Page 1
EPSON TERMINAL PRINTER
LQ-2170
SERVICE MANUAL
EPSON
4005735
Page 2

NOTICE
• All right reserved. Reproduction of any part of this manual in any form wharsoever without SEIKO EPSON’s express
written permission is forbidden.
• The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
• All efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy of the contents of this manual. However, should any errors be
detected, SEIKO EPSON would greatly appreciate being informed of them.
• The above notwithstanding SEIKO EPSON can assume no responsibility for any errors in this manual or the
consequences thereof
CORPORATION
Nagano, Japan
.
Copyright 1995 by SEIKO EPSON
Page 3

PRECAUTIONS
Precautionary notations throughout the tect are categorized relative to 1) personal injury, and 2) damage to
equipment:
DANGER Singnals a precaution which, if ignored, could ressult in serious or fatal personal
injury, Great caution should be exercised in performing procedures preceded by
a DANGER headings.
WARNING Singnals a precaution which, if ignored, could result in damage to equipment.
The precautionary measures itemized below should always be observed when performing repair
/maintenance procedures.
DANGER
1. ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE PRODUCT FROM BOTH THE POWER SOURCE AND THE
HOST COMPUTER BEFORE PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE OR REPAIR PROCEDURE.
2. NO WORK SHOULD BE PERFORMED ON THE UNIT BY PERSONS UNFAMIAR WITH
BASIC SAFETY MEASURES AS DICTATED FOR ALL ELECTRONICS TECHNICIANS IN
THEIR LINE OF WORK
3. WHEN PERFORMING TESTING AS DISCATED WITHIN THIS MANUL, DO NOT CONNECT
THE UNIT TO A POWER SOURCE UNIT INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. WHEN THE POWER
SUPPLY CABLE MUST BE CONNECTED, USE EXTREME CAUTION IN WORKING ON
POWER SUPPLY AND OTHER ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS.
WARNING
1. REPAIRS ON EPSON PRODUCT SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY BY AN EPSON
CERTIFIED REPAIR TECHNICIAN.
2. MAKE CERTAIN THAT THE SOURCE VOLTAGE IS THE SAME AS THE RATED VOLTAGE,
LISTED ON THE SERIAL NUMBER/RATIG PLATE. IF THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS A
PRIMARY-AC RATING DIFERENT FORM THE AVAILABLE POWER SOURCE, DO NOT
CONNECTE IT TO THE POWER SOURCE.
3. ALWAYS VERIFY THAT THE EPSON PRODUCT HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED FROM THE
POWER SOURCE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPLACING PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS
AND/OR INDDIVIDUAL CHIPS.
4. IN ORDER TO PROTECT SENSITIVE m P CHIPS AND CIRCUITRY, USE STATIC
DISCHARGE EQUIPMENT, SUCH AS ANTI-STATIC WRIST STRAPS, WHEN ACCESSING
INTERNAL COMPONENTS.
5. REPLACE MALFUNCTIONING COMPONENTS ONLY WITH THOSE COMPONENTS
RECOMMENTED BY THE MAANUFACTURE; INTRODUCTION OF SECOND-SOURCE ICs
OR OTHER NONAPPROVED COMPONENTS MAY DAMAGE THE PRODUCT AND VOID
ANY APPLICABLE EPSON WARRANTY.
Page 4

PREFACE
This manual describes functions, theory of electrical and mechanical operations, maintenance, and repair of
the FX-2170. The instructions and procedures included herein are intended for the experienced repair
technician, and attention should be given to the precautions on the preceding page. The chapters are
organized as follows:
Chapter 1 - Provides a general product overview, Lists specifications, and illustrates the main
components of the printer.
Chapter 2 - Describes the theory of printer operation.
Chapter 3 - Includes a step-by-step guide for product disassembly and assembly.
Chapter 4 - Includes a step-by step guide for addjustement.
Chapter 5 - Provides Epson-approved techniques for troubleshooting.
Chapter 6 - Describes prevetive maintenance techniques.
❇ The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
Page 5
REVISION SHEET
Revision Issued Date Revision Page
Rev. A December 5, 1995 1st issued
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CHAPTER 2. OPERATION PRINCIPLES
CHAPTER 3. DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER 4. ADJUSTMENTS
CHAPTER 5. TROUBLESHOOTING
CHAPTER 6. MAINTENANCE
APPENDIX
Page 7

CHAPTER 1 Product Description
Table of Contents
1.1 Specifications 1-1
1.1.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.1.2 Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.2 Hardware Specifications 1-4
1.2.1 Printing Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.2.2 Printing Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.2.3 Paper Handling Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.2.4 Paper Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.2.5 Ribbon Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-16
1.2.6 Electrical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-16
1.2.7 Environmental Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
1.2.8 Reliability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
1.2.9 Safety Approvals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
1.2.10 CE Marking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-18
1.2.11 Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-18
1.2.12 Cut Sheet Feeder Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-18
1.3 Firmware Specifications 1-20
1.3.1 Control Codes and Fonts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-20
1.3.2 Interface Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-21
1.3.2.1 Parallel Interface (Forward Channel) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-21
1.3.2.2 Parallel Interface (Reverse Channel) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-23
1.3.2.3 Interface Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-24
1.3.2.4 Preventing the Host from Data Time-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-24
1.3.3 Paper Handling Firmware Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-25
1.3.4 Paper Width Sensor Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-28
1.4 Operating Instructions 1-29
1.4.1 Control Panel Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-29
1.4.2 Status Codes Indicated by the LEDs and Beeper. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-30
1.4.3 Micro Adjustment Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-31
1.4.4 Tear Off Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-31
1.4.5 Self-test Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-32
1.4.6 Hexadecimal Dump Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-32
1.4.7 Default Setting Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-33
1.4.8 EEPROM Clear Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-33
1.4.9 Bidirectional Adjustment Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-34
1.5 Initialization 1-34
1.5.1 Software Initialization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-34
1.5.2 Operation Initialization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-34
1.5.3 Power On Initialization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-34
Page 8

1.6 MAIN COMPONENTS 1-35
1.6.1 C165 MAIN Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-36
1.6.2 C165 PSB/PSE Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-36
1.6.3 C165 PNL Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-37
1.6.4 Printer Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-37
1.6.5 Housing Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-38
List of Figures
Figure 1-1. Exterior View of the LQ-2170 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Figure 1-2. Pin Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Figure 1-3. Printable Area for Cut Sheets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
Figure 1-4. Printable Area for Envelopes and Card Stock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
Figure 1-5. Printable Area for Continuous Paper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-13
Figure 1-6. Label Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14
Figure 1-7. Printable Area for Roll Paper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15
Figure 1-8. Data Transmission Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-22
Figure 1-9. Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-29
Figure 1-10. Self-test Printout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-32
Figure 1-11. Hexadecimal Dump Printout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-32
Figure 1-12. Main Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-35
Figure 1-13. C165 MAIN Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-36
Figure 1-14. C165 PSB/PSE Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-36
Figure 1-15. C165 PNL Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-37
Figure 1-16. Printer Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-37
Figure 1-17. Housing Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-38
Page 9

List of Tables
Table 1-1. Items Included with the Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Table 1-2. Consumables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Table 1-3. Optional Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Table 1-4. Print Speed and Printable Columns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Table 1-5. Print Resolution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Table 1-6. Paper Path and Paper Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Table 1-7. Paper Thickness Lever Positions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Table 1-8. Specifications for Cut Sheets (Single Sheet, not Multipart) . . . . . . . . 1-8
Table 1-9. Specifications for Cut Sheets (Multipart). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
Table 1-10. Printable Area for Cut Sheets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
Table 1-11. Specifications for Envelopes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
Table 1-12. Specifications for Card Stock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
Table 1-13. Printable Area for Envelopes and Card Stock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-11
Table 1-14. Specifications for Continuous Paper (Single Sheet and Multipart ) 1-12
Table 1-15. Printable Area for Continuous Paper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-13
Table 1-16. Specifications for Continuous Paper with Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-14
Table 1-17. Specifications for Roll Paper. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15
Table 1-18. Printable Area for Roll Paper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-15
Table 1-19. Ribbon Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-16
Table 1-20. Electrical Specifications for 120 V Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-16
Table 1-21. Electrical Specifications for 220/240 V Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-16
Table 1-22. Environmental Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
Table 1-23. Reliability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
Table 1-24. Safety Information for Printer Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-17
Table 1-25. CE Marking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-18
Table 1-26. Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-18
Table 1-27. Hopper Capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-18
Table 1-28. Stacker Capacity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-19
Table 1-29. Environmental Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-19
Table 1-30. Character Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-20
Table 1-31. Pin Assignment of Forward Channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-21
Table 1-32. Minimum and Maximum Timings for Data Transmission . . . . . . . . 1-22
Table 1-33. Pin Assignments for Reverse Channel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-23
Table 1-34. Paper Handling Sequence 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-25
Table 1-35. Paper Handling Sequence 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-25
Table 1-36. Paper Handling Sequence 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-26
Table 1-37. Paper Handling Sequence 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-26
Table 1-38. Paper Handling Sequence 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-27
Table 1-39. Paper Handling Sequence 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-27
Table 1-40. Paper Width Sensor Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-28
Table 1-41. Operations in Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-29
Table 1-42. Operations at Power On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-30
Table 1-43. Operations for Default Setting Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-30
Table 1-44. Indicators and Beeper. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-30
Table 1-45. EEPROM Initialization Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-33
Page 10

