Page 1

Digital gateway
SMG-4, SMG-2
Operation manual, version 2.4 (15/06/2017)
Firmware version: 3.1.6.1189
Page 2

2 SMG digital gateway
Firmware version V.3.1.6.1189
SIP adapter version V.3.1.6.67
Document version
Issue date
Revisions
Version 2.4
15/06/2017
Updated:
– encoding settings and configuration of methods of subscriber name
transmission in Q.931
Added:
– insert remote name in Contact header
– SS7 channels transit via semi-permanent connection
– name transmission using AVAYA, Siemens, Windows-1251 encodings,
Translit and Unicode (UTF-8).
– name transmission methods: QSIG, Q.931 Display, CorNet and AVAYA
Display
Version 2.3
15/08/2016
Time zones updated.
New features added:
- STUN server parameters,
- public IP settings,
- Clear Channel (CLEARMODE) settings,
- English language.
Version 2.2
05/04/2016
Support added for routing modes configuration during trunk registration for
SIP interfaces.
Version 2.1
26/11/2015
SIP interfaces registration added.
Version 2.0
22/06/2015
Second issue.
Version 1.0
12/08/2014
First issue.
Page 3

SMG digital gateway 3
EXPLANATION OF THE SYMBOLS USED
Symbol
Description
Calibri
Notes, warnings, chapter headings, titles, and table titles are written in bold.
Calibri
Italic denotes important information that requires special attention.
Courier New
Courier New is used for command entry examples, command execution
results, and program output data.
<KEY>
Keyboard keys are written in upper-case and enclosed in angle brackets.
Analogue phone unit.
SMG digital gateway.
Softswitch ECSS-10 software switch.
Digital subscriber PBX.
Network connection.
Optical transmission medium.
Notes and Warnings
Notes contain important information, tips, or recommendations on device operation and
setup.
Warnings inform users about hazardous conditions, which may cause injuries or device
damage and may lead to the device malfunctioning or data loss.
Page 4

4 SMG digital gateway
TARGET AUDIENCE
This operation manual is intended for technical personnel in charge of gateway configuration and
monitoring using the web configurator, as well as of installation and maintenance. Qualified technical personnel
should be familiar with the operation basics of the ТСР/IP & UDP/IP protocol stacks and Ethernet networks
design concepts.
Page 5

SMG digital gateway 5
TABLE OF CONTENTS
EXPLANATION OF THE SYMBOLS USED ........................................................................................................... 3
TARGET AUDIENCE .......................................................................................................................................... 4
TABLE OF CONTENTS ....................................................................................................................................... 5
INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................................... 7
1 DEVICE DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................................................. 8
1.1 Purpose ............................................................................................................................................... 8
1.2 Typical Applications ............................................................................................................................ 9
1.2.1 Interface for TDM and VoIP Network Signalling and Media Streams ....................................... 9
1.3 Device Design and Operating Principle ............................................................................................ 10
1.4 Main Specifications ........................................................................................................................... 12
1.5 Design ............................................................................................................................................... 14
1.6 LED Indication ................................................................................................................................... 15
1.7 The F Function Button ...................................................................................................................... 18
1.8 Delivery Package ............................................................................................................................... 19
1.9 Safety Instructions ............................................................................................................................ 20
1.9.1 General Guidelines .................................................................................................................. 20
1.9.2 Electrical Safety Requirements ............................................................................................... 20
2 SMG INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................................. 21
2.1 Startup Procedure............................................................................................................................. 21
2.2 Opening the Casing ........................................................................................................................... 21
2.3 RTC Battery Replacement ................................................................................................................. 22
3 GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR GATEWAY OPERATION ................................................................................. 23
4 DEVICE CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................................................... 24
4.1 SMG Configuration via web Interface .............................................................................................. 24
4.1.1 System Parameters ................................................................................................................. 26
4.1.2 Monitoring .............................................................................................................................. 30
4.1.3 Synchronisation Sources ......................................................................................................... 39
4.1.4 CDR .......................................................................................................................................... 40
4.1.5 E1 Streams .............................................................................................................................. 45
4.1.6 Dial plan .................................................................................................................................. 52
4.1.7 Routing .................................................................................................................................... 58
4.1.8 Internal Resources .................................................................................................................. 79
4.1.9 Network Services .................................................................................................................... 92
4.1.10 User Configuration ............................................................................................................... 95
4.1.11 Security ................................................................................................................................ 95
4.1.12 Network Utilities .................................................................................................................. 99
4.1.13 RADIUS Configuration ........................................................................................................ 100
4.1.14 Tracing ............................................................................................................................... 107
4.1.15 Working with Objects and the Objects menu .................................................................... 111
4.1.16 Saving Configuration and the Service menu ...................................................................... 111
4.1.17 Time and Date Settings ...................................................................................................... 111
4.1.18 Firmware Upgrade via Web Interface ............................................................................... 111
4.1.19 Licence Renewal ................................................................................................................ 112
4.1.20 Help Menu ......................................................................................................................... 112
4.1.21 Password Configuration for Web Configurator Access ..................................................... 113
4.1.22 View Factory Settings and System Information ................................................................. 113
4.1.23 Configurator Exit ................................................................................................................ 114
4.2 Command Line, List of Supported Commands and Keys ................................................................ 114
4.2.1 System of Commands for SMG Gateway Operation in the Debug Mode ............................ 114
4.2.2 Tracing Commands Available Through the Debug Port ........................................................ 116
4.3 SMG Configuration via Telnet, SSH, or RS-232 ............................................................................... 116
Page 6

6 SMG digital gateway
4.3.1 List of CLI Commands ............................................................................................................ 117
4.3.2 Changing Device Access Password via CLI ............................................................................. 119
4.3.3 Statistics Mode ...................................................................................................................... 120
4.3.4 Management Mode .............................................................................................................. 123
4.3.5 General Device Configuration Mode..................................................................................... 125
4.3.6 СDR Configuration Mode ...................................................................................................... 128
4.3.7 Access Categories Configuration Mode ................................................................................ 130
4.3.8 E1 Stream Configuration Mode ............................................................................................. 130
4.3.9 Fail2ban Configuration Mode ............................................................................................... 134
4.3.10 Firewall Configuration Mode ............................................................................................. 135
4.3.11 SS7 Line Group Configuration Mode .................................................................................. 139
4.3.12 Modifier Table Configuration Mode .................................................................................. 141
4.3.13 Network Parameter Configuration Mode .......................................................................... 144
4.3.14 Numbering Schedule Configuration Mode ........................................................................ 149
4.3.15 Q.931 Timer Configuration Mode ...................................................................................... 153
4.3.16 RADIUS Configuration Mode .............................................................................................. 154
4.3.17 Static Route Configuration Mode ...................................................................................... 159
4.3.18 SIP/SIP-T General Configuration Mode .............................................................................. 159
4.3.19 SIP/SIP-T Interface Configuration Mode ............................................................................ 160
4.3.20 SS-7 Category Modification Configuration Mode .............................................................. 166
4.3.21 SS-7 Timer Configuration Mode ......................................................................................... 166
4.3.22 Sync Configuration Mode ................................................................................................... 168
4.3.23 Syslog Configuration Mode ................................................................................................ 168
4.3.24 Trunk Group and Trunk Direction Configuration Mode ..................................................... 170
5 APPENDIX A. CABLE CONTACT PIN ASSIGNMENT .................................................................................. 173
6 APPENDIX B. ALTERNATIVE METHOD OF DEVICE FIRMWARE UPDATE ................................................. 174
7 APPENDIX C. EXAMPLES OF MODIFIER OPERATION AND DEVICE CONFIGURATION VIA CLI ................. 177
8 APPENDIX D. CORRELATION BETWEEN ROUTING, SUBSCRIBERS, AND SIGNAL LINK PARAMETERS ..... 187
9 APPENDIX E. GUIDELINES FOR SMG OPERATION IN A PUBLIC NETWORK ............................................. 188
10 APPENDIX F. DEVICE INTERACTION WITH MONITORING SYSTEMS ....................................................... 189
11 APPENDIX G: CONFIGURATION OF E1 CHANNELS TRANSIT THROUGH A SEMIPERMANENT
CONNECTION ............................................................................................................................................... 192
12 TECHNICAL SUPPORT .............................................................................................................................. 197
13 ACCEPTANCE CERTIFICATE AND WARRANTY ......................................................................................... 198
Page 7

SMG digital gateway 7
INTRODUCTION
Today, means of communication employing state-of-the-art hardware and software solutions evolve
rapidly. New communication devices, which utilise alternative data transmission principles, pose a problem of
their integration into existing communication networks. The solution is to use special equipment, which
interconnects diverse segments of networks. Currently, such equipment is represented by digital gateways. They
allow gradual transition from existing communication networks to more efficient ones with alternative operation
principles.
At present, IP networks are considered to be the most efficient when they are weakly dependent from
data type and transmission medium and at the same time are flexible and manageable. Designed and
manufactured by Eltex, SMG digital gateway is intended for interfacing of traditional communication networks
based on the link switching principle with communication networks used for IP network data transmission.
This operation manual details main features of SMG-2 and SMG-4 digital gateways. The document
contains technical specifications of the gateway and its components. Also, it provides an overview of operation
and maintenance software-based procedures.
Page 8

8 SMG digital gateway
1 DEVICE DESCRIPTION
1.1 Purpose
The SMG trunk gateway is designed to interface signalling, PSTN (E1) media streams, and VoIP networks.
SMG is an optimal and robust solution that can be used to upgrade, develop, and migrate
telecommunication infrastructures from PSTN to NGN.
SMG Main Specifications
Number of E1 interfaces:
– for SMG-2: 1 or 2
1
;
– for SMG-4: 4.
Number of VoIP channels:
– for SMG-2: 104;
– for SMG-4: 128.
Maximum load intensity—40 cps.
Number of Ethernet ports:
– 1 port 10/100/1000BASE-T.
Static address and DHCP support.
IP telephony protocols: SIP, SIP-T, SIP-I.
TDM protocols: ISDN PRI(Q.931), QSIG, and CORNET for subscriber name transmission, SS-7
(quasi-associated mode operation).
DTMF transmission (SIP INFO, RFC2833, in-band).
Echo cancellation (G.168 recommendation).
Voice activity detector (VAD).
Comfortable noise generator (CNG).
Adaptive or fixed jitter buffer.
V.152 data transmission.
Fax transmission:
– G.711 pass through;
– T.38 UDP Real-Time Fax.
NTP support.
DNS support.
SNMP support.
ToS for RTP and signalling.
Firmware update: via web interface, CLI (Telnet, SSH, console (RS-232));
automatic update of firmware and device configuration.
Configuration and setup (also remotely):
– web interface;
– CLI (Telnet, SSH, console (RS-232)).
1
Only one E1 stream is available in an SMG-2 device by default. To activate another one, a special licence is required. For
more information about licences, see section 4.1.19. Licence Renewal
Page 9

SMG digital gateway 9
Remote monitoring:
– web interface;
– SNMP.
SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I Functions
RFC 2976 SIP INFO (for DTMF transmission);
RFC 3204 MIME Media Types for ISUP and QSIG (ISUP support);
RFC 3261 SIP;
RFC 3262 Reliability of Provisional Responses in SIP (PRACK);
RFC 3263 Locating SIP servers for DNS;
RFC 3264 SDP Offer/Answer Model;
RFC 3265 SIP Notify;
RFC 3311 SIP Update;
RFC 3323 Privacy Header;
RFC 3325 P-Asserted-Identity;
RFC 3372 SIP for Telephones (SIP-T);
RFC 3398 ISUP/SIP Mapping;
RFC 3515 SIP REFER;
RFC 3581 Symmetric Response Routing;
RFC 3665 Basic Call Flow Examples;
RFC 3666 SIP to PSTN Call Flows;
RFC 3891 SIP Replaces Header;
RFC 3892 SIP Referred-By Mechanism;
RFC 4028 SIP Session Timer;
RFC 4566 Session Description Protocol (SDP);
RFC 5806 SIP Diversion Header;
SIP Enable/Disable 302 Responses;
Q1912.5 SIP-I;
SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I interaction;
Delay offer;
SIP OPTIONS Keep-Alive (SIP Busy Out).
1.2 Typical Applications
This manual describes several methods of SMG connection.
1.2.1 Interface for TDM and VoIP Network Signalling and Media Streams
In this configuration, the device allows connection of up to 4 E1 streams with various signalling (SS-7, ISDN
PRI/QSIG/CORNET) and service protocols for up to 128 uncompressed channels (G.711 codec), for up to
72 compressed channels (G.729 A / 20-80), or for 54 T.38 fax channels; maximum load intensity—40 cps.
The device connects to an IP network via 10/100/1000 BASE-T network interface using SIP/SIP-T/ SIP-I
protocols.
Page 10

10 SMG digital gateway
Fig. 1.1—Interfacing of TDM and VoIP Network Signalling and Media Streams Using SMG-4
Fig. 1.2—Interfacing of TDM and VoIP Network Signalling and Media Streams Using SMG-2
Fig. 3 shows TDM and VoIP network interfacing and uses interaction between МС240 digital PBX and
ECSS-10 software switch as an example.
Fig. 1.3—Interfacing of TDM and VoIP Network Signalling and Media Streams
Fig. 4 shows scheme of semi-permanent connection over E1 channels through an Ethernet network.
Fig. 1.4 - Semi-permanent connection over E1 channels trough an Ethernet network
1.3 Device Design and Operating Principle
SMG has a submodule architecture and contains the following elements:
Page 11

SMG digital gateway 11
A controller featuring:
a controlling CPU,
flash memory of 64 MB,
512 MB RAM;
М4Е1 submodule of E1 streams;
SM-VP-M200 IP submodule for SMG-2;
SM-VP-M300 IP submodule for SMG-4;
a phase-lock-loop (PLL) frequency control system.
See the SMG functional chart in Fig. 4.
Fig. 1.5—SMG Functional Chart
In the TDM-IP direction, a signal coming to E1 streams is transferred to VoIP submodule audio codecs (a
line of 128 TDM channels) via the intrasystem backbone to be encoded using one of the selected standards and
further transferred as digital packets to the central processing unit. In the IP-TDM direction, digital packets are
transferred to the VoIP submodule to be decoded and further transferred to E1 streams via the intrasystem
backbone.
External 2 Mbps E1 streams are transmitted to framers through matching transformers. At that,
synchronisation signal is extracted from the stream and fed to the common synchronisation line of the device.
Synchronisation line priority is managed at the software level according to the defined algorithm.
See Fig. 5 for device firmware architecture.
Page 12

12 SMG digital gateway
Fig. 1.6—SMG firmware architecture
1.4 Main Specifications
The main specifications of the terminal are provided in the following tables:
Table 1.1 —Main Specifications
VoIP Protocols
Supported protocols
SIP-Т/SIP-I
SIP
T.38
Audio Codecs
Codecs
G.711 (A/U)
G.729 AB
G.723.1 (6.3 Kbps, 5.3 Kbps)
G.726 (32 Kbps)
CLEARMODE (RFC 4040)
Number of VoIP Channels Supported by a Submodule Depending on the Codec Type
Codec/packetisation time, ms
Number of channels
SMG-2/SMG-4 with SM-VP-M300
submodule
SMG-2 with SM-VP-M200
submodule
G.711 (A/U) / 20-60
G.711 (A/U) / 10
G.729 A / 20-80
G.729 A / 10
G.723.1 (6.3 Kbps, 5.3 Kbps)
G.726 / 20
G.726 / 10
Т.38
128
112
72
62
58
98
88
54
104
74
48
41
39
65
59
36
Electrical Ethernet Interface Specifications
No. of interfaces
1
Electric port
RJ-45
Data transfer rate, Mbps
Auto detection, 10/100/1000 Mbps,
duplex
Page 13

SMG digital gateway 13
Supported standards
10/100/1000BaseT
Console Parameters
RS-232 serial port
Data transfer rate, bps
115200
Electric signal parameters
Acc. to ITU-T V.28 guidelines
E1 Interface Parameters
No. of interfaces
SMG-4
SMG-2
4
1 or 2
2
Electric port
RJ-48
No. of channels
Acc. to ITU-T G.703 and G.704 guidelines
Line data transfer rate
2,048 Mbps
Line code
HDB3, AMI
Output signal to the line
3.0 V peak for 120 Ω load
2.37 V peak for 75 Ω load
(acc. to CCITT G.703 guidelines)
Input signal from the line
from 0 to -6 dB in relation to the standard output
impulse
Elastic buffer
2 frame capacity
Signalling protocol
ISDN PRI (Q.931), QSIG and CorNet to transmit user
name, SS-7
General Parameters
Operating temperature range
from +5°C to 40°C
Relative humidity
up to 80%
Power voltage
12 V DC, 2 А power adapter
Power consumption
not more than 10 W
Dimensions (W x H x D)
187x124x32
Net weight
0.3 kg
Gross weight
0.5 kg
2
Only one E1 stream is available in an SMG-2 device by default. To activate another one, a special licence is required. For
more information about licences, see section 4.1.19. Licence Renewal
Page 14

14 SMG digital gateway
1.5 Design
SMG trunk gateway is enclosed in 187x124x32 mm plastic casing.
For external view of the device panels, see Fig. 6, 7a, and 7b.
Fig. 1.7—SMG External View. Top and Side Panels
Fig. 1.8—SMG-4 External View. Rear Panel
Fig. 1.9—SMG-2 External View. Rear Panel
For ports, LEDs, and controls located on the device, see Table 2.1.
Page 15

