, AXE
will be migrated towards an open hardware
architecture that supports datacom functionality, asynchronous transfer mode
(ATM) switching, high-speed interfaces and
multiprocessor configurations.
References
1 Hägg, U., Persson, K.: New hardware
in AXE 10. Ericsson Review
63(1986):2, pp 86-92.
2 Stockman, B. and Wallers, A.:
BYB 501 metric equipment practice.
Ericsson Review 74(97):2, pp. 62-67.
3 Hansson, U., Paone, T.: The group
switch subsystem – an enhanced competitive group switch. Ericsson Review
74(1997):2, pp 68-73.
4 Eriksson, A., Eriksson, G., Karlsen, J.,
Roxström, A., Vallon Hulth, T.:
Ericsson echo cancellors – a key to
improved speech quality. Ericsson
Review 73(1996):1, pp 25-33.
100%
100% 100%
30%
40%
35%
Footprint Power Board types
Average exchange reduction
Figure 13
Average reduction in footprint, power, and
board type for an AXE exchange.
 Loading...
Loading...