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.1 Specifications
These specifications provide statistical information for the the LQ-2170 serial impact dot matrix printer.
1.1.1. Features
The LQ-2170 is a 24pin serial impact dot-matrix printer suitable for the VAR (value added reseller) market.
The major features of this printer are:
Print speed High speed draft 440 characters per second (cps)
Draft 330 cps
LQ 110 cps at 10 characters per inch (cpi)
Feeding method Friction feed (front, rear)
Push tractor feed (front, rear)
Push and pull tractor feed (front, rear)
Pull tractor feed (front, rear, bottom)
Feeder Front push tractor, rear push tractor, CSF bin 1 / bin 2 (optional)
Pull tractor (optional) , roll paper ❊ holder (optional)
Paper/media Single sheets, continuous paper, multipart paper, envelopes, card stock
labels, roll paper
Fonts 9 LQ and 1 draft bitmap typefaces
8 barcode fonts
Character tables Standard version 11 tables
NLSP version 20 tables
Input buffer 64KB
Acoustic noise 53 dB (A), ISO 7779 pattern
Reliability Total print volume 7.5 million lines, except printhead
MTBF 6000 power on hours (POH)
Printhead life 400 million strokes/wire
Ribbon life 8 million characters
Interfaces Bidirectional parallel interface (IEEE-P1284 nibble mode supported)
Type B I /F Level 2 (option)
Control codes ESC/P2 and IBM 2390/2391 plus emulation
Copy capability 1 original + 4 copies
Control panel functions Font, Pitch, Pause, Tear off, Bin, LF/FF, Load/Eject, Micro Adjust,
Default setting
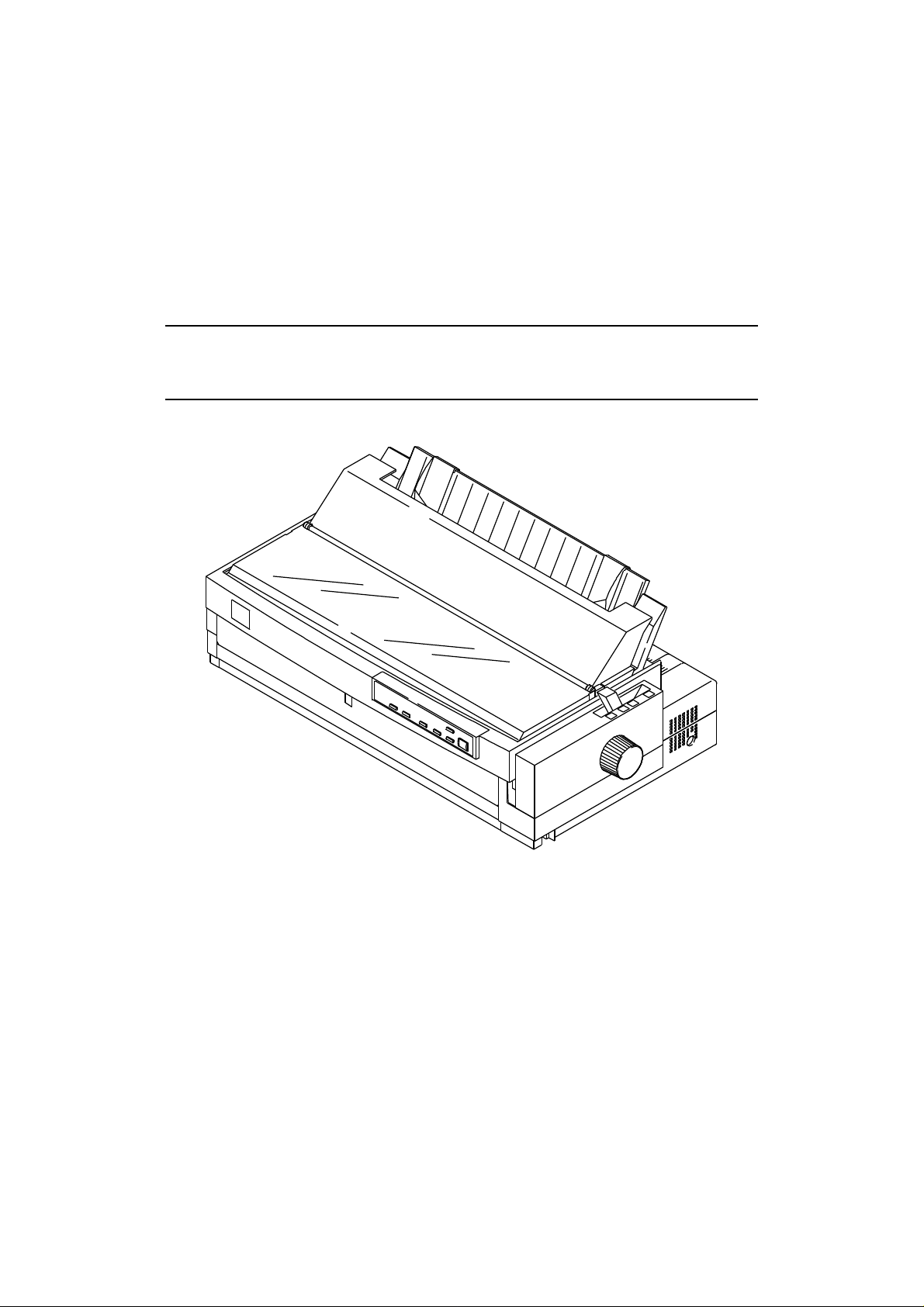
Refer to Figure 1-1 on the next page for an exterior view of the FX-2170.
❊ Roll paper is not available on all models, and not available in the U.S.
Rev.A 1-1
Page 11
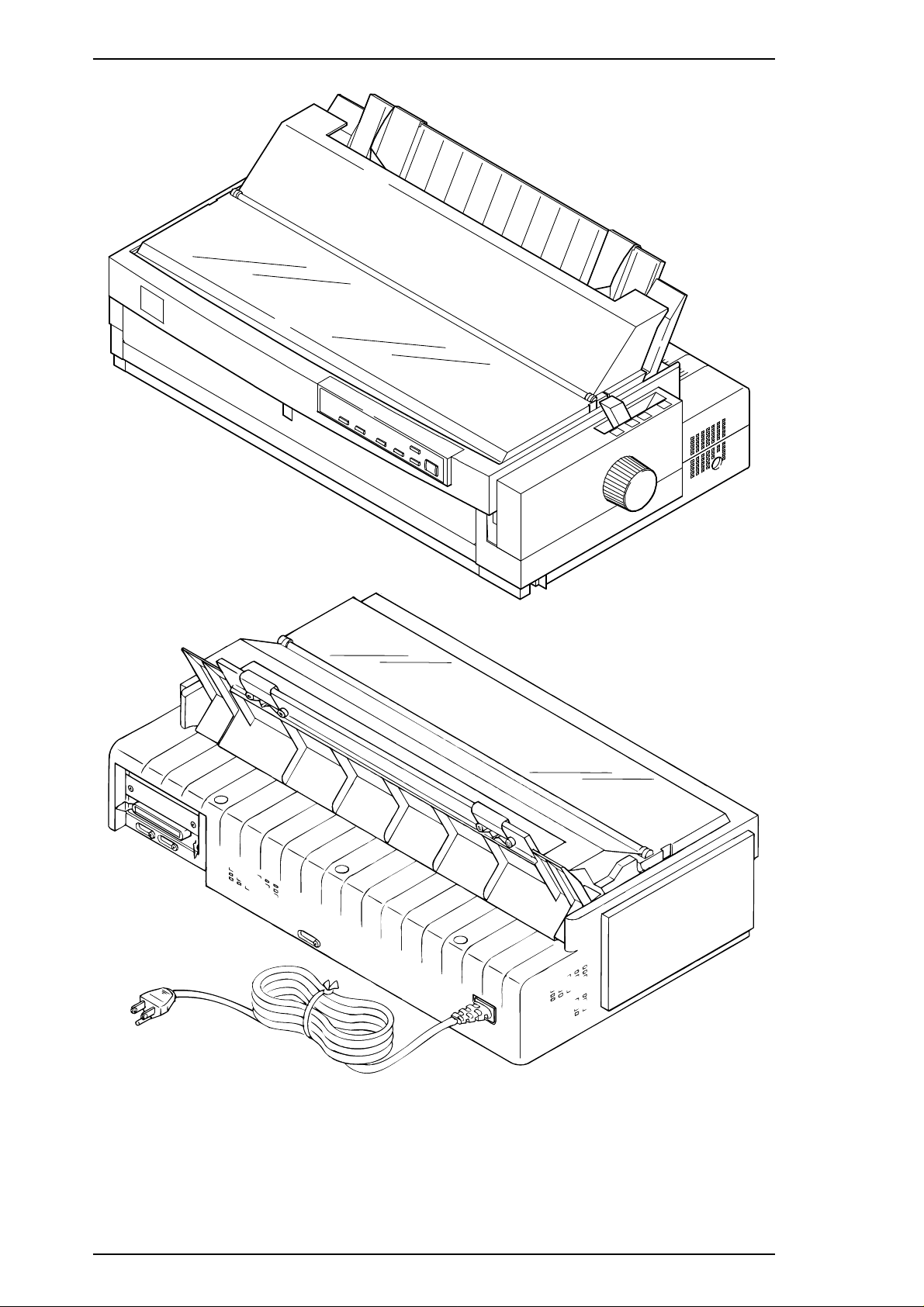
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
Figure 1-1 Exterior View of the LQ-2170
1-2 Rev.A
Page 12
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.1.2. Accessories
• Items included in the printer carton
Table 1-1 Items Included with the Printer
Enclosed Items Quantity
User’s guide 1
Driver diskette 1
Ribbon cartridge 1
Power cord 1
• Consumables
Table 1-2 Consumables
Consumable Item Part Number
Ribbon cartridge S015083
Ribbon pack S010031
• Options
Table 1-3 Optional Units
Unit
High-capacity cut sheet feeder 1 (bin 1) C80673*
Second bin cut sheet feeder 2 (bin 2) C80674*
Pull tractor unit C80032*
Roll paper holder #8310
Serial I/F card C82305* / C82306*
32KB intelligent serial I/F card C82307* / C82308*
32KB intelligent parallel I/F card C82310* / C82311*
Local Talk I/F card C82312*
32KB IEEE-488 I/F card C82313*
Coax I/F card C82314*
Description
Twinax I/F card C82315*
Ethernet I/F card C82331*
* The number represented by an asterisk varies, depending on the country.
Rev.A 1-3
Page 13
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.2 Hardware Specifications
This section provides detailed hardware specifications for the LQ-2170.
1.2.1 Printing Method
Printing method Impact dot matrix
Color Black
Number of pins 24 pins
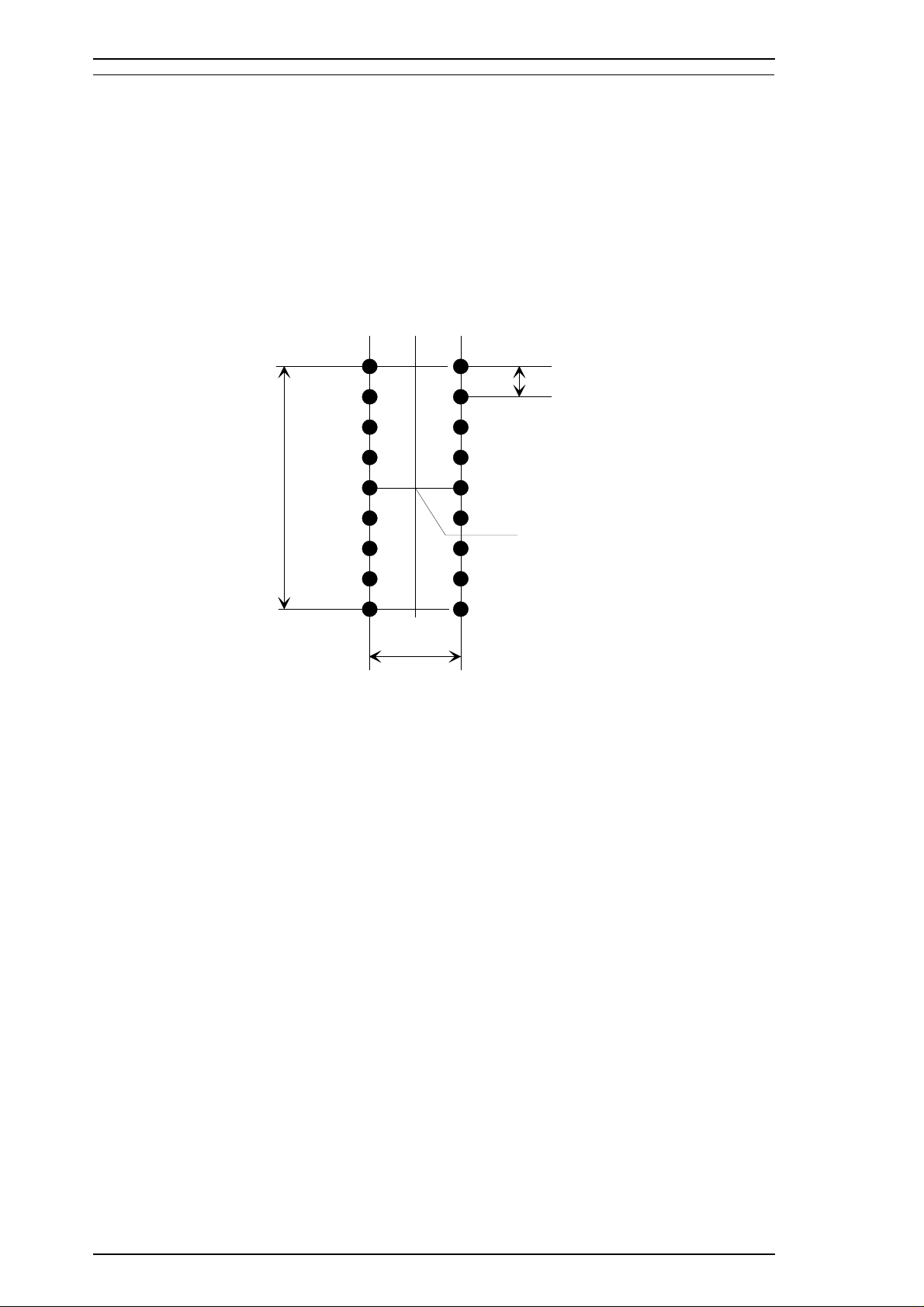
Pin arrangement
Pin diameter 0.21 mm (0.00083 inch)
12 × 2 staggered
2.822 mm
(8/72")
#1
#3 #4
#5 #6
#7 #8
#9 #10
#11 #12
#13 #14
#15 #16
#17 #18
0.847 mm
(1/30’’)
#2
0.353 mm
(1/72’’)
Head Center
Figure 1-2. Pin Configuration
❇ The figure above shows the configuration of pins on the paper.
Print direction Bidirectional, with logic seeking for text, and unidirectional for graphics.
(Bidirectional printing of graphics can be selected with a printer setting or
software command.)
1-4 Rev.A
Page 14
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.2.2 Printing Specifications
Copy capability 1 original + 4 copies
Print speed and printable columns
Table 1-4 Print Speed and Printable Columns
Print Speed (cps)
Print Mode Character Pitch Printable Columns
Normal Multipart
High-speed draft 10 cpi 136 440 293
10 cpi 136 330 220
Draft
Draft condensed
NLQ
LQ Condensed
Resolution
12 cpi 163 396 264
15 cpi 204 495 330
17 cpi 233 283 189
20 cpi 272 330 220
10 cpi 136 110 73
12 cpi 163 132 88
15 cpi 204 165 110
17 cpi 233 189 126
20 cpi 272 220 147
Table 1-5 Print Resolution
Print Mode Horizontal Density Vertical Density Adjacent Dot Printed?
High-speed draft 90 dpi 180 dpi No
Draft 120 dpi 180 dpi No
Draft condensed 240 dpi 180 dpi No
NLQ 360 dpi 180 dpi No
8 pin bit image
24 pin bit image 60, 90, 120, or 180 dpi 180 dpi Yes
Raster graphics 180 or 360 dpi 180 or 360 dpi Yes
Acoustic noise 53 dB (A), ISO 7779 pattern
60, 80, 90, or 120 dpi 60 dpi Yes
120 or 240 dpi 60 dpi No
360 dpi 180 dpi No
Rev.A 1-5
Page 15
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.2.3 Paper Handling Specifications
Feeding method Friction feed (front, rear)
Push tractor feed (front, rear)
Push and pull feed (front, rear, bottom)
Feeder Front push tractor, rear push tractor, CSF bin 1 /bin 2 (optional) Pull
tractor (optional) and roll paper holder (optional)
Paper path Manual insertion Front or rear in, top out
CSF Rear in, top out
Tractor Front, rear, or bottom in, top out
Line spacing 1/6 inch or programmable in increments of 1/360 inch.
Feed speed 1/6 inch feed 45 msec
Continuous feed 0.127 m /sec ( 5.0 inches/sec)
Release lever Set the release lever, using the following table.
Table 1-6 Paper Path and Paper Types
Paper Types
Lever
Position
Paper Entrance
Single Sheet Labels
Card Stock /
Envelopes
Multipart Roll Paper
Front insertion OK NO OK ❇ OK NO
Rear insertion OK NO OK OK NO
Friction
Front
tractor
Rear
tractor
Full
release
❇ This symbol after “OK” means you need to check the paper type before using it with this paper path.
CSF bin 1 OK NO OK OK NO
CSF bin 2 OK NO NO NO NO
Roll paper holder NO NO NO NO OK
Push OK OK ❇ NO OK NO
Push-pull OK OK ❇ NO OK NO
Push OK OK ❇ NO OK NO
Push-pull OK OK ❇ NO OK NO
Pull (front bottom) OK OK NO OK NO
Pull (rear) OK OK ❇ NO OK NO
1-6 Rev.A
Page 16
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
Paper thickness lever Set the paper thickness lever to the appropriate position, as
indicated in the following table.
Table 1-7 Paper Thickness Lever Positions
Paper Thickness ( inches) Paper Thickness (mm)
Lever Position
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
0 0.0024 0.0043 0.06 0.11
1 0.0047 0.0067 0.12 0.18
2 0.0075 0.0098 0.19 0.25
3 0.0102 0.0122 0.26 0.31
4 0.0126 0.0138 0.32 0.35
5 0.0142 0.0154 0.36 0.39
6 0.0157 0.0205 0.40 0.52
———————— Precautions for Handling Paper ————————
1. Friction feed
Set the release lever to the FRICTION position and install the paper eject assembly
Load paper from the front or top entrance. Do
not use continuous paper. Do not
perform any reverse paper feeds within the top 8.5 mm (0.33 inch) and bottom 22 mm
(0.87 inch) area.
Do not perform reverse feeds greater than 1/6 inch after the paper end has been detected.
Use the paper-tension unit.
Insert the multipart cut sheet forms only from the front.
2. Push tractor feed
Set the release lever to the REAR PUSH/FRONT PUSH position and install the paper eject
assembly.
Load paper from the rear or front entrance.
Release the friction feed mechanism.
Multipart paper must be carbonless. Use
the paper-tension unit. Do not
perform reverse feeds greater than 1/6 inch. Do not
perform reverse feeds after the paper end has been detected, because accuracy of
paper feeding cannot be assured.
3. Pull tractor feed
Set the release lever to the PULL position.
Load paper from the front, rear, or bottom entrance. (The
front or bottom entrance is recommended for thick paper or labels.)
Remove the paper eject assembly and attach the pull tractor unit.
Insert paper from either from the front or bottom.
Multipart paper must be carbonless. Do
not perform reverse feeds.
Rev.A 1-7
Page 17
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
4. Push-pull tractor feed
Set the release lever to the REAR PUSH/FRONT PUSH position.
Load paper from the front or rear entrance. Remove
the paper eject assembly and attach the pull tractor unit. Remove
any slack in the paper between the platen and pull tractor. Precisely adjust the
horizontal position of the pull tractor and push tractor. Multipart paper must be
carbonless. Do not perform reverse feeds
greater than 1/6 inch. Do not perform reverse feeds
after the paper end has been detected.
1.2.4 Paper Specifications
This section describes the printable area and types of paper that can be used in this printer.
Cut Sheets
Paper/ media specifications The following table shows specifications for cut sheets.
Table 1-8 Specifications for Cut Sheets (Single Sheet, Not Multipart)
Front Entry Rear Entry
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Width 101 mm (4.0") 420 mm (16.5") 101 mm (4.0") 420 mm (16.5")
Length 147 mm (5.8") 420 mm (16.5") 101 mm (4.0") 420 mm (16.5")
Thickness 0.065 mm(0.0025") 0.14 mm (0.0055") 0.065 mm(0.0025") 0.14 mm (0.0055")
2
Weight 52.3 g/m
Quality Plain paper, recycled paper.
Not curled, folded, or crumpled.
(14 lb) 90 g/m2(24 lb) 52.3 g/m2(14 lb) 90 g/m2(24 lb)
Plain paper, recycled paper.
Not curled, folded, or crumpled.
Table 1-9 Specifications for Cut Sheets (Multipart)
Front Entry Rear Entry
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Width 101 mm (4.0") 420 mm (16.5") 101 mm (4.0") 420 mm (16.5")
Length 147 mm (5.8") 420 mm (16.5") 101 mm(4.0") 420 mm (16.5")
Copies 1 original + 4 copies 1 original + 4 copies
Total
thickness
Weight ❇ 40 g/m
0.12 mm (0.0047") 0.39 mm (0.015") 0.12 mm (0.0047") 0.39 mm (0.015")
2
(12 lb) 58 g/m2(15 lb) 40 g/m2(12 lb) 58 g/m2(15 lb)
Quality Plain paper, recycled paper.
Not curled, folded, or crumpled.
Binding A line of glue at the top or one side of the
form.
❇ This weight is for one sheet of the multipart form.
1-8 Rev.A
Plain paper, recycled paper.
Not curled, folded, or crumpled.
A line of glue at the top of the form.
Page 18
BM
TM
PL
PW
RM
LM
Pri ntab le area
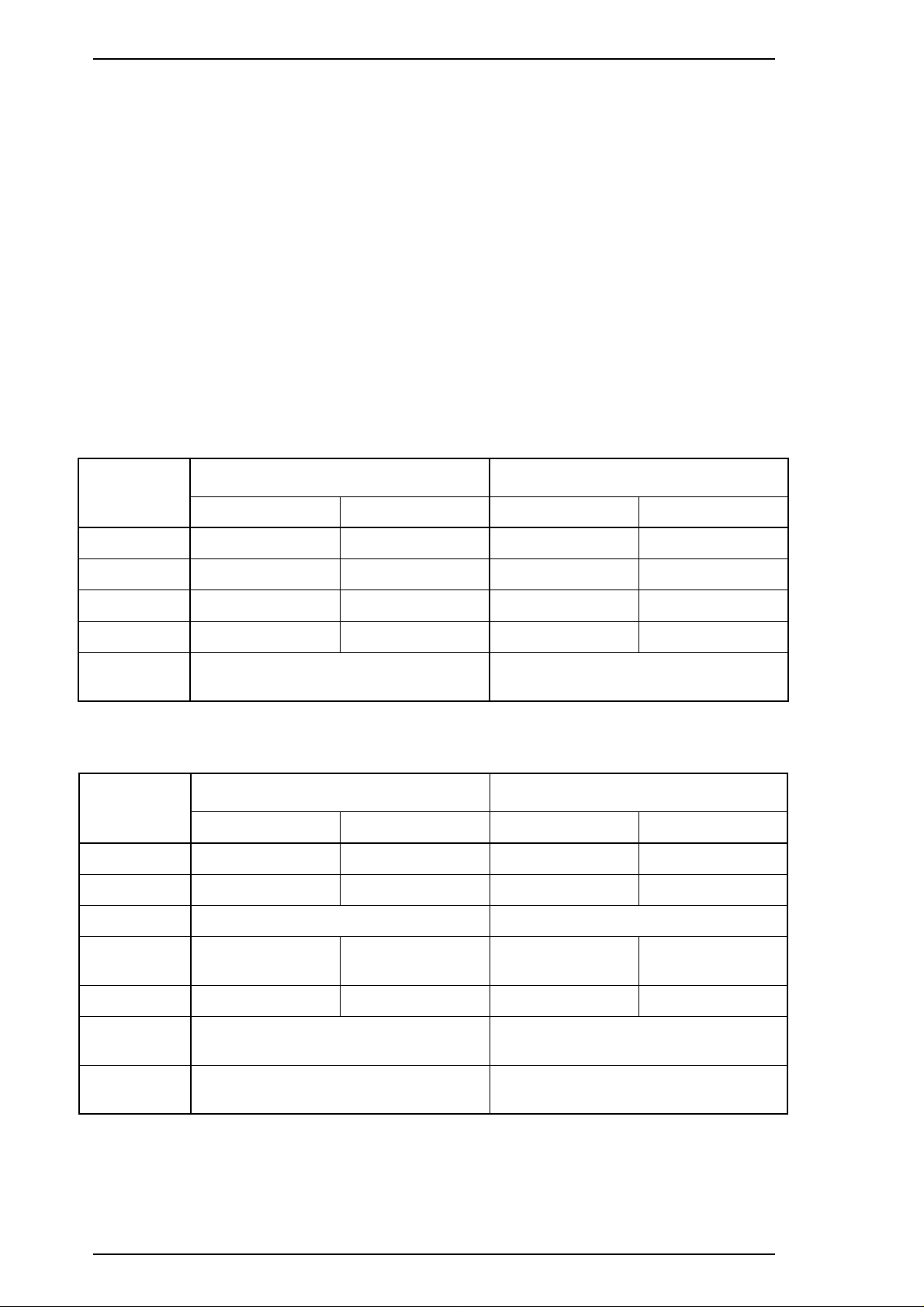
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
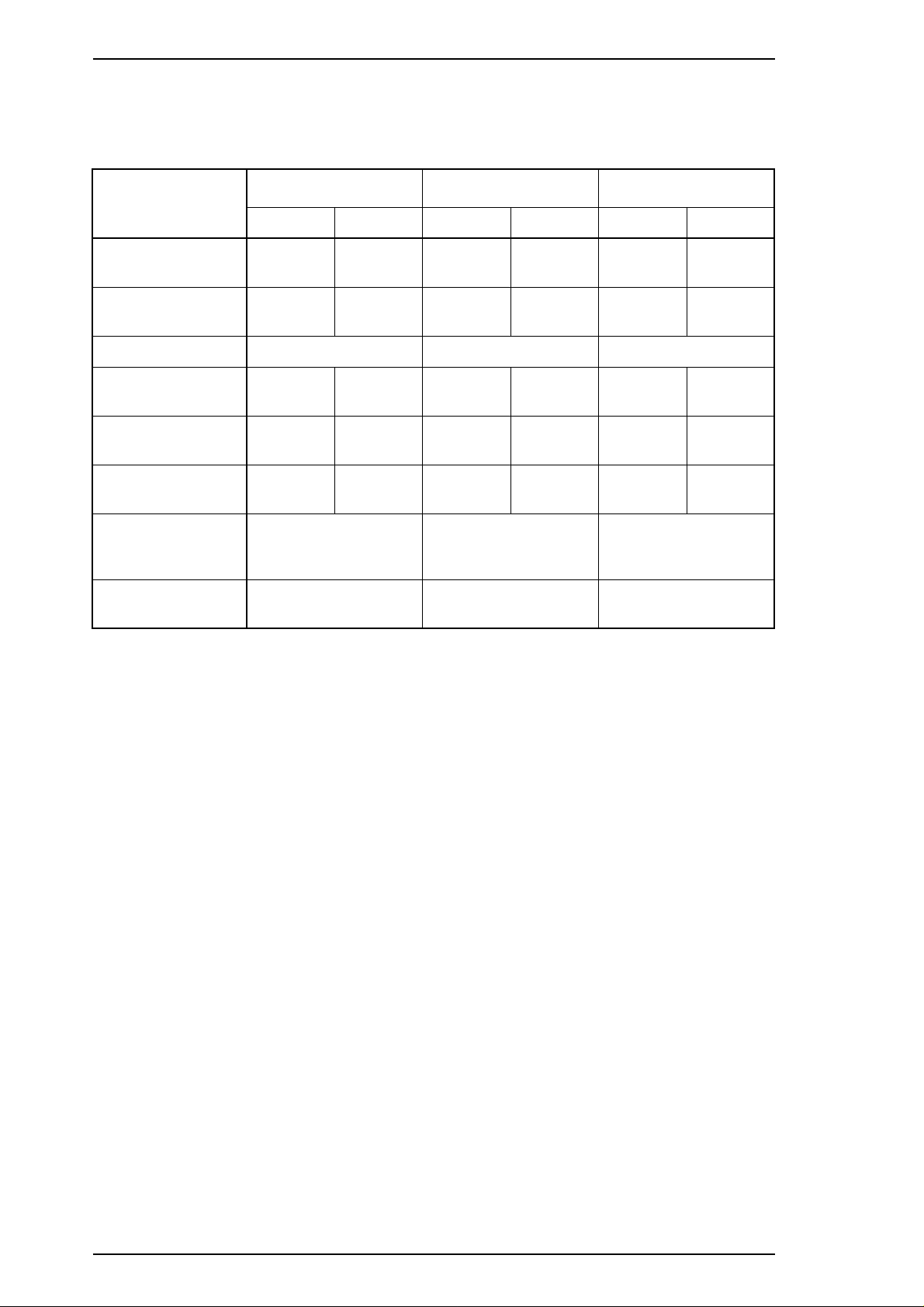
Printable area Figure 1-3 shows the printable area for cut sheets. The table
below defines the abbreviations used in the figure.
Table 1-10 Printable Area for Cut Sheets
Abbreviations Single Sheet Multipart
PW (width) Refer to Table 1-8. Refer to Table 1-9.
PL (length) Refer to Table 1-8. Refer to Table 1-9.
LM (left margin) 3 mm (0.12") or more
(PW ≤ 364 mm (14.33"))
25 mm (0.98") or more
(PW = 420 mm (16.5"))
RM (right margin) 3 mm or more
(PW ≤ 364 mm (14.33"))
25 mm (0.98") or more
(PW = 420 mm (16.5"))
TM (top margin) 4.2 mm (0.17") or more 4.2 mm (0.17") or more
BM (bottom margin) 4.2 mm (0.17") or more 4.2 mm (0.17") or more
3 mm (0.12") or more
(PW ≤ 364 mm (14.33"))
25 mm (0.98") or more
(PW = 420 mm (16.5"))
3 mm or more
(PW ≤ 364 mm (14.33"))
25 mm (0.98") or more
(PW = 420 mm (16.5"))
Figure 1-3 Printable Area for Cut Sheets
Rev.A 1-9
Page 19
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
Envelopes and Card Stock
Paper/media specifications The following tables gives specifications for envelopes and card stock.
Table 1-11 Specifications for Envelopes
Front Entry Rear Entry
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
No. 6
envelopes
No. 10
envelopes
Total thickness —— —— 0.16 mm (0.0063") 0.52 mm (0.020")
Weight —— —— 45 g/m
Quality
❇ Printing on envelopes is available only at normal temperatures and humidity.
❇ Insert envelopes from the rear entrance only.
❇ Insert the longer side of the envelope horizontally.
Width —- 166 mm (6.5")
Length —- 92 mm (3.6")
Width —- 240 mm (9.5")
Length —- 104 mm (4.1")
——
——
Differences in thickness in the printable
area must be within 0.25 mm (0.0098").
2
(12 lb) 91 g/m2(24 lb)
Bond paper, plain paper, or airmail.
No glue at the flap.
Not curled, folded, or crumpled.
Table 1-12 Specifications for Card Stock
Front Entry Rear Entry
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Width 105 mm (4.13") 148 mm (5.83") 105 mm (4.13") 148 mm (5.83")
Length 148 mm (5.83") 148 mm (5.83") 105 mm (4.13") 148 mm (5.83")
Thickness 0.22 mm (0.0087") 0.22 mm (0.0087")
2
Weight 192 g/m
Quality Plain paper, recycled paper.
Not curled, folded, or crumpled.
❇ Printing on card stock is available only at normal temperatures and humidity.
❇ When the longer side of an A6 card is to be inserted horizontally, insert it from the rear entrance.
(51 lb) 192 g/m2(51 lb)
Plain paper, recycled paper.
Not curled, folded, or crumpled.
1-10 Rev.A
Page 20
Printable area
RM
TM
BM
LM
PW
LM RM
TM
BM
PL
Print abl e ar e a
PW
PL
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
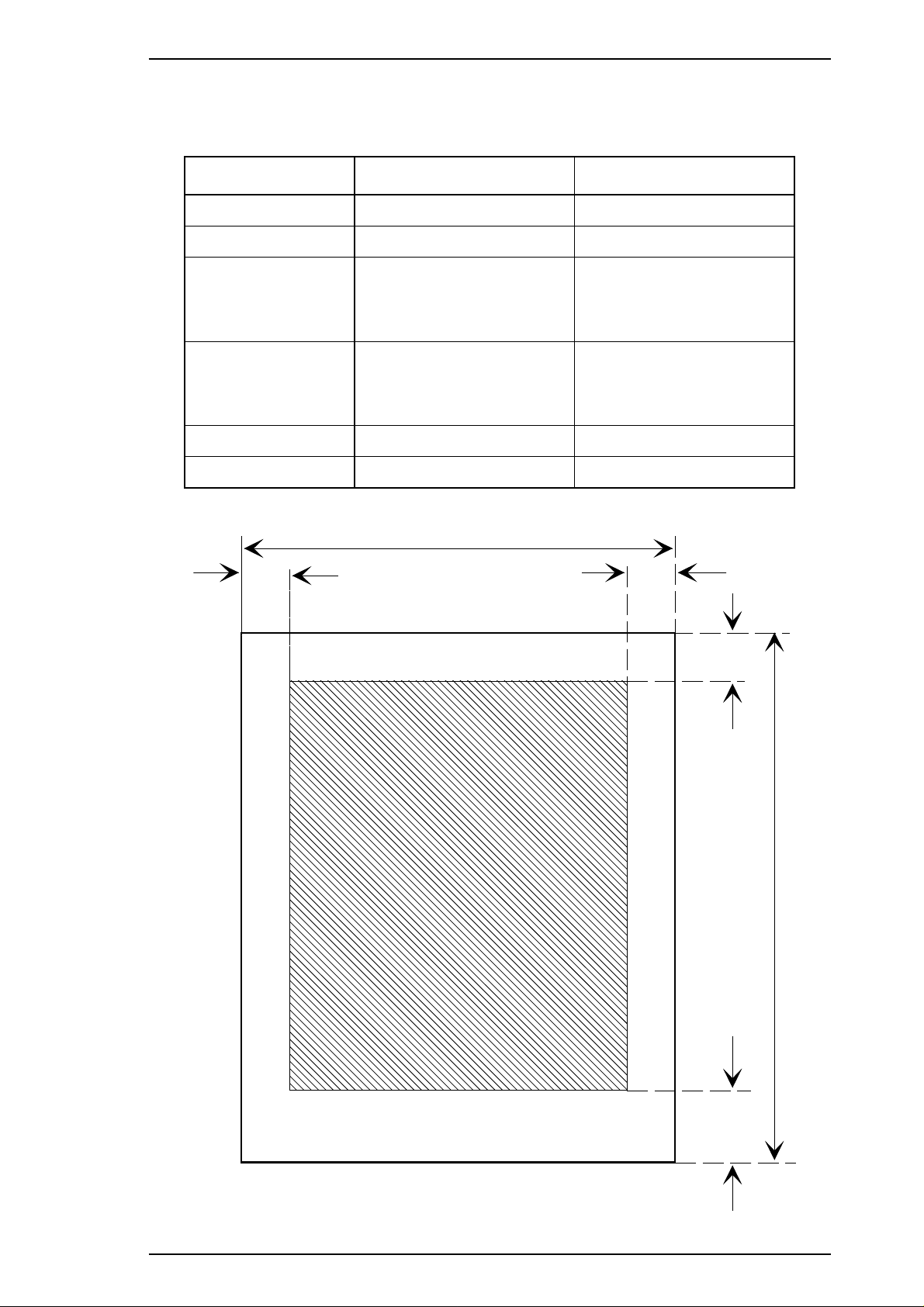
Printable area The figure below shows the printable area for envelopes and card stock.
Each abbreviation is defined in the following table.
Table 1-13 Printable Area for Envelopes and Card Stock
Abbreviations Envelopes Card Stock
PW (width) Refer to Table 1-11. Refer to Table 1-12.
PL (length) Refer to Table 1-11. Refer to Table 1-12.
LM (left margin) 3 mm (0.12") or more 3 mm (0.12") or more
RM (right margin) 3 mm (0.12") or more 3 mm (0.12") or more
TM (top margin) 4.2 mm (0.17") or more 4.2 mm (0.17") or more
BM (bottom margin) 4.2 mm (0.17") or more 4.2 mm (0.17") or more
Figure 1-4 Printable Area for Envelopes and Card Stock
Rev.A 1-11
Page 21
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
Continuous Paper
Paper/media specifications The following table gives specifications continuous paper.
Table 1-14 Specifications for Continuous Paper (Single Sheet and Multipart)
Front Entry Rear Entry Bottom Entry
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Width 101 mm
(4.0")
Length 101 mm
(4.0")
406 mm