SMG digital gateway 15
Table 2.1—Description of Ports, LEDs, and Controls Located on the Front Panel
№
Panel Element
Description
Top panel. Operation indicators
1
Power
Power indicator
2
LAN
Network activity indicator
3
USB
USB operation indicator
4
Alarm
Device critical failure indicator
5
Status
Device operation indicator
6
Sync
Synchronisation indicator
7
E1 0..3
E1 stream operation indicator; E1 2 and E1 3 LEDs are inactive
for SMG-2
Side panel. Function button
8 F Function button
Rear panel. Ports and controls
9
ON/OFF
On/off button
10
12V
Power socket (for connection to power line via the supplied
adapter)
11
LAN 10/100/1000
1 RJ-45 port for Ethernet 10/100/1000 Base-T interface
12
USB
USB port for external storage device
13
Console
RJ-45 console port for local device administration (for
connector wiring, see Appendix A)
14
E1 0..3 (for SMG-4)
4 x RJ-48 ports for Е1 streams (for connector wiring, see
Appendix A)
E1 0..1 (for SMG-2)
2 x RJ-48 ports for Е1 streams3 (for connector wiring, see
Appendix A)
1.6 LED Indication
The current status of the device is shown by the Power, LAN, USB, Alarm, Status, Sync, and E1 indicators
located on the top panel.
Indicator statuses are listed in Tables 3.1 and 3.2.
Table 3.1—LED Indication of the Device Status in Operation
LED
LED Status
Device Status
Power
Off
No power supply from 12 V adapter
Solid green
12 V power supplied to the device
LAN
Off
Link lost
Solid green / blinking green
Port is in the 10/100Base-TX mode
Solid yellow / blinking yellow
Port is in the 1000Base-T mode
USB
Off
USB device is not connected
Solid green
A high-speed USB device is connected
Solid red
A low-speed USB device is connected
Alarm
Blinking red
Critical device failure
3
Only one E1 stream is available in an SMG-2 device by default. To activate another one, a special licence is required. For
more information about licences, see section 4.1.19. Licence Renewal
Page 16

16 SMG digital gateway
Solid red
Non-critical device failure
Solid yellow
Non-critical warnings, no failures
Solid green
Normal operation
Status
Solid green
Normal operation
Off
Device power lost
Sync
Off
Synchronisation sources not defined
Solid green
Synchronisation from source available
Solid red
Synchronisation from source unavailable
Table 3.2—LED Indication During Device Startup and Reset to Factory Defaults
No.
LED
Reset to Factory Defaults
(Device Is On)
Sync
Alarm
Status
1
Yellow
Yellow
Yellow
Press the F button and hold for 1 second until the following
pattern appears, then release the button. The device reboot
will start in 3 seconds.
2
Off
Off
Yellow
The device is powered on, the operating system is not loaded.
3
Off
Green
Green
The gateway operating system is being loaded. When the
pattern appears, press the F button and hold it for 40–
45 seconds to change network parameters and restore the
device configuration to factory defaults.
4
Off
Yellow
Yellow
When the pattern appears, release the F button.
After a while, the following message will be displayed in the
console.
<<<BOOTING IN SAFE-MODE.RESTORING DEFAULT
PARAMETERS>>>
Reset to factory defaults is complete.
The device can also be reset to factory defaults during startup.
Skip step 1 in this case.
Ethernet interface status is also shown by LED indicators built in the 1000/100 connector.
Table 3.3—LED Indication for Ethernet 1000/100 Interfaces
Device Status
LED/Status
Yellow LED 1000/100
Green LED 1000/100
The port is in the 1000Base-T mode, no data transfer
Solid on
Solid on
The port is in the 1000Base-T mode, data transfer
Solid on
Blinking
The port is in the 10/100Base-TX mode, no data transfer
Off
Solid on
The port is in the 10/100Base-TX mode, data transfer
Off
Blinking
Table 3.4 shows E1 streams indication.
Page 17

SMG digital gateway 17
Table 3.4—Е1 Indication
Stream Status
E1 Indicator
Red
Yellow
Green
Е1 is disabled in the gateway configuration
Off
Off
Off
E1 stream failure
Blinking
(200 ms)
Off
Off
Loss of signal (LoS)
On
Off
Off
AIS failure
Blinking
(200 ms)
Blinking
(200 ms)
Off
LOF failure
Blinking
(200 ms)
Off
Off
LOMF failure
Blinking
(200 ms)
Off
Off
E1 stream normal operation
Off
Off
On
Failure on a remote host (RAI)
Off
On
Off
E1 stream is in operation, the stream has slips
Off
Blinking
(500 ms)
Blinking
(500 ms)
E1 stream is being tested
Blinking
(200 ms)
Off
Blinking
(200 ms)
Table 3.5 provides a detailed description of the failures shown by the Alarm indicator.
Indication of CDR Files Saving
When the FTP server is not available, CDRs will be saved to the device RAM. 30 MB are allocated
for storing CDR files. If the memory is full up to a specified value, a fault will be indicated.
Table 3.5—Alarm Indication
Alarm LED Status
Fault Level
Fault Description
Blinking red
Critical failure
Configuration error
Connection with SIP module lost
SS-7 line group fault (when the Fault indication checkbox is checked in the
Routing/SS line groups menu)
E1 stream fault (when the Alarm indication checkbox is checked in the Е1
streams/Physical parameters menu)
FTP server is unavailable, RAM utilisation for storing CDR files exceeds 50%
(15–30 MB)
CPU temperature exceeds 100 ºС
Less than 25 MB free RAM (5%)
Free storage on a connected USB drive is less than
- 5% of the total capacity (for drives with less than 5 GB storage),
- 256 MB (for drives with more than 5 GB storage)
Opposing SIP device does not respond to OPTIONS queries, when regular
checks by OPTIONS messages are enabled
setting up of semi-permanent connection over E1 channel failed
Solid red
Non-critical
failure (errors)
SS-7 link fault (when the Fault indication checkbox is checked in the
Routing/SS line groups menu)
Page 18
18 SMG digital gateway
Synchronisation fault (free-run mode operation)
FTP server is unavailable, RAM utilisation for storing CDR files is less than 50%
(5–15 MB)
No connection to one of the SM-VP-300 modules
CPU temperature reached 90 ºС
Less than 50 MB free RAM (10%)
Free storage on a connected USB drive is less than
- 10% of the total capacity (for drives with less than 5 GB storage),
- 512 MB (for drives with more than 5 GB storage)
CPU load is about or above 95% during the last 9 seconds
Solid yellow
Warnings
E1 stream remote fault
E1 stream slipping
Synchronisation from a lower priority source (a higher priority one is not
available)
FTP server is unavailable, RAM utilisation for storing CDR files is below 5 MB
CPU temperature reached 85 ºС
Less than 128 MB
free RAM (25%)
CPU load is about or above 90% during the last 9 seconds
Free storage on a connected USB drive is less than
- 15% of the total capacity (for drives with less than 5 GB storage),
- 1,024 MB (for drives with more than 5 GB storage)
1.7 The F Function Button
The F button allows device reboot, restoration to factory configuration, and recovery of forgotten
password.
For instructions on reset of an operating device to factory defaults, see Table 3.2.
When the factory configuration is restored, the device can be accessed by IP address 192.168.1.2 (mask
255.255.255.0):
– via telnet or console: login: admin, password: rootpasswd;
– via web interface: login: admin, password: rootpasswd.
After that, saving the factory configuration, restoring a password, or rebooting the device can be
performed.
Saving Factory Configuration
To save the factory configuration: connect via telnet or console using admin for login and rootpasswd for
password; enter the sh command (the device will switch from the CLI mode to the SHELL mode), enter the save
command, and restart using the reboot command. The gateway will be restarted with the factory configuration.
********************************************
* Welcome to SMG-4 *
********************************************
smg login: admin
Password: rootpasswd
********************************************
* Welcome to SMG-4 *
********************************************
Welcome! It is Thu Aug 21 11:40:40 GMT+6 2014
SMG4> sh
Page 19

SMG digital gateway 19
/home/admin # save
tar: removing leading '/' from member names
*Saved successful
New image 1
Restored successful
/home/admin # reboot
Password Recovery
To recover a password: connect via telnet, SSH, or console, enter the sh command (the device will switch
from the CLI mode to the SHELL mode), enter the restore command (the current configuration will be restored),
enter the passwd command (the device will request to enter and confirm a new password), enter the save
command, and restart using the reboot command. The gateway will be restarted with the current configuration
and the new password.
If the device is rebooted without any additional operations, the current configuration will be restored on
the device without password recovery. The gateway will be restarted with the current configuration and the old
password.
********************************************
* Welcome to SMG-4 *
********************************************
smg login: admin
Password: rootpasswd
********************************************
* Welcome to SMG-4 *
********************************************
Welcome! It is Thu Aug 21 11:40:40 GMT+6 2014
SMG4> sh
/home/admin # restore
Welcome! It is Fri Jul 2 12:57:56 UTC 2010
SMG4> sh
/home/admin # restore
New image 1
Restored successful
/home/admin # passwd admin
Changing password for admin
New password: 1q2w3e4r5t6y
Retype password: 1q2w3e4r5t6y
passwd: password for admin is changed
/home/admin # save
tar: removing leading '/' from member names
*Saved successful
New image 1
Restored successful
/home/admin # reboot
1.8 Delivery Package
SMG standard delivery package includes:
SMG-2 or SMG-4 trunk gateway,
power adapter,
operation manual and documentation package.
Page 20

20 SMG digital gateway
1.9 Safety Instructions
1.9.1 General Guidelines
Any operations with the equipment should comply to the Safety Rules for Operation of Customers'
Electrical Installations.
Operations with the equipment should be carried out only by personnel authorised in accordance
with the safety requirements.
Before operating the device, all engineers should undergo special training.
The device should only be connected to properly functioning supplementary equipment.
The SMG trunk gateway can be used 24/7 provided the following requirements are met:
– Ambient temperature from 0 to +40°C.
– Relative humidity up to 80% at +25°C.
– Atmosphere pressure from 6.0 х 10
4
to 10.7х104 Pa (from 450 to 800 mm Hg).
The device should not be exposed to mechanical shock, vibration, smoke, dust, water, and
chemicals.
To avoid components overheating, which may result in device malfunction, do not block air vents
or place objects on the equipment.
1.9.2 Electrical Safety Requirements
Prior to turning the device on, check that all cables are undamaged and securely connected.
Before dismantling and assembling the device, make sure the power supply is disabled.
Page 21

SMG digital gateway 21
2 SMG INSTALLATION
Check the device for visible mechanical damage before installing and turning it on. In case of any damage,
stop the installation, fill in the corresponding document, and contact your supplier.
If the device has been exposed to low temperatures for a long time before installation, leave it for 2 hours
at ambient temperature prior to operation. If the device has been exposed to high humidity for a long time,
leave it for at least 12 hours in normal conditions prior to turning it on.
2.1 Startup Procedure
1. Connect stream (E1) and Ethernet cables to corresponding gateway connectors.
2. Connect the power adaptor to the device.
3. Turn the device on and check the front panel LEDs to make sure the terminal is in normal
operating conditions.
2.2 Opening the Casing
Prior to proceed, disable SMG power supply and disconnect all cables.
Fig. 2.1—Opening the Casing
1. Use a screwdriver to remove 4 screws holding the bottom panel of the device as shown in the
figure.
2. Pull the top panel (cover) of the device to remove it.
To assemble the device, repeat all the steps above in the reverse order.
Page 22

22 SMG digital gateway
2.3 RTC Battery Replacement
RTC (an electric circuit designed for independent chronometric data metering—current time, date, day of
the week, etc.) installed on the device plate has a battery with the following specifications:
Battery type
Lithium
Form-factor
CR2032 (CR2024 option is possible)
Voltage
3 V
Capacity
225 mA
Diameter
20 mm
Thickness
3.2 mm
Battery life / expiration date
5 years
Storage conditions
-20 to +35 °С
Fig. 2.2—Battery Location in RTC
If battery life is expired, replace the battery with a new one to ensure correct and continuous operation of
the equipment. The replacement procedure is as follows:
1. Check if the device is energised.
2. If the voltage is present, disconnect the power supply.
3. Open the device casing (see section 2.2 Opening the Casing).
4. Remove the exhausted battery from the reverse side of the plate (Fig. 17) and install a new one in
the same position.
To assemble the device, repeat all the steps above in the reverse order.
If NTP synchronisation is disabled, the system date and time will require adjustment after
RTC battery replacement.
Used batteries should be recycled according to requirements.
Page 23

SMG digital gateway 23
3 GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR GATEWAY OPERATION
The easiest way to configure and monitor the device is to use the web interface, so it is highly
recommended.
To prevent unauthorised access to the device, it is recommended to change the password for telnet and
console access (default username: admin, password: rootpasswd) and the administrator password for the web
interface. For information on password configuration for telnet and console access, see section 4.3.2 Changing
Device Access Password via CLI. For information on password configuration for web interface access, see
section 4.1.21. It is recommended to write down and store the configured passwords in a safe place, inaccessible
for intruders.
In order to prevent the loss of device configuration data, e. g. after reset to factory defaults, it is
recommended to make configuration backups and save them on a PC each time significant changes are made.
Page 24
24 SMG digital gateway
4 DEVICE CONFIGURATION
The device provides 4 connection options: web interface, the Telnet protocol, SSH, or RS-232 cable
connection (for access via RS-232, SSH, or Telnet, use CLI).
All settings will take effect without gateway restart. To save configuration changes into the nonvolatile memory, use the Service/Save Configuration into Flash menu in the web configurator or
the COPY RUNNING_TO_STARTUP command in CLI.
4.1 SMG Configuration via web Interface
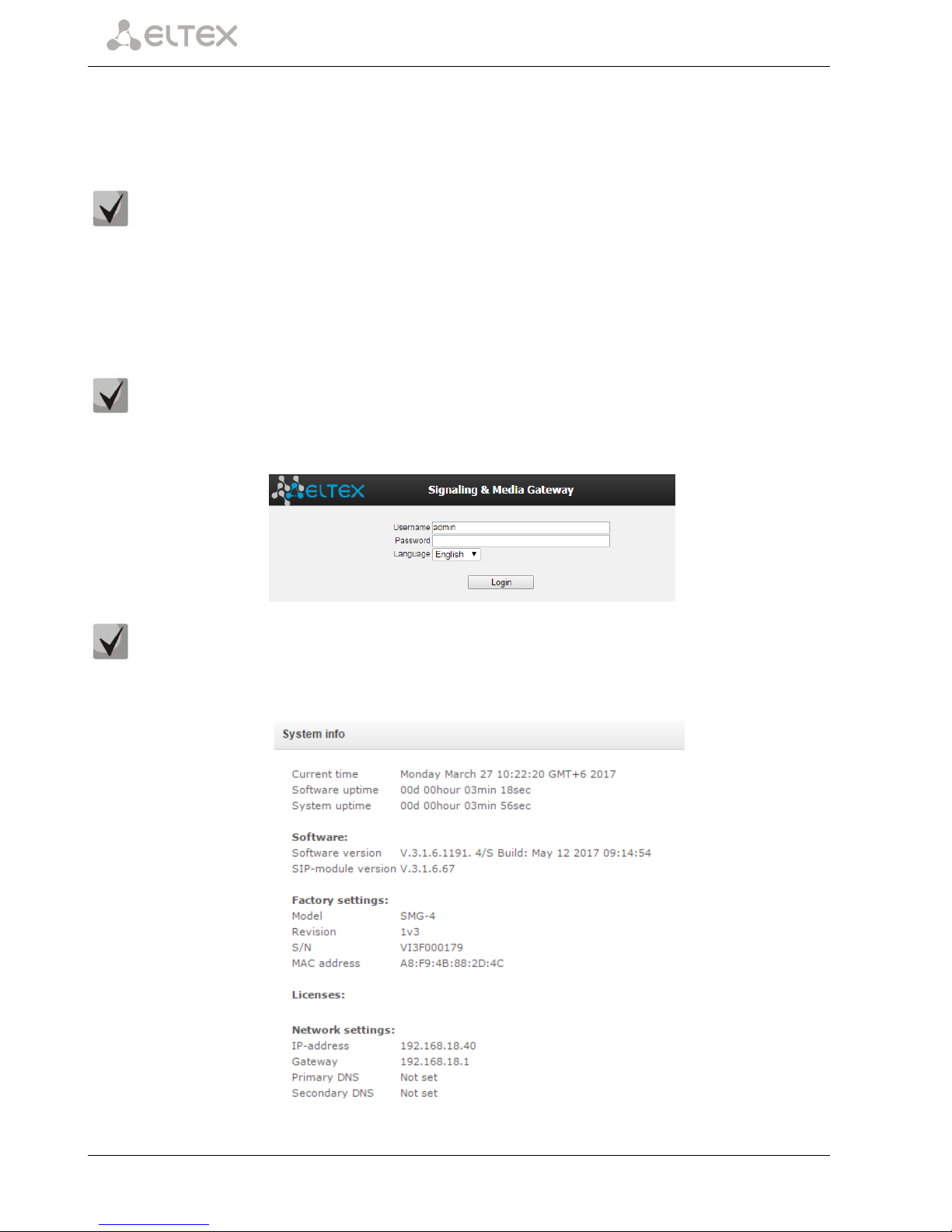
To configure the device, establish a connection to the device in a web browser (hypertext document
viewer), e. g. Firefox, Google Chrome. Enter the device IP address in the address bar of the web browser.
SMG factory default IP address: 192.168.1.2, network mask: 255.255.255.0.
As soon as the IP address is entered, the device will request username and password.
Initial startup username: admin, password: rootpasswd.
Upon access to the web configurator, the System Information menu opens.
Page 25

SMG digital gateway 25
The figure below illustrates navigation in the web configurator.
A window in user interface is divided into several areas.
Navigation tree
– enables management of the settings field. The navigation tree represents a
hierarchy of management sections and nested menus.
Settings field
– is defined by user selections. Allows user to view device settings and enter
configuration data.
Control panel
– a panel to control the settings field and firmware status.
Control menu
– drop-down menus in the control panel for the settings field and firmware status.
Alarms
– displays the current highest-priority fault and serves as a link to work with the fault
events log.
Authorisation
– a link to work with passwords, which are used to access the device via web
interface.
Control icons
– controls to work with objects in the settings field; duplicate the Objects menu of the
control panel:
– Add Object;
— Edit Object;
— Remove Object;
— View Object.
Control buttons
– controls to work with the settings field.
To prevent unauthorised access to the device during further work, it's recommended to change the
password (see section 4.1.21).
Page 26

