Page 1

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
CHAPTER▼ ONE
GETTING TO KNOW THE BASICS
This chapter introduces the features and
components of the computer.
1-1
Page 2

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Performance Features
High Performance AMD Processor with advanced ATI
Integrated Chipset
The notebook PC is equipped with the powerful Mobile
AMD Turion 64 X2 dual-core processor or the Mobile AMD
Sempron single-core processor. Together with the latest
ATI Radeon Xpress chipset and integrated graphic
technologies, the system offers very advanced PC
performances.
Wide-Screen LCD Display
The computer is equipped with a wide-screen 15.4-inch
TFT high-resolution display panel for the best cinematic
viewing experience.
Battery Performance Technology
The system uses a unique power management technology
that allows user to enjoy extended battery life without
sacrificing performance.
ExpressCard Technology
ExpressCard (type II, 54mm) is the next-generation of the
PC Card standard. The bus interface is based on the two
standards: PCI Express for high-performance I/O and
USB2.0 for variety of devices.
Expandability
The system offers upgradeable hard disk drive and 2 DDRII
SDRAM sockets for expansion, allowing the user to easily
increase the storage and system capacities as the need
arises.
Built-in Multiple Card Reader
There is built-in 4-in-1 card reader to access many of the
portable media formats (SD Card, MS Card, MMC Card,
1-2
Page 3

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
and MS-Pro Card).
Ethernet Port
The system provides built-in 10/100Mbps Ethernet network
adapter for high bandwidth network connection.
Firewire (IEEE1394 / 1394a) and USB2.0 ports
In addition to a full array of built-in I/O por
ts, the computer
offers IEEE1394 for ultra high-speed connection to high
bandwidth digital video devices and USB2.0 ports to
connect to any USB-based peripheral devices.
Wireless LAN
The internal Wireless LAN module allows your notebook to
connect wirelessly to other 802.11-enabled systems,
devices, or network.
1-3
Page 4
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
System At A Glance
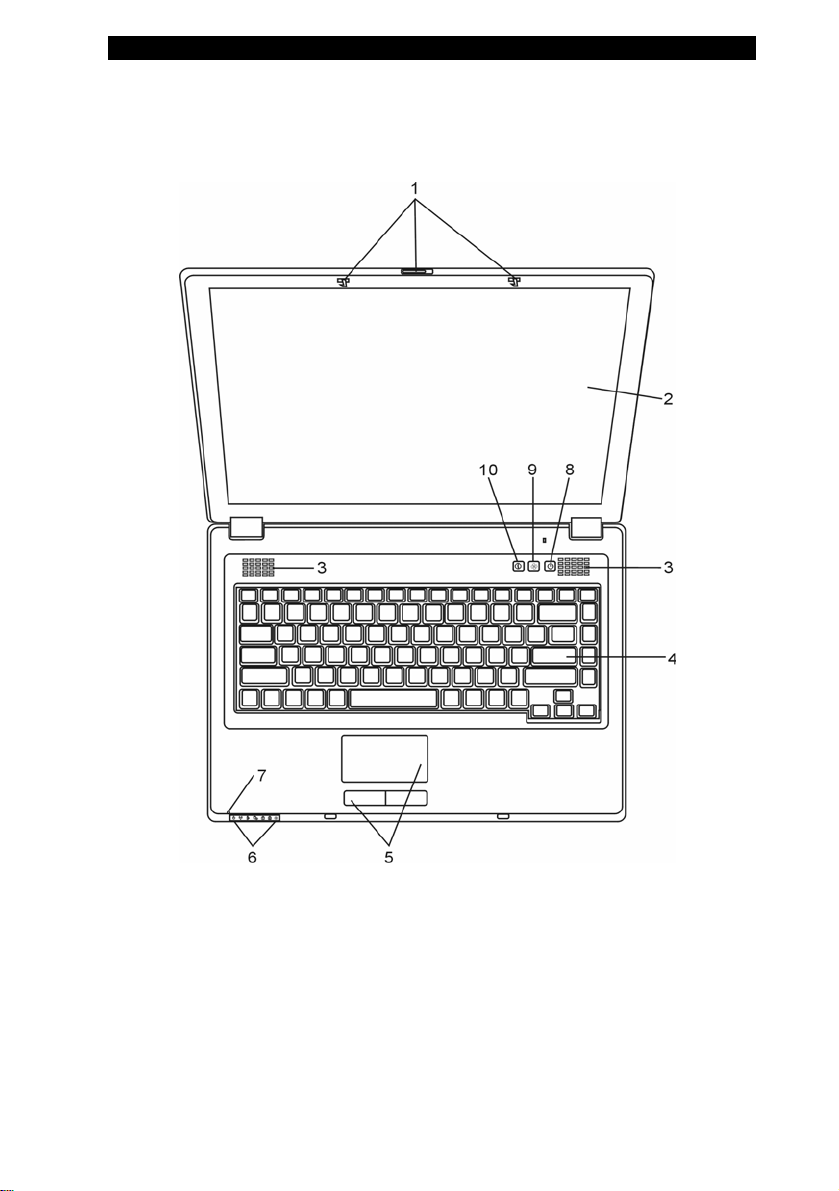
Top View
1. LCD Latch
The LCD latches lock / unlock the LCD panel.
2. LCD Display
The panel is where the system content is displayed.
1-4
Page 5