(16")
559 mm
(22")
101 mm
(4.0")
101 mm
(4.0")
406 mm
(16")
559 mm
(22")
101 mm
(4.0")
101 mm
(4.0")
406 mm
(16")
559 mm
(22")
Copies 1 original + 4 copies 1 original + 4 copies 1 original + 4 copies
Total thickness 0.065 mm
(0.0025")
Weight
(not multipart)
Weight (one sheet
of a multipart form)
52.3 g/m
(14 lb)
40 g/m
(12 lb)
Types of paper Plain paper.
Recycled paper.
Carbonless multipart.
Binding Dots of glue or paper
staples (both sides).
2
2
0.39 mm
(0.015")
82 g/m
(22 lb)
58 g/m
(15 lb)
0.065 mm
(0.0025")
2
52.3 g/m
2
(14 lb)
2
40 g/m
2
(12 lb)
Plain paper.
Recycled paper.
Carbonless multipart.
Dots of glue or paper
staples (both sides).
0.39 mm
(0.015")
82 g/m2
(22 lb)
58 g/m
(15 lb)
0.065 mm
(0.0025")
52.3 g/m
2
(14 lb)
2
40 g/m
2
(12 lb)
Plain paper.
Recycled paper.
Carbonless multipart.
Dots of glue or paper
staples (both sides).
0.39 mm
(0.015")
82 g/m2
(22 lb)
58 g/m
(15 lb)
2
1-12 Rev.A
Page 22
PW
LM
RM
TM
BM
PL
Printable area
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
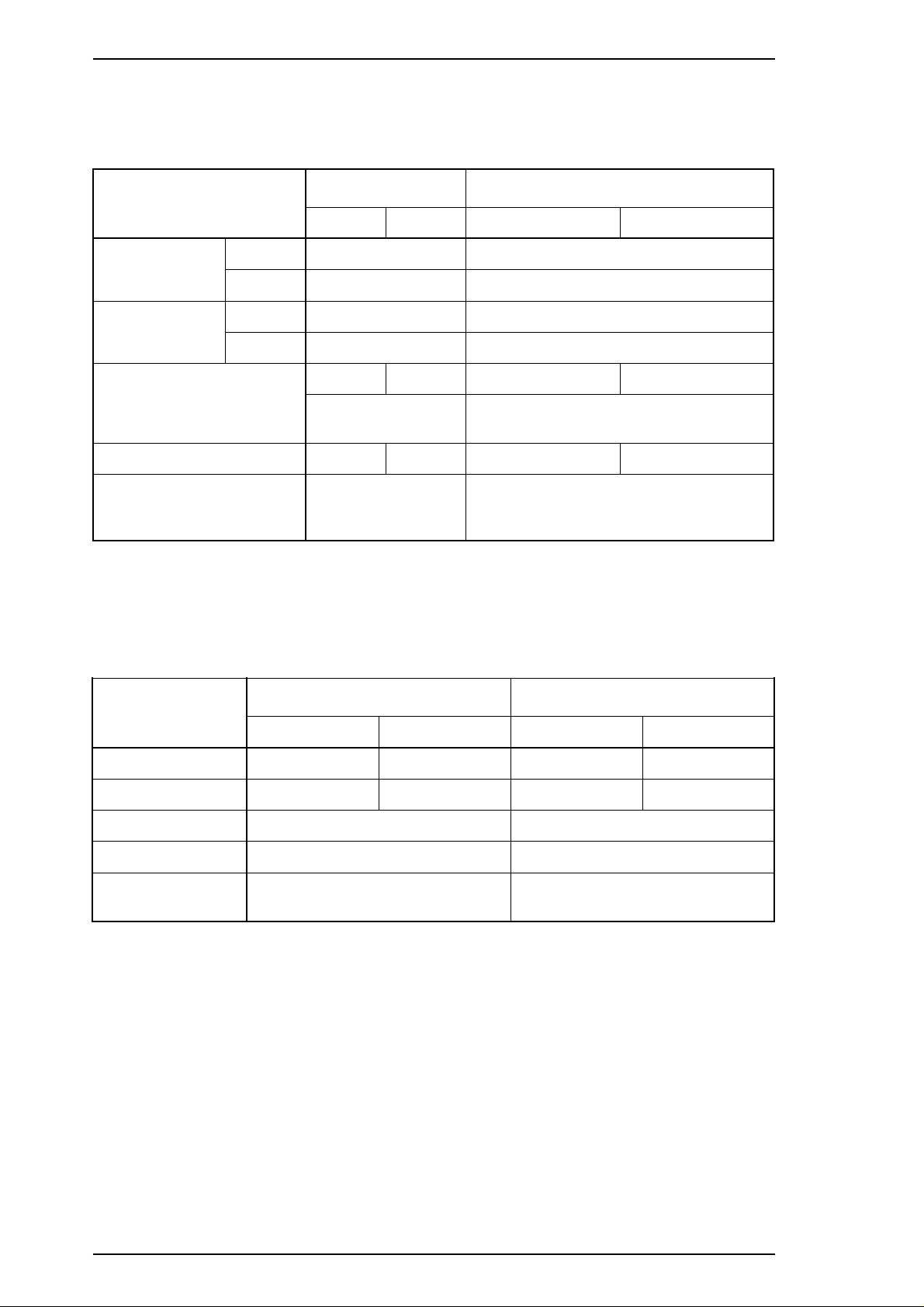
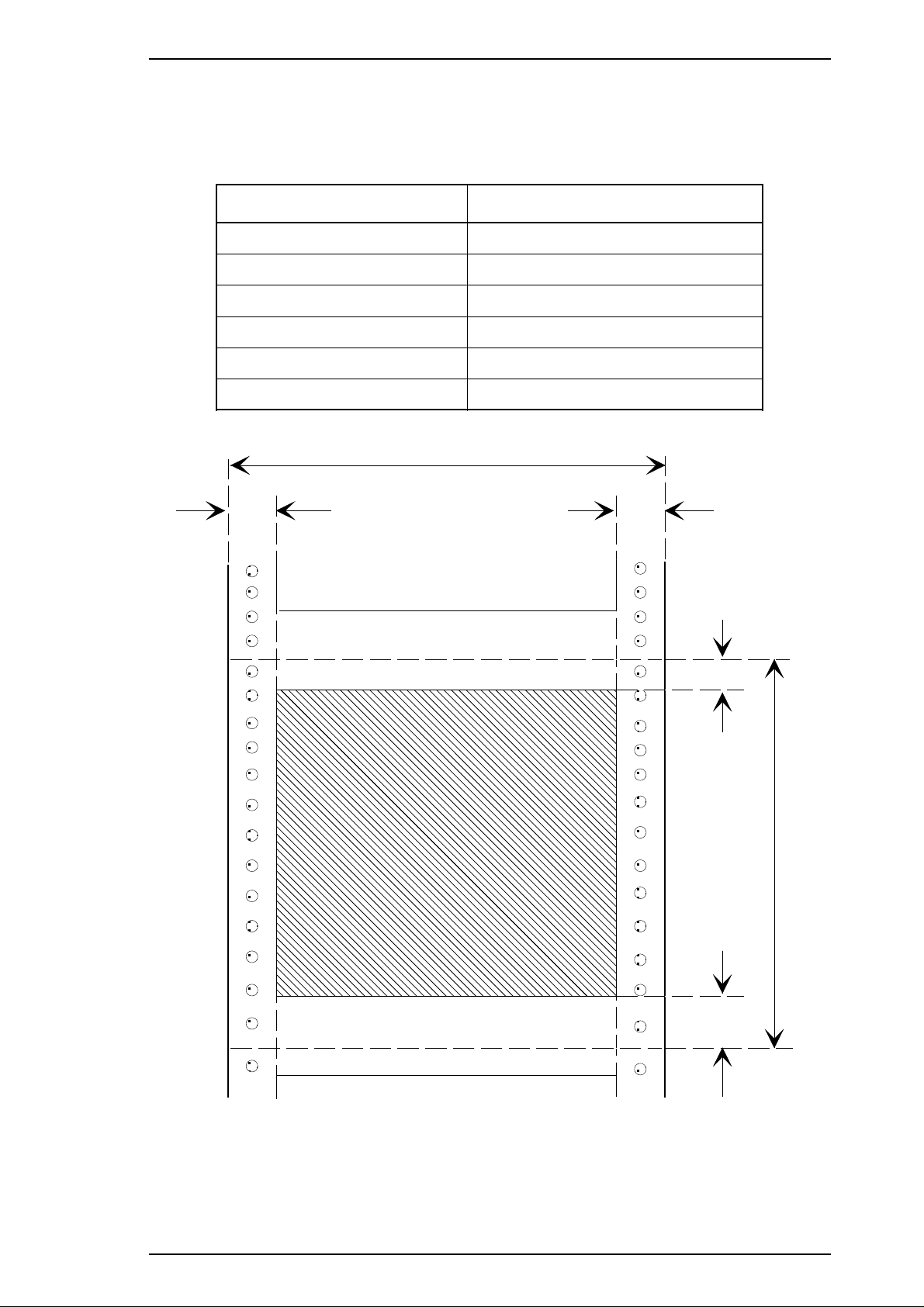
Printable area The figure below shows the printable area for continuous paper.
Each abbreviation is defined in the following table.
Table 1- 15 Printable Area for Continuous Paper
Abbreviations Continuous Paper
PW (width) Refer to Table 1-14.
PL (length) Refer to Table 1-14.
LM (left margin) 13 mm (0.51") or more
RM (right margin) 13 mm (0.51") or more
TM (top margin) 4.2 mm (0.17") or more
BM (bottom margin) 4.2 mm (0.17") or more
Figure 1-5 Printable Area for Continuous Paper
Rev.A 1-13
Page 23
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
Continuous Paper with Labels
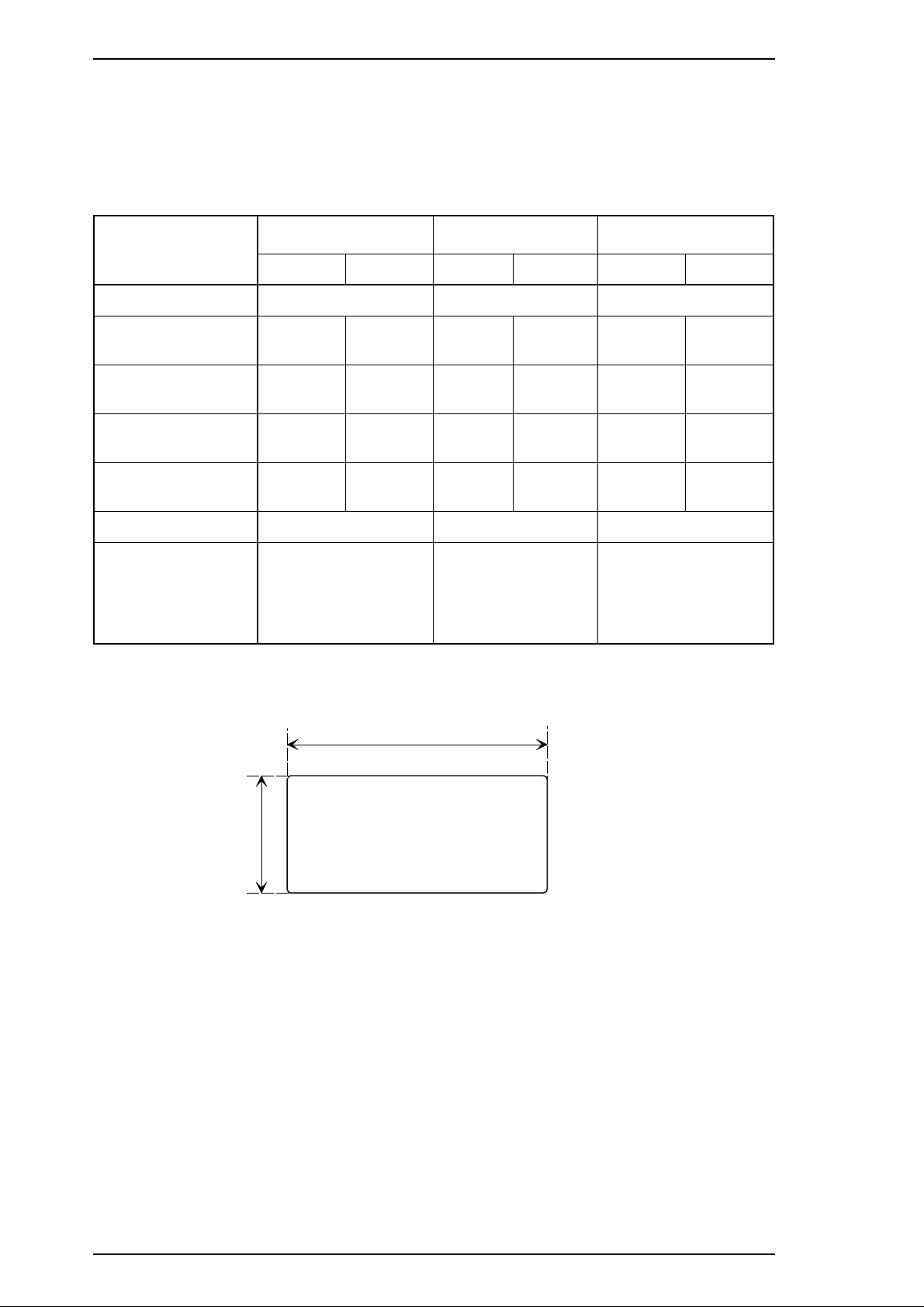
Paper/media specifications The following table gives the specifications for continuous paper with
labels.
Table 1-16 Specifications for Continuous Paper with Labels
Front Entry Rear Entry Bottom Entry
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Label size See the figure below —- See the figure below
Base sheet width 101 mm
(4.0")
Base sheet length
(one page)
101 mm
(4.0")
Base sheet thickness 0.07 mm
(0,0028")
Total thickness 0.16 mm
(0.0063")
Label weight 68 g/m
406 mm
(16")
559 mm
(22")
0.09 mm
(0.00352)
0.19 mm
(0.0075")
2
(17 lb) —- 68 g/m2(17 lb)
—- —-
—- —-
—- —-
—- —-
0.16 mm
(0.0063")
0.16 mm
(0.0063")
Quality Avery continuous
form labels
Avery mini-line or
—equivalent quality
labels
❇ Printing on labels is available only at normal temperatures and humidity.
❇ The base sheet for the labels must be continuous paper.
❇ Continuous paper with labels should be inserted from the front or bottom entrance.
2.5inch (63.5mm) min.
101 mm
406 mm
(4.0")
101 mm
559 mm
(4.0")
0.19 mm
(0.0075")
0.19 mm
(0.0075")
Avery continuous
form labels
Avery mini-line or
equivalent quality
labels
(16")
(22")
15/16inch
(23.8mm)
min.
Label
R0.1inch (2.5mm) min.
Figure 1-6 Label Size
Printable size and area The figure above is the printable size for the labels.
The printable area for the base sheet containing the labels
depends on conditions in Figure 1-5 and Table 1-15.
1-14 Rev.A
Page 24
LM
TM
BM
PL
PW
Printabl e ar e a
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
Roll Paper
Note: Roll paper is not available in all models, and not available in the U.S.
Paper/media specifications The following table shows specifications for roll paper.
Table 1-17 Specifications for Roll Paper
Front Entry Rear Entry
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Width —— 216 mm (8.5")
Length —— ——
Thickness —— —— 0.07 mm (0.0028") 0.09 mm (0.0035")
2
Weight —— —— 52.3g/m
(14 lb) 82 g/m2(22 lb)
Quality
——
Plain paper, recycled paper.
Not curled, folded, or crumpled.
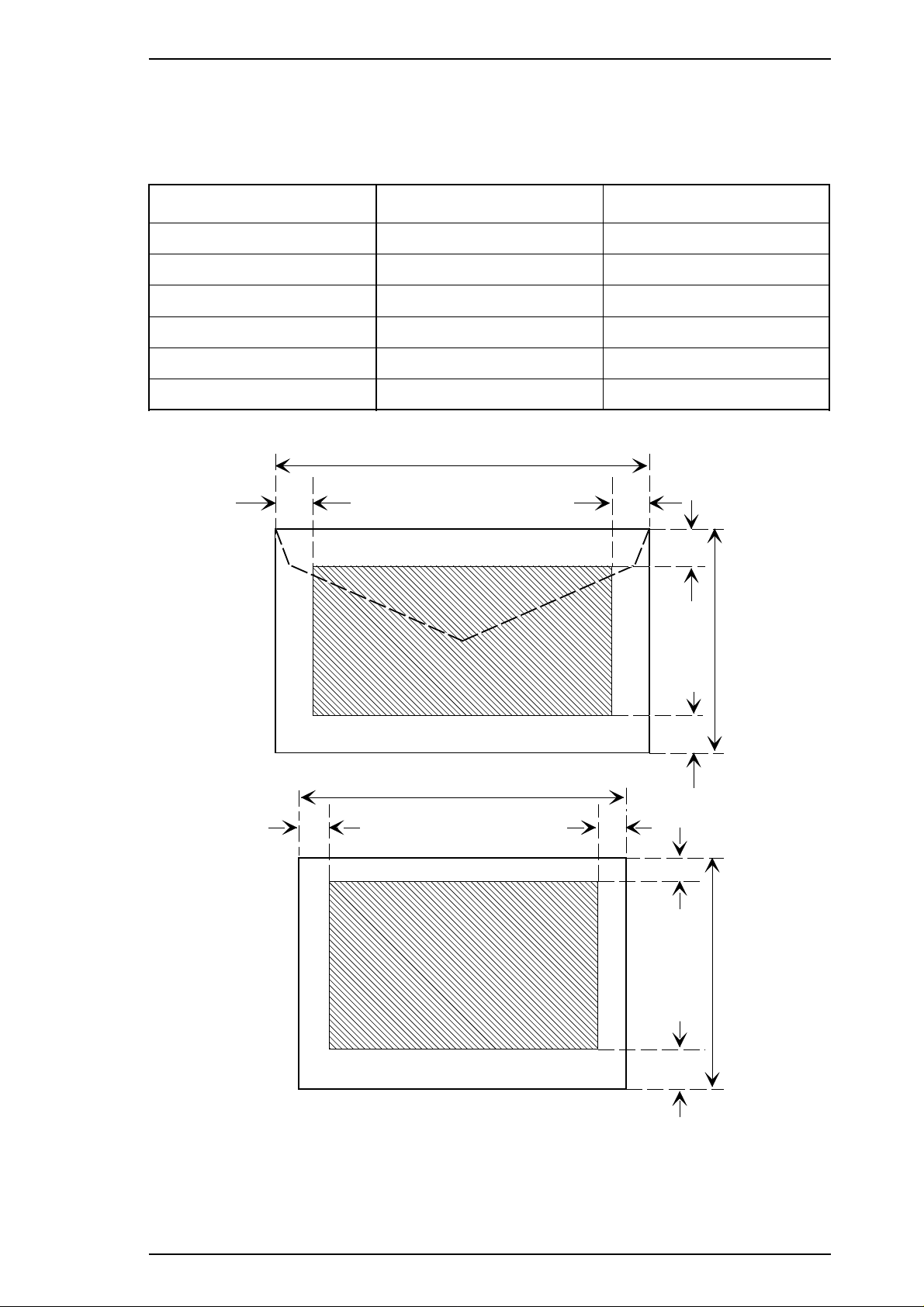
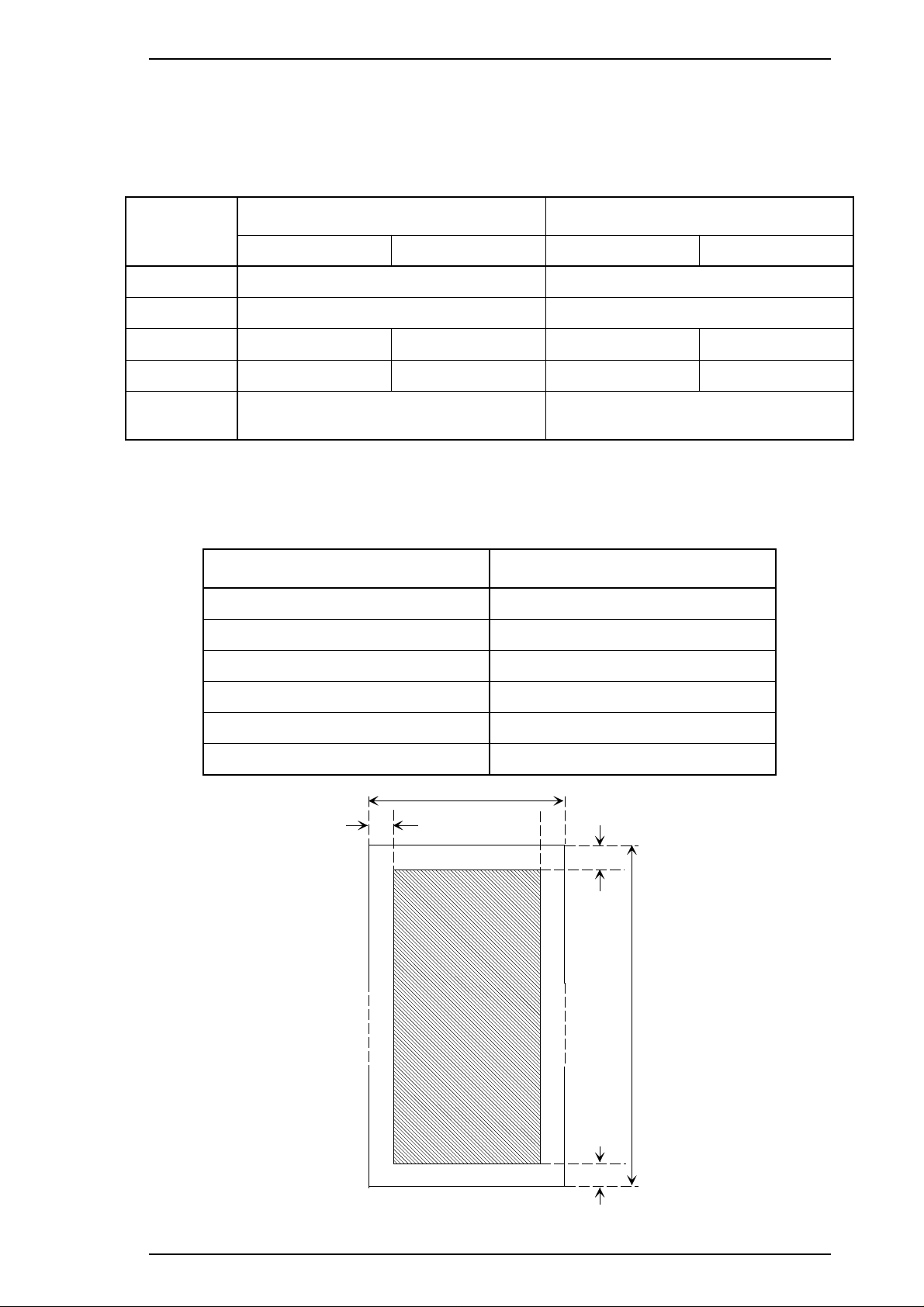
Printable area Figure 1-7 gives the printable area for roll paper.
Each abbreviation is defined in the following table.
Table 1-18 Printable Area for Roll Paper
Abbreviations Roll Paper
PW (width) See Table 1-17.
PL (length) See Table 1-17.
LM 3 mm (0.12") or more
RM 3 mm (0.12") or more
TM 4.2 mm (0.17") or more
BM 4.2 mm (0.17") or more
Rev.A 1-15
Figure 1-7 Printable Area for Roll Paper
Page 25
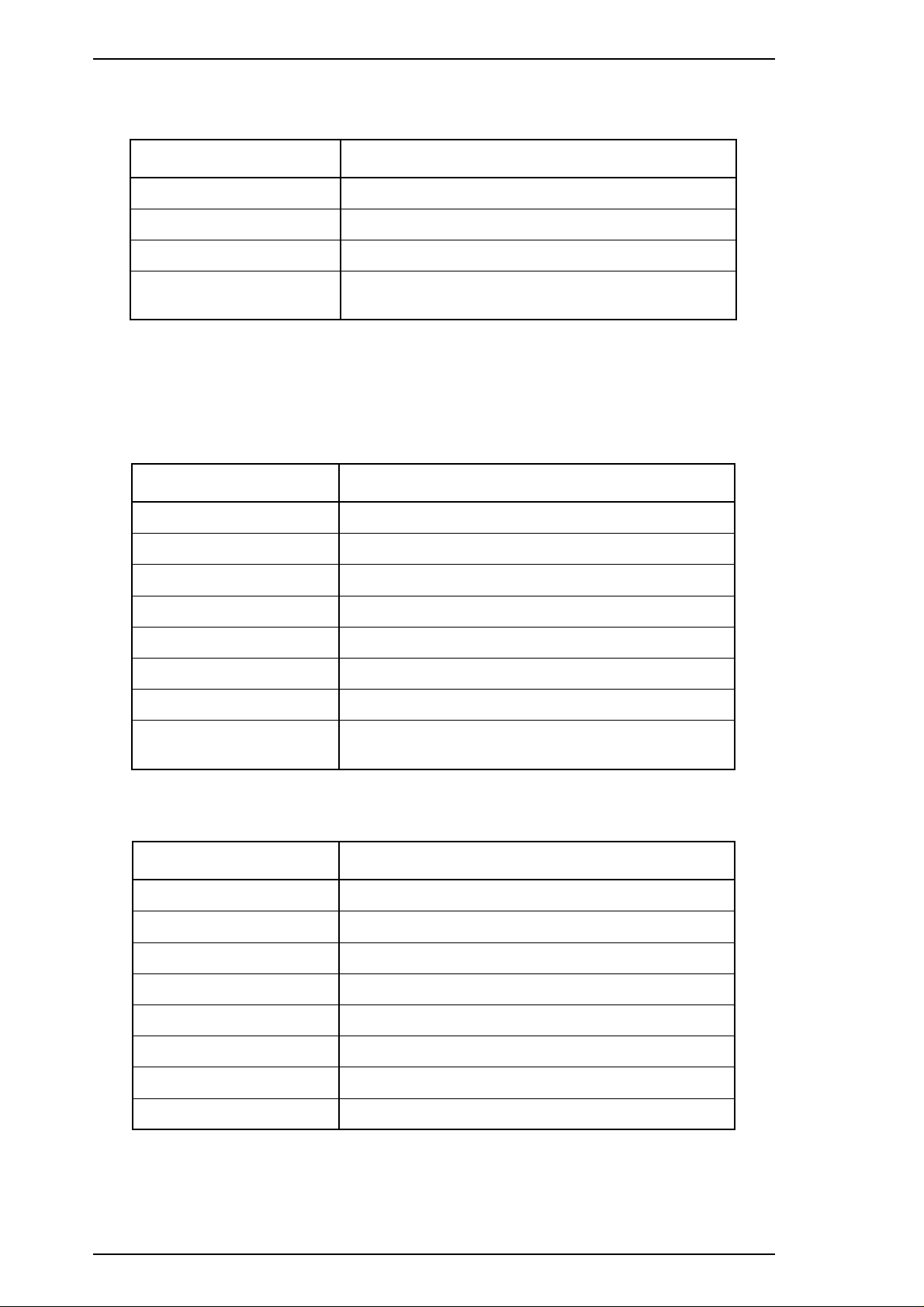
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.2.5 Ribbon Specifications
Table 1-19 Statistics on the Ribbon
Item Specification
Type Fabric
Color Black
Ribbon life 8 million characters (draft, 10 cpi, 48 dots/ character)
Dimension 506.0 mm (W) × 123.5 mm (D) × 23.0 mm (H)
19.92" (W) x 4.86" (D) x .91" (H)
1.2.6 Electrical Specifications
Tables 1-20 and 1-21 provide statistics on electrical ratings and consumption.
Table 1-20 Electrical Specifications for the 120 V Version
Item Specifications
Rated voltage 120 VAC
Input voltage range 103.5 to 132 VAC
Rated frequency range 50 to 60 Hz
Input frequency range 49.5 to 60.5 Hz
Rated current 1.0 A (max. 2.6 A)
Power consumption Approx. 62 W (self-test in draft mode at 10 cpi)
Insulation resistance 10 MΩ min. (between AC line and chassis, 500 VDC)
Dielectric strength 1000 VAC rms. 1 min. or
1200 VAC rms. 1 sec. (between AC line and chassis)
Table 1-21 Electrical Specifications for the 220/240 V Version
Item Specifications
Rated voltage 220 to 240 VAC
Input voltage range 198 to 264 VAC
Rated frequency range 50 to 60 Hz
Input frequency range 49.5 to 60.5 Hz
Rated current 0.5 A (maximum 1.3 A)
Power consumption Approx. 62 W (self-test in draft mode at 10 cpi)
Insulation resistance 10 MΩ min. (between AC line and chassis, 500 VDC)
Dielectric strength 1500 VAC rms. 1 min. (between AC line and chassis)
1-16 Rev.A
Page 26
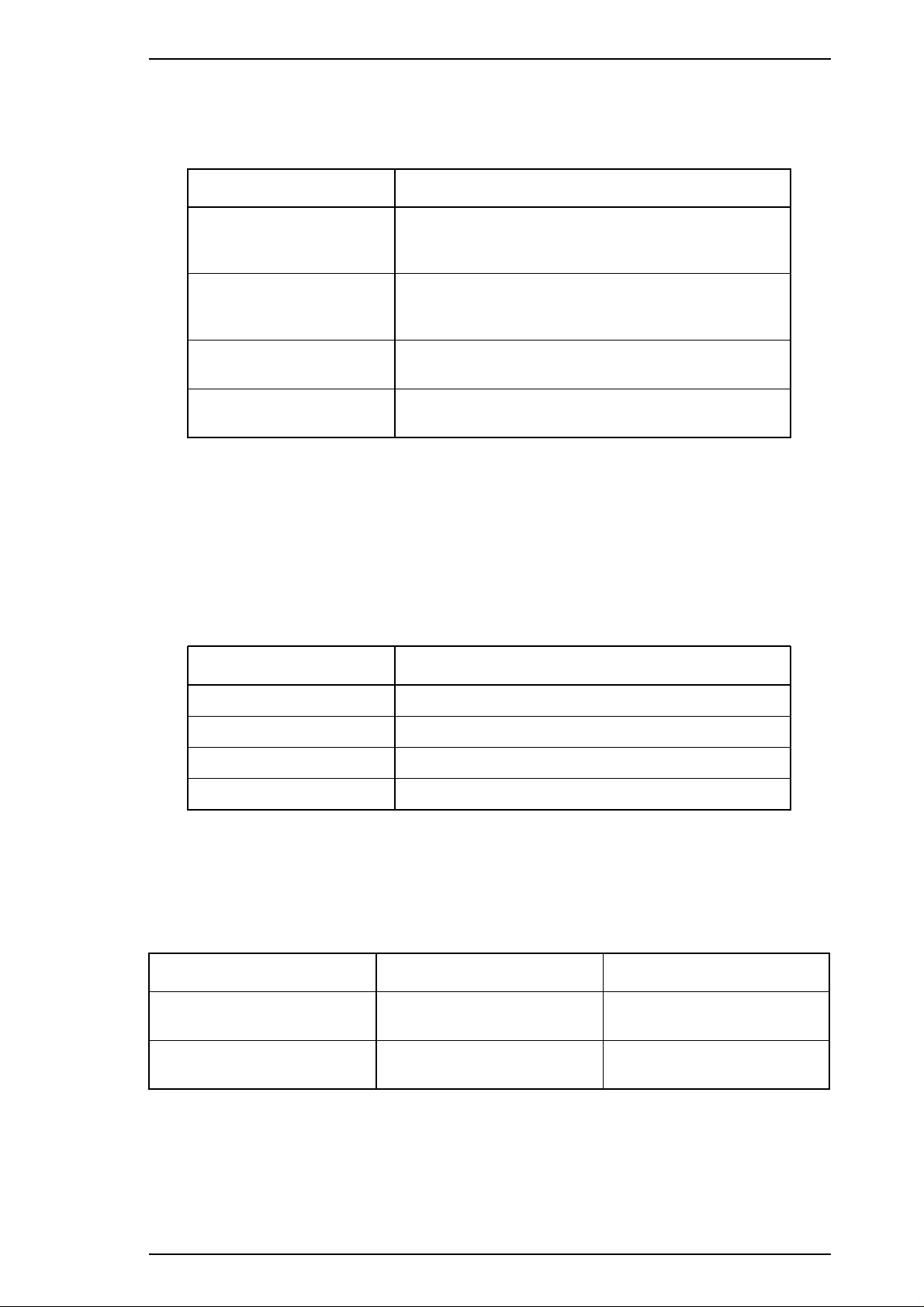
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.2.7 Environmental Conditions
Table 1-22 explains the conditions the printer requires during operation and when not operating.
Table 1-22 Environmental Requirements
Item Specifications
Temperature 5 to 35° C/41 to 95° F ( operating ❇ 1)
15 to 25° C/59 to 77° F (operating ❇ 1, ❇ 2)
ä30 to 60° C/–22 to 140° F (non-operating)
Humidity 10 to 80 % RH (operating ❇ 1)
30 to 60 % RH (operating ❇ 1, ❇ 2)
0 to 85 % RH (non-operating ❇ 1)
Resistance to shock 1 G, within 1 ms (operating)
2 G, within 2 ms (non-operating ❇ 3)
Resistance to vibration 0.25 G, 10 to 55 Hz (operating )
0.50 G, 10 to 55 Hz (non-operating ❇ 3)
❇ 1: Without condensation.
❇ 2: During printing on multipart paper, envelopes, card stock, or labels.
❇ 3: In shipment container.
1.2.8 Reliability
Table 1-23 gives maximum life and usage specifications.
Table 1-23 Reliability Statistics
Item Specification
Total print volume 7.5 million lines (except printhead)
MTBF 6000 power on hours (POH)
Printhead life 400 million strokes / wire
Ribbon life 8 million characters
1.2.9 Safety Approvals
Table 1-24 provides information about the safety approvals the printer has met.
Table 1-24 Safety Information for Printer Models
120 V 230 V
Safety Standards UL1950 with D3
CSA C22.2 No,950 with D3
EN60950 (TüV. SEMKO,
DEMKO, NEMKO, FIMKO )
EMI FCC part 15 subpart B class B
CSA C108.8
Rev.A 1-17
EN55022 (CISPR pub.22)
class B
Page 27
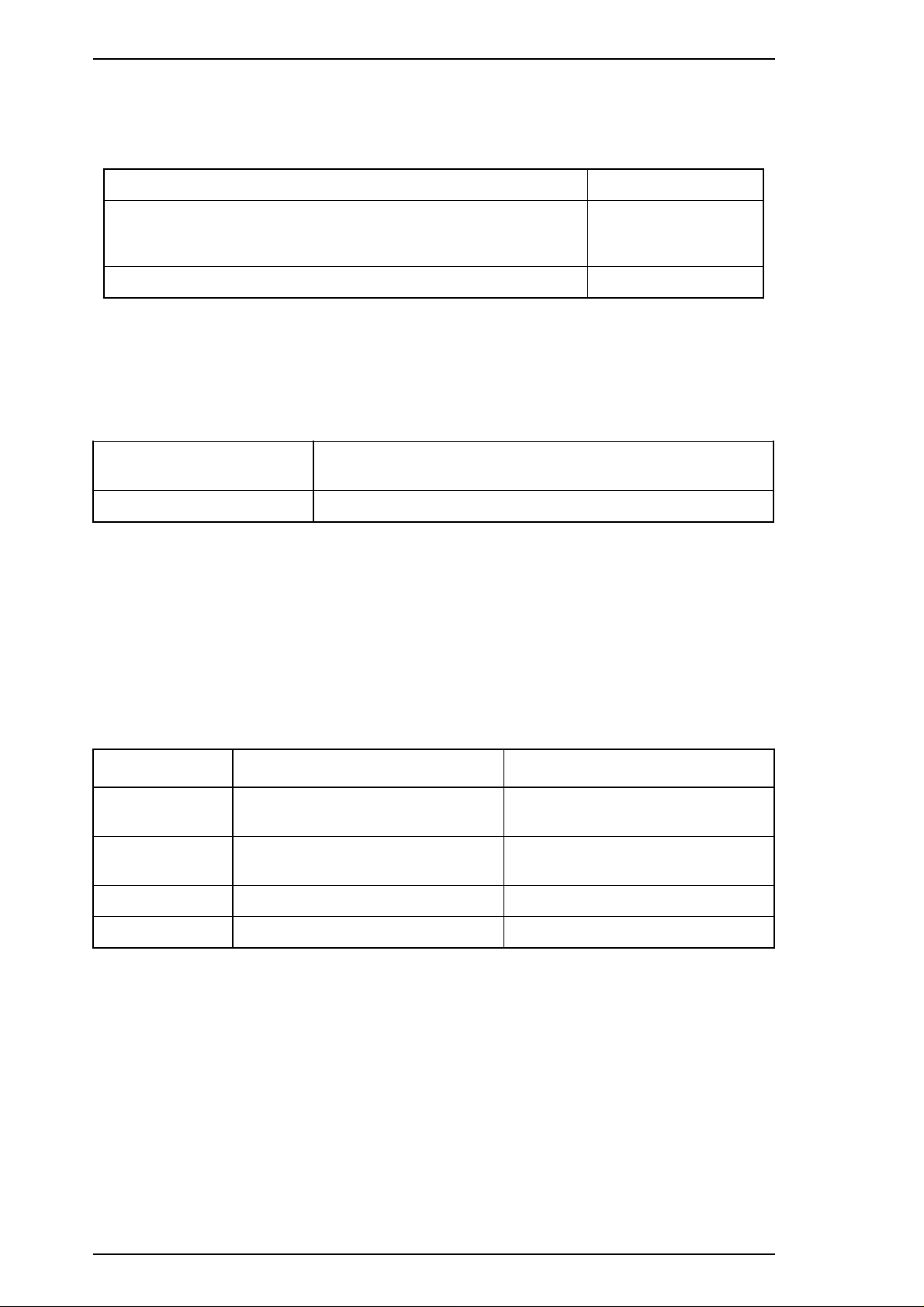
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.2.10 CE Marking
The following table lists CE marking information.
Table 1-25 CE Marking
Low Voltage Directive 73/23 / EEC EN60950
EMC Directive 89/336 / EEC EN55022 class B
EN50082-1 , IEC801-2
IEC801-3 , IEC801-4
Non-Automatic Weighing Instruments Directive 90/384/EEC EN45501
1.2.11 Physical Specifications
Table 1-26 provides printer dimensions and weight.
Table 1-26 Physical Specifications
Dimensions 639 mm (W) × 410 mm (D) × 257 mm (H)
25.16" (W) x 16.14" (D) x 10.12" (H)
Weight Approx. 13 kg (28.66 lb)
1.2.12 Cut Sheet Feeder Specifications
This printer has two CSF options: a high-capacity CSF and a 2nd bin CSF. The high-capacity CSF has
special a paper-feed motor to load the paper quickly. The 2nd bin CSF can be connected to the high-capacity
CSF to allow them to be used as a double bin CSF. The following table provides the specifications for these
CSF options.
Hopper capacity
Table 1-27 Hopper Capacity
CSF Bin 1 CSF Bin 2
Single sheets 150 sheets (❇ 1) / 110 sheets (❇ 2)
185 sheets (❇ 3) / 135 sheets (❇ 4)
Envelopes 25 sheets (❇ 5)
30 sheets (❇ 6)
Card stock 50 sheets (❇ 7) —Multipart paper 40 sheets (❇ 8) —-
2
❇ 1 : Plain paper (weight: 82 g/m
❇ 2 : Plain paper (weight: 82 g/m
❇ 3 : Plain paper (weight: 64 g/m
❇ 4 : Plain paper (weight: 64 g/m
❇ 5 : Envelopes (weight: 91 g/m
❇ 6 : Envelopes (weight: 45 g/m
❇ 7 : Card stock (weight: 192 g/m
, 22 lb) or recycled paper, except for A3-size paper.
2
, 22 lb) or recycled paper, A3 paper.
2
, 17 lb) , except for A3 paper.
2
, 17 lb), A3 paper.
2
, 24 lb)
2
, 12 lb)
2
, 51 lb; thickness: 0.22 mm, 0.0087")
❇ 8 : 1 original + 5 copies (thickness: 0.36 mm, 0.0142")
50 sheets (❇ 1) / 50 sheets (❇ 2)
60 sheets (❇ 3) / 60 sheets (❇ 4)
—-
1-18 Rev.A
Page 28
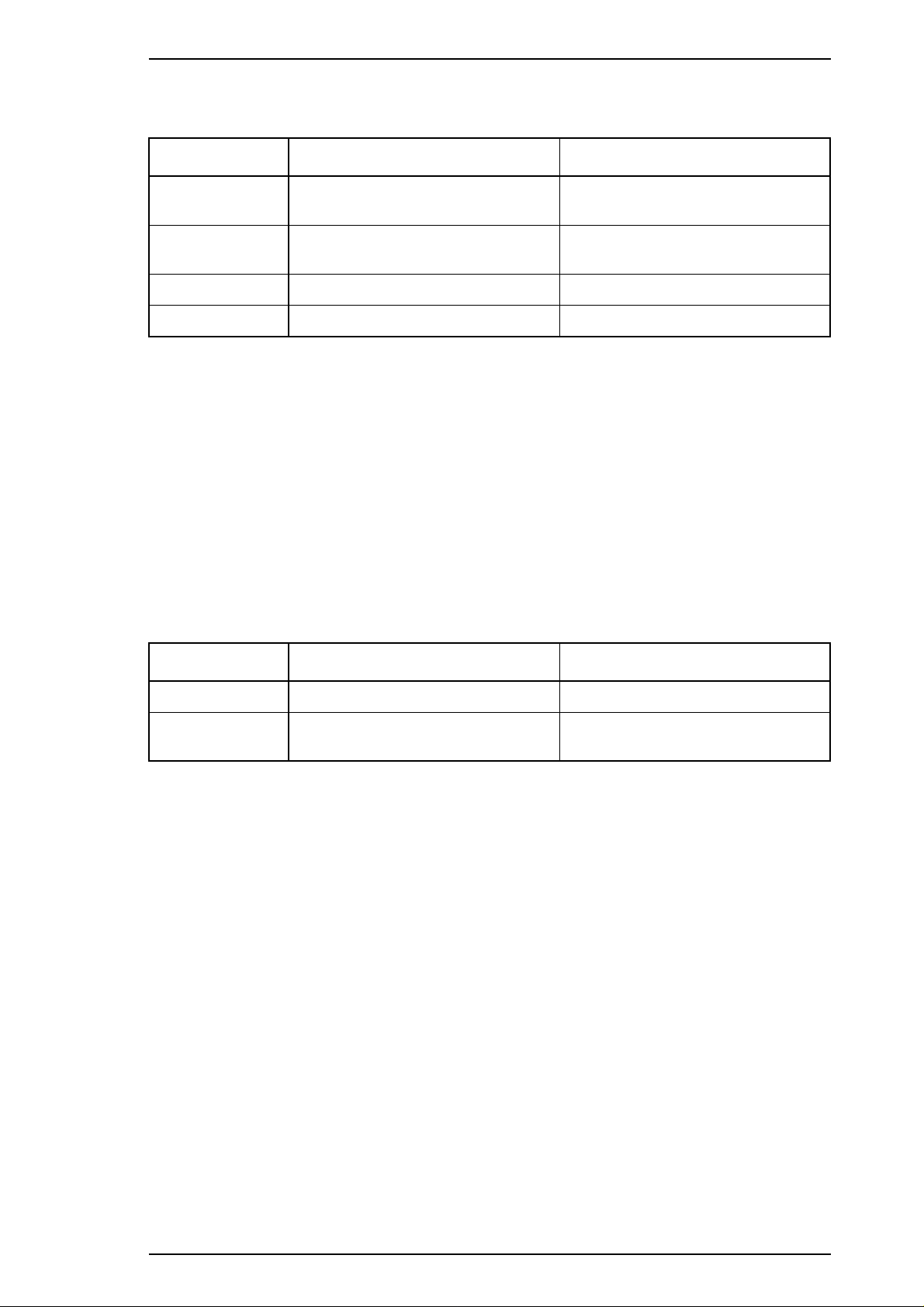
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
Stacker capacity
Table 1-28 Capacity of the Stacker
CSF Bin 1 CSF Bin 2
Single sheets 140 sheets (❇ 1)
100 sheets (❇ 2)
Envelopes 15 sheets (❇ 3)
28 sheets (❇ 4)
——-
——-
Card stock 30 sheets (❇ 5) ——Multipart 36 sheets (❇ 6) ——-
❇ 1: Single sheets (weight: 82 g/m
❇ 2: Single sheets (weight: 82 g/m
❇ 3: Envelopes (weight: 91 g/m
❇ 4: Envelopes (weight: 45 g/m
❇ 5: Card stock (weight : 192 g/m
2
, 22 lb), except for A3 paper
2
, 22 lb), A3 paper
2
, 24 lb)
2
, 12 lb)
2
, 51 lb; thickness: 0.22 mm, 0.0087")
❇ 6: 1 original + 5 copies (thickness: 0.36 mm, 0.0142")
Reliability
MCBF: 2 × 10
5
cycles
Environmental conditions
Table 1-29 Environmental Conditions
Operating Non Operating
Temperature 5 to 35° C (41 to 95° F) –30 to 60° C (–22 to 140° F)
Humidity 15 to 80% RH (❇ 1, ❇ 3)
30 to 605 RH (❇ 2, ❇ 4)
2
❇ 1: Single sheets (plain, 64 g/m
❇ 2: Single sheets (plain, weight<64 g/m2
< weight < 82 g/m2;/17 lb < weight < 22 lb)
, 82 g/m2< weight/weight < 17 lb, 22 lb < weight)
5 to 85% RH (❇ 3)
Single sheets (recycled), multipart, envelopes, and card stock
❇ 3: Without condensation
Rev.A 1-19
Page 29
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.3 Firmware Specifications
This section provides detailed information about LQ-2170 firmware.
1.3.1 Control Codes and Fonts
Control codes ESC/P2 and IBM 2390/2391 plus emulations.
Typefaces Bitmap fonts
EPSON Draft 10 cpi, 12 cpi, 15 cpi
EPSON Roman 10 cpi, 12 cpi, 15 cpi, proportional
EPSON Sans Serif 10 cpi, 12 cpi, 15 cpi, proportional
EPSON Courier 10 cpi, 12 cpi, 15 cpi,
EPSON Prestige 10 cpi, 12 cpi
EPSON Script 10 cpi
EPSON OCR-B 10 cpi
EPSON Orator 10 cpi
EPSON Orator-S 10 cpi
EPSON Script C Proportional
Scalable font
EPSON Roman 10.5pt., 8pt.~32pt. (every 2 pt.)
EPSON Sans Serif 10.5pt., 8pt.~32pt. (every 2pt.)
EPSON Roman T 10.5pt., 8pt.~32pt. (every 2pt.)
EPSON Sans Serif H 10.5pt., 8pt.~32pt. (every 2pt.)
Bar code fonts
EAN-13, EAN-8, Interleaved 2 of 5, UPC-A, UPC-E, Code 39
Code 128, POSTNET
International character sets 13 countries
U.S.A., France, Germany, U.K., Denmark 1, Sweden, Italy,
Spain 1, Japan, Norway, Denmark2, Spain2, Latin America
Character tables The standard version has 11 character tables and the NLSP version has 20
character tables, as shown in the following table.
Table 1-30 Character Tables
Version Character Tables
Italic PC-437 (U.S., Standard Eur.) PC-850 (Multilingual)
Standard Version
PC-860 (Portuguese) PC-861 (Icelandic)
PC-865 (Nordic) Abicomp BRASCII
Roman 8 ISO Latin 1
Italic PC- 437 (US, Standard Eur.) PC-850 (Multilingual)
PC- 863 (Canadian-French)
PC-437 Greek PC-852 (East Europe) PC-853 (Turkish)
PC-855 (Cyrillic) PC-857 (Turkish) PC-866 (Russian)
NLSP Version
1-20 Rev.A
PC-869 (Greek) MAZOWAI (Poland) Code MJK (CSFR)
ISO 8859-7 (Latin/Greek) ISO Latin 1T (Turkish) Bulgaria (Bulgarian)
Estonia (Estonia) PC-744(LST 1283:1993) ISO Latin 2
PC-866 LAT (Latvia) PC-864 (Arabic)
Page 30
LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.3.2 Interface Specifications
This printer provides a bidirectional 8-bit parallel interface and a Type B optional interface slot, standard.
1.3.2.1 Parallel Interface (Forward Channel)
Transmission mode 8-bit parallel, IEEE-P1284, compatibility mode
Adaptable connector 57-30360 (Amphenol) or equivalent
Synchronization
Handshaking BUSY and
Signal level TTL compatible (IEEE-P1284 level 1 device)
STROBE pulse
ACKNLG signals
Table 1-31 Pin Assignments for Forward Channel
Pin
No.
1
2 DATA1 20 In Parallel input data to the printer bit 0: LSB
3 DATA2 21 In bit 1
4 DATA3 22 In bit 2
5 DATA4 23 In bit 3
6 DATA5 24 In bit 4
7 DATA6 25 In bit 5
8 DATA7 26 In bit 6
9 DATA8 27 In bit 7: MSB
10
11 BUSY 29 Out
12 PE 28 Out
Signal
Name
STROBE 19 In
ACKNLG
Return
GND pin
28 Out
In /Out Function Description
Strobe pulse. Input data is latched at falling edge of the signal
This signal (negative pulse) indicates the printer has received
data and is ready to accept more data.
This signal’s HIGH level means the printer is not ready to
accept data.
This signal’s HIGH level means the printer has a paper-out
error.
13 SLCT 28 Out Always HIGH when the printer is powered on.
14
31
32
36
18 Logic H —— Out This line is pulled up to + 5 V through 3.3KΩ resistor.
35 +5V —— Out This line is pulled up to +5 V through 3.3KΩ resistor.
17 Chassis —— —— Chassis GND.
16, 33,
19-30
15, 34 NC —— —— Not connected.
Rev.A 1-21
AFXT 30 In
INIT 30 In
ERROR 29 Out
SLIN 30 In
GND —— ——
Not used.
This signal’s negative pulse initializes printer.
This signal’s LOW level means the printer is in an error state.
Not used.
Signal GND.
Page 31

Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
DATA
STROBE
BUSY
ACKNLG
tsetup
t
ready
data byte n
t
hold
t
stb
t
busy
t
reply t
ack
data byte n+1
t
next
t
nbusy
Figure 1-8 Data Transmission Timing
Table 1-32 Maximum and Minimum Timings for Data Transmission
Parameter Minimum Maximum
setup 500 nsec ——-
thold 500 nsec ——-
t stb 500 nsec ——-
tready 0 ——-
tbusy —— 500 nsec
treply —— ——-
tack 500 nsec
tnbusy 0 ——-
tnext 0 ——-
ttout —— 120 nsec
ttin —— 200 nsec
❒ The BUSY signal is active (HIGH level) under the conditions below:
❒ During data receipt.
❒ If the input buffer is full.
❒ If the
INIT signal is active (LOW level).
❒ During hardware initialization.
❒ In self-test mode.
❒ In adjustment mode.
❒ In default-setting mode.
10 µs
ERROR signal is active (LOW level) under the conditions below:
❒ The
❒ If there is a fatal error.
❒ If there is a paper-out error.
❒ If the cover is open (cover open error).
PE signal is active (HIGH level) under the conditions below:
❒ If there is a paper-out error.
1-22 Rev.A
Page 32

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.3.2.2 Parallel Interface (Reverse Channel)
Transmission mode IEEE-P1284 nibble mode
Adaptable connector 57-30360 (Amphenol) or equivalent
Synchronization Refer to the IEEE-P1284 Specification
Handshaking Refer to the IEEE-P1284 Specification
Signal level TTL-compatible (IEEE-P1284 level 1 device)
Data transmission timing Refer to the specification
Table 1-33 Pin Assignments for Reverse Channel
Pin
No,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Signal
Name
HostClk 19 In Host clock signal.
DATA1 20 In Parallel input data to the printer bit 0: LSB
DATA2 21 In bit 1
DATA3 22 In bit 2
DATA4 23 In bit 3
DATA5 24 In bit 4
DATA6 25 In bit 5
DATA7 26 In bit 6
DATA8 27 In bit 7: MSB
PtrClk 28 Out Printer clock signal.
PtrBusy /
DataBit-3, 7
AckDataReq/
DataBit-2, 6
Return GND
Pin
29 Out
28 Out
In /Out Function Description
Printer busy signal and reverse channel transfer of data
bits 3 or 7
Acknowledge data request signal and reverse channel
transfer of data bits 2 or 6
13
14
31
32
36
18
35
17
16, 33,
19-30
15, 34
Xflag /
DataBit-1, 5
HostBusy 30 In Host busy signal.
INIT
DataAvail /
DataBit-0, 4
1284-Active 30 In 1284 active signal.
Logic H —— Out
+5 V —— Out
Chassis —— —— Chassis GND.
GND —— —— Signal GND.
NC —— —— Not connected.
28 Out
30 In Not used.
29 Out
X-flag signal and reverse channel transfer of data bits 1
or 5
Data available signal and reverse channel transfer of
data bits 0 or 4
This line is pulled up to + 5 V through 3.3K Ω resistor.
This line is pulled up to +5 V through 3.3K Ω resistor.
Rev.A 1-23
Page 33

Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
• Extensibility request The printer responds to the extensibility request in the affirmative, when
the request is 00 H or 04 H, which means:
00 H Request nibble mode of reverse channel transfer.
04 H Request device ID in nibble mode of reverse channel transfer.
• Device ID Refer to the following descriptions:
ESC/P2 [00 H][32 H] ...... MFG: EPSON, CMD: ESCPL2-00, MDL: LQ-2170, CLS: PRINTER
IBM 2391 Plus [00 H][33 H] ..... . MGF: EPSON, CMD: PRPXL24-01, MDL: LQ-2170, CLS: PRINTER
1.3.2.3 Interface Selection
The printer has 2 interfaces: the parallel interface and Type B optional interface. These interfaces are selected
manually in default setting mode or selected automatically.
Manual selection
One of 2 interfaces can be selected in default setting mode.
Automatic selection
Automatic interface is enabled in default setting mode. In automatic interface mode, the printer is initialized
to the idle state, where it scans which interface is to be activated. The interface that receives data first is
selected. When the host stops data transfer, and the printer is in standby for a number of seconds specified in
default setting mode, the printer returns to the idle state. As long as the host sends data or the printer interface
is busy, the selected interface remains active.
Interface state and interface selection
When the parallel interface is not selected, that interface goes into a busy state. When the Type B serial
interface card is installed and it is not selected, the interface sends an XOFF code and sets the DTR signal to
MARK. When the optional interface is not selected, the printer sends disable commands to the optional
interface. When the printer is initialized or returned to the idle state, the parallel interface goes into the ready
state, the serial interface sends an XON code and sets the DTR signal to SPACE, and the printer sends an
enable command to the optional interface. Remember that interrupt signals, such as the
parallel interface, are not effective unless that interface is selected.
INIT signal on the
1.3.2.4 Prevention Hosts from Data Transfer Time-out
Generally, hosts abandon data transfer to peripherals when the peripheral is in the busy state for dozens of
seconds continuously. To prevent hosts from this kind of time-out, the printer receives data very slowly,
several bytes per minute, even if the printer is in the busy state. This slowdown is started when the rest of the
input buffer becomes several hundreds of bytes. Finally, when the input buffer is full, the printer is in busy
continuously.
1-24 Rev.A
Page 34

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.3.3 Paper Handling Sequence
In this section, paper handling firmware sequences are described in several cases.
• Printer status Printer is on line (not in the pause state).
No PE sensor detects that paper is loaded.
The release lever position is set to continuous paper.
Table 1-34 Paper Handling Sequence 1
Occurrence Result
Print command sent Continuous paper is loaded.
Pause
LF/FF
Load/Eject
Micro Adjust
Micro Adjust
Release lever set to Friction The paper path is changed for cut sheets.
• Printer status The rear PE sensor detects that paper is loaded in the rear paper path.
button pressed Printer enters pause state.
button pressed Continuous paper is loaded.
button pressed Continuous paper is loaded.
↑ button pressed No operation.
↓ button pressed No operation.
The release lever is set to continuous paper.
Table 1-35 Paper Handling Sequence 2
Occurrence Result
Pause
LF/FF
LF/FF
button pressed The printer goes off or on line.
button pressed The printer performs a line feed.
button held down continuously The printer performs a form feed after the line
feed.
Load / Eject
Load /Eject
advanced to skip area
Micro Adjust
Micro Adjust
Release lever set to Friction The beeper sounds.
Front paper end sensor detects that paper is
loaded in the front paper path.
button pressed Paper is ejected to the rear paper park position.
button pressed and paper
↑ button pressed The printer micro feeds paper forward.
↓ button pressed The printer micro feeds paper backward.
Paper is advanced to the next TOF position.
The beeper sounds.
Rev.A 1-25
Page 35

Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
• Printer status The front PE sensor detects that paper is loaded in the front paper path.
The release lever is set to continuous paper
Table 1-36 Paper Handling Sequence 3
Occurrence Result
PAUSE
LF/FF
LF/FF
Load / Eject
Load /Eject
advanced to skip area
Micro Adjust
Micro Adjust
Release lever was set to Friction
Front paper end sensor detects that paper was
loaded in the rear paper path.
• Printer status Printer is on line ( not in the pause state).
button pressed
button pressed
button held down continuously
button pressed
button pressed and the paper was
↑ button pressed
↓ button pressed
No PE sensor detects that paper is loaded. ( The printer is set to CSF .)
The release lever is set to the Friction.
Printer goes off or on line.
Printer performs a line feed.
The printer performs a form feed after the line
.
feed
Paper is ejected to the front paper park position
Paper is advanced to the next TOF position.
The printer micro feeds paper forward.
The printer micro feeds paper backward.
The beeper sounds.
The beeper sounds.
Table 1-37 Paper Handling Sequence 4
Occurrence Result
Print command sent
Pause
LF/FF
Load / Eject
Micro Adjust
Micro Adjust
Release lever set to tractor position
Rear/ Front paper end sensor detects that
paper is loaded in the rear or front paper path.
And, 3 seconds have passed.
Rear/ Front paper end sensor detects that
paper is loaded in the rear or front paper path.
And,
was pressed.
button pressed
button pressed
button pressed
↑ button pressed
↓ button pressed
Pause
, LF/FF, or
LOAD/EJECT
button
The paper is loaded from the CSF.
Printer goes off line.
Paper is loaded from the CSF.
Paper is loaded from the CSF.
No operation.
No operation.
The paper path is changed to tractor.
The printer feeds paper.
Ignored.
1-26 Rev.A
Page 36

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
• Printer status The rear PE sensor detects that paper is loaded in the rear paper path.
Release lever position is set to Friction.
Table 1-38 Paper Handling Sequence 5
Occurrence Result
Pause
LF/FF
button pressed
button pressed
Printer goes on or off line.
Printer performs a line feed.
Printer ejects paper forward after the line feed
LF/FF
button held down continuously
(except with roll paper).
The printer performs a form feed after the line
feed (roll paper).
LF / FF
over the logical paper length.
Load /Eject
Micro Adjust
Micro Adjust
Release lever set to the tractor position
Front paper end sensor detects that paper was
button pressed, and paper is advanced
button pressed
↑ button pressed
↓ button pressed
Paper is ejected forward (except with roll paper).
The printer performs a form feed (roll paper).
Paper is ejected forward (except with roll paper).
The printer performs a form feed (roll paper).
The printer micro feeds paper forward.
The printer micro feeds paper backward.
The beeper sounds.
The beeper sounds.
loaded in the rear paper path.
• Printer status Front PE sensor detects that paper is loaded in the rear paper path
The release lever position is set to Friction.
Table 1-39 Paper Handling Sequence 6
Trigger Result
Pause
LF/FF
LF/FF
LF / FF
more than the logical paper length.
Load /Eject
Micro Adjust
Micro Adjust
Release lever set to tractor position
Front paper end sensor detects that paper was
loaded on the rear paper path.
button pressed
button pressed
button held down continuously
button pressed, and paper advanced
button pressed
↑ button pressed
↓ button pressed
Printer goes on or off line.
Printer performs a line feed.
Paper is ejected forward after the line feed.
The paper is ejected forward.
The paper is ejected forward.
The printer micro feeds paper forward.
The printer micro feeds paper backward.
The beeper sounds.
The beeper sounds.
Rev.A 1-27
Page 37

Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.3.4. Paper Width (PW) Sensor Operation
The PW sensor is mounted on the ribbon mask holder to measure the paper width and detect the top
edge of the paper. However, in cases where print data is over the paper width, the image cut function
does not operate in all modes. This section describes when the image cut function is operational, as
shown in the following table.
Table 1-40 PW Sensor Operation
Paper Path
Friction Measured Executed (Only Copy Mode 2)
Push Tractor (Rear / Front) Measured Not Executed ❇ 1
Pull Tractor Measured Not Executed ❇ 1
❇ 1: The measured paper width value is used to estimate the printhead centering position.
When narrow continuous paper (fewer than 30 columns) is loaded, the printer changes the
centering position to the proper position, based on the measured paper width.
Paper Width Measurement Image Cut Function
1-28 Rev.A
Page 38

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.4 Operating Instructions
This section provides detailed information about the LQ-2170 control panel buttons and LEDs.
1.4.1 Control Panel Operations
The printer control panel contains 6 non-lock type push buttons and 10 LEDs for various printer functions.
The exterior view of the control panel is shown in the following figure.
Font
Draft
Roman
Sans S
erif
PitchFont
Pitch
10 cpi
12 cpi
15 cpi
17 cpi
20 cpi
PS
Tear Off / Bin
Tear Off / Bin
Tear Off
Bin 1
Bin 2
Card
Micro Adjust
LF/ FF Load / Eject
LED Off
LED On
LED Blinks
Figure 1-9 Control Panel
Operation in normal mode
In normal mode, pressing panel buttons executes following functions:
Table 1-41 Operation in Normal Mode
Pause
Paper Out
Operate
3 sec
Buttons and
Switches
Operation
Pause
Load / Eject
LF / FF
Tear Off / Bin
Font
Pitch
Function
Turns the printer on and off.
Alternates printing and non-printing states.
Enables the micro adjust function, when held down for 3 seconds.
Loads or ejects paper
Micro feeds forward, when that function is enabled.
Line feed, when pressed briefly.
Form feeds, when held down for a few seconds.
Micro feeds backward, when that function is enabled.
Advances continuous paper to the tear-off position.
Selects CSF bin 1 / 2 or card mode.
Selects font.
Selects pitch.
Rev.A 1-29
Page 39

Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
Operations at power on
Turning the printer on while pressing panel buttons executes the functions below:
Table 1-42 Operation at Power On
Button Function
Load / Eject
LF / FF
Load / Eject
Font
and
Operation in default setting mode
The buttons used in default setting mode are as follows:
and
LF/FF
Pitch
Tear Off / Bin
Pause
Others Not available
LQ self-test
Draft self-test
Hexadecimal data dump
Default setting
Clear EEPROM
Bi-d adjustment
Table 1-43 Operation at Default Setting Mode
Button Function
Pitch
Tear Off / Bin
Others Not available
Selects the menu.
Changes the setting
1.4.2 Status Codes Indicated by the LEDs and Beeper
Table 1-44 Indicators and Beeper
Tear Off /
Bin
Pitch Font Beeper
Pause
Paper Out
Paper Jam
Head Hot
Cover Open
Micro Adjust
Tear Off
Bin Selection
Pitch Selection
Font Selection
Fatal Error
Pause Paper Out
On —- —- —- —- —On On —- —- —- ❍❍❍
On Blinks —- —- —- ●●●●●
Blinks —- —- —- —- —On —- —- —- —- ❍❍❍
Blinks —- —- —- —- ❍
—- —- —- —- —- ❍
—- —- —- —- —- ❍
—- —- —- —- —- ❍
—- —- —- —- —- ❍
Blinks Blinks Blinks Blinks Blinks ●●●●●
❍indicates the beeper sounds for 100 ms with an interval of 100 ms.
● indicates the beeper sounds for 500 ms with an interval of 100 ms.
— indicates that the LED or beeper is not used to indicate this status condition.
1-30 Rev.A
Page 40

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.4.3 Micro Adjust Function
The micro adjust function lets you set the TOF and tear off positions. After the printer is put in this
1
⁄
mode, you can adjust the top of form (TOF) position up or down in increments of
pressing the
printer is turned off, the setting is not cleared. The function is operational in the printer under the
following conditions and within the following area:
Conditions required for the adjustment
The TOF position can be adjusted under the following conditions:
1. The data buffer is empty and the printer is on line.
2. Paper is at the TOF position.
3. The
Adjustable area
Micro adjust positions can be set within the following range from the top edge of the page:
LF/FForLoad/Eject
Pause
button is held down more than 3 seconds to put the printer in micro adjust mode.
button. The adjusted TOF position is saved to the EEPROM. If the
3 mm~ 8.5 mm , 8.5 mm ~ 2 87.9 mm
(0.12" ~ 0.33", 0.33" ~ 11.34" )
216
inch by
1.4.4 Tear Off Function
The tear off function advances continuous paper to the tear off position when the
pressed. There are two modes for this function: auto tear off and manual tear off. The tear off mode can be
selected in the default setting mode. After the paper is torn off at the perforation, it is fed back to the TOF
position when any new print data is sent to the printer. The tear off position is saved in the EEPROM, and if
the printer is turned off, the setting is not cleared.
Conditions required for the adjustment
❇ Auto tear off function
❒ Auto tear off has been set to ON in default setting mode.
❒ The release lever has been set to Tractor.
❒ The data buffer is empty, and the printer is on line.
❒ More than 3 seconds have passed after the host computer finished transferring print data.
❇ Manual tear off function
❒ Auto tear off has been set to OFF in default setting mode.
❒ The release lever has been set to Tractor.
❒ The data buffer is empty and the printer is on line, or the printer is off line.
❒ The
Paper handling with the tear off position
❒ Pressing the
❒ Pressing the
Tear Off
position for the next page and brings the printer back on line.
position for the next page and takes the printer off line.
button was pressed under all the conditions listed above.
Pause
Pause
button with the printer off line feeds the paper back to the TOF
button with the printer on line feeds the paper back to the TOF
Tear Off / Bin
button is
❒ Pressing the
page and executes a line feed.
❒ Pressing the
page and ejects paper backward.
❒ Pressing the
where you can adjust the tear off position by pressing the
❒ If the printer is turned off while in the tear off mode, the tear off position is saved, and
paper is fed back to the TOF position for the next page by turning on the printer, again.
Rev.A 1-31
LF /FF
Load /Eject
Pause
button feeds the paper back to the TOF position for the next
button more than 3 seconds puts the printer in micro adjust mode,
button feeds the paper back to the TOF position for the next
LF /FForLoad/Eject
button.
Page 41

Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.4.5 Self-test Function
Pressing the
the
LF/FF
temporarily by pressing the
When pages are printed from the CSF, the first sheet is used for scaling the sheet length. Then, the maximum
number of printable lines is printed as the bottom line of the sheet and this number is saved in non-volatile
memory as the default page length. Page lengths are saved individually when a dual-bin CSF is in use.
The self-test prints out the following:
❒ The maximum number of printable lines (only on cut sheets from the CSF)
❒ The pattern of characters shown in the figure below.
Load / Eject
button while turning on the printer puts the printer in Draft self-test mode. You can stop the self-test
button while turning on the printer puts the printer in LQ self-test mode. Pressing
Pause
button, and you can exit the self-test mode by turning off the printer.
Figure 1-10 Self-test Printout
1.4.6. Hexadecimal Dump Function
Pressing the
dump mode. In this mode, data received is printed out in hexadecimal format, along with the corresponding
ASCII characters. The function is useful to check data received from the host. If a received code is not a
printable ASCII character, the printer prints a period (.) in the ASCII column. When received data remains in
the buffer, that data is printed by pressing the
Load /Eject
and
LF/FF
buttons while turning on the printer puts the printer in hexadecimal
Pause
button.
Figure 1-11 Hexadecimal Printout
1-32 Rev.A
Page 42