26 SMG digital gateway
The button (Hint) located next to the editing element provides an explanation for a
particular parameter.
4.1.1 System Parameters
System Settings
Device name (for web pages only)—the device name used in the heading of the web configurator.
Active dial plan count —the quantity of simultaneously active numbering schedules; up to
16 independent numbering schedules can be configured with a possibility to add subscribers and
create a customised call routing table.
Alarm Indication
CPU load —when checked, the control system will be alerted about high CPU utilisation.
RAM usage—when checked, the control system will be alerted when running out of free RAM.
Local disk drive free space—when checked, the control system will be alerted when running out of
free memory on an external drive.
Auto configuration (Automatic Configuration)
Active auto-update—enables automatic updates of firmware and configuration.
Source—a method to receive parameters for automatic updates:
– Static—use automatic update parameters set in the configuration;
– DHCP—select a network interface with the configured DHCP protocol, which will be used
to retrieve Options 66 and 67 for automatic updates.
Page 27

SMG digital gateway 27
Protocol—a protocol, which will be used for automatic updates (TFTP/FTP/HTTP/HTTPS).
Authentication—setting the flag enables authentication during automatic updates via the selected
protocol (FTP/HTTP/HTTPS).
Name—a login to access the automatic update server.
Password—a password to access the automatic update server.
Server—IP address or network name of the automatic update server when the static source is
selected; update.local name is used by default.
Update configuration—specifies to use automatic configuration updates.
Configuration file name—name and path to the configuration file located on the automatic update
server; MAC.cfg by default, where MAC is the MAC address of the device in the xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx
format.
Configuration upgrade period, min—time interval in minutes between requests for a configuration
file sent to the automatic update server.
Software update—enables automatic firmware updates.
Software version file name—name of the manifest file on the automatic update server that
contains a description of the firmware version, a path to the firmware file, and time of firmware
update.
Software upgrade period, min—time interval in minutes between requests for a manifest file on
the automatic update server.
4.1.1.1 Format of Options 66 and 67
Option 66 is required to retrieve the IP address or domain name of the automatic update server.
Syntax:
“<IP address or domain name of the update server>“
Example:
“update.local“
or
“192.168.1.3“
Option 67 is required to retrieve the path to the file with firmware version description (the manifest file)
and the path to the configuration file.
Syntax:
“<Path to smg4.manifest (or smg2.manifest) file>;<Path and name of the configuration file>“
Example:
“/smg4/firmware/smg4.manifest;/smg4/conf/<MAC>.cfg“
“/smg2/firmware/smg2.manifest;/smg2/conf/<MAC>.cfg”
If a device receives a configuration file name in the format "<MAC>.cfg" from the server, it automatically
replaces <MAC> with its own MAC address in the format 11.22.33.44.55.66 when addressing the server. This
means that the server should contain a configuration file named 11.22.33.44.55.66.cfg.
Page 28

28 SMG digital gateway
Instead of using the expression "<MAC>.cfg", the server may send the configuration file name in the
following format: 11.22.33.44.55.66.cfg, where 11:22:33:44:55:66 is the factory MAC address of the device.
If no Options 66 and 67 are received from the DHCP server, their default values will be used.
For Option 66: "update.local".
For Option 67: "smg4.manifest;<MAC>.cfg";
"smg2.manifest;<MAC>.cfg".
4.1.1.2 smg4.manifest (smg2.manifest) File Format
smg4.manifest (smg2.manifest) is a text file containing information about the version and the path to the
firmware file located on the automatic update server, as well as the time to restart the device after firmware
update to a new version.
General format of the file content:
<firmware version>;<path to firmware file>; <time (in hours)>
The <firmware version> and <path to firmware file> parameters are mandatory. The <Time> parameter is
optional. If it is not specified, the device will restart as soon as there are no conversation sessions.
Example of a file with time set:
3.1.1.1076;smg4/smg4_firmware_3.1.1.1076.bin;18-21
Example of a file without time set:
3.1.1.1076;smg4/smg4_firmware_3.1.1.1076.bin
4.1.1.3 Algorithm of Automatic Configuration Loading and Checking for a New Configuration File
This procedure is used for automatic download of a new device configuration file from the server. The
configuration file contains the date and time of its creation:
SMG-config:
Version: 13
LastUpdate:
ID: 1
Date: 2015-03-30
Time: 05:59:28
While loading, SMG checks for a configuration file in the specified location on the FTP/TFTP/HTTP/HTTPS
sever (and authorises on the server if necessary). If it finds the configuration file, the gateway downloads it and
compares the creation date and time of the current file and the downloaded one's. If the downloaded file is
created later, the device saves and applies the new configuration. Otherwise, the current configuration remains
valid.
Thus, to change the gateway configuration, operator simply needs to upload a new configuration file to
the server with necessary adjustments and new date and time of creation. The configuration will be updated
automatically after the time set in the Configuration update period parameter.
Page 29

SMG digital gateway 29
4.1.1.4 Algorithm of Automatic Software Updating and Checking for New Firmware Versions
During SMG loading or after the time set in Firmware update period elapses, the gateway checks for a
version description file (smg4.manifest/smg2.manifest) in the specified location on the server. If the file is found,
SMG downloads it. The file contains information on firmware file versions available on the server, their locations
and names, as well as (optional) the time period before device restart after update. If firmware versions on the
server differ from the current ones on the gateway, the device checks for active conversation sessions. If there
are none, the gateway downloads the firmware image specified in the smg4.manifest/smg2.manifest file and
updates the firmware. After the firmware update, the gateway checks for active voice sessions and restarts if
finds none. Otherwise, a 30 seconds timer starts. When the time runs out, the gateway checks for active
conversation sessions again. If the manifest file specifies a time period for restart, a timer starts for this period.
For example, if the file specifies 18–21, the device waits till 18:00 to check for active voice sessions. If it finds
none, the gateway restarts; otherwise, the 30 seconds timer starts. When the time runs out, the gateway checks
for active conversation sessions again.
Page 30

30 SMG digital gateway
4.1.2 Monitoring
4.1.2.1 Telemetrics
This section contains information on the temperature sensors and CPU utilisation.
Temperature sensors
TempSensor #0—CPU temperature.
TempSensor #1—switch temperature.
Current CPU Utilisation
USR—percentage of CPU time utilisation by user applications.
SYS—percentage of CPU time utilisation by core processes.
NIC—percentage of CPU time utilisation by applications with a modified priority.
IDLE—percentage of unused CPU resources.
IO—percentage of CPU time spent on I/O operations.
IRQ—percentage of CPU time spent on processing of hardware interruptions.
SIRQ—percentage of CPU time spent on processing of software interruptions.
Page 31

SMG digital gateway 31
4.1.2.2 E1 Stream Monitoring
This section4 contains information on the chip installed in the M4E1 submodule, as well as on E1 stream
monitoring and statistics.
M4E1 Submodule Info—information about chip name and identifier.
Stream Parameters
State—stream status:
– WORK—stream in operation;
– LOS—signal lost;
– OFF—stream is disabled in configuration;
– NONE—submodule not installed;
– AIS—alarm state indication signal (signal that contains all units);
– LOMF—multi-frame alarm state indication signal;
– RAI—remote alarm indication;
– D channel status—status of D-channel, service management channel;
– up—D-channel is in operation;
– down—D-channel is not in operation;
– no—there is no management channel for the stream;
– off—signalling is disabled for the stream.
D-channel state - state of D channel, service management channel
– up- D-channel is in operation
– down - D-channel is not in operation
– no- there is no management channel for the stream
– off - signalling is disabled for the stream
Statistics collection time, sec—time for statistics collection in seconds.
4
Only one E1 stream is available in an SMG-2 device by default. To activate another one, a special licence is required. For
more information about licences, see section 4.1.19. Licence Renewal
Page 32

32 SMG digital gateway
Slip up—number of positive bit slips for the stream.
Slip down—number of negative bit slips for the stream.
RX bytes—number of bytes received from the stream.
TX bytes—number of bytes sent to the stream.
Short packets—number of received packets of a smaller size than the standard one.
Big packets—number of received packets of a larger size than the standard one.
RX Overflow—buffer overrun error counter.
CRC errors—CRC error counter.
TX underrun—stream transmission failure counter.
Code violations counter—signal code sequence failure counter.
CRC Error Counter / PRBS—number of CRC errors (in the PRBS test mode).
Bit error rate—number of bit errors for the stream.
Select—when checked, clicking the Reset Counters button will clear the collected statistics.
Remote loop—Е1 path test mode, where the signal received by the unit from the connected Е1
stream is transmitted directly in the same stream.
PRBS test—enables pseudorandom sequence output to the output port of the unit (transmitted
into the connected Е1 stream); at that, the error detection mode will be enabled at the unit input
port (Е1 stream reception) for this sequence in order to evaluate the signal transmission quality.
The number of errors and analysis time counter will be displayed in the stream information
window.
PRBS test and local loop—Е1 path test mode, where external line is disabled and the signal
transferred by the unit is transmitted directly in the input of the same unit. Pseudorandom
sequence output will be enabled to the unit output port; the input port will operate in the error
detection mode.
Stop test—disables the test mode.
4.1.2.3 E1 Channel Monitoring
This section5 contains information on E1 stream channel status.
5
Only one E1 stream is available in an SMG-2 device by default. To activate another one, a special licence is required. For
more information about licences, see section 4.1.19. Licence Renewal
Page 33

SMG digital gateway 33
Stream State
State—stream status:
NONE—М4Е1 submodule is missing;
OFF—stream is disabled in configuration;
ALARM—M4E1 submodule initialisation error;
LOS—signal lost;
AIS—alarm state indication signal (signal that contains all units);
LOF—loss of frame;
LOMF—multi-frame alarm state indication signal;
WORK/RAI—remote alarm indication;
WORK/SLIP—SLIP indication for the stream;
WORK—stream in operation;
TEST—stream test indication (PRBS test, local or remote loop).
Channel State
State—channel status:
OFF—channel is disabled in configuration;
Idle—channel is in initial state;
Block—port is blocked;
Incoming dialing—incoming call dialling;
Outgoing dialing—outgoing call dialling;
Incoming alerting—incoming engagement, callee is disengaged;
Outgoing alerting—outgoing engagement, callee is disengaged;
Busy, Release—channel release, sending the busy tone;
Talk, Hold—channel is in the call state, on hold;
Page 34

34 SMG digital gateway
Waiting—waiting for response from the opposite party (waiting for engagement
acknowledgement, waiting for Caller ID, waiting for call dialling).
Connection Information for Stream and Channel
Port/channel—this section is divided into two parts:
– signalling protocol (PRI/SS7);
– port location: stream #: channel #
Connected port/channel—this section is divided into two parts:
– linked port signalling protocol (PRI/SS7/VoIP);
– linked port location: stream #: PRI/SS7 channel # or VoIP submodule #: VoIP channel #.
Connected Callref—call identifier for the linked channel.
State—channel status:
– Off—channel is disabled;
– Block—port is blocked;
– Init—channel initialisation;
– Idle—channel is in initial state;
– In-Dial/Out-Dial—incoming/outgoing call dial;
– In-Call/Out-Call—incoming or outgoing engagement;
– In-Busy/Out-Busy—sending the busy tone;
– Talk—channel is in call state;
– Release—channel release;
– Wait-Ack—waiting for acknowledgement;
– Wait-CID—waiting for CgPN (Caller ID);
– Wait-Num—waiting for call dial;
– Hold—subscriber is on hold.
State timer—channel last known status duration.
Incoming SS7 category—SS7 category of an incoming call before modification.
Incoming CdPN—callee number before modification.
Incoming CgPN—caller number before modification.
Outgoing SS7 category—SS7 category of an incoming call after modification.
Outgoing CdPN—callee number after modification.
Outgoing CgPN—caller number after modification.
Channel status updates every 5 seconds.
4.1.2.4 CPU Utilisation Chart
This section contains information on CPU utilisation in real time (10-minute interval). Statistics charts are
based on average data for each 3-second device operation interval.
Page 35

SMG digital gateway 35
To navigate between specific parameters in monitoring charts, use the and buttons. To enhance
visual identification, all charts have different colours.
TOTAL—total percentage of CPU utilisation.
IO—percentage of CPU time spent on I/O operations.
IRQ—percentage of CPU time spent on processing of hardware interruptions.
SIRQ—percentage of CPU time spent on processing of software interruptions.
USR—percentage of CPU time utilisation by user applications.
SYS—percentage of CPU time utilisation by core processes.
NIC—percentage of CPU time utilisation by applications with a modified priority.
4.1.2.5 VoIP Submodule Monitoring
This section contains information on installed SM-VP submodules and their channel status.
No—SM-VP submodule serial number (SMG allows installation of only one VoIP submodule).
Type—installed submodule type.
State:
– Not Present—not installed;
– No init—not initialised, no initialisation attempts;
– Off—disabled, starting to load submodule;
– Wait Ack—waiting for acknowledgement from CPU after submodule loading;
– Failed—no response from submodule;
– Work—submodule is in normal operation;
– Recovery—no control packets coming from submodule;
Active count—the number of submodule active connections at the given moment;
Payload—percentage of submodule resource utilisation at the given moment.
To monitor the status of channels, select a submodule in the table and press the Channel Monitoring
button.
Page 36

36 SMG digital gateway
Channel Connection Information
Port/channel—port/channel data:
– signalling protocol (VoIP);
– port location: VoIP submodule #: channel #.
Callref—call identifier.
Connected port/channel— data on the linked port/channel:
– linked port signalling protocol (PRI/SS7/VoIP);
– linked port location: stream #:channel # for PRI/SS7 or VoIP submodule #:VoIP channel #.
Connected Callref—call identifier for the linked channel.
State—channel status:
– Off—channel is disabled;
– Block—port is blocked;
– Init—channel initialisation;
– Idle—channel is in initial state;
– In-Dial/Out-Dial—incoming/outgoing call dial;
– In-Call/Out-Call—incoming or outgoing engagement;
– In-Busy/Out-Busy—sending the busy tone;
– Talk—channel is in call state;
– Release—channel release;
– Wait-Ack—waiting for acknowledgement;
– Wait-CID—waiting for CgPN (Caller ID);
– Wait-Num—waiting for call dial;
– Hold—subscriber is on hold;
State timer—channel last known status duration.
Incoming SS7 category—SS7 category of an incoming call before modification.
Incoming CdPN —callee number before modification.
Incoming CgPN —caller number before modification.
Outgoing SS7 category—SS7 category of an incoming call after modification.
Outgoing CdPN —callee number after modification.
Page 37

SMG digital gateway 37
Outgoing CgPN —caller number after modification.
Channel States
Idle (grey)—initial state, the channel is ready to serve a call.
Active (green)—active state, the channel is engaged with an active call.
Reserved (yellow)—the channel is reserved for service needs (sending the busy, ringback, PBX
response tones) or for a new call. Channels cannot be reserved in SGM.
To view detailed channel information, left-click to select a channel from the table.
Information on Channel IP Connection
State—channel state (see description above).
Codec—codec used (Payload Type is specified in square brackets).
Status—media information transmission status:
– Good—channel in operation;
– Loss of RTP—loss of the opposite RTP stream (when the time in RTP packet timeout
expires);
– VBD—communication is established through the channel in the data transmission mode;
– T38—fax connection using the Т.38 protocol is established through the channel.
Mode—media channel operation mode:
– sendrecv—channel operates in the duplex mode (receipt and transmission);
– sendonly—channel operates in the simplex mode, transmission only;
– recvonly—channel operates in the simplex mode, receipt only;
– inactive—channel is not active, receipt and transmission are inactive.
SSRC—the SSRC (Synchronisation Source) field value for the RTP stream outgoing from the device.
IP:port remote—remote IP address and port of the RTP stream source.
IP:port local—local IP address and port of the RTP stream source.
MAC remote—remote MAC address of the RTP stream source.
MAC local—local MAC address of the RTP stream source.
4.1.2.6 Alarm log
When a failure occurs, all related information containing the fault stream number, SS-7 line group, signal
link, or faulty module is displayed in the header of web interface. If there are multiple active failures, the header
of web interface will alert about the current most critical one.
When there are no alarms, the message "No alarms" will be displayed.
Alarm Message Examples
Alarm Message
Meaning
Configuration has not been read
Configuration file error
No communication with SIP module
Failure of a software module responsible for VoIP
operation
No communication with VoIP submodule #
SM-VP-300 submodule failure
SS-7 line group (linkset) No. is not in operation
SS-7 line group failure
Page 38

38 SMG digital gateway
E1 stream # failure
E1 stream failure
SS-7 link failure Link set #, E1 stream #
SS-7 link failure
Synchronisation with a local source. All specified
sources are inoperable
Synchronisation source is lost
E1 stream # remote fault
E1 stream remote fault
Synchronisation from a lower priority source
Primary synchronisation source is lost, the priority of the
current source is lower
Failed to send CDR files via FTP
Failure to send a CDR file to FTP server
Running out of operating memory
One of RAM utilisation limits has been reached
High CPU temperature
One of CPU temperature limits has been reached
High CPU utilisation
One of CPU utilisation limits has been reached
Transit over E1 stream
setting up of semi-permanent connection over E1 channel
failed
The Alarm events list menu contains a list of alarm events arranged by time and date.
Alarm Table
Clear—delete the existing fault events table.
№—fault sequential number.
Time—fault occurrence time (HH:MM:SS).
Date—fault occurrence date (DD/MM/YY).
Type—a fault type:
– CONFIG—a critical fault, a configuration file fault;
– SIPT-MODULE—a critical fault, a failure of a program module responsible for VoIP
operation;
– LINKSET—a critical fault, an SS-7 line group is not in operation;
– STREAM—a critical fault, an E1 stream is not in operation;
– SM-VP DEVICE—a fault, a SM-VP module failure;
– SS7 LINK—an SS-7 signal channel failure;
– SYNC—a synchronisation fault, a synchronisation source is missing;
– STREAM-REMOTE—a warning, a remote fault of an E1 stream;
– CDR-FTP—a fault or a warning, a failure to send a CDR file to the FTP server.
– TRANSIT – critical alarm, setting up of semi-permanent connection over E1 channel failed.
State—a fault state status:
critical alarm, LED blinking red—the fault requires immediate intervention of the service
personnel and affects device operation and provisioning of communication services;
alarm, red LED—non-critical fault, intervention of the service personnel is also required;
Page 39