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
3. Built-in Stereo Speakers
The built-in speakers output the sound in stereo.
4. Keyboard
The keyboard is used to enter data. (See Keyboard Section for
details.)
5. Touch Pad
The touch pad is a built-in pointing device with functions similar
to a mouse.
6. LED Status Indicator
The LED Status indicators reveal the status of these functions:
Numeric keypad, cap lock, silent mode, WLAN module
enabling and disabling and also the ODD, HDD activities. (See
the LED Status Indicator Section for details.)
The LED Status indicators also reveal the status of the system
power state and battery-charging state. See the LED Status
Indicator Section for details.
7. Built-in Microphone
The built-in microphone records sound.
8. Power / Suspend Button
The power/suspend button turns the notebook on and off and it
also acts as a system suspend key. Press momentarily to turn
on the system. Press and hold for at least 4 seconds to turn off
the system. How this key behaves can be defined in [Start >
Settings > Control Panel > Power Options > Advanced] menu.
Press the power / suspend button again to return from the
suspend mode. (See Chapter 3 for more details on system
suspend function.)
When the system is in Suspend Mode, the
indicator shows blinking green light.
LED status
1-5
Page 6

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
9. Silent Mode Button
Pressing the key enables the system to lower its power usage;
therefore the fan speed is reduced to achieve lowest operating
noise.
When Silent Mode is enabled, the
shows steady green light.
10. Internet Explorer Quick Key
Pressing the button launches Internet Explorer in Windows.
LED status indicator
1-6
Page 7
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
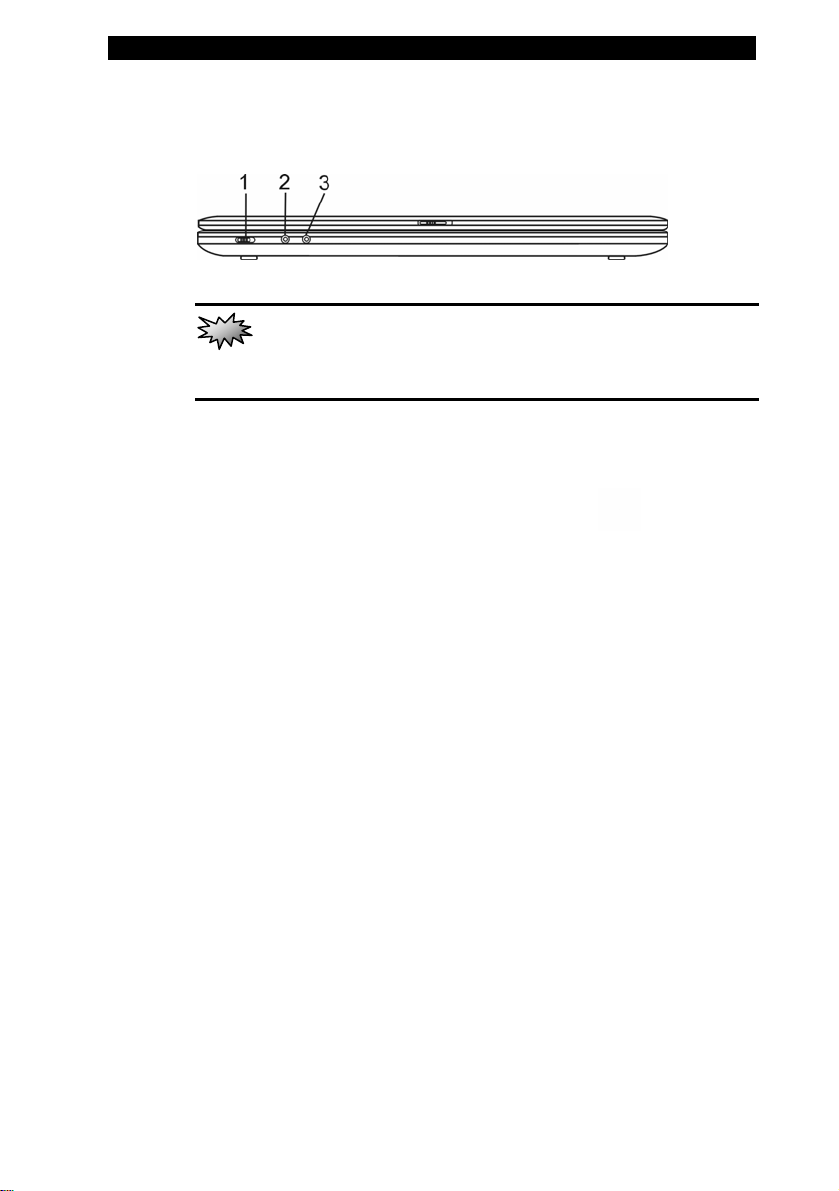
Front View
Warning:
damage the display
Do not place any heavy objects on the top of notebook. This may
1. Wireless On/Off Switch
Use the Switch to disable or enable the Wireless function.
When Wireless LAN function is enabled, the
indicator shows steady green light.
2. Microphone/Audio Line-in Jack