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.4.7 Default Setting Function
Pressing the
printer settings can be changed in this operation. The method for setting defaults is described in the
instruction sheets, which are printed out immediately after you enter the mode. You are asked to use three
buttons (
Pause
method used to set defaults.
Pitch
button while turning on the printer puts the printer in default setting mode. Some default
Font,Pitch
: 1 LED) on the control panel. Refer the instructions printed in default setting mode for the actual
, and
Tear Off / Bin
) and watch six LEDs (
Pitch
: 3 LEDs,
Tear Off/Bin
: 2 LEDs, and
1.4.8 EEPROM Clear Function
Pressing the
standard factory settings. This operation initializes the items below to the factory settings in the right-hand
column.
Font
and
Tear Off /Bin
buttons while turning on the printer resets the EEPROM to the
Table 1-45 EEPROM Initialization Settings
Setting Factory Default
Font Roman
Pitch 10 CPI
Character Table PC437
Other Font Selection Roman-T
Page Format
( Tractor Rear / Front )
Page Length: 11 inches
TOF Position: 8.5 mm (0.333 inches)
Bottom Margin : 11 inches
Page Format
(Friction , CSF Bin 1 / Bin 2 ,
Manual Feed Rear / Front )
Print Direction Bi-d
Auto LF Off
Auto Tear-Off Off
1-inch Skip Off
High Speed Draft On
Input Buffer On
BDC-ST Reply On
Roll Paper Off
I/F Selection Auto I/F Mode
Auto I/F Wait Time 10 sec.
Software ESC/P2
Slashed Zero Off
Buzzer On
Page Length: 22 inch
TOF Position: 8.5 mm (0.333 inch)
Bottom Margin: 22 inches
A.G.M (IBM Mode) Off
Auto CR ( IBM Mode ) Off
Adjust Tear-Off Position 0 inch
Paper Conditions Friction: Bin 1 , Tractor: Tear-Off: Status Off
Rev.A 1-33
Page 43

Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.4.9 Bidirectional Adjustment Function
Pressing the
this mode, you can adjust the bidirectional alignment for the following three modes:
1. High-speed draft mode
2. Draft mode
3. LQ mode
For instructions on performing the adjustment, see Chapter 4.
Pause
button while turning on the printer puts the printer in bidirectional adjustment mode. In
1.5 Initialization
1.5.1 Software Initialization
This initialization is activated by the control code
❒ Clears unprinted data.
❒ Resets the printer’s setting defaults.
1.5.2 Operation Initialization
This initialization is activated by receipt of the INIT signal (negative pulse). This initialization:
❒ Clears the buffer of all data.
❒ Cancels download character definition.
ESC@
. This initialization:
❒ Puts the printer in standby state, if no errors occur.
❒ Executes software initialization.
1.5.3 Power On Initialization
This initialization is activated by power on or by a cold-reset command (remote
initialization
❒ Initializes the printer mechanism.
❒ Executes operation initialization.
RS
command). This
1-34 Rev.A
Page 44

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.6 MAIN COMPONENTS
The main components of the LQ-2170 are designed for easy removal and repair. The
main components are:
❒ C165 MAIN Board Assembly
❒ C165 PSB/PSE Board Assembly (120 V/230 V)
❒ C165 PNL Board Assembly
❒ Printer Mechanism
❒ Housing Assembly
The following figure shows the main components of the LQ-2170.
Figure 1-12 Main Components
Rev.A 1-35
Page 45

PC1
Photo Coupler
F1
Fuse
IC51
Switching Regulator
TL494CN
Transformaer
T1
Q1
Switching FET
DB1
Diode Bridge
IC52
OP-amp
D51
Diode
Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.6.1 C165 MAIN Board Assembly
The C165 MAIN board consists of a TMP96C141AF CPU, an E05B13 gate array, a program/CG ROM, a
PS-RAM, an EEPROM, etc.
IC11 PF Motor Driver
UDN2917EB
IC3 P-ROM
IC 5 PS RAM
IC 2
GATE ARRAY
E05B13
IC12
CR Motor Driver
SLA7024M
Head Drive
TRANSISTOR
IC 1
CPU
TMP96C041AF
EEPROM
CN2 for Option I / F
Figure 1-13 C165 MAIN Board Assembly
1.6.2 C165 PSB/PSE Board Assembly
These boards have two AC input voltage ratings: 120 VAC (C165 PSB) and 230 VAC (C165 PSE). Both
boards consist of a transformer, switching FET, regulator IC, diode bridge, etc. The power supply board
provides +5 VDC and +35 VDC for the main board and printer mechanism.
Figure 1-14 C165 PSB/PSE Board Assembly
1-36 Rev.A
Page 46

LQ-2170 Service Manual Product Description
1.6.3 C165 PNL Board Assembly
This board function is the control panel for the LQ-2170. It consists of a power switch, six buttons, and 10
indicator LEDs. This board is almost same as it for the LQ-2170.
SW
LED LED LED
LED
LED
SW
SW
SW
SW SW
Power SW
Figure 1-15 Board Assembly C165 PNL
1.6.4 Printer Mechanism
The printer mechanism consists of an 24-pin impact dot head, paper feed (PF) motor, ribbon feed (RF) motor,
paper end (PE) sensor, home position (HP) sensor, platen gap (PG) sensor, release lever sensor, etc.
Figure 1-16 Printer Mechanism
Rev.A 1-37
Page 47

Product Description LQ-2170 Service Manual
1.6.5. Housing Assembly
This consists of printer cover assembly, edge guide assembly, upper housing, lower housing assembly, etc.
Figure 1-17 Housing Assembly
1-38 Rev.A
Page 48

CHAPTER 2 Operating Principles
Table of Contents
2.1 PRINTER MECHANISM OPERATION 2-1
2.1.1 Printing Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.1.2 Carriage Movement Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2.1.3. Platen Gap Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.1.4 Paper Handling Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.1.4.1 Release Lever. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.1.4.2 Paper Advance Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.1.5 Paper Paths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
2.1.6 Ribbon Advance Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
2.2 POWER SUPPLY OPERATION 2-17
2.2.1 Power Supply Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
2.2.2 Power Supply Circuit Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
2.3 CONTROL CIRCUIT 2-22
2.3.1 Control Circuit Operation Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
2.3.2 System Reset Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
2.3.3 Printhead Drive Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
2.3.4 CR Motor Drive Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
2.3.5 PF Motor Drive Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
2.3.6 EEPROM Control Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
2.3.7 Sensor Circuits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
Page 49

List of Figures
Figure 2-1. Printhead Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Figure 2-2. Carriage Movement Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Figure 2-3. Platen Gap Adjust Lever. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Figure 2-4. Release Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Figure 2-5. Friction Advance Operation Using the Top Entrance. . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Figure 2-6. Push Tractor Operation Using the Rear Paper Entrance . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Figure 2-7. Push Tractor Operation Using the Front Paper Entrance. . . . . . . . . 2-7
Figure 2-8. Pull Tractor Operation Using the Bottom Paper Entrance . . . . . . . . 2-8
Figure 2-9. Push- Pull Tractor Operation Using the Rear Paper Entrance. . . . . 2-9
Figure 2-10. Push- Pull Tractor Operation Using the Front Paper Entrance . . 2-10
Figure 2-11. Paper Path and Detector PE Sensor Location. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Figure 2-12. Friction Feeding Using the Top Entrance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Figure 2-13. Push Tractor Feeding Using the Rear Entrance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Figure 2-14. Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Rear Entrance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Figure 2-15. Push-Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Rear Entrance . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Figure 2-16. Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Bottom Entrance. . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Figure 2-17. Friction Feeding Using the Front Entrance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Figure 2-18. Push Tractor Feeding Using the Front Entrance . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Figure 2-19. Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Front Entrance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Figure 2-20. Push-Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Front Entrance. . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Figure 2-21. Ribbon Advance Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Figure 2-22. Power Supply Circuit Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Figure 2-23 Power Switch Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Figure 2-24. Over Voltage Protection Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Figure 2-25. +35V Line Constant Voltage Control Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
Figure 2-26. +35V Line Overload Detector Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
Figure 2-27. +35V Line Over Current Protection Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
Figure 2-28. +5V Line Over Current Protection Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
Figure 2-29. +5V Constant Voltage Control Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
Figure 2-30. Control Circuit Block Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
Figure 2-31. Data Flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
Figure 2-32. Reset Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
Figure 2-33. Reset Signal Output Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
Figure 2-34. Printhead Drive Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
Figure 2-35. CR Drive Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Figure 2-36. PF Motor Drive Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Figure 2-37. EEPROM Control Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Figure 2-38. Sensor Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
List of Tables
Table 2-1. CR Motor Assembly Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Table 2-2. Platen Gap and Print Speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Table 2-3. Release Lever Position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Table 2-4. Ribbon Advance Gear Linkage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Table 2-5. Power Supply Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Table 2-6. Power Supply Output Voltage and Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Table 2-7. Functions of the Main IC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
Table 2-8. CR Motor Drive Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Page 50

Platen
Ribbon Mask
Ribbon
Dot Wire
Wire Resetting Spring
Stopper
Actuat ing
Plate
Paper
Iron Core
Head Driving Coil
Actuating Spring
LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
2.1 PRINTER MECHANISM OPERATION
This section describes the printer mechanism and explains how it works.
2.1.1 Printing Mechanism
The printing mechanism is composed of the printhead, ink ribbon, and ribbon mask. The printhead is an
24-pin (12 pins × 2) head for impact dot printing. To improve the durability of the dot wires, they are
arranged on the printhead in 2 columns.
Each wire has its own drive coil, which causes the wire to move in and out of the printhead to print each dot.
The four steps below describe how these driving wires work.
1. A drive signal, transmitted from the control circuit to the printhead drive circuit, is converted to the
proper printhead driving voltage, which energizes a corresponding coil. The energized coil then causes
the iron core to become magnetized.
2. The magnetic force draws the actuating plate toward the core, and the dot wire, which is connected to
the core, rushes toward the platen.
3. When the dot wire impacts the platen, pressing against the ribbon and paper, it prints a dot.
4. When the driving voltage stops energizing the coil, the magnetic force from the iron core vanishes. The
actuating plate returns to its original position (the position before coil was energized) with spring action.
The dot wire also returns to its original position.
This is the sequence used to print a single dot.
The mechanism is equipped with a built-in thermistor for head temperature detection. The temperature
detected by the thermistor is converted to an electric signal and fed back to the control circuit.
The printhead is also used as a beeper. Head driving coils move all the dot wires back and forth at a
frequency of 1.98 KHz for 65 ± 5 µsec without impacting the platen, so that the wires vibrate.
The vibrating dot wires create the sound used for beep codes.
Rev.A 2-1
Figure 2-1 Printhead Operation Principles
Page 51

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2.1.2 Carriage Movement Mechanism
The carriage movement mechanism consists of the carriage assembly, carriage (CR) motor, timing belt,
driven pulley, home position (HP) sensor, etc. The CR motor drives the timing belt. The carriage assembly
is connected to the timing belt, which is moved by the CR motor. Figure 2-2 shows the carriage movement
mechanism.
The printer detects the carriage home position with the HP sensor. This sensor is the basis for determining
the carriage position. The HP sensor informs the CPU when the carriage is at the home position. The sensor
is ON, when the carriage is pushed to the right or left. The striker on the carriage activates the sensor to
indicate the carriage is at the home position, which toggles the sensor to OFF.
Table 2-1. CR Motor Assembly Specifications
Category Requirement
Type 4-phase, 200-pole, HB-type pulse motor
Drive Voltage 35 ± 2.1 VDC
Coil Resistance 2.7 Ω±10%, per phase, at 25° C (77° F)
Inductance 3.7 µH ± 20% (per phase, at 1K Hz 1 V rms)
Figure 2-2 Carriage Movement Mechanism
2-2 Rev.A
Page 52

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
2.1.3 Platen Gap Adjustment
You can adjust the platen gap (the gap between the platen and printhead) to allow the printer to use paper of
different weights or thicknesses. When you move the platen gap adjust lever forward or backward, the
carriage guide shaft rotates. This rotation moves the carriage either toward or away from the platen and
changes the platen gap. This adjustment function has nine ranges for the adjustment, and the adjustment
position is detected by platen gap (PG) switches.
PG Adjustment Lever
PG SW1
Close
PG SW2
Platen Gap Adjustment Slot
Open
Figure 2-3 Platen Gap Adjustment Lever
Moving the platen gap adjust lever beyond position 2 changes the print speed mode to Copy mode, and the
speed slows down to about
between the platen gap and the print speed.
2
⁄3normal to protect the printhead. The following table show you the relationship
Table 2-2. Platen Gap and Print Speed
Paper Type
Paper Thickness
(mm)
Single Sheet 0.065 0 Closed Normal
0.1 0 Closed Normal
0.14 1 Closed Normal
Continuous
0.065 0 Closed Normal
Paper (Single
Sheet)
Continuous
0.09
~0.18 1 Closed Normal
Paper (Multipart)
~0.25 2 Open Copy
~0.32 3 Open Copy
~0.39 5 Open Copy
Labels 0.07 / 0.19 2 Open Copy
Envelopes 0.16 / 0.32 2 Open Copy
0.16 / 0.40 3 Open Copy
Adjust Lever
Position
PG SW Print Speed
0 Closed Normal
0.22 / 0.44 4 Open Copy
0.23 / 0.46 4 Open Copy
0.26 / 0.52 6 Open Copy
Card Stock 0.22 2 Open Copy
Rev.A 2-3
Page 53

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2.1.4. Paper Handling Mechanisms
During the normal operation, paper is fed to the printer, advanced to the specified position, and ejected from
the printer. These paper-handling operations are performed by various paper handling mechanisms, such as
tractors, platens, rollers, and gears. This section describes the printer’s paper handling mechanisms.
2.1.4.1. Release Lever
The release lever is used to select friction for rear /front tractor feed or to release the paper for pull tractor
feed. Changing the release lever position moves the paper guide rollers, and the new lever position is
detected by 2 release switch sensors (RLSW1 and RLSW2). See the following table.
Table 2-3. Release Lever Position
Release Lever
Position
Friction mode The paper guide rollers are
Front push tractor
mode
Rear push tractor
mode
Pull tractor mode The paper guide rollers and the
Status of Paper Guide Rollers RL SW 1 RL SW 2
pressed against the platen
The paper guide rollers are
separated from the platen
The paper guide rollers are
separated from the platen
rollers for the lower paper guide
are separated from each
position.
Open Open
Closed Open
Closed Open
Closed Closed
Figure 2-4 Release Switch
2-4 Rev.A
Page 54

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
2.1.4.2. Paper Advance Mechanism
This section describes how the friction and tractor advance mechanisms work to move the paper through the
printer.
1. Friction Advance Method
Paper is held between the platen and the paper guide rollers and between the paper tension roller and paper
tension unit cover. The paper feed (PF) motor pinion gear, turns in the direction of the black arrow, driving
the paper advance reduction gear. The paper advance reduction gear turns the platen gear and paper tension
roller gear. Paper advances in the direction of the white arrow. Figure 2-5 shows the friction advance method
when paper is fed through the top paper entrance.
In the friction advance method, the paper guide roller spring holds the paper against the platen. Paper can be
released by setting the release lever to the tractor feed position.
Figure 2-5 Friction Advance Operation Using the Top Entrance
Rev.A 2-5
Page 55

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2. Push Tractor Method
The push tractor method is used with the rear or front entrance.
When the push tractor method is used with the rear entrance, the torque generated by the PF motor is
transmitted to the push tractor gear through the PF motor pinion gear, paper advance reduction gear, and
tractor reduction gear. When the PF motor pinion gear turns in the direction of the black arrow, the tractor
gear rotates in the direction of the black arrow, and thus feeds paper into the printer. Paper is advanced by the
platen and paper tension roller, which are also driven by the PF motor through the gear train.
When the push tractor method is used with the front entrance, the torque generated by the PF motor is
transmitted to the push tractor gear through the PF motor pinion gear, paper advance reduction gear, platen
gear, and gear train in the front part of the printer. When the PF motor pinion gear turns in the direction of
the black arrow, the tractor gear rotates in the direction of the black arrow and thus feeds paper into the
printer. Paper is advanced by the paper drive roller and platen, which are also driven by the PF motor through
the gear train.
In the push tractor method, the release lever is set to one of the tractor positions to release the pressure
between the paper guide roller and the platen. Figure 2-6 illustrates push tractor operation when paper is fed
through the rear paper entrance. Figure 2-7 illustrates push tractor operation when the paper is fed through
the front paper entrance.
Figure 2-6 Push Tractor Operation Using the Rear Paper Entrance
2-6 Rev.A
Page 56

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
Figure 2-7. Push Tractor Operation Using the Front Paper Entrance
Rev.A 2-7
Page 57

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
3. Pull Tractor Method
The pull tractor advances paper in basically the same way as the push tractor. The push tractor is installed at
the paper entrance and pushes paper into the printer. On the other hand, the pull tractor is installed at the
paper exit and pulls paper out of the printer mechanism. As a result, the paper tension unit is not required.
Figure 2-8 illustrates pull tractor operation when paper is fed through the bottom paper entrance.
Figure 2-8 Pull Tractor Operation Using the Bottom Paper Entrance
2-8 Rev.A
Page 58

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
4. Push-Pull Tractor Method
The push-pull tractor method is a combination of the push and pull tractor methods. Two tractors are used to
advance the paper: one at the front paper entrance and the other at the rear paper entrance. They operate
simultaneously to push and pull the paper through the printer mechanism. Figure 2-9 illustrates push-pull
tractor operation when paper is fed through the rear paper entrance. Figure 2-10 illustrate push-pull tractor
operation when paper is fed through the front entrance.
Figure. 2-9 Push-Pull Tractor Operation Using the Rear Paper Entrance
Rev.A 2-9
Page 59

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
Figure 2-10 Push-Pull Tractor Operation Using the Front Paper Entrance
2-10 Rev.A
Page 60

Up
Up
LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
2.1.5 Paper Paths
This section describes various paper paths through the printer mechanism. These paper paths are divided into
four groups, depending on which entrance (top, rear, bottom, or front) is used to feed paper. The printer has
two PE (paper end) sensors. The front PE sensor is located in front of the printer mechanism. The rear PE
sensor is located behind the printer mechanism. Refer to the following figure.
1. Top Entrance
Printhead
Paper Drive Roller
Front Paper Guide
Front PE Sensor
Paper Eject Drive Roller
(Paper Eject Assembly)
Platen
Rear Driven PF Roller
Front Driven PF Roller
Lower Driven PF Roller
Platen Cover
Middle
Paper Guide
Rear PE
Sensor
Figure 2-11. Paper Paths and PE Sensor Locations
Figure 2-12 shows the paper path for friction feed using the top entrance. The top entrance is only used with
the friction feed method. When the top entrance is used, the rear PE sensor detects when the paper is out.
Figure. 2-12. Friction Feeding Using the Top Entrance
Rev.A 2-11
Page 61

Down
Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2. Rear Entrance
Figures 2-13, 2-14, and 2-15 show the paper paths for tractor feeding using the rear entrance. You can use the
rear entrance with any of the following paper feed methods: push tractor feed, pull tractor feed, or push-pull
tractor feed. When you use the rear entrance, the rear PE sensor detects when paper is out.
Down
Figure. 2-13. Push Tractor Feeding Using the Rear Entrance
Figure. 2-14. Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Rear Entrance
As shown above in Figure 2-14, when you use the pull tractor in this printer, you must remove the paper eject
cover, which includes the paper tension roller, from the printer mechanism.
2-12 Rev.A
Page 62

Down
LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
Figure 2-15. Push-Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Rear Entrance
As shown above in Figure 2-15, when you use the pull tractor with this printer, you must remove the paper
eject cover, which includes the paper tension roller, from the printer mechanism.
3. Bottom Entrance
Figure 2-16 shows the paper path for tractor feeding using the bottom entrance. The bottom entrance is used
only for pull tractor feed. When the bottom entrance is used, the front PE sensor detects when paper is out.
Figure. 2-16. Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Bottom Entrance
Rev.A 2-13
Page 63

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
4. Front Entrance
Figures 2-17 through 2-20 show the paper paths for the front entrance. The front entrance can be used with
any of the following paper feed methods: friction feed, push tractor feed, pull tractor feed, or push-pull
tractor feed. When the front entrance is used, the front PE sensor detects when paper is out.
Figure 2-17 Friction Feeding Using the Front Entrance
Up
Up
Figure 2-18 Push Tractor Feeding Using the Front Entrance
2-14 Rev.A
Page 64

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
Down
Figure 2-19 Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Front Entrance
Figure 2-20 Push-Pull Tractor Feeding Using the Front Entrance
Rev.A 2-15
Page 65

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2.1.6 Ribbon Advance Mechanism
The ribbon is held between the ribbon advance roller (ribbon driven gear) and the ribbon pressure roller.
When the carriage moves from left to right and vice versa on the CR guide shaft, the timing belt turns the
belt-driven pulley. Then the torque is transmitted to the ribbon driving gear through the gear trains. The
ribbon driving gear rotates counterclockwise, no matter what direction the carriage moves, because a
planetary gear is used in the gear linkage.
Table 2-4. Ribbon Advance Gear Linkage
Direction of Carriage Movement Gear Linkage
Left to right
(indicated by the black arrow)
Right to light
(indicated by the white arrow)
The ribbon brake spring, attached to the exit of the cartridge case, prevents slack in the ribbon and keeps the
ribbon tension at an appropriate level. The ribbon mask prevents the ribbon from brushing against the paper.
Belt driven pulley → Gear (1) → Gear (2) →
Ribbon driving gear
Belt driven pulley → Gear (1) → Gear (3) →
Gear (4) → Ribbon driving gear
Figure 2-21 Ribbon Advance Mechanism
2-16 Rev.A
Page 66