SMG digital gateway 39
warning, yellow LED—the fault does not affect provisioning of communication services;
OK, green LED—the fault is resolved.
Parameters—detailed fault description.
4.1.2.7 Interface Monitoring
This section describes status monitoring for network interfaces and turning VPN/PPTP interfaces on and
off.
4.1.3 Synchronisation Sources
To synchronise the device with multiple sources, a priority list
algorithm has been implemented. The algorithm is as follows: when a
sync signal from the current source is lost, the system looks through
the list to find active signals from lower priority sources. When a
higher priority signal is restored, the system switches to that signal.
Also, there may be multiple sources of the same priority. When a
signal of the same priority is restored, the system does not switch to
that signal.
Up to 4 synchronisation sources are supported (from any of the
4 E1 streams).
To generate the list, use the following buttons:
—Add Source; —Remove.
To change the source priority, use the Up/Down buttons located next to each source. The highest
priority value is 0, the lowest priority value is 14.
Signal loss timeout, sec—time interval when the system does not switch to a lower priority
synchronisation source in case of a signal loss. If the signal is restored during this interval, the
system will not switch to a lower priority source.
Signal presence timeout, sec—time interval when the restored higher priority synchronisation
signal should be active for the system to switch to that signal.
If the PRI protocol is configured for the stream, from which the synchronisation signal is
received, then the PRI protocol should also be enabled for the connected stream at the other
side. Otherwise, the synchronisation signal will not be received from the stream, which will
cause slips.
Page 40

40 SMG digital gateway
4.1.4 CDR
This section describes parameters configuration to save call detail records.
CDR is a call detail record, which allows the system to save the history of calls performed through SMG.
CDR Saving Parameters
Enable CDR—when checked, the gateway will generate CDRs.
Saving period: Days, Hours, Minutes—time period for CDR generation and saving in the device
RAM.
Add header—when checked, the following header will be written at the beginning of the CDR file:
SMG4. CDR. File started at "YYYYMMDDhhmmss", where "YYYYMMDDhhmmss" is the records
saving start time.
Signature—specifies a distinctive feature to identify the device, which created the record.
Page 41

SMG digital gateway 41
FTP server settings
Store files on FTP—when checked, CDRs will be transferred to FTP server
Server address/hostname—FTP server IP address
Server port—FTP server TCP port
Path on server—defines path to FTP server folder for CDR storage
Login—username for FTP server access
Password—user password for FTP server access
Settings of Redundant FTP Server
Save files on FTP—when checked, CDRs will be transferred to a redundant FTP server.
Server address/hostname—IP address of the redundant FTP server.
Server port—TCP port of the redundant FTP server.
Path on server—a path to the redundant FTP server directory to store CDRs.
Login—username for access to the redundant FTP server.
Password—user password for access to the redundant FTP server.
When the FTP server is not available, CDRs will be saved to the device RAM. 30 MB are allocated
for storing CDR files. If the memory is full up to a specified value, a fault will be indicated. For
CDR file saving indication, see section 1.6 LED Indication.
When a certain alarm level is reached, the system sends the corresponding SNMP trap.
Other Settings
Save unsuccessful calls—when checked, stores unsuccessful calls (not resulted in conversation)
into CDR files.
Save empty files—when checked, saves CDR files containing no records.
Write redirecting number—when checked, an additional field, Redirecting Number, is added to
CDR; otherwise, the additional Redirecting Number field will not be added when a call is
redirected, and the number which originated the redirection will be saved into the Calling Party
Number parameter.
Write redirecting mark—when checked, CDR will contain an additional field, Redirection Tag.
Write call category—when checked, CDR will contain an additional field, Calling Party Category.
Modifiers for incoming numbers
Incoming number modifiers are the modifiers, which modify any CDR fields containing subscriber numbers
and apply to these fields before a call proceeds through a numbering schedule.
CdPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the callee number received from the
incoming channel.
CgPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the caller number received from the
incoming channel.
RedirPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the number of the subscriber, which
redirected the call received from the incoming channel.
Page 42

42 SMG digital gateway
Modifiers for outgoing numbers
Outgoing number modifiers are the modifiers, which modify any CDR fields containing subscriber numbers
and apply to these fields after a call proceeds through a numbering schedule.
CdPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the callee number sent to the outgoing
channel.
CgPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the caller number sent to the outgoing
channel.
RedirPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the number of the subscriber, which
redirected the call sent to the outgoing channel.
4.1.4.1 CDR Format
A general header for an entire CDR file (this parameter is displayed, if the corresponding setting is
selected).
A discriminant (this parameter is displayed, if the corresponding setting is selected).
Connection establishment time in the YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss format (in case of unsuccessful calls,
this parameter is equal to the disconnection time).
Call duration, seconds.
Cause of disconnection according to ITU-T Q.850.
Connection information.
Caller information:
– IP address;
– source type;
– subscriber/trunk name (TG).
Caller number on input.
Caller number on output.
Caller category on input.
Caller category on output.
Redirecting number (this parameter is displayed, if the corresponding setting is selected).
Callee information:
– IP address;
– destination type;
– subscriber/trunk name (TG).
Callee number on input.
Callee number on output.
Call received time in the format: YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.
Connection termination time in the format: YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.
Redirection tag (this parameter is displayed, if the corresponding setting is selected).
Source and Destination Types
SIP-user—SIP subscriber;
trunk-SIP—SIP trunk;
trunk-SS7—SS-7 trunk;
Page 43

SMG digital gateway 43
trunk-Q931—ISDN PRI trunk.
Types of Connection Information
user answer—successful call;
user called, but unanswer—unsuccessful call, no response from subscriber;
unassigned number—unsuccessful call, the number is not assigned;
user busy—unsuccessful call, the user is busy;
uncomplete number—unsuccessful call, the number is not complete;
end point equipment out of order—unsuccessful call, the terminal equipment is not available;
unavailable trunk line—unsuccessful call, the trunk is not available;
unavailable v-chan—unsuccessful call, no free voice links available;
access denied—unsuccessful call, access denied;
RADIUS-response not received—unsuccessful call, no response from the RADIUS server;
other cause—unsuccessful call, another reason.
Redirection Tag
normal—a call w/o redirection;
redirecting—a redirected call (a call containing the redirecting number after the redirection);
redirected—the received call that was redirected.
4.1.4.2 CDR File Example
Example of a CDR file containing 2 records (header and discriminant are enabled):
SMG4. CDR. File started at '20111024093328'
27;2011-10-24 09:33:37;2;16;user answer;192.168.16.200;sip-user; undef;520001;520001;
192.168.16.200;sip-user;undef;520000;520000;2011-10-24 09:33:35;2011-10-24 09:33:39;
27;2011-10-24 09:38:56;242;16;user answer;192.168.16.202;sip-user;undef;7000000;7000000;
192.168.16.200;sip-user;undef;520000;520000;2011-10-24 09:38:45;2011-10-24 09:42:58;
4.1.4.3 CDR Structure for Various Settings
By default, a CDR on SMG (checkboxes in Other Settings are not checked) contains rows of the following
format:
;2013-10-08 15:10:14;2;16;user answer;0.0.0.0;trunk-SS7;TrunkGroup00;650000;650000;0.0.0.0;trunk-
SS7;TrunkGroup00;80123456789;80123456789;2013-10-08 15:10:12;2013-10-08 15:10:16;
where
2013-10-08—call start date;
15:10:14—call start time;
2—call duration (in seconds);
16—cause of disconnection according to ITU-T Q.850;
user answer—connection information;
0.0.0.0—IP address where the call originates from (a call from TDM appears as 0.0.0.0);
trunk-SS7—source type;
Page 44

44 SMG digital gateway
TrunkGroup00—caller name or incoming trunk name (TG);
650000—caller name on SMG input (before modification on incoming TG);
650000—caller name on SMG output (after modification on incoming and outgoing TG);
0.0.0.0—IP address where the call is directed to (a call to TDM appears as 0.0.0.0);
trunk-SS7—destination type;
TrunkGroup00—callee name or outgoing trunk name (TG);
80123456789—callee number on SMG input (before modification on incoming TG);
80123456789—callee number on SMG output (after modification on incoming and outgoing TG);
2013-10-08 15:10:12—call received time;
2013-10-08 15:10:16—connection termination time.
The caller number will have the following format:
For normal calls—the number from the Calling Party Number field (the PRI and SS-7 protocols) or
the From field (SIP).
When an IAM (the SS7 protocol) or SETUP (the PRI protocol) message received with redirection
information—the number from the Redirecting Number field.
When message 302 (the SIP protocol) is received—the number from the To field.
The callee number will have the following format:
For normal calls—the number from the Called Party Number field (the PRI and SS-7 protocols) or
the To field (SIP).
When an IAM (the SS7 protocol) or SETUP (the PRI protocol) message received with redirection
information—the number from the Called Party Number field.
When message 302 (the SIP protocol) is received—the number from the Contact field.
When the Save Call Category checkbox is checked, two additional fields are added to this record:
2013-10-08 15:10:14;2;16;user answer;0.0.0.0;trunk-SS7;TrunkGroup00;650000;650000;1;3;0.0.0.0;trunkSS7;TrunkGroup00;80123456789;80123456789;2013-10-08 15:10:12;2013-10-08 15:10:16;
where
1—caller category on input (before modification on incoming TG);
3—caller category on output (after modification on incoming and outgoing TG).
When the Save Redirecting Number checkbox is checked, two additional fields are added:
;2013-10-08 18:27:13;1;16;user answer;0.0.0.0;trunkSS7;TrunkGroup00;650000;37650000;1;1;650016;3835650016;0.0.0.0;trunk-
SS7;TrunkGroup00;80123456789;58123456789;2013-10-08 18:27:09;2013-10-08 18:27:14;
where
650016—the redirecting number (the number that originated the redirection) on SMG input (before
modification on incoming TG)—the number from the Redirecting Number field (the PRI and SS-7 protocols) or
the To field (SIP).
3835650016—the redirecting number on SMG output (after modification on incoming and outgoing TG)—the
number from the Redirecting Number field (the PRI and SS-7 protocols) or the To field (SIP).
In this case, the number from the Calling Party Number field (the PRI and SS-7 protocols) or the From field
(SIP) will be specified as a caller number.
Page 45

SMG digital gateway 45
– When an IAM (the SS7 protocol) or SETUP (the PRI protocol) message received with redirection
information—the number from the Redirecting Number field.
– When message 302 (the SIP protocol) is received—the number from the To field.
When the Save Redirection Tag checkbox is checked, the following field is added for redirected calls:
;2013-10-09 17:58:26;5;16;user answer;192.168.0.2;trunkSIP;TrunkGroup01;650000;650000;1;1;001;001;0.0.0.0;trunk-SS7;TrunkGroup00;650023;650023;2013-10-09
17:58:24;2013-10-09 17:58:31;redirecting;
where
redirecting—a redirection tag.
The redirection tag may have the following values:
redirecting—the caller has redirected the call to the callee;
redirected—the call initiated by the caller has been redirected to another subscriber.
4.1.5 E1 Streams
This section6 describes configuration of signalling and parameters for each E1 stream.
4.1.5.1 Signalling Protocol Selection
To select a signalling protocol for a stream, use the
Signalling Protocol drop-down list.
The device supports the following signalling protocols:
Q.931 (User, Network);
SS7 (ОКС-7);
QSIG for subscriber name transmission;
CorNet for subscriber name transmission.
4.1.5.2 Configuration of Physical Parameters
Physical settings
Enable—the stream is physically enabled.
CRC4 xmit/control—CRC4 checksum is generated
during transmission and checked during reception.
Equalizer—when checked, amplifies the
transmitted signal.
Alarm indication—when checked, a local stream
fault results in fault indication (the ALARM LED
turns on and the alarm is registered in the alarm
log).
Remote alarm indication—when checked, a
remote stream fault results in fault indication (the
6
Only one E1 stream is available in an SMG-2 device by default. To activate another one, a special licence is required. For
more information about licences, see section 4.1.19 Licence RenewalLicence Renewal.
Page 46

46 SMG digital gateway
ALARM LED turns on and the alarm is registered in the alarm log).
Line code —the method of channel information encoding (HDB3, AMI).
Slip indication—when checked, any slips identified in the reception path result is fault indication.
Slip detection timeout—time interval for stream parameters polling on the card; if a slip is
detected in the stream, the gateway will indicate an alarm during the timeout.
4.1.5.3 Q.931 Signalling Protocol Configuration
Physical Parameters/Q.931 Tab
Page 47

SMG digital gateway 47
Q.931 LAPD—LAPD Channel-Level Parameters of Q.931 Protocol
Т200—transmission timer. The timer defines the time period when a frame response should be
received, which enables transmission of next frames. The time period should be longer than the
time required to transmit a frame and receive its acknowledgement.
Т203—the maximum time when the device may have no frames exchange with the opposite
device.
N200—the number of frame transmission retries.
Q.931 Signalling Protocol parameters
TrunkGroup—name of the trunk group this Е1 stream belongs to.
Scheduled routing profile—the selected scheduled routing profile.
Access category—the selected access category.
Dial plan —defines the numbering schedule that will be used to route calls received from this port
(required for coordination of numbering schedules).
Numbering plan type—defines the ISDN numbering schedule type. To use E.164 common
numbering schedule, select ISDN/telephony.
Calling category for incoming calls—the caller ID category assigned to the calls received from this
port.
Send calling category —enables transmission of the caller ID category as the first digit of the
number in the CgPN information element of the SETUP message.
Proper operation requires support of this mode
by the opposite party.
"End-of-dial" message—issues the "Sending Complete" information element upon the "End of
dial" event (the event received from a linked channel; the maximum number of digits is achieved
according to the prefix; the dialling timeout for the next digit).
Do not send RESTART for interface—when checked, the gateway does not send the RESTART
message into the line when a stream is restored (the channel level LAPD is established).
Do not send RESTART for channel —when checked, the gateway does not send the RESTART
message into the line upon expiration of T308 timer. The timer activates when the RELEASE
message is sent into the channel and resets upon receipt of the RELEASE COMPLETE message in
response. If the RELEASE COMPLETE message is not received while T308 timer is active, the
RESTART message is transmitted to release the channel.
Channels selection order —defines the order of physical channels provisioning for an outgoing call.
Four types are available: sequential forward, sequential back, from the first one and forward, from
the last one and back. To minimise the number of communication conflicts with adjacent PBXs,
inverse channel engagement types are recommended.
DialTone for incoming overlap-seize—when checked, the gateway sends a DialTone into the line in
case of an incoming overlap engagement (the "PBX response" ready signal). In this case, an
overlap engagement means that the SETUP message is received without "sending complete". To
switch between tracts, the SETUP message should have the progress indicator = 8.
Process PI 'In-band' in DISCONNECT — when checked, field PI In-Band contained in DISCONNECT
message will be processed for call clearback IVR voice message transmission otherwise this field is
ignored.
Page 48

48 SMG digital gateway
Names transmission parameters
In this tab you can configure method of reception/ transmission of subscriber name and type of encoding
of receiving/transmitting name.
Name transmission method:
Not set -name transmission is disabled;
Q.931 DISPLAY - transmission in Q.931 Display element with Codeset 5;
QSIG-NA - transmission via QSIG-NA (ECMA-164) protocol;
CORNET - transmission via Siemens CorNet protocol;
CORNET HICOM-350 - transmission via Siemens CorNet protocol with supplementary information
for Hicom PBX;
AVAYA DISPLAY - transmission in Q.931 Display element with Codeset 6;
Name encoding method:
Transit - transcoding is not performed (name received in UTF-8, by default);
CP 1251 - Windows-1251 encoding;
Siemens adaptation - Siemens PBX encoding;
AVAYA adaptation - AVAYA PBX encoding;
Latin transliteration - latin transliteration of Russian names.
Page 49

SMG digital gateway 49
Using Channels
This menu allows E1 stream channels to be enabled or disabled. Check or uncheck the checkbox next to
the corresponding channel. The Trunk Group column shows the number of the group where the channels are
configured (it is used when a trunk group is set for certain stream channels instead of the entire stream).
4.1.5.4 SS7 Signalling Protocol Configuration
Page 50

50 SMG digital gateway
SS-7 Settings
SS7 Linkset —linkset selection (SS-7 line group).
Channel ID (SLC)—identifier of a signal channel in the SS-7 line group.
MTP3 opposite code (DPC-MTP3)—the code of the opposite signalling transition point (STP). It is
used when SMG operates in the quasi-associated mode. If the quasi-associated mode is not
required, set the value to 0. In this case, the opposite MTP3 code is equal to the DPC-ISUP value,
which is set in the configuration of SS-7 Line Groups (section 4.1.7.2).
D-channel—the number of the channel interval (CI) to be used for signal transmission.
Bit D in LSU—sets "1" to bit D in the status field (SF) of the LSSU signal unit (bits D–F in the status
field are reserved).
Channel Settings
ISUP CIC, channel identifier code—voice link numbers (CIC).
To adjust automatic numbering of voice links, click the Set button.
This will open the following menu:
Starting number—the number of the first voice link.
Numbering increment—the channel numbering increment. Each subsequent channel will be
assigned a number, which is greater than the number of the current channel by the numbering
increment.
Channels range—this section allows numeration adjustment for all stream channels or for a
certain range of channels only.
The Trunk Group column shows the number of the group where the channels are configured (it is used
when a trunk group is set for certain stream channels instead of the entire stream).
Page 51

SMG digital gateway 51
The button for configuration of a channel transit through semi-permanent connection is displayed in
'Transit' column7. The example of configuration of the connection is represented in appendix G.
The window where you can set the following parameters is opened after clicking the button:
7
Only upon a lisence for transit
Page 52

52 SMG digital gateway
Transit enable– When you enable a transit, the channel will be excluded from SS7 stream and will
be transmitted directly over semi-permanent connection through a SIP interface;
SIP interface – interface through which transit is implemented;
Codec–voice codec, which will be used for transit. If you chose 'by default', the codecs which were
configured on the selected SIP interface will be negotiated;
Е1 stream – E1 stream on remote side , to which the channel will be connected;
Channel – channel of E1 stream on remote side to which the channel will be connected;
Active side – if you enable this option, SMG will initiate connection for the channel transit. If you
disable the option, SMG will be a receiving side for the channel.
Click 'Stream transit' button for enabling transit for all channels on the stream with the same settings. The
list of settings will be the same as for single channel, except the 'number of channel' field, which will not be
available in this mode, every channel number on the active side will be comply to channel number on remote
side.
4.1.6 Dial plan
This section defines transition prefixes to trunk groups.
The device features up to 16 independent numbering schedules. Every numbering schedule may have its
own subscribers and prefixes. To set the number of active schedules, see section 4.1.1 System Parameters.
The device routes calls using 2 criteria:
Search by caller number—CgPN (Calling Party Number).
Search by callee number—CdPN (Called Party Number).
When a call arrives to a numbering schedule, its routing begins; first of all, a search for matches to CgPN
number masks is performed. If a match is found, the call is routed and further search is stopped.
When call parameters do not match CgPN masks and the subscriber number, a search by all CdPN masks
configured in the numbering schedule is performed.
If both CgPN and CdPN number masks are configured in prefix parameters, this rule uses OR
logic, i. e. the call is not analysed for CgPN and CdPN numbers simultaneously.
Page 53