The microphone/Audio Line-in jack (3.5-mm diameter) is where
you connect a microphone or an external audio input source
such as a CD Player..
3. Stereo Headphone / SPDIF-out Jack
The stereo headphone jack (3.5-mm diameter) is where you
connect the headphones or external speakers. Alternatively,
you may connect the S/PDIF output to an external DTS, AC3,
or PCM sound processor / decoder in your home stereo
system.
LED status
1-7
Page 8

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Side Views
Warning:
damage the display
Do not place any heavy objects on the top of notebook. This may
1. USB2.0 Port (x3)
The Universal Serial Bus (USB2.0-compliant) port allows you to
connect a wide variety of devices to your computer at a rate of
up to 480 Mbps. This port conforms to the latest USB2.0
plug-and-play standards.
2. Optical Drive and Disk Eject Button and Manual Eject Key
Hole
If your computer comes with the Combo drive, DVD-Dual or
Super-Multi drive, you may save data onto a CD-R / CD-RW or
DVD RW disc. Press the eject button to eject the disk tray. The
manual eject keyhole allows you to manually eject a jammed
1-8
Page 9

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
disk.
3. Modem Port
This is where you plug the phone jack (RJ-11) for fax/modem
functions.
4. Kensington Lock Key Hole
A Kensington-type security lock latches to this keyhole for
anti-theft purpose.
5. Ventilation Grill
The fan grill is where air is exchanged to dissipate the internal
heat. Do not block this airway completely.
6. Power Jack (DC-in)
The DC-out jack of the AC Adapter connects here and powers
the computer.
7. External VGA Port
The VGA video output port is for connecting the external LCD
monitor or projector.
8. TV (S-Video) Port
The S-Video port permits you to redirect the screen output to a
television set or any analog video playback device. This TV
Port is copyright protected; when DVD movie is played, the
output is scrambled to prevent analog recording.
9. Ethernet / LAN Port
The port connects to a network hub via the RJ-45 cable and
also conforms to 10/100Base-TX transmission protocol.
1-9
Page 10