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
2.2 POWER SUPPLY OPERATION
The printer can be powered by either of two power supply boards: the C165 PSB (120 V) or C165 PSE (230
V) power supply. These boards are the same for both the LQ-2170 and FX-2170. Additionally, the PSB and
PSE boards function the same, except for a difference in primary circuitry. The power supply board outputs
the DC current necessary to drive the printer control circuits and drive mechanism. Table 2-5 shows the
input voltages and fuse ratings for these boards.
Table 2-5. Power Supply Board
Board Input Voltage Fuse F1 Rating
C165 PSB 103.5 to 132 VAC 6.3 A / 125 V
C165 PSE 198 to 264 VAC T3.15 AH / 250 V
2.2.1 Power Supply Overview
The power supply board has two power outputs for use by the various control circuits and drive mechanisms.
Table 2-6 lists the applications for the two DC output supply voltages.
Table 2-6 Power Supply Output Voltages and Applications
Output Voltage (DC) Applications
+5 V Main Board Logic Circuit Sensors Control Panel LEDs
+35 V CR Motor PF Motor Printhead Drive
Figure 2-22 shows a block diagram of the power supply circuitry.
Primary Circuit
Full Wave
Rectification
Circuit
Filter Circuit
AC input
Smoothing
Circuit
Switching
Circuit
PhotoCoupler
PhotoCoupler
Secondary Circuit
+5V Switching
Regurator
+5V Constant Voltage
Control Circuit
+5V Over current
Protection Circuit
Smoothing
Circuit
+35V Line
Over Load
Detector Circuit
+35V Line
Constant Voltage
Control Circuit
+35V Line
Over Voltage
Protection Circuit
+5V Line
Over Voltage
Protection Circuit
+35V Line
Over Current
Protection Circuit
+5V DC
+35V DC
CPU
Port 20
Operation
SW
Figure 2- 22 Power Supply Circuit Block Diagram
As shown in the figure above, when AC power enters the printer from an external power source, the filter
circuit removes the noise. The AC voltage then undergoes full-wave rectification and is smoothed to produce
direct voltage. The voltage is fed to the gate port for the switching FET (Q1: K1531 or K1692) through
resistors R18 and R31, and then the switching circuit operates. The secondary smoothing circuit produces a
stepped down +35 VDC voltage. The +5 VDC voltage is generated by feeding the +35 VDC voltage through
the +5 VDC power supply circuit, where the +35 VDC is stepped down to a stable +5 VDC from the 35 VDC
line.
Rev.A 2-17
Page 67

D85
D84
R68
R69
3
4
6
5
Q31
Operation SW
(Power SW)
PSC line
OFF
+35V Line
C55
R91
D52
8
7
PC1
Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2.2.2 Power Supply Circuit Operation
The power supply circuit is composed of an RCC (ringing choke converter) system and the power switch
circuit in the secondary circuitry. The power supply circuit has several protection and control circuits. This
section describes these circuits.
1. Power Switch Circuit
The power switch circuit is in the secondary circuitry. It is shown in the illustration below.
Figure 2-23 Power Switch Circuit
When printer power is off, the PSC line is connected to a ground line and the current is loaded from
C55 to PC1. Consequently, Q32 and Q31 are turned on, and the switching FET is shut off.
(2) +35 V/+5 VDC Line Over Voltage Protection Circuit
This circuit is shown below.
D82
Q55
C82
GND
Q81
R90
ZD52
ZD87
ZD53
ZD86
PC1
6
Q31
FET
5
3
4
Figure 2-24 Over Voltage Protection Circuit
R89
+35V Line
+5V Line
The +35 VDC over voltage protection circuit operates when voltage exceeds 42.42 V between ZD52 and
ZD87 and shuts off the switching FET (Q1: K1692 or K1531). The +5 VDC over voltage protection circuit
operates when voltage exceeds 7.5 V between ZD53, and shuts off the switching FET (Q1: K1692 or
K1531). When either of these protection circuits operate, the protection cannot be removed without turning
power off and on again.
2-18 Rev.A
Page 68

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
3. +35 V Constant Voltage Control Circuit
The +35 V constant voltage control circuit is illustrated below.
11
C15
R20 R21
Q1
R19
Q2
R16
R15
R14
R11C13
Q3
R13
C12
IC1
10+
+35V Line
ZD51
ZD81
ZD82
+
9+
R56
D81
128
7
R57
ZD83
ZD84
ZD85
GND Line
Figure 2-25 +35 V Line Constant Voltage Control Circuit
The constant voltage control circuit operates to keep the 35 V line at 35 V ± 6 %. When the voltage between
ZD51 and ZD85 becomes 32.7 V ± 2.75 %, PC1 turns on, and then Q2 also turns on. Consequently,
switching FET Q1 shuts off. When the voltage between ZD51 and ZD85 becomes less than 32.7 ± 2.75 V,
PC1 turns off, and then Q2 also turns off. Consequently, switching FET Q1 operates again. Repeating the
above operation keeps the +35 V line at 35 V ± 6%.
4. +35V Line Overload Detection Circuit
The +35 V line voltage drop protection circuit is shown in the figure below.
+35V Line
ZD51
ZD81
ZD82
ZD83
ZD84
+5V Line
ZD85
GND Line
Q31
PC1
8
7
R56
1
R57
2
D81
R20
R83
R84
R86
8
+
5
6
7
-
4
R87
PWDN
GND
Figure 2-26 +35 V Line Overload Detection Circuit
When the +35 V line is overloaded, it means that constant voltage control is not being maintained. In this
condition, the forward current of PC1 drops to 0 A. Consequently, voltage Vf between PC1 and D81 also
drops. On this circuit, when the Vf voltage drops below 1.3 V (+35 V line: 33.1 V), IC528 detects the
overload and outputs the PWDN signal (+5 V: HIGH active) to port 20 of the CPU. When the CPU receives
this PWDN signal, printing stops. When the +35 V line becomes normal again, the voltage between PC1 and
D81 also becomes normal. When the Vf voltage goes above 1.6 V (+35 V line: 33.4 V), the PWDN signal
is removed.
Rev.A 2-19
Page 69

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
5. +35 V Line Over Current Protection Circuit
The +35 V line over current control circuit is illustrated below.
R54
+35V Line
Q31
R70
D85
C57
6
5
3
4
R68
Q54
Q53
R74
R75
Q82
R71
R72
R73
GND
PSC
Figure 2-27 +35 V Line Over Current Protection Circuit
When the +35 V line becomes less than 27 V, Q82 and Q54 turn on, and PC1 turns on. Consequently, Q32
and Q31 turn off, and then switching FET Q1 shuts off. When the protection circuit operates, this protection
can only be removed by turning the power off and on again.
6. +5 V Line Over Current Protect Circuit
+5 V line over current control circuit is shown below.
+35V Line
Q51
L51
R53
+5v Line
R88
R64
R65
GND
IC51
TL494CN
-
+
R61
R51
D51
8
2
-
+
1
R67
Figure 2-28 +5 V Line Over Current Protection Circuit
Port 2 of IC51 (TL494CN) monitors the +5 V line, and this protection circuit operates when the +5 V line
goes below 4.75 V. When this circuit operates, port 8 signal output of the PWM pulse stops, and Q51 stops
its switching operation. Consequently, the +5 V line stops generating.
2-20 Rev.A
Page 70

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
7. +5 V Line Constant Voltage Control Circuit
The +5 V line constant voltage control circuit is shown below.
+35V
GND
GND
R81
16
+
IC51
TL494CN
-
R60
R59
Q51
ZD55
R61
R51
15
8
D51
L51
R53
+5v Line
R88
R64
R65
GND
Figure 2-29 +5 V Line Constant Voltage Control Circuit
Port 16 of IC51 (TL494CN) monitors the + 5 V line, and the voltage is compared with the standard voltage,
which is input into port 15. When the voltage of port 16 goes below 4.81 V or above 5.17 V, the pulse width
of the PWM signal, which is output from port 8, changes and the +5 V line is kept between 4.81 V to 5.17 V.
Rev.A 2-21
Page 71

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2.3 CONTROL CIRCUIT
The control circuit consists of the C165 MAIN board assembly and C165 PNL board This section describes
the major components and explains how the boards work.
2.3.1 Overview of Control Circuit Operation
The printer’s control circuit includes a TMP96C141AF CPU that runs at 17.20 MHz, an E05B13YA gate
array, a 1M bit PS-RAM (8-bit bus, less than 80ns) , a 2M bit PROM (8-bit bus, less than 120ns), 4M CG
(Standard Version) or 8M CG (NLSP Version). It oversees control of all the components in the printer. The
following chart shows you a block diagram of the control circuit.
Type B I/F
Parallel I/F
Panel LED
Power SW
PSC
PWDN
P/ S
Unit
5V
GL
35V
GP
IC 3
IC2
Gate Array
E05B13
IC 12
SLA7024M
ROM RAM
IC 11
PF Drv.CR Drv.
UDN2917EB
IC 5
IC 8
EEPROM
IC 10
Rest IC
IC 1
CPU
TMP96C041AF
CSF Drv.
Q5~Q22
Head Drv.
CSF
Detec tor
Head Temp.
Detector
+35V Voltage
Detector
PE-Rear
Detector
PE-Front
Detector
P-W idt h
Detector
Home
Detector
Release
Lever
Detector
Gap
Lever
Detector
: Data Bus
: Address Bus
Figure 2-30 Control Circuit Block Diagram
2-22 Rev.A
Page 72

Host
Computer
CPU
TMP96C041AF
RAM
Gate Array
E05B13
Printhead drive
circuite
Input
Buffer
Image
Buffer
Line Edit
Buffer
Print data
conversion 1
Print data
conversion 2
Data latch
and
data output
Image data
transfer
Parallel I/F
Option I/F
LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
The following figure shows the data flow from the host computer to the printhead. Data sent from the host
computer is converted to image data and transmitted to the printhead through the gate array.
Figure 2-31 Data Flow
The following table lists the each function of the main components of the C165 MAIN board.
Table 2-7 Functions of the Main Board
IC Location Function
Receives data from the host computer and sends it to the input buffer
in RAM (under interrupt processing control). Extends the input data
CPU IC1
Gate Array IC2
EEPROM IC 8
ROM IC 3
RAM IC 5 The RAM contains the CPU working area and the buffers
CG IC 6 The CG contain the bit map font of each character table
SLA7024M IC 12 Drive circuit for the CR motor
UDN2917EB IC 11 Drive circuit for the PF motor
held in the buffer to create image data. Loads this image data to the
image buffer in RAM. Transfers the image data to the printhead drive
circuit.
Controls the functions below:
• Controls output data from the internal block
• Memory management
• Address latch of the address/data bus from the CPU
• Clock control unit
• Bit manipulation
• Interface control
• Expanded parallel port
• Printhead control
• Motor control
An electrically writable and erasable ROM used to hold such
information as the TOF position and bidirectional adjustment value.
The ROM contains the program that runs the CPU and holds the
character design (also called the character generator).
Rev.A 2-23
Page 73

CPU
Gate
Array
C19
ZD1
+35V
7879
74
73
R51
R50
+35V
R49
Address
Data Line
37
44
~
28
~
21
Printhead Drive Signal
69 76~89 91~93
Printhead Dri ve Tran sist or Q 5~Q13, Q14~ 22
Print Head
HTMP
+
C9
+35V +35V
32
19
Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2.3.2 System Reset Circuit
Control circuits IC1 and IC2 are initialized when a RESET signal (LOW level) is output from port 1 (VOUT)
of IC10. IC10 monitors the +5 V line on port 3, and resets under the following conditions:
E05813YA
IC2
+5V
R47
IC10
PST5920
VOUT
MRES
VCC
GND
1K
+5V
1
2
3
4
C16
0.1U
Figure 2-32 Reset Circuit
1. When the power supply is turned on, a
+5 V line goes up to 4.2 V, and then 100 ms passes.
2. When the +5 V line goes below +4.2 V, a
+5 V line goes back up to 4.2 V and then 100 ms passes.
(v)
5
4
3
2
1
Power On
RESET signal is output. RESET is canceled when the
RESET signal is output. RESET is canceled when the
100ms
RESET
VOUT (RESET)
RESET
61
TPM96C041AF
IC1
23 RESET
100ms
RESET
VCC (+5V line)
2.3.3 Printhead Driver Circuit
The standard voltage for the A/D converter is made in ZD1 and input to CPU port 78. Based on this
standard voltage, the A/D converter in the CPU operates. Port 74 monitors the +35 V line between R50 and
R51 to determine the printhead drive pulse width. Using the monitored voltage, the CPU converts the
voltage to a digital value and decides the printhead drive pulse width, and then transports the data to the gate
array via CPU port 19. Based on the monitored voltage, the CPU decides the printing interval. Port 73
monitors the printhead temperature to protect the printhead. If the temperature exceeds 110° C (228° F) ,
printing is stopped.
2-24 Rev.A
Figure 2-33 Reset Signal Output Timing
Figure 2-34 Printhead Drive Circuit
Page 74

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
2.3.4 CR Motor Driver Circuit
The CR motor driver circuit is shown below.
6
IN A
5
IN-A
17
IN B
16
IN-B
3
14
9
10
4
15
RFA
RFB
SLA7024M
RSA
RSB
GND A
GNB B
-A
-B
A
B
+35V
CR A
CR-A
CR B
CR-B
CRCOM
+5V
CPU
Address
Data Line
Gate
Array
PG00
PG01
PG02
PG03
CRI0
CRI1
CRI2
CRI3
R72
1
2
3
4
R67
R73
65
R74
64
R75
63
R76
62
R71
R68
C29, 30
C31
R69, 70
Figure 2-35 CR Driver Circuit
The carriage motor driver circuit controls the CR motor, using an open-loop, constant drive arrangement.
2-2 and 1-2 phases excite the motor. A 2-2 phase step is equivalent to a 1-2 phase step doubled. Ports 1 to 4
of the SLA7024M are used to change the excitation phase, depending on the selected print mode. Table 2-8
describes the motor driver modes.
Table 2-8 CR Motor Driver Modes
Speed Mode
Print Speed
(CPS)
8/3 440 5280 2-2 Super Draft
3 330 3960 2-2 Draft
8/3 293.3 3520 2-2 Super Draft and Copy
2 220 5280 1-2
3/2 165 3960 1-2 Draft & Power down
1 110 2640 1-2
Drive
Frequency
(PPS)
Excitation
Phase
Applications
Super Draft & Power down
Draft & Copy
Super draft & Copy &
Power down
Draft & Copy & Power down
LQ
3/4 82.5 1980 1-2 Bit Image & Power down
2/3 73.4 1760 1-2 LQ & Copy
1/2 52.5 1320 1-2
LQ & Power down
LQ & Copy & Power down
The SLA7024M (IC12) CR motor driver circuit detects and regulates the amount of current flowing in the
carriage motor coil. The current flowing through the coil varies, depending on the speed of the CR motor.
The CPU sets the amount of current via the Address /Data line. Signals are sent to ports 3 (RFA) and 14
(RFB) of the SLA7024M. The SLA7024M sets the coil current, depending on the CR speed.
Rev.A 2-25
Page 75

Operating Principles LQ-2170 Service Manual
2.3.5 PF Motor Driver Circuit
The figure below shows the PF motor driver circuit.
IC6
74LS32
1
3
2
I10
I11
42
27
43
26
I20
I21
VREF1
VREF2
PH1
PH2
4
6
5
A
A
B
B
1
6
3
18
21
PF A
2
PF-A
3
PF B
4
PF-B
IC11
PP
G3
PG
13
7
8
Gate
Array
PP
G2
8
PG
12
PP
G1
PG
11
HOLD
9
67
PFI1
PFI2
PP
G0
PG
10
68
67
66
10
5
P27
61
CPU
UDN2917EB
Figure 2-36 PF Motor Driver Circuit
The gate array receives phase data from the CPU via ports 5 (PG10), 6 (PG11), 7 (PG12), and 8 (PG13),
converts the data to UDN2917 form, and then sends that phase data to ports 43 (PH1) and 26 (PH2). The PF
driver current is controlled by the 74LS32 using port 68 (PF1) and 67 (PF2) signals output from the gate
array and port 61 (P27) output from the CPU. These controlled drive currents are output to ports 2 (I10), 1
(I11), 23 (I20), and 24 (I21) of the UDN2917EB.
2.3.6 EEPROM Control Circuit
The EEPROM is non-volatile memory that stores information even if the printer power is off. The figure
below shows the EEPROM control circuit.
CPU
P70
P71
P72
P73
9
10
11
12
1
CS
2
CK
3
DI
4
DO
IC 8
EEPROM
Figure 2-37 EEPROM Control Circuit
The EEPROM is controlled by CPU ports 9 (P70), 10 (P71), 11 (P72), and 12 (P73). Port 11 is the data
output line used to save the information to the EEPROM, and port 12 is the data input line used to read the
saved data from the EEPROM. Port 70 is the chip select line, and port 71 is the clock timing line. When the
PWDN signal (power down) is detected on port 20 (INTO), the CPU writes the necessary data to the
EEPROM before the +5 V line drops to 4.75 V.
2-26 Rev.A
Page 76

LQ-2170 Service Manual Operating Principles
2.3.7 Sensor Circuits
The CPU detects conditions of the following sensors: home position (HP) sensor, release sensors 1 and 2,
platen gap (PG) sensor, rear and front paper end (PE) sensors, paper width (PW) sensor, and cover open
sensor.
+5V
+5V
Rear PE
Sensor
Front PE
Sensor
PW Sensor
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
70
P40
68
75
P36
AN2
CPU
P53
P32
P33
P34
P35
INT7
76
64
65
66
67
18
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
HP Sensor
Relea se
Sensor 2
Release
Sensor 1
PG Sens or 1
PG Sens or 2
Cover Open
Sensor
Figure 2-38 Sensor Circuits
Two types of sensors are used in this printer. Release sensors 1 and 2 , PG sensors, the front PE sensor, and
cover open sensor are momentary switches. Pages 2-3 and 2-4 describe the relationship between release and
PG sensor operation and actual print operation.
The other type of sensor is used for the HP sensor, rear PE sensor, and PW sensor, which are photo diode
switches. The HP sensor detects CR home position when the photo diode rays are cut off by the printhead.
The rear PE sensor detects that paper has been loaded when the photo diode rays are cut off by the sensor
plate, which is included in the rear PE sensor. The PW sensor, used for paper width measurement and paper
loading positioning, detects the paper edge by comparing the measured voltage with standard voltage, which
was measured during the power on sequence.
Additionally, as mentioned on the page 2-24, the +35 V line and head temperature are monitored to set the
pulse length of the head drive signal.
Rev.A 2-27
Page 77

CHAPTER 3 Disassembly and Assembly
Table of Contents
3.1 OVERVIEW 3-1
3.1.1 Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1.2 Tools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1.3 Service Checks After Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.1.4 Specifications for Screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.2 PRINTER DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY 3-4
3.2.1 Before Starting Disassembly Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.2.2 Removing the Panel Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.2.3 Removing the Printhead. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
3.2.4 Removing the HP Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.2.5 Removing the PW Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.2.6 Removing the Platen Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
3.2.7 Removing the Upper Housing Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
3.2.8 Removing the Case Open Sensor Assembly, . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
3.2.9 Removing the CR Motor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
3.2.10 Removing the Printer Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
3.2.10.1 Removing the PF Motor Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
3.2.10.2 Removing the PG Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
3.2.10.3 Removing the Right Frame Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
3.2.10.4 Disassembling the Right Frame Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
3.2.10.5 Removing the Left Frame Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-19
3.2.10.6 Removing the Ribbon Drive (RD) Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
3.2.10.7 Removing the CR Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-21
3.2.10.8 Removing the Rear PE Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
3.2.10.9 Removing the Front PE Sensor Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
3.2.11 Removing the C165 MAIN Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-24
3.2.12 Removing the C165 PSB/E Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-25
3.3 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY OF CSF BIN 1 3-26
3.3.1 Disassembling the Right Side Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-26
3.3.2 Disassembling the Paper Support Block Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
3.3.3 Removing the Paper Eject Cover Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
3.4 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY OF CSF BIN 2 3-31
3.4.1 Disassembly Right Side Block. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
3.4.2 Disassembly Paper Support Block Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-32
Page 78

List of Figures
Figure 3-1. Screw Types and Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Figure 3-2. Flowchart for Disassembling the Printer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Figure 3-3. Before Starting Disassembly Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Figure 3-4. Removing the Panel Board Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Figure 3-5. Lock Cover for CN1 and the FFC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Figure 3-6. Removing the Printhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Figure 3-7. Connecting the Printhead FFCs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Figure 3-8. Removing the HP Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Figure 3-9. Removing the PW Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Figure 3-10. Mounting Position for the PW Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Figure 3-11. Releasing the Locks for the Bushings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Figure 3-12. Removing the Platen Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Figure 3-13. Releasing the Upper Housing Assembly Hooks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Figure 3-14. Removing the Upper Housing Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Figure 3-15. Removing the Case Open Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Figure 3-16. Removing the CR Motor Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Figure 3-17. Removing the Printer Mechanism. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Figure 3-18. Removing the PF Motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
Figure 3-19. Removing the PG Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Figure 3-20. Removing the Right Frame Assembly.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Figure 3-21. Removing the Right Sub Frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Figure 3-22. Engaging Gears 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Figure 3-23. Engaging Gears 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Figure 3-24. Engaging the Tractor Clutch Cam . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Figure 3-25. Removing the Left Frame Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-19
Figure 3-26. Cable Connection for the Release Lever Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-19
Figure 3-27. Removing the RD Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Figure 3-28. Engaging Gears for the RD Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Figure 3-29. Disconnecting the FFC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-21
Figure 3-30. Removing the CR Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-21
Figure 3-31. Inserting the Timing Belt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Figure 3-32. Inserting the Oil Pad into the CR Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Figure 3-33. Assembling the Rear CR Guide Shaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Figure 3-34. Removing the Rear PE Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
Figure 3-35. Removing the Front PE Sensor Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
Figure 3-36. Removing the C165 MAIN Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-24
Figure 3-37. Removing the C165 PSB/E Board Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-25
Figure 3-38. Direction for Mounting the Fan Motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-25
Figure 3-39. Releasing the Clips for the Right CSF Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-26
Figure 3-40. Cable Alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-27
Figure 3-41. Engaging 13 Gears . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-27
Figure 3-42. Removing the E-ring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
Figure 3-43. Removing 1 Gear (29 mm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
Figure 3-44. Removing the CPB Tight Screw. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
Figure 3-45. Removing the Paper Support Block Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-29
Figure 3-46. Removing the Paper Feed Roller Cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-29
Figure 3-47. Removing the Paper Eject Cover Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
Figure 3-48. Assembling the Paper Eject Cover Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
Page 79

Figure 3-49. Removing the Right CSF Cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
Figure 3-50. Engaging 5 Gears . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
Figure 3-51. Removing the E-ring and 2 CBS Screws. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-32
Figure 3-52. Removing the Paper Feed Roller Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-32
List of Tables
Table 3-1. Recommended Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Table 3-2. Equipment Required for Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Table 3-3. Inspection Check List for Repaired Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Table 3-4. Screw Types and Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Page 80