SMG digital gateway 53
Dial plan settings
Name—name of the numbering schedule.
SIP domain—domain name for registration.
Check dial plan by number—checks if routing is possible for
the number entered into this field.
The check is performed by caller and callee subscriber masks.
The search results determine if call routing is possible for the caller
number (CgPN) or the callee number (CdPN) and retrieve the prefix
number, if it is.
ST—when checked, the search recognises the end
dial marker.
Search masks by template—searches a prefix by the number
template.
To create a new prefix, open the Objects menu and click Add
Object or click the button located below the list and enter prefix
parameters in the opened form:
Title—name of the numbering schedule.
Dial plan—the selected numbering schedule.
Access category—the selected access category.
Check access category—when checked, checks the
possibility of call routing by the prefix based on the rules determined by access categories.
Prefix type—the selected prefix type:
– TrunkGroup—transition to trunk group;
– Trunk Direction—transition to trunk direction.
Page 54

54 SMG digital gateway
– Change dial plan —dialling the prefix allows the system to switch to another numbering
schedule. When this prefix type is selected, the New Numbering Schedule option becomes
available which allows selection of the numbering schedule to switch to.
For a trunk group:
TrunkGroup—the trunk group the call will be routed to by this prefix.
Direction—the trunk group access type: local, emergency, zone, private, long-distance,
international. It is used to limit communication capabilities if data communication with the
RADIUS server fails (see section 4.1.13 RADIUS Configuration).
Caller ID request—defines if transition to the trunk group specified in the Trunk Group field
requires caller ID information (caller number and category). When a call arrives from a
communication node and the caller ID information is missing, a caller ID request will be sent to the
node (an INR message from SS-7 signalling).
Caller ID mandatory—indicates that caller ID information is mandatory during the direction
transition. If caller ID information cannot be retrieved from the calling party, the connection
establishment is cancelled.
Dial mode—the method of number transmission:
– enblock—wait for collection of the entire address information;
– overlap—do not wait for collection of the entire address information.
Do not send end-of-dial (ST)—when checked, the end dial marker is not sent (ST in SS or "sending
complete" in PRI).
Priority—sets the prefix priority within the range from 0 to 100. A prefix with a smaller value has a
higher priority (0 is the highest priority, 100 is the lowest).
For trunk direction:
Trunk direction—a trunk direction (a set of trunk groups united in one direction), in which a call
will be routed by this prefix.
Direction—the trunk group access type: local, emergency, zone, private, long-distance,
international. It is used to limit communication capabilities if data communication with the
RADIUS server fails (see section 4.1.13 RADIUS Configuration).
Caller ID request—defines if transition to the trunk group specified in the Trunk Group field
requires caller ID information (caller number and category). When a call arrives from a
communication node and the caller ID information is missing, a caller ID request will be sent to the
node (an INR message from SS-7 signalling).
Caller ID mandatory—indicates that caller ID information is mandatory during the direction
transition. If caller ID information cannot be retrieved from the calling party, the connection
establishment is cancelled.
Dial mode—the method of number transmission:
– enblock—wait for collection of the entire address information;
– overlap—do not wait for collection of the entire address information.
Do not send end-of-dial (ST)—when checked, the end dial marker is not sent (ST in SS or "sending
complete" in PRI).
Priority—sets the prefix priority within the range from 0 to 100. A prefix with a smaller value has a
higher priority (0 is the highest priority, 100 is the lowest).
To change the numbering schedule:
Page 55

SMG digital gateway 55
New numbering schedule—the numbering schedule the call, which is routed by this prefix, will be
directed to.
New access category—the access category to be allocated to the caller when the numbering
schedule is changed.
Priority—sets the prefix priority within the range from 0 to 100. A prefix with a smaller value has a
higher priority (0 is the highest priority, 100 is the lowest).
CdPN settings
Number type—the callee number type: unknown, subscriber number, national number,
international number, no change. The selected number type will be sent in SS-7, ISDN PRI, SIP-I/T
signalling messages during an outgoing call by a prefix ("no change" means that the number type
will not be converted, i. e. it will be sent in the form it has been received from the incoming
channel).
Numbering plan type—the callee's numbering schedule type; may take the following values:
unknown, isdn/telephony, national, privat, no change. The selected numbering schedule type will
be sent in ISDN PRI signalling messages during outgoing call by a prefix ("no change" means that
the number type will not be converted, i. e. it will be sent in the form it has been received from
the incoming channel).
Direct route timers (used when trunk groups are directly connected without prefix mask analysis—the
Direct Prefix function in trunk group settings).
These timers work only when dialling in the overlap mode:
Short timer—time interval in seconds when the digital
gateway will wait for further dialling if a part of address
information has already been received. The default value:
5 seconds.
Duration—the timer for number dialling duration. The default value: 30 seconds.
The Mask List section allows configuration of number masks for routing
by this prefix.
To generate the list, use the following buttons:
— Add Mask;
— Edit Mask;
— Remove Mask;
— View Mask.
Mask—a template or a set of templates, which is compared to
the caller or callee number received from the incoming channel.
It is used for further call routing (for mask syntax, see section
4.1.6.1).
Type—mask type. Defines the number for the call routing—caller number (calling) or callee
number (called).
Long timer—time interval in seconds when the digital gateway will wait for the next digit dialling
until a match to a sample from the numbering schedule is established. The default value:
10 seconds.
Short timer—time interval in seconds when the digital gateway will wait for further dialling if the
dialled number already matches a sample in the numbering schedule, but additional digits may be
also dialled, which will result in a match to another sample. The default value: 5 seconds.
Page 56

56 SMG digital gateway
Duration—the timer for number dialling duration. The default value: 30 seconds.
To edit a prefix, double-click the prefix row in the prefix table with the left button or select the prefix and
click the button below the list.
To delete a prefix, select the prefix and click the button below the list or open the Objects menu and
select Remove Object.
4.1.6.1 Description of Number Mask and Its Syntax
Number mask is a set of templ templates delimited by '|'. The mask should be enclosed into parentheses.
(templ) is equal to (templ1|templ2|...|templN).
Syntax:
X or —any digit;
*—an asterisk (*);
#—a sharp (#);
09—digits from 0 to 9;
D—character D.
. —the dot is a special symbol which means that the preceding character may be repeated any
number of times (30 characters max. for one number), e. g.:
– (34x.) —all possible number combinations which begin with "34".
[ ]—defines a range (with a hyphen) or an enumeration (w/o spaces, commas, and other
characters between the digits) of prefixes, e. g.:
– the range ([15])—all 4-digit numbers which begin with 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5.
– the enumeration ([138]xx)—all 3-digit numbers which begin with 1, 3, or 8.
min, max—defines the number of repetitions for the character outside the parentheses, e. g.:
(1x{3,5})—means that there may be from 3 to 5 arbitrary digits () and it corresponds to the mask
.
|—logical OR—separates templates in a mask.
(-)—the mask which is used only in CgPN number modifier tables for calls without a caller number.
Allows the caller number to be added if it was missing and also specifies indicators for that
number.
If a numbering schedule contains overlapping prefixes, then the prefix with the most precise
mask for a specific number will have a higher priority during the number processing by the
numbering schedule, e. g.:
Prefix 1: (2xxxx)
Prefix 2: (23xxx)
When the number "23456" arrives to the numbering schedule, it will be processed with
prefix 2.
Also, the masks containing an arbitrary number of repetitions (x.) or a range of repetitions
{min, max} have a lower priority than the masks with a precise number of characters, e. g.:
Page 57

SMG digital gateway 57
Prefix 1: (2x{4,7})
Prefix 2: (23xxx)
When the number "23456" arrives to the numbering schedule, it will be processed with
prefix 2.
The masks with a specified range of repetitions {min, max} have a higher priority than the
masks with an arbitrary number of repetitions (x.), e. g.:
Prefix 1: (2x.)
Prefix 2: (2x{4,7})
When the number "23456" arrives to the numbering schedule, it will be processed with
prefix 2.
4.1.6.2 Mask Operation Examples
Example 1
(#XX#|*#XX#|*XX*X.#|112|011|0[1-4]|6[2-
The mask contains 9 templates:
1. #XX#—any 4-digit number which begins and ends with #, the 2
nd
and the 3rd digits of the number
may take any values from 0 to 9, as well as * or #.
In general, this template disables VAS utilisation from the phone unit.
2. *#XX#—any 5-digit number which begins with *# and ends with #, the 3
rd
and the 4th digits of the
number may take any values from 0 to 9, as well as * or #.
In general, this template is used to control VAS utilisation from the phone unit.
3. *XX*X.# —an N-digit number which begins with * followed by two arbitrary digits (from 0 to 9, as
well as * and #), then by *, and then by any number of any digits (from 0 to 9, *) until # is met.
In general, this template is used to order VAS utilisation from the phone unit.
4. 112—dialling the specific 3-digit number (112).
5. 011—dialling the specific 3-digit number (011).
6. 0[1–4]—a 2-digit number which begins with 0 and ends with 1, 2, 3, or 4, i. e. 01, 02, 03, or 04.
7. 6[2–9]ХХХ—a 5-digit number which begins with 6, with the second digit of the number being any
digit from 2 to 9, and the last three digits being any digits from 0 to 9, as well as * and #.
8. 5[24]ХХХXX—a 7-digit number which begins with 5, with the second digit of the number being 2
or 4, and the last five digits being any digits from 0 to 9, as well as * and #.
9. 810X{11, 15}—a number which begins with 810 followed by 11 to 15 arbitrary digits from 0 to 9,
as well as * and #. Taking into account the first three digits, the length of the number according to
this rule is from 14 to 18 digits.
Example 2
A numbering schedule configuration is required to allow all numbers, which begin with 1 and have the
length of 3, to be routed to Trunk0, and number 117 to be individually routed to Trunk1.
To solve this task, configure the following prefixes:
1. Route the first prefix with the mask (117) to Trunk1.
2. Route the second prefix with the mask (11[0-689]|1[02-9]x) to Trunk0.
Templates of the second prefix overlap all "1xx" numbers except for 117.
Page 58

58 SMG digital gateway
4.1.6.3 Timer Operation Examples
Consider an example of timer operation for dialling with 011 number overlap (example 1 from the
previous section). Let us assume that the timer has the following values set:
L = 10 seconds.
S = 5 seconds.
Receiving the first digit—0. A mask for such a dial includes 2 rules: 011 and 0[1-4]. The first received digit
does not provide any complete match to any of the rules, therefore the L-timer is activated (10 seconds) to wait
for the next digit. If the next digit does not come in 10 seconds, a timeout will be registered. Since there are no
matches to the rules, the timeout will result in dial error.
Receiving the second digit—1. Receiving the second digit results in a match to rule 6: 0[1-4] (prefix 01).
Since the match is found, but there may also be a further match to rule 5 (that is 011), the S-timer is activated
(5 seconds) to wait for the next digit. If the next digit does not come in 5 seconds, a timeout will be registered.
Since there is a match to a rule, the call will be successfully directed according to this mask.
Receiving the third digit—1. There is no match to rule 6 anymore, but the number matches rule 5 now.
This match is final, since the mask has no more rules for further matches. The call is immediately routed
according to rule 5.
4.1.7 Routing
4.1.7.1 Trunk Groups
A trunk group is a set of connecting lines (trunks), such as: E1 stream channels, data transmission band (IP
channels). E1 stream channels enable Q.931 and SS-7 signalling, while IP channels enable SIP-T interface. To edit
a trunk group, double-click the corresponding row in the group table with the left button or select the group and
click the button below the list.
To delete a trunk group, select the group and click the button below the list or open the Objects menu
and select Remove Object.
Page 59

SMG digital gateway 59
Up to 64 trunk groups are supported.
Trunk Group Parameters
To access a trunk group, the device configuration should include prefixes which perform
transition to this group.
Title—name of the trunk group.
TrunkGroup members—content of the trunk group (E1 stream channels, Q.931 signalling stream,
SS line group, or SIP interface) that can be changed when editing the group.
E1 stream—an E1 stream; the parameter is specified if the group includes E1 channels. To include
a channel into a trunk group, check the checkbox next to it.
Channels selection order—channel selection order in E1 streams. This menu is available when you
chose E1 streams from SS7 Linkset;
Direct routing prefix—transition to the prefix without caller or callee number analysis. It enables
switching of all calls in a single trunk group to another group regardless of the dialled number
(without mask creation in prefixes). When a number is dialled in the overlap mode, direct dialling
timers are used, which are configured in the direct prefix.
Ingress calls
Disable ingress calls—when checked, the incoming calls are barred. Setting the call barring does
not terminate any of the established connections.
No Connected number transit—indicates that the Connected Number parameter set in the
message of the Q.931, the SS-7 protocol is not translated.
RADIUS profile—the selected RADIUS profile (see description in section 4.1.13.2).
Ingress calls modifiers
CdPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the callee number received from the
incoming channel.
Page 60

60 SMG digital gateway
CgPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the caller number received from the
incoming channel.
Egress calls
Disable egress calls—when checked, the outgoing calls are barred. Setting the call barring does
not terminate any of the established connections.
Reserve TrunkGroup—specifies the trunk group a call will be routed to when routing to the current
trunk group is not possible (all channels are engaged or inoperable).
Egress calls modifiers
CdPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the callee number sent to the outgoing
channel.
CgPN—intended for modifications based on analysis of the caller number sent to the outgoing
channel.
Original Called Number—intended for modifications based on analysis of the callee's original
number sent to the outgoing channel.
Redirecting Number—intended for modifications based on analysis of the redirecting number sent
to the outgoing channel.
Generic number—intended for modifications based on analysis of the generic number sent to the
outgoing channel.
To create, edit, or remove groups (as well as other objects), use the Objects—Add Object, Objects—Edit
Object, or Objects—Remove Object menus and the following buttons:
— Add Trunk Group;
— Edit Trunk Group Parameters;
— Remove Trunk Group.
4.1.7.2 SS7 Linksets
For SS7 signalling protocol configuration, see the E1 Streams section (section 4.1.5.4).
An SS7 line group is a signal link, which includes a group of signalling channels. To create, edit, or remove
line groups, use the Objects—Add Object, Objects—Edit Object, or Objects—Remove Object menus and the
following buttons:
– Add SS-7 Line Group (LinkSet);
– Edit SS-7 Line Group (LinkSet);
– Remove SS-7 Line Group (LinkSet).
Page 61

SMG digital gateway 61
SS-7 Line Group Parameters
SS-7 Line Group
Title —name of the SS-7 line group.
TrunkGroup—name of the trunk group the SS-7 line group operates with.
Access category—the selected access category.
Dial plan—defines the numbering schedule that will be used to route calls of this group (required
for coordination of numbering schedules).
Scheduled routing profile—the selected scheduled routing profile.
Page 62

62 SMG digital gateway
Toll
8
—means that this signal link is connected to the ALDE. This parameter is used to ensure
correct operation with long-distance calls (used in transits to signalling CAS).
Alarm indication—when checked, a fault in SS-7 signal link results in fault indication (the ALARM
LED turns on and the fault is registered in the alarm log).
Channel selection—the order of channel engagement for outgoing calls. Available options:
– sequential forward;
– sequential back;
– from the first and forward;
– from the last and back;
– sequential forward even;
– sequential back even;
– sequential forward odd;
– sequential back odd.
To minimise the number of communication conflicts with adjacent PBXs,
inverse channel engagement types are recommended.
Reserve SS7 Linkset—the selected redundant SS-7 line group. When the main SS-7 line group is not
available, the exchange of signalling messages will be entirely performed through the redundant
SS7 line group.
Combined mode—the Combined Linkset mode which means that only voice streams are used in
this SS-7 line group, while signal channels of the primary and secondary SS-7 groups are used for
signalling.
Primary SS7 Linkset —the SS-7 line group selected by signal D-channels that will be used to
exchange the signalling messages related to this particular SS-7 line group.
Secondary SS7 Linkset —the second SS7 line group selected by signal D-channels that will be used
to exchange the signalling messages related to this particular SS-7 line group.
In the combined mode, the signalling load is evenly distributed (50/50)
between the primary and secondary SS-7 line groups.
SS7 Timers profile—the selected timer profile which will be used for this SS-7 line group.
MTP2 Level
Emergency alignment for a single signal link—enables emergency phasing during SS-7 line group
commissioning, if this SS-7 line group has a single signal link.
Service Information (SIO)
Network ID—specifies the network type: international, national, local network or reserve (usually,
the Local Network value is used in the Russian Federation).
Routing Label
Own point code (OPC)—the signalling point own code.
ISUP opposite code (DPC-ISUP)—code of the communicating signalling point of the ISUP
subsystem.
8
Not supported in the current version.
Page 63