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
10. ExpressCard Slot
The slot is where ExpressCard (Type II, 54mm) is inserted.
ExpressCard integrates both the PCI-Express bus technology
and USB2.0 interface.
Press the card into the slot to insert. Press the card again to
eject.
11. Firewire / IEEE1394 / 1394a Port
This is a high-speed serial data port. You may connect any
Fire-wire-ready device to this port.
12. 4-in-1 Card Reader
The 4-in-1 Card Reader supports SD Card, MS Card, MMC
Card, and MS-Pro Card.
1-10
Page 11

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Bottom View
1. Battery Pack and Battery Latch
The battery pack is a built-in power source for the notebook.
Slide the battery latch to release the battery pack.
2. Ventilation Grill
1-11
Page 12

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
The fan grill is where air is exchanged to dissipate the internal
heat. Do not block this airway completely.
Warning:
surface only. The bottom case may get very hot.
Do not block the Fan Grill outlet. Place the machine on hard
3. System Device Cover
The system’s processor with cooler assembly, Wireless LAN
module, HDD, and DDR memory module are located under the
case cover. The system memory can be upgraded to a larger
capacity. (See Chapter 4 for instructions on the memory and
HDD upgrade.)
1-12
Page 13

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
AC Adapter
1. DC-out Connector
The DC-out connector docks to the power jack (DC-in) on the
computer.
2. Adapter
The adapter converts alternating current into constant DC
voltage for the computer.
3. AC Plug
The AC plug plugs to the AC wall outlet.
Warning:
ground pin. If not, you may feel a slight tingling sensation on any of the
computer’s metal parts such as the I/O ports. This is caused by leakage current
when the AC adapter is not properly grounded (via the ground pin). However,
the amount of leakage current is within the safety regulation and is not harmful
to human body.
Make sure you are using a standard 3-prong AC wall socket with a
1-13
Page 14

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
LED Status Indicator
The LED Status Indicator displays the operating status of your
notebook. When a certain function is enabled, an LED will light
up. The following section describes its indication.
System & Power Status Indicators
LED Graphic
Symbol
Indication
Green light indicates the system is ON.
Blinking green light indicates the
notebook is in the suspend mode.
Green light indicates the WLAN module
is active.
Persistent green light indicates the Silent
Mode is enabled.
Blinking orange light indicates the
battery is being charged.
Blinking red light indicates the battery
power is low when the system is turned
ON.
Persistent green light indicates the
battery is Full and the AC Adapter is
plugged in.
Green light indicates the hard drive
and/or optical drive is being accessed.
Green light indicates the numeric keypad
is activated.
Green light indicates the cap-lock is
activated.
1-14
Page 15

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Keyboard Features
Function Keys (Quick Keys)
Graphic
Symbol
For various system controls, press the Fn (Function) key and the Fx key
simultaneously.
Action System Control
Fn + F1 Enters Suspend Mode.
Fn + F3 Turns the battery warning beep
Fn + F4 Changes Display Mode:
Fn + F5 Turns Speaker Volume up.
Fn + F6 Turns Speaker Volume down.
Fn + F7 Increases Display Brightness.
Fn + F8 Decreases Display Brightness.
Fn+Num
Lock
Scroll Lock Press the Scroll Lock key and
off or on.
LCD-only, CRT-only and
LCD&CRT.
Enables the embedded keypad
to work in numeric mode. The
keys act like numeric keypads
in a calculator. Use this mode
when you need to do a lot of
numeric data entry. An
alternative would be to connect
an external numeric keypad.
then press ↑or ↓to move one
line up or down.
1-15
Page 16