Page 81

LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.1 OVERVIEW
This section describes various points to note when disassembling and assembling the printer.
3.1.1 Precautions
Follow the precautions below for disassembly or assembly.
WARNING
Before disassembling, assembling, or adjusting the printer, disconnect the power supply cable
from the AC power socket. Failure to do so can cause physical injury. The power switch is wired in
the secondary circuitry. Therefore, the printer’s primary circuitry remains live even after the
power switch is turned off.
Never touch primary parts of the the power supply unit (including the heat sink) while the power
supply cable is connected to the AC power socket.
CAUTION
To maintain efficient printer operation:
• Use only recommended tools for maintenance work.
• Use only recommended lubricants and adhesives (see Chapter 6).
• Adjust the printer only in the manner described in this manual.
3.1.2 Tools
Tables 3-1 and 3-2 list the tools recommended for disassembling, assembling, or adjusting the printer. Use
only tools that meet these specifications.
Table 3-1. Recommended Tools
Tool Part No.
Round-nose pliers B740400100
Nippers B740500100
Tweezers B741000100
Soldering iron B740200100
E-ring holder #2.5 B740800400
Phillips screwdriver No.2 B743800200
Standard screwdriver B743000100
Thickness gauge B776702201
Note: All tools are commercially available.
Table 3-2. Equipment Required for Maintenance
Description
Multimeter
Oscilloscope
Note: An oscilloscope is required only for servicers who repair to the component level.
Rev.A 3-1
Specification
——
50 MHz
Page 82

Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.1.3 Service Checks After Repair
Before returning the printer after service, use the check list in Table 3-3, which provides a record to make
servicing and shipping more efficient.
Table 3-3. Inspection Check List for the Repaired Printer
Category
Printer
units
^
^
^
^
^
^
Adjustment
System
upgrade
Component Item to Check Is Check Required?
Printhead Are any wires broken?
Are any wires worn out?
Carriage
mechanism
Paper
advance
mechanism
Paper path Is the
Ribbon
mask
Self-test Was the self-test successful?
On-line test Was the on-line test successful?
Printhead
printing
Default
settings
ROM
version
Shipment Has the ribbon been removed?
Does the carriage move smoothly?
Movement noisy Mechanism dirty
Mechanism oily
Is the CR motor at the
correct temperature (not overheating)
Is paper advancing smoothly?
Movement noisy Mechanism dirty
Mechanism oily
Is the paper feed motor running
at the correct temperature (not
overheating)
type
of paper in the printer
feeding smoothly?
Is the tractor feeding the paper
correctly?
Is the paper path clear of all
obstructions?
Is the platen free of damage?
Is the ribbon mask free of distortion?
Is the platen gap adjusted correctly?
Is the bidirectional print position
adjusted correctly?
Have user-changeable settings been
reset to the default values?
ROM version ________.
Have all relevant parts been included
in the shipment?
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
Checked Not necessary
3-2 Rev.A
Page 83

LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.1.4 Specifications for Screws
Table 3-4 lists the abbreviations used in the following sections for small parts, such as screws and washers.
Table 3-4. Screw Types and Abbreviations
Abbreviation Part Name
CPS Cross-recessed pan head S-tight screw
CBB Cross-recessed bind head B-tight screw
CBS Cross-recessed bind head S-tight screw
CBN Cross-recessed bind head N-tight screw
CBC Cross-recessed bind head C-Lamitite screw
CBA Cross-recessed bind head A-lamitite screw
CB(O) Cross-recessed bind head with outside-toothed lock washer
Head
Body
Top Side
Cross-recessed head
Pan
Bind
(with Notch)
S-tight
Normal
B-tight
C-lamitite
A-lamitite
Figure 3-1 Screw Types and Abbreviations
Rev.A 3-3
Page 84

Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.2. PRINTER DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
This section describes procedures for disassembling and assembling the main components of the printer.
When the procedure for installing a component is simply the reverse of removing the component, this chapter
does not describe the assembly procedure. If necessary, special notes on assembling or adjusting a component
are given at the end of the description of each procedure. Be sure to follow the instructions in these notes.
CAUTION
• Before disassembling any part of the printer, note the warnings in Section 3.1.
• Before beginning to disassemble the printer, remove the paper and the ink ribbon.
Also disconnect the interface cable.
• Whenever the printer is repaired, wipe the surface of the paper width (PW) sensor assembly
with a soft cloth, and keep it clean to avoid abnormal operation. If the surface is dirty from
any adhering material, sensor sensitivity goes down and operation is not correct.
Note: Exploded diagrams in the appendix show you how the components fit together. Refer to
them as necessary. The flowchart below shows the order you need to use to disassemble the
printer. For details of the required adjustments, refer to Chapter 4.
Page 3-6
3.2.2
Removing the Panel
Board Assembly
3.2.8
Page 3-12
Removing the Cse
Open Sensor
Disconnect the printer's power cord and interface cable.
Page 3-7
3.2.3
3.2.3
Removing the
Printhead
3.2.9
3.2.9
Removing the CR Motor
Assembly
Page 3-7
Page 3-12
START
3.2.1 Page 3-5
Before Starting Disassembly Pricedure
Page 3-8
3.2.4
Removing the
HP Sensor
3.2.7
Page 3-11
Removing Upper Housing Assembly
Page 3-13
3.2.10
Removing the
Printer Mechanism
Page 3-8
3.2.5
3.2.5
Removing the
PW Sneosr Assembly
3.2.11
Page 3-24
Removing C165 MAIN
Board
: Bi-d adjustment is required
:
PG adjustment is required
: Bi-d & PG adjustment are required
: Bi-d Adjustment & Factor y Setting
are required (when the parts is
replaced to new one)
: TPE Level Reset is required
the parts is replaced to new one)
3.2.6
Page 3-10
3.2.6 Page 3-10
Removing the
Platen Assembly
Page 3-25
3.2.12
Removing C165 PSB/E
Board
(when
3.2.10.1 Page 3-14
Removing the PFMotor
Assembly
3.2.10.6
Removing the RD
Assembly
Page 3-20
3.2.10.2 Page 3-15
Removing PG Sensor
3.2.10.7
Removing CR Assembly
Page 3-21
3.210.3
Removing the Right
Frame Assembly
3.2.10.8
Removing the Rear PE
Sensor
Page 3-16
Page 3-23
3.2.10.4
Disassemble Right
Frame Assembly
3.2.10,9 Page 3-23
Removing the Fron PE
Sensor
Page 3-16
3.2.10.5
Removing the Left
Frame Assembly
Page 3-19
Figure 3-2 Flowchart for Disassembling the Printer
3-4 Rev.A
Page 85

LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.1. Before Starting Disassembly Procedures
1. Remove the following parts:
Front edge guide assembly Front cover Bottom cover
Rear edge guide assembly Printer cover Paper eject assembly
. Front/rear tractor assembly Ribbon cartridge
Refer to the following figure.
Figure 3-3 Before Starting Disassembly Procedures
Note
Remove the paper eject cover and the front/rear tractor assembly by pushing to release the hooks
at both sides. When remounting them, be sure to snap the hooks on the projecting parts.
Rev.A 3-5
Page 86

Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.2.2. Removing the Panel Board Assembly
1. Remove the printer cover and ribbon cartridge (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Release the left clips for the panel board assembly by pushing them from the cutout located on
the inside front of the upper housing assembly.
3. Release the flexible flat cable (FFC) by pulling the lock cover for CN1, and then disconnect the
FFC for CN1 and connector CN2 from the C165 PNL board assembly.
CN1
CN2
Figure 3-4 Removing the Panel Board Assembly
4. Remove the panel board assembly from the upper housing assembly.
Assembly Notes
Before disconnecting the FFC from CN1, slide the lock cover for CN 1 as shown in Figure 3-5,
and release the FFC from CN1. After reconnecting the FFC for CN1, lock the lock cover .
The FFC must be connected properly, as shown in Figure 3-5. Exposed terminals must be
connected face upward against the C165 PNL board.
Lock Cover for CN 1
Slide
CN 1 CN 1
CN 1
Exposed terminals face
FFC
Figure 3-5 Lock Cover for CN1 and the FFC
3-6 Rev.A
Page 87

FFCs for Printhead
Direction that Explosed Terminals Face
Print Head
LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.3. Removing the Printhead
1. Remove the printer cover and ribbon cartridge (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove 2 CBS screws (3 × 10, F/Zn) securing the printhead to the CR assembly.
3. Remove the printhead from the CR assembly.
4. Disconnect 2 wide FFCs from the printhead and then disconnect the narrow FFC from the
connector on the CR cover.
CBSScrews (3X10F/Zn)
Printhead
Figure 3-6 Removing the Printhead
Assembly Notes
The FFC must be connected properly, as shown in the following figure.
The tightening torque for the 2 CBS screws (3 × 10, F/Zn) = 0.59 ~ 0.78 Nm ( 6 ~8 Kg f. cm )
Adjust the platen gap. Refer to Chapter 4.
Figure 3-7 Method for Connecting the Printhead FFC
Rev.A 3-7
Page 88

PW Sensor Assembly
CB Screw (2 x 5 F/Zn)
Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.2.4 Removing the HP Sensor
1. Remove the printer cover, ribbon cartridge, front edge guide, and front cover (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Disconnect the connector cable for the HP sensor.
3. Remove the HP sensor by pushing up and releasing the 2 clips at the bottom of the HP sensor
from the front paper entrance.
2 Clips for HP Sensor
Figure 3-8 Removing the HP Sensor
3.2.5 Removing the PW Sensor Assembly
1. Remove the printer cover and ribbon cartridge (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the CB screw (2.5 × 5, F/Zn) securing the PW sensor to the ribbon mask holder. Then,
3. Remove the PW sensor assembly along with the CR cover by pushing and releasing the 2 clips
Assembly Note
Notice the direction for mounting the HP sensor. Refer to the figure above.
remove the FFC from the PW sensor connector, mounted onto the CR cover.
for the CR cover, as shown in the following figure.
3-8 Rev.A
Figure 3-9 Removing the PW Sensor Assembly
Page 89

CB Screw ( 2.5X5 F/Zn)
PW Sensor Assembly
Ribbon Mask H older
View of PW Sensor
through Ribbon Mask Holder
Bold Perforated line is the Groove.
Micro Photo Sensor
LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
Assembly Notes
Mount the PW sensor assembly onto the ribbon mask holder groove, aligning the bottom line of
micro photo sensor to the bottom line of the groove.
Whenever you remove the PW sensor assembly, clean the surface of the sensor by wiping it with a
soft material. If the surface is not clean, abnormal operations may occur, such as printing on the
platen surface.
The tightening torque for the CB screw (2.5 × 5, F/Zn) = 0.08 ~ 0.12 Nm (0.8 ~ 0.12 Kg f-cm)
When you replace the PW sensor assembly, reset the TPE level. Refer to Chapter 4.
Figure 3-10 Mounting Position for the PW Sensor Assembly
Rev.A 3-9
Page 90

Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.2.6 Removing the Platen Assembly
1. Remove the printer cover, ribbon cartridge, and platen knob (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Release both locks for the left and right bushings (8 mm) by pushing the lever holder for the
bushings outside, and then pulling the holder lever forward.
Left and Right Bushings (8mm)
Figure 3-11 Releasing the Locks for the Bushings
3 Slide the platen assembly to the right, and move the printhead to the right edge.
4. Pull the left edge of the platen assembly upward by tilting it backward, and then pull up the
right edge of the platen assembly.
Figure 3-12 Removing the Platen Assembly
Assembly Notes
Before reinstalling the platen assembly into the printer mechanism, move the printhead to the
right edge of the CR shaft, and set the release lever to the tractor position. This pre-assembly
operation helps you mount the platen assembly more easily.
After installing the platen assembly into the printer mechanism, make sure both locks for left and
right bushings (8 mm) are locked completely.
Be careful handling the lever holders for the left and right bushings (8 mm). These are fragile.
Adjust the platen gap. Refer to Chapter 4.
3-10 Rev.A
Page 91

LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.7 Removing the Upper Housing Assembly
1 Remove the rear edge guide assembly, paper eject assembly, rear tractor unit, and printer cover
(see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board assembly (see Section 3.2.2).
3. Remove 4 CBB screws (4 × 14, F/Zn) securing the upper housing assembly.
4. Remove the platen knob.
5. Lift up the front side of the upper housing assembly by releasing 2 hooks from the holes located
on right and left of the front bottom side.
Figure 3-13 Releasing the Upper Housing Assembly Hooks
6 Remove the upper housing assembly.
Figure 3-14 Removing the Upper Housing Assembly
Assembly Note
The tightening torque for the CBB (4 × 14, F/Zn) = 0.98 Nm (10 ~ 12 Kg - cm)
Rev.A 3-11
Page 92

C.B.B. Screw
(3x8 F/Zn)
C.B.Screw
(2 x8 F/Ni)
Sensor
Holder
Case Open
Sensor Assembly
Upper Housing Assembly
CR Mounting Screws
Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.2.8 Removing the Case Open Sensor Assembly
1. Remove the rear edge guide assembly, paper eject assembly, rear tractor unit, and printer cover
(see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board (see Section 3.2.2) and upper housing assemblies (see Section 3.2.7).
3. Turn the upper housing assembly over and remove the case open sensor assembly by loosening
the CBB screw ( 3 × 8, F/Zn) fixing the sensor holder to the upper housing assembly.
Figure 3-15 Removing the Case Open Sensor Assembly
3.2.9 Removing the CR Motor Assembly
1 Remove the rear edge guide assembly, paper eject assembly, rear tractor unit, and printer cover.
(see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board (see Section 3.2.2) and upper housing assemblies (see Section 3.2.7).
3. Remove the 2 CR mounting screws securing the CR motor assembly. After releasing the
extension spring (15.7 g), disengage the timing belt from the CR motor assembly.
4. Disconnect the cable for CN11 from the C165 MAIN board assembly.
5. Remove the CR motor assembly from the printer mechanism.
Figure 3-16 Removing the CR Motor Assembly
Assembly Notes
The tightening torque for the 2 CR mounting screws = 0.78 ~ 0.98 Nm (8~10 Kg - cm)
Adjust the bidirectional print alignment. Refer to Chapter 4.
3-12 Rev.A
Page 93

Printer Mechanism Mounting Screws
LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.10 Removing the Printer Mechanism
1. Remove the rear/front edge guide assembly, front cover, paper eject assembly, rear/front tractor
units, and printer cover (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board assembly (see Section 3.2.2) and upper housing assembly (see Section
3.2.7).
3. Remove 4 printer mechanism mounting screws securing the printer mechanism.
4. Disconnect the following connectors on the C165 MAIN board assembly:
CN4 ( 3-pin, white) CN5 ( 3-pin, black) CN6 ( 2-pin, white )
CN7 (4-pin, white FFC) CN8 (18-pin, white FFC) CN9 (16-pin, white FFC)
CN10 (4-pin, blue) CN11 (5-pin, blue) CN12 (4-pin, white)
CN13 (2-pin, black)
❇ Disconnect the cables for CN10 and CN11 after releasing the connector locks by pulling up.
5. Remove the printer mechanism.
Figure 3-17 Removing the Printer Mechanism
Assembly Notes
Notice the connection for cables CN10 and CN11 and align the red colored cable to pin 1 of the
connector.
The tightening torque for the printer mechanism mounting screw=
0.98 Nm ~ 1.18 Nm (10 ~ 12 Kg - cm)
Adjust the bidirectional print alignment and reset the TPE level. Refer to Chapter 4.
Rev.A 3-13
Page 94

CBS Screws (3 x 6 F/Zn)
Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.2.10.1 Removing the PF Motor
1. Remove the rear/front edge guide assembly, front cover, paper eject assembly, rear/front tractor
unit, and printer cover (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board (see Section 3.2.2) and upper housing assemblies (see Section 3.2.7).
3. Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.10).
4. Remove the CBS screw (3 × 6, F/Zn) and CB screw (3 × 8, F/Zn) securing the PF motor.
5. Disconnect connector CN10 from the C165 MAIN board assembly.
6. Remove the PF motor from the right sub frame.
Figure 3-18 Removing the PF Motor
Assembly Note
Before attaching the PF motor to the proper position on the right sub frame, set the release lever
to the full release position.
The CB screw (3 × 8, FZ/n) is used to secure the upper part of the PF motor. The CBS screw
(3 × 6, FZ/n ) is used to secure the lower part of the PF motor.
The tightening torque for the CB and CBS screws (3 × 8, F/Zn) = 0.78 ~ 0.98 Nm (8 ~ 10 Kg cm)
3-14 Rev.A
Page 95

Hexagon Nut (Standard, M4)
LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.10.2 Removing the PG Sensor Assembly
1. Remove the rear/front edge guide assembly, front cover, paper eject assembly, rear/front tractor
unit, and printer cover (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board (see Section 3.2.2) and upper housing assemblies (see Section 3.2.7).
3. Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.10 ).
4. Remove the hexagon nut (standard, M4) securing the PG sensor assembly to the right frame
assembly.
Figure 3-19 Removing the PG Sensor Assembly
Assembly Notes
The tightening torque for the hexagon nut (standard, M4) = 1.18 ~ 1.37 Nm (12 ~ 14 Kg f - cm)
When securing the shaft, push the front CR guide shaft to the bottom of the cutout.
Rev.A 3-15
Page 96

Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.2.10.3 Removing the Right Frame Assembly
1. Remove the rear/front edge guide assembly, front cover, paper eject assembly, rear/front tractor
unit, and printer cover (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board (see Section 3.2.2) and upper housing assemblies (see Section 3.2.7).
3 Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.10 ), CR motor assembly (see Section 3.2.9), PF
motor, (see Section 3.2.10.1) and PG sensor assembly (see Section 3.2.10.2 ).
4. Remove the hexagon nut (standard, M4) securing the gap adjust lever. Then, remove the gap
adjust lever from the right frame assembly.
5. Remove 2 CBS screws (3 × 6, F/Zn) securing the platen cover.
6. Remove 3 CBS screws (3 × 6, F/Zn) securing the right frame assembly at the positions illustrated.
CBS Screw (3 x6) Securing the Right Frame Assembly
Figure 3-20 Removing the Right Frame Assembly
7. Remove the right frame assembly.
Assembly Notes
Adjust the platen gap and bidirectional print alignment. Refer to Chapter 4.
3.2.10.4 Disassembling the Right Frame Assembly
1. Remove 1 CBS screw (3 × 6, F/Zn ) and 1 CBS screw (3 × 8, F/Zn) securing the right sub frame.
(The bold line in the illustration is the right sub frame.)
Right Sub Frame
CBS Screw (3 X6 FZ/n )
Securing the Right Sub Fram
CBS Screw (3 x 8 F/Zn)
Securing the Right Sub Frame
Figure 3-21 Removing the Right Sub Frame
3-16 Rev.A
Page 97

LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
2. Remove the right sub frame from the right frame assembly.
3. Remove the following 11 parts from the right frame assembly.
2 compression springs (200 g) 2 plain washers 1 spur gear (27 mm)
2 spur gears (34.5 mm) 1 spur gear (34 mm) 1 spur gear (21 mm)
1 combination gear (8 mm, 31.5 mm) 1 intermittent gear
Assembly Notes
Adjust the bidirectional print alignment. Refer to Chapter 4.
Mount the 11 parts above on the right frame assembly, as shown in the following figures.
Compression Spring (200g)
Plan Washer
Compression Spring (200g)
Plan Washer
Spur Gear
(21 mm)
Super Gear
(34.5 mm)
Combination Gear
(8mm/ 31.5mm)
Intermittent Gear
Spur Gear (27mm)
Spur Gear (34.5mm)
Spur Gear (34mm)
Figure 3-22 Engaging Gears 1
Rev.A 3-17
Page 98

Lever, Release, Transmission
Intermittent Gear
Lever, Release
Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
Assembly Notes
When you engage the release lever and release lever transmission to the tractor clutch cam,
notice the points in the following figure.
The tightening torque for the CBS screws (3 × 6, F/Zn) and (3 × 8, F/Zn)
0.78 ~ 0.98 N.m (8 ~ 10 Kg - cm)
The tightening torque for the hexagon nut (standard, M4) =
1.18 ~ 1.37 N.m(12 ~ 14 Kg f - cm)
Notice how the intermittent gear, release lever, and release lever transmission are engaged.
Figure 3-23 Engaging Gears 2
Pay attention to how the tractor clutch cam is engaged. Refer to the following figure.
3-18 Rev.A
Tractor Clutch Cam
Figure 3-24 Engaging the Tractor Clutch Cam
Page 99

Release SW1
(White connector)
Release SW2
(Black Connector)
Platen
Left Frame Assembly
LQ-2170 Service Manual Disassembly and Assembly
3.2.10.5 Removing the Left Frame Assembly
1. Remove the rear/front edge guide assembly, front cover, paper eject assembly, rear/front tractor
unit, and printer cover (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board assembly (see Section 3.2.2), upper housing assembly (see Section 3.2.7),
and then remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.10 ).
3. Remove 2 CBS screws (3 × 6, F/Zn) securing the platen cover.
4. Remove the hexagon nut (standard, M4) securing the front CR guide shaft and left frame.
5 Remove 4 CBS screws (3 × 6, F/Zn) securing the left frame assembly.
Platen Cover
C.B.S Screw (3 X 6 FZ/n)
CBS Screw (3 X 6 FZ/n ) Securing the Left Frame Assembly
Hexagon Nut (Normal, M4)
Figure 3-25 Removing the Left Frame Assembly
6. Disconnect 2 connector cables from the 2 release lever sensors, and then disconnect the
connector cable from the HP sensor.
7. Remove the left frame assembly.
Assembly Notes
Notice the connection of the release lever sensor cables. The white conector’s cable should be
connected to the SW1 sensor, as shown in the following figure.
The tightening torque for the CBS screw (3 × 6, F/Zn) = 0.78 ~ 0.98 Nm (8 ~ 10 Kg f - cm)
The tightening torque for the hexagon nut (standard, M4) = 1.18 ~ 1.37 Nm (12 ~ 14 Kg f - cm)
Adjust the platen gap and bidirectional print alignment. Refer to Chapter 4.
Figure 3-26 Cable Connections for the Release Lever Sensors
Rev.A 3-19
Page 100

Driven Pully Assembly
RD Assembly
Timing Belt
Disassembly and Assembly LQ-2170 Service Manual
3.2.10.6 Removing the Ribbon Drive (RD) Assembly
1. Remove the rear/front edge guide assembly, front cover, paper eject assembly, rear/front tractor
unit, and printer cover (see Section 3.2.1).
2. Remove the panel board (see Section 3.2.2) and upper housing assemblies (see Section 3.2.7).
3. Remove the printer mechanism (see Section 3.2.10).
4. Remove the left frame assembly (see Section 3.2.10.5).
5. Remove 2 CBS screws (3 × 8, F/Zn ) securing the RD assembly to the front frame.
6. Remove the RD assembly from the front frame.
7. Remove the timing belt from the RD assembly.
Figure 3-27 Removing the RD Assembly
Assembly Notes
Notice how the gears in the RD assembly are engaged. Refer to the following figure.
The tightening torque for the CBS screw (3 × 8, F/Zn) = 0.78 ~ 0.98 N.m (8 ~ 10 Kg - cm)
Adjust the platen gap and perform the bidirectional print alignment. See Chapter 4.
Rachet, RD
Spur Gear
(11 mm)
Combination Spring (7 g/ 23 g)
Driven Pulley
Assembly
Spur Gear (25 mm)
Figure 3-28 Engaging Gears for the RD Assembly
3-20 Rev.A
 Loading...
Loading...