SMG digital gateway 63
ISUP Subsystem
Channels initialization mode—device operations during stream recovery:
– leave blocked—channels remain blocked (BLO);
– individual unblock—the unblock command (UBL) is sent for each channel;
– group unblock—a group command is sent to unblock a group of channels (CGU);
– group reset—the group reset command (GRS) is sent.
Send REL on receiving SUS—sends the REL message in response to the SUS message, which
notifies about channel suspension.
Add a digit in IAM for overlap—sends a single digit to the Called Party Number field of the IAM
message in the overlap dialling mode.
Restrict CdPN in IAM to 15 digits —when checked, limits the number of digits of the CdPN number
sent in the IAM message to 15, while other digits are sent in the SAM message.
Control receiving Redirecting/Original Called for incoming redirection—when checked, a call will
be cleared back if the IAM message contains the Redirection Information parameter, but has no
Redirecting Number or Original Called Number.
IAM Indicators
Transmission medium requirements—specifies the type of information to be delivered by the
transmission environment.
Forward call indications
ISUP preference —a rule that governs modification of the ISUP preference indicator. As a rule,
these bits should not be changed.
Interworking indicator—defines whether the interaction indicator should be modified (defines
whether the interaction has been established with a non-ISDN network).
Call type indicator—determines whether the call type indicator should change its value to
international or national.
Connect type indicators
Satellite indicator—identifies the presence of a satellite channel.
– Override to "no satellite"—changes the identifier value to "no satellite" regardless of the
value received from the incoming channel.
– Unchanged—keeps the indicator value unchanged.
– Add one—this setting is used if the signal link operates via a satellite channel. In this case,
the satellite channel parameter transmitted in the Nature of Connection indicators is
increased by 1.
Enable continuity check —enables integrity check support in the SS-7 line group. During an
outgoing call, the called party establishes a remote loop in the stream, SMG sends the frequency
to the channel that will be detected on receipt after signal transmission through the channel. If
the frequency is detected, the call is handled through this channel; otherwise, a similar attempt is
performed on the next channel. After 3 unsuccessful attempts (on three different channels), the
call service is stopped.
Continuity check frequency —defines the frequency of channel integrity checks during outgoing
calls performed through the SS-7 line group. For example, the value of 3 means that every third
outgoing call will be checked for channel integrity.
Page 64

64 SMG digital gateway
A correspondence between SS and Caller ID categories can be adjusted for the gateway. For
configuration, see section 4.1.8.1 SS Category.
4.1.7.2.1 Examples
An example of SMG connection for operation in the SS-7 quasi-associated mode via signalling transfer
points (STP).
Objective
A connection is required between SMG and the opposite signalling point (SP) using two signal links. The
first signal link should pass through STP 1 signalling transition point, while the second one—through STP 2.
Point code: SMG4 = 22, STP 1 = 155, STP 2 = 166, SP = 23.
Solution
In addition to basic settings, set Own Point Code (OPC) = 22 and ISUP Opposite Code (DPC-ISUP) = 23 in the
SS-7 Line Groups menu.
Let us assume that stream 0 is connected to STP 1, while stream 1—to STP 2. Specify the following in the
stream settings: SS7 Signalling protocol; configure CIC numbering correctly and select the required E1 stream
time slot for signalling D-channel; select the pre-created SS-7 line group in SS-7 Line Group settings and set MTP3
Opposite Code (DPC-MTP3) to 155 for stream 0 and to 166 for stream 1.
An example of SMG connection for operation in the SS-7 quasi-associated mode via PBX with STP features.
LS— an SS-7 line group (Link Set).
Objective
A connection is required between SMG and two PBXs with STP features (PBX/STP); when the 1LS main
circuit group between SMG and PBX/STP 1 fails, signalling messages should be sent via 2LS.
Solution
Page 65

SMG digital gateway 65
Let us assume that stream 0 of SMG is connected to PBX/STP 1 and is configured to use the first SS-7 line
group, while stream 1 is connected to PBX/STP 2 and is configured to use the second SS-7 line group. Specify the
following in the stream settings: SS7 Signalling protocol; configure CIC numbering correctly and select the
required E1 stream time slot for signalling D-channel; specify the second SS-7 line group in Redundant SS-7 Line
Group in configuration of the first SS-7 line group.
An example of SMG connection for operation in the combined mode.
Objective
Only voice channels are used for communication between SMG and PBX/SP; signalling traffic should be
transferred via PBX/STP 1 and PBX/STP 2.
Solution
Let us assume that stream 0 of SMG is connected to PBX/STP 1 and is configured to use the first SS-7 line
group, while stream 1 is connected to PBX/STP 2 and is configured to use the second SS-7 line group; stream 2 of
SMG is connected to PBX/SP and is configured to use the third SS-7 line group. Specify the following in the
stream settings: SS7 Signalling protocol; configure CIC numbering correctly and select the required E1 stream
time slot for signalling D-channel of streams 0 and 1; specify the first SS-7 line group in Primary SS-7 Line Group
in configuration of the third SS-7 line group; specify the second SS-7 line group in Secondary SS-7 Line Group in
configuration of the third SS-7 line group.
4.1.7.3 SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I Interfaces
4.1.7.3.1 Configuration
This section describes configuration of general parameters for SIP stack, custom settings for each direction
operating via SIP/SIP-Т/SIP-I protocols, and SIP subscriber profiles.
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is a signalling protocol, which used in IP telephony. It facilitates basic call
management tasks such as session start and termination.
SIP network addressing is based on the SIP URI scheme:
Page 66

66 SMG digital gateway
sip:user@host:port;uri-parameters
user—the number of a SIP subscriber.
@—a separator located between the number and domain of the SIP subscriber.
host—domain or IP address of the SIP subscriber.
port—the UDP port used for subscriber's SIP service operation.
uri parameters—additional parameters.
One of the additional SIP URI parameters is user=phone. If this parameter is specified, the syntax of the
SIP subscriber number (in the user part) should match the TEL URI syntax described in RFC 3966. In this case, the
device will process requests, which contain "+", ";", "=", "?" in the SIP subscriber number, and will automatically
add "+" before the callee number for international calls using the SIP-T protocol.
Common SIP settings
Local SIP port—the UDP port which is used to send and receive SIP messages.
Transport—the selected transport protocol which is used to send and receive SIP messages:
– TCP-prefer—the messages are received via UDP and TCP and sent via TCP. If failed to
establish a TCP connection, the messages are sent via UDP.
– UDP-prefer—the messages are received via UDP and TCP. The packets smaller than
1,300 bytes are sent via TCP, while the ones larger than 1,300 bytes—via UDP.
– UDP-only—use the UDP protocol only.
– TCP-only—use the TCP protocol only.
T1 timer—timeout for a request; upon expiration, the request is re-sent. The maximum
retranslation interval for the INVITE requests is equal to 64*T1.
T2 timer—the maximum retranslation interval for responses to the INVITE request and for all
requests except for the INVITE ones.
Page 67

SMG digital gateway 67
T4 timer—the maximum time allotted for all retranslations of the final response.
Ignore address in R-URI—specifies that only the user part of the request URI is analysed.
Up to 64 interfaces are supported. To create, edit, or remove SIP/SIP-T interfaces, use the Objects—Add
Object, Objects—Edit Object, or Objects—Remove Object menus and the following buttons:
— Add Interface;
— Edit Interface Parameters;
— Remove Interface.
The signal processor of the gateway encodes analogue voice traffic and fax/modem data into digital
signals and performs its reverse decoding. The gateway supports the following codecs: G.711A, G.711U, G.729,
the Т.38 protocol and the CLEARMODE mode.
G.711 is a PCM codec without compression of voice data. To ensure correct operation, this codec should
be supported by all manufacturers of VoIP equipment. G.711A and G.711U codecs differ from each other in
encoding law (А-law is a linear encoding and U-law is a non-linear). The U-law encoding is used in North America,
and the A-law encoding—in Europe.
G.726 is an ADPCM ITU-T standard which describes voice data transmission using 16, 24, 32, and 40 kbps
bands. G.726-32 substitutes G.721 which describes ADPCM voice data transmission using 32 kbps band.
G.723.1 is a voice data compression codec which has two operation modes: 6.3 kbps and 5.3 kbps.
G.723.1 has a voice activity detector and generates comfort noise at the remote end during the period of silence
(Annex A).
G.729 is a voice data compression codec too; it supports the rate of 8 kbps. By analogy with G.723.1,
G.729 supports a voice activity detector and generates comfort noise (Annex B).
T.38 is a standard which describes sending facsimile messages in real time over IP networks. Signals and
data sent by a fax unit are copied to T.38 protocol packets. The generated packets may include redundancy data
from previous packets that allows reliable fax transmissions through unstable channels.
CLEARMODE—a mode which does not use signals encoding/decoding. It is supported for transparent
transmission of digital information at 64 kbps (RFC4040).
The Service Type (IP DSCP) field value for RTP, T.38, and SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I
0 (DSCP 0x00, Diffserv 0x00)—the best effort—the default value.
8 (DSCP 0x08, Diffserv 0x20)—class 1.
10 (DSCP 0x0A, Diffserv 0x28)—assured forwarding, low drop precedence (Class1, AF11).
12 (DSCP 0x0A, Diffserv 0x30)—assured forwarding, medium drop precedence (Class1, AF12).
14 (DSCP 0x0E, Diffserv 0x38)—assured forwarding, high drop precedence (Class1, AF13).
16 (DSCP 0x10, Diffserv 0x40)—class 2.
18 (DSCP 0x12, Diffserv 0x48)—assured forwarding, low drop precedence (Class2, AF21).
20 (DSCP 0x14, Diffserv 0x50)—assured forwarding, medium drop precedence (Class2, AF22).
22 (DSCP 0x16, Diffserv 0x58)—assured forwarding, high drop precedence (Class2, AF23).
24 (DSCP 0x18, Diffserv 0x60)—class 3.
26 (DSCP 0x1A, Diffserv 0x68)—assured forwarding, low drop precedence (Class3, AF31).
28 (DSCP 0x1C, Diffserv 0x70)—assured forwarding, medium drop precedence (Class3, AF32).
30 (DSCP 0x1E, Diffserv 0x78)—assured forwarding, high drop precedence (Class3, AF33).
32 (DSCP 0x20, Diffserv 0x80)—class 4.
34 (DSCP 0x22, Diffserv 0x88)—assured forwarding, low drop precedence (Class4, AF41).
36 (DSCP 0x24, Diffserv 0x90)—assured forwarding, medium drop precedence (Class4, AF42).
38 (DSCP 0x26, Diffserv 0x98)—assured forwarding, high drop precedence (Class4, AF43).
40 (DSCP 0x28, Diffserv 0xA0)—class 5.
Page 68

68 SMG digital gateway
46 (DSCP 0x2E, Diffserv 0xB8)—expedited forwarding (Class5, Expedited Forwarding).
IP Precedence:
0 – IPP0 (Routine);
8 – IPP1 (Priority);
16 – IPP2 (Immediate);
24 – IPP3 (Flash);
32 – IPP4 (Flash Override);
40 – IPP5 (Critical);
48 – IPP6 (Internetwork Control);
56 – IPP7 (Network Control).
4.1.7.4 SIP Interface Configuration Tab
Title —the interface name.
Mode—the protocol selected for the interface (SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I, Transit E1).
TrunkGroup—name of the trunk group the interface in included to.
Access category—the selected access category.
Dial plan—defines the numbering schedule that will be used for dialling from this port (required
for coordination of numbering schedules).
Hostname/IP-address—IP address or name of the host communicating via the gateway's SIP/SIP-T
protocol.
Remote SIP port
9
—a UDP/TCP port of the communicating gateway that is used to receive SIP/SIP-T
signalling.
Local SIP port
9
—a local UDP/TCP port of the device that is used to receive SIP/SIP-T signalling from
the communicating device via this interface.
Public IP —the IP address which is used for outgoing SIP/SDP messages. This helps to ensure
correct operation of the device after NAT.
9
The field is disabled in the SIP profile mode.
Page 69

SMG digital gateway 69
Ignore source port for incoming calls—when checked, the signalling transmission UDP port of the
communicating gateway that is specified in the Port for SIP Signalling Reception parameter is not
checked; otherwise, the port is checked and the call is cleared back if the INVITE request is
received from another port. If the INVITE request is received via TCP, the port is not checked
regardless of the parameter value.
Trusted network—means that the interface is connected to a trusted network. This option defines
generation of the INVITE request fields for calls with hidden caller number (presentation
restricted). When checked, the caller number information is transmitted in the from and P-
Asserted-identity fields together with the information on its hidden state in the Privacy: id field;
otherwise, the caller number information is not transmitted in any fields.
Alarm indication—when checked, SMG will indicate a fault when connection to the opposite
device is lost. For correct operation of this feature, check the Opposite party availability control
using OPTIONS messages checkbox in SIP settings.
Network interface for SIP—the network interface selected to receive and transmit signalling SIP
messages.
Network interface for RTP—the network interface selected to receive and transmit voice traffic.
Q.850-cause and SIP-reply mapping table—the selected table of correspondence between Q.850-
cause and SIP-reply codes. To configure correspondence tables, use the Internal Resources menu.
Scheduled routing profile—the selected profile of the scheduled routing service, which is
configured in the Internal Resources section.
Max active calls—the maximum number of simultaneous (incoming and outgoing) connections
through this interface.
Options configurations for 'Transit E1' mode.
Some of the options are not used in this mode. Fields which are not used are not displayed and are not
available in 'Transit E1' mode. The rest of the fields are configured as in SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I mode.
Page 70

70 SMG digital gateway
4.1.7.5 SIP Protocol Configuration Tab
SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I Options Configuration
Keep-alive control by messages OPTIONS—a function that controls direction availability by sending
OPTIONS requests; when a direction is not available, the redundant trunk group is used for the call.
This function also analyses the received OPTIONS response that allows avoiding the use of the
100rel, replaces, and timer features, which are configured in this direction, in case the opposite
party does not support them. The parameter defines the request transmission period and may
take values in the range of 30–3,600 seconds.
Always transmit SDP in provisional responses—allows early forwarding of voice frequency path.
For example, when unchecked, SMG sends reply 180 without SDP session description; according
to this reply, the outgoing party plays the ringback tone; when checked, SMG sends reply 180 with
SDP session description and the ringback is played by the incoming party.
"In-band signal" with 183+SDP transmission—issues SIP-reply 183 with SDP session description for
voice frequency path forwarding upon receipt of the CALL PROCEEDING or PROGRESS messages
from ISDN PRI that contain the progress indicator = 8 (in-band signal).
Page 71

SMG digital gateway 71
Enable redirection (302) processing—when checked, the gateway is allowed to perform
redirection upon receipt of reply 302 from this interface. When unchecked and reply 302 is
received, the gateway will reject the call and perform the redirection.
Redirection server direction—this option is available when reply 302 processing is enabled (the
Enable redirection (302) parameter). This enables redirection of the call, which was sent using a
public address, to the subscriber's private address received in reply 302 without numbering
schedule routing. The call is routed directly to the address specified in the "contact" header of
reply 302 received from the redirection server.
Enable REFER processing—a REFER request is sent by the communicating gateway to enable the
Call Transfer service. When checked, the gateway is allowed to process REFER requests received
from this interface. When unchecked, the gateway clears back the call upon receipt of a REFER
request and does not provide the Call Transfer service.
Reliable provisional responses (1xx)—when checked, the INVITE request and 1хх class provisional
responses will contain the require: 100rel option, which requires assured confirmation of
provisional responses.
– off—reliable delivery of provisional responses is disabled.
– support—the INVITE request and 1хх class provisional responses will contain the support:
100rel option.
– require—the INVITE request and 1хх class provisional responses will contain the require:
100rel option, which requires assured confirmation of provisional responses.
The SIP protocol defines two types of responses to connection initiating requests (INVITE)—
provisional and final. 2хх, 3хх, 4хх, 5хх and 6хх-class responses are final, their transfer is reliable
and confirmed by the ACK message. 1хх-class responses, except for the "100 Trying" response, are
provisional and do not have a confirmation (rfc3261). These responses contain information on the
current INVITE request processing step; in SIP-T/SIP-I protocols, SS-7 messages are encapsulated
into 1xx class responses, therefore the loss of these responses is unacceptable. Utilisation of
reliable provisional responses is also realised in the SIP protocol (rfc3262) and is defined by the
"100rel" tag in the initiating request. In this case, provisional responses are confirmed by a PRACK
message.
DSCP for signalling—a service type (DSCP) for SIP signalling traffic.
DSCP settings for RTP and SIP will be ignored when a VLAN is used to transmit
RTP and signalling. In this case, "Class of Service VLAN" will be used for traffic
prioritisation.
Remote name in contact header - insert displayed name in Contact header.
SIP Session Timers (RFC 4028)
Enable—when checked, enables support of SIP session timers (RFC 4028). A session is renewed by
re-INVITE requests sent during the session.
Session Expires—a period of time in seconds before a forced session termination if the session is
not renewed in time (from 90 to 64,800 seconds; 1,800 seconds is recommended).
Min SE (Minimum session expiration)—the minimal time interval for connection health checks
(from 90 to 32,000 seconds). This value should not exceed the Sessions Expires forced termination
timeout.
Refresher side—defines the party to renew the session (client (uac)—client (caller) party, server
(uas)—server (callee) party).
Page 72

72 SMG digital gateway
Registration Settings10
Upper registration—the selected type of registration on an upstream server:
– Trunk registration—registration on the upstream server using parameters specified in this
section.
Login—the name used for authentication.
Password—the password used for authentication.
Username/Number—the user number which is used as a caller number for outgoing trunk calls.
SIP domain—the SIP domain to be used for registration and subsequent calls from this interface.
Routing mode—the selected mode for incoming calls routing in case of trunk registration:
– by RURI—routing by request-URI of the INVITE message;
– by TO—routing by the TO field of the INVITE message;
– by CdPN by default—routing by the specified CdPN number regardless of the numbers
received in the INVITE message;
Default CdPN —the CdPN number for calls routing in case of the "by CdPN by default" mode.
Replace CgPN on egress call—when checked, the caller number (CgPN) is taken from the
Username/Number parameter; otherwise, the CgPN number received in the incoming call is used.
Registration period (sec)—the time interval for registration renewal.
Registration requests interval (ms)—the minimum interval between the Register messages that is
used to protect from high traffic caused by simultaneous registration of a large number of
subscribers.
STUN Server settings
Enable—when checked, enables requests to the STUN server.
IP address—the IP address of the STUN server.
Port—the port of the STUN server.
Option configuration for 'Transit E1'
Some of the options are not used in this mode. Fields which are not used are not displayed and are
not available in 'Transit E1' mode. The rest of the fields are configured as in SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I mode.
10
This block of parameters is available only for the SIP mode.
Page 73