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Windows Keys
Your keyboard also has two Windows keys:
1. Start Key
This key allows you to pull up the Windows Start Menu at
the bottom of the taskbar.
2. Application Menu Key
This key brings up the popup menu for the application,
similar to a click of the right mouse button.
Embedded Numeric Keypad
Press Fn+Num Lock to enable the embedded numeric keypad.
The numbers are printed in upper right corner of a key, in a
color different from the alphabets. This key pad is complete
with arithmetic operators (+, -, * , /).
Press Fn+Num Lock to revert to normal character keys.
1-16
Page 17
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
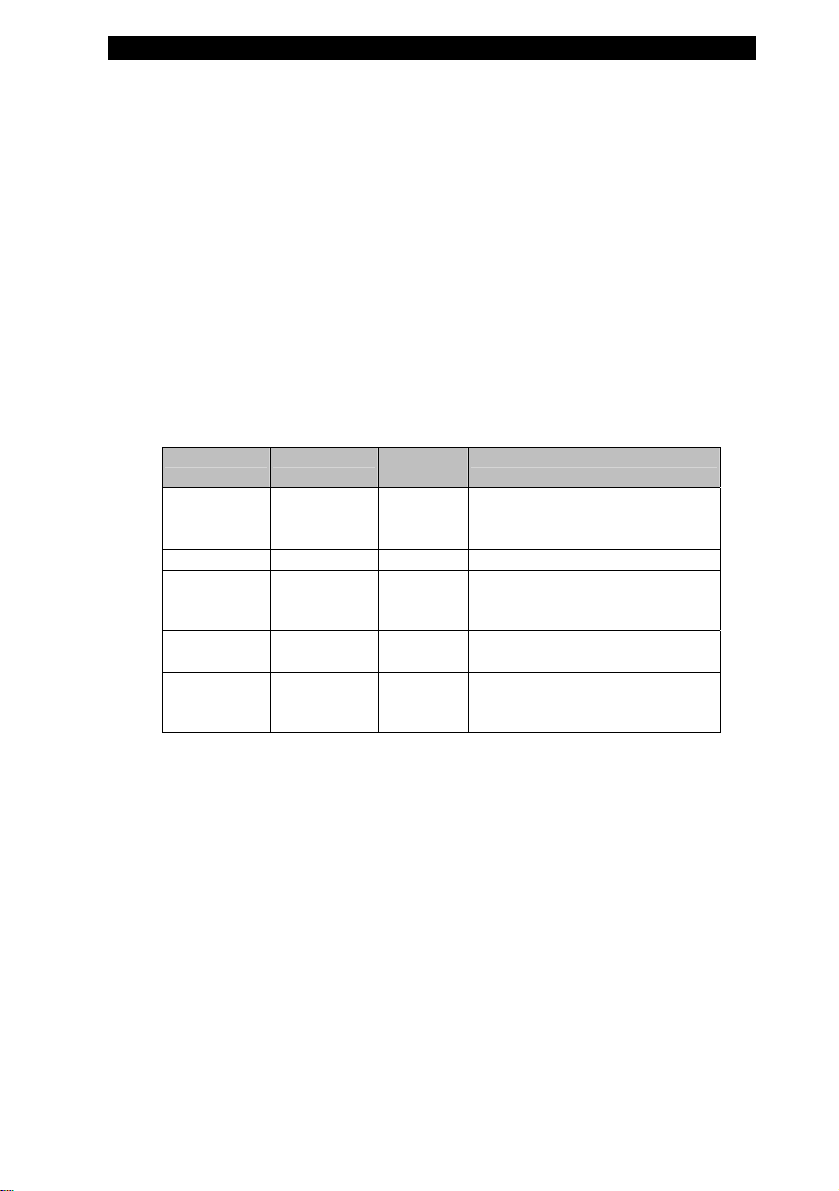
Touch Pad
The built-in touch pad, which is a PS/2-compatible pointing device,
senses movement on its surface. As you move your fingertip on the
surface of the pad, the cursor responds accordingly.
The following items teach you how to use the touch pad:
1. Move your finger across the touch pad to move the cursor.
2. Press buttons to select or execute functions. These two buttons
are similar to the left and right buttons on a mouse. Tapping on the
touch pad twice produces is similar to clicking the left button of a
mouse.
Function Left Button Right
Execution Click twice
quickly
Selection Click once Tap once
Drag Click and hold
Access
Context Menu
Move One
Page Up or
Down
to drag the
cursor
Click once
Button
Tap twice (at the same speed as
Tap twice quickly and on the
Tips on Using the Touch Pad:
1. The double-click speed is timed. If you double-click too slowly,
your notebook responds as if you single-clicked twice.
2. Keep your fingers dry and clean when using the touch pad.
Also keep the surface of touch pad clean and dry to prolong its life.
3. The touch pad is sensitive to finger movements. Hence, the
lighter the touch, the better the response. Heavy touch does not
produce better response.
Equivalent Tapping Action
double-clicking
the mouse button)
second tap hold finger to the touch
pad to drag the cursor
1-17
Page 18
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Graphic Subsystem
Your computer uses a high performance 15.4-inch active matrix
TFT panel with high resolution and multi-million colors for
comfortable viewing. The ATI Radeon Xpress integrated video
graphics accelerator, which is Microsoft DirectX 9 compatible,
performs graphic rendering at a lighting-fast speed.
Adjusting the Display Brightness
The notebook uses special key combinations, called hot keys,
to control brightness.
Press Fn+F7 to increase the brightness.
Press Fn+F8 to decrease the brightness.
Note:
To maximize your battery operating time, set the brightness to the
lowest comfortable setting, so that the internal backlight uses less power.
Extending the Life of the TFT Display Device
Observe the following guidelines to maximize the life of the
backlight in the display.
1. Set the brightness to the lowest comfortable setting
(Fn+F8).
2. When working at your desk, connect your notebook to an
external monitor and disable the internal display Fn+ F4.
3. Do not disable the suspend time-outs.
4. If you are using AC power and have no external monitor
attached, change to suspend mode when not in use.
1-18
Page 19