SMG digital gateway 73
Options of SIP-session timers (RFC 4028) will be enabled by default in 'Transit E1' mode if the values
are not set before.
4.1.7.6 RTP Codec Configuration Tab
Options
Voice activity detector / Comfort noise generator (VAD/CNG)—when checked, enables a silence
detector and a comfort noise generator. The voice activity detector allows transmission of RTP
packets to be disabled during periods of silence, thus reducing the load in data networks.
Source IP: Port verification—when checked, controls media traffic received from the IP address
and UDP port specified in the SDP communication session description; otherwise, accepts traffic
from any IP address and UDP port.
Echo cancellation—the echo cancellation mode:
– voice(default)—echo cancellers are enabled in the voice data transmission mode;
– voice nlp-off—echo cancellers are enabled in the voice mode; the non-linear processor
(NLP) is disabled. When the levels of transmission and reception signals significantly differ,
a weak signal may be suppressed by the NLP. This echo canceller mode is used to prevent
the signal suppression;
– modem—echo cancellers are enabled in the modem operation mode (direct component
filtering is disabled, NLP control is disabled, CNG is disabled);
– off—echo cancellation is disabled (this mode is set by default).
Rx gain (0.1 dB)—volume of the signal received, gain of the signal received from the
communicating gateway.
Tx gain (0.1 dB)—volume of the signal transmitted, gain of the signal transmitted in the
communicating gateway direction.
Page 74

74 SMG digital gateway
DSCP for RTP—a service type (DSCP) for RTP and UDPTL (T.38) packets.
RTP-loss timeout—a function to control voice frequency path status by monitoring the presence of
RTP traffic from the communicating device. The range of permitted values is from 10 to
300 seconds. When unchecked, RTP control is disabled; enabled when checked. The following
control is performed: if there are no RTP packets coming from the opposite device for the
duration of the timeout interval and the last packet was not a silence suppression packet, the call
is cleared back.
RTP-loss timeout after Silence-Suppression Indication (multiplier)—the RTP packet timeout for the
silence suppression option. The range of permitted values is from 1 to 30. The coefficient is a
multiplier that determines how many times the value of this timeout is larger than the RTP Packet
Timeout value. The following control is performed: if there are no RTP packets coming from the
opposite device for the duration of this time interval and the last packet was a silence suppression
packet, the call is cleared back.
RTCP period (sec.)—time period in seconds (5–65,535), after which the device sends control
packets via the RTCP protocol. When unchecked, RTCP is not used.
RTCP activity control—a function to control voice frequency path status; may take values from 5
to 65,535 seconds. The number of time periods (RTCP timer) to wait for RTCP protocol packets
from the opposite party. If no packets received during the specified period of time, the
established connection is terminated. At that, "cause 3 no route to destination" is set as a cause of
the disconnection to the TDM and IP protocols. The control period is calculated from the following
expression: RTCP timer * RTCP control period (seconds). When unchecked, the feature is disabled.
Clear Channel —a channel that is established for transparent transfer of digital data; when the
channel is established, the device does not attempt to recode it that ensures transparent
transmission. To establish a connection of this kind, the Transmission Medium Requirement field is
required with the following values:
– restricted digital info (Q.931 protocol);
– unrestricted dig.info (Q.931 protocol);
– video (Q.931 protocol);
– 64 kbit/s unrestricted (SS-7 protocol).
Clear Channel override—when checked, only one CLEARMODE codec is specified while
establishing a clear channel in SDP if operation via Clear Channel is invoked on the first call leg.
When unchecked, the complete list of selected codecs is transferred to SDP in the priority order.
DTMF Transmission
DTMF transport — the method of DTMF
transmission via IP network:
– inband—in RTP packets, in-band;
– rfc2833—in RTP packets according to
rfc2833 recommendations;
– info—out-of-band. The SIP protocol uses INFO messages; the type of DTMF signals
transferred depends on the MIME extension type in this case.
To use extension dialling during a call, make sure the similar DTMF tone transmission method
is configured in the opposite gateway.
Flash signal processing (RFC2833)—processing of the FLASH signals received according to RFC2833
method.
RFC2833 PT—the type of dynamic load used to transfer DTMF packets via RFС2833. The range of
permitted values is from 96 to 127. RFC2833 recommendation defines the transmission of DTMF
Page 75

SMG digital gateway 75
via the RTP protocol. This parameter should conform to the similar parameter of the
communicating gateway (the most frequently used values are 96, 101).
RFC2833: same PT—when checked, if SMG is the party which sends "offer SDP", RFC2833 packets
are expected for reception with a PT value sent in "answer SDP"; otherwise, RFC2833 packets are
expected for reception with the same PT value as sent by SMG "offer SDP".
DTMF MIME Type—the load type used for DTMF transmission in SIP protocol INFO packets:
– application/dtmf-relay—in SIP INFO application/dtmf-relay packets ("*" and "#" are sent
as symbols "*" and "#");
– application/dtmf—in SIP INFO application/dtmf packets ("*" and "#" are sent as digits 10
and 11).
Jitter Buffer settings
Mode—the mode of jitter buffer operation: fixed
or adaptive.
Minimum size, ms—the size of a fixed jitter buffer
or the lower limit (minimum size) of an adaptive
jitter buffer. The range of permitted values is
from 0 to 200 ms.
Initial size, ms—an initial value of the adaptive
jitter buffer. The range of permitted values is
from 0 to 200 ms.
Maximum size, ms—the upper limit (maximum
size) of the adaptive jitter buffer, in milliseconds.
The range of permitted values is from "minimum
size" to 200 ms.
Adaptation period, ms—the time of buffer adaptation to the lower limit without faults in packet
sequence order.
Removal mode—the mode of buffer adaptation. Defines the method of packet deletion during
buffer adaptation to the lower limit.
– Soft—the device uses an intelligent selection pattern to delete the packets, which exceed
the threshold.
– Hard—the packets, which delay exceeds the threshold, are deleted immediately.
Removal threshold, ms—a threshold for immediate deletion of a packet, in milliseconds. When
buffer size grows and packets delay exceeds this threshold, the packets are deleted immediately.
The range of permitted values is from "Delay max" to 500 ms.
Adjustment mode—the adjustment mode selected for increase of the adaptive jitter buffer
(gradual/instant).
Size for VBD, ms—the size of the fixed jitter buffer used for data transmission in the VBD mode
(modem communication). The range of permitted values is from 0 to 200 ms.
Options configuration for 'Transit E1' mode
Some of the options are not used in this mode. Fields which are not used are not displayed and are
not available in 'Transit E1' mode. The rest of the fields are configured as in SIP/SIP-T/SIP-I mode.
Page 76

76 SMG digital gateway
4.1.7.7 Fax and Data Transfer Configuration Tab
Data Transmission
Enable VBD—when checked, creates a VBD channel according to V.152 recommendation for
modem transmission. When a CED signal is detected, the device enters the Voice Band Data mode.
Unchecking the checkbox disables modem tone detection, but does not affect modem
Page 77

SMG digital gateway 77
communication (switching to modem codec will not be initiated, but this operation still may be
performed by the opposite gateway).
VCodec for VBD—the codec which is used for data transmission in the VBD mode.
Payload type for VBD—the load type which is used for data transmission in the VBD mode.
– Static—uses the standard value of the load type for a codec (8 for G.711A codec, 0 for
G.711U codec).
– 96–127—load types from the dynamic range.
Fax settings
Fax detector mode—detects the transmission direction for fax tone detection with subsequent
switching to a fax codec:
– no detect fax—disables fax tone detection, but does not affect fax transmission (switching
to fax codec will not be initiated, but this operation still may be performed by the opposite
gateway);
– Caller and Callee—tones are detected during both fax transmission and reception. During
fax transmission, a CNG FAX signal is detected from the subscriber's line. During fax
reception, a V.21 signal is detected from the subscriber's line;
– Caller—tones are detected only during fax transmission. During fax transmission, a CNG
FAX signal is detected from the subscriber's line;
– Callee—tones are detected only during fax reception. During fax reception, a V.21 signal is
detected from the subscriber's line.
A V.21 signal may also be detected from the transmitting fax.
Fax relay mode—the protocol selected for fax transmission.
Fax relay max rate (bps)—the maximum transfer rate of a fax transmitted via the Т.38 protocol.
This setting have influence on the gateway's ability to work with high-speed fax units. If fax units
support data transfer at 14,400 bauds and the gateway is configured to 9,600 bauds, the
maximum rate of connection between the fax units and the gateway will be limited by
9,600 bauds. And vice versa, if fax units support data transfer at 9,600 bauds and the gateway is
configured to 14,400 bauds, this setting does not affect the interaction and the maximum rate is
defined by the fax units.
Fax relay rate management —defines the method of data transfer rate management:
– local TCF—the method requires the TCF tuning signal to be locally generated by the
recipient gateway. It is generally used for T.38 transmission via TCP;
– transferred TCF—the method requires the TCF tuning signal to be sent from the sender
device to the recipient one. It is generally used for T.38 transmission via UDP.
Т.38 data fill bits removal—padding bit removals and inserts for the data which is not related to
ЕСМ (error correction mode).
Т.38 data redundancy—redundancy amount in Т.38 data packets (the number of previous packets
in the next Т.38 packet). Introduction of redundancy allows the transmitted data sequence to be
restored upon reception if some packets have been lost during transmission.
Т.38 data packetization—defines the frequency of Т.38 packets generation in milliseconds (ms).
This option allows size adjustment for a transmitted packet. If the communicating gateway is able
to receive datagrams with max. size of 72 bytes (maxdatagrammSize: 72), the packetisation time
should be set to a minimum in SMG.
Т.38 data transit—when a call is performed using two SIP interfaces with the T.38 fax transfer
protocol being used by both of them, this setting allows the T.38 packets to transit between the
interfaces with a minimum delay.
Page 78

78 SMG digital gateway
Options configuration for 'Transit E1' mode
Options of modem and fax detection are not used in 'Transit E1' mode. The tab is not available in this
mode.
4.1.7.8 Trunk Directions
A trunk direction is a set of trunk groups united in one direction. When a call is performed to a trunk
direction, the order of selection of the trunk groups in this direction can be chosen.
To create, edit, or remove trunk directions, use the Objects—Add Object, Objects—Edit Object, or
Objects—Remove Object menus and the following buttons:
— Add Direction;
— Edit Direction Parameters;
— Remove Direction.
To access a trunk direction, the device configuration should include prefixes which perform transition to
this direction.
Name—name of the trunk direction.
TrunkGroup select mode—order of trunk group selection in the direction:
– Sequential forward—all trunk groups of the direction are selected in turns beginning from
the first one in the list;
– Sequential back—all trunk groups of the direction are selected in turns beginning from the
last one in the list;
– From the first and forward—the first free trunk group of the direction is selected
beginning from the first one in the list;
– From the last and back—the first free trunk group of the direction is selected beginning
from the last one in the list.
A list of trunk groups in the direction:
Page 79

SMG digital gateway 79
To add or remove trunk groups, use the following buttons:
— Add;
— Remove.
Use the arrow buttons (up, down) to change the trunk group order in the list.
4.1.8 Internal Resources
4.1.8.1 SS7 Categories
This section specifies correspondence between Caller ID categories and SS7 protocol categories.
The generally accepted correspondence between SS7 categories and Caller ID categories is provided
below.
SS7 category 10
—
Caller ID category 1
SS7 category 11
—
Caller ID category 4
SS7 category 12
—
Caller ID category 8
SS7 category 15
—
Caller ID category 6
SS7 category 224
—
Caller ID category 0
SS7 category 225
—
Caller ID category 2
SS7 category 226
—
Caller ID category 5
SS7 category 227
—
Caller ID category 7
SS7 category 228
—
Caller ID category 3
SS7 category 229
—
Caller ID category 9
Page 80

80 SMG digital gateway
4.1.8.2 Access Categories
Access categories are used to define access privileges for subscribers, trunk groups, and other objects. The
categories enable calls from the incoming channel to the outgoing channel.
To restrict access to an object, assign the corresponding category; for other categories, this menu defines
accessibility to a category assigned to an object (to disable access, uncheck the checkbox next to the
corresponding category; to enable access, check the checkbox next to the corresponding category).
In total, up to 64 access categories can be configured. Access to the first 16 categories is provided by
default in each of the access categories.
To configure and edit a selected category, click the button.
4.1.8.3 Modifier Tables
This table contains all created modifiers and the objects they are assigned to.
To create, edit, or remove a modifier, use the Objects—Add Object, Objects—Edit Object, or Objects—
Remove Object menus and the following buttons:
— Add Modifier;
— Edit Modifier Parameters;
—Remove Modifier.
Page 81

SMG digital gateway 81
To assign or edit parameters of a created modifier, select the corresponding row and click .
To confirm changes in modifier parameters, click the Apply button; or click Cancel to exit without saving.
Number Selection Tab
Number mask—a template or a set of templates which is compared to the subscriber number (for
mask syntax, see section 4.1.6.1).
Number type—type of the subscriber number:
– Subscriber—subscriber number (SN) in Е.164 format;
– National—national number. The format: NDC + SN, where NDC—a geographical area code;
– International—international number. The format: СС + NDC + SN, where СC—a country
code;
– Network specific—specific network number;
– Unknown—unknown type of the number;
– Any—modification will be performed for any number type.
Number category—subscriber's Caller ID category.
Page 82

82 SMG digital gateway
General Modification Tab
Modification example—click the button to view modification summary after application of the
modification rules specified.
Access category—allows modification of access categories.
Dial plan —allows modification of the numbering schedule to be used for further routing (required
for coordination of numbering schedules).
CdPN/Original CdPN Modification Tab
Modification example—click the button to view modification summary after application of the
modification rules specified. It is recommended to define a number to be modified instead of
number 123456789, which is entered in the rule check example.
Modification rule for CdPN/Original CdPN—callee number modification rule. For syntax, see
section 4.1.8.3.1; for examples, see Appendix C. This rule also applies to modification of the callee
original number (original Called party number) when this modifier table is chosen in the Trunk
Group section for Original CdPN modification.
Number type—modification rule for callee number types (no change—do not modify).
Numbering plan type—modification rule for numbering schedule types (no change—do not
modify).
Page 83

SMG digital gateway 83
CgPN/RedirPN Modification Tab
Modification example—click the button to view modification summary after application of the
modification rules specified. It is recommended to define a number to be modified instead of
number 123456789, which is entered in the rule check example.
Modification rule CgPN/Redir PN—callee number modification rule. For syntax, see section
4.1.8.3.1; for examples, see Appendix C. This rule also applies to modification of the redirecting
number when this modifier table is chosen in the Trunk Group section for Redir PN modification.
Number type—modification rule for caller number types (no change—do not modify).
Presentation—modification rule for presentation of the caller (no change—do not modify).
Screen— modification rule for caller screen indicators (no change—do not modify).
Number category—modification rule for caller category (no change—do not modify).
Numbering plan type—modification rule for numbering schedule types (no change—do not
modify).
4.1.8.3.1 Modification Rule Syntax
Modification rule is a set of special characters which govern number modifications.
'.' and '-': special characters indicating that a digits is removed in the current position and other
digits, which followed the removed one, are shifted to its position.
'X', 'x': special characters indicating that a digit in the current position remains unchanged (the
position must contain a digit).
'?': a special character indicating that a digit in the current position remains unchanged(the
position may contain no digits).
'+': a special character indicating that all characters located between the current position and the
next special character (or the end of the sequence) are inserted at the specified location of the
number.
Page 84

84 SMG digital gateway
'!': a special character indicating a breakdown finish; all other digits of the number are truncated.
'$': a special character indicating a breakdown finish; all other digits of the number remain
unchanged.
09, D, #, and * (not preceded by "+"): informational characters that substitute a digit in the
specified position of the number.
4.1.8.4 Q.931 Timers
This section defines configuration of the third level timers required for
Q.931 signalling protocol operation.
Timer names and default values are described in Q.931 ITU-T
recommendation, §9 List of System Parameters.
Name
Default Value, seconds
Range,
seconds
T301
180
180 – 360
T302
15
10 – 25
T303
4
4 – 10
T304
20
20 -30
T305
30
30 – 40
T306
30
30 -40
T307
180
180 – 240
T308
4
4 – 10
T309
90
6 -90
T310
10
10 – 20
T312
6
6 -12
T313
4
4 – 10
T314
4
4 – 10
T316
120
120 – 240
T317
120
120–240
not less than
T316
T320
30
30 – 60
T321
30
30 – 60
T322
4
4 – 10
4.1.8.5 SS7 Timers
This section defines configuration of MTP2, MTP3, and ISUP level timers of the SS-7 protocol.
To create, edit, or remove a profile, use the following buttons:
— Add Profile;
— Edit Profile Parameters;
— Remove Profile.
Page 85

SMG digital gateway 85
No.—the sequence number of the SS-7 timer profile.
Profile—profile name.
SS7 Linkset—a list of SS-7 line groups which have this profile selected.
Profile Settings
Names of MTP2 level timers and their default settings are described in Q.703 ITU-T recommendation,
§12.3 Timers.
Name
Default Value, seconds
Range, seconds
T1
50
40 – 50
T2
50
5 – 150
T3 2 1 – 2
T4n
8.2
7.5 – 9.5
T4e
0.5
0.4 – 0.6
T6 6 3 – 6
T7n 2 0.5 – 2
Names of MTP3 level timers and their default settings are described in Q.704 ITU-T recommendation,
§16.8 Timers and Timer Values.
Name
Default Value, seconds
Range, seconds
T2 2 0.7 – 2
T4
1.2
0.5 – 1.2
T12
1.5
0.8 – 1.5
T13
1.5
0.8 – 1.5
T14 3 2 – 3
T17
1.5
0.8 – 1.5
T22
180
180 – 360
T23
180
180 – 360
Page 86

86 SMG digital gateway
Names of ISUP level timers and their default settings are described in Q.764 ITU-T recommendation,
Appendix A, Table A.1/Q.764 Timers in the ISDN User Part.
Name
Default Value, seconds
Range, seconds
T1
60
15 – 60
T5
900
150 – 900
T6
30
10 – 60
T7
30
20 – 30
T8
15
10 – 15
T9
180
30 – 240
T12
60
15 – 60
T13
900
150 – 900
T14
60
15 – 60
T15
900
150 – 900
T16
60
15 – 60
T17
900
150 – 900
T18
60
15 – 60
T19
900
150 – 900
T20
60
15 – 60
T21
900
150 – 900
T22
60
15 – 60
T23
900
150 – 900
T24 2 0 – 2
T25
10
1 – 10
T26
180
60 – 180
T33
15
12 – 15
T34 4 2 – 4
T35
20
15 – 20
4.1.8.6 Q.850-Cause and SIP-Reply Code Correspondence Table
This section establishes correspondence between clearback
reasons described in Q.850 recommendations for the SS-7 and PRI
protocols and 4xx, 5xx, 6xx class SIP replies.
The correspondence described in the Order No. 10 as of January
27, 2009, issued by the Ministry of Communications and Mass Media (MinComSvyaz) of the Russian Federation
is used by default; for the causes not described in this Order, the correspondence described in Q.1912.5
recommendation for SIP-I and in RFC3398 for SIP/SIP-T is used.
To create, edit, or remove rules in correspondence tables, use the following buttons:
— Add Rule;
— Edit Rule Parameters;
— Remove Rule.
Name—name of the Q.850-cause and SIP-reply correspondence table.
Page 87