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Opening and Closing the Display Panel
To open the display, push the LCD latch to the right and lift up
the lid. Then tilt it to a comfortable viewing position. The LCD
panel has a maximum opening of 135 degrees. Do not push it
down forcibly.
To close the display cover, fold it down gently.
Warning:
place any object on top of the computer when the display is closed
To avoid damaging the display, do not slam it when closing. Do not
1-19
Page 20

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Audio Subsystem
Your computer’s audio subsystem is Sound Blaster Pro-compatible.
Adjusting the Volume Manually
To increase the volume, press Fn+F5.
To decrease the volume, press Fn+F6.
Adjusting the Audio Volume in Windows
1. Click the speaker symbol in the task tray in Windows.
2. Drag the volume control bar up or down to adjust the volume.
3. To temporarily silence the speaker without changing the
volume setting, click Mute.
Voice Recording
A built-in microphone allows you to record sound. You will need
to use audio processing software to enable the built-in
microphone. For example, you may use Microsoft Sound
Recorder.
1-20
Page 21

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Modem
Your computer comes with a 56K V.92 internal fax/modem and a phone
jack (RJ-11), which is located on the left side of your computer.
Use a telephone cable to connect the computer to the telephone wall
outlet.
Connecting the Modem
1. Plug one end of the phone line into the modem port located on
the rear side of the computer. (For EMI compliance, you need to clip
the included EMI CORE to the phone line.)
2. Plug the other end of the line into the analog phone wall outlet.
Depending on where your computer is used, you may need to change
settings in the modem. Correct setting will allow you to maintain a stable
connection in a country where its telecommunication system may be
different to others.
To change the modem setting, do the following:
1. Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel > Phone and
Modem Options]. Go to Dialing Rules and Edit My Location. In
the Country/Region pull-down menu, select the appropriate
country setting. You will see a similar dialog box.
1-21
Page 22

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
2. Click on the pull-down menu and select the country where it is
applicable. Click on OK to exit.
1-22
Page 23

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Ethernet
Your computer is equipped with a 10/100Base-TX Fast Ethernet
network adapter. Connect the active LAN cable to the RJ-45 LAN
port located on the right side of the computer. This allows you to
access and transmit data in the local area network.
Connecting to the Network
Use Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Ethernet cable only.
1. Insert one end of the UTP cable into the network connector
until the connector snaps securely into the receptacle.
2. Either connect the other end of the cable to an RJ-45 jack
wall outlet or to an RJ-45 port on a UTP concentrator or hub in
the network.
Cabling Restriction for Networks
The following restrictions should be observed for
10/100BASE-TX networks:
The maximum cable run length is 100 meters(m) (328
feet[ft]).
Note:
Consult Windows manual and / or Novell Netware user’s guide for the
software installation, configuration, operation of the network.
1-23
 Loading...
Loading...