SMG digital gateway 87
Profile Settings
Direction:
– SIP reply -> Q.850 cause—direction from SIP to
Q.850.
– Q.850 cause -> SIP reply—direction from Q.850 to
SIP.
Q.850-cause—value of a Q.850 cause.
SIP-reply—value of a 4xx, 5xx, 6xx class SIP reply.
4.1.8.7 Scheduled Routing
This section configures scheduled routing that allows the use of different numbering schedules depending
on the time and day of the week.
To create, edit, or remove rules, use the following buttons:
— Add Rule;
— Edit Rule Parameters;
— Remove Rule.
Routing Rule
Start date—the selected start date for a scheduled routing rule operation.
Active days—duration of the scheduled routing rule operation.
Repeat monthly—allows monthly repetition of the routing rule.
Week days —the selected days of the week when the scheduled routing rule operates.
Page 88

88 SMG digital gateway
Active hours —the selected hours of the scheduled routing rule operation.
Dial plan—the selected routing schedule which will be used during the scheduled routing rule
operation.
4.1.8.8 TCP/IP Settings
This section configures device network settings and IP packet routing rules.
DHCP is a protocol which allows automatic retrieval of IP address and other settings required for
operation in a TCP/IP network. It allows the gateway to obtain all necessary network settings from
DHCP server.
SNMP is a simple network management protocol. It allows the gateway to send real-time
messages about failures to the controlling SNMP manager. Also, the gateway's SNMP agent
supports monitoring of gateway sensors' status on request from the SNMP manager.
DNS is a protocol which is used to retrieve domain information. It allows the gateway to obtain
the IP address of the communicating device by its network name (hostname). This may be useful,
e. g. when hosts are specified in the routing schedule or when a network name of the SIP server is
used as its address.
TELNET is a protocol which is used to establish control over network. Allows remote connection to
the gateway from a computer for configuration and management. In case of the TELNET protocol,
the data transfer process is not encrypted.
SSH is a protocol which is used to establish control over network. Unlike TELNET, this protocol
implies encryption of all data transferred through the network, including passwords.
4.1.8.9 Routing Table
This submenu can be used to configure static routes.
Static routing allows packets to be routed to specified IP networks or IP addresses through the specified
gateways. The packets sent to IP addresses, which do not belong to the gateway IP network and are outside the
scope of static routing rules, will be sent to the default gateway.
The routing table is separated into 2 parts: configured routes at the top of the table and automatically
created ones.
The automatically created routes cannot be changed as they are created automatically when the network
Page 89

SMG digital gateway 89
and VPN/PPTP interfaces are established. These routes are required for normal operation of the interfaces.
To create, edit, or remove a route, use the Objects—Add Object, Objects—Edit Object, or Objects—
Remove Object menus and the following buttons:
— Add Route;
— Edit Route Parameters;
— Remove Route.
Route Parameters
Enable—when checked, enables the route.
Destination—an IP network, an IP address or the default value (to set a default gateway).
Mask—specifies a network mask for the defined IP network (use mask 255.255.255.255 for IP
address).
Gateway (IP address or
*
)—defines an IP address of the route gateway.
Interface—the selected network transmission interface.
Metric—route metrics.
4.1.8.10 Network Settings
This submenu can be used to specify a device name and to
change the network gateway address, the DNS server address, and the
SSH/Telnet access ports.
Device Network Parameters
Hostname—device network name.
Use gateway from—network gateway address for the device.
Primary DNS—primary DNS server.
Page 90

90 SMG digital gateway
Secondary DNS—secondary DNS server.
Port for SSH—TCP port for device access via the SSH protocol, the default value is 22.
Port for Telnet—TCP port for device access via the Telnet protocol, the default value is 23.
4.1.8.11 Network Interfaces
The device allows configuration of 1 basic eth0 network interface, up to 8 additional eth0.XX VLAN
interfaces, and up to 5 additional pppX VLAN/PPP interfaces.
To create, edit, or remove rules for network interfaces, use the following buttons:
Add;
Edit;
Delete.
Network Interface Settings
Basic Settings
Network label—name of the network.
Firewall profile—shows the firewall profile selected for
this interface.
Type—interface type (always untagged for eth0
interface).
VLAN ID—VLAN identifier (1–4,095) (only for tagged
type interfaces).
Enable DHCP—specifies that an IP address is to
dynamically obtained from the DHCP server.
IP-address—network address of the device.
Network mask—subnet mask of the device.
Broadcast—address for packets broadcasting.
Gateway—do not obtain the IP address of the gateway
dynamically from the DHCP server.
DNS-address by DHCP—obtain the IP address of the
DNS server dynamically from the DHCP server.
NTP-address by DHCP—obtain the IP address of the NTP server dynamically from the DHCP server.
Services - a configuration menu for the services enabled for this interface:
Enable Web—enables access via web interface.
Enable Telnet—enables access via the Telnet protocol.
Enable SSH—enables access via the SSH protocol.
Enable SNMP—enables SNMP.
Enable SIP signalling—enables reception and transmission of the SIP signalling information
through the network interface configured in this section.
Page 91

SMG digital gateway 91
Enable RTP transmission—enables reception and transmission of the voice traffic through the
network interface configured in this section.
Enable RADIUS—enables the RADIUS protocol.
If an IP address or a network mask has been changed or the web configurator management has
been disabled for the network interface, confirm these settings by logging into the web
configurator to prevent the loss of access to the device; otherwise, the previous configuration will
be restored in two minutes.
VPN/PPP Interface Settings
Basic Settings
Network label—name of the network.
PPTPD IP—IP address of the PPTP server.
User name—the username (login) used by the
device for network connection.
Password—VPN connection password.
Options
Launch at startup—launches the interface at device
startup.
Ignore default gateway—ignores the gateway
setting in the Network Parameters section.
Enable encryption—enables encryption.
Services—a configuration menu for the services enabled for this
interface:
Enable Web—enables access via web interface.
Enable Telnet—enables access via the Telnet
protocol.
Enable SSH—enables access via the SSH protocol.
Enable SNMP—enables SNMP.
Enable RADIUS—enables the RADIUS protocol.
4.1.8.12 RTP Port Range
This section allows configuration of a UDP port range for
voice RTP packets transmission.
UDP Port Parameters
Starting port—the number of the UPD starting port for voice traffic (RTP) and data transmission
via the T.38 protocol.
Ports count—a range (quantity) of UPD ports used for voice traffic (RTP) and data transmission via
the T.38 protocol.
To avoid conflicts, make sure that the ports used for RTP and
overlap the ports used for SIP signalling (port 5060 by default).
Page 92

92 SMG digital gateway
4.1.9 Network Services
NTP is a protocol for synchronisation of real-time clock of the device. It allows synchronisation of date and
time used by the gateway against their reference values.
Enable—enables time synchronisation via NTP.
Time server (NTP)—the IP address or host name of the NTP server.
Timezone—configuration of the time zone and GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) offset:
– Manual mode—defines the GMT offset.
– Automatic mode—this mode allows selection of device location; the GMT offset will be
determined automatically. This mode also enables automatic switch to daylight saving
time.
Synchronisation period (min)—an interval between synchronisation requests.
Save—saves changes.
Cancel—discards changes.
To force time synchronisation with the server, click the ‘Restart NTP-client’ button (the NTP client will be
restarted).
4.1.9.1 SNMP Settings
SMG firmware enables device status monitoring via SNMP. The SNMP submenu allows configuration of
SNMP agent settings.
SNMP monitoring allows the following parameters to be requested from the gateway:
gateway name;
device type;
firmware version;
IP address;
E1 streams statistics;
IP submodules statistics;
linksets state;
E1 stream channels state;
Page 93

SMG digital gateway 93
IP channels state (statistics for the current calls via IP).
Statistics of the current calls performed via IP channels includes the following data:
channel number;
channel state;
call identifier;
caller MAC address;
caller IP address;
caller number;
callee MAC address;
callee IP address;
callee number;
channel engagement duration.
– Sys Name—device name.
– Sys Contact—contact information.
– Sys Location—device location.
– ro Community—parameter read password/community.
– rw Community—parameter write password/community.
– Apply—applies the changes.
– Reset—discards the settings.
4.1.9.2 SNMP Trap Configuration
For detailed monitoring parameters and traps description, see MIB files on the disk shipped
with the gateway.
The SNMP agent sends an SNMPv2-trap message in case of the following events:
configuration error;
SIP module failure;
IP submodule failure;
linkset failure;
SS-7 signal channel failure;
synchronisation loss or synchronisation from a lower priority source;
E1 stream failure;
remote stream failure;
configuration error fixed;
SIP-T module restored after a failure;
IP submodule restored after a failure;
linkset restored after a failure;
SS-7 signal channel restored after a failure;
synchronisation from a higher priority source restored;
no stream failure (after a failure or remote failure);
Page 94

94 SMG digital gateway
FTP server is unavailable, RAM utilisation for storing CDR files exceeds 50% (15–30 MB);
FTP server is unavailable, RAM utilisation for storing CDR files is less than 50% (5–15 MB);
FTP server is unavailable, RAM utilisation for storing CDR files is below 5 MB;
firmware update or configuration file upload/download status.
Restart SNMPd—click the button to restart the SNMP client.
To create, edit, or remove trap parameters, use the following buttons:
— Add;
— Edit;
— Remove.
Type—type of the SNMP message (TRAPv1, TRAPv2, INFORM).
Community—the password contained in traps.
IP address—IP address of the trap recipient.
Port—UDP port of the trap recipient (default port: 162).
4.1.9.3 FTP Server
This section allows configuration of an integrated FTP server used for provisioning FTP access to the
following directories:
cdr—a directory with CDR files.
log—a directory with tracing files and other debug data.
mnt—a directory with files located on external storage devices (SSD drives, USB flash drives).
4.1.9.4 FTP Server Settings
Enable—enables/disables the local FTP server.
Network interface—the network interface selected for the FTP server.
Port—the TCP port selected for the FTP server.
Page 95

SMG digital gateway 95
Authorization timeout, sec—a timeout for subscriber authorisation on the FTP server; when the
timeout expires, the server forces connection termination.
Idle timeout, sec—a timeout for user idle status on the FTP server; when the timeout expires, the
server forces connection termination.
Session timeout, sec—duration of a session.
4.1.10 User Configuration
By default, the device has a subscriber account created with permissions to read all directories (login:
ftpuser, password: ftppasswd).
Name—username.
Password—user password.
Access to log—log directory access configuration, read/write.
Access to mounts—mnt directory access configuration, read/write.
Access to CDR—CDR directory access configuration, read/write.
4.1.11 Security
4.1.11.1 SSL/TLS Configuration
This section is used to obtain a self-signed certificate in order to use an encrypted connection to the
gateway via the HTTP protocol and to upload/download configuration files via the FTPS protocol.
Web configurator interaction protocol—web configurator connection mode:
– HTTP or HTTPS—allows both unencrypted (HTTP) and encrypted (HTTPS) connections.
HTTPS connection is possible only when a generated certificate is available.
– HTTPS only—enables only encrypted HTTPS connection. HTTPS connection is possible only
when a generated certificate is available.
Page 96

96 SMG digital gateway
Generate New Certificates
These parameters should be entered in Latin characters.
Country code (two symbols)—country code (RU for Russia).
Region—region name.
City—city name.
Company name—organisation name.
Department—name of the organisation unit or division.
E-mail— contact e-mail address.
Hostname or IP address—IP address of the gateway.
4.1.11.2 Fail2ban
Fail2ban—a utility that monitors logs files for attempts to access various services. When fail2ban
discovers repeated unsuccessful access attempts from the same IP address/host, it blocks all further access
attempts from this IP address/host.
The following actions may be identified as an unsuccessful access attempt:
Brute forcing authentication data—reception of REGISTER requests from a known IP address but
containing wrong authentication data.
Reception of requests (REGISTER, INIVITE, SUBSCRIBE, and others) from an unknown IP address.
Reception of unknown requests via SIP port.
Fail2ban Parameters
Enable—launches Fail2ban utility.
Block time, seconds—time in seconds during which access from a suspicious address will be
banned.
Access attempts before blocking—the maximum number of host's unsuccessful access attempts
to a server before the host is banned by fail2ban.
White list (the last 30 records)—a list of IP addresses that cannot be banned by fail2ban.
Black list (the last 30 records)—a list of permanently banned addresses. A device may have up to
8,192 records in total.
Page 97

SMG digital gateway 97
To add, search, or remove an address from the list, select it in the entry field and click the Add, Search, or
Remove button.
An IP address or a subnet can be specified.
To enter a subnet, enter the data in the following format:
AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/mask
Example
192.168.0.0/24—this record corresponds to the network address 192.168.0.0 with the mask
255.255.255.0.
Download the entire white/black list of IP addresses—the web interface shows only the last
30 records in the file; click this button to download the entire white or black list to PC.
List of banned addresses—a list of addresses banned by fail2ban.
Download the entire list of banned IP addresses—allows download of the entire list of banned
addresses to PC.
To update the lists, click the Refresh button next to the header.
4.1.11.3 Firewall Profiles
Firewall is a software tools package that allows control and filtration of transmitted network packets in
accordance with defined rules to protect the device from unauthorised access.
Firewall Profiles
To create, edit, or remove firewall profiles, use the
following buttons:
Add;
Edit;
Delete.
The software allows configuration of firewall rules for incoming, outgoing and transit traffic, as well as for
specific network interfaces.
When a rule is created, the following parameters are configured:
Page 98

98 SMG digital gateway
Name—rule name.
Enable—defines whether the rule is used. When
unchecked, the rule is inactive.
Traffic type—type of traffic for the rule being created:
– egress—intended for SMG;
– ingress—sent by SMG.
Packet source—defines the network address of the
packet source either for all addresses or for a
particular IP address or network:
– any—for all addresses (the checkbox is
checked);
– IP address/mask—for a particular IP address
or network. The field is active when the any
checkbox is unchecked. The mask is
mandatory for a network, but optional for an
IP address.
Source ports—a ТСР/UDP port or port range (defined with a hyphen "-") of the packet source. This
parameter is used for TCP and UDP only; thus, select UDP, TCP, or TCP/UDP in this field to make it
active.
Destination address—defines the network address of the packet recipient either for all addresses
or for a particular IP address or network:
– any—for all addresses (the checkbox is checked);
– IP address/mask—for a particular IP address or network. The field is active when the any
checkbox is unchecked. The mask is mandatory for a network, but optional for an IP
address.
Destination ports—a ТСР/UDP port or port range (defined with a hyphen "-") of the packet
recipient. This parameter is used for TCP and UDP only; thus, select UDP, TCP, or TCP/UDP in this
field to make it active.
Protocol—the protocol the rule will be used for: UDP, TCP, ICMP, or TCP/UDP.
ICMP Message type—the ICMP message type the rule will be used for. This field is active, when
ICMP is selected in the Protocol field.
Action—an action executed by the rule:
– ACCEPT—the packets corresponding this rule will be accepted by the firewall.
– DROP—the packets corresponding this rule will be rejected by the firewall without
informing the party that has sent them.
– REJECT—the packets corresponding this rule will be rejected by the firewall. The party
that has sent the packet will receive either a TCP RST packet or "ICMP destination
unreachable".
A created rule is placed into the corresponding section: "Incoming traffic rules", "Outgoing traffic rules" or
"Transit traffic rules".
Also, the firewall profile allows specification of the network interfaces the rules of the profile will be
applied to.
Page 99

SMG digital gateway 99
Every network interface can be used only in a single firewall profile at a time. As soon as a
network interface is assigned to a new profile, it is removed from the old one.
To apply the rules, click the Apply button that appears when changes are made into the firewall settings.
4.1.11.4 List of Allowed IP Addresses
This section allows configuration of the list of IP addresses allowed to be used by administrator to connect
to the device via web interface and the Telnet/SSH protocols. By default, all addresses are allowed.
Access only for allowed IP addresses—when checked, the list of allowed IP addresses is used;
otherwise, access is allowed from any address.
Apply—applies changes.
Confirm—commits changes.
To create or remove a list of allowed addresses, use the following buttons:
Add;
— Remove.
Upon configuration of a list of addresses, click the Apply and Commit buttons; failing to confirm the
changes in 60 seconds restores the previous values. This allows user protection from loss of access to the device.
4.1.12 Network Utilities
4.1.12.1 PING
This utility is used to check device network connection (route presence).
Page 100

100 SMG digital gateway
IP Probing—used for a single-time check of device network connection.
To send a ping request (the ICMP protocol is used), enter the host IP address or network name in
the IP Probing field and click the Ping button. The result of the command execution will be shown
at the bottom of the page. The result contains information on the number the of transmitted
packets, the number of responses to the packets, the percent of lost packets, and the time of
reception/transmission (minimum/average/maximum) in milliseconds.
Periodic ping—used for periodic check of device network connection.
Enable—when checked, sends ping requests to the addresses specified in the host list.
Period, minutes—time interval between requests in minutes.
Attempts count—the number of attempts to send a request to an address.
Status
Start—launches/restarts periodic ping.
Stop—forcedly stops periodic ping.
Information—click this button to view the /tmp/log/hosttest.log log file which contains data on
the last attempt of periodic ping request transmission.
IP addresses list—a list of IP addresses to send periodic ping requests to.
To add a new address to the list, select it in the entry field and click the Add button. To remove an address,
click the Remove button next to the required address.
4.1.13 RADIUS Configuration
4.1.13.1 RADIUS Servers
The device supports up to 8 authorisation servers and up to 8 accounting servers.
Server reply timeout—amount of time to wait for a server response.
 Loading...
Loading...